All Subjects

Doing the DBQ: Thesis, Part 1
october 30, 2019
Patrick Lasseter
In this live stream, we continue our breakdown of the DBQ with an emphasis on the Thesis. We will look at what the thesis is, tips for writing a thesis, and will explore a sample DBQ in order to arrive at writing a thesis statement.

Stay Connected
© 2024 fiveable inc. all rights reserved., ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website., doing the dbq, part 2: evidence.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write a DBQ Essay: Key Strategies and Tips
Advanced Placement (AP)

The DBQ, or document-based-question, is a somewhat unusually-formatted timed essay on the AP History Exams: AP US History, AP European History, and AP World History. Because of its unfamiliarity, many students are at a loss as to how to even prepare, let alone how to write a successful DBQ essay on test day.
Never fear! I, the DBQ wizard and master, have a wealth of preparation strategies for you, as well as advice on how to cram everything you need to cover into your limited DBQ writing time on exam day. When you're done reading this guide, you'll know exactly how to write a DBQ.
For a general overview of the DBQ—what it is, its purpose, its format, etc.—see my article "What is a DBQ?"

Table of Contents
What Should My Study Timeline Be?
Preparing for the DBQ
Establish a Baseline
Foundational Skills
Rubric Breakdown
Take Another Practice DBQ
How Can I Succeed on Test Day?
Reading the Question and Documents
Planning Your Essay
Writing Your Essay
Key Takeaways
What Should My DBQ Study Timeline Be?
Your AP exam study timeline depends on a few things. First, how much time you have to study per week, and how many hours you want to study in total? If you don't have much time per week, start a little earlier; if you will be able to devote a substantial amount of time per week (10-15 hours) to prep, you can wait until later in the year.
One thing to keep in mind, though, is that the earlier you start studying for your AP test, the less material you will have covered in class. Make sure you continually review older material as the school year goes on to keep things fresh in your mind, but in terms of DBQ prep it probably doesn't make sense to start before February or January at the absolute earliest.
Another factor is how much you need to work on. I recommend you complete a baseline DBQ around early February to see where you need to focus your efforts.
If, for example, you got a six out of seven and missed one point for doing further document analysis, you won't need to spend too much time studying how to write a DBQ. Maybe just do a document analysis exercise every few weeks and check in a couple months later with another timed practice DBQ to make sure you've got it.
However, if you got a two or three out of seven, you'll know you have more work to do, and you'll probably want to devote at least an hour or two every week to honing your skills.
The general flow of your preparation should be: take a practice DBQ, do focused skills practice, take another practice DBQ, do focused skills practice, take another practice DBQ, and so on. How often you take the practice DBQs and how many times you repeat the cycle really depends on how much preparation you need, and how often you want to check your progress. Take practice DBQs often enough that the format stays familiar, but not so much that you've done barely any skills practice in between.

He's ready to start studying!
The general preparation process is to diagnose, practice, test, and repeat. First, you'll figure out what you need to work on by establishing a baseline level for your DBQ skills. Then, you'll practice building skills. Finally, you'll take another DBQ to see how you've improved and what you still need to work on.
In this next section, I'll go over the whole process. First, I'll give guidance on how to establish a baseline. Then I'll go over some basic, foundational essay-writing skills and how to build them. After that I'll break down the DBQ rubric. You'll be acing practice DBQs before you know it!
#1: Establish a Baseline
The first thing you need to do is to establish a baseline— figure out where you are at with respect to your DBQ skills. This will let you know where you need to focus your preparation efforts.
To do this, you will take a timed, practice DBQ and have a trusted teacher or advisor grade it according to the appropriate rubric.
AP US History
For the AP US History DBQ, you'll be given a 15-minute reading period and 45 minutes of writing time.
A selection of practice questions from the exam can be found online at the College Board, including a DBQ. (Go to page 136 in the linked document for the practice prompt.)
If you've already seen this practice question, perhaps in class, you might use the 2015 DBQ question .
Other available College Board DBQs are going to be in the old format (find them in the "Free-Response Questions" documents). This is fine if you need to use them, but be sure to use the new rubric (which is out of seven points, rather than nine) to grade.
I advise you to save all these links , or even download all the Free Response Questions and the Scoring Guides, for reference because you will be using them again and again for practice.
AP European History
The College Board has provided practice questions for the exam , including a DBQ (see page 200 in the linked document).
If you've already seen this question, the only other questions available through the College Board are in the old format, because the 2016 DBQ is in a new, seven-point format identical to the AP US History exam. Just be sure to use the new DBQ rubric if you want to use any of the old prompts provided by the College Board . (DBQs are in the documents titled "Free-Response Questions.")
I advise you to save all these links (or even download all the Free Response Questions and the Scoring Guides) for reference, because you will be using them again and again for practice.

Who knows—maybe this will be one of your documents!
AP World History
For this exam, you'll be given a 15-minute reading period and 45 minutes of writing time . As for the other two history exams, the College Board has provided practice questions . See page 166 for the DBQ.
If you've already seen this question, the only other questions available through the College Board are in the old format, because the 2017 World History DBQ is in a new, seven-point format identical to the AP US History and AP European History exams. So be sure to use the new DBQ rubric if you want to use any of the old prompts provided by the College Board . (DBQs are in the documents titled "Free-Response Questions.")
Finding a Trusted Advisor to Look at Your Papers
A history teacher would be a great resource, but if they are not available to you in this capacity, here are some other ideas:
- An English teacher.
- Ask a librarian at your school or public library! If they can't help you, they may be able to direct you to resources who can.
- You could also ask a school guidance counselor to direct you to in-school resources you could use.
- A tutor. This is especially helpful if they are familiar with the test, although even if they aren't, they can still advise—the DBQ is mostly testing academic writing skills under pressure.
- Your parent(s)! Again, ideally your trusted advisor will be familiar with the AP, but if you have used your parents for writing help in the past they can also assist here.
- You might try an older friend who has already taken the exam and did well...although bear in mind that some people are better at doing than scoring and/or explaining!
Can I Prepare For My Baseline?
If you know nothing about the DBQ and you'd like to do a little basic familiarization before you establish your baseline, that's completely fine. There's no point in taking a practice exam if you are going to panic and muddle your way through it; it won't give a useful picture of your skills.
For a basic orientation, check out my article for a basic introduction to the DBQ including DBQ format.
If you want to look at one or two sample essays, see my article for a list of DBQ example essay resources . Keep in mind that you should use a fresh prompt you haven't seen to establish your baseline, though, so if you do look at samples don't use those prompts to set your baseline.
I would also check out this page about the various "task" words associated with AP essay questions . This page was created primarily for the AP European History Long Essay question, but the definitions are still useful for the DBQ on all the history exams, particularly since these are the definitions provided by the College Board.
Once you feel oriented, take your practice exam!
Don't worry if you don't do well on your first practice! That's what studying is for. The point of establishing a baseline is not to make you feel bad, but to empower you to focus your efforts on the areas you need to work on. Even if you need to work on all the areas, that is completely fine and doable! Every skill you need for the DBQ can be built .
In the following section, we'll go over these skills and how to build them for each exam.

You need a stronger foundation than this sand castle.
#2: Develop Foundational Skills
In this section, I'll discuss the foundational writing skills you need to write a DBQ.
I'll start with some general information on crafting an effective thesis , since this is a skill you will need for any DBQ exam (and for your entire academic life). Then, I'll go over outlining essays, with some sample outline ideas for the DBQ. After I'll touch on time management. Finally, I'll briefly discuss how to non-awkwardly integrate information from your documents into your writing.
It sounds like a lot, but not only are these skills vital to your academic career in general, you probably already have the basic building blocks to master them in your arsenal!
Writing An Effective Thesis
Writing a good thesis is a skill you will need to develop for all your DBQs, and for any essay you write, on the AP or otherwise.
Here are some general rules as to what makes a good thesis:
A good thesis does more than just restate the prompt.
Let's say our class prompt is: "Analyze the primary factors that led to the French Revolution."
Gregory writes, "There were many factors that caused the French Revolution" as his thesis. This is not an effective thesis. All it does is vaguely restate the prompt.
A good thesis makes a plausible claim that you can defend in an essay-length piece of writing.
Maybe Karen writes, "Marie Antoinette caused the French Revolution when she said ‘Let them eat cake' because it made people mad."
This is not an effective thesis, either. For one thing, Marie Antoinette never said that. More importantly, how are you going to write an entire essay on how one offhand comment by Marie Antoinette caused the entire Revolution? This is both implausible and overly simplistic.
A good thesis answers the question .
If LaToya writes, "The Reign of Terror led to the ultimate demise of the French Revolution and ultimately paved the way for Napoleon Bonaparte to seize control of France," she may be making a reasonable, defensible claim, but it doesn't answer the question, which is not about what happened after the Revolution, but what caused it!
A good thesis makes it clear where you are going in your essay.
Let's say Juan writes, "The French Revolution, while caused by a variety of political, social, and economic factors, was primarily incited by the emergence of the highly educated Bourgeois class." This thesis provides a mini-roadmap for the entire essay, laying out that Juan is going to discuss the political, social, and economic factors that led to the Revolution, in that order, and that he will argue that the members of the Bourgeois class were the ultimate inciters of the Revolution.
This is a great thesis! It answers the question, makes an overarching point, and provides a clear idea of what the writer is going to discuss in the essay.
To review: a good thesis makes a claim, responds to the prompt, and lays out what you will discuss in your essay.
If you feel like you have trouble telling the difference between a good thesis and a not-so-good one, here are a few resources you can consult:
This site from SUNY Empire has an exercise in choosing the best thesis from several options. It's meant for research papers, but the general rules as to what makes a good thesis apply.
About.com has another exercise in choosing thesis statements specifically for short essays. Note, however, that most of the correct answers here would be "good" thesis statements as opposed to "super" thesis statements.
- This guide from the University of Iowa provides some really helpful tips on writing a thesis for a history paper.
So how do you practice your thesis statement skills for the DBQ?
While you should definitely practice looking at DBQ questions and documents and writing a thesis in response to those, you may also find it useful to write some practice thesis statements in response to the Free-Response Questions. While you won't be taking any documents into account in your argument for the Free-Response Questions, it's good practice on how to construct an effective thesis in general.
You could even try writing multiple thesis statements in response to the same prompt! It is a great exercise to see how you could approach the prompt from different angles. Time yourself for 5-10 minutes to mimic the time pressure of the AP exam.
If possible, have a trusted advisor or friend look over your practice statements and give you feedback. Barring that, looking over the scoring guidelines for old prompts (accessible from the same page on the College Board where past free-response questions can be found) will provide you with useful tips on what might make a good thesis in response to a given prompt.
Once you can write a thesis, you need to be able to support it—that's where outlining comes in!

