Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.

How to view all IE Trusted Sites when security settings are managed?
If the Security Zones for Internet Explorer are managed by my system administrator, the list of Trusted Sites is disabled and I cannot scroll through the list. Is there a way I can view the full list of Trusted Sites?

- internet-explorer
- security-policy
- Not a duplicate, but somewhat related: serverfault.com/questions/612903/… - "IE11: How to check into which zone a URL falls?" – T S Commented Apr 23 at 9:21
11 Answers 11
In the registry , perform a search for a URL that is known to be trusted. This should get you to the relevant key where you can see all of the others.
On my Windows 7 installation, the path appears to be HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey , which is slightly different from this answer .
The key should contain several string values with a name indicating the URL and numeric data indicating the zone, one of the following by default.
- 0 = My Computer
- 1 = Local Intranet Zone
- 2 = Trusted sites Zone
- 3 = Internet Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites Zone
- 8 Mine are all under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE – Richard Collette Commented Sep 26, 2014 at 18:03
Depends upon your firm whether the list is under HKLM or HKCU. Here's a quick Powershell command to get the list
- 3 +1: This is the only solution which worked for me! Thanks! – Kidburla Commented Mar 18, 2015 at 15:41
- 3 Remove the ".property" on the end of each line to see which zone the site is configured for: 1 = Local Intranet, 2 = Trusted Sites, 3 = Restricted Sites – BateTech Commented Jul 10, 2019 at 12:25
From powershell:
- 1 Can you explain this answer/flesh it out a bit more for those who don't know PS as well? – studiohack Commented Feb 10, 2015 at 16:13
- Start -> type gpedit.msc -> hit Enter
- navigate to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page
- in the right-hand panel, double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List option, then click Show...
- trusted sites are the ones with 2 in the Value column (1 = Intranet, 3 = Internet, 4 = Restricted)
If that doesn't work (that option is set to "Not Configured" or the list is empty), try the same, except instead of Computer Configuration, start with User Configuration.
- 3 Both of these settings are "Not Configured" and the lists are empty. – JustinStolle Commented Apr 18, 2012 at 22:33
- "You do not have permission to perform this action" - gpedit also locked down – LJT Commented Apr 13, 2016 at 0:10
I came up with the following solution, I hope others will find it useful as well.
I have limited rights, only local, not enough to open and view GPEDIT on AD level.
So, what I did, and works, is to open a command prompt (as Admin) and run the command:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>GPResult /V /SCOPE Computer /H c:\temp\stuff.txt
Then perform a search e.g. for the "ZoneMapKey"
C:\WINDOWS\system32>find "ZoneMapKey" c:\temp\stuff.txt >> c:\temp\sites.txt
Keep in mind there are other keys that might require your attention, like the "approvedactivexinstalsites"...
You will have an output like:
KeyName: Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey\https://www.wesayso.com
Clean it up (I use Excel, use the \ as seperator and be done with it) and you will have a great list.
- 4 I tried this but got an error "ERROR: Invalid Syntax. Options /U, /P, /R, /V, /Z cannot be specified along with /X, /H." – Kidburla Commented Mar 18, 2015 at 15:39
- C:\WINDOWS\system32>GPResult /V /SCOPE COMPUTER >> c:\temp\stuff.txt generate the file for me. "COMPUTER" in caps per the help file. Use >> to write to file instead of /H – MrChrister Commented Feb 4, 2019 at 22:58
This one works on my Windows 7 machine. It was set by my company's domain controller.
Here is an enhanced version of the script that translates the zone type number in the registry to its name as seen in the IE explorer settings dialog box.
Above we see how to gather the registry value names in a registry key and then get the data of each of those values. As each enter separates the value name and the value data with a comma, it could be further enhanced to output to a file with the csv extension and then opened in Excel. Many more possibilities if you want an actual report. But if just need to know what is the site list this will show most of them.
on windows 10 The URL are saved in Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey
to get the values you can brows to the above key or via PowerShell
My key was located here (in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, not HKEY_CURRENT_USER)
I could right-click "ZoneMapKey" and choose "Export"
This .reg file can be opened in Notepad to view (and search) the text contents.
This PowerShell script provides a list from both registry keys if they are populated and uses the out-gridview cmdlet to provide a search capability using the out-gridview filter field.
Stick this in Powershell for a list of the trusted sites:
1 = Intranet zone – sites on your local network. 2 = Trusted Sites zone – sites that have been added to your trusted sites. 3 = Internet zone – sites that are on the Internet. 4 = Restricted Sites zone – sites that have been specifically added to your restricted sites.
Answer taken from: https://blogs.sulross.edu/gfreidline/2017/06/20/show-ie-trusted-sites-from-powershell/
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged internet-explorer security-policy managed ..
- The Overflow Blog
- At scale, anything that could fail definitely will
- Featured on Meta
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
Hot Network Questions
- best way to double-bend arrows smoothly
- What is Zion's depth in the Matrix?
- Can every quantum gravity theory be equivalent to a CFT or an EFT?
- How would humans actually colonize mars?
- Does strong convergence of operators imply pointwise convergence of their unbounded inverses?
- How do I apologize to a lecturer
- Why is the stall speed of an aircraft a specific speed?
- Permutations Required to Randomly sort a deck
- Proof of the principle of explosion
- Maximizing the common value of both sides of an equation (part 2)
- Would reverse voltage kill the optocoupler over long time period?
- Why is the wiper fluid hose on the Mk7 Golf covered in cloth tape?
- How would you slow the speed of a rogue solar system?
- Driveway electric run using existing service poles
- Second Derivative for Non standard Calculus
- If a Palestinian converts to Judaism, can they get Israeli citizenship?
- Not a cross, not a word (number crossword)
- User & hostname suddenly changed after update, now sudo and internet issues
- Can a British judge convict and sentence someone for contempt in their own court on the spot?
- How to reconcile the effect of my time magic spell with my timeline
- What rules of legal ethics apply to information a lawyer learns during a consultation?
- What happens to entropy during compression?
- Risks of exposing professional email accounts?
- How can I write the following expression in LaTeX?

a blog by Sander Berkouwer
- The things that are better left unspoken
HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Local Intranet list of Internet Explorer and Edge

Most Microsoft-based Hybrid Identity implementations use Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) Servers, Web Application Proxies and Azure AD Connect installations. In this series, labeled Hardening Hybrid Identity , we’re looking at hardening these implementations, using recommended practices.
In this part of the series, we’ll look at the required Hybrid Identity URLs that you want to add to the Intranet Sites list in Internet Explorer.
Note: This is the first part for adding Microsoft Cloud URLs to Internet Explorer’s zone. In this part we look at the Local Intranet zone. In the next part we look at the Trusted Sites zone.
Note: Adding URLs to the Local Intranet zone for Internet Explorer, also applies to Microsoft Edge.
Why look at the Intranet Sites?
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), and certain functionality in Azure Active Directory leverage Windows Integrated Authentication to allow for Single Sign-on. (SSO).
Single Sign-on reduces prompt fatigue in people and thus makes them more aware of the moments when password prompts happen and (and this is the theory…) paying more attention to what they are doing with their passwords.
I’m not a psychologist, but I do know how to make Windows Integrated Authentication work with Internet Explorer.
Intranet Sites vs. Trusted Sites (with Default settings)
Internet Explorer offers built-in zones:
- Local intranet
- Trusted sites
- Restricted sites
Per zone, Internet Explorer is allowed specific functionality. Restricted Sites is the most restricted zone and Internet Explorer deploys the maximum safeguards and fewer secure features (like Windows Integrated Authentication) are enabled.
The Local intranet zone, by default, offers a medium-low level of security, where Trusted sites allows for medium-level security. By default, the Local intranet zone allows for the following functionality beyond the Trusted sites zone:
- Local intranet does not allow ActiveX Filtering
- Local intranet allows Scriptlets
- Local intranet allows accessing data sources across domains (Trusted sites prompt)
- Local intranet allows scripting of Microsoft web browser control
- Sites in the Local intranet zone don’t prompt for client certificate selection when only one certificate exists
- Sites in the Local intranet zone may launch applications and unsafe files
- Sites in the Local intranet zone may navigate windows and frames across different domains
- Local intranet sites do not use the Pop-up Blocker feature
- Local intranet sites do not use the Defender SmartScreen feature
- Local intranet sites allow programmatic clipboard access
- Local intranet sites do not use the XSS Filter feature
- Local intranet sites allow user authentication
Possible negative impact (What could go wrong?)
Internet Explorer’s zones are defined with specific default settings to lower the security features for websites added to these zones.
When you use a Group Policy object to add websites that don’t need the functionality of the Local intranet zone to the zone, the systems in scope for the Group Policy object are opened up to these websites. This may result in unwanted behavior of the browser such as browser hijacks, identity theft and remote code executions.
While this does not represent a clear and immediate danger, it is a situation to avoid.
Getting ready
The best way to manage Internet Explorer zones is to use Group Policy.
To create a Group Policy object, manage settings for the Group Policy object and link it to an Organizational Unit, Active Directory site and/or Active Directory domain, log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed with an account that is either:
- A member of the Domain Admins group, or;
- The current owner of the Group Policy Object, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked, or;
- Delegated the Edit Settings or Edit settings, delete and modify security permission on the GPO, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked.
The URLs to add
You’ll want to add the following URLs to the Local intranet zone, depending on the way you’ve setup your Hybrid Identity implementation:
https:// <YourADFSFarmName>
When you use federation with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), the URL for the AD FS Farm needs to be added to the Local Intranet zone. As AD FS is authenticated against, it need to be added to the Local intranet zone as, by default, this is the only zone for websites to allow for user authentication.
https://login.microsoftonline.com
Https://secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com.
The https://login.microsoftonline.com and https://secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com URLs are the main URLs for authenticating to Microsoft cloud services. As these URLs are used to authenticate against, they need to be added to the Local intranet zone as, by default, this is the only zone for websites to allow for user authentication.
https://aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net
- https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com
If you use the Seamless Single Sign-On (3SO) feature in Azure AD Connect, then you’ll want to add the following URLS to the Local intranet zone:
- https://aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net and
These URLs need to be added to the Local intranet zone on all devices where people in the organization use the 3SO feature, as these are the URLs where they will authenticate against. Trusted sites, by default, do not allow this functionality.
If you don’t use the 3SO functionality, don’t add the above URLs.
https://account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com
It is still one of Microsoft’s recommendation to add the https://account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com URL to the Local intranet zone. However, an enhanced experience is available that no longer points employees to this URL, but instead to the https://myprofile.microsoft.com URL, that uses the normal authentication URLs.
The new enhanced experience is available in the Azure portal, under User settings , Manage user feature preview settings (in the User feature previews area) named Users can use preview features for registering and managing security info – enhanced .
If you’ve enabled the enhanced preview, don’t add the above URL.
How to add the URLs to the Local Intranet zone
To add the URLs to the Local Intranet zone, perform these steps:
- Log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console ( gpmc.msc )
- In the left pane, navigate to the Group Policy objects node.
- Locate the Group Policy Object that you want to use and select it, or right-click the Group Policy Objects node and select New from the menu.
- Right-click the Group Policy object and select Edit… from the menu. The Group Policy Management Editor window appears.
- In the main pane of the Group Policy Management Editor window, expand the Computer Configuration node, then Policies , Administrative Templates , Windows Components , Internet Explorer , Internet Control Panel and then the Security Page node.

