- Jul 22, 2022
- 11 min read

Is a PhD Worth It? The Pros and Cons of Getting a Doctorate
To get a PhD or not to get a PhD? That is the question.
Valerie David
Lifestyle and Career Expert
Reviewed by Hayley Ramsey

Entering the job market for the first time can be a stressful experience, especially if you don't feel completely prepared. When deciding how to take those first steps toward your ultimate career , and how to give yourself a chance at the best jobs, you may find yourself asking: “Should I do a PhD?”.
While academics looking forward to a life of learning may consider this a no-brainer, there are important factors for everyone to consider. Finances, job prospects and quality of life issues can greatly affect the success of furthering your education.
To help you decide if the time and effort of a PhD is worth it, here are the major benefits and disadvantages of getting that doctorate.
After four or more years of intellectual pursuits, adding a PhD may seem like overkill. Before you make your choice, let's look at all the benefits that are exclusive to earning the most advanced degree.
1. You can contribute new knowledge to the world
Embarking on a PhD programme means delving into your preferred subject in a much deeper way than you have in any of your previous studies. The beauty of this advanced degree is that it allows you to sail in uncharted waters. Your goal is to find new information, draw new conclusions and, hopefully, make a significant contribution to your field.
Your intensive research, travel, collaboration and study will lead you on an unpredictable path to telling a story that no one has heard before. For some students, this pursuit of knowledge and discovery is enough to make all the hard work of earning a PhD worth it.
2. You'll have access to more prestigious jobs
One of the key benefits of a PhD is that it opens doors to careers at the highest levels. This can include leadership positions in science and engineering, government roles in economics and political science, and prestigious teaching posts for English and arts majors. Even if an advanced degree isn't required for the job you want, that PhD can give you an extra air of authority in your field and an edge over other candidates.
Another obvious upside to continuing your postgraduate studies is that landing these powerful positions can lead to large financial rewards. Some areas of study, like medicine and the law, tend to be more lucrative, but it can also depend on the type of job. For example, a university professor or researcher post can pay well for a wide variety of disciplines. Check out sites like the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the National Careers Service to investigate potential salaries.
3. Employers look for candidates with your superior writing skills
A study arranged by the National Commission on Writing discovered that blue-chip businesses (long-standing companies with stable stock growth) are spending more than $3 billion a year on remedial writing course for current employees. This includes staff with undergraduate degrees.
So, when a hiring manager peruses your résumé and sees that you've earned a PhD, they'll know immediately that you've spent years honing your skills at compiling research, organizing mountains of data and writing about your results in a cohesive and persuasive way. This will clearly set you apart from your competition, while landing your dream job will prove that pursuing that advanced degree was worth it.
4. You'll improve on all your soft skills
While pursuing your undergraduate degree, you likely noticed that you were learning more than just the subject matter taught in each class. Completing your studies also required time management skills , focus and problem solving .
Getting a doctorate degree requires even more of the soft skills that employers look for in applicants . Your intensive study and finished thesis should lead to improvements in your problem solving, critical thinking , patience and adaptability . These desirable skills won't just help you land a job but also excel in whatever career you choose to pursue .
5. You'll collect an extensive network of professional colleagues
When weighing the pros and cons of earning a PhD, consider all the professional contacts you'll make during the course of your studies. Working closely with professors, department heads, experts in your field, as well as fellow researchers, helps you develop an important resource. This network of colleagues can provide continual assistance with references, job leads, career advice and collaboration.
6. You can wait for a more favorable job market
Job prospects may not look that promising when you've completed your undergraduate degree, or even after you've been in the workforce for a few years. While there's no guarantee things will improve after a delay, some students may appreciate the benefit of a steady graduate assistant salary while they work on enhancing their résumé with a doctorate.
If you couldn't get a good internship during or after your undergrad studies, the PhD work also gives you the time to build that professional network . These contacts could prove to be the key to breaking into a specialized or highly competitive field.
You may still be thinking about all that time and commitment and wondering, “Is a PhD worth it?”. While there are always positive results from improving your education, there are some downsides to getting your doctorate.
1. It's expensive
This is a substantial factor for many students when weighing the merits of pursuing a PhD versus entering the job market right away. If you already have student loans , continuing your education will just increase your burden and add substantial pressure when you eventually begin your job search.
If cost is a concern, investigate graduate assistant jobs that help with expenses. Some programmes offer tuition assistance in return for teaching or research work. For those who already work full time and are hoping a PhD will help them advance in their career, consider keeping that job and pursuing your studies on a part-time basis.
2. Getting a PhD can be a lonely experience
Despite your interactions with professors and other students, pursuing a doctoral degree is ultimately a solitary pursuit. Your thesis topic is unique to you, and you'll spend a lot of time alone doing research and writing. Your social life can suffer, especially if you're also working in addition to your studies.
Career experts often talk about the necessity of work-life balance for physical and mental health, and this is just as important for PhD students as anyone else. It may take you a little longer to complete your degree, but it's worth taking the time to visit family and hang out with your friends. These positive interactions can help you stay motivated through the most tedious parts of your work.
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration
Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
A topic that seemed intriguing at first may not live up to years of scrutiny, causing boredom at best or requiring a complete thesis change at worst. Not all programmes are well-run, either, and you may have a supervisor who is too critical, offers poor advice or is just unavailable and unhelpful.
The difficulties of a PhD programme lead to rather substantial dropout rates. In the US alone, only 57% of PhD students obtained their degree within a decade of enrolling. If you want to be in the successful half of those stats, take extra time to review your choice of supervisor and topic focus. Ask every professor you have for advice on making the right decisions and talk with current graduate students to see what their experience has been.
4. There may be limited job openings
While getting a PhD can qualify you for better and higher-paying jobs , it can also put you in a position where you're competing for an extremely limited number of job openings. This is especially true of university jobs, where the number of advanced degree graduates far outpaces the need for full-time instructors, researchers and administrators.
Earning your PhD with a very obscure thesis in a niche speciality can also limit your options. When there are only a handful of jobs that suit your expertise, and they're already occupied, it can make you feel that your doctorate was a waste of time. Consider the job market before you make decisions about getting another degree. If you're determined to study in a niche area, think ahead of time about related fields or industries where your knowledge and skills will also prove useful to employers.
5. There may be little to no financial reward
While most studies concur that having a PhD increases your income potential substantially over the lifetime of your career, it's not a guarantee of job security or a financial windfall. A study by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) found that 5 years after earning their doctorates , 45% of grads in Germany were still on temporary contracts and 13% ended up in lowly occupations.
Other European countries, including Slovakia, Belgium and Spain, had similar results. In the US, in fields like engineering, the difference in pay scales between employees with a master's degree and a PhD was a mere 7%. When that small bump in salary is weighed against the amount of debt taken on in order to get your degree, you may decide it's not worth it.
6. You could lose out on valuable job experience
New forms of technology continue to change how organizations operate, and those changes can happen fast. If you've already spent several years in school, toiling away in solitary study of obscure subjects can cause you to fall further behind in learning the skills you'll actually need for a future career.
Before you invest in getting a PhD, research your chosen field and learn which type of degree will give you the most value. Many scientific, financial and computing careers rely more on skills acquired on the job, rather than in coursework that can quickly become outdated.
Questions to ask yourself
You’ve listed out the pros and cons, but that still may not be enough to help make your decision. When it comes to a life-altering change like getting a doctorate, it’s okay to take enough time to ask yourself specific questions to ensure you’re making the right move. Consider asking yourself the following:
- Why do I want to get a PhD?
- Do I have the pre-requisites to move forward to a PhD?
- What are my strengths and limitations?
- Am I financially prepared?
- Am I mentally prepared?
- How will this affect my relationship with my family or friends?
- Where will I study?
- What am I trying to achieve?
- What jobs will be available to me after I get my PhD?
- Are there other options or avenues to consider?
Unfortunately, you may not have the answer to every one of these questions, because let’s face it, you don’t know what you don’t know. You might not know how it will affect your relationship with family or friends, but why not ask them? Reach out to those closest to you and see how you pursuing this degree could trickle down to them and allow that to play into your decision. Evaluate the answers to these questions and use it to help you make an educated decision on your future moving forward.
The best PhD degrees
If you’ve weighed out the pros and cons, asked all the important questions, and now you’re set on getting your PhD, congratulations! To help you along the way, let’s look at a list of the most valuable PhD programs to start you on your way to this degree.
- Criminal Justice
- Engineering
- Cybersecurity
- Business Administration
These fields are rapidly growing and are among the highest-paying doctorate degrees in 2022 , so they might be worth considering as you start your journey.
Key takeaways
Pursuing your PhD requires an incredible amount of commitment, and it's important to take the necessary time to make the decision. As you’re evaluating a doctorate degree, remember the following:
- Evaluate the pros and cons list right from the beginning to ensure you’re weighing out both sides of the coin.
- Ask yourself the necessary questions. A doctorate degree commitment can affect more than just you, so be sure you’re factoring that into your decision.
- Review specifically which PhD would be best for you and your field progression.
- Research your chosen field carefully and evaluate the job market before you finalize your degree choice.
- Once you’ve selected your degree, stay focused and stay driven. It’s going to be a hard few years, but it will be worth the work!
Who knows, this may prompt you to move on to postgraduate study — never stop achieving!
Have you decided to pursue your PhD, or are you still considering your options? Join us in the comments below and let us know what’s stopping or encouraging you from getting a PhD.
Originally published on July 24, 2019. Updated by Shalie Reich.
Continuing Education
Courses and Qualifications

