- Physiological Processes
- Biological Science

Understanding the Types of Stress

- University of Delhi
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Psychology Discussion
Essay on stress: it’s meaning, effects and coping with stress.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Stress: It’s Meaning, Effects and Coping with Stress!
Stress is a very common problem being faced today. Every individual will experience stress in one or the other time.
The term stress has many definitions, Lazarus and Folkman (1984) have defined stress as “an internal state which can be caused by physical demands of body or by environmental and social situations, which are evaluated as potentially harmful, uncontrollable, or exceeding our resources for coping”.
According to David Fontana “stress is a demand made upon the adaptive capacities of the mind and body”.
These definitions indicate that stress represents those conditions under which individuals have demand made upon them, that they cannot physically or psychologically meet, leading to breakdown at one or other of these levels.
Stress is usually thought of in negative terms. But ii can manifest itself in both positive and negative way. It is said to be positive when the situation offers an opportunity for one, to gain something.
Eustress (the Greek word ‘eu’ means good) is the term used to describe positive stress. It is often viewed as motivator, since in its absence the individual lacks the spirit necessary for peak performance. Distress is the term used to indicate negative stress.
Almost any change in the environment- even a pleasant change such as a joyful trip- demands some coping, and a little stress is useful in helping us to adapt. But beyond some point, stress becomes a ‘distress’.
What acts to produce distress varies from person to person, but some events seem to be stressors for every person.
Examples of stressors are:
1. Injury or infections of the body, dangers in environment, major changes or transitions in life which force us to cope in new ways.
2. Physical stressors like noise, pollutions, climatic changes, etc.
3. Hustles of everyday life centering on work, family, social activities, health and finances.
4. Frustrations and conflicts.
The physical, environmental and social causes of the stress state are termed stressors. Once induced by stressors the internal stress state can then lead to various responses. On the other hand, psychological responses such as anxiety, hopelessness, depression, irritability, and a general feeling of not being able to cope with the world, can result from the stress state.
Stress cycles:
Stress has a number of immediate effects. If the stressors are maintained, long-term behavioural, physiological, emotional and cognitive effects occur. If these effects hinder adaptation to the environment or create discomfort and distress, they themselves become stressors and, tend to perpetuate a ‘cycle’ of distress.
Example, a patient spends more money on treatment, may experience continued stress even after the cure of the disease, because repayment of debt cause stress for long time in him or a patient whose leg is amputated after accident may continue to worry about it.
On the other hand, many people have developed ways of coping with stressors, so that they are able to respond adaptively. This is the ‘wellness cycle’. Teaching people adaptive ways of handling stress, so as to promote the wellness cycle is an important part of the newly emerging field of behavioural medicine.
Effects of stress:
Stress is not always harmful. In fact, it is recognised that low levels of stress can even helps for better performance. For example, a student can prepare well for forthcoming examination only if he has some stress. However, excess level of stress is undoubtedly harmful.
The effects of stress are divided into three categories:
a. Physiological effects:
Commonly appearing stress related bodily disorders are-peptic ulcers, hypertension, chronic fatigue, hormonal changes, increased heart rate, difficulty in breathing, numbness of limbs, heart disease and reduction in immunity, etc.
b. Psychological effects:
Anxiety, depression, hopelessness, helplessness, anger, nervousness, irritability, tension and boredom may be experienced.
c. Behavioural changes:
Decreasing efficiency, making mistakes, inability to take decisions, under eating or overeating, sleeplessness, increased smoking, develop addiction to alcohol and drugs, forgetfulness, hypersensitivity or passiveness, accident proneness and interpersonal difficulties are seen.
Stress is linked to disorders such as cancer and heart disorders. There are several mediating variables that determine whether stress becomes dangerous or not. For example, good coping mechanisms which can help to reduce stress, having good social support, often help in reducing stress.
Perception of stress or how a person views stress is also very important. For example, a person may not perceive a situation as stressful whereas the same situation may be perceived as highly stressful by some other person.
People with personality type ‘A’ are more prone to be affected by stress related disorders like cardiovascular diseases. Personality character like hardiness or emotional stability helps to withstand effects of stress.
Hans Selye, a renowned biological scientist defines stress as the nonspecific response of the body to any demand upon it. He termed the body’s response to stressors the “General Adaptation Syndrome” (GAS).
The GAS consists of 3 stages:
1. Alarm reaction:
It is an emergency response of the body. In this stage prompt responses of the body, many of them mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, prepare us to cope with the stressor here and now.
2. Stage of resistance:
If the stressor continues to be present, the stage of resistance begins, wherein the body resists the effects of the continuous stressor. During this stage certain hormonal responses of the body are an important line of defence in resisting the effects of stressors (For example, release of ACTH).
3. Stage of exhaustion:
In this stage, the body’s capacity to respond to both continuous and new stressors has been seriously compromised. The person will no longer be able to face stressor and he will finally succumb to it. The person may develop psychosomatic illness.
The stress leads to many psychosomatic diseases. Treatment for such diseases involves medical help for the physical problems and, at the same time, attention to the psychological factors producing the stress.
Coping with Stress :
There are different ways of coping with stress such as: confronting (facing), distancing (remoteness), self-control, seeking social support, accepting responsibility, escape or avoid (from the stressor), plan a problem solving strategy and positive reappraisal.
Usually two broad type of coping types are seen- Instrumental coping and Emotional coping.
In instrumental coping, a person focuses on the problem and tries to solve it. In emotional coping, the focus is more on the feelings generated by the problem.
Today, self- help remedies, Do to yourself approaches, weight loss clinics and diets, health foods and physical exercise are being given much attention in mass media. People are actually taking more responsibility to maintain good health.
However, some specific techniques to eliminate or to manage more effectively the inevitable, prolonged stress are as follows:
Good physical exercise like walking, jogging, swimming, riding bicycle, playing soft ball, tennis are necessary to cope with stress.
Relaxation:
Whether a person simply takes it easy once in a while or uses specific relaxation techniques such as bio-feedback, or meditation, the intent is to eliminate the immediately stressful situation or manage a prolonged stressful situation more effectively.
Taking it easy may mean curling up with a good book on an easy chair or watching some light programme on television or listening to a light music. Meditation is scientifically proved to be very useful, both physically and mentally to cope with stress.
Behavioural self-control:
By deliberately managing the antecedents and the consequence of their own behaviour, people can achieve self-control. Besides managing their own behaviour to reduce stress, people can also become more aware of their limits and of ‘red flags’ that signal trouble ahead. They can avoid people or situations that they know will put them under stress.
Maladaptive strategies, rigid strategies or relying on one type of coping method lead to increase in the stress. Social support helps reduce the effect of stress. People may provide help, advice, material support or moral support that helps to reduce stress.
In addition to the above, psychotherapy (Beck’s cognitive therapy, Ellis’s rational emotive therapy and Meichenbaum’s stress- inoculation training), skill training, environmental changes, Bio-feedback (control of physical signs such as Blood pressure, headache, etc), family therapy, group therapy, hypnosis, yoga, are found to be very useful. Finally, uses of drugs are some of the other strategies adopted in coping with stress.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Tension: Meaning, Causes and Effects
- Stress: Meaning, Causes and Suggestions to Manage It
- Essay on Stress: Top 7 Essays | Human Behaviour | Psychology
- Emotions in Children: Meaning, Effects and Hints | Term Paper | Psychology

The Three Types of Stress
There are three kinds of stress that each take a toll on the body..
Posted December 7, 2018 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- What Is Stress?
- Take our Burnout Test
- Find a therapist to overcome stress
Understanding stress can help you know more quickly when you need help.
Stress is our built-in response to danger, a surge in hormones as we choose between fighting, fleeing, or freezing. The danger may be real or imagined, immediate or farther away; our bodies don’t know the difference.
According to the American Psychological Association, the three types of stress — acute stress, episodic acute stress, and chronic stress — can all make us feel out of sorts or even ill, but chronic stress is often ignored.
Acute Stress. You know the feeling when you’re behind on a seemingly all-important deadline and then you get a call from your child’s school asking you to come by or you barely miss a serious car accident.
Your heart might race and your blood pressure might rise. Your sense of emergency might trigger a migraine or even chest pain.
Other possible symptoms include irritability, anxiety , sadness, headaches, back pain, and gut problems. These may appear for a short time and subside when the stress eases.
Our minds extend acute stress. A recent argument may replay in your mind, keeping you up at night. Or you might keep worrying about the future, a deadline ahead. You might benefit from learning techniques to calm your mind, but stress isn’t interfering with your relationships or career .
Episodic acute stress. Some people experience these mini-crises regularly and live in a state of tension. They may be taking on too much or simply be overburdened by their lives. If you tend to worry, your body will be tense or angry.
The symptoms are similar but occur more often and accumulate.
Maybe your company is poorly managed and your boss is stressed out, passing along emergencies to you. Those tight deadlines keep cropping up.
In modern life, we often can’t take big, immediate actions to solve our problems. Instead, we can take small steps that build up over time.
You might need to spend more time getting physical exercise while rethinking your finances in case you need to quit. You might need the help of a therapist to change your circumstances or your responses to them.
Over time, a pattern of episodic acute stress can wear away at your relationships and work.
That risk is greater if you turn to unhealthy coping strategies like binge drinking, overeating, or clinging to bad relationships. Many people also slowly give up pursuing pleasurable activities or meaningful goals .
If poorly managed, episodic acute stress can contribute to serious illnesses like heart disease or clinical depression .
Chronic stress. This is the grinding stress that wears us down over the years. It arises from serious life problems that may be fundamentally beyond our control: poverty, war, or racism .
The demands are unrelenting and you don’t know when they will stop. You get by day by day.
If you had a traumatic childhood , you may experience life as chronically stressful even when the surface appears okay. You believe you are perpetually threatened by poverty or illness even when this is untrue.
Whether the cause lies in your mindset or difficult circumstances, many people stop fighting for change and begin to accommodate chronic stress.
It is important to get all the help you can and not blame yourself — blame will only grind you down further. Chronic stress feeds chronic and acute serious illness.
How can you actually use this information? When you’re overwhelmed, making distinctions — how bad is it really? — may feel impossible or unsympathetic. But distinguishing between these three types of stress will help you see your own circumstances clearly. Are you overreacting, seeing a temporary situation as permanent? Or have you been ignoring the signs for years? Again, blame won’t help. Knowing the three types should also help you find perspective and feel more compassion for other people who are under stress.

A version of this story appears on Your Care Everywhere.

Temma Ehrenfeld is a New York-based science writer, and former assistant editor at Newsweek .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Benefits of Good Stress
Sometimes, stress can actually be a good thing
Hill Street Studios/Blend Images / Getty Images
What Is Good Stress?
Examples of good stress.
- When Good Stress Becomes Bad
- How Bad Stress Can Become Good
While we often think of stress as something negative to be avoided, it is a natural and expected part of daily life. You might be surprised to hear that some stress is actually considered "good stress." Also known as eustress , it is the type of stress you might feel before a first date or important competition.
When we feel good stress, our heart rate increases, our breathing rate increases, and we feel a thrill of excitement. It's a short-term change in our bodies that helps us to feel prepared, energized, and ready to perform at our best.
We rarely hear people say, "I'm really feeling stressed. Isn't that great?" But we'd feel rudderless and unhappy if we didn't have some stress in our lives—the "good stress" variety. If we define stress as anything that alters our homeostasis, then good stress, in its many forms, is vital for a healthy life. Bad stress , or distress, can even turn into good stress and vice versa, depending on the situation.
At a Glance
Good stress helps you feel excited and energized, and it's important to have it in your life. While bad stress can harm your health, good stress can promote well-being. Changing your perception of stress can help. So can adding positive activities to promote eustress (aka, the good kind of stress). Together, these strategies help you create a healthy balance in your life.
"Good stress," or what psychologists refer to as " eustress ," is the type of stress we feel when we are excited. Our pulse quickens and our hormones surge, but there is no threat or fear.
We feel this type of stress when we ride a roller coaster, compete for a promotion, or go on a first date. There are many triggers for this good stress, and it keeps us feeling alive and excited about life.
A certain level of stress helps keep your mind and body alert and ready to respond. It can be motivating and help you perform your best.
According to Yerkes-Dodson law , stress can improve performance--at least, up to a certain point. Once you pass that point, stress can take a toll on your ability to perform well.
Good Stress vs. Bad Stress
Another type of stress is acute stress. It comes from quick surprises that need a response. Acute stress triggers the body's stress response as well, but the triggers aren't always happy and exciting. This is what we normally think of as "stress" (or "bad stress").
Acute stress in itself doesn't take a heavy toll if we find ways to relax quickly. Once the stressor has been dealt with, we need to return our body to homeostasis, or its pre-stress state, to be healthy and happy.
Chronic stress is another form of bad stress. It occurs when we repeatedly face stressors that take a heavy toll and feel inescapable. A stressful job or an unhappy home life can bring chronic stress. This is what we normally think of as serious stress .
Because our bodies aren't designed for chronic stress, we can face negative health effects (both physical and emotional) if we experience chronic stress for an extended period of time.
How Can Good Stress Be Beneficial?
How exactly can stress be helpful? When you feel excited about something, your more likely to feel alert and motivated. It can improve your mood and help you perform your best. But those aren't the only benefits.
- Cognitive benefits : Research suggests that short-term stress positively impacts memory . This can be useful in some situations, such as when taking an exam.
- Better resilience : When you face a stressful situation, it can help you learn more about yourself, your skills, and your limits. As you learn more about what you are capable of, you're more likely to feel able to handle such situations in the future.
- Stronger immunity : While bad stress hurts your immune system, some research indicates that short-term stressors can help improve your body's ability to deal with illness and injury. In one study, for example, researchers found that short-term stress improves immunity in people with infections or wounds.
Yes, you can add good stress to your life! Ideally, you choose activities and set goals that make you feel good, happy, and excited. To gauge whether or not an activity is worth your time, pay attention to how the thought of it makes you feel.
Do you feel excited? Is it a "want to," or a "have to"? Be sure your "want to" activities are all things you really do want to do, and your "have to" activities are all absolutely necessary.
Examples of ways you can create more good stress in your life include:
- Taking on work projects that you are excited about : These projects allow you to use your strengths but also challenge you to learn new things.
- Learning more about something that you are passionate about : Hobbies and personal interests can be a great source of eustress. You might try out new skills or try out new things that hold your interest and challenge your current abilities.
- Engaging in physical exercise : Moving your body can be a form of good stress. As you keep working, you can add challenges that help build your physical strength, flexibility, and endurance.
- Traveling to new places : Travel brings new experiences and challenges and allows you to meet new people and learn more about different cultures. It can be stressful, but it's a good sort of stress as long as you're excited and having fun.
Life changes can also be a source of good stress. Getting married, starting a family, getting a new job, or moving to a new place are all transitions that can be stressful, often in a good way.
Sometimes these changes might not start off great, however. Losing your job or ending a relationship can create bad stress. Changing how you look at the situation, such as viewing it as a chance for growth, can help shift negative stress into good stress.
Whether something counts as good stress or bad stress can also vary from one person to the next. Something that one person experiences in a positive way might trigger distress in someone else.
How Good Stress Can Become Bad Stress
Good stress can become bad for you if you experience too much of it. ( Thrill seekers know this firsthand.) This is because your stress response is triggered either way, and if you're adding that to chronic stress, or several other stressors, there is a cumulative effect.
Be in tune with yourself and acknowledge when you've had too much. You may not be able to eliminate all stress, but there are often ways to minimize or avoid some of the stress in your life, which can make it easier to handle the rest.
If you can avoid the most taxing forms of stress , you'll have more resilience against other types of stress that are unavoidable.
How Bad Stress Can Become Good Stress
Not all forms of bad stress can become good stress, but it is possible to change your perception of some of the stressors in your life. This shift can change your experience of stress.
The body reacts strongly to perceived threats. If you don't perceive something as a threat, there is generally no threat-based stress response.
If you perceive something as a challenge instead, the fear you normally experience may turn into excitement, anticipation, or at least resolve. You can often make the shift in perception by:
- Focusing on the resources you have to meet the challenge
- Seeing the potential benefits of a situation
- Reminding yourself of your strengths
- Having a positive mindset (getting into the habit of thinking like an optimist )
As you practice looking at threats as challenges more often, it becomes more automatic, and you experience more good stress and less bad stress.
Pluut H, Curșeu PL, Fodor OC. Development and validation of a short measure of emotional, physical, and behavioral markers of eustress and distress (MEDS) . Healthcare (Basel) . 2022;10(2):339. doi:10.3390/healthcare10020339
Aschbacher K, O'Donovan A, Wolkowitz OM, Dhabhar FS, Su Y, Epel E. Good stress, bad stress and oxidative stress: insights from anticipatory cortisol reactivity . Psychoneuroendocrinology . 2013;38(9):1698-708. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.02.004
Lu S, Wei F, Li G. The evolution of the concept of stress and the framework of the stress system . Cell Stress . 2021;5(6):76-85. doi:10.15698/cst2021.06.250
Rowland DL, van Lankveld JJDM. Anxiety and performance in sex, sport, and stage: Identifying common ground . Front Psychol. 2019;10:1615. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01615
Yaribeygi H, Panahi Y, Sahraei H, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. The impact of stress on body function: A review . EXCLI J . 2017;16:1057-1072. doi:10.17179/excli2017-480
Dhabhar FS. The short-term stress response - Mother nature's mechanism for enhancing protection and performance under conditions of threat, challenge, and opportunity . Front Neuroendocrinol . 2018;49:175-192. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.03.004
Lu S, Wei F, Li G. The evolution of the concept of stress and the framework of the stress system . Cell Stress . 2021;5(6):76-85. doi:10.15698/cst2021.06.250
By Elizabeth Scott, PhD Elizabeth Scott, PhD is an author, workshop leader, educator, and award-winning blogger on stress management, positive psychology, relationships, and emotional wellbeing.