- In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting.
- Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane.
- Click the Show… button in the left pane. The Show Contents window appears.

- Add the above URLs to the Local Intranet zone by entering the URL in the Value name column and the number 1 in the Value column for each of the URLs.
- Click OK when done.
- Close the Group Policy Editor window.
- In the left navigation pane of the Group Policy Management Console, navigate to the Organization Unit (OU) where you want to link the Group Policy object.
- Right-click the OU and select Link an existing GPO… from the menu.
- In the Select GPO window, select the GPO.
- Click OK to link the GPO.
Repeat the last three steps to link the GPO to all OUs that require it. Take Block Inheritance into account for OUs by linking the GPO specifically to include all people in scope.
To enable functionality in a Hybrid Identity implementation, we need to open up the web browser to allow functionality for specific web addresses. By enabling the right URLs we minimize our efforts in enabling the functionality and also minimize the negative effect on browser security.
There is no need to add all the URLs to specific Internet Explorer zones, when you don’t need to functionality. However, do not forget to add the specific URLs when you enable specific functionality like Seamless Single Sign-on and remove specific URLs when you move away from specific functionality.
Further reading
Office 365 URLs and IP address ranges Group Policy – Internet Explorer Security Zones Add Site to Local Intranet Zone Group Policy
Posted on October 15, 2019 by Sander Berkouwer in Active Directory , Entra ID , Security
5 Responses to HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Local Intranet list of Internet Explorer and Edge

If you use the GPO methode (S2ZAL) the zone get's 'locked' so the user cannot add url's to the zone himself. If you want them to allow this ( yeah i know this shoudln't be 🙂 ) you can use a reg import with GPO Preferences instead.
Yes, indeed you can.

Very well done and written! I've only just begun writing myself just recently and realized that a lot of blogs merely rework old content but add very little of worth. It's good to see a beneficial post of some true valuue to your readers and I. It is actually going down on the list of things I need to emulate being a nnew blogger. Visitor engagement and content quality are king. Many great ideas; you've unquestionably made it on my list of sites to follow!
Continue the great work!
it's done,work fine,thanks you
Nice detail, well explained. Good work.
leave your comment cancel
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Advertisement

Search this site
Dirteam.com / activedir.org blogs.
- Strategy and Stuff
- Dave Stork's IMHO
- The way I did it
- Sergio's Shack
- Things I do
- Tomek's DS World
Microsoft MVP (2009-2025)
Veeam vanguard (2016-2024), vmware vexpert (2019-2022).

Xcitium Security MVP (2023)

Recent Posts
- On-premises Identity-related updates and fixes for August 2024
- What's New in Veeam Backup and Replication v12.2 for Identity Admins
- Entra ID Application Security – A Complex Problem with a Community Solution
- VMware addresses ‘ESX Admins’ authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2024-37085) in ESXi 8.0 Update 3
- VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 3 adds federation support for four Identity Providers
Recent Comments
- Frank Keough on Hardening SMB on Domain Controllers, Step 1: Reporting on SMBv1 connections , SMBv2 connections and SMB null sessions
- Sander Berkouwer on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
- Jeff McGowan on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
- Sander Berkouwer on Configuring Geo-Redundancy for AD FS on-premises with Azure Traffic Manager
- JB on Configuring Geo-Redundancy for AD FS on-premises with Azure Traffic Manager
The information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and the authors make no warranties, either express or implied. Information in these documents, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice. The entire risk of the use or the results from the use of this document remains with the user. Active Directory, Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, and Windows Server are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Group Policy Central
News, Tips and Tutorials for all your Group Policy needss
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites
As you know Group Policy Preferences are these fantastic new settings that allow IT administrators perform any configuration they want on a users group using Group Policy… well almost.. In this tutorial I will show you how to configured one of the few settings that are not controlled by preferences but can be configured using a native Group Policy.
The Internet Explore site zone assignment is one of the few settings you specifically can’t configured using preferences, as you can see (image below) the User Interface to this options has been disabled.
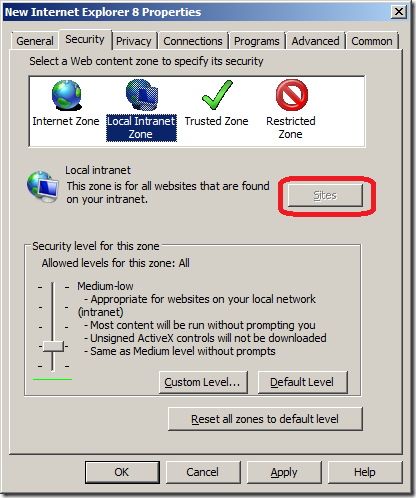
There is a native Group Policy that allows you to control Internet Explorer site zone list is called “Site to Zone Assignment List†which I will go thought below how to use.
Step 1. Edit the Group Policy Object that is targeted to the users you whish this setting to be applied.
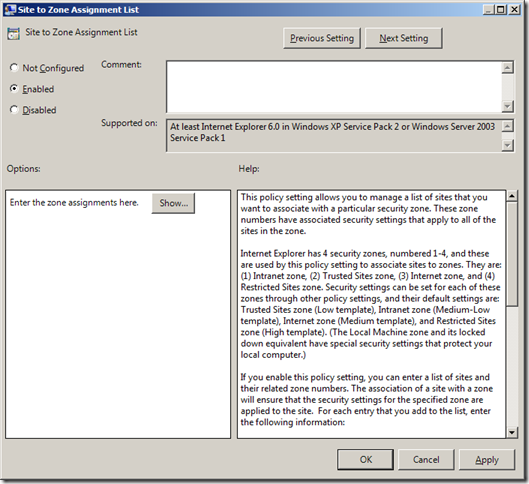
Step 2 . Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button.
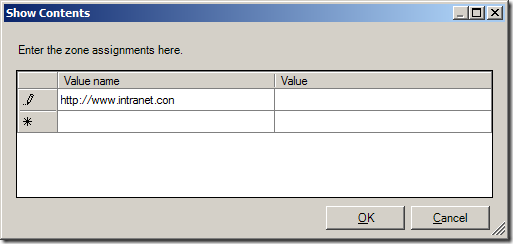
Step 3. Now type the URL in the “Value name†field with the >* on the far left and then type the zone number (see table below) you want to assign to that zone.
Internet Explorer Group Policy Zone Number Mapping
| Zone Number | Zone Name |
| 1 | Intranet Zone |
| 2 | Trusted Sites zone |
| 3 | Internet zone |
| 4 | Restricted Sites zone |
As soon as you start typing the URL a new line will appear for the next URL.
Step 4. One you have finished assigning adding the URL’s and site zone number click OK
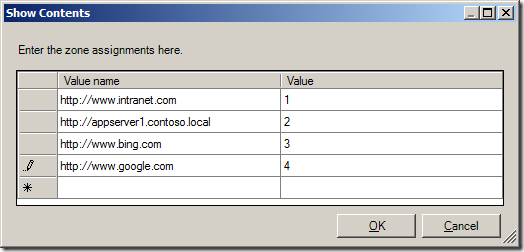
Tip: If you want to delete a row click on the button on the far left to select the row you want to delete (see image below) and then press the “Delete†key.
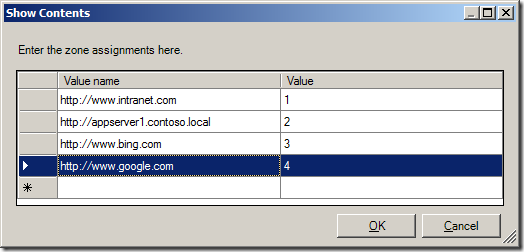
(sites in above list are example only)
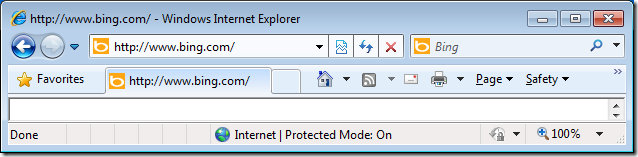
Now the Internet Explorer Site zone list will now be populated with the zone you configured above and as you can see in the images below the Internet Explorer status bar now show the correct zone based on the that the URL’s in the address bar.
Author: Alan Burchill
Related articles.