The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
Is a PhD Worth It? Should I Do a PhD?
It’s been almost a year since I was officially awarded my PhD. How time flies! I figure now is a good time to reflect on the PhD and answer some of life’s big questions. Is a PhD worth it? Does having a PhD help your future job prospects? Am I pleased that I did a PhD and would I recommend that you do a PhD?
In this post I’ll walk through some of the main points to consider. We’ll touch on some pros and cons, explore the influence it could have on your career and finally attempt to answer the ultimate question. Is a PhD worth it?
Before we get into the details, if you’re considering applying for a PhD you may also want to check out a few other posts I’ve written:
- How Hard is a PhD?
- How Much Work is a PhD?
- How Much Does a PhD Student Earn? Comparing a PhD Stipend to Grad Salaries
- Characteristics of a Researcher
Are you seated comfortably? Great! Then we’ll begin.
The Pros and Cons of PhDs
When I have a difficult decision to make I like to write a pros and cons list. So let’s start by breaking down the good and bad sides of getting a PhD. Although I’ve tried to stay objective, do take into account that I have completed a PhD and enjoyed my project a lot!
These lists certainly aren’t exhaustive, so be sure to let me know if you can think of any other points to add!
The Good Parts: Reasons to Do a PhD
Life as a phd student.
- You get to work on something really interesting . Very few people outside of academia get to dive so deep into topics they enjoy. Plus, by conducting cutting edge research you’re contributing knowledge to a field.
- It can be fun! For example: solving challenges, building things, setting up collaborations and going to conferences.
- Being a PhD student can be a fantastic opportunity for personal growth : from giving presentations and thinking critically through to making the most of being a student such as trying new sports.
- You are getting paid to be a student : I mean come on, that’s pretty good! Flexible hours, socialising and getting paid to learn can all be perks. Do make sure you consciously make the most of it!
Life As A PhD Graduate
- The main one: Having a PhD may open doors . For certain fields, such as academia itself, a PhD may be a necesity. Whilst in others having a PhD can help demonstrate expertise or competency, opening doors or helping you to leapfrog to higher positions. Your mileage may vary!
- You survived a PhD: this accomplishment can be a big confidence booster .
- You’ve got a doctorate and you can use the title Dr. Certainly not enough justification on it’s own to do a PhD, but for some people it helps!
The Bad Parts: Potential Reasons Not to Do a PhD
- It can be tough to complete a PhD! There are lots of challenges . Unless you’re careful and take good care of yourself it can take a mental and physical toll on your well being.
- A PhD can be lonely ( though doesn’t have to be ), and PhD supervisors aren’t always as supportive as you’d like them to be.
- Additionally, in particular now during the pandemic, you might not be able to get as much support from your supervisor, see your peers or even access the equipment and technical support as easily as in normal times.
- You might find that having a PhD may not bring the riches you were expecting . Have a certain career you’re looking to pursue? Consider trying to find out whether or not having a PhD actually helps.
- Getting a job with a PhD can still be tough . Let’s say you want to go for a career where having a PhD is required, even once you’ve got a PhD it might not be easy to find employment. Case in point are academic positions.
- Even though you’ve put in the work you may want to use your Dr title sparingly , it certain industries a PhD may be seen as pretencious. Also, use your title sparingly to avoid getting mistaken for a medic (unless of course you’re one of them too!)
Is a PhD Good For Your Career?
If you’re wondering “Should I do a PhD?”, part of your motivation for considering gaining a PhD may be your career prospects. Therefore I want to now dive deeper into whether or not a PhD could help with future employment.
It is difficult to give definitive answers because whether or not a PhD helps will ultimately depend a lot upon what kind of career you’re hoping to have. Anyway, let’s discuss a few specific questions.
Does a PhD Help You Get a Job?
For certain industries having a PhD may either be a requirement or a strong positive.
Some professions may require a PhD such as academia or research in certain industries like pharma. Others will see your qualification as evidence that you’re competent which could give you an edge. Of course if you’re aiming to go into a career using similar skills to your PhD then you’ll stand a better chance of your future employer appreciating the PhD.
In contrast, for other roles your PhD may not be much help in securing a job. Having a PhD may not be valued and instead your time may be better spent getting experience in a job. Even so, a PhD likely won’t have been completely useless.
When I worked at an engineering consultancy the recruitment team suggested that four years of a PhD would be considered comparable to two or three years of experience in industry. In those instances, the employer may actively prefer candidates who spent those years gaining experience on the job but still appreciates the value of a PhD.
Conclusion: Sometimes a PhD will help you get a job, othertimes it wont. Not all employers may appreciate your PhD though few employers will actively mark you down for having a PhD.
Does a PhD Increase Salary? Will it Allow You to Start at a Higher Level?
This question is very much relates to the previous one so my answer will sound slightly similar.
It’ll ultimately depend upon whether or not the industry and company value the skills or knowledge you’ve gained throughout your PhD.
I want to say from the start that none of us PhD-holders should feel entitled and above certain types of position in every profession just for having a PhD. Not all fields will appreciate your PhD and it may offer no advantage. It is better to realise this now.
Some professions will appreciate that with a PhD you’ll have developed a certain detail-orientated mindset, specialised knowledge or skills that are worth paying more for. Even if the position doesn’t really demand a PhD, it is sometimes the case that having someone with a PhD in that position is a useful badge for the company to wave at customers or competitors. Under these circumstances PhD-holders may by default be offered slightly higher starting positions than other new-starters will lower degree qualifications.
To play devil’s advocate, you could be spending those 3-4 (or more) years progressing in the job. Let’s look at a few concrete examples.
PhD Graduate Salaries in Academia
Let’s cut to the chase: currently as a postdoc at a decent university my salary is £33,787, which isn’t great. With a PhD there is potential to possibly climb the academic ladder but it’s certainly not easy. If I were still working in London I’d be earning more, and if I were speficially still working at Imperial in London I’d be earning a lot more. Browse Imperial’s pay scales here . But how much is it possible to earn with a PhD compared to not having one?
For comparison to research staff with and without PhDs:
As of 2023 research assistants (so a member of staff conducting research but with no PhD) at Imperial earn £38,194 – £ 4 1,388 and postdoctoral research associates earn £43,093 – £50,834 . Not only do you earn £5000 or more a year higher with a PhD, but without a PhD you simply can’t progress up the ladder to research fellow or tenure track positions.
Therefore in academia it pays to have a PhD, not just for the extra cash but for the potential to progress your career.
PhD Graduate Salaries in Industry
For jobs in industry, it is difficult to give a definitive answer since the variety of jobs are so wide ranging.
Certain industries will greatly reward PhD-holders with higher salaries than those without PhDs. Again it ultimately depends on how valuable your skills are. I’ve known PhD holders to do very well going into banking, science consultancy, technology and such forth.
You might not necessarily earn more money with a PhD in industry, but it might open more doors to switch industries or try new things. This doesn’t necessarily mean gaining a higher salary: I have known PhD-holders to go for graduate schemes which are open to grads with bachelors or masters degrees. Perhaps there is an argument that you’re more employable and therefore it encourages you to make more risky career moves which someone with fewer qualifications may make?
You can of course also use your PhD skills to start your own company. Compensation at a start-up varies wildly, especially if you’re a founder so it is hardly worth discussing. One example I can’t resist though is Magic Pony. The company was co-founded by a Imperial PhD graduate who applied expertise from his PhD to another domain. He sold the company two years later to Twitter for $150 million . Yes, including this example is of course taking cherry-picking to the extreme! The point stands though that you can potentially pick up some very lucrative skills during your PhD.
Conclusion: Like the previous question, not all industries will reward your PhD. Depending on what you want to go and do afterward your PhD, it isn’t always worth doing a PhD just for career progression. For professions that don’t specifically value a PhD (which is likely the majority of them!) don’t expect for your PhD to necessarily be your ticket to a higher position in the organisation.
Is a PhD Worth it?
What is “it”.
When we’re asking the question “is a PhD worth it?” it is a good idea to touch on what “it” actually is. What exactly are PhD students sacrificing in gaining a PhD? Here is my take:
- Time . 3-5 (more more) years of your life. For more see my post: how long a PhD takes .
- Energy. There is no doubt that a PhD can be mentally and physically draining, often more so than typical grad jobs. Not many of us PhD students often stick to normal office hours, though I do encourage you to !
- Money. Thankfully most of us, at least in STEM, are on funded PhD projects with tax free stipends. You can also earn some money on the side quite easily and without paying tax for a while. Even so, over the course of a PhD you are realistically likely to earn more in a grad job. For more details on how PhD stipends compare to grad salaries read my full analysis .
- Potential loss of opportunities . If you weren’t doing a PhD, what else could you be doing? As a side note, if you do go on to do a PhD, do make sure you to take advantage of the opportunities as a PhD student !
When a PhD Could Be Worth It
1. passion for a topic and sheer joy of research.
The contribution you make to progressing research is valuable in it’s own right. If you enjoy research, can get funding and are passionate about a subject by all means go and do the PhD and I doubt you’ll regret it.
2. Learning skills
If there is something really specific you want to spend three year or more years learning then a PhD can be a great opportunity. They’re also great for building soft skills such as independence, team work, presenting and making decisions.
Do be aware though that PhD projects can and do evolve so you can’t always guarantee your project will pan out as expected.
If there is the option to go into a career without a PhD I’d bet that in a lot of cases you’d learn more, faster, and with better support in industry. The speed of academic research can be painstakingly slow. There are upsides to learning skills in academia though, such as freedom and the low amount of responsibility for things outside your project and of course if you’re interested in something which hasn’t yet reached industry.
3. Helping with your career
See the section further up the page, this only applies for certain jobs. It is rare though that having a PhD would actively look bad on your CV.
When a PhD May Not Be Worth It
1. just because you can’t find another job.
Doing a PhD simply because you can’t find a job isn’t a great reason for starting one. In these circumstances having a PhD likely isn’t worth it.
2. Badge collecting
Tempted by a PhD simply to have a doctorate, or to out-do someone? Not only may you struggle with motivation but you likely won’t find the experience particularly satisfying. Sure, it can be the icing on the cake but I reckon you could lose interest pretty quickly if it is your only motivation for gaining a PhD.
Do I Feel That My Own PhD Was Worth It?
When I finished my undergrad I’d been tempted by a PhD but I wasn’t exactly sure about it. Largely I was worried about picking the wrong topic.
I spent a bit of time apprehensively applying, never being sure how I’d find the experience. Now that I’ve finished it I’m very pleased to have got my PhD!
Here are my main reasons:
- I enjoyed the research and felt relatively well fulfilled with the outcomes
- Having the opportunity to learn lots of some new things was great, and felt like time well spent
- I made new friends and generally enjoyed my time at the university
- Since I’d been interested in research and doing a PhD for so long, I feel like if I’d not done it I’d be left wondering about it and potentially end up regretting it.
In Summary, Is a PhD Worth It?
I’ve interviewed many PhD students and graduates and asked each one of them whether the PhD was worth it . The resounding answer is yes! Now of course there is some selection bias but even an interviewee who had dropped out of their PhD said that the experience had been valueable.

If you’ve got this far in the post and are still a little on the fence about whether or not a PhD is worth it, my advice is to look at the bigger picture. In comparison to your lifetime as a whole, a PhD doesn’t really take long:

People graduating now likely won’t retire until they’re in their 70s: what is 3-4 years out of a half century long career?
So Should I Do a PhD?
Whether a PhD is worth all the time and energy ultimately comes down to why you’re doing one in the first place.
There are many great reasons for wanting to do a PhD, from the sheer enjoyment of a subject through to wanting to open up new career opportunities.
Nevertheless, it is worth pointing out that practically every PhD student encounters difficult periods. Unsurprisingly, completing a PhD can be challenging and mentally draining. You’ll want to ensure you’re able to remind yourself of all the reasons why it is worth it to provide motivation to continue.
If you’re interested, here were my own reasons for wanting a PhD.
Why I decided to pursue a PhD
Saying that, if you’re interested in doing a PhD I think you should at least apply. I can’t think of any circumstances where having a PhD would be a hindrance.
It can take a while to find the right project (with funding ) so I suggest submitting some applications and see how they go. If you get interesting job offers in the meantime you don’t need to commit to the PhD. Even if you start the PhD and find you don’t enjoy it, there is no shame in leaving and you can often still walk away with a master’s degree.
My advice is that if you’re at all tempted by a PhD: go for it!
I hope this post helped you to understand if a PhD is worth it for you personally. If it is then best of luck with your application!
Considering doing a PhD? I have lots of other posts covering everything about funding , how much PhD students earn , choosing a project and the interview process through to many posts about what the life of a PhD student and graduate is like . Be sure to subscribe below!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

The Five Most Powerful Lessons I Learned During My PhD
8th August 2024 8th August 2024

PhD Salary UK: How Much Do PhD Students Get Paid Compared to Graduates?
5th February 2024 4th July 2024

The Benefits of Having a PhD
7th September 2022 30th January 2024
4 Comments on “Is a PhD Worth It? Should I Do a PhD?”
Hi Thanks for the post . I have been struggling to make a decision regarding doing a PhD or doing a second masters . I’m currently doing an msc civil engineering online (because of covid) so for my research I am not able to conduct lab experiments. Therefore my research is more of a literature review / inductive research. So I feel I’ll be at a disadvantage if I were to apply for a phd program especially at high ranking universities like oxford , imperial etc What are your thoughts?
Hey Esther,
I completely appreciate that it’s not an ideal situation at the moment so thanks for reaching out, it’s a great question. A few thoughts I have:
• If you are already tempted by a PhD and would do a second masters simply to gain lab experience, there is no harm in applying for the PhD now. At the very least I suggest considering reaching out to potential supervisors to discuss the situation with them. The universities realise that current applicants won’t have been able to gain as much research experience as normal over the last year. Practical lab experience has halted for so many people so don’t let it put you off applying!
• If you don’t get in on the first go, I don’t believe it looks bad to apply again with more experience. I applied for PhDs for three years, it doesn’t need to take this long but the point is that there’s not much reason to give it a go this year and stand a chance of getting accepted.
• Although we can be optimistic, even if you were to do a second masters it may not be guaranteed that you can gain as much lab experience as you’d like during it: even more reason to start the ball rolling now.
I hope that helps, let me know if you’d like any other further advice.
Best of luck. 🙂
Funny, every one i have talked to as well as myself when we asked ourselves and others whether the PhD was worth it is a resounding ‘No.’
I guess it comes down to a Blue or Red Pill, LoL.
Hi Joe, thanks for sharing this. I’ve spent enough time on the PhD subreddit to see many other people who haven’t had good experiences either! On the flipside many people do have positive experiences, myself included. There is perhaps an element of luck as to what your research environment turns out to be like which could somewhat dictate the PhD experience, but ultimately I do think that answering whether or not a PhD has been worth it really depends a lot on why someone is pursuing a PhD in the first place. I’m keen to make sure people don’t have unrealistic expectations for what it could bring them. I really welcome hearing about different experiences and if you’d fancy sharing your perspective for the PhD profiles series I’d love to hear from you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview

