Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk

Introduction
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
Step 1: Define the Problem
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Step 4: Workplan
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template, multi-chapter growth strategy framework (free template), lidl swot analysis: free ppt template and in-depth insights.
Discover Lidl's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with our free PowerPoint template. This in-depth SWOT analysis provides valuable insights to help you understand Lidl's market position and strategic direction.
Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Pestle analysis: decoding reddit's landscape (free ppt).
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
A guide to problem-solving techniques, steps, and skills

You might associate problem-solving with the math exercises that a seven-year-old would do at school. But problem-solving isn’t just about math — it’s a crucial skill that helps everyone make better decisions in everyday life or work.

Problem-solving involves finding effective solutions to address complex challenges, in any context they may arise.
Unfortunately, structured and systematic problem-solving methods aren’t commonly taught. Instead, when solving a problem, PMs tend to rely heavily on intuition. While for simple issues this might work well, solving a complex problem with a straightforward solution is often ineffective and can even create more problems.
In this article, you’ll learn a framework for approaching problem-solving, alongside how you can improve your problem-solving skills.
The 7 steps to problem-solving
When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication.
1. Define the problem
Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Without a well-defined problem statement, confusion and misunderstandings can hinder progress. It’s crucial to ensure that the problem statement is outcome-focused, specific, measurable whenever possible, and time-bound.
Additionally, aligning the problem definition with relevant stakeholders and decision-makers is essential to ensure efforts are directed towards addressing the actual problem rather than side issues.
2. Disaggregate
Complex issues often require deeper analysis. Instead of tackling the entire problem at once, the next step is to break it down into smaller, more manageable components.
Various types of logic trees (also known as issue trees or decision trees) can be used to break down the problem. At each stage where new branches are created, it’s important for them to be “MECE” – mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. This process of breaking down continues until manageable components are identified, allowing for individual examination.
The decomposition of the problem demands looking at the problem from various perspectives. That is why collaboration within a team often yields more valuable results, as diverse viewpoints lead to a richer pool of ideas and solutions.
3. Prioritize problem branches
The next step involves prioritization. Not all branches of the problem tree have the same impact, so it’s important to understand the significance of each and focus attention on the most impactful areas. Prioritizing helps streamline efforts and minimize the time required to solve the problem.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
4. Create an analysis plan
For prioritized components, you may need to conduct in-depth analysis. Before proceeding, a work plan is created for data gathering and analysis. If work is conducted within a team, having a plan provides guidance on what needs to be achieved, who is responsible for which tasks, and the timelines involved.
5. Conduct analysis
Data gathering and analysis are central to the problem-solving process. It’s a good practice to set time limits for this phase to prevent excessive time spent on perfecting details. You can employ heuristics and rule-of-thumb reasoning to improve efficiency and direct efforts towards the most impactful work.
6. Synthesis
After each individual branch component has been researched, the problem isn’t solved yet. The next step is synthesizing the data logically to address the initial question. The synthesis process and the logical relationship between the individual branch results depend on the logic tree used.
7. Communication
The last step is communicating the story and the solution of the problem to the stakeholders and decision-makers. Clear effective communication is necessary to build trust in the solution and facilitates understanding among all parties involved. It ensures that stakeholders grasp the intricacies of the problem and the proposed solution, leading to informed decision-making.
Exploring problem-solving in various contexts
While problem-solving has traditionally been associated with fields like engineering and science, today it has become a fundamental skill for individuals across all professions. In fact, problem-solving consistently ranks as one of the top skills required by employers.
Problem-solving techniques can be applied in diverse contexts:
- Individuals — What career path should I choose? Where should I live? These are examples of simple and common personal challenges that require effective problem-solving skills
- Organizations — Businesses also face many decisions that are not trivial to answer. Should we expand into new markets this year? How can we enhance the quality of our product development? Will our office accommodate the upcoming year’s growth in terms of capacity?
- Societal issues — The biggest world challenges are also complex problems that can be addressed with the same technique. How can we minimize the impact of climate change? How do we fight cancer?
Despite the variation in domains and contexts, the fundamental approach to solving these questions remains the same. It starts with gaining a clear understanding of the problem, followed by decomposition, conducting analysis of the decomposed branches, and synthesizing it into a result that answers the initial problem.
Real-world examples of problem-solving
Let’s now explore some examples where we can apply the problem solving framework.
Problem: In the production of electronic devices, you observe an increasing number of defects. How can you reduce the error rate and improve the quality?
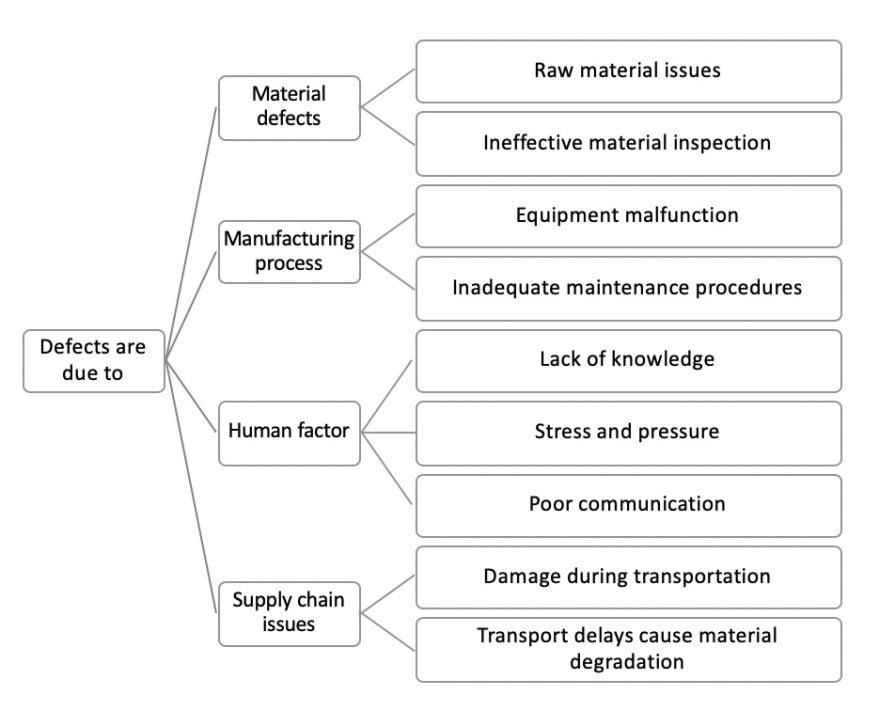
Before delving into analysis, you can deprioritize branches that you already have information for or ones you deem less important. For instance, while transportation delays may occur, the resulting material degradation is likely negligible. For other branches, additional research and data gathering may be necessary.
Once results are obtained, synthesis is crucial to address the core question: How can you decrease the defect rate?
While all factors listed may play a role, their significance varies. Your task is to prioritize effectively. Through data analysis, you may discover that altering the equipment would bring the most substantial positive outcome. However, executing a solution isn’t always straightforward. In prioritizing, you should consider both the potential impact and the level of effort needed for implementation.
By evaluating impact and effort, you can systematically prioritize areas for improvement, focusing on those with high impact and requiring minimal effort to address. This approach ensures efficient allocation of resources towards improvements that offer the greatest return on investment.
Problem : What should be my next job role?
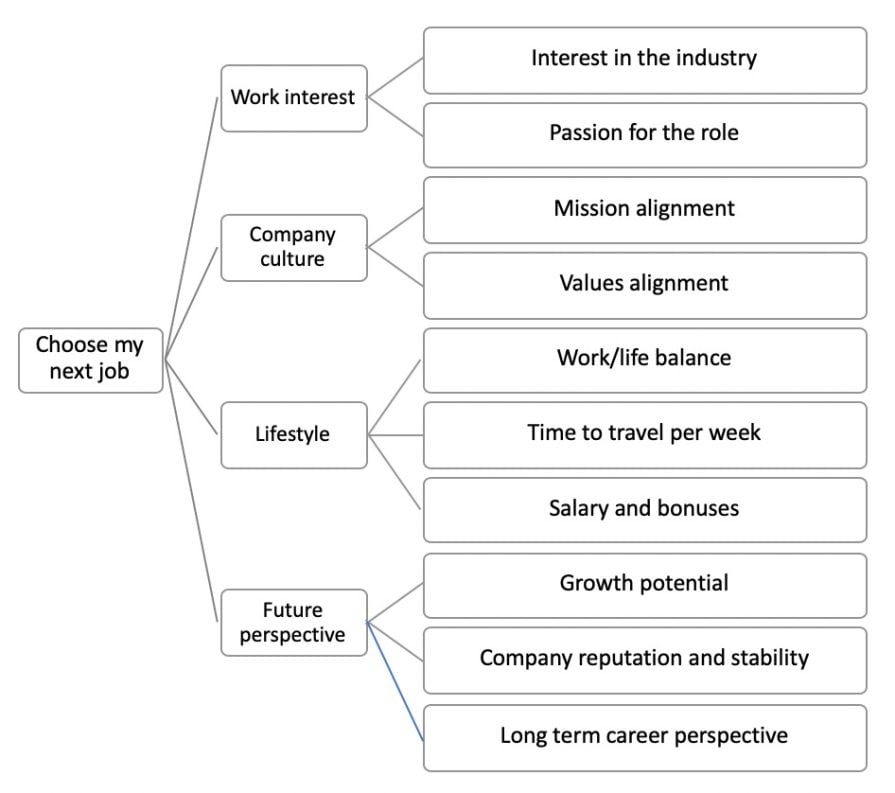
When breaking down this problem, you need to consider various factors that are important for your future happiness in the role. This includes aspects like the company culture, our interest in the work itself, and the lifestyle that you can afford with the role.
However, not all factors carry the same weight for us. To make sense of the results, we can assign a weight factor to each branch. For instance, passion for the job role may have a weight factor of 1, while interest in the industry may have a weight factor of 0.5, because that is less important for you.
By applying these weights to a specific role and summing the values, you can have an estimate of how suitable that role is for you. Moreover, you can compare two roles and make an informed decision based on these weighted indicators.
Key problem-solving skills
This framework provides the foundation and guidance needed to effectively solve problems. However, successfully applying this framework requires the following:
- Creativity — During the decomposition phase, it’s essential to approach the problem from various perspectives and think outside the box to generate innovative ideas for breaking down the problem tree
- Decision-making — Throughout the process, decisions must be made, even when full confidence is lacking. Employing rules of thumb to simplify analysis or selecting one tree cut over another requires decisiveness and comfort with choices made
- Analytical skills — Analytical and research skills are necessary for the phase following decomposition, involving data gathering and analysis on selected tree branches
- Teamwork — Collaboration and teamwork are crucial when working within a team setting. Solving problems effectively often requires collective effort and shared responsibility
- Communication — Clear and structured communication is essential to convey the problem solution to stakeholders and decision-makers and build trust
How to enhance your problem-solving skills
Problem-solving requires practice and a certain mindset. The more you practice, the easier it becomes. Here are some strategies to enhance your skills:
- Practice structured thinking in your daily life — Break down problems or questions into manageable parts. You don’t need to go through the entire problem-solving process and conduct detailed analysis. When conveying a message, simplify the conversation by breaking the message into smaller, more understandable segments
- Regularly challenging yourself with games and puzzles — Solving puzzles, riddles, or strategy games can boost your problem-solving skills and cognitive agility.
- Engage with individuals from diverse backgrounds and viewpoints — Conversing with people who offer different perspectives provides fresh insights and alternative solutions to problems. This boosts creativity and helps in approaching challenges from new angles
Final thoughts
Problem-solving extends far beyond mathematics or scientific fields; it’s a critical skill for making informed decisions in every area of life and work. The seven-step framework presented here provides a systematic approach to problem-solving, relevant across various domains.
Now, consider this: What’s one question currently on your mind? Grab a piece of paper and try to apply the problem-solving framework. You might uncover fresh insights you hadn’t considered before.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #career development
- #tools and resources

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Strategies for managing delays in development sprints
You can maintain productivity and meet your deadlines with careful planning, open communication, and a commitment to improvement.
Leader Spotlight: The relational component of product management, with Michael Park
Michael Park talks about how he worked to adapt BombBomb’s product strategy as the pandemic revolutionized remote work.
A guide to product advertising
Product advertising involves you marketing a product or set of products instead of marketing the brand itself.

Leader Spotlight: Creating a ‘choose your own adventure’ experience, with Peter Sucher
Peter talks about how he works to enable Girl Scouts to express themselves and engage their customer base at the level they desire.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving

The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Problem Solving Methodologies
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website www.learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

Beware of TIM WOODS: The Eight-Headed Monster in Your Business

8D Problem Solving: The Key to Effective Root Cause Analysis
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

Understanding Process Performance: Pp and Ppk
Understand Process Performance (Pp) and Process Performance Index (Ppk) to assess and improve manufacturing processes.…
LIFO or FIFO for Stock Management?
Choosing between LIFO and FIFO for stock management depends on factors like product nature, market…
Are There Any Official Standards for Six Sigma?
Are there any official standards for Six Sigma? While Six Sigma is a well-defined methodology…
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving, a guide to the 7-step mckinsey problem solving process.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
In this guide you'll learn:
Overview of the mckinsey approach to problem solving, problem solving process, problem definition.
- Problem Statement
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Structure the problem, hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, communicate, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, request the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem.
In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
Constraints can be a good thing (e.g., limit solutions to actions within the available budget.) And constraints can be a bad thing (e.g., eliminating the possibility of creative ideas.) So choose wisely.
The problem statement may ignore many issues to focus on the priority that should be addressed. The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution.
Example scenario – A family on Friday evening :
A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend.
The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
Potential problem definitions – A family on Friday evening :
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Given one set of facts, it is possible to come up with many possible problem statements. The choice of problem statement constrains the range of possible solutions.
Before starting to solve the problem, the family first needs to agree on what problem they want to solve.
- What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
- How can the family schedule their activities this weekend to accomplish everything planned given that they only have one vehicle available?
- How can the family increase income or reduce expenses to allow them to save $75K over the next 12 months to pay for the planned addition to their house?
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
Here are three different templates for a workplan:
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Once the recommendations have been crafted in the problem-solving process, it’s vital to effectively communicate those findings and recommendations.
An executive summary is a great slide to use for this. See more on executive summary slides, including 30 templates, at our Ultimate Guide to Executive Summary Slides .
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2024 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service

Wednesday, November 15, 2017
- The Seven Steps of Problem Solving

- Select the issue.
- Search for data to describe the situation.
- Analyze the facts to obtain root cause(s) of the performance gap.
- Select a solution.
- Conduct a pilot test.
- Evaluate performance.
- Standardize the gains, reflect, and repeat the process.
No comments:
Post a comment.
Search A Lean Journey
Twitter updates.
- Facebook Updates
- Advertising
Subscribe Now

Get new posts by email:
A Lean Journey LinkedIn Group
Recent comments, search this blog.
Top 10 Posts
- Celebrating my 500th Blog Post
- Visual Management Board
- Guest Post: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle...
- What Do We Mean By True North?
- The Six-Step Problem-Solving Process
- Five Lean Games Every Company Can Benefit From
- 10 Characteristics of a Good Measure and 7 Pitfalls to Avoid
- DOWNTIME and the Eight Wastes
- The 8 Common Wastes in an Office That Cause Downtime
- Lean Leadership: Lessons from Abe Lincoln
Blog Archive
- ► August (4)
- ► July (14)
- ► June (12)
- ► May (14)
- ► April (13)
- ► March (13)
- ► February (12)
- ► January (14)
- ► December (11)
- ► November (13)
- ► October (12)
- ► September (13)
- ► August (13)
- ► July (8)
- ► June (13)
- ► April (12)
- ► February (13)
- ► January (13)
- ► December (12)
- ► October (13)
- ► August (14)
- ► July (13)
- ► May (13)
- ► August (10)
- ► March (14)
- ► December (10)
- ► April (9)
- ► December (13)
- ► October (14)
- ► September (12)
- ► May (12)
- Lean Roundup #102 - November, 2017
- Lean Tips Edition #117 (1756-1770)
- Lean Quote: Gratitude is Something We Have to Prac...
- Happy Thanksgiving!
- Be Thankful This Thanksgiving
- Lean Quote: Developing Excellent Communication Ski...
- Guest Post: Empowering Others
- Lean Quote: Priorities and the Rule of Three
- Lean Administration: Time based Improvement Not Co...
- Guest Post: The Best Online Kanban Board Tools for...
- Lean Quote: Lean Goes Beyond Tools
- Lean Tips Edition #116 (1741 -1755)
- ► January (12)
- ► October (15)
- ► December (14)
- ► November (12)
- ► January (15)
- ► August (17)
- ► July (19)
- ► June (16)
- ► May (19)
- ► April (18)
- ► March (17)
- ► February (16)
- ► January (18)
- ► December (19)
- ► November (18)
- ► October (20)
- ► September (18)
- ► August (22)
- ► July (23)
- ► June (21)
- ► April (17)
- ► February (18)
- ► January (20)
- ► December (18)
- ► November (19)
- ► October (17)
- ► September (22)
- ► July (20)
- ► June (20)
- ► May (21)
- ► April (19)
- ► March (20)
- ► February (17)
- ► January (17)
- ► December (20)
- ► November (15)
- ► August (18)
- ► July (17)
- ► April (14)
- ► November (17)
- ► July (15)
- ► June (9)
- ► May (5)
- A Lean Journey (81)
- A Year Ago (8)
- ASQ's Influential Voices (40)
- Book Review (64)
- Change Management (53)
- Communication (13)
- Conference (10)
- Culture (38)
- Customer Focus (2)
- Daily Management (1)
- Development/Training (13)
- Empowerment (20)
- Engagement (37)
- Exercises/Games (8)
- Facilitation (2)
- Feedback (3)
- Guest Post (168)
- In the News (70)
- Innovation (2)
- kaizen (11)
- L.A.M.E. (5)
- Leadership (224)
- Lean and Green (12)
- Lean Basics (110)
- Lean Definition (25)
- Lean Fun (10)
- Lean in Practice (55)
- Lean Management (152)
- Lean Office (14)
- Lean Products (4)
- Lean Quote (735)
- Lean Resources (44)
- Lean Roundup (201)
- Lean Thinking (5)
- Lean Tips (237)
- Meet-up (34)
- Podcast (5)
- Problem Solving (21)
- Product Review (2)
- Project Management (6)
- Quality (50)
- Respect For People (57)
- Sharing Best Practices (129)
- Soft Skills (3)
- Strategy (6)
- Supply Chain (2)
- Talking Lean (1)
- Teamwork (42)
- Visual Factory (31)
- Webinar (23)
Lean Blogs I Like
- 2 Lean Principles
- 5S Supply Blog
- Avoiding The Corporate Death Spiral
- Be More Careful!
- Curious Cat
- Daily Kaizen
- Evolving Excellence
- Gemba Panta Rei
- Gemba Tales
- Got Boondoggle?
- Gotta Go Lean Blog
- Improve With Me
- Jamie Flinchbaugh
- Kaizen Notebook
- Lean Builder
- Lean Communications
- Lean For Everyone
- Lean Healthcare Exchange
- Lean Homebuilding
- Lean Insider
- Lean Is Good
- Lean Leadership
- Lean Pathways
- Lean Printing
- Lean Reflections
- Lean Simulations
- Lean Six Sigma Academy
- LeanCor Blog
- Learn Lean Manufacturing
- Learning About Lean
- Old Lean Dude Blog
- The A3 Post
- The Lean Edge
- The Lean Library
- The Lean Logistics Blog
- The Lean Thinker
- The Lean Way Consulting
- TimeBack Blog
- To The Gemba
- Training Within Industry
- Visual Management Blog
Other Sites I like
- AME's Target Magazine
- AnythingLean.com
- Art of Lean
- Bosch Rexroth Lean Production
- CIRAS - Theory of Constraints
- Chasing The Rabbit
- Corporate Event Management
- Creative Safety Supply
- Creative Safety Supply 5S Resource Page
- Fuss & O'Neill SPL
- Gemba Academy
- Grassroots Innovation
- IndustryWeek
- Lean Enterprise Institute
- Leanovations
- Learn More McGraw-Hill
- MEP University
- Manufacturers BlogNotions
- Manufacturing Business Technology
- Manufacturing Pulse
- Modern Machine Shop
- Running A Hospital
- Superfactory
- The 5S Store
- Unclutterer
- Visual Workplace
- Xtreme Lean Consulting
- catalyst for change
- freeleansite.com
wibiya widget
A lean journey blog - copyright © 2009-2024 tim mcmahon - all rights reserved.

