- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations

How to Restate a Thesis
Last Updated: February 27, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 391,862 times.
A thesis statement serves as your paper’s (or speech’s) guiding idea, alerting readers to the main points of your paper and the direction it will take. A thesis restatement, which comes in the paper’s conclusion, is the thesis’s kindred spirit, though not its identical twin. It differs from the thesis in both word choice and sentence structure. Restating your thesis at the end of the paper allows you to remind your readers of what you have proven in your body paragraphs and helps to bring your paper to a successful close.
Working out the Restatement Basics

- Sketching out a rough conclusion (the main points you want to get across) will give you an idea of the best place for the restated thesis before you actually try your hand at writing the restatement.
- Depending on the nature of your paper or of your conclusion, you may want to open your conclusion with a question or some other kind of rhetorical device, rather than a restatement of the thesis. While writing often follows prescribed formulas (such as the 5-paragraph essay), there is no one-size-fits-all approach for writing a concluding paragraph, and you may need to try out several positions for your thesis restatement to find out what works best.

- You can use the restated thesis to provide a greater level of sophistication or emotional impact to the original argument. For example, if your initial argument was that buying pets as holiday gifts is dangerous, you might restate your thesis this way: "Remember: buying that puppy as a Christmas present might seem like a good idea at the time, but it could end in the tragedy of another homeless dog by Easter."
- You can also restate your thesis to incorporate the relationship you've built with your reader. For example, if your essay was about developing business partnerships, you could begin your restatement by saying something like, "As a businessperson...." Not only will this make your restatement different from the original, but it will also help draw connections with important elements from the essay/speech.

- For example, if you have written an essay about alcohol use on college campuses, you could revisit the "So what?" question in your conclusion by providing a statement about what that means for students and for college officials. It could look something like this: "Because alcohol abuse depends on more than just the legal drinking age, it is crucial that students be educated about how alcohol abuse occurs, and also that college officials broaden their perspective to include a greater variety of aspects."

- You may be able to use something like “In conclusion” at the end of a speech, however. Signaling or signposting words—like “in conclusion” or “next”—are very important in speeches because listeners only have one chance to follow along with what you’re saying, and these words help them to keep their place.

- Avoid saying things like, “It seems like” or “It is possible that” in the restatement. One exception would be if this conditional language is part of your original thesis statement and your paper is devoted to discussing a topic that is only a possibility, not something you are stating is definitely the case. Otherwise, maintain a level of confidence.
- While maintaining confidence is crucial to the success of your paper, it’s important to acknowledge when opposition exists and not to use absolute statements which may alienate readers. Confidence in your position and in the fact that you’ve proven your point is one thing; blind certainty in your opinion is another!
Making the Restatement Distinct from the Thesis

- You can use your word processor’s thesaurus function for this, an online thesaurus, or a good old-fashioned paper thesaurus. If you use a thesaurus, however, check your chosen word in the dictionary to ensure that you know its precise meaning. Thesauruses group words very loosely by general meaning, and there is often a significant difference in connotation between them.
- It’s not necessary to change every single word, such as prepositions (“in,” “on,” “above,” “over”) and articles (“a,” “an,” and “the”). Spend your time focusing on words/phrases that receive the most emphasis, like those that are central to the points you’re making.

- Try varying your sentences by starting with different parts of speech. For example, if you began the original thesis with a prepositional phrase, start the restatement with the subject of the sentence. For instance, if the thesis starts out “Around the turn of the nineteenth century in England, women frequently…”, you might start your restatement out with something like “Women in early nineteenth-century….”
- Another way to vary the structure is to present your points in a different order. Many thesis statements include three ideas, presented in the order in which they will be discussed in the body paragraphs. When restating, you can list the points in an alternate order.

Community Q&A
- When restating your thesis, if you find that the statement doesn’t fit your paper anymore, you’ll want to go back to the body of your paper and try to find where things went off track. You may find that you need to revise the original thesis to reflect what you actually wrote in the paper, or that parts of the body of the paper need to be revised to better suit the thesis. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- While restating your thesis is essential to the conclusion of your paper or speech, it’s not enough. You will need to emphasize main points and, depending on the assignment/goal of the paper, you may also need to call your audience to action, discuss the implications of what you have talked about in the paper, or make predictions for the future. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Think of the restatement as a new, more powerful version of your thesis—you’ve written the paper and learned a lot over that process, and now you have all of this knowledge to draw on. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/writing-conclusions.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/cliches/
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/conclusion
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bob Lanchester
May 26, 2017
Did this article help you?

Madison Luoma
Mar 14, 2019
Petch Phanpha
Oct 2, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
How to Restate a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement —a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments.
But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of it—you also need to restate the thesis statement in the conclusion. Moreover, it should be paraphrased using a more diverse vocabulary.
If you’re unsure about how to restate a thesis, this article by Custom-Writing.org will be helpful for you. Here, you will find:
- various rephrasing strategies,
- a step-by-step guide,
- the most actionable thesis restatement tips.
- ✍️ Thesis Restatement Definition
- ✅ Step-By-Step Guide
- 💡 Rephrasing Strategies
- 📋 Example Sentences
- 🖼️ How to Reframe
- ✨ Bonus Tips
🔍 References
✍️ what is a restated thesis.
A restated thesis is a reworded and restructured version of the original statement. It is presented in a conclusion or any other part of the essay requiring a recap of the paper’s main idea. It shouldn’t repeat the thesis statement word for word: instead, it’s better to focus on its content.
Why Restating Your Thesis Is Necessary
For a solid, effective academic work, a restated thesis in a conclusion is a must. Here’s why:
- A restated thesis helps reintroduce your central argument, thus enhancing its perceived significance.
- A correctly restated main claim makes the transition to the implications smoother.
- A paraphrased thesis restatement signals the readers about the wrap-up of your paper.
✅ How to Restate a Thesis Step by Step
Now, let’s dwell on the restatement process in more detail. We recommend you follow the steps we described below. It will help you make your paraphrased thesis effective without undermining your persuasive arguments.
| Reread the original thesis statement carefully. | |
| Determine in which person it is written (1 , 2 , or 3 ) and preserve that point of view in the rewrite. | |
| Outline all keywords and main points that should be present in the reworded thesis. Applying synonyms and using closely related words will make the sentence look different while still rendering the same idea. | |
| Think of expanding the thesis with your original contribution without altering its meaning. | |
| Paraphrase the thesis using one of the strategies we’ve laid out below. |
💡 How to Rephrase a Thesis: Different Strategies
You can approach the restatement of thesis in several ways. Here are the best strategies that will make your argument effective and easily understood.

How to Restate a Claim by Substituting Synonyms
English is a language rich in synonyms, so you’ll hardly experience any trouble finding suitable substitutes for the words you’ve used in the original thesis. You can also try out an online reword generator or thesis statement maker to get different versions of your central claim.
For instance, imagine that this is your thesis:
People of color have achieved pronounced success in the fight for their civil rights and equality in the USA over the last century,
You may experiment with synonyms as freely as you want. Here are some variants:
- The 20-century civil rights movement gave many rights and freedoms to the minorities in the United States.
- The situation with racial equality improved significantly over the past 100 years, giving racial minorities a strong voice in American society.
Restating Your Thesis by Altering the Sentence Structure
The syntax is also a rich source of inspiration for thesis changes. If the original statement is compound, divide it into several shorter sentences. If you’ve used several simple sentences in the first version, consider combining them into one longer statement.
Here is an example of altering the thesis’ structure without changing the main points:
| Original thesis | Reworded thesis |
|---|---|
| Diabetes is a growing problem in the USA, affecting over 100 million people today. | With the number of people with diabetes exceeding 100 million these days, one can hardly deny that diabetes is a pressing public health concern. |
In the original version, we started by focusing on diabetes. In the reworded thesis, we presented the numbers as the first piece of data. This way, we’re directing the reader’s attention to the gravity of the problem.
How to Restate Your Thesis by Changing the Tense
In most cases, the original thesis statement uses future or present tense. It helps to inform the readers about what they are about to read. For instance, it can start with an introductory phrase:
I will argue that homework should be canceled to give students more free time and ease the burden of high school studies.
In this example, the thesis statement is written in the present tense. It links to the general statistics of time students spend on their homework. You can transform this statement into a past-tense sentence in the conclusion, showing that your argument has been proven.
The presented evidence showed that students benefited from homework cancellation and had more quality time for their hobbies and relaxation.
Restating a Thesis by Shortening or Lengthening It
The length of your thesis statement also matters. You may present it in a shorter way at the beginning of your paper, focusing only on the gist of your research question. Later on, once the arguments are laid out and explained in detail, you can present a more extended version of the initially formulated problem.
| Original thesis | Reworded thesis |
|---|---|
| Assigned seating in canteens can help address the problem of school bullying. | Bullying practices like refusing a seat to a classmate will become impossible if students are assigned a fixed seat in the canteen. |
In this restates thesis example, we have extended the original idea, explaining what “assigned seating” and “school bullying” mean. This way, the reworded version could embrace the evidence discussed in the argumentative essay’s body.
Restating a Thesis by Linking It to the Research Problem
The strategy we’re about to describe is suitable for use in research paper writing. You will need to tie the thesis statement to the problem you’ve outlined in the introduction, linking it to the issue you’re examining.
For instance, in an essay on child obesity in the USA, you can restate the thesis as follows:
Although preventive healthcare has witnessed much advancement in the past decade, evidence proves that child obesity is still on the rise, with alarming annual increase rates.
📋 How to Restate a Thesis: Example Sentences
Now, let’s examine how to rephrase a sentence in practice. Have a look at these examples:
Example # 1
| Original thesis | Reworded thesis |
|---|---|
| Body image distortion is a frequent symptom of eating disorders. | The way people perceive their body shape indicates how healthy their self-image is. Research proves that individuals with a distorted body image are vulnerable to developing an eating disorder or already have this condition. |
Here, we expanded the thesis statement by making it longer and adding some details.
| Original thesis | Reworded thesis |
|---|---|
| Marijuana legalization opens new paths for teenage substance abuse. | The rates of teenage cannabis use have been on the rise because of the recent recreational and medical cannabis laws. |
Here, we have changed the sentence structure by switching the first and second parts. The first example focuses on the legalization of marijuana, while the second version starts by mentioning the rising rates of teenage weed consumption.
| Original thesis | Reworded thesis |
|---|---|
| I will argue that healthy eating habits develop due to a positive family example. | The presented evidence proved the prominent role of family eating examples on the child’s development of eating habits. |
In this example, we’ve changed the thesis statement’s tense from future to past, showing how an intention transformed into a completed task.
🖼️ How to Reframe a Reworded Thesis?
Once you’ve approached the conclusion paragraph of your work, it’s time to think about reframing your main claim. It’s important not to duplicate the introductory thesis because its role in the final section is different. Here are some workable reframing suggestions:
- Reword the original thesis and put it at the beginning of your conclusion. It will bring the focus back to your initial research purpose.
- Enumerate the central claims you’ve focused on. They can be compiled from topic sentences used in the body paragraphs.
- After restating the thesis, you can dwell on the broader significance of the problem you’ve examined. Make a logically related call to action based on the cited evidence. You can also mention your study’s limitations and clarify what additional research is needed.
✨ Bonus Thesis Statement Tips
Now, it’s time to give you a bonus for careful reading: our tried-and-tested tips for good thesis rewriting. Check them out:
| ❌ | Never apologize for your opinion or research findings. Any phrases like “though I’m not an expert,” “it’s only my opinion,” and so on reduce your credibility and make the reader doubt your expertise. |
| ✔️ | Acknowledge the counterarguments. If you stick to your viewpoint only, the paper may seem biased. So, it’s always more effective to give credit to both sides of the argument. |
| ❌ | Avoid using clichés as much as you can. That point is self-explanatory. |
| ✔️ | Use effective sentence starters instead of the trivial “in conclusion…” to avoid seeming dull. Some original ideas for your conclusion are: |
As you can see, rephrasing a thesis statement requires effort. Using extensive vocabulary and syntax will help you restructure the content and retain its meaning. And, of course, make sure to follow our tips!
Further reading:
- Best Thesis Statement Examples with Expert Comments
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper: Examples & Tips
- How to Write a 5-Paragraph Essay: Outline, Examples, & Writing Steps
- What Are the 5 Different Types of Essays? A Complete Guide
❓ How to Restate Thesis in Conclusion FAQs
Restatement of your thesis involves restructuring and changing the vocabulary originally used in the introduction. However, the altered thesis should preserve your work’s meaning and central message.
You will typically need a reworded thesis in a conclusion paragraph. This part of your essay or research paper should wrap up everything you’ve said and summarize your claims in different words.
When composing your essay conclusion paragraph, it is vital to reword your thesis statement initially presented in the introduction. This strategy will help you make the conclusion sound non-redundant while preserving the original main idea.
When restating the claim, you do the same work as when you reword the thesis. You need to change the wording and syntax while preserving the overall meaning of the original claim.
A good example is as follows: “children should wear uniforms at school.” The reworded thesis would contain the same meaning rephrased in your own words: “Uniforms are recommended for all students.”
- Writing the Conclusion: Indiana University Bloomington
- Writing Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs: University of Minnesota
- How to Restate a Thesis Statement: Classroom: Synonym
- Writing a Paper: Conclusions: Walden University
- Conclusions: Purdue University
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions: Harvard University
- Thesis Statements: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

Discourse is the way people talk about any specific topic. It’s also the way in which language is used to convey social and historical meanings. Discourse analysis is the process that helps to understand the underlying message of what is being said. Sounds interesting? Keep reading to learn more. This in...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

