How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)

The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.

Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
In addition, a powerful thesis introduction is well-written, logically structured, and free of grammar and spelling errors. Reputable thesis editors can elevate the quality of your introduction to the next level. If you are in search of a trustworthy thesis or dissertation editor who upholds high-quality standards and offers efficient turnaround times, I recommend the professional thesis and dissertation editing service provided by Editage .
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
Open with a (personal) story.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
This story can be, for instance, based on one of your study participants. It can also be a very personal account of one of your own experiences, which drew you to study the thesis topic in the first place.
| |
Start by providing data or statistics
Data and statistics are another established way to immediately draw in your reader. Especially surprising or shocking numbers can highlight the importance of a thesis topic in the first few sentences!
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
| , 2022)! While awareness of marine pollution is increasing, there is a lack of concrete actions to tackle this environmental problem. In this thesis, I provide a comparative analysis of interventions to reduce marine pollution in five European countries. |
Begin with a problem
Usually, at a later stage in the introductory chapter, it is common to go more in-depth, describing the research problem (and its scientific and societal relevance) in more detail.
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Define a clear research gap
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
| “ ” (Liu and Agur, 2022: 2)*. |
Describe the scientific relevance of the thesis
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
Describe the societal relevance of the thesis
Formulating a compelling argument.
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences
Support your argument with sufficient evidence.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
Consider possible objections
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Address the empirical research context.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
| . As a consequence, the marine and terrestrial ecosystems of the Islands are increasingly disrupted. |
Give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis
Hint at the practical implications of the research.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
| . . . |
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
Provide a reading guide.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
Briefly summarise all chapters to come
Design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, the most useful academic social networking sites for phd students, 10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles, how to write a literature review introduction (+ examples), why you cannot write a phd thesis in 3-6 months, first meeting with your dissertation supervisor: what to expect, 5 inspiring phd thesis acknowledgement examples.
- AI Detector and Humanizer
- Business Solutions
- Try it Free
How to Write a Thesis Introduction (with Examples)

As Ralph Waldo Emerson once said, “Sometimes a scream is better than a thesis.” While it’s ironically the case for many, writing a thesis is basically the culmination of your hard work.
There’s a certain pride in accomplishing such a task, and many people hold it close to their hearts throughout their lifetimes.
This showcases a student’s ability to contribute original insights to their field and opens many more doors to broaden their academic and professional opportunities. Finishing a thesis certainly has weight.
The great thing about education today is that technology can help make things easier. AI tools, for instance, can assist with writing research papers and doing thesis work.
Even teachers can utilize the power of AI to improve their ways of teaching – but more on the exciting AI stuff later.
What you need to start with for your thesis is to create a strong introduction. Your thesis intro sets the tone for your entire work, so getting it right is important.
Here’s everything you need to know on how to write a thesis introduction that instantly catches the eye and informs effectively at a glance.
What Types of Information Should Be Included in Your Thesis Introduction?
After days and nights of researching, typing, and editing, the general average thesis length ends up at around 20-50 pages.
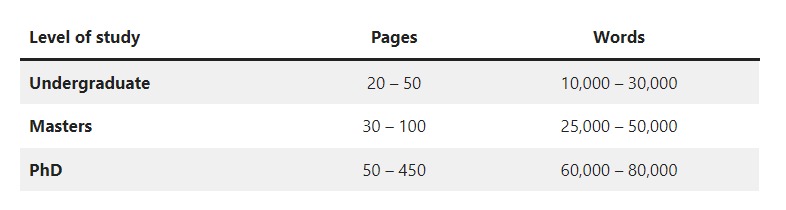
A PhD dissertation, usually tougher, can go up to 90-500 pages long. That’s a lot of work.
With so much information to showcase, your thesis intro should be able to make a big impression. A weak introduction can mislead your readers and even diminish the value of your entire thesis.
As the first impression of your work, the intro sets the stage by providing some context, highlighting the research problem, and laying out your objectives clearly.
It can be intimidating just thinking about it, so we’re here to make sure your thesis intro delivers the punch it needs. Here are some things that you should include.
Have an attention-grabbing opening
In the marketing world, you’ve only got eight seconds to grab a customer’s attention; that’s the average attention span.
While your teacher won’t drop your thesis if your introduction doesn’t grab them within seconds, having a great opening can still make a strong impact.
The main goal here is to present a compelling hook that sparks curiosity.
Include a surprising statistic, engage with a thought-provoking question, share a short but relatable anecdote, or try to be daring and make a bold statement that shocks but relates to your research topic.
There are many ways to do it, but ultimately, you want to engage your reader right from the start.
Provide context and the importance of the topic
“In this thesis, we will be exploring the effects of social media on communication.” Why, though? And what part of social media are we talking about here?
This is a bad example of a thesis intro because it lacks context.
Instead of simply choosing a controversial or topical subject to make an impact, you need to go deeper straight away.
The goal of providing context is to guide your reader in understanding why your topic is worth discussing in the first place.
You can offer a brief overview of already existing research and how you can add to it, and also show the gaps and unresolved issues that your study aims to fix.
Highlighting your topic goes to show that it’s an important matter to discuss in your field.
Engage through specific questions that your research addresses
One of the best ways to make your thesis intro stand out is by asking specific questions.
For example, if your research is about the effects of social media on traditional media, rather than just stating it outright, you can start off with an engaging question like “Is social media ending the age of the newspaper?”
In this way, you instantly grab the attention of your reader with a compelling question while still providing a sense of what your research will be about.
It’s a two-punch combo of showing immediate purpose and relevance while making your thesis intro easy to follow.
Frame your research in the form of specific and engaging questions so you can lay the groundwork for a more focused thesis.
Thesis Introduction Tips

So far, a good thesis introduction should be able to outline the main topic clearly, present some compelling questions, and provide context and significance for the study.
It’s definitely not easy, but there are ways to make it more doable. Here are some handy thesis introduction tips to help you out.
Know your audience
Knowing your audience means that you understand who will be reading your thesis. By doing this, you can create an introduction that meets their expectations and interests.
When writing a thesis intro, you should be able to consider the background, knowledge level, and interests of the thesis readers – your advisor, committee members, and other related academics.
Knowing this, you can set the right tone, which is usually formal, and engage in a way that interests them.
Refer to your thesis proposal or notes
If you want to make a seamless thesis paper, you will constantly need to refer to your proposal and notes.
You should refer to all the preliminary work that you’ve done to direct the writing of your introduction.
This can include your research questions, objectives, literature review, and methodology that you’ve outlined for your proposal.
It’s always important to go back and review your thesis notes regularly because these help you:
- Ensure that your thesis introduction is consistent with your original proposal.
- Present the main elements of your research.
- Organize your thoughts and create a well-structured introduction, contributing to your overall thesis flow.
Keep your thesis proposal and notes by your side. They will help you create a strong introduction that provides clear context for your research.
Use Assistant AI tools to help with writing and proofreading
Especially when it comes to writing, AI tools have become quite useful.
You might already be familiar with ChatGPT, which uses advanced algorithms to generate the needed content; it can even proofread text .
AI tools can be useful to writers and researchers by offering suggestions and writing parts of the work that they can improve later.
This makes the writing process a whole lot more efficient and much less time-consuming. With AI, you can essentially produce high-quality work under tight deadlines.
However, while AI tools are clearly helpful, it’s necessary that you still use them responsibly.
AI plagiarism is a growing concern that happens when any AI-generated content is presented as original work without giving the right acknowledgment.
This can severely damage the credibility of your research and even get you in trouble.
Treat AI as what it’s intended to be – a tool – rather than the main writer of your work. You should still be the writer of your own work.
To avoid any issue with AI, a reliable detector like Undetectable AI can be used to always make sure that your content passes as human-written.
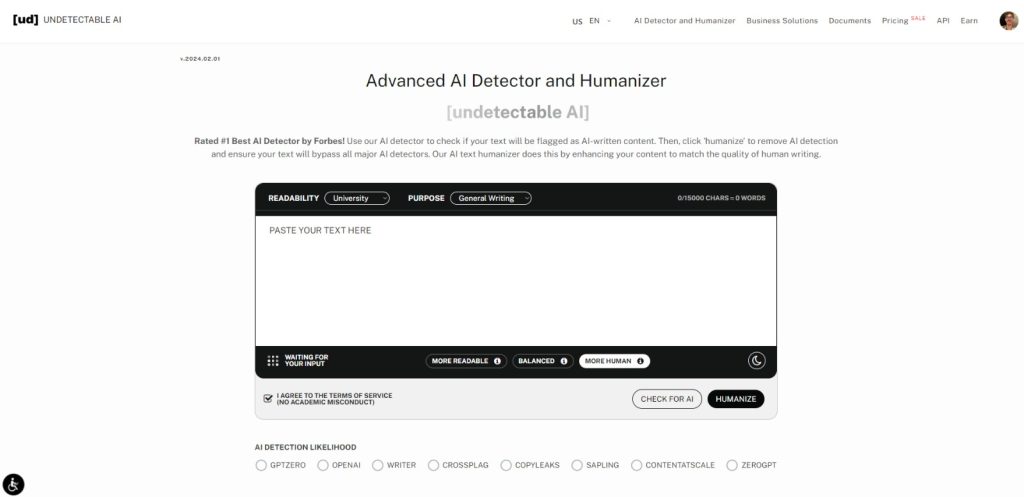
Undetectable analyzes any text you submit to effectively detect AI content. It also includes features like a humanizer that adjusts the writing to match a natural human tone .
We certainly don’t want to stop you from maximizing your potential with the help of AI, so with a useful AI detector and humanizer by your side, you can always get the results you want.
You can try Undetectable AI easily with the widget below (English only). Just input your text and see how it can transform your writing!
Make sure you clearly state your topic, aims, and objectives
This one is essential. Your thesis introduction should be able to clearly define what your research is about (topic), what you plan to accomplish (aims), and the steps you’re taking to get there (objectives).
It’s pretty straightforward and is a no-brainer, but you must do this for several reasons:
- Helps your readers understand the focus of your research right from the get-go.
- Sets clear expectations for your thesis.
- Establishes relevance, making your work highly credible.
- Easier assessment (whether you’ve achieved your goals) by your advisor and evaluators.
Remember, a well-defined introduction is your first step toward a successful thesis. Make it matter.
Explain why your research matters
If your thesis doesn’t make an impact in your field, then it might not be seen as valuable. So, from the start, be sure to explain why your research matters.
This provides a basis for why you’re choosing a specific topic in the first place and explaining why it deserves their attention.
To help, you can also link your research to real-world applications or social issues to enhance its appeal to the research community and beyond.
3 Thesis Introduction Examples to Inspire You

