- Scope And Excitement Of Physics
Physics covers an outsized area of study. Its range is extremely vast, from the molecular level to the astronomical level. Thus it’s exciting also. So, during this article, we’ll be discussing the scope and excitement of Physics. Physics is basically the study of energy , matter, and their interactions. It’s a very broad field because it is concerned with matter and energy in the least levels—from the foremost fundamental particles of interest in the whole universe.

Scope And Excitement Of Physics

What is the Scope of Physics?
Physics is a very vast subject. The scope of physics deals with the magnitude of physical quantities like energy, mass etc. The scope of physics is best understood under the three disciplines Microscopic, Mesoscopic and Macroscopic phenomena.
Microscopic Phenomena
This phenomenon takes place at the molecular or atomic level.
Mesoscopic Phenomena
It occurs between the microscopic and macroscopic phenomena. This level of physics is applicable once we enforce miniature of the macroscopic level phenomena as wiped out electronic physics.
Macroscopic Phenomena
All the theories related to classical physics is not applicable to microscopic and mesoscopic phenomena. Hence, macroscopic phenomena come into effect. It includes:
- Mechanics – The world of Physics that deals with the behaviour of bodies and their effect on the environment when subjected to external mechanical force is understood as Mechanics. For example, pushing a door or pulling a rope is an example of mechanical force.
- Electrodynamics – The world of Physics that deals with the electrical and magnetic phenomena relating to the charged and magnetic bodies are often known as Electrodynamics. Example – Response of electrical circuits to ac voltage(signal) or working of an antenna.
- Optics – The branch of Physics that deals with light related phenomena is mentioned as Optics. It covers the issues associated with optical phenomena and instruments.
- Thermodynamics – It’s the branch of physics that deals with the situations that consisted of macroscopic equilibrium and takes care of entropy change, temperature, internal energy etc. of the system through external work and warmth transfer. It’s different from mechanics because it doesn’t deal with the motion of particles as an entire. The efficiency of engines and refrigerators, the direction of physical or chemical processes are the issues of interest in Thermodynamics .
Excitement of Physics
Physics may be a very exciting subject. It excites people’s mentality in many ways. Some think that they will pose a huge magnitude of physical quantities with help of a couple of basic principles. For a few, each problem within physics may be a challenge.
Excitement results in Progress – Basically it is the excitement that results in experiment and progress. Excitement to seek out new ways of learning has made physics advance at such rapid speed. Physics is very vast with many variations and the most interesting as well as an exciting subject. Proving its laws may be a thrilling work for the lover of physics. As we move on, we’ll see many interesting parts of physics in future.
FAQs about Scope And Excitement Of Physics
Q.1. What is the two scopes of physics?
Answer – The two scopes of physics are – Classical Physics and Modern Physics. Classical physics principle works with the macroscopic phenomena while the modern physics principle works upon the microscopic phenomena.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Physical World
- Scope of Physics
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Scope and Excitement of Physics with Example
- Updated by Scienly
- On May 30, 2024
In this chapter, we will understand about the scope and excitement of physics with the help of examples. First, we will understand the scope of physics.
The scope of physics means the extent or range of view. It is truly very vast and wide. The domain of physics covers an enormous range of magnitude of physical quantities, like length, time, mass, energy, etc. For example, the range of distance varies from 10 -14 cm to 10 25 m i.e. from the size of nucleus to the size of universe. The range of masses varies from 10 -30 kg (mass of electron) to 10 55 kg (mass of a universe). The range of time varies from 10 -22 sec (time taken by electromagnetic radiation to cross a nuclear distance) to 10 18 sec (life of sun). Thus, the scope of physics is vast.
Table of Contents
Therefore, the scope of physics is broadly divided into two groups, on the basis of magnitude of physical quantities involved in it:
- Classical physics
- Modern physics

