- How to Order
Essay Writing Guide
Essay Writing Problems

Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems

People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 370+ Essay Topics for Students
Common Types of Essays - Sub-types and Examples
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
How to Write an Essay Outline in 5 Simple Steps
How to Start an Essay? Tips for an Engaging Start
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Tips On How to Make an Essay Longer: 15 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay Properly- An Easy Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
A Guide to Writing a Five-Paragraph Essay
How To Write A Strong Body Paragraph
Many writers suffer from the occasional writer’s block. Writer’s block can easily affect students who need to complete academic writing assignments as well.
However, this is only one of the many issues they may need to deal with in the essay writing process. Many students face other challenges as they strive to complete their writing assignments.
Knowing the common essay writing issues can help you rectify the situation as you complete your essay.
- 1. Top Essay Writing Problems Students Deal With
- 2. Other Writing Problems You May Face
Top Essay Writing Problems Students Deal With
Below are the top five common problems that can stop students dead in their tracks, as they begin or complete their essay writing assignments, and tips to overcome them.
#1 Lack of Confidence
The inability to believe in one’s capabilities and skills is one of the most common problems in essay writing that students have to face.
Students who think they are not good at writing will have trouble starting their papers. They doubt their capability to complete it as well. And with this self-doubt, they may never even try to start working on their paper.
As a result, these students end up not submitting an assignment or simply handing in a poorly-written one, fully accepting and expecting that they will get a low or failing grade.
How to Overcome This
There are various ways students can improve their writing skills. There are online courses they can take and they also have the option to take up traditional classes offered by local schools or tutorial centers.
Additionally, students should practice writing daily even if they make mistakes. As long as these mistakes are corrected, they will become better writers in the future.
Lastly, students who don’t know how to start an essay can always ask for assistance from their teachers, peers, and other people who are more knowledgeable and experienced in writing.
#2 Insufficient Knowledge
Many students will also have difficulties writing about an essay topic taken up in school. The main reason is that they don’t have enough knowledge about the subject matter.
This difficulty can be caused by the student failing to take notes in class or not attending classes at all. He or she may not even understand the topic completely. This will cause anyone to have poor knowledge of any topic.
This is a problem that students can easily trounce. Students simply need to put in some extra time to study whatever notes they have. They can also do extra research to understand the topic.
Students can also ask their teacher to explain the topic to them again if they are having a hard time understanding it.
#3 Lack of Writing Skills
Although some students are confident about writing and have enough ideas to write their papers, if they lack language proficiency, they won’t submit an impressive essay.
Using the wrong words, misleading language, misplacing words, phrases, and punctuation will result in a poor paper. Some students may even resort to using technical words and jargon with the hope of impressing their teacher. Of course, this technique usually backfires.
Students should learn to use simple words and construct short, concise sentences to get a good mark on their papers. Additionally, determining the type of essay you’re going to write helps you stay focused and organized. Students also need to read more since this is a good exercise for becoming a better writer.
They can also get help from the best assignment experts if they need help with polishing their papers. These writers will ensure students turn in good essays, reflective of their knowledge and abilities.
#4 Plagiarism
When all else fails, plagiarism is something that many students end up doing just so they can submit a paper. This is also their last resort if they are rushing to complete their essay at the last minute.
Teachers today check each paper for plagiarized content. Students who submit essays that contain copied paragraphs from published material will find themselves in a lot of trouble.
Students need to learn how to paraphrase the content they use for their essays. They should know when and how to use references as well.
Finally, they should make it a habit to run their essays through online plagiarism tools to ensure that they submit an original paper.
#5 Getting Stuck
Lastly, students are given a topic that has been discussed numerous times already. This can get the student stuck and unable to write anything about it. They think that there is nothing left to explore and they can’t have their own say on such topics.
Because of this, they are unable to start writing their paper, much less finish it.
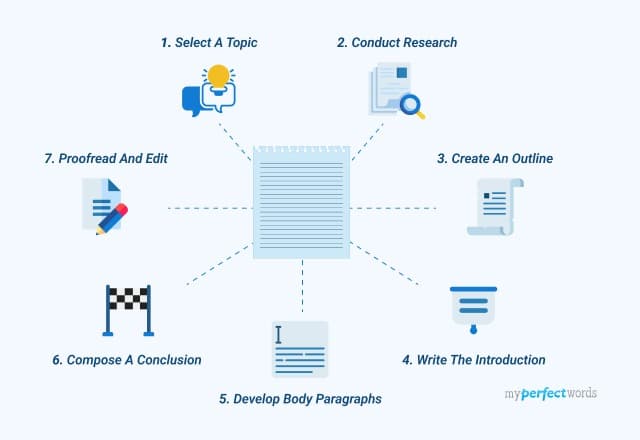
To overcome this, conduct more in-depth research to find a unique angle or perspective that interests you. After gathering sufficient information, create a detailed essay outline to organize your thoughts.
Develop body paragraphs for each main idea you will discuss, ensuring each one is supported by evidence and analysis. This approach will make the writing process smoother and more manageable.
#6 Time Management
Time management is another main problem that students face. Some students think they can get away with working at the last minute. They might be in a big hurry or simply don't know what needs to be done yet. Because of this, they will submit bad-quality work.
How to Overcome This:
If you plan ahead, you can avoid having to spend a lot of time editing your paper.
Planning ahead will help you do better research, so your analysis of the issue is stronger. This will also help you set the paper aside and come back to it later with a fresh perspective, which means you can revise it more effectively.
#7 Awkward Structure
The structure of your sentences should be clear and understandable to allow the reader to follow what you are saying. Each sentence needs a meaningful connection with the topic so they can understand it fully without confusion, ultimately making them enjoy reading more.
To improve structure and flow, you can also add transition words to make your writing flow smoothly. Make sure you’re following the standard writing conventions to avoid writing an essay that doesn’t read well.
Other Writing Problems You May Face
College students are constantly under pressure to produce high-quality work. In addition, there is the issue that low-quality papers appear because they do not have enough time or resources for their studies and so on.
Despite these problems, there are many other writing problems that students face.
- Lack of time: If you want to save time, you need to plan properly. One way to do this is by writing down all the information about your sources. This will help you avoid wasting time later on.
- Lack of inspiration: If you are having trouble coming up with an idea for your essay, try reading essays about the same topic. This can help you get your thoughts in order and come up with a good idea.
- Unclear analysis: If you want to know more, you need to study. There is no way to shortcut this process. You will have to learn everything you can about the topic if you want to be an expert.
- Poor editing and proofreading skills: People sometimes find it hard to edit and proofread their own writing. A trick to make it easier is to read the text backward, from the last word to the first. Another way is to read the paper aloud. This way, you can find where the transitions between paragraphs are not smooth and ensure your essay format remains consistent.
So these are the common problems encountered by students in writing an essay. Keep in mind that essay writing is not something that comes naturally to many students.
If you are stuck in the writing process, pinpoint the cause and follow the tips shared and the writing practice will definitely help you overcome it.
If you are still confused, whether you are still starting your essay or need help polishing it, our custom essay help is here for you. So, get in touch with our experts and get solutions to all your essay problems!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do i struggle to write essays.
Struggling with essay writing can stem from various issues such as lack of confidence, insufficient knowledge of the topic, poor writing skills, or even time management problems. Additionally, some students face difficulty due to anxiety or perfectionism, which can hinder their ability to start or complete an essay. To overcome these challenges, try setting specific, achievable goals for each writing session and take regular breaks to avoid burnout.
What are good essay writing topics?
Good essay writing topics are those that interest you and allow for ample research and analysis. They should be specific enough to be manageable yet broad enough to find sufficient information.
Examples include the impact of technology on education, the importance of mental health awareness, climate change and its effects, and the role of social media in modern communication. Additionally, consider current events, societal issues, or areas you are passionate about. Topics related to scientific advancements, cultural trends, and ethical dilemmas also offer rich material.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Because differences are our greatest strength
What is written expression disorder?

By Gail Belsky
Expert reviewed by Karen Wilson, PhD
Updated January 12, 2024

What you’ll learn
Snapshot: what written expression disorder is, written expression disorder signs and symptoms, how written expression disorder is diagnosed.
Written expression disorder is a learning disorder that makes it hard for people to put their ideas into writing. It also creates difficulty with grammar and punctuation. It’s a type of learning disability that’s common and lifelong.
Written expression disorder is a learning challenge that impacts writing. The formal diagnosis is “specific learning disorder with impairment in writing.” Schools might call it a learning disability in writing.
This lifelong disorder makes it hard to express thoughts in writing . People might have great ideas. But their writing is disorganized and full of grammar and punctuation mistakes.
Written expression disorder is caused by differences in the brain. While it’s not as well-known as dyslexia , it may actually be more common. Experts think between 8 and 15 percent of people have it.
Written expression disorder often co-occurs with other learning challenges. Two of the most common are dyslexia and ADHD .
There aren’t any major teaching programs to help with these writing challenges. But there are strategies and techniques that can help people manage the difficulties and improve their skills.
People can be tested for writing challenges at any age. Parents can request a free evaluation at school. Adults typically have them done privately. The tests are different for kids and adults.
Written expression disorder impacts learning. And it can make certain tasks at work difficult. But it’s important to know that people who have it are just as smart as other people.
Dive deeper
Learn about the six skills of written expression .
Find out when kids develop different writing skills .
Explore assistive technology for writing .
When people struggle with written expression, it doesn’t mean they also have trouble expressing themselves when speaking. They might tell a story that’s well organized and detailed. But it looks very different when they try to write it out.
The difficulties can show up in different ways . Here are some things you might see in their written work:
Words that are misused or that have the wrong meaning
The same words used over and over
Basic grammar mistakes, like missing verbs or incorrect noun-verb agreement
Sentences that don’t make sense
Disorganized essays and papers
Written work that seems incomplete
Missing facts and details
Slow writing and typing
There are behavioral signs, too. These include:
Making excuses and avoiding writing assignments
Complaining about not being able to think of what to write or not knowing where to start
Sitting for a long time at a desk without writing
Finishing a writing task quickly without giving it much thought
Learn about dictation (speech-to-text) technology .
For families: Explore ways to help your child with writing .
For teachers: Explore strategies to teach kids self-regulation in writing .
The only way to know if someone has written expression challenges is to have a full evaluation . Parents can request that the school evaluate their child. School evaluations are free.
Certain professionals do private evaluations. But they can be very costly. In some cases, there are ways to get private evaluations for free or at a low cost .
Evaluators use a series of tests to look at writing skills . They also test for strengths and challenges in other areas. Many people with written expression disorder also have other learning and thinking differences, like dyslexia or ADHD.
There are a few types of professionals who do evaluations. These include:
School psychologists
Clinical psychologists
Speech-language pathologists
Neuropsychologists
Getting a diagnosis (schools call it an identification) can lead to extra help at school. It can also lead to accommodations at college and at work.
For teachers: Explore five things to look for in your students’ IEPs .
For families: Learn how to request a free school evaluation .
For college students: Research types of accommodations at college .
Trouble with written expression can impact people of all ages and create challenges at school and work. But there are supports that can help. Find out how accommodations work . Learn how to apply for them for the SAT and ACT and how to request them at work .
Explore related topics
Essay Writing Tips: 10 Steps to Writing a Great Essay (And Have Fun Doing It!)
by Joe Bunting | 118 comments
Do you dread essay writing? Are you looking for some essay tips that will help you write an amazing essay—and have fun doing it?

