The Advantages & Disadvantages of Critical Thinking
Micah mcdunnigan.

Critical thinking is, at heart, questioning what you are told instead of taking it at face value. It is evaluating information in a rational framework where facts and reason line up to support or fail to support assertions. Critical thinking skills are highly sought, and have a number of benefits in life. However, with the upsides comes certain downsides.

Explore this article
- Academic Success
- Professional Success
- Disadvantages
1 Academic Success
Memorizing what your teacher tells you and regurgitating it verbatim will only get you so far in school. Memorizing exactly what the teacher told you gives you access to a number of discrete facts you can call on for exams. This will serve you well on questions that ask for such verbatim recitation of information, but the best grades and future success will go to students who can ask questions about those facts, draw connections between them, formulate their own thoughts on the matter, and articulate them.
2 Professional Success
Critical thinking skills will make you more effective in whatever field you choose to go into. The ability to look at your professional field and make connections to identify opportunities no one else has seen yet will give you an edge. This is the way new and innovative products come about. If you are always just following the crowd, you'll never stand out. In a competitive business world, you're in professional trouble if you can't stand on your own or make valuable contributions to your employer.
Critical thinking skills can help you get along with a wider range of people. This is because if you can step back and evaluate a situation from a perspective other than your own, you can better understand why different people do what they do. This helps you avoid the social conflict that results from two narrow-minded perspectives butting heads with one another. It can expand your social circle, and lead to more harmonious interactions with everyone around you.
4 Disadvantages
The downside of critical thinking skills is that they can lead you into new and frightening territory. You might find yourself questioning the values, even the religion, by which you were raised. There is a certain existential comfort in someone else telling you how the world works, then blindly clinging to those tenets. The price of this simple comfort is forgoing a deeper understanding of how the world works, and all the opportunities this deeper thinking provides. While you can use your thinking skills to find new tenets that make sense, a modified version of those original tenets, or a new understanding of those original tenets, you might feel lost as you move between points A and B.
- 1 McGraw Hill: Introduction to Critical Thinking
About the Author
Micah McDunnigan has been writing on politics and technology since 2007. He has written technology pieces and political op-eds for a variety of student organizations and blogs. McDunnigan earned a Bachelor of Arts in international relations from the University of California, Davis.
Related Articles

Critical Thinking in the Decision-Making Processes

How Can a College Experience Help With Achieving Future...

How to Improve Adult Reading Comprehension

Seven Key Features of Critical Thinking

Trusting Others After Being Disappointed

What Does It Mean When You Have a High Intuition?

Differences Between Analytical & Critical Thinking

What Are the Differences Between Bias & Fallacy?

How to Move on After a Long Term Relationship Without...

What Are Ethical Ramifications?

The Importance of College After High School Graduation

How to Practice the Serenity Prayer

Signs of Intelligence

Types of Argument Syles

How to Get Over Being Dumped From a Long-Term Relationship

What to Do When a Friend Tells You She's Not Your Friend...

How to Write a Philosophy Thesis

How to Control Anger If Someone Hurls Insults at Me

How to Increase Your Critical Thinking Skills

How to Make People Want to Follow You on Tumblr
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .

Advantages and Disadvantages of Critical Thinking In Education
Looking for advantages and disadvantages of Critical Thinking In Education?
We have collected some solid points that will help you understand the pros and cons of Critical Thinking In Education in detail.
But first, let’s understand the topic:
What is Critical Thinking In Education?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of critical thinking in education.
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of Critical Thinking In Education:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhances problem-solving skills | Can hinder quick decision-making |
| Promotes independent thinking | May lead to overthinking |
| Encourages open-mindedness | Requires extensive time and resources |
| Improves decision-making ability | Can cause analysis paralysis |
| Fosters effective communication | Might discourage creative spontaneity |

Advantages of Critical Thinking In Education
Disadvantages of critical thinking in education.
You can view other “advantages and disadvantages of…” posts by clicking here .
If you have a related query, feel free to let us know in the comments below.
Also, kindly share the information with your friends who you think might be interested in reading it.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
EducationalWave
Pros and Cons of Critical Thinking

Critical thinking offers numerous benefits, including improved decision-making , enhanced problem-solving capabilities , and the ability to evaluate information objectively . It enables individuals to view issues from multiple perspectives , fostering well-reasoned judgments and innovative solutions. However, challenges exist, such as the risk of overthinking, which can hinder enjoyment of humor and casual conversations. Additionally, critical thinkers may struggle with social interactions due to their preference for intellectual discussions and self-reliance. Balancing critical thinking with openness and flexibility is essential to navigate these challenges effectively. Continue to explore to uncover more insights surrounding this essential skill.
Table of Contents
- Objective Analysis : Critical thinking enables objective analysis and evaluation of information, leading to well-reasoned judgments.
- Enhanced Decision-Making : It enhances decision-making and problem-solving by scrutinizing facts and weighing options thoroughly.
- Exploration of Perspectives : Encourages exploration of various perspectives, helping to question assumptions and consider alternatives.
- Social Challenges : May lead to limited social interactions and difficulty in finding suitable conversational partners due to preference for intellectual discussions.
- Overthinking Risks : Can cause overthinking, diminishing the ability to enjoy humor and potentially leading to a disconnect in social interactions.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves the objective analysis and evaluation of information to form a well-reasoned judgment . At its core, critical thinking is the ability to scrutinize facts , question underlying assumptions, and explore various perspectives before arriving at a conclusion. This process is integral in making informed decisions , as it requires individuals to weigh options thoroughly and assess potential consequences.
In educational settings, critical thinking is paramount for students to develop the skills necessary to tackle complex problems . It enables them to move beyond rote memorization and engage in deeper understanding and analysis.
In the business world, professionals utilize critical thinking to navigate uncertainties, drive innovation , and implement effective strategies. By considering diverse viewpoints and challenging the status quo, they can identify the most viable solutions.
Proficient critical thinkers are characterized by their curiosity and research skills, enabling them to gather and analyze relevant data thoroughly. They also exhibit pattern recognition abilities , which allow them to discern trends and relationships within the information.
Open-mindedness is another essential trait, as it fosters an environment where diverse perspectives are valued and integrated into decision-making processes. Ultimately, critical thinking equips individuals with the capability to make well-reasoned and judicious decisions.
Benefits in Everyday Life

Critical thinking greatly enhances everyday life by improving decision-making and problem-solving abilities.
This cognitive approach allows individuals to assess situations more thoroughly and arrive at well-informed conclusions.
Consequently, it equips people with the skills necessary to navigate and overcome various challenges effectively.
Improved Decision Making
The practice of critical thinking enhances decision-making by thoroughly evaluating all relevant factors and potential outcomes. By employing this approach, individuals are better equipped to make well-informed decisions.
One of the primary advantages of critical thinking is its ability to help solve complex problems by dissecting them into manageable components and examining each part rigorously. This meticulous analysis enables a more thorough understanding of the situation at hand, thereby facilitating improved decision-making.
In everyday life, critical thinking reduces the likelihood of making impulsive decisions , as it encourages a rational and systematic evaluation of available options. By weighing the pros and cons of different choices, individuals can arrive at decisions that are more likely to yield favorable results.
This process of logical reasoning and evidence-based judgment is instrumental in achieving better outcomes in various aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional endeavors.
Moreover, the ability to critically assess information empowers individuals to navigate complex situations effectively. By fostering a habit of questioning assumptions and considering alternative perspectives , critical thinking ensures that decisions are grounded in reality and are adaptable to changing circumstances.
This strategic approach to decision-making ultimately leads to more successful and satisfying life experiences.
Enhanced Problem Solving
Analyzing situations from various perspectives greatly enhances problem-solving skills in everyday life. Critical thinking empowers individuals to dissect issues thoroughly , leading to the identification of root causes and the development of innovative solutions. By evaluating problems from multiple angles, critical thinkers are well-equipped to devise strategies that are both creative and effective.
One significant benefit of critical thinking is its contribution to making well-informed decisions . In everyday scenarios, from personal dilemmas to professional challenges, the ability to assess information objectively is invaluable. Critical thinkers excel at filtering out biases and irrelevant data, focusing instead on the core elements that influence outcomes. This rigorous approach ensures that the decisions made are based on solid evidence and logical reasoning .
Moreover, the application of critical thinking in problem-solving fosters resilience and adaptability. When faced with obstacles, critical thinkers are more likely to analyze the situation thoroughly, consider various potential solutions, and implement the most effective course of action. This methodical approach not only enhances their capacity to address challenges efficiently but also contributes to continuous learning and improvement.
Professional Advantages
Critical thinking greatly enhances decision-making processes , allowing professionals to evaluate options thoroughly and choose the most effective course of action.
This skill also improves problem-solving abilities , enabling individuals to address challenges methodically and efficiently.
Moreover, critical thinkers excel in strategic planning, as they can anticipate potential outcomes and develop detailed plans to achieve organizational goals.
Enhanced Decision Making
How does critical thinking serve as a cornerstone for enhanced decision-making in professional environments?
Critical thinking enhances decision-making by enabling individuals to make well-informed choices grounded in evidence, logic, and thorough analysis. This process involves weighing various options, analyzing potential consequences, and minimizing risks, making it essential in professional settings.
When professionals engage in critical thinking, they elevate their ability to navigate complex situations efficiently and effectively.
Critical thinking contributes to enhanced decision-making through:
- Evidence-Based Decisions : By relying on credible data and logical reasoning, professionals can make decisions that are not only well-informed but also more likely to yield positive outcomes.
- Risk Minimization : Weighing the pros and cons of different choices allows for the identification and mitigation of potential risks, ensuring more robust and sustainable decisions.
- Strategic Solutions : Applying critical analysis helps in formulating strategic solutions that align with organizational goals and drive innovation.
Employers highly value employees who possess strong critical thinking skills, as these individuals are adept at making decisions that boost productivity and lead to improved outcomes in the workplace.
Therefore, critical thinking remains an essential tool for professional success and innovation.
Improved Problem Solving
Utilizing critical thinking greatly enhances problem-solving capabilities in professional environments. Critical thinking empowers individuals to systematically analyze complex challenges, leading to more effective problem-solving skills.
By evaluating issues from multiple perspectives , professionals can identify root causes rather than just symptoms, enabling the development of innovative and sustainable solutions .
In workplaces that increasingly encounter multifaceted problems , the ability to think critically is invaluable. Professionals who excel in critical thinking are adept at dissecting intricate issues, which positions them as indispensable assets in their teams.
Their refined problem-solving skills not only facilitate the resolution of current challenges but also contribute to the anticipation and mitigation of potential future issues.
Moreover, the ability to think critically is linked to career advancement . Individuals who demonstrate strong problem-solving skills are often entrusted with greater responsibilities and leadership roles , as they are seen as capable of addressing complex challenges effectively.
Employers place a high value on employees with robust critical thinking skills, recognizing their significant contributions to overcoming business obstacles and driving organizational success .
Strategic Planning Skills
In the domain of strategic planning, individuals who possess strong critical thinking skills are able to effectively analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to make well-informed decisions. These skills are indispensable for professionals aiming to excel in strategic roles, as they allow for a thorough examination of data and circumstances, enabling the anticipation of potential outcomes.
Critical thinking in strategic planning involves several key advantages:
- Trend Identification: Professionals can identify trends and patterns, providing a clearer understanding of market dynamics.
- Opportunity Recognition: The ability to evaluate information helps in discovering new opportunities that may not be immediately apparent.
- Innovative Solutions: Analyzing and synthesizing information leads to creative and competitive solutions that can set a business apart.
Incorporating critical thinking into strategic planning not only enhances decision-making skills but also fosters an environment where innovative and effective strategies are developed. This proficiency is highly valued across industries, as it directly contributes to a company's success and competitive edge.
Social Interaction Challenges

Critical thinkers often encounter social interaction challenges due to their preference for intellectual discussions over casual conversations . This inclination towards deep, meaningful exchanges can make finding conversation partners who share similar interests challenging. Many individuals may not possess the same enthusiasm for intellectual exchanges, resulting in limited social interactions for critical thinkers .
The unique interests and focus on critical thinking frequently lead to a form of social isolation from peers whose conversational preferences differ . This divergence can create a barrier to forming and maintaining social connections. The self-reliance that critical thinkers develop in engaging with complex ideas often means they might not actively seek out others for such discussions, further limiting their opportunities for intellectual exchanges.
Finding suitable conversation partners who are equally passionate about deep discussions is another significant hurdle. This challenge in aligning their unique interests with those of their peers can perpetuate feelings of isolation and reduce the frequency of meaningful social interactions.
Consequently, critical thinkers may find themselves maneuvering through a social landscape that is less accommodating to their intellectual pursuits, making the cultivation of fulfilling relationships more challenging.
Potential Overthinking Issues