How to Rephrase a Thesis Statement for the Conclusion

A thesis statement is the most critical part of any essay, research paper, term paper, or academic paper.
Most professors, instructors, or teachers will look forward to reading an engaging thesis statement. Another thing they will also focus on is how you restate the thesis in the conclusion of an essay or research paper.
For every thesis in the introduction, there must be a restated thesis statement at the beginning of the conclusion.
If you are not conversant with how to restate a thesis, you came to the right place because we will look at the steps, tips, and strategies to use so that you keep the spirits of your readers high even as they exit reading your piece of written text.
Restating a Thesis
A thesis restatement comes at the beginning of the conclusion paragraph . Note that when restating the thesis, you are simply rewording, restructuring, reorganizing, and representing the original thesis statement in the introduction within your conclusion.
There are many reasons why many professors and guides for writing various types of papers will insist on having a restated thesis as part of the first section of the conclusion paragraph.
Restating the thesis helps the readers to close the loop of reading your text by seeing how you have proven the thesis in your body paragraphs.
It also helps to bring closure to the readers without leaving them in suspense. You are also reintroducing the central argument, enhancing the perceived significance your readers developed as they started reading.
A restated thesis also makes an excellent transition to other parts of the conclusion, such as a call to action, recommendations, or implications.
Steps for Restating a Thesis in a Conclusion
Understanding the thesis restatement process will go a long way in ensuring you achieve the benefits we have discussed above. You want to paraphrase your thesis so that even though they deliver the same message; they have a different organization, structure, and flow, making your writing persuasive and compelling.
1. Read the original thesis statement
After writing your introduction and body paragraphs, it is expected that you will have refined the preliminary thesis statement into a final thesis statement. Now, when you need to restate the thesis, for the purposes of concluding, begin by reading the final thesis statement of your essay or research paper, whatever writing you are undertaking. Reading the original thesis helps you to identify its focus and have a good picture of how to restate it in the conclusion.
2. Decide where you want to place it
Although many people might think that a restated thesis must appear at the beginning of the conclusion, that is not always the case. Therefore, you have to decide where you will place the restatement. At this stage, having an outline of the conclusion paragraph would be ideal, and it will help you figure out where to restate the thesis without making mistakes. All the same, having the restated thesis at the beginning of the introduction saves you time. Writing a conclusion is not cast in stone; you can take whatever approach you like as long as you achieve the intended purpose.
3. Look at the perspective of the original thesis
To restate the thesis better, consider the original thesis's point of view or perspective. You want to maintain the same person you wrote the thesis and the subject, even if it means rewriting the entire thesis.
4. Focus on the main points in the body paragraph
If you feel lost in how to restate the thesis, outline the main points and keywords you presented in the body paragraphs. An excellent way to quickly do this is by reading each topic sentence of the body paragraphs. Remember, your restatement should have the information you have discussed and portray the links you have established in your paper.
5. Express the significance of your argument
You have to justify your paper's central argument to validate the restated thesis. You should let your readers know why they should care about the topic you are writing about. Expand the thesis, so you have the original contribution without altering the intended meaning.
6. Paraphrase the thesis
Having identified everything that sets you up for successful thesis restatement, ensure that you paraphrase the thesis so that you have a restated thesis that meets all the criteria set in the rubric. Let's look at some ways to make the restated thesis stand out.
How to Rephrase or Paraphrase a thesis Effectively
Restating a thesis is about achieving different wording and flow but maintaining the meaning of the original thesis. This can be achieved in many ways. In a nutshell, you can restate the thesis using synonyms, changing the sentence structure and tenses, shortening or lengthening the thesis, and writing the message by linking it to research. Let's have a detailed look at each of these strategies.
Link your thesis to research
If you are writing a research paper or an essay, you must tie the thesis to the research problem stated in your introduction.
Change the Sentence Structure
You can take advantage of the fact that you can play around with the arrangement of words (syntax) as an inspiration to alter your original thesis statement when restarting it. You can restructure the original thesis into smaller or shorter sentences and then combine them again without altering the meaning you presented earlier in the introduction paragraph. You can rearrange the clauses in a sentence but maintain the same meaning.
Shortening or extrapolating the original thesis
A thesis statement is clear and concise. If your initial thesis statement was shorter, consider having a longer restated thesis at the end of your paper. This is always the case with most restatements. It helps spread out the main arguments or points in the body paragraph so that the readers are reminded about what they just read and how your promise in the thesis statement has been achieved. Summarizing the thesis statement when restating it should be done when focusing on the main idea.
Substitute synonyms
To effectively rephrase, paraphrase, or reword a thesis, you can use synonyms of the words used in your original thesis statement. Take advantage of dictionaries and word thesaurus but ensure that you maintain the same meaning without being ambiguous. Thanks to the richness of English in synonyms that mean the same thing, you will not have a lot of challenges restating a thesis using synonyms.
Change the tense
There is power in the way you can use tenses when restating a thesis statement. In most instances, the thesis statement is written in either present or future tense. You can take advantage of this and write a thesis statement in the past tense, emphasizing the main points you discussed in the body paragraphs.
Tips for Thesis Restatement (what works and what doesn't)
We are in the business of writing custom papers for diverse groups of clients, from students to professionals and scholars. Therefore, we keep trying, researching, and reading more about how to perfect the papers we write. Out of the many essays, theses, proposals, research papers, term papers, and dissertations we have written, we can confidently give the tips below as surefire ways to restate the thesis in the conclusion.
- Never apologize when restating a thesis. After all, you have fielded the best proof through evidence and examples supporting your claims in the essay. An apology at this point only weakens your conclusion paragraph, leaving your readers confused even more.
- When writing the thesis statement in the conclusion, acknowledge the counterarguments and counterclaims. Instead of sticking to your main point of view, show maturity by giving credit to either side of an argument.
- Don't use clichés when restating the thesis. It is the same thing as using filler words within your body paragraphs; it dilutes the sweetness of your writing.
- Use conclusion sentence starters to introduce your restatement. You should try as much to avoid the common conclusion starters such as "to sum up, in conclusion, …etc."
- You should reword the original thesis and put it effectively within the beginning of your conclusion, even though you can put it anywhere. It is the easiest approach and makes it easy to locate the restated thesis and allows readers to refocus on the research purpose or purpose of the essay.
- You should be concise while making meaning at the same time.
- You should be objective, focused, and neutral in your stance . Instead of using judgmental language, stay neutral when rewriting the thesis for your introduction.
- You can compile the topic sentences in the body paragraphs and enumerate the central claims when restating the thesis.
- After restating the thesis, you should expound on the significance of your topic . You should logically explain why your readers should care based on the findings. You should call the readers top action and discuss implications and limitations.
- Don't contradict yourself when writing the thesis a second time, as this leaves your readers confused. You should also avoid introducing new information.
- Ensure that your restated thesis has a good choice of words and sound flow and does not counter the meaning of the original thesis . Remember, the thesis and restated thesis are sisters only that have different appearances but stand for the same thing.
- You should view the restated thesis statement as a powerful version of the original thesis that cements your central idea in the readers' minds.
- Avoid using incorrect tenses and modifiers when restating the thesis. When you use the wrong tenses, you confuse the readers, as when you incorrectly modify the subject.
- Be confident as you restate the thesis to have a strong conclusion paragraph.
Examples of Original and Restates Thesis Statements
Below are examples of restating a thesis statement to help you figure out how to do it when writing your conclusion paragraph.
|
|
|
|---|---|
| Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in muscle loss and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers. | Banana Herb Tea has known effects on body weight and muscles, making it dangerous to customers. |
| While most American families would view consanguineal marriage, or marriage between people from a common ancestor, as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family | Although consanguine marriage is disdained in American culture as incest and a threat to nuclear family structure, some societies, such as Iranians, prefer it to create family cohesion. |
| Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce, and farming in infertile soil is rarely profitable. | Unemployment and lack of arable land for profitable agricultural practices are the top reasons why hunger is persistent in Glandelinia. |
| Reading develops a child's mind by fostering comprehension skills, increasing vocabulary, and exposing them to new worlds they might not otherwise encounter. | Children develop essential skills such as comprehension, critical thinking, and vocabulary memory through reading, fostering exposure. |
| Even though portrayed as a threat on account of the loss of jobs, AI is a promising solution for medical applications with efficiency and high precision compared to humans and in disaster response. | Artificial Intelligence is the much-needed savior through creating efficiency in fields such as medicine and disaster response despite cutting jobs from humans. |
| Kidney donors should be well compensated financially for their sacrifice, given the grueling tests, invasive surgeries, and lifelong changes they must endure. | Like other organ donors, kidney donors should be compensated well financially to cater to the endurance they undergo through the entire process. |
| The internet does a wonderful job of connecting people worldwide at the click of a button, while at the same time, it also leads to negative experiences such as cyberbullying and body shaming. | Despite being used by others maliciously, the internet is a tool connecting people from around the globe. |
| With the growing global population, the utilization of natural resources such as land has grown to uncontainable measures leading to the encroachment of formerly arable lands to provide space for settlement, which has immensely contributed to world hunger that ravages many people from different parts of the world. | Population explosion globally is to blame for the rising world hunger affecting millions of people. |
| Childhood obesity and diabetes are the top growing lifestyle diseases among children in the USA, affecting millions of children, some of whom are already in school. | Given the astounding number of children affected by diabetes and childhood obesity, it is no doubt that these are the most pressing public health concerns that should be prioritized. |
| Marijuana legalization for recreational use opens room for the economy to benefit while simultaneously creating space for teenagers to abuse the drug. | Teenage abuse of cannabis has been on the rise recently, and legalizing it for recreational use threatens to catapult the rates further. |
| Although many video game learning strategies are already present in many college classrooms, perhaps the most controversial and most promising technique unique to video games is that of risk-taking | The use of gamification in the classroom for learning purposes should be pursued, especially those that entail risk-taking.
|
| Although 21st-century technology might seem the most important cause of cheating, a more fundamental problem is parents of high schoolers who put too much pressure on their children to excel in school. | Putting too much pressure on high school and college students for academic excellence is to blame for the rising cases of cheating. |
| Among the many learning tools James Paul Gee explores in video games, the most significant ones—system thinking, collaborative tasks, and situated meanings- all emphasize seeing information as a whole rather than disconnected facts and ideas as education is usually taught. | As Paul Gee observes, systems thinking, situated meanings, and collaborative tasks are some of the best learning tools in video games, which impact learners' academic performance. |
What are the components of a strong thesis?
A strong thesis statement should answer the question of "how?" and "why?" about the topic and should do so with specificity. It takes a stance, justifies discussion, and is specific. Therefore, it should have a specific noun, action verb, and assertive predicate. For instance,
Example: The tax policies (specific noun) of the current administration threaten to reduce (action verb) the tax burden on the middle class by sacrificing education and healthcare programs for anyone ( assertive predicate ). These should also feature when you restate the thesis, even if you rephrase, change the structure or tenses, or shorten the original thesis.
What does rephrasing or restating the thesis statement mean?
It means reading the original thesis and expressing it differently but maintaining the original meaning. The restated thesis is placed in the conclusion paragraph, preferably in the begging immediately after the conclusion starter.
Where does the restated thesis go?
When restating the thesis, placing it at the beginning of your conclusion paragraph immediately after the conclusion paragraph starter helps you to avoid losing your readers. It is the most convenient location, although you can place it anywhere within the conclusion. Placing it at the beginning helps you to have a narrow to the broad conclusion that gives better closure to the readers.
How does one restate the thesis?
To restate the thesis statement, read the original thesis statement, then rephrase it by changing the tenses and structure, using synonyms and different vocabulary, shortening or lengthening it, and paraphrasing it but maintaining the original meaning. Avoid using a thesis generator when restating your thesis because it will not give you the correct feel if you did it alone.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How to Restate A Thesis: Your Detailed Guide

A thesis acts as your research paper’s main pillar, guiding the readers to the key points on the paper and the direction that you took. A thesis statement comes at the introduction, but you will need to restate it in the conclusion. Notably, a lot of students find this challenging and keep asking, “How do you rephrase a thesis statement?” and “Are you supposed to reword your thesis in the conclusion paragraph?”
To help you restate thesis of your paper appropriately, we have highlighted the key steps that you should follow. Make sure to also check the examples and practice the different ways to restate a thesis until you can hack it like a pro.
What Does Restate Thesis Mean?
Before we can look at the steps involved in restating a thesis, it is important to start by asking the questions, “What does restating means?” and “How long does a thesis restate have to be?”
Restating means that you are highlighting something that you had already brought out, in this case, the “thesis of your paper.” Therefore, you are simply reminding the readers about the points that you were trying to put across in the entire paper, but without sounding repetitive. When it comes to length, there is no specific rule on it, but you should try to make it approximately the same length as the original thesis.
When you restate thesis and conclude the paper well, your work will look complete, professional and earn you a better grade.
Restate Thesis Statement: Decide Where to Position It
In most cases, college students restate the thesis at the start of their conclusion. You might also want to place it on a different section of the conclusion, other than the beginning of the conclusion. When teaching students how to restate a thesis in a conclusion, we recommend them to use the method that will make their work look unique.
For example, instead of restating the thesis as the first sentence, consider starting the conclusion with a rhetoric question followed by your restated thesis statement. Here is an example below. “Will we ever appreciate the importance of saving our rainforests? Rainforests act as the largest carbon sinks on the globe, as well as home to thousands of species, and everyone can play a role in their protection.”
Note that since there is no specific formula on how to restate a thesis statement , it is advisable to start by crafting a draft conclusion and then decide where to position it. Actually, you might consider several positions until you get the perfect spot.
How to Rephrase a Thesis: Make It to have a Deeper Impact
By the time a reader gets to the conclusion of your work, it implies that he/she has already read the entire paper and has a clear idea about your stand on the topic. Therefore, you should take advantage of this and rephrase the thesis statement to deliver a deeper level of emotional effect.
One way of driving this deeper emotional impact is addressing the reader directly, and here is an example. If you were working on a paper with a topic, such as cybersecurity for startups, a good way to start restating the thesis might be:
- “As a startup enterprise owner …”
- “To strengthen your information security as a small business owner …”
Ways to Restate a Thesis: Answer the Question, “So What?”
The stated thesis at the start of your introduction might not provide the answer to the question, “so what?” However, the restated thesis , in your conclusion, should comprehensively answer the question. The answer seeks to inform the reader about the significance of the arguments in the paper to avoid leaving him/her hanging.
For example, if your paper was talking about teenage alcohol and substance abuse, make sure to answer the question “So what?” by showing what it does to teenagers. This can be something such as this; “ Additional awareness of the dangers of substance abuse, such as alcohol, should be emphasized because teenagers are more prone and likely to give in because of peer pressure rather than the implications of substance abuse.”
Avoid Making Apologies when Rewording a Thesis
When working on the conclusion of your paper, it is prudent to be confident that you provided ample proof in the body. Therefore, as you restate the thesis, you should not make apologetic statements because they undermine your argument. Such statements, which you should avoid, include:
“It appears that …. “ “It is possible that …” “It is my opinion that …”
The only time when using such statements when restating your thesis might be okay is when the topic of discussion was simply a possibility.
Restate Thesis Statement by Varying the Tense
When writing an paper, the thesis statement at the introduction might have been done in the future tense, informing the reader what to anticipate in the rest of the paper.
For example, a paper looking at coal production might have a thesis such as this, “ I will examine the effects of using coal in Azerbaijan ….” When restating the thesis, you can change the tense, and put it in the past, so that it looks something like this, “ I evaluated the how harmful the use of coal is to the environment in Azerbaijan …”
Seek Writing Help to Restate Thesis of Your Paper
When you work on any piece of assignment, how you wrap it up, especially in the conclusion, is very important to avoid leaving your reader in suspense. In this post, we have demonstrated how to restate a thesis statement, but you should consider reading a carefully done restate thesis and practice more to hone your skills. However, if you are still finding the task a challenge, even after reading a restate thesis example, consider seeking writing help from an expert.
We have a pool of qualified writers who are ready to help you with your academic assignments, and all you have to do is ask us for help to “restate my thesis.” They know how to start a paper, write the body professionally, and restate the thesis like pros. Furthermore, our services are cheap, and you can count on our writers for quality work and top grades.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Dissertation Proofreading and Editing
- Dissertation Service
- Dissertation Proposal Service
- Dissertation Chapter
- Dissertation Topic and Outline
- Statistical Analysis Services
- Model Answers and Exam Notes
- Dissertation Samples
- Essay Writing Service
- Assignment Service
- Report Service
- Coursework Service
- Literature Review Service
- Reflective Report Service
- Presentation Service
- Poster Service
- Criminal Psychology Dissertation Topics | List of Trending Ideas With Research Aims
- Cognitive Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Top Ideas For Research in 2024
- Social Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Latest Research Ideas
- Top 10 Clinical Psychology Dissertation Topics with Research Aims
- Educational Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Interesting Ideas For Research
- Customer Service Dissertation Topics | List of Latest Ideas For Students
- 15 Interesting Music Dissertation Topics
- Business Intelligence Dissertation Topics | List of Top Ideas With Research Aims
- Physical Education Dissertation Topics | 15 Interesting Title Examples
- 15 Top Forensic Science Dissertation Topics with Research Aims
- Islamic Finance Dissertation Topics | List of 15 Top Ideas With Research Aims
- Dissertation Examples
- Dissertation Proposal Examples
- Essay Examples
- Report Examples
- Coursework Examples
- Assignment Examples
- Literature Review Examples
- Dissertation Topic and Outline Examples
- Dissertation Chapter Examples
- Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Topics
- Academic Library
- Assignment Plagiarism Checker
- Coursework Plagiarism Checke
- Dissertation Plagiarism Checker
- Thesis Plagiarism Checker
- Report Plagiarism Checke
- Plagiarism Remover Service
- Plagiarism Checker Free Service
- Turnitin Plagiarism Checker Free Service
- Free Plagiarism Checker for Students
- Difference Between Paraphrasing & Plagiarism
- Free Similarity Checker
- How Plagiarism Checkers Work?
- How to Cite Sources to Avoid Plagiarism?
- Free Topics
- Get a Free Quote

