Have an account?

Suggestions for you See more

Test Frederick Douglas
Frederick douglass, the people could fly, declaration of sentiments, the road to freedom, harriett tubman, 10th - 11th , plot elements, 4th - 6th .

The Narrative of Frederick Douglass Chap...
9th - 12th grade.
The Narrative of Frederick Douglass Chapter 1
12 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
What do slaves not have knowledge about?
Age and birthdays
the name of their plantation
Who prevents slaves from having knowledge?
Slave masters
their parents
Frederick Douglass's father was...
Isaac Bailey
Harriet Bailey
Frederick Douglass Sr.
His slave master
The reason children were taken away from their mother before 12 months old was...
To improve the bond between mother and child by keeping them apart.
to hinder the temptation of playing Fortnite.
to instill the affections given to mother and a child
to prevent the affection and emotional connection between mother and child.
- 5. Multiple Choice Edit 1 minute 1 pt 1. Why is Frederick not sure when he was born? There are no records kept of slaves’ births. His mom forgot to tell him. His master burned his birth certificate. All of the above.
Why is a slaveholder who has fathered a child likely to be tougher on that child?
The slaveholder would hate the child.
The slaveholder would not want to be accused of favoritism by his white wife.
The slaveholder would not know it was his child.
All of the above.
Based on what we have read so far, what was Douglass’s main purpose in writing his autobiography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass?
To cover up his true identity
To help other slaves know how to get free
To shed light/truth on the system of slavery
To make him sound smart
- 8. Multiple Choice Edit 1 minute 1 pt Why would slaveholders want to keep a slave ignorant of such a simple thing as his birthday? It makes them feel like animals. It keeps them uneducated. It makes them easier to control. All of the above.
Why does Frederick only rarely see his mother?
She doesn't love him.
She doesn't know he's her son.
She was moved away from him at birth and is 12 miles away
Why does Frederick tell the story of Aunt Hester and Lloyd’s Ned?
It was when Frederick realized that slavery was brutal and violent at times.
It was a funny anecdote to lighten the mood.
It showed that romance could still happen between slaves.
It was when Douglass declared that he would someday be free.
What does the following quote mean?
"Cursed be Canaan (Ham's son); a servant of servants shall he be unto his brethren."
All slaves are cursed.
Canaan was the most important slave on the plantation.
Slaves would one day break free from their masters.
All people with black skin (descendants of Ham) are supposed to be slaves.
What does Frederick Douglass look like?
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Early life and enslavement
Escape from slavery, life in new bedford, and work with the american anti-slavery society, narrative of the life of frederick douglass , european travel, and the north star, involvement with john brown, abraham lincoln, elizabeth cady stanton, and susan b. anthony, move to washington, d.c., the freedman’s bank, government office-holding, and later years.

What was Frederick Douglass’s childhood like?
How did frederick douglass become involved in the abolitionist movement, how was frederick douglass involved in the american civil war and reconstruction, what are some of frederick douglass’s most famous writings and speeches.

Frederick Douglass
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Free Speech Center - Frederick Douglass
- American Battlefield Trust - Frederick Douglass
- National Park Service - Frederick Douglass National Historic Site - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Library of Congress - Frederick Douglass Timeline
- Social Studies for Kids - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- PBS LearningMedia - The Abolitionists: The Emancipation Proclamation and the Civil War
- NPR - Frederick Douglass On How Slave Owners Used Food As A Weapon Of Control
- HistoryNet - Frederick Douglass
- Humanities Libretexts - Frederick Douglass (1818–1895)
- United States History - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Frederick Douglass - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- Frederick Douglass - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Frederick Douglass was born in slavery to a Black mother and a white father. At age eight the man who owned him sent him to Baltimore, Maryland, to live in the household of Hugh Auld. There Auld’s wife taught Douglass to read. Douglass attempted to escape slavery at age 15 but was discovered before he could do so.
Frederick Douglass escaped from slavery to New York City in 1838, later settling in New Bedford, Massachusetts. At an 1841 antislavery convention, he was asked to recount his experience as an enslaved person. He so moved his audience that he became an agent for the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society. His 1845 autobiography cemented his prominence as an abolitionist .
During the American Civil War Frederick Douglass served as an adviser to Pres. Abraham Lincoln . Douglass played a crucial role in persuading Lincoln to arm enslaved people and prioritize abolition. During Reconstruction Douglass became the highest-ranking Black official of his time and advocated for full civil rights for Black people as well as for women.
Frederick Douglass published three autobiographies. The first autobiography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave, Written by Himself , catapulted him to fame and invigorated the abolitionist movement. Of Douglass’s many speeches, “What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?” was perhaps one of the most well-known.
What was Frederick Douglass’s legacy?
Frederick Douglass was a prolific writer and a masterful orator who captivated readers and listeners throughout the U.S. and Great Britain. His talents contributed to the rise of antislavery sentiments in public consciousness.
Frederick Douglass (born February 1818, Talbot county, Maryland , U.S.—died February 20, 1895, Washington, D.C.) was an African American abolitionist, orator, newspaper publisher, and author who is famous for his first autobiography , Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . He became the first Black U.S. marshal and was the most photographed American man of the 19th century.

Douglass was born enslaved as Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey on Holme Hill Farm in Talbot county, Maryland. Although the date of his birth was not recorded, Douglass estimated that he had been born in February 1818, and he later celebrated his birthday on February 14. (The best source for the events in Douglass’s life is Douglass himself in his oratory and writings, especially his three autobiographies, the details of which have been checked when possible and have largely been confirmed, though his biographers have contributed corrections and clarifications.) Douglass was owned by Capt. Aaron Anthony, who was the clerk and superintendent of overseers for Edward Lloyd V (also known as Colonel Lloyd), a wealthy landowner and slaveholder in eastern Maryland. Like many other enslaved children, Douglass was separated from his mother, Harriet Bailey, when he was very young. He spent his formative years with his maternal grandmother, Betsey Bailey, who had the responsibility of raising young enslaved children.

Harriet Bailey worked as a field hand on a neighbouring plantation and had to walk more than 12 miles (about 19 km) to visit her son, whom she met with only a few times in his life. He described her as “tall and finely proportioned, of dark, glossy complexion, with regular features, and amongst the slaves was remarkably sedate and dignified.” She died when he was about seven years old. As an adult, Douglass learned that his mother had been the only Black person in what was then Talbot county who could read, an extraordinarily rare achievement for a field hand.