Overthinking, a common trait among critical thinkers, can greatly diminish their ability to enjoy humor and jokes. This propensity to analyze everything meticulously often leads to a diminished enjoyment of humor, as the spontaneity and simplicity that make jokes amusing get lost in the scrutiny.
When one dissects humor excessively, the natural reaction of laughter is replaced by a mechanical evaluation of its components , leading to an altered perception of the joke's essence.
Constantly scrutinizing humor creates a disconnect in social interactions . Critical thinkers may struggle to resonate with their peers' humor after dissecting it, making it challenging to participate in light-hearted conversations. This disconnect can further lead to social isolation , as humor is a significant bonding mechanism in many social groups.
Analyzing jokes excessively can result in finding them less funny.
Struggle to resonate with peers' humor after dissecting jokes, critical thinkers often find it hard to connect.
Constant scrutiny alters one's perception of jokes compared to others.
Such overthinking can place critical thinkers at odds with the lighter side of human interaction, highlighting a notable downside to a generally beneficial trait.
Balancing Critical Thinking

Achieving a balance between skepticism and openness is essential for honing effective critical thinking skills . Finding this equilibrium allows individuals to critically analyze information without dismissing new and potentially valuable perspectives. This nuanced approach is particularly vital when making decisions based on complex data and multifaceted scenarios .
Critical thinking involves questioning underlying assumptions and rigorously evaluating evidence. However, these necessary tools must be balanced with a receptiveness to alternative viewpoints . Without this balance, individuals risk becoming overly skeptical, which can stifle innovation and limit the scope of analysis. Conversely, excessive openness may lead to uncritical acceptance of flawed or misleading information.
Striking this balance is key to mastering critical thinking skills. It enables individuals to evaluate information judiciously while remaining adaptable to new insights and evolving situations. This well-rounded approach equips decision-makers to navigate complex issues effectively, ensuring that their conclusions are well-founded and all-encompassing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are pros and cons critical thinking?.
The pros and cons of critical thinking involve bias identification, emotional detachment, logical consistency, and creative problem solving. These elements collectively contribute to a balanced, objective analysis, leading to well-informed decision-making and enhanced problem-solving skills.
What Are the Negative Effects of Critical Thinking?
The negative effects of critical thinking include decision fatigue, analysis paralysis, and overthinking consequences, which can lead to emotional detachment. These outcomes can impair effective decision-making and reduce overall enjoyment in social interactions.
What Are the 5 Benefits of Critical Thinking?
The five benefits of critical thinking include enhanced problem solving, improved communication, unbiased decisions, better creativity, and innovative solutions. These advantages collectively contribute to more effective decision-making and the identification of reliable information.
What Are the Weaknesses of Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking weaknesses include bias reinforcement, decision paralysis, and overthinking pitfalls. Additionally, it may lead to emotional detachment, impacting relationships and social interactions negatively by prioritizing analytical rigor over empathy and spontaneity.
Maintaining this equilibrium guarantees that critical thinking remains a valuable tool across various aspects of life, offering significant benefits such as enhanced decision-making in daily life, improved professional performance, and more informed social interactions.
However, challenges such as social friction and potential overthinking must be managed. Balancing critical thinking with emotional considerations and practical constraints is essential for maximizing its advantages while mitigating drawbacks.
This equilibrium emphasizes the importance of critical thinking in maximizing its benefits while minimizing its potential pitfalls .
Related Posts:
- Pros and Cons of Casual Employment
- Pros and Cons of Banning Books
- 20 Pros and Cons of Being a Lawyer
Related posts:
- 20 Pros and Cons of Generac Generators
- Pros and Cons of Stove Under Window
- Pros and Cons of Push Ups
Educational Wave Team
- For Individuals
- For Businesses
- For Universities
- For Governments
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Are Critical Thinking Skills and Why Are They Important?
Learn what critical thinking skills are, why they’re important, and how to develop and apply them in your workplace and everyday life.
![critical thinking advantages and disadvantages [Featured Image]: Project Manager, approaching and analyzing the latest project with a team member,](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1SOj8kON2XLXVb6u3bmDwN/62a5b68b69ec07b192de34b7ce8fa28a/GettyImages-598260236.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
We often use critical thinking skills without even realizing it. When you make a decision, such as which cereal to eat for breakfast, you're using critical thinking to determine the best option for you that day.
Critical thinking is like a muscle that can be exercised and built over time. It is a skill that can help propel your career to new heights. You'll be able to solve workplace issues, use trial and error to troubleshoot ideas, and more.
We'll take you through what it is and some examples so you can begin your journey in mastering this skill.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to interpret, evaluate, and analyze facts and information that are available, to form a judgment or decide if something is right or wrong.
More than just being curious about the world around you, critical thinkers make connections between logical ideas to see the bigger picture. Building your critical thinking skills means being able to advocate your ideas and opinions, present them in a logical fashion, and make decisions for improvement.
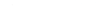
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Why is critical thinking important?
Critical thinking is useful in many areas of your life, including your career. It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice.
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]:
Crucial for the economy
Essential for improving language and presentation skills
Very helpful in promoting creativity
Important for self-reflection
The basis of science and democracy
Critical thinking skills are used every day in a myriad of ways and can be applied to situations such as a CEO approaching a group project or a nurse deciding in which order to treat their patients.
Examples of common critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills differ from individual to individual and are utilized in various ways. Examples of common critical thinking skills include:
Identification of biases: Identifying biases means knowing there are certain people or things that may have an unfair prejudice or influence on the situation at hand. Pointing out these biases helps to remove them from contention when it comes to solving the problem and allows you to see things from a different perspective.
Research: Researching details and facts allows you to be prepared when presenting your information to people. You’ll know exactly what you’re talking about due to the time you’ve spent with the subject material, and you’ll be well-spoken and know what questions to ask to gain more knowledge. When researching, always use credible sources and factual information.
Open-mindedness: Being open-minded when having a conversation or participating in a group activity is crucial to success. Dismissing someone else’s ideas before you’ve heard them will inhibit you from progressing to a solution, and will often create animosity. If you truly want to solve a problem, you need to be willing to hear everyone’s opinions and ideas if you want them to hear yours.
Analysis: Analyzing your research will lead to you having a better understanding of the things you’ve heard and read. As a true critical thinker, you’ll want to seek out the truth and get to the source of issues. It’s important to avoid taking things at face value and always dig deeper.
Problem-solving: Problem-solving is perhaps the most important skill that critical thinkers can possess. The ability to solve issues and bounce back from conflict is what helps you succeed, be a leader, and effect change. One way to properly solve problems is to first recognize there’s a problem that needs solving. By determining the issue at hand, you can then analyze it and come up with several potential solutions.
How to develop critical thinking skills
You can develop critical thinking skills every day if you approach problems in a logical manner. Here are a few ways you can start your path to improvement:
1. Ask questions.
Be inquisitive about everything. Maintain a neutral perspective and develop a natural curiosity, so you can ask questions that develop your understanding of the situation or task at hand. The more details, facts, and information you have, the better informed you are to make decisions.
2. Practice active listening.
Utilize active listening techniques, which are founded in empathy, to really listen to what the other person is saying. Critical thinking, in part, is the cognitive process of reading the situation: the words coming out of their mouth, their body language, their reactions to your own words. Then, you might paraphrase to clarify what they're saying, so both of you agree you're on the same page.
3. Develop your logic and reasoning.
This is perhaps a more abstract task that requires practice and long-term development. However, think of a schoolteacher assessing the classroom to determine how to energize the lesson. There's options such as playing a game, watching a video, or challenging the students with a reward system. Using logic, you might decide that the reward system will take up too much time and is not an immediate fix. A video is not exactly relevant at this time. So, the teacher decides to play a simple word association game.
Scenarios like this happen every day, so next time, you can be more aware of what will work and what won't. Over time, developing your logic and reasoning will strengthen your critical thinking skills.
Learn tips and tricks on how to become a better critical thinker and problem solver through online courses from notable educational institutions on Coursera. Start with Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking from Duke University or Mindware: Critical Thinking for the Information Age from the University of Michigan.
Article sources
University of the People, “ Why is Critical Thinking Important?: A Survival Guide , https://www.uopeople.edu/blog/why-is-critical-thinking-important/.” Accessed May 18, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
Defining Critical Thinking
|
| ||
|
Foundation for Critical Thinking Press, 2008)
Teacher’s College, Columbia University, 1941) | ||
| | ||

6 tips for boosting critical thinking skills to avoid biases and make more informed decisions
- Thinking critically means considering other perspectives and analyzing facts from different sources.
- Good critical thinking skills can help you avoid generalizations and decisions you later regret.
- To sharpen your skills, try asking questions, considering consequences, and practicing mindfulness.

