
- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life

PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?

Many people use the terms “PhD student” and “PhD candidate” interchangeably. However, these terms actually mean something quite different, including a different status level at universities.
We’re here to define the differences between a PhD candidate vs student, as well as other essential information, before you continue your educational journey.
Table of Contents
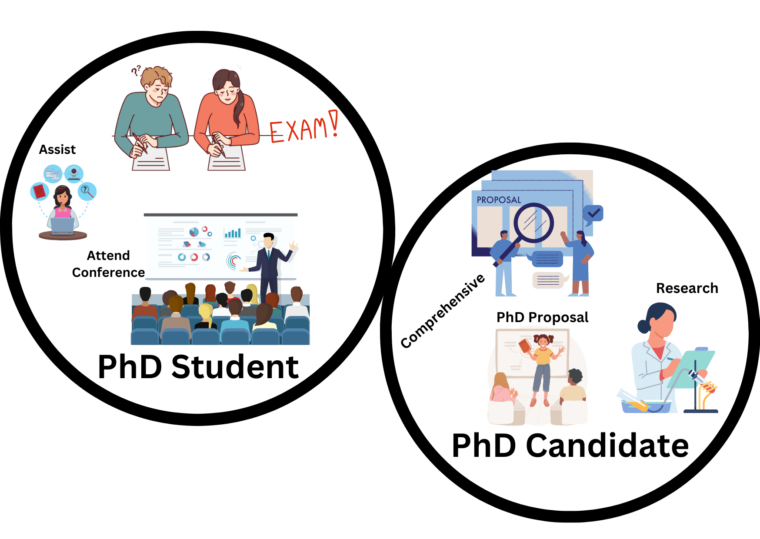
What I s a PhD student?
A doctoral student is anyone who is enrolled in a doctorate degree, also referred to as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. PhD students are typically required to complete a certain number of course credits and sit qualifying exams. Next, they can move on to conduct research and present it in the form of a dissertation.
A PhD is centered around self-directed research and possibly teaching/running tutorials, but they typically also involve a substantial amount of coursework and require attending classes, either online or in person.
Unlike candidates, PhD students are in the process of completing the required coursework for the degree. They haven’t passed the relevant qualifying exams yet.
What Is a PhD Candidate?
A PhD candidate has completed the required coursework and passed the qualifying exams for their doctorate program. They are currently working on their dissertation.
Most PhD students need to go through an application process and show they meet certain requirements such as a relevant master’s degree . To become a PhD candidate, doctoral students need to pass an internal application process, typically involving a set of exams.
This stage involves significant research usually in innovative areas and incorporating this into a dissertation (this stage is sometimes referred to as “all but dissertation” [ABD]), as they’ve completed all other aspects of the program and satisfied these requirements. To complete their doctoral journey, a PhD candidate must defend their dissertation. Once they’ve successfully done this, they will be awarded their degree and move from PhD candidate to doctor of their chosen field.
PhD Candidate vs Student: 6 Key Differences

There are a number of key differences between a PhD student vs PhD candidate, from their status to the structure and nature of study.
Note: Some universities have recently started adopting hybrid approaches (where there is no clear difference between PhD students and PhD candidates). These programs don’t involve any qualifying exams and students typically begin the dissertation as part of their coursework. Most schools, however, continue with the traditional distinction between a PhD candidate and PhD student.
1. Program Stage
A PhD student could be at any stage of the doctoral program . Coursework still needs to be completed and qualifying exams must be passed. Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research).
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it.
2. Research Progress
A PhD student may not have selected their research topic or settled on a particular research question. A candidate’s research is in progress and they should already have a clear research question.
3. Relationship with Advisors
A PhD student may not yet have an advisor. A candidate has an established working relationship with their advisor and works closely with them to complete their research and dissertation.
4. Level of Support
Although they work closely with an advisor, a PhD candidate is generally expected to work more independently than a student enrolled in a doctoral student. Once candidates reach this stage of their doctorate, they typically won’t receive as much direction or supervision.
5. Flexibility and Structure
Understandably, PhD candidates have more freedom and flexibility in their work. Most candidates choose their area of research, as well as the methods used to conduct their work. As part of their coursework, PhD students usually have to work within a set structure (e.g., completing core subjects, meeting deadlines).
Being a PhD candidate comes with a certain degree of status. If they’ve demonstrated a degree of expertise through completing qualifying exams, candidates can put the letters PhD(c) after their name.
Tips for PhD Candidates

A PhD is an advanced degree designed to demonstrate expertise in a given field, as well as high-level skills and abilities in various areas (including research and writing). As such, earning a doctorate can be a challenging process.
The following tips for doctoral candidates will help you put your best foot forward and set yourself up for success.
Stay Organized
Because PhD candidates have to balance many competing priorities, organization is essential. Using organizational tools such as calendars, note-taking apps , and project management software can help you keep track of deadlines and meet your targets.
Focus on Your Research
PhD candidates likely have busy schedules with plenty of demands (such as teaching commitments and crafting a dissertation). As it’s the backbone of any doctoral program, be sure to prioritize this part of your work and monitor progress to stay on track.
Actively Seek Out Feedback
Because PhD candidates often work independently, there’s a risk of feeling isolated. Ask your advisors, mentors, and fellow candidates for feedback and advice. This will help ensure that you’re considering all aspects of your research question and multiple solutions, rather than focusing too intensely on a single area.
Take Advantage of Networking Opportunities
Networking is one of the biggest benefits for PhD candidates, so take full advantage of these events. Use this time to build a strong network of professors, advisors, fellow candidates, and other professionals you meet at conferences and events.
Take Care of Yourself
A PhD program can be taxing, and it’s easy for your mental and physical health to take a backseat. Make sure you exercise, eat well, and get enough sleep . Remember: Resting and recharging is crucial for working on your dissertation.
How Long Is a Typical PhD Candidacy?

Most PhD students require 1-2 years to complete their coursework and pass their qualifying exams. However, the length of a PhD candidacy is much more open. In most cases, programs take between two and five years, depending on:
- the complexity of the field of research
- the candidate’s other commitments, such as teaching load
- other abilities, such as a candidate’s level of organization.
Once a PhD candidate has completed their dissertation, they have to defend it successfully before a panel of faculty members before they can earn their doctorate degree. This process of defending a PhD dissertation can take several months.
Some universities specify a maximum length for PhD candidacy duration. For example, Carnegie Mellon University limits this to six years .
Benefits of Being a PhD Candidate
Being a PhD candidate can be rewarding for several reasons:
1. Research Opportunities
You’ll be exposed to vast research opportunities in your field. You may contribute to valuable discoveries while developing advanced knowledge and skills.
2. Networking
Through your PhD candidacy, you’ll also be in a great position to build gain a stronger network of fellow professionals.
3. Critical Thinking
A PhD candidacy can help you develop high intellectual independence and critical thinking skills.
4. Career Opportunitie s
A PhD is an advanced degree that allows you to build a rewarding career in the academic, government, and private sectors. PhD-holders can also expect to earn more than other graduates and are most likely to find a job.
5. Salaries
According to Northeastern University , professionals with a doctorate degree earn an average annual salary of $99,290 on average (and much more for the highest-paid PhDs ) and have a 1.5% unemployment rate. For master’s degree holders, the average annual salary is $81,867 average annual salary and a 2.6% unemployment rate.
6. Personal Fulfillment
Being a PhD candidate can help you pursue your passions. This advanced qualification will allow you to become a specialist in your chosen field, allowing you to hone in on the exact subject thatl fulfills you the most.
Qualifying Exams to Become a PhD Candidate

While requirements vary by program, to become a PhD candidate, most students will need to pass a set of exams. These will test students’ knowledge in the field, measure their research skills, and ensure they’re ready to start their dissertation research.
Traditionally, qualifying exams for PhD candidates involved a written test and an oral exam. These will cover a range of topics related to your field of study, with the oral component designed to demonstrate your level of understanding.
Some universities have recently started to issue doctoral students with a set of questions and have them submit the answers within a set timeframe (usually around two weeks). Other schools ask prospective doctoral candidates to submit a dissertation proposal instead of an exam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a phd candidate be called a doctor.
In most cases, a doctoral candidate cannot be called a doctor until after they successfully defend their dissertation and receive their doctorate.
Can I Put ‘PhD Candidate’ after My Name?
Once you’ve passed qualifying exams and embarked on dissertation research, you’re technically entitled to put “PhD candidate” or “PhD (c)” after your name. However, this is uncommon and not always recommended. It is generally more acceptable to mention that you are pursuing a doctorate (along with the field of research and university) or that you expect to complete your PhD in a certain year (on your CV and online profiles).
How Long Can You Be a PhD Candidate?
There isn’t a set length of time that a person can be a PhD candidate. The length of candidacy depends on a range of factors, including the subject of research and program requirements. Most PhD candidates complete this phase in around 3-5 years (where some university programs have set limits).
Do PhD Students Take Classes?
Yes, most PhD students must take classes and complete coursework as part of the first 1-2 years of their doctorate program. Once they’ve completed this coursework and passed qualifying exams, they move on to work on their research dissertation. At this stage, they’ll be considered a PhD candidate.
Key Takeaways
Now that you know the differences between PhD candidates vs. students, you’ve got a deeper understanding of how to obtain a doctorate. However you slice it, both will help you build your knowledge and skills to become an expert in your field.
However the program is structured, a PhD is a highly valuable degree that allows you to become a high-level professional and build a successful career.
If you know a PhD candidate who’s celebrating their accomplishments soon? Take a look at this guide to the best PhD graduation gifts .
- 10 Best PhD Programs in Pennsylvania
- Top 10 Best PhD in Cybersecurity Online Programs
- 10 Top PhD Programs in Chemistry
- The Top 10 Easiest PhDs: Tuition, Duration, and Financial Aid
- Top 10 Fully Funded PhD Programs and Universities
- Top 10 Best PhD in Medicine Programs

Lisa Marlin
Lisa is a full-time writer specializing in career advice, further education, and personal development. She works from all over the world, and when not writing you'll find her hiking, practicing yoga, or enjoying a glass of Malbec.
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 12 Best Laptops for Computer Science Students
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ ACBSP Vs AACSB: Which Business Program Accreditations is Better?
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]
14 Cheap Spring Break Destinations for College Students in 2024
How to get a master’s without a bachelor’s: the complete guide, related posts.

- How Many Grad Schools Should I Apply To?
![what's the difference between phd candidate and student When to Apply for Grad School: The Simple Guide [2026/2027]](https://blog.thegradcafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/When-to-Apply-to-Grad-School-350x250.png)
- When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]

- 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024

- Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024

The Sassy Digital Assistant Revolutionizing Student Budgeting

Computer Science Graduate Admission Trends: Annual Results

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Last Mile Education Fund Paves the Way for Tech Students, Offers Lifeline Grants