Writing a thesis introduction can be quite a challenge, but looking at examples can help you understand how to start your research on the right foot.
Communications Example
“Is social media ending the age of the newspaper?” This question frequently arises in discussions as the communication landscape continuously evolves.
Platforms like Facebook, X (previously called Twitter), and Instagram continue to grow, and their impact on traditional media – newspapers, television, and radio – becomes more significant and complex.
Social media has drastically changed how people access information. Unlike traditional media, which professional journalists and editors usually produce, social media allows anyone to create and share content.
This shift has huge implications for both media producers and consumers. Understanding these changes is important for professionals in the field and the general population.
This thesis aims to answer several questions: How has social media affected the credibility of traditional news sources?
What strategies are traditional media adopting to compete in a digital world? And how do today’s audiences perceive news found on social media vs traditional platforms?
By addressing these questions, this research seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current media landscape and provide some discourse on the future of communication and modern-day responsible journalism.
Environmental Science Example
Food production is one of the largest contributors to environmental damage.
The methods that we traditionally use to grow and raise our food have serious implications for resource use, greenhouse gas emissions, and land use.
So, we ask the question, “Can our food choices save the planet?”
As global populations rise and climate change accelerates, understanding the environmental impact of different food production systems has never been more important.
Plant-based agriculture and animal-based agriculture differ considerably, so studying these differences can help identify sustainable practices that minimize and ultimately prevent environmental damage.
This thesis aims to address how plant-based and animal-based food production systems compare in terms of resource use and environmental impact and what practices within these systems can reduce their impact on the environment.
Education Example
The global pandemic has made a dent in how we live, and that includes the state of education.
During this difficult time, schools and universities worldwide were essentially forced to shift to online learning almost overnight.
This sudden and widespread adoption of online learning presents a unique opportunity to assess its effectiveness and impact on education – past the pandemic.
If online learning is actually shown to be effective, it could lead to more flexible, accessible, and inclusive educational practices.
Conversely, if notable shortcomings are identified, this can highlight areas that need improvement to support students and educators better.
This thesis aims to identify the effectiveness of online learning in achieving educational outcomes compared to traditional classroom settings, the major challenges faced by students and educators during this transition, and how factors such as socioeconomic status and access to technology influence the effectiveness of online learning.
With this study, we can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of online education, contributing to the broader discussion of post-pandemic learning.
How do you start an introduction for a thesis?
To start a thesis introduction, start with a hook that draws the reader in and sets the stage for your research topic. Provide context by discussing the significance of the topic. Then transition into your thesis statement, which outlines the main argument or purpose of your research.
What is an example of a thesis statement in an introduction?
An example of a thesis statement in an introduction could be: “This thesis examines how social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly Twitter) have reshaped how individuals interact and form relationships in the digital age, with an emphasis on interpersonal communication.” Clearly state the main focus and purpose of your research and provide a roadmap for the reader to understand what will be discussed in your thesis.
What is a good way to start a thesis statement?
You could start a thesis statement by introducing your topic and talking about the specific angle you plan to explore in your research. Grab the reader’s attention and establish why it’s worth investigating further.
How do you start writing a thesis?
Writing a thesis starts with choosing a topic that interests you – and then aligns with your field. Be sure that the main goal of your thesis stays relevant to gain some credibility. With this, you can create a clear thesis statement that outlines the main objective of your study. This is where you can start drafting a compelling thesis introduction and then filling your content with strong arguments that are supported by evidence and analysis. Firmly conclude with a summary of your findings and their implications. Always cite your sources accurately and follow the academic guidelines.
Maximizing the potential of your thesis always starts with an introduction, and with the help of AI tools, you can be confident to write a strong one.
When using these tools, just be sure to have Undetectable AI by your side so that any content you need assistance with stays authentic.
The humanizer feature matches real human writing styles as closely as possible so that your content speaks to your readers.
Remember to tailor your thesis introduction to your specific research topic and audience, and use examples and evidence to back up your claims.
With these strategies in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to write an impactful thesis introduction – paving the way for a great thesis.
Finding datasets of credible and well-conducted research requires a understanding deep of primary sources. In […]
You can’t escape ChatGPT. Everyone’s heard about it. It started with some steady growth, and […]
According to a recent survey, 87% of global organizations believe that artificial intelligence gives them […]
Imagine being able to utilize AI to create research papers in a fraction of the […]
At a time when personal branding has never been more important, a well-written professional bio […]
- Twin Cities
- Campus Today
- Directories
University of Minnesota Crookston
- Mission, Vision & Values
- Campus Directory
- Campus Maps/Directions
- Transportation and Lodging
- Crookston Community
- Chancellor's Office
- Quick Facts
- Tuition & Costs
- Institutional Effectiveness
- Organizational Chart
- Accreditation
- Strategic Planning
- Awards and Recognition
- Policies & Procedures
- Campus Reporting
- Public Safety
- Admissions Home
- First Year Student
- Transfer Student
- Online Student
- International Student
- Military Veteran Student
- PSEO Student
- More Student Types...
- Financial Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Request Info
- Visit Campus
- Admitted Students
- Majors, Minors & Programs
- Agriculture and Natural Resources
- Humanities, Social Sciences, and Education
- Math, Science and Technology
- Teacher Education Unit
- Class Schedules & Registration
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Organizations
- Events Calendar
- Student Activities
- Outdoor Equipment Rental
- Intramural & Club Sports
- Wellness Center
- Golden Eagle Athletics
- Health Services
- Career Services
- Counseling Services
- Success Center/Tutoring
- Computer Help Desk
- Scholarships & Aid
- Eagle's Essentials Pantry
- Transportation
- Dining Options
- Residential Life
- Safety & Security
- Crookston & NW Minnesota
- Important Dates & Deadlines
- Cross Country
- Equestrian - Jumping Seat
- Equestrian - Western
- Teambackers
- Campus News
- Student Dates & Deadlines
- Social Media
- Publications & Archives
- Summer Camps
- Alumni/Donor Awards
- Alumni and Donor Relations

Writing Center
Effective introductions and thesis statements, make them want to continue reading.
Writing an effective introduction is an art form. The introduction is the first thing that your reader sees. It is what invests the reader in your paper, and it should make them want to continue reading. You want to be creative and unique early on in your introduction; here are some strategies to help catch your reader’s attention:
- Tell a brief anecdote or story
- As a series of short rhetorical questions
- Use a powerful quotation
- Refute a common belief
- Cite a dramatic fact or statistic
Your introduction also needs to adequately explain the topic and organization of your paper.
Your thesis statement identifies the purpose of your paper. It also helps focus the reader on your central point. An effective thesis establishes a tone and a point of view for a given purpose and audience. Here are some important things to consider when constructing your thesis statement.
- Don’t just make a factual statement – your thesis is your educated opinion on a topic.
- Don’t write a highly opinionated statement that might offend your audience.
- Don’t simply make an announcement (ex. “Tuition should be lowered” is a much better thesis than “My essay will discuss if tuition should be lowered”).
- Don’t write a thesis that is too broad – be specific.
The thesis is often located in the middle or at the end of the introduction, but considerations about audience, purpose, and tone should always guide your decision about its placement.
Sometimes it’s helpful to wait to write the introduction until after you’ve written the essay’s body because, again, you want this to be one of the strongest parts of the paper.
Example of an introduction:
Innocent people murdered because of the hysteria of young girls! Many people believe that the young girls who accused citizens of Salem, Massachusetts of taking part in witchcraft were simply acting to punish their enemies. But recent evidence shows that the young girls may have been poisoned by a fungus called Ergot, which affects rye and wheat. The general public needs to learn about this possible cause for the hysteria that occurred in Salem so that society can better understand what happened in the past, how this event may change present opinion, and how the future might be changed by learning this new information.
By Rachel McCoppin, Ph.D. Last edited October 2016 by Allison Haas, M.A.
Campus MyThesis Academy
The unique, worldwide Campus where you´ll learn how to write a thesis advised by an expert who graduated summa cum laude

How to write a thesis introduction

The fundamental question of how to write a thesis introduction that leaves the reader curious and excited to find out more and keep on reading is one of the most challenging and overwhelming tasks for all thesis writing students. When you start to work on your thesis opening, you should have a clear idea of what goes into it, how to structure it and how to make a good first impression. If you struggle to formulate the crucial initial words, this post will help you. Even if there is no recipe for h ow to write a thesis introduction for every topic, the following key issues and tips will enable you to craft yours.
How to write a thesis introduction for your dissertation
Your introduction is a key section that needs special attention! Representing the opening part of your thesis, it is the point of start for your reader, indicating the direction which your work will take, presenting your thesis statement, arguments, and making him understand your ideas in a concise way , in order to showcase your writing skills. Fulfilling such an important function, you need to know, how to write a thesis introduction that is simply perfect.
Your approach: How to write a thesis introduction for chapter 1
The first chapter is the right and only place for your initial words. Your goal is not only to introduce your research to the reader, but far behind : Addressing also the main key points and sections of your dissertation, such as the Literature review, scientific method, and relevance of your topic and writing, it´s your opportunity to leave a brilliant first impression and catch the interest.
If you struggle to find initial words, or to structure your opening section and still don´t know, how to start a dissertation introduction, start to work out yours by completing the following steps and stages :
- 1 – Start with a presentation of the general topic and provide some background information.
- 2 – Continue with a short overview of the actual literature related to the topic (briefly! keep the extension for your literature review).
- 3 – Introduce the principal idea and name the scope of the topic. outline the current state of research & evaluate the situation and arrive at the gap.
- 4 – Include a topic-comment, that showcases and clearly explains the relevance and importance.
- 5 – Name your research question, and formulate aims & objectives.
- 6 – Condense and place your thesis statement & arguments (if you like to know, how to write a thesis statement in an introduction paragraph and how to introduce a thesis statement in the best manner, consult my related post).
- 7 – Provide a brief description, that explains your methodological approach.
- 8 – Finish the introduction by outlining the structure of your dissertation.
How to write a thesis introduction that is well-structured
Writing a strong introduction means providing a condensed outline and definition of the principal sections which make up your dissertation. When you think about how to write a thesis introduction, be pragmatic: Open with some words on the topic introduction and provide readers with background information . Show the reader, why the subject is important the topic is worth and the relevant topic to be discussed. Your paragraphs should follow a logical structure, leading from one point to the next, until arriving at the main arguments and contribution.
How to highlight your research question & its relevance
To explain the famous “So what” and “Why does it matter” that motivated you for this specific research, introduce some hard facts: Present a brief overview of your studies’ contextual background and current state of research, founded by citing relevant sources.
Caution: Only the relevant! Don´t stuff the section, there is plenty of time for a detailed view of all sources in the literature review of your manuscript.