- Report Generating Service
- Model Answers and Exam Notes Writing
- Reflective or Personal Report Writing
- Poster Writing
- Literature Review Writing
- Premier Sample Dissertations
- Course Work
- Cognitive Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Physical Education Dissertation Topics
- 15 Top Forensic Science Dissertation Topics
- Top 10 Clinical Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Islamic Finance Dissertation Topics
- Social Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Educational Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Business Intelligence Dissertation Topics
- Customer Service Dissertation Topics
- Criminal Psychology Dissertation Topics

- Literature Review Example
- Report Example
- Assignment Example
- Coursework Example

- Coursework Plagiarism Checker
- Turnitin Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing and Plagiarism
- Best Dissertation Plagiarism Checker
- Report Plagiarism Checker
- Similarity Checker
- Plagiarism Checker Free
- FREE Topics
Get an experienced writer start working
Review our examples before placing an order, learn how to draft academic papers, how to restate your thesis: a beginner’s guide & examples.

An Introduction to Research Paradigms: Understanding the Basics

Exploring Various Types of Dissertation

- Dissertation

Restating a thesis is often considered a complex job. The good news is that you need to come up with smart hacks to structure your thesis in a better manner.
Not only a well-structured thesis statement can help you convey your message effectively, but it also promotes better comprehensiveness. With proper formatting, positioning, and structure of a thesis, a reader is likely to grasp the idea within the first 4 seconds of reading the thesis.
Review Our Quality Dissertation Examples
Get Free 3+ Dissertation Topics Within 24 Hours
With that said, let's understand what it takes to restate a thesis that remains accurate and relevant till the end.
3-Step Dissertation Process!

Get 3+ Topics

Dissertation Proposal

Get Final Dissertation
Step 1 analyze the original thesis statement.
Proper Analysis is the key to identifying the loopholes in any thesis statement. If your original thesis statement looks incomplete or dull, repeat the initial research required for writing.
Below is a quick checklist to analyze your final thesis statement for better readability
- Identify the key ideas
- Repeat your arguments
- Present your claims
- Keep your focus in one place
- Always keep the central argument in focus
Step 2: Revise your Thesis Statement
Starting from the first thesis statement, it's a summary of your subject used to support the argument of the entire thesis.
It is the first thing a reader reads at the start of a thesis, also often considered the main idea of the essay.
How to Write A Thesis Statement? Expert Tips and Examples
The easiest way to restate a thesis is by replacing complex words with simpler nouns. Doing this work helps avoid repetition, captures the main idea of the thesis, and keeps things fresh.
To restate your thesis statement, pick one strong idea you would like to talk about in the entire thesis.
Step 3: Summarise the Main Points
Once you're done restating your thesis statement, the next step is to summarise all the other important points you're going to cover in the thesis.
Exploring the ideas will help you better convey your message in fewer words.
To summarise the main points, pick the central argument and brainstorm other related ideas that you can think of from the reader's perspective.
Summarize Well: How to Write a Good Executive Summary?
Step 4: Use Active Voice
Writing a thesis in Active voice makes it 10x more impactful than using passive voice. With a quick manual check, you can easily highlight sentences that can be changed into passive voice. Extract those abstracts and use a passive-to-active converter.
Step 5: Be Specific
Specificity is the key to a good thesis; nothing else can beat that. To be specific with your research, state strong points with references. Don't try to be vague or use fancy words that have a negative impact on the thesis.
Step 6: Build Connections
A thesis is a set of connected ideas collected to reinforce the central argument. Restating a thesis is another name for creating connections with main points.
Try to use more transitions that connect one paragraph to the other without killing the main crux of the idea.
However, make sure of the consistency so that it keeps the reader from the main idea.
Step 7: Give it a Final Thought
Adding a personal touch to your thesis statement can be the ultimate deal sealer.
After every paragraph, go through your thesis and make any changes required.
This step helps you add or subtract anything for a better restatement of your thesis.
At this point, you can also add CTAs, revise the final thoughts, shorten your concluding remarks, and add a small reflection paragraph at the end to summarise everything.
Step 8: Check for consistency
Consistency is a must-have for any thesis that has to be published online. Once you're done with your thesis, check for consistency if any paragraph of your thesis needs to be more consistent.
Some of the easy ways to make a thesis consistent are:
- Clearly state the focus of your essay.
- Use a parallel structure in your easy
- Try to add more verbs and only talk about the main point of your thesis.
- Use consistent terminology in the thesis that makes it easy for readers to understand.
- Take care of the formal tone of the essay. Avoid changing tone in between and stick to the same tone & voice for the entire thesis.
- Use traditions to feed the curiosity of your reader. Always look for ways to add logic and avoid complex terms that may confuse the reader.
Step 9: Write for the Audience
The main objective of a thesis is to inform the reader of the latest facts and updates about a topic or subject.
Take a moment to think of the language they would like to read. Keep the tone informative and friendly for better comprehension of the idea.
Make every sentence clear and complete so the reader doesn't have to research from external sources.
Step 10: Use Emoticons
Using the right emotions at the right place is key to attracting the reader in the first 10 seconds.
Whether you want to connect with the audience or reinforce the arguments for better understanding, using emotions is the key.
Ending with a Verdict
Though a research thesis doesn't allow an individual's opinion or interests, giving a neutral verdict, dissent sounds like a bad idea.
Some common examples of a verdict include.
- an ending statement that summarizes the whole idea of the thesis
- A Call to action or CTA that guides the readers on what to do next
- An unbiased recommendation discussed mutually in the thesis
- A reflection statement that describes the broader implications of the topic
Step 11: Edit, Format, and Publish
Like any content, your research thesis also needs to be revised during the final editing.
It's the time when you should edit the essay to ensure it's clear, complete, and error-free.
The good idea is to spare an hour to review any possible errors that may create an inconsistency with your content.
Once done editing, consider formatting the thesis in a way that looks read well. Avoid stuffing all the information in a single paragraph but try to break your idea into multiple sections.
Checklist for Restating a Thesis
- Be specific about the introduction and build arguments.
- Answer why, what, and how this research thesis is going to be helpful
- Choose a topic sentence that represents your thesis in less than 15 words
- Conclude the thesis to summarise the whole idea
- Offer new arguments and back them with factual information
- Try to convey more information in fewer words
- Draw a vision for the thesis before writing
- Focus on the goal and only give justification for that
- Don't hesitate to find and include new ideas in every paragraph
- Check the flow of the paragraph and delete any unnecessary information.
Acknowledgement for Thesis & Dissertation: A Guide on How to Write Acknowledgement for Dissertation
Questions to Ask Yourself Before Restating a Thesis
Unlike blogs or articles, a thesis is not just stuffing information into paragraphs, but it's more than that.
Before writing a thesis, make sure to ask yourself a few questions. Such ae
- Did I fulfil the goal of the thesis
- Have I solved the challenges for the reader
- Is it thesis specific for the target audience
- Does my thesis answer the what, why, and how to question
- Does my thesis have an impact on words
How to Know if Your Thesis is Strong
A strong thesis allows a better understanding of the idea discussed
While there are many ways to know if your thesis is strong, the easiest thing to do is review it yourself and ask a few questions.
- Have I constructed the thesis the right way?
- Have I created a connection between the A and B factor
- Have I made my thesis specific enough
- Does my thesis clarify all the objections?
- Does my thesis support the thesis or topic statement
- Is my thesis relevant to the reader's concern?
- Does my thesis propose a useful solution?
How to Improve Your Thesis?
Improving an existing thesis is not a hard nut to crack. All you need to do is run a few manual checks to ensure everything is in place.
Here are a few things you can do to improve your thesis
- Back with Strong Evidence
Having strong evidence is the only way to make your thesis effective.
Add evidence that makes sure your thesis is provable by evidence.
- Keep it Short and Precise
No one likes to read stacks of long paragraphs with overstuffed information. Try to keep your thesis strong, clear, and to the point.
Delete excess information that is of no use to the thesis.
- Focus on one Solution
A good thesis should not propose more than one solution to the reader. The simplest idea is not to give other distractions to the reader.
Stick to one idea and create more content that justifies the requirements.
Restating a thesis is not the hardest thing to o. With a small share of effort, you can easily manage to restate a thesis that doesn't seem repeated, arguable, or reinforced.
Your thesis should work around one idea or central argument only.
The process needs careful Analysis, attention to detail, and an in-depth understanding of the audience.
Start by restating your thesis statement and try to retain the original essence of your thesis without any repetition or forceful reinforcement.
FAQs about Restating Your Thesis
Get 3+ free dissertation topics within 24 hours.
Your Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Masters PhD
Area of Research
Related posts

Dissertation Interview Questions | Everything You Need To Know

Conducting Interviews for Your Dissertation | A Comprehensive Guide

What is Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle and How Can It Benefit You? | Applications and Example
Comments are closed.

- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- Writing Guides
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Writing Tips
How to Restate Your Thesis: 5 Strategies
November 22, 2023
Examining the Purpose of Restating Your Thesis
Restating your thesis in the conclusion of your essay serves a vital purpose in reinforcing the main argument and leaving a lasting impact on your readers. This section will explore the significance of restating your thesis and why it is not merely a repetitive exercise.
- Reinforcement: Restating your thesis reaffirms the central idea of your essay. By reasserting your main argument, you emphasize its importance and remind readers of the key point you want them to remember.
- Summarization: Restating your thesis allows you to summarize the main points and evidence presented in your essay. It provides a succinct overview that helps consolidate the information and reinforce your main argument.
- Closure: Restating your thesis brings a sense of closure to your essay. It signals to the reader that you have reached the end of your discussion and allows for a satisfying and cohesive conclusion.
- Lasting Impact: By restating your thesis effectively, you can leave a lasting impression on your readers. It helps solidify your argument in their minds and prompts them to reflect upon the ideas presented long after reading your essay.
In the following sections, we will explore various strategies and examples to help you master the art of restating your thesis in a compelling and impactful way.
5 Strategies for Effective Restatement of Your Thesis
Restating your thesis effectively requires more than simply repeating your thesis statement. Instead, it involves summarizing your main points and findings while communicating the overall significance of the argument.
Summarize Your Main Points
Summarizing your main points is a crucial step in restating your thesis effectively. It allows you to remind your readers of the key arguments, evidence, and examples presented in your essay. Here are some strategies to help you summarize your main points:
- Identify the main points: Review your essay and identify the main arguments or supporting points that you have made. These are the key ideas that contribute to your overall thesis.
- Condense the information: Take each main point and condense it into a concise statement that captures its essence. Avoid going into too much detail or providing new information. Focus on the core message of each point.
- Use bullet points or numbered lists: If applicable, present your main points as a list. This can help readers grasp the key arguments quickly and easily. Bullet points or numbered lists also create a visual break in the text, making it more reader-friendly.
- Order your main points strategically: Arrange your main points in a logical order that reinforces the flow of your essay. Consider prioritizing the most impactful or strongest evidence first.
- Avoid repetition: While summarizing your main points, be mindful of avoiding repetition. Restate each point in a way that adds value and emphasizes its significance without redundantly restating the exact same information.
By effectively summarizing your main points, you provide a concise overview of your essay’s key arguments and reinforce the foundation of your thesis.
Paraphrase Your Thesis Statement
Paraphrasing your thesis statement is an essential aspect of restating your thesis effectively. It involves expressing the main idea of your essay in a different way, using different words and sentence structures. Here are some strategies to help you paraphrase your thesis statement:
Change the sentence structure: Instead of using the same sentence structure as your original thesis statement, try rearranging the words and sentence structure to create a fresh and engaging restatement.
Example: Original thesis: “Climate change is a global problem that requires immediate action.” Paraphrased restatement: “Urgent measures are necessary to address the worldwide issue of climate change.”
Use synonyms and alternative words: Replace specific terms in your thesis statement with synonyms or related words. This not only helps avoid repetition but also adds depth and clarity to your restatement.
Example: Original thesis: “Education is crucial for societal progress.” Paraphrased restatement: “The advancement of societies heavily relies on the importance of education.”
Maintain the core message: While paraphrasing your thesis statement, ensure that the main idea or message remains intact. The restatement should still convey the central argument of your essay.
Example: Original thesis: “The government should implement stricter regulations on the usage of plastic to reduce environmental pollution.” Paraphrased restatement: “To combat environmental pollution, it is imperative for the government to enforce more stringent regulations regarding plastic consumption.”
By effectively paraphrasing your thesis statement, you provide a fresh perspective on your argument while staying true to the core message of your essay.
Connect Your Thesis to a Larger Idea or Context
Connecting your thesis to a larger idea or context helps emphasize the broader significance of your argument. It allows readers to understand the relevance and implications of your thesis statement in a broader context. Here are some strategies to help you connect your thesis to a larger idea or context:
Highlight the broader impact: Discuss how your thesis statement relates to a larger societal, cultural, or academic issue. Explain why understanding or addressing your thesis statement is essential in the larger scheme of things.
Example: Original thesis: “The portrayal of women in media perpetuates harmful stereotypes.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “Challenging the portrayal of women in media is an integral part of the ongoing fight for gender equality and empowering women.”
Provide historical or current examples: Demonstrate how your thesis statement connects to historical events, current affairs, or prominent figures. This highlights the relevance of your argument in a larger and recognizable context.
Example: Original thesis: “Corruption undermines the integrity of democratic systems.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “Throughout history, instances of corruption have been notorious for eroding trust in democratic institutions and fostering public disillusionment.”
Discuss the wider implications: Analyze the consequences or wider implications of your thesis statement beyond the scope of your essay. This helps readers understand the significance of your argument and its potential impact.
Example: Original thesis: “Automation in the workforce necessitates the need for reskilling and upskilling.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “The rapid advancement of automation technology not only requires individuals to adapt and acquire new skills but also poses significant challenges for educational institutions and policymakers in preparing the workforce of the future.”
By connecting your thesis to a larger idea or context, you demonstrate the broader relevance and impact of your argument, providing a deeper understanding for your readers.
Adding New Information or Ideas
While restating your thesis, you may want to introduce new information or ideas that support or expand upon your original argument. This can help enrich your restatement and provide further insight for your readers. Here are some strategies to add new information or ideas when restating your thesis:
- Present additional evidence: Introduce new evidence or examples that strengthen your argument and support your thesis statement. This shows that your original thesis is well-founded and backed by solid evidence.
- Include relevant statistics or research findings: Incorporate relevant statistics or research findings that further validate your thesis statement. This adds credibility and demonstrates a deep understanding of your topic.
- Discuss alternative perspectives: Address counterarguments or opposing viewpoints and explain how your thesis statement still holds strong despite these alternatives. This showcases critical thinking and strengthens the overall persuasiveness of your argument.
- Propose future implications or areas for further exploration: Suggest possible future developments or areas for further research and analysis related to your thesis statement. This expands the scope of your argument and encourages further engagement with the topic.
- Connect to current events or trends: Relate your thesis statement to ongoing current events or emerging trends. By highlighting the relevance of your argument to contemporary issues, you make your restatement more relatable and impactful.
Remember to integrate new information or ideas seamlessly into your restatement, ensuring they enhance and build upon your original thesis in a cohesive and logical manner.
Changing the Stance of Your Thesis
Sometimes, it can be effective to restate your thesis by presenting a different perspective or changing the stance of your original argument. This adds complexity and nuance to your restatement, engaging readers with a fresh viewpoint. Here are some strategies for changing the stance of your thesis:
- Acknowledge counterarguments: Address opposing viewpoints or critiques of your original thesis statement. Show that you have considered alternative perspectives and are open to a balanced discussion.
- Present a different angle: Introduce a related but contrasting aspect of your topic. This allows you to present a new interpretation or highlight a lesser-known aspect, challenging conventional thinking.
- Offer a qualified stance: Adjust the certainty or absoluteness of your thesis statement. Use words and phrases like “it is probable,” “it is likely,” or “there may be exceptions” to indicate a more nuanced or conditional stance.
- Explore the limitations: Discuss the limitations or constraints of your original thesis statement. This demonstrates critical thinking and an understanding of the complexities involved in your topic.
By changing the stance of your thesis, you demonstrate intellectual flexibility and engage readers with a thought-provoking restatement that encourages further exploration and discussion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Restating Your Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is a crucial step in effectively summarizing your main argument and reinforcing its significance. However, there are some common mistakes that should be avoided in order to maintain clarity and coherence. Here are some pitfalls to steer clear of when restating your thesis:
- Repetition of the exact same words: While restating your thesis, strive to express the main idea using different words and sentence structures. Repetition can make your restatement sound monotonous and redundant.
- Adding new information or ideas: Remember that restating your thesis is about summarizing and reaffirming your original argument, rather than introducing new information or ideas. Avoid incorporating unrelated or irrelevant content in your restatement.
- Changing the meaning of your thesis: Ensure that the restatement maintains the same core message or main argument as your original thesis statement. Avoid altering the meaning or taking a completely different stance without proper justification.
- Being too vague or general: Avoid being overly broad or generic when restating your thesis. Aim to provide a concise and specific restatement that accurately captures the main focus of your essay.
- Not addressing the main points of your essay: Your restatement should reflect the key points and supporting arguments discussed in your essay. Neglecting to encompass these important elements can weaken the overall effectiveness of your restatement.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can successfully restate your thesis statement in a manner that reinforces your main argument while maintaining clarity and coherence.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Debating in class or composing a persuasive paper is a fruitful intellectual practice. Doing so, participants and writers are expected...
Most students wonder whether it is possible to cite an article in an essay. The answer is “Yes”! Why not...
Let us explain what is what and how it can be used. An anthology is a published collection of poems...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
Prism's Guide: How to Restate a Thesis with Confidence
Written By:

Prism's Guide: How to Restate a Thesis with Confidence
Restating a thesis is an essential skill for any writer. It is the process of repeating the main argument of an essay or research paper using different words while maintaining the same meaning. This technique is used in the conclusion of an essay to remind the reader of the main points and leave a lasting impression. If you are wondering how to restate a thesis, this article will provide you with some effective tips and strategies.
The thesis statement is the backbone of any essay or research paper. It is a sentence or two that summarizes the main argument or point of view of the essay. Restating a thesis involves rephrasing the thesis statement in different words, but keeping the same meaning. This technique is important because it helps to reinforce the main argument and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The purpose of restating a thesis is to remind the reader of the main points and leave a lasting impression. It is important to note that restating a thesis is not the same as summarizing the main points. Instead, it involves using different words to rephrase the thesis statement while maintaining the same meaning. By doing this, you can reinforce the main argument and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Understanding Thesis Restatement
Definition and purpose.
Restating your thesis is the process of rewording the central argument of your essay or paper to remind the reader of your main point. The restated thesis should be clear and concise, and it should reflect the meaning of the original thesis. The purpose of restating your thesis is to reinforce the argument you made in your essay or paper and to help your reader remember what you said.
Differences Between Thesis and Restated Thesis
The restated thesis is not the same as the original thesis. While the original thesis is the central argument of your essay or paper, the restated thesis is a reworded version of the original thesis that reminds the reader of your main point. The restated thesis should be written in a way that is clear and concise, and it should reflect the meaning of the original thesis.
To restate your thesis, you should start by reviewing your original thesis statement and making sure you understand the main argument or assertion you presented. Then, you should determine in which person it is written (1st, 2nd, or 3rd) and preserve that point of view in the rewrite. Finally, you should outline all keywords and main points that should be present in the reworded thesis.
In conclusion, understanding how to restate a thesis is an important skill for any writer. By restating your thesis, you can reinforce the argument you made in your essay or paper and help your reader remember what you said. The restated thesis should be clear and concise, and it should reflect the meaning of the original thesis.
Strategies for Effective Restatement
Restating a thesis is an essential part of writing an effective conclusion to your paper. It provides a summary of your main argument and helps to reinforce the significance of your work. Here are some strategies to help you create an impactful restatement of your thesis.
Paraphrasing Techniques
One of the most effective ways to restate your thesis is to use paraphrasing techniques. Paraphrasing involves restating the thesis in your own words while retaining the original meaning. This technique helps to avoid plagiarism and demonstrates your understanding of the topic. To paraphrase your thesis, you can:
- Change the sentence structure
- Use synonyms
- Replace complex words with simpler ones
- Use different phrasing
Use of Synonyms and Sentence Structure
Using synonyms is another effective strategy for restating your thesis. Synonyms are words that have the same or similar meanings as the original word. By using synonyms, you can avoid repetition and add variety to your writing. Additionally, changing the sentence structure can help to emphasize different aspects of your argument. For example, you can use a rhetorical question or a conditional statement to restate your thesis.
Maintaining Originality while Restating
While restating your thesis, it is important to maintain originality. Avoid using clichés or overused phrases as they can weaken the impact of your conclusion. Instead, try to use unique and creative phrasing to reinforce your argument. You can also reflect on the journey of your essay and emphasize the significance of your work. Remember to keep your restatement concise and to the point.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a restatement that resonates with your audience and reinforces the strength of your argument. Remember to avoid common pitfalls such as using apologetic statements or vague language. With finesse and attention to detail, you can craft an effective restatement of your thesis.
Incorporating Restatement in the Conclusion
Restating the thesis statement in the conclusion is a crucial part of wrapping up your essay. It helps to summarize the central message of your essay and reinforce the main argument. Here are some tips on how to incorporate restatement in the conclusion effectively.
Transition to the Conclusion
Before restating the thesis statement, you need to transition smoothly from the body of your essay to the conclusion. You can use transitional words and phrases such as "In conclusion," "To sum up," or "Finally" to signal the reader that you are about to conclude your essay.
Summarizing Key Points
After transitioning to the conclusion, you should summarize the key points of your essay. This helps to remind the reader of the main ideas of your essay and reinforces your argument. You can use bullet points or a table to summarize the key points of your essay.
For example:
| Key Points |
|---|
| Point 1 |
| Point 2 |
| Point 3 |
Reinforcing the Main Argument
After summarizing the key points, you should restate the thesis statement in a way that reinforces the main argument of your essay. This means that you should use different words to convey the same idea as the original thesis statement.
For example, if your original thesis statement was "The use of social media has a negative impact on interpersonal communication," you could restate it as "In conclusion, social media has been shown to hinder face-to-face communication, leading to negative consequences."
By restating the thesis statement in this way, you are reinforcing the main argument of your essay and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
In conclusion, incorporating restatement in the conclusion is an essential part of wrapping up your essay. By transitioning smoothly, summarizing key points, and reinforcing the main argument, you can create a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
The Broader Implications of Your Thesis
After presenting your thesis statement and supporting it with evidence in the body of your essay, it is crucial to discuss the broader implications of your thesis in the conclusion. This section will guide you through different ways to discuss the implications of your thesis.
Discussing Research Findings and Limitations
One way to discuss the broader implications of your thesis is to summarize your research findings and limitations. This allows you to demonstrate the significance of your research and acknowledge any potential issues with your study. You can use tables or lists to summarize your findings and limitations in a clear and concise manner.
Explaining the Broader Context and Impact
Another way to discuss the broader implications of your thesis is to explain the broader context and impact of your research. This includes discussing how your research fits into the larger field of study and how it contributes to our understanding of the topic. You can also discuss how your research could be applied in real-world situations.
Offering a Call to Action or Final Thought
Finally, you can offer a call to action or final thought in your conclusion to encourage your readers to take action or think more deeply about the topic. This could include suggesting further research, proposing solutions to a problem, or encouraging readers to consider the implications of your research for their own lives.
Overall, discussing the broader implications of your thesis is an important part of any research paper or essay. By summarizing your research findings and limitations, explaining the broader context and impact of your research, and offering a call to action or final thought, you can demonstrate the significance of your research and encourage your readers to engage with your topic in a meaningful way.
Revising and Finalizing Your Restatement
Restating your thesis is not just about repeating the same words in a different order. It requires careful consideration of the main argument and an effective restatement that summarizes the key points while leaving a lasting impression on the reader. Here are some tips on how to revise and finalize your restatement:
Reviewing and Proofreading
Before finalizing your restatement, it is important to review your original thesis statement and ensure that you have covered all the main points. You can also use this opportunity to summarize the key arguments and evidence presented in your essay.
Once you have completed the review, it is essential to proofread your restatement for any errors in grammar, spelling, or punctuation. A poorly written restatement can undermine the credibility of your argument, so take the time to ensure that it is error-free.
Achieving Clarity and Closure
An effective restatement should achieve clarity and closure. It should clearly and concisely summarize the main argument and provide closure to the reader. To achieve clarity, use simple and direct language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may confuse the reader.
To achieve closure, provide a sense of finality to your restatement. This can be done by using phrases such as "In conclusion," "To summarize," or "Therefore." These phrases signal to the reader that you are wrapping up your argument and leaving them with a clear understanding of your main points.
Leaving a Lasting Impression
Your restatement should leave a lasting impression on the reader. It should be memorable and reinforce the main argument of your essay. To achieve this, consider using a powerful quote, statistic, or anecdote that relates to your thesis statement.
You can also use this opportunity to provide a call to action or suggest future research on the topic. This will leave the reader with a sense of purpose and encourage them to take action or continue exploring the topic further.
In summary, revising and finalizing your restatement requires careful consideration of the main argument, achieving clarity and closure, and leaving a lasting impression on the reader. By following these tips, you can create an effective restatement that summarizes the key points of your essay and reinforces your main argument.
Latest Articles
Ai for research paper writing with prism.

