Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What is a Conceptual Framework and How to Make It (with Examples)

A strong conceptual framework underpins good research. A conceptual framework in research is used to understand a research problem and guide the development and analysis of the research. It serves as a roadmap to conceptualize and structure the work by providing an outline that connects different ideas, concepts, and theories within the field of study. A conceptual framework pictorially or verbally depicts presumed relationships among the study variables.
The purpose of a conceptual framework is to serve as a scheme for organizing and categorizing knowledge and thereby help researchers in developing theories and hypotheses and conducting empirical studies.
In this post, we explain what is a conceptual framework, and provide expert advice on how to make a conceptual framework, along with conceptual framework examples.
Table of Contents
What is a Conceptual Framework in Research
Definition of a conceptual framework.
A conceptual framework includes key concepts, variables, relationships, and assumptions that guide the academic inquiry. It establishes the theoretical underpinnings and provides a lens through which researchers can analyze and interpret data. A conceptual framework draws upon existing theories, models, or established bodies of knowledge to provide a structure for understanding the research problem. It defines the scope of research, identifying relevant variables, establishing research questions, and guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies and data analysis techniques.
Conceptual frameworks can be written or visual. Other types of conceptual framework representations might be taxonomic (verbal description categorizing phenomena into classes without showing relationships between classes) or mathematical descriptions (expression of phenomena in the form of mathematical equations).
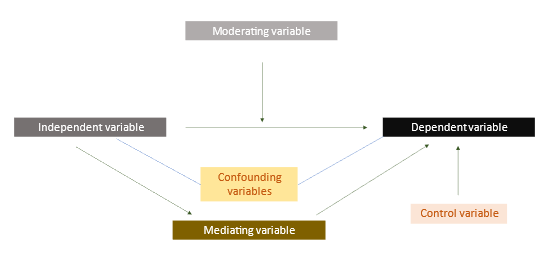
Figure 1: Definition of a conceptual framework explained diagrammatically
Conceptual Framework Origin
The term conceptual framework appears to have originated in philosophy and systems theory, being used for the first time in the 1930s by the philosopher Alfred North Whitehead. He bridged the theological, social, and physical sciences by providing a common conceptual framework. The use of the conceptual framework began early in accountancy and can be traced back to publications by William A. Paton and John B. Canning in the first quarter of the 20 th century. Thus, in the original framework, financial issues were addressed, such as useful features, basic elements, and variables needed to prepare financial statements. Nevertheless, a conceptual framework approach should be considered when starting your research journey in any field, from finance to social sciences to applied sciences.
Purpose and Importance of a Conceptual Framework in Research
The importance of a conceptual framework in research cannot be understated, irrespective of the field of study. It is important for the following reasons:
- It clarifies the context of the study.
- It justifies the study to the reader.
- It helps you check your own understanding of the problem and the need for the study.
- It illustrates the expected relationship between the variables and defines the objectives for the research.
- It helps further refine the study objectives and choose the methods appropriate to meet them.
What to Include in a Conceptual Framework
Essential elements that a conceptual framework should include are as follows:
- Overarching research question(s)
- Study parameters
- Study variables
- Potential relationships between those variables.
The sources for these elements of a conceptual framework are literature, theory, and experience or prior knowledge.
How to Make a Conceptual Framework
Now that you know the essential elements, your next question will be how to make a conceptual framework.
For this, start by identifying the most suitable set of questions that your research aims to answer. Next, categorize the various variables. Finally, perform a rigorous analysis of the collected data and compile the final results to establish connections between the variables.
In short, the steps are as follows:
- Choose appropriate research questions.
- Define the different types of variables involved.
- Determine the cause-and-effect relationships.
Be sure to make use of arrows and lines to depict the presence or absence of correlational linkages among the variables.
Developing a Conceptual Framework
Researchers should be adept at developing a conceptual framework. Here are the steps for developing a conceptual framework:
1. Identify a research question
Your research question guides your entire study, making it imperative to invest time and effort in formulating a question that aligns with your research goals and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. This step involves the following:
- Choose a broad topic of interest
- Conduct background research
- Narrow down the focus
- Define your goals
- Make it specific and answerable
- Consider significance and novelty
- Seek feedback.
2. Choose independent and dependent variables
The dependent variable is the main outcome you want to measure, explain, or predict in your study. It should be a variable that can be observed, measured, or assessed quantitatively or qualitatively. Independent variables are the factors or variables that may influence, explain, or predict changes in the dependent variable.
Choose independent and dependent variables for your study according to the research objectives, the nature of the phenomenon being studied, and the specific research design. The identification of variables is rooted in existing literature, theories, or your own observations.
3. Consider cause-and-effect relationships
To better understand and communicate the relationships between variables in your study, cause-and-effect relationships need to be visualized. This can be done by using path diagrams, cause-and-effect matrices, time series plots, scatter plots, bar charts, or heatmaps.
4. Identify other influencing variables
Besides the independent and dependent variables, researchers must understand and consider the following types of variables:
- Moderating variable: A variable that influences the strength or direction of the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable.
- Mediating variable: A variable that explains the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable and clarifies how the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
- Control variable: A variable that is kept constant or controlled to avoid the influence of other factors that may affect the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- Confounding variable: A type of unmeasured variable that is related to both the independent and dependent variables.
Example of a Conceptual Framework
Let us examine the following conceptual framework example. Let’s say your research topic is “ The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance among College Students .” Here, you want to investigate how social media usage affects academic performance in college students. Social media usage (encompassing frequency of social media use, time spent on social media platforms, and types of social media platforms used) is the independent variable, and academic performance (covering grades, exam scores, and class attendance) is the dependent variable.
This conceptual framework example also includes a mediating variable, study habits, which may explain how social media usage affects academic performance. Study habits (time spent studying, study environment, and use of study aids or resources) can act as a mechanism through which social media usage influences academic outcomes. Additionally, a moderating variable, self-discipline (level of self-control and self-regulation, ability to manage distractions, and prioritization skills), is included to examine how individual differences in self-control and discipline may influence the relationship between social media usage and academic performance.
Confounding variables are also identified (socioeconomic status, prior academic achievement), which are potential factors that may influence both social media usage and academic performance. These variables need to be considered and controlled in the study to ensure that any observed effects are specifically attributed to social media usage. A visual representation of this conceptual framework example is seen in Figure 2.
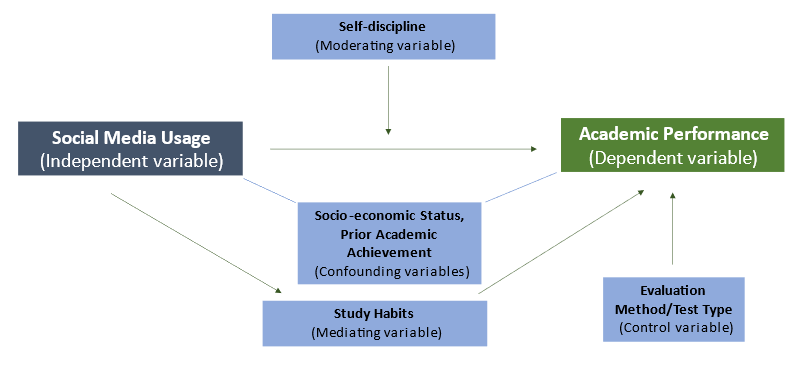
Figure 2: Visual representation of a conceptual framework for the topic “The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance among College Students”
Key Takeaways
Here is a snapshot of the basics of a conceptual framework in research:
- A conceptual framework is an idea or model representing the subject or phenomena you intend to study.
- It is primarily a researcher’s perception of the research problem. It can be used to develop hypotheses or testable research questions.
- It provides a preliminary understanding of the factors at play, their interrelationships, and the underlying reasons.
- It guides your research by aiding in the formulation of meaningful research questions, selection of appropriate methods, and identification of potential challenges to the validity of your findings.
- It provides a structure for organizing and understanding data.
- It allows you to chalk out the relationships between concepts and variables to understand them.
- Variables besides dependent and independent variables (moderating, mediating, control, and confounding variables) must be considered when developing a conceptual framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a moderating variable and a mediating variable.
Moderating and mediating variables are easily confused. A moderating variable affects the direction and strength of this relationship, whereas a mediating explains how two variables relate.
What is the difference between independent variables, dependent variables, and confounding variables?
Independent variables are the variables manipulated to affect the outcome of an experiment (e.g., the dose of a fat-loss drug administered to rats). Dependent variables are variables being measured or observed in an experiment (e.g., changes in rat body weight as a result of the drug). A confounding variable distorts or masks the effects of the variables being studied because it is associated both with dependent variable and with the independent variable. For instance, in this example, pre-existing metabolic dysfunction in some rats could interact differently with the drug being studied and also affect rat body weight.
Should I have more than one dependent or independent variable in a study?
The need for more than one dependent or independent variable in a study depends on the research question, study design, and relationships being investigated. Note the following when making this decision for your research:
- If your research question involves exploring the relationships between multiple variables or factors, it may be appropriate to have more than one dependent or independent variable.
- If you have specific hypotheses about the relationships between several variables, it may be necessary to include multiple dependent or independent variables.
- Adequate resources, sample size, and data collection methods should be considered when determining the number of dependent and independent variables to include.
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable is not the main focus of the study but can unintentionally influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Confounding variables can introduce bias and give rise to misleading conclusions. These variables must be controlled to ensure that any observed relationship is genuinely due to the independent variable.
What is a control variable?
A control variable is something not of interest to the study’s objectives but is kept constant because it could influence the outcomes. Control variables can help prevent research biases and allow for a more accurate assessment of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Examples are (i) testing all participants at the same time (e.g., in the morning) to minimize the potential effects of circadian rhythms, (ii) ensuring that instruments are calibrated consistently before each measurement to minimize the influence of measurement errors, and (iii) randomization of participants across study groups.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

Research in Shorts: R Discovery’s New Feature Helps Academics Assess Relevant Papers in 2mins

How Does R Discovery’s Interplatform Capability Enhance Research Accessibility
- Privacy Policy

Home » Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and Examples
Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and Examples
Table of Contents