- 3 . 01 . 20
- Leaving Academia
Is a PhD Worth It? I Wish I’d Asked These 6 Questions First.
- Posted by: Chris
Updated Nov. 19, 2022
Is a PhD worth it?
Should I get a PhD?
A few people admit to regretting their PhD. Most—myself included — said that they don’t ( I wrote about why in this post ).
But we often say we don’t regret stupid things we’ve done or bad things that happen to us. This means we learned from them, not that we wanted them to happen.
So just because PhDs don’t regret it, doesn’t mean it was worth it.
But if you were to ask, Is a PhD worth it, it’s a different and more complicated question.
When potential PhD students ask me for advice, I hate giving it. I can’t possibly say whether it will be worth it for them. I only know from experience that for some PhDs the answer is no.
In this post, I’ll look at this question from five different directions, five different ways that a PhD could be worth it. Then I give my opinion on each one. You can tell me if I got the right ones of if I’m way off base. So here we go.
This is post contains affiliate links. Thanks for supporting Roostervane!
tl;dr It’s up to you to make it worth it. A PhD can hurt your finances, sink you in debt, and leave you with no clear path to success in some fields. But PhDs statistically earn more than their and have lower unemployment rates. A PhD also gives you a world-class mind, a global network, and a skill set that can go just about anywhere.
Should I Get a PhD?
tl;dr Don’t get a PhD by default. Think it through. Be clear about whether it’s going to help you reach career goals, and don’t expect to be a professor. A few rules of thumb- make sure you know where you want to go and whether a PhD is the ONLY way to get there, make sure it’s FUNDED (trust me), and make sure your program has strong ties into industry and a record of helping its students get there.
1. Is a PhD worth it for your finances?
My guess: Not usually
People waste a lot of their best years living on a grad stipend. To be honest, my money situation was pretty good in grad school. I won a large national grant, I got a ton of extra money in travel grants, and my Canadian province gave me grants for students with dependents. But even with a decent income, I was still in financial limbo–not really building wealth of any sort.
And many students scrape by on very small stipends while they study.
When it comes to entering the marketplace, research from Canada and the United States shows that PhD students eventually out-earn their counterparts with Master’s degrees. It takes PhDs a few years to find their stride, but most of us eventually do fine for earnings if we leave academia. Which is great, and perhaps surprising to many PhDs who think that a barista counter is the only non-academic future they have .
The challenge is not income–it’s time. If you as a PhD grad make marginally more than a Master’s graduate, but they entered the workforce a decade earlier, it takes a long time for even an extra $10,000 a year to catch up. The Master’s grad has had the time to build their net worth and network, perhaps buy a house, pay down debt, invest, and just generally get financially healthy.
While PhDs do fine in earnings in the long run, the opportunity cost of getting the PhD is significant.
The only real way to remedy this—if you’ve done a PhD and accumulating wealth is important to you, is to strategically maximize your earnings and your value in the marketplace to close the wealth gap. This takes education, self-discipline, and creativity, but it is possible.
I tried to calculate the opportunity cost of prolonging entry into the workforce in this post .
2. Is a PhD worth it for your career?
My guess: Impossible to tell
Most of my jobs have given me the perfect opportunity to see exactly where I could be if I’d stopped at a Master’s degree, often working alongside or for those who did and are further ahead. In terms of nuts and bolts of building career experience section on a resume, which is often the most important part, a PhD is rarely worth it. (Some STEM careers do require a PhD.)
However, at the start of my post-graduate educational journey, I was working part-time running teen programs and full time as a landscaper. I had an undergraduate degree. Despite my job and a half, I was still poor. My life had no direction, and had I not begun my Master’s to PhD journey I probably would have stayed there.
The PhD transformed me personally. It did this by developing my skills, or course. But even more so, it taught me that anything is possible. It took a poor kid from a mining town in northern Canada and gave me access to the world. It made my dreams of living abroad come true. I learned that anything is possible. And that will never go away.
It’s changed the course of my life and, subsequently, my career.
It’s impossible for you to know if it’s worth it for your career. But you can build a hell of a career with it.
So it wouldn’t be fair for me to say, “don’t get a PhD.” Because it worked out for me, and for some it does.
But there are a heck of a lot of people who haven’t figured out how to build a career with this thing. Which is one of the reasons Roostervane exists in the first place.
Psst! If you’re looking at doing a PhD because you don’t know where to go next with your career–I see you. Been there. Check out my free PDF guide– How to Build a Great Career with Any Degree.
3. Is a PhD worth it for your personal brand?
My guess: Probably
There’s some debate over whether to put a Dr. or PhD before or after your name. People argue over whether it helps in the non-academic marketplace. Some feel that it just doesn’t translate to whatever their new reality is. Some have been told by some manager somewhere that they’re overqualified and pulled themselves back, sometimes wiping the PhD off their resume altogether.
The truth is, if you have a PhD, the world often won’t know what to do with it. And that’s okay. Well-meaning people won’t understand how you fit into the landscape, and you may have to fight tooth and nail for your place in it. People may tell you they can’t use you, or they might go with what they know—which is someone less qualified and less-educated.
It happens.
But someone with a PhD at the end of their name represents an indomitable leader. So grow your possibilities bigger and keep fighting. And make your personal brand match those three little letters after your name. Do this so that the world around can’t help but see you as a leader. More importantly, do it so that you don’t forget you are.
Should I put “PhD” after my name on LinkedIn?
5 reasons you need to brand yourself
4. Is a PhD worth it for your sense of purpose?
Is getting a PhD worth it? For many people the answer is no.
PhDs are hurting.
If you’ve done one, you know. Remember the sense of meaning and purpose that drew you towards a PhD program? Was it still there at the end? If yours was, you’re lucky. I directed my purpose into getting hired in a tenure-track job, and got very hurt when it didn’t happen.
And people have vastly different experiences within programs.
Some people go through crap. But for them their research is everything and putting up with crap is worth it to feel like they have a sense of purpose. Many PhDs who are drawn into programs chasing a sense of purpose leave deeply wounded and disenchanted, ironically having less purpose when they started.
While new PhDs often talk about the PhD as a path do doing “something meaningful,” those of us who have been through entire programs have often seen too much. We’ve either seen or experienced tremendous loss of self. Some have friends who didn’t make it out the other end of the PhD program.
But there are some PhDs who have a great experience in their programs and feel tremendously fulfilled.
As I reflect on it, I don’t think a sense of purpose is inherently fulfilled or disappointed by a PhD program. There are too many variables.
However, if you’re counting on a PhD program to give you a sense of purpose, I’d be very careful. I’d be even more cautious if purpose for you means “tenure-track professor.” Think broadly about what success means to you and keep an open mind .
5. Is my discipline in demand?
Okay, so you need to know that different disciplines have different experiences. Silicon Valley has fallen in love with some PhDs, and we’re seeing “PhD required” or “PhD preferred” on more and more job postings. So if your PhD is in certain, in-demand subjects… It can be a good decision.
My humanities PhD, on the other hand, was a mistake. I’m 5 years out now, and I’ve learned how to use it and make money with it. That’s the great news. But I’d never recommend that anyone get a PhD in the humanities. Sorry. I really wish I could. It’s usually a waste of years of your life, and you’ll need to figure out how to get a totally unrelated job after anyway.
TBH, most of the skills I make money with these days I taught myself on Skillshare .
6. Is a PhD worth it for your potential?
My guess: Absolutely
Every human being has unlimited potential, of course. But here’s the thing that really can make your PhD worth it. The PhD can amplify your potential. It gives you a global reach, it gives you a recognizable brand, and it gives you a mind like no other.
One of my heroes is Brené Brown. She’s taken research and transformed the world with it, speaking to everyone from Wall-Street leaders to blue-collar workers about vulnerability, shame, and purpose. She took her PhD and did amazing things with it.
Your potential at the end of your PhD is greater than it has ever been.
The question is, what will you do with that potential?
Many PhD students are held back, not by their potential, but by the fact that they’ve learned to believe that they’re worthless. Your potential is unlimited, but when you are beaten and exhausted, dragging out of a PhD program with barely any self-worth left, it’s very hard to reach your potential. You first need to repair your confidence.
But if you can do that, if you can nurture your confidence and your greatness every day until you begin to believe in yourself again, you can take your potential and do anything you want with it.
So why get a PhD?
Because it symbolizes your limitless potential. If you think strategically about how to put it to work.
PhD Graduates Don’t Need Resumes. They Need a Freaking Vision

By the way… Did you know I wrote a book about building a career with a PhD? You can read the first chapter for free on Amazon.
So if you’re asking me, “should I do a PhD,” I hope this post helps you. Try your best to check your emotion, and weigh the pros and cons.
And at the end of the day, I don’t think that whether a PhD is worth it or not is some fixed-in-stone thing. In fact, it depends on what you do with it.
So why not make it worth it? Work hard on yourself to transform into a leader worthy of the letters after your name, and don’t be afraid to learn how to leverage every asset the PhD gave you.
One of the reasons I took my PhD and launched my own company is that I saw how much more impact I could have and money I could be making as a consultant (perhaps eventually with a few employees). As long as I worked for someone else, I could see that my income would likely be capped. Working for myself was a good way to maximize my output and take control of my income.
It’s up to you to make it worth it. Pick what’s important to you and how the degree helps you get there, and chase it. Keep an open mind about where life will take you, but always be asking yourself how you can make more of it.
Check out the related post- 15 Good, Bad, and Awful Reasons People Go to Grad School. — I Answer the Question, “Should I Go to Grad School?” )

Consulting Secrets 3 – Landing Clients
Photo by Christian Sterk on Unsplash There’s a new type of post buzzing around LinkedIn. I confess, I’ve even made a few. The post is

You’re Not Good Enough… Yet
Last year, I spent $7k on a business coach. She was fantastic. She helped me through sessions of crafting my ideas to become a “thought

$200/hr Expert? Here’s the Secret!
Photo by David Monje on Unsplash I was listening to Tony Robbins this week. He was talking about being the best. Tony asks the audience,
SHARE THIS:
EMAIL UPDATES
Weekly articles, tips, and career advice
Roostervane exists to help you launch a career, find your purpose, and grow your influence
- Write for Us
Terms of Use | Privacy | Affiliate Disclaimer
©2022 All rights reserved
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window