34 thoughts on “ How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites ”
Blog Post: How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » Group Policy Setting of the Week 18 – Allow file downlaod (Internet Explorer)
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » How to use Group Policy to mitigate security issue KB981374
Yup, that is right and excately how we do it, however there is one problem that is of slight concern 🙁
Once the Zones are set via this GP the user can not add his own and as banks etc. today rely on Trusted Zones this is a slight problem. Our IT policy allow for users to use their PC for personal business as well as work and thus it is a slight problem that they cant add Zones for eg. their bank etc.
I have been thinking, maybe one could make a script to set Zones and deploy this via SCCM 2007.
I have not tried this for a while but i believe you can still do this if you configure it under the Internet Explorer Maintainence section of Group Policy…
The configuration for regular zones works fine. Bu the real pain starts when trying to cover zones for “Enahanced Security Configuration” which require other hives in the registry (e.g. “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\ESCDomains\MyDomain”). I have not seen a Microsoft solution for that so far. If anybody knows a smart solution and would share it, I’d really appreciate that.
You will not have to resort to a script and SCCM. Contrary to what this blog entry says can’t be done, we do use GPP to set sites into speicfic security zones. But we don’t set it as a GPP Internet Setting. We use GPP to assign the sites to their proper zones in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. Doing it this way we configure the sites we need configured for the organization but do not block the users’ ability to add sites they need set for their individual machines.
Ditto. This was my conclusion a few years ago when researching the various IE management methods. Have been scripting the site/zone assignment manually since then. Primarily with GPP which is fairly simple to manage Colin
GPP is server 2008 only and requires client side software correct? Anyway to do achieve the same results (managed IE Zones without disabling user access) in a 2003 AD environment?
Is there somebody who know how to do the same but with Cookies ?
Because of that, I still have to use IEM which sucks…
@AdamFowler_IT this is how you do IE zones http://t.co/uKug8h9h /cc @auteched
@alanburchill @auteched Worth noting that IE zones via this method http://t.co/qiaLSFK7 will wipe out settings from the old method!!!
with this GPO can we block all internet traffic except google and some other sites to users in the domain??
- Pingback: Best Practice: Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection (a.k.a. User State Virtualization) : The Digital Jedi's Blog
If I understand GPOs properly, configuring this policy setting will centrally manage this setting without allowing the user to add/delete/modify any of the site to zone settings. Wouldn’t it be preferable to configure these directly in the user’s registry by use of “Preference” registry settings? I.e. creating records in “User Configuration\Preferences\Windows Settings\Registry”.
Hi, Quick question. Is it possible to have multiple sites assigned to “Intranet Zone”? If I try and add additional sites with the same zone number it states that this is not allowed. Can the links be broken up with ; , or something similar? Thanks,
you add each url in separate lines and repeat the zone number code on the right as many times in the list as you like for that zone. Each url will appear listed in that zone then.
I have a question, when you apply this group policy, users cannot add trusted website anymore by themselves. Did you know how to manage that ?
For those trying to find the answer for the above this post may be useful: http://blog.thesysadmins.co.uk/group-policy-internet-explorer-security-zones.html
It covers two methods. The first method will remove the option for the end user to edit or change the security zones, the second will allow the user to add or remove sites.
- Pingback: How to configure Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection
- Pingback: genuine uggs
Is there a trick to copy/pasting in multiple Value names at once? I have like 100+ IP addresses to insert… Do I have to enter them in 1 at a time?!?
I found this extremely helpful and thank you for posting this. However, for some reason, on my PC when I test the GPO, my trusted sites are affected by the GPO but the only thing that happens is that I can no longer add them; the list is empty. I added about 10 sites to the list using the method above but they are not showing up. I checked to make sure the policy was being applied correctly and it is being applied; it is making it impossible to add to my trusted sites, but the list is empty. With IE 9, the GPO would do the opposite, it would add the sites but the end-user could still add more. I used IEAK for IE 9 years ago and never had a problem, but when I installed IEAK 10 or 11, it never worked.
OK, never mind! To answer my own question, in IE 10, it no longer displays the security zone on the status bar, which stinks, but one can right-click + properties (in an empty space in the body of the webpage) and it will tell the zone you are in. Looks like the zones I added are at least showing in trusted sites. That is good enough for me I guess. Thanks for the original post once again!
I too miss the security bar on IE 10. Will be interesting to review the browser user growths next year.
any news on the copying and pasting I have 100 ips to add need help with the distribution T
Computer specialists are often called IT experts/ advisors or business development advisors, and the division of a corporation or institution of higher education that deals with software technology is often called the IT sector. Countless IT service providers such as The Roots International are offering different facilities like real estate, IT solutions and many more.
I think I have a weird question/request. I want to include my whole domain such as http://www.domain.com as a trusted site. Although, I want to exclude a single web page such as http://www.my.domain.com .
I have *www.domain.com, can http://www.my.domain.com be excluded in any way?
Well, it will provide the internet user user better experience to use internet and surfing websites through internet explorer.
Invaluable discussion ! Coincidentally , if your company has been searching for a a form , my business discovered a blank version here http://goo.gl/eJ3ETg
دم شما گرم.
- Pingback: Allow Previously Unused ActiveX Controls To Run Without Prompt - PC Moment
- Pingback: Internet Options to add Trusted Site Greyed Out - SysPreped Windows 10 LTSB - Boot Panic
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Site sponsor, featured post.
Popular Posts

- Best Practice (40)
- Group Policy FAQ (3)
- KB Focus (5)
- Other Site Links (15)
- Podcast (2)
- ScreenCast (4)
- Security (33)
- Setting of the Week (41)
- Site News (19)
- TechEd (35)
- Tutorials (117)
- Uncategorized (6)
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments

an endpoint admin's journal
- Recent Posts
- Popular Posts
- Recent Comments

Deploy Trusted sites zone assignment using Intune
November 6, 2023

Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
October 31, 2023

Uninstall Teams chat app using remediation script and a configuration profile in Intune
October 30, 2023

Intune Last Check-in date not updating for Windows device
October 25, 2023

How to use Event Viewer to check cause of Blue screen of Death (BSOD)
October 23, 2023
5 Quick Mac OS Terminal commands to make a Mac user life easier

Powershell : Find disabled users and computers in AD
- Active Directory (1)
- Windows (7)
- November 2023
- October 2023
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users’ ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required.
Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles .
Hit the Create button and Select New policy

From the Create a profile menu, select Windows 10 and later for Platform , Templates for Profile type. Select Administrative templates and click Create .

Give the profile desired name and click Next .

In Configurations settings, select Computer Configuration and search for keyword “ Site to Zone “, Site to Zone Assignment List setting will be listed under search results. Go ahead click on it to Select it.

