- Safety Officer
- Safety Quiz
- Interview Q/A
- Online Exam
- Download PPT
- Get Certificate Online
- HSE Web Story
- NEBOSH IDIP
- Fire Engineering
- Basic Safety
- Construction Safety
- Workplace Safety
- Fire Safety
- Crane Safety
- Work At Height
- Excavation Safety
- Electrical Safety
- Confined Space
- Noise Safety
- Vibration Safety
- Scaffolding
- Radiography
- HSE Calculations & Formulas
- Safety Slogan
- Tool Box Talk
- HSE Documentation
- HSE Training
- Risk Assessment
- Safety Audit
- Accident Investigation
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions


Management Information System (MIS) | Download PPT

Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the efficient management of information is crucial for success. Enter Management Information System (MIS), a powerful tool that aids organizations in making informed decisions, streamlining operations, and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Introduction to Management Information System (MIS)
MIS refers to a computer-based system that provides managers with the tools to organize, evaluate, and efficiently manage information within an organization. It encompasses various technologies, processes, and people to collect, process, store, and distribute data for decision-making purposes.
Importance of MIS in Business Operations
Understanding mis.
MIS serves as the backbone of modern businesses, enabling them to collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data efficiently. It acts as a bridge between raw data and actionable insights, empowering decision-makers at all levels of the organization.
Role in Decision Making
One of the primary functions of MIS is to support decision-making processes by providing timely, accurate, and relevant information to managers. By accessing comprehensive reports and data analytics, managers can make informed choices that drive the organization’s success.
Efficiency and Productivity Enhancement
MIS automates routine tasks, streamlines workflows, and eliminates manual errors, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and productivity. It enables employees to focus on value-added activities while reducing redundant efforts and minimizing waste.
Components of MIS
MIS comprises four key components:
This includes computers, servers, networking devices, and other physical equipment necessary for data processing and storage.
MIS software applications facilitate data collection, processing, analysis, and reporting. Examples include database management systems, business intelligence tools, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
Data is the lifeblood of MIS, encompassing raw facts, figures, and information collected from various sources within and outside the organization.
Standardized procedures and protocols govern the collection, processing, and dissemination of information within the MIS framework. Clear guidelines ensure consistency and accuracy in data management practices.
Types of MIS
Strategic information systems.
Strategic MIS support long-term organizational goals and objectives by providing insights into market trends, competitor analysis, and strategic planning.
Management Reporting Systems
These MIS generate routine reports, dashboards, and performance metrics to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track progress towards organizational goals.
Decision Support Systems
Decision support MIS assist managers in analyzing complex data sets, conducting scenario analysis, and evaluating alternative courses of action to make informed decisions.
Benefits of Implementing MIS
Improved decision making.
MIS provides timely access to accurate and relevant information, enabling managers to make data-driven decisions aligned with organizational objectives.
Enhanced Communication
MIS facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across departments and hierarchical levels, fostering a culture of transparency and teamwork.
Streamlined Operations
By automating manual tasks and integrating disparate systems, MIS optimizes workflows, reduces inefficiencies, and minimizes operational costs.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that leverage MIS effectively gain a competitive edge by responding swiftly to market changes, identifying emerging trends, and capitalizing on new opportunities.
- Incident Reporting: Capturing information about accidents, incidents, near misses, and other safety-related events.
- Risk Assessment: Analyzing potential hazards and evaluating risks to prioritize safety measures.
- Compliance Monitoring: Tracking regulatory requirements and ensuring adherence to safety standards and protocols.
- Training Management: Managing records of safety training sessions, certifications, and competency assessments for employees.
- Performance Measurement: Monitoring safety performance indicators and key performance metrics to assess the effectiveness of safety initiatives.
- Emergency Response Planning: Developing plans and procedures for responding to emergencies and communicating critical information.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Analyzing data collected from various sources to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement, and generating reports for management and regulatory purposes.
In conclusion, Management Information System (MIS) plays a pivotal role in modern organizations, enabling them to harness the power of data for strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. By understanding the components, types, benefits, and challenges of MIS, businesses can leverage this technology to thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Documents Required for Permit To Work (PTW) | Download PPT
How to Become a Saudi Aramco Approved Safety Officer/Safety Engineer | Download PPT
Top 10 Construction Safety Interview Questions and Answers for Safety Officers | Download PPT
Important MCQs for Safety Officer | Download PPT
Near Miss Reporting by QR Code | Download PPT
- What is the role of MIS in decision making? MIS provides managers with timely access to relevant information, enabling them to make informed decisions aligned with organizational goals.
- How does MIS contribute to improving efficiency? By automating routine tasks, streamlining workflows, and minimizing manual errors, MIS enhances operational efficiency and productivity.
- What are the common challenges in implementing MIS? Integration issues, data security concerns, and user adoption are common challenges faced during the implementation of MIS.
- Can small businesses benefit from implementing MIS? Yes, small businesses can benefit from implementing MIS by improving decision-making processes, streamlining operations, and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Free download hse plan | hse plan for your project, emergency response plan (erp) | download sample copy, monsoon safety plan: free download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Popular Posts
Top 15 best safety slogan in hindi, easy nebosh igc exam questions and answers, 25 safety officer interview questions (with sample answers), hse engineer job vacancy : urgent requirement, top 25 best hindi safety slogan in 2024, 10 essential safety officer tips every workplace needs to know, industrial safety, safety officer & safety engineer, work at height | hazards | control measures, very important slip trip and fall hazards, personal fall arrest system, latest post, urgently required hse officer (aed 7000) & hse engineer (aed 9000)..., safety officer requirements for saudi: online/telephonic interview, osha worker rights and protections, hpcl rajasthan refinery limited: recruitment for fire & safety professionals, why safety officers fail in safety interviews, (nebosh) the national examination board in occupational safety and health, 03 safety officer jobs vacancy in saudi arabia: oil and gas..., 03 safety officer urgently required for saudi arabia: online interview, 05 hse officers urgently required in saudi arabia, 06 safety officer and safety engineer urgently required for oil and....

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS)
Published by Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS)"— Presentation transcript:

Chapter 3 E-Strategy.

Module 3: Business Information Systems

1 C H A P T E R CP3507 – MIS Course Introduction.

Introduction to MIS Minder Chen, Ph.D. Associate Professor Martin V. Smith School of Business and economics CSU Channel Islands

1-1 Management Information Systems for the Information Age Copyright 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved Chapter 1 THE INFORMATION.

©2002, Pearson Education Canada 1.1 c h a p t e r 1 1 MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM: CANADA AND BEYOND CANADA AND BEYOND.

1 Knowledge Management Session 4. 2 Objectives 1.What is knowledge management? Why do businesses today need knowledge management programs and systems.

McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

Database – Part 3 Dr. V.T. Raja Oregon State University External References/Sources: Data Warehousing – Mr. Sakthi Angappamudali.

GLOBAL E-BUSINESS AND COLLABORATION
E-commerce vs. E-business

Well, Sort-of.

McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Electronic Business Systems Chapter 7.

Management Information Systems
Database – Part 2b Dr. V.T. Raja Oregon State University External References/Sources: Data Warehousing – Sakthi Angappamudali at Standard Insurance; BI.

Essentials of Management Information Systems, 6e Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise 2.1 © 2005 by Prentice Hall Information Systems in the.