9 things you should consider before embarking on a PhD
June 23, 2021 | 15 min read
By Andy Greenspon
The ideal research program you envision is not what it appears to be
Editor's Note: When Andy Greenspon wrote this article, he was a first-year student in Applied Physics at Harvard. Now he has completed his PhD. — Alison Bert, June 23, 2021
If you are planning to apply for a PhD program, you're probably getting advice from dozens of students, professors, administrators your parents and the Internet. Sometimes it's hard to know which advice to focus on and what will make the biggest difference in the long-run. So before you go back to daydreaming about the day you accept that Nobel Prize, here are nine things you should give serious thought to. One or more of these tips may save you from anguish and help you make better decisions as you embark on that path to a PhD.
1. Actively seek out information about PhD programs.
Depending on your undergraduate institution, there may be more or less support to guide you in selecting a PhD program – but there is generally much less than when you applied to college.
On the website of my physics department, I found a page written by one of my professors, which listed graduate school options in physics and engineering along with resources to consult. As far as I know, my career center did not send out much information about PhD programs. Only after applying to programs did I find out that my undergraduate website had a link providing general information applicable to most PhD programs. This is the kind of information that is available all over the Internet.
So don't wait for your career center or department to lay out a plan for you. Actively seek it out from your career center counselors, your professors, the Internet — and especially from alumni from your department who are in or graduated from your desired PhD program. First-hand experiences will almost always trump the knowledge you get second-hand.
2. A PhD program is not simply a continuation of your undergraduate program.
Many students don't internalize this idea until they have jumped head-first into a PhD program. The goal is not to complete an assigned set of courses as in an undergraduate program, but to develop significant and original research in your area of expertise. You will have required courses to take, especially if you do not have a master's degree yet, but these are designed merely to compliment your research and provide a broad and deep knowledge base to support you in your research endeavors.
At the end of your PhD program, you will be judged on your research, not on how well you did in your courses. Grades are not critical as long as you maintain the minimum GPA requirement, and you should not spend too much time on courses at the expense of research projects. Graduate courses tend to be designed to allow you to take away what you will find useful to your research more than to drill a rigid set of facts and techniques into your brain.
3. Take a break between your undergraduate education and a PhD program.
You are beginning your senior year of college, and your classmates are asking you if you are applying to graduate school. You think to yourself, "Well, I like studying this topic and the associated research, and I am going to need a PhD if I want to be a professor or do independent research, so I might as well get it done as soon as possible." But are you certain about the type of research you want to do? Do you know where you want to live for the next five years? Are you prepared to stay in an academic environment for nine years straight?
Many people burn out or end up trudging through their PhD program without a thought about what lies outside of or beyond it. A break of a year or two or even more may be necessary to gain perspective. If all you know is an academic environment, how can you compare it to anything else? Many people take a job for five or more years before going back to get their PhD. It is true though that the longer you stay out of school, the harder it is to go back to an academic environment with lower pay and a lack of set work hours. A one-year break will give you six months or so after graduation before PhD applications are due. A two-year gap might be ideal to provide time to identify your priorities in life and explore different areas of research without having school work or a thesis competing for your attention.
Getting research experience outside of a degree program can help focus your interests and give you a leg up on the competition when you finally decide to apply. It can also help you determine whether you will enjoy full-time research or if you might prefer an alternative career path that still incorporates science, for example, in policy, consulting or business — or a hybrid research job that combines scientific and non-scientific skills.
I will be forever grateful that I chose to do research in a non-academic environment for a year between my undergraduate and PhD programs. It gave me the chance to get a feel for doing nothing but research for a full year. Working at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in the Space Division, I was the manager of an optics lab, performing spectroscopic experiments on rocks and minerals placed in a vacuum chamber. While my boss determined the overall experimental design, I was able to make my own suggestions for experiments and use my own discretion in how to perform them. I presented this research at two national conferences as well — a first for me. I was also able to learn about other research being performed there, determine which projects excited me the most, and thus narrow down my criteria for a PhD program.
4. Your current area of study does not dictate what you have to study in graduate school.
You might be studying the function and regulation of membrane proteins or doing a computational analysis of the conductivity of different battery designs, but that doesn't mean your PhD project must revolve around similar projects. The transition between college or another research job to a PhD program is one of the main transitions in your life when it is perfectly acceptable to completely change research areas.
If you are doing computation, you may want to switch to lab-based work or vice versa. If you are working in biology but have always had an interest in photonics research, now is the time to try it out. You may find that you love the alternative research and devote your PhD to it, you might hate it and fall back on your previous area of study — or you may even discover a unique topic that incorporates both subjects.
One of the best aspects of the PhD program is that you can make the research your own. Remember, the answer to the question "Why are you doing this research?" should not be "Well, because it's what I've been working on for the past few years already."While my undergraduate research was in atomic physics, I easily transitioned into applied physics and materials science for my PhD program and was able to apply much of what I learned as an undergraduate to my current research. If you are moving from the sciences to a non-STEM field such as social sciences or humanities, this advice can still apply, though the transition is a bit more difficult and more of a permanent commitment.
5. Make sure the PhD program has a variety of research options, and learn about as many research groups as possible in your first year.
Even if you believe you are committed to one research area, you may find that five years of such work is not quite what you expected. As such, you should find a PhD program where the professors are not all working in the same narrowly focused research area. Make sure there are at least three professors working on an array of topics you could imagine yourself working on.
In many graduate programs, you are supposed to pick a research advisor before even starting. But such arrangements often do not work out, and you may be seeking a new advisor before you know it. That's why many programs give students one or two semesters to explore different research areas before choosing a permanent research advisor.
In your first year, you should explore the research of a diverse set of groups. After touring their labs, talking to the students, or sitting in on group meetings, you may find that this group is the right one for you.
In addition, consider the importance of who your research advisor will be. This will be the person you interact with regularly for five straight years and who will have a crucial influence on your research. Do you like their advising style? Does their personality mesh with yours? Can you get along? Of course, the research your advisor works on is critical, but if you have large disagreements at every meeting or do not get helpful advice on how to proceed with your research, you may not be able to succeed. At the very least, you must be able to handle your advisor's management of the lab and advising style if you are going to be productive in your work. The Harvard program I enrolled in has professors working on research spanning from nanophotonics to energy materials and biophysics, covering my wide range of interests. By spending time in labs and offices informally chatting with graduate students, I found an advisor whose personality and research interests meshed very well with me. Their genuine enthusiasm for this advisor and their excitement when talking about their research was the best input I could have received.
6. Location is more important than you think — but name recognition is not.
The first consideration in choosing a PhD program should be, "Is there research at this university that I am passionate about?" After all, you will have to study this topic in detail for four or more years. But when considering the location of a university, your first thought should not be, "I'm going to be in the lab all the time, so what does it matter if I'm by the beach, in a city, or in the middle of nowhere." Contrary to popular belief, you will have a life outside of the lab, and you will have to be able to live with it for four or more years. Unlike when you were an undergraduate, your social and extracurricular life will revolve less around the university community, so the environment of the surrounding area is important. Do you need a city atmosphere to be productive? Or is your ideal location surrounded by forests and mountains or by a beach? Is being close to your family important? Imagine what it will be like living in the area during the times you are not doing research; consider what activities will you do and how often will you want to visit family.
While many of the PhD programs that accepted me had research that truly excited me, the only place I could envision living for five or more years was Boston, as the city I grew up near and whose environment and culture I love, and to be close to my family.
While location is more important than you think, the reputation and prestige of the university is not. In graduate school, the reputation of the individual department you are joining — and sometimes even the specific research group you work in — are more important. There, you will develop research collaborations and professional connections that will be crucial during your program and beyond. When searching for a job after graduation, other scientists will look at your specific department, the people you have worked with and the research you have done.