- Tension & Compression
- Thermal Expansion
- Pressure Vessels
- Shear Centre
- Longitudinal Shear
- Welded Connections
- Weld Groups
- Unit Conversion
- Geometric Properties
- Soil Stress Distribution
- Shallow Foundations
- Soil Properties
- Material Properties
- Design Tables
- Mathematics First Aid
- Popular Articles
- Handy Calculators

The 7 Steps to Problem Solving
Effective problem solving, document.write("page last modified on: " + document.lastmodified +"");.
Problem solving with a standardized, disciplined and methodical approach is by far the best way of understanding root causes, exploring influences and implementing solutions that not only work, but also stay effective over time. The best solution to a problem is not always the most obvious and only after careful thought and assessment can the most suitable and feasible solution or solutions be implemented. The 7 step problem solving guide provided below has been created to help solve problems where the solution or in some cases the problem itself is not obvious.
STEP 1: The Right Problem to Solve STEP 2: Analyse the Problem STEP 3: Define the Problem STEP 4: Develop Opportunities (Possible Solutions) STEP 5: Select the Best Solution STEP 6: Implement the Solution STEP 7: Evaluate and Learn
When should problem solving be used?
Anytime you have a goal to achieve or simply experience a challenge, problem solving techniques can be adopted. The steps provided can be used on any problem no matter how small and simple, or large and complex with the only difference being the amount of overall time required to be spent on the problem at hand. Unfortunately effective problem solving does take some time and attention to detail but the rewards for the time taken may far outweigh the consequences for leaving problems in place.

STEP 1: The Right Problem to Solve
Identifying the right problem to solve can be by far the most crucial element in the process and it can’t be stressed enough that for this step to work to its full potential it is important to remember to focus on the problem and not just its symptoms or possible solutions, these parts will come shortly. If dealing with multiple problems the right problem is generally the one with the most important outcome, the greatest chance for solution and the nearest deadline. When trying to determine the right problem or if only intending to confirm one, ask yourself the following questions:
- Being as specific as possible what exactly is the problem to be solved?
- a clearly and concisely defined problem avoids confusion.
- A vaguely defined problem could be interpreted as something different.
- Can the problem be broken down further?
- A problem in its most simple form is in the best state for solving.
- Complex problems are possibly multiple smaller problems.
- Is the problem exactly the same from multiple perspectives? If not, can it be reworded so that it is?
- Problems can look different to different people.
- Solving for one person will not necessarily solve for everyone.
- Is there anyone who thinks it is not a problem? Why not?
- Any doubt is worth looking into, they could know something you don’t.
- It is always a possibility that you or your perceptions are the problem.
- Is the problem a symptom of a deeper, underlying condition?
- Fixing the problem will stop future symptoms.
- Fixing a symptom is only temporary.
- Is the problem one that can be solved? If no, can the problem be redefined?
- How to get to work with a broken leg is a problem that can be solved.
- A broken leg itself is not a problem because it can’t be solved, it's broken.
- Can the problem be defined as an opportunity?
- An opportunity is something positive we generally look forward to and want to take advantage of.
- A problem is generally something negative we don’t like and simply want to get rid of.
- Is the problem a beneficial one to solve? Why?
- The most beneficial problem is often a good place to start.
- The world is full of problems and unfortunately we can’t solve them all.
- Are you trying to solve a problem? Or are you confusing cause and effect?
- Building an airstrip so a plane has somewhere to land can be solving a problem.
- Building an airstrip because you know planes land on them does not guarantee a plane.
Once the above questions can be answered concisely you should be left with a well-defined problem which can also be described as an opportunity and more importantly you should have a better understanding of what you will be going to solve or achieve. It is time for the next step, analysing the problem.
STEP 2: Analyse the Problem
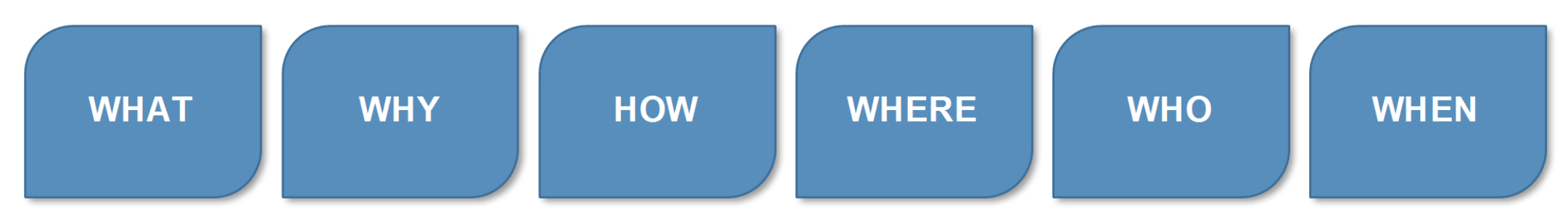
Analysing the problem starts with collecting as much information as possible relating to all aspects of the problem. This is where you find out what you already know about the situation and what areas need further looking into. To help discover all the facts it is a good idea to create a number of lists relating to the problem where you in turn list as many points as possible.
Remember that in this stage writing down anything and everything that comes to mind can be a good starting point; irrelevant items can be removed at the end. Some of the information you may find valuable may stem from the following questions. There are quite a few questions to consider, but hopefully they will guide you in the right direction. They are based on the "5 W's and 1 H".

- What does the problem currently affect?
- People or yourself?
- Environment?
- Organisation?
- What will be the benefits of solving the problem? And by how much?
- Credibility?
- Productivity?
- Reputation?
- What influences the problem?
- Does anything seem to aggravate or spread the problem?
- Does anything seem to reduce or delay the problem?
- Does anything tend to speed up / slow down the problem?
- Can the problem be simulated, recreated or acted out in another setting?
- Is there a specific example of an extreme case?
- What would be needed to solve the problem?
- Will new tools and/or policies be required?
- Will new equipment be required?
- Will new people be required?
- Could any new problems arise?
- What would happen if no solution can be found?
- Will a solution be available at a later date?
- What would be the next best thing to finding a complete solution?
- Is there a way to delay the problem?
- What would be the next best thing to solving the problem?
- Is there a chance the problem will go away on its own?
- Is there a way to change the problem for the better?

- Why do you want to achieve a solution?
- Is it something you personally want to do?
- Is it something you have been told to do?
- Is it something you feel you have to do?
- Why did the problem arise in the first place?
- Can the exact cause of the problem be pin pointed?
- Were there numerous reasons for the problem starting?
- Was a problem expected to occur at the time?
- Why was the problem allowed to escalate as far as it has?
- How much further can the problem escalate?
- Have previous attempts at solving the problem been made?
- Does the problem benefit anything/anyone else?

When you ask "How?" you are asking in what way or manner; by what means - "How does it work?" or used to ask about the condition or quality of something - How was your time there?"
- How long has the problem been around?
- Has it always been a problem?
- Has it got worse over time?
- Has the problem occurred at a previous time?
- How will the situation be different once the problem is solved?
- In particular what will be different?
- Can you guarantee the situation will be different?
- How relevant is the information available?
- Is the information up to date?
- Was the information created for the specific purpose it will be used for?
- Does the information need to be modified?
- How can I find out more information on the problem and possible solutions?
- Is all available information available?
- Is any information not available? Why not?
- Will additional research be required?
- Can additional people get involved with finding a solution?
- Is there an expert who can be approached?
- Are additional resources required?

- Where did the problem arise?
- Has the problem always existed?
- Can the exact starting point of the problem be pin pointed?
- Why did the problem arise where it did?
- Where is the problem currently located?
- Is the problem in a single or multiple locations?
- Can the problem be contained in its current location until it is dealt with?
- Is there a chance the problem will spread to different locations?
- Is the “where” component to the problem important? If so, why?

When you ask "Who?" you are asking what or which person or people are involved - "Who is that?" or "Who was there at the time?"
- Who are the stakeholders?
- Who is affected by this problem?
- Who will be affected once it is solved?
- Does anyone think that it is not a problem? What is different about their perspective?
- Who knows about the problem?
- Who has the information needed to solve or release the problem or issue?
- Who can do something or take action as a possible solution?
- Does anyone/s need to be informed about the problem?
- How do processes currently work where the problem is occurring?
- Who does what?
- With what information?
- Using what tools?
- Communicating with whom?
- In what time frame?
- Using what format?

When you ask "When?" you are asking at what time - "When did last witness it?" or at or on which time or circumstance - "Is early mornings when it happens most?"
- When did the problem first appear?
- What was its initial impact?
- How was it identified?
- Who identified it first?
- How did it start?
- Where did it start?
- Why did it start?
- What initially started it?
- When did it start?
- When does a solution need to be found?
- Would it be better to wait for a better time to implement a solution?
- Is too late to look for solutions?

Once every aspect of the problem has been looked into it is not uncommon for other potential problems to be identified as well. It may be necessary to start the entire process again for these new problems, but remember that problems are best dealt with one at a time and with that in mind it is time for the next step, defining the problem.
STEP 3: Define the Problem
Only after the right problem has been identified and analysed can one be sure of the correct definition of the problem. In most cases the definition will remain unchanged from STEP 1, but in some cases once other available information has been brought to light the problem, the opportunity or the desired outcome may have changed to accommodate either new information or a new perspective on the problem itself.
The following definitions should be written down for future reference. If there is any hesitation with any of the definitions it can be a sign that you don’t fully understand the problem at hand and that the previous step should be re-visited.
- Define exactly what the problem is.
- Define exactly what needs to be solved.
- Define your problem as an opportunity.
- Define the desired outcome.
STEP 4: Develop Opportunities (Possible Solutions)
There is always more than one way to solve a problem and in some cases simultaneous solutions may be required. As with the previous steps it is essential that time is taken to develop plenty of innovative and creative ideas. At the end of this step you can be certain you will have the best solution if you have explored all possible avenues and generated every conceivable option. To help you find the best solution the following methods can be used.
Seek advice; ask an expert In today’s day and age there is an expert on pretty much any topic you can imagine. Sometimes the best and fastest approach to getting the information we need can be simply to ask someone who knows more about the subject than we do. Of course finding that someone can be a challenge in itself, but the rewards in doing so could far outweigh other options. If the expert is unsure about the best approach for your situation they will probably be able to point you in the right direction.
Brainstorming Best done with a group of individuals brainstorming is always a good starting point. Brainstorming involves creating a list of ideas spontaneously contributed by an individual or group of individuals. With this method there is no wrong answer and wild or unexpected answers are often encouraged with all suggestions being written down. The process continues until no more suggestions can be thought of and the list of ideas can later be used to develop a solution.
The Scientific Method A method for conducting an objective investigation which is a proven approach to solving problems in a way that is reliable, consistent and non-arbitrary. The scientific method can be seen to underlay the scientific revolution and has helped to create many of the great accomplishments of recent human history. A basic flow chart of the scientific method is shown below.
Have a Guess If there is some indication, a technique you have heard of or a gut instinct about a possible solution, why not look into it further. Starting with an inkling and checking and adjusting it to suit the problem at hand could lead to the ideal solution. This method generally works better for a limited number of potential solutions where you can eliminate the options one at a time but there is no harm in employing the method in any case, it might just lead to the solution you have been looking for.
Work Backwards If the “where to start” is not obvious starting at the end goal and working backwards can be a good approach. Working backwards can sometimes offer the fastest solution because it gets you thinking with where you want to end up in mind. This approach to problem solving can also be effective when used at a point not quite at the end goal or even to back check the starting point from a different perspective.
Do the Opposite What effect does doing the opposite to what you have been doing have on the situation? If you at a dead-end or simply want to explore the opposite of something that clearly isn’t working, doing the opposite can provide a new and refreshing perspective. Rather than avoiding a situation, doing a complete 180 and diving straight in can in some cases be the best and/or fastest approach.
A Randomized Approach When all else fails or there is no indication what so ever to what sort of approach should be taken a random approach may be required. By applying random solutions and seeing how they influence the problem at hand may eventually lead to something more meaningful. You might get lucky and find the solution you have been looking for or worst possible case you may just find yourself where you started.
If after numerous attempts without success it might be necessary to go back to previous steps and try to "look outside the square". Every now and then a problem presents itself that will require a bit more creativity to come up with a feasible solution.
STEP 5: Select the Best Solution
With a list of possible solutions developed in the previous step it is time to select the best individual or best combination of solutions to be put into action and to eliminate the problem at hand. The process of selecting the best solution is a matter of ranking all of the available solutions against one another and defining each options “pluses and minuses”. Some of the key areas that might need to be evaluated and prioritised have been listed below.
- Operational validity: Can the solution actually be implemented or is it just an idea?
- Economic validity: Is the solution economical? Will the solution bring an economic result?
- Degree of Complexity: Is the solution simple to implement or are there complexities involved?
- Ease of Implementation: Is the solution ready to go and easy to install?
- Stakeholder interest: Does the solution satisfy everyone’s interests.
- Potential Risk: Does the solution bring any additional risk with it?
- Personal commitment: Is the solution something that reflects the ideals of all involved? Is the solution something you believe in?
- End result: Will the solution solve all parts of the problem or will the problem just be reduced or concealed?
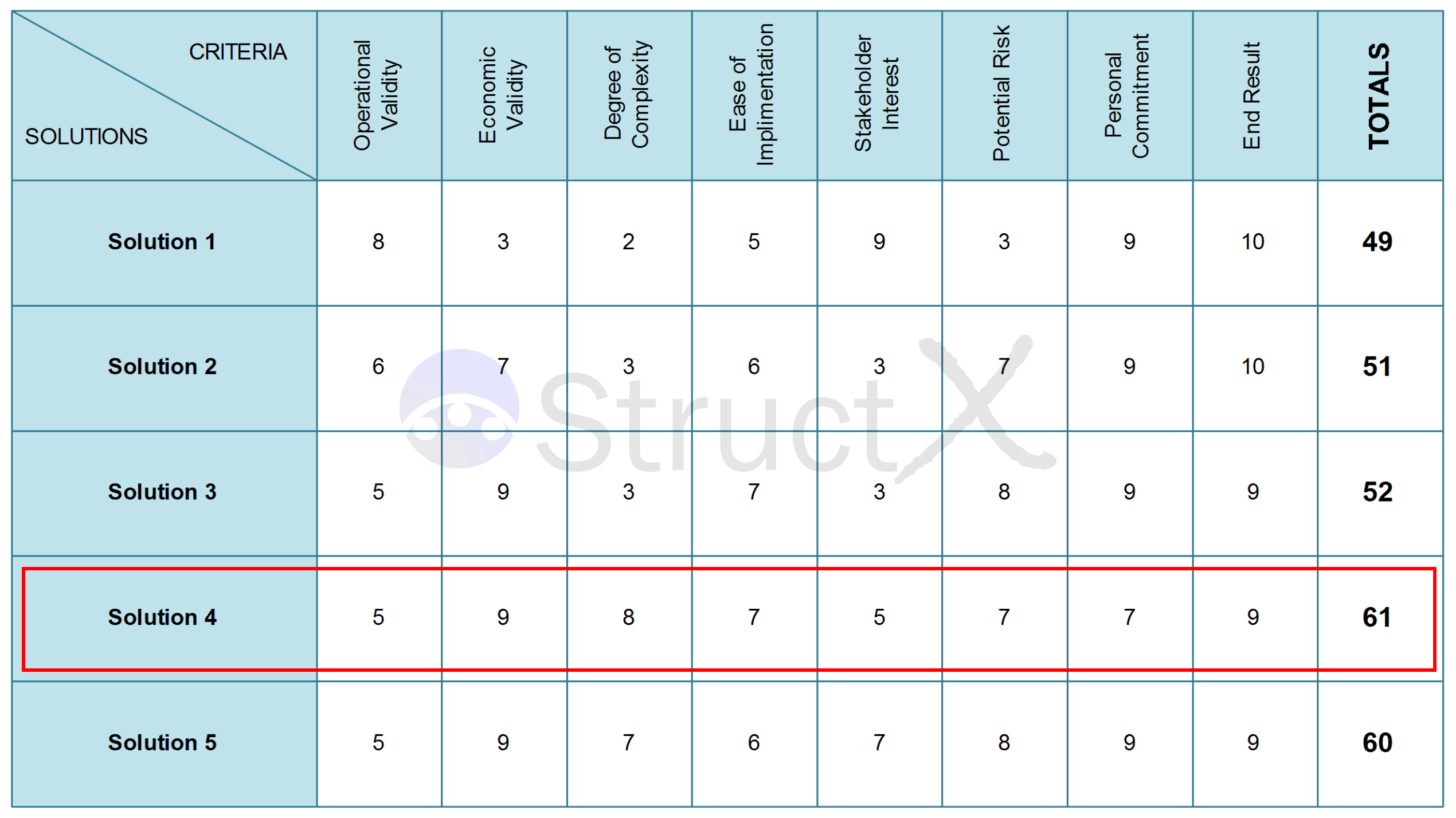
Keeping in mind that the best solution will be the result of considerable deliberation and also that one solution that is available for any problem is to simply do nothing, everything should now be in place for putting the solution into action. If something happens so that the chosen solution/s cannot be used or if the solution stops working, there will now be a list of alternatives already assessed, prioritised and ready to go.
STEP 6: Implement the Solution
The implementation plan is just as important as implementing the solution/s and monitoring the progress of this step is something that will need to be done also. A brief guide to some of the things that will need to be considered have been detailed below.
- Planning and documentation of a new solution/s
- When will the solution be implemented?
- Where will the solution be implemented?
- How is the solution to be implemented?
- What has to be done before the solution is implemented?
- How long will the solution take to start working?
- What time frame is the solution expected to take before the problem is solved?
- Have monitoring provisions been put in place?
- What are the key signs to look for to indicate the solution is working?
- Who will need to be notified about the changes about to take place?
- At what stages will the progress be reviewed?
- Have contingency arrangements been put in place for if the solution doesn’t work?
- What will be the next step if the solution doesn’t work?
- If required, have all agreements been documented and signed?
- How will it be confirmed that the problem has been solved?
- Are steps required to remove or disable the solution?
- What will happen once the problem has been solved?
- Putting the solution into action
- Put the solution into action
- Monitor the progress and effect of the solution
- Test and ensure the solution is meeting expectations and outcomes
STEP 7: Evaluate and Learn
Hopefully everything went to plan and the problem is now solved and even if it wasn’t, this step is still the same. It is vital that the whole process is evaluated from problem to solution and a good starting point is to document the 7 step procedure. This step is intended to not only provide a future reference but also a learning experience for future problem solving. At a very minimum the following questions should be answered:
- How effective was that particular solution?
- Did the solution achieve the desired outcomes?
- What consequences did problem solving activity have on my situation?
Top of Page
Problems at their most basic

Creating & Curating Early Learning Resources
Playvolution HQ
- Live Online Trainings
- Do It Yourself Ideas
- Early Learning Quotes
- Reading List
- Early Learning Glossary
- Caregiver Self-Care
- Development And Learning
- Play Sightings
- Play Space Critiques
- Roug-And-Tumble Play
- Play Advocacy
- Development
- Professional Practice
- Policy And Procedures
- School Readiness
- Observation
- Activity Reports
- Monthly Drills
- Health And Safety
- Professional Development
- Shop My Amazon Portal
- Memberships
- One Time Donation
- Contribute Content
- Other Ways To Support The Site
- Child Care Bar And Grill
- That Early Childhood Nerd
- Out Of Line
- Archived Show Episodes
- Operating Handbook Outline
- The 3 Handbook Method
- Operating Handbook
- Staff Handbook
- Parent Handbook
- Folk And Fairy Tales
- Rhymes And Songs
- Professional Practice And Advocacy
- Free Posters
- Join A Mailing List
- Types Of Schema Play
- Loose Parts That Support Schemas
- Schema Play Articles
- Loose Parts Ideas
- Loose Parts Articles
- Loose Parts Handouts
Join Our Mailing List
Like It? Share it!
The 7 Step Problem Solving Process
Revised | Originally Published: July 3, 2021 @ 4:24 pm

This handout looks at the 7 steps in the problem solving process. Problem solving is an essential skill that involves understanding a problem, devising a plan to solve it, implementing the solution, and evaluating the results. This structured approach can help you tackle problems systematically and arrive at effective solutions. Every problem is an opportunity to improve and learn, but problems are not always solved on the first attempt.
Download The 7 Step Problem Solving Process Handout
Download and share as you see fit:
Tips for Effective Problem Solving
Here are a few tips for effective problem solving:
- Stay Objective –Keep an open mind and avoid assumptions. Focus on facts and data.
- Communicate Clearly –Ensure that all stakeholders are informed and involved in the process.
- Think Creatively –Encourage innovative thinking and be open to unconventional solutions.
- Be Persistent –Problems may not always be solved on the first attempt. Be prepared to revisit and refine your approach.
Contribute content to Playvolution HQ Brought to you by Explorations Early Learning
Browse Trainings

Stay Updated
Receive regular play, professional development, and caregiver self-care updates.

Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.

Jeff Johnson
Jeff Johnson is an early learning trainer, podcaster, and author who founded Explorations Early Learning , Playvolution HQ , and Play Haven .

Support The Site
Shop My Amazon Link
I participate in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for me to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliate sites.
Thanks To Our Patrons
This post was made possible by patrons like these, who generously fund our work:
Lissadell Greene Stephanie Goloway
Lagina Kozak Michelle Hankins
Marie Messinger Tamara L. Lakin
Jen Flemming Lizz Nolasco
Susan Warner Kelly Sigalove
Vittoria Jimerson Codee Gilbert
Monica Morrell Pam Soloman Melissa Franklin
Teresa Watson Erika Felt
Melissa Taylor Jahmeela Robinson
Amber Maurina Terra Calamari Anne Jackson
Lagina Kozak Samantha Yeager-Cheevers
Elizebeth McCoy Sammy Cousens Ellen Cogan
Explore Membership Options

Join Play Haven
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

+44 (0)1335 347169
- Jul 12, 2023
The 7 step method for Practical Problem Solving skills & the 10 most common mistakes to avoid
Updated: Sep 13, 2023

Why do you need a Practical Problem Solving method?
Practical Problem Solving models are often shared online BUT the pitfalls are rarely well explained. In this blog we’ll be drawing on our own painful experience gained over 25 years, working across the world with hundreds of companies to illuminate those pitfalls. Here are the top 10 pitfalls as a list, scroll down for tips on how to avoid each.
Too big a problem
Looking in the wrong place
Brainstorming alone
Having a loose focus
Getting hung up on your fishbone
Switching between brain sides
Being rooted to the spot
Changing too much at once
Spending money too early
Not having a Plan to Check against
The Practical Problem Solving (PPS) model we learned and successfully applied from working with Toyota group, has 7 steps. We’ll show you each of those steps and the most common pitfall at each step.
We’ll even “open the kimono” and tell you about our personal biggest practical problem solving failure - more of that later. At the end we’ll share 3 secrets to help you to turbo charge your Practical Problem Solving
The initial question, as ever, has to be “Why do we need a method for Problem Solving?”
There are three main reasons
1) Containment
We’re generally okay at containment when a problem happens, at mopping up
2) Short-term countermeasure
We're not bad at coming up with a short-term countermeasure (solution) but
3) Recurrence Prevention
Most manufacturers aren't particularly strong on recurrence prevention - they don't get to the root cause
A common problem is people jumping to conclusions based on previous experiences, leading to the wrong conclusions because something is different to last time.
A Practical Problem Solving method
So, here's the Practical Problem Solving method, showing the 7 steps.

You can see that it's a funnel shape reflecting the fact that we're going from a large area, vaguely grasped and explained, down to a really focused problem that we've solved.
The 7 steps to our Practical Problem Solving method
The seven steps are:
1) “Grasp the current condition”
Understand what's going on and find your tight focus point
2) “Locate process causing the problem”
That's the process where it's caused not where it's found in in your physical process
3) “Investigate”
Using two tools often here, and for the next couple of steps - 5 why and fishbone
4) “Identify the probable causes”
Where we narrow down from our fishbone into what we think are the most likely causes – one, two or three of them and have a look at each in depth
5) “Identify the root cause”
What we as a team believe, through go-look-see observation and experimentation, is the root cause
6) “Countermeasure”
Try solutions, one at a time
7) “Confirm”
Using our PDCA cycle to make sure that we've got rid of the problem
Note the two things on the right of the funnel to look at. Firstly, it’s very important to protect the customer early and stop bad material or other problems flowing out to them. Secondly, you’ll see halfway down, after you've done a bit of investigation that you're ready to set a target: A “What?” by “How much?” by “When?”
A Problem Solving example: Fizzy drink canning factory
At Sempai we use a fizzy drink canning factory example as a Problem Solving example, along with our training materials, to help our clients start-to-finish through this process on their own shopfloor. Get in touch if you’d like us to help you this way. I’ll reference the fizzy drink can below.

10 Pitfalls in the 7 step Practical Problem Solving method
Let’s go back to the funnel model to look at the Problem Solving pitfalls
Step 1) - “Grasp the current condition” - Pitfall
The key pitfall here is NOT having a tight focus, having too broad a problem to try to solve. This is where our fizzy drink cans come in. On the picture below, having done some Data Analysis and using 80/20 thinking , if we just go after ‘dents’ our focus is too broad as there are actually 3 types of dents - 30 of one type, 8 of a second and 4 of a third. We’d pick the defect with 30 instances as it’s the highest (occasionally there are defects that have a lower frequency but cost more per defect).

Problem Solving is hard enough to do without trying to mix up and unpick a heap of variables affecting 3 different problems. If you try and do them all at once, you won't manage it. Picking 1 of the 3 to solve is good “Problem Framing”.
Step 2) - “Locate process causing the problem” - Pitfall
Critically, here you're not looking for the process where you FOUND the problem. It's where you identify that it's being CREATED. There's a very big difference between treating a symptom and a cause. Be careful that you’re not looking in the wrong spot.
Step 3) - “Investigate” - Pitfalls
This is often the area of biggest weakness, apart from Problem Framing in Step 1 above. When it comes to problem solving there are two major tools - Fishbone (aka Ishikawa diagram) and the 5 Whys. There are others, these are just the most common and useful.
The Fishbone and 5 Whys can be used together or they can be used independently. You don't always have to use both, but I'll come back to that later.
The first pitfall, in the Investigate step, is to brainstorm alone if you use a fishbone. Doing this, you only get one narrow set of ideas and experience. Involving other functions, like Maintenance for breakdowns, or Quality engineers for defects brings in other experts. Never, ever, forget to include the most important expert of all – your Operator. They know the process better than anyone as they live with it for 40 hours a week.
The second pitfall on this step is to remember is that you need a tight scope, a very tight problem well described. Not “dents” but a type of “dent” on a certain flavour of fizzy drink (if it’s made down a different line to the others!)
Step 4) - “Identify the probable causes” - Pitfalls
If you’ve used a Fishbone, you’ll then have maybe 20-40 post-it notes with possible causes on. You now go back over all of your post-it notes to identify the most probable causes. Don't get hung up trying to work out, scientifically, which are the right ones to pursue. Just agree as a team and pick the top two or three you believe. Then pursue them one at a time.
Also, don't try to critique AS YOU brainstorm as switching from one side of your brain (creative) to the other (analytical) gets the worst of both worlds. It’s mentally jarring and ideas won’t flow. Finish the brainstorm first, then critique the ideas respectfully.
Step 5) - “Identify the root cause” - Pitfall
Here you take your “probable causes” one a time and pursue the 5 whys – checking at each why stage whether what you’re suggesting is true. The pitfall here is simply staying in a training room or being rooted to the spot in the factory where you’re doing the Problem Solving. You can’t do either Step 4 or 5 in a training room or without looking at the process close up. Go-look-see and confirm on the shop floor.
Step 6) - “Countermeasure” - Pitfall
It’s really important to countermeasure (put a fix in place) for one thing at a time, otherwise you don't know which change got you the result - it's just a mix of variables. Don’t spend money too early, try solutions with old or scrapped materials, capital is scarce, thinking is free.
Step 7) - “Confirm” - Pitfall
Confirm is where we use our Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) cycle to see if our countermeasure has worked. To know if it has, you need something to compare against. So, at Plan stage, quantify the result you expect. For example, say after Step 4 “Investigate” that you have enough information to set a target. If you set that target at “20% reduction in dents in orange cans vertically across the bottom rim” and you only achieve 5% after countermeasure, you know that you’ve missed something.
Knowing when your Practical Problem Solving has worked!
There are two ways to check whether your countermeasures work:
You can recreate the problem at will
If you can turn it on and off you’ve sorted it
Data Analysis
When you do your daily or weekly Data Analysis, this specific problem doesn't occur again or is greatly reduced.
3 secrets to turbocharge your practical problem solving
We promised earlier to tell you about our biggest ever failure. That was 20 years ago when being trained by a Japanese sensei. We locked a team, for two days, in a room with a vaguely defined problem and created the world's biggest fishbone.
A fishbone that we guessed and speculated about and didn't go to the shop floor enough, to grasp and confirm. That combination of a bad focus and too many guesses meant it was a waste of time.
As promised, here’s a bonus of 3 secrets to turbocharge your practical problem solving:
Secret 1: Speed
If you can get to a problem fast it's like a fresh crime scene for a detective. It's warm, there's a body, there's a smoking gun and blood on the floor. It's easy to crack. If you get there late it's like a cold case
Secret 2: You don't always need a Fishbone
Some people love a fishbone but, to a man with a hammer, everything looks like a nail. We only use it in certain circumstances; like if we can't recreate a defect or it looks as though there are multiple variables involved, or if there's a benefit to getting a team around it.
Secret 3: Avoid problems altogether!
This is the closest we’ll get to a silver bullet. Train your people to be able to spot abnormality early, get your shop floor organised through your 5s and standardised work, so that you can react when things start to go wrong, rather than when there's a problem.
Number 3) is so powerful we've built a module dedicated to avoiding problems in SempaiGuide, our digital lean toolkit for manufacturers. Check out the demo here .
That’s the major pitfalls covered. One last piece of advice is to follow the steps, use data and verify on the gemba at every stage. Otherwise, you’re just guessing. To accompany this article, we’ve created this video on our YouTube channel
- Problem Solving
- Lean Skills
Recent Posts
How to find Abnormalities and not Problems in a lean factory
How to hone your Problem Solving Method through watching movies
80/20 Pareto rule in manufacturing – A key skill for Team Leaders
7 Steps to an Effective Problem-Solving Process
September 1, 2016 | Leadership Articles

An effective problem-solving process is one of the key attributes that separate great leaders from average ones.
Being a successful leader doesn’t mean that you don’t have any problems. Rather, it means that you know how to solve problems effectively as they arise. If you never had to deal with any problems, chances are pretty high that your company doesn’t really need you. They could hire an entry-level person to do your job!
Unfortunately, there are many examples of leaders out there who have been promoted to management or leadership positions because they are competent and excel in the technical skills needed to do the work. These people find themselves suddenly needing to “think on their feet” and solve problems that are far more high-level and complicated than they’ve ever really had to deal with before. Are there tools available to these people to help them solve the problem correctly and effectively? Absolutely!
Today, I am going to introduce you to the Seven Steps of Effective Problem Solving that Bullet Proof® Managers are learning about, developing, and implementing in their teams.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
What are things like when they are the way we want them to be?
This question helps you find the standard against which we’re going to measure where we are now. If things were going the way we want them to go, what does that look like? If this person were doing the job we want him or her to do, what would they be doing?
And then ask this important question: How much variation from the norm is tolerable?
Therein lies the problem. From an engineering perspective, you might have very little tolerance. From a behavioral perspective, you might have more tolerance. You might say it’s okay with me when this person doesn’t do it exactly as I say because I’m okay with them taking some liberty with this. Some other issue you may need 100% compliance.
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
At what stage is this problem? This helps you identify the urgency of the problem, and there are generally three stages.
The emergent stage is where the problem is just beginning to happen. It does not cause an immediate threat to the way business operates every day. It is just beginning to happen and you have time on your side to be able to correct it without it causing much damage to the processes it is affecting. The mature stage is where this problem is causing more than just minor damage. Some amount of damage has been done, and you need to jump on it immediately to fix it before it becomes a problem where the consequences may be greater, deeper, and more expensive if we don’t solve this problem fast.
The third stage is the crisis stage, when the problem is so serious it must be corrected immediately. At this stage, real damage has been done to company processes, reputation, finances, etc. that will have potentially long-term effects on your ability to do business.
Step 3: Describe the Problem
You should be able to describe a problem by writing it in the form of a statement and you should do it in 12 words or less, assuming it’s not a complicated, scientific problem. This way, you have clarity exactly what the issue is. Then, perhaps try distributing it to your team to ensure they agree that this is the root of the problem, that it makes sense, and everyone that is working toward a solution is working toward the same goal.
The most important question of all, when describing your problem: Is your premise correct?
Let me give you an example of what I mean. We’ve all heard – or read – the story of the engineer’s take on the old “half empty, half full” question. A speaker holds up the glass of water and asks if the glass is half empty or half full, a discussion within the group ensues, and you generally expect some sort of lesson in optimism, etc. from it. In this version, an engineer is in the room and answers, “I see this glass of water as being twice the size it needs to be.”
You see, sometimes when you are the one in charge of the problem, you tend to set the premise of the problem from your own perspective. But, that premise may not be accurate, or it may just need an alternate perspective from which to see it. If your premise is not correct, or at least incomplete, you are not fully understanding the problem and considering all the best options for a solution.
Step 4: Look for Root Causes
This step involves asking and answering a lot of questions. Ask questions like: What caused this problem? Who is responsible for this problem? When did this problem first emerge? Why did this happen? How did this variance from the standard come to be? Where does it hurt us the most? How do we go about resolving this problem?
Also, ask the most important question: Can we solve this problem for good so it will never occur again? Because an important aspect to leadership is coming up with solutions that people can use for a long-term benefit, rather than having to deal with the same problems over and over and over.
Step 5: Develop Alternate Solutions
Just about any problem you have to deal with has more solutions to it than the one that you think of first. So, it is best to develop a list of alternate solutions that you and your team can assess and decide which one will be the best for the particular problem. I often use the ⅓ + 1 Rule to create consensus around one – or the top two or three solutions – that will be best for everyone involved.
Then rank those solutions based on efficiency, cost, long-term value, what resources you have and that you can commit to the solution of the problem. Then, look at every one of those solutions carefully and decide what you believe to be the best solution to this problem at this time.
Step 6: Implement the Solution
Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn’t work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part in making the solution work, that there are timelines for execution, and also that you have a system in place to track whether or not the solution has corrected the problem.
Step 7: Measure the Results
From your implementation plan in step 6, make sure you track and measure the results so you can answer questions such as: Did it work? Was this a good solution? Did we learn something here in the implementation that we could apply to other potential problems?
These seven simple steps will help you become a more effective, efficient problem solver in your organization. As you practice this process and develop the skills, these steps will become more natural to you until the point that you are using them without noticing!
About Crestcom International, LLC.
Crestcom International, LLC is an international leadership development organization, training more than one million leaders for 25,000 businesses in over 60 countries across the globe. Crestcom achieves this through a blend of live-facilitated multimedia video, interactive exercises, and shared learning experiences. Crestcom implements action plans and coaching accountability sessions to ensure measured development in key leadership competency areas. For more information, please contact your local Crestcom representative found here .
Interested in a free Leadership Skills Workshop with your team?
- Address instantly fixable issues that impact customer perceptions and employee morale.
- Learn and practice a habit that will raise employee performance.
- Set actions with specific and measurable steps that they'll gladly be accountable to achieve.
- Case Studies
- Leadership Articles
- Multi-Generational Leadership
- Owning a franchise
- Press Releases
Latest Posts