© 2024 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
What is the Difference Between a PhD Candidate and a PhD Student?
Pursuing a doctoral degree is a significant academic achievement that requires years of dedicated study, research, and intellectual rigour. Within the realm of doctoral studies, the terms ‘PhD candidate’ and ‘PhD student’ are commonly used, often interchangeably. However, a closer examination reveals that there are nuanced differences between these two designations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for both prospective doctoral students and those seeking to comprehend the various stages of the doctoral journey.
In this article, we delve into the disparity between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, shedding light on the roles, responsibilities, and progression associated with each stage. We explore the specific criteria that differentiate a student from a candidate and the various milestones marking the transition. Additionally, we delve into the responsibilities and expectations that accompany each designation, illuminating the unique experiences and commitments faced by PhD candidates and students.
Furthermore, we acknowledge the variability in terminology across international boundaries, academic institutions, and disciplinary fields, providing insights into how different contexts might influence the usage of these terms. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the contrasting aspects between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, facilitating informed conversations and a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of doctoral education.
Introduction
Who is a phd student, when phd student attains status of phd candidate, variation in terminology.
Pursuing a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) degree involves conducting original research in a specific field of study, making a significant contribution to knowledge, and demonstrating a high level of expertise. It is the highest academic qualification one can attain and is highly valued in academia, research institutions, and certain industries. A PhD signifies a deep understanding of a subject area, advanced analytical and critical thinking skills, and the ability to conduct independent research.
While the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two.
A PhD student typically refers to an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program, actively engaging in coursework and other program requirements. They are in the early stages of their doctoral journey and are working towards completing the necessary academic components of their degree. On the other hand, a PhD candidate is typically someone who has progressed beyond the coursework stage and has advanced to the research phase of their program. They have usually completed comprehensive exams, passed a research proposal defense, and are actively engaged in independent research for their dissertation or thesis.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student. By exploring the criteria, milestones, and responsibilities associated with each designation, this article aims to clarify the unique experiences and progression of doctoral students. It also seeks to address the varying terminology used across different contexts and disciplines, enabling readers to grasp the intricacies of the doctoral journey and fostering informed discussions around this topic.
Through this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the journey from being a PhD student to becoming a PhD candidate and the distinct roles and responsibilities associated with each stage.
A PhD student is an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program and is actively engaged in pursuing their doctoral studies. They are at the initial stages of their doctoral journey, seeking to expand their knowledge, skills, and expertise in a specific field of study. PhD students play a vital role in academic research communities as they contribute to the generation of new knowledge and the advancement of their discipline.
PhD students are required to complete a set of coursework specific to their field of study. These courses are designed to provide a foundation in the discipline, enhance research skills, and broaden the student’s understanding of relevant theories and methodologies. Coursework may include seminars, advanced classes, and specialized topics. The specific coursework requirements can vary between programs and disciplines.
Example: Imagine a student named Alex who has just been accepted into a doctoral program in psychology. At this stage, Alex is considered a PhD student as they begin taking relevant coursework, attending seminars, and collaborating with faculty members. They are laying the foundation for their research and acquiring the necessary knowledge in their field.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
Advancement from being a PhD student to a PhD candidate typically involves meeting specific requirements set by the doctoral program. These requirements may vary depending on the institution and field of study but often include successful completion of coursework, exams, and other program-specific milestones.
One of the primary requirements for transitioning to a PhD candidate is the successful completion of coursework and exams. PhD students are expected to complete a designated set of courses, which provide a broad understanding of their field and research methodologies. They are also required to pass comprehensive exams, which assess their comprehensive knowledge and understanding of their research area.
As part of the transition to becoming a PhD candidate, students typically prepare and defend a research proposal. The research proposal outlines the scope, objectives, methodology, and significance of the intended research. The proposal defense may involve presenting the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who evaluate its feasibility, rigour, and contribution to the field. Additionally, PhD students often have to pass comprehensive exams, which test their knowledge of their research area and related disciplines.
If you are not familiar with writing PhD proposal and making PhD proposal presentation, then visit my articles on “ How to Write PhD Proposal Presentation to the University ” and ” How to Make a PhD Proposal Presentation to the University Panel” . These articles will guide you through the process of preparation and presentation of PhD proposal to the University panel.
Upon successful completion of the requirements, PhD students are often granted candidacy status. Advancement to candidacy signifies that the student has demonstrated the necessary knowledge, skills, and potential to conduct independent research and contribute to their field. This status allows students to focus more exclusively on their research and dissertation work.
Once students become PhD candidates, there is a shift towards an increased emphasis on independent research. They are expected to dedicate a significant portion of their time and effort to conducting original research, collecting data, analyzing results, and making novel contributions to their field. The focus is primarily on their dissertation or thesis work, which serves as the culmination of their doctoral studies.
Example: Let’s consider a PhD student named Alex in the field of computer science. After completing their coursework and passing comprehensive exams, Alex develops a research proposal outlining their intention to investigate the applications of machine learning in cybersecurity. They present the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who assess the feasibility and potential impact of the research.
Alex successfully defends their research proposal and is granted candidacy status, transitioning from a PhD student to a PhD candidate. With candidacy status, Alex’s focus shifts towards conducting independent research. They spend considerable time collecting and analyzing cybersecurity datasets, developing and refining machine learning algorithms, and testing their effectiveness in detecting and preventing cyber threats.
As a PhD candidate, Alex works closely with their advisor, regularly discussing research progress, seeking guidance, and receiving feedback. They collaborate with other researchers in the field, attend conferences to present their findings and contribute to the scholarly community through publications. The focus is now on producing an original and significant contribution to the field of computer science through their dissertation.
The transition to PhD candidacy marks a critical stage in the doctoral journey, as it signifies the ability to independently drive research and make scholarly contributions. PhD candidates like Alex are immersed in the world of research, expanding knowledge, and pushing the boundaries of their field.
Terminology related to PhD candidates and PhD students can vary internationally and among different academic institutions. In some countries, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” may be used interchangeably, while in others, there may be specific distinctions. For example, in the United States, “PhD student” is commonly used, while in the United Kingdom, “PhD candidate” is more frequently employed. Additionally, different universities or institutions may have their own terminology preferences, which can create further variation.
Terminology can also vary based on the disciplinary field of study. Different academic disciplines have their own conventions and terminology for referring to individuals pursuing a doctoral degree. For instance, in the sciences, one might encounter terms like “graduate researcher” or “doctoral candidate.” In the humanities and social sciences, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used. This variation reflects the specific linguistic and cultural norms within different academic domains.
In Canada, for instance, doctoral students are commonly referred to as “PhD candidates,” regardless of their stage in the program. In Australia, “PhD candidate” is the preferred term for those who have completed the required coursework and have advanced to the research phase. In contrast, in the United States, “PhD student” is frequently used to refer to individuals at all stages of their doctoral studies.
Disciplinary variations can also be observed. In engineering, individuals pursuing a doctoral degree are often referred to as “PhD students” or “doctoral students.” In contrast, in the field of education, the term “PhD candidate” is commonly used to denote those who have advanced to the research and dissertation stage.
It is important to note that these examples represent general trends, and there can still be variation within specific institutions and programs. The usage of terminology can evolve over time and may be influenced by regional or institutional preferences.
The distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student holds significant importance in the realm of doctoral education.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different stages and responsibilities within the doctoral journey. A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements.
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Best 5 Journals for Quick Review and High Impact in August 2024
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
The difference between doctoral students and doctoral candidates
This article was updated on January 2, 2024.

By Brian Fairbanks

In this article
Doctoral candidate vs. doctoral student, phd vs. practitioner doctorate.
- Explore online doctorate programs
Many people who earn a doctoral degree will, at some point, be both a doctoral student and doctoral candidate. While these roles may seem mysterious from outside the (real or virtual) halls of academia, the distinction is fairly simple.
Before we cover the distinction, however, let’s get on the same page about doctoral degrees.
What is a doctoral degree?
In academia, one degree sits at the very top: the doctoral degree. Also referred to as a doctorate, a doctoral degree is the most advanced educational credential you can earn. Though some fields of study (like journalism) don’t have a doctoral degree, most typical academic fields do, as do the fields of health, medicine, law, education and business.
Doctoral programs can lead to a PhD in a variety of fields, such as literature, philosophy and history, or a practitioner doctorate in a field like business, health administration, nursing or education. Doctoral degrees involve years of intensive study, and many require a book-length dissertation. However, practitioner doctorates have different requirements and may not entail a dissertation.
Requirements of a doctoral program
Before graduate school, you must complete years of university courses, typically two degrees, before a program will consider admitting you. However, some programs have more lenient requirements than others.
Doctoral programs tend to be intentionally difficult and rigorous courses of study. As mentioned, there are several educational levels before a doctoral degree that both students and candidates will need to pass.
The requirements for a doctoral student include:
- Prerequisite degrees: Doctoral programs usually require that students obtain a bachelor’s and a master’s degree first.
- Required coursework: Each program requires different courses, but most will be in the student’s area of study, with some focused on adjacent or complementary subjects. Additionally, foundational coursework prepares students to learn about the research process.
- Qualifying exams: Typically, students must pass qualifying exams to enter doctoral programs, but not all programs require entrance exams.
If a dissertation is part of the doctoral program, the doctoral candidate must:
- Select a dissertation advisor or committee: During your time as a doctoral student, you will come into contact with many instructors. You will typically only interact with the instructors who are your dissertation advisor or on your dissertation committee. The committee is the audience for the doctoral candidate and ensures the candidate demonstrates command of the literature and methodologies relative to their field.
- Choose your dissertation topic: This is a pivotal point in your journey to earning a PhD or doctorate. Many programs ask for a general topic as part of your initial application. Your advisors will help you to create a specific and unique dissertation topic that will fuel your work over the next several years.
- Write the dissertation: Your dissertation or thesis will normally take a couple of years to write and will be a book-length culmination of your learning and research.
- Defend your dissertation or thesis: After you submit your final draft to your dissertation committee, you will need to orally present your work to the committee, answer questions and defend your work.
The requirements for a doctorate take many years to complete. While some people complete doctoral degrees in three to five years, others take seven to 10 years. The time span depends on your specific area of study, whether you take classes on a full-time or part-time schedule and how long it takes to complete your dissertation. This also includes your level of focus and intent.
If you are interested in earning your doctorate, then it is important to understand the difference between being a doctoral candidate and a doctoral student.
What is a doctoral student?
A doctoral student is a person currently enrolled in a doctoral program at a university. Being a doctoral student involves completing a certain number of credits and coursework in an area of study and completing and passing several exams.
After students pass the qualifying exams (if the program requires it) and successfully complete required coursework, they become doctoral candidates.
What is a doctoral candidate?
A doctoral candidate leaves behind the structured learning schedule of a student. No longer does the candidate attend regular classes or take exams. Instead, they embark on a self-guided schedule for writing a dissertation. This culminates their studies and is tailored to their unique and individual areas of interest.
Doctoral candidates work closely with the advisors who make up their dissertation committee. The advisors provide guidance and critiques as the candidate writes a book-length dissertation. While the advisors can help along the way, what sets the candidate apart from the student is that, rather than simply learning what others have already discovered, they are conducting and writing about their own original, approved research — and then demonstrating what they’ve learned, as well as how it fits in the broader field of study or can be applied to tangible problems.
The meaning of candidacy in other doctoral programs
A PhD is not the only type of doctoral degree. There are also practitioner or professional doctorates, which may take the specific shape of medical doctorates, optometry doctorates, audiology doctorates, chiropractic doctorates, juris doctorates and others.
Such programs have their own conventions and terminology for various milestones. Some doctoral degrees, such as for law or medicine, focus on mastering the practice of a specific subject and the skills associated with that practice. As a result, terms such as candidate are not used universally among doctoral programs, and many of these programs do not include a dissertation.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is a doctoral degree that is focused on expanding and enriching an area of research. A PhD student typically focuses on developing new and original knowledge based on theory.
In contrast, a practitioner doctorate prepares students for leadership roles in their desired profession by applying existing knowledge to solve problems in their field or community. The practitioner doctorate generally involves rigorous curriculum, culminating in a dissertation or applied project that addresses a particular real-world problem.
Requirements of a practitioner doctorate and many practitioner programs
The requirements of a particular practitioner doctorate will vary according to the institution and the field of study. This makes sense when you consider that practitioner doctorates vary from juris doctorates to doctors of physical therapy.
While there may be similar experiences involved in the course of study, such as residencies or internships, the requirements are unique to the specific degree.
Doctorates at University of Phoenix
While University of Phoenix (UOPX) does not have PhD programs, we do offer several online doctorates. Students might choose the UOPX programs because classes are flexible and offered online, and because of our unique “ Scholar-Practitioner-Leader model .”
Our doctoral programs are:
- Doctor of Business Administration : Gain the strategic vision and skills to position yourself as a business leader. This program teaches skills such as how to solve organizational problems, design and conduct research studies, introduce innovative business ideas to the industry and more.
- Doctor of Management : This program equips you with critical thinking skills to find creative solutions to complex problems, so you can bring out the best of your leadership skills.
- Doctor of Education : Learn how to use analytical, critical and innovative thinking to improve performance and solve complex problems in education.
- Doctor of Health Administration : If you’re a health professional who is seeking greater responsibility in shaping the future of the health sector, the Doctor of Health Administration can help you get there. You’ll study the challenges inherent to today’s healthcare landscape, including economic fluctuations, burgeoning patient needs and industry-changing legislation.
- Doctor of Nursing Practice : This program is designed for working nurses who require a doctorate for advanced practice or nurses who desire their terminal degree. It does not prepare students for professional certification or state licensure as a nurse or as an advanced practice nurse.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Brian Fairbanks is a freelance writer with a background in SEO content creation and blog article development
This article has been vetted by University of Phoenix's editorial advisory committee. Read more about our editorial process.
Read more articles like this:

3 Ways to Jump-Start Your Doctoral Experience
University life.
September 28, 2022 • 5 Minutes

Doctoral Student vs. Candidate Comparison
April 26, 2023 • 7 minutes

UOPX Faculty Julie M. Ballaro
September 01, 2021 • 4 minute read

PhD Student vs. PhD Candidate

How I use gentle, digital nudges to stay current in the post-exams world
July 6, 2017 | Alison L.
Do you know the difference between a PhD student and a Ph.D. candidate?
A candidate is someone who has fulfilled all the requirements for the degree except the dissertation.
I’m a historian (see my earlier post about being a humanist at MIT ), so my path to candidacy differs a bit from other doctoral tracks at MIT. But whatever the discipline, the transition from student to candidate is an arduous process.
My department’s requirements involved: completing two years of coursework; demonstrating proficiency in a research language other than English; submitting at least one grant application; writing and revising a dissertation proposal that the dissertation committee must approve; and, most grueling of all, passing qualifying exams.
I became a candidate on November 24, 2015, after a weeklong examination period that involved three separate seven-hour written exam and a two-hour oral examination during which our committee members can grill us on anything they please.
I felt prepared for the written exams, which were open note, because I’d done nothing but read, take notes, and revise for the four months leading up to the exams.
But I lost sleep (at a time when I really couldn’t afford to be losing sleep) fretting about the oral exam. I shouldn’t have worried as much as I did. While there were a couple moments of panic—like when I blanked on the two ecozones separated by Wallace’s line—I survived “quals.”
So, what do you do once you become a candidate?
First, you take a break. I gave myself a little over a month to relax. I worked on lower-stakes projects, read fiction, attended departmental lectures, caught up with colleagues. I enjoyed the holidays at home in Chicago.
But once the New Year rolled around, a new sense of panic set in. Without the motivating pressure of exams to keep me working at a breakneck pace, how would I ever stay up-to-date in my fields? This anxiety, I’m willing to guess, is one shared by almost all academics.
While I’m actually more interested in how others have handled this pressure—comment away please!—I wanted to share a few tips I’ve picked up for keeping au courant .
1. Sign up for eTOCs That acronym stands for email Table of Contents alerts. Most journal publishers have a system that allows you to receive emails detailing the contents of their most recent releases. Sign up for a few of these and you’ll receive quarterly reminders that make it easier to stay on top of developments in the literature.
For some fields, it might not be necessary to read entire journals. In that case, pick some keywords and set up a bunch of Google Scholar alerts. Talk to your advisors and peers to see what works best in your discipline.
2. Make social media work for you Choose one social media platform and turn it into a research tool. My platform of choice is Twitter. You might be surprised by the number of scholars and professional associations that use social media. I rarely tweet myself, but I check Twitter at least once each day to find links to interesting articles, news about gatherings in my field, and to follow the work of scholars I admire. In addition to yielding worthwhile information, my Twitter sessions have the added benefit of tricking my brain into thinking it’s taking a break from work.
If you’re wondering how to curate your Twitter feed, first take a look at papers you’ve written for classes or published. See if the scholars that you cite in your own work are on Twitter and go from there. This is the most casual form of networking, but especially for introverts (like myself) these social media e-introductions facilitate in-person conference meetings, which can lead to future collaborations.
3. Listservs make life easier Most people at MIT know about the free food listserv. I’m not a member because I don’t need that kind of temptation in my life. Still, I’m a big fan of using listservs to join intellectual communities. In addition to the handful of MIT-based lists that tell me about upcoming lectures and workshops here on campus, I receive emails from communities at other Cambridge- and Boston-based schools. I’m also on a few listservs for universities in other cities. Even if I’m never able to attend those events, I know who is working on what where. If academia is about staying in the know, listservs help you do that.
I’ve written this from the perspective of a PhD candidate who needed gentle, digital nudges to stay current in the post-exams world, but I hope they prove useful for students, candidates, and beyond. Now comes the important question: What are your strategies for staying up-to-date?
Share this post:
This site uses cookies to give you the best possible experience. By browsing our website, you agree to our use of cookies.
If you require further information, please visit the Privacy Policy page.
Find A Degree

Ph.D. Student vs. Ph.D. Candidate: The Differences
Phd program rankings.
- Fully Funded PhDs in Education
- Doctor of Nursing Education
- Ph.D.: No Application Fees
- No-GRE Online Ph.D. in Psychology
- No-GRE Online Ph.D. Programs
- Fast Online Doctoral (Ph.D. and Ed.D.)
- The Most Affordable Online DBA
- Doctorate in Public Policy/Administration
- Doctor of ABA
- Transitional Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT)
- Doctorate in Marketing
- ALL Ph.D. Degree Program Rankings
Career Guides
- Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine
- Aerospace Engineering
- Behavioral Health (D.B.H.)
- Chemical Engineering (PhD CE)
- Chemistry (D.Chem.)
- Clinical Nutrition (D.C.N.)
- Speech-Language Pathology (CScD)
- Criminology (D.Crim.)
- Economics (DEc)
- Health Science (D.H.S./D.H.Sci)
- Library Science (D.L.S.)
- Molecular Biology (Phd Mol Biol)
- Occupational Safety and Health (D.O.S.H.)
- Physics (Ph.D. Physics)
- ALL PhD Career Guides
Valuable Resources
- Best Laptops for Ph.D. Students
- Gift Ideas for Ph.D. Students
- Burnout & Chronic Stress
- The Key to Free Grad School
- Ph.D. Guide for International and Domestic Students
- Habits Of Highly Effective Leaders
- Online Doctorate Reputation
- Journals for Ph.D. Students
- Earning a PhD
- Write a Perfect Essay Like a PhD
- Master’s Degree As a Bridge To Ph.D.
- Self-Funding Your PhD
- Importance of Accreditation
- Online Ph.D. Support Groups
- Getting Accepted to an Online Ph.D.
- Common Fears of Ph.D. Students
- Habits of Successful People
- US Doctoral Degrees
- ALL VALUABLE RESOURCES
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why earn a Doctorate Degree?
- What are the Ph.D. Admission Requirements?
- How Much Does a Ph.D. Cost?
- How many years will it take for me to achieve my doctorate degree online?
- Do online doctorate degree programs require campus visits?
- Ph.D. vs. Doctorate
- ALL FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
- Highest-Paying Doctoral Degrees
- Famous Ph.D. Theses In History
- Struggles Only a Ph.D. Student Would Understand
- Ph.D. Requiring Residencies
- The World’s Richest Doctors
- Academic Conferences
- Most Popular PhD Degrees
- ALL Ph.D. Highlights
Are you ready to become a Ph.D Candidate? An advanced academic or professional degree, Ph.D. is short for Doctor of Philosophy. It is a postgraduate degree awarded by accredited universities and higher education institutions after completing all of the degree requirements.
A Ph.D. degree or a doctorate or doctoral degree is globally recognized as the highest level of academic degree and presupposes the completion of an original dissertation or research.

A traditional doctorate follows a three- to four-year degree, but some institutions offer opportunities to fast-track the degree, subject to stringent requirements.
After completing your proposal, you need to impress a panel of experts in an oral defense to prove the necessity of your research. When you have defended your thesis successfully, you can move forward with writing your dissertation.
Let’s set the record straight as we define what a Ph.D. student and a Ph.D. candidate is, and find out their similarities and differences! Use these quick links to easily navigate the questions:
Why pursue a Ph.D.?
Will a ph.d. degree give me an advantage career-wise, i am not a professor nor an instructor, should i still get a ph.d., what are the basic requirements for one to become a ph.d. student, who is a ph.d. student, how long does it take for a ph.d. student to qualify as a ph.d. candidate, do i need to write a full dissertation as a ph.d. student, what are the requirements that i need to comply with for me to become a ph.d. candidate, who is a ph.d. candidate, what must i do after qualifying as a ph.d. candidate, can i now include a ph.d. in my credentials, how long does it take to finish my ph.d., i am a working professional. is there a ph.d. program designed for me, can i complete my ph.d. degree fully online.
If you are a working professional who’s in college or a typical college student thinking of advancing your academic credentials, pursuing a Ph.D. may be a wise choice!
Among the many reasons why students pursue a Ph.D. is for long-term degree goals, which ultimately lead to a career in academia. A Ph.D. is considered an essential qualification for anyone who intends to teach in the university as an instructor or professor.
While those who wish to engage in research, throughout your Ph.D., you will be allowed to conduct your research. You can make important discoveries that will bring a positive impact within your field.
Based on the data posted by the McKinsey Global Institute , we face a shortage of scientists in the world. As the global economy moves toward a more innovative approach, demand for Ph.D. degree holders will increase significantly. Most importantly, once you decide to enroll in a Ph.D. program, you will gain unparalleled analytical and research skills that will become your footstool as you move up in your career ladder.
Yes, having a Ph.D. will give you a competitive advantage . Once you complete your Ph.D. degree, you will become part of the rare commodity of people who holds an advanced degree.
The U.S. Census Bureau discloses that in 2019, only 4.5% of the American population completed a doctorate. With these statistics in mind, you will have a more competitive academic credential than 95.5% of the country.
It is worth noting that since the year 2000, this percentage has doubled. Now, it is estimated that 13.1% of American adults have obtained an advanced degree. This is a drastic increase from only 8.6% in 2000, which translates to 4.5 million Ph.D. degree holders in the United States.
Having a doctorate has a significant advantage. Doctorate holders are capable of generating new data and information that fills the gap in the body of knowledge in the field. Being trained professionals who are highly skilled in critical thinking, decision-making, and complex problem-solving are the top three skills that separate a Ph.D. degree holder from other professionals.
The Bureau of Labor and Statistics discloses that Ph.D. degree holders receive higher earnings and lower unemployment rates than bachelor’s or master’s degree holders.

Academia is a glorious field, but the belief that a Ph.D. only prepares you for academia is a myth . Professors and instructors play an equally important role in the lives of their students as they charge towards achieving their academic goals.
If you want to earn tenure as a professor in a top-tier college or university, having a Ph.D. will significantly increase your odds of securing a position. However, even if you are not a member of academia, pursuing a Ph.D. degree is still a great investment that you should seriously consider.
If you have a passion for research, you can choose to become a scholar, if not a professor. Research is central to the pursuit of an advanced degree, especially a Ph.D. Doctorate holders who do not teach in a university or higher education institutions can focus on doing research. Researchers publish peer-reviewed papers that reach students, professors, and fellow researchers who share the same interest in their specific field.
Choosing a research-focused career over a tenured teaching job allows you to pursue intellectual interests outside the academe. With a chance to apply and win research grants, you will have the resources to do extraordinary things in your field.
Admission requirements may differ from one institution to another. Your admission to any of the Ph.D. programs will depend on your academic records, both at the bachelor’s and master’s levels. Most importantly, the admissions officer will evaluate your potential research capabilities.
In the United States, universities and higher academic institutions require that applicants hold an honors degree or a master’s degree equivalent. Aside from this, having high academic standing will increase your chances of getting into the top research institutions in the country.
The admissions office will also assess an applicant’s bachelor’s degree, and graduating at the top of your class will also boost your chances. But some institutions assess applications solely based on your master’s degree academic record.
Funding for your research may also be a deciding factor on your admission. If you depend on study or research grants and loans, you need to have an exceptional academic track record to impress the admission office. But, if you are self-funded, you may have a competitive advantage over other applicants who are dependent on grants.
You also need to find a tenured professor to serve as your advisor while you complete your Ph.D. before your chosen institution may admit you to the program.
Below are the standard requirements for admission:
- Transcript of records of both your undergraduate and graduate degrees
- Resume or curriculum vitae
- Recent Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) or Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) scores
- Letters of recommendation from your peers and mentors
- Statement of purpose
After successfully complying with the admission requirements of the Ph.D. program, you are now officially a Ph.D. student. You will begin your academic journey towards completing a three- or four-year research program. Postgraduate academic institutions serve as fertile research environments that breed future scientists and experts in different fields of study.
Ph.D. students are introduced to the world of independent research. Students study under the close supervision of an academic supervisor or advisor who has a tenured position as an associate professor or higher. As Ph.D. students, collaboration with your advisor is central to developing a valuable addition to the pool of literature in a given subject.

While in graduate school, your main focus is authoring original research, which involves data analysis and evaluation. Depending on your program and department, you may be given the leeway to formulate your area for your research.
However, there are Ph.D. programs that present their students with a selection of research proposals for you to choose from. These proposals are often formulated and peer-reviewed by program supervisors.
You can complete your proposal at a certain term, or year-round, depending on your university or academic institution. Ph.D. students are required to submit a statement or a proposal to be submitted at the end of the term. This will usually take up the first two years of your journey towards your doctor of philosophy degree.
Writing original research is, arguably, the ultimate goal of hundreds of thousands of Ph.D. students. This requirement may vary from one institution to another, or even between subjects.
A doctoral program develops a student’s field of specialty to sharpen their skills to advance their position in their industry. Some doctorate programs require students to attend classes and take examinations, while some require Ph.D. students to handle a teaching load or serve as research assistants.
In the early phases of your doctoral study, you will focus on your chosen field of study. Eventually, you will dive deeper into enhancing your understanding of your specialization to better prepare you for writing your dissertation. At this point, you will start writing your proposal in preparation for your oral defense before a panel of esteemed specialists in your field.
During the final years of graduate school, your dissertation should be your priority. This way, you can move forward with your degree and become a Ph.D. Candidate.
Becoming a Ph.D. candidate from being a Ph.D. student will take time, even more so, your utmost dedication. Before you can be considered a Ph.D. Candidate, you need to submit a minimum of twenty- to thirty-page paper at the end of your first year in graduate school.
Second, you must have completed at least two years of full-time coursework. You will also be asked to show how proficient you are in the research language. In some programs, you need to submit a grant application.
Then, you need to have a draft of your dissertation prospectus. At this point, your prospectus must include your literature review and methodology.
Most importantly, you need to successfully defend your proposal before a committee or panel of experts. Once the committee approves your proposal and you pass the qualifying exams, you can now refer to yourself as a Ph.D. candidate.
After getting approval for your dissertation proposal or prospectus from the panel, you can now refer to yourself as a Ph.D. candidate. This means you get the green light to start writing your dissertation. As a Ph.D. candidate, you can use Ph.D.(c) as part of your credentials.
It signifies that you have now advanced to candidacy. You have reached the final years of your doctoral study, which will be crucial in the trajectory of your academic career.
Aside from having to defend your proposal, some institutions also require Ph.D. candidates to pass a weeklong examination. This often involves three separate written exams that may last for seven hours. You must also pass an oral examination. In this exam, your supervisor, your advisor, and a panel can ask you questions that are related to your discipline.