Information Systems In The Enterprise
The value of information is directly linked to how it helps decision makers achieve the organization’s goals Discuss why it is important to study and understand.
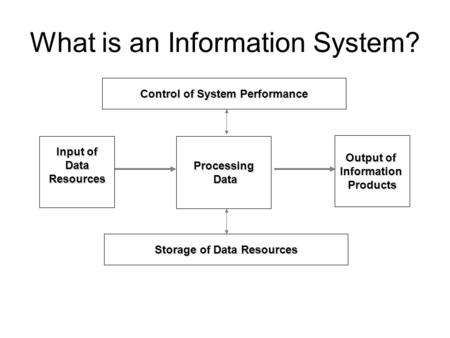
What is an Information System? Input of DataResourcesProcessing Data Data Control of System Performance Storage of Data Resources Output of InformationProducts.

Introduction to Information Systems
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS)
Jul 13, 2014
1.12k likes | 2.76k Views
Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS). Minder Chen, Ph.D. Professor of Management Information Systems Martin V. Smith School of Business and Economics CSU Channel Islands Email: [email protected]. What is MIS? . M: Management
Share Presentation
- development tool
- data warehouse
- goals objectives
- investment processes things vision
- business process source
- britannica matter

Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS) Minder Chen, Ph.D. Professor of Management Information Systems Martin V. Smith School of Business and Economics CSU Channel Islands Email: [email protected]
What is MIS? • M: Management • Business Functions/Processes, Organizations, and Human Behaviors • I: Information • Contents: Data, Information, Knowledge • Processes: Create, Gather/capture/elicit, Store, Organize, Consolidate & Condense, Filter, Deliver, and Share • S: System (Information Systems/Information Technology) • Input-Process-Output and Storage • General Systems Theory (GST) • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Management_information_system • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systems_thinking • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systems_theory
A System View of an Information System Information System Boundary Environments Information System (Producer) Data Providers Data Visualization Input Process Output Data Sources/ Business events Information Destinations • Consumers • Users • organization units Main memory Data storage Control Secondary storage (database) Procedure What are the hardware options or Inputs, Outputs, Processing, and Storages?
Characteristics of Good Information • Accurate • Timely • Relevant (provide context) to decisions • Just sufficient • Worth its cost (to justify its benefits) Information overloading • Deliver just enough accurate, relevant, and timely information to the right persons to make better decisions. • How much energy does a Google search consume? • 0.0003 kWh of energy per search; a Google search uses just about the same amount of energy that your body burns in ten seconds.
Information Quality (IA) and Categories Source: http://sloanreview.mit.edu/files/2008/12/3947-ex3-lo7.png http://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/manage-your-information-as-a-product/
Presentation of Information
Another Version
A Picture Is Worth a Thousand Words • 24 June – 14 December 1812 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Napoleons_retreat_from_moscow.jpg
Managing Information as a Resource • The resources of the industrial age were tangible things (e.g., raw materials and human resources) and easily understood. • In the emerging post-industrial society, there is little understanding of the characteristics of information – the basic yet abstract/intangible resource. • Both physical resources and information could be mined, processed, bought, sold, and managed. Harland Cleveland, "Information as Resource," The Futurist, December 1982, 34-39.
Information Life Cycle Information is processed data that is organized, meaningful, and useful. Information Data Decision • Intelligence • Design • Choice Action * http://faculty.csuci.edu/minder.chen/MIS310/Reading/20000905cleveland.pdf
Characteristic of Information • Expandable: Information explosion* Reduce information overload to reduce uncertainty in decision making. • Compressible: Sorting, categorizing, filtering, aggregating, summarizing**, and consolidating. • Substitutable: Substitute with other resources via productivity improvement. • Transportable: Data communications and networking. • Diffusive: Spreading (sharing) and leaking (Security & privacy) • Sharable: Sharing information is a shared transaction instead of an exchange transaction. * Digital Universe: The world’s information is doubling every two years. In 2011 the world will create a staggering 1.8 zettabytes. ** Summly, a news-summarizing app acquired by Yahoo for $30 millions.
Even the Caveman Needs Knowledge to Survive The information-knowledge-wisdom hierarchy. The caveman has lots of information; he selects and organizes useful information into knowledge, but he does not achieve wisdom until he has integrated his knowledge into a whole that is more than useful than the sum of its parts. Source: Harlan Cleveland, "Information as a Resource," The Futurist, December 1982, 34-39.
Source: IBM Academic Program course materials
The Knowledge Value Chain: Data Source: IBM Academic Program course materials
The Knowledge Value Chain: Information Source: IBM Academic Program course materials
The Knowledge Value Chain: Knowledge Source: IBM Academic Program course materials
Knowledge Is Not Enough Source: IBM Academic Program course materials
DIKW (Information) Hierarchy Know why Wisdom Integrating: Connect the dots Knowledge Know how Learning: Derive rules/policies through experiences & patterns Information Know what Analyzing: To support decision making Know nothing Data Observing: Description of events Happening/Doing Event
DIKW Hierarchy: version 2 • T: Tacit knowledge • E: Explicit knowledge http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DIKW_Pyramid http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:DIKW.png
Moving Up the DIKW Hierarchy • Where is the Life we have lost in living? • Where is the wisdom we have lost in knowledge? • Where is the knowledge we have lost in information? T.S. Eliot, Choruses from “The Rock”, 1934
Information as Products/Services • CarFax: CARFAX - Vehicle History Reports and VIN number check - http://www.carfax.com(1 CARFAX Report $39.99) • Britannica*: http://www.britannica.com/ • Blown to Bits: How the New Economics of Information Transforms Strategy • The printed version was blown away by three disruptive forces • A comeback act? (iPad app) • Why Britannica matter? No printed version, 2012. • Information as services • Google: Searching for information (Google would provide “access to the world's information in one click”) • Facebook: Social networking ("Facebook's mission is to give people the power to share and make the world more open and connected." ) *Source: Jorge Cauz, “Encyclopaedia Britannica's President on Killing Off a 244-Year-Old Product,” Harvard Business Review, Mar 01, 2013.
CD-ROM based Encyclopedia • Encarta (1993), Grolier, and Compton, list for $50 to $70; usually bundled with a new PC for free. • Content quality and distribution channel • Cost: • With a marginal manufacturing cost of $1.50 per copy, the CD-ROM as freebie makes good economic sense. • The marginal cost of Britannica, in contrast, is about $250 for production plus about $500 to $600 for the salesperson’s commission.
Britannica Sales WWW invented 1990 Netscape 1995 Google IPO, 2004 Google Inc. incorporated, 1999 Encarta discontinued 2008 Source: http://hbr.org/2013/03/encyclopaedia-britannicas-president-on-killing-off-a-244-year-old-product/ar/1
The Rise of Wikipedia Disruptive force
Britannica vs. Wikipedia Wiki is an open source content management system (CMS). Wikipedia uses wiki as a development tool.
Information Systems Components • Computers • Server • PC • Mobile • Networking Information Individuals, Groups, Departments, Enterprise-wide, Customers, Trading partners System SW, Application SW Data, Information, Knowledge Manual Procedures and Business Process Source: adapted from Using MIS 3e
huMan, Market, Money, Method, Machine, Material, Message • Business environments • Market demands • Technology development • Social trends • Locations/Localization Man: Human Resource, Employees Market: Customers People $$$ Who? Message: Information Money: Accounting, Finance, Investment Processes Things Vision Why? Goals/Objectives/ Performance measures How, When? What? Machine: Property, Facility, Technology Material: Raw material, Product Method: Technique, Process, Project, Task
Organizational Hierarchy and Information Aggregated OLAP External Planning Control Operation Level of Detail source Processing Detail Internal OLTP
Information Systems Triangle Operational Database Data Warehouse Data Mart Enterprise Workflow BIDSS EIS OLAP Online Analytical Processing OLTP Online Transaction Processing Business Process Workflow Data Information Messaging Systems Knowledge Workflow, Collaboration, Groupware
Classification of Information Systems • Transaction Processing System • Online transaction processing system (OLTP) • Batch, Online, real-time • Management support system • Decision support system (DSS), Executive information system (EIS), and Digital Dashboard • Data warehouse, Business intelligence (BI), and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) • Units involved • Individual, group, and departmental, enterprise-wide, inter-organizational, and social networking systems • Strategic Information Systems • Based on IT Platforms • Traditional desktop/client-server applications • Web-based applications (e.g., Electronic Commerce) • Mobile applications
The Extended Enterprise Buy Make/Add Value Sell B2B E-Commerce B2C or B2B E-Commerce Back Office Front Office Customers Suppliers E-Business: Virtual and Dynamic Enterprise Warehousing Logistic/Transportation Order Fulfillment Manufacturing Finance/Accounting Engineering HR Marketing Sales Support/Service Demand Chain Supply Chain Back Office Integration Enterprise Resource Planning Customer Relationship Management Supply Chain Management
MIS • Management BY Information Systems • Management OF Information Systems Resources Other Resources: HR, Money, Material, etc. Information Information Systems Manages As Products or Services • Managing Information as a Resource (i.e., Inventory Info. System) • Selling Information as Products (i.e., CarFax) • Offering Information/IS as Services (i.e., Facebook, Google)
Summary • What information does one may need to obtain to do his/her works? • What kinds of information systems/technologies may be the best to manage such information? • Be sensitive to the information, IS, and IT. • Know how to apply conceptual frameworks introduced this module in understanding information needs, but start with the analysis of decisions and/or business processes.
IT, IS and IM Source: Competing with Information: A Manager's Guide to Creating Business Value with Information Content
Key Frameworks
Information Systems Applications in a Firm Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Information as: Product vs. By-Product http://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/manage-your-information-as-a-product/ http://sloanreview.mit.edu/files/2008/12/3947-ex1-lo7.png
COBIT’s Information Criteria (I) • Effectiveness deals with information being relevant and pertinent to the business process as well as being delivered in a timely, correct, consistent and usable manner. • Efficiency concerns the provision of information through the optimal (most productive and economical) use of resources. • Confidentiality concerns the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure. (Sony PlayStation Network hacked) • Integrity relates to the accuracy and completeness of information as well as to its validity in accordance with business values and expectations.
COBIT’s Information Criteria (II) • Availability relates to information being available when required by the business process now and in the future. It also concerns the safeguarding of necessary resources and associated capabilities. • Compliance deals with complying with the laws, regulations and contractual arrangements to which the business process is subject, i.e., externally imposed business criteria as well as internal policies. (Sarbanes–Oxley Act) • Reliability relates to the provision of appropriate information for management to operate the entity and exercise its fiduciary and governance responsibilities.
Exercise – 20-minute break and 5-minute presentation • Describe your background and experiences • Company name and the industry it belongs to • Position and general responsibility • Three major decisions • Pick the most important decision involved in this position and find out the following: • Characteristic of the decision: Operational vs. Strategic; Structured vs. Unstructured; Routine vs. Non-routine • What information is current used to support the decision • What kind of source data should be collected to generate the information needed • Under which task is this decision performed • What is the broader business process that this task belongs. • What additional improvements can be made from the perspectives of information systems and decision making
Information System Applications
Extracting Value from Information Chaos (link)
- More by User