When Douglass was age five or six, he was taken to live on Colonel Lloyd’s home plantation, Wye House. Lloyd’s plantation functioned like a small town. Young Douglass found himself among several other enslaved children competing for food and other comforts. In 1826 at approximately age eight, he was sent to live with Hugh and Sophia Auld at Fells Point, Baltimore . Hugh’s brother Capt. Thomas Auld was the son-in-law of Douglass’s owner, Aaron Anthony. Douglass’s responsibility in Baltimore was to care for Hugh and Sophia’s young son, Thomas. Sophia began teaching Douglass how to read, along with her son. The lessons ended abruptly, however, when Hugh discovered what had been going on and informed Sophia that literacy would “spoil” a slave. According to Douglass, Hugh stated that if a slave were given an inch, he would “take an ell [a unit of measure equal to about 45 inches].” In Maryland, as in many other slaveholding states, it was forbidden to teach enslaved people how to read and write. Douglass continued his learning in secret, by exchanging bread for lessons from the poor white boys he played with in the neighbourhood and by tracing the letters in Thomas’s old schoolbooks.
In March 1832 Douglass was sent from Baltimore to St. Michaels, on Maryland’s Eastern Shore. After both Aaron Anthony and his daughter Lucretia died, her husband, Capt. Thomas Auld, became Douglass’s owner. Teenage Douglass experienced harsher living conditions with Auld, who was known for his abusive practices.
In January 1833 Douglass was leased to local farmer Edward Covey. Leasing or hiring out enslaved persons was a common revenue-generating practice. Farmers would pay slaveholders a monthly fee for enslaved people and take responsibility for their care, food, and lodging. Covey was known as a “slave breaker,” someone who abused slaves physically and psychologically in order to make them more compliant . According to Douglass, Covey’s abuse led to a climactic confrontation six months into Douglass’s time with the farmer. One day Covey attacked Douglass, and Douglass fought back. The two men engaged in an epic two-hour-long physical struggle. Douglass ultimately won the fight, and Covey never attacked him again. Douglass emerged from the incident determined to protect himself from any physical assault from anyone in the future.
In January 1834 Douglass was sent to William Freeland’s farm. Living and working conditions were better under Freeland; however, Douglass still desired his freedom. While living with Freeland, he started a Sabbath school at which he taught area Blacks how to read and write. Along with four other enslaved men, Douglass plotted to escape north by taking a large canoe up the coast of Maryland and to proceed to Pennsylvania, but their plot was discovered. Douglass and the other participants were arrested. Captain Auld then sent Douglass back to Baltimore to live again with Hugh and Sophia Auld and to learn a trade.
Hugh Auld hired out Douglass to local shipyards as a ship caulker. Now working as a skilled tradesman, Douglass was paid by the shipyards for his efforts. He would then submit his earnings to Auld, who gave Douglass a small percentage of the wages. Douglass would eventually hire out his own time, which meant that he paid Auld a set amount every week but was responsible for maintaining his own food and clothing. During this time, Douglass became more involved in Baltimore’s Black community , which led him to meet Anna Murray , a freeborn Black woman, whom he would eventually marry.
Douglass moved about Baltimore with few restrictions, but that privilege came to an end when he decided to attend a religious meeting outside of Baltimore on a Saturday evening and postpone paying Auld his weekly fee. The following Monday, when Douglass returned, Auld threatened him. After that encounter, Douglass was determined to escape his bondage. He escaped in September 1838 by dressing as a sailor and traveling from Baltimore to Wilmington , Delaware, by train, then on to Philadelphia by steamboat , and from there to New York City by train. Black sailors in the 19th century traveled with documents granting them protection under the American flag. Douglass used such documents to secure his passage north with the help of Anna, who, according to family lore , had sold her feather bed to help finance his passage.

New York City was a dangerous place for enslaved people seeking freedom. Numerous slave catchers traveled to the city to track down those who had escaped. Many locals, Black and white, were willing, for money, to tell the authorities about people trying to escape enslavement. For his own protection, Douglass (still months from assuming that name) changed his name from Frederick Bailey to Frederick Johnson. A chance meeting with Black abolitionist David Ruggles led Douglass to safety. Anna arrived in New York several days later, and the two were married by the Reverend J.W.C. Pennington.

At Ruggles’s recommendation, the couple quickly left New York City for New Bedford , Massachusetts. Ruggles had determined that New Bedford’s shipping industry would offer Douglass the best chance to find work as a ship caulker. In New Bedford the couple stayed with a local Black married couple, Nathan and Polly Johnson. Because many families in New Bedford had the surname Johnson, Douglass chose to change his name again. Nathan Johnson suggested the name Douglass, which was inspired by the name of an exiled nobleman in Sir Walter Scott ’s poem The Lady of the Lake . The newly minted Frederick Douglass earned money for the first time as a free man. However, despite Douglass’s previous work experience, racial prejudice in New Bedford prevented him from working as a ship caulker (white caulkers refused to work with Black caulkers). Consequently, Douglass spent his first years in Massachusetts working as a common labourer.

Douglass remained an avid reader throughout his adult life. When he escaped to New York, he carried with him a copy of The Columbian Orator . In New Bedford he discovered William Lloyd Garrison ’s abolitionist newspaper, The Liberator . Inspired by it, Douglass attended a Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society convention in Nantucket in the summer of 1841. At the meeting, abolitionist William C. Coffin, having heard Douglass speak in New Bedford, invited him to address the general body. Douglass’s extemporaneous speech was lauded by the audience, and he was recruited as an agent for the group.
As an agent of both the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society and the American Anti-Slavery Society , Douglass traveled the country promoting abolition and the organizations’ agenda. He and other persons who had escaped conditions of enslavement frequently described their own experiences under those conditions. The American Anti-Slavery Society supported “moral suasion” abolition, the belief that slavery was a moral wrong that should be resisted through nonviolent means. Douglass strongly promoted this philosophy during the early years of his abolitionist career. In his speech at the 1843 National Convention of Colored Citizens in Buffalo, New York, Black abolitionist and minister Henry Highland Garnet proposed a resolution that called for enslaved people to rise up against their masters. The controversial resolution ignited a tense debate at the convention, with Douglass rising in firm opposition. His belief in moral suasion would repeatedly place him at odds with other Black abolitionists during this phase of his career. Work as an agent provided Douglass with the means to support his family. He and Anna had five children: Rosetta (born 1839), Lewis (born 1840), Frederick, Jr. (born 1842), Charles (born 1844), and Annie (born 1849).

In 1845 Douglass published his first autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . Prior to its publication, audiences at Douglass’s lectures had questioned his authenticity as an ex-slave because of his eloquence, refusal to use “plantation speak,” and unwillingness to provide details about his origins. The Narrative settled these disputes by naming people and locations in Douglass’s life. The book also challenged the conventional employment of ghostwriters for slave narratives by boldly acknowledging that Douglass wrote it himself. Douglass would publish two additional autobiographies: My Bondage and My Freedom (1855) and Life and Times of Frederick Douglass (1881). The Narrative quickly became popular, especially in Europe, but the book’s success contributed to Hugh Auld’s determination to return Douglass to the conditions of enslavement.
The threat of capture, as well as the book’s excellent performance in Europe, prompted Douglass to travel abroad from August 1845 to 1847, and he lectured throughout the United Kingdom. His English supporters, led by Ellen and Anna Richardson, purchased Douglass from Hugh Auld, giving him his freedom. In the spring of 1847, Douglass returned to the United States a free man with the funding to start his own newspaper.