This is not a good outline.
Outlining and Formatting Your Essay
You may be the greatest document analyst and thesis-writer in the world, but if you don't know how to put it all together in a DBQ essay outline, you won't be able to write a cohesive, high-scoring essay on test day.
A good outline will clearly lay out your thesis and how you are going to support that thesis in your body paragraphs. It will keep your writing organized and prevent you from forgetting anything you want to mention!
For some general tips on writing outlines, this page from Roane State has some useful information. While the general principles of outlining an essay hold, the DBQ format is going to have its own unique outlining considerations.To that end, I've provided some brief sample outlines that will help you hit all the important points.
Sample DBQ Outline
- Introduction
- Thesis. The most important part of your intro!
- Body 1 - contextual information
- Any outside historical/contextual information
- Body 2 - First point
- Documents & analysis that support the first point
- If three body paragraphs: use about three documents, do deeper analysis on two
- Body 3 - Second point
- Documents & analysis that support the second point
- Use about three documents, do deeper analysis on two
- Be sure to mention your outside example if you have not done so yet!
- Body 4 (optional) - Third point
- Documents and analysis that support third point
- Re-state thesis
- Draw a comparison to another time period or situation (synthesis)
Depending on your number of body paragraphs and your main points, you may include different numbers of documents in each paragraph, or switch around where you place your contextual information, your outside example, or your synthesis.
There's no one right way to outline, just so long as each of your body paragraphs has a clear point that you support with documents, and you remember to do a deeper analysis on four documents, bring in outside historical information, and make a comparison to another historical situation or time (you will see these last points further explained in the rubric breakdown).
Of course, all the organizational skills in the world won't help you if you can't write your entire essay in the time allotted. The next section will cover time management skills.

You can be as organized as this library!
Time Management Skills for Essay Writing
Do you know all of your essay-writing skills, but just can't get a DBQ essay together in a 15-minute planning period and 40 minutes of writing?
There could be a few things at play here:
Do you find yourself spending a lot of time staring at a blank paper?
If you feel like you don't know where to start, spend one-two minutes brainstorming as soon as you read the question and the documents. Write anything here—don't censor yourself. No one will look at those notes but you!
After you've brainstormed for a bit, try to organize those thoughts into a thesis, and then into body paragraphs. It's better to start working and change things around than to waste time agonizing that you don't know the perfect thing to say.
Are you too anxious to start writing, or does anxiety distract you in the middle of your writing time? Do you just feel overwhelmed?
Sounds like test anxiety. Lots of people have this. (Including me! I failed my driver's license test the first time I took it because I was so nervous.)
You might talk to a guidance counselor about your anxiety. They will be able to provide advice and direct you to resources you can use.
There are also some valuable test anxiety resources online: try our guide to mindfulness (it's focused on the SAT, but the same concepts apply on any high-pressure test) and check out tips from Minnesota State University , these strategies from TeensHealth , or this plan for reducing anxiety from West Virginia University.
Are you only two thirds of the way through your essay when 40 minutes have passed?
You are probably spending too long on your outline, biting off more than you can chew, or both.
If you find yourself spending 20+ minutes outlining, you need to practice bringing down your outline time. Remember, an outline is just a guide for your essay—it is fine to switch things around as you are writing. It doesn't need to be perfect. To cut down on your outline time, practice just outlining for shorter and shorter time intervals. When you can write one in 20 minutes, bring it down to 18, then down to 16.
You may also be trying to cover too much in your paper. If you have five body paragraphs, you need to scale things back to three. If you are spending twenty minutes writing two paragraphs of contextual information, you need to trim it down to a few relevant sentences. Be mindful of where you are spending a lot of time, and target those areas.
You don't know the problem —you just can't get it done!
If you can't exactly pinpoint what's taking you so long, I advise you to simply practice writing DBQs in less and less time. Start with 20 minutes for your outline and 50 for your essay, (or longer, if you need). Then when you can do it in 20 and 50, move back to 18 minutes and 45 for writing, then to 15 and 40.
You absolutely can learn to manage your time effectively so that you can write a great DBQ in the time allotted. On to the next skill!
Integrating Citations
The final skill that isn't explicitly covered in the rubric, but will make a big difference in your essay quality, is integrating document citations into your essay. In other words, how do you reference the information in the documents in a clear, non-awkward way?
It is usually better to use the author or title of the document to identify a document instead of writing "Document A." So instead of writing "Document A describes the riot as...," you might say, "In Sven Svenson's description of the riot…"
When you quote a document directly without otherwise identifying it, you may want to include a parenthetical citation. For example, you might write, "The strikers were described as ‘valiant and true' by the working class citizens of the city (Document E)."

Now that we've reviewed the essential, foundational skills of the DBQ, I'll move into the rubric breakdowns. We'll discuss each skill the AP graders will be looking for when they score your exam. All of the history exams share a DBQ rubric, so the guidelines are identical.

Don't worry, you won't need a magnifying glass to examine the rubric.
#3: Learn the DBQ Rubric
The DBQ rubric has four sections for a total of seven points.
Part A: Thesis - 2 Points
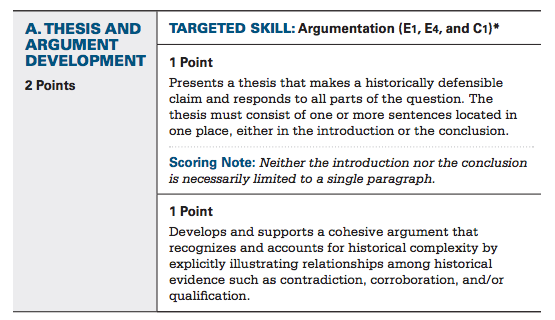
One point is for having a thesis that works and is historically defensible. This just means that your thesis can be reasonably supported by the documents and historical fact. So please don't make the main point of your essay that JFK was a member of the Illuminati or that Pope Urban II was an alien.
Per the College Board, your thesis needs to be located in your introduction or your conclusion. You've probably been taught to place your thesis in your intro, so stick with what you're used to. Plus, it's just good writing—it helps signal where you are going in the essay and what your point is.
You can receive another point for having a super thesis.
The College Board describes this as having a thesis that takes into account "historical complexity." Historical complexity is really just the idea that historical evidence does not always agree about everything, and that there are reasons for agreement, disagreement, etc.
How will you know whether the historical evidence agrees or disagrees? The documents! Suppose you are responding to a prompt about women's suffrage (suffrage is the right to vote, for those of you who haven't gotten to that unit in class yet):
"Analyze the responses to the women's suffrage movement in the United States."
Included among your documents, you have a letter from a suffragette passionately explaining why she feels women should have the vote, a copy of a suffragette's speech at a women's meeting, a letter from one congressman to another debating the pros and cons of suffrage, and a political cartoon displaying the death of society and the end of the ‘natural' order at the hands of female voters.

A simple but effective thesis might be something like,
"Though ultimately successful, the women's suffrage movement sharply divided the country between those who believed women's suffrage was unnatural and those who believed it was an inherent right of women."
This is good: it answers the question and clearly states the two responses to suffrage that are going to be analyzed in the essay.
A super thesis , however, would take the relationships between the documents (and the people behind the documents!) into account.
It might be something like,
"The dramatic contrast between those who responded in favor of women's suffrage and those who fought against it revealed a fundamental rift in American society centered on the role of women—whether women were ‘naturally' meant to be socially and civilly subordinate to men, or whether they were in fact equals."
This is a "super" thesis because it gets into the specifics of the relationship between historical factors and shows the broader picture —that is, what responses to women's suffrage revealed about the role of women in the United States overall.
It goes beyond just analyzing the specific issues to a "so what"? It doesn't just take a position about history, it tells the reader why they should care . In this case, our super thesis tells us that the reader should care about women's suffrage because the issue reveals a fundamental conflict in America over the position of women in society.
Part B: Document Analysis - 2 Points
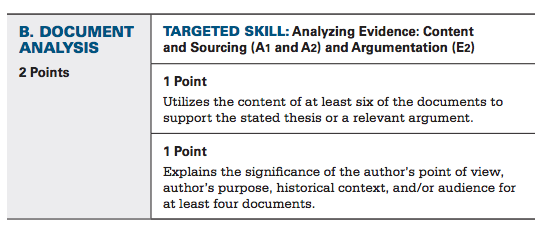
One point for using six or seven of the documents in your essay to support your argument. Easy-peasy! However, make sure you aren't just summarizing documents in a list, but are tying them back to the main points of your paragraphs.
It's best to avoid writing things like, "Document A says X, and Document B says Y, and Document C says Z." Instead, you might write something like, "The anonymous author of Document C expresses his support and admiration for the suffragettes but also expresses fear that giving women the right to vote will lead to conflict in the home, highlighting the common fear that women's suffrage would lead to upheaval in women's traditional role in society."
Any summarizing should be connected a point. Essentially, any explanation of what a document says needs to be tied to a "so what?" If it's not clear to you why what you are writing about a document is related to your main point, it's not going to be clear to the AP grader.
You can get an additional point here for doing further analysis on 4 of the documents. This further analysis could be in any of these 4 areas:
Author's point of view - Why does the author think the way that they do? What is their position in society and how does this influence what they are saying?
Author's purpose - Why is the author writing what they are writing? What are they trying to convince their audience of?
Historical context - What broader historical facts are relevant to this document?
Audience - Who is the intended audience for this document? Who is the author addressing or trying to convince?
Be sure to tie any further analysis back to your main argument! And remember, you only have to do this for four documents for full credit, but it's fine to do it for more if you can.
Practicing Document Analysis
So how do you practice document analysis? By analyzing documents!
Luckily for AP test takers everywhere, New York State has an exam called the Regents Exam that has its own DBQ section. Before they write the essay, however, New York students have to answer short answer questions about the documents.
Answering Regents exam DBQ short-answer questions is good practice for basic document analysis. While most of the questions are pretty basic, it's a good warm-up in terms of thinking more deeply about the documents and how to use them. This set of Regent-style DBQs from the Teacher's Project are mostly about US History, but the practice could be good for other tests too.
This prompt from the Morningside center also has some good document comprehensions questions about a US-History based prompt.
Note: While the document short-answer questions are useful for thinking about basic document analysis, I wouldn't advise completing entire Regents exam DBQ essay prompts for practice, because the format and rubric are both somewhat different from the AP.
Your AP history textbook may also have documents with questions that you can use to practice. Flip around in there!