Management Information Systems
2. The MIS Function and Information Systems Planning. Organization of the MIS FunctionMIS SpecialistsEstablishing Organizational MIS RequirementsEvaluating the Relative Worth of MIS ApplicationsLinking Business and systems planning. 3. The MIS Function and Information Systems Planning. Cost-Benefit AnalysisMethods of Acquiring ISThe MIS Development ProcessAgents Involved in an MIS Project Who Initiates A Project?.
1.21k views • 88 slides

Management Information Systems. In UK Higher Education. Margaret Taylor. MIS Director University of Oxford. Did I say MIS?. Management Services AISU MAISU MIS. MIS – the role. To provide Administrative and Management Systems to the University
407 views • 18 slides

Introduction to Management Information Systems
Introduction to Management Information Systems. Jason Chen, Ph.D. Professor of MIS School of Business Gonzaga University Spokane, WA 99258 [email protected]. Weekly Class Assignments. Readings and prepare for class discussion Chapter Harvard Business Cases
516 views • 35 slides

MIS. Management Information Systems. An overview of the field, our program, and career opportunities. The MIS Degree. IS offered through the Information Systems Department in the Hankamer School of Business. What is MIS?.
533 views • 27 slides

CLARK UNIVERSITY College of Professional and Continuing Education (COPACE). Management Information Systems. Lection 11 Decision support systems. Plan. Basic terms Comparison of DSS and MIS Perspectives of DSS and MIS. Basic terms.
1.1k views • 67 slides

Management Information Systems (MIS) Lecture 1: Introduction
Management Information Systems (MIS) Lecture 1: Introduction. Muhammad Ali Nasir Fall-2010. Contact Details. [email protected] [email protected] 0333-5118112 MIS Spring 2012. Grading. Management Information Systems (MIS) . Management Information Systems.
896 views • 20 slides

Management Information Systems. Islamia University of Bahawalpur Delivered by: Tasawar Javed. Management Information Systems. MIS
173 views • 8 slides

Management Information Systems. The Islamia University of Bahawalpur Delivered by: Tasawar Javed DMS. Management Information Systems. MIS
292 views • 15 slides


MIS: Management Information Systems
MIS: Management Information Systems. Yong Choi School of Business CSU, Bakersfield. What is MIS?. MIS: Management Information Systems Collect, process, store and distribute information
967 views • 8 slides

BUS 391 Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS)
BUS 391 Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS). Organizations, Processes and Information Systems. Today’s Agenda. Introductions Overview of Business Processes & Information Systems Syllabus: Course Objectives Moodle : Poly Learn Break
420 views • 21 slides

Introduction to Information Systems
Introduction to Information Systems. Soetam Rizky. First thing first…. Why you learn MIS ? Target ? What will you learn ?. Why You Learn MIS ?. We are in digital firm era…. You need to manage it properly…. Just understand it, not memorize it…
723 views • 17 slides

MIS300 An Introduction to Management of Information Systems
MIS300 An Introduction to Management of Information Systems. ?. What does MIS stand for?. Management is getting things done through other people. Information is data given shape and meaning by user. System is a way of doing things. Why is MIS important?.
177 views • 5 slides

What is MIS :- Management Information Systems
What is MIS :- Management Information Systems. Management Information Systems (MIS). Management information system (MIS) An MIS provides managers with information and support for effective decision making, and provides feedback on daily operations
848 views • 32 slides

Management Information Systems. Overview. MIS Inputs. Functions. Characteristics. MIS - Outputs. Competitive Advantage. MIS in Perspective. Without these reports , we’d be as dumb as we look. Primary Purpose of an MIS :
669 views • 43 slides