Now that you are a Ph.D. candidate, you can now start working on your dissertation, but before you begin working, you should take a well-deserved rest.
Having reached your candidacy means you have finished your doctoral studies and can now focus on your research. Writing a research paper entails that you are knowledgeable in your chosen subject.
Reading related literature will better equip you in identifying the gaps in the literature. This way, you may be able to add new knowledge to the subject and through testing your hypothesis and gathering relevant data for your research. Data collection is one of the most critical parts of research, and the viability of your study depends on it.
Moving forward, the data you have collected needs to be processed or analyzed for you to draw up a conclusion. The entire process of writing your dissertation is tedious, so you need patience, dedication, and a passion for research.
As a Ph.D. candidate, you can now use a Ph.D.(c) as part of your credentials. It signifies that you have completed all of your coursework and have now advanced to candidacy.
The (c) means you are currently working on your dissertation. However, including this title in your credentials is inappropriate, even wrong. This designation is very often misused that it has become common among candidates.
First, because a candidacy does not equate to a degree, it is not a credential or a status that is awarded by any university, college, or higher education institution. Also, you can be a candidate for a considerably long time. Unfortunately, some Ph.D. candidates never comply with the dissertation requirement and progress to earning their Ph.D. degree.
In the world of postgraduate studies, they are called Ph.D., ABD, or “all but dissertation.” Unfortunately, according to the Council of Graduate Schools , 56.6% of Ph.D. students complete the program, and the rest either drop out of graduate school or end up as Ph.D., ABD.
The answer to this will depend on the path or subject you choose.
In 2017, the median completion period for completion of a doctorate program was 5.8 years according to the Survey of Earned Doctorates. Typically, a Ph.D. degree will take four to six years to complete, but several factors may prolong this period.
One factor is your field or discipline. Programs like humanities and arts take more than seven years based on the same survey.
Another factor is your academic background. Applying for a Ph.D. program typically requires that you have already completed your master’s degree. This means more time spent in graduate school.
Yes, there are academic institutions that offer professional doctorate degrees specifically designed to accommodate working professionals.
A professional doctorate is a Ph.D. equivalent that allows experienced professionals who aim to earn a doctorate. You can leverage their industry expertise through gaining an academic degree that translates to credibility, and influence in their field.
Students in the program often bring with them years of practical work experience and expertise in various areas, including information technology, business administration, finance, and education. This background will serve as the primary focus of your doctoral research. You can apply your first-hand experience and knowledge in solving real-world problems.
Similar to a Ph.D. degree, you will learn and develop your research methods, design your proposal, and present your findings through writing your doctoral study.
Yes, you can complete your Doctor of Philosophy degree fully online. Unsurprisingly, many Americans resolve to online education to earn a degree, especially an advanced or professional degree.
In a United Nations Study, the U.S. workforce is made up of 85% males and 67% females who are working beyond 40 hours per week. Individuals with family and other obligations are also usually drawn toward online doctorate programs.

An online Ph.D. program is an attractive offering that more and more working professionals seek. Now, there are at least 205 accredited higher education institutions in the county that offer over 1,000 doctorate programs that can be completed online. Earning your Ph.D. online does not necessarily mean that it will be easy. It can easily be as demanding as the traditional format.
Most importantly, an online doctorate bears the same credibility as the one earned on-campus. It is advised that before you enroll in an online program, you check the accreditation of your college or university. This way, no time, money, or effort will be put to waste.
For additional information, check this out:
- Ph.D.’s That Pay: The 15 Highest-Paying Doctoral Degrees
- Hardest Grad School Interview Questions and Response Tips from Ph.D. Experts
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Phd candidate vs student, published by steve tippins on may 19, 2020 may 19, 2020.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 03:03 am
You make the transition from PhD student to PhD candidate after you complete all your coursework and your comprehensive exams (if required). A PhD candidate’s sole task is to conduct their research and write their dissertation.
In other words, a PhD student is still completing their coursework. They could be on the first day of their PhD program. A PhD candidate has completed all of the requirements for their degree except their dissertation (yes, that’s the infamous “ all but dissertation ” status).
PhD candidacy means you’re a PhD in training. Now you’re ready to spread your wings a little–with some guidance.
Your time as a PhD candidate is your chance to demonstrate that you are ready to be an independent scholar. It’s also your chance to screw up and have that be okay–to have support. Your committee will help you. Since it’s the first time you’ll go through the process of creating and performing a study on your own, there’s no reason to believe you’ll be perfect at it. That’s why the process is designed so that your committee can give you guidance.
But besides the simple definition above, what are the implications of being a PhD candidate vs student? Turns out, there are many important differences. Without keeping these in mind when you become a PhD candidate, it’s easy to spin out and get off track and not understand why.
PhD Candidate vs Student: What Are the Differences?

While “PhD Student” and “PhD Candidate” are both steps on the journey to getting a PhD, there are significant differences between them. Here are some of the differences between PhD candidate vs student.
Lack of Structure
When you’re doing coursework, there is structure; there are assignments and deadlines. Of course, in graduate coursework teachers aren’t on top of you to turn in assignments like they would be in an undergraduate program. However, there is a deliverable (final project, test, etc) that you have to complete each quarter. You have things to complete by a certain time in order to move forward.
Once you become a candidate, there’s no syllabus and there are no due dates. It’s completely up to you to move forward in the process.
Some people find it hard to make the transition to the lack of structure that comes with being a PhD candidate.
Academic Writing
Academic writing skills become really important when writing your dissertation –more important even than they were during the coursework phase of graduate school. Academic writing is essentially a new language, with very specific meanings and requirements.

For example, you can’t just say “people believe x or y,” you have to say who they are and how you know that, giving citations to back it up. Many words (like “significant”) have very specific meanings and can’t be used the way you might use them in speech.
As a PhD student, your professors should be teaching this language to you, so that as a PhD candidate, it will come as second nature.
How Many People Do You Have to Keep Happy?
Here’s another difference between being a PhD student vs PhD candidate: as a PhD candidate, you reduce the number of people that you have to keep happy.
As a student, you have to keep in mind the requirements from each professor teaching your classes, as well as matriculation requirements from the department, preferences and advice given by your advisor, and even the research interests of the people for whom you’re writing papers.
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
Once you become a candidate, it’s just your committee that you have to keep happy, meaning that those are the people who will hold you accountable and outline the requirements for completion of the degree. For that reason, you’ll want to choose your committee members with care.
Hopefully, by the time you need to choose your committee, you’ll have encountered professors who are intrigued by your research interests and with whom you feel personally and professionally compatible.
Freedom to Choose

When you become a PhD candidate, you get to work on what you want to work on. You can pursue the topic that interests you instead of whatever goes with the course you’re in. It’s a time to really apply all those skills you were accumulating in the classes. For example, the statistical procedures you learned in stats classes and theories you learned in the courses for your discipline.
This is the stage of culmination, when everything you’ve learned becomes not the goal, but the foundation for your own body of work. It’s one of the exhilarating (and sometimes intimidating) parts of being a PhD candidate vs a student.
Expectations and Support
Faculty often use the “go wander in the woods” approach for PhD candidates. It’s essentially like hearing, “Go find things and come back to me when you’ve got something.” They’ll usually tell you when it’s not enough, but they might not give you much direction about what they’re looking for beyond that.
The reason for this is to encourage independent scholarship. They want you to have the opportunity to build your own case for why and how this topic should be studied. But this first foray into academic independence can be quite a challenge.
When they tell you to “go wander in the woods,” they’re not even telling you what kind of tree to look for. Sometimes you get specific directions, but sometimes you get vague answers like “go look for more.” This can be frustrating. Many clients come to me because they need more direction, which is understandable.

In your coursework, you were often given studies to read or asked to find studies on particular topics that relate to the course topic. Dissertation research is more nebulous. Your committee members want you to decide which directions to go in and which kinds of studies best relate to your research questions.
They won’t be asking you for the “right answer.” They’ll be asking you, “Why? Justify what you did or plan to do.”
Here’s another difference between PhD candidate vs student: a PhD candidate can put “PhD(c)” after their name, indicating that they have achieved status as a PhD candidate. However, I suggest using caution with this designation. The APA has expressed concern that its use may be misleading to the general public and cause people to believe you have a PhD.
PhD Candidate vs Student: An Interview With a PhD(c)

Did you notice a change in how professors viewed you, once you moved from “student” to “candidate”?
Yes. It actually happened during my comprehensive exams. Before that, when I had been asked a question, the professor already knew the answer and was asking to see if I knew also. In my comprehensive exams, I had become the expert and my committee members were actually asking questions out of interest.
We were all pieces of a puzzle at that point. Instead of them saying, “tell me about John Dewy’s influence on education in the 1920s,” they asked, “How do you think Dewey influenced the school system’s openness to parental involvement in schools?” The professor who asked that was genuinely interested, because she was an expert in educational history but had not specifically studied parent involvement in schools, as I had.
That moment represented a big shift for me; it meant that as a PhD candidate, I had to then take responsibility for my own learning, because nobody knew as much as I knew about that particular thing.
It’s exhilarating on one hand, because you suddenly realize you’re the expert. On the other hand, it’s scary because we’re used to somebody else knowing the answer, being able to correct us if we’re wrong.
A Narrowing of Scope

It sounds like your topic was centered on something very particular, so maybe not a lot of other people have studied what you want to study?
Yes, that’s true. When you go through a PhD program your research area is pretty narrow. You start out with a general interest in something, but as you go through your classes, specific areas start to stand out.
I started out with an interest in egalitarianism in public education, but my own past experience combined with some seminal texts to direct me toward parent involvement in schools, specifically. Some books and articles showed me that how schools treat parents can be an indicator of egalitarianism, maybe a clearer one than any rhetoric about the students.
So, there’s this winnowing effect, as you move forward. Your professors love to watch this, too. Especially in the smaller, seminar classes, they seem to be waiting to see what makes your heart beat faster.

Speaking of your heart beating faster, is one distinction of the candidacy phase to have more passion about the work you’re doing?
I think that’s ideal, for sure. It doesn’t always happen, because some professors are really after students who will jump onto their research platform, because they can piggyback on the students’ research to get more publications. Good committee chairs, though, will want you to find your own path toward something you can happily spend a lifetime studying.

I suspect that one of the reasons people don’t finish their dissertations is because they weren’t really passionate about the topic in the first place. It’s only one possible reason, but it should give a doctoral student pause.
It’s really hard to finish a PhD, so you want to knock down any barriers to finishing. Being passionate about the topic will keep you going when things feel onerous. It’s like marrying someone with a sense of humor — even when you’re not getting along very well, there’s something you can always appreciate about your spouse.
Imposter Syndrome

What about “ imposter syndrome ”? Does that come into play when you become a candidate?
It sure did for me! To be one of the only people who’s an expert in that field feels like a huge responsibility because people are depending on you. Your research has to be accurate because people will be making policies based on your conclusions.
Even with good intentions, your conclusions can be erroneous, and there are plenty of historical examples of policies being made on the basis of erroneous conclusions. The consequences can be enormous. And that’s all on you!
So then the questions become, “Am I really up to this?” “Who am I to drive policy?” “I’m just a fallible human being, so why would (or should) anyone listen to me?” Especially right after comps, I was thinking, “How could I be the expert? Nothing really has changed about me; I’m still the same person. Yesterday, I was a student, but today I’m an expert?”