Lots of students, young and old, dread essay writing. It's a daunting assignment, one that takes research, time, and concentration.
It's also an assignment that you can break up into simple steps that make writing an essay manageable and, yes, even enjoyable.
These ten essay tips completely changed my writing process—and I hope that they can do the same for you.
Essay Writing Can Be Fun
Honestly, throughout most of high school and college, I was a mediocre essay writer.
Every once in a while, I would write a really good essay, but mostly I skated by with B's and A-minuses.
I know personally how boring writing an essay can be, and also, how hard it can be to write a good one.
However, toward the end of my time as a student, I made a breakthrough. I figured out how to not only write a great essay, I learned how to have fun while doing it .
And since then, I've become a professional writer and have written more than a dozen books. I'm not saying that these essay writing tips are going to magically turn you into a writer, but at least they can help you enjoy the process more.
I'm excited to share these ten essay writing tips with you today! But first, we need to talk about why writing an essay is so hard.
Why Writing an Essay Is So Hard
When it comes to essay writing, a lot of students find a reason to put it off. And when they tackle it, they find it difficult to string sentences together that sound like a decent stance on the assigned subject.
Here are a few reasons why essay writing is hard:
- You'd rather be scrolling through Facebook
- You're trying to write something your teacher or professor will like
- You're trying to get an A instead of writing something that's actually good
- You want to do the least amount of work possible
The biggest reason writing an essay is so hard is because we mostly focus on those external rewards like getting a passing grade, winning our teacher's approval, or just avoiding accusations of plagiarism.
The problem is that when you focus on external approval it not only makes writing much less fun, it also makes it significantly harder.
Because when you focus on external approval, you shut down your subconscious, and the subconscious is the source of your creativity.
The subconscious is the source of your creativity.
What this means practically is that when you're trying to write that perfect, A-plus-worthy sentence, you're turning off most of your best resources and writing skills.
So stop. Stop trying to write a good essay (or even a “good-enough” essay). Instead, write an interesting essay, write an essay you think is fascinating. And when you're finished, go back and edit it until it's “good” according to your teacher's standards.
Yes, you need to follow the guidelines in your assignment. If your teacher tells you to write a five-paragraph essay, then write a five-paragraph essay! If your teacher asks for a specific type of essay, like an analysis, argument, or research essay, then make sure you write that type of essay!
However, within those guidelines, find room to express something that is uniquely you .
I can't guarantee you'll get a higher grade (although, you almost certainly will), but I can absolutely promise you'll have a lot more fun writing.
The Step-by-Step Process to Writing a Great Essay: Your 10 Essay Writing Tips
Ready to get writing? You can read my ten best tips for having fun while writing an essay that earns you the top grade, or check out this presentation designed by our friends at Canva Presentations .
1. Remember your essay is just a story.
Every story is about conflict and change, and the truth is that essays are about conflict and change, too! The difference is that in an essay, the conflict is between different ideas , and the change is in the way we should perceive those ideas.
That means that the best essays are about surprise: “You probably think it's one way, but in reality, you should think of it this other way.” See tip #3 for more on this.
How do you know what story you're telling? The prompt should tell you.
Any list of essay prompts includes various topics and tasks associated with them. Within those topics are characters (historical, fictional, or topical) faced with difficult choices. Your job is to work with those choices, usually by analyzing them, arguing about them, researching them, or describing them in detail.
2. Before you start writing, ask yourself, “How can I have the most fun writing this?”
It's normal to feel unmotivated when writing an academic essay. I'm a writer, and honestly, I feel unmotivated to write all the time. But I have a super-ninja, judo-mind trick I like to use to help motivate myself.
Here's the secret trick: One of the interesting things about your subconscious is that it will answer any question you ask yourself. So whenever you feel unmotivated to write your essay, ask yourself the following question:
“How much fun can I have writing this?”
Your subconscious will immediately start thinking of strategies to make the writing process more fun.
The best time to have your fun is the first draft. Since you're just brainstorming within the topic, and exploring the possible ways of approaching it, the first draft is the perfect place to get creative and even a little scandalous. Here are some wild suggestions to make your next essay a load of fun:
- Research the most surprising or outrageous fact about the topic and use it as your hook.
- Use a thesaurus to research the topic's key words. Get crazy with your vocabulary as you write, working in each key word synonym as much as possible.
- Play devil's advocate and take the opposing or immoral side of the issue. See where the discussion takes you as you write.
3. As you research, ask yourself, “What surprises me about this subject?”
The temptation, when you're writing an essay, is to write what you think your teacher or professor wants to read.
Don't do this .
Instead, ask yourself, “What do I find interesting about this subject? What surprises me?”
If you can't think of anything that surprises you, anything you find interesting, then you're not searching well enough, because history, science, and literature are all brimming over with surprises. When you look at how great ideas actually happen, the story is always, “We used to think the world was this way. We found out we were completely wrong, and that the world is actually quite different from what we thought.”
These pieces of surprising information often make for the best topic sentences as well. Use them to outline your essay and build your body paragraphs off of each unique fact or idea. These will function as excellent hooks for your reader as you transition from one topic to the next.
(By the way, what sources should you use for research? Check out tip #10 below.)
4. Overwhelmed? Write five original sentences.
The standard three-point essay is really made up of just five original sentences surrounded by supporting paragraphs that back up those five sentences. If you're feeling overwhelmed, just write five sentences covering your most basic main points.
Here's what they might look like for this article:
- Introductory Paragraph: While most students consider writing an essay a boring task, with the right mindset, it can actually be an enjoyable experience.
- Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards.
- Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay.
- Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
- Conclusion: Writing an essay doesn't have to be simply a way to earn a good grade. Instead, it can be a means of finding fulfillment.
After you write your five sentences, it's easy to fill in the paragraphs for each one.
Now, you give it a shot!
5. Be “source heavy.”
In college, I discovered a trick that helped me go from a B-average student to an A-student, but before I explain how it works, let me warn you. This technique is powerful , but it might not work for all teachers or professors. Use with caution.
As I was writing a paper for a literature class, I realized that the articles and books I was reading said what I was trying to say much better than I ever could. So what did I do? I quoted them liberally throughout my paper. When I wasn't quoting, I re-phrased what they said in my own words, giving proper credit, of course. I found that not only did this formula create a well-written essay, it took about half the time to write.
It's good to keep in mind that using anyone else's words, even when morphed into your own phrasing, requires citation. While the definition of plagiarism is shifting with the rise of online collaboration and cooperative learning environments, always err on the side of excessive citation to be safe.
When I used this technique, my professors sometimes mentioned that my papers were very “source” heavy. However, at the same time, they always gave me A's.
To keep yourself safe, I recommend using a 60/40 approach with your body paragraphs: Make sure 60% of the words are your own analysis and argumentation, while 40% can be quoted (or text you paraphrase) from your sources.
Like the five sentence trick, this technique makes the writing process simpler. Instead of putting the main focus on writing well, it instead forces you to research well, which some students find easier.
6. Write the body first, the introduction second, and the conclusion last.
Introductions are often the hardest part to write because you're trying to summarize your entire essay before you've even written it yet. Instead, try writing your introduction last, giving yourself the body of the paper to figure out the main point of your essay.
This is especially important with an essay topic you are not personally interested in. I definitely recommend this in classes you either don't excel in or care much for. Take plenty of time to draft and revise your body paragraphs before attempting to craft a meaningful introductory paragraph.
Otherwise your opening may sound awkward, wooden, and bland.
7. Most essays answer the question, “What?” Good essays answer the “Why?” The best essays answer the “How?”
If you get stuck trying to make your argument, or you're struggling to reach the required word count, try focusing on the question, “How?”
For example:
- How did J.D. Salinger convey the theme of inauthenticity in The Catcher In the Rye ?
- How did Napoleon restore stability in France after the French Revolution?
- How does the research prove girls really do rule and boys really do drool?
If you focus on how, you'll always have enough to write about.
8. Don't be afraid to jump around.
Essay writing can be a dance. You don't have to stay in one place and write from beginning to end.
For the same reasons listed in point #6, give yourself the freedom to write as if you're circling around your topic rather than making a single, straightforward argument. Then, when you edit and proofread, you can make sure everything lines up correctly.
In fact, now is the perfect time to mention that proofreading your essay isn't just about spelling and commas.
It's about making sure your analysis or argument flows smoothly from one idea to another. (Okay, technically this comprises editing, but most students writing a high school or college essay don't take the time to complete every step of the writing process. Let's be honest.)
So as you clean up your mechanics and sentence structure, make sure your ideas flow smoothly, logically, and naturally from one to the next as you finish proofreading.
9. Here are some words and phrases you don't want to use.
- You (You'll notice I use a lot of you's, which is great for a blog post. However, in an academic essay, it's better to omit the second-person.)
- To Be verbs (is, are, was, were, am)
Don't have time to edit? Here's a lightning-quick editing technique .
A note about “I”: Some teachers say you shouldn't use “I” statements in your writing, but the truth is that professional, academic papers often use phrases like “I believe” and “in my opinion,” especially in their introductions.
10. It's okay to use Wikipedia, if…
Wikipedia is one of the top five websites in the world for a reason: it can be a great tool for research. However, most teachers and professors don't consider Wikipedia a valid source for use in essays.
Don't totally discount it, though! Here are two ways you can use Wikipedia in your essay writing:
- Background research. If you don't know enough about your topic, Wikipedia can be a great resource to quickly learn everything you need to know to get started.
- Find sources . Check the reference section of Wikipedia's articles on your topic. While you may not be able to cite Wikipedia itself, you can often find those original sources and cite them . You can locate the links to primary and secondary sources at the bottom of any Wikipedia page under the headings “Further Reading” and “References.”
You Can Enjoy Essay Writing
The thing I regret most about high school and college is that I treated it like something I had to do rather than something I wanted to do.
The truth is, education is an opportunity many people in the world don't have access to.
It's a gift, not just something that makes your life more difficult. I don't want you to make the mistake of just “getting by” through school, waiting desperately for summer breaks and, eventually, graduation.
How would your life be better if you actively enjoyed writing an essay? What would school look like if you wanted to suck it dry of all the gifts it has to give you?
All I'm saying is, don't miss out!
Looking for More Essay Writing Tips?
Looking for more essay tips to strengthen your essay writing? Try some of these resources:
- 7 Tips on Writing an Effective Essay
- Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
How about you? Do you have any tips for writing an essay? Let us know in the comments .
Need more grammar help? My favorite tool that helps find grammar problems and even generates reports to help improve my writing is ProWritingAid . Works with Word, Scrivener, Google Docs, and web browsers. Also, be sure to use my coupon code to get 20 percent off: WritePractice20
Coupon Code:WritePractice20 »
Ready to try out these ten essay tips to make your essay assignment fun? Spend fifteen minutes using tip #4 and write five original sentences that could be turned into an essay.
When you're finished, share your five sentences in the comments section. And don't forget to give feedback to your fellow writers!
[wp_ad_camp_2]
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Celebrating 25 Years
- Join ADDitude
- |

- What Is ADHD?
- The ADHD Brain
- ADHD Symptoms
- ADHD in Children
- ADHD in Adults
- ADHD in Women
- Find ADHD Specialists
- Symptom Checker Tool
- Symptom Tests
- More in Mental Health
- ADHD Medications
- Medication Reviews
- Natural Remedies
- ADHD Therapies
- Managing Treatment
- Treating Your Child
- Success @ School 2024
- Behavior & Discipline
- Positive Parenting
- Schedules & Routines
- School & Learning
- Health & Nutrition
- Teens with ADHD
- More on ADHD Parenting
- Do I Have ADD?
- Getting Things Done
- Time & Productivity
- Relationships
- Organization
- Health & Nutrition
- More for ADHD Adults
- Free Webinars
- Free Downloads
- Newsletters
- Guest Blogs
- eBooks + More
- Search Listings
- Add a Listing
- News & Research
- For Clinicians
- For Educators
- ADHD Directory
- Manage My Subscription
- Get Back Issues
- Digital Magazine
- Gift Subscription
- Renew My Subscription
- ADHD Parenting
How to Remove Hurdles to Writing for Students with ADHD
Half of all kids with adhd struggle with writing, which can make every assignment — from straightforward worksheets to full-length essays — feel like torture. boost your child’s skills with these 18 strategies for school and home..

Studies suggest that more than half of children with attention deficit disorder ( ADHD or ADD ) struggle with writing. These students may have an overflow of creative ideas , but often struggle when it comes to getting these ideas onto paper.
Children with ADHD have a hard time getting started — and following through — on writing assignments because they have difficulty picking essay topics, locating appropriate resources, holding and manipulating information in their memory, organizing and sequencing the material, and getting it down on paper — all before they forget what they wanted to say.
But these hurdles don’t have to stop them from writing. Discuss the following ADHD writing strategies with your child’s teacher so you can work together to ease the difficulties attention deficit children have with writing.
Solutions in the Classroom: Guide the Writing Process
—Set up a note system. Ask the student to write her notes about a topic on individual sticky notes. She can then group the notes together that feature similar ideas so she’ll be able to easily identify the major concepts of the subject from the groupings.
—Start small and build skills. Ask students with ADHD to write a paragraph consisting of only two or three sentences. As their skills improve, the students can start writing several paragraphs at a time.
[ Free Download: 18 Writing Tricks for Students with ADHD ]
—Demonstrate essay writing. With the use of an overhead projector, write a paragraph or an entire essay in front of the class, explaining what you are doing at each step. Students can assist you by contributing sentences as you go. Students with ADHD are often visual learners , and tend to do better when they see the teacher work on a task.
—Give writing prompts. Students with ADHD usually don’t generate as many essay ideas as their peers. Help the children with ADHD increase their options for essay assignments by collecting materials that stimulate choices. Read a poem, tell a story, show pictures in magazines, newspapers, or books.
If the student is still struggling to get started, help him by sitting down and talking about the assignment with him. Review his notes from the brainstorming session and ask, “What are some ways you could write the first sentence?” If he doesn’t have an answer, say, “Here’s an idea. How would you write that in your own words?”
—Encourage colorful description. Students with ADHD often have difficulty “dressing up” their written words. Help them add adjectives and use stronger, more active verbs in sentences.
[ How Teens with Learning Differences Can Defeat Writing Challenges ]
—Explain the editing process. Students with ADHD have a hard time writing to length and often produce essays that are too short and lacking in details. Explain how the use of adjectives and adverbs can enhance their composition. Show them how to use a thesaurus, too.
Solutions in the Classroom: Use Accommodations Where Necessary
—Allow enough time. Students with ADHD, especially those with the inattentive subtype, may take longer to process information and should receive extended time to complete assignments.
—Don’t grade early work. Sensitive students are discouraged by negative feedback as they are developing their writing skills. Wait until the paper is finished before assigning it a grade.
—Don’t deduct points for poor handwriting or bad grammar. Unless an assignment is specifically measuring handwriting and grammar skills, when a child is working hard to remember and communicate, let some things slide.
—Use a graphic organizer. A graphic organizer organizes material visually in order to help with memory recall. Distribute pre-printed blank essay forms that students with ADHD can fill in, so they’ll reserve their efforts for the most important task — writing the essay.
—Grade limited essay elements. To encourage writing mastery and avoid overwhelming students, grade only one or two elements at any given time. For example, “This week, I’m grading subject-verb agreement in sentences.” Tighter grading focus channels students’ attention to one or two writing concepts at a time.
Solutions at Home
—Encourage journals. Have your child write down his thoughts about outings to the movies, visits with relatives, or trips to museums. Add some fun to the activity by asking your child to e-mail you his thoughts or text-message you from his cell phone.
—Assist with essay topic selection. Children with ADHD have difficulty narrowing down choices and making decisions. Help your student by listening to all of his ideas and writing down three or four of his strongest topics on cards. Next, review the ideas with him and have him eliminate each topic, one by one – until only the winner is left.
—Brainstorm. Once the topic is identified, ask him for all the ideas he thinks might be related to it. Write the ideas on sticky notes, so he can cluster them together into groupings that will later become paragraphs. He can also cut and paste the ideas into a logical sequence on the computer.
—Stock up on books, movies, games. These materials will introduce new vocabulary words and stimulate thinking. Explore these with your child and ask him questions about them to solicit his views.
—Be your child’s “scribe.” Before your child loses his idea for the great American novel, or for his next English assignment, have him dictate his thoughts to you as you write them out by hand or type them into the computer. As his skills improve over time, he’ll need less of your involvement in this process.
—Go digital. Children with ADHD often write slower than their classmates. Encourage your child to start the writing process on a computer. This way, she’ll keep her work organized and won’t misplace her essay before it’s finished. Also, by working on the computer she can easily rearrange the order of sentences and paragraphs in a second draft.
—Remind your child to proofread. Let your child know that he’ll be able to catch errors if he proofreads his rough draft before handing it in.
High-Tech Writing Helpers for Kids with ADHD
Portable word processor
These battery-operated devices look like a computer keyboard with a small calculator screen. Light and durable, portable word processors can be used at school for note-taking and writing assignments. Back home, files can be transferred to a PC or Mac. Basic models cost about $20.
Speech-recognition software
Word-prediction software
Software such as Co:Writer Solo ($325) helps with spelling and builds vocabulary, providing a drop-down list of words from which a student can choose. It also fills in words to speed composition. Some programs read sentences aloud, so the writer can hear what he has written and catch mistakes as they occur.
Electronic spell-checkers and dictionaries
Enter a word phonetically, and these portable gadgets define the word and provide the correct spelling. Talking devices read the words aloud. Franklin Electronics offers models beginning at about $20.
[ The Common Problems that Lead to Writer’s Block ]
Chris Zeigler Dendy, M.S., is a member of ADDitude’s ADHD Medical Review Panel .
Learning Challenges: Read These Next