Stay Updated
Browse by topic.
[st-tag-cloud]
Privacy Overview

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

7 Steps To Problem-Solving
The 7 steps to problem-solving is a disciplined and methodical approach to identifying and then addressing the root cause of problems. Instead, a more robust approach involves working through a problem using the hypothesis-driven framework of the scientific method. Each viable hypothesis is tested using a range of specific diagnostics and then recommendations are made.
| – is a systematic approach to addressing complex challenges and making informed decisions. It provides a structured framework for , , and problems in various contexts, including , , , and everyday life. | |
| – The primary purpose of the 7 Steps is to in a logical and organized manner, increasing the likelihood of finding . It helps individuals and teams tackle problems , making the process more efficient and reducing the risk of overlooking critical factors. | |
| – : Begin by the problem or challenge. Understand its , its impact on stakeholders, and the . – : and relevant information to and causes. Use various sources and to obtain insights. – : Explore potential solutions and . Encourage and to produce a wide range of options. – : Evaluate the pros and cons of each solution. Consider factors such as feasibility, cost, impact, and potential risks. – : Choose the solution that aligns best with your problem definition and analysis. solutions based on their potential to address the problem effectively. – : Develop an for implementing the chosen solution. Assign responsibilities, allocate resources, and establish a timeline. – : After implementation, assess the results. against predefined criteria and make adjustments if necessary. Document the lessons learned for future reference. | |
| – While the 7 Steps provide a structured approach, they are not strictly linear. and can be incorporated, allowing for at any stage based on new insights or changing circumstances. The framework is adaptable to various problem types and complexities. | |
| – The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving can be applied to a wide range of challenges, including , , , , and . Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in both professional and personal contexts. | |
| – Challenges in problem-solving may include that affect decision-making, , and about outcomes. Being aware of these challenges and applying critical thinking skills can help avoid pitfalls and improve the quality of problem-solving efforts. | |
| – Effective problem-solving often involves and with others. , such as , , and , play a crucial role in the success of the 7 Steps, especially when problems involve multiple stakeholders. | |
| – Documenting each step of the problem-solving process is valuable for and . It allows organizations and individuals to learn from past experiences and apply insights to future challenges. | |
| – The integration of and can enhance problem-solving by providing and of certain tasks. These tools can assist in , , and , improving the efficiency of the 7 Steps. | |
| – Considerations related to , , and should be part of the problem-solving process. ensures that solutions align with values, respect diverse perspectives, and consider the broader impact on society and stakeholders. |
Table of Contents
Understanding the 7 steps to problem-solving
The core argument of this approach is that the most obvious solutions to a problem are often not the best solutions.
Good problem-solving in business is a skill that must be learned. Businesses that are adept at problem-solving take responsibility for their own decisions and have courage and confidence in their convictions. Ultimately, this removes doubt which can impede the growth of businesses and indeed employees alike.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving
Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically.
Step 1 – Define the problem
First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified. Actions and behaviors of individuals must be the focus – instead of a focus on the individuals themselves. Whatever the case, the problem must be clearly defined and be universally accepted by all relevant parties.
Step 2 – Disaggregate the problem
In the second step, break down the problem (challenge) into smaller parts using logic trees and develop an early hypothesis. Here, economic and scientific principles can be useful in brainstorming potential solutions. Avoid cognitive biases, such as deciding that a previous solution should be used again because it worked last time.
Step 3 – Prioritize issues
Which constituent parts could be key driving factors of the problem? Prioritize each according to those which have the biggest impact on the problem. Eliminate parts that have negligible impact. This step helps businesses use their resources wisely.
Step 4 – Plan the analyses
Before testing each hypothesis, develop a work and process plan for each. Staff should be assigned to analytical tasks with unique output and completion dates. Hypothesis testing should also be reviewed at regular intervals to measure viability and adjust strategies accordingly.
Step 5 – Conduct the analyses
In step five, gather the critical data required to accept or reject each hypothesis. Data analysis methods will vary according to the nature of the project, but each business must understand the reasons for implementing specific methods. In question-based problem solving, the Five Whys or Fishbone method may be used. More complicated problems may require the use of statistical analysis . In any case, this is often the longest and most complex step of the process.
Step 6 – Synthesise the results
Once the results have been determined, they must be synthesized in such a way that they can be tested for validity and logic. In a business context, assess the implications of the findings for a business moving forward. Does it solve the problem?
Step 7 – Communicate
In the final step, the business must present the solutions in such a way that they link back to the original problem statement. When presenting to clients, this is vital. It shows that the business understands the problem and has a solution supported by facts or hard data. Above all, the data should be woven into a convincing story that ends with recommendations for future action.
Key takeaways
- 7 steps to problem-solving is a methodical approach to problem-solving based on the scientific method.
- Although a somewhat rigorous approach, the strategy can be learned by any business willing to devote the time and resources.
- Fundamentally, the 7 steps to problem-solving method involves formulating and then testing hypotheses. Through the process of elimination, a business can narrow its focus to the likely root cause of a problem.
Key Highlights
- Definition : The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a structured methodology rooted in the scientific method. It emphasizes systematic hypothesis testing and data analysis to identify and address the root cause of problems, avoiding surface-level solutions.
- Problem-Solving Skill : Effective problem-solving is a learned skill that fosters responsible decision-making, boosts confidence, and supports business growth .
- Define the Problem : Clearly outline the problem’s scope and impact, focusing on actions and behaviors rather than individuals.
- Disaggregate the Problem : Break down the problem into smaller parts using logic trees and form early hypotheses. Avoid biases from past solutions.
- Prioritize Issues : Identify key driving factors of the problem and prioritize them by impact. Eliminate parts with minimal impact to allocate resources efficiently.
- Plan the Analyses : Develop work and process plans for hypothesis testing, assigning staff and setting completion dates. Regularly review and adjust strategies.
- Conduct the Analyses : Gather critical data to accept or reject hypotheses. Use methods like Five Whys, Fishbone diagrams, or statistical analysis .
- Synthesize the Results : Combine and analyze results to determine their validity and implications for the business . Assess if the problem is solved.
- Communicate : Present solutions that link back to the original problem statement, supported by facts. Create a compelling story ending with recommendations.
- The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is based on the scientific method.
- It requires a structured approach to formulating and testing hypotheses.
- Businesses willing to invest time and resources can learn and apply this method effectively.
| Related Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| The is a systematic approach used to address complex issues, make informed decisions, and find effective solutions to problems. These steps typically include: 1. : Clearly define the issue or challenge that needs to be resolved. 2. : Collect relevant data, facts, and insights to understand the problem’s underlying causes and implications. 3. : Brainstorm potential solutions or approaches to address the problem, considering various perspectives and creative alternatives. 4. : Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each solution based on feasibility, effectiveness, and alignment with goals and constraints. 5. : Choose the most promising solution or combination of solutions that best address the problem and achieve the desired outcomes. 6. : Develop a plan of action and execute the chosen solution, allocating resources, assigning responsibilities, and monitoring progress. 7. : Assess the effectiveness of the implemented solution by measuring outcomes, gathering feedback, and identifying lessons learned for future problem-solving endeavors. provide a structured framework for systematic thinking, collaboration, and decision-making, facilitating the resolution of complex problems and the achievement of desired objectives. | – When faced with complex challenges, issues, or decisions that require a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making. | |
| encompass a variety of approaches and techniques used to analyze problems, devise solutions, and overcome obstacles effectively. These strategies may include: 1. : Break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable tasks or components to facilitate analysis and problem-solving. 2. : Generate ideas, solutions, and alternatives through open-ended discussion, creativity, and collaboration with others. 3. : Identify the underlying causes or contributing factors of a problem to address its fundamental source rather than just treating symptoms. 4. : Construct visual diagrams or flowcharts to map out decision-making processes, options, and potential outcomes to guide informed choices. 5. : Experiment with different approaches, solutions, or strategies through iterative testing and learning from failures to refine problem-solving efforts. 6. : Apply logical reasoning, analysis, and evaluation skills to assess information, identify patterns, and draw well-founded conclusions to solve problems effectively. 7. : Engage with diverse perspectives, expertise, and stakeholders to leverage collective knowledge, insights, and resources in addressing complex problems collaboratively. enable individuals and teams to approach problems systematically, creatively, and efficiently, leading to innovative solutions and improved decision-making outcomes. | – When encountering challenges, obstacles, or issues that require analytical thinking, creativity, and strategic problem-solving to develop effective solutions and achieve desired outcomes. | |
| The is a systematic approach used to evaluate options, make choices, and take action in various personal, professional, and organizational contexts. It typically involves the following steps: 1. : Clarify the decision to be made and its significance in achieving objectives or addressing concerns. 2. : Collect relevant data, facts, and insights to understand the decision context, alternatives, and potential consequences. 3. : Assess the strengths, weaknesses, risks, and implications of available options or courses of action using criteria and decision-making tools. 4. : Evaluate the information and analysis to make a choice or commitment based on informed judgment, intuition, or consensus among decision-makers. 5. : Develop a plan of action and execute the chosen decision, allocating resources, setting timelines, and monitoring progress towards desired outcomes. 6. : Review the decision’s outcomes, impacts, and effectiveness, gathering feedback, and adjusting course if needed to improve future decision-making processes. The provides a structured framework for thoughtful analysis, evaluation, and action to make sound decisions and achieve desired objectives effectively. | – When confronted with choices, dilemmas, or opportunities that require careful consideration, analysis, and evaluation to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions. | |
| is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying causes or factors contributing to a problem or issue, rather than just addressing its symptoms. It involves the following steps: 1. : Clearly articulate the problem or issue that needs to be investigated and resolved. 2. : Gather relevant information, data, and evidence to understand the problem’s context, history, and impacts. 3. : Brainstorm and list possible causes or factors that may contribute to the problem’s occurrence or persistence. 4. : Analyze and prioritize the potential causes based on their likelihood, impact, and relevance to the problem at hand. 5. : Investigate each potential cause in depth, using techniques such as interviews, observations, or data analysis to determine its validity and significance. 6. : Determine the primary or underlying cause(s) that directly lead to the problem’s occurrence or recurrence, considering systemic, human, and organizational factors. 7. : Generate corrective actions or interventions to address the root cause(s) and prevent the problem from reoccurring in the future. helps organizations and individuals address problems systematically, improve processes, and enhance performance by addressing underlying issues rather than treating symptoms. | – When encountering recurring problems, issues, or failures that require deeper investigation and understanding to identify their underlying causes and develop effective solutions. | |
| is a holistic approach to problem-solving and decision-making that considers the interrelationships, dynamics, and feedback loops within complex systems. It involves the following principles: 1. : Recognize and explore the connections and interactions among components, elements, or variables within a system. 2. : Analyze the feedback mechanisms and loops that influence system behavior and outcomes over time. 3. : Evaluate the dynamic behavior, patterns, and emergent properties that arise from interactions within the system. 4. : Define the boundaries and scope of the system under study, including its inputs, outputs, and external influences. 5. : Identify key leverage points or intervention opportunities within the system where small changes can lead to significant impacts or outcomes. 6. : Foster a systemic mindset and awareness among stakeholders to recognize the interconnectedness of issues, anticipate unintended consequences, and collaborate effectively in addressing complex challenges. enables individuals and organizations to understand complex systems, anticipate their behavior, and leverage leverage points for effective problem-solving and decision-making. | – When dealing with complex, interconnected problems or challenges that involve multiple stakeholders, variables, and feedback loops, requiring a holistic understanding and approach to address effectively. | |
| is a cognitive process of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to form reasoned judgments, make informed decisions, and solve problems effectively. It involves the following components: 1. : Challenge assumptions, biases, and preconceptions to gain a deeper understanding of issues and perspectives. 2. : Collect relevant evidence, data, and arguments to support logical reasoning and informed decision-making. 3. : Evaluate diverse viewpoints, opinions, and interpretations to gain insights and consider alternative solutions. 4. : Identify patterns, trends, and connections within information or data to discern underlying relationships and implications. 5. : Make reasoned inferences and draw logical conclusions based on available evidence, analysis, and critical thinking. 6. : Reflect on personal biases, assumptions, and cognitive limitations that may influence thinking and decision-making processes. skills are essential for analyzing complex issues, evaluating evidence, and making informed decisions in various personal, academic, and professional contexts. | – When facing complex problems, ambiguous situations, or conflicting information that require rigorous analysis, logical reasoning, and informed judgment to arrive at well-founded conclusions and effective solutions. | |
| is an approach that emphasizes generating innovative solutions to challenges by thinking outside the box, exploring unconventional ideas, and embracing experimentation. It involves the following elements: 1. : Clearly articulate the problem or opportunity that requires creative solutions and identify desired outcomes. 2. : Encourage brainstorming and creative thinking techniques to generate a wide range of ideas, alternatives, and possibilities. 3. : Evaluate and explore unconventional or unexpected solutions that may diverge from traditional approaches or assumptions. 4. : Test and refine potential solutions through experimentation, prototyping, or pilot projects to assess feasibility and effectiveness. 5. : Embrace failure as part of the creative process and iterate on ideas based on feedback, insights, and lessons learned. 6. : Collaborate with diverse stakeholders, perspectives, and disciplines to stimulate creativity, innovation, and synergy in problem-solving efforts. fosters a culture of innovation, experimentation, and continuous improvement, enabling individuals and teams to address complex challenges with fresh perspectives and imaginative solutions. | – When seeking to break through conventional thinking, explore new possibilities, and develop innovative solutions to complex problems or opportunities that require creativity, imagination, and out-of-the-box thinking. | |
| is an approach derived from Lean principles and methodologies, focusing on identifying and eliminating waste, inefficiencies, and non-value-added activities in processes or systems. It involves the following principles: 1. : Identify the value desired by customers or stakeholders and prioritize efforts to deliver value-added outcomes. 2. : Visualize and map out the current state of processes or workflows to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement. 3. : Analyze problems systematically to identify underlying causes and factors contributing to inefficiencies or defects. 4. : Develop and implement targeted solutions or countermeasures to address root causes and streamline processes. 5. : Establish standardized work practices, procedures, or guidelines to sustain improvements and prevent recurrence of problems. 6. : Foster a culture of continuous learning, experimentation, and adaptation to drive ongoing improvements and optimize performance over time. emphasizes efficiency, effectiveness, and customer value, enabling organizations to enhance productivity, quality, and competitiveness in their operations. | – When aiming to improve operational performance, streamline processes, and eliminate waste or inefficiencies in workflows or systems by applying Lean principles and problem-solving methodologies to identify and address root causes effectively. | |
| is a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping to develop solutions that meet users’ needs and preferences. It involves the following stages: 1. : Understand users’ needs, motivations, and pain points through observation, interviews, and immersion in their experiences. 2. : Define the problem or opportunity based on insights gathered from empathizing with users and identifying their challenges or aspirations. 3. : Generate a wide range of creative ideas, concepts, and solutions to address the defined problem or opportunity, leveraging divergent thinking techniques. 4. : Develop rapid prototypes or representations of potential solutions to test and refine ideas, gathering feedback from users and stakeholders. 5. : Evaluate prototypes with users to validate assumptions, gather insights, and iteratively refine solutions based on feedback and observations. 6. : Implement and scale solutions that have been iteratively developed and validated through the design thinking process, ensuring they address users’ needs effectively. fosters innovation, collaboration, and user-centricity, enabling organizations to develop products, services, and experiences that resonate with users and create meaningful impact. | – When seeking to develop innovative solutions, products, or services that are user-centric, intuitive, and impactful by applying a human-centered approach to problem-solving and design. | |
| is an iterative, collaborative approach to addressing complex problems and adapting to changing circumstances in dynamic environments. It aligns with Agile principles and methodologies used in software development and project management. Key aspects include: 1. : Break down problems into smaller, manageable tasks or iterations that can be tackled incrementally and adaptively. 2. : Form cross-functional teams that collaborate closely, share knowledge, and work iteratively to solve problems and deliver value. 3. : Embrace feedback, experimentation, and reflection to learn from experiences, iterate on solutions, and improve outcomes over time. 4. : Respond quickly and flexibly to changes, uncertainties, and emerging insights by adjusting plans, priorities, and approaches as needed. 5. : Maintain transparency and visibility into progress, challenges, and decision-making processes to foster trust and alignment among team members and stakeholders. promotes flexibility, responsiveness, and resilience, enabling teams to navigate complexity and deliver value effectively in dynamic environments. | – When confronting complex, rapidly evolving problems or projects that require adaptive, collaborative approaches to problem-solving, decision-making, and value delivery in uncertain or changing conditions. |
Connected Decision-Making Frameworks
Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced
Read Next: Mental Models , Biases , Bounded Rationality , Mandela Effect , Dunning-Kruger Effect , Lindy Effect , Crowding Out Effect , Bandwagon Effect , Decision-Making Matrix .
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Business Model Innovation
- Platform Business Models
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Digital Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process The McKinsey Podcast
Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
- 2024 McKinsey & Company

More by McKinsey
Skip Prichard | Leadership Insights
Ideas, Insight & Inspiration
7 Steps to Problem Solving

Bulletproof Problem Solving
Complex problem solving is the core skill for 21st century teams. It’s the only way to keep up with rapid change. Winning organizations now rely on nimble, iterative problem solving, rather than the traditional planning processes. I had the opportunity to speak with Charles Conn and Robert McLean, two McKinsey alums who share a seven-step systematic approach to creative problem solving that will work in any field or industry. Their new book is BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
New Skills Required
Would you share a little about the evolution of managerial skills and what skills are needed in the current era?
This new era of focus on creative problem solving has been ushered in by massive disruption of the old order in business and society. New business models are rapidly emerging from revolutionary Internet, machine learning, and bioscience technologies that threaten the status quo in every field. Technology change is speeding business up and providing an edge for disruptive innovators.
As a consequence of accelerating change, the old model of managerial skill development and application is no longer effective. It used to be that you could learn the core skills for a career in college and graduate school – think management, accounting, law – and then apply it over forty years. Strategic planning in business assumed an existing playing field and known actors. Today savvy business leaders are prioritizing complex problem solving skills in hiring rather than old domain knowledge, and emphasizing agile team problem solving over traditional planning cycles. This approach rewards the ability to see and quickly respond to new opportunities and threats over the slower traditional big company departmental responses.
We are seeing growing awareness of this. David Brooks of the New York Times said recently, “It doesn’t matter if you are working in the cafeteria or the inspection line of a plant, companies will only hire people who can see problems and organize responses.” And The World Economic Forum in its Future of Jobs Report placed complex problem solving at #1 in its top 10 skills for jobs in 2020.
For those who feel ill-prepared for this era, what are the best ways to acquire the needed skills?
Unfortunately, despite an increasing recognition in the business press that problem solving is the core 21 st century skill, our universities and graduate schools rarely teach systematic problem solving or modern team decision making skills. This is starting to change, and we are seeing that in moves by the OECD and Council for Aid to Education (CAE) which administers the College Learning Assessment plus test.
The OECD Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) started testing individual problem solving skills in 2012 and added collaborative problem solving skills in the 2015 assessments. One of the interesting early findings is that to teach students to become better problem solvers involves other capabilities than simply teaching reading, mathematics, and science literacy well. Capabilities such as creativity, logic, and reasoning are essential contributors to students becoming better problem solvers. That is what this book is about.
You share seven steps in your bulletproof problem solving approach. How did you develop it?
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further for application more broadly to personal, social and environmental problems at all scales in later work with the Nature Conservancy, the Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation, the Rhodes Trust and in start-up companies where we are investors.
1: Define the problem.
2: Disaggregate.
3: Prioritize.
4: Workplan.
5: Analyze.
6: Synthesize.
7. Communicate.
Is there one part of it normally missed or not focused on as much as it should be?

What are some of the best methods for overcoming biases in decision making?
The most important biases to address are confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and loss aversion. These are deep seated in our psyches and often reinforced by traditional hierarchies. We use some simple team approaches to fight bias, including perspective-taking (the act of modeling another team member’s assertion or belief to the point that you can describe it as compellingly as the other), role playing (where you act out one side or the other of difficult choice, sometimes in a red team/blue team structure), team distributive voting on analyses and solution paths (one approach we have used is to assign each team member 10 votes, represented by sticky notes, and have each team member use them to vote on their favorite analysis, allowing cumulative or bullet voting, with the most senior person voting last, so as not to bias the choices of more junior members). The most important team norm to encourage is the obligation to dissent, which means every team member is required to verbally contest decisions when they disagree, regardless of seniority.
What do leadership teams most struggle with in the new environment?
The biggest challenge is the speed of change, which pressures all the management approaches we were taught in business school, particularly around planning cycles. The leadership teams that get good at this typically form and re-form cross-functional teams to deploy on issues as they arise, rather than waiting for conventional departmental responses. And they are comfortable using rapid design cycles to prototype and test products/services in the market, rather than depending on traditional marketing analysis.
How will AI impact the bulletproof approach?
We believe good organization problem solving will increasingly utilize advances in artificial intelligence to predict patterns in consumer behavior, disease, credit risk, and other complex phenomena. Machine learning is getting better at pattern recognition than most humans. But that isn’t the whole story. To meet the challenges of the twenty-first century, mental muscle and machine muscle have to work together. Machine learning frees human problem solvers from computational drudgery and amplifies the pattern recognition required for faster organizational response to external challenges. For this partnership to work, twenty-first century organizations need staff who are quick on their feet, who learn new skills quickly, and who attack emerging problems with confidence.
For more information, see BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
Continue Reading
Popular posts.

Learn the important power of prioritizing sleep
Subscribe today and receive a free e-book. Get Your Guide to a Solid Night of Sleep free when you sign up to receive blog updates via email.
Thank you! Please check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
Pin it on pinterest.
- Print Friendly

- Decision Making
- Goal Setting
- Managing Performance
- Managing Projects and Change
- Managing Through Covid
- Personal Development
- Problem Solving
- Time Management
- Workplace Well-being
- Free Downloads
7 Problem Solving Steps
In a minute!
These 7 problem solving steps provide a short outline of a process to help you solve problems effectively. A structured process helps ensure you stay on track but before you start, remember:
“Do not focus on finding an answer: focus on defining the question” Peter Drucker
Part of our manage in a minute series, read this article to gain a quick overview of the right steps for effective problem solving. We end the article with two principles that perhaps aren’t applied often enough when we set out to solve a problem.
You may also want to read our article: problem solving questions, which raises five challenging and provocative questions, based on this 7 step problem solving process:
1 Find the Right Problems to Solve
Too often our approach to problem solving is reactive, we wait for the problems to arise. Firstly in our 7 problem solving steps, we advocate taking a proactive approach, go and find problems to solve; important and valuable problems. The real starting point then for any problem solving process is to find the right problem to solve.
2 Define the Problem
It is very tempting to gloss over this step and move to analysis and solutions. However, like the first step, it is one of the secrets of effective problem solving. Combining problems that are valuable to solve, with defining exactly what you are trying to solve, can dramatically improve the effectiveness of the problem solving process. The secret to defining the problem, is really about attitude. Try to see every problem as an opportunity.
3 Analyse the Problem
Analysis is a process of discovery of the facts, finding out what you know about the situation. In doing so you are breaking down complexity, stripping away the superficial and getting to the causes/issues.
4 Develop Opportunities
There are always more than one way to solve a problem, so take time to develop plenty of creative possibilities to solve the problem.
5 Select the Best Solution
Selecting is about making choices, about deciding. To do this you need to weigh up the competing value and risk of the different options you generated in the previous step.
6 Implement
Good solutions are often only as good as the way they are implemented. Implementation requires project management and a determination to deliver the outcomes essential to solving the problem you originally defined.
7 Evaluate and Learn
You will have done some things really well through this seven step problem solving process. It would be all too easy to forget them in rushing to solve the next problem, or to implement the solution. You should evaluate at least two areas:
- How you carried out the seven step problem solving process
- The effectiveness of the solution you implemented. Did it deliver the outcomes you expected?
7 problem solving steps, 2 principles
This process provides a challenge to other problem solving techniques. It highlights the undervalued problem solving skill of applying two under-used principles, at the start of the process :
Finding the right problems to solve
Focusing on opportunities created by the “problem”
The eighth problem solving step

- Tool 1: When you don’t know what to do
- Tool 2: Defining questions for problem solving
- Tool 3: Finding the right problems to solve
- Tool 4: Problem solving check-list
- Tool 4a: Using the question check-list with your team
- Tool 5: Problem analysis in 4 steps
- Tool 5a: Using 4 Step problem analysis with your team
- Tool 6: Questions that create possibilities
- Tool 6a: Using the 5 questions with your team
- Tool 6b: Putting creativity to work – 5 alternate questions
- Tool 6c: Workshop outline
- Tool 7: Evaluating alternatives
- Tool 8: Creative thinking techniques A-Z
- Tool 9: The 5 Whys technique
Further Reading
Seven step problem solving Problem solving exercises Problem solving questions Problem solving activity
>>> Return to the Problem Solving Knowledge Hub
I am designing a new management development programme for my company and your goal setting guide has really helped..
I like the way you introduced material I haven’t seen before ( SHARP action ) & the tools to apply the learning. The price represents really good value for money and I will be checking out more of your material over the coming months.
Matthew - UK
Other e-guides you may find useful

Problem Solving Bundle

Making Better Decisions

Managing Performance Bundle

Grab a Freebie
Sign up to our newsletter and receive "How to be a Happy Manager"

Grab a Freebie!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive a free copy of "How to be a Happy Manager"
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The Happy Manager
- Testimonials
- Write For Us
- Terms & Conditions
Knowledge Hub
What's new.
- Interview Skills: How to Ace Your Job Interview
- 6 Strategies to Improve Workplace Productivity
- Boosting Workplace Performance Through Effective HR Support Services
- The Worker's Blues: Identifying and Preventing Employee Burnout
- Techniques for Crafting Powerful Team Presentations
- Why Your Business Location Has an Impact on Your Employees’ Happiness
© 2024 The Happy Manager. Part of Apex Leadership Ltd. Tel +44 (0)7572 797430
- Privacy Policy
Website by Limely
Click on the links to download your free tools
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn More
- Certifications
- Our Instructors
The 7 Stages of the Product Management Process

Carlos González De Villaumbrosia
Updated: August 7, 2024 - 17 min read
The pressures to focus on multiple ‘critical components’ of product development can be overwhelming. Honing in on your primary products is essential — of course. But, it’s also ‘crucial’ to ensure strategic alignment, use resources efficiently, stay nimble to market changes, mitigate risks, and whatnot.
In this insightful and practical piece, we explore how to be ‘holistic’ without applying direct pressure. This approach provides a deep understanding of the product management steps, from market research to roadmapping and prioritization. By examining the product management process flow, we reveal how each phase of product management contributes to all ‘critical segments’ of company’s success.
Let's explore the software product management process with clear examples and visual aids. We'll cover how to optimize each stage—market research, product specifications, roadmapping, prioritization, and more—to ensure you're maximizing opportunities for growth and innovation.
Creating a successful product involves several important steps. Each stage plays a crucial role in bringing innovative solutions to the market:

In this guide, we'll walk you through the key stages of product development, breaking down complex processes into easy-to-understand concepts. Whether you're a newcomer or an experienced professional, this overview will provide you with practical cues to navigate each phase effectively.
1. Idea Generation
The Idea Generation stage is the first step in the product development process. This is, of course, where new product ideas are brainstormed and ‘put on paper’. Unrestrained creativity and innovative thinking are the vital constituents in this phase — they encourage the collection of a wide range of ideas without immediate evaluation or criticism.
How to capture ideas?
To effectively harvest creative concepts, it’s essential to create an environment where creativity can flourish. Here are some methods to help capture innovative product ideas:
Brainstorming Sessions : Organize regular brainstorming meetings where team members can freely share their thoughts. Use techniques like mind mapping and free writing to stimulate creative thinking.
Market Research : Gather insights from market trends, key metrics , product analysis , and industry reports. Understanding market needs and gaps can spark new product ideas.
Customer Feedback : Engage with customers through surveys, interviews, and feedback forms. Customers can provide valuable insights into their needs and pain points.
Internal Suggestion Programs : Encourage all employees, not just those in product development, to contribute ideas. Create a suggestion box or an internal digital platform where ideas can be submitted.
How to make sure everyone’s in the loop?
Once ideas are generated, it’s crucial to document them in a centralized location to ensure they are accessible and not overlooked. This can be done using:
Idea Management Software : Your everyday product management tools or dedicated idea management platforms can help track and organize ideas.
Shared Documents : Use cloud-based documents (e.g., Google Docs, Microsoft OneNote) where team members can add and edit ideas in real time.
Idea Boards : Physical or digital idea boards can be used to visualize and categorize ideas.
Don’t judge, collect!
During the Idea Generation stage, the emphasis should be on quantity rather than quality. This is not the time for screening or criticism. The goal is to gather as many ideas as possible, which increases the likelihood of finding innovative solutions. Encourage team members to think outside the box and not fear sharing unconventional ideas.
Lay down the law.
To ensure ideas are well-developed and actionable, establish a set of guidelines for idea submission. These guidelines can include:
Elaboration : Ideas should be detailed enough to understand their core concept. Include descriptions of what the idea entails and how it functions.
Impact Potency : Assess the potential impact of the idea. How significant is the problem it addresses, and what benefits will the solution provide?
Channels Encompassed : Identify which channels (e.g., digital, retail, B2B) the idea affects or leverages.
Problem-Solving : Clearly state the problem the idea aims to solve. Define the target audience and their specific pain points.
Complexity : Evaluate the complexity of developing the idea. Consider the technical feasibility, required resources, and time to market.
By following these guidelines and fostering a creative, inclusive environment, the Idea Generation stage can produce a wealth of innovative ideas that serve as the foundation for successful product development.
Free Value Proposition Canvas
Learn how to take user problems as the foundation of your solution and only build products that matter with our free Value Proposition Canvas!
2. Idea Screening
The Idea Screening stage is the second step in the product development process. Here, the initial pool of ideas is evaluated to weed out the less promising ones. This phase ensures that only the most viable and valuable ideas move forward. This is where you get to be critical!
Remember though, all ideas are created equal.
It's crucial to treat all ideas equally during the screening process. Every idea, regardless of its source, should undergo the same evaluation scrutiny. This prevents bias and ensures that only the best ideas are selected based on their merit, not credit.
Product teams often make the mistake of allowing ideas from top management to bypass the screening process. This practice can lead to suboptimal decisions and missed opportunities. It is best if all ideas, whether from top management or entry-level employees, are evaluated using the same criteria.
Speaking of criteria…
Here are some key criteria to use when screening ideas:
Market Potential : Assess the potential demand for the idea. Does it address a significant need or gap in the market?
Feasibility : Evaluate whether the idea is technically and financially feasible. Do you have the resources and capabilities to develop it?
Alignment with Business Goals : Ensure the idea aligns with the company’s strategic objectives and long-term vision.
Competitive Advantage : Consider whether the idea offers a unique advantage over competitors. What sets it apart in the market?
Customer Value : Determine the value the idea provides to customers. Will it enhance their experience or solve a critical problem?
The Screening Process
Initial Review : Conduct an initial review of all ideas to filter out those that clearly do not meet the basic criteria.
Scoring System : Use a scoring system to evaluate each idea against the established criteria. Assign scores based on factors like market potential, feasibility, and alignment with business goals.
Group Discussion : Involve a cross-functional team in the screening process. Discuss each idea to gather diverse perspectives and insights.
Prioritization : Rank the ideas based on their scores and discussions. Focus on the top-ranked ideas for further development.
Feature Prioritization Template
Use this feature prioritization template to get clear direction on which features to include and which to leave out.
Tools for Screening Ideas
Evaluation Matrices : Use matrices to compare ideas against each other based on the screening criteria.
Scoring Sheets : Develop scoring sheets to systematically assess each idea's strengths and weaknesses.
Collaborative Platforms : Utilize collaborative tools to enable team discussions and input on each idea.
3. Concept Development and Testing

The Concept Development and Testing phase comes after Idea Screening and involves transforming selected ideas into detailed concepts. These concepts are then tested with target audiences to gather feedback and refine the product vision. This phase is crucial for ensuring that the product idea is viable and resonates with the intended users.
Concepts need to be detailed.
To develop detailed concepts, follow these steps:
Expand on the Idea : Take the selected idea and expand it into a full-fledged concept. This includes defining the product’s core functionality, features, and user experience.
Create Concept Prototypes : Develop prototypes or mockups to visualize the concept. These can be low-fidelity sketches or high-fidelity digital prototypes, depending on the stage of development.
Describe the Value Proposition : Clearly articulate the value proposition of the prototype or MVP . What problem does it solve? What benefits does it offer to users?
Outline the User Journey : Map out the user journey, detailing how users will interact with the product from start to finish. Identify key touchpoints and potential pain points.
Testing with target audiences
Once the concepts are developed, they need to be tested with target audiences to validate their feasibility and appeal. Here’s how to conduct effective concept testing:
Identify Test Participants : Select a representative sample of your target audience for testing. Ensure diversity to gather a wide range of feedback.
Conduct User Research : Use surveys and one-on-one interviews to gather qualitative and quantitative feedback. Ask participants about their first impressions, perceived value, and any concerns or suggestions.
Utilize Usability Testing : Conduct usability tests where participants interact with the prototypes. Observe their behavior and gather feedback on the user experience.
Analyze Feedback : Collect and analyze the feedback to identify common themes, preferences, and areas for improvement. Look for patterns that indicate the concept’s strengths and weaknesses.
Refining the Product Vision
Based on the feedback gathered, refine the product vision and concept. This iterative process ensures that the product meets user needs and expectations. Key steps include:
Incorporate Feedback : Adjust the concept to address the feedback received. This might involve adding new features, improving usability, or altering the design.
Re-evaluate Feasibility : Ensure that the refined concept is still feasible within the project’s constraints, including budget, timeline, and technical capabilities.
Iterate on Prototypes : Develop new prototypes based on the refined concept and conduct additional testing if necessary. Continue refining until the concept is well-received by the target audience.
Align with Business Goals : Make sure the refined concept aligns with the overall business goals and product strategy. Ensure it contributes to achieving the desired market position and business objectives.
4. Product Specifications
The Specification phase follows the conceptualization phase in the product development process. This phase involves detailing the selected ideas into comprehensive product specifications , which serve as a blueprint for the development team. Detailed product specs provide clear guidance, ensure alignment and communication, reduce risks, and establish quality assurance criteria.
What are Product Specifications?
Product specifications, or product specs, are detailed documents that outline the features, functionalities, design, and requirements of a product. They provide a clear and concise description of what the product is, what it will do, and how it will be built.
Questions to answer in Product Specifications
To create thorough product specifications, answer the following key questions:
What is the product? Describe the product in detail. What is its purpose? What problem does it solve?
Who is the target audience? Identify the end users. Who will use this product? What are their needs and pain points?
What are the key features and functionalities? List the primary features and functionalities of the product. What must the product be able to do?
What are the design requirements? Specify the design aspects, including user interface, aesthetics, and user experience considerations.
What are the technical requirements? Outline the technical specifications, such as platform compatibility, performance criteria, and security requirements.
What are the constraints and limitations? Identify any constraints, such as budget, timeline, regulatory requirements, and technical limitations.
How will success be measured? Define the metrics and criteria for success. How will you know if the product meets its objectives?
Know how to write product specifications
When writing product specifications, follow these guidelines to ensure clarity and completeness:
Be Detailed and Specific : Include all necessary details to avoid ambiguity. The more specific you are, the easier it will be for the development team to understand and implement the requirements.
Follow a template : Start with a template that covers all basis in order for the products specs to be detailed and digestible.
Organize Logically : Structure the document in a logical order. Start with an overview and business case then dive into specifics like features, design, and technical requirements.
Include Visuals : Use diagrams, flowcharts, and sketches to illustrate complex concepts and designs. Visuals can help communicate ideas more effectively.
Collaborate with Stakeholders : Involve key stakeholders in the specification process to ensure that all perspectives are considered and that the specs align with business goals and user needs.
By following these steps, you ensure that your product specifications provide a solid foundation for the development stages that follow. This leads to more efficient development, higher quality products, and greater success in the market.
5. Product Strategy and Roadmapping
The Product Strategy and roadmapping phase involves creating a strategic plan and a detailed roadmap that guides the product from development to launch and beyond. The strategy and roadmap ensure that the product aligns with business goals, meets market demands, and is delivered on time.
Define Product Strategy
Product Strategy is the high-level plan that outlines what the product aims to achieve and how it will do so. It provides direction and sets priorities for the product team. Aside from knowing essential frameworks and using templates , you should know the key components of a product strategy:
Vision and Mission : Define the long-term vision for the product and its mission. What is the ultimate goal of the product? What problem does it aim to solve?
Market Analysis : Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the competitive landscape, market trends, and customer needs. This helps identify opportunities and threats.
Target Audience : Clearly define the target audience for the product. Who are the primary users? What are their characteristics, needs, and pain points?
Unique Value Proposition : Identify what makes the product unique and valuable compared to competitors. Why should customers choose your product?
Business Objectives : Set clear business objectives that the product aims to achieve. These could include revenue targets, market share goals, or customer satisfaction metrics.
Product Positioning and Messaging : Develop a positioning statement and key messages that communicate the product's value to the target audience.
Creating a Product Roadmap
A product roadmap is a visual, detailed representation of the product strategy. It outlines the planned features, milestones, and timelines for the product’s development and launch. Here’s how to create an effective product roadmap:
Set Goals and Objectives : Start by setting clear goals and objectives for the product. These should be aligned with the overall product strategy and business objectives.
Prioritize Features : Based on the product specifications, prioritize the features and functionalities to be developed. Consider factors like customer needs, business value, and technical feasibility.
Define Milestones : Break down the development process into key milestones. These are significant points in the project timeline that indicate progress, such as completing a prototype or reaching beta testing.
Establish Timelines : Set realistic timelines for each milestone and feature. Consider the resources available and potential risks that could impact the schedule.
Visualize the Roadmap : Use a visual tool to create the roadmap. This can be a Gantt chart, a timeline, or a Kanban board. Ensure it is clear and easy to understand for all stakeholders.
Communicate and Collaborate : Share the roadmap with all relevant stakeholders, including the development team, marketing, sales, and upper management. Gather feedback and make adjustments as needed.
Review and Adjust : Regularly review the roadmap to track progress and make necessary adjustments. The roadmap should be a living document that evolves with the project and market conditions.
Creating a product strategy and roadmap ensures alignment and focus among team members and stakeholders, providing clear direction on what needs to be built and when. It facilitates efficient resource allocation by prioritizing features and setting realistic timelines, while also identifying potential risks early for proactive mitigation. Additionally, it enhances communication and collaboration, offering a shared understanding of the product’s progress and goals.
Product Roadmap Template
Download our easy-to-use template to help you create your Product Roadmap.
6. Agile Product Development
The Agile Product Development phase focuses on iterative and incremental development, ensuring that the product evolves through continuous collaboration, feedback, and improvement. Agile methodologies prioritize flexibility, customer satisfaction, and delivering working software frequently.
Adopting Agile methodologies
Agile product development relies on specific methodologies to manage and execute the process effectively. The most common methodologies include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP).
Scrum : Scrum divides the development process into time-boxed iterations called sprints. Each sprint typically lasts two to four weeks and involves planning, execution, review, and retrospective phases.
Kanban : Kanban focuses on visualizing the workflow, limiting work in progress (WIP), and improving efficiency. It uses a column-based board to track tasks and progress.
Extreme Programming (XP) : XP emphasizes technical excellence and good programming practices, such as pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), and continuous integration.
Key Principles of Agile Product Development
Customer Collaboration : Agile development emphasizes close collaboration with customers and stakeholders to gather feedback and ensure the product meets their needs.
Iterative Development : Development occurs in small, manageable increments. Each iteration results in a potentially shippable product increment.
Responding to Change : Agile methodologies embrace changes in requirements, even late in the development process. This flexibility allows the product to adapt to evolving market needs and customer feedback.
Agile product development keeps customers satisfied by involving them throughout the process. It's flexible and adapts easily to new information and market changes.
Agile also speeds up delivery with incremental development and frequent releases. It promotes better collaboration among developers, stakeholders, and customers. Regular feedback and retrospectives help continuously improve the product and team performance.
7. Product Launch

The Product Launch phase is the culmination of all the hard work put into developing your product. This stage involves introducing the product to the market and ensuring that everything is in place for a successful launch. A well-executed product launch plan can generate excitement, drive sales, and establish a strong market presence.
Product Launch Checklist
Launch is a critical time that can make the difference between product success and failure. Use this checklist to make sure nothing falls through the cracks.
Preparing for the launch
Before launching your product, thorough preparation is crucial. This ensures that all aspects of the product and its marketing are ready for the big day.
Finalize the Product : Ensure that the product is fully developed, tested, and ready for use. Address any final bugs or issues and confirm that the product meets all quality standards.
Develop Marketing Materials : Create compelling promotional materials , including brochures, videos, blog posts, and social media content. These materials should clearly communicate the product’s value and benefits to the target audience.
Train the Sales Team : Equip your sales team with the necessary knowledge about the product. Provide them with detailed information, including key features, benefits, and how to address common customer questions.
Set Up Customer Support : Ensure that your customer support team is prepared to handle inquiries and issues. Provide them with training and resources to effectively support new users.
Executing the launch
On launch day, it’s important to execute on your strategy to maximize impact and reach.
Launch Event : Consider hosting a launch event, either in-person or virtual, to create buzz and excitement. Invite key stakeholders, influencers, and the press to attend.
Press Releases : Distribute press releases to major media outlets to announce the product. Highlight the unique features and benefits that set your product apart from competitors.
Social Media Campaign : Leverage social media platforms to spread the word about your product. Use engaging content, hashtags, and collaborations with influencers to reach a wider audience.
Email Marketing : Send out emails to your subscriber list, announcing the product launch. Include special offers or incentives to encourage immediate purchases.
Post-Launch activities
After the initial launch, it’s essential to maintain momentum and address any issues that arise.
Monitor Performance : Track the product’s performance using analytics tools. Monitor sales, website traffic, and user engagement to gauge the success of the launch.
Gather Feedback : Collect feedback from early users to identify any problems or areas for improvement. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments and enhancements.
Customer Engagement : Continue engaging with your customers through follow-up emails, social media interactions, and community forums. Keep them informed about updates and new features.
Evaluate and Learn : Assess the overall success of the product launch. Analyze what worked well and what didn’t, and apply these lessons to future product launches.
By carefully preparing, executing, and following up on your product launch, you can maximize its impact and set the stage for ongoing success. A successful product launch not only drives initial sales but also builds a strong foundation for your product’s growth and market presence.
Product Retrospective Template
Experience continuous growth, learn from failure faster, and identify issues early with our Retrospective template.
Follow the Product Management Process!
Without a process, a team would feel like they're trying to navigate a maze in the dark. It's chaos — people are guessing the next steps, priorities are all over the place, and everyone’s just winging it.
Having a clear process helps teams stay organized, ensures all important aspects are covered, and allows for efficient use of resources.
Product management is complex enough, and there too much at stake. This structured approach not only helps in achieving business goals but also ensures that the final product meets customer needs and stands out in the market. With a solid plan and clear steps to follow, your team can handle every aspect of product management with confidence and precision.
Enroll in Product School's Product Strategy Micro-Certification (PSC)™️
The difference between a good and a great product lies in your Product Strategy, answering vital questions like: Who's the product for? What benefits does it offer? How does it further company objectives?
Updated: August 7, 2024
Enjoyed the article? You might like this too

Product Strategy
6 Steps to Supercharge Your Product Launch Strategy
Discover practical tips to refine your product launch strategy. Get expert advice and actionable insights for a successful market entry.

The Only Product Requirements Document (PRD) Template You Need
Download a free, expert-validated PRD template to set your product and team up for success. Align stakeholders, prioritize features, and plan your GTM strategy.

Product Fundamentals
Product Analysis 101: Expert Insights and Tips
Learn about product analysis, frameworks, techniques, best practices, examples, challenges, and tools in our step-by-step guide.
Subscribe to The Product Blog
Discover Where Product is Heading Next
Share this post
By sharing your email, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service
7 step problem solving technique

