- What is the PhD Viva?
Written by Mark Bennett
The viva voce is the final assessment for a PhD. It is an oral examination where the student defends their research to two academic examiners. This involves answering questions about your work, typically related to the literature, methodology, your findings and the significance of your conclusions. In some countries (like the USA ) the viva is actually referred to as a 'PhD defence', because the candidate defends their thesis from these questions.
This guide explains exactly how the viva works, what to expect on the day, how to prepare and what happens afterwards.

An overview of the PhD viva
The PhD viva can seem like an intimidating process, but it actually serves a very simple purpose: proving that your research is original, that you understand its contribution to knowledge and – most importantly – that your work is your own. It's also very rare for students to fail.
Who attends a viva?
A PhD viva usually involves two examiners: one internal examiner (from your university) and one external examiner (from another university). Both should be familiar with your field and the external examiner in particular should be a recognised expert in your specific research area.
The internal examiner usually acts as the chairperson for the exam, making sure it follows your university's procedures.
Your supervisor doesn't normally attend the viva itself, but they will help you prepare for it and should be around to provide support on the day.
How long does a PhD viva take?
There is no set length for a viva voce exam, but most take between one and three hours .
A longer viva doesn't necessarily indicate any problems with your thesis: it may simply be that the examiners are enjoying the discussion. Equally, a shorter viva may just mean that your examiners are satisfied with the thesis and your responses to their questions.
Why is the viva necessary?
The most basic function of the viva is to prove that your work is original (i.e. not plagiarised). This is especially important because the criteria for a doctorate is to offer a significant new contribution to knowledge.
By discussing your work with you directly and confirming that you fully understand your thesis, examiners can be confident that this is your own research.
Do all PhD students have to have a viva?
Almost always. One exception is for PhDs by publication (as the work in these will already have been through academic peer review). Some countries such as Australia and New Zealand also take a slightly different approach as their location makes it harder to invite external examiners for a face-to-face defence.
The viva format
Universities set their own viva voce processes, but most will follow a fairly similar format.
Before the exam
Many supervisors let you choose an external examiner . They need to have expertise in the topics you have researched, but not someone you have collaborated closely with during your PhD or who you have a strong personal friendship with (as these might create a conflict of interest).
Your supervisor will normally discuss possible options and then submit the invitation on your behalf. This usually happens just before you complete your PhD.
The next step is to submit your thesis . Nowadays most universities only ask for a digital submission which is sent out to your examiners for you.
The gap between submission and viva is usually one to three months. This allows time for both examiners to thoroughly read and consider your thesis and for you to prepare.
Your supervisor/s should offer to conduct a mock viva with you shortly before the real exam. They'll ask the sort of questions an examiner might have about your thesis so that you can practice answering and discussing them.
Your supervisor will normally meet with you before the viva begins to help you relax and ease any last minute nerves.
The exam room will be somewhere on your university campus that has been booked for the occasion. It will be laid out very similarly to a job interview, with space for you and the examiners to sit with your notes. Drinking water is also normally provided.
Most vivas are recorded and will begin with the internal examiner explaining the rules and regulations as a formality. Either they or the external will then begin asking questions about your thesis.
The examiners will usually help you relax and settle in to the discussion by asking something quite general, such as what interested you in this PhD project or what the most enjoyable part of the research was. Subsequent questions will be more specific, often referring the arguments made at particular points in your thesis.
The examiners will end the viva once they have completed their questions and feel able to come to a judgement. You will then be asked to leave the room whilst they discuss your performance and decide on a result to recommend. This normally takes around fifteen minutes or so.
After the viva
The next steps depend on your viva result. The examiners will invite you back in to explain their recommendation and provide general feedback on your work. This may include advice on whether or not you should seek to publish any of your PhD thesis and what sort of edits or further work might be required to prepare it for that.
Hopefully you'll then be able to celebrate with your supervisor, but they should be on hand to offer their to support and advise you whatever the outcome.
The majority of students have some corrections (usually minor) to make before resubmitting a final version of the thesis to be checked by the internal examiner. Once the final copy of your thesis is approved, you will be awarded your PhD! It's time to look forward to using your new title (and wearing some exceptionally elaborate robes at your graduation).
Viva preperation tips
It may feel like you're at the end of a long PhD journey by the time the viva comes around (and you are) but the oral exam is an important part of your doctorate and you should prepare accordingly.
Whatever else you do or don't do, listen to the advice of your supervisors. They'll have experience of all sides of the process, from sitting their own viva voce to preparing previous students for theirs. Chances are they've also served as internal or external examiners too and will know exactly what sort of questions they'd ask about a thesis like yours.
Here are seven tips for effective viva preparation.
#1 Take a (short) break first
Chances are you've been working very hard on your PhD recently, getting it written up, responding to feedback from your supervisor, making edits, sorting the bibliography (which you still left to the last minute, right) and getting the whole thing printed in time for the final deadline.
Whatever happens next, you've just successfully submitted a PhD thesis and you deserve a break. So take one.
A week or two away from your PhD will be ideal (no, don't take a copy of your dissertation with you). You'll get some mental rest and be in a better place to take a fresh look at your thesis and think clearly about it.
There's no need to feel guilty: the time between submission and viva is partly intended to make this possible.
#2 Read through your thesis
You may feel pretty familiar with your thesis by now but, actually, you aren't. You're familiar with a series of chapters that may well have developed separately over several years. It was probably only recently that you wrote them up in their final form, added an introduction and conclusion and turned the whole thing into a dissertation setting out your entire PhD thesis.
You need to know that thesis inside out and be completely familiar with the structure of the dissertation that contains and communicates it: which page a key concept or topic appears on for the first time, where key stages of your argument occur, where you cite or critique particular scholarship, and so on.
At the very least, this means reading your full thesis through at least once. Really though, you should be re-reading each chapter a couple of times and. . .
#3 Annotate key points
The PhD viva isn't a closed-book exam and you're expected to take a copy of your thesis with you. It's perfectly fine to consult it in response to questions, so make that process easy by annotating the most important stages of your argument.
There are lots of ways to do this, but, really, there's no substitute for sticking markers through your dissertation and scribbling in the margins.
If the copy of the thesis you take into the exam room looks like it's survived an explosion in a post-it note factory and then spent several years being read by rough-fingered undergraduate students in the library, well, you're on the right track.
#4 Note down potential questions (and answers)
You'll never be able to guess all of the questions that will come up at your viva, but you should be able to anticipate a few of them. Sketching out some bullet-point answers in advance will help you think critically about your thesis and boost your confidence going into the exam.
Spend extra time on any questions you're concerned about. If there's a point where your argument gets a bit strained or where you think your conclusions might be easy to challenge, have a think about how you'd defend them. Remember that your thesis doesn't have to be perfect, but you do need to be able to make a case for it – so practice doing that.
Incidentally, no one has been able to completely test the hypothesis that preparing for a viva question ensures it doesn't actually come up, but, well, the anecdotal evidence is strong. Prepare anyway.
#5 (Re)familiarise yourself with your examiners' work
The viva is about your thesis, but your examiners will have been selected due to the relevance of their own research and their perspectives will be at least partly informed by it.
It makes sense to consider how their work might inform their attitudes towards yours (this should also help you antitipate some questions, as above).
#6 Definitely take up the offer of a mock viva
Your supervisor/s should offer to arrange a mock viva with you shortly before the actual exam (once you've had time to prepare). This is a really helpful process.
The mock viva won't be anything like as long as the real thing and it won't cover every question your examiners will ask (or necessarily predict any of them). But it doesn't need to.
The most valuable feature of a mock viva is to get feedback on how you answer questions. Your supervisors will be able to spot whether you're coming across as too hesitant or too confident, or whether your answers are sufficiently clear.
#7 Try to enjoy it
Chances are you'll be sick of hearing this advice by the time your exam comes around, but it's true. A PhD viva voce really can be fun.
This is your chance to sit down with two experts in your academic field who have read and carefully considered your thesis and whose attention, for the duration of the exam, is entirely on your research. That's a privilege and it's one you've earned by getting to this stage.
Prepare effectively and give the viva voce the respect it deserves. But, once you get into that exam room, be confident, own your ideas and enjoy the chance to let them take centre stage in a serious academic discussion.
Viva results
The vast majority of PhD students pass their viva. By the time you're ready to submit your PhD you will be an expert in your subject area, more than capable of discussing and debating it. You'll also have done so many times before: at conferences, in conversations with your supervisor, and in your own writing.
Your supervisor will also ensure your thesis is ready for examination before they recommend you proceed to this stage. The only exceptions to this will be if you submit against the advice of your supervisor (never a good idea) or if you've over-run the time period for your PhD and have to hand in a thesis that isn't ready (you're unlikely to get to this point unless your PhD has been going badly for some time).
PhD viva outcomes
It's rare to fail a viva, but it's also rare to pass outright. Instead, most students are asked to make some corrections to their thesis.
Here are the possible outcomes of a PhD viva voce:
- Pass with no corrections – (uncommon) – Your viva has revealed no significant issues with your thesis and the dissertation itself is error-free. Congratulations, you are eligible to receive your PhD now!
- Pass with minor corrections – (very common) – Your thesis is essentially sound, but there are some minor issues with your dissertation (such as typographical errors, or missing references). You will normally have three months to submit a corrected thesis.
- Pass with major corrections – (fairly uncommon) – There are some parts of your argument that need to be clarified, expanded or otherwise rewritten. You will normally have six months to submit a revised thesis, but won't need a second viva.
- Revise and resubmit – (fairly rare) – Your thesis is potentially good enough for a PhD, but it needs some significant work, usually including some substantial additional research. You will have around a year to re-submit an improved and updated version of your dissertation for a second viva voce exam.
- Be recommended for MPhil – (rare) – Your thesis isn't good enough for a PhD, but it is sufficient for an MPhil (a research Masters that doesn't require a substantial original contribution to knowledge). You may receive the MPhil outright, or after some edits and corrections.
- Fail – (exceptionally rare) – Your thesis does not meet the required standard for a PhD (perhaps due to fundamental flaws in your data and analysis, or due to evidence of plagiarism) and it cannot be converted into an MPhil. You have failed your doctorate and cannot resubmit your thesis.
Those last couple of results may appear scary but, in practice, it's only a few % of candidates each year who don't pass with corrections. The only way a PhD is likely to fail outright is if you have run down the clock on your registration period, submitted a poorly written thesis based on insufficient data and probably done so against the advice of your supervisor/s. The entire PhD process is designed to prevent this happening.
So relax. The likelihood is that your PhD will pass with minor corrections (or better) and that your next challenge will be deciding what to use your new 'Dr' title on first.
Can you appeal a viva result?
If you think your viva outcome was incorrect or unfair, then you may be able to appeal it with your university. The first thing to do is check their guidelines and appeal process. Your students' union may also be able to support and advise you.
Note that you can't normally appeal on academic grounds . Your examiners' judgement is generally final. It is also difficult to appeal a PhD result if you submitted without the support of your supervisor/s or have otherwise ignored their advice at other points in your project.
You may have grounds for appeal if you can demonstrate that you have been poorly advised or supervised (you will need evidence of this and of the specific impact it has had) or if there was an irregularity in the conduct of your viva (such as interruptions, an unsuitable venue, or a lack of consideration for relevant disabilities or health conditions that may have impacted your performance).
Common viva questions
The questions your examiners ask will obviously be very specific to your thesis and anticipating them is a big part of your specific viva preparation . There are a few things that are likely to crop up more often than not, though.
Here are some example viva questions , along with some tips for answering them well.
"Why did you choose this PhD project?" / "What interested you most about this topic?"
This is a classic icebreaker: it's an invitation to speak generally and positively about your work. As well as being a fairly easy question to answer (after all, there must be at least something you enjoyed about your PhD) this should also help you channel your passion and enthusiasm for your research as the viva gets going.
"What was the most challenging part of the project?"
This probably won't be the first question you're asked, but it might also come up early in the viva as the examiners ease you into talking about your project. It doesn't mean that they think your PhD is flawed. All research involves overcoming obstacles. This is an invitation to talk about how you did that and reflect on the practicalities of your project.
"What is the original contribution to knowledge made by this thesis?"
This question is highly likely to come up at some point in the viva and it's one you absolutely must have a clear answer for. You should be able to explain in one or two sentences what your contribution is, how it's original and why it matters.
Some examiners might not be so explicit or direct in asking this, so be on the lookout for questions like "why is this PhD important?", "why was this project worth completing?", "what were your main findings?" or "why does this research matter?". If you hear any of those, it's time to deploy the original contribution answer.
"Why did you include / exclude X?"
All doctoral projects need to be selective about what they can and can't include, and successful PhD students need to set boundaries for their research. At some point your examiners will probably want to see the logic behind yours.
Be confident and own your decisions. If there was a particular topic or approach you didn't include, then give your reasons for that.
Remember that there are lots of reasons why something might not make the cut for a PhD and the examiners aren't trying to catch you out. They don't even need to agree 100% with your decisions, but they do need to hear that you had credible reasons for making them.
It may be that there wasn't space to cover everything (in which case you should justify prioritising the material you did include). Or perhaps you felt that there was already sufficient scholarship related to a particular source or concept and your aim was to take the field in a different direction (this is a very good answer, if you can make it convincingly).
"If you were to repeat this project, what would you do differently?"
This question (or one like it) may come towards the end of the viva as you reflect on the project as a whole.
Again, the aim isn't to try and undermine your thesis, but rather to see whether you can constructively critique your own work and approaches. Or, to put it another way, have you learned anything from the experience of doing a PhD? You should have. After all, a doctorate is partly about learning to become an effective researcher and mistakes are a great thing to learn from.
In any case, this shouldn't be too hard to answer. There are likely to be all sorts of things you would do differently in future: from adopting different approaches or directions sooner, to heading off blind alleys or methodological mistakes.
"What do you think the next steps might be for this research?"
Relax, your examiners aren't expecting you to dive straight into another PhD. But they may want to hear where you would take this research next, or what you think other scholars could do to build on your findings. After all, part of the value in a new contribution to your field should lie in what it makes possible, as well as what it is .
It's best to be modest and realistic here, rather than making sweeping claims for how your findings will allow other researchers to reinvent the wheel (unless you have actually come up with a new technique for designing wheels, in which case, go ahead).
"Do you have any questions or comments for us?"
Your examiners will probably end the viva by asking if you'd like to ask them any questions, or say anything else about your thesis. This might seem a bit odd, but it's actually a helpful way for you to revisit or clarify any of your earlier answers.
For example, you might like to acknowledge a specific critique and reiterate your reasons for believing the thesis to be valid in spite of it. Or you might want to confirm that the examiners understood what you meant at a particular point in the previous discussion.
It's not a good idea to try and rehash large chunks of the viva here, but it's fine to pick out one or two things and be assertive. This demonstrates your confidence and commitment.
Equally, you can take the opportunity to ask the examiner's opinions on areas of the thesis that haven't come up, if you wish. This is fine, provided you're confident in those sections and comfortable discussing them.
Browse current PhD opportunities
Ready to begin the journey towards your own viva? Search thousands of PhDs on our site right now.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.

PhD fees can vary based on subject, university and location. Use our guide to find out the PhD fees in the UK and other destinations, as well as doctoral living costs.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.