Write a dissertation introduction with the right length
Referring to the question of how to write a thesis introduction with adequate length, please consider, that there is no precise formula or required number of sentences or paragraphs. Try to cover all the essential points and leave all additional and unnecessary information out. Don´t overstuff the section or squeeze all points and arguments into one page. Instead, consider an extension of about five to seven pages (at least a 10% of your thesis).
Secrets to open your thesis in a brilliant way
1 – To make your dissertation an outstanding one from the very beginning, surprise your reader by including some particular and unexpected details: Introduce a unique point of view, drop some curious, special facts or surprising perspectives. I collected some further key points, which are also indicated by the Harvard University (to give you examples of how to write a good thesis introduction:
- 2 – Keep your writing short and concise.
- 3 – Check and present the best examples.
- 4 – Don’t make use of (too) specific vocabulary.
- 5 – Outline the principal key points, keep the highlights for the central body.
- 6 – Choose the right verb tense: use the present tense to state your topic, reserve the past tense for a description of the background and context.
- 7 – Avoid including a lot of quotation (this goes specially for direct quotes).
In a nutshell, the secret of how to write a thesis introduction, that will get your reader excited and interested is not an easy one, even if the components are clear. In fact, it´s a process, that requires addressing your research question and problem concisely, from different angles, and making decisions. To get to know how to start in a practical way, consult the related samples section from how to write a good thesis introduction: examples, and collect ideas to get yours done!
Frequently Asked Questions on how to write a thesis introduction
In a nutshell, the secret and best way of how to write a thesis introduction, that will get your reader excited and interested is not an easy one, even if the components are clear. In fact, it´s a process, that requires addressing your research question and problem concisely, from different angles, and making decisions. To get to know how to start a practical way, consult the related samples section from how to write a good thesis introduction: examples, and collect ideas to get yours done!
Introduce your topic, research question, and main sections/chapters of your thesis in a condensed way. Before you start writing, get a clear idea of the structure, crystallize your main arguments, and clear the contribution that your thesis will make.
The overall structure of a Ph.D. thesis introduction is very similar to an introduction for a Master´s thesis. Even though it should be a way more elaborated and the paragraphs provided with more depth and detail (extension).
Surprise your reader! That’s key if you want to keep him interested! Above the official requirements which are demanded such as a certain structure and a brief layout of your conception, the brilliance is to go behind the common expectation. Add some interesting, curious details, surprise your reader and get him excited to continue reading.
First of all, follow the steps which are provided above. Start to introduce your topic smoothly, provide some contextual background information, get over to the current state and figure out, which the gap is. Then, make clear, why it matters (research question & contribution), how you aim to approach it (methodologically) and close with a brief overview of your thesis structure.
Don´t try to squeeze all the information into one page, but avoid extending it by adding unnecessary details. There is no general rule for the length, but the expectation is around two to three pages.
There are a lot of examples provided in research papers and publications, you can also consult the section on concrete examples which is related to this post!
About the author:

Possibly you already heard of me through different media channels. My name is Dr. Friederike Jurth, and I hold a certificate from Harvard in Higher Education Teaching . Since 2010, I have given lectures on Methodology, Empirical Research, Anthropology, and Transcultural (Music) Studies in collaboration with universities in the United States, Germany, Spain, and Brazil . In 2010, I began a 7-year-long fieldwork project in Rio de Janeiro and have since presented my research at conferences worldwide, including in Japan, the United States, Australia, Brazil, Thailand, Switzerland, and many other countries. Additionally, I have worked as a lecturer and researcher with Germany’s renowned UNESCO Chair .
After completing my doctoral dissertation with summa cum laude , I aimed to unite, condense, and share the steps, ways, and details of my unique methodological and structural approach that I developed during my Ph.D. and that ultimately helped me achieve this result. By concentrating and putting them together into an elaborate academic conception, MyThesis Academy was born. Motivated by the sole aim and objective to help my students through all steps and stages of their thesis journey, MyThesis Academy enables them to achieve their best possible results in the shortest time, independent of their specific area of research.
In addition to my extensive teaching and research experience, I am part of the authors of the Cambridge Companion to Music in Brazil 2024, published by Cambridge University Press & Assessment , where I contribute as a Cambridge Author. This work is a co-operative project conducted remotely from Cambridge, England, United Kingdom.
United States & International Students
- SSL Protection
© Copyright 2024 - MyThesis Academy®. All rights reserved.

Masterclass Free

Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University
Thesis Writing
Thesis Introduction

Writing a Thesis Introduction Like a Pro - Steps & Examples
10 min read
Published on: Oct 22, 2021
Last updated on: Feb 6, 2024

People also read
Thesis Writing 101: Everything You Need to Know
100+ Thesis Topics That Will Make Your Research Stand Out
Thesis Format | Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis Proposal - Guide, Outline, Format & Tips
Share this article
Are you struggling with writing an engaging thesis introduction that grabs the attention of your readers?
Do you find yourself unsure of how to effectively introduce your research topic and present its significance?
Look no further!
In this blog, we will go through the complete process of writing the best thesis introduction.
We will also provide examples of some engaging thesis introductions along with expert tips to hook the reader's attention.
So, let's get started!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Thesis Introduction?
Writing an introduction for a thesis is one of the most important parts of writing. It sets the stage and direction for your work, and helps you stay focused on whatâs at hand. In addition, it can be used as reference points throughout your research process.
The first chapter in any thesis document starts with an introductory paragraph that narrows down broad subject matter into more specific.
Thesis introductions are usually found after the table of contents page and give a broader research context. Remember that a good opening is essential for capturing the reader's interest.
Components of a Good Thesis Introduction
The following are the important thesis introduction parts that must be covered.
- Topic and Context - What information should a reader have to grasp the thesis?
- Scope and Focus - Which elements of the topic will be covered? It might be research gaps, queries, or issues.
- Importance and Relevance - How your research work will contribute to the existing work on the same topic?
- Objectives and Questions - What are the major research aims and objectives the and how they will be achieved?
- Structure Overview - How will each chapter of the thesis contribute to the overarching goals?
How Long Should a Thesis Introduction be?
Your introduction is 10% of your paper which makes it the most important part. The PhD. thesis introduction should be between 8000 to 10000 words long. On the other hand, a Masters thesis introduction word count should be between 1500 to 2000.
However, the thesis introduction length might be extended if the writer incorporates photos, diagrams, and explanations.
Thesis Introduction Outline
The format of a thesis introduction chapter outline is as follows.
|
Take a look at the template below to get a sense of how the thesis introduction structure should be.
Thesis Introduction Outline Sample
How to Start a Thesis Introduction?
To begin a thesis introduction appropriately, follow the given steps
To write a successful paper, you must first identify an interesting topic that will keep readers engaged. Second, your introduction should be clear so they can understand what's going on between the text lines.
Brainstorm various thoughts and facts relating to your topic. Then, go through prior literature on the subject to thoroughly research it to grasp that concept or idea.
Choose the type of paper you are most comfortable using in your writing process. Keep in mind that the content should never be written in the first person.
Also, avoid including unnecessary details and be exact by utilizing correct language and grammar. When writing a thesis, using powerful phrases can assist you in defining the study objectives.
It is preferable to be aware of the audience to whom you are speaking. Similarly, work approaches, procedures, and literature should be introduced in accordance with your target audience.
In the following stage, organize and assemble the major arguments, concepts, and claims. A good idea will be useful in describing and presenting the thesis statement in the introduction.
Before beginning your thesis introduction, define the subject and the relevant themes. Going through it would make it easy for the reader to understand and get a decent idea of your topic.
How to Write a Thesis Introduction?
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you write a thesis introduction.
These steps of writing an introduction are discussed below in detail.
1. Capture the Readerâs Attention
A writer should begin the introduction with a hook sentence to draw the reader's attention. It can start with a quote, question, or an interesting transition into your argument.
Make a list of intriguing, present issues or events that are connected to your theme as well. It will assist in the development of a good opening and thesis statement .
2. Determine the Research Gap
Examine and evaluate the available literature. It will assist you in identifying and filling the research gaps.
3. Provide Background Information
An excellent thesis beginning always provides the historical context of the selected topic. It is generally referenced in the opening paragraph and illustrates the subject's present status.
4. Use Relevant Literature to Back Up Your Topic
The introduction combines previous research and the literature review. As a result, the topic should be backed up by relevant resources.
It's also used to explain the context and significance of previous research. It also acknowledges credible sources of information to back up your argument.
You can also check out this video for a better understanding:
5. Specify the Hypothesis
Create a hypothesis for your research paper . It will go through your goals as well as the options available to you.
6. Explain the Importance of Your Research
The gap will assist in assessing the situation and explaining the relevance of the current research.
Thus, provide your paper's goal, which explains why the study was conducted. It will also show the potential future contributions of the study work.
7. Outline the Research Questions
The next step is to compose an outline of your research questions. These should be relevant to the goal of your research. It will also aid you in discussing the issues you wish to address.
8. State Your Research Goals
To identify the fundamental purpose of the work, state the research goals and objectives. It should provide direction for the research by offering an outline of what it hopes to achieve.
9. Make an Outline
Make a well-structured outline to organize and assemble your ideas. Include a table of contents at the start of your dissertation as well. It could be used as a mind map to talk about the structure of your thesis proposal.
10. Examine the Research Methodology
In this stage, you have to identify and define the terms and methods you will use in your study. It is an effective method for making your research authentic, trustworthy, and valuable.
11. Complete Your Introduction
After you've finished writing the introduction, ask yourself the following questions.
- Is your introduction concerned with the issue that your thesis seeks to address?
- Does it make a case for the study?
- Is this part concerned with the research's contribution?
- Is it a thorough review of your thesis?
- Is it precise in defining research topics, issues, and hypotheses?
- Does it end by briefly addressing the topic of each chapter?
Take a look at this example and get a better understanding of writing the thesis introduction.
How to Write a Good Thesis Introduction
Thesis Introduction Examples
The following are examples of an introductory thesis paragraph to assist you in writing effective introductions.
Thesis Introduction Sample
School Canteen Thesis Introduction
Study Habits Thesis Introduction
PhD Thesis Introduction
Master Thesis Introduction Example
Bachelor Thesis Introduction Example
Thesis Defense Introduction Speech Sample
Thesis Chapter 1 Introduction Example
Thesis Introduction About Working Students Example
Useful Tips for Writing a Thesis Introduction
Here are some useful writing tips for writing a great thesis introduction.
Identify and Specify Research Parameters:
- Define the Research Scope and Boundaries
- Set Research Parameters in the Introduction
Provide Adequate Information to Back Up Claims:
- Support Claims with Relevant Information
- Present Evidence in the Introduction
Compose a Strong Introduction to Establish Scope and Goal:
- Establish the Scope and Goal of the Work in the Introduction
- Craft a Compelling Opening to Set the Tone and Direction
Solid Opening to Establish Scope and Aim:
- Establish the Scope and Aim of the Work in the Opening
- Create a Strong Opening Statement for the Introduction
Establishing Topic, Terms, and Scope:
- Establish the Context and Parameters of the Research
- Define the Topic, Terms, and Scope in the Introduction
Background Information for a Strong Foundation:
- Provide Background Information
- Establish a Solid Foundation with Background Details
Creating a Niche and Restricting Assertions:
- Establish a Niche and Limiting Assertions in the Introduction
- Create a Focused Framework for the Thesis in the Introduction
Guiding Future Research with Methodology:
- Indicate the Methodology for Future Research in the Introduction
- Guide Future Research with the Introduction's Methodological Overview
Overview of Present Research: Hypothesis, Questions, Aims:
- Present the Research Overview in the Introduction
- Introduce Hypotheses , Research Questions, and Aims in the Introduction
Unique and Plagiarism-Free Content:
- Ensure Unique and Original Content
- Maintain Academic Integrity with Plagiarism-Free Introduction
Consistent Thesis Format with Clear Facts:
- Adhere to a Consistent Thesis Format
- Present Clear Facts with a Consistent Format in the Introduction
Avoiding Technical Terms and Confusing Language:
- Write in Clear Language, Avoiding Technical Terms
- Maintain Clarity by Avoiding Confusing Language in the Introduction
Are you stuck on starting an introduction or looking for a thesis paper that will get an A? Get help from our AI writing tool to get started!
We at CollegeEssay.org understand the struggle of writing an introduction or thesis paper. This is why our college paper writing service is affordable and accessible.
We will help you with that! Our writers can produce any type of college essay, thesis , and any other writing assignment for all levels in no time.
So, order now and get help from the best academic writing service.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