Prism's Guide: How to Organize a Literature Review

AI Market Research Tools: How Prism Can Help You Stay Ahead

Prism's Social Science Research Building: A Modern Facility for Cutting-Edge Research
Social Science Research Building (SSRB) is an iconic building located on the University of Chicago campus, with a rich history and architectural significance
Schedule a demo
How to Restate a Thesis: Techniques for Clear Communication
Restate a thesis with ease! Learn how to do it with pro tips to clearly and confidently reinforce your argument.
When it comes to how to restate a thesis, write essays, or make a point, your thesis statement is like the heart of your argument. It sets the tone and direction for everything that follows. However, many people overlook the importance of bringing the thesis statement back into focus at the end.
Restating a thesis in the conclusion is crucial. It reminds the reader of the main point that has been made throughout the writing. It’s a way to reinforce the argument and leave a strong final impression.
This article examines the importance of restating a thesis. It will discuss how this practice clarifies the message, reinforces the main idea, and ensures the writing feels complete. By understanding the significance of this step, we can appreciate how it enhances the effectiveness of idea communication.
Understanding a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a concise declaration that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It typically appears near the beginning of the paper, often in the introduction, and it presents the writer’s stance on the topic being discussed.
The primary purpose of a thesis statement is to guide the reader through the writer’s argument. It is like a roadmap for the paper, outlining the main idea and the direction of the discussion that will follow. A well-crafted thesis statement helps to clarify the scope of the topic and sets the tone for the entire piece of writing.
In essence, a thesis statement not only informs the reader about the central point of the essay but also helps the writer stay focused and organized as they develop their arguments and present their evidence. It is a crucial element that shapes the coherence and effectiveness of the entire paper.
Key Elements Of A Strong Thesis
A strong thesis statement embodies several essential elements that are crucial for effective communication and argumentation:
Clear and Concise Language
A strong thesis statement written in clear and straightforward language avoids ambiguity and communicates the writer’s position or argument on the topic. This clarity helps both the writer and the reader understand the central message of the paper from the outset.
Specificity and Focus
A strong thesis statement is specific and focused. It addresses a particular aspect of the topic and provides a clear direction for the paper. By narrowing down the scope of the discussion, specificity ensures that the thesis statement remains manageable and allows for a more in-depth exploration of the issue at hand.
Argument or Main Point
A strong thesis statement presents a distinct argument or main point. It goes beyond stating a fact or observation; instead, it asserts a position that the writer intends to support and justify throughout the paper. This argumentative stance gives the thesis statement its persuasive power and guides the development of the entire essay or research paper.
A strong thesis statement combines clear and concise language with specificity and focus while presenting a clear argument or main point. These elements work to establish a strong foundation for the writer’s argument and ensure coherence and direction in the paper’s structure.
Related article: What is a Thesis Statement and How to Write It?
The thesis statement is fundamental to restating a thesis because:
Reinforces the Central Argument : The thesis statement is the core argument or claim of your essay or research paper. Restating it in the conclusion reinforces this central argument, reminding readers of the primary focus and purpose of your work.
Provides Consistency : A clear and consistent restatement of the thesis ensures that your paper maintains a coherent narrative. It ties together the introduction, body, and conclusion, providing a unified and well-structured argument.
Emphasizes Importance : By restating the thesis, you emphasize the significance of your argument or research. It helps to highlight why your work matters and what contribution it makes to the field or topic you are discussing.
Creates a Strong Conclusion : Restating the thesis in the conclusion provides a sense of closure and reinforces the main takeaways of your paper. For tips on crafting an excellent thesis conclusion, check out this helpful article: “ How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper “.
Engages the Reader : A well-restated thesis can re-engage the reader, encouraging them to reflect on the arguments and evidence presented. It ensures that the central message of your paper is effectively communicated.
Techniques for Restating a Thesis
When concluding an essay or research paper, effectively restating your thesis statement can enhance the clarity and impact of your overall argument. Here are some key techniques for restating a thesis:
Maintaining the Original Meaning
How to restate a thesis: When concluding your essay or research paper, it’s essential to maintain the original meaning of your argument in the restatement of your thesis statement. This ensures clarity and coherence throughout your writing. Here’s how to achieve this:
- Ensure the restated thesis accurately reflects the original argument: The restatement should capture the essence of your original thesis statement without altering its core message. This involves rephrasing the thesis using different words and sentence structures while preserving its central idea and intent.
- Do not introduce new ideas or concepts: Avoid introducing new information or arguments in the restated thesis. The conclusion is not the place to introduce fresh insights or expand on additional points that were not covered in the body of your essay or research paper. Instead, focus on summarizing and reinforcing the main argument that has already been developed.
Ensuring consistency and clarity in your writing involves maintaining the original meaning of your thesis statement when restating it in the conclusion. This approach reinforces your main argument and leaves a strong final impression on your reader, effectively summarizing the insights and findings presented in your paper.
Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing your thesis statement means expressing the central idea using different words and sentence structures while preserving the original meaning. This technique is used for several important purposes:
- Avoiding Repetition : Paraphrasing prevents your conclusion from sounding redundant by presenting your thesis statement in a new light. It keeps the reader engaged and shows your ability to reframe ideas without losing clarity.
- Enhancing Clarity : By using varied language and sentence structures, paraphrasing can clarify your thesis statement further, making it easier for the reader to grasp the significance of your argument.
- Maintaining Original Meaning : While rephrasing, ensure that the essence and intent of your original thesis statement remain intact. This entails conveying the same core message but in a new and insightful manner.
Example of Paraphrasing:
Original Thesis Statement: “Climate change poses a significant threat to global biodiversity.”
Paraphrased Restatement: “The impact of climate change on worldwide biodiversity is a critical concern that demands urgent attention.”
In this example, the paraphrased restatement maintains the original meaning—that climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity—while presenting it in a slightly different way to emphasize urgency and broaden the perspective.
Emphasizing Key Points
When restating your thesis, emphasizing key points means highlighting the most critical aspects of your argument and reinforcing their significance. This technique serves several important purposes:
- Reinforcement of Central Ideas : By emphasizing key points, you remind the reader of the main arguments and evidence that support your thesis statement. This reinforcement helps to solidify your argument in the reader’s mind and reinforces the validity of your perspective.
- Summarization : Emphasizing key points allows you to succinctly summarize the main ideas discussed throughout your essay or research paper. This summary helps to bring closure to your argument and provides a clear overview of the insights gained from your analysis.
- Significance and Implications : Highlighting the significance of your key points, you can discuss the broader implications of your thesis statement. This discussion can connect your argument to larger themes, contexts, or real-world applications, demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research or analysis.
Example of Emphasizing Key Points:
Original Thesis Statement: “Education is the key to empowering individuals and promoting social equality.”
Restatement with Emphasis: “Throughout this essay, we have explored how education serves as a transformative force, empowering individuals to break barriers and fostering a more equitable society. By equipping individuals with knowledge and skills, education becomes not just a tool for personal advancement but a catalyst for societal change.”
In this example, the restatement emphasizes the transformative power of education and its role in promoting social equality, while also summarizing the main points discussed in the essay.

Examples of Restated Thesis Statements
These examples demonstrate how restating the thesis statement in the conclusion can summarize the main argument while adding depth or context that reflects the insights gained throughout the essay or research paper.
- Original Thesis: “The advancement of artificial intelligence poses ethical dilemmas regarding privacy and autonomy.”
- Restated Thesis: “In conclusion, the ethical implications of advancing artificial intelligence extend beyond technological progress, raising profound concerns about individual privacy and autonomy in an increasingly interconnected world.”
- Original Thesis: “Effective communication is essential for fostering positive workplace relationships.”
- Restated Thesis: “To summarize, cultivating effective communication skills within the workplace is not merely advantageous but crucial for nurturing productive relationships and fostering a collaborative environment.”
- Original Thesis : “Renewable energy sources are necessary for reducing global dependence on fossil fuels.”
- Restated Thesis : “In conclusion, the adoption of renewable energy sources is imperative for diminishing our global reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a more sustainable future.”
- Original Thesis : “Social media platforms significantly impact the self-esteem of teenagers.”
- Restated Thesis : “To summarize, social media’s influence on teenagers’ self-esteem is profound, necessitating mindful usage and awareness to mitigate potential negative effects.”
Refining Your Thesis Restatement
Refining your thesis restatement is the process of carefully crafting and polishing the statement that summarizes the main argument presented in the conclusion of your essay or research paper. It ensures that this restated thesis accurately reflects and emphasizes the key points and findings discussed throughout your work.
The goal is to achieve clarity, coherence, and persuasive impact, reinforcing the significance of your research or essay topic to leave a strong impression on the reader. This refinement process also focuses on using clear language and tone to communicate the main ideas and conclusions of your paper effectively. It is essential for several reasons:
Refinement : This step requires careful attention to detail in adjusting and improving your thesis statement to ensure it succinctly captures the essence of your main points.
Accuracy : The restated thesis should accurately represent the core arguments and findings discussed throughout your paper, providing a clear and concise summary.
Clarity : It’s important to review the restatement for clarity and coherence, ensuring that it effectively communicates your conclusions to the reader without ambiguity.
Language and Tone : Choosing appropriate language and tone is crucial as it helps in conveying your message clearly and leaving a strong impression on the reader. This includes avoiding jargon or overly complex language that may obscure your main points.
Relevance : By refining your thesis restatement, you strengthen the relevance and persuasive impact of your central argument. This ensures that your conclusion effectively reinforces the significance of your research or essay topic.
Refining your thesis restatement through careful revision enhances the overall effectiveness of your conclusion, providing a clear and compelling summary of your paper’s key points and findings.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When restating your thesis statement in the conclusion of your essay or research paper, it’s important to steer clear of certain pitfalls that can diminish the effectiveness of your conclusion. One common pitfall to avoid is:
Avoiding Clichés
Restating your thesis with clichéd language can weaken the impact of your conclusion and make it less memorable to the reader. Here’s how to navigate this:
- Steer clear of overused phrases and terms: Phrases like “In conclusion,” “To sum up,” or “In summary” are common but can sound formulaic and uninspired if overused. Consider using alternative phrases or structuring your conclusion in a more creative manner to maintain reader engagement.
- Keep the language fresh and unique: Instead of relying on clichéd language, strive to use fresh and unique language that reflects the specific nuances of your argument. This not only keeps your conclusion engaging but also reinforces the originality and significance of your thesis statement.
Repetition Without Adding Value
Simply repeating the thesis statement without adding any new insights can make your conclusion feel redundant. Instead:
- Expand on the original thesis : Highlight the implications of your argument or how your findings contribute to the field. This approach adds depth and demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic.
- Reflect on the broader context : Discuss the broader implications of your thesis. This helps to show the significance of your argument beyond the scope of your paper.
Lack of Specificity
A vague restatement of your thesis can leave the reader unclear about your main argument. To avoid this:
- Be precise and clear : Ensure your restated thesis is specific and clearly reflects the core message of your paper. Avoid generalizations that can dilute the impact of your conclusion.
- Summarize key points : Briefly summarize the key points that support your thesis, providing a clear and concise wrap-up of your argument.
Introducing New Information
Introducing new arguments or evidence in your conclusion can confuse the reader and disrupt the flow of your paper. To maintain coherence:
- Stick to the main points : Focus on restating the thesis and summarizing the main arguments presented in the body of your paper. Avoid introducing new information that wasn’t covered earlier.
- Ensure coherence : Make sure your restatement logically follows from the preceding discussion and ties together the key points.
Overly Complex Language
Using overly complex or technical language in your restatement can alienate readers and obscure your main argument. To ensure clarity:
- Use straightforward language : Restate your thesis in clear and accessible language. This makes your conclusion more impactful and easier to understand.
- Focus on clarity : Prioritize clarity and simplicity in your language to ensure your restated thesis effectively communicates your main argument.
Online Scientific Design Tool For Your Classes, Speeches, Papers, And Much More
Mind the Graph is an online platform designed specifically for scientists, providing a rich library of scientifically accurate illustrations and customizable templates. This tool simplifies the creation of visually compelling content tailored for academic presentations, research papers, and professional materials. By enabling the integration of intricate scientific data into graphical abstracts, posters, and presentations, Mind the Graph empowers researchers to effectively convey their discoveries to diverse audiences. Its user-friendly interface and collaborative functionalities enhance efficiency in scientific communication, fostering innovative approaches to visual storytelling in research and education.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
Content tags
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Rebels Blog
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
10 Intriguing Conclusion Sentence Starters to Seal the Deal in Your Essays