Famous People with Dyslexia, Dyscalculia & Other Learning Differences


A Teacher’s Guide to NVLD: How to Support Students with Nonverbal Learning Disability

9 Things I Wish the World Knew About My Students’ ADHD

Top 25 Downloads from ADDitude’s First 25 Years
Adhd newsletter, success @ school, strategies for homework, accommodations, ieps, working with school & more..
It appears JavaScript is disabled in your browser. Please enable JavaScript and refresh the page in order to complete this form.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Writing Problems Common for Students With ADHD
damircudic / E+ / Getty Images
- ADHD and Writing Skills
- Common Challenges
- Helpful Writing Strategies
Children with ADHD are more likely to develop writing problems than children without ADHD, regardless of gender. Among both boys and girls with ADHD who also have a reading disability, however, girls have an even higher chance of developing a written language disorder, creating even more challenges for girls in the classroom.
At a Glance
ADHD is a form of neurodivergence that can make writing more challenging for some students. ADHD traits can affect a student's ability to concentrate, meet deadlines, stay on task, and stay organized, impacting their writing skills. Keep reading to learn more about how ADHD can affect children's writing skills—and how appropriate accommodations and support can help these students succeed.
ADHD Can Impact Skills Important for Writing
The technique of expressing oneself through writing is quite a complex, multi-step process. It requires integrating several skills, including:
- Planning, analyzing, and organizing thoughts
- Prioritizing and sequencing information
- Remembering and implementing correct spelling, punctuation, and grammar rules
- Fine motor coordination
As students age and move into high school and college , the expectations around writing become even more demanding. Essays and reports that require students to communicate what they know on paper factor more prominently into the curriculum.
It is no wonder that writing can create such anxiety in students with ADHD. Simply starting the process and getting ideas and thoughts out of their head in an organized manner and down on paper can feel like an uphill battle.
This can create problems for students with ADHD since research has found that writing abilities longitudinally predict the academic outcomes of kids with this form of neurodivergence .
Signs of Writing Problems in Kids With ADHD
Some of the signs that a student might be struggling with their writing due to ADHD characteristics include:
- Taking longer than their classmates to complete their work
- Producing less written work—shorter reports, less "discussion" on discussion questions, and fewer sentences on each test question—as compared to their peers without ADHD
- Struggling to turn in written assignments by the required deadline
- Making spelling errors due to rushing through the writing process or not being able to stay on task
- Failing to proofread and edit assignments before turning them in
ADHD Challenges That May Lead to Writing Difficulties
Why is it so tough for students with ADHD to produce well-crafted, thoughtful, carefully edited writing? Here are nine of the top reasons:
- Keeping ideas in mind long enough to remember what one wants to say
- Maintaining focus on the "train of thought" so the flow of the writing does not veer off course
- Keeping in mind the big picture of what you want to communicate while manipulating the ideas, details, and wording
- With the time and frustration it can take to complete work, there is often no time (or energy) remaining to check over the details, edit assignments, and make corrections.
- Students with ADHD generally have problems with focus and attention to detail, making it likely that they will make errors in spelling, grammar, or punctuation.
- If a child is impulsive, they may also rush through schoolwork. As a result, papers are often filled with "careless" mistakes.
- The whole proofreading and editing process can be quite tedious, so if students attempt to review work, they may easily lose interest and focus.
- Challenges with fine motor coordination can complicate writing ability further. Many students with ADHD struggle with fine motor coordination, resulting in slower, messier penmanship that can be very difficult to read.
- Simply sustaining the attention and mental energy required for writing can be a struggle for someone with ADHD.
Research indicates that it is less the overt behavioral traits (like restlessness and impulsivity) that influence writing problems in kids with ADHD. Instead, it is typically struggles with executive functions (such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and attentional control) that play the most significant role in causing writing problems for kids with ADHD.
Writing Strategies for Kids With ADHD
Students with ADHD can work on strategies to improve writing skills that address common learning problems that can interfere with written language expression. Appropriate accommodations and support can help students with ADHD manage the challenges that might affect their writing abilities. Some strategies that can help include:
Giving Clear Instructions
Students with ADHD benefit from having concise instructions that clearly outline the steps to follow in an assignment. Breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks can also help.
Help With Organization
Organizational strategies like outlining can help. Some people may find index cards breaking down writing tasks into small steps helpful, but students with ADHD often get bogged down if they have to deal with many smaller tasks. In such instances, setting a timer and devoting a specific block of time to writing can be a great way to make progress on writing tasks without getting overwhelmed.
Provide Extra Time
Because students with ADHD may take longer with writing assignments, providing extra time to complete these tasks can be a helpful accommodation that helps ensure academic sucess. This can give kids the time they need to produce quality work and finish their assignments.
Extra time, clear instructions, and help with organization can help kids with ADHD managing writing assignments more easily. However, it is important to remember that each kid is different. Experimenting with different methods and supports can help each child figure out what works best for them.
Keep in Mind
It is important to remember that while students with ADHD might struggle with writing skills, having the right accommodations and support can help them succeed in academic settings. Finding ways to support kids in overcoming their writing challenges can help them manage their ADHD effectively, foster more positive academic self-esteem, and strengthen their writing skills.
Molitor SJ, Langberg JM, Evans SW. The written expression abilities of adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder . Res Dev Disabil . 2016;51-52:49-59. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2016.01.005
Molitor SJ, Langberg JM, Bourchtein E, Eddy LD, Dvorsky MR, Evans SW. Writing abilities longitudinally predict academic outcomes of adolescents with ADHD . Sch Psychol Q . 2016;31(3):393-404. doi:10.1037/spq0000143
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ADHD in the classroom: Helping children succeed in school .
Mokobane M, Pillay BJ, Meyer A. Fine motor deficits and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in primary school children . S Afr J Psychiatr . 2019;25:1232. doi:10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v25i0.1232
Soto EF, Irwin LN, Chan ESM, Spiegel JA, Kofler MJ. Executive functions and writing skills in children with and without ADHD . Neuropsychology . 2021;35(8):792-808. doi:10.1037/neu0000769
By Keath Low Keath Low, MA, is a therapist and clinical scientist with the Carolina Institute for Developmental Disabilities at the University of North Carolina. She specializes in treatment of ADD/ADHD.

- Writing Help for ADHD Students
Updated 2024.
Typically, students with ADHD produce a wealth of ideas about an essay writing topic. Yet over 60% of students with ADHD struggle to get their ideas down on paper.
For most students with ADHD, writing assignments are torturous.
Because students with ADHD often have trouble separating dominant (main) ideas from less dominant (subordinate) ideas, even starting a writing assignment can be an arduous and anxiety filled experience.
But none of these difficulties needs to keep your ADHD child from writing successfully in school. Use the eight strategies below to help your child write more easily and successfully.