How To Write A Thesis Introduction Chapter
Crafting the introductory chapter of a thesis can be confusing. If you are feeling the same, you are the at right place.
This post will explore how you can write a thesis introduction chapter, by outlining the essential components of a thesis introduction. We will look at the process, one section at a time, and explain them to help you get a hang of how to craft your thesis introduction.
How To Write A Good Thesis Introduction?
| Section | Description (Point Form) |
|---|---|
| – Acts as a hook to engage readers – Provides a concise preview – Outlines the structure | |
| – Sets the research context with a narrative – Outlines literature review – Articulates focus and scope | |
| – Addresses a literature gap – Explains the significance of bridging the gap – States what is known and unknown | |
| – Defines research aim, objectives, and questions – Provides a study roadmap – Sets research scope boundaries | |
| – Demonstrates research value – Emphasises enrichment to knowledge | |
| – Outlines study boundaries – Addresses constraints – Manages reader expectations – Establishes trust with transparency | |
| – Acts as a blueprint for the thesis – Outlines each chapter succinctly – Ensures logical progression of research work |
The opening section of a thesis introduction sets the stage for what’s to come, acting as a crucial hook to capture the reader’s attention.
Unlike the broader strokes found in the table of contents, this initial foray into your research is where you must distill the essence of your thesis into a potent, digestible form.
A skillful introduction begins with a concise preview of the chapter’s terrain, delineating the structure of the thesis with a clarity that avoids overwhelming the reader.
This is not the stage for exhaustive details; rather, it’s where you prime the reader with a snapshot of the intellectual journey ahead.
In crafting this segment, insiders advise adhering to a quartet of foundational sentences that offer an academic handshake to the reader.
First Section: I ntroduces the broad field of research, such as the significance of organisational skills development in business growth.
Second Section: Narrows the focus, pinpointing a specific research problem or gap — perhaps the debate on managing skill development in fast-paced industries like web development.
Third Section: Clearly state the research aims and objectives, guiding the reader to the ‘why’ behind your study. Finally, a sentence should outline the roadmap of the introduction chapter itself, forecasting the background context, research questions, significance, and limitations that will follow.
Such a calibrated approach ensures that every element from the research objective to the hypothesis is presented with precision.
This method, a well-guarded secret amongst seasoned researchers, transforms a mundane introduction into a compelling entrée into your dissertation or thesis.
Background To The Study
This section sets the tone for the research journey ahead. The goal here is to capture the reader’s attention by threading relevant background information into a coherent narrative that aligns with the research objectives of the thesis.
To write a good thesis introduction, one must carefully describe the background to highlight the context in which the research is grounded.
This involves not just a literature review but a strategic presentation of the current state of research, pinpointing where your work will wedge itself into the existing body of knowledge.
For instance, if the research project focuses on qualitative changes in urban planning, the introduction should spotlight key developmental milestones and policy shifts that foreground the study’s aims and objectives.
When writing this section, articulate the focus and scope of the research, ensuring the reader grasps the importance of the research questions and hypothesis.
This section must not only be informative but also engaging. By the end of the introductory chapter, the reader should be compelled to continue reading, having grasped a clear and easy-to-understand summary of each chapter that will follow.
It’s a good idea to address frequently asked questions and to clearly state any industry-specific terminology, assuming no prior expertise on the reader’s part.
This approach establishes a solid foundation for the rest of the thesis or dissertation, ensuring the reader is well-prepared to dive into the nuances of your research project.
Research Problem
Crafting the nucleus of your thesis or dissertation hinges on pinpointing a compelling research problem. This step is crucial; it is the keystone of a good thesis introduction chapter, drawing the reader’s attention and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.

A well-defined research problem addresses a gap in the existing literature, underscored by a qualitative or quantitative body of research that lacks consensus or is outdated, especially in rapidly evolving fields.
Consider the dynamic sphere of organizational skills development. Established research might agree on strategies for industries where skills change at a snail’s pace.
However, if the landscape shifts more quickly—take web development for example, where new languages and platforms emerge incessantly—the literature gap becomes evident.
Herein lies the research problem: existing strategies may not suffice in industries characterized by a swift knowledge turnover.
When writing your introduction, your goal is to clearly state this gap. A great thesis introduction delineates what is known, what remains unknown, and why bridging this chasm is significant.
It should illuminate the research objectives and questions, laying out a roadmap for the reader in a language that’s clear and easy to understand, regardless of their familiarity with the topic.
You’ll be able to capture and maintain the reader’s interest by effectively communicating why your research matters—setting the scene for your hypothesis and subsequent investigation.
Remember, a good thesis introduction should not only provide background information but also articulate the focus and scope of the study, offering a preview of the structure of your thesis.
Research Aims, Objectives And Questions
This pivotal section lays out the foundation by providing relevant background information, but it is the articulation of research aims, objectives, and questions that clarifies the focus and scope of your study.
The research aim is the lighthouse of your thesis, illuminating the overarching purpose of your investigation.
For instance, a thesis exploring skills development in fast-paced industries might present an aim to evaluate the effectiveness of various strategies within UK web development companies. This broad goal sets the direction for more detailed planning.
Research objectives drill down into specifics, acting as stepping stones toward achieving your aim. They are the tangible checkpoints of your research project, often action-oriented, outlining what you will do.
Examples might include identifying common skills development strategies or evaluating their effectiveness. These objectives segment the monumental task into manageable portions, offering a clear and easy way to write a structured pathway for the research.

Equally critical are the research questions, which translate your objectives into inquiries that your thesis will answer. They narrow the focus even further, dictating the structure of the thesis.
For instance:
- “What are the prevalent skills development strategies employed by UK web development firms?”
- “How effective are these strategies?”
Such questions demand concrete responses and guide the reader through the rest of the thesis.
Significance Of The Study
The “Significance of the Study” section within the introduction chapter of your thesis or dissertation holds considerable weight in laying out the importance of your research.

This segment answers the pivotal question: “Why does this research matter?” It is strategically placed after the background information and literature review to underscore the contribution your study makes to the existing body of research.
In writing this section, you’ll be able to capture the reader’s attention by clearly stating the impact and added value your research project offers.
Whether it’s a qualitative or quantitative study, the significance must be articulated in terms of:
- Theoretical
- Academic, and
- Societal contributions.
For instance, it may fill gaps identified in the literature review, propose innovative solutions to pressing problems, or advance our understanding in a certain field.
A good thesis introduction will succinctly convey three main things: the research objective, the hypothesis or research questions, and the importance of your research.
It’s a good idea to provide your reader with a roadmap, foreshadowing the structure of the thesis and offering a summary of each chapter, thus enticing the reader to continue reading.
When you write the introduction section, it should also serve as a concise synopsis of the focus and scope of your research.
It’s often beneficial to include examples of introductions that clearly state the research objectives and questions, offering a snapshot of the whole thesis, and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.
Limitations Of The Study
A thorough thesis introduction lays out specific research objectives and questions, yet it also sheds light on the study’s inherent boundaries. This is the purpose of the Limitation of The Study section.
The limitations section is not a confession of failure; instead, it’s a good idea to see it as demonstrating academic maturity.
Here, you clearly state the parameters within which the research was conducted.
For instance, a qualitative study might face scrutiny for subjectivity, or a quantitative one for potentially oversimplifying complexities. Other common constraints include the scope—perhaps focusing on a narrow aspect without considering variable interplay—resources, and generalizability.
For example, a study concentrated on a specific industry in Florida may not hold water in a different context, for example in Tokyo, Japan.
It’s essential to write this section with transparency. A good thesis introduction doesn’t shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader’s attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter.
This honesty allows the reader to understand the research’s focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
This approach also serves to manage the reader’s expectations. By preempting frequently asked questions about the scope of your research, the introductory chapter establishes a trust that encourages the reader to continue reading, aware of the contours shaping the body of research.
Thus, a well-articulated limitations section is not just part of the thesis; it is an integral piece of a responsibly woven research narrative.
Structural Outline Of Thesis, Thesis Statement
Within the thesis or dissertation, the structural outline section is akin to a compass, orienting the reader’s journey through the academic landscape laid out within the pages.
Crafting this section is a strategic exercise, one that requires an understanding of the work’s skeleton.
In essence, it’s the blueprint for the construction of a scholarly argument, and writing a good thesis necessitates a clear and easy-to-follow outline.
When you write a thesis outline, it’s not only about catching the reader’s attention; it’s also about holding it throughout the rest of the thesis.
This is where the structural outline comes into play, often beginning with an introduction chapter that presents the thesis statement, research objectives, and the importance of your research.
Following the introduction, a typical outline might proceed with Chapter 2, offering a literature review to acquaint the reader with existing literature and how this piece of research fits within it.
Subsequent chapters, each with a paragraph in the outline, detail the methodological approach—whether it’s qualitative or quantitative—and the research’s focus and scope.
A well-thought-out outline should also preview the structure of the thesis, succinctly:
- Summarizing the main aim and objectives of each chapter, and
- Indicating the type of data and analysis that will be presented.
This roadmap reassures the reader that the dissertation or thesis will cover the necessary ground in a logical progression, continuing from where the introduction first captivated their interest.
The structural outline is not only part of the thesis—it’s a strategic framework that informs the reader what to expect in each subsequent chapter.
Done correctly, this section allows the reader to understand the whole thesis in a nutshell and can often serve as a checklist for both the reader and the writer.
This ensures that the key stages of the research project are clearly stated and that the reader is provided with a roadmap to guide them through the detailed landscape of your scholarly work.
Write An Introduction Chapter With Ease
Mastering the thesis introduction chapter is a critical step towards a successful dissertation. It’s about striking a balance between engagement and information, presenting a snapshot of your research with clarity and intrigue.
Remember to start with a hook, establish the context, clarify your aims, and highlight the significance, all while being mindful of the study’s scope and limitations.
By adhering to these principles, your introduction will not only guide but also inspire your readers, laying a strong foundation for the in-depth exploration that follows in your thesis or dissertation.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction.
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write – in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Begin by introducing your research topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualise your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.

Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an outline of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, September 09). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.

Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Feb 26, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow.

