
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development.
Case Study Question 1:
Similarly, for development, people look at a mix of goals. It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business. Hence, the developmental goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) Developmental goals means (a) goals of weaker people (b) goals of women (c) goals of all sections of the society (d) goals of working Population
(ii) …………. goals lead to decreased GDP of the country. (a) Social (b) Economic (c) Developmental (d) None of these
(iii) If women are engaged in paid work then their (a) respect (b) dignity (c) prestige (d) all of these
Related Posts
Tips to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science.
Preparing for case study and passage-based questions in class 10 social science can be challenging, but it is important to remember that with the right approach, you can effectively tackle these types of questions. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science:
- Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like history, geography, economics, or civics.
- Read and analyze the case study or passage carefully: The first step in answering case study questions is to read the scenario or passage carefully. Try to identify the main idea or theme of the passage and note down any important details that you think are relevant. Pay attention to any maps, graphs, or charts that are included as they can be helpful in answering the questions.
- Identify the type of questions being asked: After reading the case study or passage, you should analyze the questions being asked. Try to identify the type of question, whether it is a factual question or an analytical question. Factual questions require you to provide specific details from the passage, while analytical questions require you to use your critical thinking skills to analyze the information presented in the passage.
- Use your textbook and notes: To prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the topics covered in your textbook. Go through your notes and textbook to revise the relevant topics and concepts. This will help you to answer the questions more accurately.
- Practice sample questions: One of the best ways to prepare for case study questions is to practice answering sample questions. Try to find sample questions online or in your textbook and practice answering them. This will help you to get comfortable with the format of the questions and improve your speed and accuracy.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
myCBSEguide
- Social Science
- Class 10 Social Science...
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for CBSE Class 10 Social Science case study questions, myCBSEguide provides all the resources you need. We have a wide range of Class 10 Social Science case studies covering various topics, and our team of experts is on hand to provide guidance and support to Class 10 students. Whether you’re struggling with a particular topic or just need some extra help, myCBSEguide is the perfect place to turn.
Purpose of Class 10 Social Science
Up to the secondary level of schooling, social science is a core course. It is an essential component of a general education because it assists Class 10 Social Science students in comprehending the environment as a whole and acquiring a broader perspective as well as an empirical, reasonable, and humanitarian outlook. This is critical because it helps Class 10 Social Science students into well-informed and responsible citizens with the required qualities and skills to effectively engage and contribute to the process of development and nation-building.
Case Study Questions in Class 10 Social Science
Class 10 social science curriculum includes a wide range of topics. One way to help students learn and retain information from these topics is to incorporate case studies into the classroom. Case studies can provide real-world examples of the concepts being taught, and help students to understand how the theory can be applied in practice.
Incorporating case studies into the Class 10 social science curriculum can also help to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By working through a case study, Class 10 social science students can learn how to identify key issues, consider different options and make decisions. These skills will be valuable in their future studies and careers.
Whichever way case studies are used, they can be a valuable addition to the Class 10 social science curriculum.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions Samples
Students must solve a range of Class 10 Social Science case study questions in order to achieve good grades in Social Science. Students in Class 10 Social Science must be looking for some samples of case study questions in order to improve their grades. myCBSEguide has collected a variety of case study questions for Class 10 Social Science that will undoubtedly assist all students studying the subject. We’ve put created a collection of Class 10 Social Science case study questions for you.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 1
Class 10 HISTORY: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: Frederic Sorrieu prepared a series of four prints visualizing his dream of a world made up of ‘democratic and social Republics’, as he called them. The first print of the series shows the peoples of Europe and America – men and women of all ages and social classes – marching in a long train, and offering homage to the Statue of Liberty as they pass by it. Artists of the time of the French Revolution personified Liberty as a female figure. She bears the torch of Enlightenment in one hand and the Charter of the Rights of Man in the other. On the earth in the foreground of the image lie the shattered remains of the symbols of absolutist institutions. In Sorrieu’s utopian vision, the peoples of the world are grouped as distinct nations, identified through their flags and national costume. Leading the procession, way past the Statue of Liberty, are the United States and Switzerland, which by this time were already nation-states. France, identifiable by the revolutionary tricolour, has just reached the statue. She is followed by the peoples of Germany, bearing the black, red and gold flag. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Who was Frederic Sorrieu?
- French artist
- German Artist
- Italian Artist
- British Artist
In which year did Frederic Sorrier prepare a series of four prints?
Which of the following statements correctly describes “absolutist”?
- Monarchical Government
- Democratic Government
- Uncentralised Government
- Bureaucratic Government
Which of the following is correct with respect to “utopian vision”?
- Homogenous society
- Monarchical society
- Ideal society
- All are correct
Answer Key:
- (a) French artist
- (a) Monarchical Government
- (c) Ideal society
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 2
Class 10 GEOGRAPHY: Lifelines of National Economy
Read the extract and answer the question that follows:
We use different materials and services in our daily life. Some of these are available in our immediate surroundings, while other requirements are met by bringing things from other places. Goods and services do not move from supply locales to demand locales on their own. The movement of these goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport. Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to be traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation. Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space. Therefore, efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development.
The movement of these goods and services can be over three important domains of our earth i.e. land, water and air. Based on these, transport can also be classified into the land, water and air transport. For a long time, trade and transport were restricted to limited space. With the development in science and technology, the area of influence of trade and transport expanded far and wide.
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast-moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of an equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
- Explain the necessity of means of transport in modern times. (1)
- Enumerate the domains and means of transport. (2)
- Why are efficient means of transport pre-requisites for the fast development of the country? (2)
- The movement of goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport.
- The movement of these goods and services can be over three important domains of our earth i.e. land, water and air.
- Based on these, transport can also be classified into the land, water and air transport.
- (Any two relevant points)
- Efficient and good transport for speedy movement of goods and services to different parts of India and to fulfill the needs of the people is needed.
- Goods and services do not move from supply locations to demand locations on their own. This necessitates the need for transport.
- Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. They go to traders who make the products and take them to the consumers by transportation.
- Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movements over space.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 3
Class 10 POLITICAL SCIENCE: Power-sharing
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: The Belgian leaders recognised the existence of regional differences and cultural diversities. Between 1970 and 1993, they amended their constitution four times so as to work out an arrangement that would enable everyone to live together within the same country. The arrangement they worked out is different from any other country and is very innovative. Here are some of the elements of the Belgian model:
- Constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government. Some special laws require the support of the majority of members from each linguistic group.
- Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.
- Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation. The French-speaking people accepted equal representation in Brussels because the Dutch-speaking community has accepted equal representation in the Central Government.
- Apart from the Central and the State Government, there is a third kind of government. This ‘community government’ is elected by people belonging to one language community – Dutch, French and German-speaking – no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- India, Srilanka
- Belgium, Sri Lanka
- Wallonia, Brussels
- Flemish, Wallonia
- Which of the following is not the element of “Belgian model”?
- Equal number of ministers for both the groups
- Setting up of Community Government
- More power to the central government
- Equal representation at the state and central level
- “Apart from the Central and the State Government, there is a third kind of government”. Which of the following is incorrect with respect to this?
- The unique government is Community Government
- A single social group is given powers to handle community-related affairs
- Elected by people belonging to Dutch, French and German-speaking
- Power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues
- Which of the following title best describes the given passage?
- The ethnic composition of Belgium
- Accommodation in Sri Lanka
- Accommodation in Belgium
- The ethnic composition of Sri Lanka
- (b) Belgium, Sri Lanka
- (c) More power to central government. [Explanation: Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.]
- (b) Single social group is given powers to handle the community-related affairs. [Explanation: A community government is one in which different social groups are given powers to handle community-related affairs.]
- (c) Accommodation in Belgium
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 4
Class 10 ECONOMICS: Development
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: Besides seeking more income, oneway or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All of these are important goals. In fact, in some cases, these may be more important than more income or more consumption because material goods are not all that you need to live. Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things. Consider an example: If you get a job in a far-off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom. Similarly, for development, people look at a mix of goals. It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business. Hence, the developmental goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- Opportunity to learn
- Working atmosphere
- Job security
- All of the above
- The approach of living a life in bungalows, with costly cars, bikes and international tours is ________ life.
- Materialistic
- Both a and c
- “Women, who are engaged in paid jobs are an example of persons who fulfil a mix of goals.” Which of the following statement is incorrect with the given statement?
- A secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
- If there is respect for women, there would be greater acceptance of women working outside.
- If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society decreases.
- “Besides seeking more income, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security and respect of others”. What does the given statement signify?
- Mixed goals are important for people for development.
- Common goals are important for people for development.
- Conflicting goals are important for people for development.
- Similar goals are important for people for development.
- (d) All of the above
- (a) Materialistic
- (c) If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society decreases. [Explanation: If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases.]
- (a) Mixed goals are important for people for development.
Class 10 Social Science curriculum at a glance
The material of the Class 10 Social Science curriculum is mostly drawn from history, geography, politics, and economics. There are also elements of Sociology and Commerce. They provide a holistic vision of society in space and time, as well as in relation to one another. The numerous methods of inquiry used in each topic assist Class 10 Social Science students in understanding society from various perspectives and forming a comprehensive vision. Class 10 Social Science curriculum is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of various disciplines like History, Geography, Economics and Political Science.
The table below provides the complete syllabus structure for Class 10 Social Science curriculum.
Class 10 SOCIAL SCIENCE COURSE CONTENT
| 1. The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| 2. Nationalism in India: |
| 3. The Making of a Global World |
| 4. The Age of Industrialization |
| 5. Print Culture and the Modern World |
| 1. Resources and Development |
| 2. Forest and Wildlife |
| 3. Water Resources |
| 4. Agriculture |
| 5. Minerals and Energy Resources |
| 6. Manufacturing Industries |
| 7. Life Lines of National Economy |
| 1. Power Sharing |
| 2. Federalism |
| 4. Gender, Religion and Caste |
| 6. Political Parties |
| 7. Outcomes of Democracy |
| 1. Development |
| 2. Sectors of the Indian Economy |
| 3. Money and Credit |
| 4. Globalization and the Indian Economy |
| 5. Consumer Rights |
Reasons to choose myCBSEguide for class 10
There are many reasons to choose myCBSEguide for CBSE social science Class 10.
- First and foremost, myCBSEguide provides comprehensive and up-to-date study material for the entire syllabus including class 10 social science case study questions. In addition, myCBSEguide also provides practice questions, sample papers and previous year question papers to help students prepare for the exams.
- Another reason to choose myCBSEguide is the online tests. Online tests are a great way to test your knowledge and prepare for the exams.
- Finally, myCBSEguide also provides a “Home Work help” forum where students can ask questions and get answers.
In conclusion, myCBSEguide is the ideal resource for CBSE social science Class 10 students, offering everything they need to excel in their studies.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
5 thoughts on “Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions”
I want all case study questions of sst
I want case study question for maths (standard)
It helped me a lot
GK MCQ Questions
I want to case study of science and math tomorrow.
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should practise these solved case studies to get more marks in examinations.
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
On the Basis of the Status of Development Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly. Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility. Identify at least two resources from each category. Do you know that India has got the right to mine manganese nodules from the bed of the Indian Ocean from that area which lies beyond the exclusive economic zone. Identify some other resources which are international in nature. Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are included among stock. For example, water is a compound of two gases; hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced technical ‘know-how’ to use it for this purpose. Hence, it can be considered as stock. Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. River water can be used for generating hydroelectric power but presently, it is being utilised only to a limited extent. Thus, the water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Which one of the following statements is true about the term resources? (a) Resources are free gifts of nature. (b) They are the functions of human activities. (c) All those things which are found in nature. (d) Things which cannot be used to fulfill our needs.
(ii) Identify the correct basis of the Status of Development potential resources.
| (a) resources | 1. No appropriate technology to use them |
| (b) stock | 2. Not utilised |
| (c) developed resource | 3. Subset of the stock |
| (d) reserves | 4. Surveyed (quantity and quality) |
Choose the correct option-
(a) (a)-1, (b)–3, (c)–2, (d)–4 (b) (a)–2, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–3 (c) (a)–3, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–2 (d) (a)–4, (b)–2, (c)–3, (d)–1
(iii) Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation are __________. (a) Potential Resources (b) Individual Resources (c) Developed Resources (d) Stock
(iv) Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called: (a) Renewable resources (b) Reserve (c) Community resources (d) Non-renewable resources
2. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic – needs inputs of energy. The economic development plans implemented since Independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. As a result, consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country. In this background, there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the twin planks of sustainable energy. India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources. For example, as concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles; switching off electricity when not in use, using power-saving devices and using non-conventional sources of energy. After all, “energy saved is energy produced”.
(i) How will using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles help us? (a) saving resources (b) saving energy (c) saving vehicles (d) all the above
(ii) There is an urgent need of _________ development. (a) unsustainable (b) sustainable (c) non-energy (d) none of the above
(iii) Meaning of sustainable: (a) viable (b) temporary (c) conserve (d) none of the above
(iv) What is considered to be the basic requirement of economic development? (a) resources (b) energy (c) technology (d) citizens
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too. Ninety-five per cent of our basic needs for food, shelter and clothing are obtained from land. Human activities have not only brought about degradation of land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land. Some human activities such as deforestation, over grazing, mining and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation. Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country. There are many ways to solve the problems of land degradation. Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent. Planting of shelter belts of plants, control on over grazing, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes are some of the methods to check land degradation in arid areas. Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
(i) In which of the follo wing States mining has caused severe land degradation? (a) Gujarat (b) Jharkhand (c) Kerala (d) Uttarakhand
(ii) In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land degradation? (a) Jharkhand and Orissa (b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan (c) Punjab and Haryana (d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab? (a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over-irrigation (d) Overgrazing
(iv) One of the following which does not check land degradation- (a) control on overgrazing (b) creating shelter belts (c) deforestation (d) afforestation
4. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves: (i) identification and inventor of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources. (ii) evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans. (iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans. India has made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning right from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region, but mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but these are included in economically backward regions. On the contrary there are some regions which have a poor resource base but they are economically developed. The history of colonisation reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders. It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies. Therefore, resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes.
India has experienced all this in different phases of colonisation. Therefore, in India, development in general, and resource development in particular do not only involve the availability of resources, but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