This otter is ready to swim in the waters of the DBQ.
When you want to do a deeper dive on the documents, you can also pull out those old College Board DBQ prompts.
Read the documents carefully. Write down everything that comes to your attention. Do further analysis—author's point of view, purpose, audience, and historical context—on all the documents for practice, even though you will only need to do additional analysis on four on test day. Of course, you might not be able to do all kinds of further analysis on things like maps and graphs, which is fine.
You might also try thinking about how you would arrange those observations in an argument, or even try writing a practice outline! This exercise would combine your thesis and document-analysis skills practice.
When you've analyzed everything you can possibly think of for all the documents, pull up the Scoring Guide for that prompt. It helpfully has an entire list of analysis points for each document.
Consider what they identified that you missed.
Do you seem way off-base in your interpretation? If so, how did it happen?
Part C: Using Evidence Beyond the Documents - 2 Points
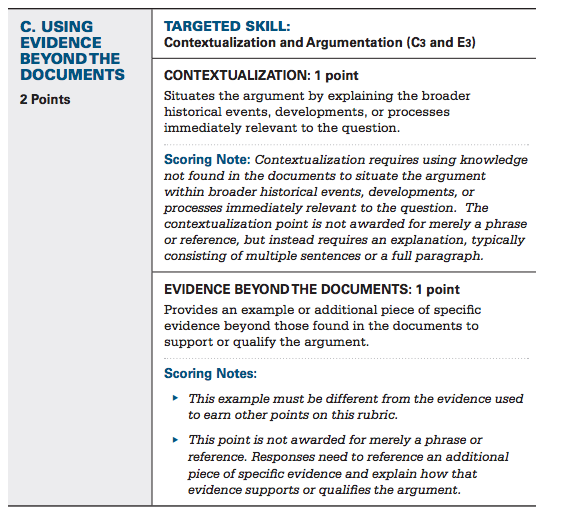
Don't be freaked out by the fact that this is two points!
One point is just for context—if you can locate the issue within its broader historical situation. You do need to write several sentences to a paragraph about it, but don't stress; all you really need to know to be able to get this point is information about major historical trends over time, and you will need to know this anyways for the multiple choice section. If the question is about the Dust Bowl during the Great Depression, for example, be sure to include some of the general information you know about the Great Depression! Boom. Contextualized.
The other point is for naming a specific, relevant example in your essay that does not appear in the documents.
To practice your outside information skills, pull up your College Board prompts!
Read through the prompt and documents and then write down all of the contextualizing facts and as many specific examples as you can think of.
I advise timing yourself—maybe 5-10 minutes to read the documents and prompt and list your outside knowledge—to imitate the time pressure of the DBQ.
When you've exhausted your knowledge, make sure to fact-check your examples and your contextual information! You don't want to use incorrect information on test day.
If you can't remember any examples or contextual information about that topic, look some up! This will help fill in holes in your knowledge.
Part D: Synthesis - 1 Point
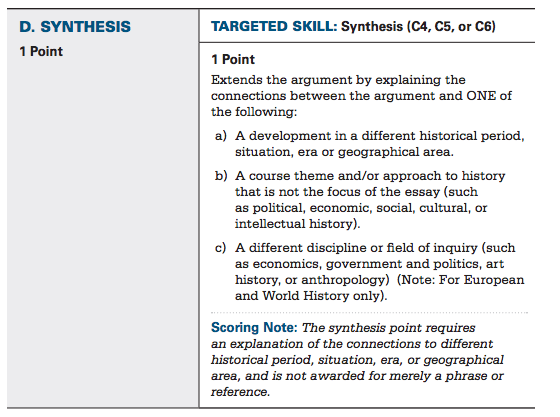
All you need to do for synthesis is relate your argument about this specific time period to a different time period, geographical area, historical movement, etc. It is probably easiest to do this in the conclusion of the essay. If your essay is about the Great Depression, you might relate it to the Great Recession of 2007-2009.
You do need to do more than just mention your synthesis connection. You need to make it meaningful. How are the two things you are comparing similar? What does one reveal about the other? Is there a key difference that highlights something important?
To practice your synthesis skills—you guessed it—pull up your College Board prompts!
- Read through the prompt and documents and then identify what historical connections you could make for your synthesis point. Be sure to write a few words on why the connection is significant!
- A great way to make sure that your synthesis connection makes sense is to explain it to someone else. If you explain what you think the connection is and they get it, you're probably on the right track.
- You can also look at sample responses and the scoring guide for the old prompts to see what other connections students and AP graders made.
That's a wrap on the rubric! Let's move on to skill-building strategy.

I know you're tired, but you can do it!
#5: Take Another Practice DBQ
So, you established a baseline, identified the skills you need to work on, and practiced writing a thesis statement and analyzing documents for hours. What now?
Take another timed, practice DBQ from a prompt you haven't seen before to check how you've improved. Recruit your same trusted advisor to grade your exam and give feedback. After, work on any skills that still need to be honed.
Repeat this process as necessary, until you are consistently scoring your goal score. Then you just need to make sure you maintain your skills until test day by doing an occasional practice DBQ.
Eventually, test day will come—read on for my DBQ-test-taking tips.
How Can I Succeed On DBQ Test Day?
Once you've prepped your brains out, you still have to take the test! I know, I know. But I've got some advice on how to make sure all of your hard work pays off on test day—both some general tips and some specific advice on how to write a DBQ.
#1: General Test-Taking Tips
Most of these are probably tips you've heard before, but they bear repeating:
Get a good night's sleep for the two nights preceding the exam. This will keep your memory sharp!
Eat a good breakfast (and lunch, if the exam is in the afternoon) before the exam with protein and whole grains. This will keep your blood sugar from crashing and making you tired during the exam.
Don't study the night before the exam if you can help it. Instead, do something relaxing. You've been preparing, and you will have an easier time on exam day if you aren't stressed from trying to cram the night before.

This dude knows he needs to get a good night's rest!
#2: DBQ Plan and Strategies
Below I've laid out how to use your time during the DBQ exam. I'll provide tips on reading the question and docs, planning your essay, and writing!
Be sure to keep an eye on the clock throughout so you can track your general progress.
Reading the Question and the Documents: 5-6 min
First thing's first: r ead the question carefully , two or even three times. You may want to circle the task words ("analyze," "describe," "evaluate," "compare") to make sure they stand out.
You could also quickly jot down some contextual information you already know before moving on to the documents, but if you can't remember any right then, move on to the docs and let them jog your memory.
It's fine to have a general idea of a thesis after you read the question, but if you don't, move on to the docs and let them guide you in the right direction.
Next, move on to the documents. Mark them as you read—circle things that seem important, jot thoughts and notes in the margins.
After you've passed over the documents once, you should choose the four documents you are going to analyze more deeply and read them again. You probably won't be analyzing the author's purpose for sources like maps and charts. Good choices are documents in which the author's social or political position and stake in the issue at hand are clear.

Get ready to go down the document rabbit hole.
Planning Your Essay: 9-11 min
Once you've read the question and you have preliminary notes on the documents, it's time to start working on a thesis. If you still aren't sure what to talk about, spend a minute or so brainstorming. Write down themes and concepts that seem important and create a thesis from those. Remember, your thesis needs to answer the question and make a claim!
When you've got a thesis, it's time to work on an outline . Once you've got some appropriate topics for your body paragraphs, use your notes on the documents to populate your outline. Which documents support which ideas? You don't need to use every little thought you had about the document when you read it, but you should be sure to use every document.
Here's three things to make sure of:
Make sure your outline notes where you are going to include your contextual information (often placed in the first body paragraph, but this is up to you), your specific example (likely in one of the body paragraphs), and your synthesis (the conclusion is a good place for this).
Make sure you've also integrated the four documents you are going to further analyze and how to analyze them.
Make sure you use all the documents! I can't stress this enough. Take a quick pass over your outline and the docs and make sure all of the docs appear in your outline.
If you go over the planning time a couple of minutes, it's not the end of the world. This probably just means you have a really thorough outline! But be ready to write pretty fast.
Writing the Essay - 45 min
If you have a good outline, the hard part is out of the way! You just need to make sure you get all of your great ideas down in the test booklet.
Don't get too bogged down in writing a super-exciting introduction. You won't get points for it, so trying to be fancy will just waste time. Spend maybe one or two sentences introducing the issue, then get right to your thesis.
For your body paragraphs, make sure your topic sentences clearly state the point of the paragraph . Then you can get right into your evidence and your document analysis.
As you write, make sure to keep an eye on the time. You want to be a little more than halfway through at the 20-minute mark of the writing period, so you have a couple minutes to go back and edit your essay at the end.
Keep in mind that it's more important to clearly lay out your argument than to use flowery language. Sentences that are shorter and to the point are completely fine.
If you are short on time, the conclusion is the least important part of your essay . Even just one sentence to wrap things up is fine just so long as you've hit all the points you need to (i.e. don't skip your conclusion if you still need to put in your synthesis example).
When you are done, make one last past through your essay. Make sure you included everything that was in your outline and hit all the rubric skills! Then take a deep breath and pat yourself on the back.