What is the purpose of a PhD thesis introduction?
1. establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context), 2. establish and justify your niche (by describing why your research is needed) , 3. explain the significance of your research (by describing how you conducted the research).
- What your thesis is about
- Why it is important
- How it was conducted
- How it is laid out
The introduction as a whole should outline the significance and relevance of the thesis. The main criteria for a PhD is its role as an original contribution to knowledge, so the introduction is the space in which you very clearly outline that contribution.
How to structure an PhD thesis introduction
A typical PhD thesis introduction follows the following format:
- Introduction to the introduction: a short version (of only a few paragraphs) of the thesis’ aims, research questions, contribution, objectives and findings.
- State the overarching topic and aims of the thesis in more detail Provide a brief review of the literature related to the topic (this will be very brief if you have a separate literature review chapter)
- Define the terms and scope of the topic
- Critically evaluate the current state of the literature on that topic and identify your gap
- Outline why the research is important and the contribution that it makes
- Outline your epistemological and ontological position
- Clearly outline the research questions and problem(s) you seek to address
- State the hypotheses (if you are using any)
- Detail the most important concepts and variables
- Briefly describe your methodology
- Discuss the main findings
- Discuss the layout of the thesis
Much like the abstract, the reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it. So, you’ll start by presenting your research in a clear, concise way in the opening few paragraphs. These opening paragraphs should briefly summarise the aims, objectives, research questions, main argument and contribution.
The reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it.
A useful exercise here is to try and write the core elements of an introduction on a Post-it note. Keep trying until they fit. When they do, use that as the basis for these first few paragraphs. This is the same technique you use when filling out the PhD Writing Template .
As you go through the chapter, you will dial down into more and more detail. That means that the next stage, after the first few paragraphs, is to provide some context (steps 2-10 above).
Here you provide all the detail necessary to situate the study and make sense of the opening few paragraphs.
But, there are two things to bear in mind.
You will need to ease into the detail gently. Don’t launch straight from your opening paragraphs into huge amounts of detail. Follow the order of the 13 steps above and you will gradually ease into your discussion.
The danger of presenting too much information too soon is that you will confuse the reader. They will struggle to understand how the information you present is relevant and will struggle to understand how it relates to your thesis aims and objectives.
Simply follow the steps above.
You need to bear in mind that the level of detail you will go into (and therefore the length of the introduction) depends on the structure of your thesis.
If you have a standalone literature review, you will go into less detail about the current state of the literature and the gaps within it.
Similarly, if you have a dedicated theory chapter, you will not need to spend too much time on developing your theory framework.
The same is true for your methods.
The goal in any case is to present enough context to situate and make sense of your research questions but not overburden the reader with information that is superfluous to the goal of situating the research and which you will repeat at a later juncture anyhow.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Common problems when writing your introduction
When we proofread PhDs , we see the same mistakes again and again.
Providing too much detail
There is a tendency to provide too much background information in the introduction. As we saw above, quite how much information you present in your thesis will depend on whether you have a standalone literature review or methods chapter. What you want to avoid is any unnecessary repetition.
Sometimes there is necessary repetition though. You need to present just enough information to contextualise your study and to be able to situate your aims, research questions an argument, but not too much that you end up confusing and bombarding the reader. Keep things simple here; it’s fine to overlook some of the more technical detail at this stage. Think of a newspaper article: the first couple of paragraphs provide a brief overview of the story. The detail comes later.
Not providing enough detail
On the flip side, some students don’t provide enough detail. The danger here is that the reader is left asking questions at the end of the introduction. Remember: they should be able to understand what your thesis is about, how it was conducted and why it is important just from reading the introduction. If you present too little detail then they won’t be able to. Read through your own introduction; is it clear what your contribution is and why it is important? If not, you haven’t got enough detail.
Launching into too much detail
Make sure you introduce gently. Don’t suddenly rush into lots of detail. Instead, you should make the aims, questions and contribution clear in the opening lines and then gradually layer on more detail. That way, the reader can keep up. Present too much detail too soon and the reader will become confused. The last place you want confusion is in the introduction; if the reader can’t follow your introduction, they won’t understand the thesis.
Not following a coherent structure so that the reader is left confused
Some students don’t follow a coherent logic when they write their introductions, which means that the reader is left confused.
For example, if you present too much background information and literature review before you outline the aim and purpose of the research, the reader will struggle to follow, because they won’t know why the background information is important.
The same is true if you discuss the methods before your research questions.
What we see often is important information being spread throughout the introduction in such a way that the reader has to hunt for it. Follow our layout guide above so that each piece of vital information is contained in its own mini section. Make your reader’s job as easy as possible.
Using too much technical language not properly defined
It’s more than likely that your research relies upon lots of technical terms, concepts and techniques. If you must talk about any of these in the introduction, be sure to offer clear and concise definitions. A failure to do so means that the reader is left confused.
Conducting a literature review
Unless you are explicitly avoiding a standalone literature review chapter, the introduction is not the place to review the literature. Sure, you will need to situate your study in a body of literature, but the introduction isn’t the place to critically discuss it or justify its inclusion in that literature. It’s enough to say that you will contribute to X body of literature and briefly discuss its core features and shortcomings. The literature review is the place to justify that decision and elaborate upon its features. Read our guide to writing literature reviews and our guide to being critical when you do so.
Finalising your thesis introduction
Once you have finished your thesis, ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the first line of the introduction discuss the problem that your thesis is addressing and the contribution that it is making?
- Does the introduction provide an overview of the thesis and end with a brief discussion on the content of each chapter?
- Does the introduction make a case for the research?
- Have the research questions/problems/hypotheses been clearly outlined (preferably early on)?
Now you know how to present your research as clearly and concisely as possible. Your reader (and examiner) will thank you, because they’ll be able to understand exactly what your study is about just from reading the introductory pages. Keep this guide to hand, whatever stage of the writing process you are at.
Have you downloaded our free one page PhD Writing Template ? It’s a really effective way to visualise your entire thesis on one page.
If you’re still struggling to structure your introduction, or you need any other support as you write your thesis, check out our one-on-one PhD coaching . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.
Share this:
12 comments.
I was struggling with writing the introduction chapter. Really had no idea on how to organise my ideas. Completely lost and desolate. I have no one to encourage or support me. I prayed to God to give me knowledge and wisdom and guide me. After a while I found this site. Praise the Lord. I can’t thank u enough for addressing exactly what’s in my mind. Thank you. Glory be to God for directing me to this site.
All we aim to do here is to make life a little bit easier for PhD students. I know how hard I found it when I was completing mine, so I want to give something back to the community. I’m so pleased you found it useful. Good luck with writing up. If you need any support or if you have any questions at all, email me: [email protected]
Thank you very very much for your information it is resourceful. I was having a problem how to start my introduction.
It’s great to hear you found it useful. Thanks!
Hey, this is so useful thankyou! I’m wondering does this apply broadly to all PhD’s including humanities?
Yep – it sure does.
I found this piece of information helpful. I am preparing for my proposal defense in two weeks and needed to refine my introduction. Thank you very much. God bless you richly. I wish we can have a skype conversation.
Thank you again.
thank you, learned from this
Your advice and guidance has become my constant companion in what has been a very stressful time. You write with empathy and understanding. What a wonderful job you are doing for those of us who are too proud to seek advice and support from supervisors or colleagues. Sincerest thanks for taking the loneliness out of writing.
Such nice words. Thank you so much.
this is really useful!!!
Thanks Nora! I’m glad you found it useful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
How do you write a good introduction to a thesis or dissertation?

The introduction to a university dissertation or thesis is an essential part of a final year project.It is the first connection you will make with your reader.It is therefore important to write a well-written introduction to your dissertation in order to
- interest the reader or the examiner,
- capture their attention ,
- give them a clear idea of the subject covered in the dissertation.
A reader or examiner in a hurry generally reads your thesis diagonally. In this case, they are particularly interested in the following 3 elements : the introduction to the thesis , the outline of the thesis and the conclusion of the thesis . It is therefore important to take care with these 3 elements to highlight the quality of your work.
In this article, we present the main elements to be included in a thesis introduction , with an example of an introduction valid for different levels of study: bachelor's thesis (bac+3), master's thesis (bac+4 and bac+5), doctoral thesis , etc.
Contents : Writing a thesis introduction at the right time The 5 main elements in the introduction to a dissertation or thesis Highlighting your thesis introduction Example of a thesis introduction

1. Writing a thesis introduction at the right time
There are 2 schools of thought on the ideal time to write a thesis introduction :
- Write your introduction after the writing plan has been finalised (at the start of the dissertation or thesis project).
- Write your introduction after you have finished writing your thesis (at the end of the project).
Writing a thesis introduction after finalising the outline
Drawing up a detailed outline for your dissertation or thesis is a crucial stage in the preparation of a university project .
It follows the definition of the subject, the choice of a thesis supervisor and the formulation of the problem statement .
Drawing up an outline for your thesis is important, because your outline sets out your response to the problem.
As soon as you have finalised and validated your dissertation or thesis plan , you can start writing your project , particularly the introduction to your thesis or dissertation .
Be careful to adjust your dissertation or thesis introduction according to the elements you include in your dissertation as you go along.

Writing a thesis introduction after you've written your thesis
Writing your thesis introduction at the end may seem counter-intuitive , but in reality it is recommended practice for a number of reasons:
When writing the different parts of your thesis, you usually have a vague idea of the points you want to cover. As you go along, your thoughts evolve and you refine your ideas . Writing the introduction at the end gives you an overview of the work as a whole, so that you can write a more precise and relevant introduction to your thesis .
Clarifying your objectives
At the end of your research, you will have a clearer idea of your objectives and the means and tools you will use to achieve them. Writing your introduction at the end makes it easier to explain your objectives.
Adjusting the problem
During the course of a research project, the subject may evolve . By writing the thesis introduction at the end, you can be sure that you are presenting the problem to which you are responding.
Consistency with the conclusion
Writing your thesis introduction at the same time as your conclusion ensures that they are aligned . This way, you can be sure that they are coherent and that they provide a good framework for your thesis .
Even if you choose to write your thesis introduction at the end of your work , you should be aware that you can write a draft introduction at the beginning of the project. This first draft will allow you to clarify your ideas and give your dissertation or thesis a direction. You can revise and finalise it once the rest of the thesis has been completed.

2. The 5 main elements of a thesis introduction
There are several elements to include in your thesis introduction , whether it's a research or professional thesis .
Make sure your introduction is structured , brief and concise . The aim is to communicate the essential information to your reader in no more than one or two pages .
The structure of a thesis introduction is also crucial in capturing the reader's attention. This structure may vary according to the requirements of your field of study or your institution.
Here are the 5 parts to be included in your thesis introduction and adapted according to the guidelines received :
Contextualisation
Start with a hook (statistics, key facts or concrete examples) to draw your reader's attention to the subject. Then go on to introduce the subject in a general way, highlighting its importance in the current context and its relevance to your field of study .
Problematic
Clearly identify the question you wish to answer. Explain why this problematic is interesting and why you have chosen to address it. A good problematic should be simple, precise and understandable!
Research objectives
Frame your study by presenting its objectives . What are you trying to measure? What are the main hypotheses you want to examine? Also describe your research methodology in this paragraph.
Structure of the thesis
Give an overview of the overall structure of your dissertation or thesis by announcing your plan. Explain your choice of sections and parts to familiarise the reader with your organisation.
Announcement of results (optional)
Finally, give a brief overview of the results you have reached at the end of your research. Indicate the main conclusions to pique the reader's interest and encourage them to want to find out more.

