Essay on Media and Violence
Introduction
Research studies indicate that media causes violence and plays a role in desensitization, aggressive behavior, fear of harm, and nightmares. Examples of media platforms include movies, video games, television, and music. Violence in media has also been associated with health concerns. The youth have been the most common victims of media exposure and thus stand higher chances of exposure to violence (Anderson, 2016). In the contemporary world, violence in media platforms has been growing, reaching heightened levels, which is dangerous for society. When you turn on the television, there is violence, social media platforms; there is violence when you go to the movies; there is violence. Studies indicate that an average person in the United States watches videos for nearly five hours in a day. In addition, three-quarters of television content contain some form of violence, and the games being played today have elements of violence. This paper intends to evaluate the concept of media messages and their influence on violent and deviant behaviors. Television networks and video games will be considered.
The Netflix effect involves the behavior of staying home all day, ordering food, and relaxing the couch to watch Netflix programs (McDonald & Smith-Rowsey, 2016). Netflix and binge-watching have become popular among the younger generation and thus are exposed to different kinds of content being aired. Studies indicate that continuous exposure to violent materials has a negative effect on the aggressive behavior of individuals. Netflix is a global platform in the entertainment industry (Lobato, 2019). Although, the company does not have the rights to air in major countries such as China, India, and Japan, it has wide audience. One of the reasons for sanctions is the issues of content being aired by the platform, which may influence the behaviors of the young generation. The primary goal of Netflix is entertainment; it’s only the viewers who have developed specific effects that affect their violent behaviors through imitation of the content.
Television Networks
Television networks focus on feeding viewers with the latest updates on different happenings across the globe. In other instances, they focus on bringing up advertisements and entertainment programs. There is little room for violent messages and content in the networks unless they are airing movie programs, which also are intended for entertainment. However, there has been evidence in the violence effect witnessed in television networks. Studies called the “Marilyn Monroe effect” established that following the airing of many suicidal cases, there has been a growth in suicides among the population (Anderson, Bushman, Donnerstein, Hummer, & Warburton, 2015). Actual suicide cases increased by 2.5%, which is linked to news coverage regarding suicide. Additionally, some coverages are filled with violence descriptions, and their aftermath with may necessitate violent behaviors in the society. For instance, if televisions are covering mass demonstrations where several people have been killed, the news may trigger other protests in other parts of the country.
Communications scholars, however, dispute these effects and link the violent behaviors to the individuals’ perception. They argue that the proportion of witnessing violent content in television networks is minimal. Some acts of violence are associated with what the individual perceives and other psychological factors that are classified into social and non-social instigators (Anderson et al., 2015). Social instigators consist of social rejection, provocation, and unjust treatment. Nonsocial instigators are physical objects present, which include weapons or guns. Also, there are environmental factors that include loud noises, overcrowding, and heat. Therefore, there is more explanation of the causes of aggressive behaviors that are not initiated by television networks but rather a combination of biological and environmental factors.
Video games
Researchers have paid more attention to television networks and less on video games. Children spend more time playing video games. According to research, more than 52% of children play video games and spend about 49 minutes per day playing. Some of the games contain violent behaviors. Playing violent games among youth can cause aggressive behaviors. The acts of kicking, hitting, and pinching in the games have influenced physical aggression. However, communication scholars argue that there is no association between aggression and video games (Krahé & Busching, 2015). Researchers have used tools such as “Competition Reaction Time Test,” and “Hot Sauce Paradigm” to assess the aggression level. The “Hot Sauce Paradigm” participants were required to make hot sauce tor tasting. They were required to taste tester must finish the cup of the hot sauce in which the tester detests spicy products. It was concluded that the more the hot sauce testers added in the cup, the more aggressive they were deemed to be.
The “Competition Reaction Time Test” required individuals to compete with another in the next room. It was required to press a button fast as soon as the flashlight appeared. Whoever won was to discipline the opponent with loud noises. They could turn up the volume as high as they wanted. However, in reality, there was no person in the room; the game was to let individuals win half of the test. Researchers intended to test how far individuals would hold the dial. In theory, individuals who punish their opponents in cruel ways are perceived to be more aggressive. Another way to test violent behaviors for gamer was done by letting participants finish some words. For instance, “M_ _ _ ER,” if an individual completes the word as “Murder” rather than “Mother,” the character was considered to possess violent behavior (Allen & Anderson, 2017). In this regard, video games have been termed as entertainment ideologies, and the determination of the players is to win, no matter how brutal the game might be.
In this paper, fixed assumptions were used to correlate violent behaviors and media objects. But that was not the case with regards to the findings. A fixed model may not be appropriate in the examination of time-sensitive causes of dependent variables. Although the model is applicable for assessing specific entities in a given industry, the results may not be precise.
Conclusion .
Based on the findings of the paper, there is no relationship between violent behaviors and media. Netflix effect does not influence the behavior of individuals. The perceptions of the viewers and players is what matters, and how they understand the message being conveyed. Individuals usually play video games and watch televisions for entertainment purposes. The same case applies to the use of social media platforms and sports competitions. Even though there is violent content, individuals focus on the primary objective of their needs.
Analysis of sources
The sources have been thoroughly researched, and they provide essential information regarding the relationship between violent behaviors and media messages. Studies conducted by various authors like Krahé & Busching did not establish any relationship between the two variables. Allen & Anderson (2017) argue that the models for testing the two variables are unreliable and invalid. The fixed assumptions effect model was utilized, and its limitations have been discussed above. Therefore, the authors of these references have not been able to conclude whether there is a connection between violence and media messages.
Allen, J. J., & Anderson, C. A. (2017). General aggression model. The International Encyclopedia of Media Effects , 1-15.
Anderson, C. A. (2016). Media violence effects on children, adolescents and young adults. Health Progress , 97 (4), 59-62.
Anderson, C. A., Bushman, B. J., Donnerstein, E., Hummer, T. A., & Warburton, W. (2015). SPSSI research summary on media violence. Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy , 15 (1), 4-19.
Krahé, B., & Busching, R. (2015). Breaking the vicious cycle of media violence use and aggression: A test of intervention effects over 30 months. Psychology of Violence , 5 (2), 217.
Lobato, R. (2019). Netflix nations: the geography of digital distribution . NYU Press.
McDonald, K., & Smith-Rowsey, D. (Eds.). (2016). The Netflix effect: Technology and entertainment in the 21st century . Bloomsbury Publishing USA.

Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- How Might We Define ‘Citizenship’ within the European context?
- Essay on Electronic Health Information Exchange Organizations (HIEs)
- Essay on How Branches of Governments Provide Checks for the President
- A discussion of the efficient market hypothesis theory
- Essay on Professional Digital Innovation in Biological Asset Managemen...
- “Keep My Memory Green”: Recycling in Dickens’ Ghost Stories

Violence in the media: Psychologists study potential harmful effects
Early research on the effects of viewing violence on television—especially among children—found a desensitizing effect and the potential for aggression. Is the same true for those who play violent video games?
- Video Games
- Physical Abuse and Violence