Critical thinking happens when you engage in reflective and independent thinking, instead of making sweeping generalizations or falling prey to cognitive biases like stereotyping.
For instance, you're thinking critically when deciding whether a story is credible by analyzing and evaluating all the information you find rather than only considering one perspective.
Consequently, critical thinkers often have a more balanced and rational view of the world.
If that sounds like something you're interested in, read on to learn how critical thinking can benefit your career, emotional health, and overall well-being, plus get a few strategies for boosting your own critical thinking skills.
The benefits of critical thinking
Since critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating all information available to you, it can help you better understand others and cultivate your own empathy.
Plus, you'll probably have an easier time getting along with people who have varying personalities, says Judy Rosenberg , Clinical Director and clinical psychologist at the Psychological Healing Center.
Critical thinking skills can help you:
- Succeed in undergraduate and graduate school across disciplines , from engineering to art.
- Identify reliable sources of information and determine which news articles or people to trust.
- Understand your own biases to better understand yourself and those around you.
- Stay invaluable in a fast-paced or knowledge-driven workplace. Critical thinking is considered a top skill for success in the fastest-growing jobs in the U.S.
- Improve other life skills like communication, creativity, and self-reflection.
Last but not least, one 2017 study of U.S. adults found that participants with higher critical thinking scores tended to experience fewer negative life events. The study authors concluded that critical thinking seemed to be a better predictor of good life decisions than intelligence.
"If we can evaluate information effectively, we can feel secure and trust ourselves in various life situations," says Amanda Butler , a licensed marriage and family therapist in private practice.
In short, critical thinking can have benefits across multiple areas of life.
If you want to reap the benefits above, try these strategies from experts to boost your critical thinking skills.
1. Slow down and ask more questions
"If you have doubts, ask yourself more questions. What is it that doesn't quite seem believable?" Butler says. Doing so can help you decide if these doubts and concerns are warning you about something important, like red flags in a romantic interest.
While you might want to believe the new person you've just met is your perfect match, it's healthy to question their behavior before deciding, Butler says.
"Let's say a potential partner is not responsive to texts, frequently says hurtful things, or is unwilling to communicate about relationship issues," Butler says. She notes that thinking critically about these behaviors can help you break things off if needed to avoid more heartbreak down the road.
You might find you've been engaging in wishful thinking , where your hopes about a particular person or situation get in the way of any tell-tale warning signs.
2. Say no to the status quo
You might feel tempted to hop on board with the latest viral trend. But by challenging the status quo, you can boost your critical thinking skills.
Fad diets, for example, tend to promise a quick way to lose weight. However, if you practice critical thinking by digging a little deeper into the research, you may find they're not only ineffective long-term but may also lead to a number of health risks, from impaired bone health and infertility to disordered eating .
To challenge the status quo in any circumstances, Butler suggests asking yourself:
- "Are the claims too good to be true or otherwise unrealistic?"
- "Have you seen similar claims made before?"
3. Do your own fact-checking
You may not always have enough information on hand to make an informed decision in the moment.
"Be willing to do more research on something if you're not sure," Rosenberg says. You might, for example, read online reviews of a product, service, or workplace you're considering.
Let's say you're trying to decide if an article your mom shared on Facebook is accurate, something you might not be able to tell from just reading the story.
Thinking critically, then, might involve checking for signs of inaccuracy and errors , such as:
- A lack of references
- Sponsored content
- Biased authors , like the founder of a supplement company stating their supplements are the solution to your health ailments
4. Consider long-term consequences
Considering how a decision might affect your future can help you make more informed decisions today.
"Look beyond the immediate situation. Something that might be advantageous now might not be in the future. Ask yourself what's on the line," Rosenberg says.
This can be particularly important when making big decisions like:
- Moving to a new city
- Selling your home
- Saying yes to a new job
- Accepting a marriage proposal
For instance, if you have two job offers where one involves more hours but higher pay than the other, then you'll need to decide whether you value financial security over more free time, or vice versa. You may also want to evaluate the day-to-day responsibilities and people you'll work with closely.
Considering all of these factors can help you decide if it's really the right fit and avoid circumstances that aren't a good match, Butler says.
5. Practice mindfulness
Mindfulness is a type of meditation where you focus on your present thoughts, feelings, body, and environment through an accepting and non-judgmental lens. In short, you let go of "good thoughts" and "bad thoughts," along with ruminations on the past or fixations on the future.
One 2016 cross-sectional study of 178 university students via questionnaires and executive functioning tasks found that dispositional mindfulness , the ability to focus on the present moment with an open attitude, facilitated critical thinking.
Studies also suggest mindfulness can help you develop self-control, knowledge, and wisdom by improving your attention and emotional regulation.
Mindfulness might feel counterintuitive to critical thinking because it involves letting go of things outside the present. But it can actually boost critical thinking, in the end, since it can help you increase your attention span and better understand your biases.
A few ways to practice mindfulness include:
- Body scans: Bring attention to each part of your body, one at a time. This helps you notice sources of tension and your body's needs gently, which can empower you to take better care of yourself and make healthier choices moving forward.
- Mindful breathing: Focus on your breath: Breathe in through the nose for three seconds, hold for two seconds, then out through the mouth for four seconds. This practice can improve your concentration and help you center yourself when big emotions threaten to overtake you.
- Walking meditation: Find a peaceful place to walk for 10 to 20 feet and pay attention to your body and environment while you move. This can help you improve your sense of control over yourself and respond in more productive ways when you feel overwhelmed.
6. Improve your skills with outside help
Like any other skill, critical thinking can improve the more you practice it.
Just know it's not unusual to hit a wall and find it tough to further critical thinking skills on your own. "You should find learning new things challenging. It's the same as working out at the gym: no pain, no gain. The discomfort and difficulty of thinking enhance your capacity for critical thought and problem-solving," Rosenberg says.
A mental health professional can offer guidance on developing critical thinking skills when you find yourself stuck, Butler says. "Many therapeutic approaches are based in looking at and changing how a client thinks about certain things in their life, so therapy can be a great resource for developing new ways of thinking," Butler says.
Insider's takeaway
Ultimately, critical thinking can help you get some distance from internal biases and emotional judgments. As a result, you might find it easier to make well-reasoned decisions and determine which sources to trust.
Developing this skill can strengthen your relationships with others and boost your professional marketability. But critical thinking can also help you make the best choices for your health, values, and long-term happiness.
"Critical thinking allows you to evaluate information for yourself and form your own opinion on it, rather than just taking it at face value. This helps you know yourself, what you want, and what you really need," Butler says.
We may receive a commission when you buy through our links, but our reporting and recommendations are always independent and objective.
- Main content
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
Published on May 30, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment .
To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources .
Critical thinking skills help you to:
- Identify credible sources
- Evaluate and respond to arguments
- Assess alternative viewpoints
- Test hypotheses against relevant criteria
Table of contents
Why is critical thinking important, critical thinking examples, how to think critically, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about critical thinking.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions.
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process . The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both.
In academic writing , critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source:
- Is free from research bias
- Provides evidence to support its research findings
- Considers alternative viewpoints
Outside of academia, critical thinking goes hand in hand with information literacy to help you form opinions rationally and engage independently and critically with popular media.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Critical thinking can help you to identify reliable sources of information that you can cite in your research paper . It can also guide your own research methods and inform your own arguments.
Outside of academia, critical thinking can help you to be aware of both your own and others’ biases and assumptions.
Academic examples
However, when you compare the findings of the study with other current research, you determine that the results seem improbable. You analyze the paper again, consulting the sources it cites.
You notice that the research was funded by the pharmaceutical company that created the treatment. Because of this, you view its results skeptically and determine that more independent research is necessary to confirm or refute them. Example: Poor critical thinking in an academic context You’re researching a paper on the impact wireless technology has had on developing countries that previously did not have large-scale communications infrastructure. You read an article that seems to confirm your hypothesis: the impact is mainly positive. Rather than evaluating the research methodology, you accept the findings uncritically.
Nonacademic examples
However, you decide to compare this review article with consumer reviews on a different site. You find that these reviews are not as positive. Some customers have had problems installing the alarm, and some have noted that it activates for no apparent reason.
You revisit the original review article. You notice that the words “sponsored content” appear in small print under the article title. Based on this, you conclude that the review is advertising and is therefore not an unbiased source. Example: Poor critical thinking in a nonacademic context You support a candidate in an upcoming election. You visit an online news site affiliated with their political party and read an article that criticizes their opponent. The article claims that the opponent is inexperienced in politics. You accept this without evidence, because it fits your preconceptions about the opponent.
There is no single way to think critically. How you engage with information will depend on the type of source you’re using and the information you need.
However, you can engage with sources in a systematic and critical way by asking certain questions when you encounter information. Like the CRAAP test , these questions focus on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
When encountering information, ask:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert in their field?
- What do they say? Is their argument clear? Can you summarize it?
- When did they say this? Is the source current?
- Where is the information published? Is it an academic article? Is it peer-reviewed ?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence? Does it rely on opinion, speculation, or appeals to emotion ? Do they address alternative arguments?
Critical thinking also involves being aware of your own biases, not only those of others. When you make an argument or draw your own conclusions, you can ask similar questions about your own writing:
- Am I only considering evidence that supports my preconceptions?
- Is my argument expressed clearly and backed up with credible sources?
- Would I be convinced by this argument coming from someone else?
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Critical thinking skills include the ability to:
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Information literacy refers to a broad range of skills, including the ability to find, evaluate, and use sources of information effectively.
Being information literate means that you:
- Know how to find credible sources
- Use relevant sources to inform your research
- Understand what constitutes plagiarism
- Know how to cite your sources correctly
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search, interpret, and recall information in a way that aligns with our pre-existing values, opinions, or beliefs. It refers to the ability to recollect information best when it amplifies what we already believe. Relatedly, we tend to forget information that contradicts our opinions.
Although selective recall is a component of confirmation bias, it should not be confused with recall bias.
On the other hand, recall bias refers to the differences in the ability between study participants to recall past events when self-reporting is used. This difference in accuracy or completeness of recollection is not related to beliefs or opinions. Rather, recall bias relates to other factors, such as the length of the recall period, age, and the characteristics of the disease under investigation.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/critical-thinking/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, student guide: information literacy | meaning & examples, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- What was education like in ancient Athens?
- How does social class affect education attainment?
- When did education become compulsory?
- What are alternative forms of education?
- Do school vouchers offer students access to better education?

critical thinking
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Critical Thinking
- Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Critical Thinking
- Monash University - Student Academic Success - What is critical thinking?
- Oklahoma State University Pressbooks - Critical Thinking - Introduction to Critical Thinking
- University of Louisville - Critical Thinking
critical thinking , in educational theory, mode of cognition using deliberative reasoning and impartial scrutiny of information to arrive at a possible solution to a problem. From the perspective of educators, critical thinking encompasses both a set of logical skills that can be taught and a disposition toward reflective open inquiry that can be cultivated . The term critical thinking was coined by American philosopher and educator John Dewey in the book How We Think (1910) and was adopted by the progressive education movement as a core instructional goal that offered a dynamic modern alternative to traditional educational methods such as rote memorization.
Critical thinking is characterized by a broad set of related skills usually including the abilities to
- break down a problem into its constituent parts to reveal its underlying logic and assumptions
- recognize and account for one’s own biases in judgment and experience
- collect and assess relevant evidence from either personal observations and experimentation or by gathering external information
- adjust and reevaluate one’s own thinking in response to what one has learned
- form a reasoned assessment in order to propose a solution to a problem or a more accurate understanding of the topic at hand

Theorists have noted that such skills are only valuable insofar as a person is inclined to use them. Consequently, they emphasize that certain habits of mind are necessary components of critical thinking. This disposition may include curiosity, open-mindedness, self-awareness, empathy , and persistence.
Although there is a generally accepted set of qualities that are associated with critical thinking, scholarly writing about the term has highlighted disagreements over its exact definition and whether and how it differs from related concepts such as problem solving . In addition, some theorists have insisted that critical thinking be regarded and valued as a process and not as a goal-oriented skill set to be used to solve problems. Critical-thinking theory has also been accused of reflecting patriarchal assumptions about knowledge and ways of knowing that are inherently biased against women.
Dewey, who also used the term reflective thinking , connected critical thinking to a tradition of rational inquiry associated with modern science . From the turn of the 20th century, he and others working in the overlapping fields of psychology , philosophy , and educational theory sought to rigorously apply the scientific method to understand and define the process of thinking. They conceived critical thinking to be related to the scientific method but more open, flexible, and self-correcting; instead of a recipe or a series of steps, critical thinking would be a wider set of skills, patterns, and strategies that allow someone to reason through an intellectual topic, constantly reassessing assumptions and potential explanations in order to arrive at a sound judgment and understanding.
In the progressive education movement in the United States , critical thinking was seen as a crucial component of raising citizens in a democratic society. Instead of imparting a particular series of lessons or teaching only canonical subject matter, theorists thought that teachers should train students in how to think. As critical thinkers, such students would be equipped to be productive and engaged citizens who could cooperate and rationally overcome differences inherent in a pluralistic society.

Beginning in the 1970s and ’80s, critical thinking as a key outcome of school and university curriculum leapt to the forefront of U.S. education policy. In an atmosphere of renewed Cold War competition and amid reports of declining U.S. test scores, there were growing fears that the quality of education in the United States was falling and that students were unprepared. In response, a concerted effort was made to systematically define curriculum goals and implement standardized testing regimens , and critical-thinking skills were frequently included as a crucially important outcome of a successful education. A notable event in this movement was the release of the 1980 report of the Rockefeller Commission on the Humanities that called for the U.S. Department of Education to include critical thinking on its list of “basic skills.” Three years later the California State University system implemented a policy that required every undergraduate student to complete a course in critical thinking.
Critical thinking continued to be put forward as a central goal of education in the early 21st century. Its ubiquity in the language of education policy and in such guidelines as the Common Core State Standards in the United States generated some criticism that the concept itself was both overused and ill-defined. In addition, an argument was made by teachers, theorists, and others that educators were not being adequately trained to teach critical thinking.
The Disadvantages of Critical Thinking: Don’t Overthink It
Sometimes, critical thinking can lead us to spend too much time and energy on analyzing every detail and possibility of a situation, which can cause stress. Overthinking can also prevent us from taking action or trusting our intuition when it is appropriate. And also make us focus on the flaws, risks, and weaknesses of an idea or a solution, rather than on its strengths, benefits, and opportunities. This can lead to a pessimistic or cynical attitude that can affect our motivation and creativity. Emphasizing the negative can also make us overlook or dismiss positive feedback. It's our duty to identify them and take actions.
Sanju Pradeepa

We’ve all had moments when we spent more time thinking than acting. And that’s usually because we got caught up in the process of critical thinking. It’s not necessarily a bad thing to indulge in. After all, it makes us analyze our decisions, weigh the pros and cons, and come out with a conclusion that is backed by facts and data.
But what if there’s a downside to critical thinking? To be clear, this isn’t an attempt to convince you to just go with your gut feeling all the time. Instead, this article is intended to provide perspective on how excessive overthinking can hinder your progress instead of helping you make an informed decision.
We’ll cover why using critical thinking too much can lead to poor decision-making, how it affects your stress levels, and when it matters most. So don’t overthink it. Let’s dive in and explore the disadvantages of critical thinking together.
Table of Contents
What is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a term you’ve probably heard bandied about, but what does it actually mean? In short, it’s a way of examining information and forming opinions or judgments based on the evidence at hand.
It’s the ability to take an analytical approach to a problem. This means that critical thinking involves analyzing information in order to form an opinion and then continuing to assess the data in order to challenge and modify that opinion.
At its best, critical thinking can lead to more informed decisions and more effective problem-solving. But there are also some disadvantages to this method of thinking. Read on for more information.
Let’s know more about Critical Thinking – 7 Types of Critical Thinking: A Guide to Analyzing Problems
Disadvantages of Critical Thinking, When You Have Too Much
We all value the power of critical thinking; it’s an invaluable skill to have in any field. But like anything, too much of a good thing can be a problem.
When we overthink things and become overly critical, the consequences can be significant. Often, it can prevent us from making decisions in a timely manner, if at all. It can also lead to missed opportunities, as we become paralyzed by our analysis and fail to seize the moment.
Furthermore, analysis paralysis can lead to high levels of stress and anxiety as we struggle to make up our minds on a given subject or action. We might even fail to recognize the real risks at hand when focusing too much on minor details and missing out on what matters most for successful outcomes.
The takeaway here is that being critical is valuable but remember to balance it with intuition and trust your instincts before you get too deep into overthinking things.
1. Difficulty in Decision-Making

One of the biggest disadvantages of critical thinking is that it can be difficult to make decisions. Because critical thinkers are constantly analyzing and evaluating data to draw conclusions, this can be a time-consuming process.
Even after all the facts and evidence have been gathered, it can take a long time to weigh the pros and cons of each option before making the best decision possible. This means that in some cases, a critical thinker will not be able to make a decision quickly or easily.
On top of that, if there is not enough data or information available about a particular decision, it can be even harder for a critical thinker to come up with a solid solution in an efficient manner. This can cause even more delays in decision-making and may lead to frustration as well as inadequate solutions.
2. You might be overthinking every situation.