At the Asgard Irish Pub in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Andy Greenspon talks with fellow graduate students from Harvard and MIT at an Ask for Evidence workshop organized by Sense About Science. He grew up near Boston and chose to go to graduate school there.
7. Those time management skills you developed in college? Develop them further.
After surviving college, you may think you have mastered the ability to squeeze in your coursework, extracurricular activities and even some sleep. In a PhD program, time management reaches a whole new level. You will not only have lectures to attend and homework to do. You will have to make time for your research, which will include spending extended periods of time in the lab, analyzing data, and scheduling time with other students to collaborate on research.
Also, you will most likely have to teach for a number of semesters, and you will want to attend any seminar that may be related to your research or that just peaks your interest. To top it all off, you will still want to do many of those extracurricular activities you did as an undergraduate. While in the abstract, it may seem simple enough to put this all into your calendar and stay organized, you will find quickly enough that the one hour you scheduled for a task might take two or three hours, putting you behind on everything else for the rest of the day or forcing you to cut other planned events. Be prepared for schedules to go awry, and be willing to sacrifice certain activities. For some, this might be sleep; for others, it might be an extracurricular activity or a few seminars they were hoping to attend. In short, don't panic when things don't go according to plan; anticipate possible delays and be ready to adapt.
8. Expect to learn research skills on the fly – or take advantage of the training your department or career center offers.
This may be the first time you will have to write fellowship or grant proposals, write scientific papers, attend conferences, present your research to others, or even peer-review scientific manuscripts. From my experience, very few college students or even PhD students receive formal training on how to perform any of these tasks. Usually people follow by example. But this is not always easy and can be quite aggravating sometimes. So seek out talks or interactive programs offered by your department or career center. The effort will be well worth it when you realize you've become quite adept at quickly and clearly explaining your research to others and at outlining scientific papers and grant proposals. Alternatively, ask a more experienced graduate student or your advisor for advice on these topics. In addition, be prepared for a learning curve when learning all the procedures and processes of the group you end up working in. There may be many new protocols to master, whether they involve synthesizing chemicals, growing bacterial cells, or aligning mirrors on an optical table. In addition, the group may use programming languages or data analysis software you are unfamiliar with. Don't get discouraged but plan to spend extra effort getting used to these procedures and systems. After working with them regularly, they will soon become second nature. When I first started my job at Johns Hopkins, I felt overwhelmed by all the intricacies of the experiment and definitely made a few mistakes, including breaking a number of optical elements. But by the end of my year there, I had written an updated protocol manual for the modifications I had made to the experimental procedures and was the "master" passing on my knowledge to the next person taking the job.
9. There are no real breaks.
In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done." You might be in the lab during regular work hours or you might be working until 10 p.m. or later to finish an experiment. And the only time you might have available to analyze data might be at 1 a.m. Expect to work during part of the weekend, too. Graduate students do go on vacations but might still have to do some data analysis or a literature search while away.
As a PhD student, it might be hard to stop thinking about the next step in an experiment or that data sitting on your computer or that paper you were meaning to start. While I imagine some students can bifurcate their mind between graduate school life and everything else, that's quite hard for many of us to do. No matter what, my research lies somewhere in the back of my head. In short, your schedule is much more flexible as a PhD student, but as a result, you never truly take a break from your work.
While this may seem like a downer, remember that you should have passion for the research you work on (most of the time), so you should be excited to think up new experiments or different ways to consider that data you have collected. Even when I'm lying in bed about to fall asleep, I am sometimes ruminating about aspects of my experiment I could modify or what information I could do a literature search on to gain new insights. A PhD program is quite the commitment and rarely lives up to expectations – but it is well worth the time and effort you will spend for something that truly excites you.
Contributor
Andy greenspon.
Big PhD questions: Should I do a PhD?
If you are reading this, chances are that you have already decided to do a PhD. Yet, you may know someone who is considering a doctoral degree (or you may be offering such a position as a supervisor to prospective students). This post is for them . In this new type of post, we will look at big questions facing any PhD student. Today, we analyze the question that precedes all the other big PhD questions: “should I do a PhD?”. Below, I offer a couple of quick, simple ways to look at this important life decision, and a list of 10 factors to consider when offered (or seeking) a PhD position.
The other day, some researcher colleagues told me about a brilliant master student of theirs, to whom they were offering the possibility of doing a PhD in their lab. However, the student was doubtful: should she embark on this long and uncertain journey, on a low income, foregoing higher salaries (and maybe more stability) if she entered the job market right away? Her family and friends, not really knowing what a PhD or academia are like, were also giving all sorts of (sometimes contradictory) advice. Should she do a PhD?
This simple question is not asked nearly as much (or as seriously) as it should. Many people (myself included!) have embarked on this challenging, marathon-like experience without a clear idea of why it is the right choice for them, for that particular moment in their lives. Given this lack of clarity, we shouldn’t be surprised by the high rates of people that drop out of doctoral programs , or that develop mental health issues , once they hit the hard parts of the journey.
So, let’s approach this big PhD question from a few different angles…
A first short answer: Thinking about the career path
When I started my PhD back in 2007, coming from a job in the industry, I only had a very nebulous idea that I might like to do research professionally (albeit, to be honest, what I liked most about research was the travelling and the working with foreign, smart people). My employer back then was encouraging us to earn doctoral degrees as a way to pump up the R&D output. Thus I started a PhD, without a clear idea of a topic, of who would be my supervisor, or what I would do with my life once I had the doctoral degree in my hands.
This is exactly what some career advice experts like Cal Newport say you should NOT do . They argue that graduate degrees (also including Master’s) should not be pursued due to a generic idea that having them will improve our “job prospects” or “hirability”, that it will help us “land a job” more easily. Rather, they propose to take a cold, hard look to what we want to do after the doctorate (do I want to be a Professor? if so, where? do I want a job in the industry? in which company? etc.). Then, pursue the PhD only if we have proof that a PhD, from the kind of university program we can get into 1 , is a necessary requisite for that job .
If you aspire to be an academic (and maybe get tenure), do not take that aspiration lightly: such positions are becoming increasingly rare and competition for them is fiercer than ever. Take a look at the latest academic positions in your field at your target university, and who filled them. Do you have a (more or less) similar profile? In some highly prestigious institutions, you need to be some kind of “superstar” student, coming from a particular kind of university, if you want to get that kind of job.
In general, I agree with Cal that we should not generically assume that a PhD will be useful or get us a job in a particular area, unless we have hard evidence on that (especially if we want a job in the industry!). Also, I agree that the opportunity cost of a PhD should not be underestimated: if you enroll in a PhD program, you will probably be in for a reduction in salary (compared with most industry jobs), for a period of four or more years!
Yet, for some of us, the plan about what to do after the PhD may not be so clear (as it was my case back in 2007). Also, being too single-minded about what our future career path should look like has its own problems 2 . Indeed, there are plenty of examples of people that started a PhD without a clear endgame in mind, who finished it happily and went on to become successful academics or researchers. Ask any researcher you know!
So, if this first answer to ‘should I do a PhD?' did not give us a clear answer, maybe we need a different approach. Read on.
A longer answer: Factors for a happy (or less sucky) PhD
If we are still unsure of whether doing a PhD is a good idea, we can do worse than to follow the decision-making advice I have proposed in a previous post for big decisions during the PhD. In those posts, I describe a three-step process in which we 1) expand our understanding of the options available (not just to do or not do a PhD, but also what PhD places are available, what are our non-PhD alternative paths, etc.); 2) analyze (and maybe prototype) and visualize the different options; and 3) take the decision and move on with it.
However, one obstacle we may face when applying that process to this particular decision is the “analytic intuition” step , in which we evaluate explicitly different aspects of each of the options, to inform our final, intuitive (i.e., “gut feeling”) decision. If we have never done a PhD or been in academia, we may be baffled about what are the most important aspects to consider when making such an evaluation about a particular PhD position, or whether a PhD is a good path for us at all.
Below, I outline ten factors that I have observed are related to better, happier (but not necessarily stress-free!) PhD processes and outcomes. Contrary to many other posts in this blog (where I focus on the factors that we have control over ), most of the items below are factors outside our direct control as PhD students, or which are hard to change all by ourselves. Things like our current life situation, what kind of person we are, or the particular supervisor/lab/topic where we would do the PhD. Such external or hard-to-change aspects are often the ones that produce most frustration (and probably lead to bad mental health or dropout outcomes) once we are on the PhD journey:
- Time . This is pretty obvious, but often overlooked. Do we have time in our days to actually do a PhD (or can we make enough time by stopping other things we currently do)? PhD programs are calibrated to take 3-4 years to complete, working at least 8 hours a day. And the sheer amount of hours spent working on thesis materials seems to be the most noticeable predictor of everyday progress in the PhD , according to (still unpublished) studies we are doing of doctoral student diaries and self-tracking (and, let’s remember, progress itself is the most important factor in completing a PhD 3 ). And there is also the issue of our mental energy : if we think that we can solve the kind of cognitively demanding tasks that a PhD entails, after 8 hours of an unrelated (and potentially stressful) day job, maybe we should think again. Abandon the idea that you can do a PhD (and actually enjoy it) while juggling two other day jobs and taking care of small kids. Paraphrasing one of my mentors, “a PhD is not a hobby”, it is a full-time job! Ignore this advice at your own risk.
- Money . This is related to the previous one (since time is money, as they say), but deserves independent evaluation. How are we going to support ourselves economically during the 3+ years that a PhD lasts? In many countries, there exist PhD positions that pay a salary (if we can get access to those). Is that salary high enough to support us (and maybe our family, depending on our situation) during those years? If we do not have access to these paid PhD positions (or the salary is too low for our needs), how will we be supported? Do we have enough savings to keep us going for the length of the PhD? can our spouse or our family support us? If we plan on taking/keeping an unrelated job for such economic support, read again point #1. Also, consider the obligations that a particular paid PhD position has: sometimes it requires us to work on a particular research project (which may or may not be related to our PhD topic), sometimes it requires us to teach at the university (which does not help us advance in our dissertation), etc. As stated in the decision process advice , it is important to talk to people currently in that kind of position or situation, to see how they actually spend their time (e.g., are they so stressed by the teaching load that they do not have time to advance in the dissertation?).
- Having social support (especially, outside academia). This one is also quite obvious, but bears mentioning anyways. Having strong social ties is one of the most important correlates of good mental health in the doctorate , and probably also helps us across the rough patches of the PhD journey towards completion. Having a supportive spouse, family, or close friends to whom we can turn when things are bad, or with whom we can go on holidays or simply unwind and disconnect from our PhD work from time to time, will be invaluable. Even having kids is associated with lower risk of mental health symptoms during the doctorate (which is somewhat counter-intuitive, and probably depends on whether you have access to childcare or not). A PhD can be a very lonely job sometimes, and there is plenty of research showing that loneliness is bad for our mental and physical health!
- An attitude of learning . Although this is a somewhat squishy factor, it is probably the first that came to my mind, stemming from my own (anecdotal, non-scientific) observation of PhD students in different labs and universities. Those that were excited to learn new things, to read the latest papers on a topic, to try a new methodology, seem to be more successful at doing the PhD (and look happier to me). People that are strong in curiosity seem a good match for a scientific career, which is in the end about answering questions (even if curiosity also has its downsides ). This personal quality can also be related to Dweck’s growth mindset (the belief that our intelligence and talents are not fixed and can be learned) 4 . If you are curious , this mindset can be measured in a variety of ways .
- A knack for systematicity and concentration. This one is, in a sense, the counterweight to the previous one. Curious people often have shorter attention spans, so sometimes they ( we , I should say) have trouble concentrating or focusing on the same thing for a long period of time. Yet, research is all about following a particular method in a systematic and consistent way, and often requires long periods of focus and concentration. Thus, if we find ourselves having trouble with staying with one task, idea or project for more than a few minutes in a row, we may be in for trouble. The PhD requires to pursue a single idea for years !
- Valuing autonomy . As I mentioned in passing above, a PhD is, by definition, an individual achievement (even if a lot of research today requires teamwork and collaboration). Thus, to be successful (and even enjoy) the process of the PhD, we have to be comfortable being and working alone, at least for some of the time. Spending years developing our own contribution to knowledge that no one else has come up with before, should not feel like a weird notion to us. Even if it occasionally comes with the uncomfortable uncertainty of not knowing whether our ideas will work out. In human values research they call this impulse to define our own direction, autonomy 5 , and many of my researcher friends tell me it is a very common trait in researchers. However, these values are very personal and very cultural. To evaluate this factor, we could simply ask ourselves how much we value this autonomy over other things in life, or use validated instruments to measure relative value importance, like the Portrait Values Questionnaire (PVQ) .
- Liking and/or being good at writing . I have written quite a bit here about the importance (and difficulty) of writing in the PhD . Be it writing journal and conference papers, or the dissertation tome itself, every PhD student spends quite a bit of time writing, as a way of conveying new knowledge in a clear, concise and systematic way. Learning to write effectively is also known to be one of the common difficulties of many PhD processes 6 , due to reasons discussed elsewhere . Hence, if we hate writing, we should think carefully about spending the next 3+ years doing something that necessarily involves quite a bit of writing, other people spotting flaws in your writing, and rewriting your ideas multiple times. Please note that I don’t consider being a good (academic or nonfiction) writer a necessary requisite for a PhD, as it can be learned like any other skill (again, the learning attitude in point #4 will help with that!). But being good at it will certainly make things easier and will let you focus on the content of the research, rather than on learning this new, complex skill.
- Compatibility (or, as they call it in the literature sometimes, the “fit”) of our and their personalities, ways of working (e.g., do they like micro-managing people, but you hate people looking over your shoulder?) and expectations about what a doctoral student and a supervisor should do.
- A concern for you as a person. Since this is difficult to evaluate as we may not know each other yet, we could use their concern about the people that work in their lab (beyond being just a source of cheap labor), as a proxy.
- Enthusiasm for the field of research or topic, its importance in the world, etc. A cynic, jaded researcher may not be the best person to guide us to be a great member of the scientific community.
- A supervisor that is well-known, an expert in the particular topic of the dissertation. Looking at the number of citations, e.g., in Google Scholar is a good initial indicator, but look at the publication titles (are they in similar topics to those they are offering you as your doctoral project? if not, that may mean that this person may also be new to your particular dissertation topic!).
- Related to the previous one, does this researcher have a good network of (international) contacts in other institutions? Do they frequently co-author papers with researchers in other labs/countries? We may be able to benefit from such contact network, and get wind of important opportunities during the dissertation and for our long-term research career.
- Openness (and time!) to talk about what the doctoral student job entails, potential barriers and difficulties , etc. This can be a proxy to both their general busyness (you will not get much guidance if they can never meet you because they have too little time) and their communication skills (something critical to consider when signing up to work closely with someone for years).
- Whether the supervisor is an ethical person. This is very important but seldom considered (maybe because it is hard to evaluate!). For sure, we don’t want to be backstabbed or exploited by our supervisor!
- Whether this person(s) is known to be a good supervisor . Have they already supervised other doctoral students to completion, in nominal time and with good grades? Do they regularly attend trainings and professional development about doctoral supervision? Do they seem to care about this part of their job for its own sake (rather than as a mere medium to get cheap labor)?
- You may be wondering how you are going to gather information about all the aspects mentioned above. Sometimes you can ask the supervisor directly, but you can also talk with current PhD students of this person, or students in the same lab/department (but do not take what they say at face value: partisanship, gossip or rivalries may be at work!). If you have the time and the opportunity, try to “prototype” (see the decision process post) the experience of working with this supervisor: do a master thesis with them, or a summer internship, or use the work on a joint PhD project proposal (a pre-requisite before being accepted as a doctoral student in some institutions). Some things we don’t know we like until we try them!
- Of course, all of the above are two-way streets. As prospective students, we also need to show to a potential supervisor that we are open to talk about expectations, that we are somewhat flexible, dependable, etc. Be very conscious of this in your interactions with supervisors and other people in their lab!
- The lab/department where you will do the dissertation . Again, there are many things to consider here. Is there an actual research group, or will we be doing our research in isolation with our supervisor? Normally, the former is preferable, since that gives us more resources to draw from if the supervisor is not available. Is the research group well known in the field (again, look at citations, invited talks, etc. of different group members)? But especially, try to get an idea of the lab’s working atmosphere : is it stressful, relaxed, collaborative, competitive…? As with the previous point, we could prototype it by spending some time working there, or we can interview one or more people working in the lab. If we do the latter, it is better to go beyond direct questions that will give vague (and maybe unreliable) answers, like “it’s good”. Rather, take a journalistic approach, and ask people to narrate concretely what the routines are in the lab, when and how did they last collaborate with another student, or the last conflict arising in the lab. Then, decide whether this kind of ambience is a good fit for you .
- The concrete PhD topic . We should find out (e.g., from our prospective supervisor) whether the topic of the dissertation is already well-defined, or rather we will have to explore and define it ourselves (both options have pros and cons, and again it depends whether we value more autonomy and exploration, or having a clear path ahead). Is the area or keywords of the PhD topic going up or down in popularity (see here for a potential way to find out)? Are there clear funding schemes that specifically target this kind of research topic, at the national or international level? How easy is it to collect evidence for this kind of research (empirical data is a critical element in almost all research fields, so we want easy and reliable access to them)? I would not evaluate a PhD topic on the basis of whether we love it right now, as we never know much about any research area when we start a doctorate (even if we think we do!). An attitude of learning and curiosity (see #4) will take care of that. Rather, talk with the supervisor about how the research process might look like, what kind of activities will take up most of our time (reading papers? doing labwork? interviewing people?): do we find those activities interesting?
Yet, after considering all these 10 factors separately, we may not be clear on the decision (maybe some aspects are good, others not so much). If, after all this thinking and gathering of information we still are not sure, there is one last idea I can offer…
One last answer: We cannot really know (the PhD as a transformative experience)
We could also frame the question of whether to do a PhD as what philosopher L.A. Paul calls a “transformative experience” 8 . Doing a PhD is a big life decision (like becoming a parent or taking a powerful drug) through which we probably will transform ourselves into another person , with different preferences and even different values.
I can think of many ways in which I am a different person now, due to the transformative experience of doing my PhD: I am now able to read and understand scientific papers (e.g., when I come across a new idea or “expert”, I go and read actual research papers about that), and I can evaluate the reliability of different types of evidence; I trust more scientific advances and consensus; I am more comfortable speaking (and writing) in English; I am more aware of culture and life in other countries, and I have less chauvinistic views of foreigners (due to my international experience gained as a researcher). Et cetera .
Paul’s argument regarding transformative experiences is that there are limitations to simulating (i.e., imagining) whether we will like the experience, as our own values and preferences may be changed by the very experience we try to simulate. For similar reasons, there are limits to the usefulness of asking others about the decision (and trusting their testimony), since they also have different values, preferences and coping strategies than us. Even looking at the latest and most reliable research on the topic (e.g., whether PhD students end up happier and/or more satisfied with their lives than people who did not take that choice) is of limited help, since such research (of which there is little!) often concentrates on average effects, and we may not be “average”.
What to do, then?
L.A. Paul’s way out of this dilemma seems to be a reframe of the question: "Will I be happier if I do a Ph?“ , "Should I do a PhD?“ . Rather, we can ask: “Do I value discovering my new self as a researcher/doctor?" . In a sense, this new question targets a key intrinsic value we may (or may not) have: Do we appreciate learning, exploring, getting novel experiences, discovering and remaking ourselves (related to point #4 above)? If yes, a PhD might be a good idea. If we prefer stability, things (and our life) as they have always been, the status quo … maybe we will not appreciate this transformation that much.
There is no right or wrong answer. Only your answer.
The diagram below summarizes the main ideas in this post. Reflect upon these questions, and make your own choice. Take responsibility for your choice… but don’t blame yourself for the outcome , i.e., if it does not work out as you expected. There are too many inherent uncertainties about this decision that cannot be known until we actually walk the path.
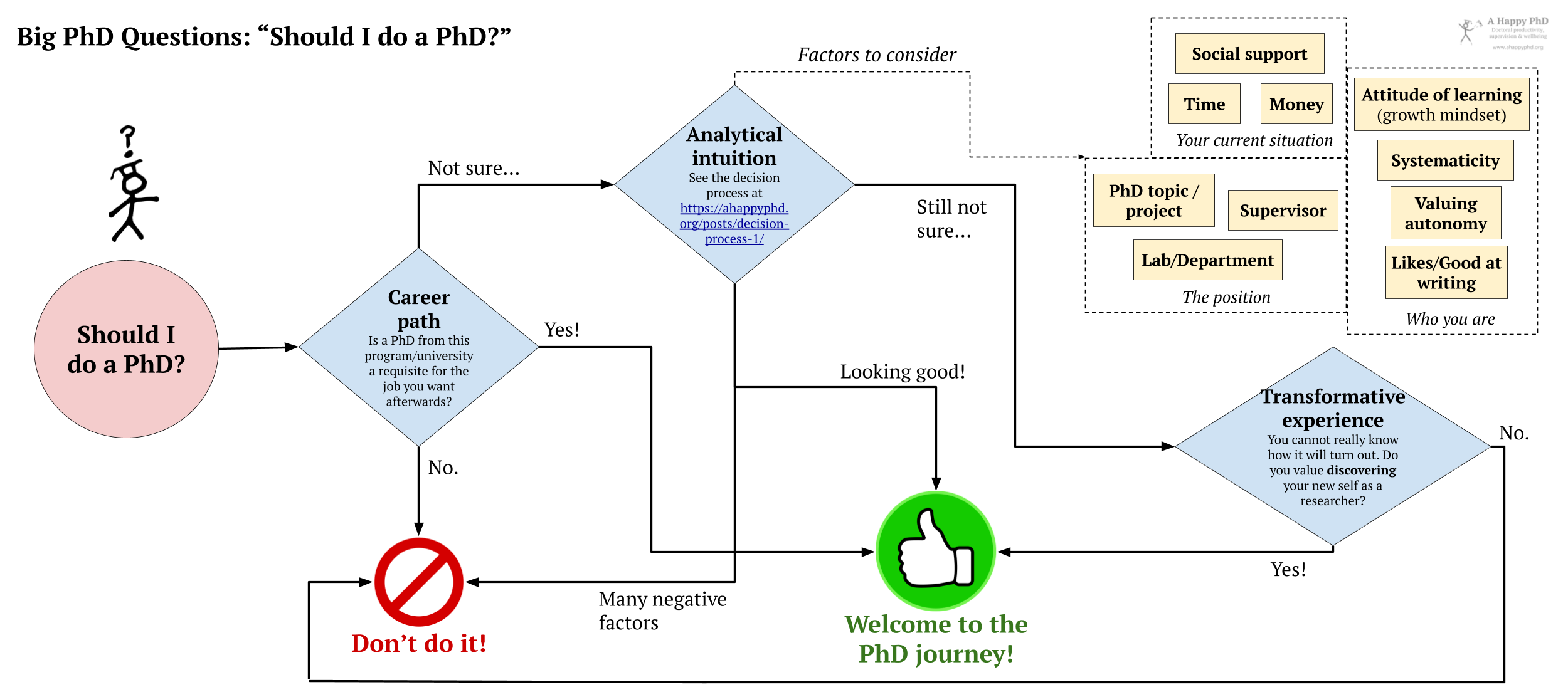
Summary of the ideas in this post
Did these arguments and factors help you think through the decision of doing (or not doing) a PhD? What did you decide in the end and why? I’d be very curious to know… Let us know in the comments section below!
Header photo by Zeevveez
This seems especially important in the U.S. higher education and research market, which is quite clearly stratified, with research-focused and more teaching-focused universities, “Ivy Leagues”, etc. ↩︎
If we get obsessed with going a particular way and we fail to achieve it (or even if we achieve it and find out that it’s not what we thought it’d be), we may end up feeling stuck and/or depressed. See Burnett, W., & Evans, D. J. (2016). Designing your life: How to build a well-lived, joyful life , for ideas on how to get “unstuck” in those cases. ↩︎
De Clercq, M., Frenay, M., Azzi, A., Klein, O., & Galand, B. (2021). All you need is self-determination: Investigation of PhD students’ motivation profiles and their impact on the doctoral completion process. International Journal of Doctoral Studies , 16 , 189–209. ↩︎
Claro, S., Paunesku, D., & Dweck, C. S. (2016). Growth mindset tempers the effects of poverty on academic achievement. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 113 (31), 8664–8668. ↩︎
Schwartz, S. H. (2012). An Overview of the Schwartz Theory of Basic Values. Online Readings in Psychology and Culture , 2 (1). https://doi.org/10.9707/2307-0919.1116 ↩︎
Sverdlik, A., Hall, N. C., McAlpine, L., & Hubbard, K. (2018). The PhD experience: A review of the factors influencing doctoral students’ completion, achievement, and well-being. International Journal of Doctoral Studies , 13 , 361–388. https://doi.org/10.28945/4113 ↩︎
Masek, A., & Alias, M. (2020). A review of effective doctoral supervision: What is it and how can we achieve it? Universal Journal of Educational Research , 8 (6), 2493–2500. ↩︎
Paul, L. A. (2014). Transformative experience . OUP Oxford. ↩︎