(i) What was main attraction of foreign invaders to India? (a) architecture (b) resource (c) irrigation method (d) spices
(ii) Resource planning is essential for __________ existence of all forms of life. (a) ecological balance (b) sustainable (c) exploitation (d) None of these
(iii) Which of the following is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life? (a) Resource planning (b) Resource management (c) Resource extraction (d) Resource generation
(iv) From which Five Year Plan has India made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning? (a) First Five Year Plan (b) Fifth Five Year Plan (c) Annual Plans (d) Tenth Five Year Plan
5. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow Non-Renewable Resources: These occur over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use. On the Basis of Ownership Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals. Make a list of resources owned by your household. Community Owned Resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there. National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(i) Which one of the following is not the community owned resource? (a) Burial grounds (b) Grazing grounds (c) Privately owned house (d) village ponds
(ii) Match the following
| 1. Renewable resource | (a) wells |
| 2. Individual resource | (b) Ocean |
| 3. National resource | (c) solar energy |
| 4. International resource | (d) plantation |
Choose the correct option:
(a) 1–(a), 2–(c), 3–(d), 4–(b) (b) 1–(c), 2–(d), 3–(a), 4–(b) (c) 1–(b), 2–(a), 3–(c), 4–(b) (d) 1–(d), 2–(c), 3–(a), 4–(b)
(iii) Which among the following is a type of resources classified on the basis of exhaustibility? (a) National and individual (b) Renewable and non-renewable (c) Biotic and abiotic (d) Potential and reserves
6. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue.
In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals.
Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.
National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land.
All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(i) Which one of the following is an example of Biotic Resources? (a) Rock (b) Mountain (c) Mineral (d) Flora
(ii) The resources which are owned by the community are: (a) plantation (b) pasture land (c) ponds (d) all the above
(iii) The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone can be termed as which of the following types of resource? (a) Individual resources (b) Community owned resources (c) National resources (d) International resources
(iv) On the basis of ownership, plantations can be better considered as which of the following types of resources? (a) Individual resource (b) Community owned resource (c) National resource (d) International resource
Resources and Development
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore? (a) Renewable (b) Biotic (c) Flow (d) Non-renewable [Answer : (d)
Question. Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put? (a) Replenishable (b) Human-made (c) Abiotic (d) Non-renewable [Answer : (a)
Question. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab? (a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over-irrigation (d) Overgrazing [Answer : (c)
Question. In which one of the following States is terrace cultivation practised? (a) Punjab (b) Plains of U.P. (c) Haryana (d) Uttaranchal [Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States is black soil found? (a) Jammu & Kashmir (b) Gujarat (c) Rajasthan (d) Jharkhand [Answer : (b)
Question. What percentage of our land should be under forest according to the National Forest Policy (1952)? (a) 33 (b) 22.5 (c) 31 (d) 30 [Answer : (a)
Question. Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have appropriate technology to access them are called: (a) Potential resource (b) Stock (c) Developed resource (d) Reserves [Answer : (b)
Question. India’s territorial water extends upto a distance of: (a) 12 km (b) 12 nautical miles (c) 200 nautical miles (d) 19.2 miles [Answer : (b)
Question. Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called: (a) Renewable resources (b) Reserve (c) Community resources (d) Non-renewable resources [Answer : (d)
Question. Land that is left uncultivated for more than five agricultural years is called: (a) Pasture land (b) Culturable waste land (c) Current fallow (d) Barren land [Answer : (b)
Question. Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as: (a) Net sown area (b) Forest cover (c) Waste land (d) Gross cropped area [Answer : (d)
Question. The total degraded land in our country is: (a) 133 million hectares (b) 130 million sq. km. (c) 140 million hectares (d) 130 million hectares [Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States mining has caused severe land degradation? (a) Gujarat (b) Jharkhand (c) Kerala (d) Uttarakhand [Answer : (b)
Question. The main cause of land degradation in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh is: (a) Mining (b) Over irrigation (c) Deforestation (d) Over grazing [Answer : (b)
Question. Which is the most common soil of Northern India? (a) Black soil (b) Laterite soil (c) Alluvial soil (d) Red soil [Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is mostly found in: (a) Parts of Jammu & Kashmir (b) Upper Ganga Plains (c) Eastern and Southern part of Deccan Plateau (d) None of the above [Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is reddish in colour due to: (a) high clay content. (b) presence of kankar nodules in the subsoil. (c) diffusion of iron in igneous and metamorphic rocks. (d) high moisture content. [Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not important for soil formation? (a) Relief (c) Parent rock (c) Climate (d) Duration of day [Answer : (d)
Question. Black soil is also called: (a) Bangar (b) Khadar (c) Regur (d) Humus [Answer : (c)
Question. Black soils are common in: (a) Deccan trap region (b) Kashmir Valley (c) Ganga Valley (d) Northern Plains [Answer : (a)
Question. Laterite soil is very useful for growing: (a) Rice, wheat and mustard (b) Tea, coffee and cashewnut (c) Pulses, sugarcane and resin (d) None of the above [Answer : (b)
Question. Black soil is deficient in (a) Calcium carbonate (b) Magnesium (c) Potash (d) Phosphoric contents [Answer : (d)
Question. Which of the following soils has self-aeration capacity? (a) Alluvial soil (b) Mountain soil (c) Black soil (d) Red soil [Answer : (c)
Question. Ploughing along the contour lines to decelerate the flow of water down the slopes is called: (a) Strip cropping (b) Sheet erosion (c) Contour ploughing (d) Terrace cultivation [Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation? (a) Strip cropping (b) Terrace cultivation (c) Shelter belts (d) Overdrawing of ground water [Answer : (d)
Assertion-Reason Questions DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable: (a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) If assertion is true but reason is false. (d) If both assertion and reason are false.
1. Assertion. Alluvial soil is ideal for growth of paddy, wheat, cereal and pulse crops. Reason. Alluvial soil is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Alluvial soil contains adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops. It is porous and this property makes it ideal for the growth of wheat, paddy, cereal and pulse crops.
2. Assertion. The availability of resources is not the only necessary condition for the development of any region. Reason. Not only availability of resources but also corresponding change in technology is necessary for the development of any region. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. Thus, both resources and advanced technologies contribute in development of a region.
3. Assertion. Resources are free gifts of nature. Reason. Resources like soil, air, water are easily available in nature. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Resources are not free gifts of nature but are present due to interaction of human beings with nature, technology and institutions. They are a function ofhuman activities. They transform material available in our environment into resources.
4. Assertion. Land is a natural resource of utmost importance. Reason. Land can be used for various purposes. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Land is a natural resource of utmost importance as it supports human life and wild life, economic activities like agriculture, mining, transport and communication system.
5. Assertion. Resource planning is an easy process in India. Reason. Resource planning involves planning structure, identification and inventory of resource across the regions. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Resource planning is not an easy but a very complex process as it involves surveying, mapping, quantitative and qualitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
6. Assertion. Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. Reason. Soil supports different types of living organisms on earth. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Soil is a living system. Soil helps to grow plants, supports natural vegetation and economic activities like agriculture. Its universal usage proves that it is the most important renewable natural resource.
7. Assertion. Processes of soil formation and erosion go simultaneously and create a balance between the two. Reason. The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is soil erosion. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Soil formation and erosion go simultaneously but this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining. Natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion.
8. Assertion. Arid soil is unsuitable for cultivation. Reason. Arid soil is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. It restricts the filtration of water. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Due to dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture that is why it becomes unfit for cultivation.
9. Assertion. Control on mining activities does not control land degradation. Reason. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, deforestation has occurred due to overgrazing, not mining. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Activities of mining cause land degradation because mining sites are abandoned after excavation work. This results in over-burdening. Mining activities in the mentioned states has contributed to deforestation.
10. Assertion. Terrace cultivation does not restrict erosion. Reason. Running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. This helps to cultivate crops. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Terraces, out on slopes in forms of steps break up the force of the wind, thus preventing erosion. The gullies render cultivation in those lands impossible
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Give one example of the main commercial crop cultivable in laterite soil. Ans. Tea/coffee.
Question. Which type of soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nut ? Ans . Soil for the growth of Cashew nuts: Red Laterite soil. Question. Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility. Ans. On the basis of exhaustibility, resources can be classified as: 1. Renewable/ Non-exhaustible resources 2. Non-renewable/ Exhaustible resources. Question. Read the features of a soil and name the related soil: 1. This soil ranges from red to brown in colour. 2. It is generally sandy in texture and is saline. 3. It lacks humus and moisture. Ans . Arid soil is the soil that has all these features.
Question. “Degradation of land is a cause of worry.” Give one reason to support the statement. Ans. Degradation of land is a cause of worry because it can cause ecological imbalance.
Question. How is overgrazing responsible for land degradation in Gujarat? Ans . Overgrazing is responsible for land degradation in Gujarat because the extensive grazing for long and repeated periods leaves less time for propre vegetation to grow and thus the land and it is soil particles are left loose thereby degrading the overall quality of the land. Related Theory Overgrazing refers to what happens when livestock feeds on pasture to the point where there is no vegetation left.
Question. “Conservation of resource is vital for development.” Give one example regarding the statement. Ans. Conservation of resources: afforestation, water treatment.
Question. How are mining activities responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand? Ans. Mining activities are responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand because mining sites are abandoned after the excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars on the land. Related Theory To get rid of this land degradation, proper management of wastelands and control of mining activities needs to be initiated.
Question. Water is a compound of two inflammable gases, hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy. However, we do not have the required technical ‘know-how’ to use them for this purpose. What kind of resources can these gases be put in? Ans. The gases can be put in: The Stock Resources.
Question. Highlight the reason for land being known as the utmost important natural resource. Ans. Land is known as the utmost important natural resource because all economic activities are performed on land and it also supports natural vegetation and wildlife.
Question. Give one example of community owned resources. Ans. Village grazing grounds, public parks and picnic spots.
Question. This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows. They are well- known for their capacity to hold moisture. in addition, they are rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime. they are made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material. Read the details given in the source above and identify the kind of soil whose features have been mentioned. Ans. Black Soil Explanation: Black soil is also known as ‘Regur Soil’ or ‘Cotton Soil’ as it is good for the cultivation of cotton crop in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat in India.
Question. Favourable conditions for wind energy exist in Western Rajasthan and Gujarat, but they have not been utilised and developed to the maximum. It falls in which category of resources? Ans. Wind energy received in Western Rajasthan exist as: Potential Resources.
Question. Which soil is most retentive of moisture? Ans . Black Soil retains the most moisture.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. ‘‘Resource planning is a complex process.’’ Support the statement with arguments. Ans. Resource planning is a complex process because: (1) Resource planning involves identifying resources which are available in different parts of the country. This is a time consuming process as it involves surveying and mapping various regions of the country. Then, the quality and quantity of the available minerals also needs to be estimated. (2) Resource planning is a complicated process as it involves the use of specialised technology, skill sets and requires setting up many institutions for the execution of resource development plans. (3) One of the daunting tasks is to match and align resource development plans with national development plans. Related Theory Resource planning is the judicious use of resources. Resource planning becomes more important in a country like India, where resources are not distributed properly.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘alluvial soil’ found in India. Ans . Features of the alluvial soil are as: (1) It is formed by the deposition of the river load as it flows from its upper to its lower course. (2) It is light and porous, therefore easily tillable. (3) It is a fertile soil as it is rich in minerals, especially potash and lime. (4) It is suitable for the growth of a large variety of rabi and kharif crops. (5) Soils in the drier areas are more alkaline.
Question. Classify resources of the basis of their origin. Ans. Types of resources on the basis of origin are as follows: (1) Biotic Resources: These resources are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc. (2) Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example, rocks and metals etc.
Question. Describe the different steps of resource planning. Ans. The different steps of resource planning are : (1) Doing proper and strategic surveying, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of resources, leading to identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. (2) Resource development plans are implemented by evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup. (3) The overall development plans are then matched and coincided with development plans.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘black soil’ found in India. Ans. Features of the black soil found in India are: (1) Black soil is black in colour and is also known as regur soil. (2) Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil. (3) It is fine textured and clayey in nature. (4) It is formed from weathered lava rocks , which also gives it its black colour. (5) It has high water retention power.
Question. Mention three problems that are associated with the indiscriminate use of resources. Ans. The following three problems are the result of indiscriminate use of resources: (1) Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals. (2) Accumulation of resources in few hands, which in turn has divided the society into two segments-rich and poor. (3) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Question. ‘Sustainable Development is a crucial step for the development of a country’. Explain with suitable examples. Ans. Sustainable development is crucial for development of a country as it: (1) Promotes use of renewable resources like solar energy, tidal energy, etc (2) Puts a check on over usage of resources (3) Promotes protection and conservation of resources for future generation
Question. Describe the importance of judicious use of resources. OR Why should we use natural resources properly and judiciously? Explain your views. Ans. The importance of judicious use of resources are : (1) Multiple environmental and socioeconomic problems may arise if resources are used in an indiscriminate manner. (2) Most of the resources are non-renewable. The continuous usage of these resources may result in exhaustion of the resources. This may stunt development and growth of the people. (3) It will enhance the status of a person and would not impede development in general for future generations. They have to be used with caution.
49. What were the main features of the Earth Summit held at Rio de Janeiro in 1992? Ans. Three main features of the Earth Summit of 1992 held at Rio de Janeiro: (1) It was the first international Earth Summit in which more than 100 heads of states met. (2) The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level. (3) This Convention endorsed the global, Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is meant by conservation of resources? Mention any four steps taken at global level to conserve resources. Ans . Resources are vital for development and also to satisfy human needs and aspirations. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important. Even once Mahatma Gandhi raised his concern about resource conservation in these words, “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses. Steps taken at global level for the conservation of resources are as follows: (1) The club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968. (2) In 1974, Gandhi ji’s philosophy was presented by Schumacher in his book ‘Small is Beautiful’. (3) In 1987, the Brundtland Commission Report introduced the concept of sustainable development as a means for resource conservation. (4) In 1992, the first Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil made significant contribution towards the conservation of resources.
Question. What is land degradation? Suggest any four steps to control land degradation. Ans. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation. This has serious repercussions on society and the environment. Following steps can be taken to control the land degradation: (1) Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent (2) Planting of shelter belts of plants. (3) Control on over grazing, stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes (4) Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Question. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development? Explain. Ans. Sustainable economic development means development that is viable keeping the requirements of both the present and future generations at par. It is a development that doesn’t compromise with the environment, provides equal opportunities to grow, utilises resources for both the present and upcoming generations. The issue of sustainability is important for development because without the same, man will use resources without care, destroying the environment, preventing all chances of survival and development in future. If not for sustainability, people would start exploiting finitely available resources and end up finishing them soon, thus destroying Earth’s balance. Global warming, ozone layer depletion and environmental pollution have been caused due to this ignorance. Sustainability is vital for maintaining global peace and quality of life. So, the need of the hour is to use resources wisely so, as to sustain our planet Earth.
Question. What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential? Explain. Ans. Resource planning is a technique of proper utilisation of resources which aimed at sustainable development. Resource planning is essential because of the following reasons: (1) Most of resources available on earth are limited in supply. (2) The resources available to us are distributed unevenly all over the country. (3) Overutilization of the resources may lead to environmental pollution and depletion of resources as well. Therefore, planning of resources can reduce pollution and overutilization of resources as well. (4) Planning of resources can lead to have a balanced development at national, state, regional and local levels.
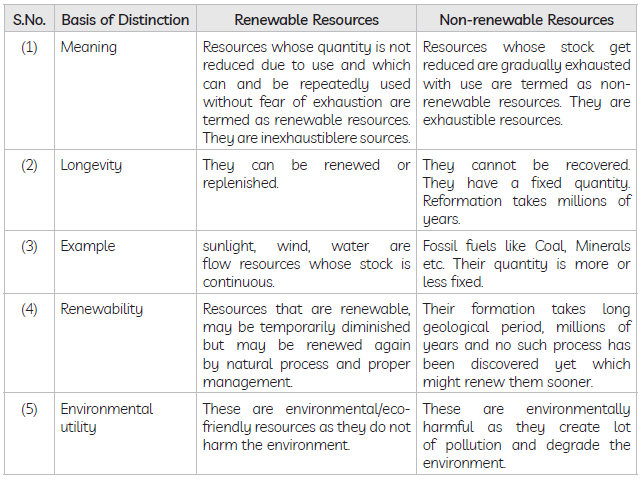
Question . Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources. Give examples.
Related Posts