Postgraduate students in the UK are not eligible for the same funding as undergraduates or the free-hours entitlement for workers. So, what childcare support are postgraduate students eligible for?
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Personal tools
- Log in/Register Register

https://www.vitae.ac.uk/doing-research/doing-a-doctorate/completing-your-doctorate/your-viva/your-phd-viva
This page has been reproduced from the Vitae website (www.vitae.ac.uk). Vitae is dedicated to realising the potential of researchers through transforming their professional and career development.
- Vitae members' area
Defending your doctoral thesis: the PhD viva
Format for defending a doctoral thesis.
Every institution will have specific regulations for the thesis defence. In some countries or institutions, the convention is for thesis defences to be public events where you will give a lecture explaining your research, followed by a discussion with a panel of examiners (opponents). Both your examiners and the audience are able to ask questions.
In other countries, including the UK, the oral examination is usually conducted behind closed doors by at least two examiners, usually with at least one being from another institution (external examiner) and an expert in your topic of research. In the UK the supervisor does not participate in the viva, but may be allowed to observe. Sometimes someone from your own institution is appointed as an independent chair. Although it is now becoming more common for the candidate to have an opportunity to give a public lecture in UK institutions, this does not form part of the examination and may or may not be attended by the examiners.
Viva preparation
Take the preparation for your viva seriously and devote a substantial amount of time to it. The viva preparation checklist may be useful to help you prepare.
Your institution may offer courses on viva preparation and there may be opportunities to organise a practice viva. Take advantage of these opportunities: they can be extremely valuable experiences.
Things you may wish to take with you
- your thesis – mildly annotated if you wish
- a list of questions that you might be asked and your planned responses
- any questions that you want to ask your examiners
- additional notes which you have made during your revision
- list of minor corrections that you have come across during your revision.
During the viva
Your study will have strengths and weaknesses: it is essential that you are prepared to discuss both. You could think of any weaknesses as an opportunity to demonstrate your skill at critical appraisal. Examiners will seek to find and discuss weaknesses in all theses. Do not interpret criticism as indication of a possible negative outcome.
Examiners have different personalities, styles and levels of experience. Sometimes a candidate may feel that a challenge is made in a confrontational way. Experienced, effective examiners will not be inappropriately confrontational, but some will. Do not take offence. A relaxed, thoughtful, and non-confrontational response from you will help re-balance the discussion. Having an independent chair can help maintain a constructive environment.
Useful tips for during your viva:
- Ask for clarification of ambiguous questions or ask for the question to be repeated if necessary
- Take time to think before answering
- Be prepared to ask questions and enter into a dialogue with your examiners
- Be prepared to discuss your research in context of other work done in your field
- Be ready to admit if you don't know the answer to a question
- Be prepared to express opinions of your own
You are not expected to have perfect recall of your thesis and everything that you have read and done. If you get flustered, or need to refer to notes your examiners will understand. They have been in your situation themselves!
After your viva
There are several possible outcomes of a thesis defence. Most commonly, your examiners will recommend to your institution that you are awarded your degree subject to minor corrections, although in some instances they might ask for more substantial work.
Bookmark & Share
Student Administration

This page contains information about preparing for your viva and viva outcomes.
The object of the viva examination is to allow you the opportunity to explore, clarify and defend your research in the presence of academic leaders in your chosen discipline. The viva examination will normally be attended by an external examiner, an internal examiner and you. Your supervisor will not be present at the viva examination.
If you are a member of University staff, two external examiners are appointed and both would attend the viva.
There is no way of telling in advance how long the examination will last but it can be several hours.
The viva examination is usually conducted behind closed doors by at least two examiners, usually with at least one being an external examiner from another institution and an expert in your topic of research.
The internal examiner is responsible for arranging the date, time and venue for the viva which is normally held within three months of submission of the thesis.
In advance of your viva, your examiners will read your thesis and prepare independent, written reports. After the examination, a formal joint report with an agreed recommendation will be produced.
If you would like a copy of the final reports please contact the Research Degree Administration Team . The internal examiner should provide you with informal feedback, and if necessary, a copy of the revisions that have been requested.
Viva outcomes
For the degrees of PhD, MPhil and MD, examiners can recommend:
| Outcome | |
|---|---|
| Pass | You will receive an email from the Research Degree Administration Team advising you on how to submit your final thesis. |
| Pass subject to minor modifications | The Internal Examiner will provide you with a list of required corrections. Once minor modifications have been made to the thesis you should send it directly to the examiner(s) for their approval. You will receive an email from the Research Degree Administration Team when the examiners have confirmed the modifications have been made to their satisfaction. Modifications are to be made usually within three months of the oral examination but can be submitted earlier than the stated deadline. |
| Pass subject to major modifications | Examiners will have the option to recommend major modifications as an outcome for first submissions submitted from 2 September 2019 onwards. This will mean that you have up to six months to revise your thesis. |
| Resubmission | The Internal Examiner will provide you with a list of required corrections. Candidates who receive a Resubmission recommendation will be contacted by their Faculty Link Officer formally notifying them of their resubmission deadline and fee. You will have one year from the date of the formal notification to submit the revised thesis. Once you have completed your revisions, you are required to submit an electronic version to . You will have a second viva, which will be attended by an independent chair. Your Internal Examiner will contact you to arrange a date and time. |
| To award MPhil subject to, if required, amendments to the thesis [PhD and MD students only] | |
| Resubmission for the award of MPhil [PhD and MD students only.] | The revisions to be made usually within one year of the date of the oral examination but can be submitted earlier than the stated deadline |
| Fail |
When considering a resubmitted thesis examiners can only use recommendations 1,2, 5 or 7. A candidate may only make two applications for a research degree award.
Back to: Student Administration
What is a PhD Viva?
- Maisie Dadswell
- July 31, 2024

After you have written and submitted your PhD thesis, the next stage in the process is to pass your PhD viva examination, which your PhD supervisor at UWS London will fully prepare you for. Your viva will happen within three months of submitting your thesis; after completing your viva, you will know if you have passed with flying colours and can call yourself a doctor in your respective field. Though the prospect may sound daunting, see it as the chance to prove that your creative knowledge makes you a peer to the academic panel that will be present for your viva; it is the perfect opportunity to establish yourself as an intellectual authority in your field.
This article will cover what a viva is, how it works, what the potential outcomes are, who will be present on the panel and provide some helpful tips that are relevant for all fields of study.
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree is the highest academic degree one can earn in most fields of study. It typically involves conducting original research, making a significant contribution to the field’s knowledge, and writing a dissertation or thesis that demonstrates expertise in a specific area. Learn more about PhD at UWS Londo n here .
A PhD viva also referred to as a Viva Voce, Latin for ‘living voice’, is an oral examination which follows the submission of your doctoral thesis, where you will showcase your knowledge and defend your research in front of a panel comprised of academic experts. This examination is compulsory for the vast majority of doctoral students.
PhD Viva Questions
All the questions asked during your viva will assess:
- Your knowledge depth in your specific area of research.
- How deep your knowledge is concerning the broader research field relevant to your PhD.
- If you can place your work in a broader context.
- If you can demonstrate how your research contributes to your field.
- If you know of any potential limitations and oversights in your work – where applicable.
If the panel has any suspicions that your work may not be your own, they may also question the authenticity of your work.
How Long Does a PhD Viva Take?
One of the most frequently asked questions is how long is a PhD Viva. The average length is around three hours, but several factors can extend or shorten your oral examination. If there are issues in your PhD thesis or if it is poorly presented or formatted, this could lead to confusion on the panel, which will necessitate more clarification for you to set the record straight and prove that you understand your field of study. Similarly, how well-prepared you are and how concisely you respond to questions will also have a bearing on the duration of the viva.
However, lengthy PhD defences don’t always need to be a sign that it is going poorly! Your examiners may enjoy the discussion enough that they will want to talk about it long after they have concluded that you have passed the examination. Even though, in some rare instances, a viva can take up to eight hours there may be university or country-specific rules on maximum duration – feel free to discuss this with your PhD supervisor beforehand.
Who Will Be on Your Viva Panel?
Your PhD examination will be carried out by one examiner from your university and an examiner from an outside university. Your PhD supervisor may also be on the panel, although this is not always the case. If you do find your supervisor on your viva panel, in the UK, it is common that they are prohibited from speaking. If they are present, they will solely act as observers.
Together, the examiners will highlight what they found when reading your PhD thesis thoroughly, focusing on the theories and key concepts you put forward in your research. To ensure that the examiners are being fair and appropriate in the viva process, there is also usually a chairperson on the panel who takes notes documenting any notable suggestions or comments. The chairperson will either be internal or external from the university.
What Are the Outcomes of a Viva Exam?
In the UK, there are six potential Viva PhD outcomes. We have listed them below from the best outcome to the worst. However, it is worth bearing in mind that even if you need to make minor or major corrections after your viva, you will be given equal credit as someone who was awarded their PhD degree without corrections.
The average pass rate for a PhD viva in the UK can vary depending on the university, field of study, and specific criteria used for evaluation. However, it is generally quite high.
In many UK universities, a significant majority of candidates who reach the viva stage pass, often with some amendments required. A “pass with minor amendments” is a common outcome, indicating that the candidate has demonstrated a sufficient understanding of the research. Recent research on viva experiences indicates that 84% of Ph.D. candidates are required to make minor revisions in order to achieve a passing grade.
1. Awarded PhD Degree with No Corrections
It is rare for students to pass their PhD degree without any corrections. So, if this is your outcome following your viva, celebrations are in order! It means you have seriously impressed your examiners with your research and examination.
2. Minor Corrections Required to Pass
Recent viva experience research has highlighted that 84% of PhD candidates must make minor corrections to pass. Typically, the minor corrections will be small issues with the thesis, such as grammatical errors, typos, typograph issues, or presentational faux pas, which can be quickly edited. Don’t be disparaged if you are presented with this outcome following your viva; it still means that you have done remarkably well with your thesis and viva.
3. Major Corrections Required to Pass
This outcome is the second most common following a viva; it means you have met the required standard to be awarded your doctorate, but some revisions or corrections need to be made. Typically, this will involve you improving the structure or clarity of your thesis by rewriting chapters or adding additional analysis. Once again, needing to make major corrections shouldn’t be seen as a failure; although it may be disparaging, it doesn’t invalidate your research or contribution to your field.
4. Revise and Represent to Pass
You will be asked to revise and represent your work if the panel can see the potential within your work and that it can meet requirements if you undertake additional research or analysis. You will be presented with this outcome if your work doesn’t quite reach the PhD degree standard; unlike with the minor and major corrections outcomes, if you are asked to revise and represent, you will need to present your revised work to the panel again.
5. Awarded an MPhil Degree
If the academic panel decide that major corrections or additional research still won’t allow your work to meet the PhD standard, you may be awarded a lower-standard MPhil degree instead. For example, philosophy PhD candidates will be awarded a Master of Psychology degree instead of a Doctor of Philosophy degree. Typically, MPhil degrees are awarded in place of PhDs if your work lacks originality or the knowledge creation that a PhD requires. An MPhil degree ranks above MA and MSc degrees as the most advanced Masters degrees. An MPhil degree still demonstrates that you have the same skill set as someone who successfully obtained a PhD, and they are still valuable to employers.
6. Immediate Fail
An immediate fail is rare; a 2022 survey found that only 3.3% of PhD candidates fail their viva outright – it certainly isn’t something you should obsess over. If when you are preparing for your viva, you find some faults in your thesis, don’t be afraid to broach them yourself in your exam; this will show that you can present a passable thesis. `
PhD Viva Tips:
Don’t work with irrelevant guidance or tips.
While brushing up on generalised tips online can help you to feel prepared for your viva, remember that there will always be variability in the process, the focus of the exam, and the questions asked. The variable factors include your field of study and the university you are obtaining your doctorate. With this in mind, always chat with your supervisor to ensure you are preparing with the right and relevant knowledge.
Treat the Examiners as Equals
Your PhD defence may technically be an exam, and naturally, many PhD candidates are stressed, daunted, or overwhelmed by the process for weeks. However, you will do much better if you go into the exam with the mindset that you are equal with the academic panel and treat the examination as a discussion rather than an inquisition. Remember, your viva is your chance to be seen as a doctor, not a student.
Mindset Matters
After spending years on your thesis, you will know your subject inside and out; it is your area of expertise; don’t go into the viva with a defensive and confrontational mindset; remain confident in your knowledge creation and how it benefits your field of study. Imposter syndrome can come in hard here, so limit your negative self-talk and silence your inner critic.
Ask for a Mock Viva with Your Supervisor
Never be shy about asking your PhD supervisor for the support you need as you prepare for your viva. They will be best placed to answer all of your questions as they will know the procedure for your university and your field of research. Your PhD supervisor will likely have already been present in viva exams; they will know the score, and more importantly, after working with you for years, they will want you to pass your viva – never be shy about asking them to arrange a mock viva to help you prepare.
How long is a PhD?
If you look for an answer to the question, how long is a PhD thesis, you will notice that there is a lot of contradictory information on the internet because there is no one-size-fits-all answer for PhD students. How long does a PhD take ? Well, we’ve got all the info you need in our other blog
You might also like

The Best London Boroughs for Home Study
Students have much to consider when viewing and moving into their student accommodation. As well as the feel of the home, it is important to

Undergraduate degree vs postgraduate degree: key differences
Going to university and choosing the right educational path are likely going to be some of the most important decisions in your life. This means

Do You Get Paid for a PhD?
Do You Get Paid for a PhD? For many students who don’t have the luxury of never worrying about money, one of the main considerations
Enquire with us
We are here to help and to make your journey to UWS London as smooth as possible. Please use the relevant button below to enquiry about a course you would like to apply, or to clarify any questions you may have about us and our admission’s process. After you submit your enquiry, one of our advisers will get back to you as soon as possible.