Television and video violence
Virtually since the dawn of television, parents, teachers, legislators, and mental health professionals have wanted to understand the impact of television programs, particularly on children. Of special concern has been the portrayal of violence, particularly given psychologist Albert Bandura’s work in the 1970s on social learning and the tendency of children to imitate what they see.
As a result of 15 years of “consistently disturbing” findings about the violent content of children’s programs, the Surgeon General’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Television and Social Behavior was formed in 1969 to assess the impact of violence on the attitudes, values, and behavior of viewers. The resulting report and a follow-up report in 1982 by the National Institute of Mental Health identified these major effects of seeing violence on television:
- Children may become less sensitive to the pain and suffering of others.
- Children may be more fearful of the world around them.
- Children may be more likely to behave in aggressive or harmful ways toward others.
Research by psychologists L. Rowell Huesmann, Leonard Eron, and others starting in the 1980s found that children who watched many hours of violence on television when they were in elementary school tended to show higher levels of aggressive behavior when they became teenagers. By observing these participants into adulthood, Huesmann and Eron found that the ones who’d watched a lot of TV violence when they were 8 years old were more likely to be arrested and prosecuted for criminal acts as adults.
Interestingly, being aggressive as a child did not predict watching more violent TV as a teenager, suggesting that TV watching could be a cause rather than a consequence of aggressive behavior. However, later research by psychologists Douglas Gentile and Brad Bushman, among others, suggested that exposure to media violence is just one of several factors that can contribute to aggressive behavior.
Other research has found that exposure to media violence can desensitize people to violence in the real world and that, for some people, watching violence in the media becomes enjoyable and does not result in the anxious arousal that would be expected from seeing such imagery.
Video game violence
The advent of video games raised new questions about the potential impact of media violence, since the video game player is an active participant rather than merely a viewer. 97% of adolescents age 12–17 play video games—on a computer, on consoles such as the Wii, Playstation, and Xbox, or on portable devices such as Gameboys, smartphones, and tablets. A Pew Research Center survey in 2008 found that half of all teens reported playing a video game “yesterday,” and those who played every day typically did so for an hour or more.
Many of the most popular video games, such as “Call of Duty” and “Grand Theft Auto,” are violent; however, as video game technology is relatively new, there are fewer empirical studies of video game violence than other forms of media violence. Still, several meta-analytic reviews have reported negative effects of exposure to violence in video games.
A 2010 review by psychologist Craig A. Anderson and others concluded that “the evidence strongly suggests that exposure to violent video games is a causal risk factor for increased aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, and aggressive affect and for decreased empathy and prosocial behavior.” Anderson’s earlier research showed that playing violent video games can increase a person’s aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior both in laboratory settings and in daily life. “One major conclusion from this and other research on violent entertainment media is that content matters,” says Anderson.
Other researchers, including psychologist Christopher J. Ferguson, have challenged the position that video game violence harms children. While his own 2009 meta-analytic review reported results similar to Anderson’s, Ferguson contends that laboratory results have not translated into real world, meaningful effects. He also claims that much of the research into video game violence has failed to control for other variables such as mental health and family life, which may have impacted the results. His work has found that children who are already at risk may be more likely to choose to play violent video games. According to Ferguson, these other risk factors, as opposed to the games, cause aggressive and violent behavior.
APA launched an analysis in 2013 of peer-reviewed research on the impact of media violence and is reviewing its policy statements in the area.
Anderson, C.A., Ihori, Nobuko, Bushman, B.J., Rothstein, H.R., Shibuya, A., Swing, E.L., Sakamoto, A., & Saleem, M. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in Eastern and Western countries: A Meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin , Vol. 126, No. 2.
Anderson, C. A., Carnagey, N. L. & Eubanks, J. (2003). Exposure to violent media: The effects of songs with violent lyrics on aggressive thoughts and feelings. Journal of Personality and Social Psycholog y, Vol. 84, No. 5.
Anderson, C. A., & Dill, K. E. (2000). Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , Vol. 78, No. 4.
Ferguson, C.J. (2011). Video games and youth violence: A Prospective analysis in adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence , Vol. 40, No. 4.
Gentile, D.A., & Bushman, B.J. (2012). Reassessing media violence effects using a risk and resilience approach to understanding aggression. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , Vol. 1, No. 3.
Huesmann, L. R., & Eron, L. D. (1986). Television and the aggressive child: A cross-national comparison. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Huesmann, L. R., Moise-Titus, J., Podolski, C. L., & Eron, L. D. (2003). Longitudinal relations between children’s exposure to TV violence and their aggressive and violent behavior in young adulthood: 1977–1992. Developmental Psychology , Vol. 39, No. 2, 201–221.
Huston, A. C., Donnerstein, E., Fairchild, H., Feshbach, N. D., Katz, P. A., Murray, J. P., Rubinstein, E. A., Wilcox, B. & Zuckerman, D. (1992). Big world, small screen: The role of television in American society. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
Krahe, B., Moller, I., Kirwil, L., Huesmann, L.R., Felber, J., & Berger, A. (2011). Desensitization to media violence: Links with habitual media violence exposure, aggressive cognitions, and aggressive behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , Vol. 100, No. 4.
Murray, J. P. (1973). Television and violence: Implications of the Surgeon General’s research program. American Psychologist , Vol. 28, 472–478.
National Institute of Mental Health (1982). Television and behavior: Ten years of scientific progress and implications for the eighties, Vol. 1. Rockville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Recommended Reading
You may also like.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Corrections
- Crime, Media, and Popular Culture
- Criminal Behavior
- Criminological Theory
- Critical Criminology
- Geography of Crime
- International Crime
- Juvenile Justice
- Prevention/Public Policy
- Race, Ethnicity, and Crime
- Research Methods
- Victimology/Criminal Victimization
- White Collar Crime
- Women, Crime, and Justice
- Share Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Violence, media effects, and criminology.
- Nickie D. Phillips Nickie D. Phillips Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice, St. Francis College
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264079.013.189
- Published online: 27 July 2017
Debate surrounding the impact of media representations on violence and crime has raged for decades and shows no sign of abating. Over the years, the targets of concern have shifted from film to comic books to television to video games, but the central questions remain the same. What is the relationship between popular media and audience emotions, attitudes, and behaviors? While media effects research covers a vast range of topics—from the study of its persuasive effects in advertising to its positive impact on emotions and behaviors—of particular interest to criminologists is the relationship between violence in popular media and real-life aggression and violence. Does media violence cause aggression and/or violence?
The study of media effects is informed by a variety of theoretical perspectives and spans many disciplines including communications and media studies, psychology, medicine, sociology, and criminology. Decades of research have amassed on the topic, yet there is no clear agreement about the impact of media or about which methodologies are most appropriate. Instead, there continues to be disagreement about whether media portrayals of violence are a serious problem and, if so, how society should respond.
Conflicting interpretations of research findings inform and shape public debate around media effects. Although there seems to be a consensus among scholars that exposure to media violence impacts aggression, there is less agreement around its potential impact on violence and criminal behavior. While a few criminologists focus on the phenomenon of copycat crimes, most rarely engage with whether media directly causes violence. Instead, they explore broader considerations of the relationship between media, popular culture, and society.
- media exposure
- criminal behavior
- popular culture
- media violence
- media and crime
- copycat crimes
Media Exposure, Violence, and Aggression
On Friday July 22, 2016 , a gunman killed nine people at a mall in Munich, Germany. The 18-year-old shooter was subsequently characterized by the media as being under psychiatric care and harboring at least two obsessions. One, an obsession with mass shootings, including that of Anders Breivik who ultimately killed 77 people in Norway in 2011 , and the other an obsession with video games. A Los Angeles, California, news report stated that the gunman was “an avid player of first-person shooter video games, including ‘Counter-Strike,’” while another headline similarly declared, “Munich gunman, a fan of violent video games, rampage killers, had planned attack for a year”(CNN Wire, 2016 ; Reuters, 2016 ). This high-profile incident was hardly the first to link popular culture to violent crime. Notably, in the aftermath of the 1999 Columbine shooting massacre, for example, media sources implicated and later discredited music, video games, and a gothic aesthetic as causal factors of the crime (Cullen, 2009 ; Yamato, 2016 ). Other, more recent, incidents have echoed similar claims suggesting that popular culture has a nefarious influence on consumers.
Media violence and its impact on audiences are among the most researched and examined topics in communications studies (Hetsroni, 2007 ). Yet, debate over whether media violence causes aggression and violence persists, particularly in response to high-profile criminal incidents. Blaming video games, and other forms of media and popular culture, as contributing to violence is not a new phenomenon. However, interpreting media effects can be difficult because commenters often seem to indicate a grand consensus that understates more contradictory and nuanced interpretations of the data.
In fact, there is a consensus among many media researchers that media violence has an impact on aggression although its impact on violence is less clear. For example, in response to the shooting in Munich, Brad Bushman, professor of communication and psychology, avoided pinning the incident solely on video games, but in the process supported the assertion that video gameplay is linked to aggression. He stated,
While there isn’t complete consensus in any scientific field, a study we conducted showed more than 90% of pediatricians and about two-thirds of media researchers surveyed agreed that violent video games increase aggression in children. (Bushman, 2016 )
Others, too, have reached similar conclusions with regard to other media. In 2008 , psychologist John Murray summarized decades of research stating, “Fifty years of research on the effect of TV violence on children leads to the inescapable conclusion that viewing media violence is related to increases in aggressive attitudes, values, and behaviors” (Murray, 2008 , p. 1212). Scholars Glenn Sparks and Cheri Sparks similarly declared that,
Despite the fact that controversy still exists about the impact of media violence, the research results reveal a dominant and consistent pattern in favor of the notion that exposure to violent media images does increase the risk of aggressive behavior. (Sparks & Sparks, 2002 , p. 273)
In 2014 , psychologist Wayne Warburton more broadly concluded that the vast majority of studies have found “that exposure to violent media increases the likelihood of aggressive behavior in the short and longterm, increases hostile perceptions and attitudes, and desensitizes individuals to violent content” (Warburton, 2014 , p. 64).
Criminologists, too, are sensitive to the impact of media exposure. For example, Jacqueline Helfgott summarized the research:
There have been over 1000 studies on the effects of TV and film violence over the past 40 years. Research on the influence of TV violence on aggression has consistently shown that TV violence increases aggression and social anxiety, cultivates a “mean view” of the world, and negatively impacts real-world behavior. (Helfgott, 2015 , p. 50)
In his book, Media Coverage of Crime and Criminal Justice , criminologist Matthew Robinson stated, “Studies of the impact of media on violence are crystal clear in their findings and implications for society” (Robinson, 2011 , p. 135). He cited studies on childhood exposure to violent media leading to aggressive behavior as evidence. In his pioneering book Media, Crime, and Criminal Justice , criminologist Ray Surette concurred that media violence is linked to aggression, but offered a nuanced interpretation. He stated,
a small to modest but genuine causal role for media violence regarding viewer aggression has been established for most beyond a reasonable doubt . . . There is certainly a connection between violent media and social aggression, but its strength and configuration is simply not known at this time. (Surette, 2011 , p. 68)
The uncertainties about the strength of the relationship and the lack of evidence linking media violence to real-world violence is often lost in the news media accounts of high-profile violent crimes.
Media Exposure and Copycat Crimes
While many scholars do seem to agree that there is evidence that media violence—whether that of film, TV, or video games—increases aggression, they disagree about its impact on violent or criminal behavior (Ferguson, 2014 ; Gunter, 2008 ; Helfgott, 2015 ; Reiner, 2002 ; Savage, 2008 ). Nonetheless, it is violent incidents that most often prompt speculation that media causes violence. More specifically, violence that appears to mimic portrayals of violent media tends to ignite controversy. For example, the idea that films contribute to violent crime is not a new assertion. Films such as A Clockwork Orange , Menace II Society , Set it Off , and Child’s Play 3 , have been linked to crimes and at least eight murders have been linked to Oliver Stone’s 1994 film Natural Born Killers (Bracci, 2010 ; Brooks, 2002 ; PBS, n.d. ). Nonetheless, pinpointing a direct, causal relationship between media and violent crime remains elusive.
Criminologist Jacqueline Helfgott defined copycat crime as a “crime that is inspired by another crime” (Helfgott, 2015 , p. 51). The idea is that offenders model their behavior on media representations of violence whether real or fictional. One case, in particular, illustrated how popular culture, media, and criminal violence converge. On July 20, 2012 , James Holmes entered the midnight premiere of The Dark Knight Rises , the third film in the massively successful Batman trilogy, in a movie theater in Aurora, Colorado. He shot and killed 12 people and wounded 70 others. At the time, the New York Times described the incident,
Witnesses told the police that Mr. Holmes said something to the effect of “I am the Joker,” according to a federal law enforcement official, and that his hair had been dyed or he was wearing a wig. Then, as people began to rise from their seats in confusion or anxiety, he began to shoot. The gunman paused at least once, several witnesses said, perhaps to reload, and continued firing. (Frosch & Johnson, 2012 ).
The dyed hair, Holme’s alleged comment, and that the incident occurred at a popular screening led many to speculate that the shooter was influenced by the earlier film in the trilogy and reignited debate around the impact about media violence. The Daily Mail pointed out that Holmes may have been motivated by a 25-year-old Batman comic in which a gunman opens fire in a movie theater—thus further suggesting the iconic villain served as motivation for the attack (Graham & Gallagher, 2012 ). Perceptions of the “Joker connection” fed into the notion that popular media has a direct causal influence on violent behavior even as press reports later indicated that Holmes had not, in fact, made reference to the Joker (Meyer, 2015 ).
A week after the Aurora shooting, the New York Daily News published an article detailing a “possible copycat” crime. A suspect was arrested in his Maryland home after making threatening phone calls to his workplace. The article reported that the suspect stated, “I am a [sic] joker” and “I’m going to load my guns and blow everybody up.” In their search, police found “a lethal arsenal of 25 guns and thousands of rounds of ammunition” in the suspect’s home (McShane, 2012 ).
Though criminologists are generally skeptical that those who commit violent crimes are motivated solely by media violence, there does seem to be some evidence that media may be influential in shaping how some offenders commit crime. In his study of serious and violent juvenile offenders, criminologist Ray Surette found “about one out of three juveniles reports having considered a copycat crime and about one out of four reports actually having attempted one.” He concluded that “those juveniles who are self-reported copycats are significantly more likely to credit the media as both a general and personal influence.” Surette contended that though violent offenses garner the most media attention, copycat criminals are more likely to be career criminals and to commit property crimes rather than violent crimes (Surette, 2002 , pp. 56, 63; Surette 2011 ).
Discerning what crimes may be classified as copycat crimes is a challenge. Jacqueline Helfgott suggested they occur on a “continuum of influence.” On one end, she said, media plays a relatively minor role in being a “component of the modus operandi” of the offender, while on the other end, she said, “personality disordered media junkies” have difficulty distinguishing reality from violent fantasy. According to Helfgott, various factors such as individual characteristics, characteristics of media sources, relationship to media, demographic factors, and cultural factors are influential. Overall, scholars suggest that rather than pushing unsuspecting viewers to commit crimes, media more often influences how , rather than why, someone commits a crime (Helfgott, 2015 ; Marsh & Melville, 2014 ).
Given the public interest, there is relatively little research devoted to exactly what copycat crimes are and how they occur. Part of the problem of studying these types of crimes is the difficulty defining and measuring the concept. In an effort to clarify and empirically measure the phenomenon, Surette offered a scale that included seven indicators of copycat crimes. He used the following factors to identify copycat crimes: time order (media exposure must occur before the crime); time proximity (a five-year cut-off point of exposure); theme consistency (“a pattern of thought, feeling or behavior in the offender which closely parallels the media model”); scene specificity (mimicking a specific scene); repetitive viewing; self-editing (repeated viewing of single scene while “the balance of the film is ignored”); and offender statements and second-party statements indicating the influence of media. Findings demonstrated that cases are often prematurely, if not erroneously, labeled as “copycat.” Surette suggested that use of the scale offers a more precise way for researchers to objectively measure trends and frequency of copycat crimes (Surette, 2016 , p. 8).
Media Exposure and Violent Crimes
Overall, a causal link between media exposure and violent criminal behavior has yet to be validated, and most researchers steer clear of making such causal assumptions. Instead, many emphasize that media does not directly cause aggression and violence so much as operate as a risk factor among other variables (Bushman & Anderson, 2015 ; Warburton, 2014 ). In their review of media effects, Brad Bushman and psychologist Craig Anderson concluded,
In sum, extant research shows that media violence is a causal risk factor not only for mild forms of aggression but also for more serious forms of aggression, including violent criminal behavior. That does not mean that violent media exposure by itself will turn a normal child or adolescent who has few or no other risk factors into a violent criminal or a school shooter. Such extreme violence is rare, and tends to occur only when multiple risk factors converge in time, space, and within an individual. (Bushman & Anderson, 2015 , p. 1817)
Surette, however, argued that there is no clear linkage between media exposure and criminal behavior—violent or otherwise. In other words, a link between media violence and aggression does not necessarily mean that exposure to violent media causes violent (or nonviolent) criminal behavior. Though there are thousands of articles addressing media effects, many of these consist of reviews or commentary about prior research findings rather than original studies (Brown, 2007 ; Murray, 2008 ; Savage, 2008 ; Surette, 2011 ). Fewer, still, are studies that specifically measure media violence and criminal behavior (Gunter, 2008 ; Strasburger & Donnerstein, 2014 ). In their meta-analysis investigating the link between media violence and criminal aggression, scholars Joanne Savage and Christina Yancey did not find support for the assertion. Instead, they concluded,
The study of most consequence for violent crime policy actually found that exposure to media violence was significantly negatively related to violent crime rates at the aggregate level . . . It is plain to us that the relationship between exposure to violent media and serious violence has yet to be established. (Savage & Yancey, 2008 , p. 786)
Researchers continue to measure the impact of media violence among various forms of media and generally stop short of drawing a direct causal link in favor of more indirect effects. For example, one study examined the increase of gun violence in films over the years and concluded that violent scenes provide scripts for youth that justify gun violence that, in turn, may amplify aggression (Bushman, Jamieson, Weitz, & Romer, 2013 ). But others report contradictory findings. Patrick Markey and colleagues studied the relationship between rates of homicide and aggravated assault and gun violence in films from 1960–2012 and found that over the years, violent content in films increased while crime rates declined . After controlling for age shifts, poverty, education, incarceration rates, and economic inequality, the relationships remained statistically non-significant (Markey, French, & Markey, 2015 , p. 165). Psychologist Christopher Ferguson also failed to find a relationship between media violence in films and video games and violence (Ferguson, 2014 ).
Another study, by Gordon Dahl and Stefano DellaVigna, examined violent films from 1995–2004 and found decreases in violent crimes coincided with violent blockbuster movie attendance. Here, it was not the content that was alleged to impact crime rates, but instead what the authors called “voluntary incapacitation,” or the shifting of daily activities from that of potential criminal behavior to movie attendance. The authors concluded, “For each million people watching a strongly or mildly violent movie, respectively, violent crime decreases by 1.9% and 2.1%. Nonviolent movies have no statistically significant impact” (Dahl & DellaVigna, p. 39).
High-profile cases over the last several years have shifted public concern toward the perceived danger of video games, but research demonstrating a link between video games and criminal violence remains scant. The American Psychiatric Association declared that “research demonstrates a consistent relation between violent video game use and increases in aggressive behavior, aggressive cognitions and aggressive affect, and decreases in prosocial behavior, empathy and sensitivity to aggression . . .” but stopped short of claiming that video games impact criminal violence. According to Breuer and colleagues, “While all of the available meta-analyses . . . found a relationship between aggression and the use of (violent) video games, the size and interpretation of this connection differ largely between these studies . . .” (APA, 2015 ; Breuer et al., 2015 ; DeCamp, 2015 ). Further, psychologists Patrick Markey, Charlotte Markey, and Juliana French conducted four time-series analyses investigating the relationship between video game habits and assault and homicide rates. The studies measured rates of violent crime, the annual and monthly video game sales, Internet searches for video game walkthroughs, and rates of violent crime occurring after the release dates of popular games. The results showed that there was no relationship between video game habits and rates of aggravated assault and homicide. Instead, there was some indication of decreases in crime (Markey, Markey, & French, 2015 ).
Another longitudinal study failed to find video games as a predictor of aggression, instead finding support for the “selection hypothesis”—that physically aggressive individuals (aged 14–17) were more likely to choose media content that contained violence than those slightly older, aged 18–21. Additionally, the researchers concluded,
that violent media do not have a substantial impact on aggressive personality or behavior, at least in the phases of late adolescence and early adulthood that we focused on. (Breuer, Vogelgesang, Quandt, & Festl, 2015 , p. 324)
Overall, the lack of a consistent finding demonstrating that media exposure causes violent crime may not be particularly surprising given that studies linking media exposure, aggression, and violence suffer from a host of general criticisms. By way of explanation, social theorist David Gauntlett maintained that researchers frequently employ problematic definitions of aggression and violence, questionable methodologies, rely too much on fictional violence, neglect the social meaning of violence, and assume the third-person effect—that is, assume that other, vulnerable people are impacted by media, but “we” are not (Ferguson & Dyck, 2012 ; Gauntlett, 2001 ).
Others, such as scholars Martin Barker and Julian Petley, flatly reject the notion that violent media exposure is a causal factor for aggression and/or violence. In their book Ill Effects , the authors stated instead that it is simply “stupid” to query about “what are the effects of [media] violence” without taking context into account (p. 2). They counter what they describe as moral campaigners who advance the idea that media violence causes violence. Instead, Barker and Petley argue that audiences interpret media violence in a variety of ways based on their histories, experiences, and knowledge, and as such, it makes little sense to claim media “cause” violence (Barker & Petley, 2001 ).
Given the seemingly inconclusive and contradictory findings regarding media effects research, to say that the debate can, at times, be contentious is an understatement. One article published in European Psychologist queried “Does Doing Media Violence Research Make One Aggressive?” and lamented that the debate had devolved into an ideological one (Elson & Ferguson, 2013 ). Another academic journal published a special issue devoted to video games and youth and included a transcript of exchanges between two scholars to demonstrate that a “peaceful debate” was, in fact, possible (Ferguson & Konijn, 2015 ).
Nonetheless, in this debate, the stakes are high and the policy consequences profound. After examining over 900 published articles, publication patterns, prominent authors and coauthors, and disciplinary interest in the topic, scholar James Anderson argued that prominent media effects scholars, whom he deems the “causationists,” had developed a cottage industry dependent on funding by agencies focused primarily on the negative effects of media on children. Anderson argued that such a focus presents media as a threat to family values and ultimately operates as a zero-sum game. As a result, attention and resources are diverted toward media and away from other priorities that are essential to understanding aggression such as social disadvantage, substance abuse, and parental conflict (Anderson, 2008 , p. 1276).
Theoretical Perspectives on Media Effects
Understanding how media may impact attitudes and behavior has been the focus of media and communications studies for decades. Numerous theoretical perspectives offer insight into how and to what extent the media impacts the audience. As scholar Jenny Kitzinger documented in 2004 , there are generally two ways to approach the study of media effects. One is to foreground the power of media. That is, to suggest that the media holds powerful sway over viewers. Another perspective is to foreground the power and heterogeneity of the audience and to recognize that it is comprised of active agents (Kitzinger, 2004 ).
The notion of an all-powerful media can be traced to the influence of scholars affiliated with the Institute for Social Research, or Frankfurt School, in the 1930–1940s and proponents of the mass society theory. The institute was originally founded in Germany but later moved to the United States. Criminologist Yvonne Jewkes outlined how mass society theory assumed that members of the public were susceptible to media messages. This, theorists argued, was a result of rapidly changing social conditions and industrialization that produced isolated, impressionable individuals “cut adrift from kinship and organic ties and lacking moral cohesion” (Jewkes, 2015 , p. 13). In this historical context, in the era of World War II, the impact of Nazi propaganda was particularly resonant. Here, the media was believed to exhibit a unidirectional flow, operating as a powerful force influencing the masses. The most useful metaphor for this perspective described the media as a “hypodermic syringe” that could “‘inject’ values, ideas and information directly into the passive receiver producing direct and unmediated ‘effects’” (Jewkes, 2015 , pp. 16, 34). Though the hypodermic syringe model seems simplistic today, the idea that the media is all-powerful continues to inform contemporary public discourse around media and violence.
Concern of the power of media captured the attention of researchers interested in its purported negative impact on children. In one of the earliest series of studies in the United States during the late 1920s–1930s, researchers attempted to quantitatively measure media effects with the Payne Fund Studies. For example, they investigated how film, a relatively new medium, impacted children’s attitudes and behaviors, including antisocial and violent behavior. At the time, the Payne Fund Studies’ findings fueled the notion that children were indeed negatively influenced by films. This prompted the film industry to adopt a self-imposed code regulating content (Sparks & Sparks, 2002 ; Surette, 2011 ). Not everyone agreed with the approach. In fact, the methodologies employed in the studies received much criticism, and ultimately, the movement was branded as a moral crusade to regulate film content. Scholars Garth Jowett, Ian Jarvie, and Kathryn Fuller wrote about the significance of the studies,
We have seen this same policy battle fought and refought over radio, television, rock and roll, music videos and video games. Their researchers looked to see if intuitive concerns could be given concrete, measurable expression in research. While they had partial success, as have all subsequent efforts, they also ran into intractable problems . . . Since that day, no way has yet been found to resolve the dilemma of cause and effect: do crime movies create more crime, or do the criminally inclined enjoy and perhaps imitate crime movies? (Jowett, Jarvie, & Fuller, 1996 , p. 12)
As the debate continued, more sophisticated theoretical perspectives emerged. Efforts to empirically measure the impact of media on aggression and violence continued, albeit with equivocal results. In the 1950s and 1960s, psychological behaviorism, or understanding psychological motivations through observable behavior, became a prominent lens through which to view the causal impact of media violence. This type of research was exemplified by Albert Bandura’s Bobo Doll studies demonstrating that children exposed to aggressive behavior, either observed in real life or on film, behaved more aggressively than those in control groups who were not exposed to the behavior. The assumption derived was that children learn through exposure and imitate behavior (Bandura, Ross, & Ross, 1963 ). Though influential, the Bandura experiments were nevertheless heavily criticized. Some argued the laboratory conditions under which children were exposed to media were not generalizable to real-life conditions. Others challenged the assumption that children absorb media content in an unsophisticated manner without being able to distinguish between fantasy and reality. In fact, later studies did find children to be more discerning consumers of media than popularly believed (Gauntlett, 2001 ).
Hugely influential in our understandings of human behavior, the concept of social learning has been at the core of more contemporary understandings of media effects. For example, scholar Christopher Ferguson noted that the General Aggression Model (GAM), rooted in social learning and cognitive theory, has for decades been a dominant model for understanding how media impacts aggression and violence. GAM is described as the idea that “aggression is learned by the activation and repetition of cognitive scripts coupled with the desensitization of emotional responses due to repeated exposure.” However, Ferguson noted that its usefulness has been debated and advocated for a paradigm shift (Ferguson, 2013 , pp. 65, 27; Krahé, 2014 ).
Though the methodologies of the Payne Fund Studies and Bandura studies were heavily criticized, concern over media effects continued to be tied to larger moral debates including the fear of moral decline and concern over the welfare of children. Most notably, in the 1950s, psychiatrist Frederic Wertham warned of the dangers of comic books, a hugely popular medium at the time, and their impact on juveniles. Based on anecdotes and his clinical experience with children, Wertham argued that images of graphic violence and sexual debauchery in comic books were linked to juvenile delinquency. Though he was far from the only critic of comic book content, his criticisms reached the masses and gained further notoriety with the publication of his 1954 book, Seduction of the Innocent . Wertham described the comic book content thusly,
The stories have a lot of crime and gunplay and, in addition, alluring advertisements of guns, some of them full-page and in bright colors, with four guns of various sizes and descriptions on a page . . . Here is the repetition of violence and sexiness which no Freud, Krafft-Ebing or Havelock Ellis ever dreamed could be offered to children, and in such profusion . . . I have come to the conclusion that this chronic stimulation, temptation and seduction by comic books, both their content and their alluring advertisements of knives and guns, are contributing factors to many children’s maladjustment. (Wertham, 1954 , p. 39)
Wertham’s work was instrumental in shaping public opinion and policies about the dangers of comic books. Concern about the impact of comics reached its apex in 1954 with the United States Senate Judiciary Subcommittee on Juvenile Delinquency. Wertham testified before the committee, arguing that comics were a leading cause of juvenile delinquency. Ultimately, the protest of graphic content in comic books by various interest groups contributed to implementation of the publishers’ self-censorship code, the Comics Code Authority, which essentially designated select books that were deemed “safe” for children (Nyberg, 1998 ). The code remained in place for decades, though it was eventually relaxed and decades later phased out by the two most dominant publishers, DC and Marvel.
Wertham’s work, however influential in impacting the comic industry, was ultimately panned by academics. Although scholar Bart Beaty characterized Wertham’s position as more nuanced, if not progressive, than the mythology that followed him, Wertham was broadly dismissed as a moral reactionary (Beaty, 2005 ; Phillips & Strobl, 2013 ). The most damning criticism of Wertham’s work came decades later, from Carol Tilley’s examination of Wertham’s files. She concluded that in Seduction of the Innocent ,
Wertham manipulated, overstated, compromised, and fabricated evidence—especially that evidence he attributed to personal clinical research with young people—for rhetorical gain. (Tilley, 2012 , p. 386)
Tilley linked Wertham’s approach to that of the Frankfurt theorists who deemed popular culture a social threat and contended that Wertham was most interested in “cultural correction” rather than scientific inquiry (Tilley, 2012 , p. 404).
Over the decades, concern about the moral impact of media remained while theoretical and methodological approaches to media effects studies continued to evolve (Rich, Bickham, & Wartella, 2015 ). In what many consider a sophisticated development, theorists began to view the audience as more active and multifaceted than the mass society perspective allowed (Kitzinger, 2004 ). One perspective, based on a “uses and gratifications” model, assumes that rather than a passive audience being injected with values and information, a more active audience selects and “uses” media as a response to their needs and desires. Studies of uses and gratifications take into account how choice of media is influenced by one’s psychological and social circumstances. In this context, media provides a variety of functions for consumers who may engage with it for the purposes of gathering information, reducing boredom, seeking enjoyment, or facilitating communication (Katz, Blumler, & Gurevitch, 1973 ; Rubin, 2002 ). This approach differs from earlier views in that it privileges the perspective and agency of the audience.
Another approach, the cultivation theory, gained momentum among researchers in the 1970s and has been of particular interest to criminologists. It focuses on how television television viewing impacts viewers’ attitudes toward social reality. The theory was first introduced by communications scholar George Gerbner, who argued the importance of understanding messages that long-term viewers absorb. Rather than examine the effect of specific content within any given programming, cultivation theory,
looks at exposure to massive flows of messages over long periods of time. The cultivation process takes place in the interaction of the viewer with the message; neither the message nor the viewer are all-powerful. (Gerbner, Gross, Morgan, Singnorielli, & Shanahan, 2002 , p. 48)
In other words, he argued, television viewers are, over time, exposed to messages about the way the world works. As Gerbner and colleagues stated, “continued exposure to its messages is likely to reiterate, confirm, and nourish—that is, cultivate—its own values and perspectives” (p. 49).
One of the most well-known consequences of heavy media exposure is what Gerbner termed the “mean world” syndrome. He coined it based on studies that found that long-term exposure to media violence among heavy television viewers, “tends to cultivate the image of a relatively mean and dangerous world” (p. 52). Inherent in Gerbner’s view was that media representations are separate and distinct entities from “real life.” That is, it is the distorted representations of crime and violence that cultivate the notion that the world is a dangerous place. In this context, Gerbner found that heavy television viewers are more likely to be fearful of crime and to overestimate their chances of being a victim of violence (Gerbner, 1994 ).
Though there is evidence in support of cultivation theory, the strength of the relationship between media exposure and fear of crime is inconclusive. This is in part due to the recognition that audience members are not homogenous. Instead, researchers have found that there are many factors that impact the cultivating process. This includes, but is not limited to, “class, race, gender, place of residence, and actual experience of crime” (Reiner, 2002 ; Sparks, 1992 ). Or, as Ted Chiricos and colleagues remarked in their study of crime news and fear of crime, “The issue is not whether media accounts of crime increase fear, but which audiences, with which experiences and interests, construct which meanings from the messages received” (Chiricos, Eschholz, & Gertz, p. 354).
Other researchers found that exposure to media violence creates a desensitizing effect, that is, that as viewers consume more violent media, they become less empathetic as well as psychologically and emotionally numb when confronted with actual violence (Bartholow, Bushman, & Sestir, 2006 ; Carnagey, Anderson, & Bushman, 2007 ; Cline, Croft, & Courrier, 1973 ; Fanti, Vanman, Henrich, & Avraamides, 2009 ; Krahé et al., 2011 ). Other scholars such as Henry Giroux, however, point out that our contemporary culture is awash in violence and “everyone is infected.” From this perspective, the focus is not on certain individuals whose exposure to violent media leads to a desensitization of real-life violence, but rather on the notion that violence so permeates society that it has become normalized in ways that are divorced from ethical and moral implications. Giroux wrote,
While it would be wrong to suggest that the violence that saturates popular culture directly causes violence in the larger society, it is arguable that such violence serves not only to produce an insensitivity to real life violence but also functions to normalize violence as both a source of pleasure and as a practice for addressing social issues. When young people and others begin to believe that a world of extreme violence, vengeance, lawlessness, and revenge is the only world they inhabit, the culture and practice of real-life violence is more difficult to scrutinize, resist, and transform . . . (Giroux, 2015 )
For Giroux, the danger is that the normalization of violence has become a threat to democracy itself. In our culture of mass consumption shaped by neoliberal logics, depoliticized narratives of violence have become desired forms of entertainment and are presented in ways that express tolerance for some forms of violence while delegitimizing other forms of violence. In their book, Disposable Futures , Brad Evans and Henry Giroux argued that as the spectacle of violence perpetuates fear of inevitable catastrophe, it reinforces expansion of police powers, increased militarization and other forms of social control, and ultimately renders marginalized members of the populace disposable (Evans & Giroux, 2015 , p. 81).
Criminology and the “Media/Crime Nexus”
Most criminologists and sociologists who focus on media and crime are generally either dismissive of the notion that media violence directly causes violence or conclude that findings are more complex than traditional media effects models allow, preferring to focus attention on the impact of media violence on society rather than individual behavior (Carrabine, 2008 ; Ferrell, Hayward, & Young, 2015 ; Jewkes, 2015 ; Kitzinger, 2004 ; Marsh & Melville, 2014 ; Rafter, 2006 ; Sternheimer, 2003 ; Sternheimer 2013 ; Surette, 2011 ). Sociologist Karen Sternheimer forcefully declared “media culture is not the root cause of American social problems, not the Big Bad Wolf, as our ongoing public discussion would suggest” (Sternheimer, 2003 , p. 3). Sternheimer rejected the idea that media causes violence and argued that a false connection has been forged between media, popular culture, and violence. Like others critical of a singular focus on media, Sternheimer posited that overemphasis on the perceived dangers of media violence serves as a red herring that directs attention away from the actual causes of violence rooted in factors such as poverty, family violence, abuse, and economic inequalities (Sternheimer, 2003 , 2013 ). Similarly, in her Media and Crime text, Yvonne Jewkes stated that U.K. scholars tend to reject findings of a causal link because the studies are too reductionist; criminal behavior cannot be reduced to a single causal factor such as media consumption. Echoing Gauntlett’s critiques of media effects research, Jewkes stated that simplistic causal assumptions ignore “the wider context of a lifetime of meaning-making” (Jewkes, 2015 , p. 17).
Although they most often reject a “violent media cause violence” relationship, criminologists do not dismiss the notion of media as influential. To the contrary, over the decades much criminological interest has focused on the construction of social problems, the ideological implications of media, and media’s potential impact on crime policies and social control. Eamonn Carrabine noted that the focus of concern is not whether media directly causes violence but on “how the media promote damaging stereotypes of social groups, especially the young, to uphold the status quo” (Carrabine, 2008 , p. 34). Theoretically, these foci have been traced to the influence of cultural and Marxist studies. For example, criminologists frequently focus on how social anxieties and class inequalities impact our understandings of the relationship between media violence and attitudes, values, and behaviors. Influential works in the 1970s, such as Policing the Crisis: Mugging, the State, and Law and Order by Stuart Hall et al. and Stanley Cohen’s Folk Devils and Moral Panics , shifted criminological critique toward understanding media as a hegemonic force that reinforces state power and social control (Brown, 2011 ; Carrabine, 2008 ; Cohen, 2005 ; Garland, 2008 ; Hall et al., 2013 /1973, 2013/1973 ). Since that time, moral panic has become a common framework applied to public discourse around a variety of social issues including road rage, child abuse, popular music, sex panics, and drug abuse among others.
Into the 21st century , advances in technology, including increased use of social media, shifted the ways that criminologists approach the study of media effects. Scholar Sheila Brown traced how research in criminology evolved from a focus on “media and crime” to what she calls the “media/crime nexus” that recognizes that “media experience is real experience” (Brown, 2011 , p. 413). In other words, many criminologists began to reject as fallacy what social media theorist Nathan Jurgenson deemed “digital dualism,” or the notion that we have an “online” existence that is separate and distinct from our “off-line” existence. Instead, we exist simultaneously both online and offline, an
augmented reality that exists at the intersection of materiality and information, physicality and digitality, bodies and technology, atoms and bits, the off and the online. It is wrong to say “IRL” [in real life] to mean offline: Facebook is real life. (Jurgenson, 2012 )
The changing media landscape has been of particular interest to cultural criminologists. Michelle Brown recognized the omnipresence of media as significant in terms of methodological preferences and urged a move away from a focus on causality and predictability toward a more fluid approach that embraces the complex, contemporary media-saturated social reality characterized by uncertainty and instability (Brown, 2007 ).
Cultural criminologists have indeed rejected direct, causal relationships in favor of the recognition that social meanings of aggression and violence are constantly in transition, flowing through the media landscape, where “bits of information reverberate and bend back on themselves, creating a fluid porosity of meaning that defines late-modern life, and the nature of crime and media within it.” In other words, there is no linear relationship between crime and its representation. Instead, crime is viewed as inseparable from the culture in which our everyday lives are constantly re-created in loops and spirals that “amplify, distort, and define the experience of crime and criminality itself” (Ferrell, Hayward, & Young, 2015 , pp. 154–155). As an example of this shift in understanding media effects, criminologist Majid Yar proposed that we consider how the transition from being primarily consumers to primarily producers of content may serve as a motivating mechanism for criminal behavior. Here, Yar is suggesting that the proliferation of user-generated content via media technologies such as social media (i.e., the desire “to be seen” and to manage self-presentation) has a criminogenic component worthy of criminological inquiry (Yar, 2012 ). Shifting attention toward the media/crime nexus and away from traditional media effects analyses opens possibilities for a deeper understanding of the ways that media remains an integral part of our everyday lives and inseparable from our understandings of and engagement with crime and violence.
Over the years, from films to comic books to television to video games to social media, concerns over media effects have shifted along with changing technologies. While there seems to be some consensus that exposure to violent media impacts aggression, there is little evidence showing its impact on violent or criminal behavior. Nonetheless, high-profile violent crimes continue to reignite public interest in media effects, particularly with regard to copycat crimes.
At times, academic debate around media effects remains contentious and one’s academic discipline informs the study and interpretation of media effects. Criminologists and sociologists are generally reluctant to attribute violence and criminal behavior directly to exposure to violence media. They are, however, not dismissive of the impact of media on attitudes, social policies, and social control as evidenced by the myriad of studies on moral panics and other research that addresses the relationship between media, social anxieties, gender, race, and class inequalities. Scholars who study media effects are also sensitive to the historical context of the debates and ways that moral concerns shape public policies. The self-regulating codes of the film industry and the comic book industry have led scholars to be wary of hyperbole and policy overreach in response to claims of media effects. Future research will continue to explore ways that changing technologies, including increasing use of social media, will impact our understandings and perceptions of crime as well as criminal behavior.
Further Reading
- American Psychological Association . (2015). Resolution on violent video games . Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/about/policy/violent-video-games.aspx
- Anderson, J. A. , & Grimes, T. (2008). Special issue: Media violence. Introduction. American Behavioral Scientist , 51 (8), 1059–1060.
- Berlatsky, N. (Ed.). (2012). Media violence: Opposing viewpoints . Farmington Hills, MI: Greenhaven.
- Elson, M. , & Ferguson, C. J. (2014). Twenty-five years of research on violence in digital games and aggression. European Psychologist , 19 (1), 33–46.
- Ferguson, C. (Ed.). (2015). Special issue: Video games and youth. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 4 (4).
- Ferguson, C. J. , Olson, C. K. , Kutner, L. A. , & Warner, D. E. (2014). Violent video games, catharsis seeking, bullying, and delinquency: A multivariate analysis of effects. Crime & Delinquency , 60 (5), 764–784.
- Gentile, D. (2013). Catharsis and media violence: A conceptual analysis. Societies , 3 (4), 491–510.
- Huesmann, L. R. (2007). The impact of electronic media violence: Scientific theory and research. Journal of Adolescent Health , 41 (6), S6–S13.
- Huesmann, L. R. , & Taylor, L. D. (2006). The role of media violence in violent behavior. Annual Review of Public Health , 27 (1), 393–415.
- Krahé, B. (Ed.). (2013). Special issue: Understanding media violence effects. Societies , 3 (3).
- Media Violence Commission, International Society for Research on Aggression (ISRA) . (2012). Report of the Media Violence Commission. Aggressive Behavior , 38 (5), 335–341.
- Rich, M. , & Bickham, D. (Eds.). (2015). Special issue: Methodological advances in the field of media influences on children. Introduction. American Behavioral Scientist , 59 (14), 1731–1735.
- American Psychological Association (APA) . (2015, August 13). APA review confirms link between playing violent video games and aggression . Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2015/08/violent-video-games.aspx
- Anderson, J. A. (2008). The production of media violence and aggression research: A cultural analysis. American Behavioral Scientist , 51 (8), 1260–1279.
- Bandura, A. , Ross, D. , & Ross, S. A. (1963). Imitation of film-mediated aggressive models. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 66 (1), 3–11.
- Barker, M. , & Petley, J. (2001). Ill effects: The media violence debate (2d ed.). London: Routledge.
- Bartholow, B. D. , Bushman, B. J. , & Sestir, M. A. (2006). Chronic violent video game exposure and desensitization to violence: Behavioral and event-related brain potential data. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 42 (4), 532–539.
- Beaty, B. (2005). Fredric Wertham and the critique of mass culture . Jackson: University Press of Mississippi.
- Bracci, P. (2010, March 12). The police were sure James Bulger’s ten-year-old killers were simply wicked. But should their parents have been in the dock? Retrieved from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-1257614/The-police-sure-James-Bulgers-year-old-killers-simply-wicked-But-parents-dock.html
- Breuer, J. , Vogelgesang, J. , Quandt, T. , & Festl, R. (2015). Violent video games and physical aggression: Evidence for a selection effect among adolescents. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 4 (4), 305–328.
- Brooks, X. (2002, December 19). Natural born copycats . Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/culture/2002/dec/20/artsfeatures1
- Brown, M. (2007). Beyond the requisites: Alternative starting points in the study of media effects and youth violence. Journal of Criminal Justice and Popular Culture , 14 (1), 1–20.
- Brown, S. (2011). Media/crime/millennium: Where are we now? A reflective review of research and theory directions in the 21st century. Sociology Compass , 5 (6), 413–425.
- Bushman, B. (2016, July 26). Violent video games and real violence: There’s a link but it’s not so simple . Retrieved from http://theconversation.com/violent-video-games-and-real-violence-theres-a-link-but-its-not-so-simple?63038
- Bushman, B. J. , & Anderson, C. A. (2015). Understanding causality in the effects of media violence. American Behavioral Scientist , 59 (14), 1807–1821.
- Bushman, B. J. , Jamieson, P. E. , Weitz, I. , & Romer, D. (2013). Gun violence trends in movies. Pediatrics , 132 (6), 1014–1018.
- Carnagey, N. L. , Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2007). The effect of video game violence on physiological desensitization to real-life violence. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 43 (3), 489–496.
- Carrabine, E. (2008). Crime, culture and the media . Cambridge, U.K.: Polity.
- Chiricos, T. , Eschholz, S. , & Gertz, M. (1997). Crime, news and fear of crime: Toward an identification of audience effects. Social Problems , 44 , 342.
- Cline, V. B. , Croft, R. G. , & Courrier, S. (1973). Desensitization of children to television violence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 27 (3), 360–365.
- CNN Wire (2016, July 24). Officials: 18-year-old suspect in Munich attack was obsessed with mass shootings . Retrieved from http://ktla.com/2016/07/24/18-year-old-suspect-in-munich-shooting-played-violent-video-games-had-mental-illness-officials/
- Cohen, S. (2005). Folk devils and moral panics (3d ed.). New York: Routledge.
- Cullen, D. (2009). Columbine . New York: Hachette.
- Dahl, G. , & DellaVigna, S. (2012). Does movie violence increase violent crime? In N. Berlatsky (Ed.), Media Violence: Opposing Viewpoints (pp. 36–43). Farmington Hills, MI: Greenhaven.
- DeCamp, W. (2015). Impersonal agencies of communication: Comparing the effects of video games and other risk factors on violence. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 4 (4), 296–304.
- Elson, M. , & Ferguson, C. J. (2013). Does doing media violence research make one aggressive? European Psychologist , 19 (1), 68–75.
- Evans, B. , & Giroux, H. (2015). Disposable futures: The seduction of violence in the age of spectacle . San Francisco: City Lights Publishers.
- Fanti, K. A. , Vanman, E. , Henrich, C. C. , & Avraamides, M. N. (2009). Desensitization to media violence over a short period of time. Aggressive Behavior , 35 (2), 179–187.
- Ferguson, C. J. (2013). Violent video games and the Supreme Court: Lessons for the scientific community in the wake of Brown v. Entertainment Merchants Association. American Psychologist , 68 (2), 57–74.
- Ferguson, C. J. (2014). Does media violence predict societal violence? It depends on what you look at and when. Journal of Communication , 65 (1), E1–E22.
- Ferguson, C. J. , & Dyck, D. (2012). Paradigm change in aggression research: The time has come to retire the general aggression model. Aggression and Violent Behavior , 17 (3), 220–228.
- Ferguson, C. J. , & Konijn, E. A. (2015). She said/he said: A peaceful debate on video game violence. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 4 (4), 397–411.
- Ferrell, J. , Hayward, K. , & Young, J. (2015). Cultural criminology: An invitation . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Frosch, D. , & Johnson, K. (2012, July 20). 12 are killed at showing of Batman movie in Colorado . Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2012/07/21/us/shooting-at-colorado-theater-showing-batman-movie.html
- Garland, D. (2008). On the concept of moral panic. Crime, Media, Culture , 4 (1), 9–30.
- Gauntlett, D. (2001). The worrying influence of “media effects” studies. In ill effects: The media violence debate (2d ed.). London: Routledge.
- Gerbner, G. (1994). TV violence and the art of asking the wrong question. Retrieved from http://www.medialit.org/reading-room/tv-violence-and-art-asking-wrong-question
- Gerbner, G. , Gross, L. , Morgan, M. , Singnorielli, N. , & Shanahan, J. (2002). Growing up with television: Cultivation process. In J. Bryant & D. Zillmann (Eds.), Media effects: Advances in theory and research (pp. 43–67). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Giroux, H. (2015, December 25). America’s addiction to violence . Retrieved from http://www.counterpunch.org/2015/12/25/americas-addiction-to-violence-2/
- Graham, C. , & Gallagher, I. (2012, July 20). Gunman who massacred 12 at movie premiere used same drugs that killed Batman star Heath Ledger . Retrieved from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2176377/James-Holmes-Colorado-shooting-Gunman-used-drugs-killed-Heath-Ledger.html
- Gunter, B. (2008). Media violence: Is there a case for causality? American Behavioral Scientist , 51 (8), 1061–1122.
- Hall, S. , Critcher, C. , Jefferson, T. , Clarke, J. , & Roberts, B. (2013/1973). Policing the crisis: Mugging, the state and law and order . Hampshire, U.K.: Palgrave.
- Helfgott, J. B. (2015). Criminal behavior and the copycat effect: Literature review and theoretical framework for empirical investigation. Aggression and Violent Behavior , 22 (C), 46–64.
- Hetsroni, A. (2007). Four decades of violent content on prime-time network programming: A longitudinal meta-analytic review. Journal of Communication , 57 (4), 759–784.
- Jewkes, Y. (2015). Media & crime . London: SAGE.
- Jowett, G. , Jarvie, I. , & Fuller, K. (1996). Children and the movies: Media influence and the Payne Fund controversy . Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Jurgenson, N. (2012, June 28). The IRL fetish . Retrieved from http://thenewinquiry.com/essays/the-irl-fetish/
- Katz, E. , Blumler, J. G. , & Gurevitch, M. (1973). Uses and gratifications research. The Public Opinion Quarterly .
- Kitzinger, J. (2004). Framing abuse: Media influence and public understanding of sexual violence against children . London: Polity.
- Krahé, B. (2014). Restoring the spirit of fair play in the debate about violent video games. European Psychologist , 19 (1), 56–59.
- Krahé, B. , Möller, I. , Huesmann, L. R. , Kirwil, L. , Felber, J. , & Berger, A. (2011). Desensitization to media violence: Links with habitual media violence exposure, aggressive cognitions, and aggressive behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 100 (4), 630–646.
- Markey, P. M. , French, J. E. , & Markey, C. N. (2015). Violent movies and severe acts of violence: Sensationalism versus science. Human Communication Research , 41 (2), 155–173.
- Markey, P. M. , Markey, C. N. , & French, J. E. (2015). Violent video games and real-world violence: Rhetoric versus data. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 4 (4), 277–295.
- Marsh, I. , & Melville, G. (2014). Crime, justice and the media . New York: Routledge.
- McShane, L. (2012, July 27). Maryland police arrest possible Aurora copycat . Retrieved from http://www.nydailynews.com/news/national/maryland-cops-thwart-aurora-theater-shooting-copycat-discover-gun-stash-included-20-weapons-400-rounds-ammo-article-1.1123265
- Meyer, J. (2015, September 18). The James Holmes “Joker” rumor . Retrieved from http://www.denverpost.com/2015/09/18/meyer-the-james-holmes-joker-rumor/
- Murray, J. P. (2008). Media violence: The effects are both real and strong. American Behavioral Scientist , 51 (8), 1212–1230.
- Nyberg, A. K. (1998). Seal of approval: The history of the comics code. Jackson: University Press of Mississippi.
- PBS . (n.d.). Culture shock: Flashpoints: Theater, film, and video: Stanley Kubrick’s A Clockwork Orange. Retrieved from http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/cultureshock/flashpoints/theater/clockworkorange.html
- Phillips, N. D. , & Strobl, S. (2013). Comic book crime: Truth, justice, and the American way . New York: New York University Press.
- Rafter, N. (2006). Shots in the mirror: Crime films and society (2d ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
- Reiner, R. (2002). Media made criminality: The representation of crime in the mass media. In R. Reiner , M. Maguire , & R. Morgan (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of criminology (pp. 302–340). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Reuters . (2016, July 24). Munich gunman, a fan of violent video games, rampage killers, had planned attack for a year . Retrieved from http://www.cnbc.com/2016/07/24/munich-gunman-a-fan-of-violent-video-games-rampage-killers-had-planned-attack-for-a-year.html
- Rich, M. , Bickham, D. S. , & Wartella, E. (2015). Methodological advances in the field of media influences on children. American Behavioral Scientist , 59 (14), 1731–1735.
- Robinson, M. B. (2011). Media coverage of crime and criminal justice. Durham, NC: Carolina Academic Press.
- Rubin, A. (2002). The uses-and-gratifications perspective of media effects. In J. Bryant & D. Zillmann (Eds.), Media effects: Advances in theory and research (pp. 525–548). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Savage, J. (2008). The role of exposure to media violence in the etiology of violent behavior: A criminologist weighs in. American Behavioral Scientist , 51 (8), 1123–1136.
- Savage, J. , & Yancey, C. (2008). The effects of media violence exposure on criminal aggression: A meta-analysis. Criminal Justice and Behavior , 35 (6), 772–791.
- Sparks, R. (1992). Television and the drama of crime: Moral tales and the place of crime in public life . Buckingham, U.K.: Open University Press.
- Sparks, G. , & Sparks, C. (2002). Effects of media violence. In J. Bryant & D. Zillmann (Eds.), Media effects: Advances in theory and research (2d ed., pp. 269–286). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Sternheimer, K. (2003). It’s not the media: The truth about pop culture’s influence on children . Boulder, CO: Westview.
- Sternheimer, K. (2013). Connecting social problems and popular culture: Why media is not the answer (2d ed.). Boulder, CO: Westview.
- Strasburger, V. C. , & Donnerstein, E. (2014). The new media of violent video games: Yet same old media problems? Clinical Pediatrics , 53 (8), 721–725.
- Surette, R. (2002). Self-reported copycat crime among a population of serious and violent juvenile offenders. Crime & Delinquency , 48 (1), 46–69.
- Surette, R. (2011). Media, crime, and criminal justice: Images, realities and policies (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Surette, R. (2016). Measuring copycat crime. Crime, Media, Culture , 12 (1), 37–64.
- Tilley, C. L. (2012). Seducing the innocent: Fredric Wertham and the falsifications that helped condemn comics. Information & Culture , 47 (4), 383–413.
- Warburton, W. (2014). Apples, oranges, and the burden of proof—putting media violence findings into context. European Psychologist , 19 (1), 60–67.
- Wertham, F. (1954). Seduction of the innocent . New York: Rinehart.
- Yamato, J. (2016, June 14). Gaming industry mourns Orlando victims at E3—and sees no link between video games and gun violence . Retrieved from http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2016/06/14/gamers-mourn-orlando-victims-at-e3-and-see-no-link-between-gaming-and-gun-violence.html
- Yar, M. (2012). Crime, media and the will-to-representation: Reconsidering relationships in the new media age. Crime, Media, Culture , 8 (3), 245–260.
Related Articles
- Intimate Partner Violence
- The Extent and Nature of Gang Crime
- Intersecting Dimensions of Violence, Abuse, and Victimization
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Criminology and Criminal Justice. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 14 September 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.66.14.236]
- 185.66.14.236
Character limit 500 /500
- About The Journalist’s Resource
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
Violent media and real-world behavior: Historical data and recent trends
2015 study from Stetson University published in Journal of Communications that explores violence in movies and video games and rates of societal violence over the same period.

Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by Devon Maylie, The Journalist's Resource February 18, 2015
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/criminal-justice/violent-media-real-world-behavior-historical-data-recent-trends/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
The relationship between violent media and real-world violence has been the subject of extensive debate and considerable academic research , yet the core question is far from answered. Do violent games and movies encourage more violence, less, or is there no effect? Complicating matters is what seems like a simultaneous rise in onscreen mayhem and the number of bloody events in our streets — according to a 2014 report from the FBI, between 2007 and 2013 there were an average of 16.4 active-shooter incidents in the U.S. every year, more than 150% higher than the annual rate between 2000 and 2006.
But as has long been observed, any correlation is not necessarily causation . While Adam Lanza and James Holmes — respectively, the perpetrators of the Newtown and Aurora mass shootings — both played violent video games , so do millions of law-abiding Americans. A 2014 study in Psychology of Popular Media Culture found no evidence of an association between violent crime and video game sales and the release dates of popular violent video games. “Unexpectedly, many of the results were suggestive of a decrease in violent crime in response to violent video games,” write the researchers, based at Villanova and Rutgers. A 2015 study from the University of Toledo showed that playing violent video games could desensitize children and youth to violence, but didn’t establish a definitive connection with real-world behavior, positive or negative.
A 2014 study in Journal of Communication , “Does Media Violence Predict Societal Violence? It Depends on What You Look at and When,” builds on prior research to look closer at media portrayals of violence and rates of violent behavior. The research, by Christopher J. Ferguson of Stetson University, had two parts: The first measured the frequency and graphicness of violence in movies between 1920 and 2005 and compared it to homicide rates, median household income, policing, population density, youth population and GDP over the same period. The second part looked at the correlation between the consumption of violent video games and youth behavior from 1996 to 2011.
The study’s findings include:
- Overall, no evidence was found to support the conclusion that media violence and societal violence are meaningfully correlated.
- Across the 20th century the frequency of movie violence followed a rough U-pattern: It was common in the 1920s, then declined before rising again in the latter part of the 20th century. This appears to correspond to the period of the Motion Picture Production Code (known as the Hays Code), in force from 1930 to the late 1960s.
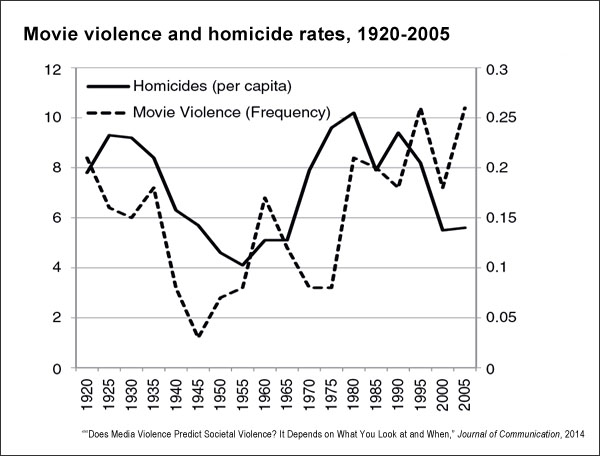
- The frequency of movie violence and murder rates were correlated in the mid-20th century, but not earlier or later in the period studied. “By the latter 20th century … movie violence [was] associated with reduced societal violence in the form of homicides. Further, the correlation between movie and societal violence was reduced when policing or real GDP were controlled.”
- The graphicness of movie violence shows an increasing pattern across the 20th century, particularly beginning in the 1950s, but did not correlate with societal violence.
- The second part of the study found that for the years 1996 to 2011, the consumption of violent video games was inversely related to youth violence.
- Youth violence decreased during the 15-year study period despite high levels of media violence in society. However, the study period is relatively short, the researcher cautioned, and therefore results could be imperfect.
“Results from the two studies suggest that socialization models of media violence may be inadequate to our understanding of the interaction between media and consumer behavior at least in regard to serious violence,” Ferguson concludes. “Adoption of a limited-effects model in which user motivations rather than content drive media experiences may help us understand how media can have influences, yet those influences result in only limited aggregate net impact in society.” Given that effects on individual users may differ widely, Ferguson suggests that policy discussion should be more focused on “more pressing” issues that influence violence in society such as poverty or mental health.
Related research: A 2015 research roundup, “The Contested Field of Violent Video Games,” gives an overview of recent scholarship on video games and societal violence, including ones that support a link and others that refute it. Also of interest is a 2014 research roundup, “Mass Murder, Shooting Sprees and Rampage Violence.”
Keywords: video games, violence, aggression, desensitization, empathy, technology, youth, cognition, guns, crime, entertainment
About The Author
Devon Maylie
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Gray Matter
Does Media Violence Lead to the Real Thing?
By Vasilis K. Pozios Praveen R. Kambam and H. Eric Bender
- Aug. 23, 2013
EARLIER this summer the actor Jim Carrey, a star of the new superhero movie “Kick-Ass 2,” tweeted that he was distancing himself from the film because, in the wake of the Sandy Hook massacre, “in all good conscience I cannot support” the movie’s extensive and graphically violent scenes.
Mark Millar, a creator of the “Kick-Ass” comic book series and one of the movie’s executive producers, responded that he has “never quite bought the notion that violence in fiction leads to violence in real life any more than Harry Potter casting a spell creates more boy wizards in real life.”
While Mr. Carrey’s point of view has its adherents, most people reflexively agree with Mr. Millar. After all, the logic goes, millions of Americans see violent imagery in films and on TV every day, but vanishingly few become killers.
But a growing body of research indicates that this reasoning may be off base. Exposure to violent imagery does not preordain violence, but it is a risk factor. We would never say: “I’ve smoked cigarettes for a long time, and I don’t have lung cancer. Therefore there’s no link between smoking cigarettes and lung cancer.” So why use such flawed reasoning when it comes to media violence?
There is now consensus that exposure to media violence is linked to actual violent behavior — a link found by many scholars to be on par with the correlation of exposure to secondhand smoke and the risk of lung cancer. In a meta-analysis of 217 studies published between 1957 and 1990, the psychologists George Comstock and Haejung Paik found that the short-term effect of exposure to media violence on actual physical violence against a person was moderate to large in strength.
Mr. Comstock and Ms. Paik also conducted a meta-analysis of studies that looked at the correlation between habitual viewing of violent media and aggressive behavior at a point in time. They found 200 studies showing a moderate, positive relationship between watching television violence and physical aggression against another person.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

The Facts on Media Violence
By Vanessa Schipani
Posted on March 8, 2018
In the wake of the Florida school shooting, politicians have raised concern over the influence of violent video games and films on young people, with the president claiming they’re “shaping young people’s thoughts.” Scientists still debate the issue, but the majority of studies show that extensive exposure to media violence is a risk factor for aggressive thoughts, feelings and behaviors.