My observation is that this happens with women more than men, probably because women in authority positions are more often questioned than are men. But even for men, this seemingly sudden transformation can make you worry that you’re not qualified for the responsibility you’re being given.
The thing is, It’s not really as sudden as it seems. You’ve been studying something for, say, four years, so you have a claim to expertise. And you’ve been narrowing your interests all along the way, so you’ve been slowly building up your expertise.
Besides, in many good schools, you get warned a lot about how easy it is to make a mistake in research and how easy it is to make false conclusions. They beat that into you so much that it can become a constant doubt.
In most primary and secondary schools, and sometimes even in college, they teach you to sit down, shut up, and learn something. For people to suddenly be saying, “tell me what you think,” can be challenging. I suspect that that’s another major reason people who finish their coursework don’t complete their dissertation: they’re not sufficiently prepared for this shift in roles.
Suggestions for PhD Candidates

Having been through this shift yourself, do you have any advice for students in this stage of their process?
Mostly, I think it’s a matter of taking personal responsibility and seeing yourself in a new light. It helps me to consider this process as a transformation — like a caterpillar into a butterfly. The “student” stage is the caterpillar stage, where you’re eating the milkweed, the knowledge, to nourish you.
Then there comes a time when you’ve got to stop being a consumer and transform into a real researcher. That’s like the metamorphosis stage when the caterpillar is in the chrysalis, melting down. (And I have had plenty of meltdowns myself in this stage!) That’s when you’re on your own, writing the dissertation.
That chrysalis stage is a real slog. You try as hard as you can, and your proposal still gets rejected — twice. Or the IRB wants you to structure the study differently, after your committee has already approved it. Or you can’t get enough participants for your quantitative study or enough data for your qualitative study — whatever. It’s the biggest challenge of most people’s life!

But if you stick with it, you actually do get this huge reward. As a butterfly, or a PhD, you bring something unique to the world. You have an important role in society that can potentially change the course of history — even if you don’t envision that in the beginning.
And that’s why the committee makes the process arduous. They want to be sure you’re great at what you do, because there is potentially an awful lot riding on your shoulders. I’m actually grateful for the rigor they demand. I want to feel ready for the role I’m taking.
Ultimately, candidacy is time in the chrysalis. It’s a time of transformation, built on one’s time as a student. It’s a time in the dark and alone, which makes it challenging, for sure. But I trust I’ll eventually emerge strong enough to spread my wings.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins

Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?

- Code of Ethics
- Dissertation Editing
- Dissertation Coaching
- Free Consultation
Ph.D. Candidate vs Ph.D. Student – What’s the Difference?
One of the most significant milestones in any doctoral education is the transition from Ph.D. student to Ph.D. candidate. While the change in title may be the difference of only one word, getting the distinction of being a Ph.D. candidate represents a major step forward on the journey to earning a dissertation. Though a Ph.D. candidate has not yet fulfilled all of the requirements for earning a doctorate, they are well on their way.
The elevation in title from Ph.D. student to Ph.D. candidate is an accomplishment recognized both within a student’s home department and institution and beyond. In addition to being that much closer to earning a Ph.D., achieving the designation of Ph.D. candidate also opens professional and academic doors to new opportunities. Prior to becoming a Ph.D. candidate, it’s a good idea to become informed about what it entails.
These are a few frequently asked questions about what it means to become a Ph.D. candidate:
- How do you become a Ph.D. candidate?
- What is the difference between being a Ph.D. student and a Ph.D. candidate?
- What are the benefits of being a Ph.D. candidate?
- How long does Ph.D. candidacy last?
Becoming a Ph.D Candidate
Transitioning from Ph.D. student to Ph.D. candidate is a fairly straightforward, if involved, process. To become a Ph.D. candidate, you must first complete all of your academic coursework–required classes, electives, colloquia, the whole nine yards. Early in a Ph.D. program, most Ph.D. students are also tested during an oral qualifying exam with two or three department faculty members to ensure they are making adequate progress in the program.

Once all classes are completed, Ph.D. most students sit for comprehensive exams. These are written exams (sometimes with an additional oral component) designed to test both broad knowledge of the field as well as narrow subject matter. Many Ph.D. students regard comprehensive exams as a major hurdle on their path to completing their Ph.D.
As a Ph.D. student, comprehensive exams (“comps” for short) were definitely my greatest source of anxiety on the road to earning my degree. I spent months studying for these exams, reading hundreds of books and articles in order to prepare myself to answer just three questions. Looking back, getting ready for these exams and passing them was definitely the most intense part of getting my Ph.D.. T he transition from Ph.D. student to Ph.D. candidate can feel like a crucible for proving yourself up to the task of writing a dissertation.
Ph.D. Student Versus Ph.D. Candidate
Though the distinctions between being a Ph.D. student and a Ph.D. candidate may seem subtle, they are significant. In some ways, becoming a Ph.D. candidate feels like entering a new world, one laden with additional expectations. As a senior member of your graduate cohort, you may take on a mentoring role for new Ph.D. students in your department. You may also be asked to serve as a department student representative on university committees.
Though Ph.D. candidates are technically finished with coursework, many opt to take independent study courses with faculty whose research aligns with their own. This helps guide the Ph.D. candidate’s own research, and may even shape their dissertation. Between researching, writing, wading into the job market, and teaching (for those on a fellowship), a Ph.D. candidate’s day is as full as ever.

Having the freedom to dedicate the bulk of my time to my own research was one of my favorite parts of being a Ph.D. candidate. There are very few opportunities in life to devote yourself wholly to the study of one narrow topic, and it can be very rewarding. In addition to writing your dissertation, this is also a great chance to map out the first couple academic articles that you’ll write after graduating.
Benefits of Being a Ph.D. Candidate
While being a Ph.D. candidate often means accepting additional responsibilities in your department, it also leads to new and exciting opportunities . Ph.D. candidates are afforded more consideration for conference papers and panels, as well as travel and research funding. In many departments, Ph.D. candidates are a priority for faculty and also receive a lot of mentoring.
Though the leviathan of the dissertation looms ahead of them, some Ph.D. candidates may also feel like the pressure on them is less intense, and for good reason. Doctoral coursework is a proving ground, and a difficult one at that. Successfully making the leap from Ph.D. student to Ph.D. candidate means that you have what it takes to go the distance and complete your degree. Keep that in mind!

Length of Ph.D. Candidacy
During the period of Ph.D. candidacy, doctoral candidates are designated as being ABD , or “all but dissertation.” The length of time that a Ph.D. candidate has to finish their dissertation is not indefinite. At most institutions, dissertations must be completed within six years, barring extenuating circumstances. Before embarking on your dissertation , it’s a good idea to check with your advisor or department chair and confirm the time limit.
The period of Ph.D. candidacy is a great time to begin the shift from student to professional. The year that I spent between coursework and graduation shaped me into a professional academic. In addition to researching and writing, I also organized department events, attended conferences, created my professional dossier, and went on the academic job market. It was a busy year, but I also learned a lot.
Regardless of the department’s timeclock for the completion of your dissertation, you’ll want to set up your own schedule and timeline for researching, writing, and defending your dissertation . For most Ph.D. candidates, this process takes 1-3 years, but it’s specific to each individual. You will be the best judge of how much time you need to complete your dissertation. Pace yourself and keep your eye on the prize!
Related posts:

Courtney Watson, Ph.D.
Courtney Watson, Ph.D. is an Associate Professor of English at Radford University Carilion, in Roanoke, Virginia. Her areas of expertise include undergraduate and graduate curriculum development for writing courses in the health sciences and American literature with a focus on literary travel, tourism, and heritage economies. Her writing and academic scholarship has been widely published in places that include Studies in American Culture , Dialogue , and The Virginia Quarterly Review . Her research on the integration of humanities into STEM education will be published by Routledge in an upcoming collection. Dr. Watson has also been nominated by the State Council for Higher Education of Virginia’s Outstanding Faculty Rising Star Award, and she is a past winner of the National Society of Arts & Letters Regional Short Story Prize, as well as institutional awards for scholarly research and excellence in teaching. Throughout her career in higher education, Dr. Watson has served in faculty governance and administration as a frequent committee chair and program chair. As a higher education consultant, she has served as a subject matter expert, an evaluator, and a contributor to white papers exploring program development, enrollment research, and educational mergers and acquisitions.
Comments are closed.

- Call: +32 485 729 359
- Email: EDAMBA EXECUTIVE SECRETARY

PhD students and PhD candidates: Know the Difference
Phd students and phd candidates: know the difference feb 20, 2023.
Who is a PhD Student?
A PhD student refers to an individual who has registered for a doctoral degree program. These students, often known as learners, may complete their coursework on campus, online, or in both settings. Students must fulfil a minimum number of academic credits and pass prerequisite tests to enroll in a standard PhD program.
Also Read, FIVE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW BEFORE YOU START A PHD
Once this phase is completed, the student progresses to the dissertation phase, which involves research, writing, and defense.
The distinction between a PhD student and a PhD candidate is that the former is still undertaking coursework and has not yet commenced the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams, although they may be in the process of doing so.
PhD students' education is defined by a predetermined structure, which also sets forth their schedules.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
A person who has finished all the necessary coursework and passed their qualifying tests is considered a PhD candidate. Once this goal is met, the individual gains the unofficial status of all but the dissertation (ABD).
In general, PhD students eagerly anticipate the transition from PhD student to PhD candidate since it will provide them with the opportunity to focus on their original research and start writing their dissertation with the help of their committee advisors.
Know more about Dissertation and Thesis and what are the major differences between these two ,
PhD student vs Candidates: What Are the Main Differences?
The main distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student is that as a student, one is still engaged in course-related activities such as attending classes, writing tests and exams, and completing assignments. On the other hand, becoming a PhD candidate puts you one step closer to earning a doctoral degree and adding the title PhD to your name after passing the tests and writing your thesis . It is important to note that you have to be a student before you become a candidate .
While the differences between being a Ph.D. student and a Ph.D. candidate may appear slight, they carry a lot of weight. Transitioning to a Ph.D. candidate can feel like stepping into a new realm, with new demands and expectations. Despite having completed their coursework, many Ph.D. candidates choose to take self-directed study courses with faculty members whose research aligns with their own, as it can help guide their own research and even influence their dissertation.
If you're part of the PhD community or considering pursuing a doctorate degree, it's important to understand the distinction between being a PhD candidate and a PhD student. Knowing where you stand in your academic journey can help you make informed decisions and set realistic expectations. Keep learning and growing as a PhD researcher , and remember to seek guidance and support from your peers and advisors along the way.
Read more about the EDAMBA PhD Students Forum
Read more about the EDAMBA Summer Research Academy
EDAMBA aims to achieve its mission through three pillars of activity: 1. The Annual Meeting 2. The Summer Research Academy 3. The EDAMBA-EIASM Consortium of Doctoral Supervision
Edamba engages in global collaboration across networks 1. european code of practice 2. equal 3. aacsb, enquiry form.
the difference between phd student and phd candidate

Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
PhD Student/Candidate distinction - European/French universities
I read an interesting topic entitled "PhD candidate vs. PhD Student". I understood that the distinction between the use of those terms is strongly linked to the structure of PhD programs in the US/Canada. I wonder how should I phrase it for an application to a doctoral workshop that requires me to mention whether I am PhD student or candidate (I completed research master's coursework, passed agrégation examinations and defended my dissertation proposal before getting into doctoral school).
To be sure I well understand how it works in North-American universities: students often get admitted in 5-6 years PhD programs after graduating from a 4 years bachelor's degree. The PhD programs, therefore, include a 1 to 2 years first step (PhD student) in which students pursue intensive training in their field. Students have to work on a dissertation proposal which is defended at the end of that first step so that the second step (PhD candidate) deal with the completing the dissertation (reviewing relevant literature, structuring research questions, designing research protocols, testing, analyzing results ... and finally, writing the dissertation).
Considering that European students often have to complete a research master + research proposal (+ for humanities and social sciences in France, having passed a competitive examination for teaching which is called agrégation is often implicitly required, those demands seem similar to final exams of N-A PhD programs) before applying to 3-4 years PhD programs, should we consider they are "PhD candidates" from their entrance into PhD programs?
- terminology
- 1 Related: PhD candidate vs PhD student – GoodDeeds Commented Sep 13, 2020 at 8:02
- Just a note: That some application requires the information whether you are student or candidate is really bad, as it assumes the whole world uses the same structure. – user111388 Commented Sep 13, 2020 at 22:00
2 Answers 2
In North America, usually PhD candidate is also called ABD (all but dissertation), so, are PhD students who has passed all PhD requirements but defending/submitting their final thesis. The distinction between a candidate and an ABD is not very clear, some say candidate may imply that one is still working on their dissertation while most candidates who quit may call themselves as ABD. I would not concern myself with the distinction between candidate and ABD on my CV as providing dates (e.g., expected finish time) can clarify it.
Now, in answer to your question, I would say if you can call yourself an ABD (nothing left but defending your final thesis) then you can call yourself a PhD candidate, else, you might count as PhD student.
In France, both terms can be used and no one would be bothered. Indeed, this can be confirmed through the residence permit status for non-EU foreign people who can make a choice between two different residence permit status.
Either you can have an étudiant residence permit which is the student residence permit or you can have the status mention chercheur scientifique which is the residence permit that shows you are a professional researcher. I think, in the first case, you can be called "PhD student" and in the second case, you are not legally considered as a student. So, you are PhD candidate.
Of course, you can have the second residence permit if your doctoral research is funded by the university, which is called contrat doctoral (doctoral contract). Otherwise, without funding, you can be registered to the doctoral school but you can only have the student residence permit and you are legally considered as a student.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd europe terminology titles france ..
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
Hot Network Questions
- Is it defamatory to publish nonsense under somebody else's name?
- Why do I often see bunches of medical helicopters hovering in clusters in various locations
- Is a thing just a class with only one member?
- For a bike with "Forged alloy crank with 44T compact disc chainring", can the chainring be removed?
- How to increase distance by a unit after every instance in Geometric Nodes array?
- Doesn't nonlocality follow from nonrealism in the EPR thought experiment and Bell tests?
- "There is a bra for every ket, but there is not a ket for every bra"
- Place with signs in Chinese & Arabic
- Why does a capacitor act as an open circuit under a DC circuit?
- Do carbon fiber wings need a wing spar?
- C++ std::function-like queue
- ASCII 2D landscape
- Why is the \[ThickSpace] character defined as 5/18 em instead of 1/4 em as in Unicode?
- Сhanging borders of shared polygon shapefile features in QGIS
- Custom PCB with Esp32-S3 isn't recognised by Device Manager for every board ordered
- Movie where a young director's student film gets made (badly) by a major studio
- How can I switch from MAG to TRU heading in a 737?
- Fast leap year check
- Rocky Mountains Elevation Cutout
- Is it true that before European modernity, there were no "nations"?
- Subject verb agreement - I as well as he is/am the culprit
- Who pays the cost of Star Alliance lounge usage for cross-airline access?
- What would be an appropriate translation of Solitude?
- Is there an essential distinction between experienced and observed consciousness?
The Common App is Open. Class of 2029, Apply Today!
PhD vs. EdD in Higher Education: Which Path Is Right for You?
- Careers for Veterans
- College Advice
- Completing Your Degree
- Dental Hygiene
- Earning a Master's in Education: A Complete Timeline
What Do Special Education Teachers Do? Three Responsibilities
- Taking Higher Education One Step Higher
- Putting his Faith in Education
What To Look For In Special Education Masters Programs
- Health Sciences
- Marketing and Communications
- Medical Imaging
- Occupational Therapy
- Online Learning
- Public Health
- Speech-Language Pathology
In today’s competitive higher education landscape, advanced degrees have become essential for those looking to enhance their leadership skills and advance to executive positions. As a result, job posting data shows that the number of institutions offering advanced higher education programs has increased by 24 percent in the last five years.