You did it!! Have a cupcake to celebrate.
Key Tips for How to Write a DBQ
I realize I've bombarded you with information, so here are the key points to take away:
Remember the drill for prep: establish a baseline, build skills, take another practice DBQ, repeat skill-building as necessary.
Make sure that you know the rubric inside and out so you will remember to hit all the necessary points on test day! It's easy to lose points just for forgetting something like your synthesis point.
On test day, keep yourself on track time-wise !
This may seem like a lot, but you can learn how to ace your DBQ! With a combination of preparation and good test-taking strategy, you will get the score you're aiming for. The more you practice, the more natural it will seem, until every DBQ is a breeze.
What's Next?
If you want more information about the DBQ, see my introductory guide to the DBQ .
Haven't registered for your AP test yet? See our article for help registering for AP exams .
For more on studying for the AP US History exam, check out the best AP US History notes to study with .
Studying for World History? See these AP World History study tips from one of our experts.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ellen has extensive education mentorship experience and is deeply committed to helping students succeed in all areas of life. She received a BA from Harvard in Folklore and Mythology and is currently pursuing graduate studies at Columbia University.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
An Overview of the Writing Process
Thesis statements, what this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can discover or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper .

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:.
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence somewhere in your first paragraph that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I get a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis,” a basic or main idea, an argument that you think you can support with evidence but that may need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following:
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question.
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough?
Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is, “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s o.k. to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on 19th-century America, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: Compare and contrast the reasons why the North and South fought the Civil War. You turn on the computer and type out the following:
The North and South fought the Civil War for many reasons, some of which were the same and some different.
This weak thesis restates the question without providing any additional information. You will expand on this new information in the body of the essay, but it is important that the reader know where you are heading. A reader of this weak thesis might think, “What reasons? How are they the same? How are they different?” Ask yourself these same questions and begin to compare Northern and Southern attitudes (perhaps you first think, “The South believed slavery was right, and the North thought slavery was wrong”). Now, push your comparison toward an interpretation—why did one side think slavery was right and the other side think it was wrong? You look again at the evidence, and you decide that you are going to argue that the North believed slavery was immoral while the South believed it upheld the Southern way of life. You write:
While both sides fought the Civil War over the issue of slavery, the North fought for moral reasons while the South fought to preserve its own institutions.
Now you have a working thesis! Included in this working thesis is a reason for the war and some idea of how the two sides disagreed over this reason. As you write the essay, you will probably begin to characterize these differences more precisely, and your working thesis may start to seem too vague. Maybe you decide that both sides fought for moral reasons, and that they just focused on different moral issues. You end up revising the working thesis into a final thesis that really captures the argument in your paper:
While both Northerners and Southerners believed they fought against tyranny and oppression, Northerners focused on the oppression of slaves while Southerners defended their own right to self-government.
Compare this to the original weak thesis. This final thesis presents a way of interpreting evidence that illuminates the significance of the question. Keep in mind that this is one of many possible interpretations of the Civil War—it is not the one and only right answer to the question . There isn’t one right answer; there are only strong and weak thesis statements and strong and weak uses of evidence.
Let’s look at another example. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
Why is this thesis weak? Think about what the reader would expect from the essay that follows: you will most likely provide a general, appreciative summary of Twain’s novel. The question did not ask you to summarize; it asked you to analyze. Your professor is probably not interested in your opinion of the novel; instead, she wants you to think about why it’s such a great novel— what do Huck’s adventures tell us about life, about America, about coming of age, about race relations, etc.? First, the question asks you to pick an aspect of the novel that you think is important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
Here’s a working thesis with potential: you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation; however, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal. Your reader is intrigued, but is still thinking, “So what? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?” Perhaps you are not sure yet, either. That’s fine—begin to work on comparing scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions. Eventually you will be able to clarify for yourself, and then for the reader, why this contrast matters. After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing the original version of this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find the latest publications on this topic. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
Anson, Chris M. and Robert A. Schwegler. The Longman Handbook for Writers. 2nd ed. New York: Longman, 2000.
Hairston, Maxine and John J. Ruszkiewicz. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers. 4th ed. New York: HarperCollins, 1996.
Lunsford, Andrea and Robert Connors. The St. Martin’s Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s, 1995.
Rosen, Leonard J. and Laurence Behrens. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook. 3rd ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1997.
- Thesis Statements. Provided by : The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Located at : http://writingcenter.unc.edu/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives

Document-Based Question (DBQ)
What is a dbq, how to read the documents:, written documents, how to answer the prompt:, compare & contrast, cause & effect, change & continuity over time, how to earn all 7 points:.
Contextualization
Analysis & Sourcing
How to start writing the dbq, how to write a dbq:.
Attached below is a worksheet with an outline organizer for your DBQ. When practicing for your DBQ, feel free to download & print this to use:
7 documents
_pn.png)
You are given 7 documents, and you are given a prompt, similar to an LEQ prompt. You need to write an essay, responding to the prompt, using evidence from the documents. You have 60 minutes in total, but of those 15 minutes are recommended for reading. The sections below describe the types of documents, types of prompts, and the rubric and how to earn each point.
You are given 7 documents. The different types are described below:
Excerpt / Written Document
Graphic, Diagram, Map, Cartoon
.png)
General Tips
Look at the sourcing before you read each doc to get an idea of what the doc might say
Write a quick summary (~3 bullet points) to summarize the content of each doc
Write a note of how each doc fits in with the prompt
Does it support or refute your thesis?
Which side of the prompt does it cover?
Which aspect (which body paragraph) of your prompt / thesis does it cover?
Any document with written paragraphs
Newspaper, letter, speech, historian's interpretation, constitution, religious text, etc.
Special tips:
Before you read, read the sourcing & title and try to get an idea of what the doc might say
Take your time to understand the content of the doc; no need to rush
Write a few notes summarizing the doc
Figure out how the doc relates to the prompt
Does it argue one side or another?
Does it provide evidence for a specific geographical region?
Does it refute your thesis?
Which sub-category of the prompt does it answer?
Any document that is a photo
Any photo that a photographer might take, or an artist's depiction of a historical event
NOT a diagram, map, or something manmade or designed by historians
Read the sourcing & title to try to figure out what the photo might depict
Look at all aspects of the photo, get an idea of what it depicts
Does it represent a historical development?
Does it represent an artistic movement?
Look for all signs of bias in the photo
Is it depicting a specific point of view?
Does it portray a certain culture as superior?
Does it portray a certain culture as inferior?
Does it represent a military victory?
This would mean one side is better than the other
Does it portray something as bigger or exaggerated?
Means that the exaggerated thing is depicted as superior
Does it portray something as smaller?
Means that the thing that's depicted smaller is portrayed as inferior
Based on the point of view (bias) and the content, figure out how it relates to the prompt
Does it support / refute your thesis?
What aspect of the prompt does it answer?
Any document that is a man-made photo
Graphic, diagram, political cartoon, map, etc.
Before you read, read the sourcing & title and try to get an idea of what the doc might depict
Look at the doc and try to figure out what it represents, or what topic it depicts
Think about the bias or point of view of the doc:
Does it represent the views of one side or another?
Is it depicting one side as exaggerated or superior to another?
Cartoons are generally biased
If it's a map, what is it representing?
Is it representing the map of industrial factories, trade routes, westward expansion, deciphered wind patterns, etc.?
Once you figure this out, understand the historical context of the map
If it's a graphic or a diagram, what information does it detail?
If it's a population growth map, what allowed for population growth?
Think of what the diagram depicts, and what allowed for that, and what's the historical context of that historical development?
Involves comparing & contrasting 2 different things
Most important thing is the argument: Not what the differences/similarities were, but HOW THEY WERE SIGNIFICANT
How to use the documents:
Some docs might explain the features of one of the comparand (the thing you compare), other docs may explain the other comparand
Some docs might cover both comparands
Figure out what the docs are saying for each comparand, and write your thesis based on that
What are they saying are similar & different about the 2?
Involves examining what a certain historical development, and what were its causes & effects
What's more important is examining the significance of the causes, or how one cause/effect was more important than other causes/effects
Generally, 2 causes and 1 or 2 effects
Some docs might explain the event
Some docs might explain the causes, others might explain the effects
Draft a thesis based on the info about the causes & effects mentioned in the docs
Try to mention which causes were more significant than other causes
Involves examining what changed & what remained the same as a result of one event
Some docs might explain the catalyst (the event that caused the changes/continuities) you write about
Some docs might describe the changes
Some docs might describe the continuities
Draft a thesis based on what the docs say about the changes & continuities
How to Earn all 7 Points:
Contextualization (1 point).
Examine the historical context of the story
Kind of like a "recap" or a "flashback"
Like at the beginning of a TV show, it shows a recap of the previous episode
How to write one
Always include the time period & possibly the location
"In Europe in the period 1450 - 1750, ..."
Provide a brief 3-5 sentence recap of how the world arrived at the situation you are writing about in your essay
The contextualization should finish with how the world arrived at the historical development you write about in your thesis, so that there is a smooth transition from contextualization to the thesis
Sample Contextualizations
Topic: Related to the industrial revolution
Before the 1750s, people were performing manual labor, making items by hand, which was very inefficient. From 1750-1900, Europe and the rest of the world underwent an economic transformation called the Industrial Revolution. Starting in Britain due to its abundance of raw materials & strong financial support, industrial capitalists built factories powered by waterwheels or coal that artificially produced goods such as textiles, eliminating the need to make them by hand. This brought a lot more people from the countryside to the cities, where they worked in factories for low wages. From Britain, the industrial revolution spread throughout Europe as well as to US, Egypt, Russia, and Japan. [Insert Thesis Here]
Topic: Related to imperialism
In the period 1750-1900, Europe underwent an economic transformation known as the industrial revolution, where people would use artificial power to cheaply & efficiently manufacture goods in commercial factories in the cities, rather than making goods by hand at home. In order for these factories to produce goods, they needed raw materials, which is why they had to look to other nations like those in Africa and Asia to supply raw materials to them. This led to European imperialism, a development where Europeans started colonizing other nations throughout the world, especially in Africa and Asia, to establish export-oriented economies to get raw materials to supply to their factories. [Insert Thesis Here]
Thesis (1 point)
This is your argument
Must be something that can be opposed
Someone else has to be able to write an essay whose thesis is the opposite of yours
Must contain an argument, and generally 2-3 examples (topics for body paragraphs)
Better to have a concession
Useful for complexity point
Format of Thesis & Examples
Color Key:
Concession / Counterargument*
Similarities / Continuities / Causes
Difference for Comparand 1 / Changes / Effects
Differences for Comparand 2
*Concession is always optional. Described in the analysis section, it can be used to get the extra complexity point
Prompt: Compare & Contrast
Although some may believe [counterargument]* , w hile [comparand 1] and [comparand 2] both [insert similarities] , [comparand 1] was [insert difference for comparand 1], and [comparand 2] was [insert difference for comparand 2], which [is why / allowed for] [insert argument].
Although the Delhi Sultanate had very strict religious authority, while the Delhi Sultanate and the Chola Kingdom both used religion to maintain stability , the Delhi Sultanate was attempting to impose Islam on a Hindu-majority population , and the Chola Kingdom imposed Hindu on a Hindu population , which allowed for the Chola Kingdom to be more successful than the Delhi Sultanate.
Prompt: Change & Continuity over Time
Although some may believe [counterargument]* , as a result of [catalyst], while [continuity] stayed the same , [change] changed, which [is why / allowed for] [insert argument].
Although some may believe the Catholic church actually became more powerful, as a result of the Protestant Reformation, while women still maintained strictly subordinate roles , there were more religious wars, and more monarchs were able to consolidate more power for themselves , which caused the Catholic church to decline in power.
Prompt: Cause & Effect
Although some may believe [counterargument]* are the most important causes of [event] , [causes] were the main causes** , which caused [effects].
Although some may believe that the desire to spread Christianity was the main cause of European imperialism , the desire to get raw materials and the need for more markets were the main causes , which led to a more integrated global economy and the development of technological infrastructure in the colonies.
**Here, the argument is that the causes you described in the blue section are more important than the causes in the yellow section. There is no need for an extra argument at the end
Evidence (3 points)
This is where you put examples / pieces of evidence to support your thesis
To get 1 point : Use evidence from 3 of the docs
To get 2 points : Use evidence from 6 of the docs, and put an extra analysis to connect it to the thesis
It's always better to use all 7 docs in case you use one incorrectly
To get 3 points : Use an extra piece of evidence (from your own knowledge, not from the docs), and put an extra analysis to connect it to the thesis
Examples of How to Write your Evidence
How to earn the first point:
To earn the 1st point, you need to describe / state evidence from 3 docs without connecting it to the thesis
According to document 3, the Chola Empire used Hinduism as the state religion.
According to document 7, there were more factories in Britain than in France.
How to earn the second point:
To earn the 2nd point, you need evidence from 6* docs, and you also need to connect it to the thesis
According to document 3, the Chola Empire used Hinduism as the state religion. Because the population was also mostly Hindu, the Chola Empire was able to maintain stability by using a common belief in Hinduism to stabilize its rule.
According to document 7, there were more factories in Britain than in France. Thus, Britain had a larger industrial output than France, which is why it was able to manufacture more weapons during World War 1 and why France relied on Britain for support.
*Always use all 7 docs to in case you use one doc incorrectly
How to earn the third point:
To earn the third point, you need to include one piece of evidence that is not in the documents and is from your own knowledge.
Think of what evidence or what viewpoint is missing
If it's a compare & contrast: is there any other similarity or difference? Do you have any other evidence to support the topics of your thesis?
If it's a change & continuity over time: Is there any other evidence to support one of your changes or continuities?
If it's a cause & effect: Is there any other evidence or historical content that can support your causes or effects?
Analysis (2 points)
This is the hardest part
For 1 point, you need to explain how the source of 3 documents affects either your argument or what the document has to say
There are 4 parts of sourcing, and you ONLY NEED TO CHOOSE ONE
Explained in more detail below
For the 2nd point, you need to use complex analysis in your argument
This is the most confusing
The easiest way is to weave a counterargument through your essay, which the concession already sets you up for
The best way is to not think about it too much and just put a bit more complex arguments into your essay rather than sticking to a strict format
Historical Context
Point of View
You need to choose ONE of the above and follow the instructions below. Each of the sections below has information about each aspect of sourcing.
You need to do this for THREE different sources to earn full points (we recommend you do 4 in case one is wrong)
Historical Context:
Explain how the historical context of any document affects what the document argues
This document was written after WW1 when everyone was feeling depressed and economically poor, which explains why the priest is talking about a revival of religion and cheerful spirits.
This document was written in a time after the Protestant Reformation when there were a lot of religious wars, which is why the document argues that Lutheranism is better than Calvinism.
Explain how the intended audience of any document affects what the document argues
This document was written for the Armenians of the Ottoman empire, a Christian minority that was believed to conspire with the Allies, which is why the document is very aggressive toward them in asserting Ottoman dominance.
This speech was written to the American people to gain support for the Treaty of Versailles, which is why it intends to boost nationalist sentiment and promote American power.
Explain how the purpose of any document affects what the document argues
This speech was written by the Republic party with the purpose of convincing its audience to vote for them, which is why it argues that Free Silver, a democratic idea, is bad.
This speech was written by John of Montecorvino, the Archbishop of Khanbaliq who sought to convert the Mongol boys to Christianity, which is why he emphasizes how Christianity allows one to achieve salvation.
Point of View:
Explain how the point of view of any document affects what the document argues
This speech was written from the point of view of an Indian cotton farmer, which is why he writes that the British completely destroyed the Indian handmade textile industry.
This document was written from the point of view of Grover Cleveland, an anti-imperialist president, which is why he writes about the harms of annexing Hawaii.
The Complexity Point
The final point is the complexity point. This is given if you have a complex argument, and it is hard to achieve. The best way to think about this is do more than the prompt asks, and add a bit of extra analysis into the essay.
The easiest way to do this is weave a counterargument through the essay. In our thesis samples above, we already set you up for this with our concession clause.
How to Start Writing the DBQ:
First step is to outline your essay. Follow the steps below:
Read through each document, write a brief summary, and figure out how it relates to the prompt (which side/aspect does it argue?)
Write your thesis. Write each aspect of the thesis (concession/counterargument, evidence 1, evidence 2, argument), and combine them
Write the outline for your body paragraphs. Write the topic for each body paragraph, and which docs you'll use in each. Also, denote where you'll use your outside evidence
Write an outline for your sourcing. Choose 4 different documents, and write the sourcing sentence following the guidelines in the sourcing section above
Start writing. Good luck!

Analytical Essay Thesis
Analytical essay thesis statement generator.
Analytical essays delve deep into the intricacies of a subject, offering insightful interpretations and evaluations. At the heart of these essays lies the analytical thesis statement – a crucial element that encapsulates the analytical perspective you’ll explore. This guide explores a range of analytical thesis statement examples, guiding you through the process of creating thought-provoking statements. Learn to dissect complex subjects, develop critical arguments, and master the art of crafting compelling analytical thesis statements.
What is an Analytical Thesis Statement? – Definition
An analytical thesis statement is a concise declaration that outlines the main focus of an analytical essay. It presents the central argument or analysis the essay will explore, providing a roadmap for readers to understand the specific perspective, interpretation, or evaluation the writer intends to present. Unlike other types of thesis statements, an analytical thesis statement does not simply present a fact but delves into the “how” and “why” of a subject.
What is an Example of an Analytical Thesis Statement?
Example: “In F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel ‘The Great Gatsby,’ Jay Gatsby’s excessive pursuit of wealth and social status serves as a commentary on the illusory nature of the American Dream, highlighting the emptiness and moral decay that often accompany unchecked ambition.”
In this analytical thesis statement, the focus is on analyzing the character of Jay Gatsby and his actions as a reflection of larger themes within the novel. The strong thesis statement goes beyond a surface-level observation and delves into the deeper analysis of Gatsby’s character and its symbolic significance in relation to the American Dream.
100 Analytical Thesis Statement Examples