The link between media violence and mass shootings is yet more tenuous. Compared with acts of aggression and violence, mass shootings are relatively rare events, which makes conducting conclusive research on them difficult.
President Donald Trump first raised the issue during a meeting on school safety with local and state officials, which took place a week after the shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Florida. The shooter, 19-year-old Nikolas Cruz, reportedly obsessively played violent video games.
Trump, Feb. 22: We have to look at the Internet because a lot of bad things are happening to young kids and young minds, and their minds are being formed. And we have to do something about maybe what they’re seeing and how they’re seeing it. And also video games. I’m hearing more and more people say the level of violence on video games is really shaping young people’s thoughts. And then you go the further step, and that’s the movies. You see these movies, they’re so violent.
Trump discussed the issue again with members of Congress on Feb. 28 during another meeting on school safety. During that discussion, Tennessee Rep. Marsha Blackburn claimed mothers have told her they’re “very concerned” that “exposure” to entertainment media has “desensitized” children to violence.
Iowa Sen. Chuck Grassley also said during the meeting: “[Y]ou see all these films about everybody being blown up. Well, just think of the impact that makes on young people.”
The points Trump and members of Congress raise aren’t unfounded, but the research on the subject is complex. Scientists who study the effect of media violence have taken issue with how the popular press has portrayed their work, arguing that the nuance of their research is often left out.
In a 2015 review of the scientific literature on video game violence, the American Psychological Association elaborates on this point.
APA, 2015: News commentators often turn to violent video game use as a potential causal contributor to acts of mass homicide. The media point to perpetrators’ gaming habits as either a reason they have chosen to commit their crimes or as a method of training. This practice extends at least as far back as the Columbine massacre (1999). … As with most areas of science, the picture presented by this research is more complex than is usually depicted in news coverage and other information prepared for the general public.
Here, we break down the facts — nuance included — on the effect of media violence on young people.
Is Media Violence a Risk Factor for Aggression?
The 2015 report by the APA on video games is a good place to start. After systematically going through the scientific literature, the report’s authors “concluded that violent video game use has an effect on aggression.”
In particular, the authors explain that this effect manifests as an increase in aggressive behaviors, thoughts and feelings and a decrease in helping others, empathy and sensitivity to aggression. Though limited, evidence also suggests that “higher amounts of exposure” to video games is linked to “higher levels of aggression,” the report said.
The report emphasized that “aggression is a complex behavior” caused by multiple factors, each of which increases the likelihood that an individual will be aggressive. “Children who experience multiple risk factors are more likely to engage in aggression,” the report said.
The authors came to their conclusions because researchers have consistently found the effect across three different kinds of studies: cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies and laboratory experiments. “One method’s limits are offset by another method’s strengths,” the APA report explains, so only together can they be used to infer a causal relationship.
Cross-sectional studies find correlations between different phenomena at one point in time. They’re relatively easy to conduct, but they can’t provide causal evidence because correlations can be spurious . For example, an increase in video game sales might correlate with a decrease in violent crime, but that doesn’t necessarily mean video games prevent violent crime. Other unknown factors might also be at play.
Longitudinal panel studies collect data on the same group over time, sometimes for decades. They’re used to investigate long-term effects, such as whether playing video games as a child might correlate with aggression as an adult. These studies also measure other risk factors for aggression, such as harsh discipline from parents, with the aim of singling out the effect of media violence. For this reason, these studies provide better evidence for causality than cross-sectional studies, but they are more difficult to conduct.
Laboratory experiments manipulate one phenomenon — in this case, exposure to media violence — and keep all others constant. Because of their controlled environment, experiments provide strong evidence for a causal effect. But for the same reason, laboratory studies may not accurately reflect how people act in the real world.
This brings us to why debate still exists among scientists studying media violence. Some researchers have found that the experimental evidence backing the causal relationship between playing video games and aggression might not be as solid as it seems.
Last July, Joseph Hilgard , an assistant professor of psychology at Illinois State University, and others published a study in the journal Psychological Bulletin that found that laboratory experiments on the topic may be subject to publication bias. This means that studies that show the effect may be more likely to be published than those that don’t, skewing the body of evidence.
After Hilgard corrected for this bias, the effect of violent video games on aggressive behavior and emotions did still exist, but it was reduced, perhaps even to near zero. However, the effect on aggressive thoughts remained relatively unaffected by this publication bias. The researchers also found that cross-sectional studies weren’t subject to publication bias. They didn’t examine longitudinal studies, which have shown that youth who play more violent video games are more likely to report aggressive behavior over time.
Hilgard looked at a 2010 literature review by Craig A. Anderson , the director of the Center for the Study of Violence at Iowa State University, and others. Published in Psychological Bulletin, this review influenced the APA’s report.
In response, Anderson took a second look at his review and found that the effect of violent video games on aggression was smaller than he originally thought, but not as small as Hilgard found. For this reason, he argued the effect was still a “societal concern.”
To be clear, Hilgard is arguing that there’s more uncertainty in the field than originally thought, not that video games have no effect on aggression. He’s also not the first to find that research on video games may be suffering from publication bias.
But what about movies and television? Reviews of the literature on these forms of media tend to be less recent, Kenneth A. Dodge , a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University, told us by email.
Dodge, also one of the authors of the 2015 APA study, pointed us to one 1994 review of the literature on television published in the journal Communication Research that concluded that television violence also “increases aggressiveness and antisocial behavior.” Dodge told us he’s “confident” the effect this analysis and others found “would hold again today.”
Dodge also pointed us to a 2006 study that reviewed the literature on violent video games, films, television and other media together. “Most contemporary studies start with the premise that children are exposed [to violence] through so many diverse media that they start to group them together,” said Dodge.
Published in JAMA Pediatrics , the review found that exposure to violent media increases the likelihood of aggressive behavior, thoughts and feelings. The review also found media decreases the likelihood of helping behavior. All of these effects were “modest,” the researchers concluded.
Overall, most of the research suggests media violence is a risk factor for aggression, but some experts in the field still question whether there’s enough evidence to conclusively say there’s a link.
Is Violent Media a Risk Factor for Violence?
There’s even less evidence to suggest media violence is a risk factor for criminal violence.
“In psychological research, aggression is usually conceptualized as behavior that is intended to harm another,” while, “[v]iolence can be defined as an extreme form of physical aggression,” the 2015 APA report explains . “Thus, all violence is aggression, but not all aggression is violence.”
The APA report said studies have been conducted on media violence’s relationship with “criminal violence,” but the authors “did not find enough evidence of sufficient utility to evaluate whether” there’s a solid link to violent video game use.
This lack of evidence is due, in part, to the fact that there are ethical limitations to conducting experiments on violence in the laboratory, especially when it comes to children and teens, the report explains. That leaves only evidence from cross-sectional studies and longitudinal studies. So what do those studies say?
One longitudinal study , published in the journal Developmental Psychology in 2003, found that, out of 153 males, those who watched the most violent television as children were more likely 15 years later “to have pushed, grabbed, or shoved their spouses, to have responded to an insult by shoving a person” or to have been “to have been convicted of a crime” during the previous year. Girls who watched the most violent television were also more likely to commit similar acts as young women. These effects persisted after controlling for other risk factors for aggression, such as parental aggression and intellectual ability.
A 2012 cross-sectional study that Anderson, at Iowa State, and others published in the journal Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice did find that the amount of violent video games juvenile delinquents played correlated with how many violent acts they had committed over the past year. The violent acts included gang fighting, hitting a teacher, hitting a parent, hitting other students and attacking another person.
However, a 2008 review of the literature published in the journal Criminal Justice and Behavior concluded that “ the effects of exposure to media violence on criminally violent behavior have not been established.” But the authors clarify: “Saying that the effect has not been established is not the same as saying that the effect does not exist.”
In contrast to the APA report, Anderson and a colleague argue in a 2015 article published in American Behavioral Scientist that “research shows that media violence is a causal risk factor not only for mild forms of aggression but also for more serious forms of aggression, including violent criminal behavior.”
Why did Anderson and his colleagues come to different conclusions than the APA? He told us that the APA “did not include the research literature on TV violence,” and excluded “several important studies on video game effects on violent behavior published since 2013.”
In their 2015 article, Anderson and his colleague clarify that, even if there is a link, it “does not mean that violent media exposure by itself will turn a normal child or adolescent who has few or no other risk factors into a violent criminal or a school shooter.” They add, “Such extreme violence is rare, and tends to occur only when multiple risk factors converge in time, space, and within an individual.”
Multiple experts we spoke with did point to one factor unique to the United States that they argue increases the risk of mass shootings and lethality of violence in general — access to guns.
For example, Anderson told us by email: “There is a pretty strong consensus among violence researchers in psychology and criminology that the main reason that U.S. homicide rates are so much higher than in most Western democracies is our easy access to guns.”
Dodge, at Duke, echoed Anderson’s point.”The single most obvious and probably largest difference between a country like the US that has many mass shootings and other developed countries is the easy access to guns,” he said.
So while scientists disagree about how much evidence is enough to sufficiently support a causal link between media violence and real world violence, Trump and other politicians’ concerns aren’t unfounded.
Editor’s note: FactCheck.org is also based at the University of Pennsylvania’s Annenberg Public Policy Center. Hilgard, now at Illinois State, was a post doctoral fellow at the APPC.

Media Violence
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2014
- pp 1685–1691
- Cite this reference work entry

- Joanne Savage 2 &
- Christopher J. Ferguson 3
241 Accesses
This essay briefly reviews theory, logic, and empirical research related to the effects of television and film violence on adolescent development. It emphasizes reports on the link between media violence and serious aggression. A brief history of research in this area is followed by conclusions based on contemporary data and observations; research methodology is stressed throughout. This essay also touches upon media literacy and media violence effects on desensitization and fear/anxiety. It is noted that research on adolescent subjects is less common than one might expect, and therefore many conclusions about adolescents are tentative at best.
Introduction
There have been, literally, thousands of articles on the topic of media violence published in recent decades. A quick electronic search shows that the vast majority of these are editorial in nature rather than empirical studies. A striking number of such editorials appear in venues such as the Journal of the American...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1963). Imitation of film-mediated aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 66 (1), 3–11.
PubMed Google Scholar
Berkowitz, L. (2008). On the consideration of automatic as well as controlled psychological processes in aggression. Aggressive Behavior, 34 (2), 117–129.
Cantor, J. (2008). Fright reactions to mass media. In J. Bryant (Ed.), Media effects: Advances in theory and research (3rd ed., pp. 287–303). Florence, KY: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Ferguson, C. J., & Hartley, R. D. (2009). The pleasure is momentary…the expense damnable? The influence of pornography on rape and sexual assault. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 14 (5), 323–329.
Ferguson, C. J., & Kilburn, J. (2009). The public health risks of media violence: A meta-analytic review. The Journal of Pediatrics, 154 (5), 759–763.
Ferguson, C. J., & Rueda, S. M. (2009). Examining the validity of the modified Taylor Competitive Reaction Time Test of Aggression. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 5 (2), 121–137.
Freedman, J. L. (2002). Media violence and its effect on aggression: Assessing the scientific evidence . Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Huesmann, L. R., & Eron, L. D. (Eds.). (1986). Television and the aggressive child: A cross-national comparison . Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Levesque, R. J. R. (2007). Adolescents, media, and the law: What developmental science reveals and free speech requires . New York: Oxford University Press.
Moffitt, T. E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100 (4), 674–701.
Paik, H., & Comstock, G. (1994). The effects of television violence on anti-social behavior: A meta-analysis. Communication Research, 21 , 516–546.
Potter, W. J. (1999). On media violence . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Potter, W. J. (2008). Media literacy (4th ed.). Los Angeles: Sage.
Savage, J. (2004). Does viewing violent media really cause criminal violence? A methodological review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 10 (1), 99–128.
Savage, J., & Yancey, C. (2008). The effects of media violence exposure on criminal aggression: A meta-analysis. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 35 (6), 772–791.
Woolley, J., & Van Reet, J. (2006). Effects of context on judgments concerning the reality status of novel entities. Child Development, 77 (6), 1778–1793.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
American University, Washington, DC, USA
Joanne Savage
Department of Behavioral, Applied Sciences and Criminal Justice, Texas A & M International University, 5201 University Blvd, Laredo, TX, USA
Christopher J. Ferguson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joanne Savage .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Indiana University, 302 Sycamore Hall, Bloomington, IN, 47405, USA
Roger J. R. Levesque
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Savage, J., Ferguson, C.J. (2011). Media Violence. In: Levesque, R.J.R. (eds) Encyclopedia of Adolescence. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1695-2_263
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1695-2_263
Published : 12 August 2014
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4419-1694-5
Online ISBN : 978-1-4419-1695-2
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Violence in the Media: What Effects on Behavior?
"You turn on the television, and violence is there. You go to a movie, and violence is there."

Agitation Assessment: The Role of Psychiatry in Acute Settings

How to Talk to Teenagers About Substance Use

The Anniversary of 9/11 Research Roundup

5 Personality Traits of Olympic Athletes

Meditation Is Not What You Think

Preventing Overdose Deaths: How to Reduce Social Stigma and Barriers to Care
2 Commerce Drive Cranbury, NJ 08512
609-716-7777

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts
- PMC10177625

Violent Media in Childhood and Seriously Violent Behavior in Adolescence and Young Adulthood
Michele l. ybarra.
Center for Innovative Public Health Research, San Clemente, California
Kimberly J. Mitchell
Crimes against Children Research Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, New Hampshire

Jay Koby Oppenheim
Independent Consultant, New York, New York
Associated Data
To quantify the relative odds of self-reported seriously violent behavior in adolescence and young adulthood given one’s self-reported violent media diet in childhood.
Baseline data were collected nationally online from 1,586 youth 10–15 years of age in 2006. Follow-up data were collected in 2010–2011 and 2016. Children reported the amount of music, video games, television, websites with real people, and cartoons that depicted “physical fighting, hurting, shooting, or killing.” Seriously violent behavior was assessed 5 and 10 years later.
887 adolescents completed the survey at baseline and 5-year follow-up. The relative odds of reporting seriously violent behavior over time were 2.45-fold higher ( P <.001) with each incremental increase in one’s baseline violent media diet. After adjusting for other potentially influential characteristics, results persisted (aOR = 1.70, P =.01). The relative odds also were elevated for those frequently exposed to violence in music (aOR = 3.28, p=0.03), television (aOR = 3.51, p<0.001), and video games (aOR = 3.27, p=0.02). 760 young adults completed measures at baseline and 10-year follow-up. The relative odds of seriously violent behavior increased 2.18-fold ( P =.001) with each incremental increase in one’s baseline violent media diet. After adjusting for other factors, the association persisted (aOR = 1.72, P=.03). Frequent exposure to violence in video games (aOR = 3.28, p=0.03) and television (aOR = 3.14, p=0.02) also were implicated.
Discussion:
Exposure to violent media in childhood may be one modifiable influence on seriously violent behavior in adolescence and adulthood, even for those who have other risk factors.
Youth violence is a significant public health issue that negatively affects individuals, families, and communities. 1 , 2 Estimated costs associated with youth violence in the United States is more than $20 billion anually. 3 Although juvenile arrests in 2019 were down 58% since 2010, 4 youth nonetheless account for a sizable proportion of perpetrators: 9% of all violent crimes were committed by juveniles, and 21% by 18–24-year-olds. 5
No single risk factor causes violent behavior. Instead, an accumulation of exposures increases one’s risk at each level of the social ecology (e.g., exposure to spousal abuse). 2 , 6 – 9 Because it could easily be modified, exposure to violent media has been researched for decades as a potential contributor to aggressive behavior. Cross-sectional and laboratory research frequently document linkages. 10 – 12 Studies that measure violent behaviors report similar effect sizes to those that measure aggression. 10 Although fewer in number, longitudinal studies also report linkages: Huesmann and Eron found that adult criminal and violent behavior was associated with exposure to television violence 15 years prior. 13 Findings were replicated in a Finnish sample. 14 Further, Anderson and colleagues found that frequent violent video game play predicted physical aggression three to six months later for children and adolescents in three separate cohorts, two from Japan and one from the United States. 15 Some exceptions are noted. 16 Coyne and colleagues looked at longer term associations between externalizing behavior and violent video game play and did not find a linkage over the 5-year observation period. 17 This may be because the measure reflecting externalizing behavior included items that did meet the definition of aggression.
Youth media use is nearly ubiquitous 18 : Music is by far the most widely used medium in adolescence: 82% listen to music daily. 19 Most - 83% of adolescent girls and 97% of boys 13–17 years of age – also play video games; 95% own or have access to a smartphone, and 85% say they go online and exchange content. 20 Cross-sectional research by Ybarra and colleagues suggests that one’s general media violence diet may explain the increased odds of engaging in seriously violent behavior. 21 As such, it is important not just to examine the association that specific media may have but also the association that one’s violent media ‘diet’ across media may have with violent behavior over time.
The current study aims to fill noted research gaps. First, while extant research examines exposure to violence on television and in video games, exposures through other media, such as music, are less well studied yet constitute a large part of youth media diets. Second, much of the literature focuses on aggressive rather than violent behavior. Aggression is any behavior enacted by someone who intends to harm the other person when the other person does not want to be harmed. 22 , 23 Violence is a more severe type of aggression that carries with it the possibility of serious physical harm to the other individual. All violent behaviors are aggressive, whereas not all aggressive behaviors are violent. Third, few studies examine these linkages longitudinally, particularly between 5 and 10 years postexposure. Based on previous literature, we posit that violent media will predict violent behavior over time and that this will be particularly true for a general media diet as it reflects an accumulation of exposures.
Growing up with Media is a longitudinal study designed to study the association between violent media exposure in childhood and adolescence - particularly exposures to new media, including the Internet and seriously violent behavior. The survey protocol was reviewed and approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Institutional Review Board (IRB) for Waves 1–3 and by Chesapeake IRB for Waves 4–7 (subsequently acquired by Advarra IRB). Parents provided informed consent for their participation and permission for their child’s participation, and youth provided informed assent by reading the assent information and then clicking either “Yes, I want to take the survey” or “No, I do not want to take the survey.”
In 2006, 1,586 child-caregiver pairs were recruited through an email sent to randomly identified adult Harris Poll OnLine (HPOL) panel members who reported having a child living in their household. HPOL was the largest online panel at the time of recruitment, including four million members. Members were recruited through online advertising, advertising at conferences and events, and referrals.
Eligible adult caregivers reported having a child 10–15 years of age living in the household, speaking English, and being equally or more knowledgeable than other adults living in the household about their youth’s daily activities. Eligible youth participants were 10–15-year-olds who read English, lived in the household at least 50% of the time, and had used the Internet at least once in the last six months. Recruitment was balanced on youth age and sex; once a demographic ‘bin’ was filled (e.g., for 10–12-year-old girls), subsequent youth who met those criteria were marked ineligible.
Seriously violent behavior.
Seriously violent behavior, as defined by the US Department of Justice, 24 includes murder, aggravated assault, robbery, and sexual violence. Youth were coded as having engaged in past-year seriously violent behavior if they endorsed any of the following five behaviors: (1) behaviors that would likely result in murder (i.e., stabbing or shooting someone); (2) aggravated assault (i.e., threatening someone with a weapon; attacking someone resulting in the need for medical care); (3) robbery (i.e., using a knife or gun or some other kind of weapon like a bat to get something from someone else); and (4) sexual assault (kissing, touching, or doing anything sexual with another person when it was not wanted by that person). This last item was written to be developmentally appropriate for 10–15-year-olds. Because it may include behaviors that extend beyond rape, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to examine the results when this measure of sexual assault was excluded.
Exposure to violent media.
Youth reported the amount of violence they were exposed to across five different types of media: Television, computer and video games, music, websites of real people, and websites of cartoons. A similar question format was used for each medium: “When you [engage with media type], how many of them [show/talk about] physical fighting, hurting, shooting, or killing?” 25 Response options were captured on a four-point Likert scale [1 (almost none/none of them) – 4 (almost all / all of them)].
To reflect a general violent media diet, a factor score that included all five media, was estimated using maximum likelihood [Eigenvalue = 1.69, factor loadings ranged from .47 - .69, α = 0.70, Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin ranges from 0.71 – 0.78].
For specific mediums, a categorical measure was created based upon data distributions to reflect those who reported that: (1) none/almost none, (2) some, or (3) many or almost all/all of each of the medium they consumed depicted violence. Because of low cell stability, for all longitudinal analyses, baseline exposure to violence on television was dichotomized to compare none/almost none or some versus many or almost all/all; baseline exposures to real people engaging in violence online was dichotomized to none/almost none versus some, many, almost all/all. Wave 7 longitudinal analyses included a measure of baseline exposures to cartoons engaging in violence online dichotomized to none/almost none versus some, many, almost all/all.
Background variables.
Youth age and sex were reported by caregivers; race and ethnicity were reported by youth. At the individual level, because trait anger can be increased by media violence 26 , we include youths’ self-reported baseline propensity to respond with anger, measured by the 10-item State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI-CA) T-Anger scale (α = 0.86). 27 At the peer level, baseline exposure to externalizing peers was measured by asking youth the number of close friends they had who “have been arrested or done things that could get them in trouble with the police.” 28 At the family level, youth were asked if: “Ever, in real life, have you seen one of your parents get hit, slapped, punched, or beat up by your other parent, or their boyfriend or girlfriend?” 29
Randomly identified adults were emailed a link to a brief online survey that assessed their eligibility. Ineligible adults were thanked for their participation; eligible adults were invited to complete a longer 5-minute survey after obtaining informed consent. They then forwarded their survey link to their child, who provided assent and completed the, on average, 21-minute survey. Youth were encouraged to return to the survey later if they were not in a space where their responses could be kept private from others, including their caregiver.
Data were collected online in 2006 (Wave 1), 2007–2008 (Wave 2), 2008 (Wave 3), 2010–2011 (Wave 4), 2011–2012 (Wave 5), 2012–2013 (Wave 6), and 2016 (Wave 7). In this paper, we examine data from baseline (Wave 1) and five years later (Wave 4, n=887); and baseline and 10 years later (Wave 7, n=779). Incentives were $10 in Wave 1 and increased to $40 in Wave 7. The Wave 1 survey response rate (31%) is consistent with well-conducted surveys using online panels at the time of baseline recruitment. The response rate at Wave 4 was 56% (i.e., 887/1586), and at Wave 7, 49% (i.e., 779/1586).
As the recruitment target, data were weighted statistically to reflect the population of adults with children ages 10 to 15 years old in the United States according to adult age, sex, race/ethnicity, region, education, household income, and child age and sex. Using data collected from random digit dial samples, propensity score weighting also was applied to adjust for adult respondents’ propensity to be online. The weight also adjusted for nonresponse across waves.
Plan of analysis
Rates of within-wave missingness were very low: Race (1.2%) had the highest rate of declination to answer. For all dichotomous variables, “decline to answer” was recoded as “symptom absent” (e.g., not having been in a physical fight). Those who declined to answer the question about race were coded as White, the majority race. For continuous variables, “decline to answer” was recoded to the cohort mean. As a sensitivity analysis, models also were estimated with missing data imputed. Youth who did not respond to Wave 4 or Wave 7, respectively, were excluded from that specific longitudinal analysis.
Analyses were conducted using Stata 15. 30 First, co-relations of violent exposure across media were explored using a correlation matrix and Cronbach’s alpha, which reflects the inter-relatedness of the items. We also examined the percent of youth who reported varying patterns of exposure across media types. Next, to understand the long-term association between media violence and later violent behavior, we first estimated direct, unadjusted logistic regression odds (Model 1). We then estimated logistic regression odds that adjusted for baseline levels of seriously violent behavior, one’s propensity to respond to stimuli with anger, exposure to externalizing peers, exposure to caregiver spousal abuse, sex, age, race, ethnicity, and self-reported dishonesty in answering survey questions (Model 2). For each time point, six unadjusted and adjusted models were estimated: One for violent media diet and five for each of the specific types of violent media of interest.
On average, youth were 12.6 years of age (SE: 0.05) at baseline, 16.7 years of age (SE: 0.07) at 5-year and 22.1 years of age (SE: 0.07) at 10-year follow-up. As shown in Table 1 , those who completed Waves 4 and 7, respectively, versus those who did not, respectively, generally had similar baseline demographic characteristics; exposure to externalizing peers was of exception.
Responses at Wave 1 (baseline) for completers and noncompleters of Wave 4 (5 years) and Wave 7 (10 years), respectively; weighted data
| Youth characteristics at baseline | Baseline All youth n=1586 | Cohort 5 years later | Cohort 10 years later | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Completer n=699 | completer n=887 | p-value | Non-Completer n=807 | completer n=779 | p-value | ||
| M(SE) | M(SE) | M(SE) | M(SE) | ||||
| Violent media diet (a factor score; M:SE) | 0.02 (0.03) | .06 (.05) | −0.02 (0.04) | 0.17 | 0.05 (0.04) | −0.02 (0.04) | 0.26 |
| Amount of violence in TV shows consumed | % (n) | % (n) | 0.03 | % (n) | % (n) | 0.36 | |
| None / almost none or some | 69.9% (1079) | 66.1% (446) | 72.8% (634) | 68.5% (545) | 71.4% (534) | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 30.1% (465) | 33.9% (229) | 27.2% (237) | 31.5% (251) | 28.6% (214) | ||
| Amount of violence in music listened to | 0.21 | 0.42 | |||||
| None/almost none | 43.1% (665) | 43.4% (293) | 42.8% (372) | 41.1% (327) | 45.2% (338) | ||
| Some | 43.0% (664) | 40.6% (274) | 44.9% (391) | 44.0% (350) | 42.0% (314) | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 14.0% (215) | 16.1% (108) | 12.3% (107) | 15.0% (119) | 12.9% (96) | ||
| Amount of violence in games played | 0.38 | 0.10 | |||||
| None / almost none | 35.2% (543) | 33.0% (222) | 36.9% (321) | 31.8% (253) | 38.7% (290) | ||
| Some | 39.8% (615) | 42.2% (285) | 37.9% (330) | 42.1% (335) | 37.4% (280) | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 25.0% (387) | 24.8% (167) | 25.2% (219) | 26.1% (208) | 23.9% (179) | ||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show real people | 0.53 | 0.79 | |||||
| None/almost none | 85.3% (1317) | 84.4% (569) | 86.0% (748) | 85.0% (677) | 85.6% (641) | ||
| Some / many / almost all / all | 14.7% (227) | 15.6% (105) | 14.0% (122) | 15.0% (120) | 14.4% (108) | ||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show cartoons | 0.68 | 0.56 | |||||
| None / almost none | 57.7% (891) | 57.6% (388) | 57.8% (503) | 56.8% (452) | 58.7% (439) | ||
| Some | 32.8% (507) | 32.0% (216) | 33.5% (291) | ||||
| Many / almost all / all | 9.5% (146) | 10.4% (70) | 8.7% (76) | 43.3% (344) | 41.3% (309) | ||
| Any seriously violent behavior | 4.8% (74) | 4.7% (31) | 4.9% (43) | 0.84 | 5.5% (44) | 4.1% (31) | 0.32 |
| Propensity to respond to stimuli with anger (M:SE) | 18.8 (0.2) | 18.8 (0.2) | 18.7 (0.2) | 0.81 | 18.8 (0.2) | 18.7 (0.2) | 0.93 |
| Exposure to caregiver spousal abuse | 9.0% (140) | 10.8% (73) | 7.7% (67) | 0.12 | 10.9% (86) | 7.1% (53) | 0.06 |
| Externalizing peers | 16.6% (257) | 19.6% (132) | 14.3% (125) | 0.03 | 20.6% (164) | 12.5% (93) | 0.00 |
| Age (M:SE) | 12.6 (0.05) | 12.7 (0.1) | 12.5 (0.1) | 0.18 | 12.6 (0.07) | 12.6 (0.08) | 0.60 |
| Female | 48.0% (741) | 49.0% (330) | 47.2% (411) | 0.61 | 46.8 % (373) | 49.2 % (368) | 0.48 |
| Race | 0.51 | 0.92 | |||||
| White | 71.2% (1099) | 71.6% (483) | 70.9% (617) | 71.6% (570) | 70.8% (530) | ||
| Black | 12.5% (193) | 10.8% (73) | 13.9% (121) | 11.8% (94) | 13.2% (99) | ||
| Mixed | 8.1% (125) | 8.7% (59) | 7.7% (67) | 8.5% (68) | 7.7% (58) | ||
| All other | 8.2% (127) | 9.0% (60) | 7.6% (66) | 8.1% (64) | 8.3% (62) | ||
| Hispanic ethnicity | 17.5% (271) | 17.6% (119) | 17.5% (152) | 0.95 | 16.7% (133) | 18.4% (138) | 0.55 |
| Dishonesty in answering the questions | 5.1% (78) | 5.6% (38) | 4.7% (40) | 0.54 | 5.3% (43) | 4.8% (36) | 0.70 |
Co-relation of violence exposure across media
The five indicators of exposure to violence in specific media were interrelated: Cronbach’s alpha, Wave 1 = 0.70 (unweighted data given the computation ability of Stata). As shown in Supplemental Table 1 , all media were significantly interrelated. The strongest correlations were noted for violence exposure in television and video games (0.46), and television and music (0.44). Although still significantly interrelated, violence exposure in video games and websites with real people was the least correlated (0.22).
As shown in Figure 1 , more than half (56%) of youth said that none of the media they consumed was mostly violent (i.e., many, almost all, or all of it depicted physical violence).