Whilst processes are generally there to protect us from issues (i.e. follow the process and get what you expect) unsurprisingly from time to time things go wrong and problems occur that affect either the output or the success of the process in question.
What do Business problems cause? Well, they can affect a whole host of things, from Quality, Schedule or Cost for example. Left alone they can impact both your customer and business and therefore resolving them is the appropriate route of action but given that there are a plethora of problem-solving tools available which one should you follow? What makes the 7 steps of problem-solving a suitable tool to utilize?
In this article, we’ll take a look at the 7 Step problem-solving tool, what it is, what the steps are, and how to avoid the key problems.
Firstly, let’s state the obvious when problems do occur it’s absolutely fundamental to have a structured method of resolving them. By providing structured problem-solving tools to your workforce, employees should be able to resolve issues in a timely and cost-effective manner and avoid stabbing around in the dark for a possible solution without having done the work to ensure it is.
Whilst we’ve covered more formal methods of problem-solving such as the 8d report , 5 whys (you can check out our post on how to create a 5 why template here) and others, the 7 steps of the problem-solving method represents another structured step by step process which can be used to analyze and resolve problems by uncovering root causes and helping to define corrective actions to fix the problem.
Why Structured problem-solving works
One of the main challenges with problem-solving is to avoid the obvious trap of thinking you know the answer and launching immediately into fix it mode. Unfortunately in many cases particularly in complex business situations the answer is rarely obvious and is often a combination of contributory factors that require a level of uncovering through following a step by step approach ahead of launching off and implementing a random “hit and hope” solutions.
The 7 step problem resolving solution offers just that a methodical approach that can be used to resolve issues by following a standard approach. It must be remembered that effective problem solving does take time. Also, consider that problem solving doesn’t have to be tied down to one tool and that you can choose to combine methods i.e the 7 step method combined with 5 why to help drill down and understand root causes.
The approach can be used in situations where you have large or small issues and works great in a team-based approach or if you’re working on your own as an individual.
What are the 7 problem-solving steps
Below is the list of steps associated with this tool
STEP 1: The Right Problem to Solve STEP 2: Analyse the Problem STEP 3: Define the Problem STEP 4: Develop Opportunities (Possible Solutions) STEP 5: Select the Best Solution STEP 6: Implement the Solution STEP 7: Evaluate and Learn
STEP 1: Identify the problem
The first step is to define the problem that you have.
Generating a robust problem definition is key to the whole process. Start your process with a poor problem definition and you’ll be wasting your time later on which is likely to result in you reworking some of the process steps – worse still you follow the entire process define a corrective action that results in other issues (or costs your firm money in implementation that may not recover!).
A good problem definition includes a clear description of the issue in contrast with the condition that it should be. For example,
- The houses were all painted green instead of blue
- The part was manufactured to a tolerance of 1cm instead of 1/2 a cm
- The part included paint on areas identified by the drawing that should not include paint.
The above show clearly what’s wrong and contrasts the “current condition” with the “should be condition”.
Of course, you could use something like – “the part is manufactured incorrectly” but that would make both developing a solution and implementation somewhat difficult as it is not clear what’s wrong.
STEP 2: Defining your Goal
Once you’re aware of what your problem is the next step is to define where you’ll be at the end of your problem-solving process.
For example – let’s look at one of our examples from above • The houses were painted green not blue.
Here the goal may be defined as “Problem root causes identified/rectified and all houses to be reworked and painted blue within the next 3 weeks.”
The goal clearly removes the problem and sets the end result to the desired condition.
Remember, your goal should be SMART (Specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound).
STEP 3: Brainstorm the solution
Brainstorming is usually a group based method where through gathering ideas the team endeavors to find an answer to the specific issue or problem. Brainstorming usually requires each member of the team to put forward their ideas.
Ideas are usually captured on a whiteboard, list, or set of post it notes in order to then evaluate them.
With Brain-storming it’s important to ensure all members of the team have an equal voice and that collection of ideas is seen as the priority. Do not let people take over this by thinking they have all the answers (especially the management!!) – you may be surprised by who in the team comes up with best contributions.
STEP 4: Assess your solutions/alternatives
Following the brainstorming session – the next step is to evaluate each idea.
In problem-solving, the best method is to assess whether the idea impacts the believed root cause of the issue and if it does how. Generating ideas is great but if they fail to help fix the thing that’s actually going wrong then they are not going to help much. So initially challenging each idea’s effect on possible root causes is usually a good initial step.
Evaluation usually means a systematic approach to reviewing the positives and negatives of each solution put forward in order that the team can then select a final solution.
STEP 5: Select a solution
Once you’ve brainstormed the possible solutions and evaluated them, you need to pick one (or a collective of some) – this is usually the key element where some teams go awry by selecting solutions that may not have the desired impact.
Using a tool such as a Solution Selection Matrix can often help simplify the process and apply some rigor in ensuring this part of the process remains focussed.
What is a Solution Selection Matrix?
The Solution Selection matrix is a tool that can be used to help review each idea by a standard process and criteria. It’s typically a table that lists the possible ideas and then has columns that then helps you evaluate them.
The Solution Selection Matrix might include evaluation of things like
- Ease of deployment
- resource requirement
- time to implement
- Impact on stakeholders etc.
See below for an example matrix that demonstrates how this can be achieved.
I’d recommend engaging your key stakeholders at this point to discuss the resolution to the problem, how you’ll implement and the impact on the implementation (discussing things like whether the implementation will take effect immediately or after a given time).
I’d also suggest that you review your KPI’s, to understand what the current situation looks like so that you’ll be able to easily demonstrate the impact post-implementation (and if you don’t have KPI”s you can always consider implementing some simple metrics at this point).
STEP 6: Implement
Once you’ve selected your solution it’s time to implement.
Here you should develop the implementation plan that takes you through the steps of the “fix” upfront of the deployment, this way the whole team understands what’s happening and how it will work. This also provides an opportunity to critique the timeline, resource requirement, and likely cost.
The plan is usually best combined with a RAIL (Rolling ActIons List) this explains what actions are active and who owns them and when they need to be done by. A simple implementation plan that shows target dates and owners is normally all that you require to help administer this stage.
Depending on the complexity of the solution you may wish to review possible risks up front of the deployment to assess where things might go wrong.
Don’t overestimate what you can achieve here, it’s best to be realistic, considering:
- Who will implement
- How you will implement
- How you will monitor the fix
- what budget/resources you might require to implement the fix
- Will the fix start working straight away (if not when)
Management can sometimes have a tendency to think that when you come up with the “fix” it impacts straight away so it’s a good time to get everyone on the same page with what your implementation actually means and when results are likely to be seen.
STEP 7: Evaluation
The final stage is to evaluate your problem’s resolution with the key question being – did your problem-solving project drive the result you wanted?
If you have KPI’s you can track them against your fix, you might involve some stakeholder engagement to understand what the fix has meant for them and their views on the implementation, what worked and what didn’t so that you can evaluate your businesses process for next time.
Alternatives to the 7 problem solving steps.
As we discussed at the outset of the article there are a number of problem-solving techniques out there, from 8d to 5 why to SWOT etc, you can check some of them
Before you settle on an approach I’d recommend that evaluate some of these approaches, examining the pros and cons and how they might fare in your industry. As ever it’s likely that one size doesn’t fit all and you and always look to tweak the process whilst keeping the basic steps. Businesses are likely to be far more accepting of a structured process that gets improved upon over time than no process at all.
Got some thoughts on problem-solving, be sure to check out our Problem Solving Guide , perhaps you have a favorite tool or method? We’d love to hear about it, fire us up on Twitter, or our feedback section below.
Our Content
- Calculators
- Career Skills
- Communications
- Human Resources
- Strategy and Leadership
- Supply Chain Management
Problem-Solving with 8D and 7STEP
An effective approach to problem-solving is crucial for success in businesses and projects of all kinds. Problems should be solved systematically and thoughtfully. One possible method for this is the 8D process, originally stemming from quality control, and the 7 steps (7STEP) for effective presentations.
Discover how these two approaches merge to not only solve problems but also create compelling presentations that convey your message clearly and effectively.
The significance of 8D and 7 STEP for PowerPoint presentations
Do you receive complaints or feedback regarding your products or services? Take these responses seriously to maintain customer satisfaction and optimize the quality of your offerings.
Both the 8D (8 Disciplines) and the 7STEP processes are similar, structured problem-solving methods that assist you in mastering product or process issues . Both methods are used for addressing customer complaints. With 8D and 7 STEP, you can bring structure, clarity, and effectiveness to the presentation process.
When we apply this structured approach to presentation development, it helps optimize the entire process . In contrast, the 7 steps for effective presentations provide clear guidance for creating compelling and targeted presentations. They help focus on the audience and the message , ensuring a meaningful structure that facilitates the conveyance of information.
In combination, 8D and 7STEP contribute to creating presentations that are not only informative but also engage and persuade the audience . This allows businesses and professionals to present their ideas, products, and projects more effectively and achieve their goals.
In the following, we will explain the processes and demonstrate how to handle your complaint management professionally.
What is 8D?
8D stands for “ 8 Disciplines ” and is originally a quality management tool developed in the automotive industry. It provides a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement. The 8D method consists of eight well-defined steps aimed at analyzing problems, identifying their root causes, and developing permanent solutions.
The history of 8D dates back to the 1980s and was initially introduced by Ford. Since then, this method has proven to be highly effective in various industries and is applied worldwide.
Applying 8D to presentation development offers a disciplined approach to ensure that presentations are well-structured, persuasive, and effective . This leads to presentations that are not only based on facts but also capable of engaging and inspiring the audience, which is crucial for the success of any presentation.
The 8 Steps of the 8D Problem-Solving Process
Step 1: Team Formation The first step in the 8D process involves carefully assembling a multidisciplinary team. Team members should bring diverse skills and perspectives to ensure comprehensive problem-solving. This team will accompany the entire journey to solve the problem and is crucial for the process’s success.
Step 2: Problem Definition This step involves defining the problem clearly and precisely. An accurate problem statement allows the team to focus on the essential aspects and ensure that resources are effectively utilized.
Step 3: Immediate Actions Immediate actions are taken in this step to limit potential damage and restore immediate stability. This may involve implementing temporary solutions to address acute issues and minimize their impact on processes or products.
Step 4: Root Cause Analysis Identifying the roots of the problem is the core of Step 4. Various analysis tools and methods are used to determine the underlying causes of the problem. This step forms the basis for developing sustainable solutions.
Step 5: Solution Generation In this step, potential solutions are developed. The team uses creative approaches and analytical techniques to create a range of possible solutions. It is essential to evaluate different ideas and select those best suited for problem resolution.
Step 6: Solution Implementation Once a solution is chosen, implementation takes place. This step requires careful planning, resource allocation, and monitoring to ensure that the solution is effectively executed.
Step 7: Prevention Prevention is key to avoiding future problems. Measures are developed and implemented to ensure that the problem does not recur. This may involve training, process changes, or quality improvements.
Step 8: Closure and Recognition The final step of the 8D process includes reviewing the entire process, documenting the results, and recognizing the team’s efforts. Thorough post-analysis is crucial to ensure that the insights gained can be applied in the future.
What is 7STEP?
The 7STEP model is a framework for improving presentations and communication skills . It is a useful tool to ensure that presentations are effective and goal-oriented . It also emphasizes the importance of systematic approaches to presentations and their preparation.
It consists of seven steps:
- Objective Setting : Clearly define the goal of your presentation. What do you want to achieve? This step helps determine the focus of your presentation.
- Audience Analysis : Understand your audience. Analyze their needs, expectations, and knowledge level to tailor your presentation to them.
- Structuring Content : Develop a clear outline and structure for your presentation. This helps present information logically and comprehensibly.
- Visualization and Design : Choose appropriate visualizations and design your slides effectively. Visual elements can support and illustrate your message.
- Presentation Techniques : Learn presentation techniques to effectively convey your message. This includes aspects such as voice, body language, and audience interaction.
- Feedback and Adjustment : Gather feedback from others and adjust your presentation accordingly. This enables continuous improvement.
- Preparation and Delivery : Thoroughly prepare for your presentation and deliver it to your audience. In this step, you apply the techniques learned to communicate your message clearly and persuasively.
Juxtaposition of 8D and 7STEP
The 8D and 7STEP methods of problem-solving have proved themselves effective in different industries, especially the automotive industry. The demands of the customer determine which method to use, however the sequences and procedures are both similar, as shown in the picture below:
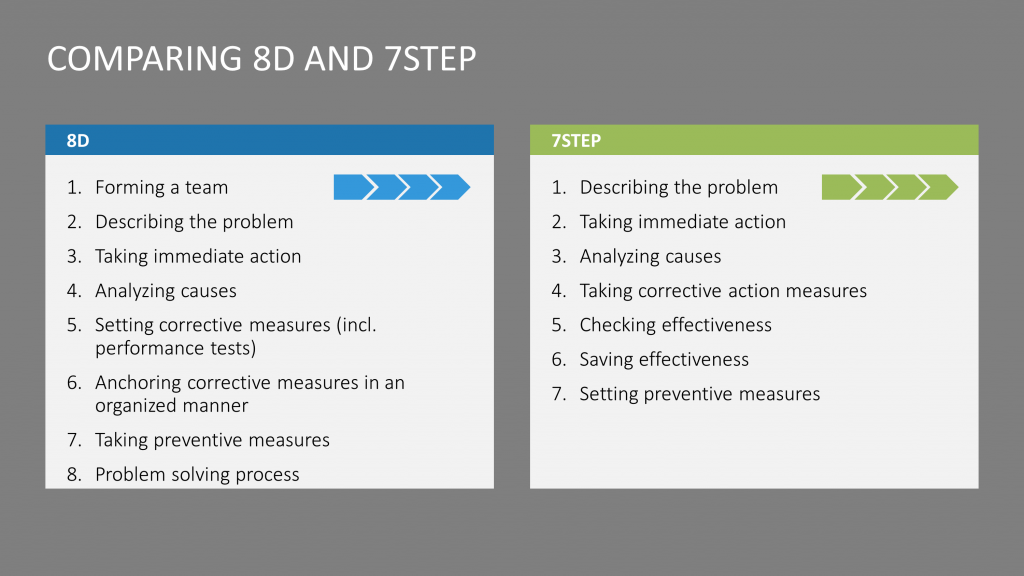
There are two main differences between the two processes. In the illustration, the team formation (step 1 in Figure 8D) and the conclusion of the problem-solving process (step 8 in 8D) are not present in 7STEP. However, in theory, these steps also exsist in 7STEP, as in you start by gathering a team and you end with a final conclusion.
In the 7STEP structure, defining, testing and implementing corrective actions are listed differently than in the 8D model. For example, efficacy testing is included in step 5 of 8D, while in 7STEP, it is its own separate step.
Step by step problem-solving
The integration of 8D, the structured problem-solving approach, and the 7 steps to effective presentation can lead to a powerful combination. Both models share the common idea of a s ystematic and disciplined approach based on clear steps and goals . Here are some ways they can be interconnected:
- Clear Objective Setting : Begin both problem-solving and presentation preparation with a clear objective. In the 8D process, you define your goal, usually resolving an issue, while in presentations, you establish the goal of your message.
- Audience Analysis : Understanding the audience is crucial in both approaches. In the 8D process, you analyze the causes of a problem, which also requires an understanding of the affected stakeholders. In presentations, you need to grasp the needs and expectations of your audience.
- Structuring : Clear structure is important in both problem-solving and presentation development. In the 8D process, you structure your approach, while in presentations, you organize your content logically and comprehensibly.
- Visualization : Visualization of information plays a role in both models. In the 8D process, you use charts and analyses to illustrate data, while in presentations, visualizations help clarify complex ideas.
- Presentation Techniques : Presentation techniques learned can also be useful in communication within the 8D process. They help in presenting your insights and solutions clearly and persuasively.
- Feedback and Adaptation : An iterative approach is essential in both models. You collect feedback and adapt your approach or presentation to achieve continuous improvements.
In general, the steps can be divided into three phases:
- The first phase aims to assemble an expert team that addresses the problem to the extent that the customer is no longer confronted with it by initiating immediate actions.
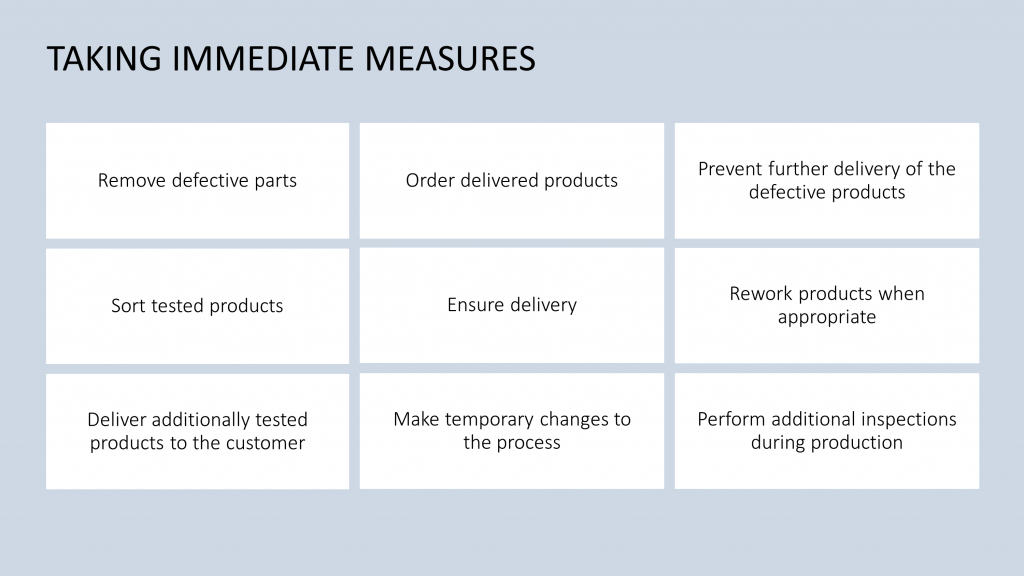
2. In the second phase, the problem is intensively analyzed until the root cause is identified . The 5 Whys method is suitable for this, as it simplifies the problem to the error-causing step through various “why” questions (it is permissible to ask more than 5 “why” questions, contrary to the method’s name). Subsequently, corrective actions are identified and tested for long-term effectiveness.

3. In the third and final phase, the found solutions are anchored organizationally (updated work instructions, training, etc.) and technically (changes to machinery, etc.) within the company. In addition, preventive measures are taken to prevent a recurrence of the same error elsewhere. The Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is often used for this purpose, to identify and eliminate weaknesses in plans for future products/processes where the identified problem may occur.
Feel free to use FMEA templates from PresentationLoad!
Customer satisfaction and loyalty
Do you wonder whether the time and energy-consuming problem-solving processes are worth the effort? Of course, considering the severity of the problem, it may be quicker to solve it without the help of 8D/ 7STEP.
Yet, every business that commits to the saying, “the customer is king” should invest in an expert team that analyzes complaints and works out problems to the full satisfaction of it’s customers.
With the help of 8D/ 7STEP, rapid emergency measures are initiated, long-term, solutions are developed and chances of repeated errors are eliminated. All of this ultimately benefits you by gaining customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and higher product quality.

Conclusion: Skillfully Combining 8D and 7STEP
The integration of 8D, the structured problem-solving approach, and the 7 steps to effective presentation represents a powerful method for optimizing internal processes and enhancing external communication. These models offer clear and disciplined approaches that can be applied in a variety of business contexts.
Emphasizing clear objectives, thorough audience analysis, and thoughtful content structuring helps efficiently address problems and create convincing presentations. This integrative approach provides companies with the opportunity to increase their effectiveness and impact in an increasingly demanding business world.
If you have any questions about the article or PowerPoint presentations in general, feel free to contact us at [email protected] . We are here to assist you!
You can find professionally designed slide templates to enhance the impact of your presentation in our shop. Take a look around; we have numerous slides on various (business) topics. ► Shop Link
You might also be interested in these articles:
- Creating a Company Presentation: 8 Tips
- Why Entrepreneurial Mission Statements Are So Important
- The Top 10 Agile Project Management Methods
Share this post
- share
- save

Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference

Why Corporate Mission Statements Are So Important

7 Tips & Learnings from the Apple Keynote
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Collaboration |
- How to build your critical thinking ski ...
How to build your critical thinking skills in 7 steps (with examples)

Critical thinking is, well, critical. By building these skills, you improve your ability to analyze information and come to the best decision possible. In this article, we cover the basics of critical thinking, as well as the seven steps you can use to implement the full critical thinking process.
Critical thinking comes from asking the right questions to come to the best conclusion possible. Strong critical thinkers analyze information from a variety of viewpoints in order to identify the best course of action.
Don’t worry if you don’t think you have strong critical thinking abilities. In this article, we’ll help you build a foundation for critical thinking so you can absorb, analyze, and make informed decisions.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to collect and analyze information to come to a conclusion. Being able to think critically is important in virtually every industry and applicable across a wide range of positions. That’s because critical thinking isn’t subject-specific—rather, it’s your ability to parse through information, data, statistics, and other details in order to identify a satisfactory solution.
Definitions of critical thinking
Various scholars have provided definitions of critical thinking, each emphasizing different aspects of this complex cognitive process:
Michael Scriven , an American philosopher, defines critical thinking as "the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication as a guide to belief and action."
Robert Ennis , professor emeritus at the University of Illinois, describes critical thinking as "reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do."
Diane Halpern , a cognitive psychologist and former president of the American Psychological Association, defines it as "the use of cognitive skills or strategies that increase the probability of a desirable outcome."
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