Classical Physics
The knowledge of physics that had collected up to about the year 1890 is called classical physics. It mainly deals with the study of macroscopic object travelling with speed as compared to much less than the speed of light. In other words, classical physics mainly deals with macroscopic phenomena.
Macroscopic Domain:
The domain which includes the phenomena at laboratory, terrestrial, and astronomical scale is called macroscopic domain. It deals with things that are large in size. It includes both terrestrial and astronomical levels. For example, all the things we can see with our naked eyes, like humans, tress, birds, animals, vehicles, buildings, etc. come under the terrestrial level. All the celestial bodies like the planets, starts, and moon, come under the astronomical level.
Macroscopic domain also helps to study of the law of nature and natural phenomena, including particle interaction, thermal expansions, and gravitational force of attraction. There are the following subject or sub-disciplines included under this domain. They are as:
- Electrodynamics
- Thermodynamics
This subject deals with the study of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitational law. It is basically related to the concepts of motion, position, and energy of particles or objects. For example, when we drop a very heavy object and a light object from the same height, both reach the ground simultaneously, appeared no less than a magic to a common person. The laws of Newton easily explained this magical observation.
Someone sitting in the train finds the persons on the platform moving in the opposite direction while a person on the platform finds the man in the train going away from him. The theory of relativity easily explained the contradiction of their observation. In mechanics, we get the knowledge of several exciting phenomena, such as the state of rest and motion of physical objects, propagation of water waves, sound waves in air, equilibrium of twisted rod, rocket propulsion by ejecting gases, etc.
Electrodynamics:
This sub-discipline deals with the study of electric and magnetic phenomena associated with magnetic and charged bodies. These phenomena are mainly based on the laws given by Coulomb, Oersted, Ampere, and Faraday. In electrodynamics, we acquire the knowledge of several exciting phenomena, such as:
- Motion of current carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
- A magnet pulling an iron piece towards itself.
- Bulb lights our house.
- Fan flows air
- Refrigerator prepares ice cream
- Air-conditioners give cool air in the room during summer seasons
- Propagation of radio waves in ionosphere and many more.
We study many of such exciting process in the electrodynamics.
Optics deals with the study of light phenomena, such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, polarization, dispersion, scattering, etc. For example:
- Why sky is blue?
- How do stars appear twinkling at night?
- Reflection and refraction of light
- Dispersion of light, etc.
Thermodynamics:
In thermodynamics, we study about the system in macroscopic equilibrium as well as changes in internal energy, temperature, entropy, etc. In thermodynamics, we get the knowledge of heat and energy and its conversion. For example, the study of heat helps us to know the rise and fall of temperature, working of heat engines, conductivity of heat, etc.
The laws of classical physics adequately explained the microscopic systems in which things are visible from the naked eye. But they were inadequate in explaining the behavior of microscopic systems. Classical physics also failed to explain the correct answer when applied to the fast moving particles. This led to the development of modern physics after the year of 1890.
Modern Physics
The knowledge of physics which had accumulated after 1890 and continued up to the present day is called modern physics. It mainly deals with microscopic phenomena.
Microscopic Domain:
The domain which includes all the phenomena at a minute scale like atomic, molecular and nuclear levels is called microscopic domain or microscopic phenomena. It mainly deals with the study of the interaction of particles at sub-atomic level like electron, proton, and other particles. For example, we know all things are made up of atoms in this universe. These atoms combine together to form molecules.
With our naked eyes, we cannot see them as atoms are very small in size. Each atom is composed of one nucleus, which helps us in understanding the microscopic domain of electron, protons, and neutrons. In modern physics, the quantum mechanics and the theory of relativity easily explained such microscopic phenomena.
E. Schrödinger, W. Heisenberg, and P.A.M. Dirac developed quantum mechanics in 1925. Quantum mechanics easily explained the behavior of sub-atomic particles and fundamental nature of matter. Einstein developed a special theory of relativity in 1905 for the particles that are moving with the speed equal to the speed of light. The theory of relativity easily explained the motion of objects moving with velocity comparable to light speed.
Under this domain, there are many discoveries classified into atomic physics, nuclear physics, quantum physics, bio-physics, medico-physics, etc.
Mesoscopic Domain:
The mesoscopic domain is the domain that lies in between the microscopic and macroscopic domains. It is also called mesoscopic physics. It deals with things which are neither small nor large in size and mainly used for research purposes. Rice, small insects, sand, etc. are some examples of the mesoscopic domain or physics.
Excitement of Physics
Physics is a very exciting subject that helps us to know the interesting facts or reasons for the day-to-day natural phenomena in our life. It helps to provide answers to exciting questions, such as:
- Why is sunset red?
- Why are atoms held together?
Beating of a drum causes vibration producing sound, and many more exciting questions. In fact, there are numerous exciting such questions that physics provides answers.
There are many laws such as the law of nature, electromagnetic induction, Faraday’s law, etc. that are crucial for practical purposes. Modern devices and machines use these laws and principles of physics.
In addition to it, with the help of physics we also come to get the knowledge numerous natural topics like
- How does the television display the movies?
- How do the satellites work?
- How do the seasons or climate change?
- What are the different types of forces and how we apply them practically?
- Phenomenon of day and night on the earth.
These are only a few examples. In fact, there are a very large number of such facts and questions of which we can get answers using the concepts of physics.
In this chapter, we have discussed the scope and excitement of physics with the help of many examples. Although, the scope of physics is a very wide concept, mainly used in analytic properties, both qualitatively and quantitatively. There are a total of three levels of scopes in physics: microscopic, macroscopic, and mesoscopic levels.
These three levels of domains cover atomic, molecular, terrestrial, and astronomical. In addition to it, physics also helps in studying the physical laws with illustrations. It excites the people in numerous ways with its interesting facts and concepts. Hope that you will have understood the basic facts related to the scope and excitement of physics.
Related Posts
What is physical quantity | types, example.
- September 16, 2023