The percent of youth who reported a specific amount of exposure to physical fighting, shooting, or killing across media types for 10–15-year-olds in the United States (n = 1,586). Different colored bars denote the number of media to which a youth were exposed to a certain level of violence. Five media were aggregated: television, video games, music, websites with real people, and websites with cartoon figures.
Relative odds of seriously violent behavior five years after exposure to youth’s general violent media diet
A factor score was estimated to reflect one’s “violent media diet,” that is, the intensity within and across youth exposures to violent content in five mediums. As shown in Table 2 and Supplemental Figure 1 , the relative odds of reporting seriously violent behavior five years later were 2.45-fold higher ( p <0.001) with each incremental increase in one’s baseline violent media diet. After adjusting for other potentially influential characteristics, the relative odds of seriously violent behavior five years later rose 1.70-fold ( p =0.01) with each incremental increase in one’s violent media diet at baseline.
The relative odds of seriously violent behavior 5 years after exposure to violence by media type and overall media diet, weighted data (n=887)
| Exposure to media violence at baseline | Seriously violent behavior 5 years later | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did not report seriously violent behavior | Reported seriously violent behavior | Unadjusted logistic regression model | Adjusted logistic regression model | |||
| % (n) | % (n) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | aOR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Violent media diet (M:SE) | −0.07 (0.03) | 0.60 (0.15) | ||||
| Amount of violence in TV shows consumed at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none or some | 75.5% (606) | 40.5% (27) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 24.5% (197) | 59.1% (39) | ||||
| Amount of violence in music listened to at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 44.9% (361) | 16.9% (11) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some | 43.8% (352) | 58.0% (39) | ||||
| Many / almost all / all | 11.3% (90) | 25.1% (17) | ||||
| Amount of violence in video games played at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 39.0% (314) | 10.9% (7) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some | 37.4% (300) | 44.6% (30) | ||||
| Many / almost all / all | 23.6% (190) | 44.5% (30) | ||||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show real people at baseline | ||||||
| None/almost none | 40.5% (27) | 73.7% (49) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some / many / almost all / all | 13.0% (105) | 26.3% (18) | 1.19 (0.53, 2.67) | 0.68 | ||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show cartoons at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 59.3% (476) | 27.0% (40) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some | 32.8% (264) | 41.4% (28) | 1.30 (0.56, 3.03) | 0.54 | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 7.9% (64) | 18.1% (12) | 1.46 (0.53, 4.05) | 0.46 | ||
OR: Odds ratio; aOR: Adjusted odds ratio. Models are adjusted for youth age, sex, race, ethnicity; and baseline seriously violent behavior and exposure to caregiver spousal abuse, propensity to respond to stimuli with anger, externalizing peers, and self-reported honesty in answering survey questions. Bolded text denotes p<0.05; italicized text denotes p<0.20.
Specific types of media also were implicated: Frequent childhood exposure to violence in television (OR = 4.44, p<0.001), music (OR = 5.91, p<0.001), video games (OR=6.73, p<0.001), websites with real people (OR = 2.39, p=0.03) and websites with cartoons (OR = 3.35, p=0.03) each was associated with significantly elevated odds of seriously violent behavior in adolescence. Findings persisted for music (aOR = 3.28, p=0.03), television (aOR = 3.51, p<0.001) and video games (aOR = 3.27, p=0.02) even after adjusting for other childhood influences on violent behavior. Importantly, too, “some” exposure in childhood was associated with seriously violent behavior in adolescence for both music (aOR = 2.34, p=0.05) and video games (aOR = 2.72, p=0.02).
Longitudinal associations a decade later
As shown in Table 3 and Supplemental Figure 1 , the relative odds of seriously violent behavior 10 years after one’s exposure in childhood increased 2.18-fold ( p =0.001) with each incremental increase in one’s violent media diet. After adjusting for other factors, the association persisted (aOR = 1.72, p=0.03). As with adolescence, frequent childhood exposure to violence in music (OR = 4.48, p=0.008), television (OR = 4.26, p=0.001) and video games (OR = 5.38, p=0.001) each were associated with seriously violent behavior in adulthood. This longitudinal association persisted for video games (aOR = 3.28, p=0.03) and television (OR = 3.14, p=0.02) even after taking into account other potentially influential factors; violence depicted in music also was implicated (aOR = 2.85, p=0.13).
The relative odds of seriously violent behavior 10 years after exposure to violence by media type, weighted data (n=760)
| Exposure to media violence at baseline | Seriously violent behavior 10 years later | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did not report seriously violent behavior | Reported seriously violent behavior | Unadjusted logistic regression model | Adjusted logistic regression model | |||
| % (n) | % (n) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | aOR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Violent media diet (M: SE) | −0.06 (0.04) | 0.63 (0.28) | ||||
| Amount of violence in TV shows consumed at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none or some | 73.5% (516) | 39.4% (18) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Many / almost all / all | 26.5% (186) | 60.6% (28) | ||||
| Amount of violence in music listened to at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 46.4% (326) | 26.2% (12) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some | 41.9% (294) | 44.1% (20) | 1.87 (0.68, 5.10) | 0.22 | 1.72 (0.63, 4.68) | 0.29 |
| Many / almost all / all | 11.8% (83) | 29.8% (14) | ||||
| Amount of violence in video games played at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 40.3% (283) | 14.2% (6) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some | 37.0% (260) | 43.0% (20) | ||||
| Many / almost all / all | 22.7% (159) | 42.8% (20) | ||||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show real people at baseline | ||||||
| None/almost none | 86.4% (607) | 73.9% (34) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some / many / almost all / all | 13.6% (96) | 26.1% (12) | 1.43 (0.43, 4.79) | 0.56 | ||
| Amount of violence seen in websites that show cartoons at baseline | ||||||
| None / almost none | 58.4% (410) | 63.8% (29) | 1.0 (RG) | 1.0 (RG) | ||
| Some / many / almost all / all | 41.6% (292) | 36.2% (17) | 0.80 (0.33, 1.91) | 0.61 | ||
RG: Reference group; OR: Odds ratio; aOR: Adjusted odds ratio. Models are adjusted for youth age, sex, race, ethnicity, baseline seriously violent behavior, concurrent propensity to respond to stimuli with anger and self-reported honesty in answering survey questions. Bolded text denotes p<0.05; italicized text denotes p<0.20.
Contrary to other trends observed, exposure to violent websites that depicted cartoons at baseline was associated with lower odds of seriously violent behavior a decade later (aOR = 0.48, p=0.09). Given that this is in the opposite direction of other violent media exposures examined, it seems likely that this may be a statistical anomaly.
Findings were replicated when seriously violent behavior was defined without the measure of sexual assault ( Supplemental Table 2 ), and when missing data were imputed ( Supplemental Table 3 ).
In this national, longitudinal study of children initially 10–15 years of age, findings suggest that exposure to violence in specific mediums and a general diet of violent media across media in childhood are associated with seriously violent behavior in adolescence and adulthood. Measured both in intensity and diversity of exposure, as one’s violent media diet increases incrementally, so too do the odds of seriously violent behavior by 70%, over time. The increased odds are evident even after taking into account other factors that could explain violent behavior later in life, such as one’s violent behaviors in childhood, exposure to caregiver spousal abuse, one’s propensity to respond with anger, and association with peers who engage in activities that could get them in trouble with the police. Pediatricians should work with parents to identify a media consumption plan for their children that is realistic and associated with the least amount of violence as possible across the online, television, game, and music content they consume. Efforts to co-view content and talk with youth about what they are being exposed to in the media they are consuming also are likely useful. 31
Youth do not experience media in a vacuum: Exposure to violence in one medium correlates highly with exposure in another medium. This saturation of messaging may be reinforcing the idea that violence is an appropriate and common tool to address situational anger across environments and stimuli. Understanding how individual types of media are affecting youth behavior is important. Current findings suggest that it may be equally important to understand how influences across media together are affecting behavior. Findings further suggest that early, intense exposure to violence in specific media, namely music, video games, and television, may be related to seriously violent behavior in adolescence and adulthood. There appears to be a stepwise association such that those who report “some” exposure in childhood are differentially at risk than those with more intense (i.e., many, almost all/all) exposures. This suggests that if parents are unable to eliminate their children’s violent media exposure entirely, pediatricians could encourage them to reduce their exposure as much as possible, and that this may still have a positive impact.
Much of the research on exposure to violent media has focused on visual media, such as television, movies, and video games; 17 , 32 , 33 or aggregated exposure across types. 34 Less is known about aural influences, like violent music, although studies exist: In one longitudinal study of adolescents, listening to aggression in music was associated with increased aggression one year later. 35 The current study builds upon this nascent research by noting associations at 5- and 10-years post-exposure, and suggests that more research attention could be focused on the content of the music to which adolescents are listening. Given the ease of digital download of music combined with the widespread ownership of smart phones among today’s adolescents, this exposure may be more hidden and require additional effort by adults to co-experience and manage their children’s consumption.
Limitations
Self-report is a less rigorous measure than objective measures of exposure to violent media. Given the length of the survey and the multitude of questions and topics queried however, it seems unlikely that youth were able to determine the study hypotheses, thereby introducing demand characteristics. Additionally, youth report the intensity of exposure to, and not the amount of time spent with, violent media. For example, some youth who primarily play violent video games may do so for 2 hours a week, whereas others may do so for 40 hours a week. This may result in an underestimate of the association between exposure and behavior. 36
Although community-based research facilitates a wider view into youth behavior than other sources, such as juvenile justice data, self-report is vulnerable to misreporting, particularly of behaviors deemed undesirable. Efforts were made to increase the validity of self-report (e.g., surveying youth online vs in person or over the telephone, reminding them their answers were private, adjusting for self-reported dishonesty in answering survey questions). The inclusion of a social desirability scale might have facilitated a more direct examination of the prevalence and impact of misreporting in the data. That said, one in twenty youth (5%) reported at least one of the seriously violent behaviors queried at baseline. This is generally consistent with base rates observed in other large self-reported surveys, 37 suggesting that under-reporting may not have been an issue in the present study.
Additionally, the multivariate models may be over-adjusting for confounders and report artificially attenuated effect sizes. 38 For example, trait anger can be increased by media violence exposure, 26 and is therefore likely interrelated with media violence exposure. Including trait anger in the multi-variate model, therefore, partially controls for prior effects that this exposure has had on behavior. Also, controlling for prior violent behavior also essentially adjusts for prior predictors of violent behavior. Moreover, youth who consume high levels of media violence may be more likely to spend time with externalizing peers. If true, then the current models may underestimate the association between media violence and violent behavior given that youth who were associating with such peers at baseline were less likely to participate in subsequent waves.
Moreover, although the data are national, they may not be representative. Survey weights were applied to adjust for this possibility. The national reach nonetheless affords a broader view of youth experiences than might not have been observed in a local setting. Moreover, given the study’s focus on mechanism, internal validity is more important than external validity. Finally, rates of attrition are suboptimal, although differential attrition generally was not apparent.
Implications
Since 2006, when baseline data were collected, technology has changed dramatically. A growing body of literature suggests that newer, peer-to-peer, and immersive technologies may positively affect health behavior change. 39 , 40 It stands to reason that a similar learning effect could be observed if content encouraged unhealthy behaviors, including violence. The current study supports this hypothesis with older technology. Future research should both replicate the current study and examine whether newer technologies are associated with an enhanced learning effect.
During childhood, exposure to violence across a variety of media, operationalized as one’s violent media “diet,” appears to be related to engaging in seriously violent behavior in adolescence and adulthood, even beyond one’s propensity to respond to situations with anger, having peers who are engaging in behaviors that could get them in trouble with the police, being exposed to caregiver spousal abuse, and engaging in violent behaviors as a child. Specific exposures to video games and television also appear to be associated with violent behavior over time; similar linkages are suggested for music. While findings should be replicated in other community-based samples, it seems reasonable to suggest that pediatricians might work with parents to identify a media consumption plan that minimizes children’s exposure to violence across media types and is realistic within the family milieu.
Implications and Contribution
In this national, longitudinal study, exposure to violent media at 10–15 years-old was associated with increased odds of seriously violent behavior 5 and 10 years later, adjusting for aggression, externalizing peers, and caregiver spousal abuse. This was true for a general ‘violent media diet;’ and video games, television and music.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements:.
We would like to thank the entire Growing up with Media study team from the Center for Innovative Public Health Research, Princeton Survey Research Associates International, Harris Interactive, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, who contributed to different parts of the planning and implementation of the study. Finally, we thank the families and youth for their time and willingness to participate in this study.
Funding/support
Research reported in this publication was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01HD083072, and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention under Award Numbers U49 CE000206; R01 CE001543. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Neither funder was involved in data analysis or manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest disclosure:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Contributor Information
Michele L. Ybarra, Center for Innovative Public Health Research, San Clemente, California.
Kimberly J. Mitchell, Crimes against Children Research Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, New Hampshire.
Jay Koby Oppenheim, Independent Consultant, New York, New York.
- A-Z Publications
Annual Review of Public Health
Volume 27, 2006, review article, the role of media violence in violent behavior.
- L. Rowell Huesmann 1 , and Laramie D. Taylor 1
- View Affiliations Hide Affiliations Affiliations: 1 Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48106-1248; email: [email protected] 2 Communication Department, University of California, Davis, California 95616; email: [email protected]
- Vol. 27:393-415 (Volume publication date April 2006) https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.26.021304.144640
- © Annual Reviews
Media violence poses a threat to public health inasmuch as it leads to an increase in real-world violence and aggression. Research shows that fictional television and film violence contribute to both a short-term and a long-term increase in aggression and violence in young viewers. Television news violence also contributes to increased violence, principally in the form of imitative suicides and acts of aggression. Video games are clearly capable of producing an increase in aggression and violence in the short term, although no long-term longitudinal studies capable of demonstrating long-term effects have been conducted. The relationship between media violence and real-world violence and aggression is moderated by the nature of the media content and characteristics of and social influences on the individual exposed to that content. Still, the average overall size of the effect is large enough to place it in the category of known threats to public health.
Article metrics loading...
Full text loading...
Literature Cited
- Abelson RP . 1985 . A variance explanation paradox: when a little is a lot. Psychol. Bull. 97 : 129– 33 [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez MM , Huston AC , Wright JC . 1988 . Gender differences in visual attention to television form and content. J . Appl. Dev. Psychol. 9 :( 4 ) 459– 75 [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA . 1997 . Effects of violent movies and trait irritability on hostile feelings and aggressive thoughts. Aggress. Behav. 23 : 161– 78 [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA , Bushman BJ . 2001 . Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol. Sci. 12 : 353– 59 [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA , Bushman BJ . 2002 . Human aggression. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 53 : 27– 51 [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA , Carnagey NL , Flanagan M , Benjamin AJ , Eubanks J , Valentine JC . 2004 . Violent video games: specific effects of violent content on aggressive thoughts and behavior. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology ed. M Zanna New York: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA , Dill KE . 2000 . Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 78 : 772– 90 [Google Scholar]
- Anderson CA , Huesmann LR . 2003 . Human aggression: a social-cognitive view. In Handbook of Social Psychology ed. MA Hogg, J Cooper pp. 296– 323 London: Sage [Google Scholar]
- Atkin C . 1983 . Effects of realistic TV violence vs. fictional violence on aggression. Journal. Q. 60 : 615– 21 [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A . 1977 . Social Learning Theory Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A . 1986 . Social Foundations of Thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A . 1994 . Social cognitive theory of mass communication. In Media Effects: Advances in Theory and Research ed. J Bryant, D Zillmann pp. 61– 90 Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A , Ross D , Ross SA . 1963 . A comparative test of the status envy, social power, and secondary reinforcement theories of identificatory learning. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 67 : 527– 34 [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A , Ross D , Ross SA . 1963 . Imitation of film-mediated aggressive models. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 67 : 3– 11 [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A , Ross D , Ross SA . 1963 . Vicarious reinforcement and imitative learning. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 67 : 601– 7 [Google Scholar]
- Bartholow BD , Anderson CA . 2002 . Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: Potential sex differences. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 38 : 283– 90 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L . 1965 . Some aspects of observed aggression. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2 : 359– 69 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L . 1993 . Aggression: Its Causes, Consequences, and Control New York: McGraw-Hill [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L , Alioto JT . 1973 . The meaning of an observed event as a determinant of its aggressive consequences. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 28 : 206– 17 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L , Geen RG . 1967 . Stimulus qualities of the target of aggression: a further study. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 5 : 364– 68 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L , LePage A . 1967 . Weapons as aggression-eliciting stimuli. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 7 : 202– 7 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L , Macaulay J . 1971 . The contagion of criminal violence. Sociometry 34 : 238– 60 [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L , Powers PC . 1979 . Effects of timing and justification of witnessed aggression on the observers' punitiveness. J. Res. Pers. 13 : 71– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkqvist K . 1985 . Violent Films, Anxiety, and Aggression Helsinki: Finn. Soc. Sci. Lett. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant J , Zillmann D . 1979 . Effect of intensification of annoyance through unrelated residual excitation on substantially delayed hostile behavior. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 15 :( 5 ) 470– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Bushman BJ . 1995 . Moderating role of trait aggressiveness in the effects of violent media on aggression. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 69 : 950– 60 [Google Scholar]
- Bushman BJ , Geen RG . 1990 . Role of cognitive-emotional mediators and individual differences in the effects of media violence on aggression. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 58 : 156– 63 [Google Scholar]
- Bushman BJ , Huesmann LR . 2001 . Effects of televised violence on aggression. In Handbook of Children and the Media ed. D Singer, J Singer pp. 223– 54 Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth G . 1999 . Neonatal imitation: existence, mechanisms and motives. In Imitation in Infancy ed. J Nadel, G Butterworth pp. 63– 88 New York: Cambridge Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Calvert SL , Tan S . 1994 . Impact of virtual reality on young adults' physiological arousal and aggressive thoughts: interaction versus observation. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 15 : 125– 39 [Google Scholar]
- Cantor J . 1994 . Confronting children's fright responses to mass media. In Media, Children, and the Family: Social Scientific, Psychodynamic, and Clinical Perspectives ed. D Zillmann, J Bryant pp. 139– 50 Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum [Google Scholar]
- Cantor J . 2002 . Fright reactions to mass media. In Media Effects: Advances in Theory and Research ed. J Bryant, D Zillmann pp. 287– 306 Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum, 2nd ed.. [Google Scholar]
- Cline VB , Croft RG , Courrier S . 1973 . Desensitization of children to television violence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 27 :( 3 ) 360– 65 [Google Scholar]
- Comstock G , Paik H . 1991 . Television and the American Child San Diego, CA: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Dodge KA . 1980 . Social cognition and children's aggressive behavior. Child Dev. 51 :( 1 ) 162– 70 [Google Scholar]
- Dodge KA . 1985 . Attributional bias in aggressive children. In Advances in Cognitive-Behavioral Research and Therapy ed. PC Kendall 4 73– 110 San Diego, CA: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Dodge KA , Pettit GS , Bates JE , Valente E . 1995 . Social information-processing patterns partially mediate the effect of early physical abuse on later conduct problems. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 104 :( 4 ) 632– 43 [Google Scholar]
- Dorr A , Kovaric P . 1980 . Some of the people some of the time—but which people? Televised violence and its effects. In Children and the Faces of Television ed. EL Palmer, A Dorr pp. 183– 99 New York: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Eron LD , Huesmann LR , Lefkowitz MM , Walder LO . 1972 . Does television violence cause aggression. Am. Psychol. 27 : 253– 63 [Google Scholar]
- Fenigstein A . 1979 . Does aggression cause a preference for viewing media violence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 37 : 2307– 17 [Google Scholar]
- Feshbach S . 1972 . Reality and fantasy in filmed violence. In Television and Social Behavior: A Technical Report to the Surgeon General's Scientific Advisory Committee on Television and Social Behavior: Vol. 3. Television and Adolescent Aggressiveness ed. GA Comstock, EA Rubinstein pp. 318–45. DHEW Publ. No. HSM 72–9058 Washington, DC: U.S. Gov. Print. Off. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich LK , Stein AH . 1973 . Aggressive and prosocial television programs and the natural behavior of preschool children. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child 38 :( 4 ) 1– 63 [Google Scholar]
- Geen RG , O'Neal EC . 1969 . Activation of cue-elicited aggression by general arousal. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 11 :( 3 ) 289– 92 [Google Scholar]
- Geen RG , Stonner R . 1973 . Context effects in observed violence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 25 : 145– 50 [Google Scholar]
- Gentile DA , Lynch PL , Linder JR , Walsh DA . 2004 . The effects of violent video game habits on adolescent hostility, aggressive behaviors, and school performance. J. Adolesc. 27 :( 1 ) 5– 22 [Google Scholar]
- Gerbner G , Gross L , Morgan M , Signorielli N . 1994 . Growing up with television: the cultivation perspective. See Ref. 12 pp. 17– 41
- Guerra NG , Huesmann LR , Hanish L . 1995 . The role of normative beliefs in children's social behavior. In Social Development ed. N Eisenberg pp. 140– 58 Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage [Google Scholar]
- Guerra NG , Huesmann LR , Spindler AJ . 2003 . Community violence exposure, social cognition, and aggression among urban elementary-school children. Child Dev. 74 :( 5 ) 1561– 76 [Google Scholar]
- Guerra NG , Huesmann LR , Tolan PH , VanAcker R , Eron L . 1995 . Stressful events and individual beliefs as correlates of economic disadvantage and aggression among urban children. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 63 :( 4 ) 518– 28 [Google Scholar]
- Gunter B . 1983 . Do aggressive people prefer violent television. Bull. Br. Psychol. Soc. 36 : 166– 68 [Google Scholar]
- Haninger K , Thompson KM . 2004 . Content and ratings of teen-rated video games. JAMA 291 :( 7 ) 856– 65 [Google Scholar]
- Hansen CH , Hansen RD . 1990 . Rock music videos and antisocial behavior. Basic Appl . Soc. Psychol. 11 :( 4 ) 357– 69 [Google Scholar]
- Hapkiewicz WG , Stone RD . 1974 . The effect of realistic versus imaginary aggressive models on children's interpersonal play. Child Study J. 4 :( 2 ) 47– 58 [Google Scholar]
- Harrison K , Cantor J . 1999 . Tales from the screen: enduring fright reactions to scary media. Media Psychol. 1 :( 2 ) 97– 116 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR . 1988 . An information processing model for the development of aggression. Aggress. Behav. 14 : 13– 24 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR . 1998 . The role of social information processing and cognitive schema in the acquisition and maintenance of habitual aggressive behavior. In Human Aggression: Theories, Research, and Implications for Social Policy ed. RG Geen, E Donnerstein pp. 73– 109 New York: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Eron LD . eds. 1986 . Television and the Aggressive Child: A Cross-National Comparison Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Eron LD , Dubow EF . 2003 . Childhood predictors of adult criminality: Are all risk factors reflected in childhood aggressiveness. Crim. Behav. Mental Health 12 : 185– 208 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Guerra NG . 1997 . Children's normative beliefs about aggression and aggressive behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72 :( 2 ) 408– 19 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Lagerspetz K , Eron LD . 1984 . Intervening variables in the TV violence-aggression relation: evidence from two countries. Dev. Psychol. 20 : 746– 75 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Miller LS . 1994 . Long-term effects of repeated exposure to media violence in childhood. In Aggressive Behavior: Current Perspectives ed. LR Huesmann pp. 153– 83 New York: Plenum [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Moise JF , Podolski CL . 1997 . The effects of media violence on the development of antisocial behavior. In Handbook of Antisocial Behavior ed. DM Stoff, J Breiling, JD Maser pp. 181– 93 New York: Wiley [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Moise-Titus J , Podolski CL , Eron LD . 2003 . Longitudinal relations between children's exposure to TV violence and their aggressive and violent behavior in young adulthood: 1977–1992. Dev. Psychol. 39 : 201– 21 [Google Scholar]
- Huesmann LR , Taylor LD . 2003 . The case against the case against media violence. In Media Violence and Children ed. DA Gentile pp. 107– 30 Westport, CT: Praeger [Google Scholar]
- Ihori N , Sakamoto A , Kobayashi K , Kimura F . 2003 . Does video game use grow children's aggressiveness? Results from a panel study. In Social Contributions and Responsibilities of Simulation and Gaming ed. K Arai pp. 221– 30 Tokyo: Jap. Assoc. Simul. Gaming [Google Scholar]
- Irwin AR , Gross AM . 1995 . Cognitive tempo, violent video games, and aggressive behavior in young boys. J. Family Violence 10 : 337– 50 [Google Scholar]
- Johnson JD , Adams MS , Ashburn L , Reed W . 1995 . Differential gender effects of exposure to rap music on African American adolescents' acceptance of teen dating violence. Sex Roles 33 : 597– 605 [Google Scholar]
- Johnson JD , Jackson LA , Gatto L . 1995 . Violent attitudes and deferred academic aspirations: deleterious effects of exposure to rap music. Basic Appl. Soc. Psychol. 16 :( 1–2 ) 27– 41 [Google Scholar]
- Johnson JG , Cohen P , Smailes EM , Kasen S , Brook JS . 2002 . Television viewing and aggressive behavior during adolescence and adulthood. Science 295 : 2468– 71 [Google Scholar]
- Josephson WL . 1987 . Television violence and children's aggression: testing the priming, social script, and disinhibition predictions. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 53 : 882– 90 [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh SJ . 1998 . Seeing the world through Mortal Kombat-colored glasses: violent video games and the development of a short-term hostile attribution bias. Childhood 5 : 177– 84 [Google Scholar]
- Kirwil L , Huesmann LR . 2003 . The relation between aggressiveness and emotional reactions to observed violence Presented at Annu. Meet. Midwest. Psych. Assoc., Chicago [Google Scholar]
- Lando HA , Donnerstein EI . 1978 . The effects of a model's success or failure on subsequent aggressive behavior. J. Res. Pers. 12 : 225– 34 [Google Scholar]
- Leyens JP , Picus S . 1973 . Identification with the winner of a fight and name mediation: their differential effects upon subsequent aggressive behavior. Br. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 12 : 374– 77 [Google Scholar]
- Lord CG , Ross L , Lepper MR . 1979 . Biased assimilation and attitude polarization: the effects of prior theories on subsequently considered evidence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 37 :( 11 ) 2098– 109 [Google Scholar]
- Malamuth NM , Check JVP . 1983 . Sexual arousal to rape depictions: individual differences. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 92 :( 1 ) 55– 67 [Google Scholar]
- Malamuth NM , Check JVP . 1985 . The effects of aggressive pornography on beliefs in rape myths: individual differences. J. Res. Personal. 19 : 299– 320 [Google Scholar]
- Meltzoff AN , Moore MK . 2000 . Imitation of facial and manual gestures by human neonates: resolving the debate about early imitation. In Infant Development: The Essential Readings ed. D Muir, A Slater pp. 167– 81 Malden, MA: Blackwell [Google Scholar]
- Milavsky JR , Kessler R , Stipp H , Rubens WS . 1982 . Television and aggression: results of a panel study. In Television and Behavior: Ten Years of Scientific Progress and Implications for the Eighties: Vol. 2. Technical Reviews ed. D Pearl, L Bouthilet, J Lazar pp. 138– 57 DHHS Publ. No. ADM 82–1196 Washington, DC: U.S. Gov. Print. Off. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt TE , Caspi A , Harrington H , Milne BJ . 2002 . Males on the life-course-persistent and adolescence-limited antisocial pathways: follow-up at age 26 years. Dev. Psychopathol. 14 :( 1 ) 179– 207 [Google Scholar]
- Moise-Titus J . 1999 . The role of negative emotions in the media violence-aggression relation Unpubl. PhD diss., Univ. Mich. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson AI . 1999 . Identifying and explaining the relationship between parental mediation and children's aggression. Commun. Res. 26 : 124– 43 [Google Scholar]
- Neely JJ , Hechel RV , Leichtman HM . 1973 . The effect of race of model and response consequences to the model on imitation in children. J. Soc. Psychol. 89 : 225– 31 [Google Scholar]
- O'Neal EC , Taylor SL . 1989 . Status of the provoker, opportunity to retaliate, and interest in video violence. Aggress. Behav. 15 : 171– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Paik H , Comstock G . 1994 . The effects of television violence on antisocial behavior: a meta-analysis. Commun. Res. 21 : 516– 46 [Google Scholar]
- Peterson DL , Pfost KS . 1989 . Influence of rock videos on attitudes of violence against women. Psychol. Rep. 64 : 319– 22 [Google Scholar]
- Phillips DP . 1979 . Suicide, motor vehicle fatalities, and the mass media: evidence toward a theory of suggestion. Am. J. Sociol. 84 : 1150– 74 [Google Scholar]
- Phillips DP . 1982 . The impact of fictional television stories on U.S. adult fatalities: new evidence on the effect of the mass media on violence. Am. J. Sociol. 87 : 1340– 59 [Google Scholar]
- Phillips DP . 1983 . The impact of mass media violence on U.S. homicides. Am. Sociol. Rev. 48 : 560– 68 [Google Scholar]
- Potts R , Huston AC , Wright JC . 1986 . The effects of television form and violent content on boys' attention and social behavior. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 41 : 1– 17 [Google Scholar]
- Prinz J . 2005 . Emotional Perception New York: Oxford Univ. Press In press [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolati G , Fadiga L , Gallese V , Fogassi L . 1996 . Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Cogn. Brain Res. 3 : 131– 41 [Google Scholar]
- Roberts DF , Foehr UG , Rideout VJ . 2005 . Generation M: Media in the Lives of 8–18 Year-Olds Menlo Park, CA: Henry J. Kaiser Family Found. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R . 1986 . Media violence, antisocial behavior, and the social consequences of small effects. J. Soc. Issues 42 :( 3 ) 141– 54 [Google Scholar]
- Simon A . 1979 . Violence in the mass media: a case of modeling. Percept. Mot. Skills 48 : 1081– 82 [Google Scholar]
- Singer JL , Singer DG . 1986 . Family experiences and television viewing as predictors of children's imagination, restlessness, and aggression. J. Soc. Issues 42 :( 3 ) 107– 24 [Google Scholar]
- Singer JL , Singer DG . 1986 . Television-viewing and family communication style as predictors of children's emotional behavior. J. Child. Contemp. Soc. 17 : 75– 91 [Google Scholar]
- Slater MD , Henry KL , Swaim RC , Anderson LL . 2003 . Violent media content and aggressiveness in adolescents: a down ward spiral model. Commun. Res. 30 :( 6 ) 713– 36 [Google Scholar]
- Stack S . 1989 . The effect of publicized mass murders and murder-suicides on lethal violence, 1968–1980: A research note. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemol. 24 : 202– 8 [Google Scholar]
- Stack S . 2000 . Media impacts on suicide: a quantitative review of 293 findings. Soc. Sci. Q. 81 :( 4 ) 957– 71 [Google Scholar]
- Thompson KM , Haninger K . 2001 . Violence in E-rated video games. JAMA 286 :( 5 ) 591– 98 [Google Scholar]
- Valentino NA , Traugott M , Hutchings V . 2002 . Group cues and ideological constraint: A replication of political advertising effects studies in the lab and in the field. Polit. Commun. 19 : 29– 48 [Google Scholar]
- Walters RH , Parke RD . 1964 . Influence of response consequences to a social model on resistance to deviation. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1 : 269– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Wilson BJ , Kunkel D , Linz D , Potter J , Donnerstein E . et al. 1997 . Violence in television programming overall: University of California, Santa Barbara study. In National Television Violence Study ed. M Seawall 1 3– 184 Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage [Google Scholar]
- Wyrwicka W . 1996 . Imitation in Human and Animal Behavior New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction [Google Scholar]
- Zajonc RB , Murphy ST , Inglehart M . 1989 . Feeling and facial efference: implications of the vascular theory of emotion. Psychol. Rev. 96 : 395– 416 [Google Scholar]
Data & Media loading...
- Article Type: Review Article
Most Read This Month
Most cited most cited rss feed, review of community-based research: assessing partnership approaches to improve public health, nature and health, measuring social class in us public health research: concepts, methodologies, and guidelines, the epidemiology of depression across cultures, acute respiratory effects of particulate air pollution, racism and health: evidence and needed research, the social determinants of health: coming of age, the role of behavioral science theory in development and implementation of public health interventions, mediation analysis: a practitioner's guide, the prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction.
Violence in the Media and Entertainment (Position Paper)
The prevalence and impact of violence portrayed in media and entertainment have long been a topic of debate in the United States. In 1972, the U.S. surgeon general issued a special report on the large and growing body of evidence on the public health effects of media violence. 1 At the time, the report was largely focused on television as the prevailing form of media and entertainment in the United States. However, even as the landscape of media has changed throughout the intervening decades to include other forms of digital media and entertainment, the near-ubiquitous portrayals of violence in various forms of media have remained a topic of intense scrutiny.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined violence as “the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation.” 2 Violence occurs at an alarming rate in the United States. 3 Among Americans aged 15 to 34 years, two of the top three causes of death are homicide and suicide, and many of these deaths involve firearms. 4,5 In a given year, more U.S. children will die from gun violence than will die from cancer, pneumonia, influenza, asthma, HIV/AIDS, and opioids combined. 6 According to the Children’s Defense Fund, “U.S. children and teens are 15 times more likely to die from gunfire than their peers in 31 other high-income countries combined.” 7 In fact, the overall rate of firearm-related death or injury in the United States is higher than the rate in most other industrialized countries. 8 There were 39,740 firearm-related deaths in the United States in 2018, which averages to approximately 109 people dying each day from homicides, suicides, and unintentional deaths involving firearms. 5 Further, the number of nonfatal injuries due to firearms is more than double the number of deaths. 9
While multiple factors can lead to violent actions, a growing body of literature shows a strong association between the perpetration of violence and exposure to violence in media, digital media, and entertainment. This is a serious public health issue that should concern all family physicians, particularly as it affects young patients and their parents or guardians. Children, adolescents, and young adults consume digital media from a variety of sources, many of which are mobile, are accessible 24 hours a day, and offer both passive and active engagement. Many of these media platforms feature entertainment that contains significant doses of violence and portrays sexual and interpersonal aggression.
Multiple studies have shown either a strong association or a suspicion or suggestion of causality between exposure to violence in media and aggressive or violent thoughts, emotions, and behavior in those exposed. 10 It is incumbent on family physicians to recognize the intersectionality of risk factors for exposure to violence in media, digital media, and entertainment, particularly for vulnerable populations. For example, some studies have shown that independent risk factors for exposure to extremely violent movies include male gender, racial or ethnic minority status, low socioeconomic status, and poor school performance. 11
Call to Action
Family physicians have a unique opportunity to encourage safer use of digital media by working closely with patients and their parents or guardians during well-child and well-adolescent visits. They can connect patients and parents or guardians to resources to promote healthier habits, such as creating a family technology use plan that considers the quality and quantity of media being consumed at home. Family physicians can also engage in local, state, and national advocacy to highlight ongoing concerns regarding violence in media, digital media, and entertainment and support continued research in this field.
Physician Level
● Promote a family technology use plan. This allows parents and guardians to consider the quality and quantity of digital media that is consumed at home and establish guidelines for age-appropriate media exposure. 12 Parental use of digital media has been shown to influence media use behaviors in children. 13
● Increase personal knowledge of the types of digital media being consumed in households, particularly among children and adolescents.
● Encourage patients, children, families, and caregivers to participate in media education and media literacy programs.
● Encourage parents or guardians to monitor content and not to rely solely on media ratings or advisory labels. Parental monitoring has been shown to have protective effects on several academic, social, and physical outcomes for children, including aggressive behaviors. 14
● Advise adults to consume digital media with their children and help them process media violence. Recording programs in advance makes it possible to pause for discussion or processing.
● Consider asking questions regarding media use during well-child and well-adolescent visits, such as:
- How much entertainment media does the child or teen consume each day?
- Does the child or teen have a television or digital media access in their bedroom?
● Consider asking patients and parents or guardians about exposure to violence in digital media. If you identify heavy exposure (i.e., more than two hours daily), take additional history of aggressive behaviors, sleep problems, fears, and depression. Be ready to discuss the health risks associated with consumption of violent media.
● Work with patients and parents or guardians to create a list of healthy alternatives to consumption of violent media.
● Counsel parents or guardians and caregivers of children younger than two years of age to limit their child's screen time to no more than two hours a day. Discourage routine digital media exposure.
● Encourage use of technology that restricts certain content and turns off the device after a certain amount of time.
Practice Level
● Create a nonjudgmental and culturally proficient environment in which patients and parents or guardians can ask questions and express concerns.
● Provide and/or promote nonviolent media choices in outpatient waiting rooms and inpatient settings.
● Display promotional information for community media literacy education opportunities.
Education Level
● Become familiar with research on trends in media use and the effects of media violence on individuals.
● Align medical education and residency program training to deliver evidence-based information on the potential health effects of consumption of violent media.
● Expand current continuing medical education (CME) offerings to include evidence-based information on best practices to promote media education and healthy media consumption.
● Support the development of media literacy education programs that focus on understanding the divide between real and fictionalized violence on television, in movies, and in other forms of digital media, as well as the responsibility, complexity, and consequences of real-life violence. Media literacy programs have been shown to be effective in limiting the negative effects of media and exploring potential positive social uses of media. 14,15,16
Advocacy Level
● Partner with medical organizations, government entities, and educators to advocate to keep this issue on the public health agenda.
● Partner with families and community-based organizations to demand that media producers limit the amount and type of violence portrayed in mass media.
● Advocate for research funding to continue studying this topic.
● Advocate for enhancements to media rating systems to help parents or guardians and caregivers guide children to make healthy media choices.
Media Violence in the United States
The term “digital media” refers to all types of electronic data, including text, databases, images, audio, and video; it may also refer to the electronic devices that store the data and to the communications methods that transmit the data. 17 Examples include streaming video, messaging and social networking platforms, video games, television, music, music videos, and social media. The expansion of media to include more and more forms of digital media has made it easier to access and be exposed to portrayals of violence. The advent of the internet has further expanded the reach and impact of digital media by encouraging interactivity and group forming through media such as online gaming, virtual reality, digital art, and social media. 18
As the cost of televisions and other screen media devices has continued to drop in recent years, screen media, streaming media, and other digital media have become more accessible than ever. In the United States, 84% of households contain at least one smartphone, with the median U.S. household containing five connected devices (e.g., smartphone, laptop or desktop computer, streaming media device) and one in five households containing 10 or more of these devices. 19
For decades, watching television was the most common form of daily media consumption, but that changed in 2019, with time on the internet exceeding time spent watching television. 20 Research suggests that young people in the United States spend more time interacting with various digital media than in any other activity except sleeping, with a typical 8- to 18-year-old using some form of media for an average of 50 hours per week or more. 21 On average, U.S. teens spend more than seven hours per day consuming a variety of entertainment screen media (e.g., smartphone, social media, gaming, music) and 8- to 12-year-olds spend more than four hours per day. 22
Studies demonstrating an association between exposure to violence in the media and real-life aggression and violence began appearing in the 1950s. Since then, various government agencies and organizations have examined the relationship, reporting their findings in publications including the surgeon general’s 1972 report, a 1982 National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) review, and a joint statement on the impact of entertainment violence on children issued following a 2000 congressional summit. 1,23,24 In 2000, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) released a report noting that media violence is a risk factor in shootings in school. 25 A 2003 review identified media violence as a significant causal factor in aggression and violence. 26 The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) issued a 2007 report on violent programming on television and noted that there is “strong evidence” that exposure to violence through media can increase aggressive behavior in children. 27
These reports and others are based on a body of literature that includes more than 2,000 scientific papers, studies, and reviews demonstrating the various effects that exposure to media violence can have on children and adolescents. These include increases in aggressive behavior, desensitization to violence, bullying, fear, depression, nightmares, and sleep disturbances. 28,29,30 Some studies found the strength of association between consumption of violent media and these behaviors to be nearly as strong as the association between cigarette smoking and lung cancer, and stronger than the well-established associations between calcium intake and bone mass, lead ingestion and IQ, and failure to use condoms and acquisition of HIV. 31
Seventy-one percent of 8- to 18-year-olds have a television in their bedroom. 21 In addition, 50% of individuals in this age group access television content online and/or on mobile platforms during a typical day. 21 Researchers have found that 8- to 12-year-olds watch television programming for an average of 1 hour and 23 minutes per day and 13- to 18-year-olds watch for an average of 1 hour and 45 minutes per day, with approximately 19 minutes and 38 minutes of this time, respectively, spent viewing television content on other devices (e.g., computer, smartphone, tablet, MP3 player). 22
An average American youth will witness 200,000 violent acts on television before age 18. 32 Weapons appear on prime-time television an average of nine times each hour. 33 The violence depicted in television content is often considerable, even in programs not advertised as violent, and children’s shows are particularly violent. Watching Saturday morning cartoons used to be a common aspect of American life. Now, children can access cartoons on demand. Studies analyzing the content of popular cartoons noted that they contain 20 to 25 violent acts per hour, which is about five times as many as prime-time programs. 34 Overall, 46% of television violence occurs in cartoons. 35,36,37 Additionally, these programs are more likely to juxtapose violence with humor (67%) and less likely to show the long-term consequences of violence (5%). 34,35,36 Although some claim that cartoon violence is not as “real,” and therefore not as damaging, it has been shown to increase the likelihood of aggressive, antisocial behavior in youth. 38 This association makes sense in light of children’s developmental difficulty discerning the real from the fantastic. 39
Video Games
Nearly all American teens—97% of males and 83% of females—play video games. 40 Eighty percent of teens play at least three hours of video games per week on a game console, with 25% of teens playing 11 hours or more per week. 41 Additional exposure occurs among teens who identify as fans of competitive video gaming, or esports; among 14- to 21-year-olds, nearly as many identified themselves as esports fans as professional football fans. 42
Many video games contain violent content, and studies have shown a significant association between violent video game exposure and increased aggression, increased desensitization to violence, and decreased empathy. 43 Video games that involve assuming the roles of aggressors or soldiers offer players the opportunity to be “virtual perpetrators.” These games also reward players for successfully carrying out violent behavior. Studies have shown that the general effects of violence may be more profound when children play these interactive games than when they are exposed to violence in a more passive manner, such as when watching television. 44,45
Music plays a central role in the lives of many adolescents and young adults, helping them sort through their emotions, identify with peer groups, and develop a sense of self. Forty-seven percent of 8- to 12-year-olds listen to music every day, with an average of 43 minutes of listening time per day, and 82% of 13- to 18-year-olds listen to music every day, with an average of slightly more than two hours of listening time per day. 22
There have been fewer studies of the effects of violent portrayals in music than studies of violence in other forms of media. One study found a correlation between violent lyrics and aggressive thoughts and emotions, but not actions. 46 Additional studies have shown that individuals who prefer heavy metal or rap music are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, have lower grades in elementary school and during adolescence, and have a history of counseling in elementary school for academic problems, compared with peers who prefer other types of music. 47
Music videos have been sources of violent content for decades. Content analysis has shown that more than 80% of the violence in music videos is perpetrated by attractive role models and that music videos mainly depict acts of violence against women and people in minority groups. 48 In many music videos, violent scenes are of a sexual nature. In addition, artistic choices and editing may juxtapose violence with images such as beautiful scenery, potentially linking violence to pleasurable experiences. 49 Several studies that focused on violence in rap music found that this genre contains more violent content than other genres. They also found that viewers of rap music videos were more likely to accept the use of violence, to accept violence against women, and to commit violent or aggressive acts themselves. 49
Several researchers have described an increase in violent content in movies, despite a national rating system. For example, studies have found that 91% of movies on television contain violence, including extreme violence. 11,36 Although film ratings and advisory labels can help parents decide on movies to avoid, certain labels, such as “parental discretion advised” and the R rating, have been shown to attract children, especially boys. 33,35,36 In 2003, 10 million adolescents aged 10 to 14 years, including 1 million 10-year-olds, had been exposed to that year’s most popular R-rated film. 11 One study found that between 2012 and 2017, there were twice as many negative themes—most commonly associated with violence—as positive themes depicted in the 25 top-grossing R-rated films. 50 Researchers have also noted that the amount of gun violence in top-grossing PG-13 films has more than tripled since the introduction of the rating in 1985. 51 In 2012, PG-13 films actually contained more gun violence than R-rated films. 52 Further, violence is even present in movies that are not considered to be violent, such as animated films. 53
1. Surgeon General’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Television and Social Behavior. Television and growing up: the impact of televised violence. Report to the Surgeon General, United States Public Health Service. U.S. Government Printing Office; 1972. DHEW publication no. HSM 72-9090. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://collections.nlm.nih.gov/ext/document/101584932X543/PDF/101584932X543.pdf
2. World Health Organization. Definition and typology of violence. Accessed July 19, 2020.
3. American Academy of Family Physicians. Violence (reviewed and approved 2014). Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/violence-position-paper.html
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 10 leading causes of death by age group, United States -- 2018. Accessed July 19, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_by_age_group_2018_1100w850h.jpg
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Firearm violence prevention. Accessed October 20, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/firearms/fastfact.html
6. Children’s Defense Fund. Protect children, not guns 2019. Accessed July 31, 2020. https://www.childrensdefense.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Protect-Children-Not-Guns-2019.pdf
7. Children’s Defense Fund. The state of America’s children 2020. Accessed July 19, 2020. https://www.childrensdefense.org/policy/resources/soac-2020-overview
8. Gramlich J. What the data says about gun deaths in the U.S. Pew Research Center; 2019. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/08/16/what-the-data-says-about-gun-deaths-in-the-u-s/
9. Fowler KA, Dahlberg LL, Haileyesus T, et al. Firearm injuries in the United States. Prev Med . 2015;79:5-14.
10. Huesmann LR. The impact of electronic media violence: scientific theory and research. J Adolesc Health . 2007;41(6 Suppl 1):S6-S13.
11. Worth KA, et al. Exposure of US adolescents to extremely violent movies. Pediatrics . 2008;(122)2:306-312.
12. American Academy of Pediatrics. Family media plan. Accessed October 19, 2020. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/media/Pages/default.aspx
13. Jago R, Sebire SJ, Edwards MJ, et al. Parental TV viewing, parental self-efficacy, media equipment and TV viewing among preschool children. Eur J Pediatr . 2013;172(11):1543-1545.
14. Gentile DA, Reimer RA, Nathanson AI, et al. Protective effects of parental monitoring of children's media use: a prospective study, JAMA Pediatr. 2014;(168)5:479-484. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/1852609
15. American Academy Pediatrics Committee on Public Education. Media education. Pediatrics . 1999;104(2):341-343.
16. Brown JA. Television “Critical Viewing Skills” Education: Major Media Literacy Projects in the United States and Selected Countries. Routledge; 1991.
17. PC Magazine Encyclopedia. Digital media. Accessed October 20, 2020. https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/digital-media
18. Smith R. What is digital media? Centre for Digital Media; 2013. Accessed August 22, 2020. https://thecdm.ca/news/what-is-digital-media
19. Pew Research Center. A third of Americans live in a household with three or more smartphones. May 25, 2017. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/05/25/a-third-of-americans-live-in-a-household-with-three-or-more-smartphones/
20. Dolliver M. U.S. time spent with media 2019. eMarketer; 2019. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.emarketer.com/content/us-time-spent-with-media-2019
21. Rideout VJ, Foehr UG, Roberts DF. Generation M 2 : media in the lives of 8- to 18-year-olds. The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation; 2010. Accessed July 19, 2020. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED527859.pdf
22. Rideout V, Robb MB. The Common Sense census: media use by tweens and teens, 2019. Common Sense Media; 2019. Accessed October 16, 2020.
23. National Institute of Mental Health. Television and behavior: ten years of scientific progress and implications for the eighties. Vol. I: summary report. U.S. Government Printing Office; 1982. DHHS publication no. ADM 82-1195. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED222186.pdf
24. American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, American Psychological Association, et al. Joint statement on the impact of entertainment violence on children. Congressional Public Health Summit. 2000.
25. O’Toole ME. The school shooter: a threat assessment perspective. Federal Bureau of Investigation; 1999. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.fbi.gov/file-repository/stats-services-publications-school-shooter-school-shooter/view
26. Anderson CA, Berkowitz L, Donnerstein E, et al. The influence of media violence on youth. Psychol Sci Public Interest . 2003(4)3:81-110.
27. Federal Communications Commission. Violent television programming and its impact on children. 2007. Accessed October 16, 2020. https://www.fcc.gov/document/violent-television-programming-and-its-impact-children
28. Gentile DA. Media Violence and Children: A Complete Guide for Parents and Professionals . 2 nd ed. Praeger; 2014.
29. Coker TR, Elliott MN, Schwebel DC, et al. Media violence exposure and physical aggression in fifth-grade children. Acad Pediatr . 2015;15(1):82-88.
30. Ybarra ML, Diener-West M, Markow D. Linkages between internet and other media violence with seriously violent behavior by youth. Pediatrics . 2008;(122)5:929-937.
31. Singer DG, Singer JL, eds. Handbook of Children and the Media . 2 nd ed. Sage Publications, Inc.; 2011.
32. American Psychological Association. Violence & youth: psychology’s response. Vol. I: summary report of the American Psychological Association Commission on Violence and Youth. 1993. Accessed October 19, 2020. https://www.apa.org/pi/prevent-violence/resources/violence-youth.pdf
33. Strasburger VC, Donnerstein E. Children, adolescents, and the media in the 21 st century. Adolesc Med . 2000;11(1):51-68.
34. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Communications. Media violence. Pediatrics . 1995(6):949-951.
35. Seawell M, ed. National Television Violence Study. Volume 1. Sage Publications, Inc.; 1996.
36. Federman J, ed. National Television Violence Study. Volume 2. Sage Publications, Inc.; 1997.
37. Seawell M, ed. National Television Violence Study. Volume 3. Sage Publications, Inc.; 1998.
38. Leung LR, Fagan JE, Cho H. Children and television. Am Fam Physician . 1994;50:909-912, 915-918.
39. Huesmann LR, Eron LD, Klein R, et al. Mitigating the imitation of aggressive behaviors by changing children’s attitudes about media violence. J Pers Soc Psychol . 1983;44(5):899-910.
40. Pew Research Center. Teens, social media & technology 2018. Accessed October 19, 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/wp-content/uploads/sites/9/2018/05/PI_2018.05.31_TeensTech_FINAL.pdf
41. PricewaterhouseCoopers. The evolution of video gaming and content consumption. 2012. Accessed October 20, 2020. https://www.pwc.com/sg/en/tice/assets/ticenews201206/evolutionvideogame201206.pdf
42. UMass Lowell Center for Public Opinion. 2017 sports poll release – esports and competitive video gaming. Accessed October 19, 2020. https://www.uml.edu/docs/esports-highlights_tcm18-288117.pdf
43. Calvert SL, Appelbaum M, Dodge KA, et al. The American Psychological Association Task Force assessment of violent video games: science in the service of public interest. Am Psychol . 2017;72(2):126-143.
44. Hollingdale J, Greitemeyer T. The effect of online violence video games on levels of aggression. PLoS ONE . 2014;9(11):e111790.
45. Anderson, CA, Gentile DA, Buckley KE. Violent Video Game Effects on Children and Adolescents . Oxford University Press; 2007.
46. Anderson CA, Carangey NL, Eubanks J. Exposure to violent media: the effects of songs with violent lyrics on aggressive thoughts and feelings. J Pers Soc Psychol . 2003;(84)5:960-971.
47. American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Communications and Media. Impact of music, music lyrics, and music videos on children and youth. Pediatrics . 2009;124(5):1488-1494.
48. Rich M, Woods ER, Goodman E, et al. Aggressors or victims: gender and race in music video violence. Pediatrics . 1998;101(4 Pt 1):669-674.
49. Ashby SL, Rich M. Video killed the radio star: the effects of music videos on adolescent health. Adolesc Med Clin . 2005;(16)2:371-393.
50. Watts A, Loloi J, Lessner K, et al. Themes depicted in top-grossing rated-R films released from 2012 to 2017. Cureus . 2020;12(2):e6844.
51. Romer D, Jamieson PE, Bushman BJ, et al. Parental desensitization to violence and sex in movies. Pediatrics . 2014;(134)5:877-884.
52. Bushman BJ, Jamieson PE, Weitz I, et al. Gun violence trends in movies. Pediatrics . 2013;132(6):1014-1018.
53. Kirsh SJ. Cartoon violence and aggression in youth. Aggression and Violent Behavior . 2006;11:547-557.
(2004) (January 2022 COD)
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
- Fake News Research Topics Topics: 60
- Journalism Paper Topics Topics: 84
- Advertising Paper Topics Topics: 312
- Television Topics Topics: 222
- Social Media Topics Topics: 431
- TV Show Research Topics Topics: 67
- Media Analysis Topics Topics: 67
- Gender Stereotypes Paper Topics Topics: 94
- Social Networking Topics Topics: 148
- Color Blindness Topics Topics: 49
- Animal Rights Research Topics Topics: 55
- Facebook Essay Topics Topics: 124
- Gender Inequality Topics Topics: 75
- Social Inequality Research Topics Topics: 77
- Gender Equality Research Topics Topics: 77
55 Media Violence Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on media violence, 🎓 most interesting media violence research titles, 💡 simple media violence essay ideas.
- Does Media Violence Cause Violent Behavior?
- Media Violence and Children
- The Representation of the Violence in the Media
- Violence in Media and Its Impact on Children
- The Issue of Violence in Media and Movies
- “Ordinary” Sexual Violence in Media and Society
- Aggression and Violence in the Media
- Media Violence in ‘Witnessing’ by C. Rentschler
- Media Violence Effects on Brain Development
- Understanding Causality in the Effects of Media Violence
- The Effects of Media Violence Exposure on Criminal Aggression
- Television Commercial Violence: Potential Effects on Children
- The Media Violence Debate and the Risks It Holds for Social Science
- The Disempowering Effects of Media Violence Against Women
- Examining Facilitative Effects of Media Violence on Helping
- The Just Do It Riots: A Critical Interpretation of the Media’s Violence
- The Impact of Mass Media Violence on Suicide and Homicide
- Priming Effects of Media Violence on the Accessibility of Aggressive Constructs in Memory
- Graphic Violence on Social Media and Its Impact on Young Adults
- The Influence of Media Violence on Intimate Partner Violence Perpetration
- The Effects of Media Violence Exposure and Dark Personality Traits
- A Sociological Perspective on Television Violence and Aggression
- The Effects of Media Violence on Anxiety in Emerging Adults
- Long-Term Effects of Repeated Exposure to Media Violence in Childhood
- Desensitizing Effects of Violent Media on Helping Others
- Aggression and Popular Media: From Violence in Entertainment Media to News Coverage of Violence
- The Impact of Mass Media Violence on Homicides in the US
- Media Violence and Judgments of Offensiveness: A Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
- Examining Media Violence Effects on Cooperative Behavior
- Reassessing Media Violence Effects Using a Risk and Resilience Approach to Understanding Aggression
- The Relationship Between Exposure to Media Violence and School Bullying
- Examining the Immediate Effects of Media Violence on Behavior
- Direct and Indirect Relationship Between Media Violence Exposure and Cyberbullying Perpetration
- The Mediating Role of Sympathy in the Relationship Between Media Violence and Adolescents’ Social Behaviors
- The Evolution of Scientific Skepticism in the Media Violence Debate
- Media Violence in Inducing Neural Changes During Emotional Face Processing
- Catharsis and Media Violence: A Conceptual Analysis
- Examining Exposure to Graphic Media Violence Through a Theory of Vivid Media Violence
- Media Violence and Adolescents’ ADHD-Related Behaviors: A Genetic Susceptibility Perspective
- Types of Media Violence and Degree of Acceptance in Under‐18s
- The Effects of a Media Literacy Program on Critical Attitudes Toward Media Violence
- Investigating How Media Violence Causes Antisocial Behavior
- The Role of Attention Problems and Impulsiveness in Media Violence Effects on Aggression
- Early Exposure to Media Violence and Later Child Adjustment
- Transportation Into Vivid Media Violence: Attention, Emotions, and Mental Rumination
- The Proliferation of Media Violence and Its Economic Underpinnings
- A Meta-Analytical Review of Selective Exposure to and the Enjoyment of Media Violence
- Public Policy and the Effects of Media Violence on Children
- Fronto-Parietal Regulation of Media Violence Exposure in Adolescents
- Exploring the Public Health Risks of Media Violence
- Repeated Exposure: Desensitization to Media Violence Over a Short Period
- Imitation and the Effects of Observing Media Violence on Behavior
- The Interplay of Media Violence Effects and Behaviorally Disordered Individuals
- Violent Video Games as the Newest Media Violence Hazard
- Aggression‐Consistent, ‐Inconsistent, and ‐Irrelevant Priming Effects on Selective Exposure to Media Violence
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2024, August 21). 55 Media Violence Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/media-violence-essay-topics/
"55 Media Violence Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 21 Aug. 2024, studycorgi.com/ideas/media-violence-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2024) '55 Media Violence Essay Topics'. 21 August.
1. StudyCorgi . "55 Media Violence Essay Topics." August 21, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/media-violence-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "55 Media Violence Essay Topics." August 21, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/media-violence-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2024. "55 Media Violence Essay Topics." August 21, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/media-violence-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Media Violence were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on September 10, 2024 .
How the Media Sanitizes Trump’s Insanity
The political press’s efforts to rationalize trump’s incoherent statements are eroding our shared reality and threatening informed democracy..