How stress affects your health
Stress can be brief, situational, and a positive force motivating performance, but if experienced over an extended period of time it can become chronic stress, which negatively impacts health and well-being.
- Chronic Illness

Stress : We’ve all felt it. Sometimes stress can be a positive force, motivating you to perform well at your piano recital or job interview. But often—like when you’re stuck in traffic—it’s a negative force. If you experience stress over a prolonged period of time, it could become chronic—unless you take action.
A natural reaction
Have you ever found yourself with sweaty hands on a first date or felt your heart pound during a scary movie? Then you know you can feel stress in both your mind and body.
This automatic response developed in our ancient ancestors as a way to protect them from predators and other threats. Faced with danger, the body kicks into gear, flooding the body with stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol that elevate your heart rate, increase your blood pressure, boost your energy, and prepare you to deal with the problem.
These days, you’re not likely to face the threat of being eaten. But you probably do confront multiple challenges every day, such as meeting deadlines, paying bills, and juggling childcare that make your body react the same way. As a result, your body’s natural alarm system—the “fight or flight” response—may be stuck in the on position. And that can have serious consequences for your health.
Pressure points
Even short-lived, minor stress can have an impact. You might get a stomachache before you have to give a presentation, for example. More major acute stress, whether caused by a fight with your spouse or an event like an earthquake or terrorist attack, can have an even bigger impact.
Repeated acute stress may also contribute to inflammation in the circulatory system , particularly in the coronary arteries, and this is one pathway that is thought to tie stress to a heart attack. It also appears that how a person responds to stress can affect cholesterol levels.
Chronic stress
When stress starts interfering with your ability to live a normal life for an extended period, it becomes even more dangerous. The longer the stress lasts, the worse it is for both your mind and body. You might feel fatigued, unable to concentrate, or irritable for no good reason, for example. But chronic stress causes wear and tear on your body, too.
The long-term activation of the stress response system and the overexposure to cortisol and other stress hormones that come with it can disrupt almost all of your body's processes. This can put you at increased risk for a variety of physical and mental health problems, including anxiety, depression, digestive issues, headaches, muscle tension and pain, heart disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, stroke, sleep problems, weight gain, and memory and concentration impairment.
Chronic stress may also cause disease, either because of changes in your body or the overeating, smoking, and other bad habits people use to cope with stress. Job strain—high demands coupled with low decision-making latitude—is associated with increased risk of coronary disease , for example. Other forms of chronic stress, such as depression and low levels of social support, have also been implicated in increased cardiovascular risk.
Chronic stress also suppresses the body's immune system , making it harder to recover from illnesses.
What you can do
Reducing your stress levels can not only make you feel better right now, but may also protect your health long-term. Several research studies have demonstrated, for example, that interventions to improve psychological health can have a beneficial impact on cardiovascular health . As a result, researchers recommend boosting your positive affect—feelings like happiness, joy, contentment, and enthusiasm—by making time for enjoyable activities every day.
Other strategies for reducing stress include:
- Identify what’s causing stress. Monitor your state of mind throughout the day. If you feel stressed, write down the cause, your thoughts, and your mood. Once you know what’s bothering you, develop a plan for addressing it. That might mean setting more reasonable expectations for yourself and others or asking for help with household responsibilities, job assignments, or other tasks. List all your commitments, assess your priorities, and then eliminate any tasks that are not absolutely essential.
- Build strong relationships. Relationships can be a source of stress. Research has found that negative, hostile reactions with your spouse cause immediate changes in stress-sensitive hormones, for example. But relationships can also serve as stress buffers. Reach out to family members or close friends and let them know you’re having a tough time. They may be able to offer practical assistance and support, useful ideas, or just a fresh perspective as you begin to tackle whatever’s causing your stress.
- Walk away when you’re angry. Before you react, take time to regroup by counting to 10. Then reconsider. Walking or other physical activities can also help you work off steam. Plus, exercise increases the production of endorphins, your body’s natural mood booster. Commit to a daily walk or other form of exercise—a small step that can make a big difference in reducing stress levels.
- Rest your mind. To help ensure you get the recommended seven or eight hours of shut-eye, cut back on caffeine, remove distractions such as television or computers from your bedroom, and go to bed at the same time each night. Research shows that activities like yoga and relaxation exercises not only help reduce stress, but also boost immune functioning .
- Get help. If you continue to feel overwhelmed, consult with a psychologist or other licensed mental health professional who can help you learn how to manage stress effectively. They can help you identify situations or behaviors that contribute to your chronic stress and then develop an action plan for changing them.
Recommended Reading

Related reading
- Stress effects on the body
- Stress in America
You may also like
Stress and Its Effects on Health Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Physical effects, psychological effects, behavioral effects.
Stress is the emotional strain or tension experienced by an individual due to a reaction toward various demanding and influential situations. The challenging or compelling situations are termed stressors. Stressors can be internal or external and include life changes such as losing a significant figure, low socioeconomic status, relationship problems, occupational challenges, and familial or environmental factors. An individual’s response to stressors influences the outcome of their life. Health is a state of complete social, emotional, and physical well-being and not merely the absence of disease. Stress is a common risk factor for negative health status secondary to negative adaptation and coping with the stressors. Stressors can create a strain on one’s physical, psychological and behavioral well-being, leading to lasting effects that are detrimental to one’s health.
Stress is associated with various physical health impacts on an individual. In an online cross-sectional survey by Keech et al. (2020) to determine the association between stress and the physical and psychological health of police officers, the findings illustrate that stress negatively impacts physical and psychological well-being. One hundred and thirty-four police officers were involved in the study (Keech et al., 2020). The findings demonstrate that stress resulted in various short and long-term physical effects that included increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. In addition, stress resulted in the development of gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer and irritable bowel syndrome. Keech et al. (2020) note that stress’s associated physical health effects are explained by various mechanisms that include overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis.
Overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system results in increased sympathetic actions on the peripheral body organs leading to increased sweat production, heart rate, respiration rate, and urinary and bowel elimination. The study notes that chronic stress without positive adaptation measures results in the progressive development of hypertension, peptic ulcers, and irritable bowel syndrome as long-term effects (Keech et al., 2020). Within the gastrointestinal tract, chronic stress activity on the sympathetic nervous system results in increased parietal cell action. Overactivity of the parietal cells results in excessive gastric acid production, gradually eroding the mucosa, and ulceration occurs.
The effects of stress on the cardiovascular system are explained in a review by Kivimäki & Steptoe (2017) to determine the impact of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. In the review, stress is identified to cause cardiovascular conditions secondary to the effects of sustained sympathetic action on heart contractility and peripheral vascular resistance (Kivimäki & Steptoe, 2017). The sympathetic nervous system contributes to normal heart and blood vessel contractility. However, when the system is overstimulated, a surge in contractility above the normal limits ensues, leading to the progressive development of heart conditions.
Psychological well-being incorporates a positive mental health status evidenced by an individual’s satisfaction with life, happiness, rational thinking and decision-making, and positive mood patterns. Stress has been associated with alterations in an individual’s psychological wellness. An explanation for alteration in an individual’s psychological well-being secondary to stress is negative adaptation. Keech et al. (2020) note that an individual’s response to a stressor determines whether stress results in positive or negative effects. In the online cross-sectional survey by Keech et al. (2020), the findings illustrate that pressure resulted in the development of anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorders as long-term effects among the participants. Exposure to stressful situations resulted in progressively developing anxiety among the individual secondary to persistent worry over the issue. The anxiety results in other physical manifestations, including increased heart rate, palpitations, sweating, and altered mobility. Depression and bipolar conditions were also associated with chronic stress secondary to the impacts of stress on neurotransmitter function and nerves.
Similar findings are noted in a cross-sectional study by Zhang et al. (2020) to compare the prevalence and severity of stress-associated mental health symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and insomnia among healthcare workers during the COVID pandemic. Five hundred and twenty-four healthcare workers were involved in the study. The study findings illustrate that 31.3% of the participants developed depression secondary to the stressful working environment, 41.2% reported anxiety, and 39.3% reported sleep disturbances (Zhang et al., 2020). The scientific explanation for the relationship between stress and depression was attributed to the effects of stressful periods on neurotransmitter homeostasis. Chronic stress results in the altered regulation of neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. Alterations in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine resulted in the progressive development of depression and anxiety. Sleep disturbances reported by the participants are attributed to alterations in cortisol hormone homeostasis secondary to overstimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis.
Stressful situations can also lead to alterations in the behavioral patterns of an individual. The most common behavioral effects secondary to stress include the development of eating disorders, altered sleeping patterns, impaired concentration, and drug abuse especially alcohol. Alterations in sleep and eating patterns are linked to stress’s effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis (HPA). Exposure to stressful events leads to increased activation of the HPA axis with a net effect of increased catecholamine production (adrenaline and noradrenaline) (Moustafa et al., 2018). Increased adrenaline and noradrenaline production results in dysregulation in the eating and sleeping patterns. Sustained high levels of cortisol results in difficulty falling asleep and increased metabolic processes. The biological clock regulates the typical sleeping pattern that relies on producing the sleep hormone melatonin. Melatonin production by the pineal gland is regulated indirectly by the concentration of serum cortisol levels and directly by light perception. Imbalances in the serum concentration cycle secondary to stress results in imbalanced melatonin production and concentration with a net effect of sleeping difficulties.
The emotional strain caused by stress increases the risk of alcohol and other illicit drug use and dependence. Moustafa et al. (2018) conducted an integrative literature review to determine the relationship between childhood trauma, early-life stress, alcohol and drug use, addiction, and abuse. The review findings illustrate that stress increases the risk of alcohol and drug use, addiction, and abuse among the victims. An explanation for the increased risk is the individuals’ lack of identification and implementation of effective coping strategies (Moustafa et al., 2018). Lack of effective coping strategies results in maladaptive measures such as illicit drug use and alcohol consumption. Extensive use of the maladaptive measures results in progressive addiction and drug abuse among individuals with an increased predisposition to other health effects. Alcohol consumption and other illicit drug use over time increase the risk of developing cardiac, respiratory, and liver conditions.
Stress is the emotional strain or tension experienced by an individual due to a reaction toward various demanding and influential situations. Individual response to stressors influences their health. Maladaptive response to stress results in various physical, psychological, and behavioral negative effects. Negative effects of stress on physical health include increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. Psychological effects include the development of anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorders. The behavioral effects of stress on an individual include the development of eating disorders, altered sleeping patterns, impaired concentration, and abuse of alcohol and other drugs. Based on the research findings, it is essential for healthcare providers to identify strategic measures and health initiatives to educate and sensitize the community members on effective stress management approaches in all settings to aid in combating the health effects.
Keech, J. J., Cole, K. L., Hagger, M. S., & Hamilton, K. (2020). The association between stress mindset and physical and psychological well being: Testing a stress beliefs model in police officers . Psychology & Health , 35 (11), 1306-1325. Web.
Kivimäki, M., & Steptoe, A. (2017). Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease . Nature Reviews Cardiology , 15 (4), 215–229. Web.
Moustafa, A. A., Parkes, D., Fitzgerald, L., Underhill, D., Garami, J., Levy-Gigi, E., Stramecki, F., Valikhani, A., Frydecka, D., & Misiak, B. (2018). The relationship between childhood trauma, early-life stress, and alcohol and drug use, abuse, and addiction: An integrative review . Current Psychology , 40 (2), 579–584. Web.
Zhang, X., Zhao, K., Zhang, G., Feng, R., Chen, J., Xu, D., Liu, X., Ngoubene-Italy, A. J., Huang, H., Liu, Y., Chen, L., & Wang, W. (2020). Occupational Stress and Mental Health: A comparison between frontline medical staff and non-frontline medical staff during the 2019 novel Coronavirus Disease outbreak . Frontiers in Psychiatry , 11 . Web.
- Midlife Crisis in a 55-Year-Old Man
- Aspects of the Mental Health Essentials
- AUD: Psychopharmacologic Treatments
- Mood and Stress Psychology: Causes, Effects and Treatments
- Jessie as the Most Sympathetic Character of “Night, Mother” by Marsha Norman
- Intergenerational Trauma and Traumatic Memory
- The Lifespan Theory Applied to a Grieving Case
- Psychological Conditions in Addition to Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory
- Self-Control: Individual Development Plan
- Arachnophobia: Systematic Desensitization Project
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 19). Stress and Its Effects on Health. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/
"Stress and Its Effects on Health." IvyPanda , 19 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Stress and Its Effects on Health'. 19 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
1. IvyPanda . "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