- Support LUC
- Directories
- KRONOS Timecard
- Employee Self-Service
- Password Self-service
- Academic Affairs
- Advancement
- Admission: Adult B.A.
- Admission: Grad/Prof
- Admission: International
- Admission: Undergrad
- Alumni Email
- Alumni Relations
- Arrupe College
- Bursar's Office
- Campus Ministry
- Career Centers
- Center for Student Assistance and Advocacy
- Colleges and Schools
- Commencement
- Conference Services
- Continuing Education
- Course Evaluations IDEA
- Cuneo Mansion & Gardens
- Dining Services
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Emeriti Faculty Caucus
- Enterprise Learning Hub
- Executive and Professional Education
- Faculty Activity System
- Financial Aid
- Human Resources
- IBHE Institutional Complaint System
- Information Technology Services
- Learning Portfolio
- Loyola Health App
- Loyola University Chicago Retiree Association (LUCRA)
- Madonna della Strada Chapel
- Media Relations
- Navigate Staff
- Office of First Year Experience
- Office of Institutional Effectiveness
- President's Office
- Rambler Buzz
- Registration and Records
- Residence Life
- Retreat & Ecology Campus
- Rome Center
- School of Environmental Sustainability
- Security/Police
- Staff Council
- Student Achievement
- Student Consumer Information
- Student Development
- Study Abroad
- Summer Sessions
- University Policies
- Writing Center
Loyola University Chicago
English tutoring at the literacy center, common writing problems & how to fix them.
Thanks to Professor Allen Frantzen for this extensive guide.
GRAMMAR. A guide to modern English grammar is available. CITATIONS. Guide to writing correct citations QUESTIONS? Email J Heckman at [email protected] .
Here are brief descriptions of common writing problems. Check them and email any questions you have about how they apply to your work. You may be required to rewrite certain sentences showing that you understand and can make the necessary corrections. Your paper may have two grades, lower and higher. If you make satisfactory corrections to the problems singled out in comments at the end of the paper, the higher grade will be recorded; if you do not make the corrections, the lower grade will be recorded. The corrections will be due one week after the date on which papers are returned. Problems marked with * will be especially important to correct.
| * * * * | * * * | * * * * * | * * * * | * |
1. Agreement Check carefully for errors in agreement; don't shift person (especially third person [he, she, it] to second [you]); number, or tense, without reason. If you are using the singular, stick to it unless you have cause to switch to the plural. Example: Everyone should know what they want. Correction: Everyone should know what he or she wants. Watch collectives—e.g., the Socialist Party is "it" not "they"; General Motors is "it" not “they.” Switches in tense are very annoying: "She drove to the mall and looks around for a store."
2. Awkward constructions Awkward constructions contain errors in logic or are so imprecise that they can't be readily understood. Sometimes a sentence is awkward because a key term is obscure—e.g., you write that "the poem follows a decision-type format." What is that supposed to mean? If you know what it is supposed to mean, then say it clearly. Awkwardness is not only a matter of incorrect expression—although errors are awkward, of course. Awkwardness usually indicates a gap in expectations between you and your reader, created when you say something you don't need to, or fail to say something you should, fail to explain something completely. Very often a sentence is marked "awkward" because it is too long; the sentence can perhaps be divided into two sentences for clarity.
3. Citation Style Please pay special attention to how you handle quoted material. Look at a citation style sheet and follow it carefully for books, articles, and websites. Avoid using filler in your citations: e.g., In her article, "The Triumph of Time," Mary McGregory discusses the last act of Hamlet . The reader can see that "The Triumph of Time" is an article (because the title is in quotes; if it were a book, it would be in italics). But why does the reader need to know the title in any case? Include the title only if the location of the reference has something to do with your argument (e.g., if the author said one thing in a book, another in an article, or something like that). Just write, for the above, Mary McGregory discusses the last act of Hamlet . That's all you're saying. My response: "And?"
4. Clichés, trite expressions Trite language belongs to everybody and therefore to nobody in particular, especially not to you. The #1 cliché in undergraduate writing in English classes is that "the author sends a message." Authors are not radio stations; they communicate complex ideas in complex ways. Only propaganda sends "a message"—and even then it is very difficult to control meaning so tightly that only one "message" is sent. Even a t.v. commercial sends more than one "message." Texts don't "send messages" so much as readers find "messages" in them—but even so, do all readers find the same "message"? It is odd, in this age of the individual, to find students automatically reducing a complex work of art to a single statement—as if everybody who read a text found the same "message" in it; as if the "message" one person found were the only "message" to be found. Do you really think so? There are better ways to address the main point you think the author is making, the argument the author makes, the author's rhetorical objective, and so on. As soon as you get away from the mechanical model (sends a message), you have to think about what you want to say the author is doing. The #2 cliché in undergraduate writing in English classes is that someone "could / could not identify with" a character. Characters are tools; you should think of a character as an "it," not a "he" or a "she." A character is a device used by an author for manipulating ideas and for setting ideas and emotions into a fictional context. You can or cannot "identify" with the character, as you wish, but you should realize what you are saying, which is that you do or don't agree with what the author is using that character to say and / or show. If you think "identify with" means anything else, you're suggesting that you think literary characters are real people. Literary characters might have been real people once, but they aren't when you are reading about them. In general, trite expressions are revealing of an uncritical disposition. For example, people may "iron out their differences," may "drift apart," may find revising their essays "as easy as rolling off a log." But these tired expressions simply replace your own thoughts and reactions with prefabricated slogans and catch-phrases. Your language should be appropriate to your subject, and it should be your own. The stuff of great satire, after all, is a scene in which characters speak in nothing but clichés—all form, no content.
5. Combining sentences Combine short sentences into longer, more varied structures; avoid choppy effects. Example of choppy effects: "This is the ultimate difficulty. It developed from the evasion of responsibility for decades. Now the price has to be paid. We must come to terms with the it." Try something like: "This, the ultimate difficulty, developed because our predecessors evaded their responsibilities for decades. Now we have to pay the price." Note that subordinate clauses help combine sentences—here instead of a list of short sentences we get a clear cause/effect process.
6. Comma Splices Independent clauses, or complete sentences, should not be strung together with commas. A comma cannot ordinarily separate two independent clauses (i.e., complete sentences). That error is called a "comma splice." For example, "The book is on the desk, it once belonged to my father." or "The merchant repeats himself many times, he does not have a good memory." The comma in each example should be replaced with a semi-colon or period; a dash is also possible—but not always recommended. Or, remembering that variety in sentence length and rhythm is important, use subordination: "The book, which once belonged to my father, is on the desk." "Because he often repeats himself, we see that the merchant does not have a good memory."
7. Dangling modifier A modifier dangles when it does not modify the noun which immediately follows it. You might as well have written, "Looking out the window, the leaves began to fall" or "Sitting in the bathtub, the telephone rang." The introductory elements, "Looking" and "Sitting," cannot modify "leaves" and "bathtub." Leaves do not look and telephones do not sit in tubs. Keep these admittedly silly examples in mind, especially if your sentence is something like, "Reading the poem carefully, irony shows what the author intended." Irony does not read poems. "Reading the poem carefully, we see that the author's irony suggests is intent."
8. Documentation Be sure that you understand the documentation system, MLA, used in this course; never manufacture your own style for notation. If you do not understand the system we are using, please ask; you are assumed to understand and have a copy of the Department of English statement on use of sources. Be warned that documentation is expected whenever you cite some else's words or ideas. There are ample warnings on the syllabus about fair use of other people's work and academic dishonesty. You are responsible for asking questions if you are unsure about fair use of sources; you cannot plead ignorance. By attending class once and signing in, you indicate that you understand and agree to abide by Department and University regulations on use of sources. No excuses. Plagiarism is academic dishonesty and will result in a student’s failing the paper or the entire course. See the Department of English website for examples of what is and what is not the correct use of sources.
9. Dummy subjects Be careful about overusing dummy subjects—beginning sentences with "It is" or "There is/There are"; these are "dummy" subjects because they stand in for real subjects. The reader should not have to guess what your "it" refers to or where your "there" can be found. Sometimes it is not easy to avoid the dummy subject—perhaps this sentence is a case in point, but I could have written, "Sometimes the dummy subject is not easily avoided"—a bit shorter and more compact. When you see that you use "It is" or "There is/are" often, rethink the sentence and try to eliminate the dummy subject.
10. Edit for economy
Edit for economy. Learn how to omit needless words and get to the point. For "She fell down due to the fact that she hurried" write "She fell because she hurried." Be concise; don't take ten words when you need only five. But being concise does not mean being abrupt; say only what needs saying, but say all that needs to be said. Wordiness results from redundant expressions and/or repetition; both problems can be corrected once you realize that you must search for them. Note too that wordiness may result from uncertainty about what you want to say. Learn to recognize this "exploratory style" as a stage in writing a good sentence, as part of the process, but not the final form. Revise the evasive, indecisive quality out of your prose.
11. Emphasis Structure sentences so that the important words and ideas stand out. Put important ideas and words in slots which stress their value. Sometimes by reversing the order of clauses you can shift the focus of the sentence to the main idea away from a less important one. For example, "We learn that he values nothing more than success when we see him kill his own brother." This sentence would be more emphatic if we reordered the clauses: "When we see him kill his own brother, we learn that he values nothing more than success" (emphasis falls on "brother" and "success").
12. Evidence Your paper must supply evidence for your argument. In the main, this should come from the primary text/s you cite. If you think a passage reveals an important idea about the aspect of the work you discuss, you should cite it. Just as it's important to avoid paraphrasing a work (summing up its plot), it's important to select evidence carefully (don't string quotes together one after another to fill up space with redundant examples). Your paper must argue the details of the text, not general ideas; the more detailed the evidence, the more persuasive the case. Your evidence will reveal your sensitivity to language and how authors use it.
13. Sentence fragments A fragment is a group of words or a phrase (a dependent clause) used as if it were a complete sentence (an independent clause). A fragment can be a dependent clause—a clause which must depend on, be connected to, a main or independent clause to form a complete sentence. "His first novel." is a fragment; "It was his first novel." is a complete sentence. "That he would leave soon" is a dependent clause and a sentence fragment if used as a complete sentence. "He decided that he would leave soon" is complete—here the dependent clause, "that he would leave soon," is linked to an independent clause ("He decided"). Sometimes fragments are used for effect—as in "She left the house in good order. Or so she thought." But don't take a chance unless you're sure you need the effect of the fragment. See #1 above.
14. Generalizations General statements have the unexpected effect of undercutting the writer's authority and causing the reader to question his or her judgment. "Since time began," one might write, "women have been deprived of all their rights." One would immediately focus on the word "all" and take exception to such a statement—the sentence tries to claim lots of ground but overreaches, and in the end it has very little authority; "since time began" is another gross generality: a statement about all time is likely to require qualification. General statements tend to be abstract, categorical, and liable to be false.
15. Nominalization Reduce wordiness by writing with strong verbs rather than weak verbs and nouns. Verbs should convey the main idea and action of the sentence. Using nouns to name actions and weak verbs when strong verbs could carry the action (and meaning) of the sentence is called "nominalization." Instead of saying "The resolution to the problem can be seen in author's attempt to reconcile..." try: "The author resolves the problem by reconciling..." Here, "resolves" replaces "resolution" and accompanying baggage.
16. Paragraph design Every paragraph needs a central idea; the definition of a paragraph is A distinct passage or section of a discourse, chapter, or book, dealing with a particular point of the subject, the words of a distinct speaker, etc., whether consisting of one sentence or of a number of sentences that are more closely connected with each other than with what stands before and after. ( Oxford English Dictionary ) A paragraph a page long does not have ONE key idea but probably contains several somewhat related ideas run together. Examine the structure of every paragraph before you hand in a paper. What's the topic sentence? How do subsequent sentences relate to it?
17. Parallel constructions Employ parallel constructions for parallel ideas. Parallel constructions are easy to read and often express ideas elegantly and effectively. Strive to create them when they serve your purpose. Example: "His objective was to win, but playing fair also mattered to him." Correction: "His objective was not only to win, but also to play fair." Make nouns parallel to nouns, verbs to verbs: "The author shows the reader the path to being virtuous rather than to vice." Correct: "the path to virtue rather than to vice."
18. Parenthetical phrases and restrictive clauses
Parenthetical expressions—phrases in apposition to a subject or to another phrase—must be set off by TWO commas, not one. For example, "In the third chapter, which he actually wrote first, the author claimed to have discovered the cure for cancer." (Incorrect: "In the third chapter, which he actually wrote first the author . . . .) The "which" clause is set off by commas correctly here. These are also known as "nonrestrictive clauses" since they do not define the noun modified but add extra information.
19. Passive voice Watch overuse of the passive voice (structures in which the subject receives rather than initiates or performs the action: The ball was caught). Sometimes the passive is necessary and helpful, but too often it is abused and it obscures the real subject and action of the sentence. The passive voice also becomes general and vague. It's usually better to write about people who do things than things which are done by an undefined somebody, especially if the whole point of writing is to write about people who ACT. "The ball was caught" may be the better way in some contexts, but "She caught the ball" describes the meaningful action more effectively.
20. Possessives and plurals Contractions are a matter of correctness rather than style. The plural of man is men, and the possessive of men is men's, not mens'. Don't confuse "it is," contracted as "it's," with "its," the possessive adjective. Example of the confusion: The cup lost it's handle. For "it's" here read "its." Don't confuse the possessive with the plural, either: Example: The boy's came home late. Read "boys." The possessive of "their" is theirs, not "their's."
21. Pronouns Beware of vague or confusing pronouns and antecedents. Is it clear to what or to whom pronouns refer? Is the referent suppressed? Example: The disaster was reported in the papers. They still didn't act. Who is "they"? Not papers, surely. If you write "Government officials still didn't act" the reader understands. Be careful, when you begin sentences or paragraphs with "This," that the reader knows which noun "This" refers back to—if I've written "This what?" in the margin, it means that the referent is either vague or unnamed (that it exists somewhere in your mind, perhaps, a collective "This," rather than on paper). The test? Always supply a noun to follow: "This point," for example, "This issue," or whatever. Get into the habit of questioning your use of "This" in the sentence-initial position.
Make sure that a pronoun refers back to the correct noun and that the pronoun is not ambiguous (if two men have just been named, "he" could refer to either one of them. Make sure that you use "who" to refer back to people and "that" to refer back to things. "The woman who wrote the book," not "The woman that wrote the book."
22. Punctuation Ordinarily, use commas only where you pause when reading a sentence aloud: "Williams' first book, was very successful." No need for a comma there. Use a semi-colon (;) as you would a period, not a comma. Use a semi-colon to separate items in a list or to separate two closely related independent clauses, not a dependent and an independent clause. Correct: "Williams wrote several books; none of them, however, were as successful as the first." Incorrect: "Williams wrote several books; The Triad being first. Do not isolate a dependent clause by putting a semi-colon ( ; ) before it, e.g., "He walked to school; a triumph over fear." Instead: "He walked to school—a triumph over fear." Use a comma, a colon ( : ), or (less often) a dash ( — ) to integrate that dependent clause into your sentence; a semi-colon is a full-stop, closer to a period than a comma.
23. Repetition Edit for economy; remove repetitious words and phrases. Repetition undercuts the progress of the paper and causes the reader to lose interest. Look at each sentence in isolation from its context and learn to identify the new information a new sentence adds to the one before. When there isn't enough—or any—new information, you are repeating the old.
24. Redundancy Avoid redundant and obvious expressions. Don't tell the reader what he or she doesn't need to know. Example: "In our modern world of today...." or "The author begins with an introduction...." "Today" and "modern" overlap, and so do "our" and "modern." Likewise, "In Twain's first chapter, he argues . . ." ("Twain's first chapter argues," or "In the first chapter, Twain argues . . . .). Other examples: "Both Smith and Jones took different views of the war." or "Both Smith and Jones took the same view of the war." Both/different and Both/same are redundant. Since Smith and Jones are different people, the reader assumes that they took differing views and has to reread the sentence to see if something has been missed (it hasn't, except by the author-as-editor). Try, "Smith and Jones took different views of the war." Or, "Smith and Jones took the same view of the war." Another example: "For his young readers, the author must avoid intimidating them by taking too much for granted." Here, "For his young readers" and "them" are redundant. Try: "The author must avoid intimidating young readers by taking too much for granted."
25. Run-on sentences Example: Run-on sentence are series of short sentences linked by "and" or some other conjunction these are very annoying to the reader they are easy to fix. Revised: Run-on sentences are series of short sentences linked by "and" or some other conjunction; annoying to the readers, they are easily fixed.
26. Quotations Two points here: * 1) See the citation guide on punctuating quotations. Indent quotes of 5 lines or more; don't italicize them, shrink the font, or anything else; just indent them. If you indent, use quotation marks ONLY if the material is dialogue or direct discourse (otherwise the quotation marks are redundant). In every case, integrate quotations into your prose. Don't turn your paper into a patch-work in which your voice suddenly stops, and, without a transition, another voice begins. Such devices as "According to . . ." and others are useful in bridging your prose and the prose you quote. If you quote a sentence or two from any source, enclose the quoted material within quotation marks (" ") and give the page number outside the quotation marks. Example: The narrator says that Janice stood "at six feet,"with "shining eyes, blond hair, and a warm smile" (323). Do not write "smile, p. 323," since the narrator did not say "page 323." Omit any sentence punctuation before the parenthesis. EXAMPLE: "a warm smile," (323). Omit that comma! * 2) Use single quotes ( ' ' ) only when you quote something inside a quotation ("The smith objected to the 'silly' game he was forced to play," Austen wrote); you might see single quotes used throughout some articles, but those articles are following a British style sheet, not an American style sheet; British and American usage is exactly the opposite in this matter. See also the special link to citations above. A note about citations from web sources: If you are quoting SEAFARER, you only need to cite module and part (e.g., Magic, Narrative, part 1; or Rank, Lexicon). For non-Loyola University Chicago-based material (excepting Anglo-Saxon.net), give the full web address: http://www. —and so forth. Web sites cited will be checked.
27. Quote marks Avoid random quotes to set off imprecise or trite language, e.g., Elizabeth might be the queen, but this scene shows that she doesn't "get it." "Get it" is loose slang; try to express this more precisely. She doesn't understand, or doesn't grasp the importance of something. If you use quotation marks, make sure you are quoting a source. Don't use quotation marks to "telegraph" to the reader that you aren't exactly sure what you mean or to allude to a slangy or loose definition and leave matters there.
28. Subjunctive mood Learn to distinguish the subjunctive mood from the indicative. The indicative refers to facts, the subjunctive to conditions contrary to fact. Example: "If I were you, . . ." (correct); "If I was you, . . ." (allowed conversationally, but "were" would be better).
29. Summarizing the plot? Don't summarize the plot. Summary has a purpose, but only a limited one, in a critical paper; the objective of a critical paper is analysis of the material from a certain perspective. Unless the reader knows what will be argued—which is to say, unless an analytical objective is in view—he or she will have no context for an elaborate discussion of plot summary. Short summaries are necessary to support arguments; but you should expect in this case that your reader knows the material about as well as you do. Set up critical framework that clarifies the objectives of your paper; then, where necessary, fit brief summaries into that framework.
30. Thesis and plan Two points here: 1) Every paper must have an identifiable thesis statement. That statement can be more or less direct, but it must be prominent in the paper's first paragraphs. Failure to provide a thesis statement is a strong indication that the paper is a description or a summary rather than an argument. A topic is something you write about; a thesis is an argument about a topic. 2) Along with a thesis, your paper should always convey a plan for pursuing the thesis. It is better to be mechanical (safe) than arbitrary and unclear (sorry) when you indicate the direction of your argument to the reader. A good thesis statement does not necessarily suggest how the argument will be organized. It might seem mechanical to write "First I will, and then I will, etc.," and you can always revise that kind of writing out of later drafts. However, a good structure helps the reader grasp the main points of the paper. Less mechanical ways of generating a plan include such phrases as, "By comparing X to Y in three key instances, I will show that . . .," "In order to explain this claim, I will focus on two aspects of X," and so forth. (Most teachers do not have a phobia about using the first person pronoun, by the way; they expect you to write in your own voice.)
31. Titles Be sure you title your paper. A good title will suggest that the paper has a specific focus and will say something about the thesis. Never title a paper something like "Second paper" or "The House of Mirth" (or whatever is the name of the novel or short-story or poem you are writing about). That shows a sad lack of imagination and effort.
32. Topic vs. thesis Distinguish a topic—which is simply a subject—from a thesis. A topic can be complex and still be a topic: the need to repent and save the soul is a topic, not a thesis. The need to save the soul before death and judgment is still just a topic. A topic is something we discuss or argue or debate; it is not, itself, an argument, but you can't have an argument without it. A THESIS is defined as "A proposition laid down or stated, esp. as a theme to be discussed and proved, or to be maintained against attack (in Logic sometimes as distinct from HYPOTHESIS; in Rhetoric from ANTITHESIS) 2); a statement, assertion, tenet" ( OED ). Note: "To be discussed and proved." A thesis requires proof. What proof does "the need to save the soul" require? None. Does any source in Old or Middle English literature say that the soul does not need to be saved? What, then, is there to argue about? If you use a topic as your thesis, all you will do is summarize the work or explain what it already explains (see #23 above, Plot summary).
33. Transitions One of your major tasks is to let the reader know what your paper will attempt, and how you will go about it. The reader should not be in doubt about the direction your paper takes. Connections between sentences and between paragraphs should be unambiguously clear, for in order to make those connections, you need transition markers to indicate contrast or qualification; illustration; ("for example, for instance"); development ("furthermore, again also"); conclusion or result ("Consequently, Therefore"), and so forth. Your direction should always be apparent to the reader.
34. Word choice The reader depends on the writer's ability to choose words carefully, to say exactly what he or she means. If word choice is inexact, the reader will easily form the wrong impression. And even if the reader can second guess the writer, and think to himself, "Oh, this must mean ——," the reader has a right to be annoyed: he or she shouldn't have to do the writer's work. Be sure you know the meanings of the words you use and be sure that they are appropriate to the context (not too informal or slangy, not pretentious or fancy). Sometimes word choice is a problem because the words are used incorrectly; sometimes word choice is merely inappropriate. Reading aloud is a good way to test word choice. "Unique" is a special case. Remember that you cannot qualify "unique": something either is, or is not, unique, and uniqueness does not come in degrees like smallness does—"quite unique, very unique," and so forth.
- Undergraduate
- Graduate/ Professional
- Adult Education