Once selected, a Site to Zone Assignment List page will appear on right side explaining different zones and values required for these zone for setup. Since this profile is being used for trusted sites, we will use the Value “2” . Go ahead and select Enabled button and start entering the trusted sites as required. please ensure to set each value to “2” . See example below:
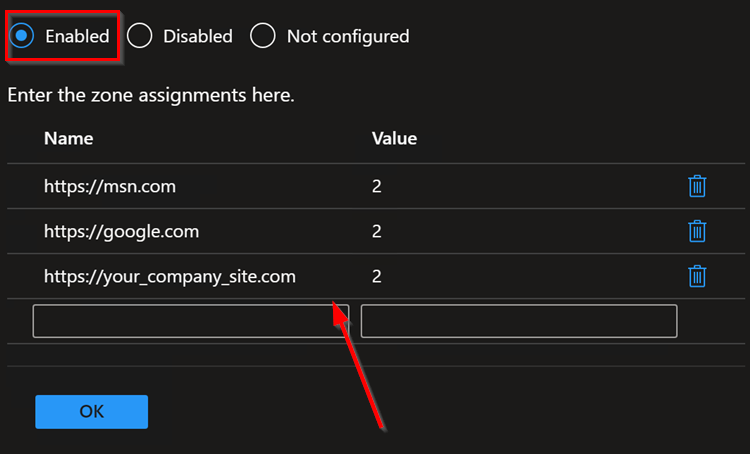
Once done adding the list of sites, click OK to close it and Hit Next on Configuration settings page.
Add Scope tags if needed.
Under Assignments , Click Add groups to target the policy deployment to specific group of devices/users. You can also select Add all users / All all devices .
Hit Next . Then Hit Review + Save button to save.
Tags: Intune Windows
You may also like...

[Windows 10] How to completely uninstall Flash player
- Previous Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
thanks! I was just looking for this exact solution!
- ManageEngine Products
Securing zone levels in Internet Explorer
Managing and configuring Internet Explorer can be complicated. This is especially true when users meddle with the numerous settings it houses. Users may even unknowingly enable the execution of malicious codes. This highlights the importance of securing Internet Explorer.
In this blog, we’ll talk about restricting users from changing security settings, setting trusted sites, preventing them from changing security zone policies, adding or deleting sites from security zones, and removing the Security tab altogether to ensure that users have a secure environment when using their browser.
Restricting users from changing security settings
A security zone is a list of websites at the same security level. These zones can be thought of as invisible boundaries that prevent certain web-based applications from performing unauthorized actions. These zones easily provide the appropriate level of security for the various types of web content that users are likely to encounter. Usually, sites are added or removed from a zone depending on the functionality available to users on that particular site.
To set trusted sites via GPO
- Open the Group Policy Management Editor .
- Go to User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page .
- Select the Site to Zone Assignment List .
- Select Enabled and click Show to edit the list. Refer to Figure 1 below. The zone values are as follows: 1 — intranet, 2 — trusted sites, 3 — internet zone, 4 — restricted sites.
- Click Apply and OK .
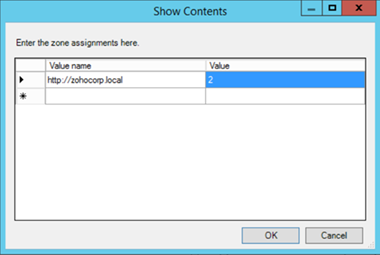
Figure 1. Assigning sites to the Trusted Sites zone.
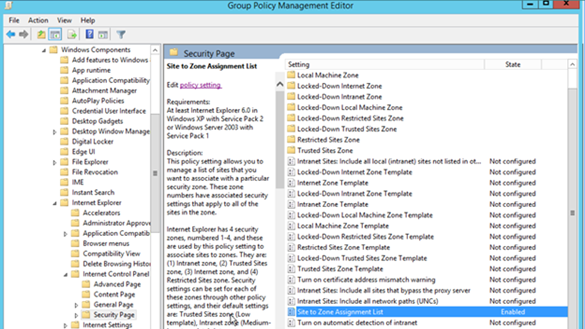
Figure 2. Enabling the Site to Zone Assignment List policy.
By enabling this policy setting, you can manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. See Figure 2.
Restricting users from changing security zone policies
- Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer .
- Double-click Security Zones: Do not allow users to change policies .
- Select Enabled .
This prevents users from changing the security zone settings set by the administrator. Once enabled, this policy disables the Custom Level button and the security-level slider on the Security tab in the Internet Options dialog box. See Figure 3.
Restricting users from adding/deleting sites from security zones
- Double-click Security Zones: Do not allow users to add/delete sites .
This disables the site management settings for security zones, and prevents users from changing site management settings for security zones established by the administrator. Users won’t be able to add or remove websites from the Trusted Sites and Restricted Sites zones or alter settings for the Local Intranet zone. See Figure 3.
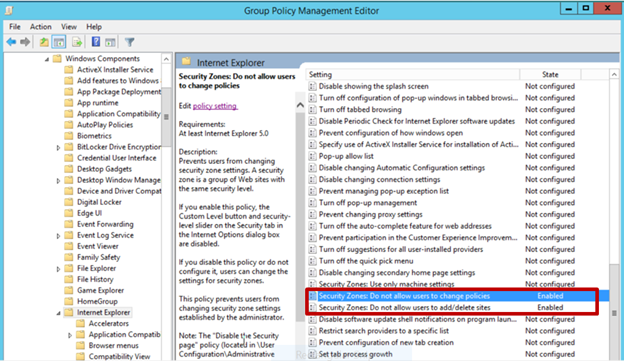
Figure 3. Enabling Security Zones: Do not allow users to change policies and Security Zones: Do not allow users to add/delete sites .
Removing the Security tab
The Security tab in Internet Explorer’s options controls access to websites by applying security settings to various download and browsing options, including defining security levels for respective security zones. By removing this tab, users will no longer be able to see or change the settings established by the administrator.
- Go to User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel .
- Double-click Disable the Security page .
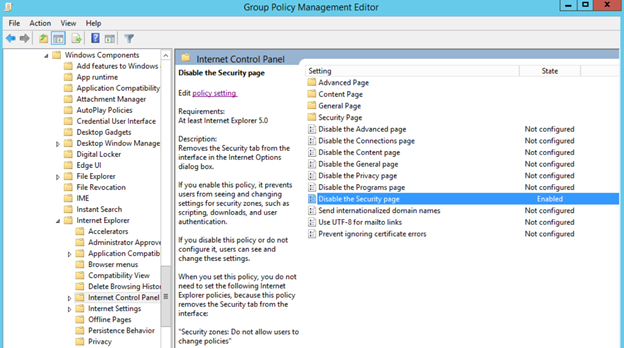
Figure 4. Enabling the Disable the Security page policy. Enabling this policy prevents users from seeing and changing settings for security zones such as scripting, downloads, and user authentication. See Figure 4.
There’s no denying the importance of securing Internet Explorer for any enterprise. By setting security levels, restricting users from changing security zone policies, preventing them from adding or deleting sites from security zones, and removing the Security tab, users will not be able to change any security settings in Microsoft Internet Explorer that have been established by the administrator. This helps you gain more control over Internet Explorer’s settings in your environment.
Derek Melber
Cancel reply.
Is there a way to enable Site to Zone assignment list and still let the user enter their own sites to the trusted list?
Hi Joe. You need to disable the below setting to achieve the requirement.
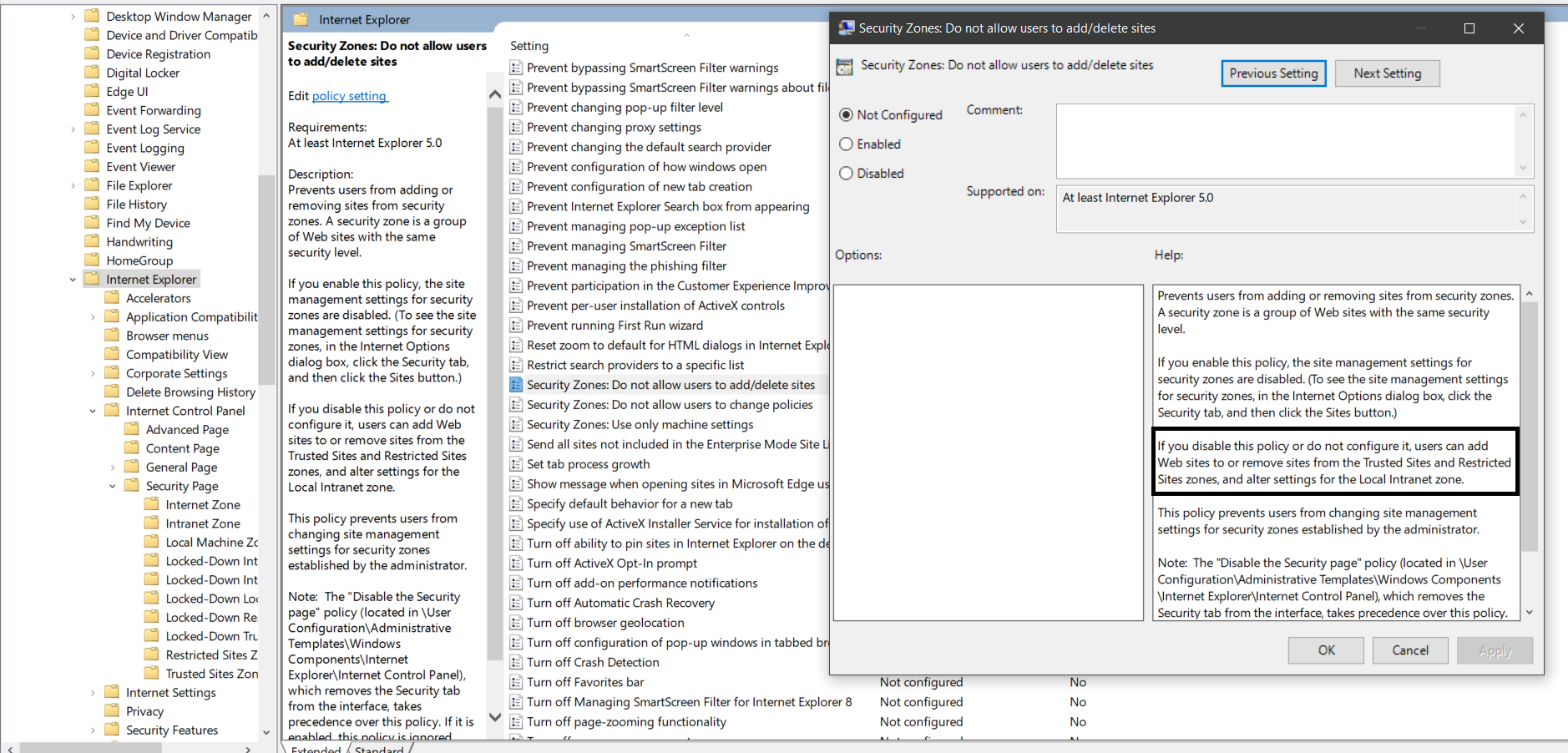
Note: Even if the policy is not configured, users can add their own sites. Only when the policy is enabled, users can’t add their own sites to trusted sites.
Thanks a lot.