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Undergraduate and Postgraduate Taught
- Postgraduate examinations
- Writing, submitting and examination
- PhD, EdD, MSc, MLitt
- Cambridge students
- New students overview
- Pre-arrival courses
- Student registration overview
- Information for New Students overview
- Step-by-step guide for new students
- Information for Continuing Students overview
- Step-by-step guide for continuing students
- Frequently Asked Questions overview
- Who needs to register
- When to register
- Received registration in error/not received registration email
- Problems creating an account
- Problems logging in
- Problems with screen display
- Personal details changed/incorrectly displayed
- Course details changed/incorrectly displayed
- Accessing email and other services
- Miscellaneous questions
- Contact Form
- First few weeks
- Manage your student information overview
- Student record overview
- Camsis overview
- Extended Self-Service (ESS)
- Logging into CamSIS
- What CamSIS can do for you
- Personal information overview
- Changing your name
- Changing Colleges
- Residing outside the University's precincts
- Applying for person(s) to join you in Cambridge
- Postgraduate students overview
- Code of Practice for Master's students
- Code of Practice for Research Students
- Postgraduate student information
- Requirements for research degrees
- Terms of study
- Your progress
- Rules and legal compliance overview
- Freedom of speech
- Public gatherings
- Disclosure and barring service overview
- Cambridge life overview
- Student unions
- Extra-curricular activities overview
- Registering societies
- Military, air, and sea training
- Food and accommodation
- Transport overview
- Bicycles and boats
- Your course overview
- Undergraduate study
- Postgraduate study overview
- Changes to your student status (postgraduates only) overview
- Applying for a change in your student status (postgraduates only)
- Changing your mode of study
- Withdrawing from the University
- Allowance/exemption of research terms
- Withdrawal from Study
- Reinstatement
- Changing your course registration
- Changing your department/faculty
- Changing your supervisor
- Exemption from the University composition fee
- Confirmation of Study: Academic Verification Letters
- Extending your submission date
- Medical intermission (postgraduates)
- Non-medical intermission (postgraduates)
- Returning from medical intermission
- Working away
- Working while you study
- Postgraduate by Research Exam Information
- Research passports
- Engagement and feedback
- Student elections
- Graduation and what next? overview
- Degree Ceremonies overview
- The ceremony
- Academical dress
- Photography
- Degree ceremony dates
- Eligibility
- The Cambridge MA
- Degree certificates and transcripts overview
- Academic Transcripts
- Degree Certificates
- After Graduation
- Verification of Cambridge degrees
- After your examination
- Exams overview
- Undergraduate and Postgraduate Taught overview
- All students timetable
- Undergraduate exam information overview
- Postgraduate examinations overview
- Examination access arrangements overview
- Research programmes
- Taught programmes
- Writing, submitting and examination overview
- PhD, EdD, MSc, MLitt overview
- Research Best Practice
- Preparing to submit your thesis
- Submitting your thesis
- Word limits
- The oral examination (viva)
- After the viva (oral examination)
- After the examination overview
- Degree approval and conferment overview
- Final thesis submission
- Examination allowances for certain Postgraduate degrees (except PhD, MSc, MLitt and MPhil by thesis degrees)
- Requesting a review of the results of an examination (postgraduate qualifications)
- Higher degrees overview
- Higher doctorates
- Bachelor of divinity
- PhD under Special Regulations
- Faith-provision in University exams
- Publication of Results
- Exam Support
- Postgraduate by Research
- EAMC overview
- Annual Reports of the EAMC
- Dates of meetings
- Frequently asked questions
- Guidance notes and application forms
- Resources overview
- Build your skills overview
- Skills Homepage
- What skills can I develop? overview
- Digital, technology use and technical skills
- Entrepreneurship & Enterprise
- Interpersonal, communication and social skills
- Leadership & Management
- Learning, thinking, and reasoning skills
- Planning and organisation skills
- Presentation, negotiation and influencing skills
- Self-management skills
- Writing, analytical and reporting skills
- Development activities overview
- Academic study
- Community and Volunteering
- Entrepreneurship
- Professional Development
- Societies & Committees
- Theatre & Arts
- Research students
- Fees and financial assistance overview
- Financial assistance overview
- General eligibility principles and guidance
- Cambridge Bursary Scheme funding overview
- What you could get
- Scottish students
- EU students
- Clinical medics and vets
- Independent students
- Extra scholarships and awards
- Crane Fund overview
- Postgraduate Wellbeing Advice
- Undergraduate Financial Assistance Fund
- Postgraduate Financial Assistance Fund
- Realise Financial Assistance Fund
- Loan Fund I
- External Support
- Support from your Funding Sponsor
- Guidance for Academic Supervisors and College Tutors
- Fees overview
- Funding overview
- Mosley, Worts, and Frere Travel Funds
- Support for UKRI Studentship Holders
- Student loans overview
- US loans overview
- Application procedure
- Entrance and Exit Counselling
- Cost of attendance
- What type of loan and how much you can borrow
- Interest rates for federal student loans
- Proof of funding for visa purposes
- Disbursement
- Satisfactory academic progress policy
- In-School Deferment Forms
- Leave of absence
- Withdrawing and return to Title IV policy
- Rights and Responsibilities as a Borrower
- Managing Repayment
- Consumer information
- Submitting a thesis — information for PhD students
- Private loans
- Veteran affairs benefits
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Student support
The Oral Examination (viva) - Doctoral degrees, MSc, MLitt, MPhil by Thesis
What is a viva.
The viva (short for viva voce) is an oral examination which gives the opportunity for:
- you to defend your thesis and clarify any matters raised by your examiners
- the examiners to probe your knowledge in the field
- the examiners to assure themselves that the work presented is your own and to clarify matters of any collaboration
- the examiners to come to a definite conclusion about the outcome of the examination
Your examiners will determine if you meet the requirements for award of the research degree for which you are a candidate.
Preparation
Talk to your supervisor and/or Academic Adviser for guidance on how to prepare for your viva.
The Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (QAA) has produced a series of videos to help PGR students prepare for their viva. Note that the procedures for examination at the University of Cambridge may be different to those referred to by other Higher Education Institutions featured in the videos.
You will have been told the identity of your examiners. This will normally be one examiner internal to the University of Cambridge and one external examiner, but you may have two external examiners. The Degree Committee may also appoint an Independent Chair to be present during your viva and/or additional examiner(s). Your examiners will be in touch to make arrangements for your viva . If you have not been advised of the date for your viva within six weeks of submitting your thesis, you should contact your Degree Committee.
Location of the viva
The viva will normally take place in-person in Cambridge, but you may choose to be examined remotely by video conference. You should inform your Degree Committee of your preference when you notify them of your intention to submit/apply for appointment of examiners. Please also make your supervisor aware of your preference as it may affect the choice of available examiners.
Arrangements where you and one examiner are co-located in Cambridge, with the second examiner participating by video conference, where both examiners are co-located and you participate by video conference, or where you and the examiners are all in separate locations, are permissible provided all parties agree.
In-person oral examination: In-person examinations may be delayed depending on the availability of the examiners as travel time will need to be factored in. Students who are overseas and returning to Cambridge for their viva should contact the International Student Office for visa advice if their student visa has expired or will be expiring soon.
Video conference oral examination: A guide to conducting vivas by video conference can be found here .
The choice of in-person or video conference viva does not constitute procedural irregularity grounds for complaint should you fail the examination.
Adjustments to the oral examination on the grounds of disability
If you wish to notify examiners of a disability or request adjustments on account of a disability for your viva (either your first year assessment or final examination), you can do this via your Degree Committee by completing and submitting the voluntary disclosure form . It is recommended you do this at least four weeks before your expected date of examination to allow time for appropriate recommendations and adjustments to be made.
Once you have submitted the form, your Degree Committee will contact the University’s Accessibility and Disability Resource Centre (ADRC) who will advise the Degree Committee on the appropriate course of action. You may be contacted by the ADRC if additional information is required or to provide you with an offer of additional support.
The information provided on the voluntary disclosure form will be kept confidential and will not be used for any other purpose.
If you already have a Student Support Document (SSD) that includes recommendations for adjustments to the viva , and you have given permission for the SSD to be shared with the Degree Committee, you do not have to complete the voluntary disclosure form but may do so if you wish.
There is no specific dress code. You can wear whatever you feel comfortable in.
What can I take in to my viva?
You may take the following into your viva:
- A copy of your thesis (the same as that you submitted)
- plain paper or blank notebook and a pen/pencil for taking notes or sketching ideas
- a presentation in the form specified by your Examiners – your Examiners will advise you in advance if a presentation is required
- any other provision that is agreed in advance with the Degree Committee as a reasonable adjustment for disability.
What happens at the viva?
- It is carried out between yourself and the two examiners and is conducted in English
- It may include an Independent Chairperson if the Degree Committee requires this
- There is no set duration, but a viva will normally last between 90 minutes and three hours
- You may be required to do a presentation - please check with your Department whether this is the case. If you are required to give a presentation, you should be informed at least two weeks in advance of the viva
- The viva cannot be recorded
- Your supervisor cannot attend the viva
Your Department should advise on any department-specific conventions or procedures.
Possible outcomes of the viva
The possible outcomes are:
- Conditional approval - pass without correction (but for doctoral degrees subject to submission of hardbound and electronic copies of the thesis ); or pass, subject to minor or major corrections
- Revision and resubmission of the work for a fresh examination
- [Doctoral examination only] Revision and resubmission of the work for a fresh examination or acceptance of the MSc/MLitt without further examination (but possibly subject to corrections)
- [Doctoral examination only] Not to be allowed to revise the thesis, but offered the MSc/MLitt without further revision or examination (but possibly subject to corrections)
- [Doctoral examination only] Revision and resubmission of the thesis for examination for the MSc/MLitt degree
- Outright failure
Notification of the result of the viva
Your examiners are asked not to give any direct indication of the likely outcome of the examination as the official result of examination can be confirmed only by the Postgraduate Committee or by Student Registry acting on its behalf (or the Degree Committee for the MPhil by Thesis). The Degree Committee will forward their decision to the Student Registry who will notify you of the outcome and email your reports to you, copying in your Supervisor.
Process following the viva
Information about the process following your viva can be found here.
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...

The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
How to Defend a Thesis: An Introduction to the PhD Viva

The prospect of defending your PhD work can be more than a little daunting. It represents the climax of many years of hard work, you’ll have to defend a thesis in front of experts in your field and the whole PhD viva process can seem cloaked in mystery.
Maybe you’ve seen a labmate go for their PhD viva to then emerge several hours later, relieved but perhaps slightly dazed. Often it’ll be the case that they’ll have forgotten the specifics by the time they’ve left the room. On top of that, horror stories of bad PhD viva experiences pass through many research groups which are enough to make even the most confident and positive PhD students shake in their boots.
Having had my own PhD viva earlier this year, in addition to discussing experiences with many other PhD graduates, I now want to help you through the process.
Before we begin, I want to offer some reassurance. For most people the PhD viva is not at all the horrible experience we occasionally hear about. Even so, it’s still useful to know what to expect. I’ve therefore put together a series to help others understand the PhD viva process and how to defend a thesis.
Defend a Thesis: Overview of the PhD Viva Series
This first post will be an introduction to the PhD viva process and how to defend a thesis. Upcoming posts will cover:
- Viva Preparation: Common PhD Viva Questions
- What is a PhD Viva Like? Sharing Graduates’ Experiences
- How to Choose Your Examiners
If there is anything specific you’d like covered, please let me know! I’ll be sure to include it. If you’d like to subscribe to get notified of upcoming posts as they’re released you can do so here:
How is a PhD Assessed?
Typically the main output expected at the end of your PhD project is a thesis. You’ve put years of work into your PhD and the thesis details your contributions to your chosen research field. But how is the thesis “marked”? Who will decide if what you’ve written is actually any good?
This is where the PhD viva comes in!
The PhD viva involves you discussing and defending your work with experts in your field. The experts act as examiners to determine whether or not the university should award you a PhD based on your thesis and viva performance. The thesis is the written report submitted for a PhD, and the viva is a means of quality control to ensure that only suitable candidates are awarded a PhD by the university.
Although part of the purpose of a PhD viva is to ensure that the work is of a high quality, just as importantly it’s to check that you were the one who carried it out and that you understand what you were doing!
The PhD viva is therefore essentially an exam during which you’ll have to defend a thesis.
Here is the official “mark scheme” for a PhD at Imperial:

I recommend looking at the presentation which this screenshot came from: sadly I only came across it after my own PhD viva whilst putting together this post!
Steps to Completing a PhD
- Submit your thesis for the examiners to read ahead of the viva.
- Have the viva , where you’ll defend a thesis and discuss your research. The examiners will decide from a list of possible outcomes as detailed later in this post.
- Make amendments to the thesis as necessary.
- Optional celebration.
- Have the thesis amendments approved by the examiners and/or your supervisor and confirmation sent to the university.
- Upload the final copy of your thesis to the university.
- Eagerly await notification that you’ve been awarded a PhD by the university!
- Celebrate, Dr!
All celebrations except for the one after making changes to your thesis are mandatory!
PhD Viva vs PhD Defence
The words viva and defence are sometimes used interchangeably, but often are used to reference the different ways that the a PhD is concluded around the world.
A PhD viva (technically a viva voce ) is a formal examination of a PhD. It’s typical in the UK (amongst other countries) and it is a closed-event between yourself and some examiners.
Across much of Europe it is common instead to have a PhD defence . This still involves expert questioning but can be more of a ceremony and may even be open to the public. You can read about Siddartha’s experience , who completed his PhD in the Netherlands.
I went through a PhD viva and that’ll be the focus of this series. Nevertheless, there is overlap and you may still have difficult questions in a PhD defence, so the content in this series should still be useful no matter where you’re based.
In both a PhD viva and a PhD defence you’ll be expected to defend a thesis which represents the culmination of your work during the PhD.
Who is Present During the PhD Viva?
In the UK it is typical for the PhD viva to include:
- One or more experts from your university ( internal examiner ).
- One or more experts in your field from another institution to your own ( external examiner ).
- And sometimes your supervisor, though in my experience this is quite rare unless you actively ask them to be there.
The main role of the internal examiner is to act as a moderator and ensure that the university’s protocols are upheld. They’ll usually still have some questions for you, but on top of that they’ll make sure that the external examiner(s) are reasonable. They will also take charge of documenting the viva.
Often the external examiner will be more specialised to your field than the internal examiner, so expect them to potentially ask more tricky and technical questions.
As mentioned in the previous section, for PhD defences in other countries the event may be less of an exam (viva) and more of a celebration of your work. These can be a lot more open, with access granted to your friends, family or anyone else who is interested in the topic. I quite like this idea, especially when the research has been publicly funded!
How the PhD Viva is Structured
The structure of the viva will vary but a typical format is shown below. The times in brackets are how long the sections for my own viva were, thankfully not all vivas are over five hours long!
- Introductions (2 minutes) – greeting the examiners and they’ll usually quickly give an overview for how they want the viva to go.
- Presentation (10 minutes) – Not all examiners will want you to give a presentation, it’s best to ask them in advance. I believe many examiners like asking for presentations: both to ease into the exam and also to see how you do at distilling years of work into a short presentation.
- Discussion (Over 5 hours, yes, really!) – the long and potentially scary bit.
- A short break (~10 minutes) . You’ll leave the room (or video call!) and the examiners will come to a decision for your PhD outcome.
- Decision and final comments (10 minutes) – where the examiners will tell you what the outcome is of the viva – we’ll cover this in more depth in the next section.
The discussion in the middle of course is the main guts of the PhD viva, and the potentially scary bit. This is where you’ll get questioned about your work and thesis. What you get asked could vary considerably depending on your thesis and examiners.
I’ll save an in-depth discussion of my own viva for another post. In short, I received very few questions relating to the work or any fundamental underlying science. There were practically no questions to quiz my knowledge.
Rather than checking my understanding of the work, the viva was much more of a discussion of how best to present the work in the thesis. We spent roughly an hour going page by page through each chapter. This included suggestions for improvements to figures, changes in terminology and the like.
Possible PhD Viva Outcomes
At the end of the viva the examiners will give you feedback. This will include feedback on your performance in the viva. But as long as they’re satisfied that you carried out the work and that you knew what you’re doing, the bulk of the feedback will in fact revolve around your PhD thesis.
Technically there are lots of potential outcomes, as detailed here:

In reality here are the four main possible outcomes from the viva:
- Pass with no amendments . The examiners didn’t want to make a single alteration to your thesis. Well done you just have to submit the finalised thesis to the university and you’ve finished your PhD! I know a few people who’ve had no revisions but it’s rare.
- Pass with minor amendments Minor amendments include things such as correcting typos, rewording sentences and small alterations to data analysis and presentation. This is by far the most common outcome.
- Referral for resubmission ( major amendments). More substantial changes to the thesis are required or further experimental work is required to fulfil the requirements of a PhD. The examiners will decide whether or not this means having another viva too.
- Fail . Unless there are glaring issues or you didn’t actually do any of the research in your thesis yourself, you should be relieved to hear that practically no one ever fails. If you have failed, it usually points to systematic issues revolving around your supervisor: you shouldn’t have been allowed to get to this point. Usually the examiners would recommend that you be awarded a lower degree, such as a masters in research (MRes).
Slightly up the page is a screenshot from my own examiners’ report. You’ll see that I, like most people, passed with minor amendments.
2022 Update: Starting to prepare for your PhD viva? A set of viva preparation worksheets are now available in the resource library. Click the image below for free access!

Making Changes to Your PhD Thesis
Shortly after the viva you should receive the examiner’s report which includes a list of revisions for you to make.
If you’ve got through the viva with a pass, you can breathe a sigh of relief because the hard work is over! In a separate post I’ll be covering how the process to make my own minor amendments went.
No matter the outcome, it is possible that you’d like to make your own changes to the thesis since it’ll have been many weeks (or months) since submitting the draft copy for your viva. On reflection there may be things you’re not happy with. You are welcome to make changes to the document yourself.
If you’re interested in reading more about how to make the corrections to your thesis, read the article dedicated to it here: Minor Corrections: How To Make Them and Succeed With Your PhD Thesis.
After you’ve made changes, the final stage in getting awarded the PhD is submitting your finalised version of the thesis to the university. Shortly afterwards you’ll get the long-awaited notification that you’ve got your PhD!