Luis P. Prieto
Luis P. is a Ramón y Cajal research fellow at the University of Valladolid (Spain), investigating learning technologies, especially learning analytics. He is also an avid learner about doctoral education and supervision, and he's the main author at the A Happy PhD blog.
Google Scholar profile
- Career Advice
Do You Really Need a Ph.D.?
By Arie Spirgel
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

chinga_11/istock/getty images plus
Relative to the fire that it is today, when I earned my Ph.D. in 2011, the alternative-academic community was a crackling ember. At the time, finding information about career paths outside the academy felt like driving through a rainstorm in an unfamiliar town: it was not that my destination was not out there, it was that it was not easy to find.
Today, having a Ph.D. and openly seeking a career outside academe is a mainstream phenomenon. There are books, blogs, hashtags, Twitter accounts, articles and vibrant online communities dedicated to helping you make the most of your Ph.D. in a nonacademic setting. Quit lit is a genre. Even academe itself has gotten in the game, with institutions like Stanford University , the University of Michigan and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill providing resources for those considering the nonacademic career path. The movement gives voice, emotional support and practical advice to people with Ph.D.s interested in exploring nonacademic career paths. If you have a Ph.D. and can imagine a life for yourself outside academe, there is someone out there to help you find it.
As empowering as the notion of the alternative-academic path is, deciding to pursue a Ph.D. when the career you want doesn't require a doctorate may not be the best choice. In his recent memoir, Eat a Peach , the chef and restaurateur David Chang’s first piece of advice to aspiring chefs is this: if there is anything else you can do for a living, then do that. It is my wish that Chang’s advice be appropriated for the Ph.D.-curious as follows: unless the only career you can imagine yourself having requires or appropriately values a doctorate, I would strongly advise against getting one. At the very least, I urge you to have honest conversations -- with friends, family, a therapist, yourself -- about why it is that you want to pursue a doctorate. Whether it be validation, not being sure what else to do or something else, I suspect that when you look deep enough, you will find the reasons unconvincing.
The counterargument to this advice is that although a Ph.D. degree is generally designed to prepare you for a career as a professor, the skills you obtain are invaluable to other domains. It would be foolish to argue against this assertion, particularly if you already have a Ph.D. But it also ignores a more relevant point: your time is finite, which means that making one choice means forgoing countless others. So saying that a Ph.D. program offers useful skills in the nonacademic job market does not mean that a Ph.D. is the best -- or most satisfying -- way to obtain skills that are valued in the nonacademic job market.
Take my own experience in pursuing a doctorate in cognitive psychology, and notice how the skills that some might say prepared me for the nonacademic job market often fell short.
- Writing. I read articles by people who never learned to write well, and I learned to write from the same people who wrote said articles.
- Presenting information. I taught undergraduate sections to students who evaluated me once per semester, and if the research is right, on characteristics that had little to do with my ability to teach.
- Critical thinking. Academics do not have a monopoly on critical thinking, and unlike nonacademic settings, the problems are often too remote for there to be any consequences to errors in thinking.
- Leadership . Explaining to a group of high-achieving and reliable undergraduates how to run an experiment hardly qualifies as leadership training.
I could go on, but you get the point.
I cite these examples as someone who had a positive graduate experience and was mentored by professors who, in addition to achieving their own impressive levels of success, genuinely cared about the success of their students. And if it was an academic career I wanted, then I chose the right program. But I did not want a career in academe, which means that I was forgoing the opportunity to learn the skills that would best prepare me for the nonacademic job market.
If I wanted to learn to write, I could have read the works of the best writers and taken courses taught by trained writers. If I wanted to learn to present information, I could have gotten a job in sales. If I wanted to learn to “think,” I could have gone to the library and checked out books on Lovelace and Kant. If I wanted to learn leadership, I could have volunteered to help manage the local cat shelter.
Above all, if I wanted to learn the skills that would help me succeed in a nonacademic environment, I could have gotten a job in a nonacademic environment -- making more money with less work, to boot. To make it more concrete, of the skills that have been most important to my career -- for example, statistical computing, an understanding of databases, designing effective data visualizations -- I learned all of them after graduate school.
For all that they have offered the world, colleges and universities are one of humanity’s greatest inventions. A career in academe can be a noble and fulfilling profession, and if that is what you want, I hope you succeed. The world needs people like you. But if it is not what you want, you may find that a Ph.D. is not only unnecessary but also counterproductive to your goals. Academics are really good at producing other academics, yet much less so at preparing you for nonacademic work.
So rather than twist your credentials to suit the nonacademic job market, my advice is to not get a Ph.D. in the first place. Yes, a Ph.D. will introduce you to interesting people and ideas, but interesting people and ideas exist outside academe, and a choice to go in one direction is also a choice to not go in so many others.

Too Few Middle-Skills Credentials to Meet Future Job Demand
Most providers have to double the number of credentials they produce for well-paying jobs that don't require a bachel
Share This Article
More from career advice.

How to Mitigate Bias and Hire the Best People
Patrick Arens shares an approach to reviewing candidates that helps you select those most suited to do the job rather

The Warning Signs of Academic Layoffs
Ryan Anderson advises on how to tell if your institution is gearing up for them and how you can prepare and protect y