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
8 Overcoming Challenges College Essay Examples
The purpose of the Overcoming Challenges essay is for schools to see how you might handle the difficulties of college. They want to know how you grow, evolve, and learn when you face adversity. For this topic, there are many clichés , such as getting a bad grade or losing a sports game, so be sure to steer clear of those and focus on a topic that’s unique to you. (See our full guide on the Overcoming Challenges Essay for more tips).
These overcoming challenges essay examples were all written by real students. Read through them to get a sense of what makes a strong essay. At the end, we’ll present the revision process for the first essay and share some resources for improving your essay.
Please note: Looking at examples of real essays students have submitted to colleges can be very beneficial to get inspiration for your essays. You should never copy or plagiarize from these examples when writing your own essays. Colleges can tell when an essay isn’t genuine and will not view students favorably if they plagiarized.
Essay 1: Becoming a Coach
“Advanced females ages 13 to 14 please proceed to staging with your coaches at this time.” Skittering around the room, eyes wide and pleading, I frantically explained my situation to nearby coaches. The seconds ticked away in my head; every polite refusal increased my desperation.
Despair weighed me down. I sank to my knees as a stream of competitors, coaches, and officials flowed around me. My dojang had no coach, and the tournament rules prohibited me from competing without one.
Although I wanted to remain strong, doubts began to cloud my mind. I could not help wondering: what was the point of perfecting my skills if I would never even compete? The other members of my team, who had found coaches minutes earlier, attempted to comfort me, but I barely heard their words. They couldn’t understand my despair at being left on the outside, and I never wanted them to understand.
Since my first lesson 12 years ago, the members of my dojang have become family. I have watched them grow up, finding my own happiness in theirs. Together, we have honed our kicks, blocks, and strikes. We have pushed one another to aim higher and become better martial artists. Although my dojang had searched for a reliable coach for years, we had not found one. When we attended competitions in the past, my teammates and I had always gotten lucky and found a sympathetic coach. Now, I knew this practice was unsustainable. It would devastate me to see the other members of my dojang in my situation, unable to compete and losing hope as a result. My dojang needed a coach, and I decided it was up to me to find one.
I first approached the adults in the dojang – both instructors and members’ parents. However, these attempts only reacquainted me with polite refusals. Everyone I asked told me they couldn’t devote multiple weekends per year to competitions. I soon realized that I would have become the coach myself.
At first, the inner workings of tournaments were a mystery to me. To prepare myself for success as a coach, I spent the next year as an official and took coaching classes on the side. I learned everything from motivational strategies to technical, behind-the-scenes components of Taekwondo competitions. Though I emerged with new knowledge and confidence in my capabilities, others did not share this faith.
Parents threw me disbelieving looks when they learned that their children’s coach was only a child herself. My self-confidence was my armor, deflecting their surly glances. Every armor is penetrable, however, and as the relentless barrage of doubts pounded my resilience, it began to wear down. I grew unsure of my own abilities.
Despite the attack, I refused to give up. When I saw the shining eyes of the youngest students preparing for their first competition, I knew I couldn’t let them down. To quit would be to set them up to be barred from competing like I was. The knowledge that I could solve my dojang’s longtime problem motivated me to overcome my apprehension.
Now that my dojang flourishes at competitions, the attacks on me have weakened, but not ended. I may never win the approval of every parent; at times, I am still tormented by doubts, but I find solace in the fact that members of my dojang now only worry about competing to the best of their abilities.
Now, as I arrive at a tournament with my students, I close my eyes and remember the past. I visualize the frantic search for a coach and the chaos amongst my teammates as we competed with one another to find coaches before the staging calls for our respective divisions. I open my eyes to the exact opposite scene. Lacking a coach hurt my ability to compete, but I am proud to know that no member of my dojang will have to face that problem again.
This essay begins with an in-the-moment narrative that really illustrates the chaos of looking for a coach last-minute. We feel the writer’s emotions, particularly their dejectedness, at not being able to compete.
Through this essay, we can see how gutsy and determined the student is in deciding to become a coach themselves. The writer shows us these characteristics through their actions, rather than explicitly telling us: To prepare myself for success as a coach, I spent the next year as an official and took coaching classes on the side.
One area of improvement of this essay would be the “attack” wording. The author likely uses this word as a metaphor for martial arts, but it feels too strong to describe the adults’ doubt of the student’s abilities as a coach, and can even be confusing at first.
Still, we see the student’s resilience as they are able to move past the disbelieving looks to help their team. The essay is kept real and vulnerable, however, as the writer admits having doubts: Every armor is penetrable, however, and as the relentless barrage of doubts pounded my resilience, it began to wear down. I grew unsure of my own abilities.
The essay comes full circle as the author recalls the frantic situations in seeking out a coach, but this is no longer a concern for them and their team. Overall, this essay is extremely effective in painting this student as mature, bold, and compassionate.
Essay 2: Starting a Fire
Was I no longer the beloved daughter of nature, whisperer of trees? Knee-high rubber boots, camouflage, bug spray—I wore the garb and perfume of a proud wild woman, yet there I was, hunched over the pathetic pile of stubborn sticks, utterly stumped, on the verge of tears. As a child, I had considered myself a kind of rustic princess, a cradler of spiders and centipedes, who was serenaded by mourning doves and chickadees, who could glide through tick-infested meadows and emerge Lyme-free. I knew the cracks of the earth like the scars on my own rough palms. Yet here I was, ten years later, incapable of performing the most fundamental outdoor task: I could not, for the life of me, start a fire.
Furiously I rubbed the twigs together—rubbed and rubbed until shreds of skin flaked from my fingers. No smoke. The twigs were too young, too sticky-green; I tossed them away with a shower of curses, and began tearing through the underbrush in search of a more flammable collection. My efforts were fruitless. Livid, I bit a rejected twig, determined to prove that the forest had spurned me, offering only young, wet bones that would never burn. But the wood cracked like carrots between my teeth—old, brittle, and bitter. Roaring and nursing my aching palms, I retreated to the tent, where I sulked and awaited the jeers of my family.
Rattling their empty worm cans and reeking of fat fish, my brother and cousins swaggered into the campsite. Immediately, they noticed the minor stick massacre by the fire pit and called to me, their deep voices already sharp with contempt.
“Where’s the fire, Princess Clara?” they taunted. “Having some trouble?” They prodded me with the ends of the chewed branches and, with a few effortless scrapes of wood on rock, sparked a red and roaring flame. My face burned long after I left the fire pit. The camp stank of salmon and shame.
In the tent, I pondered my failure. Was I so dainty? Was I that incapable? I thought of my hands, how calloused and capable they had been, how tender and smooth they had become. It had been years since I’d kneaded mud between my fingers; instead of scaling a white pine, I’d practiced scales on my piano, my hands softening into those of a musician—fleshy and sensitive. And I’d gotten glasses, having grown horrifically nearsighted; long nights of dim lighting and thick books had done this. I couldn’t remember the last time I had lain down on a hill, barefaced, and seen the stars without having to squint. Crawling along the edge of the tent, a spider confirmed my transformation—he disgusted me, and I felt an overwhelming urge to squash him.
Yet, I realized I hadn’t really changed—I had only shifted perspective. I still eagerly explored new worlds, but through poems and prose rather than pastures and puddles. I’d grown to prefer the boom of a bass over that of a bullfrog, learned to coax a different kind of fire from wood, having developed a burn for writing rhymes and scrawling hypotheses.
That night, I stayed up late with my journal and wrote about the spider I had decided not to kill. I had tolerated him just barely, only shrieking when he jumped—it helped to watch him decorate the corners of the tent with his delicate webs, knowing that he couldn’t start fires, either. When the night grew cold and the embers died, my words still smoked—my hands burned from all that scrawling—and even when I fell asleep, the ideas kept sparking—I was on fire, always on fire.
This essay is an excellent example because the writer turns an everyday challenge—starting a fire—into an exploration of her identity. The writer was once “a kind of rustic princess, a cradler of spiders and centipedes,” but has since traded her love of the outdoors for a love of music, writing, and reading.
The story begins in media res , or in the middle of the action, allowing readers to feel as if we’re there with the writer. One of the essay’s biggest strengths is its use of imagery. We can easily visualize the writer’s childhood and the present day. For instance, she states that she “rubbed and rubbed [the twigs] until shreds of skin flaked from my fingers.”
The writing has an extremely literary quality, particularly with its wordplay. The writer reappropriates words and meanings, and even appeals to the senses: “My face burned long after I left the fire pit. The camp stank of salmon and shame.” She later uses a parallelism to cleverly juxtapose her changed interests: “instead of scaling a white pine, I’d practiced scales on my piano.”
One of the essay’s main areas of improvement is its overemphasis on the “story” and lack of emphasis on the reflection. The second to last paragraph about changing perspective is crucial to the essay, as it ties the anecdote to larger lessons in the writer’s life. She states that she hasn’t changed, but has only shifted perspective. Yet, we don’t get a good sense of where this realization comes from and how it impacts her life going forward.
The end of the essay offers a satisfying return to the fire imagery, and highlights the writer’s passion—the one thing that has remained constant in her life.
Essay 3: Last-Minute Switch
The morning of the Model United Nation conference, I walked into Committee feeling confident about my research. We were simulating the Nuremberg Trials – a series of post-World War II proceedings for war crimes – and my portfolio was of the Soviet Judge Major General Iona Nikitchenko. Until that day, the infamous Nazi regime had only been a chapter in my history textbook; however, the conference’s unveiling of each defendant’s crimes brought those horrors to life. The previous night, I had organized my research, proofread my position paper and gone over Judge Nikitchenko’s pertinent statements. I aimed to find the perfect balance between his stance and my own.
As I walked into committee anticipating a battle of wits, my director abruptly called out to me. “I’m afraid we’ve received a late confirmation from another delegate who will be representing Judge Nikitchenko. You, on the other hand, are now the defense attorney, Otto Stahmer.” Everyone around me buzzed around the room in excitement, coordinating with their allies and developing strategies against their enemies, oblivious to the bomb that had just dropped on me. I felt frozen in my tracks, and it seemed that only rage against the careless delegate who had confirmed her presence so late could pull me out of my trance. After having spent a month painstakingly crafting my verdicts and gathering evidence against the Nazis, I now needed to reverse my stance only three hours before the first session.
Gradually, anger gave way to utter panic. My research was fundamental to my performance, and without it, I knew I could add little to the Trials. But confident in my ability, my director optimistically recommended constructing an impromptu defense. Nervously, I began my research anew. Despite feeling hopeless, as I read through the prosecution’s arguments, I uncovered substantial loopholes. I noticed a lack of conclusive evidence against the defendants and certain inconsistencies in testimonies. My discovery energized me, inspiring me to revisit the historical overview in my conference “Background Guide” and to search the web for other relevant articles. Some Nazi prisoners had been treated as “guilty” before their court dates. While I had brushed this information under the carpet while developing my position as a judge, i t now became the focus of my defense. I began scratching out a new argument, centered on the premise that the allied countries had violated the fundamental rule that, a defendant was “not guilty” until proven otherwise.
At the end of the three hours, I felt better prepared. The first session began, and with bravado, I raised my placard to speak. Microphone in hand, I turned to face my audience. “Greetings delegates. I, Otto Stahmer would like to…….” I suddenly blanked. Utter dread permeated my body as I tried to recall my thoughts in vain. “Defence Attorney, Stahmer we’ll come back to you,” my Committee Director broke the silence as I tottered back to my seat, flushed with embarrassment. Despite my shame, I was undeterred. I needed to vindicate my director’s faith in me. I pulled out my notes, refocused, and began outlining my arguments in a more clear and direct manner. Thereafter, I spoke articulately, confidently putting forth my points. I was overjoyed when Secretariat members congratulated me on my fine performance.
Going into the conference, I believed that preparation was the key to success. I wouldn’t say I disagree with that statement now, but I believe adaptability is equally important. My ability to problem-solve in the face of an unforeseen challenge proved advantageous in the art of diplomacy. Not only did this experience transform me into a confident and eloquent delegate at that conference, but it also helped me become a more flexible and creative thinker in a variety of other capacities. Now that I know I can adapt under pressure, I look forward to engaging in activities that will push me to be even quicker on my feet.
This essay is an excellent example because it focuses on a unique challenge and is highly engaging. The writer details their experience reversing their stance in a Model UN trial with only a few hours notice, after having researched and prepared to argue the opposite perspective for a month.
Their essay is written in media res , or in the middle of the action, allowing readers to feel as if we’re there with the writer. The student openly shares their internal thoughts with us — we feel their anger and panic upon the reversal of roles. We empathize with their emotions of “utter dread” and embarrassment when they’re unable to speak.
From the essay, we learn that the student believes in thorough preparation, but can also adapt to unforeseen obstacles. They’re able to rise to the challenge and put together an impromptu argument, think critically under pressure, and recover after their initial inability to speak.
Essay 4: Music as a Coping Mechanism
CW: This essay mentions self-harm.
Sobbing uncontrollably, I parked around the corner from my best friend’s house. As I sat in the driver’s seat, I whispered the most earnest prayer I had ever offered.
Minutes before, I had driven to Colin’s house to pick up a prop for our upcoming spring musical. When I got there, his older brother, Tom, came to the door and informed me that no one else was home. “No,” I corrected, “Colin is here. He’s got a migraine.” Tom shook his head and gently told me where Colin actually was: the psychiatric unit of the local hospital. I felt a weight on my chest as I connected the dots; the terrifying picture rocked my safe little world. Tom’s words blurred as he explained Colin’s self-harm, but all I could think of was whether I could have stopped him. Those cuts on his arms had never been accidents. Colin had lied, very convincingly, many times. How could I have ignored the signs in front of me? Somehow, I managed to ask Tom whether I could see him, but he told me that visiting hours for non-family members were over for the day. I would have to move on with my afternoon.
Once my tears had subsided a little, I drove to the theater, trying to pull myself together and warm up to sing. How would I rehearse? I couldn’t sing three notes without bursting into tears. “I can’t do this,” I thought. But then I realized that the question wasn’t whether I could do it. I knew Colin would want me to push through, and something deep inside told me that music was the best way for me to process my grief. I needed to sing.
I practiced the lyrics throughout my whole drive. The first few times, I broke down in sobs. By the time I reached the theater, however, the music had calmed me. While Colin would never be far from my mind, I had to focus on the task ahead: recording vocals and then producing the video trailer that would be shown to my high school classmates. I fought to channel my worry into my recording. If my voice shook during the particularly heartfelt moments, it only added emotion and depth to my performance. I felt Colin’s absence next to me, but even before I listened to that first take, I knew it was a keeper.
With one of my hurdles behind me, I steeled myself again and prepared for the musical’s trailer. In a floor-length black cape and purple dress, I swept regally down the steps to my director, who waited outside. Under a gloomy sky that threatened to turn stormy, I boldly strode across the street, tossed a dainty yellow bouquet, and flashed confident grins at all those staring. My grief lurched inside, but I felt powerful. Despite my sadness, I could still make art.
To my own surprise, I successfully took back the day. I had felt pain, but I had not let it drown me – making music was a productive way to express my feelings than worrying. Since then, I have been learning to take better care of myself in difficult situations. That day before rehearsal, I found myself in the most troubling circumstances of my life thus far, but they did not sink me because I refused to sink. When my aunt developed cancer several months later, I knew that resolution would not come quickly, but that I could rely on music to cope with the agony, even when it would be easier to fall apart. Thankfully, Colin recovered from his injuries and was home within days. The next week, we stood together on stage at our show’s opening night. As our eyes met and our voices joined in song, I knew that music would always be our greatest mechanism for transforming pain into strength.
This essay is well-written, as we can feel the writer’s emotions through the thoughts they share, and visualize the night of the performance through their rich descriptions. Their varied sentence length also makes the essay more engaging.
That said, this essay is not a great example because of the framing of the topic. The writer can come off as insensitive since they make their friend’s struggle about themself and their emotions (and this is only worsened by the mention of their aunt’s cancer and how it was tough on them ). The essay would’ve been stronger if it focused on their guilt of not recognizing their friend’s struggles and spanned a longer period of time to demonstrate gradual relationship building and reflection. Still, this would’ve been difficult to do well.