Should You Strive For No Amendments?
In my opinion it’s not worth the effort of trying to get no amendments.
I’d personally rather spend slightly less time up front, knowing that more than likely I would have to made some amendments. You can never put in enough work to ensure there will be nothing your examiners want changed!
You could spent hundreds of extra hours endlessly going through your thesis meticulously before submission but your examiners can always find something they want you to change. In comparison, my own minor amendments only took two days of work.
Sometimes you’ll see someone mention on their CV that they passed with no revisions but it doesn’t really have any bearing on your PhD. Unlike most other qualifications, there aren’t really grades for PhDs: you either have one or you don’t.
During an early PhD assessment my assessor made a poignant joke about medical degrees: “What do you call the person who graduates bottom of their class in medical school? A doctor!” And it’s essentially the same with PhDs!
If you’d like personalised help with preparing for your PhD viva I am now starting to offer a small number of one-to-one sessions. Please contact me to find out more or click here to book a call.
I hope this introduction to PhD vivas and how to defend a thesis has been useful. Let me know if you have any specific questions or concerns you’d like to see addressed in the following posts.
As always you can stay up to date with content by subscribing here:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

The Five Most Powerful Lessons I Learned During My PhD
8th August 2024 8th August 2024

Minor Corrections: How To Make Them and Succeed With Your PhD Thesis
2nd June 2024 2nd June 2024

How to Master Data Management in Research
25th April 2024 4th August 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
Finishing Your Doctorate - a guide for students approaching the end of their studies
Learn about the different stages you will go through to complete your doctorate. find out about the timescales and the issues you will need to consider..
- Introduction
As you approach the end of your doctoral studies there are many things to consider including finishing off your research, writing and submitting your thesis, preparing for your viva voce examination and completing any corrections before your doctorate is awarded.
This step-by-step guide will help you understand the different stages you will need to go through. If you are completing an MPhil, please contact your supervisor or the Doctoral Programmes Administrator in the Doctoral College for specific advice for finishing your award as the process will be different. They are on hand to provide help and further detailed information about each step.
- Timeline for completion of your doctorate
The timeline from when you formally tell us that you intend to submit your thesis or portfolio to when your award is approved, can vary from six to 18 months, depending on the outcome of your viva voce examination. You can see the timeline in full on this diagram .
You should aim to submit in advance of your expected registration end date, in order to allow time for the examination process to be completed before your registration period runs out.
Funding and visa issues
If you are in receipt of funding for a fixed period, you should bear this in mind when considering when to submit. Whilst technically it is still possible to submit your thesis on the last day of your formal registration period, or after your funding ends, you are strongly advised not to do this: you will need extensions to cover the examination period and you will still be required to pay fees until the date you submit your thesis. If you are a student visa holder, you may also need to consider that your visa could expire before your viva examination can be held.
For those students who find themselves in financial difficulty, The University of Bath Financial Support Fund is available.
- Step 1: Decide how to submit your thesis
A doctoral thesis submitted for the award of MPhil, PhD, DBA, DPRP or DHealth may be submitted in one of two differing formats:
a traditional thesis consisting of chapters
an alternative format thesis which integrates academic papers into the text.
You will need to decide, if you haven’t already, which format you plan to submit. Ideally, you will have discussed with your supervisory team at an appropriately early stage in your studies how you wish to present your work.
The programme regulations for each Degree will describe how the research work may be presented: in a thesis, a portfolio (EngD, and DClinPsy only) or via a body of published works (MD MS only). Only students registered on an EdD prior to 2014 are able to present their work in either a thesis or portfolio format.
Further details of the University’s specifications for Higher Degree Theses and Portfolios can be found in Appendix 6 of QA7 . You may also want to read the Alternative Format Thesis FAQs .
You can access the Library’s collection of successful thesis submissions online via the Research Portal. You may wish to look at a few from your department as examples, taking note of content and organisation.
- Step 2: Transfer to Submission Pending Status
Once you have completed the minimum period of study required for your particular degree as stipulated in Regulation 16 , and you have finished the specified amount of work, you may be able to apply for transfer to 'Submission Pending' status, subject to approval by Board of Studies (Doctoral).
In determining whether the status should be adjusted, the Board of Studies (Doctoral) will consider a number of factors, including but not limited to:
- Whether any active research is complete
- Whether data collection is complete (incl. use of laboratories)
- Whether the student’s workplan supports their case that they are in the final stages of preparing for submission of their thesis/portfolio
The fee associated with submission pending status represents a significant drop from the regular fee rate. Students will need to submit a workplan to accompany their request, including a detailed timeline to submission, which will need to be supported by both supervisor and Director of Studies (DoS) to provide assurance that the application is appropriate and timescale realistic.
Students granted ‘submission-pending’ status will continue to receive supervision and submit progress reports, retain access to Library resources, remain registered, and their university email remains active.
Approval process
You should consider making an application for transfer to submission pending status at the earliest point, as changes of status may take time to be approved. In order to apply to transfer to submission pending status and for your fee status to be changed you must:
complete the PGR10 form
ask your lead supervisor and your Director of Studies to sign the form to support the change in your status
submit the form to your Doctoral Programmes Administrator in the Doctoral College for consideration by Board of Studies (Doctoral) for formal approval.
Impact of change of status
You should note that if you are in receipt of funding, such as a full studentship or a fee waiver, this funding will end at the point at which you transfer to submission pending status. You should also be aware that a change in your status may impact on your liability to pay Council Tax .
- Step 3: Notice of intention to submit
At least two months before you intend to submit your thesis or portfolio, and before your registration period ends, you should complete the HD1 form, which can be accessed through your SAMIS in-tray.
By completing this form you are providing formal notice of your intention to submit, which then prompts your supervisors and Director of Studies to start the appointment of examiners process by nominating an appropriate internal and an external examiner. It will also alert the graduation team that you are likely to be completing in the near future, so your name can be added to the invitation list for the next available graduation ceremony.
Most students will receive an email notification, reminding them to complete the HD1 form, six months prior to their registration end date. Students on the DClinPsy programme will be told by their Programme team when and how to complete a version of HD1. If you wish to submit your HD1 form earlier than six months before your end date, please contact your Doctoral Programme Administrator in the Doctoral College.
- Step 4: Restriction of access to your thesis
You should talk to your supervisor and/or funder about whether there is a need to restrict access to your thesis. Typical reasons for restricting access can include:
contractual agreements with companies or funders to not make findings public for a fixed period
deferral of open release of the e-thesis until after a paper’s publication
delay in making results public as they are being used to prepare patent applications.
If, for reasons of confidentiality, you want to restrict access to your thesis, it is possible to request a 12 month restriction. This applies to the electronic copy of the final thesis at the point when it is uploaded to the Library repository, Pure .
If you wish to secure a more comprehensive restriction of both the electronic and printed copies, or would like a restriction of a longer duration, you will need to make a formal request for approval from the Board of Studies (Doctoral) using the PGR7 form . On this form you will need to indicate why you need access to be restricted, and for how long.
The University has an open access policy on research outputs, and the expectation is that all theses/ portfolios will be available within the Library repository, therefore you will need to provide some details about why your work should not be shared. You will then need to submit the form to your Doctoral Programmes Administrator in the Doctoral College.
- Step 5: Appointment and role of examiners
Your supervisors and your departmental Director of Studies are responsible for nominating a Board of Examiners for the viva voce examination of your thesis or portfolio. This team will consist of an internal examiner who is usually, but not always, an academic from your department, and an external examiner from another university or organisation.
The team of examiners may also consist of an additional examiner, as a condition of funding, or an independent chairperson who can be appointed when the Director of Studies considers that the presence of an additional academic would be of assistance.
Criteria for appointment and role of examiners
For information on the criteria for the appointment of examiners, see section 27 of Regulation 16. You can also find further information in QA7 (section 13) .
Nominations for doctoral examiners will be submitted using the PGR13 form: Appointment of Examiners for Doctoral Research Degrees. This form includes details of who the proposed examiners are and what previous examination experience they have, and it is signed by the lead supervisor and the Director of Studies.
The appointment of examiners needs to be approved by Board of Studies (Doctoral) before a viva voce examination can take place, so this form should be submitted to your Doctoral Programmes Administrator in the Doctoral College in good time prior to the submission of your thesis or portfolio. When you submit your Notice of Intention to Submit form you might want to also check with your lead supervisor that they have begun the process of identifying potential examiners.
- Step 6: Final preparation for submission
Word counts
The guidelines on word limits for final theses/portfolios vary by faculty or department. In order to be sure that you stay within any prescribed limits please consult the Doctoral College guidance document on word counts .
Plagiarism is a serious academic offence. You will have by now completed the academic integrity training and are expected to be aware of the rules around plagiarism.
All theses are checked for plagiarism using appropriate software. Whether it is detected by the supervisor when proof-reading a draft copy, or by the examiners in a thesis actually submitted for examination, the procedure for inquiring into Allegations of Misconduct in Research outlines the investigation process that will be followed if a suspected plagiarism offence is detected. The viva examination cannot go ahead until the investigation is completed, and where plagiarism is found to have taken place this may result in a disciplinary hearing where an appropriate penalty will be decided.
For a refresher on academic integrity whilst writing your thesis, see the Library guide on citing references and how to avoid plagiarism .
Seeking advice from your supervisor on draft(s)
The lead supervisor is responsible for advising you on the format of the thesis to be adopted and for carrying out a critical reading of the draft. When you are ready, your lead supervisor should read a complete draft of your thesis or portfolio and advise you of any changes or additions that should be made prior to submission. You may need to produce more than one draft before it is finalised.
You should give your supervisors not less than two weeks notice that you will be providing them with a copy of the draft thesis. They will need at least six weeks to read the draft and make their comments. The supervisor’s opinion is only advisory, and you have the right to decide whether to make any of the edits they recommend, and to decide when you are ready to submit your work for examination (subject to the requirements of the Regulations for the degree for which you are registered). Addressing the comments made by your supervisor does not guarantee that your thesis/portfolio will subsequently be passed by the examiners.
Specification for submission
There are detailed specifications for the presentation of a thesis or portfolio for examination and these can be found in Appendix 6 of QA7 . Please take note of these before submitting your work.
- Step 7: Submission of your thesis/portfolio
What do I submit?
You are required to submit your thesis/portfolio in electronic format to the Doctoral College Submission page in Moodle where it will be checked for plagiarism. If an investigation into a potential plagiarism offence has to take place, the examination process will be stopped until this is concluded.
You will also need to complete the HD2 form: Record of submission of a thesis or portfolio , and email it to your Doctoral Programmes Administrator. Upon receipt of the HD2 form, and your submission onto Moodle, the Doctoral College will email you, your supervisor and the Director of Studies to formally confirm receipt of your submission.
When do I submit?
You are strongly advised to submit before the last day of your formal registration period so that the examination process can be completed before your registration ends, and if you are a Student visa holder, before your visa runs out.
If you do not submit before your registration end date, you will have to seek permission from Board of Studies to re-register as a student.
Your registration end date can be found on your SAMIS page or you can check this with your Doctoral College Programme Administrator.
If your visa runs out before the examination process is complete, you may be required to obtain a new visa (such as a short-term study visa) or return to your home country. If this happens, it may be possible to return to the UK at a later date to attend the viva voce examination in person, or alternatively a video conference can be arranged to facilitate the examination. Find out more about visas .
What happens to my tuition fees after I submit?
Tuition fees will no longer be incurred but may still be charged from the point of submission. Depending on the outcome of your viva examination, and the level of access you may need to supervision and resources in order to complete your corrections/revisions, you may be charged a writing up fee for the corrections period.
Do I have to start paying Council Tax after I submit?
Full-time students are exempt from paying Council Tax until their expected, or actual, end date of registration. If you submit your thesis/portfolio on, or close to, your end date, you will need to contact your Doctoral Programmes Administrator to request an examination extension, which will extend your end of registration date. The actual end date of registration will then be the day of the Board of Studies (Doctoral) meeting where your final award is approved.
- Step 8: Preparing for the viva voce examination
Purpose of the viva voce
The main purpose of the viva voce is for you to defend the content of your thesis/portfolio and demonstrate your understanding of the broader aspects of the field of research and the subject of the thesis. It is an essential part of the examination process, and you must pass the viva as well as present a satisfactory thesis/portfolio in order to gain the award.
The examiners will test your ability to defend the work presented for examination. They need to ensure that your work is robust and that you fully understand the implications of your findings. They want to check the foundations of your research to ensure that the basic assumptions underpinning the work are sound, and that nothing major has been overlooked. Being able to discuss the work with you in person is of particular help if there is disagreement between the examiners about the outcome, or when the decision is marginal.
Think about the viva voce as more than an examination. It is an opportunity for you to discuss and develop ideas with experts in the field, to receive guidance on future publication plans and to receive constructive feedback on your work.
When should the examination take place?
The viva voce examination should normally take place within three months of the submission of the thesis/portfolio. Efforts will be made, where possible, to arrange the viva examination on a date convenient to all parties involved, and to minimise the amount of time a student has to wait for a viva examination.
You will be advised of the date of the examination as soon as possible after the thesis has been submitted. As a minimum, you will be given at least one week’s notice of the date of the exam. Those Student visa students on an Academic Technology Approval Scheme (ATAS) course who are coming back to the UK for their viva examination may require more notice, so that they can apply and receive their new ATAS certificate. The Doctoral Programmes Administrator for your department or programme/supervisor will work with the examiners to check availability and agree a date and time.
Where should the examination take place?
The venue for the viva voce examination will vary by discipline. In some cases it will take place in the office of the internal examiner. In other cases a room may be booked. In all cases, the venue should be a quiet, comfortable environment free from interruptions.
Video Conferencing
In certain circumstances, the use of video conferencing facilities may be permitted for your viva examination, although some programmes may have their own expectations with regards to the use of these facilities. This might be an option if you or your examiner are based outside the UK and for reasons of cost, time or restricted mobility are unable to travel to the University of Bath in order to participate in the viva exam at an appropriate time. Should you require further advice on this, or should you want to take advantage of this facility, you should contact your Doctoral Programmes Administrator as soon as you are notified of your viva date.
For further information on the use of video conferencing in viva examinations see QA7 Appendix 3 .