Size: 264 KB
- “In Shakespeare’s ‘Hamlet,’ the protagonist’s internal conflict reflects the complex interplay between duty, morality, and personal desires.”
- “Through symbolic imagery and character development, ‘The Scarlet Letter’ by Nathaniel Hawthorne explores the destructive power of guilt on individuals and society.”
- “Analyzing the juxtaposition of innocence and corruption in ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ Harper Lee critiques the pervasive societal biases that perpetuate injustice.”
- “The film ‘Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind’ employs nonlinear narrative structure to delve into the complexities of memory, love, and human connection.”
- “Through the lens of Marxist theory, George Orwell’s ‘1984’ unveils a dystopian world that critiques totalitarianism and the manipulation of truth.”
- “In Emily Dickinson’s poetry, the recurring theme of death serves as a means of contemplating the transient nature of life and the human condition.”
- “Analyzing Frida Kahlo’s self-portraits reveals her use of visual symbolism to convey her physical and emotional pain as well as her feminist ideals.”
- “Through intricate narrative structure and character development, ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ by Gabriel García Márquez explores the cyclical nature of history and human experience.”
- “The painting ‘Starry Night’ by Vincent van Gogh conveys the artist’s emotional turmoil and inner conflict through its vivid color palette and swirling forms.”
- “Through the analysis of ‘The Catcher in the Rye,’ J.D. Salinger portrays the protagonist Holden Caulfield’s alienation as a manifestation of his fear of adulthood and societal conformity.
- “Exploring the use of metaphors and allegory in ‘Animal Farm,’ George Orwell satirizes political ideologies and the corruption of power.”
- “The poem ‘The Road Not Taken’ by Robert Frost delves into the concept of choices and regret, using a diverging path as a metaphor for life’s decisions.”
- “Analyzing the historical context and literary techniques in ‘The Grapes of Wrath,’ John Steinbeck critiques the exploitation of the working class during the Great Depression.”
- “In Mary Shelley’s ‘Frankenstein,’ the creature’s isolation and rejection serve as a commentary on the consequences of unchecked scientific ambition.”
- “Through visual elements and composition, Leonardo da Vinci’s ‘Mona Lisa’ conveys a sense of mystery and psychological depth, captivating viewers for centuries.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and social commentary in Jonathan Swift’s ‘A Modest Proposal,’ one can understand his satirical critique of British colonialism.”
- “The play ‘Death of a Salesman’ by Arthur Miller explores the disillusionment of the American Dream through the tragic downfall of the protagonist Willy Loman.”
- “Through the lens of feminist theory, Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s ‘The Yellow Wallpaper’ critiques the societal constraints placed on women’s mental and emotional well-being.”
- “Analyzing the motifs of light and darkness in Joseph Conrad’s ‘Heart of Darkness,’ one can interpret them as representations of morality and the human psyche.”
- “Edgar Allan Poe’s ‘The Tell-Tale Heart’ uses unreliable narration and symbolism to delve into the narrator’s descent into madness and guilt.”
- “In the film ‘Citizen Kane,’ Orson Welles employs non-linear storytelling and deep focus cinematography to explore the enigmatic life of the titular character.”
- “Analyzing the use of repetition and imagery in Langston Hughes’ ‘Dream Deferred,’ one can interpret the poem as a commentary on the consequences of unfulfilled dreams.”
- “Through allegorical elements and character interactions, William Golding’s ‘Lord of the Flies’ examines the inherent capacity for savagery within human nature.”
- “The painting ‘Guernica’ by Pablo Picasso serves as a powerful anti-war statement, depicting the horrors of conflict and the suffering of innocent civilians.”
- “Analyzing the themes of identity and societal conformity in Jhumpa Lahiri’s ‘The Namesake,’ one can uncover the struggles faced by immigrant families in adapting to new cultures.”
- “In ‘The Picture of Dorian Gray’ by Oscar Wilde, the portrait serves as a symbol of the protagonist’s moral decay and the consequences of pursuing eternal youth.”
- “Analyzing the use of color symbolism in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s ‘The Great Gatsby,’ one can interpret colors as reflections of characters’ personalities and societal decadence.”
- “Through the examination of allegorical elements in George Orwell’s ‘Animal Farm,’ one can uncover the representation of historical events and political ideologies.”
- “In ‘Brave New World’ by Aldous Huxley, the dystopian society’s use of technology and conditioning raises questions about the cost of sacrificing individuality for stability.”
- “Analyzing the character of Lady Macbeth in Shakespeare’s ‘Macbeth,’ one can discern her ambition-driven transformation and the psychological toll of her actions.
- “In ‘Pride and Prejudice’ by Jane Austen, the social commentary and character interactions illuminate the societal norms and expectations of the Regency era.”
- “Analyzing the use of religious symbolism in Herman Melville’s ‘Moby-Dick,’ one can interpret the white whale as a representation of the unattainable and the divine.”
- “The film ‘The Shawshank Redemption’ explores themes of hope and redemption through the friendship between two inmates, offering a commentary on the human spirit.”
- “Analyzing the motif of the American Dream in ‘The Great Gatsby,’ F. Scott Fitzgerald critiques the pursuit of materialism and the illusion of social mobility.”
- “In ‘Othello’ by William Shakespeare, the tragic downfall of the titular character is driven by jealousy and manipulation, revealing the destructive power of unchecked emotions.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in T.S. Eliot’s poem ‘The Waste Land,’ one can interpret various images and references as reflections of societal decay and spiritual desolation.”
- “The painting ‘American Gothic’ by Grant Wood conveys a complex narrative through the stern expressions and juxtaposition of the farmer and his daughter.”
- “Analyzing the character development in Jane Eyre’s journey, Charlotte Brontë examines themes of independence, feminism, and self-discovery.”
- “In ‘The Metamorphosis’ by Franz Kafka, the protagonist’s transformation into a giant insect serves as a metaphor for alienation and the absurdity of modern life.”
- “Analyzing the use of foreshadowing and symbolism in William Faulkner’s ‘A Rose for Emily,’ one can interpret the decayed mansion as a representation of the past and its lingering impact.”
- “Through allegorical elements in ‘The Alchemist’ by Paulo Coelho, one can uncover themes of personal legend and the transformative power of following one’s dreams.”
- “Analyzing the narrative structure in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Chronicle of a Death Foretold,’ one can discern the multi-perspective exploration of truth and collective guilt.”
- “The sculpture ‘The Thinker’ by Auguste Rodin captures the contemplative nature of human thought and the complexity of philosophical introspection.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and satire in Voltaire’s ‘Candide,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s misadventures as a commentary on the irrationality of human behavior.”
- “Through the exploration of nature and human experience in Ralph Waldo Emerson’s essays, transcendentalism emerges as a celebration of individual intuition and connection.”
- “Analyzing the use of narrative structure in Vladimir Nabokov’s ‘Lolita,’ one can discern the unreliable narration that challenges readers’ perceptions of truth and morality.”
- “In ‘The Awakening’ by Kate Chopin, the protagonist’s journey towards self-discovery and liberation reflects the constraints placed on women in the 19th-century society.”
- “Analyzing the use of dramatic monologue in Robert Browning’s ‘My Last Duchess,’ one can uncover the psychological complexity and possessive nature of the speaker.”
- “Through allegorical elements and philosophical themes in Albert Camus’ ‘The Stranger,’ the protagonist’s indifference to societal norms questions the absurdity of existence.”
- “Analyzing the use of myth and symbolism in Toni Morrison’s ‘Beloved,’ one can interpret the haunting presence of the titular character as a representation of historical trauma.”
- “In ‘Crime and Punishment’ by Fyodor Dostoevsky, the psychological turmoil of the protagonist Raskolnikov reflects the tension between morality and rationality.”
- “Analyzing the narrative techniques in Salman Rushdie’s ‘Midnight’s Children,’ one can discern the blending of history and magical realism to explore India’s postcolonial identity.”
- “Through the examination of imagery and metaphor in Sylvia Plath’s poetry, themes of mental illness, identity, and gender roles come to the forefront.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in E.M. Forster’s ‘A Passage to India,’ one can interpret the Marabar Caves as a metaphor for the complexity of cultural misunderstandings.”
- “The short story ‘The Lottery’ by Shirley Jackson employs irony and social commentary to critique blind adherence to tradition and the potential for collective cruelty.”
- “Analyzing the use of allegory in John Bunyan’s ‘The Pilgrim’s Progress,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s journey as a representation of spiritual enlightenment and salvation.”
- “In ‘Their Eyes Were Watching God’ by Zora Neale Hurston, the protagonist Janie’s journey towards self-discovery reflects her search for autonomy and empowerment.”
- “Analyzing the use of literary devices in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Love in the Time of Cholera,’ one can uncover the exploration of enduring love and the passage of time.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘The Trial,’ one can interpret the absurdity of the bureaucratic legal system as a commentary on the human struggle for control.”
- “Analyzing the use of dramatic irony in Shakespeare’s ‘Romeo and Juliet,’ one can discern the tragic irony that underscores the lovers’ fate and the societal feud.”
- “In ‘The Road’ by Cormac McCarthy, the post-apocalyptic landscape serves as a metaphor for the fragility of human existence and the pursuit of hope.”
- “Analyzing the themes of colonization and cultural clash in Chinua Achebe’s ‘Things Fall Apart,’ one can interpret the protagonist Okonkwo’s downfall as a representation of societal upheaval.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Jack London’s ‘To Build a Fire,’ the protagonist’s struggle against nature serves as a reflection of human hubris and vulnerability.”
- “In ‘Invisible Man’ by Ralph Ellison, the protagonist’s invisibility becomes a metaphor for social marginalization and the dehumanizing effects of racial prejudice.”
- “Analyzing the use of motifs and symbolism in Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s liberation as a commentary on societal expectations.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘Metamorphosis,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s transformation as a representation of alienation and the absurdity of modern life.”
- “In ‘Gulliver’s Travels’ by Jonathan Swift, the protagonist’s encounters with different societies serve as satirical commentaries on various aspects of human behavior.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in William Faulkner’s ‘As I Lay Dying,’ one can interpret the journey to bury Addie Bundren’s body as a representation of family dynamics and individual motivations.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Herman Melville’s ‘Bartleby, the Scrivener,’ one can interpret the enigmatic character Bartleby as a representation of passive resistance and societal alienation.”
- “In ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ by Margaret Atwood, the dystopian society serves as a critique of patriarchal control and the erosion of women’s rights.”
- “Analyzing the use of foreshadowing and symbolism in Shirley Jackson’s ‘The Haunting of Hill House,’ one can interpret the house itself as a representation of psychological trauma.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Albert Camus’ ‘The Plague,’ one can interpret the outbreak of plague as a metaphor for the absurdity of human existence and the inevitability of suffering.”
- “In ‘The Sun Also Rises’ by Ernest Hemingway, the Lost Generation’s disillusionment serves as a commentary on the aftermath of World War I.”