STRESS AND HEALTH: Psychological, Behavioral, and Biological Determinants
Stressors have a major influence upon mood, our sense of well-being, behavior, and health. Acute stress responses in young, healthy individuals may be adaptive and typically do not impose a health burden. However, if the threat is unremitting, particularly in older or unhealthy individuals, the long-term effects of stressors can damage health. The relationship between psychosocial stressors and disease is affected by the nature, number, and persistence of the stressors as well as by the individual’s biological vulnerability (i.e., genetics, constitutional factors), psychosocial resources, and learned patterns of coping. Psychosocial interventions have proven useful for treating stress-related disorders and may influence the course of chronic diseases.
INTRODUCTION
Claude Bernard (1865/1961) noted that the maintenance of life is critically dependent on keeping our internal milieu constant in the face of a changing environment. Cannon (1929) called this “homeostasis.” Selye (1956) used the term “stress” to represent the effects of anything that seriously threatens homeostasis. The actual or perceived threat to an organism is referred to as the “stressor” and the response to the stressor is called the “stress response.” Although stress responses evolved as adaptive processes, Selye observed that severe, prolonged stress responses might lead to tissue damage and disease.
Based on the appraisal of perceived threat, humans and other animals invoke coping responses ( Lazarus & Folkman 1984 ). Our central nervous system (CNS) tends to produce integrated coping responses rather than single, isolated response changes ( Hilton 1975 ). Thus, when immediate fight-or-flight appears feasible, mammals tend to show increased autonomic and hormonal activities that maximize the possibilities for muscular exertion ( Cannon 1929 , Hess 1957 ). In contrast, during aversive situations in which an active coping response is not available, mammals may engage in a vigilance response that involves sympathetic nervous system (SNS) arousal accompanied by an active inhibition of movement and shunting of blood away from the periphery ( Adams et al. 1968 ). The extent to which various situations elicit different patterns of biologic response is called “situational stereotypy” ( Lacey 1967 ).
Although various situations tend to elicit different patterns of stress responses, there are also individual differences in stress responses to the same situation. This tendency to exhibit a particular pattern of stress responses across a variety of stressors is referred to as “response stereotypy” ( Lacey & Lacey 1958 ). Across a variety of situations, some individuals tend to show stress responses associated with active coping, whereas others tend to show stress responses more associated with aversive vigilance ( Kasprowicz et al. 1990 , Llabre et al. 1998 ).
Although genetic inheritance undoubtedly plays a role in determining individual differences in response stereotypy, neonatal experiences in rats have been shown to produce long-term effects in cognitive-emotional responses ( Levine 1957 ). For example, Meaney et al. (1993) showed that rats raised by nurturing mothers have increased levels of central serotonin activity compared with rats raised by less nurturing mothers. The increased serotonin activity leads to increased expression of a central glucocorticoid receptor gene. This, in turn, leads to higher numbers of glucocorticoid receptors in the limbic system and improved glucocorticoid feedback into the CNS throughout the rat’s life. Interestingly, female rats who receive a high level of nurturing in turn become highly nurturing mothers whose offspring also have high levels of glucocorticoid receptors. This example of behaviorally induced gene expression shows how highly nurtured rats develop into low-anxiety adults, who in turn become nurturing mothers with reduced stress responses.
In contrast to highly nurtured rats, pups separated from their mothers for several hours per day during early life have a highly active hypothalamic-pituitary adrenocortical axis and elevated SNS arousal ( Ladd et al. 2000 ). These deprived rats tend to show larger and more frequent stress responses to the environment than do less deprived animals.
Because evolution has provided mammals with reasonably effective homeostatic mechanisms (e.g., baroreceptor reflex) for dealing with short-term stressors, acute stress responses in young, healthy individuals typically do not impose a health burden. However, if the threat is persistent, particularly in older or unhealthy individuals, the long-term effects of the response to stress may damage health ( Schneiderman 1983 ). Adverse effects of chronic stressors are particularly common in humans, possibly because their high capacity for symbolic thought may elicit persistent stress responses to a broad range of adverse living and working conditions. The relationship between psychosocial stressors and chronic disease is complex. It is affected, for example, by the nature, number, and persistence of the stressors as well as by the individual’s biological vulnerability (i.e., genetics, constitutional factors) and learned patterns of coping. In this review, we focus on some of the psychological, behavioral, and biological effects of specific stressors, the mediating psychophysiological pathways, and the variables known to mediate these relationships. We conclude with a consideration of treatment implications.
PSYCHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF STRESS
Stressors during childhood and adolescence and their psychological sequelae.
The most widely studied stressors in children and adolescents are exposure to violence, abuse (sexual, physical, emotional, or neglect), and divorce/marital conflict (see Cicchetti 2005 ). McMahon et al. (2003) also provide an excellent review of the psychological consequences of such stressors. Psychological effects of maltreatment/abuse include the dysregulation of affect, provocative behaviors, the avoidance of intimacy, and disturbances in attachment ( Haviland et al. 1995 , Lowenthal 1998 ). Survivors of childhood sexual abuse have higher levels of both general distress and major psychological disturbances including personality disorders ( Polusny & Follett 1995 ). Childhood abuse is also associated with negative views toward learning and poor school performance ( Lowenthal 1998 ). Children of divorced parents have more reported antisocial behavior, anxiety, and depression than their peers ( Short 2002 ). Adult offspring of divorced parents report more current life stress, family conflict, and lack of friend support compared with those whose parents did not divorce ( Short 2002 ). Exposure to nonresponsive environments has also been described as a stressor leading to learned helplessness ( Peterson & Seligman 1984 ).
Studies have also addressed the psychological consequences of exposure to war and terrorism during childhood ( Shaw 2003 ). A majority of children exposed to war experience significant psychological morbidity, including both post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depressive symptoms. For example, Nader et al. (1993) found that 70% of Kuwaiti children reported mild to severe PTSD symptoms after the Gulf War. Some effects are long lasting: Macksound & Aber (1996) found that 43% of Lebanese children continued to manifest post-traumatic stress symptoms 10 years after exposure to war-related trauma.
Exposure to intense and chronic stressors during the developmental years has long-lasting neurobiological effects and puts one at increased risk for anxiety and mood disorders, aggressive dyscontrol problems, hypo-immune dysfunction, medical morbidity, structural changes in the CNS, and early death ( Shaw 2003 ).
Stressors During Adulthood and Their Psychological Sequelae
Life stress, anxiety, and depression.
It is well known that first depressive episodes often develop following the occurrence of a major negative life event ( Paykel 2001 ). Furthermore, there is evidence that stressful life events are causal for the onset of depression (see Hammen 2005 , Kendler et al. 1999 ). A study of 13,006 patients in Denmark, with first psychiatric admissions diagnosed with depression, found more recent divorces, unemployment, and suicides by relatives compared with age- and gender-matched controls ( Kessing et al. 2003 ). The diagnosis of a major medical illness often has been considered a severe life stressor and often is accompanied by high rates of depression ( Cassem 1995 ). For example, a meta-analysis found that 24% of cancer patients are diagnosed with major depression ( McDaniel et al. 1995 ).
Stressful life events often precede anxiety disorders as well ( Faravelli & Pallanti 1989 , Finlay-Jones & Brown 1981 ). Interestingly, long-term follow-up studies have shown that anxiety occurs more commonly before depression ( Angst &Vollrath 1991 , Breslau et al. 1995 ). In fact, in prospective studies, patients with anxiety are most likely to develop major depression after stressful life events occur ( Brown et al. 1986 ).
DISORDERS RELATED TO TRAUMA
Lifetime exposure to traumatic events in the general population is high, with estimates ranging from 40% to 70% ( Norris 1992 ). Of note, an estimated 13% of adult women in the United States have been exposed to sexual assault ( Kilpatrick et al. 1992 ). The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-IV-TR; American Psychiatric Association 2000 ) includes two primary diagnoses related to trauma: Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) and PTSD. Both these disorders have as prominent features a traumatic event involving actual or threatened death or serious injury and symptom clusters including re-experiencing of the traumatic event (e.g., intrusive thoughts), avoidance of reminders/numbing, and hyperarousal (e.g., difficulty falling or staying asleep). The time frame for ASD is shorter (lasting two days to four weeks), with diagnosis limited to within one month of the incident. ASD was introduced in 1994 to describe initial trauma reactions, but it has come under criticism ( Harvey & Bryant 2002 ) for weak empirical and theoretical support. Most people who have symptoms of PTSD shortly after a traumatic event recover and do not develop PTSD. In a comprehensive review, Green (1994) estimates that approximately 25% of those exposed to traumatic events develop PTSD. Surveys of the general population indicate that PTSD affects 1 in 12 adults at some time in their life ( Kessler et al. 1995 ). Trauma and disasters are related not only to PTSD, but also to concurrent depression, other anxiety disorders, cognitive impairment, and substance abuse ( David et al. 1996 , Schnurr et al. 2002 , Shalev 2001 ).
Other consequences of stress that could provide linkages to health have been identified, such as increases in smoking, substance use, accidents, sleep problems, and eating disorders. Populations that live in more stressful environments (communities with higher divorce rates, business failures, natural disasters, etc.) smoke more heavily and experience higher mortality from lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder ( Colby et al. 1994 ). A longitudinal study following seamen in a naval training center found that more cigarette smoking occurred on high-stress days ( Conway et al. 1981 ). Life events stress and chronically stressful conditions have also been linked to higher consumption of alcohol ( Linsky et al. 1985 ). In addition, the possibility that alcohol may be used as self-medication for stress-related disorders such as anxiety has been proposed. For example, a prospective community study of 3021 adolescents and young adults ( Zimmerman et al. 2003 ) found that those with certain anxiety disorders (social phobia and panic attacks) were more likely to develop substance abuse or dependence prospectively over four years of follow-up. Life in stressful environments has also been linked to fatal accidents ( Linsky & Strauss 1986 ) and to the onset of bulimia ( Welch et al. 1997 ). Another variable related to stress that could provide a link to health is the increased sleep problems that have been reported after sychological trauma ( Harvey et al. 2003 ). New onset of sleep problems mediated the relationship between post-traumatic stress symptoms and decreased natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity in Hurricane Andrew victims ( Ironson et al. 1997 ).
Variations in Stress Responses
Certain characteristics of a situation are associated with greater stress responses. These include the intensity or severity of the stressor and controllability of the stressor, as well as features that determine the nature of the cognitive responses or appraisals. Life event dimensions of loss, humiliation, and danger are related to the development of major depression and generalized anxiety ( Kendler et al. 2003 ). Factors associated with the development of symptoms of PTSD and mental health disorders include injury, damage to property, loss of resources, bereavement, and perceived life threat ( Freedy et al. 1992 , Ironson et al. 1997 , McNally 2003 ). Recovery from a stressor can also be affected by secondary traumatization ( Pfefferbaum et al. 2003 ). Other studies have found that multiple facets of stress that may work synergistically are more potent than a single facet; for example, in the area of work stress, time pressure in combination with threat ( Stanton et al. 2001 ), or high demand in combination with low control ( Karasek & Theorell 1990 ).
Stress-related outcomes also vary according to personal and environmental factors. Personal risk factors for the development of depression, anxiety, or PTSD after a serious life event, disaster, or trauma include prior psychiatric history, neuroticism, female gender, and other sociodemographic variables ( Green 1996 , McNally 2003 , Patton et al. 2003 ). There is also some evidence that the relationship between personality and environmental adversity may be bidirectional ( Kendler et al. 2003 ). Levels of neuroticism, emotionality, and reactivity correlate with poor interpersonal relationships as well as “event proneness.” Protective factors that have been identified include, but are not limited to, coping, resources (e.g., social support, self-esteem, optimism), and finding meaning. For example, those with social support fare better after a natural disaster ( Madakaisira & O’Brien 1987 ) or after myocardial infarction ( Frasure-Smith et al. 2000 ). Pruessner et al. (1999) found that people with higher self-esteem performed better and had lower cortisol responses to acute stressors (difficult math problems). Attaching meaning to the event is another protective factor against the development of PTSD, even when horrific torture has occurred. Left-wing political activists who were tortured by Turkey’s military regime had lower rates of PTSD than did nonactivists who were arrested and tortured by the police ( Basoğlu et al. 1994 ).
Finally, human beings are resilient and in general are able to cope with adverse situations. A recent illustration is provided by a study of a nationally representative sample of Israelis after 19 months of ongoing exposure to the Palestinian intifada. Despite considerable distress, most Israelis reported adapting to the situation without substantial mental health symptoms or impairment ( Bleich et al. 2003 ).
BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES TO STRESSORS
Acute stress responses.
Following the perception of an acute stressful event, there is a cascade of changes in the nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems. These changes constitute the stress response and are generally adaptive, at least in the short term ( Selye 1956 ). Two features in particular make the stress response adaptive. First, stress hormones are released to make energy stores available for the body’s immediate use. Second, a new pattern of energy distribution emerges. Energy is diverted to the tissues that become more active during stress, primarily the skeletal muscles and the brain. Cells of the immune system are also activated and migrate to “battle stations” ( Dhabar & McEwen 1997 ). Less critical activities are suspended, such as digestion and the production of growth and gonadal hormones. Simply put, during times of acute crisis, eating, growth, and sexual activity may be a detriment to physical integrity and even survival.
Stress hormones are produced by the SNS and hypothalamic-pituitary adrenocortical axis. The SNS stimulates the adrenal medulla to produce catecholamines (e.g., epinephrine). In parallel, the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus produces corticotropin releasing factor, which in turn stimulates the pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropin. Adrenocorticotropin then stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol. Together, catecholamines and cortisol increase available sources of energy by promoting lipolysis and the conversion of glycogen into glucose (i.e., blood sugar). Lipolysis is the process of breaking down fats into usable sources of energy (i.e., fatty acids and glycerol; Brindley & Rollan 1989 ).
Energy is then distributed to the organs that need it most by increasing blood pressure levels and contracting certain blood vessels while dilating others. Blood pressure is increased with one of two hemodynamic mechanisms ( Llabre et al.1998 , Schneiderman & McCabe 1989 ). The myocardial mechanism increases blood pressure through enhanced cardiac output; that is, increases in heart rate and stroke volume (i.e., the amount of blood pumped with each heart beat). The vascular mechanism constricts the vasculature, thereby increasing blood pressure much like constricting a hose increases water pressure. Specific stressors tend to elicit either myocardial or vascular responses, providing evidence of situational stereotypy ( Saab et al. 1992 , 1993 ). Laboratory stressors that call for active coping strategies, such as giving a speech or performing mental arithmetic, require the participant to do something and are associated with myocardial responses. In contrast, laboratory stressors that call for more vigilant coping strategies in the absence of movement, such as viewing a distressing video or keeping one’s foot in a bucket of ice water, are associated with vascular responses. From an evolutionary perspective, cardiac responses are believed to facilitate active coping by shunting blood to skeletal muscles, consistent with the fight-or-flight response. In situations where decisive action would not be appropriate, but instead skeletal muscle inhibition and vigilance are called for, a vascular hemodynamic response is adaptive. The vascular response shunts blood away from the periphery to the internal organs, thereby minimizing potential bleeding in the case of physical assault.
Finally, in addition to the increased availability and redistribution of energy, the acute stress response includes activation of the immune system. Cells of the innate immune system (e.g., macrophages and natural killer cells), the first line of defense, depart from lymphatic tissue and spleen and enter the bloodstream, temporarily raising the number of immune cells in circulation (i.e., leukocytosis). From there, the immune cells migrate into tissues that are most likely to suffer damage during physical confrontation (e.g., the skin). Once at “battle stations,” these cells are in position to contain microbes that may enter the body through wounds and thereby facilitate healing ( Dhabar & McEwen 1997 ).
Chronic Stress Responses
The acute stress response can become maladaptive if it is repeatedly or continuously activated ( Selye 1956 ). For example, chronic SNS stimulation of the cardiovascular system due to stress leads to sustained increases in blood pressure and vascular hypertrophy ( Henry et al. 1975 ). That is, the muscles that constrict the vasculature thicken, producing elevated resting blood pressure and response stereotypy, or a tendency to respond to all types of stressors with a vascular response. Chronically elevated blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, which leads to hypertrophy of the left ventricle ( Brownley et al. 2000 ). Over time, the chronically elevated and rapidly shifting levels of blood pressure can lead to damaged arteries and plaque formation.
The elevated basal levels of stress hormones associated with chronic stress also suppress immunity by directly affecting cytokine profiles. Cytokines are communicatory molecules produced primarily by immune cells (see Roitt et al. 1998 ). There are three classes of cytokines. Proinflammatory cytokines mediate acute inflammatory reactions. Th1 cytokines mediate cellular immunity by stimulating natural killer cells and cytotoxic T cells, immune cells that target intracellular pathogens (e.g., viruses). Finally, Th2 cytokines mediate humoral immunity by stimulating B cells to produce antibody, which “tags” extracellular pathogens (e.g., bacteria) for removal. In a meta-analysis of over 30 years of research, Segerstrom & Miller (2004) found that intermediate stressors, such as academic examinations, could promote a Th2 shift (i.e., an increase in Th2 cytokines relative to Th1 cytokines). A Th2 shift has the effect of suppressing cellular immunity in favor of humoral immunity. In response to more chronic stressors (e.g., long-term caregiving for a dementia patient), Segerstrom & Miller found that proinflammatory, Th1, and Th2 cytokines become dysregulated and lead both to suppressed humoral and cellular immunity. Intermediate and chronic stressors are associated with slower wound healing and recovery from surgery, poorer antibody responses to vaccination, and antiviral deficits that are believed to contribute to increased vulnerability to viral infections (e.g., reductions in natural killer cell cytotoxicity; see Kiecolt-Glaser et al. 2002 ).
Chronic stress is particularly problematic for elderly people in light of immunosenescence, the gradual loss of immune function associated with aging. Older adults are less able to produce antibody responses to vaccinations or combat viral infections ( Ferguson et al. 1995 ), and there is also evidence of a Th2 shift ( Glaser et al. 2001 ). Although research has yet to link poor vaccination responses to early mortality, influenza and other infectious illnesses are a major cause of mortality in the elderly, even among those who have received vaccinations (e.g., Voordouw et al. 2003 ).
PSYCHOSOCIAL STRESSORS AND HEALTH
Cardiovascular disease.
Both epidemiological and controlled studies have demonstrated relationships between psychosocial stressors and disease. The underlying mediators, however, are unclear in most cases, although possible mechanisms have been explored in some experimental studies. An occupational gradient in coronary heart disease (CHD) risk has been documented in which men with relatively low socioeconomic status have the poorest health outcomes ( Marmot 2003 ). Much of the risk gradient in CHD can be eliminated, however, by taking into account lack of perceived job control, which is a potent stressor ( Marmot et al. 1997 ). Other factors include risky behaviors such as smoking, alcohol use, and sedentary lifestyle ( Lantz et al. 1998 ), which may be facilitated by stress. Among men ( Schnall et al. 1994 ) and women ( Eaker 1998 ), work stress has been reported to be a predictor of incident CHD and hypertension ( Ironson 1992 ). However, in women with existing CHD, marital stress is a better predictor of poor prognosis than is work stress ( Orth-Gomer et al. 2000 ).
Although the observational studies cited thus far reveal provocative associations between psychosocial stressors and disease, they are limited in what they can tell us about the exact contribution of these stressors or about how stress mediates disease processes. Animal models provide an important tool for helping to understand the specific influences of stressors on disease processes. This is especially true of atherosclerotic CHD, which takes multiple decades to develop in humans and is influenced by a great many constitutional, demographic, and environmental factors. It would also be unethical to induce disease in humans by experimental means.
Perhaps the best-known animal model relating stress to atherosclerosis was developed by Kaplan et al. (1982) . Their study was carried out on male cynomolgus monkeys, who normally live in social groups. The investigators stressed half the animals by reorganizing five-member social groups at one- to three-month intervals on a schedule that ensured that each monkey would be housed with several new animals during each reorganization. The other half of the animals lived in stable social groups. All animals were maintained on a moderately atherogenic diet for 22 months. Animals were also assessed for their social status (i.e., relative dominance) within each group. The major findings were that ( a ) socially dominant animals living in unstable groups had significantly more atherosclerosis than did less dominant animals living in unstable groups; and ( b ) socially dominant male animals living in unstable groups had significantly more atherosclerosis than did socially dominant animals living in stable groups. Other important findings based upon this model have been that heart-rate reactivity to the threat of capture predicts severity of atherosclerosis ( Manuck et al. 1983 ) and that administration of the SNS-blocking agent propranolol decreases the progression of atherosclerosis ( Kaplan et al. 1987 ). In contrast to the findings in males, subordinate premenstrual females develop greater atherosclerosis than do dominant females ( Kaplan et al. 1984 ) because they are relatively estrogen deficient, tending to miss ovulatory cycles ( Adams et al. 1985 ).
Whereas the studies in cynomolgus monkeys indicate that emotionally stressful behavior can accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, McCabe et al. (2002) have provided evidence that affiliative social behavior can slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. This rabbit model has a genetic defect in lipoprotein clearance such that it exhibits hypercholesterolemia and severe atherosclerosis. The rabbits were assigned to one of three social or behavioral groups: ( a ) an unstable group in which unfamiliar rabbits were paired daily, with the pairing switched each week; ( b ) a stable group, in which littermates were paired daily for the entire study; and ( c ) an individually caged group. The stable group exhibited more affiliative behavior and less agonistic behavior than the unstable group and significantly less atherosclerosis than each of the other two groups. The study emphasizes the importance of behavioral factors in atherogenesis, even in a model of disease with extremely strong genetic determinants.
Upper Respiratory Diseases
The hypothesis that stress predicts susceptibility to the common cold received support from observational studies ( Graham et al. 1986 , Meyer & Haggerty 1962 ). One problem with such studies is that they do not control for exposure. Stressed people, for instance, might seek more outside contact and thus be exposed to more viruses. Therefore, in a more controlled study, people were exposed to a rhinovirus and then quarantined to control for exposure to other viruses ( Cohen et al. 1991 ). Those individuals with the most stressful life events and highest levels of perceived stress and negative affect had the greatest probability of developing cold symptoms. In a subsequent study of volunteers inoculated with a cold virus, it was found that people enduring chronic, stressful life events (i.e., events lasting a month or longer including unemployment, chronic underemployment, or continued interpersonal difficulties) had a high likelihood of catching cold, whereas people subjected to stressful events lasting less than a month did not ( Cohen et al. 1998 ).