The Proposal Class 10 English Important Questions

Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Science Important Questions

The Making of a Global World Class 10 Social Science Important Questions
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 10 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science
- Understanding Economic Development

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics (Understanding Economic Development) - FREE PDF Download
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics offers clear and detailed answers to all the questions in the textbook. These solutions help students straightforwardly understand important economic concepts. Understanding Economic Development is a crucial part of this subject which comprises five chapters covering the different aspects of the Indian economy, global rights, and consumer rights. This section is entirely based on economics and the terms related to the economic development of a country. In this subject, you will find several notions related to the economic development of a country and how it is calculated.

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science is also great for exam preparation, covering all key topics and questions from the textbook. Using CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus, students can clear up doubts, reinforce their understanding, and build a strong base in economics. This resource is designed to improve performance, making it essential for any Class 10 students.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter-wise Links - Download the FREE PDF
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter-wise Links |
|
|
|
|
|
Below is the pictorial representation of the Class 10 NCERT Economics Syllabus for better understanding.
Quick Overview of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics
NCERT Economics Class 10 answers all chapters in the NCERT textbook, ensuring complete coverage.
NCERT Class 10 Economics solutions help students practice and evaluate their understanding of economic concepts, improving retention and clarity.
Each solution offers detailed explanations, including step-by-step methods and relevant examples, facilitating effective learning and revision.
This resource is essential for exam preparation, helping students build a strong foundation in economics and their confidence in tackling exam questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics: Chapter Details, Concepts, and Important Links
Chapter 1: development.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 examines the concept of development and its societal importance.
NCERT Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 Development introduces the concept of development, highlighting its economic, social, and environmental aspects.
It discusses various development indicators like income, health, and education, and their role in the growth of society.
This chapter compares developed, developing, and underdeveloped nations, explaining the reasons behind these differences.
It focuses on sustainable development, stressing the need to balance economic growth with environmental care.
Students will explore traditional and modern development approaches and the impact of policies and international organisations.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 1: Development
Understanding Development
Different People, Different Goals
Income and Other Goals
National Development
Comparing Different Countries or States
Income and Other Criteria
Public Facilities
Sustainability of Development
Along with Class 10 Economics NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 10 Development Revision Notes .
Chapter 2: Sectors of The Indian Economy
NCERT Economics Class 10 Chapter 2 explores the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors and their economic roles.
Chapter 1 Development explains the different sectors of the Indian economy and their roles.
It describes the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors, detailing their functions and significance.
The chapter discusses how each sector contributes to the overall economy and employment.
It explores the concept of the organised and unorganised sectors, highlighting their differences.
This chapter also examines the changes in the importance of different sectors over time and their impact on economic development.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 2: Sectors of The Indian Economy
Introduction to the Sectors of the Economy
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Sectors
Organised and Unorganised Sectors
Interdependence of Sectors
Role of Government in Different Sectors
Along with Class 10 Economics NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 10 Sectors of The Indian Economy Revision Notes
Chapter 3: Money and Credit
NCERT Economics Class 10 Chapter 3 establishes the significance of money and credit, fostering an understanding of financial systems.
This chapter explains the role of money in everyday transactions and the need for a proper financial system.
It discusses the concepts of formal and informal credit, highlighting their differences and impacts on society.
The Money And Credit chapter covers the functioning of various financial institutions and their role in providing credit.
It explores the importance of credit in economic development and the issues related to credit accessibility.
This chapter emphasises the significance of responsible borrowing and lending practices for future financial stability.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 3: Money and Credit
Evolution and Functions of Money
Formal and Informal Credit Sources
Role of Banks and Financial Institutions
Challenges in Credit Accessibility and Responsible Borrowing
Along with Class 10 Economics NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 10 Money And Credit Revision Notes
Chapter 4: Globalisation and The Indian Economy
NCERT Economics Class 10 Chapter 4 explains the concept of globalisation and its impact on the Indian economy.
It discusses how globalisation has affected the agriculture, industry, and services sectors in India.
The chapter explores the benefits and challenges of globalisation for workers, consumers, and businesses.
It provides insights into the role of multinational corporations (MNCs) in the Indian market.
The chapter outlines the measures taken by the Indian government to promote globalisation and its importance for economic development.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 4: Globalisation and The Indian Economy
Definition and Meaning of Globalisation
Factors Enabling Globalisation
Impact on Agriculture, Industry, and Services
Role of Multinational Corporations (MNCs)
Benefits and Challenges of Globalisation
Government Policies and Measures
Case Studies on Globalisation
Future Prospects for Globalisation in India
Along with Class 10 Economics NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 10 Globalisation and The Indian Economy Revision Notes
Chapter 5: Consumer Rights
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 lays a strong foundation for understanding consumer rights and the importance of being informed and vigilant as a consumer.
This chapter educates students about their rights and responsibilities in the marketplace.
It covers various consumer protection laws and the mechanisms available for safeguarding consumer interests.
The chapter explains how consumers can address grievances and the role of consumer courts.
It emphasises the importance of consumer awareness and how informed choices impact the economy.
This chapter highlights the need for ethical business practices and the role of vigilant consumers.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 5: Consumer Rights
Understanding Consumer Rights
Consumer Protection Laws
Mechanisms for Grievance Redressal
Role of Consumer Courts
Importance of Consumer Awareness
Impact of Informed Consumer Choices
Ethical Business Practices
Consumer Vigilance and Responsibility
Along with Class 10 Economics NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 10 Consumer Rights Revision Notes
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics
Economic Class 10 provides clear and extensive explanations for each topic, allowing students to better understand the concepts.
These solutions cover all important topics and questions from the textbook, which is helpful for thorough exam preparation.
Problems are solved step-by-step, making it simple for students to learn and apply problem-solving techniques.
Practising these solutions can help students improve their speed and accuracy, aiding in better time management during exams.
The solutions help clear up any doubts students may have, ensuring a strong grasp of economic principles.
Regular practice with Economic Class 10 solutions boosts students' confidence, making them well-prepared for their exams.
Economic Class 10 equips students with essential knowledge about economic principles and practices. Understanding consumer rights, various economic policies, and market dynamics helps students become informed citizens. The comprehensive study of these topics not only prepares students for exams but also lays a strong foundation for future economic studies and practical life applications. This subject is crucial for personal and professional growth.
Related Important Links for Class 6 Economics
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for CBSE Class 10 Economics –
S. No | Important Links for Class 10 Economics |
1. |
|
2. |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 10 2024-25
1. What is the best way to understand Economic Development in Economic Class 10?
Focus on the class lectures. Read the subject repeatedly to understand the definitions and concepts well. Follow the Economic Development Class 10 PDF solution file for framing the best answers to the exercise questions and make your knowledge more fortified.
2. How can you find the right answers to Economic Class 10 questions?
If you follow how the experienced teachers of Vedantu have framed the right answers to the exercise questions and practice, you will be able to do the same. Download NCERT Solutions for Social Science Economic Class 10 PDF for your convenience.
3. How can you develop knowledge related to Economics in Class 10?
CBSE Class 10 Social Science understanding of Economic Development should be studied with proper attention. You will need good study material and a proper solution to the exercise questions to develop your knowledge.
4. Is it important to study Economics in Class 10?
The syllabus of Economics Class 10 NCERT is relatively short when compared to other subjects under Social Science. Hence, this makes it even more important. You must make notes and go through all the NCERT Solutions for Class 10th Economics to score the maximum marks. You must also keep in mind the important terms and definitions as they are very essential while framing an answer.
5. Which is the most important Chapter in Class 10th Economics?
All the chapters are equally important and you must prepare all of them. You must also practise all the Ncert questions from the page NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics on Vedantu’s website (vedantu.com) and revise all the key concepts. The definitions and key features are extremely important as they give weight to your answers. All the resources are also available on the Vedantu app free of cost.
6. Do I need to practise all the questions provided in NCERT Solutions Class 10th Economics?
All the questions are extremely important as they are from Economics Class 10 NCERT and they have a higher rate of coming in the board examinations. Also, the solutions are written in such a way that they are best suited to the exam pattern and if one studies carefully and thoroughly, they will surely get full marks. The answers cover all the important points and the keywords that are used now and then. The answers can either be seen or downloaded from the page NCERT Class 10 Economics free of cost.
7. How can I understand Class 10th Economics?
The best way to understand Economics is to start with NCERT Solutions for Class 10th Economics. A thorough read followed by noting down all the important concepts is the ideal approach to tackling Economics. Once you are through with the syllabus, you must then attempt the NCERT questions and check them using the Economics NCERT Class 10 provided by Vedantu. This will not only improve your answers but will also help you figure out where you went wrong so that you don't repeat those mistakes.
8. Can NCERT Class 10 Economics improve my performance in exams?
Yes, Economics NCERT Class 10 is designed to cover all important topics and questions from the textbook, which are often reflected in exams. By practising these solutions, students can familiarise themselves with the question patterns and improve their answering techniques. This thorough preparation can lead to better performance in exams.
9. Are NCERT Class 10 Economics useful for clearing doubts about economic concepts?
Economics NCERT Class 10 is very helpful in clearing doubts. They provide detailed explanations and step-by-step solutions that address common student queries. By studying these solutions, students can resolve their misunderstandings and reinforce their knowledge, leading to a stronger grasp of economic concepts.
NCERT SOLUTIONS FOR CLASS 10
Cbse class 10 study materials, home tuitions in india.
Development Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these questions will help you to score excellent marks in the board exams.
Development Class 10 Extra Questions Economics Chapter 1
Very short answer type questions (1 mark).
1. What is development?
Answer: It is a comprehensive term which includes increase in real per capita income, improvement in living standard of people, reduction in poverty etc.
2. Mention any two developmental goals of a landless rural labourer.
Answer: (i) More days of work and better wages. (ii) Quality education for his children.
3. Mention any two developmental goals of a girl.
Answer: (i) Gender equality (ii) Girls empowerment
4. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for other. Give one example.
Answer: Construction of a dam may be good for an industrialist as he will get more electricity but construction of dam submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced.
5. Mention any two developmental goals of people other than income.
Answer: (i) Equal treatment (ii) Respect of others
6. Mention any two developmental goals of a rural women.
Answer: (i) Dignity in the household. (ii) A safe and secure environment.
7. What is national development? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: National development is a comprehensive term which includes improvement in living standard. of the people, increase in per capita income, providing social amenities like education, medical care, social services, etc. to the citizens of the country.
8. Mention any two national development goals of India. Answer: (i) Corruption free society. (ii) High per capita income.
9. Which is the most important attribute for national development? Answer: National income or per capita income of the nation.
10. ‘For comparing countries, total income or national income is not a useful measure. Give reason.
Answer: Since countries have different population, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn.
11. What is average income or per capita income? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: When the total national income is divided by the total population, it is called the per capita income. Per Capita Income = National Income / Population
12. What is the most important component for comparing different countries? [CBSE 2010, 12] Answer: Per capita income.
13. Which criteria is used by the World Bank to classify different countries? Answer: Per capita income.
Q.14. Which countries have been categorised as rich countries according to the World Development Report? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: Countries with per capita income of US $ 12276 per annum and above in 2010 are called rich countries.
15. Which countries have been categorised as low income countries according to World Development Report?
Answer: Countries with per capita income of US $ 1005 or less are called low income countries.
16. Under which category India has been placed by the World Bank Development Report?
Answer: Low middle income countries as India’s per capita income is less than JUS $ 1005. or less.
17. What are developed countries according to World Development Report ?
Answer: All the countries excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries which have per capita income of US $ 12276 per annum or above have been termed as developed countries.
18. What is Infant Mortality Rate? [CBSE 2009, 2013 (D)]
Answer: It indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year.
19. What is Literacy Rate? [CBSE 2009 (D)]
Answer: It measures the proportion of literate population in the seven and above age group.
20. What is Net Attendance ratio? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: It is the total number of children of the age group 6-10, attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.
21. What is Gross Enrolment Ratio?
Answer: It is the enrolment ratio for primary, secondary and higher education.
22. Which Indian state has the lowest Infant Mortality Rate ? Answer: Kerala.
23. Why Kerala has a low Infant Mortality Rate ? [CBSE 2008, 2013 (F)]
Answer: Kerala has low IMR because : (i) It has very high literacy rate and literate people take care of their children better as compared to illiterate. (ii) Literate people also have high earning capacity so they can afford basic necessities for their children.
24. Mention any two things which money cannot buy. Answer: (i) Peace (ii) Freedom
25. What is Public Distribution System?
Answer: It is a food security programme under which government provide foodgrains and other essential items to the poor at an affordable price.
26. What is Human Development Index?
Answer: It is an index prepared by the World Bank Under which all the nations of the world are indexed or ranked according to their performance in various parameters like per ‘—’capita income, life expectancy, literacy rate etc.
27. What are the three components of human Development Index? Answer: (i) Per Capita Income (ii) Life Expectancy (iii) Literacy Rate
28. What is India’s rank according to 2013 HDI ? Answer: 136
29. Mention any two parameters where Sri Lanka has scored over India in HDI. Answer: (i) Per capita income (ii) Literacy rate
30. Define life expectancy. [CBSE 2013] Answer: Average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
31. What is life expectancy in India? Answer: 65.8 years
32. What is Sustainable Development?
Answer: Sustainable development is that process of economic development which aims at maintaining the quality of life of both the present and the future generations without harming the natural resources and environment.
33. What are non-renewable resources? Give one example.
Answer: “Non-renewable resources are the natural resources that cannot be replaced at all or within a reasonable time.” Fossil fuels such as oil, gas and coal are examples of non-renewable resources. These resources accumulated over millions of years.
34. Name the region of world which has large crude oil reserves. Answer: Middle East.
Short Answer Type Questions (3 Marks)
1. (i) What is development? Mention any two features of development. (ii) What is national income? [CBSE 2009 (D)] (iii) What is per capita income? [CBSE Sept. 2011] Or Define the term, ‘average income.’ [CBSE 2008, 2009 (D)]
Answer: (i) Development is a comprehensive term which include increase in real per capita income, improvement in living standard of people, reduction in poverty, illiteracy, crime rate, etc. Features (a) Different persons have different developmental goals. (b) Income is a major component of development. (ii) National income is defined as the total value of all the goods and services produced within a country plus net income coming from abroad. (iii) When the total national income is divided by the total population, it is called the per capita income. Per Capita Income = National Income / Population
2. (f) State the criteria used to compare the different countries by the Human Development Report published by the United National Development Programme (UNDP). (ii) Which is the new area of knowledge in which scientists, economists, philosophers and other social scientists are working together? (iii) What is meant by Human Development? [CBSE Sept. 2011, 2012] (iv) What is Sustainable Development? [CBSE Comp. (D) 2008, 2009 (F), Sept. 2011] (v) Which organisation measures HDR? Mention any three major indicators of / HDR. [CBSE Sept. 2012]
Answer: (i) Per capita income, life expectancy at birth, literacy rate and other basic necessities like clean drinking water, sanitation etc. (ii) Sustainability of development.
(iii) It is the process of enlarging people’s choices as well as raising the level of wellbeing so that they can lead a purposeful and a creative life. Though the national income and the per capita income are the indicators of human development, but it includes many other elements like consumption, health, environment, education, freedom, security, non-violent atmosphere, etc.
(iv) Sustainable Development is that process of economic development which aims at maintaining the quality of life of both the present and the future generations without harming the natural resources and environment.
(v) UNDP : (a) Educational level (b) Health status (c) Per capita income
3. (i) Mention any two important aspects of our lives other than income. [CBSE 2008 (D)] (ii) How can we achieve our hopes and possibilities in the present world ? [CBSE Comp. (D) 2008] (iii) What is ‘Public Distribution System ’ (PDS) ? [CBSE Sept. 2011] [CBSE2009 (F) Sept. 2010] (iv) Mention two developmental goals of landless rural labourers. [CBSE Comp. (O) 2008] (iv) Why has Kerala a higher Human Development Index than Punjab in spite of low per capita income? [CBSE 2009 (F) Sept. 2011]
Answer: (i) Health and Education. (ii) Through Democratic political process. (iii) It is a system through which the Government distributes ration to the poor at a reasonable rate through the ration shops. (iv) (a) More days of work and better wages. (b) Quality education for the children. (v) (a) Because it has low infant mortality rate, (b) It has higher literacy rate.
4. Mention any four characteristics of development. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011]
Answer: (i) Different people have different developmental goals. (ii) What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may be destructive for the other. (iii) Income is the most important component of development, but along with income, people also seek equal treatment, good health, peace, literacy, etc. (iu) For development, people look at mixed goals.
5. Describe any three features of developed country. [CBSE 2013, 14]
Answer: (i) As per the World Bank Report 2012 any country with per capita income of US$ 12,276 per annum and above is termed as rich or developed country. ‘ (ii) Such countries have high literacy rate. (iii) Most of the people of these countries are engaged in service sector.
6. What is PCI? Where it is used?
Answer: PCI is Per Capita Income. It is calculated by dividing the National Income of the country by population. Uses: (i) It is used to compare different countries. (ii) The World Bank has divided the countries into rich or low income countries on the basis of per Capita income.
7. What are the development goals of the following : (i) Labourer (ii) Rich farmer (iii) Trader
Answer:
- more days of work better wages
- low price food grains
- cheap labour
8. ‘What may be development for one may not be development for the other.’ Explain by giving examples. [CBSE Sept. 2012] Or With the help of an example show two groups who may have different notions of development. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: It is true that development for one may not be development for the other. (i) More wages means development for a worker, but it can go against the entrepreneur. (ii) A rich farmer or trader wants to sell foodgrains at a higher price but a poor worker wants to purchase it for low prices. (iii) Construction of a dam means more and cheap power, but people, who will lose their habitat will demonstrate. (iu) To get more electricity, the industrialists may want more dams. But this may submerge the agricultural land, and disrupt the lives of the people.