Related Posts

Gear up to combat data theft by securing user access permissions
ADManager Plus , General 2 min read Read

MEM – Deploying Trusted Sites
In this post, we will demonstrate how to deploy IE trusted sites via Microsoft Endpoint Manager (aka Intune), we will demonstrate two methods, one for complete control which will lock down the trusted sites location within Internet Settings and the other to maintain user choice, by simply adding an additional trusted sites to end users existing configuration.
- Force standard list of trusted sites and prevent end users from editing (Full Control)
- Add additional trusted sites to existing setup and allow end users to edit (One-time entry)
Full Control Method
As mentioned above, this the full control method is so administrators can control which sites are to be added to the trusted sites list, end users will not be able to add, edit or delete the entries, to get started, log into the MEM portal with your administrative account and browse to Devices , then Configuration Profiles and select Create Profile :

Select the platform to Windows 10 and later and profile to Administrative Templates :

Name and create the profile description :

In the next section, decide if this is going to be a Computer or User settings, in my case, I’m going to chose computer, browse to Computer Configuration, then Windows Components , Internet Explorer , Internet Control Panel and finally Security Page . From here select the Site to Zone Assignment List setting:

Within the setting, select Enabled and enter in the domains that you wish to add to the zone, in my case, I am going to add in https://letsconfigmgr.com/ and select a value of 2 :

The available values are as follows:
- 1 = Intranet
- 2 = Trusted Sites
- 3 = Internet Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites
Deploy the configuration profile to a test computer group and verify the results on the device, by going to Control Panel, Internet Settings , Security , Trusted Sites and confirm that the desired sites are listed, note that you cannot add \ edit \ remove configurations:

One-Time Entry Method
Some administrators may want to allow end users to control the trusted sites list, a great way to allow this via MEM and still add entries is to deploy a PowerShell script, to do this within the MEM portal , go to Devices, Scripts and select Add :

Select Windows 10 , name and set a description:

Copy the below code and save as a .ps1 file, edit lines 1, 5 and 7 to the domain that you wish to add to zones, for an example, I have added letsconfigmgr.com, note the value of 2 on the 7th line, which reflects adding the site to the trusted sites zone, the options are:
Within script settings, upload your script and select Run this script using the logged on credentials :

Once completed, assign the script to your test device and verify the results, by going to Control Panel, Internet Settings , Security , Trusted Sites and confirm that the desired sites are listed, note that you can add \ edit \ remove configurations:

A quick note on PowerShell scripts, once the scripts have run successfully, they won’t execute again, so be aware of this if an end-user removes an entry, the only way to execute the script again, if successful previously, is to edit the existing script and re-upload or create a new script with the same contents and redeploy.
Additionally, if you’re also using security baselines within MEM, I have discovered that the Windows 10 MDM baseline for May 2019 will block the ability for end-users to add \ edit \ remove \ view trusted sites with the default settings applied, if you wish for this ability then the following settings need to be edited within the baseline to allow this:
- Internet Explorer security zones use only machine settings = Disabled
- Internet Explorer users adding sites = Enabled
- Internet Explorer users changing policies = Enabled
Be sure to check the above settings with your security team to ensure that there are no security concerns before making changes to the security baselines and ensure that all settings have been tested fully prior to rolling out to production clients.
- Deploying Adobe Reader DC via ConfigMgr and Intune.
- MEM – Removing MS Teams Desktop Shortcuts
You May Also Like