Human Immunodeficiency Virus
The impact of life stressors has also been studied within the context of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) spectrum disease. Leserman et al. (2000) followed men with HIV for up to 7.5 years and found that faster progression to AIDS was associated with higher cumulative stressful life events, use of denial as a coping mechanism, lower satisfaction with social support, and elevated serum cortisol.
Inflammation, the Immune System, and Physical Health
Despite the stress-mediated immunosuppressive effects reviewed above, stress has also been associated with exacerbations of autoimmune disease ( Harbuz et al. 2003 ) and other conditions in which excessive inflammation is a central feature, such as CHD ( Appels et al. 2000 ). Evidence suggests that a chronically activated, dysregulated acute stress response is responsible for these associations. Recall that the acute stress response includes the activation and migration of cells of the innate immune system. This effect is mediated by proinflammatory cytokines. During periods of chronic stress, in the otherwise healthy individual, cortisol eventually suppresses proinflammatory cytokine production. But in individuals with autoimmune disease or CHD, prolonged stress can cause proinflammatory cytokine production to remain chronically activated, leading to an exacerbation of pathophysiology and symptomatology.
Miller et al. (2002) proposed the glucocorticoid-resistance model to account for this deficit in proinflammatory cytokine regulation. They argue that immune cells become “resistant” to the effects of cortisol (i.e., a type of glucocorticoid), primarily through a reduction, or downregulation, in the number of expressed cortisol receptors. With cortisol unable to suppress inflammation, stress continues to promote proinflammatory cytokine production indefinitely. Although there is only preliminary empirical support for this model, it could have implications for diseases of inflammation. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, excessive inflammation is responsible for joint damage, swelling, pain, and reduced mobility. Stress is associated with more swelling and reduced mobility in rheumatoid arthritis patients ( Affleck et al. 1997 ). Similarly, in multiple sclerosis (MS), an overactive immune system targets and destroys the myelin surrounding nerves, contributing to a host of symptoms that include paralysis and blindness. Again, stress is associated with an exacerbation of disease ( Mohr et al. 2004 ). Even in CHD, inflammation plays a role. The immune system responds to vascular injury just as it would any other wound: Immune cells migrate to and infiltrate the arterial wall, setting off a cascade of biochemical processes that can ultimately lead to a thrombosis (i.e., clot; Ross 1999 ). Elevated levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), are predictive of heart attacks, even when controlling for other traditional risk factors (e.g., cholesterol, blood pressure, and smoking; Morrow & Ridker 2000 ). Interestingly, a history of major depressive episodes has been associated with elevated levels of CRP in men ( Danner et al. 2003 ).
Inflammation, Cytokine Production, and Mental Health
In addition to its effects on physical health, prolonged proinflammatory cytokine production may also adversely affect mental health in vulnerable individuals. During times of illness (e.g., the flu), proinflammatory cytokines feed back to the CNS and produce symptoms of fatigue, malaise, diminished appetite, and listlessness, which are symptoms usually associated with depression. It was once thought that these symptoms were directly caused by infectious pathogens, but more recently, it has become clear that proinflammatory cytokines are both sufficient and necessary (i.e., even absent infection or fever) to generate sickness behavior ( Dantzer 2001 , Larson & Dunn 2001 ).
Sickness behavior has been suggested to be a highly organized strategy that mammals use to combat infection ( Dantzer 2001 ). Symptoms of illness, as previously thought, are not inconsequential or even maladaptive. On the contrary, sickness behavior is thought to promote resistance and facilitate recovery. For example, an overall decrease in activity allows the sick individual to preserve energy resources that can be redirected toward enhancing immune activity. Similarly, limiting exploration, mating, and foraging further preserves energy resources and reduces the likelihood of risky encounters (e.g., fighting over a mate). Furthermore, decreasing food intake also decreases the level of iron in the blood, thereby decreasing bacterial replication. Thus, for a limited period, sickness behavior may be looked upon as an adaptive response to the stress of illness.
Much like other aspects of the acute stress response, however, sickness behavior can become maladaptive when repeatedly or continuously activated. Many features of the sickness behavior response overlap with major depression. Indeed, compared with healthy controls, elevated rates of depression are reported in patients with inflammatory diseases such as MS ( Mohr et al. 2004 ) or CHD ( Carney et al. 1987 ). Granted, MS patients face a number of stressors and reports of depression are not surprising. However, when compared with individuals facing similar disability who do not have MS (e.g., car accident victims), MS patients still report higher levels of depression ( Ron & Logsdail 1989 ). In both MS ( Fassbender et al. 1998 ) and CHD ( Danner et al. 2003 ), indicators of inflammation have been found to be correlated with depressive symptomatology. Thus, there is evidence to suggest that stress contributes to both physical and mental disease through the mediating effects of proinflammatory cytokines.
HOST VULNERABILITY-STRESSOR INTERACTIONS AND DISEASE
The changes in biological set points that occur across the life span as a function of chronic stressors are referred to as allostasis, and the biological cost of these adjustments is known as allostatic load ( McEwen 1998 ). McEwen has also suggested that cumulative increases in allostatic load are related to chronic illness. These are intriguing hypotheses that emphasize the role that stressors may play in disease. The challenge, however, is to show the exact interactions that occur among stressors, pathogens, host vulnerability (both constitutional and genetic), and such poor health behaviors as smoking, alcohol abuse, and excessive caloric consumption. Evidence of a lifetime trajectory of comorbidities does not necessarily imply that allostatic load is involved since immunosenescence, genetic predisposition, pathogen exposure, and poor health behaviors may act as culprits.
It is not clear, for example, that changes in set point for variables such as blood pressure are related to cumulative stressors per se, at least in healthy young individuals. Thus, for example, British soldiers subjected to battlefield conditions for more than a year in World War II showed chronic elevations in blood pressure, which returned to normal after a couple of months away from the front ( Graham 1945 ). In contrast, individuals with chronic illnesses such as chronic fatigue syndrome may show a high rate of relapse after a relatively acute stressor such as a hurricane ( Lutgendorf et al. 1995 ). Nevertheless, by emphasizing the role that chronic stressors may play in multiple disease outcomes, McEwen has helped to emphasize an important area of study.
TREATMENT FOR STRESS-RELATED DISORDERS
For PTSD, useful treatments include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), along with exposure and the more controversial Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing ( Foa & Meadows 1997 , Ironson et al. 2002 , Shapiro 1995 ). Psychopharmacological approaches have also been suggested ( Berlant 2001 ). In addition, writing about trauma has been helpful both for affective recovery and for potential health benefit ( Pennebaker 1997 ). For outpatients with major depression, Beck’s CBT ( Beck 1976 ) and interpersonal therapy ( Klerman et al. 1984 ) are as effective as psychopharmacotherapy ( Clinical Practice Guidelines 1993 ). However, the presence of sleep problems or hypercortisolemia is associated with poorer response to psychotherapy ( Thase 2000 ). The combination of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy seems to offer a substantial advantage over psychotherapy alone for the subset of patients who are more severely depressed or have recurrent depression ( Thase et al. 1997 ). For the treatment of anxiety, it depends partly on the specific disorder [e.g., generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social phobia], although CBT including relaxation training has demonstrated efficacy in several subtypes of anxiety ( Borkovec & Ruscio 2001 ). Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors also show efficacy in anxiety ( Ballenger et al. 2001 ), especially when GAD is comorbid with major depression, which is the case in 39% of subjects with current GAD ( Judd et al. 1998 ).
BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTIONS IN CHRONIC DISEASE
Patients dealing with chronic, life-threatening diseases must often confront daily stressors that can threaten to undermine even the most resilient coping strategies and overwhelm the most abundant interpersonal resources. Psychosocial interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM), have a positive effect on the quality of life of patients with chronic disease ( Schneiderman et al. 2001 ). Such interventions decrease perceived stress and negative mood (e.g., depression), improve perceived social support, facilitate problem-focused coping, and change cognitive appraisals, as well as decrease SNS arousal and the release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex. Psychosocial interventions also appear to help chronic pain patients reduce their distress and perceived pain as well as increase their physical activity and ability to return to work ( Morley et al. 1999 ). These psychosocial interventions can also decrease patients’ overuse of medications and utilization of the health care system. There is also some evidence that psychosocial interventions may have a favorable influence on disease progression ( Schneiderman et al. 2001 ).
Morbidity, Mortality, and Markers of Disease Progression
Psychosocial intervention trials conducted upon patients following acute myocardial infarction (MI) have reported both positive and null results. Two meta-analyses have reported a reduction in both mortality and morbidity of approximately 20% to 40% ( Dusseldorp et al. 1999 , Linden et al. 1996 ). Most of these studies were carried out in men. The major study reporting positive results was the Recurrent Coronary Prevention Project (RCPP), which employed group-based CBT, and decreased hostility and depressed affect ( Mendes de Leon et al. 1991 ), as well as the composite medical end point of cardiac death and nonfatal MI ( Friedman et al. 1986 ).
In contrast, the major study reporting null results for medical end points was the Enhancing Recovery in Coronary Heart Disease (ENRICHD) clinical trial ( Writing Committee for ENRICHD Investigators 2003 ), which found that the intervention modestly decreased depression and increased perceived social support, but did not affect the composite medical end point of death and nonfatal MI. However, a secondary analysis, which examined the effects of the psychosocial intervention within gender by ethnicity subgroups, found significant decreases approaching 40% in both cardiac death and nonfatal MI for white men but not for other subgroups such as minority women ( Schneiderman et al. 2004 ). Although there were important differences between the RCPP and ENRICHD in terms of the objectives of psychosocial intervention and the duration and timing of treatment, it should also be noted that more than 90% of the patients in the RCPP were white men. Thus, because primarily white men, but not other subgroups, may have benefited from the ENRICHD intervention, future studies need to attend to variables that may have prevented morbidity and mortality benefits among gender and ethnic subgroups other than white men.
Psychosocial intervention trials conducted upon patients with cancer have reported both positive and null results with regard to survival ( Classen 1998 ). A number of factors that generally characterized intervention trials that observed significant positive effects on survival were relatively absent in trials that failed to show improved survival. These included: ( a ) having only patients with the same type and severity of cancer within each group, ( b ) creation of a supportive environment, ( c ) having an educational component, and ( d ) provision of stress-management and coping-skills training. In one study that reported positive results, Fawzy et al. (1993) found that patients with early stage melanoma assigned to a six-week cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) group showed significantly longer survival and longer time to recurrence over a six-year follow-up period compared with those receiving surgery and standard care alone. The intervention also significantly reduced distress, enhanced active coping, and increased NK cell cytotoxicity compared with controls.
Although published studies have not yet shown that psychosocial interventions can decrease disease progression in HIV/AIDS, several studies have significantly influenced factors that have been associated with HIV/AIDS disease progression ( Schneiderman & Antoni 2003 ). These variables associated with disease progression include distress, depressed affect, denial coping, low perceived social support, and elevated serum cortisol ( Ickovics et al. 2001 , Leserman et al. 2000 ). Antoni et al. have used group-based CBSM (i.e., CBT plus relaxation training) to decrease the stress-related effects of HIV+ serostatus notification. Those in the intervention condition showed lower distress, anxiety, and depressed mood than did those in the control condition as well as lower antibody titers of herpesviruses and higher levels of T-helper (CD4) cells, NK cells, and lymphocyte proliferation ( Antoni et al. 1991 , Esterling et al. 1992 ). In subsequent studies conducted upon symptomatic HIV+ men who were not attempting to determine their HIV serostatus, CBSM decreased distress, dysphoria, anxiety, herpesvirus antibody titers, cortisol, and epinephrine ( Antoni et al. 2000a , b ; Lutgendorf et al. 1997 ). Improvement in perceived social support and adaptive coping skills mediated the decreases in distress ( Lutgendorf et al. 1998 ). In summary, it appears that CBSM can positively influence stress-related variables that have been associated with HIV/AIDS progression. Only a randomized clinical trial, however, could document that CBSM can specifically decrease HIV/AIDS disease progression.
Stress is a central concept for understanding both life and evolution. All creatures face threats to homeostasis, which must be met with adaptive responses. Our future as individuals and as a species depends on our ability to adapt to potent stressors. At a societal level, we face a lack of institutional resources (e.g., inadequate health insurance), pestilence (e.g., HIV/AIDS), war, and international terrorism that has reached our shores. At an individual level, we live with the insecurities of our daily existence including job stress, marital stress, and unsafe schools and neighborhoods. These are not an entirely new condition as, in the last century alone, the world suffered from instances of mass starvation, genocide, revolutions, civil wars, major infectious disease epidemics, two world wars, and a pernicious cold war that threatened the world order. Although we have chosen not to focus on these global threats in this paper, they do provide the backdrop for our consideration of the relationship between stress and health.
A widely used definition of stressful situations is one in which the demands of the situation threaten to exceed the resources of the individual ( Lazarus & Folkman 1984 ). It is clear that all of us are exposed to stressful situations at the societal, community, and interpersonal level. How we meet these challenges will tell us about the health of our society and ourselves. Acute stress responses in young, healthy individuals may be adaptive and typically do not impose a health burden. Indeed, individuals who are optimistic and have good coping responses may benefit from such experiences and do well dealing with chronic stressors ( Garmezy 1991 , Glanz & Johnson 1999 ). In contrast, if stressors are too strong and too persistent in individuals who are biologically vulnerable because of age, genetic, or constitutional factors, stressors may lead to disease. This is particularly the case if the person has few psychosocial resources and poor coping skills. In this chapter, we have documented associations between stressors and disease and have described how endocrine-immune interactions appear to mediate the relationship. We have also described how psychosocial stressors influence mental health and how psychosocial treatments may ameliorate both mental and physical disorders. There is much we do not yet know about the relationship between stress and health, but scientific findings being made in the areas of cognitive-emotional psychology, molecular biology, neuroscience, clinical psychology, and medicine will undoubtedly lead to improved health outcomes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Preparation of this manuscript was supported by NIH grants P01-MH49548, P01- HL04726, T32-HL36588, R01-MH66697, and R01-AT02035. We thank Elizabeth Balbin, Adam Carrico, and Orit Weitzman for library research.
LITERATURE CITED
- Adams DB, Bacelli G, Mancia G, Zanchetti A. Cardiovascular changes during naturally elicited fighting behavior in the cat. Am. J. Physiol. 1968; 216 :1226–1235. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adams MR, Kaplan JR, Koritnik DR. Psychosocial influences on ovarian, endocrine and ovulatory function in Macaca fascicularis . Physiol. Behav. 1985; 35 :935–940. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Affleck G, Urrows S, Tennen H, Higgins P, Pav D, Aloisi R. A dual pathway model of daily stressor effects on rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Behav. Med. 1997; 19 :161–170. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV-TR. 4th ed. Washington, DC: Am. Psychiatr. Assoc.; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Angst J, Vollrath M. The natural history of anxiety disorders. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1991; 84 :446–452. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Antoni MH, Baggett L, Ironson G, LaPerriere A, Klimas N, et al. Cognitive behavioral stress management intervention buffers distress responses and elevates immunologic markers following notification of HIV-1 seropositivity. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1991; 59 :906–915. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Antoni MH, Cruess DG, Cruess S, Lutgendorf S, Kumar M, et al. Cognitive behavioral stress management intervention effects on anxiety, 24-hour urinary catecholamine output, and T-cytotoxic/suppressor cells over time among symptomatic HIV-infected gay men. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2000a; 68 :31–45. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Antoni MH, Cruess S, Cruess DG, Kumar M, Lutgendorf S, et al. Cognitive-behavioral stress management reduces distress and 24-hour urinary free cortisol output among symptomatic HIV-infected gay men. Ann. Behav. Med. 2000b; 22 :29–37. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Appels A, Bar FW, Bar J, Bruggeman C, de Bates M. Inflammation, depressive symptomatology, and coronary artery disease. Psychosom. Med. 2000; 62 :601–605. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ballenger JC, Davidson JRT, Lecrubier Y, Nutt DJ, Borkovec TD, et al. Consensus statement on generalized anxiety disorder from the international consensus group on depression and anxiety. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001; 62 :53–58. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Başoğlu M, Parker M, Parker Ö, Özmen E, Marks I, et al. Psychological effects of torture: a comparison of tortured with non-tortured political activists in Turkey. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1994; 151 :76–81. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baum A. Stress, intrusive imagery, and chronic distress. Health Psychol. 1990; 9 :653–675. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beck AT. Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders. New York: Int. Univ. Press; 1976. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berlant JL. Topiramate in posttraumatic stress disorder: preliminary clinical observations. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001; 62 :60–63. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bernard C. An Introduction to the Study of Experimental Medicine. Transl. HC Greene. New York: Collier; 18651961. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bleich A, Gelkopf M, Solomon Z. Exposure to terrorism, stress-related mental health symptoms, and coping behaviors among a nationally representative sample in Israel. JAMA. 2003; 290 :612–620. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borkovec TD, Ruscio AM. Psychotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001; 61 :37–42. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Breslau N, Davis GC, Andreski P, Peterson E. Sex differences in depression: a role for preexisting anxiety. Psychiatr. Res. 1995; 58 :1–12. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brindley D, Rollan Y. Possible connections between stress, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and altered lipoprotein metabolism that may result in atherosclerosis. Clin. Sci. 1989; 77 :453–461. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown GW, Bifulco A, Harris T, Bridge L. Life stress, chronic subclinical symptoms and vulnerability to clinical depression. J. Affect. Disord. 1986; 11 :1–19. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownley KA, Hurwitz BE, Schneiderman N. Cardiovascular psychophysiology. In: Cacioppo JT, Tassinary LG, Berntson GG, editors. Handbook of Psychophysiology. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge Univ.; 2000. pp. 224–264. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cannon WB. Bodily Changes in Pain, Hunger, Fear and Rage. 2nd ed. New York: Appleton; 1929. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carney RM, Rich MW, Tevelde A, Saini J, Clark K, Jaffe AS. Major depressive disorder in coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987; 60 :1273–1275. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cassem EH. Depressive disorders in the medically ill: an overview. Psychosomatics. 1995; 36 :S2–S10. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cicchetti D. Child maltreatment. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005; 1 :409–438. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Classen C, Sephton SE, Diamond S, Spiegel D. Studies of life-extending psychosocial interventions. In: Holland J, editor. Textbook of Psycho-Oncology. New York: Oxford Univ. Press; 1998. pp. 730–742. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clinical Practice Guidelines. No. 5. Depression in Primary Care. Vol. 2: Treatment of Major Depression. Rockville, MD: US Dept. Health Hum. Serv., Agency Health Care Policy Res.; 1993. AHCPR Publ. 93-0551.