Douglass moved to Rochester , New York, to publish his newspaper, The North Star , despite objections from Garrison and others. Basing the newspaper in Rochester ensured that The North Star did not compete with the distribution of The Liberator and the National Anti-Slavery Standard in New England . The North Star ’s first issue appeared on December 3, 1847. In 1851 the paper merged with the Liberty Party Paper to form Frederick Douglass’ Paper , which ran until 1860. Douglass would publish two additional newspapers during his life, Douglass’ Monthly (1859–63) and New National Era (1870–74).
The move to Rochester surrounded Douglass with political abolitionists such as Gerrit Smith . During his first few years in Rochester, Douglass remained loyal to Garrison’s philosophy, which promoted moral suasion, stated that the U.S. Constitution was an invalid document, and discouraged participation in American politics because it was a system corrupted by slavery. In 1851, however, Douglass announced his split from Garrison when he declared that the Constitution was a valid legal document that could be used on behalf of emancipation. Consequently, Douglass became more engaged in American politics and constitutional interpretation.

The country’s tension around slavery rapidly increased in the 1850s. Douglass’s Rochester home was part of the Underground Railroad and hosted numerous fellow abolitionists. In 1859 Douglass met with abolitionist John Brown in a quarry in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania. Brown invited Douglass to participate in the planned raid on the federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry , Virginia (now in West Virginia), which Brown hoped would inspire a massive uprising by enslaved people. Douglass declined the invitation. Shortly after the raid (October 16–19), Douglass received word that the authorities were looking to arrest him as an accomplice . He quickly fled to Canada before heading to Europe for a scheduled lecture tour. Douglass returned home in April 1860 after learning that his youngest daughter, Annie, had died.

With the outbreak of the Civil War , Douglass strongly advocated for inclusion of Black soldiers in the Union army. He became a recruiter for the Massachusetts 54th, an all-Black infantry regiment in which his sons Lewis and Charles served. In 1863 Douglass visited the White House to meet with Pres. Abraham Lincoln to advocate for better pay and conditions for the soldiers. Lincoln then invited Douglass to the White House in 1864 to discuss what could be done for Blacks in the case of a Union loss. Douglass would meet with Lincoln a third time, after the president’s second inauguration and about a month before his assassination.
The Emancipation Proclamation and the Union’s victory presented a new reality: millions of Black people were free. Douglass dedicated himself to securing the community’s rights to this new freedom. He strongly supported the Fourteenth Amendment , which granted Blacks citizenship, but he realized that this new citizenship status needed to be protected by suffrage. Initially Douglass supported a constitutional amendment supporting suffrage for all men and women. Having attended the 1848 women’s rights convention in Seneca Falls , New York, he was a longtime supporter of women’s rights, joining Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony in this stance. Reconstruction politics, however, indicated that a universal suffrage amendment would fail. Douglass then supported Black male suffrage with the idea that Black men could help women secure the right to vote later. This placed him at odds with Stanton and Anthony. Douglass hoped that the passage of the Fifteenth Amendment would encourage African Americans to stay in the South to consolidate their power as a voting bloc, but the region’s high levels of violence against African Americans led him to support Black migration to safer areas of the country.

After a fire destroyed his Rochester home, Douglass moved in 1872 to Washington, D.C. , where he published his latest newspaper venture, New National Era . The newspaper folded in 1874 because of its poor fiscal health. That same year Douglass was appointed president of the Freedman’s Savings & Trust, also known as the Freedman’s Bank. The bank failed four months after he became president because of the years of corruption that predated his association with the bank. The bank’s failure harmed his reputation, but Douglass worked with the U.S. Congress to remedy the damage caused by the bank.

After the Freedman’s Bank debacle , Douglass held numerous government appointments. He became the first Black U.S. marshal in 1877 when he was appointed to that post for the District of Columbia by Pres. Rutherford B. Hayes . He served in that capacity until 1881, when Pres. James A. Garfield appointed him to the high-paying position of recorder of deeds for the District of Columbia. In 1889 Pres. Benjamin Harrison selected Douglass as the U.S. minister resident and consul general to the Republic of Haiti . The major controversy during Douglass’s tenure was the quest by the United States to acquire the port town of Môle Saint-Nicolas as a refueling station for the U.S. Navy. Douglass disagreed with the Harrison administration’s approach, preferring to promote the autonomy of the Haitian government. He resigned the position in 1891 and returned to his home in Washington, D.C.

Douglass spent the last 17 years of his life at Cedar Hill, his home in the Anacostia neighbourhood of Washington, D.C., to which he had moved in 1878. On August 4, 1882, Anna Murray Douglass died in the home after suffering a stroke. In 1884 Douglass married Helen Pitts, his white secretary, who was about 20 years younger than her husband. The marriage was controversial for its time, and it resulted in Douglass’s temporary estrangement from some friends and family.

During the latter years of his life, Douglass remained committed to social justice and the African American community. His prominence and work resulted in his being the most photographed American man in the 19th century . His distinguished photographs were deliberate contradictions to the visual stereotypes of African Americans at the time, which often exaggerated their facial features, skin colour, and physical bodies and demeaned their intelligence. He served on Howard University ’s board of trustees from 1871 to 1895. Douglass cultivated relationships with younger activists, most notably Ida B. Wells , who featured his letter to her in her book Southern Horrors: Lynch Law in All Its Phases. He also contributed to her pamphlet protesting the exclusion of exhibits dedicated to African American culture from the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition , The Reason Why the Colored American Is Not in the World’s Columbian Exposition .