Units and Measurement Notes for Class 11
- September 14, 2023

Law of Conservation of Energy with Example
- August 28, 2023

Conservation Laws in Physics
- August 26, 2023
- Units And Dimensions
- Scope And Excitement Of Physics
- Active page
Units And Dimensions of Class 11
The domain of physics consists of wide variety and large number of natural phenomena. Hence, the scope of physics is very vast and obviously the excitement that one gets from the careful study of physics has got no boundaries.
Scope of Physics
For example, when we study one of the basic physical quantities called mass, we come across the values ranging from minute masses like mass of an electron (of the order of 10−30 kg) to heavy masses like mass of universe (1055 kg). Similarly, in case of other basic quantities like length and time also the range is very wide.
Hence, the scope of physics can be understood easily, only when we can classify the study of physics chiefly into three levels. They are
(a) Macroscopic level study of physics.
(b) Mesoscopic level study of physics.
(c) Microscopic level study of physics.
Macroscopic level study of physics: Macroscopic level study of physics mainly includes the study of basic laws of nature and several natural phenomena like gravitational force of attraction between any two bodies in the universe (in mechanics), variation of quantities like pressure, volume, temperature, etc. of gases on their thermal expansion or contraction (in thermodynamics), etc.
Microscopic level study of physics: The microscopic level study of physics deals with constitution and structure of matter at the level of atoms or nuclei. For example, in case of nucleus interaction between elementary particles like electrons, protons and other particles , and in the case of materials point of view particle size and structure. Since the bulk properties of the material is different from the microscopic level properties. .
Mesoscopic level study of physics: The mesoscopic level study of physics deals with the intermediate domain of macroscopic and microscopic, where we study various physical phenomena of atoms in bulk.
So, the edifice of physics is beautiful and one can appreciate the subject as and when one pursues the same seriously.

Excitement of Physics
The study of physics is exciting in many ways as it explains us the reason behind several interesting features like (a) how days and nights are formed? (b) how different climatic conditions are formed in different seasons? (c) how satellite works and helps in using several devices like television, telephones, etc.? (d) how an astronaut travels to celestial space ? (e) how we can convert one form of energy to another ? (f) how different types of forces are governing different types of motion in universe ? (g) how different type of materials are used in the present day-SMART science technology?
It is quite common and simple that every human being on the earth will be interested to know the answers for at least few of the above questions. As physics is the subject which answers them, naturally the study of physics will be exciting.
- Introduction
- Technology And Society
- Fundamental Forces In Nature
- Conservation Laws
- Measurement And Units
- Measurement Of Mass
- Errors In Measurement
- Physical Quantities

Talk to Our counsellor

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Scope and Excitement of Physics for IIT JEE
- Scope And Excitement Of Physics