- Cohen S, Frank E, Doyle WJ, Skoner DP, Rabin BS, Gwaltney JM., Jr Types of stressors that increase susceptibility to the common cold in healthy adults. Health Psychol. 1998; 17 :214–223. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen S, Tyrrell DA, Smith AP. Psychological stress and susceptibility to the common cold. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991; 325 :606–612. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Colby JP, Linsky AS, Straus MA. Social stress and state-to-state differences in smoking-related mortality in the United States. Soc. Sci. Med. 1994; 38 :373–381. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Conway TL, Vickers RR, Ward HW, Rahe RH. Occupational stress and variation in cigarette, coffee and alcohol consumption. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1981; 22 :156–165. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Danner M, Kasl SV, Abramson JL, Vaccarion V. Association between depression and elevated C-reactive protein. Psychosom. Med. 2003; 65 :347–356. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dantzer R. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior: Where do we stand? Brain Behav. Immun. 2001; 15 :7–24. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- David D, Mellman TA, Mendoza LM, Kulick-Bell R, Ironson G, Schneiderman N. Psychiatric morbidity following Hurricane Andrew. Int. Soc. Trauma. Stress Stud. 1996; 9 :607–612. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dhabar FS, McEwen BS. Acute stress enhances while chronic stress suppresses cell-mediated immunity in vivo: a potential role for leukocyte trafficking. Brain Behav. Immun. 1997; 11 :286–306. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dusseldorp E, van Elderen T, Maes S, Meulman J, Kraaij V. A meta-analysis of psychoeducational programs for coronary heart disease patients. Health Psychol. 1999; 18 :506–519. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eaker ED. Psychosocial risk factors for coronary heart disease in women. Cardiovasc. Clin. 1998; 16 :103–111. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Esterling BA, Antoni MH, Schneiderman N, Carver CS, LaPerriere A, et al. Psychosocial modulation of antibody to Epstein-Barr viral capsid antigen and herpes virus type-6 HIV-1 infected and at-risk gay men. Psychosom. Med. 1992; 54 :354–371. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Faravelli C, Pallanti S. Recent life events and panic disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1989; 146 :622–626. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fassbender K, Schmidt R, Mossner R, Kischka U, Kuhnen J, et al. Mood disorders and dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in multiple sclerosis: associations with cerebral inflammation. Arch. Neurol. 1998; 55 :66–72. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fawzy FI, Fawzy NW, Hyun CS, Elashoff R, Guthrie D, et al. Malignant melanoma. Effects of an early structured psychiatric intervention, coping and affective state on recurrence and survival 6 years later. Arch. Gen. Psychol. 1993; 50 :681–689. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferguson RG, Wikby A, Maxson P, Olsson J, Johansson B. Immune parameters in a longitudinal study of a very old population of Swedish people: a comparison between survivors and nonsurvivors. J. Gerontol. 1995; 50 :B378–B382. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Finlay-Jones R, Brown GW. Types of stressful life events and the onset of anxiety and depressive disorders. Psychol. Med. 1981; 11 :803–815. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foa EB, Meadows EA. Psychosocial treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: critical review. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1997; 48 :449–480. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frasure-Smith N, Lespérance F, Gravel G, Masson A, Juneau M, et al. Social support, depression, and mortality during the first year after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2000; 101 :1919–1924. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freedy JR, Shaw DL, Jarrell MP, Masters CR. Towards an understanding of the psychological impact of natural disasters: an application of the conservation of resources stress model. J. Trauma. Stress. 1992; 5 :441–454. [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman M, Thoresen CE, Gill JJ, Ulmer D, Powell LH, et al. Alteration of type A behavior and its effects on cardiac recurrences in post myocardial patients: summary results of the Recurrent Coronary Prevention Project. Am. Heart J. 1986; 112 :653–665. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garmezy N. Resiliency and vulnerability to adverse developmental outcomes associated with poverty. Am. Behav. Sci. 1991; 34 :416–430. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glanz MD, Johnson JL. Resilience and Development: Positive Life Adaptations. New York: Kluwer Acad./Plenum; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser R, MacCallum RC, Laskowski BF, Malarkey WB, Sheridan JF, Kiecolt-Glaser JK. Evidence for a shift in the Th-1 to Th-2 cytokine response associated with chronic stress and aging. J. Gerontol. 2001; 56 :M477–M482. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Graham JDP. High blood pressure after battle. Lancet. 1945; 248 :239–240. [ Google Scholar ]
- Graham NMH, Douglas RB, Ryan P. Stress and acute respiratory infection. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986; 124 :389–401. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green BL. Psychosocial research in traumatic stress: an update. J. Trauma. Stress. 1994; 7 :341–362. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green BL. Traumatic stress and disaster: mental health effects and factors influencing adaptation. In: Mak FL, Nadelson C, editors. International Review of Psychiatry. Washington, DC: Am. Psychiatr. Press; 1996. pp. 177–211. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammen C. Stress and depression. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005; 1 :293–319. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harbuz MS, Chover-Gonzalez AJ, Jessop DS. Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and chronic immune activation. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2003; 992 :99–106. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harvey AG, Bryant RA. Acute stress disorder: a synthesis and critique. Psychol. Bull. 2002; 128 :886–902. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harvey AG, Jones C, Schmidt DA. Sleep and posttraumatic stress disorder: a review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2003; 23 :377–407. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haviland MG, Sonne JL, Woods LR. Beyond posttraumatic stress disorder: object relations and reality testing disturbances in physically and sexually abused adolescents. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 1995; 34 :1054–1059. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henry JP, Stephens PM, Santisteban GA. A model of psychosocial hypertension showing reversibility and progression of cardiovascular complications. Circ. Res. 1975; 36 :156–164. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hess WR. Functional Organization of the Diencephalons. New York: Grune & Stratton; 1957. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hilton SM. Ways of viewing the central nervous control of the circulation—old and new. Brain Res. 1975; 87 :213–228. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ickovics JR, Hamburger ME, Vlahov D, Schoenbaum EE, Schumm P, Boland RJ. Mortality, CD4 cell count decline, and depressive symptoms among HIV-seropositive women. JAMA. 2001; 285 :1466–1474. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ironson GH. Job stress and health. In: Cranny CJ, Smith PC, Stone EF, editors. Job Satisfaction: How People Feel About Their Jobs and How It Affects Their Performance. New York: Lexington; 1992. pp. 219–239. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ironson GH, Freund B, Strauss JL, Williams J. Comparison of two treatments for traumatic stress: a community-based study of EMDR and prolonged exposure. J. Clin. Psychol. 2002; 58 :113–128. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ironson GH, Wynings C, Schneiderman N, Baum A, Rodriguez M, et al. Posttraumatic stress symptoms, intrusive thoughts, loss, and immune function after Hurricane Andrew. Psychosom. Med. 1997; 59 :128–141. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Judd LL, Kessler RC, Paulus MP, Zeller PV, Whittchen HU, Kunovac JL. Comorbidity as a fundamental feature of generalized anxiety disorders: results from the National Comorbidity Survey (NCS) Acta Psychiatr. Scand. Suppl. 1998; 393 :6–11. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaplan JR, Adams MR, Clarkson TB, Koritnik DR. Psychosocial influences on female “protection” among cynomolgues macaques. Atherosclerosis. 1984; 53 :283–295. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaplan JR, Manuck SB, Adams MR, Weingard KW, Clarkson TB. Inhibition of coronary atherosclerosis by propranolol in behaviorally predisposed monkeys fed an atherogenic diet. Circulation. 1987; 76 :1364–1372. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaplan JR, Manuck SB, Clarkson TB, Lusso FM, Taub DM. Social status, environment and atherosclerosis in cynomolgus monkeys. Arteriosclerosis. 1982; 2 :359–368. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karasek RA, Theorell TG. Healthy Work. New York: Basic Books; 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kasprowicz AL, Manuck SB, Malkoff SB, Krantz DS. Individual differences in behaviorally evoked cardiovascular response: temporal stability and hemodynamic patterning. Psychophysiology. 1990; 27 :605–619. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Prescott CA. Personality and the experience of environmental adversity. Psychol. Med. 2003; 33 :1193–1202. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kendler KS, Hettema JM, Butera F, Gardner CO, Prescott CA. Life event dimensions of loss, humiliation, entrapment and danger in the prediction of onsets of major depression and generalized anxiety. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2003; 60 :789–796. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kendler KS, Karkowski LM, Prescott CA. Causal relationship between stressful life events and the onset of major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1999; 156 :837–841. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kessing LV, Agerbro E, Mortensen PB. Does the impact of major stressful life events on the risk of developing depression change throughout life? Psychol. Med. 2003; 33 :1177–1184. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kessler RC, Sonnega A, Bromet E, Hughes M, Nelson CB. Posttraumatic stress disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1995; 52 :1048–1060. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiecolt-Glaser JK, McGuire L, Robles TF, Glaser R. Psychoneuroimmunology: psychological influences on immune function and health. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2002; 70 :537–547. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kilpatrick DG, Edmunds CN, Seymour AK. Rape in America: A Report to the Nation. Arlington, VA: Natl. Victims Cent.; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Klerman GL, Weissman MM, Rounsaville BJ, Chevron ES. Interpersonal Psycho-Therapy of Depression. New York: Basic Books; 1984. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lacey JI. Somatic response patterning and stress: some revisions of activation theory. In: Appleyo MH, Trumble R, editors. Psychological Stress. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1967. p. 14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lacey JL, Lacey BC. Verification and extension of the principle of autonomic response stereotyping. Am. J. Psychol. 1958; 71 :50–73. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ladd CO, Huot RL, Thrivikraman P, Nemeroff CB, Meaney MJ, Plotsky PM. Long-term behavioral and neuroendocrine adaptations to adverse early experience. Prog. Brain Res. 2000; 122 :79–101. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lantz PM, House JS, Lepkowski JM, Williams DR, Mero RP, Chen J. Socioeconomic factors, health behaviors, and mortality: results from nationally representative prospective study of US adults. JAMA. 1998; 279 :1703–1708. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Larson SJ, Dunn AJ. Behavioral effects of cytokines. Brain Behav. Immun. 2001; 15 :371–387. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, Appraisal and Coping. New York: Springer; 1984. [ Google Scholar ]
- Leserman J, Pettito JM, Golden RN, Gaynes BN, Gu H, Perkins DO. The impact of stressful life events, depression, social support, coping and cortisol on progression to AIDS. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2000; 57 :1221–1228. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levine S. Infantile experience and resistance to physiological stress. Science. 1957; 126 :405–406. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Linden W, Stossel C, Maurice J. Psychosocial interventions for patients with coronary artery disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996; 156 :745–752. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Linsky AS, Strauss M. Social Stress in the United States: Links to Regional Patterns in Crime and Illness. Dover, MA: Auburn House; 1986. [ Google Scholar ]
- Linsky AS, Strauss MA, Colby JP. Stressful events, stressful conditions, and alcohol problems in the United States: a partial test of the Bales theory of alcoholism. J. Stud. Alcohol. 1985; 46 :72–80. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Llabre MM, Klein BR, Saab PG, McCalla JB, Schneiderman N. Classification of individual differences in cardiovascular responsivity. The contribution of reactor type controlling for race and gender. Int. J. Behav. Med. 1998; 5 :213–229. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lowenthal B. The effects of early childhood abuse and the development of resiliency. Early Child Dev. Care. 1998; 142 :43–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lutgendorf S, Antoni MH, Ironson G, Fletcher MA, Penedo F, Van Riel F. Physical symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome are exacerbated by the stress of Hurricane Andrew. Psychiatr. Med. 1995; 57 :310–325. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lutgendorf S, Antoni MH, Ironson G, Klimas N, Fletcher MA, Schneiderman N. Cognitive processing style, mood, and immune function following HIV seropositivity notification. Cogn. Ther. Res. 1997; 21 :157–184. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lutgendorf S, Antoni MH, Ironson G, Starr K, Costello N, et al. Changes in cognitive coping skills and social support mediate distress outcomes in symptomatic HIV-seropositive gay men during a cognitive behavioral stress management intervention. Psychosom. Med. 1998; 60 :204–214. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macksound M, Aber J. The war experience and psychosocial development of children in Lebanon. Child Dev. 1996; 67 :70–88. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Madakasira S, O’Brien KF. Acute post-traumatic stress disorder in victims of a natural disaster. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1987; 175 :286–290. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Manuck SB, Kamarack TW, Kasprowica AS, Waldstein SR. Stability and patterning of behaviorally evoked cardiovascular reactivity. In: Blascovich J, Katkin ES, editors. Cardiovascular Reactivity to Psychological Stress and Disease. Washington, DC: Am. Psychol. Assoc.; 1993. pp. 111–134. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manuck SB, Kaplan JR, Clarkson TB. Behaviorally induced heart rate reactivity and atherosclerosis in cynomolgus monkeys. Psychosom. Med. 1983; 45 :95–108. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marmot M. Social resources and health. In: Kessel F, Rosenfield PL, Anderson NB, editors. Expanding the Boundaries of Health and Social Science. New York: Oxford Univ. Press; 2003. pp. 259–285. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marmot MG, Bosma H, Hemingway H, Brunner EJ, Stansfeld S. Contribution of job control and other risk factors to social variations in coronary heart disease incidence. Lancet. 1997; 350 :235–239. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCabe PM, Gonzalez JA, Zaias J, Szeto A, Kumar M, et al. Social environment influences the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Circulation. 2002; 105 :354–359. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McDaniel JS, Musselman DL, Porter MR, Reed DA, Nemeroff CB. Depression in patients with cancer. diagnosis biology and treatment. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1995; 2 :89–99. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McEwen BS. Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998; 338 :171–179. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McEwen BS, Steller E. Stress and the individual: mechanisms leading to disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993; 153 :2093–2101. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McMahon SD, Grant KE, Compas BE, Thurm AE, Ey S. Stress and psychopathology in children and adolescents: Is there evidence of specificity? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2003; 44 :107–133. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McNally RJ. Psychological mechanisms in acute response to trauma. Biol. Psychiatry. 2003; 53 :779–788. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meaney MJ, Bhatnagan S, Dioria J, Larogue S, Francis D, et al. Molecular basis for the development of individual differences in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress response. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1993; 13 :321–347. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mendes de Leon CF, Powell LH, Kaplan BH. Change in coronary-prone behaviors in the recurrent coronary prevention project. Psychosom. Med. 1991; 53 :407–419. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyer RJ, Haggerty RJ. Streptococcal infection in families. Pediatrics. 1962; 29 :539–549. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller GE, Cohen S, Ritchey AK. Chronic psychological stress and regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines: a glucocorticoid-resistance model. Health Psychol. 2002; 21 :531–541. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohr DC, Classen C, Barrera M. The relationship between social support, depression and treatment for depression in people with multiple sclerosis. Psychol. Med. 2004; 34 :533–541. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohr DC, Hart SL, Julian L, Cox D, Pelletier D. Association between stressful life events and exacerbation in multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Br. Med. J. 2004; 328 :731. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morley S, Eccleston C, Williams A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of cognitive behavior therapy and behavior therapy for chronic pain in adults, excluding headache. Pain. 1999; 80 :1–13. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrow DA, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein, inflammation, and coronary disease. Med. Clin. North Am. 2000; 81 :149–161. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nader KO, Pynoos RS, Fairbanks LA, al Ajeel M, al-Asfour A. A preliminary study of PTSD and grief among the children of Kuwait following the Gulf crisis. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1993; 32 :407–416. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Norris FH. Epidemiology of trauma: frequency and impact of different potentially traumatic events on different demographic groups. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1992; 60 :409–418. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Donnell ML, Creamer M, Bryant RA, Schnyder U, Shalev A. Posttraumatic disorders following injury: an empirical and methodological review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2003; 23 :587–603. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orth-Gomér K, Wamala SP, Horsten M, Schenk-Gustafsson K, Schneiderman N, Mittleman MA. Marital stress worsens prognosis in women with coronary heart disease. JAMA. 2000; 284 :3008–3014. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton GC, Coffey C, Posterino M, Carlin JB, Bowes G. Life events and early onset depression: cause or consequence? Psychol. Med. 2003; 33 :1203–1210. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paykel ES. Stress and affective disorders in humans. Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry. 2001; 6 :4–11. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pennebaker JW. Writing about emotional experiences as a therapeutic process. Psychol. Sci. 1997; 8 :162–164. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson C, Seligman MEP. Causal explanations as a risk factor for depression: theory and evidence. Psychol. Rev. 1984; 91 :347–374. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pfefferbaum B, Sconzo GM, Flynn BW, Kearns LJ, Doughty DE, et al. Case finding and mental health services for children in the aftermath of the Oklahoma City bombing. J. Behav. Health Serv. Res. 2003; 30 :215–227. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Polusny MA, Follette VM. Long-term correlates of childhood sexual abuse: theory and review of the empirical literature. Appl. Prev. Psychol. 1995; 4 :143–166. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pruessner JC, Hellhammer DH, Kirschbaum C. Low self-esteem, induced failure and the adrenocortical stress response. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1999; 27 :477–489. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roitt I, Brostoff J, Male D. Immunology. 5th ed. London: Mosby Int.; 1998. p. 125. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ron M, Logsdail S. Psychiatric morbidity in multiple sclerosis: a clinical and MRI study. Psychol. Med. 1989; 19 :887–895. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999; 340 :115–126. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saab PG, Llabre MM, Hurwitz BE, Frame CA, Reineke LJ, et al. Myocardial and peripheral vascular responses to behavioral changes and their stability in black and white Americans. Psychophysiology. 1992; 29 :384–397. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saab PG, Llabre MM, Hurwitz BE, Schneiderman N, Wohlgemuth W, et al. The cold pressor test: vascular and myocardial response patterns and their stability. Psychophysiology. 1993; 30 :366–373. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schnall PL, Landsbergis PA, Baker D. Job strain and cardiovascular disease. Annu. Rev. Public Health. 1994; 15 :381–411. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N. Pathophysiology in animals. In: Dembroski TM, Schmidt TH, Blümhen G, editors. Biobehavioral Bases of Coronary Heart Disease. Basel: Karger; 1983. pp. 304–364. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N, Antoni MH. Learning to cope with HIV/AIDS. In: Kessel F, Rosenfield PL, Anderson NB, editors. Expanding the Boundaries of Health and Social Science. New York: Oxford Univ. Press; 2003. pp. 316–347. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N, Antoni MH, Saab PG, Ironson G. Health psychology: psychosocial and biobehavioral aspects of chronic disease management. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001; 52 :555–580. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N, McCabe P. Psychophysiologic strategies in laboratory research. In: Schneiderman N, Weiss SM, Kaufmann PG, editors. Handbook of Research Methods in Cardiovascular Behavioral Medicine. New York: Plenum; 1989. pp. 349–364. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneiderman N, Saab PG, Catellier DJ, Powell LH, DeBusk RF, et al. Psychosocial treatment within gender by ethnicity subgroups in the enhancing recovery in coronary heart disease (ENRICHD) clinic trial. Psychosom. Med. 2004; 66 :475–483. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schnurr PP, Friedman J, Bernardy NC. Research on posttraumatic stress disorder: epidemiology, pathophysiology and assessment. Psychother. Pract. 2002; 58 :877–889. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Segerstrom SC, Miller GE. Psychological stress and the human immune system: a meta-analysis of 30 years of inquiry. Psychol. Bull. 2004; 130 :601–630. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Selye H. The Stress of Life. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1956. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shalev AY. What is posttraumatic stress disorder? J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001; 62 :4–10. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shapiro F. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing: Basic Principles, Protocols, and Procedures. New York: Guilford; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaw JA. Children exposed to war/terrorism. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2003; 6 :237–246. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Short JL. The effects of parental divorce during childhood on college students. J. Divorce Remarriage. 2002; 38 :143–156. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanton JM, Balzer WK, Smith PC, Parra LF, Ironson G. A general measure of work stress: the stress in general scale. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2001; 61 :866–888. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thase ME. Treatment of severe depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2000; 61 :17–25. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thase ME, Greenhouse JB, Frank E. Treatment of major depression with psychotherapy or psychotherapy-pharmacotherapy combinations. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1997; 54 :1009–1015. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Voordouw BC, van der Linden PD, Simonia S, van der Lei J, Sturkenboom MC, Stricker BH. Influenza vaccination in community-dwelling elderly: impact on mortality and influenza-associated morbidity. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003; 163 :1089–1094. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Welch SL, Doll HA, Fairburn CG. Life events and the onset of bulimia nervosa: a controlled study. Psychol. Med. 1997; 27 :515–522. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Writing Committee for ENRICHD Investigators. Effects of treating depression and low perceived social support on clinical events after myocardial infarction: the Enhancing Recovery in Coronary Heart Disease patients (ENRICHD) randomized trial. JAMA. 2003; 289 :3106–3116. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman P, Wittchen HU, Hofler M, Pfister H, Kessler RC, Lieb R. Primary anxiety disorders and the development of subsequent alcohol use disorders: a 4-year community study of adolescents and young adults. Psychol. Med. 2003; 33 :1211–1222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Types of Stress That Impact Mental & Physical Health