In general, you should try to choose a challenge that is undeniably your own, and you should get at least one or two people to read your essay to give you candid feedback.
Essay 5: Dedicating a Track
“Getting beat is one thing – it’s part of competing – but I want no part in losing.” Coach Rob Stark’s motto never fails to remind me of his encouragement on early-morning bus rides to track meets around the state. I’ve always appreciated the phrase, but an experience last June helped me understand its more profound, universal meaning.
Stark, as we affectionately call him, has coached track at my high school for 25 years. His care, dedication, and emphasis on developing good character has left an enduring impact on me and hundreds of other students. Not only did he help me discover my talent and love for running, but he also taught me the importance of commitment and discipline and to approach every endeavor with the passion and intensity that I bring to running. When I learned a neighboring high school had dedicated their track to a longtime coach, I felt that Stark deserved similar honors.
Our school district’s board of education indicated they would only dedicate our track to Stark if I could demonstrate that he was extraordinary. I took charge and mobilized my teammates to distribute petitions, reach out to alumni, and compile statistics on the many team and individual champions Stark had coached over the years. We received astounding support, collecting almost 3,000 signatures and pages of endorsements from across the community. With help from my teammates, I presented this evidence to the board.
They didn’t bite.
Most members argued that dedicating the track was a low priority. Knowing that we had to act quickly to convince them of its importance, I called a team meeting where we drafted a rebuttal for the next board meeting. To my surprise, they chose me to deliver it. I was far from the best public speaker in the group, and I felt nervous about going before the unsympathetic board again. However, at that second meeting, I discovered that I enjoy articulating and arguing for something that I’m passionate about.
Public speaking resembles a cross country race. Walking to the starting line, you have to trust your training and quell your last minute doubts. When the gun fires, you can’t think too hard about anything; your performance has to be instinctual, natural, even relaxed. At the next board meeting, the podium was my starting line. As I walked up to it, familiar butterflies fluttered in my stomach. Instead of the track stretching out in front of me, I faced the vast audience of teachers, board members, and my teammates. I felt my adrenaline build, and reassured myself: I’ve put in the work, my argument is powerful and sound. As the board president told me to introduce myself, I heard, “runners set” in the back of my mind. She finished speaking, and Bang! The brief silence was the gunshot for me to begin.
The next few minutes blurred together, but when the dust settled, I knew from the board members’ expressions and the audience’s thunderous approval that I had run quite a race. Unfortunately, it wasn’t enough; the board voted down our proposal. I was disappointed, but proud of myself, my team, and our collaboration off the track. We stood up for a cause we believed in, and I overcame my worries about being a leader. Although I discovered that changing the status quo through an elected body can be a painstakingly difficult process and requires perseverance, I learned that I enjoy the challenges this effort offers. Last month, one of the school board members joked that I had become a “regular” – I now often show up to meetings to advocate for a variety of causes, including better environmental practices in cafeterias and safer equipment for athletes.
Just as Stark taught me, I worked passionately to achieve my goal. I may have been beaten when I appealed to the board, but I certainly didn’t lose, and that would have made Stark proud.
While the writer didn’t succeed in getting the track dedicated to Coach Stark, their essay is certainly successful in showing their willingness to push themselves and take initiative.
The essay opens with a quote from Coach Stark that later comes full circle at the end of the essay. We learn about Stark’s impact and the motivation for trying to get the track dedicated to him.
One of the biggest areas of improvement in the intro, however, is how the essay tells us Stark’s impact rather than showing us: His care, dedication, and emphasis on developing good character has left an enduring impact on me and hundreds of other students. Not only did he help me discover my talent and love for running, but he also taught me the importance of commitment and discipline and to approach every endeavor with the passion and intensity that I bring to running.
The writer could’ve helped us feel a stronger emotional connection to Stark if they had included examples of Stark’s qualities, rather than explicitly stating them. For example, they could’ve written something like: Stark was the kind of person who would give you gas money if you told him your parents couldn’t afford to pick you up from practice. And he actually did that—several times. At track meets, alumni regularly would come talk to him and tell him how he’d changed their lives. Before Stark, I was ambivalent about running and was on the JV team, but his encouragement motivated me to run longer and harder and eventually make varsity. Because of him, I approach every endeavor with the passion and intensity that I bring to running.
The essay goes on to explain how the writer overcame their apprehension of public speaking, and likens the process of submitting an appeal to the school board to running a race. This metaphor makes the writing more engaging and allows us to feel the student’s emotions.
While the student didn’t ultimately succeed in getting the track dedicated, we learn about their resilience and initiative: I now often show up to meetings to advocate for a variety of causes, including better environmental practices in cafeterias and safer equipment for athletes.
Overall, this essay is well-done. It demonstrates growth despite failing to meet a goal, which is a unique essay structure. The running metaphor and full-circle intro/ending also elevate the writing in this essay.
Essay 6: Body Image
CW: This essay mentions eating disorders.
I press the “discover” button on my Instagram app, hoping to find enticing pictures to satisfy my boredom. Scrolling through, I see funny videos and mouth-watering pictures of food. However, one image stops me immediately. A fit teenage girl with a “perfect body” relaxes in a bikini on a beach. Beneath it, I see a slew of flattering comments. I shake with disapproval over the image’s unrealistic quality. However, part of me still wants to have a body like hers so that others will make similar comments to me.
I would like to resolve a silent issue that harms many teenagers and adults: negative self image and low self-esteem in a world where social media shapes how people view each other. When people see the façades others wear to create an “ideal” image, they can develop poor thought patterns rooted in negative self-talk. The constant comparisons to “perfect” others make people feel small. In this new digital age, it is hard to distinguish authentic from artificial representations.
When I was 11, I developed anorexia nervosa. Though I was already thin, I wanted to be skinny like the models that I saw on the magazine covers on the grocery store stands. Little did I know that those models probably also suffered from disorders, and that photoshop erased their flaws. I preferred being underweight to being healthy. No matter how little I ate or how thin I was, I always thought that I was too fat. I became obsessed with the number on the scale and would try to eat the least that I could without my parents urging me to take more. Fortunately, I stopped engaging in anorexic behaviors before middle school. However, my underlying mental habits did not change. The images that had provoked my disorder in the first place were still a constant presence in my life.
By age 15, I was in recovery from anorexia, but suffered from depression. While I used to only compare myself to models, the growth of social media meant I also compared myself to my friends and acquaintances. I felt left out when I saw my friends’ excitement about lake trips they had taken without me. As I scrolled past endless photos of my flawless, thin classmates with hundreds of likes and affirming comments, I felt my jealousy spiral. I wanted to be admired and loved by other people too. However, I felt that I could never be enough. I began to hate the way that I looked, and felt nothing in my life was good enough. I wanted to be called “perfect” and “body goals,” so I tried to only post at certain times of day to maximize my “likes.” When that didn’t work, I started to feel too anxious to post anything at all.
Body image insecurities and social media comparisons affect thousands of people – men, women, children, and adults – every day. I am lucky – after a few months of my destructive social media habits, I came across a video that pointed out the illusory nature of social media; many Instagram posts only show off good things while people hide their flaws. I began going to therapy, and recovered from my depression. To address the problem of self-image and social media, we can all focus on what matters on the inside and not what is on the surface. As an effort to become healthy internally, I started a club at my school to promote clean eating and radiating beauty from within. It has helped me grow in my confidence, and today I’m not afraid to show others my struggles by sharing my experience with eating disorders. Someday, I hope to make this club a national organization to help teenagers and adults across the country. I support the idea of body positivity and embracing difference, not “perfection.” After all, how can we be ourselves if we all look the same?
This essay covers the difficult topics of eating disorders and mental health. If you’re thinking about covering similar topics in your essay, we recommend reading our post Should You Talk About Mental Health in College Essays?
The short answer is that, yes, you can talk about mental health, but it can be risky. If you do go that route, it’s important to focus on what you learned from the experience.
We can see that the writer of this essay has been through a lot, and a strength of their essay is their vulnerability, in excerpts such as this: I wanted to be admired and loved by other people too. However, I felt that I could never be enough. I began to hate the way that I looked, and felt nothing in my life was good enough. I wanted to be called “perfect” and “body goals,” so I tried to only post at certain times of day to maximize my “likes.”
The student goes on to share how they recovered from their depression through an eye-opening video and therapy sessions, and they’re now helping others find their self-worth as well. It’s great that this essay looks towards the future and shares the writer’s goals of making their club a national organization; we can see their ambition and compassion.
The main weakness of this essay is that it doesn’t focus enough on their recovery process, which is arguably the most important part. They could’ve told us more about the video they watched or the process of starting their club and the interactions they’ve had with other members.
Still, this essay shows us that this student is honest, self-aware, and caring, which are all qualities admissions officer are looking for.
Essay 7: Health Crisis
Tears streamed down my face and my mind was paralyzed with fear. Sirens blared, but the silent panic in my own head was deafening. I was muted by shock. A few hours earlier, I had anticipated a vacation in Washington, D.C., but unexpectedly, I was rushing to the hospital behind an ambulance carrying my mother. As a fourteen-year-old from a single mother household, without a driver’s license, and seven hours from home, I was distraught over the prospect of losing the only parent I had. My fear turned into action as I made some of the bravest decisions of my life.
Three blood transfusions later, my mother’s condition was stable, but we were still states away from home, so I coordinated with my mother’s doctors in North Carolina to schedule the emergency operation that would save her life. Throughout her surgery, I anxiously awaited any word from her surgeon, but each time I asked, I was told that there had been another complication or delay. Relying on my faith and positive attitude, I remained optimistic that my mother would survive and that I could embrace new responsibilities.
My mother had been a source of strength for me, and now I would be strong for her through her long recovery ahead. As I started high school, everyone thought the crisis was over, but it had really just started to impact my life. My mother was often fatigued, so I assumed more responsibility, juggling family duties, school, athletics, and work. I made countless trips to the neighborhood pharmacy, cooked dinner, biked to the grocery store, supported my concerned sister, and provided the loving care my mother needed to recover. I didn’t know I was capable of such maturity and resourcefulness until it was called upon. Each day was a stage in my gradual transformation from dependence to relative independence.
Throughout my mother’s health crisis, I matured by learning to put others’ needs before my own. As I worried about my mother’s health, I took nothing for granted, cherished what I had, and used my daily activities as motivation to move forward. I now take ownership over small decisions such as scheduling daily appointments and managing my time but also over major decisions involving my future, including the college admissions process. Although I have become more independent, my mother and I are inseparably close, and the realization that I almost lost her affects me daily. Each morning, I wake up ten minutes early simply to eat breakfast with my mother and spend time with her before our busy days begin. I am aware of how quickly life can change. My mother remains a guiding force in my life, but the feeling of empowerment I discovered within myself is the ultimate form of my independence. Though I thought the summer before my freshman year would be a transition from middle school to high school, it was a transformation from childhood to adulthood.
This essay feels real and tells readers a lot about the writer. To start at the beginning, the intro is 10/10. It has drama, it has emotions, and it has the reader wanting more.
And, when you keep going, you get to learn a lot about a very resilient and mature student. Through sentences like “I made countless trips to the neighborhood pharmacy, cooked dinner, biked to the grocery store, supported my concerned sister, and provided the loving care my mother needed to recover” and “Relying on my faith and positive attitude, I remained optimistic that my mother would survive and that I could embrace new responsibilities,” the reader shows us that they are aware of their resilience and maturity, but are not arrogant about it. It is simply a fact that they have proven through their actions!
This essay makes us want to cheer for the writer, and they certainly seem like someone who would thrive in a more independent college environment.
Essay 8: Turned Tables
“You ruined my life!” After months of quiet anger, my brother finally confronted me. To my shame, I had been appallingly ignorant of his pain.
Despite being twins, Max and I are profoundly different. Having intellectual interests from a young age that, well, interested very few of my peers, I often felt out of step in comparison with my highly-social brother. Everything appeared to come effortlessly for Max and, while we share an extremely tight bond, his frequent time away with friends left me feeling more and more alone as we grew older.
When my parents learned about The Green Academy, we hoped it would be an opportunity for me to find not only an academically challenging environment, but also – perhaps more importantly – a community. This meant transferring the family from Drumfield to Kingston. And while there was concern about Max, we all believed that given his sociable nature, moving would be far less impactful on him than staying put might be on me.
As it turned out, Green Academy was everything I’d hoped for. I was ecstatic to discover a group of students with whom I shared interests and could truly engage. Preoccupied with new friends and a rigorous course load, I failed to notice that the tables had turned. Max, lost in the fray and grappling with how to make connections in his enormous new high school, had become withdrawn and lonely. It took me until Christmas time – and a massive argument – to recognize how difficult the transition had been for my brother, let alone that he blamed me for it.
Through my own journey of searching for academic peers, in addition to coming out as gay when I was 12, I had developed deep empathy for those who had trouble fitting in. It was a pain I knew well and could easily relate to. Yet after Max’s outburst, my first response was to protest that our parents – not I – had chosen to move us here. In my heart, though, I knew that regardless of who had made the decision, we ended up in Kingston for my benefit. I was ashamed that, while I saw myself as genuinely compassionate, I had been oblivious to the heartache of the person closest to me. I could no longer ignore it – and I didn’t want to.
We stayed up half the night talking, and the conversation took an unexpected turn. Max opened up and shared that it wasn’t just about the move. He told me how challenging school had always been for him, due to his dyslexia, and that the ever-present comparison to me had only deepened his pain.
We had been in parallel battles the whole time and, yet, I only saw that Max was in distress once he experienced problems with which I directly identified. I’d long thought Max had it so easy – all because he had friends. The truth was, he didn’t need to experience my personal brand of sorrow in order for me to relate – he had felt plenty of his own.
My failure to recognize Max’s suffering brought home for me the profound universality and diversity of personal struggle; everyone has insecurities, everyone has woes, and everyone – most certainly – has pain. I am acutely grateful for the conversations he and I shared around all of this, because I believe our relationship has been fundamentally strengthened by a deeper understanding of one another. Further, this experience has reinforced the value of constantly striving for deeper sensitivity to the hidden struggles of those around me. I won’t make the mistake again of assuming that the surface of someone’s life reflects their underlying story.
Here you can find a prime example that you don’t have to have fabulous imagery or flowery prose to write a successful essay. You just have to be clear and say something that matters. This essay is simple and beautiful. It almost feels like having a conversation with a friend and learning that they are an even better person than you already thought they were.
Through this narrative, readers learn a lot about the writer—where they’re from, what their family life is like, what their challenges were as a kid, and even their sexuality. We also learn a lot about their values—notably, the value they place on awareness, improvement, and consideration of others. Though they never explicitly state it (which is great because it is still crystal clear!), this student’s ending of “I won’t make the mistake again of assuming that the surface of someone’s life reflects their underlying story” shows that they are constantly striving for improvement and finding lessons anywhere they can get them in life.
Where to Get Your Overcoming Challenges Essays Edited
Do you want feedback on your Overcoming Challenges essays? After rereading your essays countless times, it can be difficult to evaluate your writing objectively. That’s why we created our free Peer Essay Review tool , where you can get a free review of your essay from another student. You can also improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
If you want a college admissions expert to review your essay, advisors on CollegeVine have helped students refine their writing and submit successful applications to top schools. Find the right advisor for you to improve your chances of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
Want to write a college essay that sets you apart? Three tips to give you a head start