Conceptual Framework
Definition:
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and understanding complex ideas, theories, or concepts. It provides a systematic and coherent way of thinking about a problem or topic, and helps to guide research or analysis in a particular field.
A conceptual framework typically includes a set of assumptions, concepts, and propositions that form a theoretical framework for understanding a particular phenomenon. It can be used to develop hypotheses, guide empirical research, or provide a framework for evaluating and interpreting data.
Conceptual Framework in Research
In research, a conceptual framework is a theoretical structure that provides a framework for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It is a key component of any research project and helps to guide the research process from start to finish.
A conceptual framework provides a clear understanding of the variables, relationships, and assumptions that underpin a research study. It outlines the key concepts that the study is investigating and how they are related to each other. It also defines the scope of the study and sets out the research questions or hypotheses.
Types of Conceptual Framework
Types of Conceptual Framework are as follows:
Theoretical Framework
A theoretical framework is an overarching set of concepts, ideas, and assumptions that help to explain and interpret a phenomenon. It provides a theoretical perspective on the phenomenon being studied and helps researchers to identify the relationships between different concepts. For example, a theoretical framework for a study on the impact of social media on mental health might draw on theories of communication, social influence, and psychological well-being.
Conceptual Model
A conceptual model is a visual or written representation of a complex system or phenomenon. It helps to identify the main components of the system and the relationships between them. For example, a conceptual model for a study on the factors that influence employee turnover might include factors such as job satisfaction, salary, work-life balance, and job security, and the relationships between them.
Empirical Framework
An empirical framework is based on empirical data and helps to explain a particular phenomenon. It involves collecting data, analyzing it, and developing a framework to explain the results. For example, an empirical framework for a study on the impact of a new health intervention might involve collecting data on the intervention’s effectiveness, cost, and acceptability to patients.
Descriptive Framework
A descriptive framework is used to describe a particular phenomenon. It helps to identify the main characteristics of the phenomenon and to develop a vocabulary to describe it. For example, a descriptive framework for a study on different types of musical genres might include descriptions of the instruments used, the rhythms and beats, the vocal styles, and the cultural contexts of each genre.
Analytical Framework
An analytical framework is used to analyze a particular phenomenon. It involves breaking down the phenomenon into its constituent parts and analyzing them separately. This type of framework is often used in social science research. For example, an analytical framework for a study on the impact of race on police brutality might involve analyzing the historical and cultural factors that contribute to racial bias, the organizational factors that influence police behavior, and the psychological factors that influence individual officers’ behavior.
Conceptual Framework for Policy Analysis
A conceptual framework for policy analysis is used to guide the development of policies or programs. It helps policymakers to identify the key issues and to develop strategies to address them. For example, a conceptual framework for a policy analysis on climate change might involve identifying the key stakeholders, assessing their interests and concerns, and developing policy options to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Logical Frameworks
Logical frameworks are used to plan and evaluate projects and programs. They provide a structured approach to identifying project goals, objectives, and outcomes, and help to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Conceptual Frameworks for Program Evaluation
These frameworks are used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions. They provide a structure for identifying program goals, objectives, and outcomes, and help to measure the impact of the program on its intended beneficiaries.
Conceptual Frameworks for Organizational Analysis
These frameworks are used to analyze and evaluate organizational structures, processes, and performance. They provide a structured approach to understanding the relationships between different departments, functions, and stakeholders within an organization.
Conceptual Frameworks for Strategic Planning
These frameworks are used to develop and implement strategic plans for organizations or businesses. They help to identify the key factors and stakeholders that will impact the success of the plan, and provide a structure for setting goals, developing strategies, and monitoring progress.
Components of Conceptual Framework
The components of a conceptual framework typically include:
- Research question or problem statement : This component defines the problem or question that the conceptual framework seeks to address. It sets the stage for the development of the framework and guides the selection of the relevant concepts and constructs.
- Concepts : These are the general ideas, principles, or categories that are used to describe and explain the phenomenon or problem under investigation. Concepts provide the building blocks of the framework and help to establish a common language for discussing the issue.
- Constructs : Constructs are the specific variables or concepts that are used to operationalize the general concepts. They are measurable or observable and serve as indicators of the underlying concept.
- Propositions or hypotheses : These are statements that describe the relationships between the concepts or constructs in the framework. They provide a basis for testing the validity of the framework and for generating new insights or theories.
- Assumptions : These are the underlying beliefs or values that shape the framework. They may be explicit or implicit and may influence the selection and interpretation of the concepts and constructs.
- Boundaries : These are the limits or scope of the framework. They define the focus of the investigation and help to clarify what is included and excluded from the analysis.
- Context : This component refers to the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape the phenomenon or problem under investigation. It helps to situate the framework within a larger theoretical or empirical context and to identify the relevant variables and factors that may affect the phenomenon.
- Relationships and connections: These are the connections and interrelationships between the different components of the conceptual framework. They describe how the concepts and constructs are linked and how they contribute to the overall understanding of the phenomenon or problem.
- Variables : These are the factors that are being measured or observed in the study. They are often operationalized as constructs and are used to test the propositions or hypotheses.
- Methodology : This component describes the research methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes the sampling strategy, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and ethical considerations.
- Literature review : This component provides an overview of the existing research and theories related to the phenomenon or problem under investigation. It helps to identify the gaps in the literature and to situate the framework within the broader theoretical and empirical context.
- Outcomes and implications: These are the expected outcomes or implications of the study. They describe the potential contributions of the study to the theoretical and empirical knowledge in the field and the practical implications for policy and practice.
Conceptual Framework Methodology
Conceptual Framework Methodology is a research method that is commonly used in academic and scientific research to develop a theoretical framework for a study. It is a systematic approach that helps researchers to organize their thoughts and ideas, identify the variables that are relevant to their study, and establish the relationships between these variables.
Here are the steps involved in the conceptual framework methodology:
Identify the Research Problem
The first step is to identify the research problem or question that the study aims to answer. This involves identifying the gaps in the existing literature and determining what specific issue the study aims to address.
Conduct a Literature Review
The second step involves conducting a thorough literature review to identify the existing theories, models, and frameworks that are relevant to the research question. This will help the researcher to identify the key concepts and variables that need to be considered in the study.
Define key Concepts and Variables
The next step is to define the key concepts and variables that are relevant to the study. This involves clearly defining the terms used in the study, and identifying the factors that will be measured or observed in the study.
Develop a Theoretical Framework
Once the key concepts and variables have been identified, the researcher can develop a theoretical framework. This involves establishing the relationships between the key concepts and variables, and creating a visual representation of these relationships.
Test the Framework
The final step is to test the theoretical framework using empirical data. This involves collecting and analyzing data to determine whether the relationships between the key concepts and variables that were identified in the framework are accurate and valid.
Examples of Conceptual Framework
Some realtime Examples of Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- In economics , the concept of supply and demand is a well-known conceptual framework. It provides a structure for understanding how prices are set in a market, based on the interplay of the quantity of goods supplied by producers and the quantity of goods demanded by consumers.
- In psychology , the cognitive-behavioral framework is a widely used conceptual framework for understanding mental health and illness. It emphasizes the role of thoughts and behaviors in shaping emotions and the importance of cognitive restructuring and behavior change in treatment.
- In sociology , the social determinants of health framework provides a way of understanding how social and economic factors such as income, education, and race influence health outcomes. This framework is widely used in public health research and policy.
- In environmental science , the ecosystem services framework is a way of understanding the benefits that humans derive from natural ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination, and carbon storage. This framework is used to guide conservation and land-use decisions.
- In education, the constructivist framework is a way of understanding how learners construct knowledge through active engagement with their environment. This framework is used to guide instructional design and teaching strategies.
Applications of Conceptual Framework
Some of the applications of Conceptual Frameworks are as follows:
- Research : Conceptual frameworks are used in research to guide the design, implementation, and interpretation of studies. Researchers use conceptual frameworks to develop hypotheses, identify research questions, and select appropriate methods for collecting and analyzing data.
- Policy: Conceptual frameworks are used in policy-making to guide the development of policies and programs. Policymakers use conceptual frameworks to identify key factors that influence a particular problem or issue, and to develop strategies for addressing them.
- Education : Conceptual frameworks are used in education to guide the design and implementation of instructional strategies and curriculum. Educators use conceptual frameworks to identify learning objectives, select appropriate teaching methods, and assess student learning.
- Management : Conceptual frameworks are used in management to guide decision-making and strategy development. Managers use conceptual frameworks to understand the internal and external factors that influence their organizations, and to develop strategies for achieving their goals.
- Evaluation : Conceptual frameworks are used in evaluation to guide the development of evaluation plans and to interpret evaluation results. Evaluators use conceptual frameworks to identify key outcomes, indicators, and measures, and to develop a logic model for their evaluation.
Purpose of Conceptual Framework
The purpose of a conceptual framework is to provide a theoretical foundation for understanding and analyzing complex phenomena. Conceptual frameworks help to:
- Guide research : Conceptual frameworks provide a framework for researchers to develop hypotheses, identify research questions, and select appropriate methods for collecting and analyzing data. By providing a theoretical foundation for research, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that research is rigorous, systematic, and valid.
- Provide clarity: Conceptual frameworks help to provide clarity and structure to complex phenomena by identifying key concepts, relationships, and processes. By providing a clear and systematic understanding of a phenomenon, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that researchers, policymakers, and practitioners are all on the same page when it comes to understanding the issue at hand.
- Inform decision-making : Conceptual frameworks can be used to inform decision-making and strategy development by identifying key factors that influence a particular problem or issue. By understanding the complex interplay of factors that contribute to a particular issue, decision-makers can develop more effective strategies for addressing the problem.
- Facilitate communication : Conceptual frameworks provide a common language and conceptual framework for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners to communicate and collaborate on complex issues. By providing a shared understanding of a phenomenon, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal.
When to use Conceptual Framework
There are several situations when it is appropriate to use a conceptual framework:
- To guide the research : A conceptual framework can be used to guide the research process by providing a clear roadmap for the research project. It can help researchers identify key variables and relationships, and develop hypotheses or research questions.
- To clarify concepts : A conceptual framework can be used to clarify and define key concepts and terms used in a research project. It can help ensure that all researchers are using the same language and have a shared understanding of the concepts being studied.
- To provide a theoretical basis: A conceptual framework can provide a theoretical basis for a research project by linking it to existing theories or conceptual models. This can help researchers build on previous research and contribute to the development of a field.
- To identify gaps in knowledge : A conceptual framework can help identify gaps in existing knowledge by highlighting areas that require further research or investigation.
- To communicate findings : A conceptual framework can be used to communicate research findings by providing a clear and concise summary of the key variables, relationships, and assumptions that underpin the research project.
Characteristics of Conceptual Framework
key characteristics of a conceptual framework are:
- Clear definition of key concepts : A conceptual framework should clearly define the key concepts and terms being used in a research project. This ensures that all researchers have a shared understanding of the concepts being studied.
- Identification of key variables: A conceptual framework should identify the key variables that are being studied and how they are related to each other. This helps to organize the research project and provides a clear focus for the study.
- Logical structure: A conceptual framework should have a logical structure that connects the key concepts and variables being studied. This helps to ensure that the research project is coherent and consistent.
- Based on existing theory : A conceptual framework should be based on existing theory or conceptual models. This helps to ensure that the research project is grounded in existing knowledge and builds on previous research.
- Testable hypotheses or research questions: A conceptual framework should include testable hypotheses or research questions that can be answered through empirical research. This helps to ensure that the research project is rigorous and scientifically valid.
- Flexibility : A conceptual framework should be flexible enough to allow for modifications as new information is gathered during the research process. This helps to ensure that the research project is responsive to new findings and is able to adapt to changing circumstances.
Advantages of Conceptual Framework
Advantages of the Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- Clarity : A conceptual framework provides clarity to researchers by outlining the key concepts and variables that are relevant to the research project. This clarity helps researchers to focus on the most important aspects of the research problem and develop a clear plan for investigating it.
- Direction : A conceptual framework provides direction to researchers by helping them to develop hypotheses or research questions that are grounded in existing theory or conceptual models. This direction ensures that the research project is relevant and contributes to the development of the field.
- Efficiency : A conceptual framework can increase efficiency in the research process by providing a structure for organizing ideas and data. This structure can help researchers to avoid redundancies and inconsistencies in their work, saving time and effort.
- Rigor : A conceptual framework can help to ensure the rigor of a research project by providing a theoretical basis for the investigation. This rigor is essential for ensuring that the research project is scientifically valid and produces meaningful results.
- Communication : A conceptual framework can facilitate communication between researchers by providing a shared language and understanding of the key concepts and variables being studied. This communication is essential for collaboration and the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Generalization : A conceptual framework can help to generalize research findings beyond the specific study by providing a theoretical basis for the investigation. This generalization is essential for the development of knowledge in the field and for informing future research.
Limitations of Conceptual Framework
Limitations of Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- Limited applicability: Conceptual frameworks are often based on existing theory or conceptual models, which may not be applicable to all research problems or contexts. This can limit the usefulness of a conceptual framework in certain situations.
- Lack of empirical support : While a conceptual framework can provide a theoretical basis for a research project, it may not be supported by empirical evidence. This can limit the usefulness of a conceptual framework in guiding empirical research.
- Narrow focus: A conceptual framework can provide a clear focus for a research project, but it may also limit the scope of the investigation. This can make it difficult to address broader research questions or to consider alternative perspectives.
- Over-simplification: A conceptual framework can help to organize and structure research ideas, but it may also over-simplify complex phenomena. This can limit the depth of the investigation and the richness of the data collected.
- Inflexibility : A conceptual framework can provide a structure for organizing research ideas, but it may also be inflexible in the face of new data or unexpected findings. This can limit the ability of researchers to adapt their research project to new information or changing circumstances.
- Difficulty in development : Developing a conceptual framework can be a challenging and time-consuming process. It requires a thorough understanding of existing theory or conceptual models, and may require collaboration with other researchers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Appendix in Research Paper – Examples and...