Management Information Systems ( business information systems)
Management Information Systems ( business information systems). Fatemah Alhusayni PSU 006 – Spring 2006 Instructor: ANDREW BERGSTEIN TA:LINDSI M SCANLAN Pennsylvania State University. What is MIS?.
517 views • 15 slides

Introduction to Management Information Systems Chapter 1 MIS and You
Introduction to Management Information Systems Chapter 1 MIS and You. HTM 304 Spring 06. Definition of MIS. The Development and Use of Information Systems that Achieve Business Goals and Objectives. Three Key Elements: Components of an Info Sys Development and use of the IS
1.04k views • 27 slides

Management Information Systems. An overview of the field, our program, and career opportunities. MIS. The MIS Degree. IS offered through the Information Systems Department in the Hankamer School of Business. What is MIS?.
458 views • 26 slides
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Management Information System Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Corporation or other organization MIS is the safest electronic storing of information. The objective of a management information system is to build a treasure mine of historical data that can be accessed and analyzed to offer helpful insight into the business operations. Grab our professionally designed Management Information system MIS template that presents the companys current situation, gap analysis, the need for a data warehouse in the business, OLAP, OLTP, ETL, Schemas, MPP, etc. In this template, we have covered the features of MIS in different architectures such as primary, three tier, etc. Moreover, in this MIS template, we have included various types of data warehouses, cloud and modern data warehouses, components, general stages, etc. In addition, this PPT contains a working management information system, data warehouse design guidelines, approaches such as top down and bottom up, implementation of MIS, etc. Furthermore, this template compares MIS with other storage systems such as databases, operational database systems, Data Lake, and data mart. Lastly, this deck comprises the impacts of MIS implementation on business, a 30 60 90 days plan, a roadmap to implement a management information system, and a dashboard. Download it now.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Deliver this complete deck to your team members and other collaborators. Encompassed with stylized slides presenting various concepts, this Management Information System Powerpoint Presentation Slides is the best tool you can utilize. Personalize its content and graphics to make it unique and thought-provoking. All the eighty eight slides are editable and modifiable, so feel free to adjust them to your business setting. The font, color, and other components also come in an editable format making this PPT design the best choice for your next presentation. So, download now.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Complete Decks , All Decks , IT
- Data Warehouse Architecture ,
- Data Warehouse Vs Database ,
- Types Of Data Warehouse ,
- Decision Support System DSS ,
- Executive Information System ,
- Management Information System ,
- Business Intelligence Solution
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
We put our trust in God. Everyone else needs to bring data. - W. Edwards Deming, American economist.
Do you find it difficult to turn that data into insights that you can use in your presentations? You are not alone.
Immersed in a sea of information: you wage a relentless battle, striving for the precise data that weaves the narrative you seek.
Losing the Crowd: When you barrage your crowd with perplexing graphs and technical terminology, the audience becomes exhausted and uninterested.
Limited Impact: Neither important conversations nor well-informed decisions are sparked by your presentations.
What was the outcome? Missed possibilities for your organization and frustration on your part.
Want to access the work breakdown structure of the management information system? Click on the link provided.
This is your opportunity to create an impact! We'll furnish you with the strategies and assets you want to turn your MIS data from a devastating weight into a powerful advantage. We'll exhibit how to connect with presentations that:
Put Experiences First: Find how to gather confounded information into data that is reasonable and interesting to your crowd.
Initiate Your Watchers: Get familiar with the methods for making outwardly striking slides that convey a drawing in narrative.
Persuade Activity: Change experiences into practical suggestions that support informed independent decisions, going past just giving information.
Address key issues in your management information system with our template. Click on the link to access the same.
Management Information System Templates
In a company or other organization, MIS is the safest method for storing data digitally. A management information framework's goal is to fabricate a valuable chronicle of verifiable information that can be used to offer insightful analyses of corporate tasks. Get your hands on our masterfully planned template, which incorporates a gap analysis, a company's requirement for data warehouses, OLAP, OLTP, ETL, Outlines, and MPP. From there, the sky’s the limit. The MIS aspects in primary and three-tier architectures are covered by our template.
It also comprises components, general stages, cloud and contemporary data warehouses, and a variety of other data warehouse types. A functional management information system, data warehouse design principles, top-down and bottom-up approaches, MIS implementation, database comparisons, operational database systems, Data Lake, and data mart are also included in this presentation. Ultimately, this deck has a dashboard, an arrangement for the initial 30, 60, and 90 days, a manual for fostering an administration data framework, and the impacts of MIS establishment on associations. Get it immediately.
Template 1: Where’s The Gap in The Organization

Find the progressive capability of our Template, intended to overcome any barrier in your organization's data management. This layout frames the difficulties presented by the storm of large information and shows how a concentrated data storehouse can possibly change your business. Our template fulfills users’ need for proficient data administration by offering a deliberate way to deal with sorting out and overseeing enormous volumes of data. Focusing on the social occasion of fundamental data and encouraging a thorough environment, engages chiefs to use precise data to make well-informed and better decisions. Bid farewell to disconnected joints of knowledge and dispersed information for the efficient base of our template.
Template 2: Why We Need Data Warehouse