1. Keep it real. It’s normal to want to make a good impression on the school of your choice, but it’s also important to show who you really are. So just be yourself! Compelling stories might not be perfectly linear or have a happy ending, and that’s OK. It’s best to be authentic instead of telling schools what you think they want to hear.
2. Be reflective . Think about how you’ve changed during high school. How have you grown and improved? What makes you feel ready for college, and how do you hope to contribute to the campus community and society at large?
3. Look to the future. Consider your reasons for attending college. What do you hope to gain from your education? What about college excites you the most, and what would you like to do after you graduate? Answering these questions will not only give colleges insight into the kind of student you’ll be, but it will also give you the personal insight you’ll need to choose the school that’s right for you.
Have questions about college prep? We're here to help.
Written by CU Boulder Office of Admissions
- College-Prep
The University of Colorado does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, pregnancy, disability, creed, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, veteran status, political affiliation, or political philosophy. All qualified individuals are encouraged to apply. You may view the list of ADA and Title IX coordinators and review the Regent policy .
As a student or prospective student at CU Boulder, you have a right to certain information pertaining to financial aid programs, the Clery Act, crime and safety, graduation rates, athletics and other general information such as the costs associated with attending CU Boulder. To view this information visit colorado.edu/your-right-know .
Apply for Admission
Visit Campus
Support CU Boulder
- Safety & Health Services
- COVID-19 Information
- Campus Communications
- Emergency Alert System
- New Student & Family Programs
Getting Around
- Campus Events
- Parking & Transportation
- Visit Information
Information for
- Faculty & Staff
- Journalists
Initiatives
- Business & Industry Collaborations
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Free Speech
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship
- Public & Outreach Programs
- Sustainability
- Understanding Your Cost of Attendance
Essays About Challenges: Top 11 Examples and Prompts
We come across many challenges we must endure throughout life. If you want to write essays about challenges, start by reading some of our top essay examples.
Everyone has had to deal with obstacles or challenges at some point. Some people can overcome hurdles with confidence and bravery, while many others have difficulty trying to face them. However, the challenges we have faced are, without a doubt, a central part of who we are today. Overcoming challenges can make you a better person. The lessons you learn from them are essential for future success, and as with all other experiences, these challenges help form you into the person you are today. They can also be exciting to some, as they test your skills and capabilities.
If you are writing essays about challenges, look at our featured essay examples below.
1. Personal Challenges by Delores Goodwin
2. life’s struggles make us stronger – and happier – if we let them by helen g. rousseau, 3. how to overcome your challenges with openness and courage by tony fahkry.
- 4. Life: full of challenges by Vaibhav Jain
5. Challenges Facing Public Schools by Lewis Rios
1. challenges i have faced, 2. lessons learned from challenges, 3. how to change your attitude towards challenge, 4. helping others overcome challenges and adversity, 5. challenges faced in your home country, 6. challenges the world currently faces.
| IMAGE | PRODUCT | |
|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | ||
| ProWritingAid |
“A challenge will tell an individual more about themselves than anything else in life. Am I a quitter? How much adversity can I take? How badly do I want this? What is my breaking point? Where does my loyalty end? Challenge can ask us hundreds of questions and forces us to answer honestly. Challenges end the talk and make one walk the walk. Create challenges for yourself, it will cause you to see who you really are.”
Challenges are a necessity of life despite the hardship and stress they come with, and Goodwin discusses this in her essay. A great accomplishment cannot be made without a challenge. Without challenges, one becomes complacent, so we must keep facing challenges to keep us mentally and physically strong. Goodwin encourages readers to challenge themselves more to help them delve deeper into who they are. For more, check out these essays about life challenges .
“Every human being has been in this place at one time or another. Sometimes depression can make it more difficult to get away from the edge but any spark of light or encouragement should be used to seek help physically, emotionally or spiritually. When we face a crisis, it effects the all of who we are and thus must be met with our total beings.”
Rousseau reflects on overcoming adversity, recalling when she met with two former coworkers. They talked about their lives, families, and struggles during lunch. They could bond over their shared positive, confident mindset, allowing them to overcome challenges. Rousseau clarifies that if you put your mind to it, you can overcome anything and closes her essay with two of her poems about resilience.
“Instead of running away from your emotions, lean into them and experience them fully. This transforms your fears and anxiety into empowering emotions. Let go of what you believe life owes you. It owes you nothing since you are the expression of life. Rise to your challenges armed with courage and an open mind. Remain confident that your experiences are serving your personal growth.”
Fahkry explains how to face challenges without stress and suffering. He reminds us that, first of all, we have free will, so we do not have to feel the way we do if we put our minds to it. We cannot change our reality once it is already there, so feeling sad or angry for prolonged periods is useless. If we change our mindsets for the better, we can overcome all adversity. Our fear and anxiety can be turned into confidence, empowerment, and courage. Check out these essays about competition .
4. Life: full of challenges by Vaibhav Jain
“A person who has not encountered difficulties in life can never achieve success. Difficulties test the courage, patience, perseverance, and true character of a human being. Adversity and hardships make a person strong and ready to face the challenges of life with equanimity. There is no doubt that there can be no gain without pain. It is only when one toils and sweats it out that success is nourished and sustained.”
In his short essay, Jain writes about the wonders of life as well as its challenges. He likens life to a bed of roses, complete with painful thorns. In general, life is good, but adversity and challenges are prevalent. These two concepts seem different, but one cannot exist without the other. As with the previous essays, Jain explains that challenges make us stronger and help us feel successful and relieved: “there can be no gain without pain.” Without challenges, we take the better parts of life for granted; if we accept and overcome our struggles, we can live life to the fullest.
“In conclusion, public educational institutions experience many challenges ranging from budgetary constraints, student violence and low parental involvement. Much research needs to be done to establish why these problems exist in the first place and lasting solutions for these institutions.”
Rios’ essay explores challenges in an education system; he proposes research on the constraints of the U.S. public school system. Public schools face several economic and social challenges, such as insufficient funding and lack of parental involvement due to many students’ working-class backgrounds. Rios wishes for more research on these problems and possible solutions.
Writing Prompts On Essays about Challenges
In this essay, write about a challenge you previously encountered and how you dealt with it. Provide context by describing the events leading up to it, how it happened, and, most importantly, how you overcame it. Then, describe how you felt after- were you relieved, stressed, or tired? You can also discuss how this experience has affected you today.
Challenges can teach us a lot about life and the world. Reflect on a challenge you faced previously and what you learned from it, whether positive or negative. As with the previous prompt, feel free to include ways in which the lesson you learned affects you today.
How can you best handle the challenges you may face? Describe the ideal attitude one would need to overcome complex challenges. For example, what qualities would you need to have- courage, prudence, or sensibility? Regardless of what type of attitude you choose to write about, your essay will be substantive if you can adequately support your argument.