Legislation Isn’t All That Negatively Impacts DEI Practitioners
Many experience incivility, bullying, belittling and a disregard for their views and feelings on their own campuses,
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- Master’s vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Published on November 27, 2020 by Lauren Thomas . Revised on May 10, 2024.
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master’s and doctoral degrees:
- A master’s is a 1–2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers.
- A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3–7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research.
A master’s is also the necessary first step to a PhD. In the US, the master’s is built into PhD programs, while in most other countries, a separate master’s degree is required before applying for PhDs.
Master’s are far more common than PhDs. In the US, 24 million people have master’s or professional degrees, whereas only 4.5 million have doctorates.
Table of contents
Master’s vs phd at a glance, which is right for you, length of time required, career prospects, costs and salaries, application process, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about master's and phd degrees.
The table below shows the key differences between the two.
| Master’s | PhD | |
|---|---|---|
| Career prospects | Usually intended for a career outside of academia. | Prepares for a research career, ideally as a university professor. |
| Length of time | 1–2 years | 5–7 in the US (master’s degree included); 3–5 outside the US (after a separate master’s degree) |
| Structure | Mostly coursework, often with a semester-long or capstone project at the end. | 2 years of coursework (in the US), followed by 3–5 years of preparing a dissertation, which should make a significant original contribution to current knowledge. |
| Cost | Varies by country, university and program; usually higher upfront cost with limited financial aid available. | Tuition fees are usually waived and a living stipend provided in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. |
| Graduate salaries | Wage premium (compared to earnings with a high school education) is 23% on average. | Wage premium is 26% on average. |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A PhD is right for you if:
- Your goal is to become a professor at a university or some other type of professional researcher.
- You love research and are passionate about discovering the answer to a particular question.
- You are willing to spend years pursuing your research even if you have to put up with a lot of dead ends and roadblocks.
A master’s degree is the better choice if any of the following apply:
- You want to continue studies in your field, but you’re not committed to a career as a professional researcher.
- You want to develop professional skills for a specific career.
- You are willing to pay a higher upfront cost if it means finishing with your degree (and thus being able to work) much faster.
- You want the option to study part-time while working.
The length of time required to complete a PhD or master’s degree varies. Unsurprisingly, PhDs take much longer, usually between 3–7 years. Master’s degrees are usually only 1–2 years.
Length of a master’s
Master’s degrees are usually 2 years, although 1-year master’s degrees also exist, mainly in the UK.
Most of the degree consists of classes and coursework, although many master’s programs include an intensive, semester-long master’s thesis or capstone project in which students bring together all they’ve learned to produce an original piece of work.
Length of a PhD
In the US, a PhD usually takes between 5 and 7 years to complete. The first 2 years are spent on coursework. Students, even those who choose to leave without finishing the program, usually receive a master’s degree at this point.
The next 3–5 years are spent preparing a dissertation —a lengthy piece of writing based on independent research, which aims to make a significant original contribution to one’s field.
Master’s degrees tend to prepare you for a career outside of academia, while PhDs are designed to lead to a career in research.
Careers for master’s graduates
There are two types of master’s degrees: terminal and research-intensive. The career prospects are different for each.
Terminal master’s degrees are intended to prepare students for careers outside of academia. Some degrees, known as professional degrees, specifically prepare students for particular professions; these include the Master of Public Policy (MPP), Master of Business Administration (MBA), Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT), Master of Fine Arts (MFA), and Master of Public Health (MPH) degrees.
Other master’s degrees, usually Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Sciences (MS or MSc) degrees, do not necessarily lead to a specific career, but are intended to be a final degree. Examples include an MS in Communications or MS in Data Analytics.
In research-intensive master’s programs, students take coursework intended to prepare them for writing an original piece of research known as the master’s thesis . Such programs are usually intended to prepare for further study in a doctoral program.
Careers for PhD graduates
As research degrees, PhDs are usually intended to lead to an academic career. A PhD can be thought of like an apprenticeship, where students learn from professional researchers (academics) how to produce their own research.
Most students aspire to become a university professor upon the completion of their degree. However, careers in academia are highly competitive, and the skills learned in a doctoral program often lend themselves well to other types of careers.
Some graduates who find they prefer teaching to producing research go on to be teachers at liberal arts colleges or even secondary schools. Others work in research-intensive careers in the government, private sector, or at think tanks.
Below are a few examples of specific fields and non-academic careers that are common destinations of graduates of those fields.
- Computer Science
- Lab Sciences
Many government jobs, including economists at a country’s central bank, are research-intensive and require a PhD. Think tanks also hire economists to carry out independent research.
In the private sector, economic consulting and technology firms frequently hire PhDs to solve real-world problems that require complex mathematical modeling.
Graduate students from the humanities are sometimes hired by museums, who can make use of their research and writing skills to curate exhibits and run public outreach.
Humanities PhDs are often well-suited to research and grant-writing roles at nonprofits. Since so much of research is funded by grants, PhD students often gain a lot of experience applying for them, which is a useful skill in the nonprofit sector.
There are a wide range of non-academic research jobs for lab scientists with doctorates in subjects like chemistry, biology, ecology and physics.
Many PhD graduates are hired by pharmaceutical companies that need to perform research to create and test their products. Government agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), also hire lab scientists to work on research projects.
Job prospects after graduation vary widely based on the field. In fields like management, computer science, statistics, and economics, there’s little underemployment—even graduates from less well-known programs can easily find jobs that pay well and use the skills they’ve gained from the PhD.
However, in other fields, particularly in the humanities, many PhD graduates have difficulty in the job market. Unfortunately, there are far more PhD graduates than assistant professor roles, so many instead take on part-time and low-paid roles as adjunct instructors. Even non-academic careers can sometimes be difficult for PhDs to move into, as they may be seen as “overqualified” or as lacking in relevant professional experience.
Because career options post-PhD vary so much, you should take the time to figure out what the career prospects are in your field. Doctoral programs often have detailed “placement” records online in which they list the career outcomes of their graduates immediately upon leaving the program. If you can’t find these records, contact the program and ask for them—placement information should play an important role in your choice of PhD program.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Although PhDs take far longer to complete, students often receive a living stipend in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. Master’s degrees are shorter but less likely to be funded.
Both master’s degrees and PhDs lead to increased salaries upon graduation. While PhDs usually earn a bit more than those with a master’s degree, in some fields, the wages are identical, meaning that no financial benefit is gained from going on to a PhD.
Cost of a master’s
The upfront cost of a master’s degree is usually higher than a doctoral degree due to the lower amount of financial aid available. However, increased salaries also arrive faster than with a doctoral degree, because people graduate much earlier from a master’s program.
Some master’s students do receive stipends for their degrees, usually as compensation for being a teaching or research assistant. In addition, many people complete master’s degrees part time while working full-time, which allows them to fund their living costs as well as tuition.
The cost varies significantly by school and program. Public schools are usually cheaper than private ones. Some master’s degrees, such as MBAs, are notoriously expensive, but also result in much higher wages afterwards that make up for the high cost.
The master’s wage premium , or the extra amount that someone with a master’s degree makes than someone with just a high school diploma, is 23% on average. Many universities provide detailed statistics on the career and salary outcomes of their students. If they do not have this online, you should feel free to contact an administrator of the program and ask.
Cost of a PhD
PhDs, particularly outside the humanities, are usually (though not always) funded, meaning that tuition fees are fully waived and students receive a small living stipend. During the last 3–5 years of a PhD, after finishing their coursework (and sometimes before), students are usually expected to work as graduate instructors or research assistants in exchange for the stipend.
Sometimes students can apply for a fellowship (such as the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Program in the United States) that relieves them of any obligations to be a teaching or research assistant. Doctoral programs in the US tend to be better funded than in the rest of the world.
Sometimes, PhD degrees can be completed part-time, but this is rare. Students are usually expected to devote at least 40 hours a week to their research and work as teaching or research assistants.
The main cost of doctoral programs comes in the form of opportunity cost—all the years that students could be working a regular, full-time job, which usually pays much better than a graduate school stipend.
The average wage premium for PhDs is 26%, which is not much higher than the master’s degree premium.
In the US, the application process is similar for master’s and PhD programs. Both will generally ask for:
- At least one application essay, often called a personal statement or statement of purpose .
- Letters of recommendation .
- A resume or CV .
- Transcripts.
- Writing samples.
Applications for both types of programs also often require a standardized test. PhDs usually require the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), which tries to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative, critical thinking , and analytical writing skills. Many master’s programs require this test as well.
Applying for a master’s
Master’s degrees programs will often ask you to respond to specific essay prompts that may ask you to reflect upon not just your academic background, but also your personal character and future career ambitions.
Northwestern University’s Kellogg Business School requires Master’s of Business Administration (MBA) applicants write two essays, one about a recent time they demonstrated leadership and the second about their personal values.
Who you should ask for your letters of recommendation varies by program. If you are applying to a research-intensive master’s program, then you should choose former professors or research supervisors. For other programs, particularly business school, current work supervisors may be a better choice.
Some professional master’s programs require a specific test. For example, to apply to law school, you must take the Law School Admissions Test, or LSAT. For business school, you must take either the GRE or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT).
Applying for a PhD
When applying for a PhD, your resume should focus more on your research background—you should especially emphasize any publications you’ve authored or presentations that you’ve given.
Similarly, your statement of purpose should discuss research that you’ve participated in, whether as an assistant or the lead author. You should detail what exactly you did in projects you’ve contributed to, whether that’s conducting a literature review, coding regressions, or writing an entire article.
Your letters of recommendations should be from former professors or supervisors who can speak to your abilities and potential as a researcher. A good rule of thumb is to avoid asking for recommendations from anyone who does not themselves have a PhD.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Thomas, L. (2024, May 09). Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/masters-vs-phd/
Is this article helpful?

Lauren Thomas
Other students also liked, when to apply for graduate school | month-by-month timeline, how to write a statement of purpose | example, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
The best answers to “Why do you want to do a PhD?”