Who will attend?
In line with UK practice, the viva voce will be a closed examination rather than a public event. You and the examiners will attend, along with an independent Chairperson if they have been appointed. You may ask that your supervisor is permitted to attend the viva voce examination to provide moral support or reassurance, but they must not play an active role in the examination. If you want your supervisor to be in attendance you will need to notify the Doctoral College on your HD2 form at the point of submission.
Some departments may also require you to undertake a public lecture or presentation before your viva voce. Please contact your supervisor for further information about whether this applies to you.
Can I ask for adjustments to help me participate in the viva examination?
The University is responsible for ensuring that appropriate facilities are made available should you need them. Please raise details of any reasonable adjustments that you may require to enable you to participate fully in the viva examination at your earliest opportunity. These adjustments can be related to a long-standing disability or a short-term medical issue, for example a back problem. Student Support can provide you with advice about adjustments and will generate a Disability Action Plan to record the adjustments where appropriate.
- Tips and advice for your viva voce
The following tips and advice will help you to prepare:
- expect to be challenged!
- be active - anticipate the questions that are likely to be asked in the viva examination
- use your research skills to identify commonly asked questions, and, after they’ve proof-read the thesis, ask your supervisors to suggest some potential questions too
- be prepared to discuss both the strengths and weaknesses of your work
- if you’ve presented your work at a conference or departmental seminar consider the questions that other researchers have raised about your work
- re-familiarise yourself with your examiners’ work in the field, as this can help you anticipate some of their likely questions
- be ready to summarise their most significant findings or area of greatest strength in your thesis
- be objective, and identify any areas of weaknesses within the body of work and be ready to discuss these, too
- ask your supervisory team, fellow researchers, or doctoral students in your office to hold a practice viva voce examination, in order to gain experience in answering questions about your work.
- re-read the thesis, particularly the first chapters that you wrote, in order to familiarise yourself with the contents once more
- attend the DoctoralSkills workshop ' Preparing for your doctoral viva '. You'll discuss what is expected of you in the examination and there will be a Q&A session with experienced examiners. Alternatively, you can complete the online learning module . Find out more by emailing DoctoralSkills .
- Further information about the viva voce
There are several useful resources in the library catalogue, the following list may be accessed online: Murray, R., (2009) How to Survive Your Viva: Defending a Thesis in an Oral Examination. Mansfield, N., (2007) Final hurdle: a guide to a successful viva. Potter, S., (2006) Doing postgraduate research.
The following Vitae guides may also prove helpful:
- Finishing your doctorate
- Completing your doctorate
- Writing and submitting your doctoral thesis
- Defending your thesis: the PhD viva
- Thesis defence checklist
- Thesis outcomes and corrections
- I had my doctoral viva and I enjoyed it
ATAS requirements
If you are a visa-holding student on an Academic Technology Approval Scheme (ATAS) course coming back to the UK for your viva voce examination on a short-term study visa, you will need to ensure that a new ATAS certificate has been applied for, and received, in good time before making your new visa application. This includes nationals who are able to ask for permission to enter the UK on arrival at the border, rather than apply for a visa in advance. If you return to the UK for your viva voce without having a new ATAS certificate in place then it may not be possible to proceed with the examination.
- Step 9: Examiners' role in the viva voce
What do the examiners do?
Once appointed, internal and external examiners will read your thesis and each complete a preliminary report which records their initial independent thoughts on the work presented for examination. The examiners will refer back to these reports when they ask you questions in the viva voce examination. After the viva examination is concluded, the examiners will ask you to leave the room whilst they make their decision. You will be called back in, with your supervisor, to hear the examiners’ recommended outcome of the examination.
Examiners are asked to assess doctoral candidates' research and confirm their research as:
- making an original and significant contribution to knowledge
- giving evidence of originality of mind and critical judgement in a particular subject
- containing material worthy of peer-reviewed publication
- being satisfactory in its literary and/or technical presentation and structure with a full bibliography and references
- demonstrating an understanding of the context of the research: this must include, as appropriate for the subject of the thesis, the scientific, engineering, commercial and social contexts
And passing a viva voce examination on the broader aspects of the field of research in addition to the subject of the thesis
Examiners' Report
On the day of the viva the examiners will complete an Examiners’ Report, which summarises how the examination went, their recommended outcome, and any minor corrections or revisions that are required. It is not always possible for these to be outlined in detail on the day of the examination, so the full list of corrections/revisions may be supplied by the examiners up to two weeks later.
The Examiners Report, and corrections list, goes to Board of Studies (Doctoral) for consideration and approval, and until this point their recommendations are only provisional. The official outcome of the examination will be confirmed to you by email from the Doctoral College/Secretary of the Board of Studies (Doctoral).
More information about the role and responsibilities of the Board of Examiners and how the examination will be conducted can be found in the Guidelines for Research Examiners .
Contact with examiners
You should have no contact with your examiners prior to the viva voce examination, other than with the internal examiner to arrange the date and time of your examination. After the examination, advice and supervision in support of any required corrections or revisions will be provided by your supervisors, not the examiners. If needed, your supervisor or the Doctoral College can liaise with examiners on your behalf.
Please note that examiners usually need between four and six weeks to read a thesis and prepare for the examination. Later, when presented with a corrected thesis, the internal examiner may take up to four weeks to determine whether the corrections have been done satisfactorily. Examiners should not be pressured to set an early viva date, or examine to a foreshortened schedule.
- Step 10: Possible outcomes of the viva voce examination
The Board of Examiners will agree a recommended outcome following your viva examination. The list of potential outcomes of the examination are set out fully in both QA7 Section 17 and Regulation 16 but in summary, the examiners can recommend the following outcomes:
- Pass with minor corrections (3 months)
- Pass with major corrections (6 months)
- Fail viva but pass thesis/portfolio element (possibly with minor or major corrections), and require repeat of the viva voce for overall pass
- Fail with permission to resubmit thesis/portfolio (within 12 months). A second viva voce may be held at the discretion of the Board of Examiners.
- Fail, but recommendation to award Master of Philosophy (MPhil) with minor or major corrections
Communication of the recommendation
You will be informed verbally of the recommended outcome by your examiners following the viva examination. Your supervisor should be in attendance at this point. The outcome is unconfirmed, and subject to approval by the Board of Studies (Doctoral).
In cases where the examiners require substantial amounts of work to be completed, the examiners will send their report and the details of the corrections/revisions to the Board of Studies (Doctoral) for consideration.
The Board of Studies (Doctoral) is responsible for checking that the examiners’ recommended outcome is supported by what is written in their report, and that any significant minor corrections or thesis revisions specified by the examiners may reasonably be expected to be completed within the time allowed. Written notification of the outcome of the exam will then be sent to you, and you will have up to 3 months to complete minor corrections, up to 6 months to complete major corrections, or up to 12 months to complete a revised thesis. You can find out more about Corrections in Step 12.
It is important that you meet the deadline for submission of your corrections or revised thesis, failure to do so may result in a fail outcome. In exceptional circumstances you may request an extension to the deadline for submitting the corrected or revised thesis/portfolio. Please contact your Doctoral Programme Administrator for information. If you have a disability access plan that relates to your ability to meet the deadline, please contact your Doctoral Programme Administrator.
- Step 11: Approval by Board of Studies (Doctoral)
The Board of Studies (Doctoral) normally meets approximately every four-six weeks. You will receive formal notification of the outcome of your examination shortly after it is approved by Committee.
You are permitted to use your new academic title of ‘Doctor’ from the point at which you are awarded your degree by the Board of Studies (Doctoral). You will no longer hold student status from the date of the Board of Studies meeting where your award is approved.
You can appeal against an academic decision made by the Board of Studies (Doctoral) about your degree award. Regulation 17 sets out the grounds, process and timescales for which you can do this.
If you wish to raise an issue you are encouraged to:
speak with your supervisor or Director of Studies
seek independent advice from the Students’ Union Advice and Support Centre
-seek advice from the University Independent Advisors for Postgraduate Research Students
- seek support from Student Services
-speak to the Doctoral College .
- Step 12: Corrections to your Thesis or Portfolio
No Corrections
If no corrections are required, you will need to submit an electronic copy of your final thesis/ portfolio via Moodle and to Pure , before the outcome of your viva examination can be approved by the Board of Studies (Doctoral) - see Step 13, below.
Minor Corrections
Depending on the outcome of your examination, you may be required to complete some minor corrections. It is uncommon for a thesis or portfolio to be accepted without requiring some form of correction following the examination. You will normally receive up to 3 months to complete minor corrections.
When the minor corrections are completed, you will need to submit the corrected thesis to Moodle.
The internal examiner will then determine, on behalf of the Board of Examiners, whether the corrections have been completed satisfactorily, and whether you may now receive the award. It may help your examiner to do this if you complete the corrections in a different colour ink, and/or provide a document listing how each of the required changes has been addressed.
The internal examiner will update the examiners’ recommended outcome, and inform the Doctoral College. The Doctoral College will email you to inform you of the recommended final outcome that will go to Board of Studies (Doctoral) for approval. When you receive this email, you should start the process of uploading an electronic version to Moodle and to PURE (see Step 13 below).
Major Corrections
Depending on the outcome of your examination, you may be required to complete some major corrections. It is uncommon for a thesis or portfolio to be accepted without requiring some form of correction following the examination. You will normally receive up to 6 months to complete major corrections.
When the major corrections are completed, you will need to submit the corrected thesis to Moodle.
Revised thesis/portfolio
If the recommendation is to submit a revised thesis/portfolio, you will be given a reasonable time frame to complete the work, usually up to 12 months. You may also be required to attend a second viva. Before this deadline expires, the revised thesis or portfolio should be submitted to Moodle in the same way as you did for the first submission.
Extension to your deadline
- Step 13: Submitting Your Final Thesis or Portfolio
Submitting an electronic thesis/portfolio
Once your examination has been successfully completed, the final version of your thesis or portfolio should be submitted in electronic format via Moodle along with a completed HD3 form to your Doctoral Programmes Administrator in the Doctoral College, before the final outcome can be approved by the Board of Studies (Doctoral).
Uploading electronic thesis/portfolio to Pure
You will need to make the electronic copy of your thesis or portfolio publicly available by uploading it to the University’s research information system Pure . The Library provides guidance on how to deposit your thesis with the library , including details on how to request a 12 month restriction to the electronic version.
- Step 14: Graduation
You will be contacted about the graduation ceremonies by email.
If you receive an invitation but have yet to have your final award approved, these invitations will be provisional. Deadlines for actions that must be completed before you are eligible to attend a graduation ceremony can be found here .
Your Bath student email address will be deactivated a short time after the Board of Studies (Doctoral) approves your award, so it is really important that you provide an alternate contact address within your SAMIS record. You may wish to switch to BathMail which is an @bath.edu email address that is exclusive to University of Bath graduates. Graduating students will automatically be sent a BathMail username and password to their student email account before it is deactivated.
Graduation Ceremony
The University holds graduation ceremonies twice a year, in December/January and July. Find more information on the dates of future ceremonies .
See eligibility to attend graduation ceremonies and doctoral deadlines for graduation ceremonies for more information.
If you are interested in attending a specific ceremony, please contact your Doctoral Programmes Administrator who will be able to inform you of the deadline for that ceremony.
See doctoral deadlines for graduation ceremonies , for more information on the next ceremony.
Preparation for Graduation
You can find out further information about how to prepare for your graduation ceremony . You should not book your travel until you have received confirmation that your successful outcome has been approved by Board of Studies (Doctoral) and the Graduation team have confirmed you have a place at the ceremony.
Certificate
Your degree certificate will be generated once the Vice Chancellor formally confers the award, following Board of Studies approval. Conferment is timed so that certificates can be released for the graduation ceremonies. If you decide not to attend a ceremony, or your ceremony is a while away, you can find out more information about receiving your certificate here .
Your Graduation certificate will include the following information: - your full name
degree awarded (such as Doctor of Philosophy)
date awarded
signatures from the Vice Chancellor, Director of Academic Registry and the Pro-Vice-Chancellor (International & Doctoral)
Please note that the University of Bath Doctoral certificate does not specify the subject studied.
Alumnus status
All graduates, former staff and students who have studied at Bath for at least one semester are members of our alumni community . Alumni receive invitations to events, regular updates about the latest news from campus and opportunities to get involved with University life.
There are University of Bath alumni groups or networks in more than 40 different locations around the world. Activities vary in each city or country, from an online network to a Chapter - where an international volunteer committee organises a programme of events for local alumni. Getting involved can be a great way to make new contacts and widen your social or professional circle.
University of Bath alumni can use the Sports Training Village and Library, which offer discounted membership and special rates to alumni. Alumni are also able to use the University Careers Service. To access these services you will need to provide your alumni ID number or other proof of alumni status, available by contacting the Alumni Relations team .
- Further information
During the above timeline, you may also be thinking about your next steps after your doctorate, in terms of your career. The University Careers Service can provide support and guidance and specialist careers information.
On this page
- Academic life
- Registration
- Module Enrolment
- Discovery Modules
- Creating Sustainable Futures
- Enterprise and Innovation
- Ethics, Religion and Law
- Exploring the Sciences
- Languages and Intercultural understanding
- Media, Culture and Creativity
- Mind and Body
- Personal and Professional Development
- Power and Conflict
- Technology and its Impacts
- Making changes
- Attendance and Absences
- Academic Dates and Deadlines
- Study Support
- Leeds for Life
- Plus Programme
- Higher and Degree Apprenticeships
- School of Medicine
- Lifelong learning centre
- Online learning support
- Navigating online learning systems
- Key dates and locations
- Preparing for your assessments
- Online assessments
- On-campus assessments
- I need help during the assessment period
- What happens after the assessment period?
- Classification
- Academic Integrity
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Postgraduate research
- Starting your research
- During your research
- Thesis Submission and the Viva
- Postgraduate researcher policies and procedures
- Funding for postgraduate researchers
- The Doctoral College
- Research practice
- If your research is disrupted
- Prepare for your graduation ceremony
- Leaving the university
- Official documentation and regulations
- Feedback and complaints
- Responding to your feedback
- Research student policies and procedures
- Taught student policies and procedures
- Paying fees and charges
- University scholarships and funds
- Leeds Bursary
- University Financial Assistance Fund
- External funding
- Student loans
- American and Canadian student funding
- Funding for medics and dentists
- NHS Learning Support Fund
- Study abroad and work placements
- Finding work
- Opportunities
- Languages for All
- The Turing Scheme
- Leadership programmes
- Support and wellbeing
- Counselling and wellbeing
- Groups and workshops
- Togetherall, resources and self help
- Your emotional wellbeing
- Healthy relationships with yourself and others
- Dealing with academic challenges and life stress
- Academic stress and challenges
- Life stress and challenges
- Support for our diverse students
- Disabled student support
- Who we support
- Setting up your support
- Funding for disabled students
- Support for disabled students
- Your safety
- Fraud, phishing, scams; don't lose your money
- Safety at home
- Your personal safety
- Bereavement
- Medical services and what to do if you're ill
- Harassment and misconduct
- Sexual Violence
- Your campus experience and life in Leeds
- Study abroad
- Where can I go?
- Prepare to apply
- Get ready to go
- Study Abroad funding and costs
- During your Study Abroad year
- Returning to Leeds
- Summer abroad
- International students
- Prepare for Leeds
- Your first weeks at Leeds
- International orientation
- Complete start-up processes
- Opening a bank account
- Settle into life at Leeds
- Global Community
- Intercultural work and volunteering
- Intercultural experiences
- Explore Languages and Cultures
- Living in the UK
- International families
- Work volunteering and your visa
- Student Life
- Your time in Leeds
- Finding Your Way Around
- Children and Family
- Staying Safe
- Health and wellbeing
- The Leeds Partnership
- Laidlaw Leadership and Research Programme
- Undergraduate research opportunities
- Applications and interviews
- Career options
- Starting your own business (SPARK)
- Jobs and work experience
- Discover your future
- Final year support
- Leadership programme
The outcome of the viva
Find out the possible recommendations examiners can make on your thesis and what to do in each case.
The outcome of the viva is normally given informally to you immediately and by no later than 24 hours after the viva has taken place. Please see the Guide to the thesis submission process on the Research student guidance page of the For Students website for more information on the processes explained on this webpage.
Possible recommendations
After the viva, your examiners produce a joint report which outlines their recommendation. The recommendation of the examiners is subject to final approval by the Graduate Board's Progress and Examinations Group, which must consider the examiners’ report at its next meeting. The examiners will inform you of the recommendation they are sending forward on your thesis. The possible recommendations are:
Where your thesis satisfies the requirements for the award and no further corrections are required. You will need to submit your final eThesis to the University within one month of the viva date.
Pass (subject to the correction of ‘editorial and presentational corrections’)
Where your thesis satisfies the requirements for the award of the degree but is found to contain minor editorial and presentational errors (trivial errors, typographical errors, simple mistakes of fact or the insertion of headings or other ‘signpost’ material for the sake of clarity). Your corrections must be completed and returned to your internal examiner for approval within four weeks from the viva.
Pass (subject to the correction of minor deficiencies)
Where your thesis satisfies the requirements for the award of the degree but is found to contain minor deficiencies (rewriting of sections, correcting calculations or clarifying arguments and the correction of minor typographical errors). Your corrections must be completed and returned to your internal examiner for approval within 12 weeks from the viva.
Where your thesis is potentially of a standard to merit the award of the degree, but it does not, at this stage, satisfy the requirements for award. You will be required to revise your thesis, which may entail further research, or any other activity required by the examiners, and resubmit this for re-examination. Please see the Referral and resubmission page of the For Students website for further guidance.
If the examiners recommend that your thesis be failed there is no further opportunity to revise and resubmit the work.
MPhil award on PhD submission
For candidates submitting for PhD only, the examiners may recommend the award of MPhil (with or without minor corrections) in cases where the thesis fails to achieve the standard for the award of a PhD but does satisfy the criteria for the award of the degree of MPhil.
Appealing
In some circumstances, you may wish to appeal against an adverse academic decision. You will receive details of the appeals process in an email sent to you notifying you of the outcome of your viva, so please read it carefully. You can also read further details of the procedure governing the consideration of postgraduate researcher appeals on the Academic appeals page of the University of Leeds Secretariat website . If you are considering an appeal against the outcome of the examination, you are strongly encouraged to seek independent advice and support from the Leeds University Union Student Advice team . You should also speak to your supervisory team and your Graduate School .
- The Library
- Leeds University Union
- Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Privacy and cookies
- Freedom of Information
© 2024 University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT
Browser does not support script.
- Student intranet
- Staff intranet