Focus on the presentation of research methodology
What is the research methodology for a thesis.
The choice of academic research methodology depends on the nature of the project: research dissertation , professional dissertation , doctoral thesis .
There are several academic research methods : quantitative studies , qualitative studies , empirical studies , comparative studies , etc.
Why present your research methodology in the thesis introduction?
By presenting your research methodology in your thesis introduction , you situate your work in a specific methodological context . You give the reader more information to u nderstand your approach and assess the validity of your results.
Focus on announcing the plan in a thesis introduction
Why include the outline in the introduction to a thesis.
To orientate the reader, we strongly advise you to announce the overall plan of your thesis in your introduction. This gives them an overview and helps them to follow your argument coherently.
By announcing the plan, you also help the reader to understand what to expect in each part. This can be particularly useful when your work is long.

How do you announce a thesis plan in the introduction?
Here are some ideas for announcing the plan in the introduction to your thesis :
Simple enumeration
List the main parts of your thesis .
For example : "This thesis is divided into four main parts: Part I - Background and problematic, Part II - Review of the literature, Part III...".
Explanatory sentences
To give more context to each part, you can add a brief explanatory sentence for each of them.
For example: "This thesis is structured in four main parts. In the first part, we will examine the context and problematic of our research. The second part will be devoted to an in-depth review of the existing literature on the subject...".
3. Highlighting the thesis introduction: the layout
It is important to highlight the thesis introduction . To do this, an appropriate layout is necessary.
The layout of the thesis introduction must be carefully thought out and well structured in order to capture the reader's attention and guide them through the text clearly and concisely.
Here is an example of the layout for the first few pages of a thesis (including the introduction):
Page 1: cover page of the thesis
name of the university or institution,
- title of the thesis,
- first name and surname of the author,
- date of submission.
Page 2: acknowledgement page
acknowledgements to all the people who contributed to the smooth running of your academic year,
- thanks to all those who contributed to the writing of your dissertation or university thesis.
Page 3: table of contents
A detailed list of the sections and subsections of the thesis, with the corresponding page numbers.
Page 4: thesis introduction
title of the introduction,
- catchphrase or relevant quotation to capture the reader's attention (contextualisation),
- context in which the research topic is justified (contextualisation),
- problematic and research questions (problematic),
- research objectives and methodology used,
- outline of the plan.

4. Example of a thesis introduction
The following is an example of a thesis introduction that can be adapted to deliverables for different levels of study: bachelor's thesis , master's thesis , doctoral thesis , etc.
Example of a thesis introduction for a dissertation or doctoral thesis on the subject of artificial intelligence and its impact on education :
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up new perspectives in many fields, including education. AI-based technologies have the potential to transform educational practices , improve learning processes and prepare learners for the challenges of our digital society. In this doctoral thesis, we propose to explore the impact of artificial intelligences on education , taking an in-depth look at the opportunities, challenges and implications of these emerging technologies.
The problematic of this research lies in the growing need to adapt education to the demands of the 21st century , integrating technological innovations to deliver a more effective, personalised and relevant learning experience. Artificial intelligences represent a promising response to this problematic, but their integration into the field of education raises fundamental questions about the pedagogical, ethical and social consequences of these technological advances.
Research objective
The main objective of this thesis is therefore to analyse in depth the impact of artificial intelligences on education , focusing on their applications, their potential benefits, and the challenges and concerns they raise. To achieve this aim, we will adopt a multidisciplinary approach, combining conceptual analyses , case studies and empirical investigations .
Structure of the dissertation
This thesis is structured in six main parts . In the first part , we present the context and the problematic linked to the use of artificial intelligences in education . We will raise the current educational issues and the needs that AIs can meet, identifying the research questions that guide our work.
The second part will be devoted to an in-depth literature review , where we will analyse previous work and existing research on the impact of artificial intelligences in education. We will examine the different applications of AIs , such as intelligent tutoring systems , learning data analysis , personalisation of teaching , etc.
In the third part , we will describe our research methodology , explaining how we designed our case studies and empirical investigations . We will discuss the tools and methods used to collect and analyse the data, as well as the measures taken to ensure the validity and reliability of our research .
Then, in the fourth section , we will present the results of our case studies and surveys , analysing them in the light of our research problematic. We will examine the potential benefits of AI in terms of improved learner performance, adaptation to individual needs, personalised feedback, and so on.
In the fifth part , we will address the challenges and concerns associated with the use of AI .

Write your student work with peace of mind
With Compilatio Studium, make sure to cite all your sources and submit quality assignments, compliant with academic requirements . This way, you can easily avoid plagiarism penalties and prove the integrity of your work .
To sum up, the introduction is an important part of the thesis. It captures the reader's attention by presenting the context, subject, problematic and structure of the thesis. By following these few tips, you can write an effective and relevant thesis introduction to encourage your reader or your examiner to read your deliverable.
Sources for further reading : " Thesis or Dissertation Cover Page: How to create it? " Compilatio, consulted on 23/07/2024. " How to Write a Thesis Introduction " UNSW, consulted on 13/07/2023. " How to write a good thesis introduction " Paperpile, consulted on 13/07/2023. " How to write a fantastic thesis introduction " Master Academia, consulted on 13/07/2023. Information: this informative article, which does not require any personal reflection, was written in part with the help of ChatGPT. We have reworked the automatically generated content (correcting repetitions, correcting turns of phrase, adding clarifications, adding quotations, checking the veracity of the information, etc.).
Studium Newsletter
Receive tips on writing and citations and don't miss our promotional offers by subscribing to the Studium newsletter.
By clicking "Subscribe", I agree that Compilatio processes the data provided in this form for the following purpose: "Information on the topic of plagiarism". Learn more about how we manage your data and your rights.
How to Write an Introduction
An introduction for an essay or research paper is the first paragraph, which explains the topic and prepares the reader for the rest of the work. Because it’s responsible for both the reader’s first impression and setting the stage for the rest of the work, the introduction paragraph is arguably the most important paragraph in the work.
Knowing how to write an introduction paragraph is a great skill, not just for writers, but for students and researchers as well. Here, we explain everything you need to know to write the best introduction, such as what to include and a step-by-step process, with some introduction paragraph examples.
Give your writing extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
What is an introduction?
Your introduction is a way of preparing your reader for your paper. As the first paragraph of your writing , it makes the first impression and sets the reader’s expectations for tone, voice, and writing style. More importantly, your introduction provides the necessary background for your reader to understand your paper’s purpose and key points.
The introduction is also a way to engage and captivate your reader. An interesting, thought-provoking, or generally entertaining introduction makes your reader excited to keep reading—and an eager reader is an attentive reader.
What to include in an introduction
Introductions generally follow the writing style of the author and the format for the type of paper—for example, opening with a joke is appropriate for some essays, but not research papers . However, no matter what your writing style is or what kind of paper you’re writing, a good introduction includes at least three parts:
- A hook to capture the reader’s attention
- Background for context
- A clearly defined thesis statement or main point of your paper
How to write a hook
The hook refers to anything that grabs (or “hooks”) your reader’s attention and makes them interested. This could be a mystery, such as posing a question and only answering it at the end of your paper. Or it could be a shocking statistic, something that makes your reader rethink what they thought they knew and become curious for more information.
Hooks can be even more creative. Some papers start with an analogy or parable to present complicated topics in a way that someone with little experience can understand. Likewise, many writers opt to use personal anecdotes to show a more human side and spark an emotional connection with the reader.
When all else fails, you can use a poignant quote. If you’re having trouble putting your thoughts into words, maybe one of the great minds from history has already said it well.
You can read all about how to write a hook here, including more detailed instructions and examples.
How to add background information
Not every paper requires background knowledge, but sometimes your reader needs to catch up or understand the context before you make your original points.
If you’re writing about something factual, such as a scientific or historical paper, you may need to provide a small lesson on the basics. For example, if you’re writing about the conflict between ancient Egypt and Nubia, you might want to establish the time period and where each party was located geographically.
Just don’t give too much away in the introduction. In general, introductions should be short. If your topic requires extensive background to understand, it’s best to dedicate a few paragraphs to this after the introduction.
How to write a thesis statement
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement , a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence, your thesis statement could be:
Despite the rhetoric and finger-pointing, no evidence has connected live-action role-play violence with real-world violence, but there is plenty of evidence for exoneration, as I explain here.
Learning to write a good thesis statement is an essential writing skill, both in college and the world of work, so it’s worth taking the time to learn. The rule of thumb for thesis statements is not to give everything away all at once. Thesis statements, and more broadly introductions, should be short and to the point, so save the details for the rest of the paper.
How to write an introduction paragraph in 6 steps
1 decide on the overall tone and formality of your paper.
Often what you’re writing determines the style: The guidelines for how to write an introduction for a report are different from those for how to write an English essay introduction. Even the different types of essays have their own limitations; for example, slang might be acceptable for a personal essay, but not a serious argumentative essay.
Don’t force yourself to write in a style that’s uncomfortable to you. If you’re not good at making jokes, you don’t need to. As long as your writing is interesting and your points are clear, your readers won’t mind.
2 Write your thesis statement
At the beginning of writing a paper, even before writing the research paper outline , you should know what your thesis is. If you haven’t already, now is the time to put that thesis into words by writing your thesis statement.
Thesis statements are just one sentence, but they are usually the most important sentence in your entire work. When your thesis is clearly defined, your readers will often use it as an anchor to understand the rest of the writing.
The key to writing a good thesis statement is knowing what to ignore. Your thesis statement should be an overview, not an outline. Save the details, evidence, and personal opinions for the body of the paper.
If you’re still having trouble, ask yourself how you’d explain this topic to a child. When you’re forced to use small words and simplify complex ideas, your writing comes across more clearly and is easier to understand. This technique also helps you know which details are necessary up front and which can wait until later .
3 Consider what background information your reader needs
Don’t take your own experience for granted. By this point in the writing process , you’ve probably already finished your research, which means you’re somewhat of an expert on the topic. Think back to what it was like before you learned: What did you wish you had known then?
Even if your topic is abstract, such as an ethical debate, consider including some context on the debate itself. How long has the ethical debate been happening? Was there a specific event that started it? Information like this can help set the scene so your reader doesn’t feel like they’re missing something.
4 Think of a good hook
Writing a hook can be the most difficult part of writing an introduction because it calls for some creativity. While the rest of your paper might be presenting fact after fact, the hook in your introduction often requires creating something from nothing.
Luckily, there are already plenty of tried-and-true strategies for how to start an essay . If you’re not feeling very creative, you can use a method that’s already been proven effective.
Just remember that the best hooks create an emotional connection—which emotion is up to you and your topic.
5 Write a rough draft of your introduction without pressure
It’s normal to clam up when writing a rough draft of your introduction. After all, the introduction always comes first, so it’s the first thing you write when you finally begin.
As explained in our guide to writing a rough draft , the best advice is not to pressure yourself. It’s OK to write something that’s messy—that’s what makes this draft rough . The idea here is to get words on paper that make your point. They don’t have to be the perfect words; that’s what revisions are for.
At the beginning, just worry about saying what needs to be said. Get down your hook and thesis statement, and background information if necessary, without worrying about how it sounds. You’ll be able to fix the problems later.
6 Revise your introduction after you’ve written your whole paper.
We recommend finishing the first draft of your entire paper before revising the introduction. You may make some changes in your paper’s structure when writing the first draft, and those changes should be reflected in the introduction.
After the first draft, it’s easier to focus on minutiae like word choice and sentence structure, not to mention finding spelling and grammar mistakes.
Introduction for an essay example
While other kids’ memories of circuses are happy and fun, what I recall most from my first time at a circus was feeling sorry for the animals—I can still remember the sadness in their eyes. [HOOK] Although animal rights in the circus have come a long way, their treatment of animals even under the new laws is still cruelty plain and simple. [BACKGROUND] The way circuses abuse animals needs to be abolished immediately, and we need to entirely rethink the way we use animals for entertainment. [THESIS STATEMENT]
Introduction for a research paper example
What would happen to humanity if everyone just stopped having babies? [HOOK] Although more endemic in some places than others, the global decline in birth rates has become a major issue since the end of the pandemic. [BACKGROUND] My research here shows not only that birth rates are declining all over the world, but also that unless the threats are addressed, these drastic declines will only get worse. [THESIS STATEMENT]
Introduction FAQs
An introduction is the first paragraph in an essay or research paper. It prepares the reader for what follows.
What’s the purpose of an introduction?
The goal of the introduction is to both provide the necessary context for the topic so the reader can follow along and also create an emotional connection so the reader wants to keep reading.
What should an introduction include?
An introduction should include three things: a hook to interest the reader, some background on the topic so the reader can understand it, and a thesis statement that clearly and quickly summarizes your main point.