9. What is national development? What are the aspects covered under the national development? [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: National development is a comprehensive term which includes improvement in living standard of the people, increase in per capita income, providing social amenities like education, medical care, social services, etc. to the citizens of the country. (i) Under national development, a country uses its resources in a fair and just way. (ii) Under this only those programmes and policies are implemented which would benefit a large number of people. (iii) Under national development, countries focus more on social infrastructure which includes education, health and other social services.
10. What contributes to the human development?
Answer: There are many economic as well as non-economic factors which contribute to the human development. (i) Living a long and a healthy life. (ii) To have education, information and knowledge. (iii) Enjoying a decent standard of living. (iv) Enjoying basic fundamental rights like freedom, security, education, etc. (v) To have equality and enjoyment of human rights.
11. What is the significance of Human Development Index? [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) HDI is used to measure level of development of a country. (ii) It has been published by UNDP and according to it countries has been ranked. (iii) It is a comprehensive approach which cover all the major aspects of life. (iv) Apart from income, education, health status, life expectancy, etc., are considered for measuring economic development of a nation.
12. ‘Human development is the essence of social development.’ Explain.
Answer: (i) Human development focuses on the people. (ii) It is concerned with the well-being of the people, their needs, choices and aspirations. All these help in building a right kind of society. (iii) It is all about the enlarging or widening the choices for the people. It is the building of human capabilities, such as to lead a long and a healthy life, to have education, information and knowledge, to have opportunities of livelihood, etc. (iv) Human development focuses on the expansion of basic choices.
13. ‘Money cannot buy all the goods and services that one needs to live well.’ Explain. [CBSE 2010(0), Sept. 2013]
Answer: (i) Money or material things that one can buy with it is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends upon non-material things like equal treatment, freedom, security, respect of others, etc. (ii) Money cannot buy us a pollution free environment, unadulterated medicines, peace, etc. (iii) There are many facilities like schools, colleges, parks, hospitals which an individual cannot afford. All these are to be provided by the government/society. (iv) Money possessed by an individual even can not provide us a type of government which take decisions for the welfare of the common people.
14. What are the limitations of the per capita income criteria of development ? [CBSE 2014] Or What is Per Capita Income? Can it be regarded as the sole indicator of economic development of a country? Give four valid arguments to support your answer. [CBSE 2012]
Answer: (i) Per capita income is the average income of a country. (ii) Per capita income criteria takes into account only the economic aspect of life and ignores the social, aspect of life. (iii) Per capita income criteria ignores education, health, life expectancy, sanitation etc. (iv) Per capita income criteria also ignores non material things like peace, pollution free environment, democracy, etc. (v) Though Punjab has higher per capita income as compared to Kerala but it has been ranked lower on Human Development Index because it is far behind than Kerala in literacy rate and has higher infant mortality rate than Kerala.
15. “Average income is an important criterion for development.” Explain.
Answer: (i) Average income gives us an idea what an average person is likely to get out of the total national income. (ii) Average income is used to classify the countries into rich, poor or developing nations. (iii) Average income is used to make economic policies.
16. Besides income, what can be the other attributes to compare economic development? [CBSE 2013, 14]
Answer: (1) Of course, for comparing economic development of countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need. That is why, the World Bank uses Per Capita Income to compare economic development.
(2) Apart from income, educational levels of the people and their health status are considered as measures to compare economic development of a nation. (i) Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) : This indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1,000 live children born in that particular year. ‘ (ii) Literacy Rate : This measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 years and above age group. (iii) Net Attendance Ratio : This is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group. (iv) Life Expectancy at birth : It denotes average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
17. What is infant mortality rate ? Suggest two measures to keep the infant mortality rate low. [CBSE 2013, 14] Or What is the meaning of ‘Infant Mortality Rate ’ (IMR) ? Give two main reasons for low IMR in Kerala. [CBSE 2010]
Answer: (1) The number of children that die before the age of one year per 1,000 children born alive in a particular year is called Infant Mortality Rate. (2) Measures to keep Infant Mortality Rate low : (i) Provision of basic health. (ii) Provision of proper educational facility. (iii) Proper functioning of Public Distribution System.
18. Define the following terms: (i) IMR (ii) Literacy Rate (iii) NAR [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011]
Answer: (i) Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR) indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year. (ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 years and above age group. (iii) Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 years attending school as a percentage of the total number of children in the same age group.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
1. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What are the limitations of this criterion? [CBSE Sept. 2010] Or Explain the meaning of the term ‘Rich Countries’ and ‘Low Income Countries’ according to the World Development Report of 2006. What is India’s position in this respect? [CBSE 2013]
Answer: The World Development Report, 2012, brought out by the World Bank has given the following criteria in classifying countries : (i) Rich or High income countries : Countries with the per capita income of US $12276 per annum and above in 2010, are called rich countries. (ii) Poor or Low income countries: The countries with the per capita income of US $ 1005 or less, are called low income countries. India comes in the category of low middle income countries because its per capita income in 2010 was just US $1340.4 per annum. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called the developed countries.
Limitations : (i) It covers only the economic aspect ignoring peace, health, environment, education, longevity, etc. (ii) The method does not provide us the distribution of income.
2. Compare India and Sri Lanka on the basis of any three indicators of the Human Development Index for 2004. [CBSE 2009 (O), Sept. 2012]
Answer: (1) Per capita income : The per capita income of Sri Lanka is higher than that of India. The per capita income of India is about $ 3285, whereas it is around $ 5170 for Sri Lanka. (2) Life expectancy at birth : Life expectancy at birth in Sri Lanka is also higher as compared to India. In Sri Lanka, the life expectancy is around 75.1 whereas in India it is about 65.8. (3) Literacy rate : Literacy rate in Sri Lanka is also higher than India. It is 90.6 in Sri Lanka whereas it is 62.8 in India.
3. Why are the countries of the Middle East not called ‘developed’ inspite of high per capita income ?[CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: (i) These are small countries. (ii) The gap between rich and poor is very high, (iii) Though per capita income in Middle East countries is very high but there is unequal distribution of wealth. (iv) These countries have high per capita income due to oil production. So they have only one major source of income. (v) The World Development Report brought out by the World Bank has excluded these countries from the list of developed countries.
4. Highlight any three advantages of public facilities. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: (i) Public facilities is the cheapest way to provide basic services collectively. (ii) Most of the poor people survive only because of public facilities. (iii) There are many services like police, education, transportation, etc., which become affordable only if they are part of public facilities.
5. Why are public facilities needed for the development of the country ? Explain four public facilities. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2012]
Answer: Public facilities play very important role in the development of a country as these include education, health, transportation, banking which are the base for any kind of development. (i) Education : Education is the most important public facility which is required both by the rich as well as the poor. (ii) Public Distribution System (PDS) : Public distribution system is another important facility which plays an important role in providing food security to the people. (iii) Transportation : Many transport facilities like railway, airways, waterways, banking become affordable only if they are provided collectively.
6. Explain common, different and conflicting goals by giving appropriate examples. [CBSE 2012]
Answer: Development goals may be common, different or conflicting. (i) Common goals : There are some needs which are common to all like income, freedom, equality, security, respect, friendship, etc. (ii) Different goals : Development or progress does not mean the same thing for every individual. Each individual has his own idea of development. For example, development for a farmer might be better irrigation facilities; for an unemployed youth it may mean better employment opportunities, etc. (ii) Conflicting goals : What may be development for some, may become destruction for some others. For example, industrialists may want dams for electricity but such dams would displace the natives of the region.
7. Mention any four aspects of comparison notions of development between different countries. [CBSE 2010, 14] Or Explain three attributes for comparing nations development between different countries. [CBSE 2010] Or What are the two basic criteria used for comparing an underdeveloped country with developed one ? [CBSE 2010] Or Give examples to prove that there are other important developmental goals than income. [CBSE 2012]
Answer: Development of a country can generally be determined by: per capita income; average literacy level; and health status of its people. (i) Per Capita Income means average income generated by each person in a given group of people. Its limitation is that it does not show the disparities among the people of the group. ‘ (ii) Amount of literacy achieved is also a measure of development. Literacy rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group. The more the people are educated, the more developed the group is. (iii) Health indicators are Infant Mortality Rate, Birth Rate, etc. Lower the amount of Infant Mortality Rate, higher is the rate of people being healthy. , (iv) Net Attendance Ratio is also the indicator of economic development of a nation. It is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group, (v) Life Expectancy at birth denotes average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth. Higher the life expectancy at birth, higher is considered the development of a nation.
8. How is BMI used to determine the undernourishment of a person ? Explain. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) One way to find out if adults are undernourished is to calculate what nutrition scientists call Body Mass Index or BMI. (ii) In order to calculate, first of all the weight of the person in kg is taken. Then, the height in metres is measured. The weight is divided by the square of the height. (ii) If this figure is less than 18.5, then the person would be considered undernourished. However, if this BMI is more than 25, then a person is overweight.
9. What is the criterion to determine if adults are undernourished? [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) The criterion to determine if adults are undernourished is Body Mass Index, popularly known as BMI. (ii) In order to calculate it, first the weight of the person in kg is taken. Then, we take height in meters. The weight is divided by the square of the height. (iii) If this figure is less than 18.5, then the person would be considered undernourished. However, if this BMI is more than 25, then a person is overweight.
10. What is meant by ‘Overusing a Resource’ ? Explain with examples. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) ‘Overusing a Resource’ means more uses of the resource than it is replenished by the nature. (ii) Let us consider groundwater. It is an example of renewable resources. These resources are replenished by nature. However, even these resources may be overused. In the case of groundwater, if we use more than what is being replenished by rain then we would be overusing this resource. (iii) This is what Indian states have done. For example, farmers of Punjab have overused the groundwater. This has lead to lowering of the water table.
11. Explain the importance of sustainable development with reference to groundwater by giving example. [CBSE 2013] Or What is meant by sustainable development? Explain it by taking the case study of water. [CBSE 2011, 14]
Answer: (i) Sustainable development is the development of a country or world not only at present, but the development which is to be continued and maintained for future generations. (ii) For example, groundwater is a natural resource which is replenished by nature. People of a particular generation must use water in such a way that people of future generation may also be able to use groundwater. People should not overuse and degrade the quality of water so that water is exhausted or if it remains, it is contaminated to such an extent that it becomes unusable for people of future generations.
12. “Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries.” Justify the statement. [CBSE 2012, 14]
Answer: (i) Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries. This issue is no longer a regional or national issue. (ii) Our future is linked together. Sustainability of development is essential for all the mankind and it is our common responsibility to save the environment. (iii) These days it is a matter of discussion among different countries of the world. (iv) Global warming, acid rain, etc., are not to be controlled by one nation. It is a global matter of thinking and finding the solutions.
13. Explain the term ‘Development’. How is it linked with sustainability ? Explain with example. [CBSE 2012, 14]
Answer: (i) Development is a process which has a notion of going further up and improving the quality of life. (ii) It is linked to sustainability since it has to be maintained for future generations. (iii) Resources need to be used wisely so that they can be replenished. (iv) Overuse of resources exhaust them. For example, petroleum. (v) If development is not sustainable, it will give rise to environmental degradation and become a global problem.
Value Based Questions
1.‘The development goals that people have me not only about better Income but also about other Important things in life.’ Explain. Mention any two goals of a student. Or ‘ ‘For development people look at a mix of goals’. Support the statement with suitable examples. [CBSE Sept. 2011] Or Apart from income, which other six things people look for? [CBSE 2012] Though income is one of the most important
Answer: components of development but there are other important things, such as : (i) People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security and respect. (ii) Women need safe and secure environment to take up a variety of jobs or run a business. (iii) People also need political rights. (iv) People seek a pollution-free environment. Students goal : (i) Better Education. (ii) Pollution free environment.
2. What do you mean by public facilities ? Why are they important ? Name two public facilities available in India.
Answer: Public facilities are the essential facilities for the community at large and are provided by the government. Important : They are important because there are many services like education, health, transportation etc., which have become cheap and affordable if provided, collectively. Public facilities : Rail transport and – . government schools.
3. Why is literacy essential for the economic ‘ development ? Explain. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: (i) Illiterate people are easily cheated and exploited by the traders, shopkeepers and employers. (ii) There is shortage of skilled workers in India, this shortage can be reduced only through literacy. (iii) Most of the illiterate people are engaged in primary and unorganised sector so their earning is very low.
4. ‘Money in your pocket cannot buy all the goods and services that one need’. With reference to the given statement mention any four things which money can not buy for an individual.
Answer: (i) Peace (ii) Pollution free environment (iii) Good health (iu) Freedom
5. The annual Per Capita Incomes of three countries are given below. Based on the guidelines set by the World Bank Report (2012), classify these countries as high income, low income or developing. • Country A : US $ 5,000 • Country B : US $ 15,580 • Country C : US $ 12,280 [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) Country A with Per Capita Income of US $ 5,000 comes under Low Income Countries. (ii) Country B with Per Capita Income of US $ 15,580 lies in the category of High Income Countries. (iii) Country C with Per Capita Income of US $ 12,280 falls in the category of Developing countries.
6. Think of any three developmental goals of a boy from a rich urban family. Describe them. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) He may think to get quality education and pursue his studies abroad. (ii) He may require the availability of vocational education and training. (iii) He may require capital to start his own business.
7. Apart from salary, what other goals can you have in mind while taking up a new job? Explain. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) Security (ii) Working Environment (iii) Opportunity to learn (iv) Pollution from environment.
8. How do the women engaged in paid jobs fulfill mix of goals? Explain. [CBSE 2014]
Answer: (i) Economic independence: If a women is working she will get economic independency. (ii) Equality: As per the law working women need to be treated equally. (iii) Respected: A working women will get respect not only in the family but in the society also.
Study Material
.avif)
Home > Class 10 SST Subject-wise Material
Class 10 SST Economics Chapter 1 Development
Students study the components contributing to the advancement of cultures and countries as they look into the notion of economic development in eco class 10 ch 1. The goal of this chapter is to provide students with the fundamental information they need to understand the differences between the economies of developed and emerging nations.
By providing a basis for understanding the intricacies of economic growth, the first chapter prepares students for more in-depth discussions of certain subjects in later chapters. The eco class 10 ch 1 development study material provided by Educart includes chapter-wise notes, DoE worksheets, question banks, and much more for students to prepare effectively for exams.
| S.No. | Table Of Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 |
CBSE Class 10 Development Notes
Below we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of class 10th development notes for every typology.
<red> ➜ <red>Development Notes
📈 Trending: Class 10 CBSE Syllabus 2024-25
📺 Recommended: Educart One Shots for Class 10
📚 Don't Miss: CBSE Class 10 Open Book Test
CBSE Class 10 Development DoE Worksheets
Below we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of class 10 eco ch 1 worksheets to help students practice every typology question.
<red> ➜ <red>Worksheet 17
<red> ➜ <red>worksheet 18, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 59, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 60, cbse class 10 development experiential activities.
Below we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of Experiential Learning Activity for class 10 eco ch 1 to help students implement their acquired knowledge in the real world.
<red> ➜ <red>Development Experiential Activities
Cbse class 10 development important questions.
Below we have provided Class 10 SST Important Questions that cover all the important questions in Development.
<red> ➜ <red>Development Important Questions(View)
Cbse class 10 development mind maps.
Below we have provided Class 10 SST Mind maps that include mind maps of the related concepts in Development.
<red> ➜ <red>Development Mind Maps
Cbse class 10 development question bank.
Below we have provided Class 10 SST Question Banks that cover every typology question with detailed explanations from various resources in one place.
<red> ➜ <red>Kendriya Vidyalaya Question Bank
Cbse class 10 development support material.
Below we have provided Class 10 SST Support Materials that cover Case Study-based questions from the various concepts explained in Science NCERT chapters.
<red> ➜ <red>Development Support Material
Why download these chapter-wise pdfs.
The eco class 10 ch 1 download links are provided above to help students prepare for their exams with the relevant materials. We comprehend topics more easily when there are images, tables, and graphs present because our brains process visual information faster than written text.
- Chapter-wise PDFs offer an organized approach to learning. It is simpler for students to organize their learning and monitor their progress when they can concentrate on one chapter at a time.
- Chapter-wise PDFs make it simple for students to access particular subjects or chapters. Without needing to carry along the complete textbook, users may download and understand any content they require.
- PDFs that have been downloaded may be viewed offline, which is very helpful in places with spotty or nonexistent internet access. Regardless of whether they are not online, students may still learn.
- Numerous devices, including PCs, tablets, and smartphones, are compatible with PDFs. Students may easily bring their learning materials alongside them anywhere they go thanks to this.
- A paper copy of a particular chapter is preferred by certain students to better annotate and take notes. It is simple to print PDFs that have been downloaded for this use.
How Can This Chapter-wise Material Help Students?
The chapter-wise material for SST Development will help in preparing the chapter from the 10th NCERT textbook along with the additional study material. Students may efficiently practice for the chapter by downloading crucial questions, question banks, chapter notes, and a plethora of additional study materials.
- The economics class 10 notes Chapter 1 Development comprehensive account of a student's comprehension and analysis of the subject matter. This customized approach encourages a more meaningful engagement with the information.
- Mind maps are a useful tool for helping students link the concepts they have learned. It will be very helpful in aligning your existing knowledge with the newly learned information, which will improve your understanding of the chapter.
- The question banks can be used to prepare for every type of question that will be asked on the 10th board test. Students can make a timetable and practice answering pertinent questions if they have a good understanding of the subject matter.
- You need to study not just for the examination's topic questions but also for the Class 10 CBSE important questions, which contain recurring questions. You may improve your chances of receiving higher exam results by practicing important questions.
Chapter-organized study materials are crucial for learning because they help improve understanding, memory, and test-taking readiness. It is a valuable tool that is advantageous to teachers as well as students.
Extra 10% Discount