Viva outcome
When will i hear about the outcome of my viva.
Although your examiners may informally tell you the outcome at the end of the viva, the official confirmation of the outcome will be emailed to you (copying in your department) by the Doctoral School team once the examiners have submitted their report forms.
Examiners are asked to submit their report forms to the Doctoral School within two weeks of the viva and the Doctoral School aims to inform you of the outcome within one week of receiving the report forms.
What are the possible outcomes of the viva?
Your examiners will discuss the outcome of your thesis submission and will decide on one of the following outcomes of the submission:
- Pass PhD subject to minor corrections in 3 months
- Pass PhD subject to amendments to address errors of substance or omission in 9 months
- Resubmit for PhD within 18 months (with or without a second viva)
- Re-viva on the same thesis within 18 months
- Pass MPhil subject to minor corrections in 3 months
- Pass MPhil subject to amendments to address errors of substance or omission in 9 months
- Resubmit for MPhil within 12 months
- Fail at PhD and MPhil
The corrections period applies irrespective of your mode of study, and therefore applies to both full and part time students.
What are the most common outcomes?
The most common of these outcomes are:
- Pass PhD - please visit the Final thesis submission and Award process pages for information about the next stages.
- Pass subject to minor corrections in 3 months
- Pass subject to amendments to address errors of substance or omission in 9 months
- Resubmission within 12 / 18 months (with or without a second viva)
|
|
Quick links
|
|
- Home »
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
How to prepare for a phd viva.
Preparing for your PhD viva can be a daunting task. You'll want to ensure that you are ready to defend your thesis successfully.
To help, we've rounded up some useful tips on what to expect during your viva experience, how you can fully prepare for the process and what to expect after viva is done.
What is a PhD viva?
For the majority of PhD students, finishing the dissertation is a seminal moment. After all, knowing that such a long project has come to an end may seem almost surreal.
However, a hard copy of the dissertation is not the end of the PhD experience , each dissertation will have to be orally ‘defended’ in an examination called a viva, which usually takes between one and two hours to complete.
A PhD is an oral examination in the form of a discussion in which PhD students present their PhD thesis and defend their research methods and outcomes to a panel of academic experts.
The word ’viva’ is a shortened form of the Latin term ‘viva voce’ which means ‘live voice’.
How to prepare for a PhD viva
A key way to ensure success in your PhD viva is to make sure you are properly prepared – this can be done in four simple ways:
1. Know your research project inside out.
2. Find out about your viva examiners if you can. If you know about their areas of expertise, you may be able to anticipate their lines of questioning and even work out what they’d like to hear more about.
3. Compile a list of possible questions and practice your explanation/defence of methods used and outcomes discovered.
4. Prepare properly for the actual day by planning your journey to the PhD viva, knowing what you’re going to wear and compiling all the documentation that you need to have with you.
How to prepare ahead of your PhD viva – 5 steps to success
After you hand in your thesis/dissertation, you will usually have a few free weeks before undertaking the PhD viva. It is important that you prepare well during this period and walk out of your examination with at least a “pass mark subject to minor corrections”.
We have compiled a list of some of the most important PhD viva preparation steps to help you succeed in your viva.
STEP 1 – Take a break
After you have submitted your thesis, it is good to take a one or two week break and avoid thinking about your work. This will allow you to see your thesis from a third-person perspective and to understand your own shortcomings more clearly when you read it once again.
STEP 2 – Get to know your thesis
Read each section carefully and summarise its main points. You need to know how to explain and justify the main aspects of your thesis including the research question, methodology and data analysis. Writing any thoughts that come to your mind while reading the thesis as comments will help you to establish a "personal connection" with the thesis and understand it in greater depth.
STEP 3 – Critically examine your thesis
The crucial step of preparation is to lose any "compassion" towards your own work and criticise any weak points that you find in your thesis. It is very likely that your examiners will focus on some of these points in your viva, and you need to find out how to justify them.
STEP 4 – Learn how to defend your thesis!
Write a list of possible critical questions regarding your research and learn how to answer them convincingly. Try to think of yourself as a lawyer and of your thesis as the defendant whom you need to defend!
STEP 5 – Arrange a mock viva with your supervisor around 1-2 weeks before the actual viva
This will help you determine whether your preparation has been complete or there are still some aspects to be prepared before you can successfully defend your thesis. And don't forget to do something enjoyable and relax on the day before your actual viva!
PhD viva tips
We have compiled some of the most useful PhD viva tips to help you understand what is awaiting you if you ever decide to become a PhD student or if you already are one.
| long is a viva? | There is no formal time limit. A viva can last between 1 and 2 hours but can sometimes event take 3 hours. |
| will examine me? | You will usually be examined by 2 examiners. One of them will be a member of your own university (internal examiner) and the other will be an external examiner from another university. Your supervisor may also be present during the examination but is not allowed to ask any questions or impact the outcome. |
| is the purpose of a viva? | A viva is an academic discussion between you and 2 senior researchers in your field of study. It is your opportunity to show them that you possess a thorough understanding of your topic and that you can defend your own research ideas. It is a challenging experience that many students enjoy and are inspired by as it is refreshing to talk to someone about your academic knowledge instead of just spending hours at your desk writing on your own. |
| will I know the outcome? | After the viva has ended, your examiners will ask you to leave the room so they can make the decision. Sometimes it can take them just 10 minutes to reach the decision, however it may take them up to an hour or even longer. Please note, the amount of the time they take to reach a decision doesn’t reflect on the quality of your viva performance. |
| are the possible outcomes of a viva? | – this result is very rare and usually only happens if you have plagiarised your thesis. – if the examiners feel that the amount of work you’ve done is not sufficient for a doctoral degree they may award you an MPhil. – if the examiners think your thesis is not sufficient for an MPhil, they may allow you to do more work and resubmit for an MPhil. – if the examiners think your thesis is of a high standard but the amount of work is insufficient for a doctoral degree, they’ll give you the opportunity to do further research – this is the most frequent decision and usually requires you to do some minor revisions before being awarded your doctorate. – to get a PhD without having to do any corrections is rare but not impossible. Hard work really does pay off! |
Who will be at a PhD viva?
A viva is attended by the PhD student and at least two academic experts.
In some universities, in addition to the student and the two examiners, there may be a senior member of academic staff present to act as chair of the examination. Your supervisor may also be present, although some universities do not allow this.
If there is a chair or your supervisor present at your PhD viva, they are not allowed to ask you questions or to take part in any of the discussion about the outcome.
What questions are asked at a PhD viva?
The examiners will usually start by trying to make you feel comfortable, perhaps by welcoming you and having some polite ‘social’ conversation to start with, for they will understand that you are nervous.
They will soon move on to the range of questions they have planned. These questions could cover anything about the thesis. They might ask you about the methods you have used, the results and findings or the conclusions you have drawn.
They may ask very detailed questions, or they may ask about the overall methods or findings. They will certainly want to explore any areas they feel you have not explained clearly enough or in enough detail in your thesis.
You may be asked to justify some of the conclusions you have made and to show exactly how your data has led you to draw those conclusions. In the area of methodology, you may be asked to justify your choice of the overall method you used, as well as explaining the decisions you made about the detailed methods you chose.
You may also be asked to show how well you know the range of literature and previous research in your field and how your findings add to the literature. In most vivas you will be asked to explain carefully what you believe to be your distinctive ‘contribution to knowledge’ from your research.
What will the PhD examiners want to know?
Understanding what PhD examiners might ask during your viva and having your answers is one way to prepare for success.
How do you justify the critical aspects of your work?
No dissertation is perfect and there will be some aspects of your PhD research that your examiners will be specifically critical about. Thus, it will be important for them to ask you some of the questions regarding these 'critical' aspects of your work to see if you can justify them. These questions will probably be decisive in determining the outcome of your viva.
Can you elaborate on specific sections of your research?
Besides focusing on some 'critical' aspects of your work, the examiners may ask you to give some more elaborate explanations of specific sections of your thesis or specific techniques used in your research. This will help them determine whether you really understand your own work and can think critically about your research.
How does your research contribute to your field of study?
Last, but not least, your examiners will be interested in how well you understand the place of your work within your field of research , and they will ask you to explain the overall contribution of your research to your discipline. As an aspiring student, you will always need to see the big picture and understand how your ideas can shape your academic field.
PhD viva – an academic discussion
A helpful way to think of the viva is as a serious academic discussion. It is an opportunity to sit and talk about your work and your field with two senior academics who know the field well.
As such, it should be challenging and stimulating, and should give you a chance to show that you can engage in serious academic discussion and debate at a very high level.
After the examination many students look back on their viva and see it as a stimulating and enjoyable experience, and they forget the nerves they felt when they first entered the viva room.
The dos and don’ts of a PhD viva
After you have carefully prepared how to defend the content of your thesis, it is important to think of how you should behave during the actual viva.
We have a whole host of PhD viva tips for you. From how to answer properly and be convincing to what to say and what not to say – here, we have clarified these things in our list of PhD viva dos and don’ts .
|
|
|
| Speak clearly and slowly to make sure | Don’t talk incoherently and formulate answers without giving them any structure. |
| Make eye contact and try not to be too | Don’t behave arrogantly and act like you know more than the examiners – remember, they are the experts! |
| Remain quiet after you have answered a question to give the examiners some time to consider your answer. | Don’t start answering before your examiners have finished their question. |
| If you don’t understand a question, ask | Don’t try and use jargon, especially to bluff your way out of a question you don’t know the answer to. |
| Take your time before speaking so you can structure your answers clearly | Don’t digress in your answers or talk about something you haven’t been asked about. |
| Answer with confidence to demonstrate faith in your research – even if you do | Don’t blame your supervisor for any weaknesses the examiners notice in your research. |
| Avoid simple yes or no answers. | Don’t take your examiners’ criticism too personally or get angry. |
| Dress smartly. | Try not to look at your watch. |
Are you a Doctor after your viva?
Once you have passed your PhD viva, you cannot officially use the title ‘Dr’ until you receive official documentation from your university stating that you are a ‘Doctor’.
Can you fail a PhD viva?
Although the majority of PhD students are happy with the outcome of their PhD viva, things don’t always go as expected, and some of the least appealing outcomes do happen. You can fail a PhD viva – although according to recent research by Discover PhDs this number is only 4%. It is more common for borderline students to be awarded a provisional pass pending amends to their research project.
If, as a PhD student, you feel that your own work is not of very high quality and you are aware that the unfavourable outcome is your fault, there is not much you can do except for complying with the decision of your examiners.
Appealing a PhD viva decision
If you feel that your viva has not been appropriately conducted and the outcome doesn’t match the quality of your performance, there are some things you can do.
Universities in the UK will usually allow you to appeal against how your examination was conducted and if you do appeal, a panel of researchers within your university will be appointed to investigate the issue, but you must possess clear evidence in your support.
If your appeal is successful, you will get a chance to undertake another viva with different examiners.
If the university hasn’t decided in your favour, you will be able to appeal to an external organisation, such as the Office of the Independent Adjudicator for Higher Education (OIA). But remember, appeals are usually not very successful, and it is always better to make sure that your thesis is of high quality and that you have done the right amount of PhD viva preparation.
Related articles
What Is A PhD?
How Long Is A PhD?
PhD In The USA
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course

- PhD Failure Rate – A Study of 26,076 PhD Candidates
- Doing a PhD
The PhD failure rate in the UK is 19.5%, with 16.2% of students leaving their PhD programme early, and 3.3% of students failing their viva. 80.5% of all students who enrol onto a PhD programme successfully complete it and are awarded a doctorate.
Introduction
One of the biggest concerns for doctoral students is the ongoing fear of failing their PhD.
After all those years of research, the long days in the lab and the endless nights in the library, it’s no surprise to find many agonising over the possibility of it all being for nothing. While this fear will always exist, it would help you to know how likely failure is, and what you can do to increase your chances of success.
Read on to learn how PhDs can be failed, what the true failure rates are based on an analysis of 26,067 PhD candidates from 14 UK universities, and what your options are if you’re unsuccessful in obtaining your PhD.
Ways You Can Fail A PhD
There are essentially two ways in which you can fail a PhD; non-completion or failing your viva (also known as your thesis defence ).
Non-completion
Non-completion is when a student leaves their PhD programme before having sat their viva examination. Since vivas take place at the end of the PhD journey, typically between the 3rd and 4th year for most full-time programmes, most failed PhDs fall within the ‘non-completion’ category because of the long duration it covers.
There are many reasons why a student may decide to leave a programme early, though these can usually be grouped into two categories:
- Motives – The individual may no longer believe undertaking a PhD is for them. This might be because it isn’t what they had imagined, or they’ve decided on an alternative path.
- Extenuating circumstances – The student may face unforeseen problems beyond their control, such as poor health, bereavement or family difficulties, preventing them from completing their research.
In both cases, a good supervisor will always try their best to help the student continue with their studies. In the former case, this may mean considering alternative research questions or, in the latter case, encouraging you to seek academic support from the university through one of their student care policies.
Besides the student deciding to end their programme early, the university can also make this decision. On these occasions, the student’s supervisor may not believe they’ve made enough progress for the time they’ve been on the project. If the problem can’t be corrected, the supervisor may ask the university to remove the student from the programme.
Failing The Viva
Assuming you make it to the end of your programme, there are still two ways you can be unsuccessful.
The first is an unsatisfactory thesis. For whatever reason, your thesis may be deemed not good enough, lacking originality, reliable data, conclusive findings, or be of poor overall quality. In such cases, your examiners may request an extensive rework of your thesis before agreeing to perform your viva examination. Although this will rarely be the case, it is possible that you may exceed the permissible length of programme registration and if you don’t have valid grounds for an extension, you may not have enough time to be able to sit your viva.
The more common scenario, while still being uncommon itself, is that you sit and fail your viva examination. The examiners may decide that your research project is severely flawed, to the point where it can’t possibly be remedied even with major revisions. This could happen for reasons such as basing your study on an incorrect fundamental assumption; this should not happen however if there is a proper supervisory support system in place.
PhD Failure Rate – UK & EU Statistics
According to 2010-11 data published by the Higher Education Funding Council for England (now replaced by UK Research and Innovation ), 72.9% of students enrolled in a PhD programme in the UK or EU complete their degree within seven years. Following this, 80.5% of PhD students complete their degree within 25 years.
This means that four out of every five students who register onto a PhD programme successfully complete their doctorate.
While a failure rate of one in five students may seem a little high, most of these are those who exit their programme early as opposed to those who fail at the viva stage.
Failing Doesn’t Happen Often
Although a PhD is an independent project, you will be appointed a supervisor to support you. Each university will have its own system for how your supervisor is to support you , but regardless of this, they will all require regular communication between the two of you. This could be in the form of annual reviews, quarterly interim reviews or regular meetings. The majority of students also have a secondary academic supervisor (and in some cases a thesis committee of supervisors); the role of these can vary from having a hands-on role in regular supervision, to being another useful person to bounce ideas off of.
These frequent check-ins are designed to help you stay on track with your project. For example, if any issues are identified, you and your supervisor can discuss how to rectify them in order to refocus your research. This reduces the likelihood of a problem going undetected for several years, only for it to be unearthed after it’s too late to address.
In addition, the thesis you submit to your examiners will likely be your third or fourth iteration, with your supervisor having critiqued each earlier version. As a result, your thesis will typically only be submitted to the examiners after your supervisor approves it; many UK universities require a formal, signed document to be submitted by the primary academic supervisor at the same time as the student submits the thesis, confirming that he or she has approved the submission.
Failed Viva – Outcomes of 26,076 Students
Despite what you may have heard, the failing PhD rate amongst students who sit their viva is low.
This, combined with ongoing guidance from your supervisor, is because vivas don’t have a strict pass/fail outcome. You can find a detailed breakdown of all viva outcomes in our viva guide, but to summarise – the most common outcome will be for you to revise your thesis in accordance with the comments from your examiners and resubmit it.
This means that as long as the review of your thesis and your viva examination uncovers no significant issues, you’re almost certain to be awarded a provisional pass on the basis you make the necessary corrections to your thesis.
To give you an indication of the viva failure rate, we’ve analysed the outcomes of 26,076 PhD candidates from 14 UK universities who sat a viva between 2006 and 2017.
The analysis shows that of the 26,076 students who sat their viva, 25,063 succeeded; this is just over 96% of the total students as shown in the chart below.
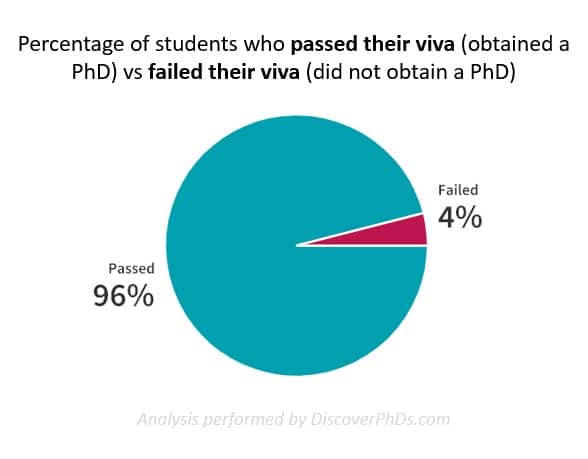
Students Who Passed
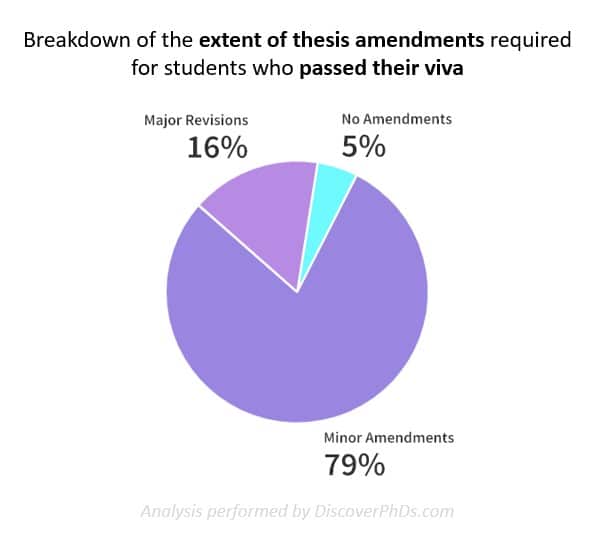
The analysis shows that of the 96% of students who passed, approximately 5% required no amendments, 79% required minor amendments and the remaining 16% required major revisions. This supports our earlier discussion on how the most common outcome of a viva is a ‘pass with minor amendments’.
Students Who Failed

Of the 4% of unsuccessful students, approximately 97% were awarded an MPhil (Master of Philosophy), and 3% weren’t awarded a degree.
Note : It should be noted that while the data provides the student’s overall outcome, i.e. whether they passed or failed, they didn’t all provide the students specific outcome, i.e. whether they had to make amendments, or with a failure, whether they were awarded an MPhil. Therefore, while the breakdowns represent the current known data, the exact breakdown may differ.
Summary of Findings
By using our data in combination with the earlier statistic provided by HEFCE, we can gain an overall picture of the PhD journey as summarised in the image below.