When you engage in critical thinking, you may find yourself overthinking every situation and making an issue out of things that don’t need your attention. Going back to our earlier example, if you were to critically analyze the situation of your friend sleeping at your house, you might start to worry about the extra resources it may consume or about how it may affect your relationship. While this could be true, it might also be a bit excessive. In certain situations, it’s better to accept certain things and not overthink them.
This is one of the most common disadvantages of critical thinking: overthinking can lead to analysis paralysis, where one is so focused on analyzing a situation that one becomes unable to make any decisions at all. This can lead to frustration and decreased productivity as no progress is made. Additionally, engaging in too much critical thinking can lead to stress and burnout , which are both counterproductive in any situation.
Therefore, while it’s important to engage in critical thinking when necessary and appropriate, it’s also important not to overdo it. Otherwise, the outcomes you’re hoping for will never be achieved.
3. Unavoidable biases and prejudices

You may think that critical thinking is the answer to everything, but it has its disadvantages too. Most notably, it’s impossible to completely remove our biases and prejudices when looking at the facts. We all have a unique way of looking at things , and these biases may affect how we interpret evidence.
Confirmation Bias – One of the most common biases is called “ confirmation bias,” where people seek out evidence that supports what they already believe or look for fault in evidence that contradicts it. This often leads to people discrediting any evidence they don’t agree with.
Overconfidence – Another common bias is overconfidence, which can lead us to make more decisions than necessary or, worse yet, poor decisions based on what we think we know.
These biases can affect how people interpret evidence and make decisions, regardless of how logical and reasoned those decisions might seem. That’s why we need to be aware of our own prior beliefs , values, and experiences to prevent our biases from affecting our judgment when using critical thinking skills.
4. Disruption of Imagination and Creativity

As great as it may sound, critical thinking can have its downsides, particularly in the area of imagination and creativity. The process of critical thinking often encourages a strict focus on facts and evidence, which can lead to tunnel vision and the inability to think outside the box.
When we focus too much on analysis and facts, we can become stifled in our creative pursuits. This means that instead of creating something new or being able to think of novel solutions to problems, we are confined by existing thought patterns that don’t allow for exploration or experimentation outside of what is already known.
Limiting Ourselves – Critical thinking is great when it comes to evaluating or assessing existing information or situations, but when it comes to innovating, critical thinking can be limiting. After all, if we are stuck looking at the same evidence from different perspectives, how much further can we go? We need to be open to new ideas and experiences if we want to move forward in our creative pursuits.
Training our brain for critical thinking – An over-reliance on critical thinking skills means that our brains get trained over time to do less imaginative things because our brains become accustomed to relying on a certain pattern of thinking. This means that our brains become so accustomed to certain types of analysis that there is little room left for coming up with unique solutions or uncovering innovative ideas.
It’s true; critical thinking has its advantages. But relying too heavily on this form of thinking could mean that you’re missing out on opportunities for growth and creativity.
5. Lack of Emotional Engagement

Another possible disadvantage of critical thinking is a lack of emotional engagement. The process of critical thinking involves looking at a problem objectively, dispassionately analyzing the facts, and logically concluding. This can be helpful, but it can also lead to a disconnect with the emotional aspect of the problem or issue at hand.
At times, emotional engagement is essential for tackling certain problems. For example, certain social issues might require individuals to tap into their emotions and empathy to come up with solutions that can bring about positive change without harming anyone or anything.
Moreover, emotional understanding is important for developing solutions that take into account different perspectives and experiences. This can help create solutions that are more inclusive and equitable for everyone involved.
Ultimately, critical thinking should not be used as an exclusive method for problem solving or decision-making; it should be used in conjunction with emotional understanding and empathy. This balance between intellectual analysis and emotional engagement can help to ensure solutions that are highly effective and satisfying for everyone involved.

6. Potential for stress and anxiety

As discussed previously, critical thinking can be a great skill to have. However, it does come with disadvantages. For instance, people who engage in critical thinking can experience significant stress and anxiety as a result of constantly evaluating complex ideas and situations.
This is especially true for those who are very good at it, as they may feel pressure to always think critically and make the “right” decision. Additionally, when you’re constantly taking a hard look at problems from all angles, it can be easier to become overwhelmed. It can be difficult to decide which way to go when you have so many options available.
The constant search for evidence – People who think critically often spend a lot of time searching for evidence or trying to find the correct interpretation of facts. While this might lead to effective problem-solving and decision-making, it can also be exhausting psychologically. When you’re constantly sifting through evidence looking for the right answer, it can be hard not to become overwhelmed or discouraged if you don’t find what you’re looking for right away.
The struggle between intuition and logic – It’s also common for critical thinkers to struggle with integrating intuition into their thought processes since they tend to rely heavily on logic and evidence-based reasoning. While this type of thinking is valuable in certain scenarios, relying solely on logic can lead to overlooking potential solutions that may be based more on emotion or instinct than on facts. This can make it difficult for critical thinkers to make decisions without feeling like they’ve overlooked something important.
7. Critical thinking can be time-consuming.

You know that critical thinking is important, but have you ever considered the time it takes to think critically? Well, thinking critically can be a time-consuming endeavor .
You might not think twice about making a quick decision based on intuition or reverting to old habits, but truly making a thoughtful, well-informed decision requires more effort. It’s easy to underestimate the amount of time it can take to dig into the facts and look at an issue from all angles, but that’s what critical thinking is all about.
To ensure that you get the best possible outcome, there are several steps in critical thinking:
- Identify and analyze the problem.
- Research and gather data from reliable sources.
- Generate alternative solutions and evaluate them logically.
- Choose the most suitable option.
- Implement your chosen option, then evaluate its effectiveness and impact.
- Adjust your plan as needed.
This type of process uses up more of our precious time, but it is worth it when you come out with an informed, well-reasoned solution that you can confidently stand behind. That’s why so many organizations prioritize this way of thinking when faced with tough decisions.
8. Critical thinking can lead to uncertainty.

One of the major disadvantages of critical thinking is that it often leads to uncertainty. When you’re looking at a problem or issue from all angles and considering all the available evidence, it can be difficult to come to a definitive solution. It can be hard to know exactly what steps to take as there may be multiple potential solutions.
This can lead to indecision and doubt, which can slow down progress on any project you’re working on. Furthermore, if there are many possible solutions available, it can take time and effort to evaluate each one fully before coming to a decision.
Another downside of critical thinking is that it requires a lot of mental energy and effort. Balancing this with other aspects of work or life can be tricky, as focusing too much on one area at the expense of others is not desirable. It’s important to remember that there are limits to how much critical thinking you should do in any given situation.
While there are certain disadvantages to critical thinking, it is certainly a skill worth having. It can enable you to see past false claims and identify logical fallacies, form your own well-reasoned opinions, and spot when others might be attempting to manipulate or deceive you.
That said, it’s important to remember that critical thinking doesn’t necessarily lead to the “right” answer. It’s important to keep an open mind and be willing to have your beliefs challenged. When used responsibly, critical thinking can be an invaluable asset to anyone.
- The Advantages & Disadvantages of Critical Thinking by MICAH MCDUNNIGAN published in CLASSROOM (https://classroom.synonym.com/)
- Is Critical Thinking Overrated? Disadvantages Of Critical Thinking published in EGGCELLENT Work (https://eggcellentwork.com/)
Call to Action
If you want to learn more about this types of topic and discover some tips and tricks to boost your brain power, click the link below and subscribe to our newsletter. You will also get access to exclusive content and offers that will help you achieve your goals and become smarter every day.

Let’s boost your self-growth with Believe in Mind.
Interested in self-reflection tips, learning hacks, and knowing ways to calm down your mind? We offer you the best content which you have been looking for.
Sanju Danthanarayana
Follow Me on
You May Like Also
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

To appreciate the benefits of Critical thinking, its worthwhile to ask the psychologists about 'how we think', and then see where Critical thinking actually fits in.
two systems of thinking.
Over the decades there has been plenty of research into how we think and make decisions. Daniel Kahneman is a noble prize winning researcher who did a lot of research on the cognitive processes of the brain and how it makes judgments under various conditions.
Kahneman in his book ‘Thinking fast and Slow’ states that we need to look at our thinking processes as consisting of two distinct and different types of processes. He calls them ‘System 1 thinking’ and System 2 thinking’.
System 1 and system 2 are not associated with the left or right brains or with creativity or any physical parts of the brain in the human body. But these are names given to two different types of thinking.
Kahneman gives some examples to illustrate the two types of thinking:
The Angry woman

When you look at the picture above, and are asked what is the woman thinking or emotion that she is experiencing, you are most likely to find that your brain has deciphered the emotion to be one of anger - and this understanding that the woman is angry is almost instantaneous. You did not have to concentrate, analyze or mentally compare with past interpretations of the look to arrive at your conclusion that she is angry.

Numerical example
Or lets take a look at another example that Kahneman gives. Take a look at the problem below, and decide whether each of the answers below is correct
17x24 = ?
- 120068 ?
In the first three answers you would have found that you did not need any time to decide that the answers are wrong. But when you came to 568, its quite likely that your brain paused for a moment and considered the answer. Could this be correct?
And as I have seen in several workshops, most people declare that it is the right answer. The number of digits look right, the number ends in a ‘8’ which the right answer should end in.
Critical thinking benefits- at a glance
There is a qualitative difference in the way our thinking operates while negating the first three numbers, and while considering and evaluating whether 568 is the right answer. In the first three instances, we did not need to pause to think - we knew the answers were wrong. But in the last instance - we paused, evaluated for short or long, and then delivered a verdict - of right or wrong.
The brain focused on the problem, put in some concentration and effort in the evaluation. Kahneman calls this deliberate, attention giving type of thinking as System 2 thinking.
- System 2 thinking requires attention and effort, and the activity suffers if attention is disrupted. System 2 thinking is also associated with the feeling of agency. When we think of ourselves as a person, it is system 2 thinking.
- System 1 operates automatically and quickly with little or no effort and no sense of voluntary control
- system 2 allocates attention to the effortful mental activities that demand it including complex computations
- The operations of system two are often associated with the subjective experience of agency choice and concentration