- “Analyzing the use of metaphors and allegory in John Milton’s ‘Paradise Lost,’ one can interpret Satan’s rebellion as a representation of the dangers of pride and ambition.”
- “Through allegorical elements in H.G. Wells’ ‘The Time Machine,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s journey to the distant future as a commentary on societal evolution and the consequences of unchecked progress.”
- “In ‘Wuthering Heights’ by Emily Brontë, the tumultuous relationship between Heathcliff and Catherine serves as a metaphor for the destructive power of passionate obsession.”
- “Analyzing the use of irony and satire in Mark Twain’s ‘The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn,’ one can interpret the river as a symbol of freedom and a commentary on the racial tensions of the time.”
- “Through allegorical elements in John Steinbeck’s ‘Of Mice and Men,’ one can interpret the dream of owning a piece of land as a representation of companionship and the American Dream.”
- “In ‘The Kite Runner’ by Khaled Hosseini, the protagonist’s journey towards redemption serves as a commentary on guilt, betrayal, and the complexities of friendship.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World,’ one can interpret the conditioning and drug-induced happiness as a representation of societal control and the loss of individuality.”
- “Through allegorical elements in William Golding’s ‘Lord of the Flies,’ the descent into savagery among the stranded boys serves as a commentary on the inherent darkness within humanity.”
- “In Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘Love in the Time of Cholera,’ the protagonist’s enduring love and pursuit of lost opportunities serve as a reflection of the passage of time and the complexities of relationships.”
- “Analyzing the use of narrative structure in Leo Tolstoy’s ‘Anna Karenina,’ one can discern the parallel narratives of different characters as a commentary on societal norms and the consequences of personal choices.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Franz Kafka’s ‘The Castle,’ one can interpret the protagonist’s futile attempts to reach the inaccessible castle as a representation of the human struggle for meaning and belonging.”
- “In George Orwell’s ‘Down and Out in Paris and London,’ the protagonist’s experiences of poverty and social alienation serve as a commentary on the disparities within society.”
- “Analyzing the use of symbolism in E.E. Cummings’ poetry, one can interpret his innovative typography and language as a representation of individualism and breaking away from convention.”
- “Through allegorical elements in Jean-Paul Sartre’s play ‘No Exit,’ the characters’ confinement in a room becomes a metaphor for existential anguish and the consequences of human choices.”
- “In William Shakespeare’s ‘Julius Caesar,’ the manipulation of public opinion serves as a commentary on the dynamics of power, loyalty, and the consequences of political ambition.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for High School
An analytical essay’s thesis statement for high school sets the stage for the examination of a topic, delving into its complexities and drawing insights based on evidence.
- In Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet,” the theme of fate challenges the power of free will as seen through the tragic end of the young lovers.
- The portrayal of friendship in “The Outsiders” demonstrates the significance of social class divides in the 1960s.
- Through symbolism and imagery, Emily Dickinson’s poems convey profound themes about life, death, and eternity.
- Atticus Finch’s moral integrity in “To Kill a Mockingbird” stands as a beacon of hope in a racially divided society.
- “Lord of the Flies” uses the island as a microcosm to examine the inherent evil in human nature.
- George Orwell’s “1984” delves deep into the dangers of totalitarian governments and the loss of individuality.
- The character development of Elizabeth Bennet in “Pride and Prejudice” sheds light on the societal constraints of women during the Regency era.
- “The Catcher in the Rye” critiques the phoniness of adulthood while highlighting the vulnerability of adolescence.
- The journey of Bilbo Baggins in “The Hobbit” is a testament to personal growth and the discovery of inner courage.
- In “Fahrenheit 451,” Bradbury warns about the consequences of censorship and the loss of intellectual freedom.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for Middle School
Middle school thesis statements for analytical essays examine topics in a straightforward manner, building critical thinking skills.
- “Bridge to Terabithia” shows that friendship can help overcome personal challenges and grief.
- The challenges faced by Percy Jackson highlight the complexities of growing up with a unique identity.
- Matilda uses her intellect and supernatural powers to combat negativity and find her place in the world.
- “The Giver” reveals the dangers of a seemingly perfect society devoid of memories and emotions.
- Through “The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe,” the Pevensie siblings learn about bravery, sacrifice, and loyalty.
- In “Holes,” the interwoven stories demonstrate the impact of family legacies and the power of redemption.
- “Charlotte’s Web” uses the farm setting to explore themes of friendship, sacrifice, and the cycle of life.
- “Diary of a Wimpy Kid” humorously addresses the challenges and intricacies of middle school life.
- Through “Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone,” Rowling discusses the importance of choices in shaping one’s destiny.
- “A Wrinkle in Time” showcases the battle between good and evil, emphasizing the power of love.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for College
College-level thesis statements delve deeper into complex topics, offering nuanced insights and arguments.
- “Moby Dick” serves as a profound exploration of obsession, illustrating its destructive consequences and moral ambiguities.
- In “The Great Gatsby,” Fitzgerald critiques the American Dream, revealing its inherent flaws and the disillusionment of the Jazz Age.
- “One Hundred Years of Solitude” portrays the cyclical nature of history through the Buendía family’s experiences.
- Virginia Woolf’s “To the Lighthouse” delves into the human consciousness, capturing fleeting emotions and moments.
- In “Brave New World,” Huxley showcases the dehumanizing effects of technological advancements and societal uniformity.
- “Heart of Darkness” explores the impact of colonialism, presenting a dark reflection on human nature and moral corruption.
- Toni Morrison’s “Beloved” addresses the haunting legacy of slavery and its lasting psychological effects.
- Through “The Handmaid’s Tale,” Atwood critiques patriarchal societies, illustrating the dangers of religious extremism and loss of female agency.
- “Crime and Punishment” offers a deep psychological analysis of guilt and redemption through Raskolnikov’s actions and motivations.
- Franz Kafka’s “The Metamorphosis” provides an existential view of alienation and identity crisis in the modern world.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Example for Beginners
Beginner-level thesis statements offer clear and simple insights, setting the foundation for deeper analytical thinking.
- “The Little Prince” teaches readers about the importance of relationships and seeing with the heart.
- “Charlotte’s Web” illustrates the value of friendship and the inevitability of life’s cycles.
- “The Very Hungry Caterpillar” uses vibrant illustrations to show the process of metamorphosis in nature.
- In “Where the Wild Things Are,” Max learns about emotions and the comfort of home.
- “The Rainbow Fish” highlights the joy of sharing and the essence of true beauty.
- “Green Eggs and Ham” humorously emphasizes the idea of trying new things and overcoming initial hesitations.
- Through “The Cat in the Hat,” Dr. Seuss illustrates the fun and chaos that arise from breaking rules.
- “Goodnight Moon” uses repetitive structure and rhymes to convey the calming ritual of bedtime.
- “Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See?” introduces young readers to colors and animals through patterned text.
- “Corduroy” portrays the desire for belonging and the importance of friendship and acceptance.
How do you start an analytical thesis?
Starting an analytical thesis requires a clear understanding of the topic, a comprehensive evaluation of the relevant materials, and identifying the primary elements to be analyzed.
- Select a Topic: The first step in starting an analytical thesis is to select a specific topic or aspect you want to explore in-depth.
- Research the Topic: Before drafting your thesis, it’s important to delve into your topic. Familiarize yourself with the primary sources, secondary analyses, and any related discussions.
- Identify a Focus: Determine the specific aspect of the topic you want to analyze. This could be a character in a novel, a historical event’s cause and effect, or a particular trend in science.
- Ask Analytical Questions: Pose questions that will guide your analysis. For example, “What is the significance of this character’s actions?” or “How does this event influence the larger narrative?”
What makes a good analytical thesis?
A good analytical thesis possesses several characteristics:
- Clear and Concise: A thesis should clearly convey your main argument without being overly wordy.
- Specific: It should narrow down your topic to a specific aspect or element that can be thoroughly explored in your essay.
- Arguable: A good thesis presents an argument or an interpretation that could be challenged by others.
- Evidence-Based: It should be based on evidence from the source material.
- Relevant: The thesis should be pertinent to the assignment or topic at hand.
- Original: Your thesis should offer a fresh perspective or insight, rather than simply stating the obvious.
How do you write a thesis statement for an analytical essay? – Step by Step Guide
- Read Your Source Material: Engage with your primary source, noting key elements, themes, or patterns that emerge.
- Identify Your Main Argument: What primary message or insight do you wish to convey about your topic?
- Gather Supporting Evidence: List down the pieces of evidence from the source that support your main argument.
- Formulate a Working Thesis: Draft a tentative thesis statement that encapsulates your main argument and supporting evidence.
- Refine and Narrow: Make sure your thesis is specific and focuses on a particular aspect of your topic.
- Ensure It’s Debatable: Your thesis should present a perspective or interpretation that can be debated.
- Seek Feedback: Discuss your thesis with peers, instructors, or mentors to get feedback and further refine it.
- Finalize the Statement: Once refined, finalize your thesis statement, ensuring it accurately represents your analytical insights.
Tips for Writing an Analytical Thesis Statement Example
- Start Broad, then Narrow Down: Begin with a broad perspective on your topic and then hone in on the specific area you want to analyze.
- Avoid Subjectivity: While an analytical thesis represents your interpretation, it should be based on evidence and not personal biases.
- Stay Active: Use active voice for a more assertive and clear thesis.
- Revisit and Revise: As you write your essay, you might find more insights that can refine your thesis. Be open to revisiting and tweaking your statement.
- Avoid Vague Language: Words like “might,” “could,” or “possibly” can weaken your thesis. Be assertive in your statement.
- Test Your Thesis: A good practice is to try to counter-argue your thesis. If you can find valid counter-arguments, it might be too weak or broad.
- Keep it Focused: Your thesis should only cover what you will discuss in your essay, not introduce new topics.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Write multiple versions of your thesis before settling on the final one. This practice will help you refine your analytical skills over time.
An analytical essay thesis statement is the cornerstone of any analytical essay, offering a concise insight into the writer’s analysis. Crafting it requires a clear understanding of the topic, supporting evidence, and a focused approach. By adopting best practices and refining one’s skills, a writer can effectively convey their analytical insights, enhancing the overall impact of their essay.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Analytical Essay Thesis Statement on the symbolism in
Create an Analytical Essay Thesis Statement analyzing the effects of global warming.