There ar e many types of stress in life. All of them can impact your mental and physical health. For example, if you have financial stress, it could lead to anxiety or depression . If you have relationship stress, it may cause anger or resentment . All of these are important to address for your overall well-being. In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of stress that can negatively affect our lives You will also learn how to cope with them better!
- 1 What is Stress?
- 2.1 Types of Stress
- 2.2 Acute Stress
- 2.3 Episodic Acute Stress
- 2.4 Chronic Stress
- 2.5 Post Traumatic Stress
- 2.6 Chronic Stress vs. Acute Stress
- 2.7 Tips for Stress Management
- 2.8 Conclusion
What is Stress?
Stress is a response the body has to any kind of demand. It can be caused by anything, whether it’s mental or physical, and even emotional. Stress isn’t always bad for you. In fact, short-term stress can actually enhance your performance. This is so because it increases alertness and motivation levels while suppressing pain sensitivity. However, chronic stress is a different story. It can have negative effects on the body.
Types of Stress
Broadly, there are four types of stress, which are:
Acute Stress
Episodic acute stress, chronic stress, post traumatic stress.
You can read about all the different types of stress in detail, further in this article.

Acute stress is the body’s response to a short-term demand or change. This type of stress can last anywhere from minutes, hours, days, and even weeks. The duration depends on how long you’re exposed to an intense situation. Acute stress occurs when we need to fight off danger such as having a near-fatal experience or completing a marathon.
- Physical Symptoms: – Tightened muscles or muscle tension, chest pain or discomfort, trembling and shakiness, increased heart rate (heart palpitations ), sweating more than normal, rapid breaths.
- Emotional Symptoms: Anxiousness fearfulness, feeling overwhelmed or helpless; overwhelming feelings of panic; irritability; restlessness; and/or difficulty concentrating.
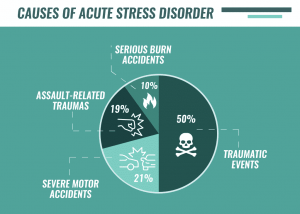
- Physical: Being in a dangerous situation, such as being close to someone or something that could cause you harm.
- Emotional: Getting bad news; thinking about life changes and their possible outcomes (i.e., death of a loved one), getting into an argument with your significant other, academic stress from school.
- Medication: Some people with chronic or severe stress may be prescribed medication to help calm them down.
- Relaxation Techniques : Meditation, deep breathing exercises , yoga , etc. can lower your heart rate and blood pressure . They send more oxygen throughout the body.
Some easy ways to avoid acute stress are:
- Staying with a friend or family member when traveling.
- Going outside for at least 30 minutes every day. Exposure to nature can help lower your levels of cortisol It is the hormone that releases during chronic stress and increases your heart rate. This high level of cortisol over a long period of time can lead to a slew of health problems.