Discover the potency of data aggregation and optimization through our Data Warehouse blueprint. This blueprint presents a comprehensive remedy that fulfills the organization's requisites for security, accessibility, and data integrity. Through the consolidation of information sourced from origins into a unified, easily accessible platform, individuals can bid farewell to the frustration of overseeing numerous systems. Guaranteed data integrity and uniform semantics enhance effectiveness, as in this slide, while also reducing risks.
Template 3: Data Warehouse is Non-volatile
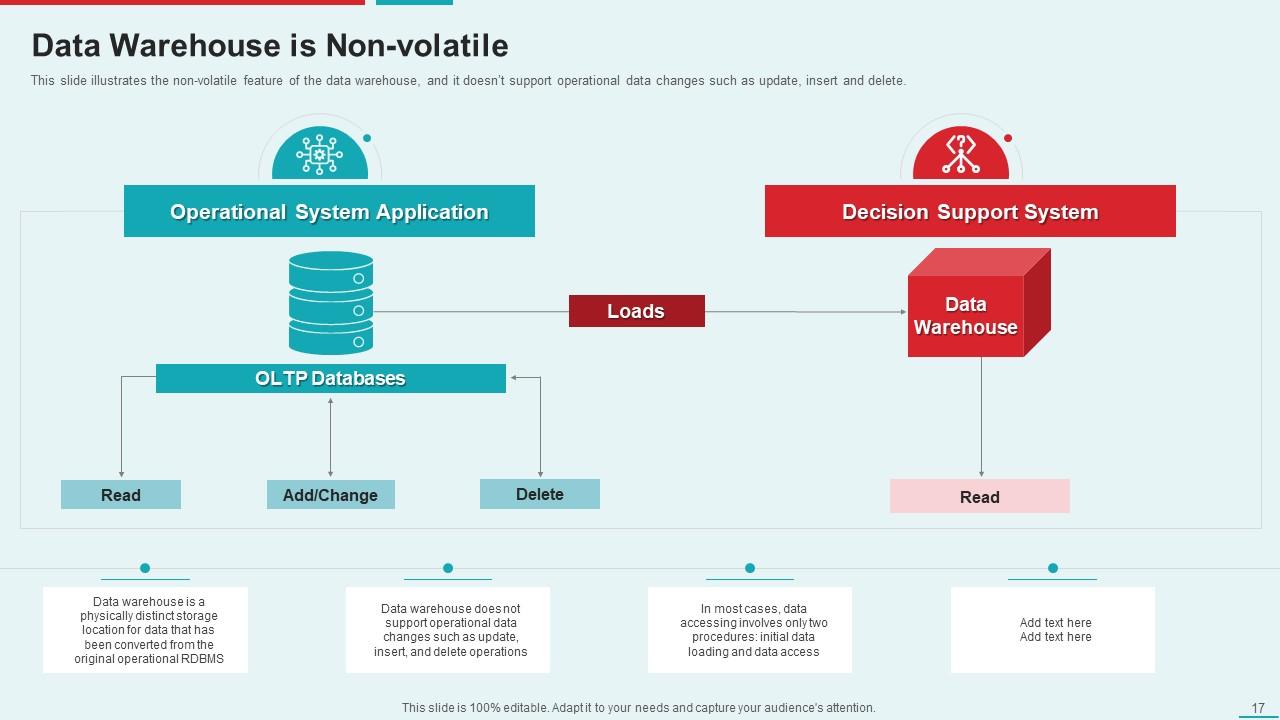
Presenting our template, an adaptable instrument to assist you with working on the productivity of your data management procedures. This layout stresses how information warehousing contrasts with functional frameworks like OLTP data sets in that it isn't unstable. With our template, you can work on your presentation, excite your crowd, and establish a long-term connection.
Template 4: Basic Architecture of Data Warehouse
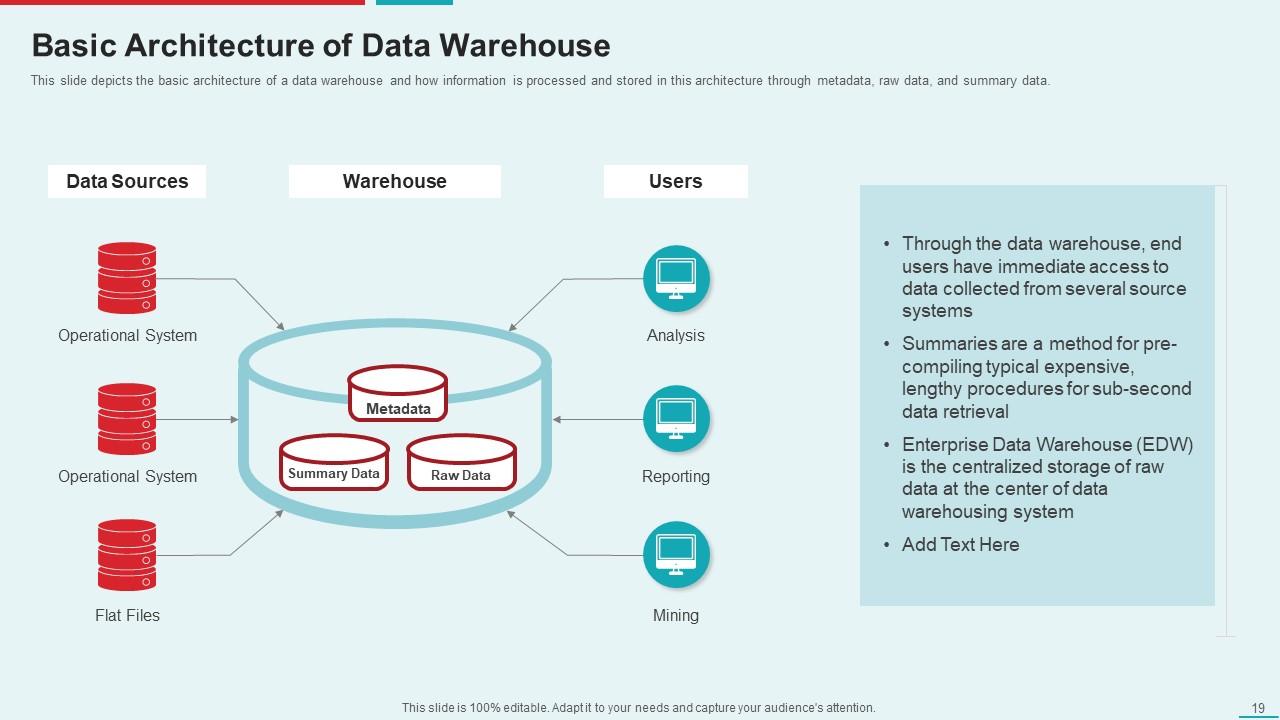
The fundamental concepts underpinning the design of an information dissemination hub are elucidated in this presentation. Delve into the evolution of information, transitioning from rudimentary data sources such as flat files and operational structures to enlightening narratives and thorough analyses. Perceive how metadata orchestrates this material and how troublesome enquiries are pre-figured for speedier recovery while utilizing summed-up information. The brought-together capability of the Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) in crude information stockpiling is clarified by this template.