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Theoretical Framework
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounded assumptions or predictions of behavior. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that summarizes concepts, ideas, and theories derived from prior research studies and which was synthesized in order to form a conceptual basis for your analysis and interpretation of meaning found within your research.
Abend, Gabriel. "The Meaning of Theory." Sociological Theory 26 (June 2008): 173–199; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (December 2018): 44-53; Swanson, Richard A. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines . San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers 2013; Varpio, Lara, Elise Paradis, Sebastian Uijtdehaage, and Meredith Young. "The Distinctions between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework." Academic Medicine 95 (July 2020): 989-994.
Importance of Theory and a Theoretical Framework
Theories can be unfamiliar to the beginning researcher because they are rarely applied in high school social studies curriculum and, as a result, can come across as unfamiliar and imprecise when first introduced as part of a writing assignment. However, in their most simplified form, a theory is simply a set of assumptions or predictions about something you think will happen based on existing evidence and that can be tested to see if those outcomes turn out to be true. Of course, it is slightly more deliberate than that, therefore, summarized from Kivunja (2018, p. 46), here are the essential characteristics of a theory.
- It is logical and coherent
- It has clear definitions of terms or variables, and has boundary conditions [i.e., it is not an open-ended statement]
- It has a domain where it applies
- It has clearly described relationships among variables
- It describes, explains, and makes specific predictions
- It comprises of concepts, themes, principles, and constructs
- It must have been based on empirical data [i.e., it is not a guess]
- It must have made claims that are subject to testing, been tested and verified
- It must be clear and concise
- Its assertions or predictions must be different and better than those in existing theories
- Its predictions must be general enough to be applicable to and understood within multiple contexts
- Its assertions or predictions are relevant, and if applied as predicted, will result in the predicted outcome
- The assertions and predictions are not immutable, but subject to revision and improvement as researchers use the theory to make sense of phenomena
- Its concepts and principles explain what is going on and why
- Its concepts and principles are substantive enough to enable us to predict a future
Given these characteristics, a theory can best be understood as the foundation from which you investigate assumptions or predictions derived from previous studies about the research problem, but in a way that leads to new knowledge and understanding as well as, in some cases, discovering how to improve the relevance of the theory itself or to argue that the theory is outdated and a new theory needs to be formulated based on new evidence.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
- The theoretical framework adds context around the theory itself based on how scholars had previously tested the theory in relation their overall research design [i.e., purpose of the study, methods of collecting data or information, methods of analysis, the time frame in which information is collected, study setting, and the methodological strategy used to conduct the research].
By virtue of its applicative nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges associated with a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Corvellec, Hervé, ed. What is Theory?: Answers from the Social and Cultural Sciences . Stockholm: Copenhagen Business School Press, 2013; Asher, Herbert B. Theory-Building and Data Analysis in the Social Sciences . Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1984; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (2018): 44-53; Omodan, Bunmi Isaiah. "A Model for Selecting Theoretical Framework through Epistemology of Research Paradigms." African Journal of Inter/Multidisciplinary Studies 4 (2022): 275-285; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Jarvis, Peter. The Practitioner-Researcher. Developing Theory from Practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1999.
Strategies for Developing the Theoretical Framework
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research problem. Identify the assumptions from which the author(s) addressed the problem.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
Structure and Writing Style
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, your work is expected to test the validity of that existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism Theory, which categorizes perceived differences among nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism Theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the disputed split between southern and northern Sudan that led to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Based upon the above example, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as an answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [i.e., justify the application of your choice of a particular theory and explain why alternative constructs were rejected. I could choose instead to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among ethnic conflict theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
Just as a research problem in your paper requires contextualization and background information, a theory requires a framework for understanding its application to the topic being investigated. When writing and revising this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks, concepts, models, or theories . As noted in the example above, there will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the theory you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory. Although the past tense can be used to describe the history of a theory or the role of key theorists, the construction of your theoretical framework is happening now.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory inadequately explains a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. "A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research." Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Weick, Karl E. “The Work of Theorizing.” In Theorizing in Social Science: The Context of Discovery . Richard Swedberg, editor. (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2014), pp. 177-194.
Writing Tip
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Other Disciplines
An increasingly important trend in the social and behavioral sciences is to think about and attempt to understand research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories developed within your particular discipline, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbents in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be more engaged in the research topic.
CohenMiller, A. S. and P. Elizabeth Pate. "A Model for Developing Interdisciplinary Research Theoretical Frameworks." The Qualitative Researcher 24 (2019): 1211-1226; Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Undertheorize!
Do not leave the theory hanging out there in the introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you describe should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the review of pertinent literature and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose supports analysis of the research problem or, if appropriate, how the theoretical framework was found to be inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.
Yet Another Writing Tip
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in newspapers and popular magazines and in non-academic settings. However, the difference between theory and hypothesis in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested assumptions that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory; critical race theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among a set of scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis. About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis. Slideshare presentation.
Still Yet Another Writing Tip
Be Prepared to Challenge the Validity of an Existing Theory
Theories are meant to be tested and their underlying assumptions challenged; they are not rigid or intransigent, but are meant to set forth general principles for explaining phenomena or predicting outcomes. Given this, testing theoretical assumptions is an important way that knowledge in any discipline develops and grows. If you're asked to apply an existing theory to a research problem, the analysis will likely include the expectation by your professor that you should offer modifications to the theory based on your research findings.
Indications that theoretical assumptions may need to be modified can include the following:
- Your findings suggest that the theory does not explain or account for current conditions or circumstances or the passage of time,
- The study reveals a finding that is incompatible with what the theory attempts to explain or predict, or
- Your analysis reveals that the theory overly generalizes behaviors or actions without taking into consideration specific factors revealed from your analysis [e.g., factors related to culture, nationality, history, gender, ethnicity, age, geographic location, legal norms or customs , religion, social class, socioeconomic status, etc.].
Philipsen, Kristian. "Theory Building: Using Abductive Search Strategies." In Collaborative Research Design: Working with Business for Meaningful Findings . Per Vagn Freytag and Louise Young, editors. (Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018), pp. 45-71; Shepherd, Dean A. and Roy Suddaby. "Theory Building: A Review and Integration." Journal of Management 43 (2017): 59-86.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 4, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George.
Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review .
A strong theoretical framework gives your research direction. It allows you to convincingly interpret, explain, and generalize from your findings and show the relevance of your thesis or dissertation topic in your field.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Sample problem statement and research questions, sample theoretical framework, your theoretical framework, other interesting articles.
Your theoretical framework is based on:
- Your problem statement
- Your research questions
- Your literature review
A new boutique downtown is struggling with the fact that many of their online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases. This is a big issue for the otherwise fast-growing store.Management wants to increase customer loyalty. They believe that improved customer satisfaction will play a major role in achieving their goal of increased return customers.
To investigate this problem, you have zeroed in on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
- Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
- Research question : How can the satisfaction of the boutique’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
The concepts of “customer loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” are clearly central to this study, along with their relationship to the likelihood that a customer will return. Your theoretical framework should define these concepts and discuss theories about the relationship between these variables.
Some sub-questions could include:
- What is the relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction?
- How satisfied and loyal are the boutique’s online customers currently?
- What factors affect the satisfaction and loyalty of the boutique’s online customers?
As the concepts of “loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” play a major role in the investigation and will later be measured, they are essential concepts to define within your theoretical framework .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Below is a simplified example showing how you can describe and compare theories in your thesis or dissertation . In this example, we focus on the concept of customer satisfaction introduced above.
Customer satisfaction
Thomassen (2003, p. 69) defines customer satisfaction as “the perception of the customer as a result of consciously or unconsciously comparing their experiences with their expectations.” Kotler & Keller (2008, p. 80) build on this definition, stating that customer satisfaction is determined by “the degree to which someone is happy or disappointed with the observed performance of a product in relation to his or her expectations.”
Performance that is below expectations leads to a dissatisfied customer, while performance that satisfies expectations produces satisfied customers (Kotler & Keller, 2003, p. 80).
The definition of Zeithaml and Bitner (2003, p. 86) is slightly different from that of Thomassen. They posit that “satisfaction is the consumer fulfillment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product of service itself, provides a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfillment.” Zeithaml and Bitner’s emphasis is thus on obtaining a certain satisfaction in relation to purchasing.
Thomassen’s definition is the most relevant to the aims of this study, given the emphasis it places on unconscious perception. Although Zeithaml and Bitner, like Thomassen, say that customer satisfaction is a reaction to the experience gained, there is no distinction between conscious and unconscious comparisons in their definition.
The boutique claims in its mission statement that it wants to sell not only a product, but also a feeling. As a result, unconscious comparison will play an important role in the satisfaction of its customers. Thomassen’s definition is therefore more relevant.
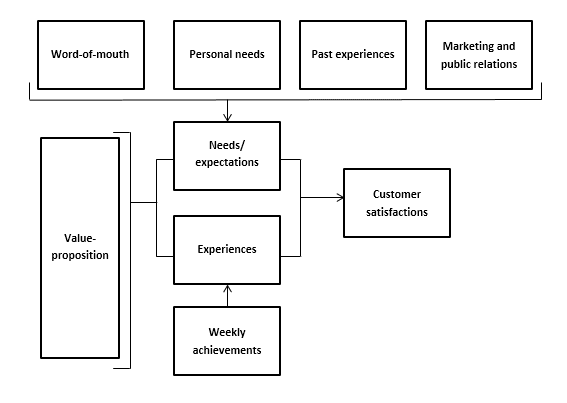
Thomassen’s Customer Satisfaction Model
According to Thomassen, both the so-called “value proposition” and other influences have an impact on final customer satisfaction. In his satisfaction model (Fig. 1), Thomassen shows that word-of-mouth, personal needs, past experiences, and marketing and public relations determine customers’ needs and expectations.
These factors are compared to their experiences, with the interplay between expectations and experiences determining a customer’s satisfaction level. Thomassen’s model is important for this study as it allows us to determine both the extent to which the boutique’s customers are satisfied, as well as where improvements can be made.
Figure 1 Customer satisfaction creation
Of course, you could analyze the concepts more thoroughly and compare additional definitions to each other. You could also discuss the theories and ideas of key authors in greater detail and provide several models to illustrate different concepts.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Vinz, S. (2023, July 18). Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Scribbr. Retrieved September 6, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework-example/
Is this article helpful?
Sarah's academic background includes a Master of Arts in English, a Master of International Affairs degree, and a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science. She loves the challenge of finding the perfect formulation or wording and derives much satisfaction from helping students take their academic writing up a notch.
Other students also liked
What is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Use a Conceptual Framework for Better Research
A conceptual framework in research is not just a tool but a vital roadmap that guides the entire research process. It integrates various theories, assumptions, and beliefs to provide a structured approach to research. By defining a conceptual framework, researchers can focus their inquiries and clarify their hypotheses, leading to more effective and meaningful research outcomes.
What is a Conceptual Framework?
A conceptual framework is essentially an analytical tool that combines concepts and sets them within an appropriate theoretical structure. It serves as a lens through which researchers view the complexities of the real world. The importance of a conceptual framework lies in its ability to serve as a guide, helping researchers to not only visualize but also systematically approach their study.
Key Components and to be Analyzed During Research
- Theories: These are the underlying principles that guide the hypotheses and assumptions of the research.
- Assumptions: These are the accepted truths that are not tested within the scope of the research but are essential for framing the study.
- Beliefs: These often reflect the subjective viewpoints that may influence the interpretation of data.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Together, these components help to define the conceptual framework that directs the research towards its ultimate goal. This structured approach not only improves clarity but also enhances the validity and reliability of the research outcomes. By using a conceptual framework, researchers can avoid common pitfalls and focus on essential variables and relationships.
For practical examples and to see how different frameworks can be applied in various research scenarios, you can Explore Conceptual Framework Examples .
Different Types of Conceptual Frameworks Used in Research
Understanding the various types of conceptual frameworks is crucial for researchers aiming to align their studies with the most effective structure. Conceptual frameworks in research vary primarily between theoretical and operational frameworks, each serving distinct purposes and suiting different research methodologies.
Theoretical vs Operational Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks are built upon existing theories and literature, providing a broad and abstract understanding of the research topic. They help in forming the basis of the study by linking the research to already established scholarly works. On the other hand, operational frameworks are more practical, focusing on how the study’s theories will be tested through specific procedures and variables.
- Theoretical frameworks are ideal for exploratory studies and can help in understanding complex phenomena.
- Operational frameworks suit studies requiring precise measurement and data analysis.
Choosing the Right Framework
Selecting the appropriate conceptual framework is pivotal for the success of a research project. It involves matching the research questions with the framework that best addresses the methodological needs of the study. For instance, a theoretical framework might be chosen for studies that aim to generate new theories, while an operational framework would be better suited for testing specific hypotheses.
Benefits of choosing the right framework include enhanced clarity, better alignment with research goals, and improved validity of research outcomes. Tools like Table Chart Maker can be instrumental in visually comparing the strengths and weaknesses of different frameworks, aiding in this crucial decision-making process.
Real-World Examples of Conceptual Frameworks in Research
Understanding the practical application of conceptual frameworks in research can significantly enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your studies. Here, we explore several real-world case studies that demonstrate the pivotal role of conceptual frameworks in achieving robust research conclusions.
- Healthcare Research: In a study examining the impact of lifestyle choices on chronic diseases, researchers used a conceptual framework to link dietary habits, exercise, and genetic predispositions. This framework helped in identifying key variables and their interrelations, leading to more targeted interventions.
- Educational Development: Educational theorists often employ conceptual frameworks to explore the dynamics between teaching methods and student learning outcomes. One notable study mapped out the influences of digital tools on learning engagement, providing insights that shaped educational policies.
- Environmental Policy: Conceptual frameworks have been crucial in environmental research, particularly in studies on climate change adaptation. By framing the relationships between human activity, ecological changes, and policy responses, researchers have been able to propose more effective sustainability strategies.
Adapting conceptual frameworks based on evolving research data is also critical. As new information becomes available, it’s essential to revisit and adjust the framework to maintain its relevance and accuracy, ensuring that the research remains aligned with real-world conditions.
For those looking to visualize and better comprehend their research frameworks, Graphic Organizers for Conceptual Frameworks can be an invaluable tool. These organizers help in structuring and presenting research findings clearly, enhancing both the process and the presentation of your research.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your Own Conceptual Framework
Creating a conceptual framework is a critical step in structuring your research to ensure clarity and focus. This guide will walk you through the process of building a robust framework, from identifying key concepts to refining your approach as your research evolves.
Building Blocks of a Conceptual Framework
- Identify and Define Main Concepts and Variables: Start by clearly identifying the main concepts, variables, and their relationships that will form the basis of your research. This could include defining key terms and establishing the scope of your study.
- Develop a Hypothesis or Primary Research Question: Formulate a central hypothesis or question that guides the direction of your research. This will serve as the foundation upon which your conceptual framework is built.
- Link Theories and Concepts Logically: Connect your identified concepts and variables with existing theories to create a coherent structure. This logical linking helps in forming a strong theoretical base for your research.
Visualizing and Refining Your Framework
Using visual tools can significantly enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your conceptual framework. Decision Tree Templates for Conceptual Frameworks can be particularly useful in mapping out the relationships between variables and hypotheses.
Map Your Framework: Utilize tools like Creately’s visual canvas to diagram your framework. This visual representation helps in identifying gaps or overlaps in your framework and provides a clear overview of your research structure.
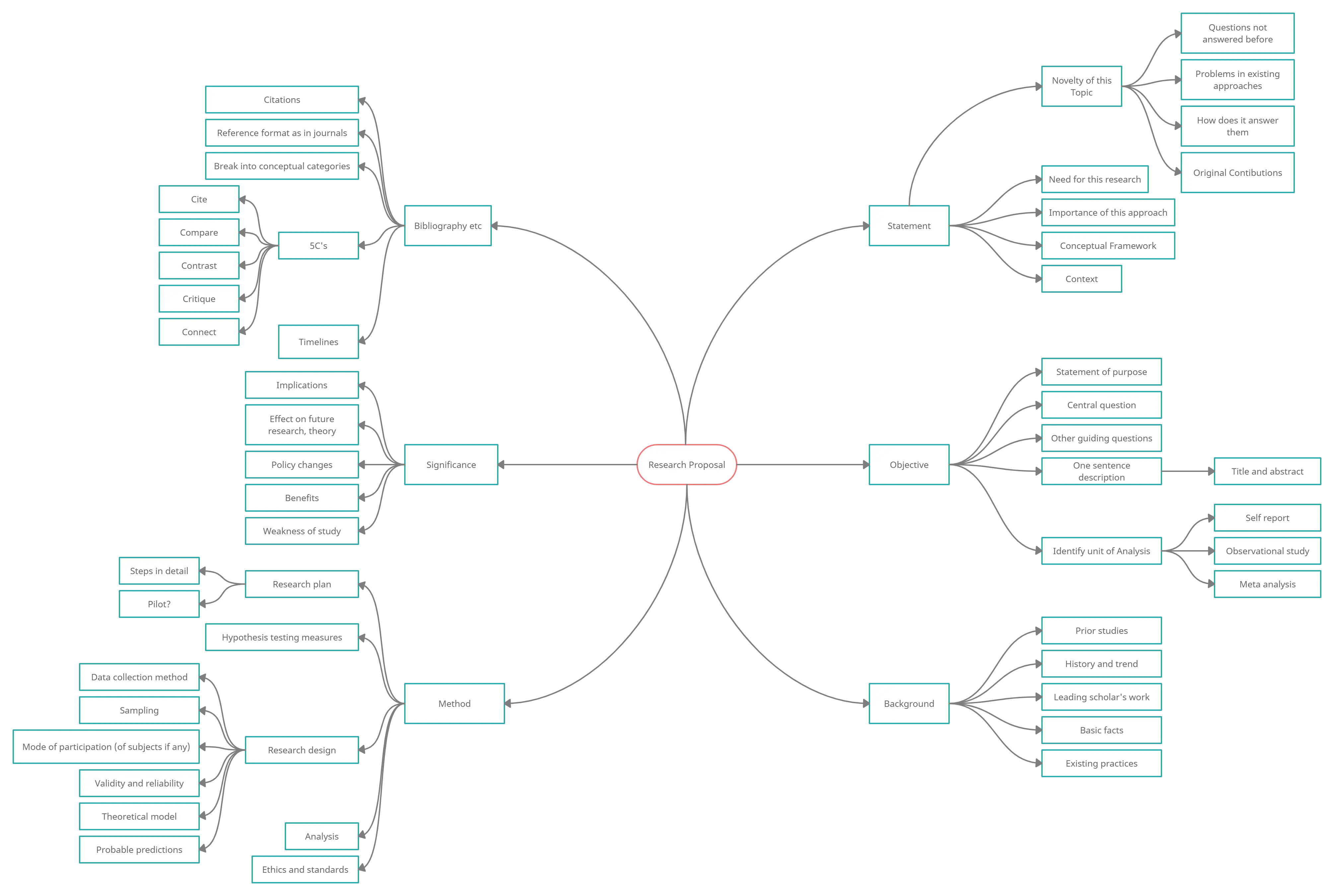
Analyze and Refine: As your research progresses, continuously evaluate and refine your framework. Adjustments may be necessary as new data comes to light or as initial assumptions are challenged.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your conceptual framework is not only well-defined but also adaptable to the changing dynamics of your research.
Practical Tips for Utilizing Conceptual Frameworks in Research
Effectively utilizing a conceptual framework in research not only streamlines the process but also enhances the clarity and coherence of your findings. Here are some practical tips to maximize the use of conceptual frameworks in your research endeavors.
- Setting Clear Research Goals: Begin by defining precise objectives that are aligned with your research questions. This clarity will guide your entire research process, ensuring that every step you take is purposeful and directly contributes to your overall study aims. \
- Maintaining Focus and Coherence: Throughout the research, consistently refer back to your conceptual framework to maintain focus. This will help in keeping your research aligned with the initial goals and prevent deviations that could dilute the effectiveness of your findings.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Use your conceptual framework as a lens through which to view and interpret data. This approach ensures that the data analysis is not only systematic but also meaningful in the context of your research objectives. For more insights, explore Research Data Analysis Methods .
- Presenting Research Findings: When it comes time to present your findings, structure your presentation around the conceptual framework . This will help your audience understand the logical flow of your research and how each part contributes to the whole.
- Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Be vigilant about common errors such as overcomplicating the framework or misaligning the research methods with the framework’s structure. Keeping it simple and aligned ensures that the framework effectively supports your research.
By adhering to these tips and utilizing tools like 7 Essential Visual Tools for Social Work Assessment , researchers can ensure that their conceptual frameworks are not only robust but also practically applicable in their studies.
How Creately Enhances the Creation and Use of Conceptual Frameworks
Creating a robust conceptual framework is pivotal for effective research, and Creately’s suite of visual tools offers unparalleled support in this endeavor. By leveraging Creately’s features, researchers can visualize, organize, and analyze their research frameworks more efficiently.
- Visual Mapping of Research Plans: Creately’s infinite visual canvas allows researchers to map out their entire research plan visually. This helps in understanding the complex relationships between different research variables and theories, enhancing the clarity and effectiveness of the research process.
- Brainstorming with Mind Maps: Using Mind Mapping Software , researchers can generate and organize ideas dynamically. Creately’s intelligent formatting helps in brainstorming sessions, making it easier to explore multiple topics or delve deeply into specific concepts.
- Centralized Data Management: Creately enables the importation of data from multiple sources, which can be integrated into the visual research framework. This centralization aids in maintaining a cohesive and comprehensive overview of all research elements, ensuring that no critical information is overlooked.
- Communication and Collaboration: The platform supports real-time collaboration, allowing teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location. This feature is crucial for research teams spread across different geographies, facilitating effective communication and iterative feedback throughout the research process.
Moreover, the ability t Explore Conceptual Framework Examples directly within Creately inspires researchers by providing practical templates and examples that can be customized to suit specific research needs. This not only saves time but also enhances the quality of the conceptual framework developed.
In conclusion, Creately’s tools for creating and managing conceptual frameworks are indispensable for researchers aiming to achieve clear, structured, and impactful research outcomes.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Patient Cent Res Rev
- v.11(1); Spring 2024
- PMC11000705