To summarise, based on the analysis of 26,076 PhD candidates at 14 universities between 2006 and 2017, the PhD pass rate in the UK is 80.5%. Of the 19.5% of students who fail, 3.3% is attributed to students failing their viva and the remaining 16.2% is attributed to students leaving their programme early.
The above statistics indicate that while 1 in every 5 students fail their PhD, the failure rate for the viva process itself is low. Specifically, only 4% of all students who sit their viva fail; in other words, 96% of the students pass it.
What Are Your Options After an Unsuccessful PhD?
Appeal your outcome.
If you believe you had a valid case, you can try to appeal against your outcome . The appeal process will be different for each university, so ensure you consult the guidelines published by your university before taking any action.
While making an appeal may be an option, it should only be considered if you genuinely believe you have a legitimate case. Most examiners have a lot of experience in assessing PhD candidates and follow strict guidelines when making their decisions. Therefore, your claim for appeal will need to be strong if it is to stand up in front of committee members in the adjudication process.
Downgrade to MPhil
If you are unsuccessful in being awarded a PhD, an MPhil may be awarded instead. For this to happen, your work would need to be considered worthy of an MPhil, as although it is a Master’s degree, it is still an advanced postgraduate research degree.
Unfortunately, there’s a lot of stigma around MPhil degrees, with many worrying that it will be seen as a sign of a failed PhD. While not as advanced as a PhD, an MPhil is still an advanced research degree, and being awarded one shows that you’ve successfully carried out an independent research project which is an undertaking to be admired.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Additional Resources
Hopefully now knowing the overall picture your mind will feel slightly more at ease. Regardless, there are several good practices you can adopt to ensure you’re always in the best possible position. The key of these includes developing a good working relationship with your supervisor, working to a project schedule, having your thesis checked by several other academics aside from your supervisor, and thoroughly preparing for your viva examination.
We’ve developed a number of resources which should help you in the above:
- What to Expect from Your Supervisor – Find out what to look for in a Supervisor, how they will typically support you, and how often you should meet with them.
- How to Write a Research Proposal – Find an outline of how you can go about putting a project plan together.
- What is a PhD Viva? – Learn exactly what a viva is, their purpose and what you can expect on the day. We’ve also provided a full breakdown of all the possible outcomes of a viva and tips to help you prepare for your own.
Data for Statistics
- Cardiff University – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- Imperial College London – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- London School of Economics (LSE) – 2006/07 to 2015/16
- Queen Mary University of London – 2009/10 to 2015/16
- University College London (UCL) – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- University of Aberdeen – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- University of Birmingham – 2006/07 to 2015/16
- University of Bristol – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- University of Edinburgh – 2006/07 to 2016/17
- University of Nottingham – 2006/07 to 2015/16
- University of Oxford – 2007/08 to 2016/17
- University of York – 2009/10 to 2016/17
- University of Manchester – 2008/09 to 2017/18
- University of Sheffield – 2006/07 to 2016/17
Note : The data used for this analysis was obtained from the above universities under the Freedom of Information Act. As per the Act, the information was provided in such a way that no specific individual can be identified from the data.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What makes one fail a PhD viva?
I do not ask about special cases, e.g. supervisor does not approve the thesis, there is rivalry between the supervisor and the examiners and so on. Is there any general standard for viva, e.g. one needs to be able to answer 2/3 of the questions, etc.
I'm waiting for my viva, and I'm only worried about questions about related work. For example, my thesis only addresses a problem on deterministic programs, do I need to know all approaches to the same problem on probabilistic programs? (at the moment I don't).
I would like to emphasize again that I do not ask about special cases, e.g. plagiarism, wrong methodology etc. I believe theses cases are extremely rare. I just want to ask about a normal case where one managed to publish some papers, and advisor (happily) approved the thesis.
- This depends a lot on the culture, country, school etc. For instance if I want to do my state exams, I have to pass all previous 5 doctoral exams, and also pass 3 additional ones on the spot. Failing to say anything there would cause me to fail the exam quite for sure. – yo' Commented May 6, 2015 at 9:26
- 19 The problem is that your "framing" is wrong: the special cases probably comprise the majority of cases when a doctoral defense "fails." If the thesis advisor is happy, and the thesis is acceptable, it is extremely rare for someone to fail. – aeismail Commented May 6, 2015 at 11:18
- 1 Perhaps you should ask your institution or adviser about how you are expected to prepare? – Superbest Commented May 6, 2015 at 12:23
- Related: How would one fail a master thesis defense? – Wrzlprmft ♦ Commented May 6, 2015 at 12:50
- 2 Given your caveats about special cases, I think the most accurate answer to the title question is "nothing". – Lazzaro Campeotti Commented May 6, 2015 at 13:34
5 Answers 5
No, there are no general worldwide standards, other than "the examiners should be satisfied".
Your advisor is probably the best person to answer questions like this for your specific case.
- 3 Additionally, rules about what the examiners should be checking vary from institution to institution. – Charles Stewart Commented May 6, 2015 at 6:54
The following are some reasons that come to mind that might justify a failure in the viva:
For the thesis:
- evidence of academic malpractice (plagiarism, etc.)
- fundamental methodological flaws, such as a poorly chosen method or a misapplied method that calls into question the scientific validity of the thesis. My guess is that this is probably the most common reason for failure: that the work is just generally not a good piece of science and needs further development before it can be considered convincing.
- a significant failure to engage with preexisting literature, which casts into doubt the significance and originality of the thesis' contribution to knowledge.
- a general lack of academic substance such that the thesis is not of sufficient scope or novelty to merit the award of a PhD.
For the viva itself:
- a general inability to answer questions about the thesis—to a such a degree that the examiners are led to question whether it is really the candidate's own work.
- a significant deficiency in the candidate's knowledge of the literature, such that s/he cannot confidently be held to understand the relationship between his/her work and that literature.
- a significant inability to justify the decisions made in the course of the PhD, calling into question the candidate's ability to construct a successful research project. For example, you should be able to say why you chose the approach you did, rather than some alternative.
- repeatedly giving answers that are so severely wrong that they call into question the candidate's competency in the field.
The use of the words fundamental, significant, etc. in the above is quite deliberate. Examiners will forgive basic problems with the thesis or a somewhat flakey viva performance because they understand that passing the viva marks the start (rather than the end) of one's education. The option of minor corrections exists to deal with such issues.
- One additional thing you should watch out for is a callous or inherent attitude towards the viva. – user34114 Commented May 6, 2015 at 11:14
- 5 Most of these are usually failures of the candidate's advisor more than the candidate, as the advisor should never let an unready candidate defend... – jakebeal Commented May 6, 2015 at 12:02
- 1 @jakebeal yet sometimes the candidate will insist, for a number of legitimate reasons: visa issues, financial duress, change of lifestyle (pregnancy, getting married, getting divorced). Life does get in the way. – ZeroTheHero Commented Jun 30 at 1:14
I assume that the aim of a vivia is generally 'to establish whether the aims of the PhD program have been achieved', although I guess some will be more restricted than that (with another grouping checking the overall picture).
Therefore generally there won't be a specific question-proportion to pass, since there's no set list of questions. You need to demonstrate that you wrote your thesis, that it is right (well, close enough, since there will usually be some mistakes somewhere), and that it is of a suitable standard. You probably also need to demonstrate that you've engaged with the professional development part of the program (as a PhD student you are essentially an apprentice professor/researcher). You should know stuff about your field other than your immediate thesis question, you should know how the research community works, and you should be able to communicate your ideas (in writing, in a planned presentation, and in answering questions). Having some realistic plans for the future might also not be a bad idea.
As a former PhD student, now lecturer, it's very rare to hear of one failing a PhD viva. The most common outcome is to grant the PhD subject to minor corrections, which will be checked off by the internal examiner. Occasionally candidates will have to make major corrections for review by the external examiner, and much more rarely, candidates will be told to revise and resubmit where the process may or may not include an additional oral examination. Only the last outcome would be generally regarded as "failure".
In the first instance the student's advisor would not recommend/allow (depending on the institution) the candidate to go forward for a viva unless the work was to the standard required. In many universities, this means publishable in whole or in part, and making a non-trivial novel contribution. One way to satisfy yourself about these criteria is whether you've published anything at all to date: if you have, it answers the question that the thesis is publishable at least in part. It's very hard to "fail" (see above) if these basic criteria are met.
About related approaches, you would probably be expected to have a rationale for choosing your own approach. This would imply that you know your chosen method well, and know enough about the others to be able to make a comparative choice. E.g. if you were working in electromagnetics and chose the Finite Element Method to solve a Partial Differential Equation, you would probably want to be able to point out why you rejected Finite Differences and/or Analytical methods. But I would not expect you to be able to discuss the intricacies of Finite Differences in any great detail. The working knowledge you already have of your own approach and that of others is probably quite sufficient, as long as you can provide a strong justification for why you chose the methods you did. It's quite OK to justify based on ease of use, local availability, expediency etc.
Further to Nate and Jessica's answers, you can get an idea as to what the risks are in your institution and your subject area by asking around for examples of people who have failed their viva.
'Failing' is also relative: the 'do not darken our doors, no option to resubmit' outcome is only likely to be a risk in case of plagiarism or moral turpitude . The difference between acceptance pending corrections (regarded as a 'pass') and asking for a 2nd viva (often regarded as a 'fail') may not be huge in terms of the amount of effort on your part that is required to satisfy your examiners.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd thesis ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Is this a new result about hexagon?
- What to do when 2 light switches are too far apart for the light switch cover plate?
- How can judicial independence be jeopardised by politicians' criticism?
- Distinctive form of "לאהוב ל-" instead of "לאהוב את"
- How does \vdotswithin work?
- If inflation/cost of living is such a complex difficult problem, then why has the price of drugs been absoultly perfectly stable my whole life?
- Regression techniques for a “triangular” scatterplot
- How do eradicated diseases make a comeback?
- Is it possible to have a planet that's gaslike in some areas and rocky in others?
- I'm trying to remember a novel about an asteroid threatening to destroy the earth. I remember seeing the phrase "SHIVA IS COMING" on the cover
- My visit is for two weeks but my host bought insurance for two months is it okay
- Can a 2-sphere be squashed flat?
- Slicing Graph by path
- What happens if all nine Supreme Justices recuse themselves?
- Parse Minecraft's VarInt
- What is the difference between a "Complaint for Civil Protection Order" and a "Motion for Civil Protection Order"?
- about flag changes in 16-bit calculations on the MC6800
- Product of rings are Morita equivalent implies the rings are Morita equivalent.
- Using "no" at the end of a statement instead of "isn't it"?
- Encode a VarInt
- Command-line script that strips out all comments in given source files
- How can I install an application in Ubuntu Server and ensure only it runs in the GUI?
- Chromatic homotopy + algebraic geometry =?
- Why was this lighting fixture smoking? What do I do about it?
Doctoral examiners’ narratives of learning to examine in the PhD viva: a call for support
- Published: 12 August 2022
- Volume 86 , pages 527–539, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Wee Chun Tan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6521-5748 1
683 Accesses
3 Citations
Explore all metrics
This study aims to better understand the learning experiences of doctoral examiners in relation to their assessment practices in the PhD viva, which directly impacts the PhD candidates’ success in doctoral assessment. A narrative approach was employed to uncover the narratives of learning to examine in the PhD viva from twelve doctoral examiners in Malaysia. Based on the thematic analysis, examiners mainly learned from their own experiences and trial and error. Additionally, they hardly receive any institutional training on how to examine in the PhD viva. This suggests a need to support examiners, especially novice examiners, in their assessment endeavours. The findings contribute to the literature on doctoral examiner experiences by raising several important questions regarding examiner practices in the PhD viva and calling for institutional support. The study provides insights into how academic developers can support doctoral examiners more effectively in the PhD viva to ensure quality in doctoral assessment and a positive examination experience for doctoral examiners and candidates.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

The Retrospective PhD by Publication: A Lesser Doctorate?

Rethinking Evidence: Assessment in the History Discipline in Australian Universities
Introduction: demystifying the phd by publication, explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Arnkoff, D. B., Glass, C. R., & Robinson, A. S. (1992). Cognitive processes, anxiety, and performance on doctoral dissertation oral examinations. Journal of Counselling Psychology, 39 (3), 382–388.
Article Google Scholar
Ary, D., Jacobs, C. L., & Sorensen, I. C. & Walker, D. A. (2018). Introduction to research in education (10th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Badaruddin, M. (2010, June 17). Managing international students in Malaysia: Issues & strategies [Paper presentation]. Internationalization and Marketing of Higher Education Malaysia Seminar, Ministry of Higher Education and Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia.
Baldacchino, G. (1995). Reflections on the status of a doctoral defence. Journal of Graduate Education, 1 (3), 71–76.
Google Scholar
Boud, D., Keogh, R., & Walker, D. (1985). Reflection: Turning experience into learning . Kogan Page.
Boyd, E., & Fales, A. (1983). Reflective learning: The key to learning from experience. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 23 (2), 99–117.
Bruner, J. (1991). The narrative construction of reality. Critical Inquiry, 18 (1), 121.
Carter, S. (2008). Examining the doctoral thesis: A discussion. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 45 (4), 365–374.
Chen, S. (2011). Making sense of the doctoral dissertation defense: A student-experience-based perspective. In L. McAlphine & C. Amundsen (Eds.), doctoral. Education: Research-Based Strategies for Doctoral Students, Supervisors and Administrators. Springer, Netherlands.
Chen, S. (2014). Balancing knowing and not-knowing: An exploration of doctoral candidates’ performance of researcher selves in the dissertation defence. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 39 (3), 364–379.
Clandinin, D. J., & Connelly, F. M. (2000). Narrative inquiry: Experience and story in qualitative research. Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Clarke, G., & Lunt, I. (2014). The concept of ‘originality’ in the Ph.D.: How is it interpreted by examiners? Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 39 (7), 803–820. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.870970
Cooksey, R. & McDonald, G. (2011). Surviving and thriving in postgraduate research . Tilde Publishing.
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
Cresswell, J. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.) . Sage Publications.
Denicolo, P., Duke, D. & Reeves, J. (2020). Delivering inspiring doctoral assessment. Sage Publications.
Denzin, N.K. & Lincoln, Y.S. (2011). The sage handbook of qualitative research (4th ed.). Sage publications.
Dewey, J. (1933). How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process . Heath and Company.
Gergen, K. J. (2009). An invitation to social construction (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
Gibbs, G. (1988). Learning by doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods . Further Education Unit.
Golding, C., Sharmini, S., & Lazarovitch, A. (2014). What examiners do: What thesis students should know. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 39 (5), 563–576.
Houston, G. (2021). Doctoral examiners’ judgements: Do examiners agree on doctoral attributes and how important are professional and personal characteristics? In A. Lee and R Bongaardt (eds). The Future of Doctoral Research: Challenges and Opportunities. Routledge.
Jackson, C., & Tinkler, P. (2001). Back to basics: A consideration of the purposes of the PhD viva. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education, 26 (4), 355–366.
Jarvis, P. (1992). Reflective practice and nursing. Nurse Education Today, 12 , 174–181.
Kelly, F. (2010). Reflecting on the purpose of the PhD oral examination. New Zealand Journal of Educational Studies., 45 (1), 77–85.
Kiley, M. (2009). ‘You don’t want a smart Alec’: Selecting examiners to assess doctoral dissertations. Studies in Higher Education, 34 (8), 889–903.
Kolb, A. D. (2015). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development (2nd ed.). Pearson FT Press.
Kumar, V., Kaur, A., & Sanderson, L. J. (2022). PhD orals from the convenors’ perspective: Implications for academics and candidates. International Journal for Academic Development. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/1360144X.2022.2051516
Kyvik, S. (2014). Assessment procedures of Norwegian PhD theses as viewed by examiners from the USA, the UK and Sweden. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 39 (2), 140–153.
Mezirow, J. (1981). A critical theory of adult learning and education. Adult Education Quarterly, 32 (3), 3–24.
Ministry of Education Malaysia. (2015, August 21). Malaysia education blueprint 2015–2025 . https://www.um.edu.my/docs/um-magazine/4-executive-summary-pppm-2015-2025.pdf
Ministry of Higher Education. (2018, September 1). Statistik pendidikan tinggi 2018 . https://www.mohe.gov.my/muat-turun/statistik/stat-2018/224-statistik-pt-2018-03-bab-1-makro-institusi-pendidikan-tinggi/file
Mullins, G., & Kiley, M. (2002). “It’s a PhD, not a Nobel Prize”: How experienced examiners assess research theses. Studies in Higher Education, 27 (4), 369–386.
Murray, R. (2009). How to survive your viva: Defending a thesis in an oral examination. Open University Press.
Nir, A., & Bogler, R. (2021). International examiners’ participation of the Viva: A ritual or an actual indicator of research quality? Quality Assurance in Education., 29 (2/3), 183–197. https://doi.org/10.1108/QAE-01-2021-0005
Pearce, L. (2005). How to examine a thesis . Open University Press-McGraw-Hill.
Powell, S., & Green, H. (2007). The doctorate worldwide . McGraw-Hill.
Quacquarelli Symonds (2022, June 13). QS World University Rankings 2023 . https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/world-university-rankings/2023
Recski, L. (2005). Interpersonal engagement in academic spoken discourse: A functional account of dissertation defences. English for Specific Purposes, 24 (1), 5–23.
Schön, D. (1983). The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action. Temple Smith.
Sikes, P. (2017). And then he threatened to kill himself: Nightmare viva stories as opportunities for learning. Qualitative Research Journal., 17 (4), 230–242.
Share, M. (2016). The PhD viva: A space for academic development. International Journal for Academic Development., 21 (3), 178–193.
Smith, P. (2014). The PhD viva: How to prepare for your oral examination . Palgrave Macmillan.
Swales, J. M. (2004). The Ph.D. defense . In J. M. Swales (Ed.), Research genres: Explorations and applications (pp. 145–172). Cambridge University Press.
Tan, W. C. (2022). Speaking the language of defence: Narratives of doctoral examiners on the PhD viva . Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1108/QRJ-01-2022-0009
Book Google Scholar
Tinkler, P., & Jackson, C. (2000). Examining the doctorate: Institutional policy and the PhD examination process in Britain. Studies in Higher Education, 25 (2), 167–180.
Tinkler, P., & Jackson, C. (2002). In the dark? Preparing for the PhD viva. Quality Assurance in Education, 10 (2), 86–97.
Tinkler, P., & Jackson, C. (2004). The doctoral examination process: A handbook for students, examiners and supervisors . Open University Press.
Trafford, V. (2003). Questions in doctoral vivas: Views from the inside. Quality Assurance in Education, 11 (2), 114–122.
Trafford, V., & Leshlem, S. (2008). Stepping stones to achieving your doctorate: Focusing on your viva from the start. Open University Press.
Wallace, S. (2003). Figuratively speaking: Six accounts of the PhD viva. Quality Assurance in Education, 11 (2), 100–108.
Wellington, J. (2010). Supporting students preparation for the viva: Their preconceptions and implications for practice. Teaching in Higher Education, 15 (1), 71–84.
Wisker, G., & Kiley, M. (2014). Professional learning: Lessons for supervision from doctoral examining. International Journal for Academic Development, 19 (2), 125–138.
Wisker, G., Highman, L., Spronken-Smith, R., & Waghorne, J. (2022). Across time and space: Examiner and candidate experiences of online doctoral vivas. Innovations in Education and Teaching International., 59 (2), 131–141. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2021.2022528
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Wee Chun Tan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wee Chun Tan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tan, W.C. Doctoral examiners’ narratives of learning to examine in the PhD viva: a call for support. High Educ 86 , 527–539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-022-00913-w
Download citation
Accepted : 08 August 2022
Published : 12 August 2022
Issue Date : September 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-022-00913-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Examiner practices
- Professional learning
- Doctoral assessment
- Doctoral education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Peoples' Friendship University of Russia
- Maria Korneykova