Douglass died in his Cedar Hill home on February 20, 1895. After his death, Helen Pitts Douglass established the Frederick Douglass Memorial and Historical Association to preserve his legacy . She bequeathed the home and its belongings to the organization in her will. Cedar Hill became part of the National Park system in 1962, and it was designated the Frederick Douglass National Historic Site in 1988. The U.S. Library of Congress digitized its holdings of Douglass’s papers , which include letters, speeches, and personal documents.
At the end of his life, Douglass, an American icon who fought for social justice and equity , became known as the “Lion of Anacostia.” Through his writings, speeches, and photographs, he boldly challenged the racial stereotypes of African Americans. Douglass’s contributions to the Black American community and American history were recognized in the early 20th century during Negro History Week, the predecessor of Black History Month , which many communities anchored to the day on which his birthday was celebrated, February 14. Today Douglass is renowned not just for his rise from slavery to the highest levels of American society but also for his dedication to challenging the country to recognize the rights of all people and be consistent with its ideals.
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass was a leader in the abolitionist movement, an early champion of women’s rights and author of ‘Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.’
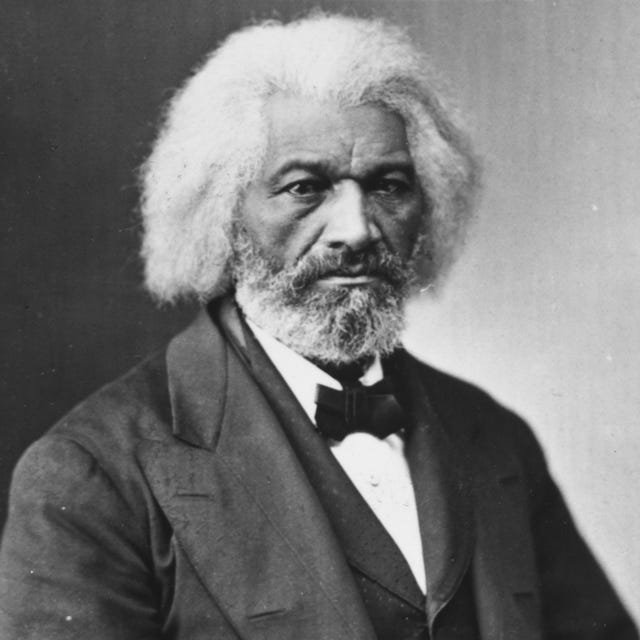

(1818-1895)
Who Was Frederick Douglass?
Among Douglass’ writings are several autobiographies eloquently describing his experiences in slavery and his life after the Civil War , including the well-known work Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave .
Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey was born around 1818 into slavery in Talbot County, Maryland. As was often the case with slaves, the exact year and date of Douglass' birth are unknown, though later in life he chose to celebrate it on February 14.
Douglass initially lived with his maternal grandmother, Betty Bailey. At a young age, Douglass was selected to live in the home of the plantation owners, one of whom may have been his father.
His mother, who was an intermittent presence in his life, died when he was around 10.
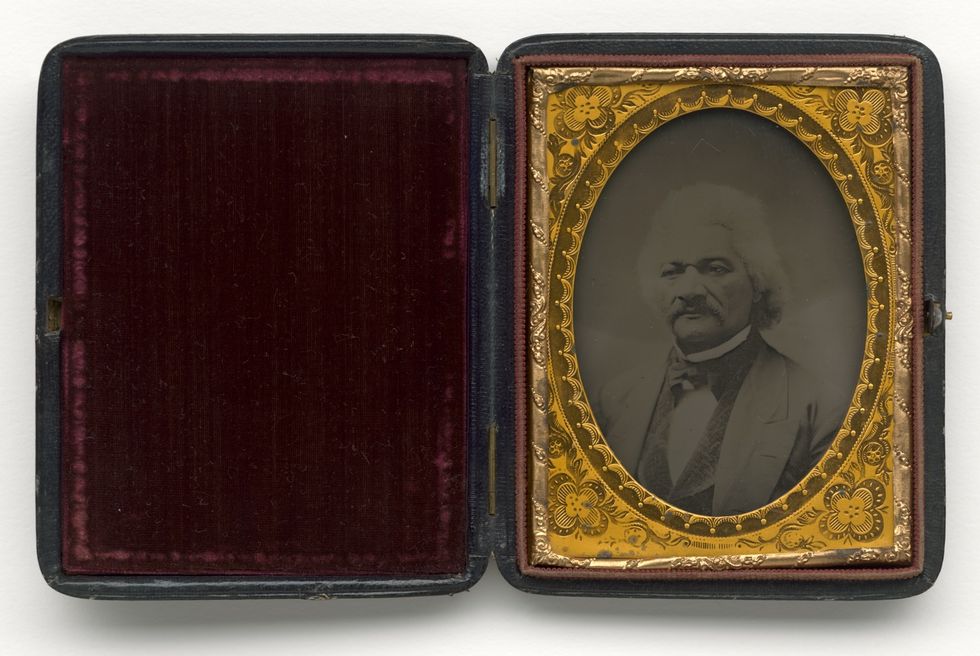

Learning to Read and Write
Defying a ban on teaching slaves to read and write, Baltimore slaveholder Hugh Auld’s wife Sophia taught Douglass the alphabet when he was around 12. When Auld forbade his wife to offer more lessons, Douglass continued to learn from white children and others in the neighborhood.
It was through reading that Douglass’ ideological opposition to slavery began to take shape. He read newspapers avidly and sought out political writing and literature as much as possible. In later years, Douglass credited The Columbian Orator with clarifying and defining his views on human rights.
Douglass shared his newfound knowledge with other enslaved people. Hired out to William Freeland, he taught other slaves on the plantation to read the New Testament at a weekly church service.
Interest was so great that in any week, more than 40 slaves would attend lessons. Although Freeland did not interfere with the lessons, other local slave owners were less understanding. Armed with clubs and stones, they dispersed the congregation permanently.
With Douglass moving between the Aulds, he was later made to work for Edward Covey, who had a reputation as a "slave-breaker.” Covey’s constant abuse nearly broke the 16-year-old Douglass psychologically. Eventually, however, Douglass fought back, in a scene rendered powerfully in his first autobiography.
After losing a physical confrontation with Douglass, Covey never beat him again. Douglass tried to escape from slavery twice before he finally succeeded.
Wife and Children
Douglass married Anna Murray, a free Black woman, on September 15, 1838. Douglass had fallen in love with Murray, who assisted him in his final attempt to escape slavery in Baltimore.
On September 3, 1838, Douglass boarded a train to Havre de Grace, Maryland. Murray had provided him with some of her savings and a sailor's uniform. He carried identification papers obtained from a free Black seaman. Douglass made his way to the safe house of abolitionist David Ruggles in New York in less than 24 hours.
Once he had arrived, Douglass sent for Murray to meet him in New York, where they married and adopted the name of Johnson to disguise Douglass’ identity. Anna and Frederick then settled in New Bedford, Massachusetts, which had a thriving free Black community. There they adopted Douglass as their married name.
Douglass and Anna had five children together: Rosetta, Lewis Henry, Frederick Jr., Charles Redmond and Annie, who died at the age of 10. Charles and Rosetta assisted their father in the production of his newspaper The North Star . Anna remained a loyal supporter of Douglass' public work, despite marital strife caused by his relationships with several other women.
After Anna’s death, Douglass married Helen Pitts, a feminist from Honeoye, New York. Pitts was the daughter of Gideon Pitts Jr., an abolitionist colleague. A graduate of Mount Holyoke College , Pitts worked on a radical feminist publication and shared many of Douglass’ moral principles.
Their marriage caused considerable controversy, since Pitts was white and nearly 20 years younger than Douglass. Douglass’ children were especially displeased with the relationship. Nonetheless, Douglass and Pitts remained married until his death 11 years later.
Abolitionist
After settling as a free man with his wife Anna in New Bedford in 1838, Douglass was eventually asked to tell his story at abolitionist meetings, and he became a regular anti-slavery lecturer.
The founder of the weekly journal The Liberator , William Lloyd Garrison , was impressed with Douglass’ strength and rhetorical skill and wrote of him in his newspaper. Several days after the story ran, Douglass delivered his first speech at the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society's annual convention in Nantucket.
Crowds were not always hospitable to Douglass. While participating in an 1843 lecture tour through the Midwest, Douglass was chased and beaten by an angry mob before being rescued by a local Quaker family.
Following the publication of his first autobiography in 1845, Douglass traveled overseas to evade recapture. He set sail for Liverpool on August 16, 1845, and eventually arrived in Ireland as the Potato Famine was beginning. He remained in Ireland and Britain for two years, speaking to large crowds on the evils of slavery.
During this time, Douglass’ British supporters gathered funds to purchase his legal freedom. In 1847, the famed writer and orator returned to the United States a free man.
'The North Star'
Upon his return, Douglass produced some abolitionist newspapers: The North Star , Frederick Douglass Weekly , Frederick Douglass' Paper , Douglass' Monthly and New National Era .
The motto of The North Star was "Right is of no Sex – Truth is of no Color – God is the Father of us all, and we are all brethren."
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S FREDERICK DOUGLASS FACT CARD

'Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass'
In New Bedford, Massachusetts, Douglass joined a Black church and regularly attended abolitionist meetings. He also subscribed to Garrison's The Liberator .
At the urging of Garrison, Douglass wrote and published his first autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave , in 1845. The book was a bestseller in the United States and was translated into several European languages.
Although the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass garnered Douglass many fans, some critics expressed doubt that a former enslaved person with no formal education could have produced such elegant prose.
Other Books by Frederick Douglass
Douglass published three versions of his autobiography during his lifetime, revising and expanding on his work each time. My Bondage and My Freedom appeared in 1855.
In 1881, Douglass published Life and Times of Frederick Douglass , which he revised in 1892.
Women’s Rights
In addition to abolition, Douglass became an outspoken supporter of women’s rights. In 1848, he was the only African American to attend the Seneca Falls convention on women's rights. Elizabeth Cady Stanton asked the assembly to pass a resolution stating the goal of women's suffrage. Many attendees opposed the idea.
Douglass, however, stood and spoke eloquently in favor, arguing that he could not accept the right to vote as a Black man if women could not also claim that right. The resolution passed.
Yet Douglass would later come into conflict with women’s rights activists for supporting the Fifteenth Amendment , which banned suffrage discrimination based on race while upholding sex-based restrictions.
Civil War and Reconstruction
By the time of the Civil War , Douglass was one of the most famous Black men in the country. He used his status to influence the role of African Americans in the war and their status in the country. In 1863, Douglass conferred with President Abraham Lincoln regarding the treatment of Black soldiers, and later with President Andrew Johnson on the subject of Black suffrage.
President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation , which took effect on January 1, 1863, declared the freedom of enslaved people in Confederate territory. Despite this victory, Douglass supported John C. Frémont over Lincoln in the 1864 election, citing his disappointment that Lincoln did not publicly endorse suffrage for Black freedmen.
Slavery everywhere in the United States was subsequently outlawed by the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution .
Douglass was appointed to several political positions following the war. He served as president of the Freedman's Savings Bank and as chargé d'affaires for the Dominican Republic.
After two years, he resigned from his ambassadorship over objections to the particulars of U.S. government policy. He was later appointed minister-resident and consul-general to the Republic of Haiti, a post he held between 1889 and 1891.
In 1877, Douglass visited one of his former owners, Thomas Auld. Douglass had met with Auld's daughter, Amanda Auld Sears, years before. The visit held personal significance for Douglass, although some criticized him for the reconciliation.
Vice Presidential Candidate
Douglass became the first African American nominated for vice president of the United States as Victoria Woodhull 's running mate on the Equal Rights Party ticket in 1872.
Nominated without his knowledge or consent, Douglass never campaigned. Nonetheless, his nomination marked the first time that an African American appeared on a presidential ballot.
Douglass died on February 20, 1895, of a massive heart attack or stroke shortly after returning from a meeting of the National Council of Women in Washington, D.C. He was buried in Mount Hope Cemetery in Rochester, New York.
QUICK FACTS
- Name: Frederick Douglass
- Birth Year: 1818
- Birth State: Maryland
- Birth City: Tuckahoe
- Birth Country: United States
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Frederick Douglass was a leader in the abolitionist movement, an early champion of women’s rights and author of ‘Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.’
- Interesting Facts
- Frederick Douglass first learned to read and write at the age of 12 from a Baltimore slaveholder's wife.
- To much controversy, Douglass married white abolitionist feminist Helen Pitts.
- Douglass became the first African American nominated for vice president of the United States.
- Death Year: 1895
- Death date: February 20, 1895
- Death City: Washington, D.C.
- Death Country: United States
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Frederick Douglass Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/activists/frederick-douglass
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E Television Networks
- Last Updated: July 15, 2021
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- If there is no struggle there is no progress. . . . Power concedes nothing without a demand. It never did and it never will.
- Find out just what any people will quietly submit to and you have the exact measure of the injustice and wrong which will be imposed on them.
- I prefer to be true to myself, even at the hazard of incurring the ridicule of others, rather than to be false, and to incur my own abhorrence.
- No man can put a chain about the ankle of his fellow man without at last finding the other end fastened about his own neck.
- People might not get all they work for in this world, but they must certainly work for all they get.
- I would unite with anybody to do right and with nobody to do wrong.
- Where justice is denied, where poverty is enforced, where ignorance prevails, and where any one class is made to feel that society is an organized conspiracy to oppress, rob and degrade them, neither persons nor property will be safe.
- The life of the nation is secure only while the nation is honest, truthful, and virtuous.
- [I]n all the relations of life and death, we are met by the color line. We cannot ignore it if we would, and ought not if we could.
- If I ever had any patriotism, or any capacity for the feeling, it was whipt out of me long since by the lash of the American soul-drivers.
- The ground which a colored man occupies in this country is, every inch of it, sternly disputed.
- The lesson of all the ages on this point is, that a wrong done to one man is a wrong done to all men. It may not be felt at the moment, and the evil day may be long delayed, but so sure as there is a moral government of the universe, so sure will the harvest of evil come.
- Believing, as I do firmly believe, that human nature, as a whole, contains more good than evil, I am willing to trust the whole, rather than a part, in the conduct of human affairs.
- To educate a man is to unfit him to be a slave.
- To deny education to any people is one of the greatest crimes against human nature. It is easy to deny them the means of freedom and the rightful pursuit of happiness and to defeat the very end of their being.
- There is no negro problem. The problem is whether the American people have loyalty enough, honor enough, patriotism enough, to live up to their own constitution.
- Let us have no country but a free country, liberty for all and chains for none. Let us have one law, one gospel, equal rights for all, and I am sure God's blessing will be upon us and we shall be a prosperous and glorious nation.