Research Frameworks: Critical Components for Reporting Qualitative Health Care Research
Qualitative health care research can provide insights into health care practices that quantitative studies cannot. However, the potential of qualitative research to improve health care is undermined by reporting that does not explain or justify the research questions and design. The vital role of research frameworks for designing and conducting quality research is widely accepted, but despite many articles and books on the topic, confusion persists about what constitutes an adequate underpinning framework, what to call it, and how to use one. This editorial clarifies some of the terminology and reinforces why research frameworks are essential for good-quality reporting of all research, especially qualitative research.
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes – for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have. 1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and citation rates of qualitative research than those of contemporaneous quantitative research. 2 The Greenhalgh et al. article was subsequently supported by an open letter from 76 senior academics spanning 11 countries to the editors of the British Medical Journal . 3 Despite greater recognition and acceptance, qualitative research continues to have an “uneasy relationship with theory,” 4 which contributes to poor reporting.
As an editor for the Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Reviews , as well as Human Resources for Health , I have seen several exemplary qualitative articles with clear and coherent reporting. On the other hand, I have often been concerned by a lack of rigorous reporting, which may reflect and reinforce the outdated perception of qualitative research as the “soft option.” 5 Qualitative research is more than conducting a few semi-structured interviews, transcribing the audio recordings verbatim, coding the transcripts, and developing and reporting themes, including a few quotes. Qualitative research that benefits health care is time-consuming and labor-intensive, requires robust design, and is rooted in theory, along with comprehensive reporting. 6
What Is “Theory”?
So fundamental is theory to qualitative research that I initially toyed with titling this editorial, “ Theory: the missing link in qualitative health care research articles ,” before deeming that focus too broad. As far back as 1967, Merton 6 warned that “the word theory threatens to become meaningless.” While it cannot be overstated that “atheoretical” studies lack the underlying logic that justifies researchers’ design choices, the word theory is so overused that it is difficult to understand what constitutes an adequate theoretical foundation and what to call it.
Theory, as used in the term theoretical foundation , refers to the existing body of knowledge. 7 , 8 The existing body of knowledge consists of more than formal theories , with their explanatory and predictive characteristics, so theory implies more than just theories . Box 1 9 – 12 defines the “building blocks of formal theories.” 9 Theorizing or theory-building starts with concepts at the most concrete, experiential level, becoming progressively more abstract until a higher-level theory is developed that explains the relationships between the building blocks. 9 Grand theories are broad, representing the most abstract level of theorizing. Middle-range and explanatory theories are progressively less abstract, more specific to particular phenomena or cases (middle-range) or variables (explanatory), and testable.
The Building Blocks of Formal Theories 9
| words we assign to mental representations of events or phenomena , | |
| higher-order clusters of concepts | |
| expressions of relationships among several constructs | |
| “sets of interrelated constructs, definitions, and propositions that present a systematic view of phenomena by specifying relations among variables and phenomena” general sets “of principles that are independent of the specific case, situation, phenomenon or observation to be explained” |
The Importance of Research Frameworks
Researchers may draw on several elements to frame their research. Generally, a framework is regarded as “a set of ideas that you use when you are forming your decisions and judgements” 13 or “a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is used to plan or decide something.” 14 Research frameworks may consist of a single formal theory or part thereof, any combination of several theories or relevant constructs from different theories, models (as simplified representations of formal theories), concepts from the literature and researchers’ experiences.
Although Merriam 15 was of the view that every study has a framework, whether explicit or not, there are advantages to using an explicit framework. Research frameworks map “the territory being investigated,” 8 thus helping researchers to be explicit about what informed their research design, from developing research questions and choosing appropriate methods to data analysis and interpretation. Using a framework makes research findings more meaningful 12 and promotes generalizability by situating the study and interpreting data in more general terms than the study itself. 16
Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks
The variation in how the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks are used may be confusing. Some researchers refer to only theoretical frameworks 17 , 18 or conceptual frameworks, 19 – 21 while others use the terms interchangeably. 7 Other researchers distinguish between the two. For example, Miles, Huberman & Saldana 8 see theoretical frameworks as based on formal theories and conceptual frameworks derived inductively from locally relevant concepts and variables, although they may include theoretical aspects. Conversely, some researchers believe that theoretical frameworks include formal theories and concepts. 18 Others argue that any differences between the two types of frameworks are semantic and, instead, emphasize using a research framework to provide coherence across the research questions, methods and interpretation of the results, irrespective of what that framework is called.
Like Ravitch and Riggan, 22 I regard conceptual frameworks (CFs) as the broader term. Including researchers’ perspectives and experiences in CFs provides valuable sources of originality. Novel perspectives guard against research repeating what has already been stated. 23 The term theoretical framework (TF) may be appropriate where formal published and identifiable theories or parts of such theories are used. 24 However, existing formal theories alone may not provide the current state of relevant concepts essential to understanding the motivation for and logic underlying a study. Some researchers may argue that relevant concepts may be covered in the literature review, but what is the point of literature reviews and prior findings unless authors connect them to the research questions and design? Indeed, Sutton & Straw 25 exclude literature reviews and lists of prior findings as an adequate foundation for a study, along with individual lists of variables or constructs (even when the constructs are defined), predictions or hypotheses, and diagrams that do not propose relationships. One or more of these aspects could be used in a research framework (eg, in a TF), and the literature review could (and should) focus on the theories or parts of theories (constructs), offer some critique of the theory and point out how they intend to use the theory. This would be more meaningful than merely describing the theory as the “background” to the study, without explicitly stating why and how it is being used. Similarly, a CF may include a discussion of the theories being used (basically, a TF) and a literature review of the current understanding of any relevant concepts that are not regarded as formal theory.
It may be helpful for authors to specify whether they are using a theoretical or a conceptual framework, but more importantly, authors should make explicit how they constructed and used their research framework. Some studies start with research frameworks of one type and end up with another type, 8 , 22 underscoring the need for authors to clarify the type of framework used and how it informed their research. Accepting the sheer complexity surrounding research frameworks and lamenting the difficulty of reducing the confusion around these terms, Box 2 26 – 31 and Box 3 offer examples highlighting the fundamental elements of theoretical and conceptual frameworks while acknowledging that they share a common purpose.
Examples of How Theoretical Frameworks May Be Used
| The Southern African Association of Health Educationalist’s best publication of 2023 reported on a non-inferiority randomized control trial comparing video demonstrations and bedside tutorials for teaching pediatric clinical skills. The authors combined the social cognitive of sequential skill acquisition , and Peyton’s approach to teaching procedural and physical examination skills , to provide the justification for skill demonstrations forming the first step in bedside teaching. This premise formed the basis for the study and informed the interpretation of the results. | |
| Maxwell describes how a researcher used a theoretical framework based on three formal theories to understand the “day-to-day work” of a medical group practice and to emphasize aspects of his results. This example illustrates the use of existing formal theories (one of which Maxwell describes as being less “identified than the other two”) to understand the phenomenon of interest and provide a frame of reference for interpreting the results. |
Examples of How Conceptual Frameworks May Be Used
| There is complexity around how conceptual frameworks are developed and used to inform research design, so consider the following examples: the first is based on the work of one of my doctoral students in medical education (with permission from Dr. Neetha Erumeda). The second is a fictitious account based on the normalization process model, which has been used in qualitative health care research. | |
| In a study evaluating a postgraduate medical training program, Dr. Erumeda constructed a conceptual framework based on a logic . Logic models graphically represent causal relationships between programmatic inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes linearly, and they can be based on different , eg, theories of action, which focus on programmatic inputs and activities, or theories of change, which focus on programmatic outcomes. Dr. Erumeda based her initial CF on a formal of change. She then selected to include in her logic model, based on the literature and of teaching in the program being evaluated. Once she had a diagrammatic representation of her logic model and the concepts she would focus on, she discussed the current understanding of each concept from the literature. After an analysis of her results, Dr. Erumeda modified her initial CF by incorporating her findings and the insights. Her final logic model represented a theory of action, allowing her to offer recommendations to improve the training program. | |
| To study the implementation of a complex innovation into a health care system, one might employ the normalization process , which is a representation of . The model consists of four constructs regarding the innovation: 1) how it is enacted by the people doing it (interactional workability), 2) how it is understood within the networks of people around it (relational integration), 3) how it fits with existing divisions of labor (skill set workability), and 4) how it is sponsored or controlled by the organization in which it is taking place (contextual integration). Constructing a would require researchers to consider how the innovation relates to each of the constructs in the model, to identify that make up the constructs and to consider their of the concepts (eg, how they conceive the prevailing work ethic or experience the managerial hierarchy). They may also be able to postulate between different constructs or concepts or decide to focus on particular aspects of the model, which they could explore conceptually using the literature. Their research design would be influenced by their areas of interest, which would, in turn, determine their research methods. The findings could allow them to modify their model with evidence-based relationships and new concepts. | |
Misconceptions About Qualitative Research
Qualitative research’s “uneasy relationship with theory” 4 may be due to several misconceptions. One possible misconception is that qualitative research aims to build theory and thus does not need theoretical grounding. The reality is that all qualitative research methods, not just Grounded Theory studies focused on theory building, may lead to theory construction. 16 Similarly, all types of qualitative research, including Grounded Theory studies, should be guided by research frameworks. 16
Not using a research framework may also be due to misconceptions that qualitative research aims to understand people’s perspectives and experiences without examining them from a particular theoretical perspective or that theoretical foundations may influence researchers’ interpretations of participants’ meanings. In fact, in the same way that participants’ meanings vary, qualitative researchers’ interpretations (as opposed to descriptions) of participants’ meaning-making will differ. 32 , 33 Research frameworks thus provide a frame of reference for “making sense of the data.” 34
Studies informed by well-defined research frameworks can make a world of difference in alleviating misconceptions. Good qualitative reporting requires research frameworks that make explicit the combination of relevant theories, theoretical constructs and concepts that will permeate every aspect of the research. Irrespective of the term used, research frameworks are critical components of reporting not only qualitative but also all types of research.
Acknowledgments
In memory of Martie Sanders: supervisor, mentor, and colleague. My deepest gratitude for your unfailing support and guidance. I feel your loss.
Conflicts of Interest: None.