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
Ncert books for class 10, class 10 subject-wise material.
Buy Latest Books
Teacher's Corner
To Download PDF
Please verify your Whatsapp number first, so you can download this pdf immediately
Please type a valid 10 digit whatsapp number

OTP sent, check your whatsapp
Your OTP is incorrect, Please enter valid OTP

- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- English L&L
- English Communicative
- Social Science
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Computer Application
- Science (Hindi )
- Maths (Hindi)
- Social Science (Hindi )
- Applied Maths
- Physical Education
- History & Civics
- Literature in English
- English Language
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 PCB Combo
- Class 12 PCM Combo
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 English

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science
Understanding Economic Development is a lesson in Class 10 Social Science from which case study questions are often asked in the Class 10 Social Science exam. There are several possible questions that can be asked from this alone chapter and therefore, for the practice purpose here we provide Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science.
Practising the case study questions on Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development can benefit students in a variety of ways as well as enable them to feel confident in answering such questions. Continue reading to learn more about the Understanding Economic Development Case Study for Class 10 Social Science .
Understanding Economic Development Case Study for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions in PDF
The PDF file of the Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science is prepared by the Selfstudys subject experts team who has years of experience. They revise the case study questions on Understanding Economic Development very often with solutions. Here on this website, we offer Understanding Economic Development Case Study for Class 10 Social Science with solutions in PDF for free of cost.
The PDF file can be accessed for free of cost and it is available 24×7 to learn and practise the questions from.
Salient Features of Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science PDF
Some salient features of the Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science PDF are mentioned below:
- Questions with Answers: One of the best and most useful features of the Understanding Economic Development Case Study for Class 10 Social Science is that the PDF file contains case-based questions as well as answers. The answers are prepared by a subject matter expert.
- Available in PDF: Another great feature of Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science is that it is available in a PDF file format which students can download as well as can read them online for free of cost.
- Prepared by Subject Matter Experts: Above all the features mentioned, this feature is the most helpful because this feature ensures that students are only getting access to the Understanding Economic Development case study questions which have a higher level of accuracy and are prepared to keep in mind the syllabus of Class 10 Social Science.
How to Download PDF of Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science?
This step-by-step process will help you download PDF file of case study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science.
- Open Selfstudys.com and click on the navigation button available beside the Selfstudys logo
- Click on CBSE from the given options
- Navigate to the Case Study and click on that
- It will further open a webpage where you need to choose Class 10
- At this stage, you are required to click on Social Science to expand it further and then get access to the case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science.
Why Practice Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science?
Case study questions are part of the Class 10 Social Science exam paper and therefore all the students should prepare and be ready for this type of question no matter the chapter name. However, there are certainly more reasons to practice case study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science discussed below:
- To Deepen the Understanding of Understanding Economic Development: Practising the Case Study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science questions is not only helpful for the board exam preparation but enables the students to deepen their level of understanding of Understanding Economic Development. Solving questions will also help students to clear their doubts about Understanding Economic Development.
- For Class 10 Social Science Board Exam Preparation: There is no doubt case study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science PDF file is prepared for students so that they can better prepare for the exam because the more practice the better command of the case-based questions. Therefore, those students who are looking for a separate PDF file of the Case Study on Understanding Economic Development to better prepare for the exam can use the PDF file.
- To Boost Confidence in Understanding Economic Development Topic: A regular and thorough practice of Class 10 Understanding Economic Development case study questions help students gain confidence in answering the questions. Whether it is in the Class 10 Social Science board exam hall or in general. Not only in solving the case-based questions but practising the Understanding Economic Development Case Study for Class 10 Social Science boost the overall confidence of the students in the topic of Understanding Economic Development.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


NCERT Solutions for Class 10th: Ch 1 Development Economics
Ncert solutions for class 10th: ch 1 development economics social studies (s.st).
| Bangladesh | |||||
Contact Form

Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions

Written By Avinash Sharan
1 comment(s), 28th june 2023, economics chapter 1 development source based questions.
Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions shed light on the economic growth and progress of nations. These questions often revolve around the factors that contribute to or hinder development, such as access to education, healthcare, infrastructure, and technology. They explore the impact of government policies, foreign aid, and trade on economic development . Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions also analyze the role of institutions, governance, and income inequality in shaping development outcomes. By examining empirical data, statistical indicators, and case studies, economists can unravel the complex dynamics of development, providing valuable insights into the strategies and policies necessary for sustainable and inclusive growth in economies around the world. So let’s begin Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions.
Besides seeking more income, one way or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All these are important goals. In fact, in some cases, these may be more important than more income or more consumption because material goods are not all that you need to live. Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above. If it is not obvious to you, then just think of the role of your friends in your life. You may desire their friendship. Similarly, there are many things that are not easily measured but they mean a lot to our lives. It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases.
Read the above passage and answer the following questions:
- What are material and non-material goods? 1.
Ans) Material commodities are physical, observable items like real estate, construction projects, furniture, pens, and the like.
However, non-material products can encompass a variety of invisible and intangible services.
2. Mention any two factors on which quality of life depends other than money? 1.
Ans) The factors on which quality of life depends other than money are”
i) the presence of friends, family, and relatives
ii) a good atmosphere, Knowledge, safety and security, Respect and dignity.
3. Do you agree that “if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases.” 2.
Ans) Yes, I agree that that “if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases.”
Women’s status in the home and society rises if they work for a living.
However, it is also true that more housework would be shared and more women would be accepted of outside employment if there was respect for
“Building a Strong Foundation Through Class IX Economics Lesson Plan”
CBSE Class IX Economics Chapter 2 People As Resource Lesson Plan
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of a country? Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country.
However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such an useful measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income. In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, this criterion is used in classifying countries.
Countries with per capita income of US$ 12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich countries and those with per capita income of US$ 1035 or less are called low-income countries. India comes in the category of low middle income countries because its per capita income in 2012 was just US$1530 per annum. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
- Do you think that “Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income.” 1.
Ans) Yes, to some extent I agree with this statement. It is because more income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income.
2. What is the criterion used by the world bank in classifying the countries? 1.
Ans) The average income is also called per capita income is the criterion used by the world bank in classifying the countries.
3. Why are the middle-east countries excluded from the list of developed countries? 2.
Ans) The Middle East nations are not counted among the developed nations despite having high GNI per capita.
This is because before classifying nations as developed, the World Bank also takes into account other elements including human development, Sex ratio,
Literacy, infrastructure, and economic diversity.
Economics Project On Income Inequality: A Comprehensive Analysis For Class X
Money in your pocket cannot buy all the goods and services that you may need to live well. So, income by itself is not a completely adequate indicator of material goods and services that citizens are able to use. For example, normally, your money cannot buy you a pollution-free environment or ensure that you get unadulterated medicines, unless you can afford to shift to a community that already has all these things. Money may also not be able to protect you from infectious diseases, unless the whole of your community takes preventive steps.
The problem does not end with Infant Mortality Rate. in Bihar are not attending school beyond Class 8. This means that if you went to school in Bihar more than two-thirds of your class would be missing. Those who could have been in school are not there! If this had happened to you, you would not be able to read what you are reading now. Actually for many of the important things in life the best way, also the cheapest way, is to provide these goods and services collectively. Just think will it be cheaper to have collective security for the whole locality or for each house to have its own security man? What if no one, other than you, in your village or locality is interested in studying? Would you be able to study? Not unless your parents could afford to send you to some private school elsewhere.
- What is Infant Mortality Rate? 1.
Ans) The number of newborn deaths for every 1,000 live births is known as the infant mortality rate. The infant mortality rate is a significant indicator of the general health of a society in addition to providing us with valuable information on maternal and baby health.
2. Why do you think that in Bihar the Net Attendance Ratio is very poor? 1.
Ans) Bihar has very poor Net Attendance Ratio because of the following reasons:
ii) Lack of quality education in government schools.
3. Mention any two things what money in your pocket cannot buy? 2.
Ans) T wo things what money in my pocket cannot buy are:
i) pollution-free environment
ii) Good health (protection from infectious diseases)
How To Write a Project On Globalization And It’s Impact On Economic Development Worldwide
Conclusion:
Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions are important for a number of reasons. First and foremost, they enable us to confirm the accuracy and legitimacy of information. We can evaluate the source’s knowledge, any potential biases, and general credibility by challenging it. Second, Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions promote critical thinking and a more thorough comprehension of the material. We can find informational gaps, discrepancies, or opposing points of view by analyzing the source. Last but not least, Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions support ethical research practices and academic integrity. They support proper citations, avoiding plagiarism, and acknowledging others’ contributions.
In conclusion, Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions are crucial in ensuring that information is gathered and analyzed in a way that is accurate, comprehensive, and ethical.
Online Fraud And Prevention – A Consumer Awareness Project
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

“From Polls to Parliament: The Mechanics of Lok Sabha Elections in India”
Jun 20, 2024
How Are Lok Sabha Elections Conducted in India? As a student, you must be curious to know How Lok Sabha Elections are...

“From Waste to Wonder: The Power of Recycling in Carbon Footprint Reduction”
Jun 9, 2024
Carbon Footprint Reduction: A School Project On a Greener Planet Are you looking to make a positive impact on the...
Mapping The Elevation: How To Read and Use Topographic Maps?
Jun 4, 2024
Topographic Maps: A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners Topographic maps are an essential tool for hikers, outdoor...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment
Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 4 Globalization and The Indian Economy
Case study 1:, case study 2:, case study 3:.
| Pros | Cons |
| Economic Growth: It can stimulate economic growth by attracting investments and fostering entrepreneurship. Efficiency: Competition and market-driven policies can enhance efficiency in industries. | Inequality: It may exacerbate income inequality.
Vulnerability: Over-reliance on global markets can make the economy vulnerable to external shocks. |

Case Study 4:
Case study 5:.
Although the concepts of fair trade and free trade have little to do with one another, in the context of public procurement, the two come into conflict. Advocates of free trade argue that governments should act as private market actors when making purchases, while others believe that governments have a duty to promote justice and equality through procurement “linkages” to social policies like fair trade. The growing recognition of the importance of sustainability has reopened the debate on whether governments should align their spending with social concerns. In Europe, a sustainable approach to public procurement is common, and the enthusiasm for this approach has spread to the World Trade Organization (WTO). A Revised Government Procurement Agreement (GPA) aims to encourage broader acceptance of the agreement by allowing exceptions for environmental and social policy linkages. These exceptions include a general exception in cases where derogation is necessary to protect human, animal, or plant life or health, exclusion of public procurement in international development assistance from the scope of the agreement, and explicit permission for governments to apply technical specifications for environmental protection. A recent case in the Netherlands involving sustainable public procurement demonstrates the flexibility given to European countries in selecting and implementing their own procurement practices. There is significant variation among countries in their government procurement practices.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, dav class 5 math solution chapter 4 fractional numbers, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 4 – the donkey and the dog, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 1 – learning together, national war memorial class 6 extra questions and answers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
Ncert solutions for class 10 economics chapter 1 – development.
According to several students, Economics is a tiresome subject. Also, they find it irrelevant. But economics is a very helpful subject. It helps students to learn about how an economy works. Apart from that, our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 will help you to easily realize the topics of the Chapter. Above all, NCERT Solutions will also assist you with other subjects also.
Toppr’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 is outlined by our team of experts who have worked in the field of economics. Also, they have years of experience in teaching. Besides, the NCERT solution is available in PDF format for free. Also, we have previous years question papers to help you gather all the required data for your study. Download the Toppr’s Android , iOS app or Signup for free.
Download NCERT Solutions for other chapters of Class 10 Social Science here.
Download NCERT Solutions for other subjects here.
CBSE Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 – Development NCERT Solutions
First of all, we have to understand what is development? In general terms, the word development means a process that makes changes to improve the living. But, in Economic term development means the process of change in social, economic and political comfort of the people of a country.
Overview- This topic deals with what we have learned till now and what we are going to learn from this Chapter.

Sub-topics covered under NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 PDF Download
1.1 What Development Promises- Different People, Different Goals- The topic includes a table by which it explains how different people goals and objective related to development varies.
1.2 Income and Other Goals- This topic deals with the basic needs or goals that people want to get fulfilled. Also, these goals mention some common demands like an increase in salary or wage, equal treatment, security, and freedom. Apart from that, an example is also given to make you understand it easily.
1.3 National Development- In the previous sub-heading discusses individual goals. But, this topic discusses national goals. Also, it is a government duty to decide the best path for a nation’s development. National development means thinking about the development of all.
1.4 How to Compare Different Countries or States? – This topic discusses the various criteria which help to compare things between countries or states. Usually, it is done with the help of specific categories which help to measure all of them.
1.5 Income and Other Criteria- This topic discusses how to measure income and other criteria like literacy rate, mortality rate, etc. with the help of an example.
1.6 Public Facilities- The topic quotes the above example and talks about the basic facilities that should be provided to all equally like education, healthcare, etc. After that heir is a sub-heading “Human development Report” which talks about the other criteria of Human Development Index.
1.7 Sustainability of Development- This topic talks about how to use the resources of the country. So, that they can be available for future generation and also over-exploitation of resources can be used.
You can download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 PDF by clicking on the button below

Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
Toppr not only provides free PDF solutions of NCERT but also provide other features like a 360o adaptive learning platform, recorded classes at your convenience, live doubt clearance that resolves your issue 24×7 and mock test to judge your performance. Above all, these features will help you improve your grades and knowledge. So, hurry up and download the Toppr Android , iOS app or Signup free.
Solved Questions For You:
Question 1. Employment in the service sector increased to the same extent as production.
Question 2. Do you think the classification of economic activities into the primary, secondary and tertiary sector is useful? Explain how.
If the tertiary sector is developing much faster than the primary sector, then it implies that agriculture is depleting, and the government must take measures to rectify this. The knowledge that the agricultural profession is becoming unpopular or regressive can only come if we know which sector it belongs to. Hence it is necessary to classify economic activities into these three sectors for smooth economic administration and development.
Question 3. What factors gave birth to the consumer movement in India? Trace its evolution.
Question 4. What do you understand by globalisation? Explain in your own words.
Answer: Globalisation means integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries under conditions of a free flow of trade, capital and movement of persons across borders. It includes (i) Increase in foreign trade (ii) Export and import of techniques of production. (iii) The flow of capital and finance from one country to another (iv) Migration of people from one country to another.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 4 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Free PDF Download
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Economics Chapter 1 Development
September 30, 2019 by phani
Formulae Handbook for Class 10 Maths and Science
Page 16 Q1. Development of a country can generally be determined by (i) its per capita income (ii) its average literacy level (iii) health status of its people (iv) all the above Answer: (iv) all the above
Q2. Which of the following neighbouring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India? (i) Bangladesh (ii) Sri Lanka (iii) Nepal (iv) Pakistan Answer: (ii) Sri Lanka
More Resources for CBSE Class 10
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of IT
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Q3. Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is Rs 5000. If the income of three families is Rs 4000, Rs 7000 and Rs 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family? (i) Rs 7500 (ii) Rs 3000 (iii) Rs 2000 (iv) Rs 6000 Answer: (iii) Rs 6000
Q4. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What are the limitations of this criterion, if any?
- In the World Development Report, 2006, the World Bank has used the criterion of average income or per capita income in classifying different countries.
- The average income or the per capita income is the total income of the country divided by its population.
(2) According to the WDR 2006, countries are classified as mentioned below :
- Rich countries : Countries with per capital income of? 4,53,000 per annum and above in 2004 are called rich countries
- Low-income countries : Countries with per capital income of? 37,000 or less are called low-income countries.
- India comes in the category of low-income countries because its per capital income in 2004 was just ? 28,000 per annum.
- Rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries are generally called developed countries.
(3) Limitations of the criterion are as mentioned below :
- It does not tell us how this income is distributed among people. A country may have more equitable distribution. People may be neither very rich nor extremely poor.
- In another country with same average income, one person may be extremely rich while others may be very poor. So, the method of average income does not give correct picture of a country.
- This system hides disparities among people.
Q5. In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank?
- The criterion used by World Bank: The average income, i.e. per capita income is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries. According to the World Development Report 2006 , published by the World Bank, countries with per capita income of $10066 per annum and above in 2004 are called rich or developed countries. On the other hand, countries with per capita income of $825 or less are called low-income countries.
- The UNDP compares countries based on HDI e., on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capital income or average income.
- Human Development Index used by UNDP is better because it is a wider indicator in which besides per capital income, health and education are also included.
Q6. Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate with your own examples related to the development.
(1) We use averages for comparison between two countries, two persons or any two or more things. (2) There are the following limitations to the use of averages :
- Averages do not tell us about similarities or differences between two countries or persons or things.
- By averages only one aspect income, size etc. in case of country, marks or participation in sports activities etc. in case of student, can be compared. All aspects or achievements are not compared.
- As only one aspect is compared, it does not give true picture of different countries, persons or things. For example, students differ in height, health, talents and interests. The healthiest student may not be the most intelligent or topper in studies. Similar is the case in respect of countries or states. A country may be ahead than the other country in one field but may lag behind in the other field. So averages do not give the correct picture.
Q7. Kerala, with lower per capita income, has a better human development ranking than Punjab. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
It is correct to say that per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states due to reasons as mentioned below :
- Money cannot buy all the goods and services that you need to live well. Income by itself is not a completely adequate indicator of material goods and services that citizens are able to use.
- There cannot be a pollution-free environment in a colony of rich people unless the whole community takes preventive steps.
- Sometimes, it is better to have collective services like security for the whole locality than to have individual security for one’s own house. Again a school may be opened for the children of the whole community than for one or two children of a rich person.
- Kerala has a better human development ranking than Punjab.
- In Kerala, Infant Mortality Rate is 11 in comparison to 49 in Punjab, where the per capita income is much more than Kerala. It is ? 26000 whereas in Kerala it is ? 22800. It is because Kerala has adequate basic health and educational facilities.
- Similarly in some states, the Public Distribution System (PDS) functions well and people get ration regularly whereas in some states ration shops do not function properly. At such places, people face a shortage of grains that affect their health. Thus it is clear that the states should not be compared on the basis of per capita income – alone.
Q8. Find out the present sources of energy that are used by the people in India. What could be the other possibilities fifty years from now? The present sources of energy that are used by the people of India are electricity, coal, crude oil, cowdung and solar energy. Other possibilities fifty years from now, could include ethanol, bio-diesel, nuclear energy and better utilization of wind energy, especially with the imminent danger of oil resources running out.
Q9. Why is the issue of sustainability is important for development?
Sustainable development means that development should meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. However, since the second half of the twentieth century, a number of scientists have been warning that the present type and levels of development are not sustainable. The issue of sustainable development has emerged from rapid industrialization of the world in the past century. It is felt that economic growth and industrialization have led to the reckless exploitation of natural resources. On the other hand, the stock of natural resources are limited. So, the growth of all countries in the future is likely to be endangered if the limited resources are completely exhausted.
Under these circumstances, the issue of sustainability has become important for development. A number of resources are being overused. For example, groundwater is under serious threat of overuse in many parts of the country i.e., Punjab, Haryana and western U.P. The water level has declined over 4 meters. As a result of it if we go on overusing there will be a water crisis in future. Similarly, if non-renewable resources are used recklessly these will also be exhausted.
Page 17: Q10. “The Earth has enough resources to meet the need of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person.” How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss. This statement is relevant to the discussion of development since both resources and development go hand in hand. As the statement claims, our earth has enough resources – renewable and non-renewable to satisfy everyone’s need if we use them in an economic manner. For the sustainability of development, the consumption and maintenance of resources is also crucial. We have to use the resources keeping our environment protected and clear so that there is a balance between the development and use of our resources. As otherwise after a certain point of time in future the development will be stagnated.
Q11. List a few examples of environmental degradation that you may have observed around you. Some of the examples of environmental degradation in the area are as follows :
- Air pollution has increased due to the emission of smoke from factories and vehicles.
- There is an increase in water pollution due to shops and small factories in residential areas.
- There is noise pollution due to the use of loudspeakers at night and blowing of horns unnecessarily on the roads by different vehicles.
- People throw garbage wherever they want. Perhaps there is no provision for dustbins in the streets or roadsides.
- Sometimes people urinate in the open on the roadside due to a lack of public conveniences.
Multiple Choice Questions
Previous Years’ Questions 1. Which one of the following countries has the largest size of the illiterate population in the age group of 15 + in the world? [CBSE (CCE) 2011] (a) India (b) Sri Lanka (c) Myanmar (d) Bangladesh
2. Development of a country can generally be determined by its: [CBSE (CCE) 2011] (a) per capita income (b) average.literacy Ieve4 (c) health status of its people (d) none of these
3. We can obtain per capita income of a country by calculating: [CBSE (CCE) 2010] (a) the total income of a person (b) by dividing the national income by the total population of a country (c) the total value of all goods and services (d) the total exports of the country
4. Kerala has low infant Mortality Rate because: [CBSE (CCE) 2010] (a) it has good climatic condition (b) it has adequate infrastructure (c) it has adequate provision of basic health and educational facilities (d) it has poor net attendance ratio
NCERT Questions 5. Which of the following neighbouring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India? (a) Bangladesh (b) Sri Lanka (c) Nepal (d) Pakistan
6. Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is ₹ 5000. If the income of three families is ₹ 4000, ₹ 7000 and ₹ 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family? (a) ₹ 7,500 (b) ₹ 3,000 (c) ₹ 2,000 (d) ₹ 6,000
Additional Questions 7. According to the World Development Report 2004, low-income countries are those which have per capita income of (a) $ 900 or less. (b) $ 1000 or less (c) $ 825 or less (d) $ 500 or less
8. Identify which of the following cannot be a development goal for a landless rural labourer? (a) More days of work (b) Better wages (c) Quality education for children (d) Foreign tours
9. Besides seeking more income, one way or the other, people also seek things like (a) equal treatment (b) freedom (c) security (d) all of them
10. Different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development. A fair and just path for all should be achieved. Interpret the concept being discussed here. (a) Social development (b) Cultural development (c) National development (d) Economic development
11. List how many tonnes of liquid toxic wastes a vessel dumped in a city called Abidjan in Ivory Coast, a country in Africa? (a) 500 tonnes (b) 600 tonnes (c) 900 tonnes (d) 1000 tonnes
12. Countries with higher income are ………….. than others with less income. (a) Less developed (b) More developed (c) Less stronger (d) More organised
13. Income of the country divided by its total population is known as (a) Capital Income (b) National Income (c) Per capita income (d) GDP
14. In the World Development Report 2006, Rich Countries were those which in 2004 had the per capita income of (a) ₹ 2,53,000 per annum & above (b) ₹ 14,50,000 per annum & above (c) ₹ 4,53,000 per annum & above (d) ₹ 13,53,000 per annum & above
15. In the World Development Report 2006, low-income countries were those which in 2004 had the per capita income of (a) ₹ 37,000 or less (b) ₹ 47,000 or less (c) ₹ 50,000 or less (d) ₹ 39,000 or less
16. In 2004, India came in the category of (a) Rich countries (b) Low-income countries (c) Developed countries (d) Medium income countries
17. Comparing all states, identify the state which had the highest per capita income in 2002 – 2003. (a) Kerala (b) Punjab (c) Delhi (d) Bihar
18. Which state had the least per capita income in 2002-03? (a) Bihar (b) Rajasthan (c) Kerala (d) Delhi
19. Number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year is known as (a) Death rate (b) Survival rate (c) Infant mortality rate (d) Life death rate
20. Proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group is called as (a) Knowledge rate (b) Literacy rate (c) Attendance rate (d) Excellence Rate
21. Which age group of children is included for calculating Net Attendance Ratio? (a) 6 – 10 (b) 7 – 11 (c) 5 – 9 (d) 10 – 15
22. In 2003, Infant Mortality Rate in Kerala was (a) 49 (b) 11 (c) 60 (d) 22
23. For the year 1995 – 96, the Net Attendance Ratio for class I to V in Bihar was (a) 81 (b) 51 (c) 41 (d) 31
24. Literacy rate for the rural male population of Uttar Pradesh is (a) 62 % (b) 59 % (c) 52 % (d) 42 %
25. For calculating Body Mass Index (BMI), the weight of the person is divided by the (a) Square of the weight (b) Square of the height (c) Square root of the height (d) Square of the sum of height and weight
26. If BMI is less than 18.5 then the person would be considered (a) overweight (b) long height (c) under nourished (d) short height
27. Report published by UNDP which compares countries based on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capita income is (a) Human Education Report (b) Human Development Report (c) Human Population Report (d) Human Quality Report
28. HDI Rank of India in the world out of 177 countries in 2004 was (a) 93 (b) 126 (c) 130 (d) 125
29. India’s per capita income in US $ is …………… Sri Lanka (in 2004) (a) less than (b) more than (c) equal to (d) less than or equal to
30. Nepal has nearly ……………. the per capita income of India (in 2004) (a) one – fourth (b) three – fourth (c) equal (d) half
31. What proportion of the country is overusing their groundwater reserves? (a) One – Fourth (b) One-Tenth (c) One – Third (d) half
32. Resources which will get exhausted after years of use is called …………… (a) Renewable resources (b) Non – durable resources (c) Non – renewable resources (d) Competing resources

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics: Understanding Economic Development – II
- Chapter 1 Understanding Economic Development
- Chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy
- Chapter 3 Money and Credit
- Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
- Chapter 5 Consumer Rights
Free Resources
Quick Resources
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 Economics
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics
Ncert solutions for class 10 economics – understanding economic development – free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics are based on Economics and the terms related to the economic development of a country. Notions based on the economic development of a country and its calculation are explained in brief in this subject. To get a clear idea of the technical terms, students should first understand the subject using the NCERT Solutions available at BYJU’S. The top experts prepare the solutions with the aim of helping students ace the exam without fear. Students will also get to know about the national income, the average income of a country, economic growth and per capita income.
In Class 10 Economics, students will learn the process of development of the Indian Economy. They will first see the beginnings of development in terms of the emergence of agriculture, manufacturing and services as three distinct sectors of the economy. Then, they will learn the concept of human development, which includes the development of health and education and other indicators that, along with income, broadly define the quality of life of people. To help to understand all these concepts in an effective way, we have provided the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics. These solutions offer chapter-wise answers to all the exercise questions.
The faculty mainly focus on the basic concepts and terminology of Economics so that students get a grip on the subject. These new concepts cannot be understood easily without the support of proper study material. The best way to learn the syllabus is to make use of the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics designed by the subject experts at BYJU’S. This is one of the crucial subjects when it comes to board exam preparation. Students are highly recommended to complete the syllabus prior to the exam so that sufficient time is remaining for revision.
The Class 10 Economics book “Understanding Economic Development” contains 5 chapters. Students can find the NCERT Solutions of all these chapters in the table below.
After reading these chapters, students would be able to understand the economic life around them. Also, they can comprehend what is meant by economic development for people. Many examples and case studies from the NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science have been used as an aid for conceptual clarity to ensure students can easily relate these ideas to reality.
NCERT Solution for Class 10 Economics Chapters Overview
The important terminology and concepts from the NCERT Social Science Class 10 Book are explained in simple language in the NCERT Solutions. The faculty provides chapter-wise solutions with the aim of helping students prepare well and manage their study schedules accordingly. Students will also understand how to calculate the economic condition of a country and how it is compared with other countries. After learning the chapter, students are advised to answer the exercise questions on their own. You can have a look at the summary of each chapter below.
Chapter 1: Development
This chapter helps students understand the idea of development for a nation’s growth. The chapter has a total of 13 questions, out of which the first 3 are of objective type, and the remaining 10 are descriptive. Students can find the answers to all these questions in the solution file.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development
- What Development Promises – Different People, Different Goals
- Income and Other Goals
- National Development
- How to Compare Different Countries or States?
- Income and Other Criteria
- Public Facilities
- Sustainability of Development
Chapter 2: Sectors of the Indian Economy
An economy is best understood when students study its components or sectors. Sectoral classification is done on the basis of several criteria. In this chapter, three types of classifications are discussed here: primary/secondary/tertiary, organised/unorganised, and public/private. The exercise contains questions related to these sectors. This chapter has a total of 14 questions, 2 are MCQs, 1 is match the following, one is odd one out, and the remaining are of descriptive nature.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors of the Indian Economy
- Sectors of Economic Activities
- Comparing the Three Sectors
- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors in India
- Division of Sectors as Organised and Unorganised
- Sectors in Terms of Ownership: Public and Private Sectors
Chapter 3: Money and Credit
In this chapter, students will study the history of money. Here, they will find the questions related to credit, the functioning of banks, different sources of credit in India, Self-Help Groups, borrowers, etc. The exercise contains a total of 13 questions, out of which one is MCQ and one is fill in the blank. Some of the questions are short, while some are descriptive type of questions.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit
- Money as a Medium of Exchange
- Modern Forms of Money
- Loan Activities of Banks
- Two Different Credit situations
- Terms of Credit
- Formal Sector Credit in India
- Self-Help Groups for the Poor
Chapter 4: Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Most regions of the world are getting increasingly interconnected. One of the major reasons for this is globalisation. In this chapter, students must have learned about globalisation in depth. The exercise contains questions based on the definition of globalisation and factors which impact and enable globalisation in India. There are a total of 13 questions in this chapter, out of which one is MCQ, one is fill in the blank, one is based on match the following and the remaining are descriptive ones.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
- Production across Countries
- Interlinking Production across Countries
- Foreign Trade and Integration of Markets
- What Is Globalisation?
- Factors that Have Enabled Globalisation
- World Trade Organisation
- Impact of Globalisation in India
- The Struggle for a Fair Globalisation
Chapter 5: Consumer Rights
After studying this chapter, students will know that the awareness of a well-informed consumer arises from the consumer movement and active participation of people in struggle movements. They will also get to know about some of the organisations which have helped the consumer by making them aware of the product. Finally, the chapter ends with some critical issues of the consumer movement in India. The exercise contains a total of 13 questions. Out of which, one question is match the following, and one is true and false. Students will find the answers to all questions in the solutions PDF.
We hope students have found these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics helpful in their studies. Keep learning and stay tuned for further updates on CBSE and other competitive exams. Download BYJU’S – The Learning App and subscribe to the YouTube channel to get interactive Maths and Science videos.
For more answers related to the subject, students can download the solutions using the links given below.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Political Science
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics
What are the chapters present in the ncert solutions for class 10 economics, what are the chances that the questions asked in the board exam are from ncert solutions for class 10 economics, are the ncert solutions for class 10 economics pdfs sufficient to ace the board exam, which are the important chapters in the ncert solutions for class 10 economics, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Case Based Questions
- MCQ Questions (1 Mark)
- Assertion Reasoning
- Picture Based Questions (MCQ)
- True or False
- Match the following
- Fill in the blanks (MCQ)
- Questions by analyzing tables
- Past Year Questions - 1 Mark
- Past Year Questions - 2 Marks
- Past Year Questions - 3 Marks
- Past Year Questions - 5 Marks
Question 1 - Case Based Questions - Chapter 1 Class 10 Economics - Development - Economics
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
Different persons can have different developmental goals. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other. Each one of us seeks different things. We seek things that are most important for them, i.e., that which can fulfil their aspirations or desires. In fact, at times, two persons or groups of persons may seek things which are conflicting. A girl expects as much freedom and opportunity as her brother, and that he also shares in the household work. Her brother may not like this. Similarly, to get more electricity, industrialists may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced — such as tribal. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land. Besides seeking more income, one way or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All these are important goals. In fact, in some cases, these may be more important than more income or more consumption because material goods are not all that you need to live. Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above. For development, people look at a mix of goals. Hence, the developmental goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
Question (i)
What can be the development goals for landless rural laborers.
(a) More days of work and better wages
(b) Local school is able to provide quality education for their children
(c) No social discrimination
(d) All of the above
Development goals of a landless rural laborer could be-
- More days of work and better wages.
- local school to provide quality education for their children.
- No social discrimination and they too can become leaders in the village.
So, the correct answer is (d).
Question (ii)
Which of the following statement is true with respect to development .
(a) Different persons can have different developmental goals
(b) What may be development for one may not be development for The other.
(c) Development may even be destructive for the other.
Aspects of development-
- Different persons have different notions of development and development goals because the life situations of people are different .
- People have conflicting development gols.
- What may be developed for one may not be developed for the other . It may even be destructive to others.
Question (iii)
Apart from income, which of the following people do not look for development .
(a) Equal treatment
(b) Discrimination
(c) Freedom
(d) Security
Apart from income, people look for-
Respect, equality in workplace, freedom, security and opportunity to learn.
So, the correct answer is (b).
Question (iv)
why do different persons have different notions of development .
(a) Because people are different.
(b) Because life situations of persons are different.
(c) Both (a) and (b).
(d) None of the above.
Different people have different notions of development because-
- People are different. They seek things as per their own goals and aspirations.
- Life situations of people are not the same.