Writing a compelling conclusion is the final flourish of your essay, leaving a lasting impact on your reader. Just as an essay's introduction sets the tone for what is to come, the conclusion seals the deal, underscoring the main points and providing a sense of closure. In this article, we explore 10 intriguing conclusion sentence starters that can help you eloquently wrap up your essays and ensure that your final words resonate with your audience.
Key Takeaways
- Effective conclusion sentence starters can elevate the ending of an essay, ensuring it is memorable and impactful.
- Each sentence starter serves as a unique way to signal the end of an essay while reinforcing the core message.
- Using varied and thoughtful conclusion starters can help maintain the reader's interest until the very last word.
1. In Conclusion
When you reach the final paragraph of your essay, 'In Conclusion' serves as a signal to your readers that you are about to wrap up your thoughts. It's a moment to underscore the significance of your findings and to leave a lasting impression. Here are a few strategies you might employ:
- Restate your thesis to remind the audience of your central argument.
- Offer a call-to-action , encouraging readers to apply your insights or continue the conversation.
- Present a warning or implication, suggesting what might happen if your ideas are ignored.
Remember, the goal is to synthesize your points , not just to summarize them. This is your final opportunity to not only reiterate your position but also to demonstrate its relevance and impact. Websites that offer tools for thesis writing emphasize the importance of a well-crafted conclusion . They provide resources such as worksheets and templates, which can serve as a roadmap for your research journey and ensure your essay concludes on a strong note.
2. To Sum Up
To sum up, your essay should not only restate the thesis but also highlight the journey that led to your conclusion. Thesis statements are crucial in academic writing, as they provide a roadmap and focus for your argument. By including supporting evidence , you encourage further research and exploration, demonstrating the depth of your analysis.
Consider the following steps to ensure your conclusion is impactful:
- Restate your thesis in a fresh way, reflecting on the evidence presented.
- Synthesize the main points, showing how they interconnect.
- Propose areas for future research, acknowledging the limitations of your study.
- End with a final thought or call to action that resonates with your reader.
Remember, a powerful conclusion is your last chance to leave a lasting impression on your audience. Make it count by succinctly summarizing your points and underscoring the significance of your work.
3. Ultimately
Ultimately, your conclusion serves as the final chance to leave your reader with a lasting impression. It is the crescendo of your symphony, the final act in your play. Use this opportunity to not only restate your thesis but to synthesize the insights you've shared throughout your essay. Consider the broader implications of your argument and how it contributes to the larger conversation on the topic.
For instance, if your essay addresses the complexities of climate change, your conclusion might highlight the urgent need for action, drawing on the evidence presented. Here's how you might structure your final thoughts:
- Recap the main points of your argument.
- Emphasize the significance of your findings.
- Propose a call to action or suggest further research.
Remember, a powerful conclusion can reinforce an argument or wrap up a complex idea. If your thesis contains multiple ideas or references, a clincher sentence can effectively tie them all together, ensuring that your reader grasps the full scope of your discussion.
4. In Summary
In summary, your essay's conclusion is your final opportunity to synthesize your arguments and leave a lasting impression. It's essential to summarize the main points without merely repeating what has already been said. Consider the following steps to craft a compelling conclusion :
- Restate your thesis in a fresh, assertive manner.
- Summarize the key arguments you've presented.
- Highlight the significance of your findings.
- Propose areas for future research or questions left unanswered.
- End with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
Remember, a well-crafted conclusion can elevate your essay from good to great. It starts by reminding the reader of the contents and importance of your findings , then moves out gradually to more general topics, ensuring a smooth and logical transition to the end of your discourse.
When you reach the point of drawing your essay to a close, finally signals to your readers that you are bringing together the threads of your argument. It's a cue that the culmination of your points is about to be presented, offering a sense of completion and satisfaction. You use finally when you want to emphasize the amount of time it took to arrive at this juncture, underscoring the thoroughness of your exploration.
Consider the following when crafting your final sentence:
- Restate your thesis in a fresh way, reflecting on the journey of your argument.
- Synthesize the key points, showing how they interlock to support your thesis.
- Propose a call to action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impact.
Remember, the final sentence is your last opportunity to leave an impression on your reader. Make it count by being concise, powerful, and reflective of the essay's content.
6. As Demonstrated
When you reach the culmination of your argument, as demonstrated throughout your essay, it's crucial to reiterate the strength of your evidence. This phrase not only signals the conclusion but also reinforces the logical progression of your points. For instance, if your essay discussed the effectiveness of a particular teaching method, you might conclude with:
As demonstrated, the interactive teaching approach significantly improved student engagement and comprehension.
In academic writing, the power of a well-supported argument is undeniable. Consider the following key points that were substantiated in your essay:
- The initial hypothesis or thesis statement
- The methodology employed for data collection
- The analysis and interpretation of results
By using 'as demonstrated,' you remind the reader of the empirical foundation upon which your conclusions are built. It's a subtle yet powerful way to assert the credibility of your findings and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
7. To Conclude
To conclude, your essay should bring the reader full circle to the initial thesis presented. It's your final opportunity to synthesize your points and leave a lasting impression . Avoid introducing new ideas ; instead, aim to reinforce your thesis statement and remind the reader of the supporting points you've made throughout your work.
Consider these steps for a compelling conclusion:
- Restate your thesis in a fresh, yet succinct manner.
- Summarize the key arguments or points you've discussed.
- Connect your conclusion back to the introduction to give a sense of closure.
Remember, a well-crafted conclusion can elevate your essay from good to great. It's not just a summary but a final pitch for your argument, a chance to resonate with your reader long after they've finished reading.
8. In Retrospect
When you look back upon the arguments and evidence presented in your essay, in retrospect , it becomes clear that the conclusions drawn are not just fleeting thoughts but are deeply rooted in factual analysis. Reflecting on the journey of your essay allows you to see the bigger picture and understand the implications of your findings.
Consider employing a ' Start, Stop, Continue ' approach to your retrospective conclusion:
- Start : Introduce new perspectives or questions that arose from your research.
- Stop : Ackoint the limitations of your study and suggest areas for improvement.
- Continue : Reinforce the key findings and their relevance to the field.
By adopting this method, you ensure that your conclusion is not merely a summary, but a thoughtful reflection that adds value to your work and encourages ongoing dialogue.
9. Upon Reflection
Upon reflection, you realize that the journey of your essay is as significant as its conclusion. Reflective writing is not merely a summary but a chance to offer a deeper insight into the subject at hand. It's an opportunity to underscore the importance of your arguments and the weight of your evidence.
Consider these steps to effectively conclude with reflection:
- Write a brief recap of the key points.
- Reflect on the significance of these points in the broader context.
- Pose questions that may guide further inquiry or contemplation.
By integrating these elements, you ensure that your essay resonates with the reader, leaving a lasting impression of your analytical prowess. Websites that offer tools for thesis writing , such as worksheets and templates, emphasize the importance of structured conversations in conducting effective interviews, which can be a valuable part of your reflective process.
10. In Closing
As you approach the end of your essay, 'In Closing' offers a final opportunity to underscore the significance of your argument. This phrase signals to your reader that you are drawing together the threads of your discussion and preparing to leave them with a lasting impression . It's essential to not only restate your thesis but to also reflect on the broader implications of your work. Consider the following steps to craft a compelling conclusion :
- Tie in your thesis statement .
- Restate your main points.
- Connect to your opening statements.
- End with a powerful closing statement.
By following these steps, you ensure that your essay resonates with the reader, reinforcing the importance of your insights. Remember, a well-crafted conclusion can transform your essay from a mere collection of arguments into a cohesive and persuasive narrative. In closing, let your essay not just conclude, but conclude with conviction.
As we wrap up this insightful journey, remember that the path to conquering your thesis doesn't have to be a solitary one. Join the ranks of successful students who have transformed their academic challenges into triumphs with Research Rebels. Don't let another sleepless night pass you by—take the first step towards clarity, confidence, and a stress-free thesis experience. Visit our website now and claim your special offer to embark on a journey that turns overwhelming anxiety into overwhelming success.
In conclusion, the art of crafting a compelling essay conclusion is pivotal in leaving a lasting impression on the reader. The final sentences of an essay are not just a summary but an opportunity to reinforce the central thesis and leave the audience pondering the broader implications of your argument. By utilizing the ten intriguing conclusion sentence starters discussed in this article, writers can effectively seal the deal, ensuring their essays resonate with clarity and purpose. Whether through a call to action, a poignant quote, or a thought-provoking question, these starters serve as a bridge, connecting the essay's content with the reader's ongoing reflection. As we strive for academic excellence, let us not underestimate the power of a well-crafted conclusion to transform a good essay into an unforgettable one.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective strategies for writing a strong conclusion.
Effective strategies for writing a strong conclusion include restating your thesis in a new light, summarizing your main points, providing a call to action, and leaving your reader with a thought-provoking question or statement.
Can a conclusion sentence starter affect the impact of an essay's conclusion?
Yes, a conclusion sentence starter can set the tone for the final thoughts and influence how the reader perceives the overall argument. It can provide a sense of closure and emphasize the significance of the essay's points.
Is it necessary to use a different conclusion sentence starter for each essay?
While it's not strictly necessary, varying your conclusion sentence starters can help tailor the ending to the specific tone and content of your essay, making it feel more personalized and impactful.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

Understanding the Difference Between Research Objectives and Research Questions
Transitioning Beyond Academia: Life After Completing Your Thesis

Trending Topics for Your Thesis: What's Hot in 2024

Thesis Action Plan

- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
How to restate a thesis: basic steps and key strategies
Updated 05 Sep 2024