Template 5: Data Warehouse Architecture with Staging Area and Data Marts
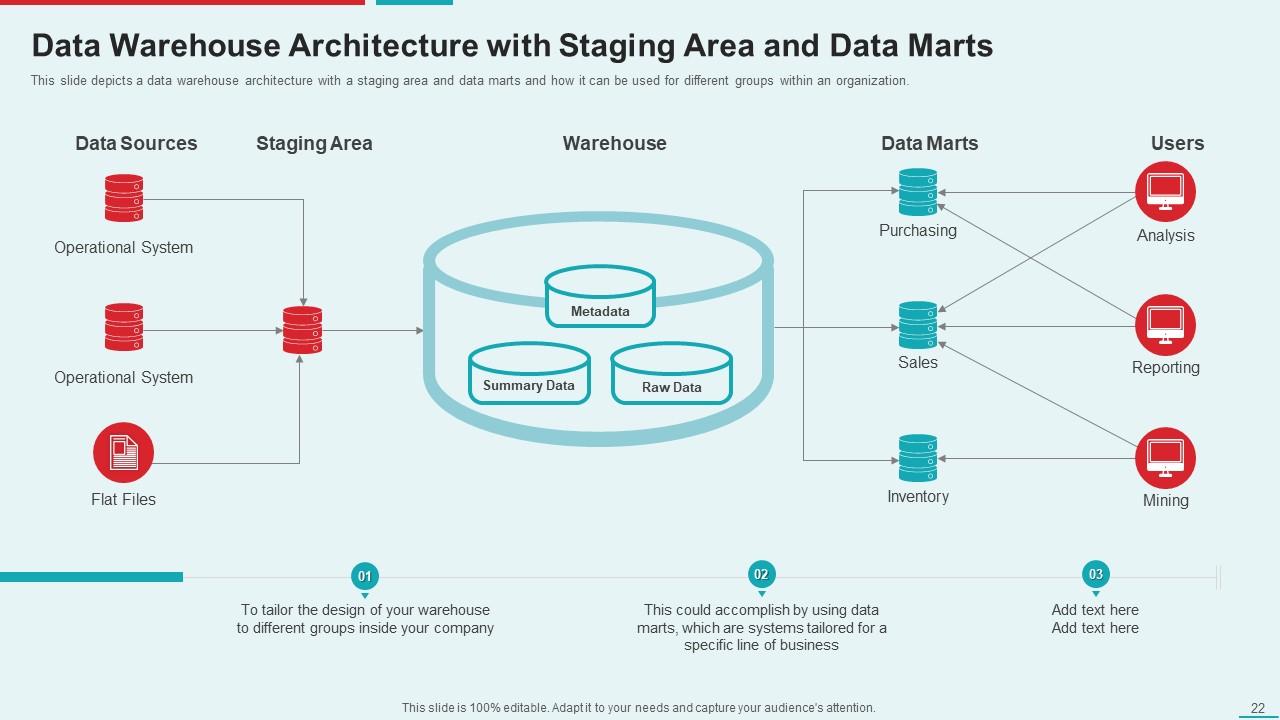
Figure out how to tailor information access for organization divisions, like sales and purchasing. Functional information is purged in the arranging region prior to being sent into the division's explicit data marts or the central warehouse. This makes reporting and analysis easier, allowing each group to focus on the data that they need most. This presentation will demonstrate your unique data flow and make the decision-making process within your organization function more smoothly.
Template 6: What is Operational Data Store
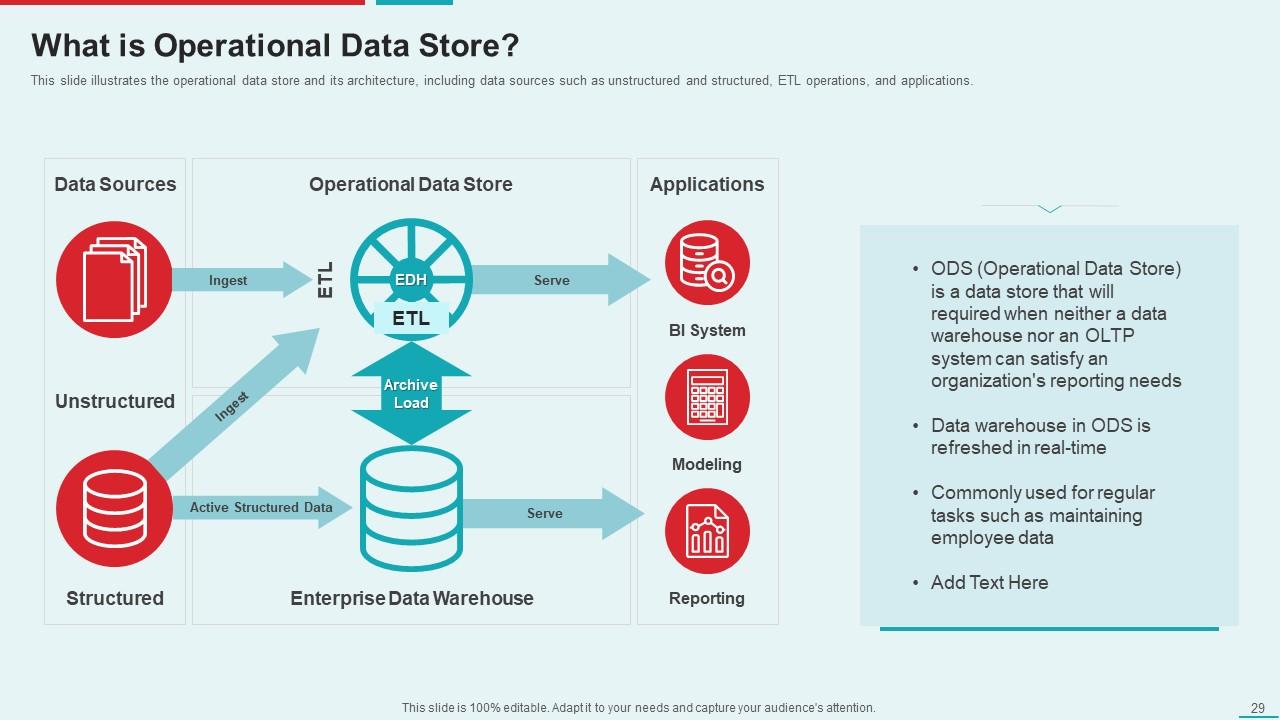
The main elements of an ODS are deconstructed in this slide, along with real-time data sources (both structured and unstructured) and how they integrate with apps. Analyze the ETL method, which stacks and changes crude information for investigation. See the development of information from the live data set into the ODS and, in the end, into the information distribution center for long-haul chronicling. Underscore the demonstrating and revealing elements, situating the ODS as the connection between the latest data and insightful investigation. Make good use of this presentation to introduce this important data management tool.
Template 7: What is Data Mart