Whether you are starting a new career path or seeking to become a leader in the higher education industry, you may be considering furthering your education and are unsure whether a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) or a Doctor of Education (EdD) in higher education leadership is right for you.
Understanding the differences between these two degrees is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with your career goals.
Key Takeaways
- A PhD is ideal for individuals interested in academic research, teaching at a Research 1 university, and contributing to educational theory.
- An EdD emphasizes practical application and leadership in educational settings, preparing graduates for roles such as college presidents, deans, and policy-makers.
- Deciding between a PhD and an EdD requires you to reflect on your personal and professional goals, considering factors such as career aspirations, program flexibility, and institutional reputation.
What Is a PhD in Higher Education?
A PhD in Higher Education is a research-focused degree designed for those who wish to contribute to academic scholarship through theoretical research. This degree is ideal for individuals who aspire to teach full time at a university, engage in scholarly research, or take on academic administration roles.
Therefore, the primary focus of a PhD program is to prepare graduates to generate new knowledge and theories in the field of education.
According to Lauren Bent, Associate Professor of the EdD in Higher Education Leadership program at Regis College , “A PhD is ideal for those who are interested in theoretical research and academic scholarship. Generally speaking, if a student aspires to teach in a Research 1 institution, a PhD is a better option for them.”
PhD candidates typically explore subjects such as educational theory, policy analysis, and higher education research. They are trained to conduct rigorous research, often aiming to publish their findings in academic journals and present at conferences.
What Is an EdD in Higher Education?
An EdD in Higher Education, on the other hand, is a professional doctorate focused on the practical application of research to solve real-world problems in educational settings. The EdD is tailored for those looking to take on leadership roles within educational institutions.
“The EdD aims to develop scholar practitioners and leaders who use applied research to improve problems in schools, institutions of higher education, other educational organizations, and educational policy,“ Bent explains.
The EdD emphasizes the application of research to practice, preparing graduates to implement changes and improvements within their organizations.
Regis College, a member of the Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate (CPED) , emphasizes that scholarly practitioners blend practical wisdom with professional skills and knowledge to address and solve problems in practice. They utilize practical research and applied theories as tools for change, understanding the importance of equity and social justice.
According to Lightcast data, EdD programs prepare students with specialized skills needed in various areas of higher education leadership such as:
- Academic affairs
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Enrollment management
- Fundraising
- Program development
- Project management
- Student recruitment
- Student services

Four Differences Between a PhD and an EdD in Higher Education Leadership
1. curriculum and coursework.
The PhD and EdD programs differ significantly in their curriculum and coursework. PhD programs are heavily research-oriented, with courses centered around research methodologies, statistical analysis, and theoretical frameworks.
Typical classes might include:
- Advanced Research Methods
- Statistical Analysis in Education
- Educational Theory and Philosophy
- Policy Analysis in Higher Education
In contrast, EdD programs focus on the practical application of research to address real-world challenges. Coursework is designed to develop leadership skills and practical knowledge. Classes may include:
- Organizational Leadership in Education
- Strategic Planning and Implementation
- Applied Research in Education
- Equity and Social Justice in Higher Education
“Within the program, there are courses where students are learning to design their own research studies, and they have lots of opportunities to develop a scholar practitioner mindset,” Bent adds. “The activities and assignments in our courses are intentionally designed to be relevant, pragmatic, and applicable to what our students are doing—and will do—in their professions.”
2. Program Length and Structure
The length and structure of PhD and EdD programs can vary, but generally, PhD programs take longer to complete due to their extensive research requirements. On average, a PhD program can take anywhere from four to seven years to complete, including time spent on coursework, comprehensive exams, and the dissertation.
EdD programs are typically designed to be more flexible and manageable for working professionals. They can often be completed in three to five years, with a structure that accommodates part-time or online study options.
3. Dissertation Requirements
Both PhD and EdD programs require a dissertation, an extensive research project that is a key component of doctoral programs. Both programs require that dissertations focus on identifying a research question, conducting a literature review, designing and executing a study, and presenting the findings in a written document.
However, the nature of the dissertation can differ depending on the program.
PhD dissertations are typically theoretical, contributing new knowledge to the field. They often involve original research and aim to be published in academic journals.
EdD dissertations, on the other hand, are more practical and focus on solving real-world problems within educational institutions. These projects often involve applied research that can be directly implemented in practice.
4. Career Outcomes
The career outcomes for PhD and EdD graduates also differ. PhD graduates often pursue careers in research, higher education teaching, and academic administration. They are well-suited for roles that require deep theoretical knowledge and extensive research skills.
EdD graduates, in contrast, are prepared for leadership roles in educational administration, policy-making, and executive leadership. They are equipped to implement change and drive improvements within their organizations.
“Our EdD prepares students to be leaders in schools, colleges and universities, and other organizations connected to educational policy,” Bent explains. “Our graduates have become college presidents, vice presidents of enrollment management and student affairs, deans, and founders and CEOs of non-profit organizations.”
If you are ready to take the next step in your career in higher education, here are a few factors you should consider before enrolling in a PhD or EdD degree program.
Factors to Consider When Making Your Decision
Personal and professional goals.
When deciding between a PhD and an EdD, consider your long-term career objectives and personal interests.
“People who aspire to higher leadership roles often find that a doctorate is required to advance their careers,” Bent says.
Reflect on how each program aligns with your aspirations and whether it provides the opportunities and experiences that will help you reach your goals. Understanding your personal and professional motivations will guide you to the program that best supports your future ambitions.
Program Flexibility
Consider the flexibility of the program, including the availability of part-time or online options, which can help you balance your education with professional and personal responsibilities.
“The modality of learning is important,” Bent adds. “Whether it's online, in-person, or hybrid, it needs to suit the students’ learning styles and lifestyles.”
Evaluating how the program's structure fits into your current lifestyle and commitments can help. Flexible options can make it easier to manage your studies alongside work and family, ensuring you can fully engage with and benefit from the program.
Institutional Reputation and Resources
Choose a reputable institution that offers access to faculty expertise, research facilities, and professional networks.
“Students should consider the faculty who are teaching and advising them,” Bent concludes. “What are their backgrounds and areas of expertise?”
You can research an institution’s reputation through a general internet search. Those top results should give you the key accomplishments and differentiators for the programs you are considering.
Take the Next Step in Your Career in Higher Education
Both the PhD and EdD in higher education offer unique advantages and can help you advance your career in different ways. Remember to reflect on your career goals and personal interests to determine which program best aligns with your aspirations.
If you’re looking for a degree that combines practical leadership skills with scholarly research, consider Regis College’s EdD in Higher Education Leadership program .
To learn more about the program, contact an admissions counselor to find out how an education at Regis can serve your professional goals.
Related Blogs

If you’re interested in providing support for children with learning challenges, here’s an overview of what a special education teacher does.

Earning a Master's in Education: A Complete Timeline
If you want to earn a master's degree in education, it's essential to understand whether or not this education will fit into your current schedule.

Considering a Master’s degree in Special Education? Here are five things you should look for when choosing the right master’s program for your needs.
September 13, 2024
- 235 Wellesley Street, Weston MA 02493
- 781.768.7000
- © 2024
- Privacy Policy
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 12 September 2024
Tap the potential of PhD students
Nature Physics volume 20 , page 1361 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
PhD students can face many challenges, such as a lack of confidence in their newly acquired skills or the uncertainty about which career path to choose. We highlight some ways to empower students in their doctoral journey.
The overall development of PhD students during their doctoral studies is important for their personal and professional growth, as well as for the success of their project. However, they are often encouraged to focus on their research project, with other aspects of academic and professional training receiving less attention. As a result, many students face difficulties in moving forward after finishing their doctoral studies. Thus, a well-rounded approach is necessary to empower PhD students with the abilities to confidently choose their career path.

A lack of research autonomy can stifle creativity and hold PhD students back in their development. By granting them control over certain aspects of their research — for example, by allowing them to steer parts of their projects or by encouraging independent exploration within the broader scope of their work — students will learn to become more self-reliant researchers.
Supervisors can further promote their students’ independence by encouraging them to propose their own hypotheses or conduct additional simulations or laboratory-based experiments. In this way, PhD students learn how to develop a research problem and how to tackle it — an invaluable skill not just in academia but in all walks of life.
In addition to conducting research, students must also learn to communicate their findings and develop presentation skills. Universities can facilitate training programmes on soft skills, such as writing research articles and presenting research to a broader audience. This will enhance students' ability to convey their ideas with confidence. It is particularly important when they present posters or give oral presentations in larger forums, such as conferences or seminars, or when they engage with their peers in the research field.
Networking is a vital component of a successful academic and professional career. It allows students to find collaborators, seek advice, and discover new research and job opportunities. However, many PhD students struggle to build and maintain professional relationships, often because of a lack of guidance on how to approach networking effectively. It is not uncommon for PhD students to be unaware of the research activities of their colleagues, whether from other departments or even the same department.
Institutions can help in this regard by organizing frequent workshops or seminars in which students can engage with peers and experts in their field. Conferences and summer schools also offer invaluable networking opportunities, while commonly providing students with the chance to present their research, which in turn enhances their presentation skills. Universities should actively support their students' participation in such events through travel grants. In addition, organizers of conferences and schools should also provide funding opportunities, especially for PhD students from developing countries where principal investigators may not have enough resources to support their students’ travel.
Another crucial aspect of a PhD student’s journey is the process of publishing their work. However, many students feel ill-equipped to handle the steps of academic publishing. They often rely on their supervisors to lead the process, which can leave them unprepared for the demands of publishing as they transition to more independent roles.
To address this, supervisors should actively involve students in every step of the publication process, from the discussion of a suitable target journal to the writing of a manuscript’s first draft and cover letter, to the actual submission and preparation of the response to reviewers' comments. Although this may require additional back-and-forth, it is an invaluable learning experience that prepares the students for future academic challenges and enhances the quality of their research output. These skills are also transferable and will undoubtedly benefit students in any future career path, whether in academia, industry or other sectors.
Uncertainty about future career paths is a common concern among PhD students. Many are unsure whether to pursue research positions or explore opportunities outside academia. Unfortunately, students often lack access to adequate career training, which hinders their ability to prepare for future employment. For example, many students don’t know how to tailor CVs for future employment options or are unsure for which non-academic positions their skills make them suitable applicants.
By facilitating career-oriented workshops, seminars and mentoring programmes, institutions could help guide PhD students on their career path. For example, students would benefit from the interaction with alumni, sharing their career stories. Career counselling and interactions with industry panels can provide insights into possible career choices, helping students understand the range of opportunities available to them. Additionally, workshops on CV writing, interview preparation, and transferable skills, such as project management and data analysis, can boost students' confidence in their abilities and prepare them for diverse career options.
Although the majority of the suggestions discussed above are well known within the academic community, they have not always been given the attention they deserve. By providing the necessary tools and opportunities to PhD students, we can tap their full potential and put them in a better position to contribute to the advancement of knowledge, to drive innovation and to make meaningful contributions to society.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tap the potential of PhD students. Nat. Phys. 20 , 1361 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-024-02654-2
Download citation
Published : 12 September 2024
Issue Date : September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-024-02654-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Why peer-to-peer conferences benefit doctoral students and their institutions
Solid research skills aside, PhD students need to master the art of collaboration and communicating their ideas. A student-led conference can offer that support