Watch Next .css-16toot1:after{background-color:#262626;color:#fff;margin-left:1.8rem;margin-top:1.25rem;width:1.5rem;height:0.063rem;content:'';display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;}

Abolitionists

Harriet Tubman

Ralph Waldo Emerson

Abraham Lincoln

Susan B. Anthony

Lucretia Mott

Harriet Beecher Stowe

Alexandre Dumas

Henry David Thoreau

Mary Ann Shadd Cary

James Garfield

Jean-Jacques Dessalines
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Frederick Douglass
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 8, 2024 | Original: October 27, 2009

Frederick Douglass was a formerly enslaved man who became a prominent activist, author and public speaker. He became a leader in the abolitionist movement , which sought to end the practice of slavery, before and during the Civil War . After that conflict and the Emancipation Proclamation of 1862, he continued to push for equality and human rights until his death in 1895.
Douglass’ 1845 autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave , described his time as an enslaved worker in Maryland . It was one of three autobiographies he penned, along with dozens of noteworthy speeches, despite receiving minimal formal education.
An advocate for women’s rights, and specifically the right of women to vote , Douglass’ legacy as an author and leader lives on. His work served as an inspiration to the civil rights movement of the 1960s and beyond.
Who Was Frederick Douglass?
Frederick Douglass was born into slavery in or around 1818 in Talbot County, Maryland. Douglass himself was never sure of his exact birth date.
His mother was an enslaved Black women and his father was white and of European descent. He was actually born Frederick Bailey (his mother’s name), and took the name Douglass only after he escaped. His full name at birth was “Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey.”
After he was separated from his mother as an infant, Douglass lived for a time with his maternal grandmother, Betty Bailey. However, at the age of six, he was moved away from her to live and work on the Wye House plantation in Maryland.
From there, Douglass was “given” to Lucretia Auld, whose husband, Thomas, sent him to work with his brother Hugh in Baltimore. Douglass credits Hugh’s wife Sophia with first teaching him the alphabet. With that foundation, Douglass then taught himself to read and write. By the time he was hired out to work under William Freeland, he was teaching other enslaved people to read using the Bible .
As word spread of his efforts to educate fellow enslaved people, Thomas Auld took him back and transferred him to Edward Covey, a farmer who was known for his brutal treatment of the enslaved people in his charge. Roughly 16 at this time, Douglass was regularly whipped by Covey.
Frederick Douglass Escapes from Slavery
After several failed attempts at escape, Douglass finally left Covey’s farm in 1838, first boarding a train to Havre de Grace, Maryland. From there he traveled through Delaware , another slave state, before arriving in New York and the safe house of abolitionist David Ruggles.
Once settled in New York, he sent for Anna Murray, a free Black woman from Baltimore he met while in captivity with the Aulds. She joined him, and the two were married in September 1838. They had five children together.
From Slavery to Abolitionist Leader
After their marriage, the young couple moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts , where they met Nathan and Mary Johnson, a married couple who were born “free persons of color.” It was the Johnsons who inspired the couple to take the surname Douglass, after the character in the Sir Walter Scott poem, “The Lady of the Lake.”
In New Bedford, Douglass began attending meetings of the abolitionist movement . During these meetings, he was exposed to the writings of abolitionist and journalist William Lloyd Garrison.
The two men eventually met when both were asked to speak at an abolitionist meeting, during which Douglass shared his story of slavery and escape. It was Garrison who encouraged Douglass to become a speaker and leader in the abolitionist movement.
By 1843, Douglass had become part of the American Anti-Slavery Society’s “Hundred Conventions” project, a six-month tour through the United States. Douglass was physically assaulted several times during the tour by those opposed to the abolitionist movement.
In one particularly brutal attack, in Pendleton, Indiana , Douglass’ hand was broken. The injuries never fully healed, and he never regained full use of his hand.
In 1858, radical abolitionist John Brown stayed with Frederick Douglass in Rochester, New York, as he planned his raid on the U.S. military arsenal at Harper’s Ferry , part of his attempt to establish a stronghold of formerly enslaved people in the mountains of Maryland and Virginia. Brown was caught and hanged for masterminding the attack, offering the following prophetic words as his final statement: “I, John Brown, am now quite certain that the crimes of this guilty land will never be purged away but with blood.”
'Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass'
Two years later, Douglass published the first and most famous of his autobiographies, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave . (He also authored My Bondage and My Freedom and Life and Times of Frederick Douglass).
In it Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , he wrote: “From my earliest recollection, I date the entertainment of a deep conviction that slavery would not always be able to hold me within its foul embrace; and in the darkest hours of my career in slavery, this living word of faith and spirit of hope departed not from me, but remained like ministering angels to cheer me through the gloom.”
He also noted, “Thus is slavery the enemy of both the slave and the slaveholder.”
Frederick Douglass in Ireland and Great Britain
Later that same year, Douglass would travel to Ireland and Great Britain. At the time, the former country was just entering the early stages of the Irish Potato Famine , or the Great Hunger.
While overseas, he was impressed by the relative freedom he had as a man of color, compared to what he had experienced in the United States. During his time in Ireland, he met the Irish nationalist Daniel O’Connell , who became an inspiration for his later work.
In England, Douglass also delivered what would later be viewed as one of his most famous speeches, the so-called “London Reception Speech.”
In the speech, he said, “What is to be thought of a nation boasting of its liberty, boasting of its humanity, boasting of its Christianity , boasting of its love of justice and purity, and yet having within its own borders three millions of persons denied by law the right of marriage?… I need not lift up the veil by giving you any experience of my own. Every one that can put two ideas together, must see the most fearful results from such a state of things…”
Frederick Douglass’ Abolitionist Paper
When he returned to the United States in 1847, Douglass began publishing his own abolitionist newsletter, the North Star . He also became involved in the movement for women’s rights .
He was the only African American to attend the Seneca Falls Convention , a gathering of women’s rights activists in New York, in 1848.
He spoke forcefully during the meeting and said, “In this denial of the right to participate in government, not merely the degradation of woman and the perpetuation of a great injustice happens, but the maiming and repudiation of one-half of the moral and intellectual power of the government of the world.”
He later included coverage of women’s rights issues in the pages of the North Star . The newsletter’s name was changed to Frederick Douglass’ Paper in 1851, and was published until 1860, just before the start of the Civil War .
Frederick Douglass Quotes
In 1852, he delivered another of his more famous speeches, one that later came to be called “What to a slave is the 4th of July?”
In one section of the speech, Douglass noted, “What, to the American slave, is your 4th of July? I answer: a day that reveals to him, more than all other days in the year, the gross injustice and cruelty to which he is the constant victim. To him, your celebration is a sham; your boasted liberty, an unholy license; your national greatness, swelling vanity; your sounds of rejoicing are empty and heartless; your denunciations of tyrants, brass fronted impudence; your shouts of liberty and equality, hollow mockery; your prayers and hymns, your sermons and thanksgivings, with all your religious parade, and solemnity, are, to him, mere bombast, fraud, deception, impiety, and hypocrisy—a thin veil to cover up crimes which would disgrace a nation of savages.”
For the 24th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation , in 1886, Douglass delivered a rousing address in Washington, D.C., during which he said, “where justice is denied, where poverty is enforced, where ignorance prevails, and where any one class is made to feel that society is an organized conspiracy to oppress, rob and degrade them, neither persons nor property will be safe.”
Frederick Douglass During the Civil War
During the brutal conflict that divided the still-young United States, Douglass continued to speak and worked tirelessly for the end of slavery and the right of newly freed Black Americans to vote.
Although he supported President Abraham Lincoln in the early years of the Civil War, Douglass fell into disagreement with the politician after the Emancipation Proclamation of 1863, which effectively ended the practice of slavery. Douglass was disappointed that Lincoln didn’t use the proclamation to grant formerly enslaved people the right to vote, particularly after they had fought bravely alongside soldiers for the Union army.
It is said, though, that Douglass and Lincoln later reconciled and, following Lincoln’s assassination in 1865, and the passage of the 13th amendment , 14th amendment , and 15th amendment to the U.S. Constitution (which, respectively, outlawed slavery, granted formerly enslaved people citizenship and equal protection under the law, and protected all citizens from racial discrimination in voting), Douglass was asked to speak at the dedication of the Emancipation Memorial in Washington, D.C.’s Lincoln Park in 1876.
Historians, in fact, suggest that Lincoln’s widow, Mary Todd Lincoln , bequeathed the late-president’s favorite walking stick to Douglass after that speech.
In the post-war Reconstruction era, Douglass served in many official positions in government, including as an ambassador to the Dominican Republic, thereby becoming the first Black man to hold high office. He also continued speaking and advocating for African American and women’s rights.
In the 1868 presidential election, he supported the candidacy of former Union general Ulysses S. Grant , who promised to take a hard line against white supremacist-led insurgencies in the post-war South. Grant notably also oversaw passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1871 , which was designed to suppress the growing Ku Klux Klan movement.
Frederick Douglass: Later Life and Death
In 1877, Douglass met with Thomas Auld , the man who once “owned” him, and the two reportedly reconciled.
Douglass’ wife Anna died in 1882, and he married white activist Helen Pitts in 1884.
In 1888, he became the first African American to receive a vote for President of the United States, during the Republican National Convention. Ultimately, though, Benjamin Harrison received the party nomination.
Douglass remained an active speaker, writer and activist until his death in 1895. He died after suffering a heart attack at home after arriving back from a meeting of the National Council of Women , a women’s rights group still in its infancy at the time, in Washington, D.C.
His life’s work still serves as an inspiration to those who seek equality and a more just society.