Episodic acute stress is the body’s response to a single, isolated stressful event. These types of events include traffic accidents and other kinds of emergencies. They may also involve some kind of physical danger. Episodic or time-limited stress can be short or long-term. This depends on how you deal with it emotionally.
Symptoms of episodic acute stress include:
- Muscle tension in the back, shoulders, and neck
- Rapid heartbeat
- Thirst or dry mouth
Symptoms of episodic acute stress typically resolve themselves within about 30 minutes. However, symptoms are likely to return if you do not find a way to manage your emotional response. If symptoms remain after six months, you should see a doctor.
- Traffic accidents and other kinds of emergencies involve some kind of physical danger.
- Trouble at home or work can cause stress. Any sudden change in your life such as a new job, marriage , divorce , birth, or death of a loved one.
- Health-related issues such as surgery, cancer diagnosis, and treatment can also cause stress.
To treat episodic acute stress, it is important to find ways to cope with the emotional experience. Specific therapies that can help include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Interpersonal therapy
If you are suffering from an episode of high levels of stress, relaxation techniques. These techniques include deep breathing or meditation can be helpful in reducing your symptoms. You may also want to consider seeing a therapist .
Rather than treating episodic acute stress, it is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. Some of these include:
- Try to create a daily schedule that allows plenty of time for relaxation and reflection.
- Maintain good sleeping habits by going to bed at around the same time each night . Wake up at about the same time each morning.
- Don’t overload yourself with work and other responsibilities when you are already feeling stressed about something in your life.
- Eat a healthy diet and stay active.
If you are experiencing episodic acute stress, it is important to practice self-care. You can try relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. You may also want to consider seeing a therapist if symptoms continue for more than six months. It can be helpful to create a daily schedule that allows plenty of time for relaxation and reflection.

Chronic stress is when your body experiences low-grade demands and threats on daily basis. This may include things, such as traffic jams/delays, having an argument with someone close to you. Working multiple jobs while trying to get by in life can also cause chronic stress. It’s often caused by the pressure you put on yourself to meet all of your own expectations.
Symptoms of chronic stress include:
- Muscle tension in the back, neck, and shoulders
- Difficulty sleeping
Chronic stress can lead to serious health problems if left untreated including diabetes, high blood pressure, digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome, and heart disease.
- Overwhelming responsibilities at work, home, or school
- Problems with relationships such as divorce and death
To treat chronic stress, it is important to find ways to reduce your emotional response. Specific therapies that can help include:
It is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. Some of these include:
- Setting realistic expectations for yourself and those around you
- Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep at night
- Having strong support from friends and family can also help to prevent chronic stress.
In order to prevent chronic stress from occurring, it is often helpful to set realistic expectations. You can do it for those around you as well as yourself. You should also try eating a healthy diet and staying active. Getting enough sleep at night also prevents chronic stress. Having strong support from friends and family can also help in preventing chronic stress from taking hold of your life.
Post-traumatic stress disorder is a mental health condition. It is one of the most dangerous types of stress. It can develop after the experience or witnessing of traumatic events. Traumatic events are war, violent personal assaults like rape and mugging, or natural disasters. When your brain processes what has happened to you, it goes through three stages:
- The first stage occurs right after the traumatic event, usually within two days of it occurring. It’s called hyperarousal.
- The second stage occurs when you experience repeated memories and nightmares about what happened to you or if people in your environment trigger reminders of the trauma
- Finally, the third stage is when you isolate yourself from others and avoid things that trigger your memories.
Symptoms of PTSD
- Flashbacks and nightmares about what happened to you
- Being easily startled or frightened even when there is no threat around
- Feeling as though the world feels unsafe, constantly on guard for danger. You might also experience social withdrawal and isolation from family and friends which can lead to depression. There may be difficulty sleeping due to recurring nightmares or intrusive thoughts which can lead to you feeling tired and irritable.
- You may have a hard time concentrating, making decisions, or remembering things
- Your body might feel tense as the result of becoming easily startled by loud noises
- One might also experience feelings of guilt about what happened or whether it could have been prevented.
- You might also feel like you are always in danger even when there is no current threat. You may constantly be on guard for another attack
Causes of PTSD
- PTSD is caused by severe trauma, especially the type that threatens one’s life or survival.
- Severe childhood neglect and abuse are also associated with PTSD in adulthood.
Treatment of PTSD
Treatment for PTSD can include psychotherapy which includes cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) as well as medications to help reduce anxiety symptoms . Support groups can also help with socialization and grieving.
Prevention of PTSD
If you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is important to seek treatment right away. However, there are some things that can be done on your own to reduce stress and anxiety levels before they escalate into full-blown PTSD. Some ways include:
- Having a support system in place with friends or family members who understand what you are going through.
- Managing your time well so you can reduce feelings of being overwhelmed and having too much to do at once. This could include making a list of tasks for the day, prioritizing them, or setting deadlines for yourself when tackling large projects that are due soon
- Getting plenty of sleep every night because stress hormones spike during periods of sleep deprivation
- Practicing meditation or relaxation techniques like deep breathing to help reduce physical symptoms that accompany stress, such as muscle tension and tightness in the chest
- Exercising regularly because it releases endorphins which can relieve feelings of pain and depression . It also boosts your immune system so you are less likely to get sick and miss out on important appointments or events
- Eating a well-balanced diet to get the nutrients you need for your body to function properly. This will also help reduce feelings of fatigue and improve your energy levels
Chronic Stress vs. Acute Stress
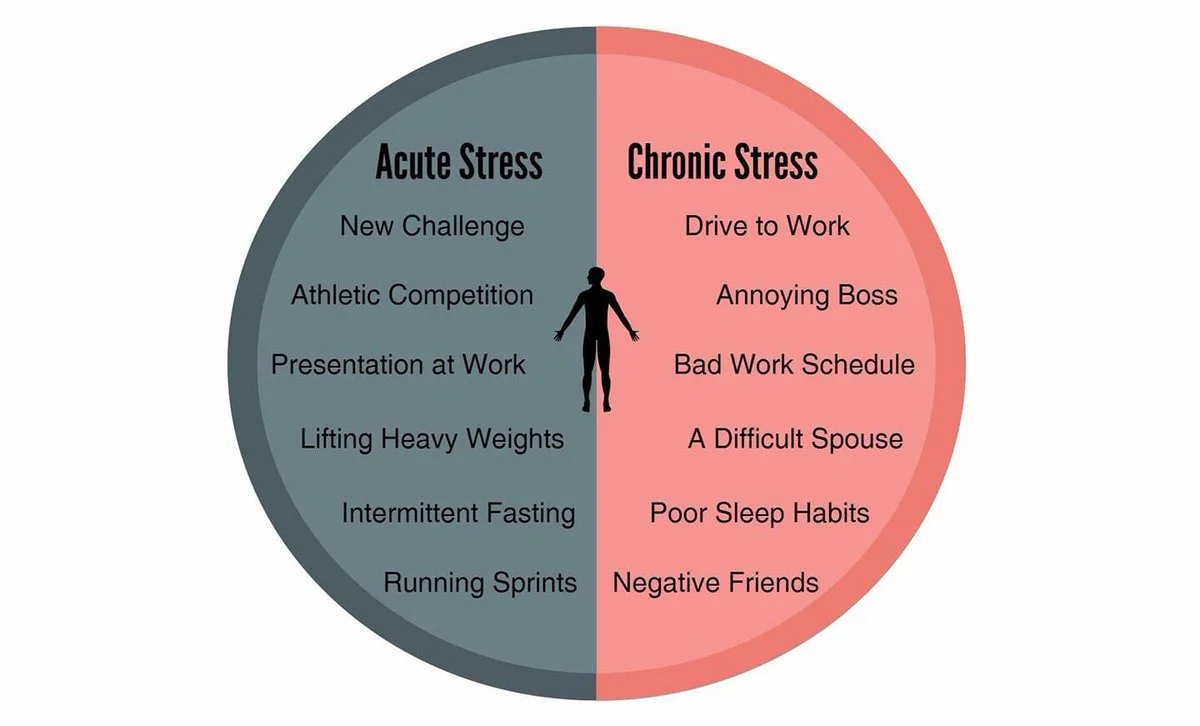
For many people, being able to identify the types of stress in their lives makes it easier for them to cope with difficult situations when they arise. Although both types of stress can impact your mental and physical health if you’re not careful, chronic stress is much more serious and can lead to health problems if left untreated.
Tips for Stress Management