- Leeds University Business School
- Research and innovation
- Research and innovation blog
How to write an introduction chapter for a thesis
Louisa Hill is a Senior Teaching Fellow and delivers workshops for Postgraduate Researchers who want to teach.

When writing a thesis, you will need to write an introductory chapter. This chapter is critical as it is the first thing that the examiner will read and it is therefore important to make a good first impression.
A good introduction chapter should incite the reader to read the rest of the thesis by establishing the context of your topic, the motivation for undertaking your work and the importance of your research.
As a lecturer and supervisor, I have read many introductory chapters for research projects such as theses. Here is my advice to those undertaking a research project and writing a thesis.
Capture the reader’s interest
Initially you need to capture the reader’s attention with a discussion of a broader theme relating to your research. To add impact draw on research, data and quotations from international or national professional bodies, governmental organisations or key authors on the topic of study.
Give an overview of your research topic
Your discussion should then begin by detailing the broader aspects of the topic more, before focussing on the specific topic of your research. It is a good idea when you do this to assume that the reader knows nothing about your topic. Therefore definitions, drawing on key research, need to be clarified and explained. Alternatively, if having read key literature for the literature review chapter, you are not satisfied with existing definitions, then draw on these, to devise your own (but make it clear you have done this).
Detail how your research is going to make a contribution
You must then sell your idea for undertaking the research topic, demonstrating the main reasons why the research will make a significant contribution to the current body of research. This can be achieved by demonstrating a gap or limitation with existing research, then showing how your research will resolve this. There are different types of contribution (see Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research ).
Explain what your interest is in the topic
Next you need to demonstrate your personal reasons for choosing the topic. These could relate to your previous research, work or experiences.
List your research objectives
You need to include your three or four overarching research objectives. Also include corresponding research questions if it is a qualitative piece of research or hypotheses if it is quantitative-based. The former are usually derivatives of the research objectives. Note though that these objectives and questions or hypotheses are fluid in nature and can be tweaked as you undertake the research.
Give a forthcoming chapter overview
The final part of the introduction is an overview of the rest of the chapters in the thesis. The other sections can go in any order, providing it is a logical sequence.
Learn from others
Look at other theses for example from White Rose etheses or your university library’s website. The majority of journal articles that you will read in the content of your topic will also provide useful insights.
Speak with your supervisor
Remember to always speak with your supervisor and have regular catch-ups. They will be able to offer guidance and encouragement, and steer you in the right direction.
Related content
- Writing a research PhD proposal
- Presenting with impact
- The benefits of undertaking a placement alongside your PhD
If you would like to get in touch regarding any of these blog entries, or are interested in contributing to the blog, please contact:
Email: [email protected] Phone: +44 (0)113 343 8754
Click here to view our privacy statement. You can repost this blog article, following the terms listed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International licence .
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and may not reflect the views of Leeds University Business School or the University of Leeds.

Thesis Introduction
Ai generator.

After coming up with your desired topic for your thesis, it is about time that you began preparing that introduction. Just like every good speech or story, you need to have an introduction as to what your thesis outline is all about and what aspects your research will be covering.
In the introduction part of your thesis, you should be trying to focus on three main things, which are called Moves, according to the University of New South Wales database:

Move 1. E stablish your territory
By marking your territory, you begin to elaborate on what your topic is about and its present situation at hand. In doing so, there is also a need for you to point out that your area of research will only be limited to this scope, and for it to go beyond your area of responsibility would be out of the context. You may also see essay examples .
Move 2. E stablish a niche
This section is the heart and soul of your introduction. Without this, why was there even the need to conduct your research in the first place if you do not know what for?
Move 3. Introduce the current research
In conclusion to your introduction, this is where your research steps into the spotlight. In this part, you will be giving the panel a glimpse of the questions the researchers would be tackling during the course of the thesis journey. Aside from stating the hypotheses in this section, it is also important for the researchers to identify early on the end goals the study wants to achieve. You may also see thesis statement .
Each Move has a number of stages. Depending on what you need to say in your introduction, you might use one or more stages. You will also find examples of introductions, divided into stages with sample sentence extracts.
Most thesis introductions include some (but not all) of the stages listed below. There are variations between different schools and between different thesis, depending on the purpose of the thesis. You may also see essay writings .
Stages in a thesis introduction
- State the general topic and give some background.
- Provide a review of the literature related to the topic.
- Define the terms and scope of the topic.
- Outline the current situation.
- Evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap.
- Identify the importance of the proposed research.
- State the research problem/questions.
- State the research aims and/or research objectives
- State the hypotheses.
- Outline the order of information in the thesis.
- Outline the methodology.
Listed below is a sample thesis introduction that was made by me and my partner during our college days. You may notice in the introduction, proponents of previous researchers who have conducted a similar study before since the opinion of experts gives the study basis and grounds as to why this topic requires more future studies. You may also see thesis proposal .
Introduction
Even as traditional media continues to be overshadowed by the insurmountable rise of electronic technology such as internet and mobile phones to access online information, daily newspapers have remained to be a key platform in disseminating public information which incites public discourse. A banner story of a newspaper is considered the highlight and most important news story of the day as newspapers follow an order of stories by arranging them of importance from front to inside pages (Tewksbury, 2002). You may also see personal essay .
At present, however, the media is confronted with issues such as making sensationalized, misleading, and satirical news stories not primarily to provide what the readers need to know, but rather to increase the issue’s marketability and compensate for the company’s production cost. Its gigantic headline running from corner to corner accompanied by its banner picture along with the story itself are put in place to draw readers’ attention and set the tone of the issue (Saxena, 2013). These existing practices greatly affect the placement of news stories from the most relevant and significant ones to the least leaving behind many substantial stories given less attention or least, under-reported. Moreover, this dilemma defeats the purpose of the main objectiveof journalism which is to provide the citizenry with information that is vital in shaping their realities and guide them in their decision making which then collates to a more systematic society. You may also see persuasive essay .
For instance, a local English daily placed the slain Bohol town mayor’s story, which reached national coverage, as its banner story of the issue while placing the progress of Cebu City’s Bus Rail Transit (BRT) project, which offers an opportunity for citizens to escape from the almost unmanageable metropolitan traffic jam when pushed through, in the latter pages of the issue. More so, with the long-aged flood problem in the metropolis especially during rainy season, a local English daily published on its second page an article entitled “Garganera: No program to solve flooding” due to the lack of comprehensive programs. You may also see short essay .
However, this did not land in the banner story, despite the relevance and the problem it seeks to raise; instead, a story about a landslide that killed two people was the highlight of the day. Hence, as it can be observed, politics, crime or disaster-based news which would likely create a stir among readers are most often than not picked as the banner story of the day. There are other news stories in other news categories that if written with the right angle and is deemed timely, can have its chance at the banner story. The news is a by-product of a journalist’s job of gathering enough evidence, conducting interviews and constant research in pursuit of the truth. In a newsroom, it is the editorial board that decides what news should be placed as the banner story which they perceive to be the most relevant news for the public to know. You may also see essay examples .
But sometimes, what the newspapers present as their banner story may not really align with the readers’ interests or perhaps may not strike as the most important or critical issue of the day. According to MacGregor (2007), journalists have been known to stray from their audiences in the context of traditional media. Gieber asserts (1960: 2004) that “news selection has no direct relationship to the wants of readers.” Gans (1979) further emphasizes Gieber’s point saying that journalists pay little to no attention to audience feedback, but place certain news together based on what they think would interest their audiences. You may also see reflective essay .
However, most, if not all of the reading public has no clue on how the editorial board decides each story’s position and inclusion. A proof of the abovementioned issues encompassing the news media industry is the presence of internal watchdogs that specialize on in-depth journalism to cover that under-reported news that is often overlooked by the mainstream news media. The Reuters Foundation is among those that provide the public with stories unlikely read or seen in the mainstream news such as humanitarian, women’s rights, human trafficking-based news. You may also see student essay .
One way or another, the media, in whatever form that it takes will never be perfect and will always be accused of bias and sensationalism which leads to public distrust. According to the analysis of some scholars, (Blumler and Gurevitch, 1995; McManus, 1994; Grabe et al., 2001) they have observed that the news is becoming more sensational or ‘tabloid-like’ over time. These kinds of stories may render the news more ‘colorful’ but are not exactly more informative (Blumler and Gurevitch, 1995; Franklin, 2005). You may also see analytical essay
Which is why one other end goal that the study wants to achieve is for each newspaper editorial board to be transparent on how the body decides each story should be written as well as the selection process of the news stories that determine which page each story belongs to. At the same time, it is also crucial that the public themselves understand how the editorial process is being done to grasp the concept behind story selection and editorial judgment in hopes that the strong trust between the public and the media will be restored once more as the media continues to deliver the news to the reading public with the challenge that they remain loyal and trustworthy by them.You may also see concept essay .
Only front-page studies are available for the researchers’ basis for their research as there were very minimal studies on banner stories. This study will be conducted for the purpose of understanding the present landscape of Cebu’s three local English newspapers. As compared to other media researchers, this will focus on identifying the most frequent news category published in the banner story of Cebu’s three local English newspapers: Cebu Daily News, SunStar Cebu, and The Freeman. Additionally, the researchers would also analyze the rhetoric of the dailies based on 1) the news values assigned by the journalists in every news story, and 2) the standard basis utilized by each newspaper’s editorial board in the selection process of news stories.You may also see comparative essay .
If you think the Introduction part of the thesis is exhausting, just wait until you get to the theoretical background and the review of related literature. They say those parts just crushes the soul out of you during the first half of your thesis writing. But do not fret. Because even though writing a thesis is like taking a walk in the park (Jurassic Park), all that hassle is really worth the tassel. Good luck!
Thesis Table Of Contents Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
- MS Publisher
Size: 36 KB
Thesis Proposal Template

Size: 80 KB
Thesis Proposal Gantt Chart Template

Size: 30 KB
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Luyện thi IELTS
- Luyện thi TOEIC
- Luyện thi HSK
- Tiếng Anh Giao Tiếp
- Luyện đề IELTS
- Luyện đề TOEIC
- Luyện đề THPTQG
Search blog
The ultimate guide to mastering the detailed approach to writing ielts writing task 2: introduction.
Writing a captivating IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction is one of the topics that many IELTS test takers are interested in while preparing for the exam. How can you create an effective IELTS Task 2 introduction to impress the examiner during the actual IELTS test? Refer to the article below to fully grasp the art of writing an Introduction for Writing Task 2!