If you are interviewing for a PhD position, chances are high that you will be asked about your motivation to do a PhD. And sometimes, simple questions are the hardest to answer. Therefore, it is smart to prepare an excellent response to this question in advance.
Creating your unique answer to “Why do you want to do a PhD?”
While this diversity is a good thing, the lack of clarity on what a good answer to the question “Why do you want to do a PhD?” constitutes, makes it particularly daunting.
A convincing response during a PhD application interview increases your chance of securing the position: it clarifies your ambition and can leave a memorable impression.
Write down everything that comes to your mind. Your notes could include words like “ curiosity” , and short sentences such as “ to be able to become a professor in the future” but also honest reflections such as “ I want to be able to call myself Dr”.
The following categories are some of the best to frame your unique answer to the question:
Doing a PhD to satisfy your scientific curiosity
There are different ways to emphasise your scientific curiosity. For instance, you could explain how a specific topic caught your interest. For example by reading the work of a specific scholar, following a course, or listening to a talk.
Doing a PhD because of your societal or environmental ambitions
Many people connect their answers to “Why do you want to do a PhD?” to societal or environmental ambitions. And for a reason: These answers can be very powerful!
You can, for instance, tell a short personal story about why you find something important. Did you have a life-changing experience? Or do you maybe know someone who has been affected by a societal shortcoming?
Doing a PhD for self-development
On the contrary, openness and a drive to improve yourself and learn new skills are highly valued by PhD supervisors. Thus, self-development can be another good framework for your answer.
Doing a PhD to improve your (academic) career prospects
Ambitions to work within academia are more straightforward to explain. For example, in most cases, you simply need a PhD to secure a lecturer position or professorship.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, key quotes to motivate and drive academic success, how to select a journal for publication as a phd student, related articles, are summer schools for master’s students worth it, 100 things to do before university starts, writing a successful academic cv (and a free template), why do you deserve a scholarship 10 outstanding justifications.
Please enable JavaScript
Get the Reddit app
We are a place for students of psychology to discuss study methods, receive assistance with homework, enquire for job-searching advice, and all else that come to mind. This community is aimed at those at the beginner to intermediate level, generally in or around undergraduate studies. Graduate students and professionals are recommended to our sister subreddit, r/AcademicPsychology.
Should I do all my readings in my PhD program?
Do you read ALL of your required readings? Every single word? If yes, what is your system? If not, why not and explain what you do instead.
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
If I have a low GPA in undergrad, and want to get into top PhD programs, should I do an MS degree or redo my undergrad degree?
I want to get into specifically top schools (in materials science and engineering) because I want to have a decent shot at being a professor.
I am aware that quite a few people have successfully done an MS and went on to top PhD programs, but my concern is that because the MS GPA is so inflated, it won't help me in my case. I already have a first author publication soon to be submitted, so my research experiences have been covered well, and my uGPA of 3.1 is my only weakness. Remember, I am trying to get into top schools, where they get so many applications that they are seeking any reason to throw them out.
Because undergrad GPAs are less inflated, I was thinking that doing a whole another undergrad might be more helpful in letting me demonstrate an improvement academically. In addition, some schools require specifically an undergrad GPA limit, apparently without regards to whether the applicant has an MS degree or not . But at the same time, since I would be repeating the same thing, they might not see it as that much of an improvement.
What do you think?
- graduate-admissions
- 18 A second undergrad degree would be a colossal waste of time. Go do a masters degree, get stellar grades, more research experience, and strong letters of recommendation while you're there, and you'll be fine. – ff524 Commented Jul 20, 2016 at 6:13
- 2 Also see How do you get a bad transcript past Ph.D. admissions? and How does the admissions process work for Ph.D. programs in the US, particularly for weak or borderline students? – ff524 Commented Jul 20, 2016 at 6:14
- 3 I was thinking that an MS wasn't such a bad idea, and it would have been what I would have decided to do without hesitation, but the classes are curved higher, and apparently not taken very seriously. From your 2nd link, a reply by JeffE: "In particular, at many universities, classes taken by terminal master's students are easier than the corresponding classes taken by undergraduates". – J. Doe Commented Jul 20, 2016 at 6:18
- 11 You're not going to get into a top PhD program because of amazing masters grades. You'll get into a top PhD program because the additional research you do and glowing letters of recommendation you get during the masters will show that your undergrad grades are irrelevant to your ability to do high quality research. (And also show that by the way, in case you were worried, the grades won't be a problem because you've turned that situation around.) – ff524 Commented Jul 20, 2016 at 6:28
- 2 Research is important, but it's quite well known that GPA is used as a cutoff, so that is why I am concerned. Do you think that the inflated MS GPA won't be much of a problem? – J. Doe Commented Jul 20, 2016 at 14:45
4 Answers 4
As others have said, getting a second undergrad degree is a waste of time. Don't bother.
The unfortunate truth is that your undergrad GPA may keep you out of top PhD programs even if you have a Master's degree with a perfect GPA and multiple journal publications.
Top engineering graduate programs receive hundreds or even thousands of applicants every year. Despite what others may tell you, they're not looking for an excuse to reject applicants because it keeps their US News rating high. They're looking for excuses to reject because there are far too many applications to judge each one on its merits, and far too many highly qualified applicants to admit them all, and the committee members are faculty who have many other demands on their time and who want sleep occasionally. In some departments, applications are filtered by GPA even before the first human committee member reads them.
By far the best way over that hurdle is to cultivate a champion -- a faculty member who is active and visible in their research community, who will write you glowing letters describing your strong potential for independent research (in personal, technical, and credible detail), and who will call up their colleagues in other departments to tell them to watch for your application. The goal here is to interest someone in your target department enough to rescue your application from knee-jerk rejection and evaluate it on its own merits.
And then your application needs to shine on its own merits. It must provide compelling evidence of your strong potential for independent research. Yes, your graduate GPA is a (small) part of this, but you need to sell yourself primarily as a future researcher , if not a current researcher, not just someone who excels at classes. Moreover, this evidence needs to be stronger than for other applicants with higher undergraduate GPAs. Do not assume that one first-author publication is enough.
All that said... Focusing on research and finding a champion will improve your chances of being admitted to a top program, but they will not guarantee anything. In particular, even with a strong research record and vocal champions, you may still be rejected because of your undergrad GPA. Admissions is best considered a random process; the most you (or anyone) can do is improve your odds.
Incidentally, the same advice goes for your longer-term goal of getting a faculty position. Yes, having a degree from a non-top-10 department makes it harder to get an academic position, but you can work against that disadvantage by developing a killer research portfolio and multiple champions (not just your advisor). Conversely, a PhD from a top-10 department will not guarantee you success on the faculty job market; you also need a killer research portfolio and multiple champions (not just your advisor). Start developing that now.
- 4 The idea of a champion is key. Everyone knows someone who punched far above what their resume might have suggested. This works even better if they have active connections at schools you are targeting. – Roger Fan Commented Jul 21, 2016 at 19:52
First, let me state that I am currently in a PhD program in a top school in the US. My undergrad GPA was from an engineering program in the top engineering school in my home country. It was 3.65. Compared to others who applied to my PhD program my GPA was probably below average. (Engineering is hard, yo!, and my school graded on a strict curve that permitted only 20% of the class to get A's)
I agree with others who have said that doing another undergraduate degree would be a waste of time. Having said that, you may want to do a post-bac or something similar if you don't want to go the masters route. This will at least allow you to get some more undergrad grades to bring your GPA up and cross the cutoff threshold. I also think that this would be a waste of time though, assuming you have at least the minimum GPA to get past the first review.
The issue with GPA is that many top schools use undergrad GPA to make themselves seem highly selective, and this is a stat that they are judged on in US News and World Report (That's my perception having talked with my program director in my PhD program). They like to have students with high undergrad GPAs, but not every student needs to have a stellar undergrad GPA.
The downside of doing the post-bac is that if you don't get into the program you want, all you have are some extra undergrad classes and a new student loan, and no "network".
Here's my suggestion.
talk with the program directors for the PhD programs you're interested in and ask them what they suggest. They may say that your undergrad GPA is super important, or they may say focus on the GRE and letters of recommendation and your research. They may also tell you if they think your GPA would completely preclude you from consideration.
Assuming the undergrad GPA isn't going to kill your application immediately, consider doing a masters at one of your preferred PhD universities. make sure you crush the GRE, since that's a relevant entry criteria for most schools. This will do a couple of things.
First, it will give you another set of grades, at the university to which you're applying. These grades will mean something and provide easy context for the admissions committee. e.g. if you do classes at Harvard and apply to Harvard, they should know what your Harvard grades mean. If you do classes at USC and apply to Harvard, Harvard may not know what your USC grades mean. e.g. is an A at USC the same as one at Harvard?
Second, it will allow you to become acquainted with professors at your preferred school. This could be the thing that gets you in. If you have someone on the admissions committee who would vouch for you and agrees to be your adviser, you have a much stronger shot of getting in no matter what the rest of your application looks like. If the faculty know you, they are more likely to admit you assuming you're a good student among your peers!
Lastly, if all else fails, when you graduate the masters, you'll have a masters from a good school, and even if you don't get accepted to that school for your PhD, your masters at a good school with good grades will signal to other schools that you are a competitive applicant (again, this presumes your undergrad GPA doesn't torpedo your app before the admissions committee even looks at it.
All this being said, it's still a bit of a crapshoot. I'm in a PhD program at a good school. I teach a class that many of the masters students who want to go on to the PhD program take. The class is regarded as the hardest quantitative class in the school. It's a requirement for the PhD students. Several of the masters students who have done exceptionally well in this class who have applied to the PhD program have been rejected in their PhD application (but ended up at other great schools). Others have been accepted. I'm not sure how much of an influence this class has, but I haven't seen anyone who has done badly in the class get accepted. At the school you apply to, there will probably be one or two classes like this. Typically they are classes you'd have to take in the PhD program if you're accepted anyway. Make sure you take those and do well. This reduces the uncertainty both for you and the faculty about your ability to succeed in the PhD program should you be accepted.
- 1 Thank you for your response. Are there any actual post-bac programs for engineering though? I have a hard time finding them, as opposed to MS programs or just retaking undergrad courses as a non-degree seeking student. And the fact that undergrad GPA, not Masters GPA, is being used to calculate rankings seems like another reason to do something that is closer to undergrad. – J. Doe Commented Jul 21, 2016 at 10:23
- 3 my GPA was probably below average — I wouldn't take that bet. – JeffE Commented Jul 21, 2016 at 18:42
- 1 and no "network". — If you're going through any degree program without creating a network, you're doing it wrong. – JeffE Commented Jul 21, 2016 at 18:44
- +1 for If you have someone on the admissions committee who would vouch for you and agrees to be your adviser, you have a much stronger shot of getting in no matter what the rest of your application looks like. — This is by far the most important point. – JeffE Commented Jul 21, 2016 at 18:59
Moreover, it has been indicated by many that yes a solid gpa in a masters degree program and an excellent explanation describing why your undergraduate gpa is low might help in certain circumstances. Research experience is a big plus as well. Not all is dead!
I have an answer for you, but you and other people might not like it.
In my opinion, you would look exceedingly foolish and naïve to re-do your undergraduate program or do another undergraduate program.
Understand, I'm almost 50 years old. Nobody is going to give a damn about your 3.1 GPA if you excel at your master level work. If you get a 3.9 or higher in your master level work, that will look very good. But if you create a phenomenal master paper on top of that , you'll be good-to-go. Don't worry about "the top school". Instead, worry about whether or not it's accredited.
Long ago, one of my professors told me that students are way too worried about their GPAs. This professor was highly respected in the structural engineering field and had written his own textbook on structural analysis.
In my opinion, if you re-do your undergraduate program or complete another undergraduate degree, I'd say you're not exhibiting mature, adult judgment. It would look very amateurish and inexperienced in life.
- 3 worry about whether or not it's accredited — "Accredited" is a pretty low bar, especially for someone aiming for an academic position. – JeffE Commented Jul 22, 2016 at 15:36
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged graduate-admissions ..
- Featured on Meta
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
Hot Network Questions
- Can someone confirm this observed bug for `bc`? `scale=0` has no effect!
- Getting lost on a Circular Track
- Can the brick opening for an exterior door be close to the same size as the door?
- Can I land on the "EuroAirport Basel-Mulhouse-Freiburg" with a German National Visa as first destination (NON-EU Citizen)?
- Confusions about Figure 16.1 in Munkres' "Analysis on Manifolds"
- How Would I Interpret This Harmonically?
- Where Does Rashi Mention the Streets of Venice?
- Error: Function Stack offset of 7256 exceeded max offset of 4096 by 3160 bytes, please minimize large stack variables
- Why does my LED bulb light up dimly when I touch it?
- Why do "modern" languages not provide argv and exit code in main?
- Understanding the parabolic state of a quantum particle in the infinite square well
- The pronoun in short yes/no answers to rhetorical tag-questions with the generic "you"
- What exactly was Teddy KGB's tell that Mike identified?
- Does Poincare recurrence show that Gibbs entropy is not strictly increasing?
- If a friend hands me a marijuana edible then dies of a heart attack am I guilty of felony murder?
- Why wasn't Randall Stevens caught?
- Is there any benefit to declaring an index that contains a primary key as unique?
- How cheap would rocket fuel have to be to make Mars colonization feasible (according to Musk)?
- Could they free up a docking port on ISS by undocking the emergency vehicle and letting it float next to the station for a little while
- Bathroom fan venting options
- Thread-safe write-efficient register() method for a Load balancer
- Extract geometry information from a .shp file without the associated files
- Is there a result allowing to seperate two connected components
- Is quantum computation effectiveness dependent on EPR non-locality?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Is a PhD really worth it?
Similarly, a PhD student is expected to know a lot more theory/background knowledge in the field and research skills compared to an undergrad. PhD students are also expected to do research contributing to their dissertation, which means they must work with their advisor to keep focused on their topic and their scope.
Though, with an MD, you can always jump back into research, but with a PhD, you can't jump into a clinical position. Though, do be aware the further experienced you are in research, the less time you will spend at the bench. Your time becomes more valuable analyzing data and designing the next set of experiments. Good luck OP.
I wasted six years of my life getting a PhD degree. What ...
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration. Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
Is a PhD Worth It? Should I Do a PhD?
If you do a PhD, after you graduate, you'll need to find a job. If you get a job now, you'll already have a job. If you do well you might even command a higher salary in 5 years' time compared to entering the market as a fresh PhD. You might find you don't need a PhD. This could especially be the case if you work with other PhD-holders.
In terms of nuts and bolts of building career experience section on a resume, which is often the most important part, a PhD is rarely worth it. (Some STEM careers do require a PhD.) However, at the start of my post-graduate educational journey, I was working part-time running teen programs and full time as a landscaper.
TL;DR: Young graduate student in his first year of a PhD program who has lost a passion for the academic world.Seriously considering quitting but don't know what to do. Science background. My background I'm 21-25, with a Science background, B.Sc in Physics.
A PhD has a pretty high opportunity cost with benefits mostly regarding job opportunities within the academy. I would think it may be easier/cheaper to get the job you want by just taking an entry level role in public policy (which you are surely qualified for, if you can spin your transition well in a cover letter), and working your way up from there.
9 things you should consider before embarking on a PhD
Big PhD questions: Should I do a PhD?
Is PhD worth it when considering your career in industry
So rather than twist your credentials to suit the nonacademic job market, my advice is to not get a Ph.D. in the first place. Yes, a Ph.D. will introduce you to interesting people and ideas, but interesting people and ideas exist outside academe, and a choice to go in one direction is also a choice to not go in so many others.
For people who have completed PhD programs, was it ...
Because I'm an idiot. Because I wanted the MD first. The PhD helps make the MD more sciency. Can't see patients without an MD. (Not a current student, just prospective applicant) I asked a physician-scientist at my university about this and I got the impression that the frame of my question was off.
Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
In short, the main difference between having a PhD and not having a PhD is that if you have a PhD you can be a professional researcher. If you don't want to do that, you probably don't need a PhD, so why go to the trouble of getting one? That said, I personally don't agree that you should never get a PhD unless you want a career as a researcher.
It may be, it may not be. You could look at getting a Doctorate in Education, which is an EdD. That's what I thought initially, but two things. An edD is different from a PhD. From what I've read, an edD is a professional degree, whereas the phD is a research degree. Also, edD's are not funded, but PhD's are.
Hence, answers to "Why do you want to do a PhD?" that centre around ambitions to satisfy your scientific curiosity are usually appreciated during PhD interviews. There are different ways to emphasise your scientific curiosity. For instance, you could explain how a specific topic caught your interest.
I just read an incredibly disheartening post on reddit about Grad School admissions in the Biological sciences. The post basically makes it sound like I have no chance of getting into a good PhD program. I graduated from UC Berkeley with a Degree in Biochemistry in 2012. While in school I worked as an undergraduate researcher for 3.5 years.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
You're not going to get into a top PhD program because of amazing masters grades. You'll get into a top PhD program because the additional research you do and glowing letters of recommendation you get during the masters will show that your undergrad grades are irrelevant to your ability to do high quality research. (And also show that by the way, in case you were worried, the grades won't be a ...