Davneet Singh
Davneet Singh has done his B.Tech from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. He has been teaching from the past 14 years. He provides courses for Maths, Science, Social Science, Physics, Chemistry, Computer Science at Teachoo.
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- School Guide
- Class 10 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 10
- Science Notes Class 10
- History Notes Class 10
- Geography Notes Class 10
- Political Science Notes Class 10
- NCERT Soln. Class 10 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 10
- Math Formulas Class 10
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Social Science Chapter 1 : Development
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 provides information on the economic development which takes place in the economy of the country and about the idea of progress and development and about how a country should function. In this chapter, students will understand the values and aspects of development which is needed by the company. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development contains the answers to the questions and will help the students to perform better in the examinations.
.webp)
NCERT Solutions Economics Class 10 Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Social Science Chapter 1: Development
The solutions from Chapter 1 of Understanding of Economic Development are given below and students can also check NCERT Solutions for Class 10 for other subjects as well.
Exercise Page No. 16
1. development of a country can generally be determined by.
(i) It’s per capita income
(ii) its average literacy level
(iii) health status of its people
(iv) all of the above
(iv) All of the above.
2. Which of the following neighboring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India?
(i) Bangladesh
(ii) Sri Lanka
(iii) Nepal
(iv) Pakistan
(ii) Sri Lanka. According to the latest report(2023) of HDI published by UNDP, India scores 132 out of 191 countries which is 0.633. Whereas other neighboring countries’ scores are Sri Lanka (73rd), China (79th), Bangladesh (129th), Bhutan (127th), Pakistan (161st), Nepal (143rd), and Myanmar (149th).
3. Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families ₹ 5000. If the income of three families is ₹ 4000, ₹ 7000 and ₹ 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family?
(ii) ₹ 3000
(iii) ₹ 2000
(iv) ₹ 6000
(4000+7000+3000+x)/ 4= 5000
14000+x= 5000*4
x= 20000-14000
4. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What are the limitations of this criterion, if any?
- The World Bank stated that a country’s level of development is closely correlated with its per capita income in World Development Reports (2006). Higher per capita income is frequently associated with increased economic growth and an improvement in the standard of living for the populace.
- Rich countries : nations with per-capita incomes of at least US$12616 in 2012.
- Countries with a per capita income of $1035 or less are considered low-income countries. India falls under the low- to middle-income category because the country’s per capita income in 2012 was only US$ 1530.
The term “developed countries” generally refers to wealthy nations, excluding Middle Eastern nations and some other minor nations.
Limitations
- Income inequality within a population is not taken into account by per capita income.
- Indicators of per capita income do not take into account the cost of living in various areas or nations.
- The economic activities that take place in the informal sector may not be fully reflected in calculations of per capita income.
- An in-depth understanding of a nation’s development might not be possible with just per capita income.
5. In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank?
The criteria used by the World Bank :
- The UNDP focuses on multifaceted aspects of development, such as income, health, and education, to capture the general well-being of people.
- When evaluating development, the UNDP takes social indicators like life expectancy and literacy rates into account.
- By comparing nations using a standardized index, the UNDP’s HDI offers a global perspective on development.
- The primary development indicator used by the UNDP is the Human Development Index (HDI).
6. Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate with your own examples related to development.
- We use averages because averages can be used to compare different quantities of the same category, we often use them.
- In order to calculate a country’s per capita income, for instance, averages must be used because different groups of people have different incomes.
- The use of averages does come with some restrictions, though. This does not depict how things are distributed among people. For illustration, consider a nation where an auto driver earns ₹ 10,000 per year while receiving ₹1,00,000 per year. Consequently, this nation’s average income will be ₹ 5,05,000 per year. In this case, the actual income or status is unknown. This country can be categorically regarded as wealthy by ignoring the income gap between the two people. Averages can be used for comparison while also hiding the differences.
7. Kerala, with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
No, I do not concur that per capita income is not at all a useful criterion. Kerala, which has a lower per capita income than Maharashtra, is ranked higher in terms of HDI because this measure takes into account factors like income, health, and education. Therefore, this is not to say that per capita income is not important. Instead, per capita income should not be overlooked as one of the development factors. The World Bank compares and measures states based on their per capita income as a measure of their level of development. However, this criterion has some limitations, so it is used in conjunction with other development factors like health, education, and other factors to determine the HDI. If a country’s national income decrease than its population growth, it will result in a decline in the number of goods and services available per person and the nation’s economic welfare.
8. Find out the present sources of energy that are used by the people in India. What could be the other possibilities fifty years from now?
India’s population currently uses electricity, coal, crude oil, cow dung, and solar energy as energy sources. The estimated lifespan of India’s known oil reserves is only 30–40 years. So, given the impending threat of oil resources running out, other options in fifty years could include ethanol, nuclear energy, biodiesel, and better utilization of wind, solar, wave, hydrogen, biomass energy, geothermal, hydroelectric, and tidal.
9. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development?
Sustainable Development is important because:
- Economic resilience and sustainability go hand in hand.
- It recognizes the significance of encouraging economic systems.
- By being sustainable, development meets current needs without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- It acknowledges that all societal groups, especially the weak and marginalized ones, should benefit from development.
- Human welfare and the health of the natural environment are interdependent, and sustainable development acknowledges this.
10. “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person”. How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss.
The resources on Earth are sufficient to meet all needs, but they must be used wisely.
- Excessive usage of resources will cause environmental deterioration, which will eventually influence both the current and coming generations.
- The development should not be excessively invasive or exploitative, but rather sustainable.
- Allowing for the practice of “green economic development” will allow for the sustainment of resources.
11. List a few examples of environmental degradation that you may have observed around you.
As carbon dioxide levels rise in the atmosphere, human activity worsens environmental degradation. Environmental aspects, such as the availability of water, may be impacted by global warming. The transpiration of plants is increased by warming. The likelihood of flooding and drought both rise with earlier snowmelt. Following are some additional instances of environmental degradation: Soil erosion. Deforestation Lowering groundwater levels. Depletion of the ozone layer due to combustion from automobiles. Water Pollution. Making use of pesticides and fertilizers made of chemicals.
12. For each of the items given in Table 1.6, find out which country is at the top and which is at the bottom.
| 12,707 | 77 | 10.6 | 73 | |
| 6,681 | 69.7 | 6.5 | 130 | |
| 4,961 | 67.1 | 5.0 | 148 | |
| 5,005 | 67.3 | 5.2 | 154 | |
| 3,457 | 70.8 | 5.0 | 143 | |
| 4,976 | 72.6 | 6.2 | 134 |
- Per capita income(GNI) in USD : Top Country – Sri Lanka; Bottom Country – Nepal
- Life Expectancy at birth: Top Country – Sri Lanka; Bottom Country – Myanmar
- Literacy Rate for 25+yrs population 2005-2012: Top Country – Sri Lanka; Bottom – Nepal & Myanmar
- HDI Rank in the World: Top Country – Sri Lanka; Bottom – Pakistan
As per Table 1.6, Sri Lanka tops in all four categories and has the highest Gross National Income, Life Expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling of people aged 25 or above, and HDI rank in the world.
13. The following table shows the proportion of undernourished adults in India. It is based on a survey of various states for the year 2001. Look at the table and answer the following questions.
| State | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Kerala |
|
|
| Karnataka |
|
|
(i) Compare the nutritional level of people in Kerala and Madhya Pradesh.
(ii) can you guess why around 40 percent of people in the country are undernourished even though it is argued that there is enough food in the country describe in your own words..
i) People in Madhya Pradesh and Kerala have different nutritional levels. In Kerala, there are 22% and 19% of men and women are undernourished, whereas, in Madhya Pradesh, it is 43% and 42% of men and women, respectively. This suggests that Kerala has better nutrition than Madhya Pradesh, where the average is lower than the national average and the latter is higher.
ii) Nearly 40% of India’s population is undernourished, despite the availability of sufficient food in the nation. This is a result of the uneven and chaotic distribution of food. Ration shops and other public distribution systems run smoothly in some states of the nation. This guarantees that no one goes hungry, especially the poor for whom food grains are provided by ration shops at reduced prices.
Important Topics Covered in this Chapter
- Introduction to Development
- What Development Promises- Different people have different goals
- Income and Other Goals
- National Development and How to Compare Different Countries or States?
- Public Facilities
- Sustainability of Development
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Social Science Chapter 1
Q 1. what are the topics covered in ncert solutions for class 10 economics chapter 1.
The topics covered in the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 include: Introduction to Development What Development Promises- Different people have different goals Income and Other Goals National Development and How to Compare Different Countries or States? Public Facilities Sustainability of Development
Q 2. What are the key highlights of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1?
The important points of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 include all the important topics and sub-topics related to the chapter and the students get a concise knowledge about the text questions and also answer the questions accurately.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Economics
- School Learning
- NCERT Solutions Class-10
- SUMIF in Google Sheets with formula examples
- How to Get a Free SSL Certificate
- Best SSL Certificates Provider in India
- Elon Musk's xAI releases Grok-2 AI assistant
- Content Improvement League 2024: From Good To A Great Article
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
about founders
2 friends, 1 dream, millions of supporters march 2020, covid times: while everyone focused on pockets, pranay & atharva focused on how student's can be helped in these tough times. from anxiety, to quality study material, everything was taken care of by padhle. more than academics, students needed guidance and moral support. that's why from 1 subscriber to 1 million, we have served "the bhaiya vibe" rather than a teacher's vibe.

Contact Info
Papergist innovations private limited, 66, ramnagar extension, dewas (madhya pradesh) – 455001 india, [email protected], ncert solutions class 10 for social science economics chapter 1 development, not that ordinary classroom vibe, literally..
the most interesting learning p̷l̷a̷t̷f̷o̷r̷m̷, family on the internet.

NCERT Solutions Class 10 for Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development : In this post, we will share with you all the detailed NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development . This will contain both in-text and back-exercise questions for Science and Social Science, and all exercise questions for Mathematics. For all school and board level examinations, doing all the NCERT Questions is a must.
Why are NCERT Questions Important?
NCERT Questions and Answers not only help you get hold of concepts firmly and enhance your understanding, but also form the base of all types of questions asked in exams. Questions asked in exam are more or less the same type as mentioned in NCERT. Moreover, sometimes the questions in NCERT are directly asked in exams, as it is, without any changes.
Hence, it’s very important to understand NCERT Questions and Answers.
- Get NCERT Solutions of all Science Chapters of Class 10
- Get NCERT Solutions of all Mathematics Chapters of Class 10
- Get NCERT Solutions of all Social Science Chapters of Class 10
- Get Notes, PYQs, Free E-Books, and other material for Class 10
- Join our Telegram Channel for Latest Updates here
[adinserter block=”3″]
Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 – Development
[twy_show_add_bookmark]
Exercise Questions (Page 16-17)
Question 1: Development of a country can generally be determined by a.its per capita income b.its average literacy level c.health status of its people d.all the above
Answer 1: d. all the above
Question 2: Which of the following neighbouring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India? a.Bangladesh b.Sri Lanka c.Nepal d.Pakistan
Answer 2: b. Sri Lanka
Question 3: Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is Rs 5000. If the income of three families is Rs 4000, Rs 7000 and Rs 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family? (i) Rs 7500 (ii) Rs 3000 (iii) Rs 2000 (iv) Rs 6000
Answer 3: (iv).Rs 6000
(4000+7000+3000+x) ÷ 4 = 5000 14000+x = 5000 × 4 x = 20000-14000 x = 6000
Question 4: What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What are the limitations of this criterion, if any?
Answer 4: World Bank uses the per capita income to classify different countries. The per capita income is calculated by dividing the total income of the country by the population of the country. For the year 2017, the countries with per capita income of US $12,056 per annum were declared rich countries and the countries with per capita income of US $ 955 or less are called low-income countries.
The limitations of the criterion are:
1.Other important factors, including literacy rate, infant mortality rate, healthcare, are ignored while classifying the countries. 2.Information about the unequal distribution of income is not mentioned by The World Bank 3.The economy of the country cannot determine the development of the country.
Question 5: In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank?
Answer 5: The criterion used by UNDP is different from the one used by the World Bank because UNDP compares countries based on the educational level of the people, their health status and per capita income. This is in contrast with the method used by the World Bank because the World Bank only calculates the per capita income for measuring development.
Question 6: Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate with your own examples related to the development.
Answer 6: (1) We use averages for comparison between two countries, two persons or any two or more things. (2) There are the following limitations to the use of averages :
i).Averages do not tell us about similarities or differences between two countries or persons or things. ii).By averages only one aspect income, size etc. in case of country, marks or participation in sports activities etc. in case of student, can be compared. All aspects or achievements are not compared. iii).As only one aspect is compared, it does not give true picture of different countries, persons or things. For example, students differ in height, health, talents and interests. The healthiest student may not be the most intelligent or topper in studies. Similar is the case in respect of countries or states. A country may be ahead than the other country in one field but may lag behind in the other field. So averages do not give the correct picture.
Question 7: Kerala, with lower per capita income, has a better human development ranking than Punjab. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
Answer 7: Kerala, with lower per capita income, has a better human development ranking than Haryana. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. This is true because the literacy rate, infant mortality rate, healthcare facilities, etc. are better in Kerala in comparison to Haryana. The per capita income is only calculated by calculating the average income of the state, irrespective of any other factor.
Question 8: Find out the present sources of energy that are used by the people in India. What could be the other possibilities fifty years from now?
Answer 8: The present sources of energy that are used by the people of India are electricity, coal, crude oil, cowdung and solar energy. Other possibilities fifty years from now, could include ethanol, bio-diesel, nuclear energy and better utilization of wind energy, especially with the imminent danger of oil resources running out.
Question 9: Why is the issue of sustainability is important for development?
Answer 9: Sustainable development means that development should meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. However, since the second half of the twentieth century, a number of scientists have been warning that the present type and levels of development are not sustainable. The issue of sustainable development has emerged from rapid industrialization of the world in the past century. It is felt that economic growth and industrialization have led to the reckless exploitation of natural resources. On the other hand, the stock of natural resources are limited. So, the growth of all countries in the future is likely to be endangered if the limited resources are completely exhausted.
Under these circumstances, the issue of sustainability has become important for development. A number of resources are being overused. For example, groundwater is under serious threat of overuse in many parts of the country i.e., Punjab, Haryana and western U.P. The water level has declined over 4 meters. As a result of it if we go on overusing there will be a water crisis in future. Similarly, if non-renewable resources are used recklessly these will also be exhausted.
Question 10: “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person”. How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss.
Answer 10: Development not just depends on the economic factors of a country, but is also dependent on resources that are available for the people of a country to use. The statement: “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person” is completely relevant in terms of the development of a country because natural resources are non-renewable resources. It is the responsibility of the people to use them only to meet their needs and not to satisfy their greed. If natural resources are not used wisely now, the future generations may not be able to use them for their needs, which will result in the downfall of development of a country.
Question 11: List a few examples of environmental degradation that you may have observed around you.
Answer 11: 1.Air pollution has increased due to the emission of smoke from factories and vehicles. 2.There is an increase in water pollution due to shops and small factories in residential areas. 3.There is noise pollution due to the use of loudspeakers at night and blowing of horns unnecessarily on the roads by different vehicles. 4.People throw garbage wherever they want. Perhaps there is no provision for dustbins in the streets or roadsides. 5.Sometimes people urinate in the open on the roadside due to a lack of public conveniences.
Question 12: For each of the items given in Table 1.6, find out which country is at the top and which is at the bottom.
Answer 12: As per table 1.6, Sri Lanka tops in all the four categories. It has the highest Gross National Income, Life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling of people aged 25 and above and HDI rank in the world. Nepal has the lowest Gross National Income among the given countries. Pakistan has the least Life Expectancy at birth and ranks the lowest HDI rank in the world among the given countries. Mean years of schooling of people aged 25 and above is the lowest for Myanmar and Nepal.
Question 13: The following table shows the proportion of adults (aged 15-49 years) whose BMI is below normal (BMI <18.5 kg/m2) in India. It is based on a survey of various states for the year 2015-16. Look at the table and answer the following questions.

a.Compare the nutritional level of people in Kerala and Madhya Pradesh. b.Can you guess why around one-fifth of people in the country are undernourished even though it is argued that there is enough food in the country? Describe in your own words.
Answer 13: a.The nutritional level of people in Kerala is higher than the nutritional level of people in Madhya Pradesh.
b.One-fifth of the population in the country are undernourished even though it is argued that there is enough food in the country because of the following reasons:
1.The disparity in the distribution of food grains by Public Distribution System (PDS). 2.Nutritious food cannot be afforded by the poor population in the country. 3.Educational backwardness of people results in unemployment because of which people cannot afford the basic necessity of food. 4.There is no proper distribution of ration at the fixed price stores.
For More Content related to Class 10 –
Related posts.