HISTORY Vault: Black History
Watch acclaimed Black History documentaries on HISTORY Vault.
Frederick Douglas, PBS.org . Frederick Douglas, National Parks Service, nps.gov . Frederick Douglas, 1818-1895, Documenting the South, University of North Carolina , docsouth.unc.edu . Frederick Douglass Quotes, brainyquote.com . “Reception Speech. At Finsbury Chapel, Moorfields, England, May 12, 1846.” USF.edu . “What to the slave is the 4th of July?” TeachingAmericanHistory.org . Graham, D.A. (2017). “Donald Trump’s Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.” The Atlantic .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Secondary Classrooms 6 Historical Letters for Secondary Students

Dorothy Hodges
Creating opportunities for students to meaningfully engage with primary sources can take considerable time to plan and sometimes feel dry for students. That’s why we’ve put together a roundup of captivating historical letters that bring the voices of historical figures directly to secondary students! Students will love each letter from our digital literacy program, as they bring voices from the past to life with thought-providing discussion and provide robust opportunities for reading comprehension practice.
Whether you’re new to CommonLit’s free literacy program or a longtime CommonLit fan looking to add some spice to your usage of primary source documents, you’re sure to find a great text for your students from this list.
“ Letter from Frederick Douglass to Harriet Tubman ” by Frederick Douglass (8th Grade)
Harriet Tubman asked Frederick Douglass to write to her biographer, speaking about her accomplishments. This letter is Douglass’ response – and it may surprise students. Throughout his pointed yet polite letter, Douglass explains the difference between private and public abolitionist work, revealing that he views himself very differently than Tubman.
After reading the letter, invite students to discuss the merits of contributing to something publicly or privately with Discussion Question 1, “Frederick Douglass discusses how Harriet Tubman does not receive applause for her private actions in the abolitionist movement - what are the benefits of contributing privately to a cause? What are the disadvantages or dangers?”
“ Letter to the Treasurer of Spain ” by Christopher Columbus (8th Grade)
This 1493 letter to the Treasurer of Spain, Columbus recounts his experiences exploring the “New World.” Columbus describes not only how he was greeted but also the geography and culture he saw, creating a beautifully detailed report for those back in Spain.
Assessment Question 3 asks students to consider Columbus’s audience as well, asking, “To whom does Columbus address the letter? Why is this an important aspect of the letter in connection to its purpose? What other details from the letter can be used to support this?”
“ Letter from Mary Mallon: On Being ‘Typhoid Mary’ ” by Mary Mallon (10th Grade)
Mary Malloon was an Irish-American immigrant, cook, and the first person identified as an asymptomatic carrier of a disease in the United States. She is presumed to have infected 51 people with typhoid, three of whom died, despite showing no symptoms herself. As a result, she was forced to quarantine and undergo numerous medical procedures. In this letter addressed to her lawyer, Mary discusses her treatment and the toll it has taken on her.
After reading, ask your students Discussion Question 1, “Were the authorities who quarantined Mary Mallon justified at the time for their actions? Do you think Mary was at fault? Explain your answer.”
“ Letter From Birmingham Jail ” by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. (10th Grade)
After refusing to stop protesting during a civil rights gathering in 1963, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. and many others were arrested in Birmingham, Alabama. In this letter, written from jail, King responds to the criticism he received from a group of white religious leaders who blamed King for the unrest. In his response, King argues for a nonviolent response in order to repair the harms of prejudice and racism.
Students can also extend their knowledge by reading the paired text A Call for Unity . This primary source builds students’ knowledge of the context for “Letter from Birmingham Jail,” as it is the public statement to which King is responding.
“ I Am Very Real ”by Kurt Vonnegut (10th Grade)
In 1973, the head of the school board in a North Dakota town decided to burn all of Drake High School’s copies of Slaughterhouse-Five . The novel’s author, Kurt Vonnegut, wrote this letter in response.
After reading this text, have students watch the Related Media video “Kurt Vonnegut Interview on Censorship.” Ask students, “Do his views in 1973 match up with the points he makes in this video, recorded 30 years later? Why or why not?”
“ Washington’s Farewell Address ” by President George Washington (12th Grade)
In this letter, Washington announced his intent to decline a third term in office and left many words of wisdom for Americans and future presidents..
After reading the text, have students reflect on how America has done heeding Washington’s advice with Discussion Question 4, “According to Washington, how can America prosper as a peaceful nation moving forward? Do you think America has followed Washington’s advice or not, and what has the effect been on America’s status as a peaceful or warring nation?”
Looking for more great texts and primary sources for secondary students? Check out these text sets focused on Influential Speeches or specific time periods such as The Cold War !
If you’re interested in learning all about CommonLit’s free digital literacy program, join one of our upcoming webinars !
Chat with CommonLit
CommonLit’s team will reach out with more information on our school and district partnerships.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Frederick Douglass was born in, Sophia Auld was Frederick's first teacher. As Frederick was starting to learn, Hugh Auld stopped him because he was a ..., How did Douglass use voluntary exchange to teach himself to read, even though the law restricted the education of enslaved people? and more.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Why is Frederick not sure when he was born?, Why would slaveholders want to keep an enslaved person ignorant of something as simple as their birth date?, Why does Frederick make the point that a slaveholder who has fathered a child is likely to be tougher on that child? and more.