Top 8 critical thinking skills
Critical thinking is essential for success in everyday life, higher education, and professional settings. The handbook "Foundation for Critical Thinking" defines it as a process of conceptualization, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation of information.
In no particular order, here are eight key critical thinking abilities that can help you excel in any situation:
1. Analytical thinking
Analytical thinking involves evaluating data from multiple sources in order to come to the best conclusions. Analytical thinking allows people to reject cognitive biases and strive to gather and analyze intricate subject matter while solving complex problems. Analytical thinkers who thrive at critical thinking can:
Identify patterns and trends in the data
Break down complex issues into manageable components
Recognize cause-and-effect relationships
Evaluate the strength of arguments and evidence
Example: A data analyst breaks down complex sales figures to identify trends and patterns that inform the company's marketing strategy.
2. Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness is the willingness to consider new ideas, arguments, and information without prejudice. This critical thinking skill helps you analyze and process information to come to an unbiased conclusion. Part of the critical thinking process is letting your personal biases go, taking information at face value and coming to a conclusion based on multiple points of view .
Open-minded critical thinkers demonstrate:
Willingness to consider alternative viewpoints
Ability to suspend judgment until sufficient evidence is gathered
Receptiveness to constructive criticism and feedback
Flexibility in updating beliefs based on new information
Example: During a product development meeting, a team leader actively considers unconventional ideas from junior members, leading to an innovative solution.
3. Problem-solving
Effective problem solving is a cornerstone of critical thinking. It requires the ability to identify issues, generate possible solutions, evaluate alternatives, and implement the best course of action. This critical thinking skill is particularly valuable in fields like project management and entrepreneurship.
Key aspects of problem-solving include:
Clearly defining the problem
Gathering relevant information
Brainstorming potential solutions
Evaluating the pros and cons of each option
Implementing and monitoring the chosen solution
Reflecting on the outcome and adjusting as necessary
Example: A high school principal uses problem-solving skills to address declining student engagement by surveying learners, consulting with higher education experts, and implementing a new curriculum that balances academic rigor with practical, real-world applications.
4. Reasoned judgment
Reasoned judgment is a key component of higher order thinking that involves making thoughtful decisions based on logical analysis of evidence and thorough consideration of alternatives. This critical thinking skill is important in both academic and professional settings. Key aspects reasoned judgment include:
Objectively gathering and analyzing information
Evaluating the credibility and relevance of evidence
Considering multiple perspectives before drawing conclusions
Making decisions based on logical inference and sound reasoning
Example: A high school science teacher uses reasoned judgment to design an experiment, carefully observing and analyzing results before drawing conclusions about the hypothesis.
5. Reflective thinking
Reflective thinking is the process of analyzing one's own thought processes, actions, and outcomes to gain deeper understanding and improve future performance. Good critical thinking requires analyzing and synthesizing information to form a coherent understanding of a problem. It's an essential critical thinking skill for continuous learning and improvement.
Key aspects of reflective thinking include:
Critically examining one's own assumptions and cognitive biases
Considering diverse viewpoints and perspectives
Synthesizing information from various experiences and sources
Applying insights to improve future decision-making and actions
Continuously evaluating and adjusting one's thinking processes
Example: A community organizer reflects on the outcomes of a recent public event, considering what worked well and what could be improved for future initiatives.
6. Communication
Strong communication skills help critical thinkers articulate ideas clearly and persuasively. Communication in the workplace is crucial for effective teamwork, leadership, and knowledge dissemination. Key aspects of communication in critical thinking include:
Clearly expressing complex ideas
Active listening and comprehension
Adapting communication styles to different audiences
Constructing and delivering persuasive arguments
Example: A manager effectively explains a new company policy to her team, addressing their concerns and ensuring everyone understands its implications.
7. Research
Critical thinkers with strong research skills gather, evaluate, and synthesize information from various sources of information. This is particularly important in academic settings and in professional fields that require continuous learning. Effective research involves:
Identifying reliable and relevant sources of information
Evaluating the credibility and bias of sources
Synthesizing information from multiple sources
Recognizing gaps in existing knowledge
Example: A journalist verifies information from multiple credible sources before publishing an article on a controversial topic.
8. Decision-making
Effective decision making is the culmination of various critical thinking skills that allow an individual to draw logical conclusions and generalizations. It involves weighing options, considering consequences, and choosing the best course of action. Key aspects of decision-making include:
Defining clear criteria for evaluation
Gathering and analyzing relevant information
Considering short-term and long-term consequences
Managing uncertainty and risk
Balancing logic and intuition
Example: A homeowner weighs the costs, benefits, and long-term implications before deciding to invest in solar panels for their house.
7 steps to improve critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that you can build by following these seven steps. The seven steps to critical thinking help you ensure you’re approaching a problem from the right angle, considering every alternative, and coming to an unbiased conclusion.
First things first: When to use the 7 step critical thinking process
There’s a lot that goes into the full critical thinking process, and not every decision needs to be this thought out. Sometimes, it’s enough to put aside bias and approach a process logically. In other, more complex cases, the best way to identify the ideal outcome is to go through the entire critical thinking process.
The seven-step critical thinking process is useful for complex decisions in areas you are less familiar with. Alternatively, the seven critical thinking steps can help you look at a problem you’re familiar with from a different angle, without any bias.
If you need to make a less complex decision, consider another problem solving strategy instead. Decision matrices are a great way to identify the best option between different choices. Check out our article on 7 steps to creating a decision matrix .
1. Identify the problem or question
Before you put those critical thinking skills to work, you first need to identify the problem you’re solving. This step includes taking a look at the problem from a few different perspectives and asking questions like:
What’s happening?
Why is this happening?
What assumptions am I making?
At first glance, how do I think we can solve this problem?
A big part of developing your critical thinking skills is learning how to come to unbiased conclusions. In order to do that, you first need to acknowledge the biases that you currently have. Does someone on your team think they know the answer? Are you making assumptions that aren’t necessarily true? Identifying these details helps you later on in the process.
2. Gather relevant information
At this point, you likely have a general idea of the problem—but in order to come up with the best solution, you need to dig deeper.
During the research process, collect information relating to the problem, including data, statistics, historical project information, team input, and more. Make sure you gather information from a variety of sources, especially if those sources go against your personal ideas about what the problem is or how to solve it.
Gathering varied information is essential for your ability to apply the critical thinking process. If you don’t get enough information, your ability to make a final decision will be skewed. Remember that critical thinking is about helping you identify the objective best conclusion. You aren’t going with your gut—you’re doing research to find the best option
3. Analyze and evaluate data
Just as it’s important to gather a variety of information, it is also important to determine how relevant the different information sources are. After all, just because there is data doesn’t mean it’s relevant.
Once you’ve gathered all of the information, sift through the noise and identify what information is relevant and what information isn’t. Synthesizing all of this information and establishing significance helps you weigh different data sources and come to the best conclusion later on in the critical thinking process.
To determine data relevance, ask yourself:
How reliable is this information?
How significant is this information?
Is this information outdated? Is it specialized in a specific field?
4. Consider alternative points of view
One of the most useful parts of the critical thinking process is coming to a decision without bias. In order to do so, you need to take a step back from the process and challenge the assumptions you’re making.
We all have bias—and that isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Unconscious biases (also known as cognitive biases) often serve as mental shortcuts to simplify problem solving and aid decision making. But even when biases aren’t inherently bad, you must be aware of your biases in order to put them aside when necessary.
Before coming to a solution, ask yourself:
Am I making any assumptions about this information?
Are there additional variables I haven’t considered?
Have I evaluated the information from every perspective?
Are there any viewpoints I missed?
5. Draw logical conclusions
Finally, you’re ready to come to a conclusion. To identify the best solution, draw connections between causes and effects. Use the facts you’ve gathered to evaluate the most objective conclusion.
Keep in mind that there may be more than one solution. Often, the problems you’re facing are complex and intricate. The critical thinking process doesn’t necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision.
6. Develop and communication solutions
Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers. It isn’t enough to think for yourself—you also need to share your conclusion with other project stakeholders. If there are multiple solutions, present them all. There may be a case where you implement one solution, then test to see if it works before implementing another solution.
This process of communicating and sharing ideas is key in promoting critical thinking within a team or organization. By encouraging open dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, you create an environment that fosters the development of critical thinking skills in others.
7. Reflect and learn from the process
The seven-step critical thinking process yields a result—and you then need to put that solution into place. After you’ve implemented your decision, evaluate whether or not it was effective. Did it solve the initial problem? What lessons—whether positive or negative—can you learn from this experience to improve your critical thinking for next time?
By engaging in this metacognitive reflective thinking process, you're essentially teaching critical thinking to yourself, refining your methodology with each iteration. This reflective practice is fundamental in developing a more robust and adaptable approach to problem-solving.
Depending on how your team shares information, consider documenting lessons learned in a central source of truth. That way, team members that are making similar or related decisions in the future can understand why you made the decision you made and what the outcome was.
Example of critical thinking in the workplace
Imagine you work in user experience design (UX). Your team is focused on pricing and packaging and ensuring customers have a clear understanding of the different services your company offers. Here’s how to apply the critical thinking process in the workplace in seven steps:
Step 1: Start by identifying the problem
Your current pricing page isn’t performing as well as you want. You’ve heard from customers that your services aren’t clear, and that the page doesn’t answer the questions they have. This page is really important for your company, since it’s where your customers sign up for your service. You and your team have a few theories about why your current page isn’t performing well, but you decide to apply the critical thinking process to ensure you come to the best decision for the page.
Gather information about how the problem started
Part of identifying the problem includes understanding how the problem started. The pricing and packaging page is important—so when your team initially designed the page, they certainly put a lot of thought into it. Before you begin researching how to improve the page, ask yourself:
Why did you design the pricing page the way you did?
Which stakeholders need to be involved in the decision making process?
Where are users getting stuck on the page?
Are any features currently working?
Step 2: Then gather information and research
In addition to understanding the history of the pricing and packaging page, it’s important to understand what works well. Part of this research means taking a look at what your competitor’s pricing pages look like.
Ask yourself:
How have our competitors set up their pricing pages?
Are there any pricing page best practices?
How does color, positioning, and animation impact navigation?
Are there any standard page layouts customers expect to see?
Step 3: Organize and analyze information
You’ve gathered all of the information you need—now you need to organize and analyze it. What trends, if any, are you noticing? Is there any particularly relevant or important information that you have to consider?
Step 4: Consider alternative viewpoints to reduce bias
In the case of critical thinking, it’s important to address and set bias aside as much as possible. Ask yourself:
Is there anything I’m missing?
Have I connected with the right stakeholders?
Are there any other viewpoints I should consider?
Step 5: Determine the most logical solution for your team
You now have all of the information you need to design the best pricing page. Depending on the complexity of the design, you may want to design a few options to present to a small group of customers or A/B test on the live website.
Step 6: Communicate your solution to stakeholders
Critical thinking can help you in every element of your life, but in the workplace, you must also involve key project stakeholders . Stakeholders help you determine next steps, like whether you’ll A/B test the page first. Depending on the complexity of the issue, consider hosting a meeting or sharing a status report to get everyone on the same page.
Step 7: Reflect on the results
No process is complete without evaluating the results. Once the new page has been live for some time, evaluate whether it did better than the previous page. What worked? What didn’t? This also helps you make better critical decisions later on.
Tools and techniques to improve critical thinking skills
As the importance of critical thinking continues to grow in academic and professional settings, numerous tools and resources have been developed to help individuals enhance their critical thinking skills. Here are some notable contributions from experts and institutions in the field:
Mind mapping for better analysis
Mind mapping is a visual technique that helps organize and structure information. It's particularly useful for synthesizing complex ideas and identifying connections between different concepts. The benefits of mind mapping include:
Enhancing creativity by encouraging non-linear thinking
Improving memory and retention of information
Facilitating brainstorming and idea generation
Providing a clear overview of complex topics
To create a mind map:
Start with a central idea or concept.
Branch out with related sub topics or ideas.
Use colors, symbols, and images to enhance visual appeal and memorability.
Draw connections between related ideas across different branches.
Mind mapping can be particularly effective in project planning , content creation, and studying complex subjects.
The Socratic Method for deeper understanding
The Socratic Method, named after the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, involves asking probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas. This technique is widely used in higher education to teach critical thinking. Key aspects of the Socratic Method include:
Asking open-ended questions that encourage deeper reflection
Challenging assumptions and preconceived notions
Exploring the implications and consequences of ideas
Fostering intellectual curiosity and continuous inquiry
The Socratic Method can be applied in various settings:
In education, to encourage students to think deeply about subject matter
In business, it is important to challenge team members to consider multiple points of view.
In personal development, to examine one's own beliefs and decisions
Example: A high school teacher might use the Socratic Method to guide students through a complex ethical dilemma, asking questions like "What principles are at stake here?" and "How might this decision affect different stakeholders?"
SWOT analysis for comprehensive evaluation
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a strategic planning tool that can be applied to critical thinking. It helps in evaluating situations from multiple angles, promoting a more thorough understanding of complex issues. The components of SWOT analysis are:
Strengths: internal positive attributes or assets
Weaknesses: internal negative attributes or limitations
Opportunities: External factors that could be beneficial
Threats: External factors that could be harmful
To conduct a SWOT analysis:
Clearly define the subject of analysis (e.g., a project, organization, or decision).
Brainstorm and list items for each category.
Analyze the interactions between different factors.
Use the analysis to inform strategy or decision-making.
Example: A startup might use SWOT analysis to evaluate its position before seeking investment, identifying its innovative technology as a strength, limited capital as a weakness, growing market demand as an opportunity, and established competitors as a threat.
Critical thinking resources
The Foundation for Critical Thinking : Based in California, this organization offers a wide range of resources, including books, articles, and workshops on critical thinking.
The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking : This council provides guidelines and standards for critical thinking instruction and assessment.
University of Louisville : Their Critical Thinking Initiative offers various resources and tools for developing critical thinking skills.
The New York Times Learning Network provides lesson plans and activities to help develop critical thinking skills through current events and news analysis.
Critical thinking frameworks and tools
Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework : Developed by Dr. Richard Paul and Dr. Linda Elder, this framework provides a comprehensive approach to developing critical thinking skills.
Bloom's Taxonomy : While not exclusively for critical thinking, this classification system is widely used in education to promote higher-order thinking skills.
The California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory (CCTDI) : This assessment tool measures the disposition to engage in problems and make decisions using critical thinking.
The Ennis-Weir Critical Thinking Essay Test : Developed by Robert Ennis, this test assesses a person's ability to appraise an argument and to formulate a written argument.
By incorporating these tools and techniques into regular practice, individuals can significantly enhance their critical thinking capabilities, leading to more effective problem-solving, decision-making, and overall cognitive performance.
Critically successful
Critical thinking takes time to build, but with effort and patience you can apply an unbiased, analytical mind to any situation. Critical thinking makes up one of many soft skills that makes you an effective team member, manager, and worker. If you’re looking to hone your skills further, read our article on the 25 project management skills you need to succeed .
Related resources

10 tips to improve nonverbal communication

Scaling clinical trial management software with PM solutions
4 ways to establish roles and responsibilities for team success
6 ways to develop adaptability in the workplace and embrace change

Thesoldiersproject is supported by its audience. When you buy through our links, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
All About the 7-Step Military Problem Solving Process
Written by Everett Bledsoe / Fact checked by Brain Bartell

In addition to power and strength, the military relies on quick and decisive thinking. Members in service must be able to think on their feet and craft solutions in the blink of an eye. Obviously, this is not easy to do. But it is not too far-fetched when you realize that countless lives depend on a single personnel’s decision and course of action.
As such, every recruit coming into the military is taught and trained about the 7-step military problem solving process. This systematic approach is believed to be the best way for military members to address any problems that they encounter.
In short, the 7 steps to solve problems are:
- Pinpoint the Problem
- Identify the Facts and Assumptions
- Craft Alternatives
- Analyze the Generated Alternatives
- Weigh Between the Generated Alternatives
- Make and Carry Out Your Final Decision
- Evaluate the Results From Your Decision
To make it easier for you to comprehend and follow along, we have elaborated on each of the above steps in this article. So, continue reading by scrolling down!
Table of Contents
Step 1: Pinpoint the Problem
Step 2: identify the facts and assumptions, step 3: craft alternatives, step 4: analyze the generated alternatives, step 5: weigh between the generated alternatives, step 6: make and carry out your final decision, step 7: evaluate the results from your decision, army problem solving & decision making process, seven step military problem solving process.

The first step is to ID the problem, which means recognizing and identifying what needs fixing. Needless to say, you cannot attempt to seek a solution without first knowing what has to be addressed. By pinpointing your problem, you will have a clear goal or end destination in mind. Only then can you come up with the right steps to take.
To effectively define the problem, ask yourself the 5Ws—who, what, where, and when. In detail:
- Who is affected? Who is involved?
- What is affected? What is in the overall picture?
- When is/did this happen?
- Where is/did this happen?
Always be crystal clear about the problem and try to view it in the most objective way as much as possible. Imagine you are the third person looking at It rather than from it. It also helps to organize your answers into a coherent and concise problem statement.
The next step is to ID the facts and assumptions. This entails that you get whatever additional information you can in the time that you have. Try to garner more facts than assumptions by reviewing all the possible factors, internal and external, and use them together with what you have thought out in the step above to determine the cause of the problem. You should also be aware of the nature and scope of the problem from this step.
From here, you take a sub-step: think about what you want the final result to be. This does not have to be complicated but it has to be very clear. For instance, one of your troop members may be lost and uncontactable. Your ultimate goal is to find him/her and return to your base together. Remember, having a wishy-washy end state will only make your problem solving process more difficult.
These first two steps constitute situation assessment, which serves as the basis for you to work towards the remaining steps of the military problem solving process.
Onto the third step, strive to develop as many potential solutions as possible. Here, you will have to exercise your imagining and visualizing skills. Brainstorm and refine any ideas simultaneously. Engage both critical and critical thinking in this step. If possible, take note of what you have come up with. Do not be hesitant and brush off any ideas.
Then, analyze your options. Consider all of your possible courses of action with all the available information that you have compiled in the previous steps. Take into account your experiences, intuitions, and emotions. This does not have to be a purely rational or mathematical procedure. Nevertheless, this does not mean that you are 100% guided by your instincts and emotions. You must have a good balance between the two.
This step naturally lends itself to the next: compare between your generated alternatives. Weigh between their respective pros and cons. In particular, look at their cost and benefit of success. Are there any limiting factors or potential for unintended consequences? Evaluate carefully and ask yourself a lot of questions. You can also consider using a table, T-chart, or matrix to compare visually.
Try to settle for the “best” solution or course of action that is both logical and feels “right”. Apart from picking the best, select two or three more workable solutions as backups. Keep them handy in case you need to refer back to them. During this process, you may merge ideas and mix-match bits and pieces—that’s perfectly fine!
Once you have made your decision, craft your action plans. Know the details—what exactly do you have to do to solve the problem? If it is a long-term problem that you have to address, set milestones and timelines with clear methods of measuring progress and success. On the other hand, if it is a short, instantaneous problem, communicate your plans clearly to anyone else involved. Be aware of the specifics and be brutally honest. Execute your course of action with care. But do not be rigid. If something happens out of the plan, be willing to adjust and adapt.
After your solution implementation, wrap up by assessing the results. Was it what you envisioned? Were there deviations? What did you take away? Answer all of the questions so you can be even more equipped for future endeavors. Think of it as a reflection stage. The 7 steps to problem solving in the military are a continuous process—you will be confronted with challenges over and over, so do not skip this strengthening step. It will further your skills and expertise to handle problems going forward.

Another set of seven steps that you may come across during your service is the army problem solving steps. Needless to say, this is applied to the army problem solving process.
- Receiving the Mission
- Analyzing the Mission
- Developing the Course of Action
- Analyzing the Course of Action
- Comparing the Course of Action
- Getting Approval for the Course of Action
- Producing, Disseminating, and Transitioning Orders
This is a part of the MDMP, short for the military decision making process. In each step, there are inputs and outputs. In general, it is more specific than the above set of steps.
These seven steps focus on collaborative planning and performance. Plus, set the stage for interactions between different military agents, including commanders, staff, headquarters, etc.
COA is an abbreviation for a course of action. Thus, these steps are relatively similar to the steps that we have gone through earlier; specifically steps two: mission analysis, three: COA development, four: COA analysis, and five: COA comparison. Like the previous seven steps, these are carried out sequentially but can be revisited when needed.
The main difference is that these 7 steps to problem solving in the army are more explicitly directed to junior personnel. Hence, the mentioning of orders from higher-ranks, the significant role of commanders, and the need to earn approval before execution.
A mnemonic that service members use to remember this process is M.A.D.A.C.A.P. for:
- A: Analysis
You might want to remember this for an exam at military school, at NCO, or soldier of the month board.
You can learn more about the MDMP here:
So, there you have it—the 7-step military problem solving process. You should now be aware of two different but equally important sets of steps to problem solving and decision making. If you have any follow-up questions or thoughts, let us know in the comments. We look forward to hearing from you!