Deploy WVD Client in System Context via MSIntune

Increasing SharePoint Site Size via PowerShell

Deploy Edge Favourites via Microsoft Intune

Customise Google Chrome using Admin Templates via Intune

Block USB Drives within Microsoft Intune
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Assign DFS share to intranet zone via GPO?
This seems like it shouldn't be hard, but I haven't had any luck with either guessing or searching. I'll admit I'm no Windows guru, so forgive me if the answer should be obvious.
I'm trying to get Windows to stop giving me security warnings when I open files or links from a DFS share. I already have a GPO in place which does this for a couple of other network shares:
Here, I've added host1.mydomain.org and host2.mydomain.org to zone 1 (intranet), and the network shares from these hosts are correctly treated as trusted intranet sites.
However, I now want to add \\mydomain.org\shares to the intranet zone as well. Adding it just like that appears not to work (and on my client machine it appears in the list as file://*.mydomain.org ). Other things I've tried include *.mydomain.org and explicitly listing the hosts where the DFS shares originate.
"Turn on automatic detection of the intranet" is also enabled, although I've never been clear on how that actually works.
Servers and DCs are 2008 R2 and clients are (mostly) 7 Pro.
Edit: The next day, it appears that the listing of mydomain.org is in fact having the desired effect. I hadn't logged out and back in during testing; I just did a gpupdate /force and confirmed that the GPO settings appeared in the Internet Options dialog. Is this a bug or just another arcane Windows thing that I don't quite understand?
- group-policy
- For those finding this via a search: run gpedit.msc to edit the policy nicely enumerated above, then gpupdate /force – Stan Commented May 12, 2016 at 22:48
2 Answers 2
When refreshing group policy it is usually necessary to log out and for some settings a restart (sometimes 2!) is necessary. I wouldn't call it arcane but it won't be obvious if you haven't documentation regarding group policy processing.
- 1 I understand that, but when I saw that the GPO settings appeared properly in the Internet Settings after the gpupdate, I naturally assumed they had been applied. – eaj Commented Oct 6, 2011 at 14:30
- 1 Ok. I wonder if the network connection to the share was still alive, then had to be recreated to be recognized under the new security zone setting for the policy to take affect? – will Commented Oct 6, 2011 at 15:20
- 1 That sounds like a pretty good theory to me. You win the green checkmark. :) – eaj Commented Oct 6, 2011 at 15:27
The shell (explorer.exe) is caching the policy. Simply restart the shell and many settings will start to be applied. There is no need to log out/back in for many scenarios.
Exiting the shell:
- Windows 7: Ctrl+Shift+right click on blank area of Start Menu | Exit Explorer
- Windows 8: Ctrl+Shift+right click on Start Menu button | Exit Explorer
Restarting shell:
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc, File | New Task (Run...) | "explorer"
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged windows group-policy dfs ..
- The Overflow Blog
- At scale, anything that could fail definitely will
- Featured on Meta
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
Hot Network Questions
- Can it be acceptable to take over CTRL + F shortcut in web app
- Can my employer require me to wear a dirty uniform and refuse to provide additional shirts?
- How many ways can you make change?
- Why is there so much salt in cheese?
- How do Trinitarian Christians defend the unfalsifiability of the Trinity?
- Does an unseen creature with a burrow speed have advantage when attacking from underground?
- Can a quadrilateral polygon have 3 obtuse angles?
- Risks of exposing professional email accounts?
- How to substitute URLs?
- Why is the stall speed of an aircraft a specific speed?
- Proof of the principle of explosion
- Marie-Sklodowska-Curie actions: publish a part of the proposal just after the deadline?
- What rules of legal ethics apply to information a lawyer learns during a consultation?
- Is it possible to travel to USA with legal cannabis?
- Light switch that is flush or recessed (next to fridge door)
- When trying to find the quartiles for discrete data, do we round to the nearest whole number?
- Difference between 失敬する and 盗む
- Admissibility of withdrawn confession
- Why are poverty definitions not based off a person's access to necessities rather than a fixed number?
- How to find the x-coordinate of the point circled(non-differentiable points) in this trigonometric function graph?
- What would happen if the voltage dropped below one volt and the button was not hit?
- Boost Converter Efficiency Input Current
- Velocity dispersion of stars in galaxies
- What is the translation of a code monkey in French?
techlauve.com – a knowledge base for IT professionals.
Inhale problems, exhale solutions..
- Nick’s Blog
- Active Directory
- Privacy Policy
« Outlook: “Sending and Receiving reported error (OX80040600)”
Terminal Server Does Not Accept Enough Client Connections »
Adding Sites to Internet Security Zones Using Group Policy
Sometimes it is useful to leverage the power of Group Policy in Active Directory to add sites to certain security zones in Internet Explorer. This can save the network admin the trouble of managing the security zone lists for each computer (or user) separately. In the following example, each user on the network needs to have a specific site added to the Trusted Sites list.
This tutorial assumes that group policy is in good working order on the domain and that all client users and computers can access the directory.
- Open the Group Policy Management MMC console.
- Right-click the organization unit (OU) that the policy should apply to, taking special care to consider whether the policy should apply to computers or users on this particular network.
- Select “Create and Link a GPO Here…” to create a new group policy object.
- In the “New GPO” window, enter a good, descriptive name for this new policy and click “OK”. (ex. “Trusted Sites Zone – Users” or something even more descriptive)
- Locate the newly created GPO in the left-side navigation pane, right-click it and select “Edit…”
- Expand “Administrative Templates” under either “Computer Configuration” or “User Configuration” depending on which type of OU the new policy was linked to in step 2.
- The path to the settings that this example will be using is: Administrative Templates -- Windows Components -- Internet Explorer -- Internet Control Panel -- Security Page
- In the right-hand pane, double-click “Site to Zone Assignment List”.
- Enable the policy and click the “Show…” button next to “Enter the zone assignments here.” This will pop up the “Show Contents” window.
- Click the “Add…” button. This will pop up the “Add Item” window.
- In the first box, labeled “Enter the name of the item to be added:”, enter the URL to the site. (ex. https://secure.ourimportantwebapp.com) . Keep in mind that wildcards can be used. (ex. https://*.ourimportantdomain.com) . Leave off any trailing slashes or sub-folders unless that type of specific control is called for.
- 1 – Intranet Zone
- 2 – Trusted Sites Zone
- 3 – Internet Zone
- 4 – Restricted Sites Zone
- Once the zone assignment has been entered, click “OK”. This will once again show the “Show Contents” window and the new entry should be present.
- Click “OK” and “OK” again to get back to the Group Policy Management Console.
The new policy will take effect at the next group policy refresh interval, which is usually 15 minutes. To test immediately, run a gpupdate /force on a user/computer that falls into the scope of the new policy and go to “Tools -> Internet Options -> Security -> Trusted Sites -> Sites”. The site(s) added should be in the list. If the sites do not show up, check the event logs for any group policy processing errors.
Related content:
- How To: Time Sync Across Windows Network
- Group Policy Not Applied To Remote VPN Users
- QuickBooks Payroll Opens/Saves the Wrong W2 Form
- Microsoft Virtual Server Web Console Constantly Asks For Password
- Group Policy: Applying Different User Policies to the Same User for Workstations and Terminal Server
No comment yet
Juicer breville says:.
November 26, 2012 at 12:11 am (UTC -5)
Hurrah, that’s what I was looking for, what a information! existing here at this web site, thanks admin of this web page.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these HTML tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Remember Me
Connect With Us
Connect with us.
Social Connect by NewsPress
Not finding the answer that you're looking for? Need more help with a problem that is addressed in one of our articles?
techlauve.com is affiliated with Rent-A-Nerd, Inc. in New Orleans, LA.
- DFS Replication (1)
- Group Policy (1)
- Microsoft Exhange (3)
- Microsoft Outlook (11)
- Copiers (1)
- Multi Function Devices (1)
- Printers (2)
- Scanners (1)
- Blackberry (1)
- Firewalls (2)
- Wireless (2)
- Hard Drives (1)
- SAN Systems (1)
- Hyper-V (3)
- Virtual Server (1)
- WordPress (1)
- Security (7)
- QuickBooks (2)
- Quicken (1)
- Antivirus/Antimalware (4)
- Backup Exec (2)
- Internet Explorer (5)
- Microsoft SQL (1)
- Licensing (2)
- Steinberg Nuendo (1)
- Mac OS X (1)
- Server 2003 (12)
- Server 2008 (14)
- Small Business Server 2003 (7)
- Terminal Server (6)
- Updates (2)
- Windows 7 (9)
- Windows XP (11)
- Reviews (1)
- Rent-A-Nerd, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence .
Valid XHTML 1.0 Strict Valid CSS Level 2.1
techlauve.com - a knowledge base for IT professionals. uses Graphene theme by Syahir Hakim.
ericlaw talks about security, the web, and software in general
Security Zones in Edge
Last updated: 19 June 2024
Browsers As Decision Makers
As a part of every page load, browsers have to make dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of decisions — should a particular API be available? Should a resource load be permitted? Should script be allowed to run? Should video be allowed to start playing automatically? Should cookies or credentials be sent on network requests? The list is long.
In many cases, decisions are governed by two inputs: a user setting, and the URL of the page for which the decision is being made.
In the old Internet Explorer web platform, each of these decisions was called an URLAction , and the ProcessUrlAction(url, action,…) API allowed the browser or another web client to query its security manager for guidance on how to behave.