- AP Calculus
- AP Chemistry
- AP U.S. History
- AP World History
- Free AP Practice Questions
- AP Exam Prep

How to Approach AP World History: Modern DBQs
Question 1 in Section II of the AP World History: Modern Exam is the document-based question (DBQ). It will always include seven documents offering a variety of perspectives on a historical development or process that took place between 1450 and 2001.
What does a high-scoring Document-Based Question response contain?
Make a thesis or claim that responds to the prompt. The thesis or claim must be based on historical facts and must establish a line of reasoning.
Provide context relevant to the prompt by describing a broader historical development or process.
Use at least six of the provided documents to support an argument in response to the prompt.
Additional Evidence
Use a historical example not found in the documents as evidence relevant to an argument about the prompt.
Explain how the context or situation of at least three documents is relevant to an argument. This could address the relevance of the document’s point of view, purpose, historical situation, and/or audience.
Complex Understanding
Demonstrate a nuanced understanding of an argument that responds to the prompt by using evidence to corroborate, qualify, or modify the argument.
While this may sound like a lot of factors to keep in mind, the strategies below will help you plan your response in such a way to address all the scoring requirements.
AP World History: Modern DBQ Strategies
Consider the following special strategies for the DBQ. Score requirements are highlighted in bold.
DBQ Strategy 1: Analyze the Prompt
- Most prompts will test one of the following historical reasoning skills: causation, continuity and change over time, or comparison. Look for keywords in the prompt that indicate which skill is being tested (for instance, “changes” often indicates continuity and change over time, while phrases such as “transformed” or “led to” often indicate causation); keep the skill in mind as you read the documents and consider organizing your essay according to the skill.
- Use the 15-minute reading period to read the documents and organize them into groups for analysis.
- Feel free to write notes in the test booklet and underline important words in both the source lines and the documents themselves. Nothing in the booklet is read as part of the essay scoring.
- Assume that each document provides only a snapshot of the topic—just one perspective.
- For each document, jot down brief notes to help you solidify your understanding of it. Use your notes to make your plan and write your essay. Take short notes about: the main idea(s) of the source, the purpose of the source (why it was written), and the background of the author and/or the context in which the source was created. Thinking about these factors will help you address several DQB requirements.
- Reread the prompt, thinking about how each of the documents relates to the prompt. Group the documents by their similarities: perhaps they present two or more major viewpoints, causes, or types of changes. When you plan the organization of your essay, each group may correspond with one body paragraph.
- If the 15-minute reading period has passed and you need a few more minutes to review the documents and organize your thoughts, go ahead! The 15 minutes is a suggested amount of time. That said, you will want to give yourself as much time as possible to write a thoughtful response.
DBQ Strategy 2: Plan Your Response
- Making a careful plan can help ensure that you address all the scoring requirements.
- Paraphrase your thesis statement. Knowing your claim will make it easier for you to plan an effective argument in your essay. In light of the documents, you must make a claim that demonstrates a line of reasoning in response to the prompt. Avoid statements that are vague or general (“The Industrial Revolution was very significant”), and make a specific claim that responds to the prompt using both the documents and your historical knowledge and sets up the rest of your essay (“The Industrial Revolution not only resulted in new capitalist economies but also brought about fundamental changes in social structures by creating new social classes and new roles for women”).
- Be sure your thesis or overall plan incorporates a complex understanding . You need to demonstrate that you have more than just a basic understanding of the content, so your essay should address the complexity of the historical development—perhaps by including multiple variables, by considering both causes and effects, or by making an insightful connection to another time period.
- Make a note about how you will provide context for the topic of the prompt. This may fit well in the introduction or first body paragraph.
- List the documents you will use as evidence —remember that you must use six or seven to earn the maximum number of points for using the documents.
- Consider whether the paragraph is a good place to provide additional evidence —you must include one additional historical example.
- Think about when it would be beneficial to explain sourcing , or how a document’s context or situation is relevant to the argument—you must do so for three documents.
- Finally, review your plan and check off each requirement in your test booklet to ensure you addressed all six.
For more help prepping for the AP World History: Modern exam, check out our AP World History: Modern Prep Plus Book .
DBQ Strategy 3: Action! Write Your Response
- Nothing is more important in the first paragraph than the clear statement of an analytical thesis. The reader is most interested in seeing a strong thesis as soon as possible.
- Your thesis can be more than just one sentence. With the compound questions often asked by the DBQ, two sentences might be needed to complete the idea.
- Each paragraph should address one component of your thesis claim. Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence.
- Refer to the authors of the documents, not just the document numbers.
- Including short quotes is an effective way to use the documents to support your claims. However, avoid copying long sentences; use only the words or phrases that are relevant to your essay. The reader is interested in your ideas, not those of the documents’ authors.
- A good idea is to write a concluding paragraph that might extend your original thesis. Think of a way to restate your thesis, adding information from your analysis of the documents.
DBQ Strategy 4: Proofread
Skim for any glaring errors and, if you have time, check again to make sure your response meets each of the DBQ requirements.
You might also like

Call 1-800-KAP-TEST or email [email protected]
Prep for an Exam
MCAT Test Prep
LSAT Test Prep
GRE Test Prep
GMAT Test Prep
SAT Test Prep
ACT Test Prep
DAT Test Prep
NCLEX Test Prep
USMLE Test Prep
Courses by Location
NCLEX Locations
GRE Locations
SAT Locations
LSAT Locations
MCAT Locations
GMAT Locations
Useful Links
Kaplan Test Prep Contact Us Partner Solutions Work for Kaplan Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy CA Privacy Policy Trademark Directory

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip #2: Your thesis should be 1-2 sentences. If your thesis is longer than 1-2 sentences, it's probably way too wordy and overly complex. Tip #3: Your thesis should be in the introduction or conclusion. According to the AP DBQ rubric, your thesis must be in the introductory or concluding paragraph.
Let's take a look at a sample AP World History DBQ question and techniques to construct a solid thesis. Using the following documents, analyze how the Ottoman government viewed ethnic and religious groups within its empire for the period 1876-1908. Identify an additional document and explain how it would help you analyze the views of the ...
Resources from Heimler's History: To master all the WRITING SKILLS you need, get my ESSAY CRAM COURSE: +AP Essay CRAM Course (DBQ, LEQ, SAQ Help): https://bi...
How DBQs Work on the AP World History Exam. The DBQ format AP World History uses consists of a single open-ended prompt, and will focus on the time period of 1450-2001. Question Type. # of Questions. % of Total Score. Multiple Choice. 55 questions. 40%. Short Answer.
The intent of this question was to assess students' ability to articulate and defend an argument based on evidence provided by a select set of historical documents. The Document-Based Question (DBQ) asked students to evaluate the extent to which European imperialism had an impact on the economies of Africa and/or Asia.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. On the actual exam, you will read three questions and determine which you can answer most confidently. For this sample question, note that you will be evaluating how changes in the spread of ideas impacted societies. The words "changes," "impacted," and "the extent" indicate that this prompt is testing ...
Now that you've crafted a thesis statement, you'll need to develop a plan for how to incorporate the given documents into your DBQ essay. Review the prompt and the documents below: ... AP World History: Modern—Period 2 Notes (1450-1750) AP World History Exam: Document-Based Question.
Overview. The question required students to identify developments and processes related to changing social norms for Muslim women in the Middle East from 1850-1950. This included the ability to place those norms in a broader historical context and to describe and analyze the content of documents.
For students taking AP World History: Modern. All Subjects. Light. Before 1200 CE. The Global Tapestry (1200-1450) Networks of Exchange (1200-1450) ... look at what the thesis is, tips for writing a thesis, and will explore a sample DBQ in order to arrive at writing a thesis statement. ... AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College ...
Responses earn 1 point by responding to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis that establishes a line of reasoning about the topic. To earn this point the thesis must make a claim that responds to the prompt rather than simply restating or rephrasing the prompt. The thesis must suggest at least one main line of
Unfortunately, this is not good enough for the AP World exam. It is too general and more or less repeats the prompt. With a simple addition and a bit of tweaking, you can make this thesis work: "There were many similarities and differences between the Han Empire during 206 B.C.E.- 220 B.C.E. and the Spanish empire of the sixteenth century.
Start with 20 minutes for your outline and 50 for your essay, (or longer, if you need). Then when you can do it in 20 and 50, move back to 18 minutes and 45 for writing, then to 15 and 40. You absolutely can learn to manage your time effectively so that you can write a great DBQ in the time allotted.
Step 2: Plan Your Response. Next, take time to plan your response. Focus on formulating a strong thesis, and check your plan against the six DBQ requirements. See the sample plan that a high-scoring writer might make. Scoring requirements are written in bold for reference; note that the writer includes six of the seven documents and plans to ...
AP®WORLD HISTORY 2018 SCORING GUIDELINES. ©2018 The College Board Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.org. Question 1 — Document-Based Question. Maximum Possible Points: 7. "Evaluate the extent to which railroads affected the process of empire -building in Afro-Eurasia between 1860 and 1918.".
Support your thesis statement. Make your overarching statement or argument, then position your supporting evidence so that it is obviously directed to answering the question. State your points clearly and explicitly connect them to the larger thesis, rather than making generalizations. Elaborate on the evidence.
Note: The thesis does not need to refer to a specific religion or belief system. The three religions listed in the introductory statement are provided as examples; it is not required that a successful thesis focus on one of these three religions.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. ... or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel. makes a claim that others might dispute. is usually a single sentence somewhere in your first ...
he first part of the thesis statement.Basic Complex-split thesis formula:Although (oth. r example) , ultimately (claim responding to prompt specifying 3 examples).Once you get used to writing a complex-split in th. anner, you can tweak the wording - but for now, stick to this formula. Example: Evaluate the main causes of World War 1 Simple ...
During Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. Each long essay question begins with a general statement that provides context about the tested time period, and then the second sentence identifies your task, which will always entail developing an evaluative argument. Make sure to read all three prompts carefully. Think of the evidence you could use and the ...
This page details all aspects of writing a DBQ including how to earn the contextualization, thesis, evidence, analysis, and sourcing points, how to write a compare & contrast essay, cause & effect essay, and change & continuity over time (CCOT) essay. It also has a free downloadable worksheet linked to it to help you organize your DBQ.
Finalize the Statement: Once refined, finalize your thesis statement, ensuring it accurately represents your analytical insights. Tips for Writing an Analytical Thesis Statement Example. Start Broad, then Narrow Down: Begin with a broad perspective on your topic and then hone in on the specific area you want to analyze.
AP World History: Modern DBQ Strategies. Consider the following special strategies for the DBQ. Score requirements are highlighted in bold. ... Paraphrase your thesis statement. Knowing your claim will make it easier for you to plan an effective argument in your essay. In light of the documents, you must make a claim that demonstrates a line of ...