I. Structure of the IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction
1. writing the general statement, 2. writing the thesis statement.
In writing the introduction for IELTS Writing Task 2, it is important to adopt a mindset of being concise and avoiding excessive elaboration and vague statements. The primary objective of the introduction is to effectively introduce the content of the essay and provide a clear direction for the reader regarding the upcoming discussion.
Firstly, it is crucial to understand the components of the introduction. The introduction in Task 2, known as the IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction, consists of two parts: the General Statement and the Thesis Statement.
- General Statement: This introductory sentence or two serves to introduce the topic of the essay. It should provide enough context to orient the reader and establish the relevance of the chosen subject matter. However, it is important to avoid going into too much detail or introducing specific arguments at this stage. Instead, focus on providing a broad overview that sets the stage for the subsequent discussion.
- Thesis Statement: Following the general statement, the thesis statement provides a roadmap for both the writer and the reader. It succinctly outlines the main points or arguments that will be addressed in the essay, serving as a preview of the forthcoming analysis. The thesis statement should be clear, concise, and directly relevant to the essay prompt, outlining the writer's stance or position on the topic.
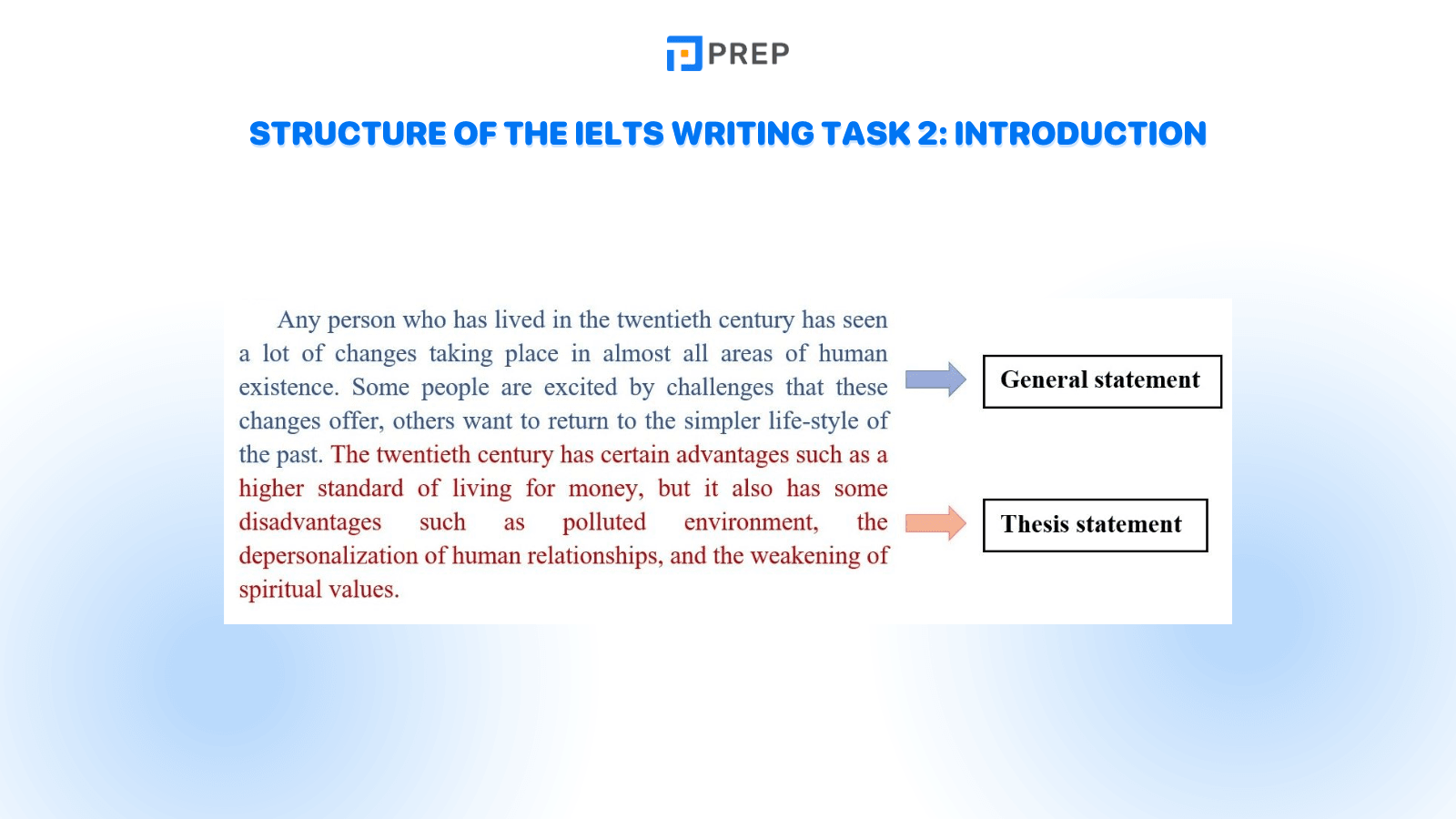
For further reference, please consult the following article:
- How to Write a Topic Sentence in IELTS Writing Task 2!
II. How to Write an IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction
The topic sentence in IELTS Writing Task 2 introduces the topic of the essay. Since the essay topic is provided in the task's prompt, you can simply paraphrase it to write the General Statement.
Task: Some people think that children must be given homework everyday to be successful at school. Others think they should be allowed to enjoy their leisure time after school without homework. Discuss both views and give your opinion.

For the given prompt, which presents two contrasting views, you can use the following structure to incorporate both views into the General Statement in the IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction:
There is an argument about whether SV
Since the prompt discusses two opposing viewpoints but generally focuses on the same subject (in this case, "young children"), this structure allows you to express both ideas in one sentence without repeating the subject. Applying this structure to the prompt, we have the following sentence:
➡ There is an argument about whether young students should be assigned homework on a daily basis or allowed to enjoy their leisure time free of extra work from school.
The Thesis Statement serves as a roadmap for both the writer and the reader. In this sentence, when writing the IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction, you have two options:
Task: Some people think that children must be given homework every day to be successful at school. Others think they should be allowed to enjoy their leisure time after school without homework. Discuss both views and give your opinion.

- For prompts that ask for personal opinion (e.g., "Discuss both views and give your opinion") ➡ Express your personal standpoint. A note to consider is that we often write a contrasting sentence to indicate that we acknowledge viewpoint A but still support viewpoint B. The following sentence uses the structure "Although SV, SV" to convey this idea: ➡ Although some may advocate the latter view, I would contend that the practice of accomplishing given homework is highly beneficial to students.
- For prompts that do not ask for personal opinion (e.g., "Discuss both views") ➡ Simply outline the plan for the essay without expressing a personal opinion ➡ This essay will discuss both sides of the issues before a conclusion is drawn.
Hopefully, the insights on writing an IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction shared by PREP above will be helpful for IELTS test takers. If you have any further questions or concerns regarding the knowledge presented in the above section, please leave a comment below the article to receive the most helpful response from PREP.

Đăng ký tư vấn lộ trình học
Bạn hãy để lại thông tin, Prep sẽ liên hệ tư vấn cho mình ngay nha!

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
2. Hook the reader and grab their attention. 3. Provide relevant background. 4. Give the reader a sense of what the paper is about. 5. Preview key points and lead into your thesis statement. Frequently Asked Questions about writing a good thesis introduction.
An example of a thesis statement in an introduction could be: "This thesis examines how social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly Twitter) have reshaped how individuals interact and form relationships in the digital age, with an emphasis on interpersonal communication."Clearly state the main focus and purpose of your research and provide a roadmap for the reader to ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Cite a dramatic fact or statistic. Your introduction also needs to adequately explain the topic and organization of your paper. Your thesis statement identifies the purpose of your paper. It also helps focus the reader on your central point. An effective thesis establishes a tone and a point of view for a given purpose and audience.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
I collected some further key points, which are also indicated by the Harvard University (to give you examples of how to write a good thesis introduction: 2 - Keep your writing short and concise. 3 - Check and present the best examples. 4 - Don't make use of (too) specific vocabulary. 5 - Outline the principal key points, keep the ...
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction.
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
Here are some useful writing tips for writing a great thesis introduction. Identify and Specify Research Parameters: Define the Research Scope and Boundaries. Set Research Parameters in the Introduction. Provide Adequate Information to Back Up Claims: Support Claims with Relevant Information.
Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide. Is a thesis statement a question? A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
A good thesis introduction doesn't shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader's attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter. This honesty allows the reader to understand the research's focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
An effective PhD thesis introduction does three things: 1. Establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context) One of the first things the introduction should do is to provide general statements that outline the importance of the topic and provide enough background information so that the reader can understand ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
1. Writing a thesis introduction at the right time. There are 2 schools of thought on the ideal time to write a thesis introduction: Write your introduction after the writing plan has been finalised (at the start of the dissertation or thesis project). Write your introduction after you have finished writing your thesis (at the end of the project).
In general, introductions should be short. If your topic requires extensive background to understand, it's best to dedicate a few paragraphs to this after the introduction. How to write a thesis statement. Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are ...
When writing a thesis, you will need to write an introductory chapter. This chapter is critical as it is the first thing that the examiner will read and it is therefore important to make a good first impression. A good introduction chapter should incite the reader to read the rest of the thesis by establishing the context of your topic, the ...
Identify the importance of the proposed research. State the research problem/questions. State the research aims and/or research objectives. State the hypotheses. Outline the order of information in the thesis. Outline the methodology. Listed below is a sample thesis introduction that was made by me and my partner during our college days.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan. A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay.It usually comes near the end of your introduction.. Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you're writing.
2. Writing the Thesis Statement. The Thesis Statement serves as a roadmap for both the writer and the reader. In this sentence, when writing the IELTS Writing Task 2: Introduction, you have two options: Task: Some people think that children must be given homework every day to be successful at school.