The Scope And Excitement Of Physics
Scope of physics:.
The scope of classical Physics deals with the following branches in Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Thermodynamics
- Electromagnetism
Modern-day Physics (after the 19th century) deals with concepts of Relativity and Quantum Mechanics. Relativity as we know was something explored by Albert Einstein. The scope of physics grew as the theory of relativity changed the way we used to think about the world and atmosphere. It is most probably the most comprehensive theories which the whole world has acknowledged. The renowned physicist Richard Feynman introduced the world to Quantum Mechanics. It is the study of motion and interaction of subatomic particles, wave-particle duality with the help of a suitable mathematical description.
The diagram given below illustrates the different domains based on speed and size of matter in consideration.
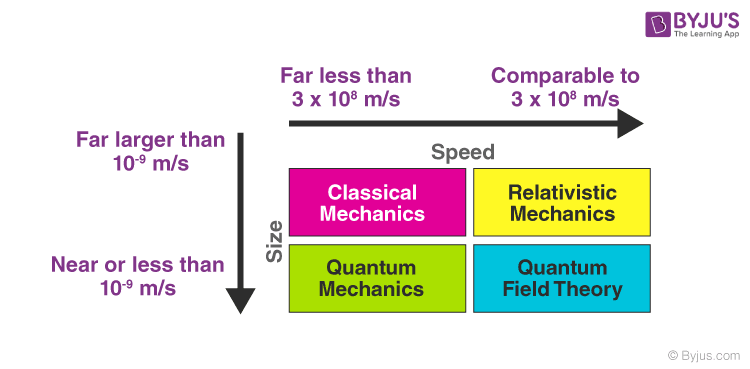
Excitement of Physics:
Do you think teleportation is possible? If your answer is yes, how would that work? I’ll get back to this. If your answer is no, why not? Did people living five hundred years ago know that there will exist a device that can tell you the position of any planet or constellation or such celestial bodies in seconds, should you wish to look for them? I’m talking about Sky Maps of course.
All this has been achieved only because of those people who were curious enough to know why everything exists as it does. The way to teleport is already out there, we just have to find that way how. Where there is a will there is a way, and the will is found through excitement!
Regarding my question on teleportation, we have already achieved the ability of quantum teleportation. In this process, the quantum information (exact information about atom or photon) can be transmitted from one location to another. We may be at this stage now, but who’s to say macroscopic beings like us won’t be able to transport ourselves from one location to another in the future!

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Physics related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Scope and Excitement of Physics
Physics is the branch of science that deals with the study of matter, force and energy. It is concerned with a wide variety of subjects like magnetism, heat, light, sound, electricity etc. Thus there exists many theories that are developed by various physicists. These theories will be experimentally tested several times and only then they are accepted as it fits as description of nature. These theories continue to be areas of active research.
Scope of Physics
Physics has a very wide scope. There are three domains of interest which are macroscopic domain, mesoscopic and microscopic domain. The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or processes are of a size that is measurable and observable by the naked eye. The microscopic scale is the scale of size or length used to describe objects smaller than those that are easily be seen by the naked eye and which require a lens or microscope to see them clearly.
Mesoscopic domain comes between the macroscopic and microscopic domain. Mesoscopic domain deals with a few tens or hundreds of atoms. It deals with several groups of atoms. Now a days this is an exciting field of research.
Physics tries to reach out the complete understanding of the universe and thus the various natural phenomena. It attempts to find the elementary particles that make the matter, forces that guide the phenomena and the various forms of energy.
Physics has its scope in Classical physics and Modern physics.
Classification in physics
Classical Physics
Classical physics is a traditional physics. Over the centuries our understanding of the universe progressed until we arrived at figures like Galileo and Newton. These two scientists brought about the birth of classical physics. Classical physics mainly deals with forces in nature. It is concerned with the matter and energy under normal conditions. It deals in terms of human observation.
Classical physics has sub branches like mechanics, thermodynamics, electrodynamics and optics. Classical mechanics can be also called as Newtonian Mechanics . We know that it was Sir Isaac Newton who introduced the laws of motion. It involves a classical kind of approach which were given by Hamiltonian and Lagrange methods.
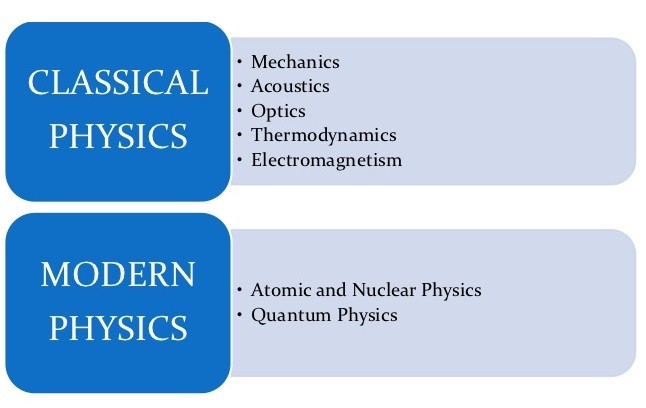
Classical physics and modern physics
Mechanics is one branch of classical physics that deals with the study of motion of various objects and particles. It deals with the study of forces that act on bodies, whether it is at static or in motion. The three sub branches are Statics, Dynamics and Kinematics. Statics deals with the forces that act on bodies at rest. Dynamics deals with the forces that affect the body in motion. Kinematics refers to the description and analysis on the cause of forces.
Acoustics Physics is another branch of classical physics. It is concerned with the study of the production of sound waves. The branch Optics refers to the study of the light. It has other sub branches. Physical optics involves the study on the production, nature and properties of light. Physiological optics refers on the part that is played by light in vision. Geometrical optics deals with the refraction and reflection of light as experienced in the study of mirrors and lenses. These principles were later used to focus light in telescopes, cameras and microscopes.
Thermodynamics is the study of the connection between heat and other forms of energy. The effects of changes in temperature, pressure and volume on physical system and their relation to energy and work will all be covered under thermodynamics. The kinetic theory of gases is based upon classical thermodynamics. It was also possible to increase the efficiency of steam engines by thermodynamics in early days. It mentions the existence of quantity called entropy.
Electromagnetism deals with the study of the properties of the electric current and magnetism and their relationship. Electrostatics refers to the electric charges at rest. Electrodynamics deals with the moving charges. Magneto statics deals with the magnetic poles at rest. The relationship between electromagnetism and mechanics can be described by the special theory of relativity. Maxwell’s equations are derived from the principle of relativity and the principle of stationary action in mechanics.
It was Albert Einstein who proposed the theory of special relativity on one of his article named ‘On the electrodynamics of moving bodies. The theory depends on two postulates. The mathematical forms of the laws of physics are invariant in all inertial systems. In vacuum the speed of the light is found to be constant and is also independent of the source or the observer. General relativity says that the space and time are part of same fabric called space time and that the force of gravity comes from objects bending space-time that makes other objects fall in towards them.