To simplify the configuration for the user or their administrator, the legacy platform classified sites into five 1 different Security Zones :
- Local Machine
- Local Intranet
Users could use the Internet Control Panel to assign specific sites to Zones and to configure the permission results for each zone. When making a decision, the browser would first map the execution context (site) to a Zone, then consult the setting for that URLAction for that Zone to decide what to do.
Reasonable defaults like “ Automatically satisfy authentication challenges from my Intranet ” meant that most users never needed to change any settings away from their defaults.
In corporate or other managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via “Site to Zone Assignment List” policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis. This allowed Microsoft IT, for instance, to configure the browser with rules like “ Treat https://mail.microsoft.com as a part of my Intranet and allow popups and file downloads without warning messages. “
Beyond manual administrative or user assignment of sites to Zones, the platform used additional heuristics that could assign sites to the Local Intranet Zone . In particular, the browser would assign dotless hostnames (e.g. https://payroll ) to the Intranet Zone, and if a Proxy Configuration script was used, any sites configured to bypass the proxy would be mapped to the Intranet Zone.
Applications hosting Web Browser Controls, by default, inherit the Windows Zone configuration settings, meaning that changes made for Internet Explorer are inherited by other applications. In relatively rare cases, the host application might supply its own Security Manager and override URL Policy decisions for embedded Web Browser Control instances.
The Trouble with Zones
While powerful and convenient, Zones are simultaneously problematic bug farms :
- Users might find that their mission critical corporate sites stopped working if their computer’s Group Policy configuration was outdated.
- Users might manually set configuration options to unsafe values without realizing it.
- Attempts to automatically provide isolation of cookies and other data by Zone led to unexpected behavior , especially for federated authentication scenarios .
Zone-mapping heuristics are extra problematic
- A Web Developer working on a site locally might find that it worked fine (Intranet Zone), but failed spectacularly for their users when deployed to production (Internet Zone).
- Users were often completely flummoxed to find that the same page on a single server behaved very differently depending on how they referred to it — e.g. http://localhost/ (Intranet Zone) vs. http://127.0.0.1/ (Internet Zone).
The fact that proxy configuration scripts can push sites into the Intranet zone proves especially challenging, because:
- A synchronous API call might need to know what Zone a caller is in, but determining that could, in the worst case, take tens of seconds — the time needed to discover the location of the proxy configuration script, download it, and run the FindProxyForUrl() function within it. This could lead to a hang and unresponsive UI.
- A site’s Zone can change at runtime without restarting the browser (say, when moving a laptop between home and work networks, or when connecting or disconnecting from a VPN).
- An IT Department might not realize the implications of returning DIRECT from a proxy configuration script and accidentally map the entire untrusted web into the highly-privileged Intranet Zone. (Microsoft IT accidentally did this circa 2011, and Google IT accidentally did it circa 2016).
- Some features like AppContainer Network Isolation are based on firewall configuration and have no inherent relationship to the browser’s Zone settings.
Legacy Edge
The legacy Edge browser (aka Spartan, Edge 18 and below) inherited the Zone architecture from its Internet Explorer predecessor with a few simplifying changes:
- Windows’ five built-in Zones were collapsed to three: Internet (Internet), the Trusted Zone (Intranet+Trusted), and the Local Computer Zone. The Restricted Zone was removed.
- Zone to URLAction mappings were hardcoded into the browser, ignoring group policies and settings in the Internet Control Panel.
Use of Zones in Chromium
Chromium goes further and favors making decisions based on explicitly-configured site lists and/or command-line arguments.
Nevertheless, in the interest of expediency, Chromium today uses Windows’ Security Zones by default in two places:
- When deciding how to handle File Downloads, and
- When deciding whether or not to release Windows Integrated Authentication (Kerberos/NTLM) credentials automatically.
For the first one, if you’ve configured the setting Launching applications and unsafe files to Disable in your Internet Control Panel’s Security tab, Chromium will block file downloads with a note: Couldn't download - Blocked .
Similarly, because Chrome uses the Windows Attachment Execute Services API to write a Mark-of-the-Web on downloaded files , the Launching applications and unsafe files setting (aka URLACTION_SHELL_EXECUTE_HIGHRISK ) for the download’s originating Zone controls whether the MoTW is written. If this setting is set to Enable (as it is for LMZ and Intranet), no MoTW is written to the file’s Zone.Identifier alternate data stream. If the Zone’s URLAction value is set to Prompt (as it is for Trusted Sites and Internet zones), the Security Zone identifier is written to the ZoneId property in the Zone.Identifier file.
By setting a policy, Administrators can optionally configure Edge or configure Chrome to skip SmartScreen/SafeBrowsing reputation checks for File Downloads that original from the Intranet/Trusted Zone.
For the second use of Zones, Chromium will process URLACTION_CREDENTIALS_USE to decide whether Windows Integrated Authentication is used automatically, or the user should instead see a manual authentication prompt. By setting the AuthServerAllowList policy , an admin may prevent Zone Mapping from being used to decide whether credentials should be sent. Aside: the manual authentication prompt is really a bit of a mistake– the browser should instead just show a prompt: “Would you like to [Send Credentials] or [Stay Anonymous]” dialog box, rather than forcing the user to retype credentials that Windows already has.
Even Limited Use is Controversial
Any respect for Zones (or network addresses 2 ) in Chromium remains controversial— the Chrome team has launched and abandoned plans to remove all support a few times, but ultimately given up under the weight of enterprise compat concerns. The arguments for complete removal include:
- Zones are poorly documented, and Windows Zone behavior is poorly understood.
- The performance/deadlock risks mentioned earlier ( Intranet Zone mappings can come from a WPAD-discovered proxy script).
- Zones are Windows-only (meaning they prevent drop-in replacement of Windows by ChromeOS).
A sort of compromise was reached: By configuring an explicit site list policy for Windows Authentication, an administrator disables the browser’s URLACTION_CREDENTIALS_USE check, so Zones Policy is not consulted. A similar option is not presently available for Downloads.
Zones in the New Edge
Beyond the two usages of Zones inherited from upstream (Downloads and Auth), the new Chromium-based Edge browser adds three more:
- Administrators can configure Internet Explorer Mode to open all Intranet sites in IEMode . Those IEMode tabs are really running Internet Explorer, and they use Zones for everything that IE did.
- Administrators can configure Intranet Zone sites to navigate to file:// URIs which is otherwise forbidden .
- Administrators can configure Intranet Zone sites to not be put into Enhanced Security Mode .
Update: This is very much a corner case, but I’ll mention it anyway. On downlevel operating systems (Windows 7/8/8.1), logging into the browser for sync makes use of a Windows dialog box that contains a Web Browser Control (based on MSHTML) that loads the login page. If you adjust your Windows Security Zones settings to block JavaScript from running in the Internet Zone, you will find that you’re unable to log into the new browser .
Downsides/Limitations
While it’s somewhat liberating that we’ve moved away from the bug farm of Security Zones, it also gives us one less tool to make things convenient or compatible for our users and IT admins.
We’ve already heard from some customers that they’d like to have a different security and privacy posture for sites on their “Intranet”, with behaviors like:
- Disable the Tracking Prevention , “Block 3rd party cookie”, and other privacy-related controls for the Intranet (like IE/Edge did).
- Allow navigation to file:// URIs from the Intranet like IE/Edge did (policy was added to Edge 95).
- Disable “ HTTP and mixed content are unsafe ” and “ TLS/1.0 and TLS/1.1 are deprecated ” nags. ( Update: Now pretty obsolete as these no longer exist )
- Skip SmartScreen website checks for the Trusted/Intranet zones ( available for Download checks only).
- Allow ClickOnce/DirectInvoke / Auto-opening Downloads from the Intranet without a prompt. Previously, Edge (Spartan)/IE respected the FTA_OpenIsSafe bit in the EditFlags for the application.manifest progid if-and-only-if the download source was in the Intranet/Trusted Sites Zone. As of Edge 94, other policies can be used.
- Allow launching application protocols from the Intranet without a prompt .
- Drop all Referrers when navigating from the Intranet to the Internet; leave Referrers alone when browsing the Intranet. (Update: less relevant now ).
- Internet Explorer and legacy Edge automatically send your client certificate to Intranet sites that ask for it. The AutoSelectCertificateForUrls policy permits Edge to send a client certificate to specified sites without a prompt, but this policy requires the administrator to manually specify the site list.
- Block all (or most) extensions from touching Intranet pages to reduce the threat of data leaks ( runtime_blocked_hosts policy).
- Guide all Intranet navigations into an appropriate profile or container (a la Detangle ).
- Upstream , there’s a longstanding desire to help protect intranets/local machine from cross-site-request-forgery attacks; blocking loads and navigations of private resources from the Internet Zone is somewhat simpler than blocking them from Intranet Sites. The current plan is to protect RFC1918-reserved address space .
At present, only AutoSelectCertificateForUrls , AutoOpenFileTypes, AutoLaunchProtocolsFromOrigins . manual cookie controls, and mixed content nags support policy-pushed site lists, but their list syntax doesn’t have any concept of “the entire Intranet” (all dotless hosts, hosts that bypass proxy).
You’ll notice that each of these has potential security impact (e.g. an XSS on a privileged “Intranet” page becomes more dangerous; unqualified hostnames can result in name collisions ), but having the ability to scope some powerful features to only “Intranet” sites might also improve security by reducing attack surface.
As browser designers, we must weigh the enterprise impact of every change we make, and being able to say “ This won’t apply to your intranet if you don’t want it to ” would be very liberating. Unfortunately, building such an escape hatch is also the recipe for accumulating technical debt and permitting the corporate intranets to “rust” to the point that they barely resemble the modern public web.
Best Practices
Throughout Chromium, many features are designed respect an individual policy-pushed list of sites to control their behavior. If you were forward-thinking enough to structure your intranet such that your hostnames are of the form:
- https://payroll. contoso-intranet.com
- https://timecard. contoso-intranet.com
- https://sharepoint. contoso-intranet.com
…Congratulations, you’ve lucked into a best practice. You can configure each desired policy with a *.contoso-intranet.com entry and your entire Intranet will be opted in.
Unfortunately, while wildcards are supported, there’s presently no way to express the concept of “any dotless hostname.”
Why is that unfortunate? For over twenty years, Internet Explorer and legacy Edge mapped domain names like https://payroll , https://timecard , and https://sharepoint/ to the Intranet Zone by default. As a result, many smaller companies have benefitted from this simple heuristic that requires no configuration changes by the user or the IT department.
Opportunity: Maybe such a DOTLESS_HOSTS token should exist in the Chromium policy syntax. This seems unlikely to happen. Edge has been on Chromium for over two years now, and there’s no active plan to introduce such a feature.
- Internet Explorer and Legacy Edge use a system of five Zones and 88+ URLActions to make security decisions for web content, based on the host of a target site.