When we think of others we identify with system 2
- let's take a look at some of the system one activities
- detect that one object is more distant than another
- Orient to the source of a certain sound
- Complete the phrase bread an
- detect hostility in a voice
- answer to 2 + 2 is equal to
- Read words on large billboards
- Drive a car on an empty Rd
- Find a strong move in chess especially if you're a chess master. those who might not be experts in chess uh they would not necessarily have an operation of system one thinking they but they would need system 2 thinking
The highly diverse operations of System 2 have one feature in common: they require attention and are disrupted when attention is drawn away. Here are some examples:
- Check the validity of a complex logical argument.
- Budgeting for building a house
- Developing a marketing strategy
- Fill out a Tax return
- Brace for the starter gun in a race.
- Focus on the voice of a particular person in a crowded and noisy room.
Critical thinking is a system 2 activity. It is a consciously directed activity and needs attention and effort. If attention is taken away from the activity on hand the activity gets disrupted.
....And now for the benefits of Critical thinking skills
Enhanced problem-solving: Critical thinking helps individuals break down complex problems into manageable parts, identify underlying issues, and generate effective solutions. It promotes a systematic approach to problem-solving, reducing reliance on assumptions or biases.
Improved decision-making: Critical thinking involves evaluating evidence, considering multiple perspectives, and weighing the pros and cons of different options. This leads to more informed and rational decision-making, minimizing the influence of emotions or personal biases.
Increased creativity: Critical thinking encourages individuals to think outside the box, challenge established norms, and explore alternative viewpoints. It fosters creativity and innovation by promoting open-mindedness and the ability to generate unique ideas.
Effective communication: Critical thinking helps individuals express their thoughts and ideas clearly, logically, and persuasively. It enables them to analyze and construct arguments, recognize fallacies, and communicate their viewpoints with evidence-based reasoning.
Stronger analytical skills: Critical thinking enhances analytical skills by training individuals to gather relevant information, evaluate its credibility and validity, and draw logical conclusions. It enables them to identify patterns, make connections, and think critically about the implications of data.
Increased self-awareness: Critical thinking involves self-reflection and the examination of one's own beliefs, biases, and assumptions. It allows individuals to become more aware of their cognitive processes, biases, and areas for improvement, fostering personal growth and intellectual humility.
Effective problem prevention: Critical thinking is not only about solving existing problems but also about preventing them. By critically evaluating situations and potential outcomes, individuals can anticipate problems, identify potential risks, and take proactive measures to avoid or mitigate them.
Better academic and professional performance: Critical thinking is highly valued in academic and professional settings. It equips individuals with the skills necessary for research, analysis, and argumentation, leading to improved academic performance, better job prospects, and career advancement.
Enhanced empathy and understanding: Critical thinking involves considering diverse perspectives and evaluating evidence objectively. This fosters empathy, tolerance, and a willingness to understand viewpoints different from one's own. It promotes respectful dialogue and effective collaboration with others.
Lifelong learning: Critical thinking is essential for continuous learning and intellectual growth. It encourages individuals to question assumptions, seek out reliable information, and remain open to new ideas and knowledge. It empowers individuals to become lifelong learners, adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
Critical thinking training in Sales
Sales leaders trained in critical thinking would appreciate Aristotle's triangle of persuasion, and easily apply the relevant modes of convincing required for different sales situations. They would also realize that every sales proposal is an inductive argument which answers the questions' why this solution' and 'why my company'. Structuring logically strong proposals is a breeze once you understand inductive reasoning. Read about how critical thinking applies in B2B sales.
Critical thinking training for HR
HR professionals who are aware of fallacies and tactics such as 'Poisoning the well', 'hasty generalization' and selection bias will find it easier to understand and deal with employees and get better at evaluating people and situations. An understanding of various fallacies and cognitive biases would mitigate the risks of bad decisions due to faulty reasoning. They would also understand that 'Resume's are an exercise in Inductive arguments to prove why a candidate is the best fit for the job, and this would help in better shortlisting, interviewing and selection of candidates.
Critical thinking training for Analysts and Consultants
Business analysts, Consultants would find an understanding of Causal reasoning extremely useful, and an appreciation of common errors would result in better diagnosis of root causes of problems, and also provide a good framework for understanding whether the recommended solution would indeed address the problem identified. Regular application of the Critical thinking framework to problem solving and decision making ensures that the issue is examined from all relevant angles and perspectives before a solution is accepted.
Critical thinking training for Managers
Managers are called to make decisions and solve problems and devise strategies on an ongoing basis. While domain knowledge and experience have a great role to play in being successful, knowledge of fallacies and cognitive biases will ensure that they do not make errors in reasoning, and also whet their solutions for eliminating any cognitive biases they may have. The Critical thinking framework will assist in systematic analysis and problem solving for addressing complex issues
Why Critical thinking is important for students
A 2013 Survey of Employers by “The Association Of American Colleges And Universities” revealed that : Nearly all employers surveyed (93 percent) say that “a demonstrated capacity to think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more important than [a candidate’s] undergraduate major.” More than 75 percent of those surveyed say they want more emphasis (In teaching) on five key areas including: critical thinking, complex problem solving, written and oral communication, and applied knowledge in real world settings.
Critical thinking in academics
A knowledge of inductive reasoning and causal reasoning helps students break down any theory or subject into logical segments, and they are also able to build connections between what they learn and their existing knowledge. This makes them better students who develop a deeper understanding of the subject, and by virtue of reasoning while learning, they tend to retain their learning for longer periods of time. All writing tasks are an exercise in persuasion - presenting arguments and supporting them (excepting story writing and pure narrative writing). Developing, evaluating and presenting arguments are the skills developed while doing a course in Critical thinking. Combined with the knowledge of writing argumentative essays, and applying critical thinking frameworks, students are well equipped to deal with a variety of analyses and writing tasks. Knowledge of Causal reasoning helps research students develop sharp hypotheses and set up experiments or surveys to test their hypothesis. Causal reasoning is at the root of all research. Critical thinking skills also makes students better at discussions and debates. Having learnt to apply logic, and veer clear of fallacies and cognitive biases, students with leadership qualities find themselves equipped to productively lead and manage teams in various projects.
Critical thinking and Resume's
Aristotle had said there are three ways of persuading human beings: With logic, credibility or emotions. A candidate's Resume is a written document that attempts to persuade a potential employer of 'Why he is the best candidate for the job'. The tools of persuasion employed in a Resume are logic and credibility. As a matter of fact, it consists of a chain of inductive arguments reinforcing each other, and credibility established with certifications, awards and recommendations. A student of Critical thinking would find it very easy to structure and write a Resume to persuasively present their credentials and suitability for the job.
Critical thinking in Group discussions and Personal interviews
In group discussions, participants are presenting arguments for or against a topic or just evaluating a situation. At the heart of any discussion is the ability to reason logically and conduct a 360 degree examination of any issue to ensure that all the dimensions of the issue are explored and analyzed. Those who do not understand logical reasoning do not have the benefit of approaching or arguing any topic in a logical and progressive manner. Critical thinking teaches students how to define and analyze problems, while avoiding fallacies and cognitive biases. They develop the ability to make very strong and persuasive arguments based on logic and evidence. They are also good at finding holes and gaps and unwarranted assumptions in others arguments. In personal interviews , you will find trained students answering pretty much to the question, and clarifying questions where required. Their answers are logical and their training guides them in strengthening their arguments with evidence or examples..
All applicants to foreign universities are required to submit a SOP (Statement of Purpose) along with their applications and GRE/GMAT scores. Many students have difficulty with writing a SOP for two reasons: (1) they are not clear what needs to go into the SOP and (2) how to actually structure and write the SOP. For a student who has studies logical reasoning and inductive arguments in particular, writing a persuasive essay is an easy task. Further, those who learn how to structure and write an argumentative essay will never have a problem with any writing task.
Critical thinking in GRE & GMAT
Critical reasoning questions in gre and gmat.
GRE and GMAT have complete sections in their tests dedicated to test the logical reasoning capabilities of applicants. They are called 'Critical reasoning' tests and are designed to test the ability of test takers to analyze arguments logically. The questions revolve around : Strengthening or weakening arguments, revealing unstated assumptions or assumptions which if proved wrong or right could make a significant difference to the strength of the argument. Some questions relate to an understanding of the arguments presented. Most test takers answer these questions using intuition, experience from past tests or guess-work. Very few if any actually have learnt the fundamentals of logical reasoning, and as a result, answers generally are a 'hit or miss'. On the contrary, if test takers have studied and understood logical reasoning and fallacies, they would be able to take a knowledgable and structured approach to these questions which minimizes the chances of making any errors. The current approach is akin to asking someone to read a balance sheet without understanding accounting. Training in Critical thinking helps students answer the Critical reasoning questions with the confidence that comes with knowledge on how to scientifically evaluate and answer these questions.
Back to Blogs
The Benefits of Critical Thinking & How to develop it
April 02, 2024
Before we proceed to understand the importance and benefits of critical thinking for students, it is important to understand what critical thinking is.
Critical thinking is the mode of thinking about any subject, problem, or content. It skillfully thinks. Later, it implements and inherent those intellectual thoughts upon them. The best part of critical thinking is, it improves the quality of thinking.
It has intellectual values like clarity, sound evidence, precision, good reasons, relevance, consistency, depth, breadth, and fairness.
Critical thinking requires a proper process, it involves skillfully conceptualizing, analyzing different aspects, synthesizing, most importantly evaluating whatever information is gathered, keenly observing all factors, and experiencing the overall view.
Now let us understand the benefits of critical thinking.
1] it helps to improve decision-making.
Critical thinking will let you make decisions by yourself. It will help you improve decision-making.
For students, while making career decisions or making a new career move, it is crucial to make quick decisions, and hence critical thinking plays a vital role here.
2] Enhances problem-solving ability
Problem-solving is the key skill required for adapting to changes and facing challenges.
This skill of critical thinking should be developed by students to avoid making any situation complex and help find a solution to it.
For instance, two people in the same situation have been given a task and asked to find a solution. One person might take 5 minutes yet can’t give a relevant solution, whereas another person with problem-solving ability will dedicate enough time to research and provide a relevant solution.
Read Here: The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills & How to Develop Them
3] refine your research skills.
Critical Thinking will refine your research skills, moreover will help you research accurately by observing, analyzing, synthesizing, and experimenting with every aspect in detail for a better result.
4] Polishes your creativity
It will help you polish your creative side. Creativity unquestionably defines itself as a requisite skill in the collaborative modern workforce. As critical thinking will surely polish your creativity.
5] Stimulates Curiosity
It stimulates curiosity in you to find the right solution for the problem or the subject you are working on. Curiosity will let you dig and delve deeper to get a better result. This factor will let you stay a lifelong learner.
All these aspects of critical thinking play a vital role in Banking and financial sector. If you are seeking to develop these crucial skills, then you must certainly opt for ‘ Thadomal Shahani Centre for Management ’ institute based in Mulund, Mumbai.
It is one of the Best institutes, aids in developing critical thinking with its innovative teaching methodology, and focuses on comprehensive development, providing students with a globally relevant curriculum, and international faculty members who have hands-on business leadership.
Additionally, If you want to enroll in Certificate in Banking and Financial Services (CBFS) or top global MBA courses, you can contact us for detailed information where you will find the program, curriculum, specializations, certifications, eligibility criteria, and everything related to it.
Consult a Career Advisor
Now lets us learn how to develop Critical Thinking skills
– ask questions.
For developing critical skills, it is important to ask more questions. The more you ask questions, the more the curiosity and quest to learn increase. The questions will clarify your thinking, and conceptualizing and analyzing will become more accessible through it.
– Scrutinize the consequences
By asking questions, you have the availability of various options. However, you must not make a hasty decision. You have to scrutinize the consequences of each option and accordingly take a decision. Therefore, it will lead to solving your problems.
– Become Active Listener
To be a critical thinker, you need to first be an active listener. You will ask numerous questions to satisfy your quest, but to know the answers, you need to be a good listener too. Listen to different people’s thoughts, views, and opinions; these will help you form your own decisions.
Know what are the advantages of developing Critical Thinking Skills

Now that you know the importance and advantages of critical thinking.
Important Links:
- Certificate in Banking and Financial Services (CBFS): https://tscfm.org/courses/certificate-in-banking-and-financial-services/
- 4-IN-1 Professional Diploma in Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (PDBFSI): https://tscfm.org/courses/4-in-1-professional-diploma-in-banking-financial-services-insurance-pdbfsi/
Previous post
5 Time Management Tips for Students to Study Effectively and Crack Exams Better
How to crack the campus placement interview, want a successful career.
Fill up this form for a free career psychometric test & a 30 min career guidance session with our advisor.
Business Management Program
Banking and finance, digital marketing, mba for working professionals, business english, career advice, master of business administration (mba), certificate in wealth management (cwm), mba from uk university, certificate in banking and financial services (cbfs), 4-in-1 professional diploma in banking, financial services & insurance (pdbfsi), professional diploma in investment banking, certificate in business english, most popular posts, how to choose the perfect mba college, benefits of studying banking and finance course, what is customer relationship management (crm) in wealth management.

Related Post

September 10, 2024

September 05, 2024

August 30, 2024
About TSCFM
TSCFM is a brand of SMART Institute Pvt. Ltd., which is a part of The Shahani Group of Institutions. We are the only B-school in Mumbai to bring the best of international management education to India. We are ranked No. 3 among colleges offering Global Business Courses in India by Outlook.
- Awards & Affiliation
- Career Advices
- Industry News
- Testimonials
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Refund and Cancellation Policy
+91 9930978000

Kindly Fill up the details to receive a call from our Career expert
- The Open University
- Accessibility hub
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
1 Barriers to critical thinking
First, let’s briefly examine some barriers to critical thinking.
Take another look at the visual summary below on critical and analytical thinking, which was introduced at the end of Session 3. Note the warning sign next to the ‘black pit’ to the lower right of this figure.
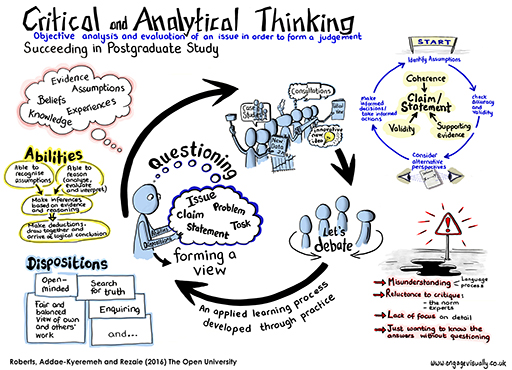
This figure shows a visual summary of critical and analytical thinking. It includes phrases such as ‘objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement’, ‘abilities’, ‘dispositions’ and ‘questioning’.
We have provided you with a larger version of this image in PDF format [ Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. ( Hide tip ) ] .
What are the common pitfalls or barriers to thinking critically and analytically? Some of these were highlighted in the visual summary, and include:
- Misunderstanding . This can arise due to language or cultural differences, a lack of awareness of the ‘processes’ involved, or a misunderstanding that critical thinking means making ‘negative’ comments (as discussed in Sessions 3 and 4).
- Reluctance to critique the ‘norm’ or experts in a field and consider alternative views (feeling out of your ‘comfort zone’ or fearful of being wrong).
- Lack of detailed knowledge . Superficial knowledge (not having read deeply enough around the subject).
- Wanting to know the answers without having to ask questions .
Why do you think being aware of these potential pitfalls is important?
As a critical and reflective thinker, you will need to be aware of the barriers, acknowledge the challenges they may present, and overcome these as best you can. This starts with an understanding of expectations. Some students feel anxious about questioning the work of experts. Critical thinking does not mean that you are challenging someone’s work or telling them that they are wrong, but encourages a deeper understanding, a consideration of alternative views, and engagement in thought, discourse or research that informs your independent judgement. At postgraduate level you will also need to read widely around a subject in order to engage effectively with critical and analytical thinking, and to ask questions: there are no ‘right’ or ‘wrong’ answers, only supported arguments. This is at the heart of postgraduate study.
Critical thinking encourages you to be constructive, by considering the strengths and weaknesses of a claim and differing sides to an argument. It helps you to clarify points, encourages deeper thought, and allows you to determine whether information that you come across is accurate and reliable. This helps you to form your own judgement, and drives research forward.
People can find it difficult to think critically, irrespective of their education or intellectual ability. The key to understanding critical thinking is not only knowing and making sure that you understand the process, but also being able to put this into practice by applying your knowledge.
Critical and reflective thinking are complex and lifelong skills that you continue to develop as part of your personal and professional growth. In your everyday life, you may also come across those who do not exercise critical thinking, and this might impact on decisions that affect you. It is important to recognise this, and to use critical and reflective thinking to ensure that your own view is informed by reasoned judgement, supported by evidence.
Take another look at the visual summary. You will see two aspects to critical thinking: one focusing on the disposition of the person engaged in critical and reflective thinking, and the other concerning their abilities. Let’s focus here on dispositions. At a personal level, barriers to critical thinking can arise through:
- an over-reliance on feelings or emotions
- self-centred or societal/cultural-centred thinking (conformism, dogma and peer-pressure)
- unconscious bias, or selective perception
- an inability to be receptive to an idea or point of view that differs from your own (close-mindedness)
- unwarranted assumptions or lack of relevant information
- fear of being wrong (anxious about being taken out of your ‘comfort zone’)
- poor communication skills or apathy
- lack of personal honesty.
Be aware that thinking critically is not simply adhering to a formula. For example, reflect on the following questions:
- How can you communicate with those who do not actively engage with critical thinking and are unwilling to engage in a meaningful dialogue?
- How would you react or respond when you experience a lack of critical thinking in the media, amongst your own family members, colleagues at work, or on your course?
Practicing Critical Thinking: Issues and Challenges
- First Online: 04 September 2024
Cite this chapter