Developing a Conceptual Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide for Researchers
- July 5, 2024
Dr. Marvin L. Smith
In academic research, conceptual frameworks serve as essential blueprints, guiding scholars through the complex landscape of their studies. This article will explore how to construct powerful conceptual frameworks that elevate research design and execution.
Whether a seasoned researcher or new to academia, you’ll learn to craft frameworks that clarify objectives, map relationships between variables, and provide a solid foundation for data collection and analysis.
Ready to transform your approach to research design?
Let’s explore the critical role of conceptual frameworks in shaping successful research projects!
Definition of a conceptual framework
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and presenting the key ideas, theories, and relationships that underpin a research study or academic argument.
It serves as a roadmap for the researcher, guiding the investigation and helping to connect various concepts logically and coherently.
For example, in a study examining the factors influencing student academic performance, a conceptual framework might include concepts such as socioeconomic status, parental involvement, teacher quality, and school resources. The framework would illustrate how these factors are thought to interact and influence the outcome of academic performance.
Developing conceptual framework in research
Developing a conceptual framework is a crucial step in the research process that helps researchers organize their thoughts, identify key variables, and visualize the relationships between different concepts in their study.
This process involves synthesizing existing literature, personal observations, and theoretical knowledge to create a structured representation of the research problem and its potential solutions.
A well-crafted conceptual framework serves as a roadmap for the entire research project, guiding the researcher through data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
It also helps in communicating complex ideas to readers, making the research more accessible and understandable.
By clearly defining the key concepts and their interconnections, researchers can ensure that their study remains focused and coherent throughout its execution.
Developing a conceptual framework is an iterative process that often evolves as the research progresses. It requires critical thinking, creativity, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. Researchers must be prepared to revise and refine their framework as they gain new insights or encounter unexpected findings during their study.
Creating a conceptual framework not only benefits the researcher but also adds credibility to the research by demonstrating a thoughtful and systematic approach to addressing the research question. It helps in identifying potential gaps in existing knowledge and can highlight areas where the study may contribute to the broader field of research.
Here’s a step-by-step guide can create a conceptual framework.
Related reading: How to write a research proposal
Ready to transform your writing experience?
Sign up for Blainy today and start writing your papers with confidence!
Step#1: Select your research question
Selecting a research question is the crucial first step in developing a conceptual framework. This step lays the foundation for your entire research project and guides the development of your conceptual framework.
Here’s a detailed explanation of this step:
The research question is the central inquiry that your study aims to answer. It should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study. When selecting your research question:
1. Identify your area of interest:
Begin by considering topics that genuinely interest you within your field. This ensures that you’ll remain motivated throughout the research process.
2. Review existing literature:
Conduct a preliminary literature review to understand what’s already known about your topic and identify gaps in current knowledge.
3. Consider relevance and significance:
Ensure that your question addresses a meaningful issue or problem in your field. It should contribute to existing knowledge or have practical implications.
4. Assess feasibility:
Consider whether you have access to the necessary resources, data, and time to answer the question effectively.
5. Be specific:
Narrow down your question to make it manageable. Avoid overly broad or vague questions that could lead to unfocused research.
6. Formulate the question:
Craft your question using clear, concise language. It should be open-ended enough to allow for in-depth exploration but specific enough to guide your research.
7. Test your question:
Ask yourself if the question can be researched, analyzed, and potentially answered within the scope of your study.
For example, instead of a broad question like “How does social media affect teenagers?”, you might refine it to “How does daily Instagram use impact self-esteem in female high school students aged 14-18 in urban areas?”
Step#2: Select and define your independent and dependent variables
This step is crucial in developing your conceptual framework as it helps clarify the relationships you’ll be exploring in your research. Let’s break down each component:
Independent Variables:
These are the factors you manipulate or control in your study. They are presumed to cause or influence the dependent variable. In your conceptual framework, independent variables are typically positioned on the left or at the beginning of your model.
For example, in a study on academic performance, independent variables might include:
- Study hours per week
- Teaching methods
Dependent Variables:
These are the outcomes or effects you’re measuring in your study. They are influenced by the independent variables. In your conceptual framework, dependent variables are usually positioned on the right or at the end of your model.
Using the same example, the dependent variable might be:
- Student grades
- Test scores
Moderator Variables:
These are variables that affect the strength or direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They can amplify or diminish the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
For instance, a moderator in our academic performance study could be:
- Student motivation level
Mediator Variables:
These variables explain how or why an independent variable affects the dependent variable. They serve as a link in the causal chain between the independent and dependent variables.
An example of a mediator in our study might be:
- Student engagement level
Moderator vs. Mediator:
The key difference is that moderators affect the strength of the relationship, while mediators explain the process through which the independent variable influences the dependent variable.
Control Variables:
These are variables that you hold constant or control for in your study to ensure that they don’t interfere with the relationship between your main variables of interest. They help isolate the effects of your independent variables on the dependent variables.
In our academic performance example, control variables might include:
- Socioeconomic status
- Prior academic achievement
When selecting and defining these variables:
- Ensure they are related to your research question.
- Choose variables that can be measured or observed.
- Consider how these variables interact with each other.
- Be precise in your definitions to avoid ambiguity.
Related reading: How to find research articles
Step#3: Determine your cause-and-effect relationship
Determining the cause-and-effect relationship is a critical step in developing your conceptual framework. This step involves identifying and clarifying how your independent variables (causes) are expected to influence your dependent variables (effects).
1. Identify potential causal relationships:
Based on your research question and the variables you’ve selected, hypothesize how your independent variables might affect your dependent variables. Consider both direct and indirect relationships.
2. Review existing theories and literature:
Examine established theories and previous research in your field to support your hypothesized relationships. This helps ground your framework in existing knowledge and can provide insights into potential causal mechanisms.
3. Consider the direction of relationships:
Determine whether the relationships are positive (as one variable increases, the other increases) or negative (as one variable increases, the other decreases).
4. Account for complexity:
Recognize that cause-and-effect relationships in social sciences are often complex. Multiple causes might lead to a single effect, or a single cause might have multiple effects.
5. Consider time factors:
Think about whether the effects are immediate or if there’s a time lag between the cause and the effect. This is particularly important in longitudinal studies.
6. Examine potential mediators and moderators:
Consider how mediator variables might explain the mechanism of the cause-effect relationship, and how moderator variables might influence the strength or direction of these relationships.
7. Be aware of spurious relationships:
Consider whether any apparent cause-effect relationships might be due to other, unmeasured variables. This is where your control variables become important.
8. Use logical reasoning:
Ensure that your proposed cause-effect relationships make logical sense and can be explained theoretically.
9. Consider alternative explanations:
Think critically about other possible explanations for the relationships you’re proposing. This helps in developing a more robust framework.
10. Visualize the relationships:
Start sketching out how these cause-and-effect relationships might look in a diagram. This can help you see potential gaps or inconsistencies in your logic.
- In our academic performance study, we might hypothesize that:
- Increased study hours (independent variable) lead to improved grades (dependent variable).
- This relationship might be mediated by an improved understanding of the subject matter.
- The relationship might be moderated by student motivation, where highly motivated students see a stronger effect of study hours on grades.
- Teaching methods (another independent variable) might also influence grades, possibly through increased student engagement.
Remember, at this stage, you’re proposing these relationships based on theory and prior research. Your actual study will test these proposed cause-and-effect relationships. Be prepared to revise your framework if your findings don’t support your initial hypotheses.
Example of a conceptual framework
An example of a conceptual framework can help illustrate how all the elements we’ve discussed come together.
Let’s use our academic performance study to create a sample conceptual framework.
Research Question:
“How do study hours and teaching methods affect high school students’ academic performance, and what role does student motivation play in this relationship?”
Conceptual Framework Example:
Explanation of the framework:
1. Independent Variables:
- Study Hours per Week
- Teaching Methods (Traditional vs. Interactive)
2. Dependent Variable:
- Academic Performance (measured by GPA and Standardized Test Scores)
3. Mediator:
- Understanding of Subject Matter (explains how study hours and teaching methods affect performance)
4. Moderator:
- Student Motivation (affects the strength of the relationship between independent and dependent variables)
5. Control Variables:
- Socioeconomic Status
- Prior Academic Achievement
Proposed Relationships:
- Increased study hours are expected to lead to better academic performance.
- Interactive teaching methods are hypothesized to result in higher academic performance compared to traditional methods.
- The effect of study hours and teaching methods on academic performance is mediated by the student’s understanding of the subject matter.
- Student motivation moderates these relationships. For highly motivated students, the positive effects of study hours and interactive teaching methods on academic performance are expected to be stronger.
- The control variables are held constant to isolate the effects of the main variables of interest.
This conceptual framework visually represents the hypothesized relationships between variables.
It shows how study hours and teaching methods (independent variables) are expected to influence academic performance (dependent variable), with the understanding of the subject matter as a mediator.
Student motivation serves as a moderator, potentially affecting the strength of these relationships.
The framework also acknowledges the presence of control variables, which are important for the study but not the primary focus of the research question.
Conclusion
Developing a conceptual framework is a critical step in research, providing structure and clarity to complex investigations. This article has outlined key steps in creating robust frameworks, emphasizing variable selection, relationship determination, and visual representation.
A well-constructed framework, as illustrated in our academic performance example, integrates various elements into a comprehensive model.
It’s important to remember that conceptual frameworks are dynamic, evolving with new insights.
Ultimately, they serve as invaluable tools, guiding research processes and effectively communicating ideas, thus forming a solid foundation for knowledge advancement in any field.
Frequently asked questions
What is a conceptual framework in research.
A conceptual framework in research is a structured approach to organizing and presenting the theoretical and conceptual underpinnings of a study. It visually or narratively explains the main variables, concepts, or constructs in a research project and how they are expected to relate to one another. Essentially, it’s a researcher’s map of the territory they plan to explore, showing the anticipated relationships between key elements of their study.
What are the 3 components of conceptual framework in research?
The three main components of a conceptual framework in research are:
- Variables: These include independent variables (factors that influence outcomes), dependent variables (outcomes being studied), and potentially mediating or moderating variables.
- Relationships: This component describes how the variables are expected to interact or influence each other, often based on existing theories or previous research.
- Context: This includes the broader theoretical background, assumptions, and limitations that frame the study and help explain why certain variables and relationships are being examined.
What are the three main types of conceptual frameworks for research?
The three main types of conceptual frameworks in research are:
- Descriptive Frameworks: These aim to identify, define, and describe the key concepts or variables in a study without necessarily proposing specific relationships between them.
- Explanatory Frameworks: These go beyond description to propose and explain relationships between variables, often drawing on existing theories to predict how and why certain factors influence outcomes.
- Predictive Frameworks: These frameworks not only describe and explain relationships but also aim to predict outcomes based on specific conditions or interventions.
What is the difference between theoretical and conceptual frameworks?
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks serve different roles in research. A theoretical framework focuses on existing theories relevant to the research topic , providing a broader context for understanding the problem. It draws from multiple theories to explain phenomena and positions the study within the larger body of knowledge in the field.
A conceptual framework, however , is specific to the particular study being conducted. It identifies and defines the key variables and concepts in the study, showing how these variables are expected to relate to each other. While it often incorporates elements from the theoretical framework, it applies them to the specific research context.
The conceptual framework is more practical, serving as a roadmap for the study by guiding data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It helps researchers visualize relationships between variables and clarify their hypotheses, bridging the gap between broad theories and the practical aspects of the research.
About the Author:
Related posts.

How to Write a Term Paper: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

Paraphrasing vs Summarizing: What’s the Difference?

Write a Winning Scholarship Essay: Tips and Examples

How to Write an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide

What is Argumentative Writing? | Learn the Basics

What is Narrative Writing? (With Types & Example)

Unlock effortless writing excellence with the world's #1 AI-powered essay and research paper writer. Experience instant research paper perfection and elevate your writing to the next level.
Discover more.
50+ Free AI Tools
Terms & Condition
Privacy Policy
✉ [email protected]
✆ +971 50 760 0820
📍190 Hackett Inlet, Eastern Region, Dubai, UAE.
Copyright © 2024 Blainy
THEORETICAL AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS IN RESEARCH: CONCEPTUAL CLARIFICATION
- September 2023
- European Chemical Bulletin 12(12):2103-2117
- 12(12):2103-2117

- Obafemi Awolowo University

- Islamic University in Uganda (IUIU)
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Asiya Khattak
- Taskeen Haider
- Bisma Javed
- Susilawati Latif

- Fathu Rahman
- Buyisani Dube

- Joe Adu-Agyem

- W. P. J. Fisher

- Matthew B Miles
- Michael A. Huberman

- Judith Preissle Goetz

- Matthew Riggan
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work.
Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research, showing that your work is grounded in established ideas.
In other words, your theoretical framework justifies and contextualises your later research, and it’s a crucial first step for your research paper , thesis, or dissertation . A well-rounded theoretical framework sets you up for success later on in your research and writing process.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why do you need a theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework, structuring your theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, frequently asked questions about theoretical frameworks.
Before you start your own research, it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with the theories and models that other researchers have already developed. Your theoretical framework is your opportunity to present and explain what you’ve learned, situated within your future research topic.
There’s a good chance that many different theories about your topic already exist, especially if the topic is broad. In your theoretical framework, you will evaluate, compare, and select the most relevant ones.
By “framing” your research within a clearly defined field, you make the reader aware of the assumptions that inform your approach, showing the rationale behind your choices for later sections, like methodology and discussion . This part of your dissertation lays the foundations that will support your analysis, helping you interpret your results and make broader generalisations .
- In literature , a scholar using postmodernist literary theory would analyse The Great Gatsby differently than a scholar using Marxist literary theory.
- In psychology , a behaviourist approach to depression would involve different research methods and assumptions than a psychoanalytic approach.
- In economics , wealth inequality would be explained and interpreted differently based on a classical economics approach than based on a Keynesian economics one.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To create your own theoretical framework, you can follow these three steps:
- Identifying your key concepts
- Evaluating and explaining relevant theories
- Showing how your research fits into existing research
1. Identify your key concepts
The first step is to pick out the key terms from your problem statement and research questions . Concepts often have multiple definitions, so your theoretical framework should also clearly define what you mean by each term.
To investigate this problem, you have identified and plan to focus on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
Research question : How can the satisfaction of company X’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
2. Evaluate and explain relevant theories
By conducting a thorough literature review , you can determine how other researchers have defined these key concepts and drawn connections between them. As you write your theoretical framework, your aim is to compare and critically evaluate the approaches that different authors have taken.
After discussing different models and theories, you can establish the definitions that best fit your research and justify why. You can even combine theories from different fields to build your own unique framework if this better suits your topic.
Make sure to at least briefly mention each of the most important theories related to your key concepts. If there is a well-established theory that you don’t want to apply to your own research, explain why it isn’t suitable for your purposes.
3. Show how your research fits into existing research
Apart from summarising and discussing existing theories, your theoretical framework should show how your project will make use of these ideas and take them a step further.
You might aim to do one or more of the following:
- Test whether a theory holds in a specific, previously unexamined context
- Use an existing theory as a basis for interpreting your results
- Critique or challenge a theory
- Combine different theories in a new or unique way
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation. As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
There are no fixed rules for structuring your theoretical framework, but it’s best to double-check with your department or institution to make sure they don’t have any formatting guidelines. The most important thing is to create a clear, logical structure. There are a few ways to do this:
- Draw on your research questions, structuring each section around a question or key concept
- Organise by theory cluster
- Organise by date
As in all other parts of your research paper , thesis, or dissertation , make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
To get a sense of what this part of your thesis or dissertation might look like, take a look at our full example .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/the-theoretical-framework/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples.
info This is a space for the teal alert bar.
notifications This is a space for the yellow alert bar.