- Chromium (New Edge, Chrome) uses a system of Site Lists and permission checks to make security decisions for web content, based on the hostname of a target site.
There does not exist an exact mapping between these two systems, which exist for similar reasons but implemented using very different mechanisms.
In general, users should expect to be able to use the new Edge without configuring anything; many of the URLActions that were exposed by IE/Spartan have no logical equivalent in modern browsers.
If the new Edge browser does not behave in the desired way for some customer scenario, then we must examine the details of what isn’t working as desired to determine whether there exists a setting (e.g. a Group Policy-pushed SiteList) that provides the desired experience.
1 Technically, it was possible for an administrator to create “Custom Security Zones” (with increasing ZoneIds starting at #5), but such a configuration has not been officially supported for at least fifteen years, and it’s been a periodic source of never-will-be-fixed bugs.
2 Beyond those explicit uses of Windows’ Zone Manager, various components in Chromium have special handling for localhost/loopback addresses, and some have special recognition of RFC1918 private IP Address ranges, e.g. SafeBrowsing handling, navigation restrictions, and Network Quality Estimation. As of 2022, Chrome did a big refactor to allow determination of whether or not the target site’s IP address is in the public IP Address space or the private IP address space (e.g. inherently Intranet) as a part of the Private Network Access spec . This check should now be basically free (it’s getting used on every resource load) and it may make sense to start using it in a lot of places to approximate the “ This target is not on the public Internet ” check. Within Edge, the EMIE List is another mechanism by which sites’ hostnames may result in different handling.
Ancient History
Security Zones were introduced with Internet Explorer 4, released back in 1997:
The UI has only changed a little bit since that time, with most of the changes happening in IE5. There were only tiny tweaks in IE6, 7, and 8.
Share this:
Published by ericlaw.
Impatient optimist. Dad. Author/speaker. Created Fiddler & SlickRun. PM @ Microsoft 2001-2012, and 2018-, working on Office, IE, and Edge. Now a GPM for Microsoft Defender. My words are my own, I do not speak for any other entity. View more posts
2 thoughts on “ Security Zones in Edge ”
In IE it is possible to see which zone is active on a page you’re currently viewing (alt to show menu bar, -> file -> properties).
Is it possible to see this in the new Edge?
No, although as noted, the Zone isn’t used for very much. To see the Zone, you’d have to reload the same page in IE (or use a command line utility or similar).
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
How to add a server to trusted sites
I’m not quite sure how to add a server as a trusted site with group policy. I know how to add URLs to trusted sites. I’m more confused on the syntax.
Do i just type in “serverA” or “\serverA” or do i just put the IP address? If it’s an IP address do i enter “file://10.0.0.1”?
Open the Group Policy Management Console.
Navigate to the Group Policy Object that you want to edit.
Expand the Computer Configuration or User Configuration folder, depending on whether you want to apply the policy to all users or just specific users.
Expand the Administrative Templates folder.
Expand the Windows Components folder.
Expand the Internet Explorer folder.
Click on the Security Zones and Content Ratings folder.
Double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List policy.
Click the Enabled radio button.
Click the Show button.
In the Value name field, enter the server name in the following format: “file://servername” (replace “servername” with the actual name of the server).
In the Value field, enter the corresponding zone number for the zone that you want to add the server to:
1 for Intranet zone
2 for Trusted Sites zone
3 for Internet zone
4 for Restricted Sites zone
Click the OK button.
@spiceuser-9i0os
Thank you! I just didn’t know what to enter for the value.
Related Topics
| Topic | Replies | Views | Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows , , , | 5 | 833 | March 6, 2016 | |
| Windows , | 4 | 209 | November 20, 2014 | |
| Windows , , , | 0 | 109 | February 24, 2010 | |
| Windows , | 11 | 18616 | November 2, 2017 | |
| Windows , | 8 | 1239 | October 11, 2016 |
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Group Policy and compatibility with Internet Explorer 11
- 2 contributors
Update: The retired, out-of-support Internet Explorer 11 desktop application has been permanently disabled through a Microsoft Edge update on certain versions of Windows 10. For more information, see Internet Explorer 11 desktop app retirement FAQ .
Internet Explorer 11 has many Group Policy entries that can be configured for keeping your environment managed and safe. This table includes all of our recommendations around security, performance, and compatibility with the previous versions of Internet Explorer, regardless of which Zone the website is in.
| Activity | Location | Setting the policy object |
|---|---|---|
| Turn on Compatibility View for all intranet zones | Double-click , and then click . | |
| Turn on Compatibility View for selected websites, using Group Policy | Double-click , and then click .Users will be able to add or remove sites manually to their local Compatibility View list, but they won’t be able to remove the sites you specifically added. | |
| Turn on Quirks mode for selected websites, using Group Policy | Double-click , and then click . | |
| Ensure your users are using the most up-to-date version of Microsoft’s compatibility list. | Double-click , and then click . | |
| Restrict users from making security zone configuration changes. | Double-click , and then click . | |
| Control which security zone settings are applied to specific websites. | Double-click , click , and then enter your list of websites and their applicable security zones. | |
| Turn off Data Execution Prevention (DEP). | Double-click , and then click . |
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
in the right-hand panel, double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List option, then click Show... trusted sites are the ones with 2 in the Value column (1 = Intranet, 3 = Internet, 4 = Restricted) ... 1 = Intranet zone - sites on your local network. 2 = Trusted Sites zone - sites that have been added to your trusted sites. 3 = Internet ...
In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting. Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane. Click the Show ... Group Policy - Internet Explorer Security Zones Add Site to Local Intranet Zone Group Policy. Posted on October 17, 2019 by Sander Berkouwer in Active Directory, Entra ID ...
In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis. ... If a Proxy Configuration script was used, any sites configured to bypass the proxy would be mapped to the Intranet Zone. EdgeHTML, used in ...
In this part of the series, we'll look at the required Hybrid Identity URLs that you want to add to the Intranet Sites list in Internet Explorer. Note: ... In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting. Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane. Click the Show ...
Right-click 'Site to Zone Assignment List' and click 'Edit' Select 'Enabled' and click 'Show' in the options pane; ... To Edit an Existing Group Policy Object (i.e. add your IP to the Local Intranet Zone) Click Start → Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Group Policy Management;
Re: Site to Zone Assignment List - Powershell. # Step 2: Navigate to the Site to Zone Assignment List # This step is manual and requires navigating through the Group Policy Management Editor interface. # Step 3: Enable the Policy and Specify Zone Assignments # Define the list of URLs and their corresponding zone assignments.
Value Setting ----- 0 My Computer 1 Local Intranet Zone 2 Trusted sites Zone 3 Internet Zone 4 Restricted Sites Zone Note. By default, My Computer does not appear in the Zone box on the Security tab as it is locked down to help improve security. Each of these keys contains the following DWORD values that represent corresponding settings on the ...
Step 2. Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button. Step 3.
4. Add one URL to Intranet Zone and Another Url To trusted Site Zone through GPO Requirement: Add one URL to Intranet Zone and Another Url To trusted Site Zone. The above requirement can be achieved in three ways. Option 1: Computer Configuration ""> Administrative Tools ""> Windows Components ""> Internet Explorer ""> Internet ...
Site to Zone Assignment List: Location: Computer and User Configuration: Path: Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page: ... If you don't configure this policy setting, users choose whether to force local sites into the Intranet Zone. Description framework properties: Property name Property value; Format ...
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users' ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required. Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles. Hit the Create button and Select New ...
Select the Site to Zone Assignment List. Select Enabled and click Show to edit the list. Refer to Figure 1 below. The zone values are as follows: 1 — intranet, 2 — trusted sites, 3 — internet zone, 4 — restricted sites. Click OK. Click Apply and OK. Figure 1. Assigning sites to the Trusted Sites zone. Figure 2.
Value = 1 (Intranet zone) Intranet Zone. Show security warning for potentially unsafe files > Enabled > Enable. If you enable this policy setting and set the drop-down box to Enable, these files open without a security warning. If you set the drop-down box to Prompt, a security warning appears before the files open. Share.
If you want to lock it down and add as needed, GPO will work just fine, just go to Win Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page - Site to Zone Assignment - enable the policy, click List and add the sites as needed, a value of 1 is Intranet a value of 2 would be Trusted. Yes. I want to lock it down so I will do it in ...
From here select the Site to Zone Assignment List setting: Within the setting, select Enabled and enter in the domains that you wish to add to the zone, in my case, ... which reflects adding the site to the trusted sites zone, the options are: 1 = Intranet; 2 = Trusted Sites; 3 = Internet Zone;
Policies Administrative Templates Windows Components Internet Explorer Internet Control Panel Security Page Site to Zone Assignment List Here, I've added host1.mydomain.org and host2.mydomain.org to zone 1 (intranet), and the network shares from these hosts are correctly treated as trusted intranet sites.
In the right-hand pane, double-click "Site to Zone Assignment List". Enable the policy and click the "Show…" button next to "Enter the zone assignments here." This will pop up the "Show Contents" window. Click the "Add…" button. This will pop up the "Add Item" window.
The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. ... Local Intranet zone; Trusted Sites zone; Internet zone; Restricted Sites zone; The security settings can be set for each of these zones ...
Beyond manual administrative or user assignment of sites to Zones, the platform used additional heuristics that could assign sites to the Local Intranet Zone. In particular, the browser would assign dotless hostnames (e.g. https://payroll ) to the Intranet Zone, and if a Proxy Configuration script was used, any sites configured to bypass the ...
Steps performed: 1- Configuration Profiles --> Site to Zone Assignment List completed (\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page) --> no changes in sites under Internet options-> Trusted sites, still shows the old ones. 2- Security Baseline, IE (users adding sites / changing policies set to "NOT Configured" ).
Click on the Security Zones and Content Ratings folder. Double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List policy. Click the Enabled radio button. Click the Show button. In the Value name field, enter the server name in the following format: "file://servername" (replace "servername" with the actual name of the server).
Control which security zone settings are applied to specific websites. Administrative Templates\ Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page: Double-click Site to Zone Assignment List, click Enabled, and then enter your list of websites and their applicable security zones. Turn off Data Execution Prevention (DEP).
Hello, I want to make one unified list of all URL which should be added to Trusted Sites and Local Intranet Zones and after that publish it to TechNet Wiki or Gallery. There are a couple of pages, KB and different service URL for different services and each of them talks about different assignments. Like KB2507767 and Office 365 URL and IP ...