- K. Venkat Reddy 3 &
- G. Suvarna Lakshmi 4
Despite acknowledging the importance of teaching or promoting critical thinking as part of education, practicing critical thinking in the real world and life has its own challenges to be resolved. Some of them are presented in the studies included in this chapter. The first article is on the gap between the perceptions on cognitive active learning of teachers and learners. The focus of the study is on exploring learners’ perceptions on deep learning particularly in Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). Instructors facing organizational difficulties, lack of experience in synchronous learning for the students, unable to have peer interaction while learning in VLE, inadequate training for the instructors and students to teach and learning virtually, students’ not experiencing the benefits of deep learning are among the major gaps or problems identified in this study. The second article is about techniques that enhance higher order thinking skills in EFL learners by using post-reading strategies resulting in better speech production and reasoning power. The output of the research states that concept mapping and argumentation enhance EFL learners’ reasoning power when private speech is used to understand the process of thinking. The third article in this chapter is on cross-cultural psychology where the cultural influence on making inferences and participating in debates by Asian students who are studying in western institutions. Though there are intercultural differences in the inferences made because of cultural backgrounds and first language variations, they are insignificant. Then the reasons for obvious differences could be learning environment, literacy and higher education. The statement that Asian students are unable to perform well in western logic might be true not because the Asian students are less capable of thinking critically but because they are not trained in or used to western logical problems. The last article of this chapter is on assessment of critical thinking in first year dental curriculum that establishes the importance of critical thinking in dental education. The assessment is on the importance of critical thinking and the need to change the curriculum incorporating critical thinking.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Smith, T. W., & Colby, S. A. (2007). Teaching for deep learning. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 80 (5), 205–210.
Article Google Scholar
Platow, M. J., Mavor, K. I., & Grace, D. M. (2013). On the role of discipline-related self-concept in deep and surface approaches to learning among university students. Instructional Science, 41 (2), 271–285.
Reinhardt, M. M. (2010). The use of deep learning strategies in online business courses to impact student retention. American Journal of Business Education, 3 (12), 49.
Google Scholar
Mimirinis, M., & Bhattacharya, M. (2007). Design of virtual learning environments for deep learning. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 18 (1), 55–64.
Smart, K., & Cappel, J. (2006). Students’ perceptions of online learning: A comparative study. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 5 (1), 201–219.
Jain, P. (2015). Virtual learning environment. International Journal in IT & Engineering, 3 (5), 75–84.
Molnár, G. (2013). Challenges and opportunities in virtual and electronic learning environments. In IEEE 11th international symposium on intelligent systems and informatics .
Riley, S. K. L. (2008). Teaching in virtual worlds: Opportunities and challenges. Setting Knowledge Free: The Journal of Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology, 5 (5), 127–135.
Warden, C. A., Stanworth, J. O., Ren, J. B., & Warden, A. R. (2013). Synchronous learning best practices: An action research study. Computers & Education, 63 , 197–207.
Yamagata-Lynch, L. C. (2014). Blending online asynchronous and synchronous learning. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 15 (2), 189–212.
Cole, M. (2009). Using wiki technology to support student engagement: Lessons from the trenches. Computers & Education, 52 (1), 141–146.
Tyler, J., & Zurick, A. (2014). Synchronous versus asynchronous learning-is there a measurable difference? In Proceedings of the 2014 Institute for Behavioral and Applied Management Conference, IBAM22 . October 9–11, 2014, 52.
Asikainen, H., & Gijbels, D. (2017). Do students develop towards more deep approaches to learning during studies? A systematic review on the development of students’ deep and surface approaches to learning in higher education. Educational Psychology Review, 29 (2), 205–234.
Biggs, J. B. (1993). From theory to practice: A cognitive systems approach. Higher Education Research and Development, 12 (1), 73–86.
Garrison, D. R., & Cleveland-Innes, M. (2005). Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough. The American Journal of Distance Education, 19 (3), 133–148.
Van Raaij, E. M., & Schepers, J. J. (2008). The acceptance and use of a virtual learning environment in China. Computers & Education, 50 (3), 838–852.
Postareff, L., Parpala, A., & Lindblom-Ylänne, S. (2015). Factors contributing to changes in a deep approach to learning in different learning environments. Learning Environments Research, 18 , 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-015-9186-1
Dolmans, D., Loyens, S., Marcq, H., & Gijbels, D. (2016). Deep and surface learning in problem-based learning: A review of the literature. Advances in Health Science Education, 21 (5), 1087–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-015-9645-6
Wildemuth, B. M. (Ed.). (2016). Applications of social research methods to questions in information and library science . ABC-CLIO.
Silverman, D. (Ed.). (2016). Qualitative research . Sage.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25 (1), 54–67.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1986). Thought and language . MIT Press.
McCafferty, S. G. (1994). The use of private speech by adult ESL learners at different levels of proficiency. In J. P. Lantolf & G. Appel (Eds.), Vygotskian approaches to second language research (pp. 135–156). Ablex.
Centeno-Cortes, B., & Jimenez Jimenez, A. F. (2004). Problem-solving tasks in a foreign language: The importance of the L1 in private verbal thinking. International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 14 (1), 7–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-4192.2004.00052.x
Ghanizadeh, A., & Mirzaee, S. (2012). Critical thinking: How to enhance it in language classes . Lambert Academic Publishing.
Choi, I., Nisbett, R., & Smith, E. E. (1997a). Culture, categorization and inductive reasoning. Cognition, 65 (1), 15–32.
Nisbett, R. E., Peng, K., Choi, I., & Norenzayan, A. (2001). Culture and systems of thought: Holistic versus analytic cognition. Psychological Review, 108 (2), 291–310.
Peng, K. (1997). Naive dialecticism and its effects on reasoning and judgement about contradiction . University of Michigan.
Peng, K., & Nisbett, R. (1996). Cross-cultural similarities and differences in the understanding of physical causality. In Paper presented at the science and culture: Proceedings of the seventh interdisciplinary conference on science and culture .
Cole, M. (1996). Cultural psychology: A once and future discipline . Belknap Press of Harvard University Press.
Nisbett, R. E. (2003). The geography of thought: How Asians and westerners think differently … and why . Free Press.
Ji, L.-J., Zhang, Z., & Nisbett, R. E. (2004). Is it culture or is it language? Examination of language effects in cross-cultural research on categorisation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87 (1), 57–65.
Norenzayan, A. (2001). Rule-based and experience-based thinking: The cognitive consequences of intellectual traditions. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences & Engineering, 62 (6-B), 2992.
Norenzayan, A., Smith, E. E., Kim, B. J., & Nisbett, R. E. (2002). Cultural preferences for formal versus intuitive reasoning. Cognitive Science, 26 (5), 653–684.
Peng, K., Ames, D. R., & Knowles, E. D. (2000). Culture and human inference: Perspectives from three traditions. In D. Matsumoto (Ed.), Handbook of cross-cultural psychology (pp. 1–2). Oxford University Press.
Whorf, B. L. (1962b). The relation of habitual thought to language, and an American Indian model of the universe from language. In J. B. Carroll (Ed.), Language, thought and reality: Selected writings of Benjamin . MIT Press.
Davidson, D. (1984). On the very idea of a conceptual scheme. In inquiries into truth and interpretation . Oxford University Press.
Devitt, M., & Sterelny, K. (1997). Language and reality . MIT Press.
Gellatly, A. (1995). Colourful whorfian ideas: Linguistic and cultural influences on the perception and cognition of colour and on the investigation of time. Mind and Language, 10 (3).
Pinker, S. (1994). The language instinct . Penguin Books.
Book Google Scholar
Davies, W. M. (2006b). Intensive teaching formats: A review. Issues in Educational Research, 16 (1), 1–20.
Felix, U., & Lawson, M. (1994). Evaluation of an integrated bridging program course on academic writing for overseas postgraduate students. Higher Education Research and Development, 13 (1), 59–70.
Felix, U., & Martin, C. (1991). A report on the program of instruction in essay writing techniques for overseas post-graduate students . School of Education, Flinders University.
Brand, D. (1987). The new whizz kids: Why Asian Americans are doing well and what it costs them. Time, August (42–50) .
Murphy, D. (1987). Offshore education: A Hong Kong perspective. Australian Universities Review, 30 (2), 43–44.
Wong, N.-Y. (2002). Conceptions of doing and learning mathematics among Chinese. Journal of Intercultural Studies, 23 (2), 211–229.
Accreditation standards for dental education programs. Commission on dental accreditation. Commission on dental Education 2019.
Elangovan, S., Venugopalan, S. R., Srinivasan, S., Karimbux, N. Y., Weistroffer, P., & Allareddy, V. (2016). Integration of basic-clinical sciences, PBL, CBL, and IPE in U.S. dental schools’ curricula and a proposed integrated curriculum model for the future. Journal of Dental Education, 80 , 281–290.
Duong, M. T., Cothron, A. E., Lawson, N. C., & Doherty, E. H. (2018). U.S. Dental schools’ preparation for the integrated national board dental examination. Journal of Dental Education, 82 , 252–259.
Annansingh, F. (2019). Mind the gap: Cognitive active learning in virtual learning environment perception of instructors and students. Education and Information Technologies . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09949-5
Mirzaee, S., & Maftoon, P. (2016). An examination of Vygotsky’s socio-cultural theory in second language acquisition: The role of higher order thinking enhancing techniques and the EFL learners’ use of private speech in the construction of reasoning. Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education . https://doi.org/10.1186/s40862-016-0022-7
Martin Davies, W. (2006). Cognitive contours: Recent work on cross-cultural psychology and its relevance for education. Studies in Philosophy and Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11217-006-9012-4
van der Hoeven, D., Truong, T. T. L. A., Holland, J. N., & Quock, R. L. (2020). Assessment of critical thinking in a first-year dental curriculum. Medical. Science Educator . https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-020-00914-3
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Training and Development, The English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
K. Venkat Reddy
Department of English Language Teaching, The English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
G. Suvarna Lakshmi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of English Language Teaching, English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reddy, K.V., Lakshmi, G.S. (2024). Practicing Critical Thinking: Issues and Challenges. In: Reddy, K.V., Lakshmi, G.S. (eds) Critical Thinking for Professional and Language Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37951-2_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37951-2_5
Published : 04 September 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-37950-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-37951-2
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Obsidian Iceberg

🌲The Difficulties of Teaching Critical Thinking
Teaching critical thinking in an optimal way is pretty hard when a course has a strict content or assessment focused pacing guide..

Note: This blog post was originally written for my Master Degree’s in Leadership in Teaching via Notre Dame of Maryland University. For readability, I’ve removed some of the inline citations, added some clarification, and omitted some of the academic formatting. If anybody wants my full references list or a copy of the original paper,…
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Obsidian Iceberg to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.
5 Advantages of Critical Thinking… or Disadvantages?

How often do you hear the phrase, “Come down to earth and think critically”? Probably, it is common to hear from parents, teachers, professors and other adults who have already seen the world and can say that the process of thinking carefully about a subject or idea without allowing feelings or opinions to affect you is the best way to deal with this world. But is it always true? This article is aimed at giving the reasonable answer to this questions providing you with both advantages of critical thinking and its disadvantages. Be sure you’ll find the golden mean of how to use critical thinking skills in everyday life. Go on reading this article to the end!
Table of Contents
One Side of the Coin: 5 Advantages of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves many useful abilities:
- The ability to think clearly and rationally;
- The ability to analyze information objectively;
- The ability to understand the logical connection between ideas;
- The ability to make reasoned judgments, etc.
Let’s find out why these abilities are considered to be useful.