Four years ago, in an article for Media Matters for America , I warned that journalists were sanitizing Donald Trump’s incoherent ramblings to make them more palatable for the average voter. The general practice went like this: The press would take something Trump said or did—for instance, using a visit to the Centers for Disease Control to ask about Fox News’s ratings, insult then–Washington Governor Jay Inslee, rant about his attempt to extort Ukraine into digging up dirt on Joe Biden, and downplay the rising number of Covid-19 cases in the U.S.—and write them up as The New York Times did : “Trump Says ‘People Have to Remain Calm’ Amid Coronavirus Outbreak.” This had the effect of making it seem like Trump’s words and actions seemed cogent and sensible for the vast majority of Americans who didn’t happen to watch his rant live.
Flash-forward to today, and it’s clear this problem has only worsened. As Trump’s statements grow increasingly unhinged in his old age, major news outlets continue to reframe his words, presenting a dangerously misleading picture to the public.
For instance, last week, Trump posted the following to his Truth Social account:
I have reached an agreement with the Radical Left Democrats for a Debate with Comrade Kamala Harris. It will be Broadcast Live on ABC FAKE NEWS, by far the nastiest and most unfair newscaster in the business, on Tuesday, September 10th, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The Rules will be the same as the last CNN Debate, which seemed to work out well for everyone except, perhaps, Crooked Joe Biden. The Debate will be “stand up,” and Candidates cannot bring notes, or “cheat sheets.” We have also been given assurance by ABC that this will be a “fair and equitable” Debate, and that neither side will be given the questions in advance (No Donna Brazile!). Harris would not agree to the FoxNews Debate on September 4th, but that date will be held open in case she changes her mind or, Flip Flops, as she has done on every single one of her long held and cherished policy beliefs. A possible third Debate, which would go to NBC FAKE NEWS, has not been agreed to by the Radical Left. GOD BLESS AMERICA!
CNN described that rambling, insult-laden, conspiracy-riddled wall of text—itself a pretty good example of what he spends his time off the campaign trail doing—by writing, “Former President Donald Trump on Tuesday announced he has ‘reached an agreement’ to participate in a September 10 debate with Vice President Kamala Harris, noting that ‘the rules will be the same as the last CNN debate, which seemed to work out well for everyone.’”
Does that really capture what Trump posted?
Days earlier, Trump heralded the endorsement of Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a man who has long pushed baseless claims that vaccines cause autism, by saying that “a panel of top experts, working with Bobby,” would “investigate what is causing the decades-long increase in chronic health problems and childhood diseases, including autoimmune disorders, autism, obesity, infertility, and more.”
In its write-up of that portion of Trump’s speech, The New York Times omitted Trump’s mention of autism, simply writing that “Mr. Trump said that, if elected to a second term, a panel of experts ‘working with Bobby’ would investigate obesity rates and other chronic health issues in the United States.” By removing the mention of autism, which should be a red flag whenever paired with a mention of Kennedy, the Times took an obvious nod to a conspiracy theory and turned it into a normal-sounding policy proposal.
While speaking at an event put on by the extremist group Moms for Liberty, Trump spread a baseless conspiracy theory that “your kid goes to school and comes home a few days later with an operation,” referring to transition-related surgeries for trans people. In their write-up of the event , a glowing piece about how Trump “charmed” this group of “conservative moms,” the Times didn’t even mention the moment where he blathered on and on about a crazy conspiracy that has and will never happen.
This “sanewashing” of Trump’s statements isn’t just poor journalism; it’s a form of misinformation that poses a threat to democracy. By continually reframing Trump’s incoherent and often dangerous rhetoric as conventional political discourse, major news outlets are failing in their duty to inform the public and are instead providing cover for increasingly erratic behavior from a former—and potentially future—president.
The consequences of this journalistic malpractice extend far beyond misleading headlines. By laundering Trump’s words in this fashion, the media is actively participating in the erosion of our shared reality. When major news outlets consistently present a polished version of Trump’s statements, they create an alternate narrative that exists alongside the unfiltered truth available on social media and in unedited footage.
Voters who rely solely on traditional news sources are presented with a version of Trump that bears little resemblance to reality. They see a former president who, while controversial, appears to operate within the bounds of normal political discourse—or at worst, is breaking with it in some kind of refreshing manner. You can see this folie à deux at work in a recent Times piece occasioned by Trump’s amplification of social media posts alleging that Harris owed her career to the provision of “blowjobs”: “Though he has a history of making crass insults about his opponents, the reposts signal Mr. Trump’s willingness to continue to shatter longstanding norms of political speech.” Meanwhile, those who seek out primary sources encounter a starkly different figure—one prone to conspiracy theories, personal attacks, and extreme rhetoric.
The Atlantic ’s Jeffrey Goldberg wrote about this in a June newsletter , explaining the role the press plays in this sanitation of Trump by journalists while remarking on a rambling speech in which Trump went on a tangent about shark attacks and using some sort of electrocution device to fend them off:
It works like this: Trump sounds nuts, but he can’t be nuts, because he’s the presumptive nominee for president of a major party, and no major party would nominate someone who is nuts. Therefore, it is our responsibility to sand down his rhetoric, to identify any kernel of meaning, to make light of his bizarro statements, to rationalize. Which is why, after the electric-shark speech, much of the coverage revolved around the high temperatures in Las Vegas, and other extraneities. The Associated Press headline on a story about the event read this way: “Trump Complains About His Teleprompters at a Scorching Las Vegas Rally.” The New York Times headlined its story thus: “In Las Vegas, Trump Appeals to Local Workers and Avoids Talk of Conviction.” CNN’s headline: “Trump Proposes Eliminating Taxes on Tips at Las Vegas Campaign Rally.”
Over the weekend, the Times seemed intent on validating Goldberg’s words with a questionable “campaign notebook” article titled “ Meandering? Off-Script? Trump Insists His ‘Weave’ Is Oratorical Genius. ”
Writer Shawn McCreesh drew generous parallels between Trump’s speaking style and celebrated wordsmiths:
Certainly, in the history of narrative, there have been writers celebrated for their ability to be discursive only to cleverly tie together all their themes with a neat bow at the end—William Shakespeare, Charles Dickens and Larry David come to mind.
He then added, “But in the case of Mr. Trump, it is difficult to find the hermeneutic methods with which to parse the linguistic flights that take him from electrocuted sharks to Hannibal Lecter’s cannibalism, windmills and Rosie O’Donnell.”
McCreesh didn’t stop there. He went on to liken Trump to literary giants James Joyce and William Faulkner, and even psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud.
“In a world of canned political speeches, Mr. Trump’s style is beloved by his supporters, who enjoy these frequent glimpses into his id.”
This analysis goes beyond mere sanitization; it ventures into the realm of the absurd. By framing Trump’s incoherent ramblings as some form of avant-garde oratory, the Times isn’t just failing to accurately report—it’s actively warping reality to its readers.
The consequences of this extend beyond misleading headlines or sanitized quotes. It’s creating a dangerous disconnect between reality and reported news, fostering an environment where extreme rhetoric becomes normalized and conspiracy theories gain unwarranted legitimacy.
This won’t remain just a Trump problem. As other politicians observe the media’s willingness to soften and reframe inflammatory statements, we risk further degradation of political discourse. The bar for what’s considered acceptable rhetoric continues to lower, while the public’s ability to discern fact from fiction erodes.
To combat this, we need a paradigm shift in political reporting. Instead of contorting themselves to find rationality in incoherence, journalists should simply present politicians’ words and actions plainly, complete with fact-checks. This might mean rethinking traditional notions of “objectivity” that often lead to false equivalencies and misrepresentation.
Readers, too, have a role to play. We must seek out primary sources, demand more comprehensive reporting, and support news outlets that prioritize accuracy over access or the appearance of “balance.”
As we approach another critical election, the quality of our discourse hangs in the balance. The health of our democracy depends on an electorate that’s truly informed, not just placated with sanitized versions of reality. It’s time for both the media and the public to recommit to the pursuit of truth, however uncomfortable that may be.
Parker Molloy writes The Present Age on Substack.