A good thesis statement is a vital skill in academic writing, as it provides closure to an essay while reinforcing the central message. However, many writers often fall into the trap of repetition or cannot add new insight. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the strategies and techniques of how to restate a thesis. We will also explore various approaches to this task, from subtle rephrasing to offering fresh perspectives. By understanding the purpose of rephrasing a thesis and learning how to craft a compelling restatement, writers can elevate the impact of their essays and leave a lasting impression on their readers.
What is a thesis statement, and why must it be restated?
A thesis statement is a concise, declarative sentence that presents the main idea or argument of an essay or other piece of writing. It typically appears in the introduction of college papers and provides the reader with a clear understanding of the writer’s position.
For a robust and impactful academic piece, it’s imperative to include a restated thesis statement in the conclusion for several reasons:
- Reformulating the essential claim at the end of your work reintroduces your argument, emphasizing its importance.
- Rephrasing the thesis statement effectively in slightly different words or with additional commentary facilitates a smoother transition to discussing the implications.
- This technique ties together the various argumentative points and ideas presented throughout the text, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of the writer’s position.
- Paraphrasing the thesis statement in a research paper signals that your paper is coming to a close and leaves the reader with a lasting impression.
How to restate a thesis in a conclusion paragraph: step-by-step guidelines
How to restate a thesis statement is a critical step to ensure clarity and reinforce your essential message. Here are effective steps on how to create an effective restated thesis statement:
Step 1. Review your statement.
Begin by revisiting your original phrase from the introduction of your argumentative essay . Ensure you understand the main argument or assertion you presented.
Step 2. Identify essential points and keywords.
Reflect on the main points and arguments you've discussed in your writing. Consider how these points support and contribute to your key idea.
Step 3. Paraphrase your argument.
Restate thesis in new words, aiming to capture the essence of your original assertion. Use synonyms and alternative phrasing while retaining the core meaning of your thesis.
Step 4. Provide a summary.
Briefly summarize the main points of your persuasive essay , emphasizing how the body paragraphs collectively support your thesis. This summary helps to reinforce your argument’s significance.
Step 5. Reflect on implications.
Consider the broader implications of your thesis statement and persuasive arguments in your writing. Discuss the relevance and importance of your findings in the context of the broader topic or field of study.
Step 6. Connect to the introduction.
Tie your conclusion back to the introduction by referencing key ideas or phrases, ensuring you convey the same idea in a different way. This connection helps to create cohesion and closure in your writing.
Step 7. End with a final thought.
Conclude your work with a final thought or reflection in the conclusion paragraph that reinforces the significance of your thesis statement. This closing remark should leave a lasting impression on your reader.
Step 8. Proofread and revise.
Review your paper's conclusion to restate the thesis for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Make any necessary revisions to ensure your message is effectively communicated.
By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can effectively paraphrase your key idea, providing closure and reinforcing the central message of your writing.
Get plagiarism-free papers in just 3 hours
- Zero AI - 100% human-crafted content
- Tailored to your writing style
- Sourced from the latest, reliable sources
Guaranteed Turnitin success ✌️
8 strategies for thesis restatement
When performing a thesis restatement, simply changing every word isn’t enough. The goal is to craft a captivating restatement. To achieve this, mastering the art of writing thesis statement and rewording is essential. Our EduBirdie specialists have prepared a list with recommendations and examples on how to effectively restate a thesis.
- Restructure your statement: Ensure your restated assertion differs from the original. Experiment with altering the word structure, clauses, vocabulary choices, and parts of speech. Consider starting with a prepositional phrase if the original statement begins with a subject.
- Utilize synonyms: When rephrasing your thesis, maintain its meaning while avoiding repetition. Employ synonyms or alternative expressions to convey the same message. Consulting a thesaurus can enrich your vocabulary and aid in this process.
- Break it down: Modify sentence structure by breaking up lengthy sentences into shorter, more digestible segments. This not only enhances clarity but also makes comprehension easier for your readers.
- Adjust tenses: Experiment with changing verb tenses in your essay. Switch between past and present tenses to breathe new life into your reformulated thesis. For instance, if your original sentence uses the past tense, consider restating it in the present tense and vice versa.
- Mind the length: If you don’t know how to restate a claim, adhere to guidelines on paragraph length. Aim to keep your rephrased sentence concise, comprising no more than 5-7% of the total word count. Prioritize quality over quantity, ensuring your rephrasing aligns with your text’s overall tone and style.
- Sum up your essential idea: Summarizing involves analyzing the original thesis statement to capture its main meaning concisely. By distilling the essence of the argument, this technique creates a clear and informative reformulated assertion. It condenses complex ideas, ensuring clarity and impact for the reader.
- Use rhetorical devices: Stylistic techniques, like parallelism and repetition, enhance your thesis statement’s persuasiveness and originality. By employing these techniques, your restated thesis gains impact and cohesion, captivating the reader and improving your paper’s overall quality and persuasiveness.
- Provide broader context: Offering a relevant context involves explaining the historical, social, or conceptual background that shapes your perspective. By providing this overview, you enrich the reader’s understanding and establish the relevance of your argument. This contextualization helps situate your ideas within a larger framework, enhancing the reader’s appreciation of the complexities and encouraging deeper engagement with your work.
By mastering these techniques, you’ll be equipped to craft a compelling restated sentence that reinforces your argument while captivating your readers. If you’re unsure about word count, prioritize crafting a high-quality restatement over adhering strictly to length guidelines.
Restating the Thesis in Different Types of Essays
The approach to restating a thesis can vary depending on the type of essay you are writing. While the core principles of rephrasing the central argument and reinforcing the main points remain the same, different essay types require different focuses in the conclusion. Below are some guidelines for restating the thesis in various essay formats:
Argumentative Essays
In an argumentative essay , your goal is to persuade the reader to adopt your viewpoint or at least recognize the validity of your argument. When restating the thesis, emphasize the strength of your argument and highlight how the evidence and reasoning presented in the body of the essay support your position. The restatement should reinforce the urgency or importance of the argument.
Example : Original Thesis: "Renewable energy is the only viable solution to combat climate change." Restated Thesis: "Given the overwhelming evidence, it’s clear that transitioning to renewable energy is crucial in the fight against climate change."
Expository Essays
In an expository essay , the thesis explains a concept or provides information on a subject. When restating the thesis, reinforce the explanation and summarize the key insights or explanations provided throughout the essay. The restated thesis should underline the clarity and significance of the subject.
Example : Original Thesis: "Photosynthesis is a complex process that is essential for plant life." Restated Thesis: "The detailed breakdown of photosynthesis reveals its crucial role in sustaining plant life and the ecosystem."
Compare-and-Contrast Essays
In a compare-and-contrast essay , the thesis highlights the similarities and differences between two subjects. When restating the thesis, focus on summarizing the main points of comparison and how these comparisons or contrasts lead to a broader understanding of the subject matter.
Example : Original Thesis: "While online learning offers flexibility, traditional classroom education provides a more structured learning environment." Restated Thesis: "Ultimately, both online learning and traditional classrooms have their unique advantages, but the choice depends on the student’s individual learning needs."
Analytical Essays
In an analytical essay , the thesis presents an analysis of a text, event, or concept. When restating the thesis, focus on the key points of analysis and how they contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject. The restatement should reflect the insights gained from the analysis and their broader implications.
Example : Original Thesis: "In Shakespeare's 'Hamlet,' the protagonist’s indecision serves as a metaphor for human uncertainty." Restated Thesis: "Through Hamlet’s indecision, Shakespeare effectively captures the complexities of human thought and the universal struggle with uncertainty."
By adapting your thesis restatement to the specific type of essay you’re writing, you can create a conclusion that not only reaffirms your argument but also aligns with the essay's broader purpose. This tailored approach helps ensure clarity, cohesion, and impact in your writing.
Common Mistakes in Restating a Thesis
When restating a thesis in the conclusion, it's easy to fall into common traps that undermine the effectiveness of your final argument. Understanding and avoiding these mistakes can significantly strengthen your conclusion and leave a lasting impression on your reader. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
Repeating the Thesis Verbatim
One of the most frequent mistakes writers make is simply repeating the thesis from the introduction word for word. While the purpose of restating is to reinforce your argument, direct repetition adds no new value to the conclusion. Instead, rephrase the thesis using different wording and synonyms to provide a fresh take on the same core idea.
Example of Mistake : Original thesis: "Climate change is the most pressing global issue because it affects the environment, economies, and human health." Restated thesis: "Climate change is the most pressing global issue because it affects the environment, economies, and human health."
Improved Restatement : "With its profound impact on ecosystems, economies, and public health, climate change remains the greatest challenge facing the world today."
Introducing New Ideas
Another common error is introducing new arguments or information in the restatement. The conclusion is not the place to present fresh ideas that haven't been discussed in the body of the essay. Introducing new points can confuse your reader and disrupt the flow of your argument. Stick to summarizing the ideas already covered in the essay to provide a sense of closure.
Example of Mistake : Restated thesis introducing a new idea: "Climate change, driven by industrial pollution, will lead to severe economic downturns and even societal collapse."
Correct Approach : "Throughout this paper, we’ve seen how climate change threatens the environment, destabilizes economies, and endangers human health, underscoring the urgency of taking action."
Overcomplicating the Restatement
Some writers may overcomplicate their thesis restatement, using overly complex language or sentence structures. This can make the restated thesis difficult to understand, diluting the clarity of the original argument. Your restatement should be concise and easy to follow , mirroring the tone and clarity of the rest of your essay.
Example of Mistake : "Given the multifaceted interdependencies of global economic frameworks, environmental sustainability metrics, and societal well-being indices, the phenomena of climate change demand immediate intervention."
Simplified Restatement : "Climate change continues to pose significant threats to global stability, making it essential for societies to take immediate action."
Neglecting to Summarize Main Points
A strong restated thesis ties together the main points of the essay. Some writers may forget to summarize or connect back to the central arguments, leaving the conclusion feeling disjointed. Ensure your restated thesis emphasizes how the supporting points in the body of the essay reinforce the thesis.
Example of Mistake : Restated thesis without summarizing main points: "Climate change is a global issue that requires attention."
Improved Restatement : "By exploring the effects of climate change on the environment, the economy, and public health, we can see why immediate action is necessary to address this global challenge."
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure your thesis restatement reinforces your argument, providing a clear and compelling conclusion to your writing.
Dos and don’ts
If you need help with my assignment as soon as the restatement of the thesis is concerned, discover the essential dos and don’ts you should keep in mind.
Pose the “so what” question.
Effective thesis statements should elucidate the importance of your argument, clarifying why readers should engage with your paper. If you’re uncertain about your restatement, consider addressing the “so what” question. To effectively address this query, elaborate on the initial assumptions embedded within your thesis. By expanding upon these foundational premises, you provide readers with a deeper understanding of the significance and implications of your argument.
Think about the purpose of your restated thesis example.
Understanding this action's underlying purpose and intent is crucial for effectively rephrasing your statement. By comprehending the primary objective of reformulating your thesis, you can articulate it more clearly. This writing technique strengthens your arguments and enhances readers' reception.
Decide where to restate your thesis.
While the conclusion is the typical location, the exact placement within this section requires careful consideration. Consider incorporating a restatement towards the end as the final sentence. Alternatively, you may opt to weave it into a broader context or support your argument elsewhere in the conclusion.
Craft compelling and robust conclusions.
Despite the potential challenges of not fully substantiating your initial thesis, it’s important not to sound apologetic. Factors such as the unavailability of expert opinions or primary data or the absence of consensus on the subject matter among published sources may contribute to this. In this case, restate your main idea and provide readers with insights into why your original promise may not have been fully fulfilled.
Don’ts
Avoid apologies.
Avoid weakening your stance by apologizing in your reformulated thesis. Phrases like “It is possible that” or “It seems like” suggest uncertainty and can undermine your argument’s impact. Confidence should emanate from your restatement. Address counter-arguments logically rather than using absolute statements, maintaining the strength of your position.
Steer clear of clichés.
Refrain from using clichéd and overused phrases such as “in conclusion” or “as these college papers for sale explain” in your restated thesis example. Your readers will already be familiar with the paper’s content by the conclusion. Repetition of the same information can render the thesis redundant and may be perceived as lacking creativity. Inject fresh perspectives into your restatement, ensuring transparency and appeal.
Avoid vague language.
Ensure specificity and steer clear of vague language in your writing. Vagueness, conditional expressions, lengthy sentences, and oversimplified ideas can detract from the clarity and engagement of your thesis. Respect your reader’s intelligence by offering thought-provoking content. Additionally, vary your sentence structure and word choice to maintain diversity and prevent reader fatigue.
Refrain from introducing new ideas.
While novel insights are valuable, they should be integrated into your paper from the outset. A sudden and unrelated conclusion can leave readers confused. Maintain coherence by adhering to your original concepts. Instead of introducing fresh ideas, focus on revisiting and reinforcing existing ideas to strengthen the connection with your introduction.
Final thoughts
Understanding how to restate a thesis word is vital for writers creating compelling essays. By adhering to the strategies in this guide, you can craft restatements that reinforce your central message and provide new perspectives. Whether concluding an academic essay, blog post, or professional report, clarity, creativity, and conviction in restating a thesis word will captivate the audience and provide a sense of closure and satisfaction.
For additional support and guidance in your writing endeavors, consider leveraging the expertise of paper writing service EduBirdie, the premier writing helper. With our team of experienced writers and commitment to excellence, we provide invaluable assistance to writers at every stage of their journey. So, take the next step in refining your writing skills and partner with EduBirdie to unlock your full writing potential!
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Meredith Anderson
Meredith, a dedicated editor at EduBirdie, specializes in academic writing. Her keen eye for grammar and structure ensures flawless papers, while her insightful feedback helps students improve their writing skills and achieve higher grades.
Related Blog Posts
Best capstone project ideas for students across subjects.
The most challenging aspect of crafting a top-tier capstone project is often getting started. The initial hurdle involves selecting a strong, impac...
How to Write a Movie Review: Tips for Aspiring Critics
If you wish to know how to write a movie review, then you are on the right page. A movie review forms part of essays college students writes. While...
Learn how to write an annotated bibliography to achieve the best grades!
Writing an annotated bibliography is one of academic work's most challenging yet essential parts. This helpful EduBirdie guide will tell you all ab...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
How to Restate a Thesis: Various Approaches to Restating Your Thesis
Table of contents
- 1 Understanding the Purpose of Restating a Thesis
- 2.1 Paraphrasing.
- 2.2 Summarizing.
- 2.3 Reflecting.
- 2.4 Significance.
- 2.5 Rhetorical Devices.
- 2.6 Emotional Appeal.
- 2.7 Call to Action.
- 2.8 Broader Context.
- 2.9 Engaging Language.
- 2.10 Memorable Statement.
- 3.1 Understand the purpose of restatement
- 3.2 Avoid clichés and overused phrases
- 3.3 Be specific and avoid vague language
- 3.4 Keep it concise
- 3.5 Reflect on the essay’s journey
- 3.6 Emphasize the significance
- 3.7 Check for coherence
- 3.8 Avoid introducing new ideas
A thesis statement guarantees that your essay will be read, and a paraphrased thesis states that the main points of your essay will be remembered. Students have already heard about the importance of formulating a thesis statement to interest the reader in your written work. However, inexperienced authors often forget to restate the thesis.
The purpose of the successful thesis restatement is to reinforce the essay’s main idea. This way, you intensify the original argument and influence the reader’s mind. For your research paper to be convincing, it must be coherent. For this reason, the thesis and the restated thesis should not contradict but complement each other.
In this article, detailed instructions will help you restate your thesis and make your essay memorable. Our experienced specialists are ready to share with you the most working strategies for high-quality rewording of the thesis. Moreover, we want to make it easier for you and have created a checklist of the necessary details to consider to restate your thesis effectively.
Understanding the Purpose of Restating a Thesis
We remind you that the thesis statement is a claim that summarizes the main idea of your essay. It is often used as the first sentence in the introductory paragraph to dedicate the reader to the context of the written work. However, a good thesis statement is not limited to the first paragraph. In academic and persuasive writing, for example, there is a need to restate the original thesis to maintain coherence.
What does restate thesis mean? Let’s start with the fact that a restated thesis is a statement based on the original thesis used in the concluding paragraph or throughout the body paragraphs. Quoting the original thesis statement word by word will not be effective, so you have to analyze the original meaning and reword it. You may use a paraphrasing tool in case you struggle with an issue of how to restate a thesis.
You must be wondering why restating a thesis statement in the conclusion paragraph is so important. It is sometimes difficult for the reader to follow your thought course while reading. Remember when you read a book, then by the last page, you begin to forget about what happened at the beginning. To regularly refresh the reader’s memory of your argument, you need to recall it by restating the original thesis statement in the essay’s conclusion paragraph and body paragraphs.
Thus, the thesis claim should permeate your essay. Each part should contain a reminder of the central idea to reinforce the perceived significance of the thesis word. The restated thesis acts as a link between the main components of your essay. It’s necessary to restate the thesis in conclusion, connect it with topic sentences and provide a logical analysis flow.
Strategies for Restating a Thesis Effectively
Unfortunately, a simple understanding of the importance of restructuring the thesis is insufficient. It is also necessary to understand the primary strategies for good restating. Our PapersOwl experts have prepared a list with good examples for you on how to restate a thesis statement effectively. The most effective strategies are:
Paraphrasing.
Reword your original thesis statement using different words and changing the sentence structure. With this technique, the form changes, but not the main point.
Initial thesis: The desegregation of public schools is considered to be the key purpose of the Civil Rights Movement.
Restatement: The anti-segregation movement in America was aimed at equalizing public schools.
Summarizing.
In this technique, you should analyze and summarize the overall meaning of the original point in the introduction. Thus, the statement will be concise and informative.
Initial thesis: Increased anxiety and stress exposure by the mother during pregnancy can negatively affect the intrauterine development of the child, making his nervous system more vulnerable to stress.
Restatement: A pregnant mother’s stress can make a child more anxious.
Reflecting.
Link your restated thesis to the ideas you uncovered in the body paragraph of the paper.
Initial thesis: The opportunities for women to develop professionally were historically equal to the career prospects of men, or were they?
Restatement of thesis: In the nineteenth century, the inequality in the career opportunities of the two sexes was drastic.
Significance.
Emphasize that the thought you expressed in the original thesis statement is so crucial that it is worth developing in restating the thesis.
Initial thesis: The lack of sex education in schools and families leads to increased unwanted pregnancies among adolescents.
Restatement: Again, 50% of pregnancies among teenagers are unwanted. As a result of the lack of sex education, the total number of teenage pregnancies continues to grow.
Rhetorical Devices.
Use rhetorical techniques in your thesis statement, such as parallelism and repetition, to enhance the persuasiveness of the paper and rephrase the original contribution.
Initial thesis: The film provides a detailed picture for our eyes.
Restatement: The film provides a detailed picture for our eyes, and a book provides an even more detailed image for our mind.
Emotional Appeal.
Use a moving phrase or concept to appeal to the reader’s emotions to enhance interaction. If you don’t know how to apply this technique, try asking for help with college papers , and get expert help.
e.g. How long must pass before people realize that their grandchildren will suffer from the consequences of environmental disasters.
Call to Action.
Formulate your paper’s central argument, and motivate the reader to take action by introducing a thesis restatement in the conclusion.
Example: Do not delay, nature needs your intervention right now, sort garbage responsibly!
Broader Context.
Explain to the reader the background of your thought.
Example: Initial thesis: The world was a millimeter far from a nuclear war.
Restatement: In the 20th century, the development of the nuclear industry reached such a level that the advanced countries were on the verge of starting a nuclear war.
Engaging Language.
Use vocabulary that is close and understandable to the reader.
Example: Lack of sleep is the major reason for heart diseases, so don’t worry, go take a nap!
Memorable Statement.
A powerful version of your original claim has a good potential to be remembered by readers.
Example: Realizing that you owe nothing to anyone is difficult, but only by recognizing this do you begin to live for real.
Checklist to help you ensure an effective restatement of your thesis

Now that you’re familiar with working strategies for paraphrasing a thesis statement, as well as with illustrative examples, it’s time to stock up on all the tips from our experienced writers. We have created a checklist of eight points you need to follow to know how to write a thesis statement for the conclusion section so that most professors truly value your writing.
Understand the purpose of restatement
Understanding the reasons and motivation for your actions gives you the key to rephrase a thesis right. Having realized the primary goal of restating your thesis statement will help you articulate it more clearly. Remember that this writing technique exists to strengthen your arguments and improve their perception by readers. So let’s see how to restate a thesis for your conclusion and write a perfect paper.
Avoid clichés and overused phrases
The reader will not be interested in hackneyed formulations, absolute statements, and overused concepts in your thesis restatement. Our brain always demands novelty, so unique information will attract more attention and arouse interest in your research paper. Try to make your thesis restatement look fresh and intriguing.
Be specific and avoid vague language
Vague concepts, conditional language, overly long sentences, and oversimplification of information will make your thesis statements more boring. Do not think that your reader is a fool. On the contrary, provide him with food for thought. Also, reconsider the sentence structure, for it not to be too weary, use different words to be diverse.
Keep it concise
An excellent conclusion thesis restatement should be concise, giving only the most necessary context to make it easier to understand. You can expand on your idea in more detail in the following main paragraphs. To get a perfect reworded thesis, use the thesis statement generator to make the process easier. Still, to make rephrasing effective, it should be concise, write shorter sentences and use different words.
Reflect on the essay’s journey
Summarize your main ideas. After all, the thesis restatement is precisely the information you want the reader to remember the most. Why don’t you recall once again the main points and central claims of your writing? Use grammar tenses to convey your point. Perhaps your original statement was written in the present or future tense, then use past tense to show you’ve accomplished your ideas. Or, at the beginning of your writing, you used a sentence with a subject. So, restate the thesis in the conclusion with a prepositional phrase instead.
Emphasize the significance
Your opinion and your words must be heard. Emphasize the importance of your ideas with a strong conclusion paragraph thesis restatement. Choose the right strategy for your body paragraphs and paper’s conclusion to sound more convincing. Restate the thesis so that the reader has no doubts regarding the expertise of your writing and the words you say.
Check for coherence
Do not forget about the connection between the thesis sentence in the introduction paragraph and the restatement in the essay conclusion section and the main body. Follow the logic of the presentation of your thoughts when you restate claim. Your paper should not contain contradictory words and statements.
Avoid introducing new ideas
New and creative ideas are good, but they should be pre-planned as part of your paper. An unexpected and unforeseen conclusion that isn’t related to the research problem can confuse the reader at the end of the essay. Stick to your original concepts and the same meaning for the coherence of your writing. Rewrite existing concepts to reinforce your introduction thesis statement.
A thesis statement is an effective technique for attracting the attention of the reader, as well as ensuring his interest. However, using a thesis statement only in the introductory paragraph will not provide you with the desired result. For a more comprehensive result, you will have to rephrase a thesis statement a few more times in the writing process.
No strong conclusion is complete without a good reworded thesis. Remember to connect the rephrasing to the main research question. Use our strategies to write an effective thesis and get a well-deserved assessment from the teacher. Stick to our recommendations to make your paraphrased thesis effective.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Concluding Sentence: Starters, Tips, & Examples