1. You Are Able to Evaluate Issues without Bias
Most people approach issues in a different way – someone relies on his/her beliefs, experiences, emotions or someone else’s opinions. All that influences how you deal with one or another issue, especially it concerns such controversial topics as abortion, capital punishment, animal testing or immigration. There are a lot of questions to be answered with reference to solid evidence. And what can help you gather it? Right, it’s critical thinking that helps you gather and assess relevant information to interpret it effectively for well-reasoned conclusions and solutions.
2. You Can Foresee How Things Will Turn out
Will-power, knowledge, skills, motivation, knowing the right people, being at the right time and in the right place is all that makes a person succeed in the modern world. And yet, there is one more point that allows achieving success – it is the ability to predict what will happen or be needed in the future. How is it possible? You learn the current issues in an objective and critical way understanding the logical links between ideas and arguments. For example, Heather A. Butler with her colleagues, Christopher Pentoney, Mabelle P. Bong conducted research among 244 participants to explore the contribution of critical thinking and intelligence to the prediction of real-world outcomes. As a result, critical thinking is considered to be a better predictor of real-world outcomes than intelligence. So start to develop your critical thinking skills right now to know what will occur to various important fields – economics, business, marketing and sales, etc.
3. You Communicate with Others Sharing Your Ideas Effectively
After you evaluate an issue and predict all possible outcomes, it is important to get out a message to the target audience – be it your chief, colleagues or professors. As a rule, critical thinking detaches all our emotions from expressing an idea in public. You just take a practical view of the situation at hand – how to solve a problem in mutual collaboration with colleagues or other people. At the same time, open mind for a different view that you can also perceive with the help of the ability to recognize valid logic.
4. You Are Trusted to Figure Out Solutions to Complex Problems
When a person is able to identify, analyze problems and even predict and solve them systematically rather than by intuition or instinct, it is particularly valuable. You still have to hope for the best – once you’ll be trusted to perform complex tasks in a company, for example. It means that the career promotion is guaranteed to you in this case. Additionally, it will influence your life in general. Yes, it is a great responsibility to solve complex problems. But just imagine how many difficult questions could be answered if you applied your critical thinking skills in practice.
5. You Are Highly Appreciated by Employers
You have been already explained the perspectives in a professional career when critical thinking is one of your strengths. What do usually students do when graduating from a college or university? “Where to find a job of my dream?” is a common question for graduates. That’s why if you want to succeed in a job search quickly, start succeeding in critical thinking. Be sure most doors of top business companies will be open to you if an HR specialist notices your good critical thinking skills in resumes, cover letters, or during job interviews. Most companies call for job applicants that are critical thinkers, communicative, collaborative, and creative. It means that besides being equipped with good reading, writing, and arithmetic skills, don’t neglect four specific skills that are known as the “ Four Cs ” – critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity.
The Flip Side to the Coin: 5 Disadvantages of Critical Thinking

In some cases, critical thinking is deemed as important as breathing. Like in an interview or maybe when you are taking a test, but not always. When you were asked in childhood, “What would you like to be?” and you might automatically reply, “I want to be a journalist when I grow up.” or “I dream to become an artist.” But then you really did grow up and all the innocence and positive outlook were destroyed when the realities and practicalities of life came crashing down on you. Critical thinking is the killer of dreams. One minute you will be dreaming about being the greatest artist of all times, and when you start to analyze it critically, you will notice the huge, gaping holes in that plan of yours. You will start to have second thoughts and will be confronted with countless dilemmas. Will you have to move to another city for that? Do you have an aptitude for becoming an artist? Are you competitive enough? The list goes on and on. You might be proud of your ability to think critically at every turn, but here are some ways it can be more harmful than you think.
1. Your Peers’ Jokes Are Not Funny Anymore
Hanging out with your friends can be a surreal experience. But when you analyze everything, their jokes suddenly don’t make any sense to you and neither are they funny anymore. How many times have you rolled your eyes at them because whenever you hear one of their repetitive jokes, you automatically think “amateur hour!” and when they expect you to laugh, you’re simply frowning.
2. You Think about Gender Equality too Much
When your girlfriend/boyfriend is gushing about that awesome invite you got to an upcoming party and you think about gender equality. A little bit different ideas, don’t you think?
3. You Feel Shame When Your Group Mates Speak
And when they are unable to communicate their ideas in a decent and intellectual way, like you would have done, you feel sorry for your group mates and secretly feel ashamed that you are thinking about them that way and you are like.
4. You Are Alone with Your Books
Not only you like books that your friends would totally hate, but you can’t discuss the finer points in the plot with them, because they are probably going to think you have gone crazy. And they look at you like
5. Your Only Adequate Companion Is You
It is hard to admit but you can speak on truly interesting matters only with … yourself. Who can talk about the biocultural approach to climate change? Who knows why it is important to support solar energy? Who defends Severus Snape because he did everything to save Harry? Right, only you.
Well, all in all, critical thinking has its uses and, in some cases, it is quite beneficial (think about Sherlock Holmes, guys!). But most times it’s going to leach the fun out of everything and exasperate your friends around you. Remember the words of Dr. Richard Paul : “Critical thinking is thinking about your thinking while you’re thinking in order to make your thinking better.” and improve the way you think today!

Too busy to write your paper by yourself?

- HR Most Influential
- HR Excellence Awards
- Advertising
Search menu
Helen Lee Bouygues
Reboot Foundation
View articles
Improving the workplace through critical thinking

A lot of the problems in business — and in human resources — can be traced back to a single root: bad thinking. Over the course of my career as a consultant, I’ve seen business leaders make abysmal decisions based on faulty reasoning, and I’ve seen HR managers fail to recognise their own innate biases when addressing employee complaints and hiring decisions.
Let me give you an example. I was once asked to help turn around a large, but faltering, lingerie company in Europe. It didn’t take too long for me to see what the problem was: the company’s strategy assumed that all their customers everywhere pretty much wanted the same products.
Company leaders hadn’t done their research and didn’t really understand how their customers’ preferences varied from country to country.
In the UK, for example, lacy bras in bright colours sold the best; Italians seemed to prefer beige bras without lace; and Americans opted for sports bras in much, much larger numbers.
Transformations and turnarounds:
What to do when leadership fails
How HR can prioritise procedure using automation and digital processes
How to transform dysfunctional teams
Without realising it, they were making business decisions on faulty assumptions and bad information. However, a new strategy based on market-dependent research quickly helped turn things around.
Using feedback to get outside of your own head
One huge advantage consultants have over internal employees is simply that they are outsiders. Consultants obviously won’t know the ins and outs of the business as well as internal managers, but because of that, they also haven’t developed the biases and assumptions that can constrain employee thinking. In short, employees are sometimes too close to the problem.
Now, there are a lot of exercises and routines you can employ to make sure you don’t have blinders on when you’re confronting new problems or challenges.
Perhaps the easiest way to do this is through feedback. Of course, feedback can be tricky. No one likes to be evaluated harshly, and without the proper mechanisms in place the value of feedback may be lost amid negative interpersonal dynamics.
One of the best things an organisation can do is to implement clear and explicit practices and guidelines for feedback between managers and employees.
Feedback should be cooperative rather than antagonistic. It should give both parties the opportunity to reflect on, explain, and refine their reasoning. And it should be explicit, preferably using both written and oral communication to find flaws in reasoning and tease out new solutions.
Making conflict productive
Conflict is inevitable in a workplace. It’s how conflict is managed that can determine whether an organisation thrives. The key to good decision-making in group settings is productive, rather than destructive, conflict.
The best decisions emerge from a process in which ideas have to do battle with one another and prove their worth in group discussions. Without some conflict, organisations fall prey to group-think , where everyone goes along with the consensus.
Again, process is crucial here. The best organisations have clear guidelines and structures in place to ensure decision-making proceeds productively.
Decision-making practices should also include mechanisms for avoiding groupthink, by, for example, soliciting opinions in writing before a discussion and by composing groups with a diverse range of backgrounds and opinions.
Finally, leaders must truly value dissenting opinions. Special consideration should be given to ideas that go against the grain. Even if they lose out in the end, dissenting opinions make the final decision stronger.
Dissenters will also be more likely to buy into a decision that goes against their views if they feel their voice has been genuinely heard.
Thinking through individual goals critically and creatively
A key component of workplace happiness is employees’ sense that they are working toward something , both in terms of overall organisational goals and in terms of personal and professional growth.
Regular reflection on individual goals is vital to sustaining a healthy workplace culture. It also encourages more thoughtful work and allows employees to see day-to-day tasks in a broader context, helping them avoid burnout and monotony .
HR professionals can implement regular systems that allow employees to intentionally formulate these types of goals and understand how their work can be integrated more fully into achieving those goals.
Organisations can also grant employees time to pursue passion projects, like Google has, to give workers the freedom to develop ideas and products beneficial to both themselves and the company.
Creative and critical thinking is integral to organisational success, but it is too often assumed that employees and organisations either have it or they don’t.
The truth is that good thinking can be fostered with intentional, structured systems in place for feedback, argument, and reflection.
Helen Lee Bouygues is founder of the Reboot Foundation
Further reading

LinkedIn’s dyslexic thinking skill: de-stigmatisation or discrimination?

Six top tips for navigating challenging conversations in the workplace

What’s in a name: supporting workplace inclusivity through #MyNameIs

The power of design thinking

Why microclimates have the power to change workplace culture

Why we need to ditch the job description

Managing the upside-down: lessons from Stranger Things

The 'power partnership': why CPOs and CMOs have a common cause
5 Advantages and Disadvantages of Problem-Based Learning [+ Activity Design Steps]
Written by Marcus Guido
- Teaching Strategies

- Advantages of Problem-Based Learning
- Disadvantages of Problem-Based Learning
- Steps to Designing Problem-Based Learning Activities
Used since the 1960s, many teachers express concerns about the effectiveness of problem-based learning (PBL) in certain classroom settings.
Whether you introduce the student-centred pedagogy as a one-time activity or mainstay exercise, grouping students together to solve open-ended problems can present pros and cons.
Below are five advantages and disadvantages of problem-based learning to help you determine if it can work in your classroom.
If you decide to introduce an activity, there are also design creation steps and a downloadable guide to keep at your desk for easy reference.
1. Development of Long-Term Knowledge Retention
Students who participate in problem-based learning activities can improve their abilities to retain and recall information, according to a literature review of studies about the pedagogy .
The literature review states “elaboration of knowledge at the time of learning” -- by sharing facts and ideas through discussion and answering questions -- “enhances subsequent retrieval.” This form of elaborating reinforces understanding of subject matter , making it easier to remember.
Small-group discussion can be especially beneficial -- ideally, each student will get chances to participate.
But regardless of group size, problem-based learning promotes long-term knowledge retention by encouraging students to discuss -- and answer questions about -- new concepts as they’re learning them.
2. Use of Diverse Instruction Types
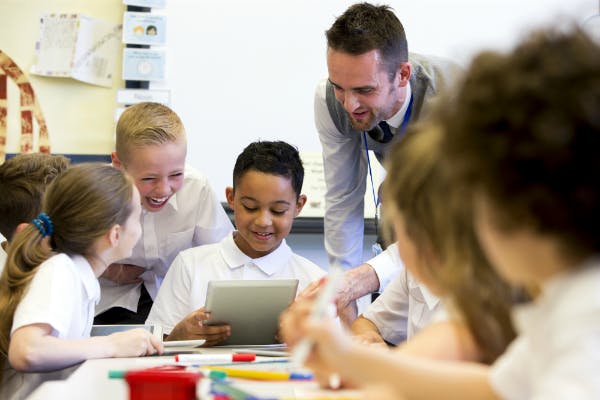

You can use problem-based learning activities to the meet the diverse learning needs and styles of your students, effectively engaging a diverse classroom in the process. In general, grouping students together for problem-based learning will allow them to:
- Address real-life issues that require real-life solutions, appealing to students who struggle to grasp abstract concepts
- Participate in small-group and large-group learning, helping students who don’t excel during solo work grasp new material
- Talk about their ideas and challenge each other in a constructive manner, giving participatory learners an avenue to excel
- Tackle a problem using a range of content you provide -- such as videos, audio recordings, news articles and other applicable material -- allowing the lesson to appeal to distinct learning styles
Since running a problem-based learning scenario will give you a way to use these differentiated instruction approaches , it can be especially worthwhile if your students don’t have similar learning preferences.
3. Continuous Engagement
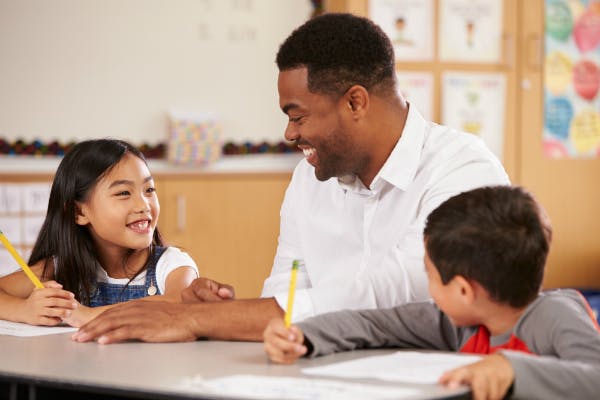