Threats of violence made to California schools in social media trend
Several school districts in Northern California fell victim to a nationwide social media trend threatening schools Friday.
In the North Bay , the Tamalpais Union High School District in Marin County canceled classes at all schools after the district's main office received a threat of violence around 7:30 a.m. via text.
Shortly after receiving the threat, the district's five schools evacuated the campuses and contacted local law enforcement. District officials said the threat didn't name which school or target site. They didn't specify the danger, but a spokesperson did tell KTVU that the threat was not a shooting.
At the time, district officials said students should remain home and those on the way or at campus should return home as they closed down the schools.
An all-clear was announced hours later when district officials said police searched and cleared all schools and offices in their district.
On the other side of the North Bay, Fairfield police said they, with the Fairfield- Suisun Unified School District, were aware of the social media trend of threats to schools and said they were not credible.
"Despite the social media post's circulation in Fairfield and other Bay Area communities, there's no credible connection to our local community or FSUSD schools," Fairfield police said.
Police said despite the threat not being credible, officers and district personnel were present.
Also in Solano County were threats made to Vacaville Unified District Schools, Vacaville police said.
District Superintendent Ed Santopadre addressed the concerns, saying the district worked closely with Vacaville police and found the threats also not credible.
"Unfortunately, a national social media trend involving alleged threats to school campuses is impacting schools across the country," Santopadre told community members in a letter.
In the South Bay, a threat was made shortly after 7 a.m. to Mt. Pleasant High School in San Jose on social media, according to the San Jose Police Department . Police increased patrol checks at the school.
Outside the Bay Area, Sacramento police shared a notice that they were aware of the trend threatening schools, and shortly before 11 a.m. in Tracy, a bomb threat was made to North School, police said.
Police conducted security checks on the campus, and found the threat not to be credible after the search.
"These threats are against the law, and anyone making any threats will be disciplined and prosecuted to the highest extent of the law," Tracy police said.
Earlier in the week, Casa Grande and Petaluma High Schools in Petaluma were threatened with acts of violence that would occur on Friday afternoon.
Police received several reports but said they did not think the threat was genuine.
"Outside of the social media post, there has been no information that leads us to believe that the threat is credible," said the department in a Wednesday night release. "However, the Petaluma Police Department treats all threats seriously and will be diligently investigating the incident thoroughly."
The Petaluma Police Department provided an extra police presence at each of the involved schools.
The Fairfield-Suisun Unified School District, East Side Union High School District, Vacaville Unified School District, and Tracy Unified School District did not immediately respond to KTVU's request for comment.
This story was reported out of Oakland, Calif.
What's happening with all the online threats of school violence? Bay County coverage.