- Exercise is a great way to help manage stress. Exercise gets your blood pumping and releases endorphins. These endorphins have been shown to promote feelings of happiness .
- Listen to calming music or take some time for yourself each day. This way you can practice relaxation techniques. These techniques include activities such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation. However, it’s important not to rely on these techniques alone.
- Maintain good sleeping habits by going to bed at about the same time each night. Also, you should not wake up around the same time every morning as well. You should also try eating a healthy diet, staying active, and getting enough sleep at night.
You can try all the above things if you want to prevent stress from occurring in your life.
In order to manage both episodic acute stress and chronic stress, it is helpful to exercise regularly. You can also listen to calming music or take some time for yourself. It is also important not to rely on these techniques alone. You should try eating a healthy diet, staying active, and getting enough sleep at night.
Stress can be a very unpredictable thing that impacts many people’s lives. However, it is often more helpful to focus on the ways you can prevent its onset. This can keep you from treating symptoms after the stress has already taken hold of your life. Set realistic expectations for yourself. Take help from those who are around you. Stay active, eat healthy food/meals regularly, get enough sleep at night, and have strong support from friends and family. You can prevent stress from negatively impacting your mental health.
We all experience different types of stress, but it’s important to understand what type you’re feeling so that you can take the proper steps for recovery. If your stress is coming from a lack of work-life balance, consider doing things like planning out your day or getting more sleep at night. For those experiencing physical symptoms due to their job, try taking time off and using meditation apps on your phone during stressful moments. There are many ways to help manage your level of stress in order to feel less overwhelmed by life! What kind of stress has been affecting you lately?
For more information, please contact MantraCare. Stress can have both physical and mental effects on the body, leading to negative consequences such as anxiety, depression, and even physical illnesses. If you have any queries regarding Online Stress Counseling experienced therapists at MantraCare can help: Book a trial Stress therapy session
Mantra Care aims at providing affordable, accessible, and professional health care treatment to people across the globe.
Online Therapy Physiotherapy Diabetes Hypertension Weight Loss / Gain Primary Care
Employers / Corporates Health plans Doctors / Providers Therapists
About Mantracare Careers Blog Contact Us
Download Our App

Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Refund Policy | Our Locations
Try MantraCare Wellness Program free
" * " indicates required fields
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Stress — Stress: Definition, Types And Impact
Stress: Definition, Types and Impact
- Categories: Stress
About this sample

Words: 821 |
Published: May 7, 2019
Words: 821 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Table of contents
What is stress, major types of stress, stress & its impact on men and women, acute stress, chronic stress, impact of stress on women.
- Reduced Sex Drive
- Irregular Periods
- Weight Gain
- Risk of Heart Diseases and Strokes.
Impact of Stress on Men
- Early Heart Disease Risk
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Lower Sperm Count
- Social Withdrawal
- High Blood Pressure.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 931 words
4 pages / 1906 words
2 pages / 797 words
3 pages / 1393 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Stress
Well, today I’d like to share with you what social anxiety is, the symptoms and who are most affected by it, and how to relax when your anxiety starts to kick in. To begin, let me first explain what social anxiety is. Social [...]
In the realm of education, academic stress has emerged as a pervasive concern, casting a shadow on the lives of students worldwide. This essay delves into the multifaceted aspects of academic stress, shedding light on its [...]
American Heart Association. (2018, April 4). Stress and Heart Health. American Heart Association. https://www.sleepeducation.org/sleep-topics/stress-and-sleep
Psychopathology refers to the study of mental disorders and the factors that contribute to their development. Understanding the causes and development of psychopathology is crucial for effective prevention and intervention [...]
In today’s world, stress is unavoidable especially for people who work or study in universities. Studying in a university is very stressful for most of students especially for those who come from another country with different [...]
When you’re living with high stress levels, you’re putting your entire well being at risk. Stress damages your emotional equilibrium, also it ruins your physical health. It narrows your ability to think clearly, function [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Occupational Stress on Employees in Information Technology Organizations
Asian Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities Vol. 6(3) August 2017
Posted: 2 Aug 2024
Sherry Sabbarwal
Panjab University, Chandigarh
Monica Munjial Singh
Mohammad amiri.
Panjab University, Chandigarh ; Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune; Qazvin Islamic Azad University
Date Written: July 01, 2017
Now a days, the occupational stress is becoming an issue of concern for all types of organizations. Information Technology based organizations are not an exception in this regard. In Pune which is an IT hub, Information Technology (IT) sector is among the top ten workplaces in India where stress levels due to work are very high. Though, there is an adoption of modern technology and innovation in IT sector, employees have overload of work and are stressed out. Employees of IT sector are not able to cope with the new rapid changes in this sector which results in stress. Through this study, an attempt has been made to identify the causes of stress among the IT employees. This study highlights the impact of stress on the physical and psychological conditions of IT employees. Through this study an attempt has also been made to focus on the stress reducing programs (stress management) implemented by selected IT organizations. The result of the study shows that there are several causes of stress in spite of the efforts made to reduce occupational stress among the IT employees. This study indicates that, majority of employees faced physical as well as psychological stress due to heavy work load.
Keywords: Occupational stress, Stress management, Types of stress
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Panjab University, Chandigarh ( email )
Sector 14 Chandigarh, 160014 India
Dr Mohammad Amiri (Contact Author)
Bharati vidyapeeth deemed university, pune ( email ), qazvin islamic azad university ( email ), do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on ssrn, paper statistics, related ejournals, comparative studies of leadership ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Corporate Governance & Psychology eJournal
Social entrepreneurship ejournal, nonprofit organizations ejournal, change management & organizational behavior ejournal.
Comparative analysis of calculations in thin-walled structure design
- Hodovanets, Elvira
- Kvocak, Vincent
This article focuses on reproducing normative calculation conditions through numerical methods and comparing these with outcomes obtained using specialized software for structural engineers. We analyse the basis of normative critical forces and stress values, including conditions of fixity, types of structures, and materials, and how these are represented in practical calculations and numerical modelling. The investigation is intended to enhance understanding between normative assumptions and their practical application in design, offering valuable guidelines for refining calculation methods.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Acute stress: Acute stress is a very short-term type of stress that can be upsetting or traumatic; this is the type of stress that is out of the ordinary, such as a car accident, assault, or natural disaster.; Chronic stress: Chronic stress is what we most often encounter in day-to-day life and seems never-ending and inescapable, like the stress of a bad marriage or an extremely taxing job.
The three main types of stress, present in any environment are physical, emotional, and cognitive (psychological). Any of these stresses incur as a result of work overload, repetitive tasks that underestimate individual's capability, and job mismatch. Problems of work overload are directly or indirectly associated with psychological or ...
The psychological stress is the stress that takes place as a result of various types of. psychological problems, i.e. anger, depression, trauma, anxiety and frustration. In the. personal as well ...
1. Injury or infections of the body, dangers in environment, major changes or transitions in life which force us to cope in new ways. 2. Physical stressors like noise, pollutions, climatic changes, etc. 3. Hustles of everyday life centering on work, family, social activities, health and finances. 4.
Stress. Stress is a normal reaction to everyday pressures, but can become unhealthy when it upsets your day-to-day functioning. Stress involves changes affecting nearly every system of the body, influencing how people feel and behave. By causing mind-body changes, stress contributes directly to psychological and physiological disorder and ...
loss of your sense of humor. feelings of overwhelm. depression. loss of interest in life or activities. existing mental health conditions get worse. Physical symptoms of stress may include the ...
Get original essay. Body Paragraph 1: One of the most important ways to cope with stress is to practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques. Engaging in activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help individuals reduce their stress levels and create a sense of calmness and inner peace.
Understanding stress can help you know more quickly when you need help. Stress is our built-in response to danger, a surge in hormones as we choose between fighting, fleeing, or freezing. The ...
Good Stress vs. Bad Stress . Another type of stress is acute stress. It comes from quick surprises that need a response. Acute stress triggers the body's stress response as well, but the triggers aren't always happy and exciting. This is what we normally think of as "stress" (or "bad stress").
The longer the stress lasts, the worse it is for both your mind and body. You might feel fatigued, unable to concentrate, or irritable for no good reason, for example. But chronic stress causes wear and tear on your body, too. The long-term activation of the stress response system and the overexposure to cortisol and other stress hormones that ...
The effects of stress on individuals can be profound and far-reaching, impacting both physical and mental health. Chronic stress has been linked to a range of health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and digestive issues. The constant activation of the body's stress response can lead to a weakened immune system, making ...
Individual response to stressors influences their health. Maladaptive response to stress results in various physical, psychological, and behavioral negative effects. Negative effects of stress on physical health include increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. Psychological ...
Abstract. Stressors have a major influence upon mood, our sense of well-being, behavior, and health. Acute stress responses in young, healthy individuals may be adaptive and typically do not impose a health burden. However, if the threat is unremitting, particularly in older or unhealthy individuals, the long-term effects of stressors can ...
In contrast to acute stress, chronic stress is your body's response to a prolonged stressful event or a series of events. In these cases, the stressor is long-term and often difficult to solve.
There are many different types of stress. Stress can be a good thing or a bad thing. For example, a little stress could help a person ace an interview, but on the other hand long-term stress can cause the stress response to shut down causing many negative physical and mental effects. ... The essay "Stress and Its Role in Our Life" is a useful ...
Often, cutting back on work can literally make you more productive due to the reduced stress. Source of stress changes as we age. Stress may appear up in a child as tantrums. What creates stress in a teenager? A teenager may become stressed because of acne, their body types such as weight and height, peer pressure, school assignments and family
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques. Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Types of Stress. Broadly, there are four types of stress, which are: Acute Stress; Episodic Acute Stress; Chronic Stress; Post Traumatic Stress; You can read about all the different types of stress in detail, further in this article. Acute Stress. Acute stress is the body's response to a short-term demand or change. This type of stress can ...
The right type and amount of stress can actually sharpen the mind and reflexes. The result in the physical manifestations of stress is when hormones are released from when stress produces a physiological reaction in your body. The four primary types of symptoms of stress are known as; physical, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral.
The essay "Stress: Definition, Types and Impact" provides a comprehensive overview of stress, but there are several shortcomings that can be addressed to improve the quality of the essay. Firstly, the essay lacks a clear thesis statement that summarizes the main argument of the essay. Secondly, there are several grammatical errors and awkward ...
Stress and Effects on Brain. 55). In other words, stress can create a life-long physiological change in and impairment of brain and body functioning. uch recent findings suggest that victims of stress may in fact suffer from a neurological disorder rather than just from a character flaw, mental weakness, or bad luck.
Now a days, the occupational stress is becoming an issue of concern for all types of organizations. Information Technology based organizations are not an exception in this regard. In Pune which is an IT hub, Information Technology (IT) sector is among the top ten workplaces in India where stress levels due to work are very high.
At baseline and every 3 months for 18 months, adolescents completed measures of suicidal ideation and behavior, depressive symptoms, and stress. RESULTS: Multilevel models examined within-person mean, deviations from within-person mean, depression, and stress and their interactions with abuse as predictors of suicidal ideation and behavior.
This article focuses on reproducing normative calculation conditions through numerical methods and comparing these with outcomes obtained using specialized software for structural engineers. We analyse the basis of normative critical forces and stress values, including conditions of fixity, types of structures, and materials, and how these are represented in practical calculations and ...