Created in partnership with
.png?itok=8Xu1tWen)
You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Change is coming, whether higher education likes it or not
Is it worth paying for genai, emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, teaching international students about academic integrity, ai and assessment redesign: a four-step process.
The PhD experience puts fledgling researchers on the path to becoming seasoned academics. This transformative journey demands not only scholarly rigour but also the resilience and adaptability to navigate challenges, from researching uncharted domains to mastering the art of communicating complex ideas with clarity and conviction. PhD students need not only hard skills in research but also soft skills , such as the ability to present research persuasively and network strategically .
Because PhD education extends beyond solitary pursuit, collaborative endeavours and supportive networks are indispensable, as I have learned from taking this journey myself.
Engaging with peers from diverse disciplines and cultural backgrounds broadens intellectual horizons and nurtures a sense of community essential for sustaining motivation and resilience during the average five-year journey. Establishing these networks early equips PhD candidates with potentially lifelong professional relationships that facilitate collaboration and career advancement.
- Advice for effective cross-team collaboration for research
- Read more: So you want to host an international online conference?
- How to make enterprise activities enjoyable and impactful
Strong communication skills also enhance employability and career prospects , preparing students for job interviews , professional settings and effective teaching .
A peer-to-peer conference led by doctoral students for doctoral students is a way to give PhD candidates the opportunity to exercise their collaboration and communication skills.
How a scholars conference enhances PhD education
Student-led conferences such as the Singapore Rising Scholars Conference (SRSC) can be a valuable complement to major field-specific conferences, where professors and established scholars are the main participants. While major conferences offer the opportunity to learn from and be inspired by seasoned academics, student conferences allow PhD candidates to take charge, practise leadership and refine their networking skills among peers. The combination of learning from established scholars and leading within peer-driven platforms provides a well-rounded preparation for academic and professional success.
The SRSC, initiated by Singapore Management University’s (SMU’s) College of Graduate Research Studies, fosters a constructive learning environment for doctoral students in management and social sciences. By encouraging constructive dialogue among emerging scholars from diverse backgrounds, the conference nurtures collaborations that transcend institutional boundaries and inspires interdisciplinary research. This annual event, which has evolved since its debut in 2023 into a two-day programme showcasing research from 60 paper presenters across 22 global institutions, not only enriches participants’ research but also cultivates essential skills in academic presentation, networking and collaboration while providing a platform for exploring new research avenues and expanding professional networks.
Jian Hu, a first-year PhD student at SMU’s Lee Kong Chian School of Business, describes the thrill of presenting his research among peers, a sentiment that mirrors my own experience as a doctoral student. I vividly remember the excitement and nerves of sharing my research with an audience for the first time, an experience that sharpened my communication skills and expanded my academic horizons through the valuable feedback I received. For Srishti Arora, from the Singapore campus of the French business school INSEAD, the conference inspired her to seek out interdisciplinary collaboration.
By promoting dialogue, collaboration and innovation, peer-to-peer conferences empower young scholars to push boundaries and make meaningful contributions to their fields and beyond.
The role of academic institutions: commitment, resources and reputation
Academic institutions can nurture PhD students through platforms such as student-led conferences. However, establishing such events requires a significant commitment of resources – financial, logistical and human – and a long-term vision. The rewards, however, can be substantial, not just for the participants but for the institution itself.
At SMU, the SRSC shows how a single institution can create and sustain such a platform. For other institutions looking to replicate this model, it is essential to recognise that success hinges on consistent execution and a commitment to quality. Over time, such a conference can become a cornerstone of an institution’s brand , attracting high-calibre faculty and students. Institutions should simultaneously consider investing in marketing, alumni outreach and continuous improvement processes to ensure that the conference grows in stature and impact over time.
Alternatively, institutions might consider a collaborative model, in which multiple universities join forces to create a rotating conference. Each institution could take turns hosting the event, sharing the burden of resources while also benefiting from the diverse expertise and perspectives that collaboration brings. This approach can also strengthen inter-institutional relationships and provide students with broader networking opportunities. However, it is important to establish clear guidelines and expectations among the participating institutions to ensure the quality and continuity of the event. Collaborative conferences can also serve as a testing ground for joint research initiatives and cross-institutional projects, further amplifying the benefits.
Whether choosing to go it alone or to collaborate, the key is for institutions to view these conferences not just as events but as strategic investments in their academic communities. They offer a tangible way to build institutional reputation while providing invaluable development opportunities for students.
The SRSC exemplifies the profound impact of peer-to-peer conferences on PhD education. By placing students at the helm, these events provide a platform to develop the collaboration and communication skills that are critical for academic and professional success. Leading discussions, presenting research and engaging in cross-disciplinary dialogues empower PhD students to become confident communicators and effective collaborators. Additionally, the networks formed during these conferences foster enduring professional relationships that can lead to future collaborations and career opportunities. Ultimately, peer-to-peer conferences such as the SRSC transform the PhD experience, equipping students with the practical skills and networks necessary for long-term success.
Heli Wang is dean of the College of Graduate Research Studies and the Janice Bellace professor of strategic management in the Lee Kong Chian School of Business at Singapore Management University.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
The iScanner app supports the academic community in information sharing and management
Change is coming, whether higher education likes it or not, use ai to get your students thinking critically, a diy guide to starting your own journal, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
The Ethics of Developing Voice Biometrics
Share this page, get the latest updates, join our newsletter, subscribe to colloquy podcast, connect with us, related news.

Medieval Google
How notaries—publicly licensed scribes who wrote contracts—were the computers of the Middle Ages.
Elevating Teacher Voices
A new study co-authored by PhD candidate Megan Satterthwaite-Freiman highlights the need for more effective and personalized training on leading conversations about sensitive topics in the classroom.

What to Know about the Space Economy
Outer space has come a long way since the 1960s. HBS Professor Matthew Weinzierl, PhD '08, explains the current state of the space economy, highlighting the various opportunities for businesses hidden among the stars.

Honoring the Cultural Backgrounds of All Students
New research from PhD candidate Emily Meland provides a model for social and emotional learning in schools that is culturally sustaining

PhD Student vs Graduate Student [Correct terminologies]
As you progress down the academic pathway it can become confusing to work out what the appropriate terminology is for your current level of education. Is it PhD student? Is it graduate student? Is the PhD student the same as a graduate? Well, this article will answer all your questions.
Graduate student is an umbrella term for someone with an undergraduate qualification (bachelors, diploma), they are often performing graduate research in a Masters or PhD program. All PhD students are graduate students but not all graduate students are PhD students.
To fully get our heads around each of these definitions, we need to understand exactly what each term really means.
This is where we can look at the actual definitions of PhD student vs graduate student.