This PowerPoint Template examines data marts, which are department-specific data warehouses that have been simplified. View the processes involved in transforming and organizing internal and external data (spreadsheets, databases) for reports and alerts (ETL). Because they carefully concentrate on specific domains, like sales or marketing, rather than including the totality of a data warehouse, data marts are more manageable and understandable. This presentation template serves as an excellent tool for sharing knowledge across departments.
Template 8: What is Dependent Data Mart?
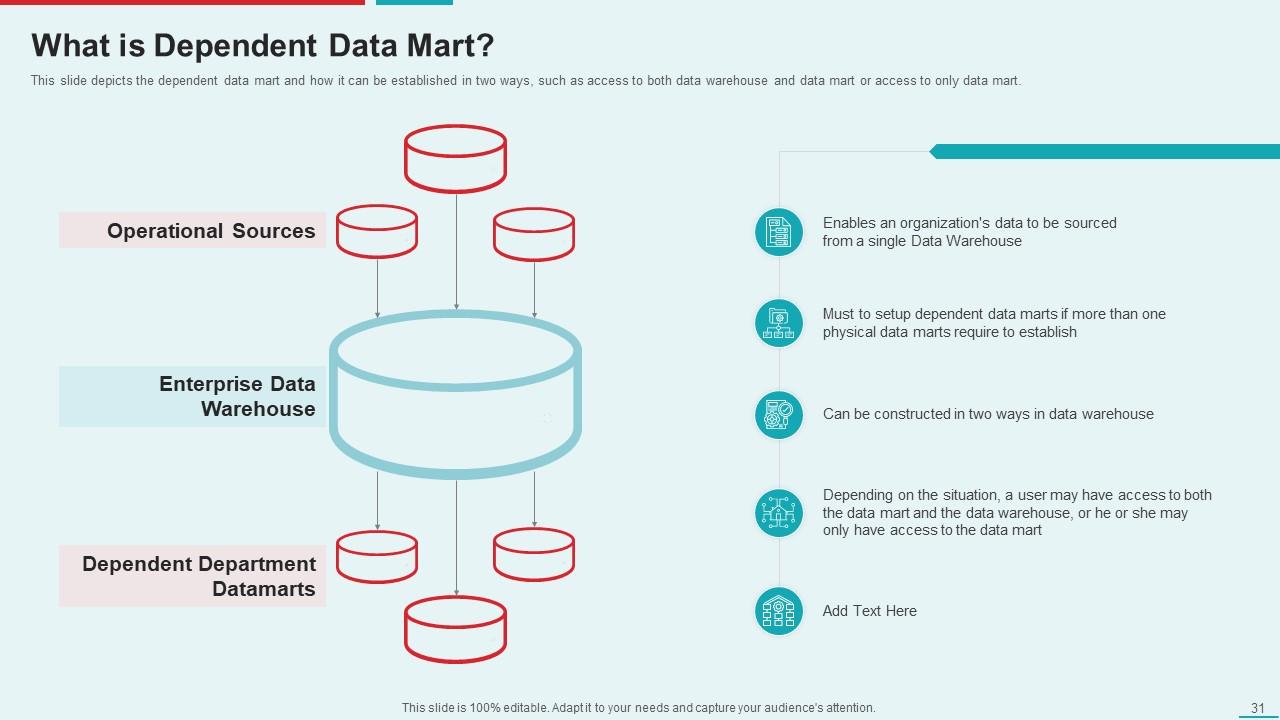
Grab hold of our Dependent Data Mart template to unleash the potential of targeted data analysis! This educational presentation explains the two ways to set up a dependent data mart, giving users access to the mart by itself or to the mart and central data warehouse together. See the flow of operational data to departmental data marts from the enterprise data warehouse, a single source. Make use of the user access area to meet your unique requirements and make sure users can access pertinent information. Improve decision-making and data exploration with this extensive template.
Template 9: What is Hybrid Data Mart?
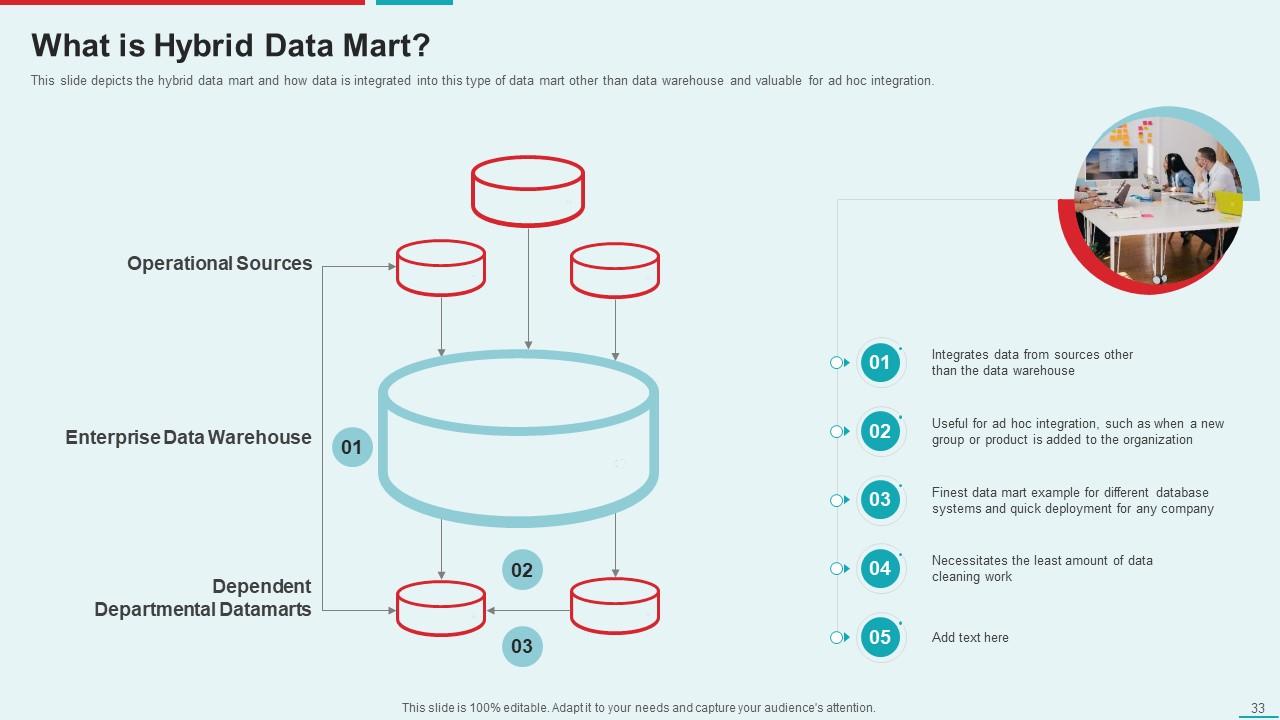
Utilize the template to unlock your agility! This exposition elucidates how data seamlessly traverses between the enterprise data warehouse and operational areas to erect a departmental juggernaut. By amalgamating external data, in contradistinction to conventional data marts, hybrid data marts prove ideal for impromptu analysis amid burgeoning business sectors. The primary merits of this blueprint entail minimal data purification exigencies, expedited deployment, and compatibility with a plethora of database systems.
Template 10: What is Cloud Data Warehouse?
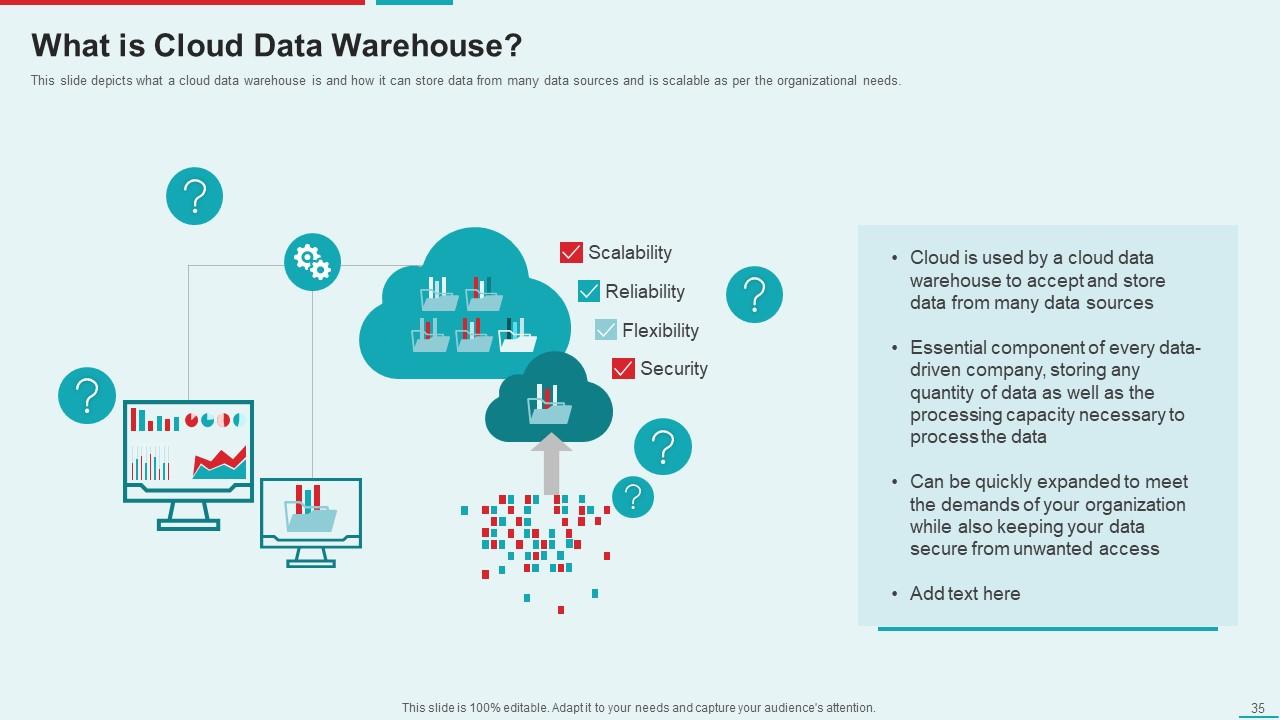
Utilize our template to unlock the potential of data! This versatile PowerPoint elucidates how it seamlessly consolidates vast reservoirs of data from diverse origins. Emphasize unwavering reliability and impregnable security protocols to safeguard your data. Showcase its flexibility by tailoring it meticulously for each data-driven project. Captivate your audience by showcasing a profound comprehension of cloud data warehousing, the key to uncovering profound insights.
Stop Drowning in Data, Start Making Waves!
This presentation offers tools and hands-on expertise to help businesses use data as an input for strategy. Use our decision-making heuristics with our Management Information System templates.
See a sample diagram outlining the limitations of Management Information Systems ON SlideTeam .
Management Information System Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 93 slides:
Use our Management Information System Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