Research Process
- Brainstorming
- Explore Google This link opens in a new window
- Explore Web Resources
- Explore Background Information
- Explore Books
- Explore Scholarly Articles
- Narrowing a Topic
- Primary and Secondary Resources
- Academic, Popular & Trade Publications
- Scholarly and Peer-Reviewed Journals
- Grey Literature
- Clinical Trials
- Evidence Based Treatment
- Scholarly Research
- Database Research Log
- Search Limits
- Keyword Searching
- Boolean Operators
- Phrase Searching
- Truncation & Wildcard Symbols
- Proximity Searching
- Field Codes
- Subject Terms and Database Thesauri
- Reading a Scientific Article
- Website Evaluation
- Article Keywords and Subject Terms
- Cited References
- Citing Articles
- Related Results
- Search Within Publication
- Database Alerts & RSS Feeds
- Personal Database Accounts
- Persistent URLs
- Literature Gap and Future Research
- Web of Knowledge
- Annual Reviews
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- Finding Seminal Works
- Exhausting the Literature
- Finding Dissertations
- Researching Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology & Design
- Tests and Measurements
- Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Picking Where to Publish
- Bibliometrics
- Learn the Library This link opens in a new window

Learn Frameworks via Email
Over the course of 7 days, you will receive bite-sized lessons in your email about researching theoretical and conceptual frameworks.
- Click on the link below.
- Complete the very short registration form.
- Check your email!
- Theoretical & Conceptual Frameworks - email series
Additional Guidance
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Theoretical Framework University of Southern California
- The Research Planning Process: Theoretical Framework (video)
- Theoretical Framework (video)
- Understanding, selecting, and integrating a Theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your “house” Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your "House". Administrative Issues Journal: Connecting Education, Practice, And Research, 4(2), 12-26.
- What is a Theoretical Framework? Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2015). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. John Wiley & Sons.
NU Dissertation Center
If you are looking for a document in the Dissertation Center or Applied Doctoral Center and can't find it please contact your Chair or The Center for Teaching and Learning at [email protected]
- NCU Dissertation Center Find valuable resources and support materials to help you through your doctoral journey.
- Applied Doctoral Center Collection of resources to support students in completing their project/dissertation-in-practice as part of the Applied Doctoral Experience (ADE).
Researching Frameworks

Research frameworks provide a foundation for your study and keeps it focused and concise. Think of a framework as a roadmap or blueprint for developing your study and supporting research.
This short video series will help you help you identify, locate, and retrieve theoretical and conceptual frameworks through the library databases and/or Google.
Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks provide a particular perspective, or lens, through which to examine a topic. There are many different lenses, such as psychological theories, social theories, organizational theories and economic theories, which may be used to define concepts and explain phenomena. Sometimes these frameworks may come from an area outside of your immediate academic discipline. Using a theoretical framework for your dissertation can help you to better analyze past events by providing a particular set of questions to ask, and a particular perspective to use when examining your topic.
Traditionally, Ph.D. and Applied Degree research must include relevant theoretical framework(s) to frame, or inform, every aspect of the dissertation. Further, Ph.D. dissertations should make an original contribution to the field by adding support for the theory, or, conversely, demonstrating ways in which the theory may not be as explanatory as originally thought. You can learn more about the theoretical framework requirements in the NU Dissertation Center .
It can be difficult to find scholarly work that takes a particular theoretical approach because articles, books, and book chapters are typically described according to the topics they tackle rather than the methods they use to tackle them. Further, there is no single database or search technique for locating theoretical information. However, the suggestions below provide techniques for locating possible theoretical frameworks and theorists in the Library databases. In addition to your Library research, you should discuss possible theories your Dissertation Chair to ensure they align with your study. Also, keep in mind that you will probably find and discard several potential theoretical frameworks before one is finally chosen.
- The Theoretical Framework Guide from the NU Center for Teaching and Learning
- Theoretical Frameworks Entry from the The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods
- Theoretical Frameworks in Qualitative Research Book effectively explains, through discussion and example, what a theoretical framework is, how it is used in qualitative research, and the effects it has on the research process.
Conceptual Frameworks
A conceptual framework provides the concept or set of related concepts supporting the basis or foundation of a study. It creates a conceptual model for possible strategies or courses of action identified as important for researching a particular problem or issue. While a conceptual framework is often referred to interchangeably with a theoretical framework, it maintains a distinct purpose. A conceptual framework is used to clarify concepts, organize ideas, and identify relationships with which to frame a study. Concepts are logically developed and organized to support an overall framework and often exhibited graphically within dissertation research. Note that a dissertation may include both a theoretical framework and a conceptual framework.
The suggestions below provide techniques for locating possible conceptual frameworks in the Library databases. Note when examples may use the term "theoretical framework," you may change your search terms to "conceptual framework." In addition to your Library research, you should discuss possible frameworks your Dissertation Chair to ensure they align with your study. Also, keep in mind that you will probably find and discard several potential conceptual frameworks before one is finally chosen.
- The Conceptual Framework Guide from the NU Center for Teaching and Learning
- Conceptual Framework Entry from the SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation
- Biographical Dictionaries
- E-Book Databases
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- NavigatorSearch
- SAGE Research Methods
- Web of Science
Biographical dictionaries can be useful if you are looking for basic background information on a particular theorist or scientist.

Content: A reference database useful for accessing scholarly definitions, background and contextual information. Subjects covered include art, biography, business, economics, education, history, literature, music, psychology, religion, and science and technology.
Purpose: An excellent starting point for brainstorming a research topic and building out your initial search terms list.
Special Features: Mindmap; related articles; image search
Content: Ebooks with coverage across all academic disciplines. The collection offers a critical mass of more than 150,000 foundational scholarly ebooks with balanced quantity and quality to improve teaching, learning and research workflow and outcomes.
Purpose: Provides access to multidisciplinary ebooks for download or to be read online.
Special Features: Browse by subject option; highlight and take notes in text.
Help using this database.
Content: Reference e-book collection
Purpose: Users may read the full text of e-books from a range of academic disciplines
Special Features: Includes a visualization tool and browse-by-topic feature that aids in brainstorming topics, a Lexile feature that filters texts by difficulty, the ability to highlight and add notes to text, and a read-aloud feature.
Content : Books, chapters, and peer-reviewed content about a diverse range of topics.
Purpose: Users may access full text, and authoritative information about many topics.
Special Features: Users may explore topics and subjects.
Content: Reference sources, primarily books but also videos and business cases.
Purpose: Use for finding reference sources like encyclopedias and handbooks that provide contextual or explanatory material.
Special Features: Includes Sage Navigator
Use the Library’s e-book databases to gather background information on a particular theory or theorist. Since the e-book databases will contain fewer resources than a database containing thousands of scholarly journal articles, it is best to keep your search terms a little more broad.
For example, a search for education theory in the Ebook Central database results in many relevant e-books, as shown below. Expanding the Table of Contents will provide additional details about the e-book.

Encyclopedias and handbooks will also provide reliable background information on particular theories. For example, a search for cognitive developmental theory in the Credo Reference database results in a number of reference entries which discuss the history of the theory, identify relevant theorists, and cite seminal research studies.

You may search for theorists and theoretical information using Google and Google Scholar , as well. However, please keep in mind that you will need to be more discriminating when it comes to using material found on open access websites. We recommend reviewing the Website Evaluation guidelines when considering online sources.
One method that may be used in Google is limiting your search by a particular domain name. If a website ends in .org, .gov, or .edu, it is more likely to be a scholarly source. If it ends in .com or .net it is less likely to be a scholarly source. In the search below, for example, we have limited our search for "leadership theories" to just those websites ending with .edu. You may also find this domain limiter under Tools>Advanced Search.
Note: Limiting to a particular domain is not necessary in Google Scholar, as all results in Google Scholar may be considered scholarly. This may include articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions, material from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other web sites.

For additional information, see the following:
- Google for School LibGuide
- Google Scholar Quick Tutorial Video A short video demonstration of using Google Scholar for academic research.
- Limit By Domain FAQ
Content: National University & NCU student dissertations and literature reviews.
Purpose: Use for foundational research, to locate test instruments and data, and more.
Special Features: Search by advisor (chair), degree, degree level, or department. Includes a read-aloud feature.
Content: Global student dissertations and literature reviews.
Special Features: Search by advisor (chair), degree, degree level, or department. Includes a read-aloud feature
The ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database (PQDT) is the world's most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses. It is the database of record for graduate research, with over 2.3 million dissertations and theses included from around the world.
Since most doctoral research requires a theoretical framework, looking at completed dissertations related to your topic is an effective way to identify relevant theories and theorists. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global provides access to over 3 million full text doctoral dissertations and graduate theses. You may limit your search to only doctoral dissertations by using the Advanced Search screen. Look at the table of contents or abstract for reference to theoretical framework, as shown below. The dissertation’s references/bibliography will have a full citation to the original theorist’s research.

Content: Scholarly journals, e-books, videos and more.
Purpose: A key multidisciplinary database for most topics. It is one of the library’s main search engines and the most comprehensive single search.
Note: Certain library databases and publisher content are not searchable in NavigatorSearch, and individual databases may need to be searched to retrieve information due to unique content. NavigatorSearch can be found at https://resources.nu.edu .
On the NavigatorSearchscreen, include theor* as one your search terms, as shown below. It will retrieve results that include one of the following keywords: theory, theories, theoretical, theorist, or theorists . It is important to keep in mind, however, that this is not a foolproof method for locating theoretical frameworks. Scholars will often cite theory or theorists in order to refute them, or because they are saying something that's tangentially related, or they may even just refer to theory briefly in passing. In our example, we have selected the field for AB Abstract because if theory is mentioned within the abstract, the study is more likely to take a theoretical approach.

As shown below, results from our example search clearly include articles which apply theory to the topic of curriculum design.

Remember to look past the article title. Theoretical information may be mentioned in a subheading, or referred to elsewhere in the document. Use the FIND feature in your PDF viewer or internet browser to scan the document for terms such as theor* (to pull up theory, theorist, theoretical), framework, conceptual, perspective , etc., as shown below.

Content: Books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos on research methods and design.
Purpose: Use to learn more about qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research.
Special Features: Includes a methods map, project planner, and "which stats" test
SAGE Research Methods is a multimedia database containing more than 1,000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos covering every step of the research process. It includes e-books and e-book chapters which may help you better understand the theoretical framework aspect of your research study. A selection of resources is included below:
Searching in SAGE Research Methods
Use the main search bar to locate information about theoretical frameworks. Search the general phrase "theoretical frameworks," or the name of a specific theoretical framework like "social cognitive theory," in quotation marks to yield results with that specific phrase. See the example below.

You may also browse content in this database by Discipline . Select Browse on the top navigation to view a list of key topics.

- Anfara, V. (2008). Theoretical frameworks. In L. M. Given (Ed.), The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods. (pp. 870-874). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Anfara, V. A., & Mertz, N. T. (Eds.). (2006). Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Theoretical framework. (2014). In Walker, R., & Solvason, C. Success with your early years research project (pp. 21-32). London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
Content: Citations and articles in multi-disciplines not found through a NavigatorSearch.
Purpose: Used to conduct topic searches as well as find additional resources that have cited a specific resource (citation network).
You may conduct a Cited Reference Search in Web of Science to find articles that cite a primary theorist in your area. These articles are likely to tackle your topic through your theoretical lens, or will point you toward another article that does. To access Web of Knowledge, go to A-Z Databases from the Library’s home page.
On the Web of Science home page, click on Cited Reference Search to search for articles that cite a person's work.
Enter the name of a key theorist in your area (in our example, John Dewey) in the format they specify (in this case Dewey J*), as shown below, and press "Search."

On the results screen, select the appropriate Web of Science category under Refine Results. For example, we could select “Education Educational Research” and then click “Refine.” You may wish to further refine by Document Type, Research Area, Author, etc. (also located on the left hand menu). Sorting your results by “Times Cited - Oldest to Newest" is an effective way to discover the most frequently cited works.