I am Everett Bledsoe, taking on the responsibility of content producer for The Soldiers Project. My purpose in this project is to give honest reviews on the gear utilized and tested over time. Of course, you cannot go wrong when checking out our package of information and guide, too, as they come from reliable sources and years of experience.
What are the 7 Steps to Problem-Solving? & Its Examples
By Teach Educator
Published on: February 4, 2024
7 Steps to Problem-Solving
7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a systematic process that involves analyzing a situation, generating possible solutions, and implementing the best course of action. While different problem-solving models exist, a common approach often involves the following seven steps:
Define the Problem:
- Clearly articulate and understand the nature of the problem. Define the issue, its scope, and its impact on individuals or the organization.
Gather Information:
- Collect relevant data and information related to the problem. This may involve research, observation, interviews, or any other method to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Generate Possible Solutions:
- Brainstorm and generate a variety of potential solutions to the problem. Encourage creativity and consider different perspectives during this phase.
Evaluate Options:
- Assess the strengths and weaknesses of each potential solution. Consider the feasibility, potential risks, and the likely outcomes associated with each option.
Make a Decision:
- Based on the evaluation, choose the most suitable solution. This decision should align with the goals and values of the individual or organization facing the problem.
Implement the Solution:
- Put the chosen solution into action. Develop an implementation plan, allocate resources, and carry out the necessary steps to address the problem effectively.
Evaluate the Results:
- Assess the outcomes of the implemented solution. Did it solve the problem as intended? What can be learned from the process? Use this information to refine future problem-solving efforts.
It’s important to note that these steps are not always linear and may involve iteration. Problem-solving is often an ongoing process, and feedback from the implementation and evaluation stages may lead to adjustments in the chosen solution or the identification of new issues that need to be addressed.
Problem-Solving Example in Education
- Certainly: Let’s consider a problem-solving example in the context of education.
- Problem: Declining Student Engagement in Mathematics Classes
Background:
A high school has noticed a decline in student engagement and performance in mathematics classes over the past few years. Students seem disinterested, and there is a noticeable decrease in test scores. The traditional teaching methods are not effectively capturing students’ attention, and there’s a need for innovative solutions to rekindle interest in mathematics.
Steps in Problem-Solving
Identify the problem:.
- Clearly define the issue: declining student engagement and performance in mathematics classes.
- Gather data on student performance, attendance, and feedback from teachers and students.
Root Cause Analysis
- Conduct surveys, interviews, and classroom observations to identify the root causes of disengagement.
- Identify potential factors such as teaching methods, curriculum relevance, or lack of real-world applications.
Brainstorm Solutions
- Organize a team of educators, administrators, and even students to brainstorm creative solutions.
- Consider integrating technology, real-world applications, project-based learning, or other interactive teaching methods.
Evaluate and Prioritize Solutions
- Evaluate each solution based on feasibility, cost, and potential impact.
- Prioritize solutions that are likely to address the root causes and have a positive impact on student engagement.
Implement the Chosen Solution
- Develop an action plan for implementing the chosen solution.
- Provide training and resources for teachers to adapt to new teaching methods or technologies.
Monitor and Evaluate
- Continuously monitor the implementation of the solution.
- Collect feedback from teachers and students to assess the effectiveness of the changes.
Adjust as Needed
- Be willing to make adjustments based on ongoing feedback and data analysis.
- Fine-tune the solution to address any unforeseen challenges or issues.
Example Solution
- Introduce a project-based learning approach in mathematics classes, where students work on real-world problems that require mathematical skills.
- Incorporate technology, such as educational apps or interactive simulations, to make learning more engaging.
- Provide professional development for teachers to enhance their skills in implementing these new teaching methods.
Expected Outcomes:
- Increased student engagement and interest in mathematics.
- Improvement in test scores and overall academic performance.
- Positive feedback from both teachers and students.
Final Words
This problem-solving approach in education involves a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and addressing issues to enhance the learning experience for students.
Related Post
Use of youtube in education and its benefits – latest update.
Use of YouTube in Education YouTube in education refers to the use of YouTube videos and the YouTube platform for educational purposes. It involves integrating YouTube videos into ...
How is YouTube used in the classroom? New Update
YouTube used in the classroom YouTube used in the classroom: YouTube is used in various ways in classrooms to enhance learning experiences and engage students. Here are some ...
What are the 4 types of chatbots? And Its Benefits – Latest
The 4 types of chatbots 4 types of chatbots: A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate conversation with human users, especially over the internet. Chatbots are ...
What are a chatbot and what example?
A chatbot and what example A chatbot is a computer program or artificial intelligence (AI) system designed to simulate conversation with human users through text or voice interactions. ...
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest Post
What is the purpose of youtube for students new update, why is youtube important to us, teach educator.
"Teach Educator aims to empower learners and educators alike through its comprehensive services. Dedicated to bridging educational gaps, it offers a range of resources designed to enhance teaching methodologies, provide updated curriculum insights, and foster professional development. With a commitment to accessibility, Teach Educator ensures that educational tools and information are readily available to all, promoting inclusivity in learning.
© Teach Educator 2021 - 2024 | All Rights Reserved
Privacy policy
Product Marketing Strategy: Definition, Steps, and Examples
12 min read

Product marketing is the process of bringing a product to market, and a well-curated product marketing strategy is key to understanding customer needs and driving adoption.
In this article, we explore the key steps product managers follow to create a successful product marketing strategy, including some successful real-world examples. Let’s dive in!
- A product marketing strategy is a roadmap for how a new product will be positioned, priced, and marketed.
- Product marketing focuses on getting products into the hands of the right users, whereas product management focuses on developing the product.
- The first step to creating a successful product marketing strategy is to set SMART goals and define your objectives.
- Next, you need to conduct market research to understand your competition and business landscape and to define your target audience and user personas .
- You’ll also need to outline your product’s positioning and messaging, decide on a pricing strategy , and create a comprehensive go-to-market strategy.
- Finally, put together the elements needed to launch your product and select key metrics for measuring your performance.
- There are different types of product marketing strategies that you can combine to drive user acquisition and retention .
- Customer acquisition strategies include strategies like content marketing , free trial offers , attractive lead magnets, referral programs, and partnerships with other SaaS companies.
- For retention purposes, you can implement growth loops , host interactive webinars , provide personalized user experiences, and announce new features in-app to existing customers.
- Whether your goal is retention or acquisition, your product marketing efforts can benefit from Userpilot’s extensive features. Book a demo today to learn more!
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

What is a product marketing strategy?
A product marketing strategy is a roadmap for how a new product will be positioned, priced, marketed, and launched.
It is a merger between product development and sales to ensure a product satisfies specific customer needs and business goals.
Product marketing vs. product management
Although they’re often intertwined, product marketing and product management serve different roles.
Product management focuses on product development. It is concerned with identifying customer needs, defining the product vision and roadmap, and ensuring accurate and timely delivery of the product.
Conversely, product marketing focuses on getting the product into the hands of the right users. It’s concerned with the product’s positioning and messaging, pricing strategy, and go-to-market strategy.
Thus, the goal of product managers is to build the right product and get it ready for launch, while a product marketing manager aims to launch the product successfully and make it into a revenue-generating asset.

How to create a successful product marketing strategy
Although there’s no one-size-fits-all product marketing strategy template, the steps below can guide your process.
1. Set SMART product marketing goals
Setting goals for your efforts will guide your strategy and keep you on track.
Of course, goals for different businesses will vary. It’s important, however, that your goals are always SMART : S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound.
For example, rather than just setting a vague goal of “increasing revenue,” you can set a SMART goal of “increasing the monthly recurring revenue (MRR) by 20% over the next quarter.
This goal is specific and measurable (20% increase in MRR). It is also realistic and achievable (depending on your business) and bound by a defined timeframe (a quarter).

2. Conduct market research
With your goals firmly in mind, it’s time to begin your research. First, you want to understand your competitors and the business landscape you’re coming into.
Conduct in-depth research into your competitor’s products, marketing strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. Your research should answer questions like:
- How do customers perceive their product?
- What customer needs have they failed to meet?
- How do they communicate their messaging?
- What are their pricing strategies and how are they perceived?
Known as landscape research, this should help you identify market opportunities, assess market potential (including its overall size and growth potential), and mitigate risks (such as changing regulations).
3. Define your target audience and user personas
Once you understand the overall market and competition, you can enter phase two of your market research: your potential customers . Your goal for this phase is to identify your target market and user/buyer personas .
A user persona highlights the profile(s) of the ideal person who will use your product, while a buyer persona highlights the profile(s) of your product’s ideal buyer .
Depending on your product, these may not be the same persons. However, both can serve the same purpose of defining your marketing direction.
If your product has more than one “ideal” group of users, create a persona for each. Each persona should highlight the user’s unique needs, challenges, and pain points .
Understanding your customers and creating a specific profile for them will help ensure that all aspects of your product marketing strategy resonate with your target audience.

4. Solidify your product positioning and messaging
Finally, you can turn your attention to your product. For this step, you need to answer questions like:
- What challenges does our product solve?
- What sets it apart from the competition?
- Which key features address customers’ needs?
- Why should customers trust the product?
The answers to these questions will help you identify your product’s differentiators and define its positioning. This positioning defines where your product fits in the market and its unique value proposition (UVP).
Sum up these points in a product positioning statement . This concise document highlights your target customers, problems solved, and UVP.

Armed with this, you can then craft your product’s messaging . Unlike the positioning statement, your messaging is external-facing. It builds on the positioning statement using taglines, slogans, and other messages that can be tailored to specific customer needs.
5. Decide on your pricing strategy
So, you’ve completed your analysis, positioned your product, and defined your personas. Next up is your pricing strategy – a crucial aspect of any successful product marketing strategy.
A very high price may cost out customers, while a meager price could be considered low quality. To help you get it right, you can choose from several pricing strategies, including:
- Competitor-based pricing : Also known as “competitive pricing,” this strategy involves setting your prices based on what your competitors charge for similar products.
- Cost-plus pricing : This strategy involves summing up the total production cost (materials, overhead, and labor) and adding a markup (percentage profit) to determine your selling price.
- Value-based pricing : Value-based pricing is based on what customers are willing to pay, rather than the cost of production. It, therefore, depends on the product’s perceived value to the customer.
- Penetration pricing : This strategy involves setting a low initial price to penetrate the market, which is increased once a significant market share is established.
- Price skimming : The opposite of penetration pricing, this strategy involves setting a high initial price to capture early adopters willing to pay a premium. The price is then lowered over time to attract more customers.
6. Create a product launch plan
The product launch plan is the most important part of any product marketing strategy. Known also as the go-to-market strategy , it provides an exhaustive plan for the internal and external aspects of the launch.
The internal aspect covers the roles of your product, marketing, and sales teams during the launch. It should also outline the timelines for different launch activities and the launch budget.
Your sales and marketing teams will then come together to define the external aspects of the launch. This involves answering questions like:
- Will you be deploying social media marketing – and how?
- What other marketing channels do you need?
- Which promotional materials do you need (website landing pages, blog articles, demo videos, etc.)?
- Should there be a big public launch event?
7. Launch the product
This part of your strategy covers the execution of your product launch plan. This is also the time to organize all the materials needed for the launch.
For instance, you may choose to launch in-app to reach your existing customers. In this case, you’ll need an in-app messaging platform to convey your message and a copy that encourages engagement.

You may also want to reach a wider audience using external platforms. SaaS products, for example, can especially benefit from launching to the tech community on ProductHunt .
Again, you’ll need a concise copy announcing the product’s features. You can also provide a demo video and images to boost interaction.

8. Measure product performance to identify gaps
Following the launch, product marketers need to track the product’s success and identify gaps. This means monitoring metrics like adoption rates, sign-ups, engagement, etc.
If you settled for a free trial pricing model, for example, you can compare the number of free trial sign-ups to the number of users that convert to paying customers .
A high conversion rate indicates your product’s acceptance among your target audience. If the rate is low, however, you’ll need to dig further (through surveys, interviews, etc.) to understand why.
9. Continuously Iterate and refine your product marketing strategy
The final part of your post-launch strategy should highlight what you can do to improve your product’s adoption. This involves creating plans for data-driven adjustments to your product marketing strategy.
When you identify a gap, for instance, you can conduct A/B tests to experiment with what works and what doesn’t.
For example, if the response to your new feature announcement is low, you can experiment with its placement, copy, media, or CTA to better encourage engagement.

13 Best product marketing strategies to implement
Now that you know how to create a product marketing strategy, let’s explore some strategies that can inspire your own.
1. Create product-led content to attract potential customers
The content marketing strategy focuses on creating content around your product’s features, benefits, and use cases. The goal is to educate potential customers and establish your product as a valuable solution.
For example, you can develop blog posts highlighting how your product solves specific customer pain points while implementing SEO best practices to optimize your content for search engines.
Userpilot, for instance, creates content around topics like user onboarding to address the needs of its target audience – product marketers.

Try Userpilot and Take Your Marketing Strategy to the Next Level
2. implement growth loops for your saas products.
Growth loops are self-sustaining cycles that drive user acquisition, activation, retention, and revenue. A growth loop depends on certain key user actions to trigger growth.
For instance, you can include features encouraging users to invite others, such as collaboration tools or social sharing options. This increases your market share while reducing your customer acquisition costs .
Calendly does this by making its tool into one huge promotional material. Upon sharing your Calendly link with someone, a small banner notifies the viewer that the service is provided by Calendly.

3. Provide free trials to showcase product value
Offering a free trial allows potential customers to experience your product firsthand. During the free trial, customers can test your product’s features and see how it solves their problems.
It, thus, enables you to showcase the product’s value and increase the likelihood of conversion.
This free trial approach is central to the product marketing strategy of the social media management platform, Later. As soon as you reach their landing page , you’re invited to sign up for a free trial.

4. Conduct webinars to engage users
As a product marketing strategy, webinars enable you to educate, engage, and build a relationship with your audience.
Their video-based nature, storytelling capability, and interactive features make them well-suited to driving user engagement and improving retention.
Userpilot takes advantage of this to the fullest, incorporating webinars addressing pertinent industry topics or showcasing product features into its marketing strategy.

5. Provide personalized experiences to your customers
For SaaS products, a good customer experience is one of your greatest marketing assets. By tracking user behavior , you can tailor their experience to better suit their needs, enhancing customer satisfaction.
For example, you can make product recommendations based on user behavior. You can also target specific user groups with surveys, onboarding tutorials, etc., that improve their experience.

6. Announce new features in-app to existing customers
While you may aim to attract new customers with new feature announcements , do not neglect your already existing customers. In-app announcements generate excitement and aid feature discovery .
It also ensures that users who need the feature or may have requested it know of its existence. This improves user satisfaction, boosts adoption and engagement rates, and reduces churn.

7. Create efficient lead magnets to attract customers
Lead magnets are a trade-by-barter approach to marketing. You offer a potential customer some valuable information, and they share their contact in exchange.
Lead magnets can take different shapes, including:
- Industry reports.
- Industry reports
- Checklists, etc.
For example, Userpilot conducts an extensive annual study to determine the product metric averages for different SaaS products and industries.
This valuable resource helps product marketers examine how their product is faring within their industry and is only offered for the “price” of an email address.

8. Leverage referral programs to attract prospective customers
Referral marketing aims to turn your customers into your biggest marketers by offering them certain incentives. These incentives could come in the form of useful loyalty points, discounts, or other rewards.
Dropbox, for example, offers 500MB of free space for customer referrals. Customers can earn up to 16GB of free storage through referrals, making it an attractive “side quest” for them.

9. Use contextual emails to reengage inactive users
Send targeted emails based on user behavior to remind them of the product’s value and encourage them to return.
To be successful, your re-engagement email should highlight your product’s benefits, be tailored to their needs, and include a clear call-to-action (CTA).
For example, this email from Grammarly aims to create a nostalgic feeling around their product while providing a huge CTA button.

10. Share case studies from successful customers
Sharing your product’s success stories as case studies taps into the human need for social proof to build trust and credibility. A good case study should highlight your product’s success and how it was used.
For example, this case study explains how Attention Insight – an AI-powered tool offering heatmap analysis – improved its user activation rate by 47% within 6 months of using Userpilot.

11. Showcase your SaaS product through strategic video marketing
Videos are powerful tools for demonstrating your product features, telling your brand story, and connecting with your audience.
Ahrefs uses them to good effect, providing a huge catalog of videos on YouTube. These videos offer free education on SEO basics and best practices while positioning Ahrefs as the user’s best SEO support tool.

12. Partner with other companies to reach a wider target market
Collaborating with complementary businesses can expand your reach and introduce your product to a new audience.
One of the simplest ways to do this is by identifying complementary businesses and creating co-marketing campaigns, such as joint webinars or content collaborations.
You can also offer integrations with other tools to make it easier for users to use your product. This is what Bonjoro, a video engagement platform, did when it integrated ActiveCampaign, tripling its user base in the process.

13. Prompt upgrades with contextual in-app messages
Tracking your user’s in-app behaviors enables you to identify opportunities for upsell or cross-sell. You can offer them premium features or additional products that fit their contextual need.
For example, Loom offers only 5 minutes of recording time to freemium users. When a user hits the 5-minute mark, a contextual prompt informs them they can record for longer with a premium upgrade.

There are many different approaches to product marketing. By combining some of the strategies above, you can create a comprehensive plan that drives customer acquisition, engagement, and retention.
From segmentation to contextual messaging, in-app analytics, and more, Userpilot provides valuable tools for executing your strategy. Book a demo to learn more!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Product marketing messaging framework: key elements & examples.
Aazar Ali Shad
16 Best Product Marketing Campaigns To Inspire Your Own

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data ...
The 7 steps to problem-solving. When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication. 1. Define the problem. Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand.
To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn. This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process ...
CIRCLES stands for the 7 steps it takes to solve a problem: C omprehend the situation. I dentify the Customer. R eport the customer's needs. C ut, through prioritization. L ist solutions. E valuate tradeoffs. S ummarize recommendation. CIRCLES framework for problem-solving.
Analyze the facts to obtain root cause (s) of the performance gap. Select a solution. Conduct a pilot test. Evaluate performance. Standardize the gains, reflect, and repeat the process. Let's cover each of these steps in a little more detail. 1. Select the Issue. Start with the voice of the customer.
The 7 step problem solving guide provided below has been created to help solve problems where the solution or in some cases the problem itself is not obvious. STEP 1: The Right Problem to Solve. STEP 2: Analyse the Problem. STEP 3: Define the Problem. STEP 4: Develop Opportunities (Possible Solutions)
Here are a few tips for effective problem solving: Stay Objective -Keep an open mind and avoid assumptions. Focus on facts and data. Communicate Clearly -Ensure that all stakeholders are informed and involved in the process. Think Creatively -Encourage innovative thinking and be open to unconventional solutions.
Step 3) - "Investigate" - Pitfalls. This is often the area of biggest weakness, apart from Problem Framing in Step 1 above. When it comes to problem solving there are two major tools - Fishbone (aka Ishikawa diagram) and the 5 Whys. There are others, these are just the most common and useful.
Step 6: Implement the Solution. Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn't work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part ...
When to use the 7-Step Problem Solving Method •The 7-Step Method is used for solving problems where the solution is not obvious. •Quality Improvement teams most commonly use the 7- Steps to respond to a known defect or weakness such as late deliveries, yield loss or product failure. •Managers can use the 7-Steps process to make sure
The 7 steps to problem-solving is a disciplined and methodical approach to identifying and then addressing the root cause of problems. Instead, a more robust approach involves working through a problem using the hypothesis-driven framework of the scientific method. Each viable hypothesis is tested using a range of specific diagnostics and then recommendations are made.
The McKinsey Podcast. Management. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges. Episode Website. More Episodes. 2024 McKinsey & Company. More ways to shop: Find an Apple Store or other retailer near you. Or call 1-800-MY-APPLE. Choose your country or region.
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further ...
The detailed step-by-step process is as follows: Step 1: This step aims to identify the problem and then assess its impact on end-users (e.g., product buyers, product users). Sometimes, there may not be a problem. For instance, an experiment with an engineering work or negative testing took place. Step 2: Once it's identified as a problem, we ...
A comprehensive guide to problem solving, complete with these 9 essential tools: Tool 1: When you don't know what to do. Tool 2: Defining questions for problem solving. Tool 3: Finding the right problems to solve. Tool 4: Problem solving check-list. Tool 4a: Using the question check-list with your team.
A comprehensive guide to problem solving, complete with these 9 essential tools: Tool 1: When you don't know what to do. Tool 2: Defining questions for problem solving. Tool 3: Finding the right problems to solve. Tool 4: Problem solving check-list. Tool 4a: Using the question check-list with your team. Tool 5: Problem analysis in 4 steps.
The Idea Generation stage is the first step in the product development process. This is, of course, where new product ideas are brainstormed and 'put on paper'. ... Problem-Solving: Clearly state the problem the idea aims to solve. Define the target audience and their specific pain points. Complexity: Evaluate the complexity of developing ...
STEP 3: Define the Problem. STEP 4: Develop Opportunities (Possible Solutions) STEP 5: Select the Best Solution. STEP 6: Implement the Solution. STEP 7: Evaluate and Learn. STEP 1: Identify the problem. The first step is to define the problem that you have. Generating a robust problem definition is key to the whole process.
There are two main differences between the two processes. In the illustration, the team formation (step 1 in Figure 8D) and the conclusion of the problem-solving process (step 8 in 8D) are not present in 7STEP. However, in theory, these steps also exsist in 7STEP, as in you start by gathering a team and you end with a final conclusion.
This process of communicating and sharing ideas is key in promoting critical thinking within a team or organization. By encouraging open dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, you create an environment that fosters the development of critical thinking skills in others. 7. Reflect and learn from the process.
So, continue reading by scrolling down! Table of Contents. Seven Step Military Problem Solving Process. Step 1: Pinpoint the Problem. Step 2: Identify the Facts and Assumptions. Step 3: Craft Alternatives. Step 4: Analyze the Generated Alternatives. Step 5: Weigh Between the Generated Alternatives.
7 Steps to Problem-Solving. 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a systematic process that involves analyzing a situation, generating possible solutions, and implementing the best course of action. While different problem-solving models exist, a common approach often involves the following seven steps: Define the Problem: Clearly articulate and ...
Title: Five Steps of Problem Solving Author: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Keywords: problem solving Created Date: 8/1/2024 6:48:36 PM
Product marketing is the process of bringing a product to market, and a well-curated product marketing strategy is key to understanding customer needs and driving adoption. In this article, we explore the key steps product managers follow to create a successful product marketing strategy, including some successful real-world examples.