Definition of PhD student
A PhD student is someone who is currently enrolled in a doctorate degree program and is in the early stages of their course.
Some institutions require students to undergo a coursework component of their graduate program and are called a PhD student .
After the completion of the coursework component, with the research component still to go, they can be called a PhD candidate .
Definition of Graduate student
A graduate student is a known for a student who continues their studies after completion of their undergraduate degree.
The Cambridge dictionary defines it as:
A student who is studying for a degree that is higher than the one received after four years of study at a college or university.
Who is considered a graduate student?
Graduate students can include:
- Masters students
- PhD students
- Professional Masters
- Graduate academic certificate programs
- undergraduate/graduate hybrid degree programs
Even if you have got an undergraduate degree, there are many more options for you to obtain many more qualifications and build on your education. In these instances, you will be known as a graduate student.
Is a PhD student a graduate student?
Yes, a PhD student is a graduate student.
They have spent up to 4 years in their undergraduate programs in order to qualify for admission into a PhD program.
PhD students are able to call themselves graduate students but many choose to refer to themselves as PhD students or candidates.
Is PhD the same as graduate?
A PhD is the highest education attainable as a graduate.
In order to obtain a PhD one must graduate from an undergraduate degree. From the moment of graduating in their undergraduate degree they are known as a graduate.
The order of becoming a PhD from a graduate is shown in the table below. It also includes what happens after you get a PhD.
| Stage of education | Important notes |
|---|---|
| Obtaining a bachelor degree | someone undergoing their undergraduate degree, referred to as an undergraduate. |
| Obtaining a Masters degree | referred to as a graduate student or a Masters student. |
| Becoming a PhD student | a PhD student is someone who is in the early stage of their degree and has two complete the coursework (common in the USA). |
| Becoming a PhD candidate | a PhD candidate is someone who has completed the coursework component of their degree and has to perform research and submit their thesis. |
| Becoming a PhD graduate | |
| Becoming a post-doc | After your PhD degree you can choose to enter the University as a postdoctoral researcher. |
| Becoming a lecturer | The first level of employment for a university tenure position is as a lecturer or reader at a university. |
| Becoming an associate professor | The next level of promotion is to an associate professor level. |
| Becoming a professor | A tenured professor has shown excellence in teaching, research, and administrative duties to the University. |
Is a doctoral student the same as a PhD student?
Strictly speaking, a PhD student is someone who is pursuing a doctor of philosophy.
A PhD student is a type of doctoral student but not all doctoral students are PhD students. Anyone aiming to achieve the title of ‘Dr’ is a doctoral student.
There are many other different types of doctoral students including:
- Doctor of Arts (DA)
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- Doctor of Design (DDes)
- Doctor of Engineering or Engineering Science (DEng, DESc, DES)
- Doctor of Education (EdD)
- Doctor of Fine Arts (DFA.)
- Doctor of Juridical Science (JSD, SJD)
- Doctor of Musical Arts (DMA)
- Doctor of Music Education (DME)
- Doctor of Modern Languages (DML)
- Doctor of Nursing Science (DNSc)
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
- Doctor of Public Health (DPH)
- Doctor of Sacred Theology (STD)
- Doctor of Science (DSc, ScD)
- Doctor of Theology (ThD)
There are also professional degrees that lead to the person being called Doctor. These professional degrees result in honorific doctor titles, including those found in the table below.
| Medical doctors | Pharmacists | Dentists |
| Veterinary surgeons | Lawyers (Doctor of Juris) | Podiatrists |
| Naturopath’s | Chiropractors |
In my 15 years in academia, I would only really refer to someone as a PhD student. However, if someone was to introduce themselves as a doctoral student I would understand them to be a PhD student.
Wrapping up
In this article, we have learned the difference between PhD student vs graduate student.
In summary, a graduate student is an umbrella term that includes anyone that has done an undergraduate qualification and is continuing their education. It includes Masters students, PhD students and others.
All PhD students are graduate students but not all graduate students are PhD students.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Government News
3 Key Economic Issues Addressed in the Debate Between Kamala Harris and Donald Trump
Taylor Tompkins has worked for more than a decade as a journalist covering business, finance, and the economy. She has logged thousands of hours interviewing experts, analyzing data, and writing articles to help readers understand economic forces. She is the Economics Editor for news at Investopedia.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TaylorTompkins-d4efdf4238614788b1848f0fc17170f3.jpg)
Doug Mills / The New York Times / Bloomberg / Getty Images
Key Takeaways
- Vice President Kamala Harris and former President Donald Trump faced off in their first debate Tuesday.
- The candidates reiterated their economic platforms and didn't introduce new proposals.
- They sparred on economic topics including tariffs, inflation and student loans.
Vice President Kamala Harris and Former President Donald Trump met for the first time as presidential candidates Tuesday, and economic issues were a central topic of debate.
Investors and other market watchers tuned in as the pair debated for an hour and a half in Philadelphia. The economy was the first topic of the night, and both took the opportunity to repeat their platforms.
Here's how the candidates sparred over three key economic topics Tuesday night.
Republican candidate Donald Trump doubled down on his tariffs plan at the beginning of the debate.
Trump has called for a broad 20% tariff on all foreign goods and tariffs of 60% or higher on Chinese products. Most economists say tariffs would damage the economy more than they would help since merchants would pass the cost of tariffs along to consumers and give domestic manufacturers cover to raise prices.
He argued his tariffs would take in hundreds of billions of dollars and not cost the American people anything.
"Other countries are going to finally, after 75 years, pay us back for all that we've done for the world," Trump said. "And the tariff will be substantial."
For her part, Harris said the tariffs would equate to a "sales tax" and said it would cost the average person more money. She said his policies on trade with other countries put the economy at risk during his presidency.
"Well, let's be clear that the Trump administration resulted in a trade deficit, one of the highest we've ever seen in the history of America," Harris said. "He invited trade wars."
Each candidate blamed their opponent for inflation.
The cost of living has risen significantly since the start of the pandemic, up 21% on average, according to the Consumer Price Index. At the same time, wages grew more than 23%, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Economists largely say inflation was spurred by constraints in the supply chain during the pandemic and, to a lesser extent, relief programs such as stimulus checks enacted by former President Trump and his successor, President Joe Biden.
Trump said there was "virtually no inflation" during his presidency (prices rose 7.5% over the time he was in office) and inflation has been a disaster for people of every class. For her part, Harris laid out her economic policies and said Trump's proposals would increase inflation.
Student Loans
Harris has supported Biden’s program of student loan debt forgiveness for federal borrowers, which has forgiven $168.5 billion in student debt, with other proposed relief blocked or delayed by Republican-led legal challenges . The legal challenges to these have left students in limbo as the cases wind their way through the courts .
While student loans weren't a main focus of the debate, Trump did bring up Supreme Court rejections of Biden's loan forgiveness plans. "So all these students got taunted with this whole thing. And how unfair that would have been, part of the reason they lost, to the millions and millions of people that had to pay off their student loans. They didn't get it for free."
Peterson Institute for International Economics. " Trump's bigger tariff proposals would cost the typical American household over $2,600 a year ."
Bureau of Economic Statistics via the Federal Reserve Economic Data. " Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees, Total Private ."
Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco. " Global Supply Chain Pressures and U.S. Inflation ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Harris-Trump-e3d01d675ad54e7d97650e64a646b662.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Watch CBS News
How ABC presidential debate rules work for tonight's Trump vs. Harris showdown
By Kathryn Watson
Updated on: September 11, 2024 / 1:02 AM EDT / CBS News
The rules have been released for the first — and possibly only — debate between former President Donald Trump and Vice President Kamala Harris. The two will face each other Tuesday at Philadelphia's National Constitution Center in a showdown that could define the rest of the presidential campaign.
The debate begins at 9 p.m. ET and ABC News is the network hosting it. There will be no live audience and no opening statements, according to the rules released by the network last week.
The candidates will have two minutes to answer questions, two minutes for rebuttals and an additional minute for follow-ups and clarifications. The two candidates will also have up to two minutes to deliver closing statements at the end.
Harris and Trump won't be able to ask questions of each other. Only the moderators — ABC's David Muir and Linsey Davis — are permitted to ask questions.
The debate will last 90 minutes and will include two commercial breaks.
Candidates aren't allowed to take prewritten notes or props on stage, and they won't receive topics or questions in advance.
ABC is allowing other television networks to simulcast the debate. CBS News will air the full debate on the CBS television stations and the streaming network CBS News 24/7 , followed by post-debate analysis.
The debate will be the first time Harris and Trump meet face to face.
Debate microphones
There was a tussle last month between the Harris and Trump camps about whether to mute the candidates' microphones when it wasn't their turn to speak. In the first debate , Trump and President Biden's mics were muted, which was requested by the Biden campaign.
The Harris campaign requested a change to allow open mics, saying in a letter to ABC News that Harris is "fundamentally disadvantaged by this format, which will serve to shield Donald Trump from direct exchanges with the Vice President."
Although the Harris campaign said the Trump campaign insisted on muted mics, Trump said on Aug. 26 that it "doesn't matter to me."
"I'd rather have it probably on, but the agreement was that it would be the same as it was last time," Trump said. "In that case, it was muted. I didn't like it the last time but it worked out fine."
The Harris campaign agreed in the end to have the muted microphones.
The Harris campaign also told CBS News that it was offered assurances that the microphones may be unmuted if there is significant crosstalk between the candidates. A candidate who constantly interrupts their opponent will be warned by the moderator and their comments may be relayed to the audience. And, if the microphones don't pick up the exchanges, a group of reporters who will be in the room would be able to report anything noteworthy.
Notes and debate preparation
The campaigns have taken different approaches to debate preparation. Harris traveled to Pittsburgh on Sept. 5 and spent the time there focusing on strategy, a senior campaign official said. While Harris had planned to pepper Trump with questions, her campaign has had to seek out a new approach, fearing that her ability to most effectively engage with the former president will be hampered by the microphone restrictions.
The vice president is practicing with extended mock debates, with a focus on policy and an effort to draw a contrast with the former president. A former aide to Hillary Clinton, who played Trump in the mock 2016 debate prep with Clinton, is playing Trump again in these sessions, with a source saying the aide is even dressing like Trump. Harris has also been practicing on a stage with lights to recreate the debate environment, a source familiar with the preparations told CBS News.
While Harris participated in several Democratic debates ahead of the 2020 primaries, this is her first presidential debate, while it is Trump's seventh debate. Trump told "Good Morning New Hampshire" last week that he's "been preparing all my life for this debate."
"So, you know, I do. I have meetings on it," Trump added. "We talk about it, but there's not a lot you can do."
Trump has been reviewing policy positions with advisers in the lead-up to the debate, sources familiar with the former president's preparation told CBS News, though his preparations are characterized as somewhat informal and include speaking with voters and engaging with the media.
Closing statements
A coin toss was held virtually on Sept. 3, with the candidate who won the coin toss allowed to choose the order of the closing statement or podium placement. Trump won the coin toss and chose to select the order of statements, ABC News said. The former president chose to offer the last closing statement.
Podium placement and candidate stage positions
After the coin toss, Harris was allowed to chose podium placement. She selected the podium position to the right on screen, ABC News said.
The rules also state that candidates will stand behind their lecterns for the "duration" of the debate, a rule that may remind viewers of a 2016 debate between Trump and former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, when Trump left his place to linger near Clinton, a move some viewed as an intimidation tactic.
Aaron Navarro , Kaia Hubbard and Ed O'Keefe contributed to this report.
- Presidential Debate
- Kamala Harris
- Democratic Party
- Donald Trump
- Republican Party
- 2024 Elections
- Philadelphia
Kathryn Watson is a politics reporter for CBS News Digital, based in Washington, D.C.
More from CBS News

Trump-Harris debate draws 67 million viewers, surpassing first matchup

Trump says he would deport migrants in Springfield, Ohio, to Venezuela

Civil rights icon endorses Kamala Harris "who follows in our footsteps"

Pope Francis says Kamala Harris and Donald Trump "both against life"

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research). On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it. 2.
A PhD student is in the initial stages of their doctoral journey, undertaking coursework and preparing for exams. A PhD candidate, having passed these exams, focuses on original research and writing a dissertation. The difference between a PhD candidate and a PhD student becomes more evident at this stage.
A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements. On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.
Let's take a closer look at a few of the key differences between PhD students and candidates. 1. Type of Learning. PhD students spend time completing courses and candidacy exams, learning from the pool of knowledge that already exists. They have completed graduate school courses and are now taking classes at the highest level possible.
The main difference between a PhD student vs. candidate is that the student is still working through the coursework. They have not yet begun the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams. A PhD student may also be in the process of taking the qualifying exams, but not yet finished with them. Many people believe that earning a doctoral ...
A doctoral student is a person currently enrolled in a doctoral program at a university. Being a doctoral student involves completing a certain number of credits and coursework in an area of study and completing and passing several exams. After students pass the qualifying exams (if the program requires it) and successfully complete required ...
What's the difference between a PhD Candidate and a PhD Student? According to two posters on the WordReferences forums: This terms vary from university to university, usually a PhD student is granted the candidate status after completion of a "comprehensive examination", which occurs sometime after the first year. and
Do you know the difference between a PhD student and a Ph.D. candidate? A candidate is someone who has fulfilled all the requirements for the degree except the dissertation. I'm a historian (see my earlier post about being a humanist at MIT), so my path to candidacy differs a bit from other doctoral tracks at MIT.
A PhD Candidate is an individual who is currently enrolled in a doctoral program at a university or other tertiary education institution. They are usually referred to as " PhD students" or "PhD candidates.". In order to qualify for the PhD, a candidate must complete all of the program's coursework requirements and write and defend a ...
A Ph.D. degree or a doctorate or doctoral degree is globally recognized as the highest level of academic degree and presupposes the completion of an original dissertation or research. A traditional doctorate follows a three- to four-year degree, but some institutions offer opportunities to fast-track the degree, subject to stringent requirements.
In other words, a PhD student is still completing their coursework. They could be on the first day of their PhD program. A PhD candidate has completed all of the requirements for their degree except their dissertation (yes, that's the infamous " all but dissertation " status). PhD candidacy means you're a PhD in training.
PhD student vs candidate. A PhD student is currently enrolled in a PhD program. The learning style for these students is hybrid, meaning that a student can learn either online, on-site, or both. Students who are enrolled in this type of program are often required to complete certain course credit loads and pass exams. The program involves a ton ...
While the change in title may be the difference of only one word, getting the distinction of being a Ph.D. candidate represents a major step forward on the journey to earning a dissertation. Though a Ph.D. candidate has not yet fulfilled all of the requirements for earning a doctorate, they are well on their way.
A PhD research student takes on a project focusing on a particular topic. They will zone in on a research hypothesis, explore it and write up the results. Once they complete this they obtain a Doctor of Philosophy degree - which is the highest level of higher education. A PhD research student will spend between three to seven years - full or ...
The main distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student is that as a student, one is still engaged in course-related activities such as attending classes, writing tests and exams, and completing assignments. On the other hand, becoming a PhD candidate puts you one step closer to earning a doctoral degree and adding the title PhD to your ...
The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries. A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as "candidates", to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
A PhD student is a student pursuing a doctoral degree, while a PhD researcher can be anyone who is conducting research at the doctoral level, including PhD students, postdocs, and faculty members. However, in practice, the terms PhD student and PhD researcher are often used interchangeably. The confusion comes from the fact that a PhD research ...
What is the difference between a PhD Candidate and a PhD Student? A PhD student is someone in a graduate program to get their PhD. I'm sharing the biggest ...
1. PhD students and PhD researchers are not the same thing. A "PhD researcher" is a researcher who has a PhD, while a PhD student is working on a project in order to obtain a PhD (i.e. does not have the degree yet). I agree with you, that the term "PhD student" in English is rather unfortunate - in reality, it is much closer to an ...
Majors & Careers; Online Grad School; Preparing For Grad School; Student Life; PhD Candidate vs Student: What's the Difference? Many people use the terms "PhD student" and P
2. In North America, usually PhD candidate is also called ABD (all but dissertation), so, are PhD students who has passed all PhD requirements but defending/submitting their final thesis. The distinction between a candidate and an ABD is not very clear, some say candidate may imply that one is still working on their dissertation while most ...
Four Differences Between a PhD and an EdD in Higher Education Leadership 1. Curriculum and Coursework. The PhD and EdD programs differ significantly in their curriculum and coursework. PhD programs are heavily research-oriented, with courses centered around research methodologies, statistical analysis, and theoretical frameworks.
PhD students can face many challenges, such as a lack of confidence in their newly acquired skills or the uncertainty about which career path to choose. We highlight some ways to empower students ...
A peer-to-peer conference led by doctoral students for doctoral students is a way to give PhD candidates the opportunity to exercise their collaboration and communication skills. How a scholars conference enhances PhD education. Student-led conferences such as the Singapore Rising Scholars Conference (SRSC) can be a valuable complement to major ...
PhD candidate Juana Catalina Becerra Sandoval explores the ethical considerations that must be applied to the development of artificial intelligence technologies like voice biometrics to ensure ... offering PhD and select master's degrees as well as opportunities to study without pursuing a degree as a visiting student. Harvard University ...
In our tests, the next model update performs similarly to PhD students on challenging benchmark tasks in physics, chemistry, and biology. We also found that it excels in math and coding. In a qualifying exam for the International Mathematics Olympiad (IMO), GPT-4o correctly solved only 13% of problems, while the reasoning model scored 83%.
Yes, a PhD student is a graduate student. They have spent up to 4 years in their undergraduate programs in order to qualify for admission into a PhD program. PhD students are able to call themselves graduate students but many choose to refer to themselves as PhD students or candidates.
While student loans weren't a main focus of the debate, Trump did bring up Supreme Court rejections of Biden's loan forgiveness plans. "So all these students got taunted with this whole thing.
The decision threatened the availability of IVF services in Alabama and thrust access to fertility treatments into the national conversation, including among the presidential candidates.
Candidates aren't allowed to take prewritten notes or props on stage, and they won't receive topics or questions in advance. ABC is allowing other television networks to simulcast the debate.