Do you feel your text isn’t as smooth and readable as you wanted it to be? If so, consider working on concluding sentences in your paragraphs. They summarize a section, connect various ideas, and enhance writing flow.
How to write a good conclusion sentence?
Read on to find the answer to this question.
What Is a Concluding Sentence?
- How to Write It?
- Concluding Sentence Starters
A concluding sentence is the final sentence in each paragraph. It is essential to every section in academic writing, as a well-structured paragraph consists of:
- A topic sentence
- Several supporting sentences
- A conclusion sentence
Concluding Sentence Functions
A good concluding sentence performs several functions in your writing:
| A concluding sentence “mirrors” a topic sentence that opens your paragraph. | |
| It wraps up all the arguments, evidence, and ideas used in the paragraph. | |
| It signals that the section is finished, allowing readers to move on to the next one. | |
| It creates smooth transitions between paragraphs, making the text easier to read. |
How to Write a Concluding Sentence for a Body Paragraph
Let’s now look at the steps necessary to write a good paragraph conclusion sentence.
- Restate the main idea. The first thing you should do is think of the key issue that your paragraph addresses. This issue should be expressed in the topic sentence that your concluding sentence will mirror.
- Formulate your findings. The second thing is to formulate your conclusion regarding the above issue. What do you want your readers to know about it?
- Indicate the evidence. To reinforce your point, you should mention evidence supporting your findings. By doing so, you will provide a logical basis for your conclusion.
- Indicate the geographical scope and the time frame. If the topic you’re discussing has a specific space dimension and time period, you can add them. However, this step is optional.
You can take these steps manually or use an automated conclusion sentence maker to speed up the writing process.
Ways to Start a Concluding Sentence
A good starter is one more essential element of an impressive and clear closing sentence. Let’s now look at some good and not-so-good ways to start concluding sentences.
Good Concluding Sentence Starters
A good conclusion sentence starter should be short, clear, and informative. In other words, it should clearly indicate that the readers have reached the final sentence of the section and will now pass to the next one.
Some good conclusion sentence starters are:
- Given all these points
- In light of this information
- In my opinion
- Upon considering all the facts
- With all this in mind
Concluding sentence: Words to Avoid
A very obvious starter is a not-so-good idea for a concluding sentence. Monotonous texts are difficult to read, so you should change the patterns, choosing more catchy words and phrases.
Here are some words that might be too obvious for concluding sentences:
- In conclusion
- To summarize
Concluding Sentence Examples
You might want to see good concluding sentence examples to enhance your understanding of what has already been said.
Let’s now look at a couple of examples.
Concluding Sentence Example 1
Here is an example of a well-structured paragraph about depression that contains all the necessary components.
| Being a serious mental health problem, depression causes significant consequences on individual and social levels. | |
| According to the WHO, worldwide. It is essential to understand that this condition affects not only one’s mental state but also physical health, leading to chronic diseases like diabetes and obesity. Moreover, depression places a substantial economic burden on society by reducing productivity and raising healthcare costs. | |
| Given all these points, depression should be addressed as a serious societal issue because it impacts individuals and social groups. |
Concluding Sentence Example 2
Here is another example of a paragraph about the negative impact of social media.
| Social media overuse has given rise to several negative consequences for individuals, relationships, and society at large. | |
| First, studies have shown that excessive use of Facebook and Instagram might cause a decreased sense of real-world social connection, leading to the feeling of isolation. Other detrimental consequences include disturbed sleep, reduced focus, and increased stress. Finally, social media is a place for the spread of misinformation and cyberbullying. | |
| In light of these facts, unchecked proliferation of social media must be critically examined because it negatively impacts individual people and society as a whole. |
As you can see from the above examples, an impressive topic sentence is another essential component of a well-written paragraph. Check a topic sentence generator if you’re stuck writing it by yourself.
Thank you for reading this article till the end! We hope that the guide and examples above will help you to quickly formulate a nice, clear, and informative concluding sentence for a paragraph. If you wish to polish other sections of your assignment, you are welcome to use the writing tools we’ve developed:
- Thesis statement maker
- Summary tool
- Paragraph & word changer
- Concluding Sentence | Overview, Examples & Starters
- Good Conclusion Starters for Final Paragraphs
- Concluding Sentence | SEA – Supporting English Acquisition
- Paragraphs & Topic Sentences: Writing Guides
- How to Write Strong Paragraphs – Grammarly
Related Posts
Fiction writing: have a fascinating travel to virtual reality.

How to Write a Critique: Offering You a Proven Model of Success
Critique essay: clarification and five steps to success, movie analysis tips: how to study cinematography as an art, art critique: advanced formula of effective art criticism.
How can I restate a thesis statement effectively?

This is the second of three chapters about Thesis Restatements . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce four tips for writing effective thesis restatements
– Explore the four elements of a thesis restatement
– Provide guidance on restating a thesis restatement using paraphrasing techniques
Chapter 1: Why are concluding thesis restatements important?
Chapter 2: How can I restate a thesis statement effectively?
Chapter 3: Can I see example academic thesis restatements?
Before you begin reading...
- video and audio texts
- knowledge checks and quizzes
- skills practices, tasks and assignments
In Chapter 1 of this short reader we introduced the basic elements of a concluding paragraph and compared the introductory thesis statement with the concluding thesis restatement . In Chapter 2, we next attempt to deconstruct and reconstruct some example thesis restatements to exemplify how these elements can be written most effectively. This exemplification can be broken down into four tips. Continue reading to learn about how to apply these simple tips to your own writing.
Tip 1: Include the Elements
As was mentioned at the end of Chapter 1, there are four key elements that build a thesis statement – and these same elements can be used to build thesis restatements too. The first is the inclusion of task language. The task language provided in the table below works to inform the reader of both the format of the assignment ( essay , dissertation , etc) and its type ( discuss , evaluate , etc.). From this information, an experienced reader should then be able to predict the likely structure of the essay based on their experience:
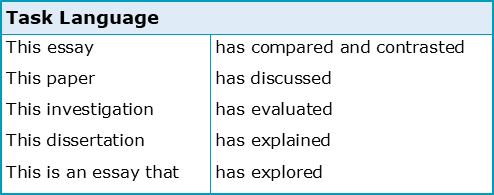
The second and third aspects are usually constructed from the topic of the essay and its key arguments. While the topic is simple as it’s often taken directly from the essay question, the writer’s key arguments are somewhat more complex as they’re drawn from the body-paragraph main ideas – as outlined in the essay’s topic sentences . As can be seen in the following table, however, these aspects are straightforward enough to write once the body section is complete (a thesis restatement should not be written before this stage):

When writing a thesis restatement, students should also remember to provide their main ideas in the same order as presented in the body section of their essay, also including stance (writer opinion) as the fourth element wherever required:
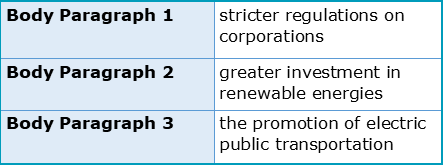
Tip 2: Paraphrase the Thesis Statement
While it’s important that the meaning of the original thesis is restated by the writer in the concluding paragraph , this doesn’t mean that precisely the same words should be used. In fact, doing so might appear lazy or repetitive to the reader. Instead, writers should use a wide variety of techniques to help them restate their thesis in different words and linguistic structures.

The most helpful techniques are listed for students below:
- alter the grammar
- alter the sentence structure
- change the order of information
- change the word order
- modify the word forms
- use antonyms and synonyms

Students should remember, of course, that it’s not necessary to paraphrase every word. Names, collocates and subject-specific words should be maintained, as can small grammatical words such as prepositions and determiners .
Tip 3: Be Specific and Concise
An effective thesis restatement should always be specific and concise . Specificity is critical as being vague will only confuse your reader or lead them to believe that you’re as unsure about your topic as they are. Likewise, overwritten text may be tiring for the reader and will use up your limited word count . To see this in action, take a look at the two example thesis restatements below and see why example A has the best balance of specificity and concision:

Tip 4: Edit Carefully
Finally, remember to check every aspect of your essay carefully for grammar and spelling errors before submission, including your concluding thesis restatement. Should a reader spot too many errors in your writing, their confidence in your argumentation will be reduced (and so too may your grade).
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) Thesis Restatements . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/concluding-paragraphs/thesis-restatements/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- Harvard University Writing Center
- University of North Carolina Writing Center
- University of New England
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters in this short reader about Thesis Restatements , you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Chapter 1 explores the topic: Why are concluding thesis restatements important? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: How can I restate a thesis statement effectively? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 3 explores the topic: Can I see example academic thesis restatements? Our Chapter 3 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 2 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our Thesis Restatements Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related to this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Another way to vary the structure is to present your points in a different order. Many thesis statements include three ideas, presented in the order in which they will be discussed in the body paragraphs. When restating, you can list the points in an alternate order. 3. Split the points up.
Step #1. Reread the original thesis statement carefully. Step #2. Determine in which person it is written (1 st, 2 nd, or 3 rd) and preserve that point of view in the rewrite. Step #3. Outline all keywords and main points that should be present in the reworded thesis.
Don't use clichés when restating the thesis. It is the same thing as using filler words within your body paragraphs; it dilutes the sweetness of your writing. Use conclusion sentence starters to introduce your restatement. You should try as much to avoid the common conclusion starters such as "to sum up, in conclusion, …etc."
Therefore, as you restate the thesis, you should not make apologetic statements because they undermine your argument. Such statements, which you should avoid, include: "It appears that …. "It is possible that …". "It is my opinion that …". The only time when using such statements when restating your thesis might be okay is when ...
Checklist for Restating a Thesis . Be specific about the introduction and build arguments. Answer why, what, and how this research thesis is going to be helpful; Choose a topic sentence that represents your thesis in less than 15 words; Conclude the thesis to summarise the whole idea; Offer new arguments and back them with factual information
Avoid incorporating unrelated or irrelevant content in your restatement. Changing the meaning of your thesis: Ensure that the restatement maintains the same core message or main argument as your original thesis statement. Avoid altering the meaning or taking a completely different stance without proper justification.
Definition and Purpose. Restating your thesis is the process of rewording the central argument of your essay or paper to remind the reader of your main point. The restated thesis should be clear and concise, and it should reflect the meaning of the original thesis. The purpose of restating your thesis is to reinforce the argument you made in ...
Be precise and clear: Ensure your restated thesis is specific and clearly reflects the core message of your paper. Avoid generalizations that can dilute the impact of your conclusion. Summarize key points: Briefly summarize the key points that support your thesis, providing a clear and concise wrap-up of your argument.
In this article, we explore 10 intriguing conclusion sentence starters that can help you eloquently wrap up your essays and ensure that your final words resonate with your audience. ... Effective strategies for writing a strong conclusion include restating your thesis in a new light, summarizing your main points, providing a call to action, and ...
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile.
The approach to restating a thesis can vary depending on the type of essay you are writing. While the core principles of rephrasing the central argument and reinforcing the main points remain the same, different essay types require different focuses in the conclusion. Below are some guidelines for restating the thesis in various essay formats:
3 Checklist to help you ensure an effective restatement of your thesis. 3.1 Understand the purpose of restatement. 3.2 Avoid clichés and overused phrases. 3.3 Be specific and avoid vague language. 3.4 Keep it concise. 3.5 Reflect on the essay's journey. 3.6 Emphasize the significance.
Following are 10 good conclusion starters, with examples. 1. While concluding, I would like to say…. Example: While concluding, I would like to say that, with the rising population fear is that, there is not enough time to take measures and avert this situation. Action is required right now.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
A concluding sentence "mirrors" a topic sentence that opens your paragraph. 📝 Summarizes the ideas. It wraps up all the arguments, evidence, and ideas used in the paragraph. 🪢 Connects the sections. It signals that the section is finished, allowing readers to move on to the next one. 🏄 Enhances writing flow.
Instead, writers should use a wide variety of techniques to help them restate their thesis in different words and linguistic structures. The most helpful techniques are listed for students below: alter the grammar. alter the sentence structure. change the order of information. change the word order. modify the word forms.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
•A topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph that signals to the reader what the para- graph's main idea will be. •Topic sentences should: » relate back to the argument of the thesis; » concisely summarize the key idea of the paragraph; » can even contain key words from the thesis statement. ToPic SenTenceS and comPrehen Sion
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
It should be intriguing and crystal clear all at the same time. As for the length, it should take around 10-20 % of the whole text. In the introduction, you put up your thesis firstly. There is no need to make the restatement yet. Body paragraph — you reveal everything you were about to say on one particular subject.
If you do this, your reading might forget what you are writing about. Second, variation is the key to restating your thesis. In other words, the best way to restate your thesis in the conclusion ...
The first sentence of the second body paragraph should state the second reason presented in your thesis. As with the previous paragraph, include supporting evidence after stating your topic sentence. Explain what the evidence means. Show the reader how this entire paragraph connects back to the thesis statement. Paragraph #3