Providing a problem-based learning challenge can engage students by acting as a break from normal lessons and common exercises.
It’s not hard to see the potential for engagement, as kids collaborate to solve real-world problems that directly affect or heavily interest them.
Although conducted with post-secondary students, a study published by the Association for the Study of Medical Education reported increased student attendance to -- and better attitudes towards -- courses that feature problem-based learning.
These activities may lose some inherent engagement if you repeat them too often, but can certainly inject excitement into class.
4. Development of Transferable Skills
Problem-based learning can help students develop skills they can transfer to real-world scenarios, according to a 2015 book that outlines theories and characteristics of the pedagogy .
The tangible contexts and consequences presented in a problem-based learning activity “allow learning to become more profound and durable.” As you present lessons through these real-life scenarios, students should be able to apply learnings if they eventually face similar issues.
For example, if they work together to address a dispute within the school, they may develop lifelong skills related to negotiation and communicating their thoughts with others.
As long as the problem’s context applies to out-of-class scenarios, students should be able to build skills they can use again.
5. Improvement of Teamwork and Interpersonal Skills

Successful completion of a problem-based learning challenge hinges on interaction and communication, meaning students should also build transferable skills based on teamwork and collaboration . Instead of memorizing facts, they get chances to present their ideas to a group, defending and revising them when needed.
What’s more, this should help them understand a group dynamic. Depending on a given student, this can involve developing listening skills and a sense of responsibility when completing one��’s tasks. Such skills and knowledge should serve your students well when they enter higher education levels and, eventually, the working world.
1. Potentially Poorer Performance on Tests

Devoting too much time to problem-based learning can cause issues when students take standardized tests, as they may not have the breadth of knowledge needed to achieve high scores. Whereas problem-based learners develop skills related to collaboration and justifying their reasoning, many tests reward fact-based learning with multiple choice and short answer questions. Despite offering many advantages, you could spot this problem develop if you run problem-based learning activities too regularly.
2. Student Unpreparedness
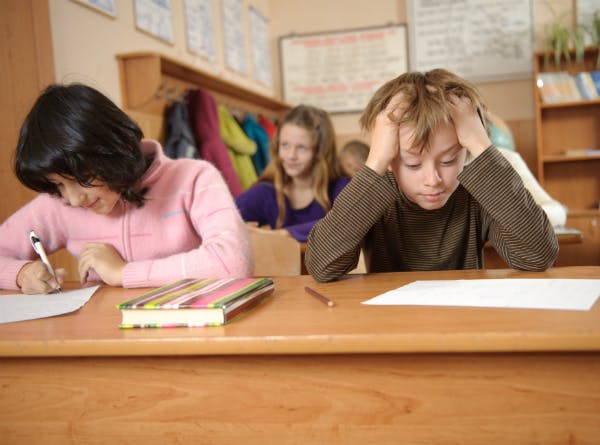

Problem-based learning exercises can engage many of your kids, but others may feel disengaged as a result of not being ready to handle this type of exercise for a number of reasons. On a class-by-class and activity-by-activity basis, participation may be hindered due to:
- Immaturity -- Some students may not display enough maturity to effectively work in a group, not fulfilling expectations and distracting other students.
- Unfamiliarity -- Some kids may struggle to grasp the concept of an open problem, since they can’t rely on you for answers.
- Lack of Prerequisite Knowledge -- Although the activity should address a relevant and tangible problem, students may require new or abstract information to create an effective solution.
You can partially mitigate these issues by actively monitoring the classroom and distributing helpful resources, such as guiding questions and articles to read. This should keep students focused and help them overcome knowledge gaps. But if you foresee facing these challenges too frequently, you may decide to avoid or seldom introduce problem-based learning exercises.
3. Teacher Unpreparedness
If supervising a problem-based learning activity is a new experience, you may have to prepare to adjust some teaching habits . For example, overtly correcting students who make flawed assumptions or statements can prevent them from thinking through difficult concepts and questions. Similarly, you shouldn’t teach to promote the fast recall of facts. Instead, you should concentrate on:
- Giving hints to help fix improper reasoning
- Questioning student logic and ideas in a constructive manner
- Distributing content for research and to reinforce new concepts
- Asking targeted questions to a group or the class, focusing their attention on a specific aspect of the problem
Depending on your teaching style, it may take time to prepare yourself to successfully run a problem-based learning lesson.
4. Time-Consuming Assessment

If you choose to give marks, assessing a student’s performance throughout a problem-based learning exercise demands constant monitoring and note-taking. You must take factors into account such as:
- Completed tasks
- The quality of those tasks
- The group’s overall work and solution
- Communication among team members
- Anything you outlined on the activity’s rubric
Monitoring these criteria is required for each student, making it time-consuming to give and justify a mark for everyone.
5. Varying Degrees of Relevancy and Applicability
It can be difficult to identify a tangible problem that students can solve with content they’re studying and skills they’re mastering. This introduces two clear issues. First, if it is easy for students to divert from the challenge’s objectives, they may miss pertinent information. Second, you could veer off the problem’s focus and purpose as students run into unanticipated obstacles. Overcoming obstacles has benefits, but may compromise the planning you did. It can also make it hard to get back on track once the activity is complete. Because of the difficulty associated with keeping activities relevant and applicable, you may see problem-based learning as too taxing.
If the advantages outweigh the disadvantages -- or you just want to give problem-based learning a shot -- follow these steps:
1. Identify an Applicable Real-Life Problem

Find a tangible problem that’s relevant to your students, allowing them to easily contextualize it and hopefully apply it to future challenges. To identify an appropriate real-world problem, look at issues related to your:
- Students’ shared interests
You must also ensure that students understand the problem and the information around it. So, not all problems are appropriate for all grade levels.
2. Determine the Overarching Purpose of the Activity
Depending on the problem you choose, determine what you want to accomplish by running the challenge. For example, you may intend to help your students improve skills related to:
- Collaboration
- Problem-solving
- Curriculum-aligned topics
- Processing diverse content
A more precise example, you may prioritize collaboration skills by assigning specific tasks to pairs of students within each team. In doing so, students will continuously develop communication and collaboration abilities by working as a couple and part of a small group. By defining a clear purpose, you’ll also have an easier time following the next step.
3. Create and Distribute Helpful Material

Handouts and other content not only act as a set of resources, but help students stay focused on the activity and its purpose. For example, if you want them to improve a certain math skill , you should make material that highlights the mathematical aspects of the problem. You may decide to provide items such as:
- Data that helps quantify and add context to the problem
- Videos, presentations and other audio-visual material
- A list of preliminary questions to investigate
Providing a range of resources can be especially important for elementary students and struggling students in higher grades, who may not have self-direction skills to work without them.
4. Set Goals and Expectations for Your Students
Along with the aforementioned materials, give students a guide or rubric that details goals and expectations. It will allow you to further highlight the purpose of the problem-based learning exercise, as you can explain what you’re looking for in terms of collaboration, the final product and anything else. It should also help students stay on track by acting as a reference throughout the activity.
5. Participate

Although explicitly correcting students may be discouraged, you can still help them and ask questions to dig into their thought processes. When you see an opportunity, consider if it’s worthwhile to:
- Fill gaps in knowledge
- Provide hints, not answers
- Question a student’s conclusion or logic regarding a certain point, helping them think through tough spots
By participating in these ways, you can provide insight when students need it most, encouraging them to effectively analyze the problem.
6. Have Students Present Ideas and Findings
If you divided them into small groups, requiring students to present their thoughts and results in front the class adds a large-group learning component to the lesson. Encourage other students to ask questions, allowing the presenting group to elaborate and provide evidence for their thoughts. This wraps up the activity and gives your class a final chance to find solutions to the problem.
Wrapping Up
The effectiveness of problem-based learning may differ between classrooms and individual students, depending on how significant specific advantages and disadvantages are to you. Evaluative research consistently shows value in giving students a question and letting them take control of their learning. But the extent of this value can depend on the difficulties you face.It may be wise to try a problem-based learning activity, and go forward based on results.
Create or log into your teacher account on Prodigy -- an adaptive math game that adjusts content to accommodate player trouble spots and learning speeds. Aligned to US and Canadian curricula, it’s used by more than 350,000 teachers and 10 million students. It may be wise to try a problem-based learning activity, and go forward based on results.
Share this article
Table of Contents
Easily differentiate learning and engage your students with Prodigy Math.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is, at heart, questioning what you are told instead of taking it at face value. It is evaluating information in a rational framework where facts and reason line up to support or fail to support assertions. Critical thinking skills are highly sought, and have a number of benefits in life. However, ...
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of Critical Thinking In Education: Advantages. Disadvantages. Enhances problem-solving skills. Can hinder quick decision-making. Promotes independent thinking. May lead to overthinking. Encourages open-mindedness. Requires extensive time and resources.
The five benefits of critical thinking include enhanced problem solving, improved communication, unbiased decisions, better creativity, and innovative solutions. These advantages collectively contribute to more effective decision-making and the identification of reliable information.
Critical thinking capacity does all that and more. 4. It's a multi-faceted practice. Critical thinking is known for encompassing a wide array of disciplines, and cultivating a broad range of cognitive talents. One could indeed say that it's a cross-curricular activity for the mind, and the mind must be exercised just like a muscle to stay ...
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [1]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
Foundation for Critical Thinking. PO Box 31080 • Santa Barbara, CA 93130 . Toll Free 800.833.3645 • Fax 707.878.9111. [email protected]
Critical Thinking is the process of using and assessing reasons to evaluate statements, assumptions, and arguments in ordinary situations. The goal of this process is to help us have good beliefs, where "good" means that our beliefs meet certain goals of thought, such as truth, usefulness, or rationality. Critical thinking is widely ...
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well. Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly ...
Walking meditation: Find a peaceful place to walk for 10 to 20 feet and pay attention to your body and environment while you move. This can help you improve your sense of control over yourself and ...
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
The countless advantages of critical thinking extend far beyond the realms of academia. For starters, critical thinking fosters superior decision-making by equipping individuals with the tools to weigh options, assess consequences, and arrive at better choices. Critical thinkers also benefit from heightened self-reflection, gaining a profound ...
Theorists have noted that such skills are only valuable insofar as a person is inclined to use them. Consequently, they emphasize that certain habits of mind are necessary components of critical thinking. This disposition may include curiosity, open-mindedness, self-awareness, empathy, and persistence. Although there is a generally accepted set of qualities that are associated with critical ...
1. Difficulty in Decision-Making. Difficulty in Decision-Making. One of the biggest disadvantages of critical thinking is that it can be difficult to make decisions. Because critical thinkers are constantly analyzing and evaluating data to draw conclusions, this can be a time-consuming process.
The number of digits look right, the number ends in a '8' which the right answer should end in. Critical thinking benefits- at a glance. Make better decisions | Solve problems better | Become a persuasive communicator | Protect yourself from Cognitive biases and fallacies | Better team management | Become immune to rhetoric.
Decision-making improves. Applying critical thinking helps you make decisions that require a lot of thought. Big, life-changing decisions, like whether or not to make a career move, are aided by critical thinking, which encourages you to research and favor objective logic over your initial emotional response.
5] Stimulates Curiosity. It stimulates curiosity in you to find the right solution for the problem or the subject you are working on. Curiosity will let you dig and delve deeper to get a better result. This factor will let you stay a lifelong learner. All these aspects of critical thinking play a vital role in Banking and financial sector.
1 Barriers to critical thinking. First, let's briefly examine some barriers to critical thinking. Take another look at the visual summary below on critical and analytical thinking, which was introduced at the end of Session 3. Note the warning sign next to the 'black pit' to the lower right of this figure. Figure 1A visual summary of ...
The extensive research on teaching critical thinking at all levels in education and incorporating critical thinking in the curriculum of various courses help us conclude that most of the initial challenges and barriers to teach critical thinking are resolved now as various techniques to enhance critical thinking are proposed by researchers/studies.
The Critical-thinking Assessment Test (CAT) looks for the skills relating to. evaluating information. creative thinking. learning and problem solving. communication. ... it is useful to investigate the relevant advantages and disadvantages students bring with them into the classroom. From an equity perspective, inherent and pre-existing factors ...
One Side of the Coin: 5 Advantages of Critical Thinking. 1. You Are Able to Evaluate Issues without Bias. 2. You Can Foresee How Things Will Turn out. 3. You Communicate with Others Sharing Your Ideas Effectively. 4. You Are Trusted to Figure Out Solutions to Complex Problems.
Thinking through individual goals critically and creatively. A key component of workplace happiness is employees' sense that they are working toward something, both in terms of overall organisational goals and in terms of personal and professional growth. Regular reflection on individual goals is vital to sustaining a healthy workplace culture.
Conclusion. Critical thinking and problem solving are essential life skills that can help us make better decisions, handle conflicts more constructively, and solve complex problems more efficiently. Training and practice can help us develop these skills, and there are a number of resources available for those looking to learn more.
Used since the 1960s, many teachers express concerns about the effectiveness of problem-based learning (PBL) in certain classroom settings. Whether you introduce the student-centred pedagogy as a one-time activity or mainstay exercise, grouping students together to solve open-ended problems can present pros and cons.. Below are five advantages and disadvantages of problem-based learning to ...
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Critical Thinking Skills. 774 Words4 Pages. great bond or a rapport between the manager and his employee which eventually results in employee satisfaction. Fourth skill: Critical Thinking; Critical thinking is a very strategic tool that humans can use in their lives. Specifically, it must be done by managers ...