- 12Manage Global knowledge platform on management and business administration, including descriptions of frameworks. Requires free email sign up.
- Academic Theories Includes alphabetical listing of theories, as well as grouping by type.
- Communication Theories Provides list of communication theories grouped according to topic.
- Psychological Theories Browse alphabetically or use the clusters feature to view theories grouped by similar topics or approaches.
- Theories Used in Information Systems (IS) Research Click on a linked theory name to find details about the theory, some examples of IS papers using the theory, and links to related sites.
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Finding Dissertations
- Next: Research Methodology & Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 12, 2024 7:35 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchprocess

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
Building and Using Theoretical Frameworks
- Open Access
- First Online: 03 December 2022
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- James Hiebert 6 ,
- Jinfa Cai 7 ,
- Stephen Hwang 7 ,
- Anne K Morris 6 &
- Charles Hohensee 6
Part of the book series: Research in Mathematics Education ((RME))
19k Accesses
1 Citations
Theoretical frameworks can be confounding. They are supposed to be very important, but it is not always clear what they are or why you need them. Using ideas from Chaps. 1 and 2 , we describe them as local theories that are custom-designed for your study. Although they might use parts of larger well-known theories, they are created by individual researchers for particular studies. They are developed through the cyclic process of creating more precise and meaningful hypotheses. Building directly on constructs from the previous chapters, you can think of theoretical frameworks as equivalent to the most compelling, complete rationales you can develop for the predictions you make. Theoretical frameworks are important because they do lots of work for you. They incorporate the literature into your rationale, they explain why your study matters, they suggest how you can best test your predictions, and they help you interpret what you find. Your theoretical framework creates an essential coherence for your study and for the paper you are writing to report the study.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Part I. What Are Theoretical Frameworks?
As the name implies, a theoretical framework is a type of theory. We will define it as the custom-made theory that focuses specifically on the hypotheses you want to test and the research questions you want to answer. It is custom-made for your study because it explains why your predictions are plausible. It does no more and no less. Building directly on Chap. 2 , as you develop more complete rationales for your predictions, you are actually building a theory to support your predictions. Our goal in this chapter is for you to become comfortable with what theoretical frameworks are, with how they relate to the general concept of theory, with what role they play in scientific inquiry, and with why and how to create one for your study.

As you read this chapter, it will be helpful to remember that our definitions of terms in this book, such as theoretical framework, are based on our view of scientific inquiry as formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses. We define theoretical framework in ways that continue the coherent story we lay out across all phases of scientific inquiry and all the chapters this book. You are likely to find descriptions of theoretical frameworks in other sources that differ in some ways from our description. In addition, you are likely to see other terms that we would include as synonyms for theoretical framework, including conceptual framework. We suggest that when you encounter these special terms, make sure you understand how the authors are defining them.
|
|
Definitions of Theories
We begin by stepping back and considering how theoretical frameworks fit within the concept of theory, as usually defined. There are many definitions of theory; you can find a huge number simply by googling “theory.” Educational researchers and theorists often propose their own definitions but many of these are quite similar. Praetorius and Charalambous ( 2022 ) reviewed a number of definitions to set the stage for examining theories of teaching. Here are a few, beginning with a dictionary definition:
Lexico.com Dictionary (Oxford University Press, 2021 ): “A supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained.”
Biddle and Anderson ( 1986 ): “By scientific theory we mean the system of concepts and propositions that is used to represent, think about, and predict observable events. Within a mature science that theory is also explanatory and formalized. It does not represent ultimate ‘truth,’ however; indeed, it will be superseded by other theories presently. Instead, it represents the best explanation we have, at present, for those events we have so far observed” (p. 241).
Kerlinger ( 1964 ): “A theory is a set of interrelated constructs (concepts), definitions and propositions which presents a systematic view of phenomena by specifying relations among variables, with the purpose of explaining and predicting phenomena” (p. 11).
Colquitt and Zapata-Phelan ( 2007 ): The authors say that theories allow researchers to understand and predict outcomes of interest, describe and explain a process or sequence of events, raise consciousness about a specific set of concepts as well as prevent scholars from “being dazzled by the complexity of the empirical world by providing a linguistic tool for organizing it” (p. 1281).
For our purposes, it is important to notice two things that most definitions of theories share: They are descriptions of a connected set of facts and concepts, and they are created to predict and/or explain observed events. You can connect these ideas to Chaps. 1 and 2 by noticing that the language for the descriptors of scientific inquiry we suggested in Chap. 1 are reflected in the definitions of theories. In particular, notice in the definitions two of the descriptors: “Observing something and trying to explain why it is the way it is” and “Updating everyone’s thinking in response to more and better information.” Notice also in the definitions the emphasis on the elements of a theory similar to the elements of a rationale described in Chap. 2 : definitions, variables, and mechanisms that explain relationships.
Exercise 3.1
Before you continue reading, in your own words, write down a definition for “theoretical framework.”
Theoretical Frameworks Are Local Theories
There are strong similarities between building theories and doing scientific inquiry (formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses). In both cases, the researcher (or theorist) develops explanations for phenomena of interest. Building theories involves describing the concepts and conjectures that predict and later explain the events, and specifying the predictions by identifying the variables that will be measured. Doing scientific inquiry involves many of the same activities: formulating predictions for answers to questions about the research problem and building rationales to explain why the predictions are appropriate and reasonable.
As you move through the cycles described in Chap. 2 —cycles of asking questions, making predictions, writing out the reasons for these predictions, imagining how you would test the predictions, reading more about what scholars know and have hypothesized, revising your predictions (and maybe your questions), and so on—your theoretical rationales will become both more complete and more precise. They will become more complete as you find new arguments and new data in the literature and through talking with others, and they will become sharper as you remove parts of the rationales that originally seemed relevant but now create mostly distractions and noise. They will become increasingly customized local theories that support your predictions.
In the end, your framework should be as clean and frugal as possible without missing arguments or data that are directly relevant. In the language of mathematics, you should use an idea if and only if it makes your framework stronger, more convincing. On the one hand, including more than you need becomes a distraction and can confuse both you, as you try to conceptualize and conduct your research, and others, as they read your reports of your research. On the other hand, including less than you need means your rationale is not yet as convincing as it could be.
The set of rationales, blended together, constitute a precisely targeted custom-made theory that supports your predictions. Custom designing your rationales for your specific predictions means you probably will be drawing ideas from lots of sources and combining them in new ways. You are likely to end up with a unique local theory, a theoretical framework that has not been proposed in exactly the same way before.
A common misconception among beginning researchers is that they should borrow a theoretical framework from somewhere else, especially from well-known scholars who have theories named after them or well-known general theories of learning or teaching. You are likely to use ideas from these theories (e.g., Vygotsky’s theory of learning, Maslow’s theory of motivation, constructivist theories of learning), but you will combine specific ideas from multiple sources to create your own framework. When someone asks, “What theoretical framework are you using?” you would not say, “A Vygotskian framework.” Rather, you would say something like, “I created my framework by combining ideas from different sources so it explains why I am making these predictions.”