3.0 (1 review) Frederick Douglass. Click the card to flip 👆. •Born as a slave in Maryland. •Escaped from slavery at age 20. Renamed himself and dedicated his future to antislavery activism. •Came out when slavery was still legal = precarious situation. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 16.
Haiti. When does Frederick Douglass pass away? February 20th 1895. What was the name of his newspaper? The North Star; Frederick Douglass' Paper. What was the name of William Garrison Lloyd's newspaper? The Liberator. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Why does Douglass have no knowledge of his birth date?, What is ...
Frederick Douglass Born February 1818 and died in February 20, 1895, he was a renowned social reformer, Orator, writer, statesman, and leader in the abolitionist movement. Abolitionism
evil, cruel. Who were put into jail along with Douglass? Henry, John, Charles, and Henry Bailey. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Why does Douglass not know his birth date?, What is most likely Douglass's father's name?, Why is it worse off to be a child of a slave-owning father and slave mother? and more.
National Park Service. 2017. 7th Grade Lexile: 1120. Font Size. Frederick Douglass by George Kendall Warren is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. [1] In his journey from captive slave to internationally renowned. 1. activist, Frederick Douglass (1818-1895) has been a source of inspiration and hope for millions.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Douglass speaks mostly in..., Who writes Douglass intro?, Date and place of Douglass Biography and more. Scheduled maintenance: March 23, 2024 from 11:00 PM to 12:00 AM
He realized there was a connection between literacy and freedom. He realized that he would never be able to read or write without asking for help. He realized that reading and writing were simply a way that the white man felt superiod. He realized that reading and writing were a waste of his time. According to the text, where did Douglass teach ...
Frederick is nearly 8 years old before he is given a pair of pants. Frederick trusts no one as he makes plans to escape from the plantation. Frederick becomes a man when he fights back when Mr. Covey tries to beat him. Frederick's grandmother is left alone to die in the woods after she is too old to work.
1. swearer, and a savage monster. He always went armed with a cowskin and a heavy cudgel. 2. I have known him to cut and slash the women's heads so horribly, that even master would be enraged at his cruelty, and would threaten to whip him if he did not mind himself. Q 1. Master, however, was not a humane slaveholder.
After reading this biography on Frederick Douglass, have students read an excerpt from his autobiography, "The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass: Excerpt from Chapter 1," in the Paired Texts tab. Douglas is described as a powerful writer and speaker in the National Park Service biography.
Explore insightful questions and answers on Frederick Douglass at eNotes. Enhance your understanding today!
Frederick Douglass 1868. Passage Summary: In this "Letter from Frederick Douglass to Harriet Tubman," Douglass praises Tubman for her work in the abolitionist movement as a biography about her life is being prepared. When and How to Pair: Introduce "Letter from Frederick Douglass to Harriet Tubman" after students have read Chapter XI, after ...
However, I can provide you with some general information about Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman. Frederick Douglass was an African American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. He was born into slavery but escaped to the North, where he became a prominent leader in the abolitionist movement.
1 pt. Why is a slaveholder who has fathered a child likely to be tougher on that child? The slaveholder would hate the child. The slaveholder would not want to be accused of favoritism by his white wife. The slaveholder would not know it was his child. All of the above.
Frederick Douglass (born February 1818, Talbot county, Maryland, U.S.—died February 20, 1895, Washington, D.C.) was an African American abolitionist, orator, newspaper publisher, and author who is famous for his first autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself.
D. Douglass and Cooper were both successful African American teachers. 1. Which statement best describes a central idea within both "The Narrative Life of Frederick Douglass: Excerpts from Chapters 1-7" and "A Child of Slavery Who Taught a Generation"? [RI.2, RI.9] 2. Compare and contrast Cooper's and Douglass' education.
Frederick Douglass was a leader in the abolitionist movement, an early champion of women's rights and author of 'Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.' Updated: Jul 15, 2021 2:49 PM EDT
Frederick Douglass was born into slavery in or around 1818 in Talbot County, Maryland. Douglass himself was never sure of his exact birth date. His mother was an enslaved Black women and his ...
Whether you're new to CommonLit's free literacy program or a longtime CommonLit fan looking to add some spice to your usage of primary source documents, you're sure to find a great text for your students from this list. "Letter from Frederick Douglass to Harriet Tubman" by Frederick Douglass (8th Grade)
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, c. February 1817 or February 1818 - February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman.He became the most important leader of the movement for African-American civil rights in the 19th century.. After escaping from slavery in Maryland in 1838, Douglass became a national leader of the ...
"Frederick Douglass" by George Kendall Warren is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. Frederick Douglass: A Biography By National Park Service 2017 Frederick Douglass (1818-1895) was born a slave but died an accomplished and respected individual. This short biography traces his life's work and involvement in the abolition movement, which worked to end