Maria Korneykova Peoples' Friendship University of Russia | rudn
Connect with experts in your field
Join ResearchGate to contact this researcher and connect with your scientific community.
Publications

- Lomonosov Moscow State University

- Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca

- The Ohio State University

- Radboud University Medical Center Nijmegen The Netherlands
- Winogradsky Institute of Microbiology, Research Center of Biotechnology of the Russian Academy of Sciences
- Italian National Research Council

- Saint Petersburg State University

- Russian Academy of Sciences

- Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- DOI: 10.17323/1814-9545-2019-1-87-108
- Corpus ID: 164614365
Who is Happy at Doctoral Programs: The Connection between Employment and Learning Outcomes of PhD Students
- S. Bekova , Zibeyda Dzhafarova
- Published in Voprosy obrazovaniya… 2019
- Voprosy obrazovaniya / Educational Studies Moscow
30 Citations
Does employment during doctoral training reduce the phd completion rate.
- Highly Influenced
Alexander V. Kabanov , PhD
Adjunct Professor Director Mescal Swain Ferguson Distinguished Prof
Alexander V. Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci.
Director, center for nanotechnology in drug delivery, mescal swain ferguson distinguished professor, center for nanotechnology in drug delivery, adjunct professor, unc department of biomedical engineering, current projects, honors and awards.
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., D.Sc., is the Mescal S. Ferguson Distinguished Professor and director of the Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy and co-director of the Carolina Institute for Nanomedicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Kabanov began his academic journey at M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU), where he graduated in 1984. He continued his studies at the same institution, earning a Ph.D. in 1987 and a D.Sc. in 1990. His scientific career took root in the Soviet Union and later transitioned to the United States. From 1994 to 2012, Kabanov was affiliated with the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha, Nebraska. During his tenure there, he established the first academic nanomedicine center in the United States in 2004.
In 2012, Kabanov moved to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill where his research focuses on several key areas.
- Polymeric Micelles : Kabanov co-developed the first polymeric micelle drug that entered clinical trials for cancer treatment, thereby establishing polymeric micelles as a clinically approved drug delivery platform.
- Polyplexes : Kabanov was among the first to use polycations and later, cationic block copolymers for delivering nucleic acids into cells. He evaluated core-shell polyelectrolyte complexes of nucleic acids and polypeptides, now known as “polyplexes”, for therapeutic drug and gene delivery.
- Nanogels, Nanoparticle-Macrophage Carriers, and Exosomes : These have been utilized for delivering small drugs, nucleic acids, and polypeptides to treat cancers and diseases of the central nervous system.
Kabanov is a highly cited researcher, with over 340 scientific papers (garnering over 50,000 citations, and a Google h-index greater than 115), 36 US patents, and has co-founded several pharmaceutical companies. His cumulative research support in academia has been over $120 million.
Kabanov has mentored more than 80 graduate students and postdocs, half of whom are women and underrepresented minorities. Nineteen past members of Kabanov laboratory hold faculty appointments. He is the director of the NCI’s T32 training program in Cancer Nanotechnology .
Kabanov also established symposium series in nanomedicine and drug delivery , chaired Gordon Research Conferences, and received numerous honors and awards, including the Lenin Komsomol Prize, NSF Career award, George Gamow award, and the Controlled Release Society (CRS) Founders award.
Kabanov is an elected member or fellow of prestigious academies and organizations, including Academia Europaea, Russian Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Inventors, American Association for the Advancement of Science, American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering, and CRS. He has served as the past President and current CEO of the Russian American Science Association, director-at-large for CRS (2019-2022), and chair of the CRS College of Fellows sub-committee (2022-2023).
Education, Certification and Licensure
- 1990: Doctor of Chemical Sciences (D.Sc.) in Chemical Kinetics and Catalysis and Biochemistry at Moscow State University
- 1984 – 1987: Candidate of Chemical Sciences (Ph.D. equivalent) in Chemical Kinetics and Catalysis at Moscow State University
- 1979 – 1984: Diploma with distinction (M.S. equivalent) in Chemistry at Moscow State University
Courses and Lectures
DPMP 862/863 “Special Topics in Advanced Pharmaceutics” 3 cr.
Office Hours
By appointment only
Google Scholar
Lab Website
Twitter @alkabanov
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-3665-946X
- Carolina Cancer Nanotechnology Training Program (C-CNTP)
- Towards Translation of Nanoformulated Paclitaxel-Platinum Combination
- Extracellular Vesicles for CNS Delivery of Therapeutic Enzymes to Treat Lysosomal Storage Disorders
- Cell-based Platform for Gene Delivery to the Brain
| 2022 | Founders Award, The Controlled Release Society |
| 2021 | Fellow, |
| 2019 | Corresponding member, Russian Academy of Sciences |
| 2018 | Fellow, |
| Life Sciences Award, Triangle Business Journal | |
| 2017 | Fellow, |
| RASA George Gamow Award | |
| 2016 | RUSNANOPRIZE Short List |
| 2015 | Dresden Senior Fellow |
| 2014 | Fellow, |
| 2013 | Member, (The Academy of Europe) |
| 2010 | |
| 2009 | |
| 2007 | |
| 1995 | NSF CAREER Award |
| 1988 | Lenin Komsomol Prize |
Highly Cited Researcher: Thompson Reuters/Clarivate Analytics – Pharmacology & Toxicology (2014, 2018, 2021)
Huang, Kabanov and Roth Recognized for Research Influence
Three faculty members from the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy were recognized on the Clarivate Analytics list of Highly Cited Researchers for 2018. Leaf Huang, Ph.D., Alexander Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci., and Bryan Roth, Ph.D., M.D., were among 6,000 scientists worldwide … Read more
Kabanov Named President of Russian-American Scientists Association
Alexander Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci., assumed office as president of the Russian-American Scientists Association (RASA-America) on Nov. 5. Kabanov is the Mescal S. Ferguson Distinguished Professor and director of the Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy and … Read more
Kabanov Elected 2018 Controlled Release Society Fellow
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr. Sci., has been selected for membership in the College of Fellows of the Controlled Release Society for his “outstanding contributions to the field of delivery science and technology.” Kabanov will be inducted into the college … Read more
Kabanov Receives TBJ Life Sciences Award
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr. Sci., is a recipient of a 2018 Life Sciences Award from the Triangle Business Journal. Kabanov was nominated in the category of Outstanding Individual Research from Universities or Research Institutes. The award was presented at … Read more
Third Carolina Nanoformulation Workshop Shares Discoveries in Nanomedicine
From March 12 to 16, scientists from industry and academia came together at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy to learn about the latest advances in nanomedicine and to get hands-on experience with advanced nanoformulations at the third annual Carolina … Read more
Kabanov to Lead Russian-American Science Society
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci., is the president-elect of the Russian-American Science Association. Kabanov was elected to his new post at the organization’s annual meeting at Northwestern University in Chicago on Nov. 4 and 5, where he also received the … Read more
Kabanov Elected to National Academy of Inventors
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci., Mescal Swaim Feruguson Distinguished Professor at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, has been named a Fellow of the National Academy of Inventors, the organization announced Tuesday. Kabanov is the director of the School’s Center … Read more
Kabanov Meets with President of Armenia
Alexander “Sasha” Kabanov, Ph.D., met with the president of Armenia on Nov. 8 as part of a group of participants in the second All-Armenian Scientific Conference held in the capital city of Yerevan on November 5-8. The delegation consisted of … Read more
Postdoc Elizabeth Wayne Reflects on TED Experience
Elizabeth Wayne, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow studying how immune cells can be used to fight cancer, gave a TED talk on the main stage at TED 2017 in Vancouver, Canada. Wayne was announced as a TED fellow in January 2017. … Read more
Yuhang Jiang Wins UNC Grad School Impact Award
Yuhang Jiang, Ph.D., a December 2016 graduate of the pharmaceutical sciences doctoral program at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, has received a 2017 Horizon Award from the UNC Graduate School for his research into a treatment to repair the … Read more

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) downgrade to MPhil with no amendments, (5) downgrade to MPhil subject to amendments, (6) immediate fail. Almost all students who sit their viva pass it, with the most common outcome being ' (2 ...
Learn about the possible outcomes of UK-based oral examinations of doctoral theses, such as outright pass, minor or major corrections, resubmission or fail. Find out how to deal with the corrections and resubmit your thesis after the viva.
The viva voce is the final assessment for a PhD. It is an oral examination where the student defends their research to two academic examiners. This involves answering questions about your work, typically related to the literature, methodology, your findings and the significance of your conclusions. In some countries (like the USA) the viva is ...
The viva voce, shortened to viva, is an oral examination where you are expected to 'defend' your thesis, and the quality of your research will be assessed. The viva will take place usually within 3 months of submitting your thesis; it is a required examination in order to achieve a postgraduate research degree.
This guidance explains the viva process, how to prepare, what will happen on the day and what the possible outcomes are. This information is for postgraduate research students. It covers: before your viva; preparing for your viva; during your viva; outcomes of the examination; Before your viva Entry forms
Learn how to prepare for and conduct your oral examination (viva) at the end of your PhD. Find out the possible outcomes of the viva and what to do after it.
The viva examination is usually conducted behind closed doors by at least two examiners, usually with at least one being an external examiner from another institution and an expert in your topic of research. ... Viva outcomes. For the degrees of PhD, MPhil and MD, examiners can recommend: Outcome ;
A PhD viva also referred to as a Viva Voce, Latin for 'living voice', is an oral examination which follows the submission of your doctoral thesis, where you will showcase your knowledge and defend your research in front of a panel comprised of academic experts. This examination is compulsory for the vast majority of doctoral students.
The viva (short for viva voce) is an oral examination which gives the opportunity for: you to defend your thesis and clarify any matters raised by your examiners. the examiners to probe your knowledge in the field. the examiners to assure themselves that the work presented is your own and to clarify matters of any collaboration.
Possible PhD Viva Outcomes. At the end of the viva the examiners will give you feedback. This will include feedback on your performance in the viva. But as long as they're satisfied that you carried out the work and that you knew what you're doing, the bulk of the feedback will in fact revolve around your PhD thesis.
Step 10: Possible outcomes of the viva voce examination. The Board of Examiners will agree a recommended outcome following your viva examination. The list of potential outcomes of the examination are set out fully in both QA7 Section 17 and Regulation 16 but in summary, the examiners can recommend to: award the degree
The outcome of the viva should normally be given informally to you immediately and by no later than 24 hours after the viva has taken place. ... For candidates submitting for PhD only, the examiners may recommend the award of MPhil (with or without minor corrections) in cases where the thesis fails to achieve the standard for the award of a PhD ...
Learn about the possible outcomes of your PhD or MPhil viva and how long you have to submit your corrections or resubmit your thesis. Find out when and how you will receive the official confirmation of the outcome by email.
A PhD is an oral examination in the form of a discussion in which PhD students present their PhD thesis and defend their research methods and outcomes to a panel of academic experts. The word 'viva' is a shortened form of the Latin term 'viva voce' which means 'live voice'.
Failed Viva - Outcomes of 26,076 Students. ... To give you an indication of the viva failure rate, we've analysed the outcomes of 26,076 PhD candidates from 14 UK universities who sat a viva between 2006 and 2017. The analysis shows that of the 26,076 students who sat their viva, 25,063 succeeded; this is just over 96% of the total students ...
interests of the candidate, UCL expects that the viva examination will be conducted in a professional and open manner. 6.5 Although there is no formal limit, typically viva examinations should last for around 2-3 hours and be a positive experience for the candidate, regardless of the examination outcome, as the examiners explore the original ideas
In general, there are six potential outcomes out of your PhD viva (at least in the UK!). Your examiners need to select one outcome from: award PhD degree without corrections - this outcome means you've impressed your examiners and you've passed your PhD degree without any corrections. This is a rare recommendations so if you do receive it ...
As a former PhD student, now lecturer, it's very rare to hear of one failing a PhD viva. The most common outcome is to grant the PhD subject to minor corrections, which will be checked off by the internal examiner. Occasionally candidates will have to make major corrections for review by the external examiner, and much more rarely, candidates ...
Examining in the PhD viva is regarded as high-stakes as examiners are expected to reach an assessment outcome of either pass or fail, with an option of re-viva in some universities. When the PhD viva is carried out properly, it drives improvement in research quality, shapes learner behaviour and identity as a researcher (Chen, 2014 ), and ...
Based on a 2016 survey of PhD students of the leading Russian universities the authors assess the scope and types of employment of postgraduates, as well as the experience of those PhD students, who balance study time with work. ... "Who Is Happy at Doctoral Programs: The Connection Between Employment and Learning Outcomes of PhD Students ...
Maria KORNEYKOVA, Principal Investigator | Cited by 288 | of Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, Moscow (rudn) | Read 75 publications | Contact Maria KORNEYKOVA
DOI: 10.17323/1814-9545-2019-1-87-108 Corpus ID: 164614365; Who is Happy at Doctoral Programs: The Connection between Employment and Learning Outcomes of PhD Students @article{Bekova2019WhoIH, title={Who is Happy at Doctoral Programs: The Connection between Employment and Learning Outcomes of PhD Students}, author={Saule Bekova and Zibeyda Dzhafarova}, journal={Voprosy obrazovaniya ...
Alexander "Sasha" Kabanov, Ph.D., Dr.Sci., is the Mescal Swaim Ferguson Distinguished Professor and director of the Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy and codirector of the Carolina Institute for Nanomedicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Prior to joining UNC-Chapel Hill in July 2012, Kabanov served for nearly eighteen ...