A data warehouse is a central repository for all data in an organization, which is designed to support business intelligence activities. It is needed to improve data quality, provide a single point for all data for all users, and make strategic decisions easier.
Data warehouses are subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile, whereas operational databases are transaction-oriented, not integrated, and volatile. Data warehouses store historical data, while operational databases store real-time data.
A cloud data warehouse is a type of data warehouse that stores data from many sources and is scalable as per organizational needs. Its benefits include cost reduction, data security, high reliability, and scalability.
A data warehouse is a central repository for structured data, whereas a data lake is a central repository for both structured and unstructured data. A data warehouse is designed for business intelligence, while a data lake is designed for big data processing.
The critical components of a data warehouse include load manager, warehouse manager, query manager, and end-user access tools. The load manager is responsible for extracting, transforming, and loading data into the warehouse. The warehouse manager is responsible for storing and managing the data in the warehouse. The query manager is responsible for retrieving data from the warehouse, and end-user access tools are used by end-users to access the data stored in the warehouse.
Ratings and Reviews
by Donald Peters
June 6, 2022
by Dan Marshall
June 5, 2022

An Introduction to Management Information System (MIS)
Last updated: March 18, 2024
- Software Architecture
Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode , for a clean learning experience:
>> Explore a clean Baeldung
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
1. Introduction
Management Information System (MIS) is a set of information technology tools and techniques used to gather, store, and analyze information aiming to support the decision-making process.
Nowadays, MIS is an essential component, especially for modern business operations, that provides managers with timely and accurate information to make informed decisions.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the purpose and components of the MIS, as well as the benefits it provides to organizations.
2. Purpose of Management Information System
The main purpose of MIS is to provide managers with the necessary information to make decisions.
MIS is responsible for gathering data from several sources, such as internal and external sources. In addition, it converts the data into useful information. This information is then utilized to monitor business operations, identify trends, and predict future outcomes.
The key functions of MIS may include data collection, where we can gather data from multiple sources, including internal and external sources. Internal sources, for example, accounting, finance, and human resources. On the other hand, external sources include market research reports and customer feedback. In addition, we can collect data using various techniques, including online surveys, face-to-face interviews, and focused groups.
It also allows data preprocessing. Once data is collected, it is processed using various tools and techniques. The processing step includes sorting, classifying, and analyzing data to produce meaningful information.
After that, this information is stored in a database for future use.
3. Components of Management Information System
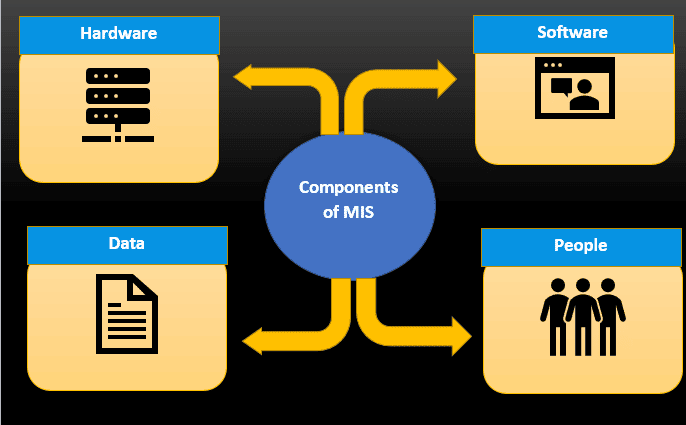
To enable decision-making, the MIS consists of four primary components that equip managers with essential information. These components are hardware, software, data, and people.
Hardware refers to the physical components of the MIS, such as computers, servers, and other devices that store and process data.
The software includes the programs used to process and analyze data. This includes various applications like databases, spreadsheets, and business intelligence tools.
Data serves as the fundamental resource for the MIS. It is collected from various sources and processed using advanced techniques to generate significant insights.
People are a crucial component of MIS. They are responsible for collecting, processing, and analyzing data. People who work in MIS have different abilities, such as looking at data, organizing databases, and keeping information safe.
The following figure shows the components of MIS:
4. Pros and Cons of MIS
While MIS provides several benefits to organizations, such as improved decision-making, increased efficiency, and reduced costs, its implementation can pose challenges for organizations due to various factors.
The table shown below addresses the pros and cons of MIS:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| MIS helps managers make better decisions by providing real-time and accurate information for trend identification and predicting future outcomes | MIS has technical challenges, including selecting the appropriate hardware and software, integrating MIS with existing systems, and ensuring data security |
| MIS automates many manual processes, reducing the time and effort required to collect and process data. This automation improves efficiency and reduces costs | However, MIS professionals need specialized skills, and the lack of proper training for employees is a challenge that organizations must address |
| MIS reduces costs by eliminating manual processes and improving efficiency. This reduces the time and effort required to complete tasks, which translates into lower costs for the organization | To successfully implement MIS, organizations must overcome employee resistance to change problems by communicating the benefits of the new system and providing adequate training |
6. Conclusion
In this article, we discussed Management Information Systems as a crucial component of modern business operations, providing managers with timely and accurate information to make informed decisions.
Through data collection from various sources, processing it to produce meaningful insights, and storing it for future use, MIS offers numerous benefits to organizations, including improved decision-making, increased efficiency, and reduced costs.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Management Information System (MIS) collects, processes, stores, and analyzes data from internal and external sources to provide information to support decision making across all levels of management. It ensures the right information is delivered to the right people at the right time.
The role of MIS is to supply managers with accurate, timely information needed for planning, controlling, and decision-making. An effective MIS is vital for organizational management, operations, and achieving strategic business goals. Read more.
MIS refers to a set of interrelated components that collects, stores, processes, generates and disseminates information for effective business decision making. MIS collects data from various resources, processes it and transforms that data into meaningful and useful information.
An MIS provides managers with tools to organize, evaluate, and manage departments efficiently. It integrates hardware, software, data, people, and procedures to provide relevant information to support organizational functions like planning, staffing, directing, and controlling.
In safety management, a Management Information System (MIS) refers to a comprehensive framework for collecting, processing, storing, and disseminating data and information related to safety within an organization.
4 Characteristics of Good Information. Accurate Timely Relevant (provide context) to decisions Just sufficient Worth its cost (to justify its benefits) Information overloading Deliver just enough accurate, relevant, and timely information to the right persons to make better decisions.
Management information systems (MIS) provide managers with information to help make efficient and effective decisions. MIS involve people, technology, and information. They analyze operational data to help manage organizations.
Characteristics of Good Information • Accurate • Timely • Relevant (provide context) to decisions • Just sufficient • Worth its cost (to justify its benefits) Information overloading • Deliver just enough accurate, relevant, and timely information to the right persons to make better decisions.
This presentation offers tools and hands-on expertise to help businesses use data as an input for strategy. Use our decision-making heuristics with our Management Information System templates. See a sample diagram outlining the limitations of Management Information Systems ON SlideTeam.
Nowadays, MIS is an essential component, especially for modern business operations, that provides managers with timely and accurate information to make informed decisions. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the purpose and components of the MIS, as well as the benefits it provides to organizations.