Theory of relativity
Modern Physics
Modern physics refers to the behavior of matter and energy under extreme conditions. It has several branches. Atomic and nuclear physics is the study of the components, structure and behavior of the nucleus of the atom. Quantum physics is concerned with the study of the individual nature of the phenomena at the atomic levels. It focuses on the indivisible units or discrete units of energy called Quanta which is as described by the quantum theory. Quantum mechanics is one branch that comprises the atomic and sub atomic systems and also their interaction with radiation.

Atomic physics
When an electron moves from one allowed level to another, an amount of energy is either emitted or absorbed. Here the frequency is directly proportional to the energy difference between two levels. The photo electric effect confirmed the quantization of light. Louie de Broglie has found out that not only light waves exhibit particle like nature, but also particles exhibit wave like nature. An important discovery of quantum theory is the uncertainty principle which places a theoretical limit on the accuracy of certain measurements.
Relativistic physics is the study of phenomena that takes place in the frame of reference that is in motion with respect to an observer. Solid state physics is the study of all properties of solid materials. It comprises of things like electrical conduction in crystals of semi-conductors and metals, superconductivity and photoconductivity. Condensed matter physics is a topic in solid state physics. It is the study of all properties of condensed materials which are solids, liquids, and dense gas, thus developing new materials with better properties. From this evolved the great technologies like computers, lasers etc.
Astrophysics is the physics in the universe that deals with the nature of stars and other celestial bodies in astronomy. Biophysics is the study of the physical behaviors of biological processes. Chemical Physics is the science of physical relations in chemistry. Econophysics deals with the physical processes and their relations in the science of economy. Geophysics is the science of physical relations that happens in our planet. Medical physics which is also known as bio medical physics is the application, prevention, diagnosis and treatment in the medical field.
We know that plasma is the fourth state of matter. Plasma physics is the study of the plasma. Low temperature physics is the study of the production and maintenance of temperatures down to almost absolute zero, and the various phenomena which occur only at that temperature.
Thus we can say that the scope of physics is very vast.
Excitement of Physics
The excitement of physics comes from the challenge in conducting new experiments for revealing the secrets of nature. The scientific progress is not only qualitative but also quantitative analysis. The basics levels, laws and theories of physics are universal. There is good strategy of approximation. A good strategy is means that we will focus and observe on the necessary facts. Then we will discover and later do the needful corrections to construct a well - defined theory. We will apply the laws of physics for practical purposes.
Physics is a huge subject that covers many different topics that ranges from galaxies in the depths of space to the sub atomic particles.
There are three domains of interest in the field of physics. They are macroscopic domain, mesoscopic and microscopic domain.
Macroscopic domain deals with matter and objects that are measurable and can be observed by the naked eye.
Microscopic domain deals with molecules, atoms and nucleus. It deals with objects which require a lens or microscope to see them clearly.
Mesoscopic domain lies between the microscopic domain and macroscopic domain.
Physics has its scope in Classical and Modern physics.
Classical physics has sub divisions like mechanics, thermodynamics, electrodynamics and optics. Classical physics is the traditional physics.
Modern physics includes atomic physics, nuclear physics, quantum physics etc.
The excitement of physics comes in conducting new experiments, discover the different secrets of nature and then applying the laws of physics for practical purposes.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings

View courses by askIITians

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask a doubt.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Class 11 Physics Physical World – Scope and Excitement of Physics
Previous <<< Introduction to Physics
Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 – Physical World
Next >>> Fundamental Forces in Nature
Scope and Excitement of Physics
[Watch Video for Understanding More with Explanation and Examples]
The scope of physics lies in its various sub-disciplines. .
Physics can be divided mainly into three domains: macroscopic, microscopic and mesoscopic.
Macroscopic domain
This domain deals with something big. Includes phenomena at the laboratory, terrestrial and astronomical scales. Which includes objects and phenomena we can see with our eyes and which we can see with the help of a telescope.
Classical physics deals mainly with macroscopic phenomena and includes subjects like Mechanics, Electrodynamics, Optics and Thermodynamics.
Microscopic domain
This domain related to something very small in size which is of the order of atoms and nuclei or smaller than this. Thus, the microscopic domain includes atomic, molecular and nuclear phenomena.
Mesoscopic domain
Mesoscopic means something of size in between microscopic and macroscopic. That is, it deals with a few tens or hundreds of atoms. This field is developing these days and has emerged as an exciting field of research. Example nanophysics or nanotechnology.
Excitement of Physics
Four points Physics is exciting:
- Elegance and universality of its basic theories. Eg: Newton’s laws of gravitation
- Carry out interesting experiments. Eg. Split light into seven colors.
- To understand more about nature and its phenomena. Eg. How rainbow occurred?
- Applying laws of physics in practical life. Eg. How engine works.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the scope and excitement of physics assignment, the next segment is about macroscopic physics. It deals with the study and understanding of finite size objects and terrestrial bodies. In contrast to modern physics, it is known as classical physics.
The scope of physics deals with the magnitude of physical quantities like energy, mass etc. The scope of physics is best understood under the three disciplines Microscopic, Mesoscopic and Macroscopic phenomena. Microscopic Phenomena. This phenomenon takes place at the molecular or atomic level.
In this chapter, we have discussed the scope and excitement of physics with the help of many examples. Although, the scope of physics is a very wide concept, mainly used in analytic properties, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Scope of Physics. For example, when we study one of the basic physical quantities called mass, we come across the values ranging from minute masses like mass of an electron (of the order of 10−30 kg) to heavy masses like mass of universe (1055 kg).
Scope And Excitement Of Physics. Download PDF. Study Material. Exam Info. Syllabus. Courses. Previous Year Question Paper. Practice Materials. Latest Updates. JEE : Online JEE Coaching. Brаnсh of Sсіеnсе - Classical, Modern and Evolution of Physics.
The Scope And Excitement Of Physics. Scope of Physics: The scope of classical Physics deals with the following branches in Physics. Classical Mechanics. Thermodynamics. Electromagnetism. Optics. Modern-day Physics (after the 19th century) deals with concepts of Relativity and Quantum Mechanics.
Scope and Excitement of Physics Physical World Class 11th by Suraj Sir. 2,345 views. 91. #physicalworld #class11 #scope #excitement #physicsClass 11th Chapter number -1 Physical...
Explore the vast scope of Physics, from Classical Mechanics to Quantum Mechanics, and the excitement it brings with its potential, such as quantum teleportation.
Now a days this is an exciting field of research. Physics tries to reach out the complete understanding of the universe and thus the various natural phenomena. It attempts to find the elementary particles that make the matter, forces that guide the phenomena and the various forms of energy.
Scope and Excitement of Physics. [Watch Video for Understanding More with Explanation and Examples] The scope of physics lies in its various sub-disciplines. . Physics can be divided mainly into three domains: macroscopic, microscopic and mesoscopic.