PANAMA CITY — School safety has been a big issue for Bay District Schools in the first month of the 2024-25 school year. The issue rose again Friday morning, when law enforcement investigated what turned out to be a false threat of gun violence mentioned online concerning Bay High School.
Here's a look at some of the News Herald's previous coverage:
Bay District Schools highlight security measures
Bay District Schools is aware of the recent safety issues, and officials have assured parents and the community that safety remains the top priority. Read more here.
North Bay Haven Charter Academy threat
A North Bay Haven Charter Academy juvenile has been arrested and charged after passing along a fake gun violence threat on social media. Read more here:
More on school violence threats: Wave of school shooting threats erupt in Florida, US. Can teens go to jail? How to report
Bay District Schools student arrested
A Bay District Schools student was arrested for allegedly threatening a staff member online. The district did not provide the student's age or school, nor any specifics about the threat. Read more here .
Online school threats have been an issue in Florida
School threats have been the trend all across Florida as of late. At least 13 students have been arrested in the state in recent days, as the USA TODAY NETWORK-Florida has reported.
If you need to report an emergency or a threat, you can always call 911. If you need more resources, the Florida Department of Juvenile Justice has a resource guide to school threats.
C.A. Bridges and Lianna Norman from USA TODAY NETWORK-Florida and Dylan Gentile from the News Herald contributed to this report
- Watch Live: Law & Crime Network
- WATCH LIVE: Young Thug YSL racketeering trial
- 9 Shocking Times Defendants Testified at Trial
- 10 Most Memorable Law&Crime Network Trials
- Watch Live: Brevard County Bond Court
- Where to Watch
- TV Schedule
- Bodycam Videos
- Justice Rules
- Buried with Love
- Prime Crime
- Cops Reloaded
- Law&Crime Productions
Husband who whispered in wife’s ear before murdering the mom of 5 during family Bible study at sister’s home, as divorce papers sat in car, is locked up for decades

Left: Corrina Woodhull, Woodhull as seen in a photo taken with her children (GoFundMe). Right: Robert Castillo (Ramsey County Sheriff’s Office)
Months after pleading guilty to second-degree murder, a Minnesota man with was sentenced to serve more than three decades in state prison for stabbing his wife, a mom of five, 10 to 20 times with a hunting knife in front of family members at a Bible study. The violence unfolded just moments after he whispered something in the victim’s ear that prompted her to “sh[ake] her head no.”
The defendant, 40-year-old Robert Castillo , was sentenced Friday to spend 33 years in prison for murdering 41-year-old Corrina Woodhull, and he must serve at least two-thirds of that sentence before he can be released, local CBS affiliate WCCO reported. At sentencing, Woodhull’s still grieving mother reportedly revealed that she found divorce papers in her daughter’s car after the murder.
“She knew it was time to walk away, and that’s why she’s dead,” Linda Castle reportedly said.
According to a the St. Paul Police Department , cops were called to the home of Castillo’s sister, where the Bible study was held, around 9:00 p.m. on March 21, 2023, more than a year ago now.
“When officers arrived, they located an adult female who was suffering from apparent stab wounds to her upper body,” cops said, noting that family members tackled and disarmed her admitted killer until authorities arrived. “Multiple witnesses on scene were holding an adult male suspect.”
Castillo’s sister told police that she hosted the Bible study group at the home on Tuesday nights, and that Woodhull and Castillo had arrived together and sat on the couch, local WCCO reported . Once there, Castillo, a man with numerous felony convictions on his record, had apparently been holding Woodhull’s hand, kissed her, and whispered something into her ear before pulling out the hunting knife and stabbing her repeatedly.
Castillo’s brother, who was also at the Bible study, reportedly told police that Woodhull and Castillo had been having marital issues, hence the discovery of the divorce papers.
Witnesses reportedly told police that they saw Castillo stab his wife 10 to 20 times and that Woodhull had pleaded for her life.
“Don’t let me die,” one witness recalled Woodhull saying, according to a Kansas City Star report .
According to WCCO, Castillo had an active warrant out for his arrest at the time of the stabbing, and he had failed to appear in court in connection with charges that he had assaulted a prison guard while an inmate at a correctional facility in Stillwater, some 20 miles east of St. Paul. Castillo reportedly had eight prior felony convictions, including an assault charge for allegedly beating the purported mother of his child with a hammer.
Prior to her death, Corrina Woodhull had worked for Juel Fairbanks Recovery Services and helped others with substance abuse.
“We are sad to report that one of our employees, Corrina Woodhull was tragically killed last night. Corrina had so much light and she spread that light and positivity each and every day to our clients and staff. Corrina was a force to be reckoned with. She had so much strength and was strong minded. She had a huge heart and genuinely wanted to help others,” the company said after news of her murder. “She leaves behind a legacy here at Juel Fairbanks and she will be truly missed. Please keep her family, our clients, and staff in your prayers.”
Family said that Woodhull was the mom of five “beautiful children” and had a “had a passion to help others experiencing substance use disorder and domestic abuse and violence.”
Castillo’s lawyer had asserted that his client was a meth and heroin user who was in a state of psychosis when he stabbed Woodhull, KARE reported .
Marisa Sarnoff contributed to this report.
Have a tip we should know? [email protected]
Filed Under:
Follow law&crime:.

Matt Naham is the Senior A.M. Editor of Law&Crime.

Fugitive nabbed in beating, strangling death of kindergarten teacher and mother of 3 whose body was found in a shallow grave

Husband stabbed wife to death while she was 5 months pregnant and attacked their 2 young daughters during rampage at home: Cops

Teen forced to take a photo with noose around his neck did it to ‘keep the peace’: Complaint

‘No Fake Love’ gang member admits to shooting outside ex-congressman’s house as daughters were in kitchen doing homework

Woman who used ‘tire plug tool with a metal spike’ to stab a man instead of showering with him, claiming he put ‘stuff down my throat,’ could be in even bigger trouble now

‘I’m not going to get closure’: Officer forced into retirement after cop killer leaves bullet fragments in his neck and murders his partner
Frederick Your Local News for Frederick, Maryland
Officers Suffering 'Serious Injuries' Arresting Domestic Violence Suspect In Frederick: Police
Two officers from the Frederick Police Department will be on the shelf for an undisclosed amount of time after being assaulted by a suspect.
Frederick Police
Marcus Deandre Taylor, 36, first attempted flight, then decided to fight a pair of officers chasing him during an investigation into a reported domestic disturbance.
At around 8 p.m. on Tuesday, Sept. 10, officers were called to the 1000 block of Heather Ridge Drive, where there was a reported domestic violence incident.
Upon arrival, the officers were provided a description of Taylor, fled fled before they arrived, but was quickly apprehended.
According to a department spokesperson, Taylor initially tried to pull a fast one on the officers by providing a fake name before taking off on foot again, this time assaulting two officers, causing "significant injuries" to both.
Backup officers responded to the area and were able to apprehend Taylor without further incident.
Paramedics were called to the scene and took the officers to Frederick Health Hospital, where one was treated for a dislocated shoulder and the other for a broken thumb.
Both were placed on restricted duty as they recover from the injuries sustained in the scuffle. Taylor was also taken to the hospital for a medical evaluation and was subsequently taken to the Frederick County Adult Detention Center.
Taylor was served on two outstanding warrants and now also faces charges that include:
First- and third-degree burglary;
- Fourth-degree theft;
- Two counts of second-degree assault;
- Second-degree assault on a Law Enforcement Officer;
- Resisting arrest;
- Obstructing and hindering;
- Possession of a controlled dangerous substance;
- Possession of drug paraphernalia.
"Every day, our officers place themselves in harm's way to keep this city safe," Frederick Police Chief Jason Lando said. "Two of those officers were assaulted by a suspect who chose to fight and flee rather than surrender peacefully.
"Because of (his) actions, these officers will be off the street for several weeks while they recover from their injuries."
Want breaking news in the DMV as it happens, or want to contribute? Join the DMV All Incidents Facebook group .
Click here to follow Daily Voice Frederick and receive free news updates.
SCROLL TO NEXT ARTICLE

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Essay on Media and Violence. Introduction. Research studies indicate that media causes violence and plays a role in desensitization, aggressive behavior, fear of harm, and nightmares. Examples of media platforms include movies, video games, television, and music. Violence in media has also been associated with health concerns.
The advent of video games raised new questions about the potential impact of media violence, since the video game player is an active participant rather than merely a viewer. 97% of adolescents age 12-17 play video games—on a computer, on consoles such as the Wii, Playstation, and Xbox, or on portable devices such as Gameboys, smartphones, and tablets.
Media violence and its impact on audiences are among the most researched and examined topics in communications studies (Hetsroni, 2007). Yet, debate over whether media violence causes aggression and violence persists, particularly in response to high-profile criminal incidents. Blaming video games, and other forms of media and popular culture ...
Youth violence decreased during the 15-year study period despite high levels of media violence in society. However, the study period is relatively short, the researcher cautioned, and therefore results could be imperfect. ... These papers look at aggressive behavior on stage, the likelihood candidates' performance will change voters' minds ...
Most media violence research involves youth aggression rather than violence, noted Douglas Gentile (Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA). Aggression is defined as any behaviour—physical, verbal, or relational—that is intended to do harm, he said, whereas violence is "a very narrow subtype of aggression that is physical and extreme, [and ...
Secondly, the effect size of media violence is the same or larger than the effect size of many other recognized threats to public health. In Figure 1 from Bushman and Huesmann , the effect sizes for many common threats to public health are compared with the effect that media violence has on aggression. The only effect slightly larger than the ...
Naturally, debate over media violence stirs up strong emotions because it raises concerns about the balance between public safety and freedom of speech. Even if violent media are conclusively ...
Published in JAMA Pediatrics, the review found that exposure to violent media increases the likelihood of aggressive behavior, thoughts and feelings. The review also found media decreases the ...
Violent media and aggression. In 2015, the American Psychological Association published a press release stating that playing violent video games is linked to aggression (APA, Citation 2015).This decision proved controversial, as some believe that there is no link between violent media and aggression (Ferguson et al., Citation 2020).In particular, it has been argued that experimental studies of ...
Violent content appears frequently in screen and audio media and takes many forms, including physical and relational aggression, gory images, violent stereotypes, and cyberbullying. Over six decades of research demonstrates that different types of media violence have significant detrimental effects, both immediately and in the long term.
Abstract. Fifty years of research on the effect of TV violence on children leads to the inescapable conclusion that viewing media violence is related to increases in aggressive attitudes, values, and behaviors. The changes in aggression are both short term and long term, and these changes may be mediated by neurological changes in the young viewer.
The notion that violence in the media contributes to the development of aggressive behaviour has been supported by meta-analyses 1 of relevant research. 2,3 However, there is continuing debate about (1) methodological approaches used in the research and their generalisability, and (2) the extent to which media violence affects children and young people. 4-8 This debate shows the typical ...
Media Violence and Aggression. The major debate in the media effects area concerns the effects of exposure to violent media on serious aggression. A major point of contention is the likelihood that the level of violent media in society causes higher levels of violent crime. There are several empirical observations from the field of criminology ...
In a 2009 Policy Statement on Media Violence, the American Academy of Pediatrics said, "Extensive research evidence indicates that media violence can contribute to aggressive behavior, desensitization to violence, nightmares, and fear of being harmed." 3. This year, the Media Violence Commission of the International Society for Research on ...
Youth violence is a significant public health issue that negatively affects individuals, families, and communities. 1,2 Estimated costs associated with youth violence in the United States is more than $20 billion anually. 3 Although juvenile arrests in 2019 were down 58% since 2010, 4 youth nonetheless account for a sizable proportion of perpetrators: 9% of all violent crimes were committed by ...
Media researchers have just begun to aggressively investigate desensitization to violence as an outcome of exposure to media violence (Funk, 2005; Huesmann & Kirwil, 2007; Krahe et al., 2010).One logical next step is to determine what factors might lead one person to become desensitized to violence and another to remain unaffected.
Numerous research studies identify an association between exposure to violence in entertainment and violent behaviour, but do not prove that exposure causes violent behaviour. Rather, there is a risk that exposure to media violence will increase the likelihood of subsequent aggressive behaviour. This risk can be increased or decreased by a large number of other factors. Appropriate policy ...
Abstract Media violence poses a threat to public health inasmuch as it leads to an increase in real-world violence and aggression. Research shows that fictional television and film violence contribute to both a short-term and a long-term increase in aggression and violence in young viewers. Television news violence also contributes to increased violence, principally in the form of imitative ...
The Influence Of Media Violence On The Youth Media Essay. Aggression in the media has been under a lot of scrutiny in recent times. It has resurfaced as the pinnacle of countless debates among politicians, parents and educators despite the fact that it is a current trend. The youth are increasingly becoming more hostile.
The prevalence and impact of violence portrayed in media and entertainment have long been a topic of debate in the United States. In 1972, the U.S. surgeon general issued a special report on the ...
Prolonged exposure to such media portrayals results in increased acceptance of violence as an appropriate means of solving problems and achieving one's goals. 2,3,9 American media, in particular, tend to portray heroes using violence as a justified means of resolving conflict and prevailing over others. 24,31 Television, movies, and music videos normalize carrying and using weapons and ...
Second, short-term effects are highly linked to the imitation of violent visual images. People witness, read, or hear of an event through the mass media. There are many effects of media violence that not all people know of. These effects can damage a human being's thinking, especially a child's. I. Violent messages in the media.
Media violence is believed to be causing aggression in today's youth and society. This paper will examine the potential reasons on how media violence is causing aggression Review of Literature In a study conducted, media psychologists, mass communication scientists, pediatricians, and parents all completed an anonymous online survey that ...
These essay examples and topics on Media Violence were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy.
Four years ago, in an article for Media Matters for America, I warned that journalists were sanitizing Donald Trump's incoherent ramblings to make them more palatable for the average voter.The ...
The threats were part of a social media trend nationwide targeting schools Several school districts in Northern California fell victim to a nationwide social media trend threatening schools Friday.
The study also highlighted racial disparities in the impact of gun violence. Black children and teens were found to have a homicide death rate 18 times greater than white peers, while the overall firearm death rate, taking into account both homicide and suicide, among Hispanic/Latino youth was more than three times higher than whites.
A North Bay Haven Charter Academy juvenile has been arrested and charged after passing along a fake gun violence threat on social media. Read more here: More on school violence threats: Wave of ...
Months after pleading guilty to second-degree murder, a Minnesota man with was sentenced to serve more than three decades in state prison for stabbing his wife, a mom of five, 10 to 20 times with a hunting knife in front of family members at a Bible study. The violence unfolded just moments after he whispered something in the victim's ear that prompted her to "sh[ake] her head no."
Upon arrival, the officers were provided a description of Taylor, fled fled before they arrived, but was quickly apprehended. According to a department spokesperson, Taylor initially tried to pull a fast one on the officers by providing a fake name before taking off on foot again, this time assaulting two officers, causing "significant injuries" to both.