In your essay, you can write about a time you were able to help someone facing a challenge. Who did you help- a friend, family member, or someone else? Then, write about how you helped them, how it made you feel, and how it has impacted your life.
Research one particular challenge your country is facing today, whether that be an economic, social, or political issue. Discuss how this challenge occurred and what began the difficulties. If applicable, include multiple viewpoints on the issue and include information from credible sources. You can also propose possible solutions to this issue.
Humanity faces challenges on a massive scale, from a climate change crisis to possible third world war to a global pandemic. Choose one challenge the world faces today and write your essay about it. As with the previous prompt, write about the causes and responses to this challenge, and feel free to propose a solution.
Check out our guide packed full of transition words for essays .
ProWritingAid is one of our top grammar checkers. Find out why in this ProWritingAid review .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Writing Curriculum
Teach Writing With The New York Times: Our 2024-25 Curriculum
Our nine writing units are based on real-world features like reviews, photo essays, narratives, podcasts and more.

By The Learning Network
Please note: Fully updated versions of each unit, as well as all supporting materials, will be published before each related contest opens for submissions.
What can the news, features, essays, interviews, photos, videos, podcasts and graphics in The New York Times teach your students about composing for a real audience? So much, we hope, that the units we detail below are just a beginning.
Our writing curriculum is a road map for teachers as well as an invitation to students. For teachers, it organizes our offerings into nine units, each of which focuses on a different genre or type of composing that your students can find not just in The Times but also in all kinds of real-world sources.
For students, these units offer confirmation that they have something valuable to say, choices about how to say it and a global audience eager to listen. Promoting student voices has always been a pillar of our site, and through the opportunities for publication woven into each unit, we want to encourage students to go beyond simply consuming media to becoming creators themselves.
Though some of the units spotlight mediums like photography or podcasting, writing is at the heart of each one. All our units begin and end with written reflection and depend on writing throughout — to plan and organize, to outline and script, to summarize and process. Increasingly, Times journalists are composing in multimedia, weaving photos, illustrations, video and audio into their written reports. We’re inviting students to do the same.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
- Do Not Sell My Personal Info

- ⋅
Free WordPress AI Writing Assistant By Jetpack
Jetpack’s free AI writing assistant for WordPress improves content conciseness and readability while maintaining authenticity

Jetpack announced a free WordPress writing tool called Write Brief With AI that improves the clarity and conciseness of content. The AI writing assistant is based on an internal tool used at Automattic and is now available without limitations regardless of whether a user is subscribed to Jetpack AI Assistant or not.
Write Brief With AI Is Free
The new AI tool started as an internal writing tool used at Automattic, the company behind WordPress.com, Jetpack, WooCommerce, and other companies. They are now integrating as part of the Jetpack AI plugin. Although Jetpack AI is a premium plugin (with a limited free trial), the functionality and usage of Write Brief with AI is available to all users both free and paid.
What It Does
The new Jetpack AI writing tool does three important things that can improve engagement and the overall quality of the content.
- It measures the readability of the text.
- Flags long-winded sentences.
- Highlights words that convey uncertainty.
Importance Of Readability
Readability and a direct writing style are important for clearly expressing the content’s topic, which can indirectly benefit SEO, conversions, and engagement. This is because clarity and conciseness make the topic more evident and easily understood by search algorithms.
Why Removing Uncertainty Is Important
Regarding flagging words that sound uncertain, that has the effect of encouraging the writer to consider revisions that make the content more definitive and confident.
Here are examples of how confident writing improves content:
This sentence expresses uncertainty:
I think we should consider expanding our marketing efforts.
This improved version of the same sentence is more confident:
We should expand our marketing efforts.
This sentence is unconfident:
Maybe we should review the budget before making a decision.
This sentence is direct and definitive:
We should review the budget before making a decision.
The above examples show how improving directness and making sentences more decisive removes a level of ambiguity and makes them more understandable.
Will that help a web page rank better? Communicating without ambiguity makes it easy for search-related algorithms to understand content which in turn makes it easier to rank for the respective topic.
See also: The 10 Best AI Writers & Content Generators Compared
Embedded Within The WordPress Editor
The editor is located within the WordPress editor. Blocks must be enabled because it won’t work within the Classic Editor. Additionally, the functionality is turned off by default and has to be activated by toggling on within the AI Assistant Settings sidebar.
Should You Try Write Brief With AI?
If your site is already using blocks then it may be convenient to give the new writing assistant a try. The tool is focused on improving content according to best practices but not actually doing the writing itself. That’s a good use of AI because it preserves the authenticity of human authored content .
Download Jetpack and activate the free trial of the AI Assistant. Write Brief With AI is switched off by default, so toggle it on in the AI Assistant settings. While AI Assistant is limited in how many times it can be used, Write Brief With AI is in Beta and can be used without limitations.
Download Jetpack here:
Jetpack by Automattic
Learn More About Write Brief With AI
Read more at the official WordPress.com announcement:
Clearer Writing at Your Fingertips: Introducing Write Brief with AI (Beta)
Read the documentation on requirements, activation instructions and how to use it:
Create Better Content with Jetpack AI
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Velishchuk Yevhen
I have 25 years hands-on experience in SEO and have kept on top of the evolution of search every step ...
Subscribe To Our Newsletter.
Conquer your day with daily search marketing news.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Struggling with essay writing can stem from various issues such as lack of confidence, insufficient knowledge of the topic, poor writing skills, or even time management problems. Additionally, some students face difficulty due to anxiety or perfectionism, which can hinder their ability to start or complete an essay.
9. Isolation and Loneliness. Creative writing is a lonely profession, after all writers spend a lot of time alone with their ideas and words. However, this doesn't mean you shouldn't make time to socialize with friends and family and meet new people. Socializing is a skill.
While some excellent writers can produce great essays without much advance planning, the majority of struggling writers start writing without an effective plan for organization and structure. ... They may have difficulty with writing fluency and knowing how to effectively start a piece of writing without significant prompting. 7. Struggling ...
Here are 7 common challenges you may face while writing, plus action steps to overcome each one. 1. You're anxious or insecure about your writing. Writing requires courage in the obvious ways, like being brave enough to share your work with the world, send it to publishers and reviewers, or read it aloud.
1. Avoid trivial or common topics. While there aren't many hard-and-fast rules for choosing an essay topic, students should avoid overdone topics. These include: Working hard in a challenging class. Overcoming a sports injury. Moving schools or immigrating to the US. Tragedy (divorce, death, abuse)
Written expression disorder is a learning challenge that impacts writing. The formal diagnosis is "specific learning disorder with impairment in writing.". Schools might call it a learning disability in writing. This lifelong disorder makes it hard to express thoughts in writing. People might have great ideas.
So, when presented with a writing task, the following symptoms may hinder your progress: difficulty organizing tasks. difficulty sustaining attention. inattention to details. procrastination ...
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards. Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay. Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
Studies suggest that more than half of children with attention deficit disorder (ADHD or ADD) struggle with writing.These students may have an overflow of creative ideas, but often struggle when it comes to getting these ideas onto paper.. Children with ADHD have a hard time getting started — and following through — on writing assignments because they have difficulty picking essay topics ...
That's an added bonus with using simple and direct language—doing so allows you to set up your challenges in the first paragraph or two, so you can then move on and dedicate most of the essay to a) what you did about it and b) what you learned. So just tell us, with clear and direct language. 2. WITH A LITTLE HUMOR.
ADHD is a form of neurodivergence that can make writing more challenging for some students. ADHD traits can affect a student's ability to concentrate, meet deadlines, stay on task, and stay organized, impacting their writing skills. Keep reading to learn more about how ADHD can affect children's writing skills—and how appropriate ...
A willing, positive, and committed attitude, and taking the time each day to read text, practice writing, and produce written text with keyboarding on a mobile or desktop device can help students become increasingly more productive in generating prose. 5. Making Technology Tools Part of the Writing Process.
This research aims to investigate the difficulties in English essay writing and its factors. Framed in a narrative inquiry, 33 students and one lecturer volunteered to participate. Data were ...
Use the eight strategies below to help your child write more easily and successfully. ADHD students have difficulty narrowing down choices and making decisions. Help your child determine the focus of her response by asking her to dictate to you all the ideas she has that are related to the essay topic. Words or short phrases will do.
Abstract. Analyzing students' difficulties in writing essays is a valuable tool for educators to enhance their teaching methods, provide personalized support, and ultimately improve students ...
The #1 cliché in undergraduate writing in English classes is that "the author sends a message." ... people may "iron out their differences," may "drift apart," may find revising their essays "as easy as rolling off a log." ... Example of choppy effects: "This is the ultimate difficulty. It developed from the evasion of responsibility for ...
The purpose of the Overcoming Challenges essay is for schools to see how you might handle the difficulties of college. They want to know how you grow, evolve, and learn when you face adversity. For this topic, there are many clichés, such as getting a bad grade or losing a sports game, so be sure to steer clear of those and focus on a topic ...
A language problem may manifest itself in a child's writing as: poor vocabulary. awkward phrasing and unconventional grammar. inappropriate use of colloquial language. difficulty with sentence ...
Bulqiyah, S., et.al (Investigating writing difficulties in essay writing) strategy while writing (Bakry & Alsamadani, 2015). Consequently, they could not produce their ideas in well-written paragraphs or essays. Okpe & Onjewu (2017) pinpointed that acquiring essay writing skills may be the one of great
Writing the personal essay for your college application can be tough, but we're here to help. Sometimes the hardest part is just getting started, but the sooner you begin, the more time and thought you can put into an essay that stands out. Check out some tips: 1. Keep it real.
Abstract and Figures. This study is primarily designed for investigating the tertiary students' perspectives on the writing difficulties of essays. This study was conducted in explanatory ...
Each paragraph should start with an introduction and end with some sort of link to the next paragraph. Last paragraph: Conclusion, restates thesis and reiterate how your supporting details prove said thesis. This was just a brief overview let me know if you need any help and I'll try to get back to you. 1.
Goodwin encourages readers to challenge themselves more to help them delve deeper into who they are. For more, check out these essays about life challenges. 2. Life's struggles make us stronger - and happier - if we let them by Helen G. Rousseau. "Every human being has been in this place at one time or another.
If your class is writing essays of 600 words or longer, our unit Teach Narrative Writing With The New York Times links to dozens of free resources, including six lessons that use Times mentor ...
If it helps, leave a placeholder and start in the body of the essay, where the story truly takes off and you get to the things you most want to say. READ: 7 Deciding Factors in Law School Admissions
Sometimes, writing about poems here at CNN, I felt like a stealth poetry whisperer. But those of you who joined me in this space seemed to savor the whispering, writes Tess Taylor.
The new Jetpack AI writing tool does three important things that can improve engagement and the overall quality of the content. It measures the readability of the text. Flags long-winded sentences.
Essays Uplift in Annual Writing Center Contest. Written By: Judith Hansen. The experience is so satisfying that people who judge the Writing Center's annual writing contest routinely ask Dr. Mary Lutze to invite them to judge again. Each year, writing prompts ask students - students in any major, students who use the Writing Center or don ...
Essay Topics- In the CAPF Paper 2, 6 topics were given for the essay writing, out of which candidates have to attempt any 4. Here are the topics of Essay Writing asked in the UPSC CAPF Paper 2. Digital Economy: Opportunities and Challenges; Global Peace and National Defence Budget; Tribal Resistance to Colonial Rule; Importance of Tropical Rain ...