Learn With Memes? How 2 Friends Use YouTube to Make Complicated Lessons ‘Not Boring’

Do you really need to study 8-10 hours straight for your board exams?

How to deal with academic pressure in class 10

Ed-tech platform Padhle aims to double its net revenue in FY24; targets students in grades 9th-10th
Ledger class 11 accountancy best handwritten notes for cbse, journal class 11 accountancy best handwritten notes for cbse, origin of transactions class 11 accountancy best handwritten notes for cbse, food security in india class 9 economics social science best handwritten notes.

Get Access to our new batches now

- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Social Science MCQs 2024-25: Download Chapter-Wise PDF
Mcqs for class 10 sst: check the chapter-wise important mcqs for cbse class 10 social science here. these questions are important for the upcoming mid-term and cbse board exam. .

MCQs for CBSE Class 10 Social Science (SSt): Get chapter-wise important Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) for CBSE Class 10 Social Science in PDF format. We have provided questions for Class 10 History, Geography, Civics and Economics here. These questions are based on the new CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus and follow the revised NCERT Books. You will also get answers to all questions for reference.
Chapter-wise MCQs for CBSE Class 10 Social Science are given in the table below and can be downloaded in PDF for quick revision and effective preparations for the upcoming mid-term and CBSE Board Exam.
Also Check CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus 2024-25
Preparation Tips for CBSE Class 10 Social Science MCQs
Practising multiple-choice questions (MCQs) is an effective way to prepare for class 10 social science exams. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you practice MCQs effectively:
1. Understand the Syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the syllabus and the topics that will be covered in the social science exam. This will help you focus your preparation and identify the areas where you need more practice.
2. Gather Resources: Collect a variety of study resources, including textbooks, reference books, past question papers, and online sources. You can refer to the best study resources available at the school section of Jagran Josh.
3. Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that allocates dedicated time for practising MCQs. Break down the topics into manageable sections and allocate specific days or time slots to practice questions from each topic.
4. Practice Topic-wise: Divide the social science subjects (History, Geography, Political Science, and Economics) into different sections and practice MCQs topic-wise. Start with one topic at a time, answering questions related to that specific topic before moving on to the next.
5. Time Management: Set a time limit for each MCQ set, simulating exam conditions. This will help you practice answering questions within the allotted time, improving your speed and efficiency.
6. Review Mistakes: After attempting a set of MCQs, carefully review your answers. Identify the questions you answered incorrectly and understand why you made those mistakes. Refer back to your study materials to reinforce your understanding of the concepts.
7. Seek Clarification: If you encounter any concepts or questions that you find difficult to understand, don't hesitate to seek clarification from your teacher, classmates, or online resources. It's essential to have a clear understanding of the topics before moving forward.
NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science (Revised)
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
MCQs for other Subjects of Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Maths Important MCQs
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- India Post GDS Merit List 2024
- RBI Grade B Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Admit Card 2024
- UGC NET Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2025
- India GDS Merit List 2024 PDF
- UP Police Exam Analysis 2024 Live Updates
- OPSC OCS Result 2024
- Sri Krishna
- Janmashtami Wishes in Hindi
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
Paris Paralympics 2024 India Medal Tally, Check Total Medals Count List
NEET PG Scorecard 2024 Out: NBEMS Releases NEET PG Score Card at nbe.edu.in, Check Details
Who is Manish Narwal? The Golden Boy of Indian Shooting
SSC CGL Tier 1 Admit Card 2024: ssc.nic.in पर जारी, यहाँ से करें टियर-1 परीक्षा के सभी रीजन के एडमिट कार्ड Download
UP NEET UG Counselling 2024: Uttar Pradesh NEET UG Round 1 Seat Allotment Result Anytime Soon at upneet.gov.in
Calcutta University Result 2024 OUT at wbresults.nic.in; Direct Link to Download Semester 6 Marksheet
BEEI Teacher Recruitment 2024: Apply For Teaching Staff Posts, Check Eligibility
SHe-Box Portal: Central Government's Initiative to Ensure Safer Workplaces for Women
Today Current Affairs Hindi One Liners: 30 अगस्त 2024- अवनी लेखरा ने जीता गोल्ड
UP Police Constable Exam Analysis 2024 LIVE: 30 August Shift 1, 2 UPPRPB Paper Review, Difficulty Level
CG SET Answer Key 2024 OUT at vyapam.cgstate.gov.in: Download CG Vyapam Subject Wise Papers
CBSE Class 12 Physics Competency-Based Questions With Answer Key 2024-25: Chapter 5 Atoms and Nuclei FREE PDF Download
CG NEET UG Counselling 2024: Chhattisgarh NEET UG MBBS/BDS Round 1 Seat Allotment Result Out at cgdme.in, Get PDF
MDU Result 2024 OUT on mdu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG, PG Marksheet
Madhya Pradesh MP Board Class 12 Subject Wise Syllabus 2024-25: Download Detailed Syllabus PDF!
यूपी पुलिस कांस्टेबल आंसर की 2024: सभी शिफ्टों के लिए UPPRPB अनौपचारिक पेपर PDF यहां से करें डाउनलोड
Today’s School Assembly News Headlines (31th August): Pakistan Invites PM Modi To Attend SCO Meeting In Islamabad In October, PM Modi Lays Foundation For ₹76,200-Crore Vadhvan Port In Maharashtra
Find 3 differences between the girl painting pictures in 19 seconds!
KLEE Result 2024 Date: Kerala 5-year and 3-year LLB Exam Results Soon at cee.kerala.gov.in, Check Qualifying Marks Here
Today Current Affairs Quiz In Hindi: 30 अगस्त 2024- पेरिस पैरालंपिक 2024
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Geography & Travel
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts

- Introduction
- Economic development as an objective of policy
- A survey of development theories
- Lessons from development experience
- Development in a broader perspective

economic development

economic development , the process whereby simple, low-income national economies are transformed into modern industrial economies. Although the term is sometimes used as a synonym for economic growth , generally it is employed to describe a change in a country’s economy involving qualitative as well as quantitative improvements. The theory of economic development—how primitive and poor economies can evolve into sophisticated and relatively prosperous ones—is of critical importance to underdeveloped countries, and it is usually in this context that the issues of economic development are discussed.
Economic development first became a major concern after World War II . As the era of European colonialism ended, many former colonies and other countries with low living standards came to be termed underdeveloped countries, to contrast their economies with those of the developed countries, which were understood to be Canada, the United States , those of western Europe, most eastern European countries, the then Soviet Union , Japan, South Africa , Australia, and New Zealand . As living standards in most poor countries began to rise in subsequent decades, they were renamed the developing countries .
There is no universally accepted definition of what a developing country is; neither is there one of what constitutes the process of economic development. Developing countries are usually categorized by a per capita income criterion, and economic development is usually thought to occur as per capita incomes rise. A country’s per capita income (which is almost synonymous with per capita output) is the best available measure of the value of the goods and services available, per person, to the society per year. Although there are a number of problems of measurement of both the level of per capita income and its rate of growth, these two indicators are the best available to provide estimates of the level of economic well-being within a country and of its economic growth.
It is well to consider some of the statistical and conceptual difficulties of using the conventional criterion of underdevelopment before analyzing the causes of underdevelopment. The statistical difficulties are well known. To begin with, there are the awkward borderline cases. Even if analysis is confined to the underdeveloped and developing countries in Asia , Africa, and Latin America, there are rich oil countries that have per capita incomes well above the rest but that are otherwise underdeveloped in their general economic characteristics. Second, there are a number of technical difficulties that make the per capita incomes of many underdeveloped countries (expressed in terms of an international currency, such as the U.S. dollar) a very crude measure of their per capita real income. These difficulties include the defectiveness of the basic national income and population statistics, the inappropriateness of the official exchange rates at which the national incomes in terms of the respective domestic currencies are converted into the common denominator of the U.S. dollar, and the problems of estimating the value of the noncash components of real incomes in the underdeveloped countries. Finally, there are conceptual problems in interpreting the meaning of the international differences in the per capita income levels.
Although the difficulties with income measures are well established, measures of per capita income correlate reasonably well with other measures of economic well-being, such as life expectancy , infant mortality rates, and literacy rates. Other indicators, such as nutritional status and the per capita availability of hospital beds, physicians, and teachers, are also closely related to per capita income levels. While a difference of, say, 10 percent in per capita incomes between two countries would not be regarded as necessarily indicative of a difference in living standards between them, actual observed differences are of a much larger magnitude. India’s per capita income, for example, was estimated at $270 in 1985. In contrast, Brazil’s was estimated to be $1,640, and Italy’s was $6,520. While economists have cited a number of reasons why the implication that Italy’s living standard was 24 times greater than India’s might be biased upward, no one would doubt that the Italian living standard was significantly higher than that of Brazil, which in turn was higher than India’s by a wide margin.
The interpretation of a low per capita income level as an index of poverty in a material sense may be accepted with two qualifications. First, the level of material living depends not on per capita income as such but on per capita consumption. The two may differ considerably when a large proportion of the national income is diverted from consumption to other purposes; for example, through a policy of forced saving. Second, the poverty of a country is more faithfully reflected by the representative standard of living of the great mass of its people. This may be well below the simple arithmetic average of per capita income or consumption when national income is very unequally distributed and there is a wide gap in the standard of living between the rich and the poor.
The usual definition of a developing country is that adopted by the World Bank: “ low-income developing countries ” in 1985 were defined as those with per capita incomes below $400; “ middle-income developing countries ” were defined as those with per capita incomes between $400 and $4,000. To be sure, countries with the same per capita income may not otherwise resemble one another: some countries may derive much of their incomes from capital-intensive enterprises, such as the extraction of oil, whereas other countries with similar per capita incomes may have more numerous and more productive uses of their labour force to compensate for the absence of wealth in resources. Kuwait , for example, was estimated to have a per capita income of $14,480 in 1985, but 50 percent of that income originated from oil. In most regards, Kuwait’s economic and social indicators fell well below what other countries with similar per capita incomes had achieved. Centrally planned economies are also generally regarded as a separate class, although China and North Korea are universally considered developing countries. A major difficulty is that prices serve less as indicators of relative scarcity in centrally planned economies and hence are less reliable as indicators of the per capita availability of goods and services than in market-oriented economies.
Estimates of percentage increases in real per capita income are subject to a somewhat smaller margin of error than are estimates of income levels. While year-to-year changes in per capita income are heavily influenced by such factors as weather (which affects agricultural output, a large component of income in most developing countries), a country’s terms of trade , and other factors, growth rates of per capita income over periods of a decade or more are strongly indicative of the rate at which average economic well-being has increased in a country.
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 31 | ||
Comments and moderation policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Development. Contents. Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development Case Study 1: Case Study 2: Case Study 3: Case Study 4: Case Study 5: At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph.
Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should practise these ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development Here we are providing case study questions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development. Case Study Question 1: Similarly, for development, people look at a mix of goals. It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social ...
Contents. Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy Case Study 1: Case Study 2: Case Study 3: Case Study 4: Case Study 5: At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 4. Class 10 ECONOMICS: Development. Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: Besides seeking more income, oneway or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination.
Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should ...
For Class 10, development is defined as a term that includes an increase in the per capita income, improvement in the standard of living of people in a country, decrease in poverty, illiteracy, and crime rate. Students can find all answers toStudents can find such related questions in the Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 PDF at Vedantu.
In this chapter, students will understand the various aspects of development that a country needs. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 - Development contain the answers to the exercises given at the end of the book of Chapter 1. These solutions will help students to write their answers in an effective way during the CBSE exams.
Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions. Question 1. Development of a country can generally be determined by. (i) its per capita income. (ii) its average literacy level. (iii) health status of its people. (iv) all the above. Answer: (iv) all the above. Explanation: UNDP publishes its human development report comparing the ...
These tests are unlimited in nature…take as many as you like. You will be able to view the solutions only after you end the test. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Economics Development chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 10 2024-25 provides chapter-wise answers to all questions in the NCERT textbook, explained systematically. ... NCERT Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 Development introduces the concept of development, highlighting its economic, social, and environmental aspects. ... Case Studies on Globalisation.
Explain. [CBSE 2014] Answer: (i) Economic independence: If a women is working she will get economic independency. (ii) Equality: As per the law working women need to be treated equally. (iii) Respected: A working women will get respect not only in the family but in the society also. CBSE Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development Extra Questions ...
The economics class 10 notes Chapter 1 Development comprehensive account of a student's comprehension and analysis of the subject matter. This customized approach encourages a more meaningful engagement with the information. Mind maps are a useful tool for helping students link the concepts they have learned. It will be very helpful in aligning ...
This step-by-step process will help you download PDF file of case study on Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Social Science. Open Selfstudys.com and click on the navigation button available beside the Selfstudys logo. Click on CBSE from the given options. Navigate to the Case Study and click on that.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10th: Ch 1 Development Economics Social Studies (S.St) Page No: 16. Exercises. 1. Development of a country can generally be determined by. (i) its per capita income. (ii) its average literacy level. (iii) health status of its people. (iv) all the above.
Economics Chapter 1 Development Source Based Questions also analyze the role of institutions, governance, and income inequality in shaping development outcomes. By examining empirical data, statistical indicators, and case studies, economists can unravel the complex dynamics of development, providing valuable insights into the strategies and ...
Contents. Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 4 Globalization and The Indian Economy Case Study 1: Case Study 2: Case Study 3: Case Study 4: Case Study 5: At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study.
Toppr's NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 is outlined by our team of experts who have worked in the field of economics. Also, they have years of experience in teaching. Besides, the NCERT solution is available in PDF format for free. Also, we have previous years question papers to help you gather all the required data for your ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Economics Chapter 1 Development. Page 16. Q1. Development of a country can generally be determined by. (i) its per capita income. (ii) its average literacy level. (iii) health status of its people. (iv) all the above. Answer:
The Class 10 Economics book "Understanding Economic Development" contains 5 chapters. Students can find the NCERT Solutions of all these chapters in the table below. Chapter 1: Development. Chapter 2: Sectors of the Indian Economy. Chapter 3: Money and Credit. Chapter 4: Globalisation and the Indian Economy.
Answer: Aspects of development-. Different persons have different notions of development and development goals because the life situations of people are different . People have conflicting development gols. What may be developed for one may not be developed for the other . It may even be destructive to others.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development contains the answers to the questions and will help the students to perform better in the examinations. ... this nation's average income will be ₹ 5,05,000 per year. In this case, the actual income or status is unknown. ... Students may use this resource to study for exams and ...
1.Other important factors, including literacy rate, infant mortality rate, healthcare, are ignored while classifying the countries. 2.Information about the unequal distribution of income is not mentioned by The World Bank. 3.The economy of the country cannot determine the development of the country. Question 5:
MCQs for CBSE Class 10 SSt: Download PDF of chapter-wise important MCQs for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Exam 2024-25. These questions are based on latest CBSE Syllabus.
economic development, the process whereby simple, low-income national economies are transformed into modern industrial economies.Although the term is sometimes used as a synonym for economic growth, generally it is employed to describe a change in a country's economy involving qualitative as well as quantitative improvements.The theory of economic development—how primitive and poor ...
Addressing this challenge, our study introduces an innovative entrepreneurial market trend prediction model based on deep learning principles. Through detailed case studies and performance evaluations, this paper demonstrates the model's effectiveness and its potential to enhance decision-making capabilities in a competitive business environment.
The Committee for Economic Development (CED) is the policy Center of The Conference Board that delivers timely insights and reasoned solutions to our nation's most critical economic and geopolitical challenges. ... Centers offer access to world-class experts, research, events, and senior executive communities. Our Centers. Committee for ...
Results revealed that student competence significantly and positively affects TVET Socio-economic development contribution (p < 0.05, t = 6.997). This implies that when there is an increased but good perception of student's competence, the eventual contribution of their training towards socio-economic development will also increase.
On examination, the patient was thin (body mass index = 17). Oral examination revealed an ulceroproliferative, rough, irregular-shaped ulcer on the right border of the tongue measuring 2 cm × 2 cm in size that extends anteriorly 1 cm from the tip of the tongue and laterally extends up to the margins of the tongue.
You'll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more. Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media ...