You should think of your theoretical framework as a potential contribution to the field, all on its own. Although it is unique to your study, there are elements of your framework that other researchers could draw from to construct theoretical frameworks for their studies, just as you drew from others’ frameworks. In rare cases, other researchers could use your framework as is. This might happen if they want to replicate your study or extend it in very specific ways. Usually, however, researchers borrow parts of frameworks or modify them in ways that better fit their own studies. And, just as you are doing with your own theoretical framework, those researchers will need to justify why borrowing or modifying parts of your framework will help them explain the predictions they are making.
Considering your theoretical framework as a contribution to the field means you should treat it as a central part of scientific inquiry, not just as a required step that must be completed before moving to the next phase. To be useful, the theoretical framework should be constructed as a critical part of conceptualizing and carrying out the research (Cai et al., 2019c ). This also means you should write out your framework as you are developing it. This will be a key part of your evolving research paper. Because your framework will be adjusted multiple times, your written document will go through many drafts.
If you are a graduate student, do not think of the potential audience for your written framework as only your advisor and committee members. Rather, consider your audience to be the larger community of education researchers. You will need to be sure all the key terms are defined and each part of your argument is clear, even to those who are not familiar with your study. This is one place where writing out your framework can benefit your study—it is easy to assume key terms are clear, but then you find out they are not so clear, even to you, when trying to communicate them. Failing to notice this lack of clarity can create lots of problems down the road.
Exercise 3.2
Researchers have used a number of different metaphors to describe theoretical frameworks. Maxwell (2005) referred to a theoretical framework as a “coat closet” that provides “places to ‘hang’ data, showing their relationship to other data,” although he cautioned that “a theory that neatly organizes some data will leave other data disheveled and lying on the floor, with no place to put them” (p. 49). Lester (2005) referred to a framework as a “scaffold” (p. 458), and others have called it a “blueprint” (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). Eisenhart (1991) described the framework as a “skeletal structure of justification” (p. 209). Spangler and Williams (2019) drew an analogy to the role that a house frame provides in preventing the house from collapsing in on itself. What aspects of a theoretical framework does each of these metaphors capture? What aspects does each fail to capture? Which metaphor do you find best fits your definition of a theoretical framework? Why? Can you think of another metaphor to describe a theoretical framework?
Part II. Why Do You Need Theoretical Frameworks?
Theoretical frameworks do lots of work for you. They have four primary purposes. They ensure (1) you have sound reasons to expect your predictions will be accurate, (2) you will craft appropriate methods to test your predictions, (3) you can interpret appropriately what you find, and (4) your interpretations will contribute to the accumulation of a knowledge base that can improve education. How do they do this?
Supporting Your Predictions
In previous chapters and earlier in this chapter, we described how theoretical frameworks are built along with your predictions. In fact, the rationales you develop for convincing others (and yourself) that your predictions are accurate are used to refine your predictions, and vice versa. So, it is not surprising that your refined framework provides a rationale that is fully aligned with your predictions. In fact, you could think of your theoretical framework as your best explanation, at any given moment during scientific inquiry, for why you will find what you think you will find.
Throughout this book, we are using “explanation” in a broad sense. As we noted earlier, an explanation for why your predictions are accurate includes all the concepts and definitions about mechanisms (Kerlinger’s, 1964 definition of “theory”) that help you describe why you think the predictions you are making are the best predictions possible. The explanation also identifies and describes all the variables that make up your predictions, variables that will be measured to test your predictions.
Crafting Appropriate Methods
Critical decisions you make to test your hypotheses form the methods for your scientific inquiry. As we have noted, imagining how you will test your hypotheses helps you decide whether the empirical observations you make can be compared with your predictions or whether you need to revise the methods (or your predictions). Remember, the theoretical framework is the coherent argument built from the rationales you develop as part of each hypothesis you formulate. Because each rationale explains why you make that prediction, it contains helpful cues for which methods would provide the fairest and most complete test of that prediction. In fact, your theoretical framework provides a logic against which you can check every aspect of the methods you imagine using.
You might find it helpful to ask yourself two questions as you think about which methods are best aligned with your theoretical framework. One is, “After reading my theoretical framework, will anyone be surprised by the methods I use?” If so, you should look back at your framework and make sure the predictions are clear and the rationales include all the reasons for your predictions. Your framework should telegraph the methods that make the most sense. The other question is, “Are there some predictions for which I can’t imagine appropriate methods?” If so, we recommend you return to your hypotheses—to your predictions and rationales (theoretical framework)—to make sure the predictions are phrased as precisely as possible and your framework is fully developed. In most cases, this will help you imagine methods that could be used. If not, you might need to revise your hypotheses.
Exercise 3.3
Kerlinger ( 1964 ) stated, “A theory is a set of interrelated constructs (concepts), definitions and propositions which presents a systematic view of phenomena by specifying relations among variables, with the purpose of explaining and predicting phenomena” (p. 11). What role do definitions play in a theoretical framework and how do they help in crafting appropriate methods?
Exercise 3.4
Sarah is in the beginning stages of developing a study. Her initial prediction is: There is a relationship between pedagogical content knowledge and ambitious teaching. She realizes that in order to craft appropriate measures, she needs to develop definitions of these constructs. Sarah’s original definitions are: Pedagogical content knowledge is knowledge about subject matter that is relevant to teaching. Ambitious teaching is teaching that is responsive to students’ thinking and develops a deep knowledge of content. Sarah recognizes that her prediction and her definitions are too broad and too general to work with. She wants to refine the definitions so they can guide the refinement of her prediction and the design of the study. Develop definitions of these two constructs that have clearer implications for the design and that would help Sarah to refine her prediction. (tip: Sarah may need to reduce the scope of her prediction by choosing to focus only on one aspect of pedagogical content knowledge and one aspect of ambitious teaching. Then, she can more precisely define those aspects.)
Guiding Interpretations of the Data
By providing rationales for your predictions, your theoretical framework explains why you think your predictions will be accurate. In education, researchers almost always find that if they make specific predictions (which they should), the predictions are not entirely accurate. This is a consequence of the fact that theoretical frameworks are never complete. Recall the definition of theories from Biddle and Anderson ( 1986 ): A theory “does not represent ultimate ‘truth,’ however; indeed, it will be superseded by other theories presently. Instead, it represents the best explanation we have, at present, for those events we have so far observed” (p. 241). If you have created your best developed and clearly stated theoretical framework that explains why you expected certain results, you can focus your interpretation on the ways in which your theoretical framework should be revised.
Focusing on realigning your theoretical framework with the data you collected produces the richest interpretation of your results. And it prevents you from making one of the most common errors of beginning researchers (and veteran researchers, as well): claiming that your results say more than they really do. Without this anchor to ground your interpretation of the data, it is easy to overgeneralize and make claims that go beyond the evidence.
In one of the definitions of theory presented earlier, Colquitt and Zapata-Phelan ( 2007 ) say that theories prevent scholars from “being dazzled by the complexity of the empirical world” (p. 1281). Theoretical frameworks keep researchers grounded by setting parameters within which the empirical world can be interpreted.
Exercise 3.5
Find two published articles that explicitly present theoretical frameworks (not all articles do). Where do you see evidence of the researchers using their theoretical frameworks to inform, shape, and connect other parts of their articles?
Showing the Contribution of Your Study
Theoretical frameworks contain the arguments that define the contribution of research studies. They do this in two ways, by showing how your study extends what is known and by setting the parameters for your contribution.
Showing How Your Study Extends What Is Known
Because your theoretical framework is built from what is already known or has been proposed, it situates your study in work that has occurred before. A clearly written framework shows readers how your study will take advantage of what is known to extend it further. It reveals what is new about what you are studying. The predictions that are generated from your framework are predictions that have never been made in quite the same way. They predict you will find something that has not been found previously in exactly this way. Your theoretical framework allows others to see the contributions that your study is likely to make even before the study has been conducted.
Setting the Parameters for Your Contribution
Earlier we noted that theoretical frameworks keep researchers grounded by setting parameters within which they should interpret their data. They do this by providing an initial explanation for why researchers expect to find particular results. The explanation is custom-built for each study. This means it uniquely explains the expected results. The results will almost surely turn out somewhat differently than predicted. Interpreting the data includes revising the initial explanation. So, you will end up with two versions of your theoretical framework, one that explains what you expected to find plus a second, updated framework that explains what you actually found.
The two frameworks—the initial version and the updated version—define the parameters of your study’s contribution. The difference between the two frameworks is what can be learned from your study. The first framework is a claim about what is known before you conduct your study about the phenomenon you are studying; the updated framework is a claim about how what is known has changed based on your results. It is the new aspects of the updated framework that capture the important contribution of your work.
Here is a brief example. Suppose you study the errors fourth graders make after receiving ordinary instruction on adding and subtracting decimal fractions. Based on empirical findings from past research, on theories of student learning, and on your own experience, you develop a rationale which predicts that a common error on “ragged” addition problems will be adding the wrong numerals. One of the reasons for this prediction is that students are likely to ignore the values of the digit positions and “line up” the numerals as they do with whole numbers. For instance, if they are asked to add 53.2 + .16, they are likely to answer either 5.48 or 54.8.
When you conduct your study, you present problems, handwritten, in both horizontal and vertical form. The horizontal form presents the numbers using the format shown above. The vertical form places one numeral over the other but not carefully aligned:
You find the predicted error occurs, but only for problems written in vertical form. To interpret these data, you look back at your theoretical framework and realize that students might ignore the value of the digits if the format reminded them of the way they lined up digits for whole number addition but might consider the value of the digits if they are forced to align the digits themselves, either by rewriting the problem or by just adding in their heads. A measure of what you (and others) learned from this study is the change in possible explanations (your theoretical frameworks). This does not mean your updated theoretical framework is “correct” or will make perfectly accurate predictions next time. But, it does mean that you are very likely moving toward more accurate predictions and toward a deeper understanding of how students think about adding decimal fractions.
Anchoring the Coherence of Your Study (and Your Evolving Research Paper)
Your theoretical framework serves as the anchor or center point around which all other aspects of your study should be aligned. This does not mean it is created first or that all other aspects are changed to align with the framework after it is created. The framework also changes as other aspects are considered. However, it is useful to always check alignment by beginning with the framework and asking whether other aspects are aligned and, if not, adjusting one or the other. This process of checking alignment is equally true when writing your evolving research paper as when planning and conducting your study.
Part III. How Do You Construct a Theoretical Framework for Your Study?
How do you start the process? Because constructing a theoretical framework is a natural extension of constructing rationales for your predictions, you already started as soon as you began formulating hypotheses: making predictions for what you will find and writing down reasons for why you are making these predictions. In Chap. 2 , we talked about beginning this process. In this section, we will explore how you can continue building out your rationales into a full-fledged theoretical framework.
Building a Theoretical Framework in Phases
Building your framework will occur in phases and proceed through cycles of clarifying your questions, making more precise and explicit your predictions, articulating reasons for making these predictions, and imagining ways of testing the predictions. The major source for ideas that will shape the framework is the research literature. That said, conversations with colleagues and other experts can help clarify your predictions and the rationales you develop to justify the predictions.
As you read relevant literature, you can ask: What have researchers found that help me predict what I will find? How have they explained their findings, and how might those explanations help me develop reasons for my predictions? Are there new ways to interpret past results so they better inform my predictions? Are there ways to look across previous results (and claims) and see new patterns that I can use to refine my predictions and enrich my rationales? How can theories that have credibility in the research community help me understand what I might find and help me explain why this is the case? As we have said, this process will go back and forth between clarifying your predictions, adjusting your rationales, reading, clarifying more, adjusting, reading, and so on.
One Researcher’s Experience Constructing a Theoretical Framework: The Continuing Case of Martha
In Chap. 2 , we followed Martha, a doctoral student in mathematics education, as she was working out the topic for her study, asking questions she wanted to answer, predicting the answers, and developing rationales for these predictions. Our story concluded with a research question, a sample set of predictions, and some reasons for Martha’s predictions. The question was: “Under what conditions do middle school teachers who lack conceptual knowledge of linear functions benefit from five 2-hour learning opportunity (LO) sessions that engage them in conceptual learning of linear functions as assessed by changes in their teaching toward a more conceptual emphasis of linear functions?” Her predictions focused on particular conditions that would affect the outcomes in particular ways. She was beginning to build rationales for these predictions by returning to the literature and identifying previous research and theory that were relevant. We continue the story here.
Imagine Martha continuing to read as she develops her theoretical framework—the rationales for her predictions. She tweaks some of her predictions based on what other researchers have already found. As she continues reading, she comes across some related literature on learning opportunities for teachers. A number of articles describe the potential of another form of LOs that might help teachers teach mathematics more conceptually—analyzing videos of mathematics lessons.
The data suggested that teachers can improve their teaching by analyzing videos of other teachers’ lessons as well as their own. However, the results were mixed so researchers did not seem to know exactly what makes the difference. Martha also read that teachers who already can analyze videos of lessons and spontaneously describe the mathematics that students are struggling with and offer useful suggestions for how to improve learning opportunities for students teach toward more conceptual learning goals, and their students learn more (Kersting et al., 2010 , 2012 ). These findings caught Martha’s attention because it is unusual to find correlates with conceptual teaching and better achievement. What is not known, realized Martha, is whether teachers who learn to analyze videos in this way, through specially designed LOs, would look like the teachers who already could analyze them. Would teachers who learned to analyze videos teach more conceptually?
It occurred to Martha she could bring these lines of research together by extending what is known along both lines. Recall our earlier suggestion of looking across the literature and noticing new patterns that can inform your work. Martha thought about studying how, exactly, these two skills are related: analyzing videos in particular ways and teaching conceptually. Would the relationships reported in the literature hold up for teachers who learn to describe the mathematics students are struggling with and make useful suggestions for improving students’ LOs?
Martha was now conflicted. She was well on her way to developing a testable hypothesis about the effects of learning about linear functions, but she was really intrigued by the work on analyzing videos of teaching. In addition, she saw several advantages of switching to this new topic:
The research question could be formulated quite easily. It would be something like: “What are the relationships between learning to analyze videos of mathematics teaching in particular ways (specified from prior research) and teaching for conceptual understanding?”
She could imagine predicting the answers to this question based directly on previous research. She would predict connections between particular kinds of analysis skills and levels of conceptual teaching of mathematics in ways that employed these skills.
The level of conceptual teaching, a challenging construct to define with her previous topic (the effects of professional development on the teaching of linear functions), was already defined in the work on analyzing videos of mathematics teaching, so that would solve a big problem. The definition foregrounded particular sets of behaviors and skills such as identifying key learning moments in a lesson and focusing on students’ thinking about the key mathematical idea during these moments. In other words, Martha saw ways to adapt a definition that had already been used and tested.
The issue of transfer—another challenging issue in her original hypothesis—was addressed more directly in this setting because the learning environment—analyzing videos of classroom teaching—is quite close to the classroom environment in which participants’ conceptual teaching would be observed.
Finally, the nature of learning opportunities, an aspect of her original idea she still needed to work through, had been explored in previous studies on this new topic, and connections were found between studying videos and changes in teaching.
Given all these advantages, Martha decided to change her topic and her research question. We applaud this decision for two major reasons. First, Martha’s interest grew as she explored this new topic. She became excited about conducting a study that might answer the research question she posed. It is always good to be passionate about what you study. Second, Martha was more likely to contribute important new insights if she could extend what is already known rather than explore a new area. Exploring something quite new requires lots of effort defining terms, creating measures, making new predictions, developing reasons for the predictions, and so on. Sometimes, exploring a new area has payoffs. But, as a beginning researcher, we suggest you take advantage of work that has already been done and extend it in creative ways.
Although Martha’s idea of extending previous work came with real advantages, she still faced a number of challenges. A first, major challenge was to decide whether she could build a rationale that would predict learning to analyze videos caused more conceptual teaching. Or, could she only build a rationale that would predict that there was a relationship between changes in analyzing videos and level of conceptual teaching? Perhaps a cause-effect relationship existed but in the opposite direction: If teachers learned to teach more conceptually, their analysis of teaching videos would improve. Although most of the literature described learning to analyze videos as the potential cause of teaching conceptually, Martha did not believe there was sufficient evidence to build a rationale for this prediction. Instead, she decided to first determine if a relationship existed and, if so, to understand the relationship. Then, if warranted, she could develop and test a hypothesis of causation in a future study. In fact, the direction of the causation might become clearer when she understood the relationship more clearly.
A second major challenge was whether to study the relationship as it existed or as one (or both) of the constructs was changing. Past research had explored the relationship as it existed, without inducing changes in either analyzing videos or teaching conceptually. So, Martha decided she could learn more about the relationship if one of the constructs was changing in a planned way. Because researchers had argued that teachers’ analysis of video could be changed with appropriate LOs, and because changing teachers’ teaching practices has resisted simple interventions, Martha decided to study the relationship as she facilitated changes in teachers’ analysis of videos. This would require gathering data on the relationship at more than one point in time.
Even after resolving these thorny issues, Martha faced many additional challenges. Should she predict a closer relationship between learning to analyze video and teaching for conceptual understanding before teachers began learning to analyze videos or after? Perhaps the relationship increases over time because conceptual teaching often changes slowly. Should she predict a closer relationship if the content of the videos teachers analyzed was the same as the content they would be teaching? Should she predict the relationship will be similar across pairs of similar topics? Should she predict that some analysis skills will show closer relationships to levels of conceptual teaching than others? These questions and others occurred to Martha as she was formulating her predictions, developing justifications for her predictions, and considering how she would test the predictions.
Based on her reading and discussions with colleagues, Martha phrased her initial predictions as follows:
There will be a significant positive correlation between teachers’ performance on analysis of videos and the extent to which they create conceptual learning opportunities for their students both before and after proposed learning experiences.
The relationship will be stronger:
Before the proposed opportunities to learn to analyze videos of teaching;
When the videos and the instruction are about similar mathematical topics; and,
When the videos analyzed display conceptual misunderstandings among students.
Of the video analysis skills that will be assessed, the two that will show the strongest relationship are spontaneously describing (1) the mathematics that students are struggling with and (2) useful suggestions for how to improve the conceptual learning opportunities for students.
Martha’s rationales for these predictions—her theoretical framework—evolved along with her predictions. We will not detail the framework here, but we will note that the rationale for the first prediction was based on findings from past research. In particular, the prediction is generated by reasoning that if there has been no special intervention, the tendency to analyze videos in particular ways and to teach conceptually develop together. This might explain Kersting’s findings described earlier. The second and third predictions were based on the literature on teachers’ learning, especially their learning from analyzing videos of teaching.
Before leaving Martha at this point in her journey, we want to make an important point about the change she made to her research topic. Changes like this occur quite often as researchers do the hard intellectual work of developing testable hypotheses that guide research studies. When this happens to you, it can feel like you have lost ground. You might feel like you wasted your time on the original topic. In Chap. 1 , we described inevitable “failure” when engaged in scientific inquiry. Failure is often associated with realizing the data you collected do not come close to supporting your predictions. But a common kind of failure occurs when researchers realize the direction they have been pursuing should change before they collect data. This happened in Martha’s case because she came across a topic that was more intriguing to her and because it helped solve some problems she was facing with the previous topic. This is an example of “failing productively” (see Chap. 1 ). Martha did not succeed in pursuing her original idea, but while she was recognizing the problems, she was also seeing new possibilities.
Constantly Improving Your Framework
We will use Martha’s experience to be more specific about the back-and-forth process in which you will engage as you flesh out your framework. We mentioned earlier your review of the literature as a major source of ideas and evidence that will affect your framework.
Reviewing Published Empirical Evidence
One of the best sources for helping you specify your predictions are studies that have been conducted on related topics. The closer to your topic, the more helpful will be the evidence for anticipating what you will find. Many beginning researchers worry they will locate a study just like the one they are planning. This (almost) never happens. Your study will be different in some ways, and a study that is very similar to yours can be extraordinarily helpful in specifying your predictions. Be excited instead of terrified when you come across a study with a title similar to yours.
Try to locate all the published research that has been conducted on your topic. What does “on your topic” mean? How widely should you cast your net? There are no rules here; you will need to use your professional judgment. However, here is a general guide: If the study does not help you clarify your predictions, change your confidence in them, or strengthen your rationale, then it falls outside your net.
In addition to helping specify your predictions, prior research studies can be a goldmine for developing and strengthening your theoretical framework. How did researchers justify their predictions or explain why they found what they did? How can you use these ideas to support (or change) your own predictions?
By reading research on similar topics, you might also imagine ways of testing your predictions. Maybe you learn of ways you could design your study, measures you could use to collect data, or strategies you could use to analyze your data. As you find helpful ideas, you will want to keep track of where you found these ideas so you can cite the appropriate sources as you write drafts of your evolving research paper.
Examining Theories
You will read a wide range of theories that provide insights into why things might work like they do. When the phenomena addressed by the theory are similar to those you will study, the associated theories can help you think through your own predictions and why you are making them. Returning to Martha’s situation, she could benefit from reading theories on adult learning, especially teacher learning, on transferring knowledge from one setting to another, on professional development for teachers, on the role of videos in learning, on the knowledge needed to teach conceptually, and so on.
Focusing on Variables and Mechanisms
As you review the literature and search for evidence and ideas that could strengthen your predictions and rationales, it is useful to keep your eyes on two components: the variables you will attend to and the mechanisms that might explain the relationships between the variables. Predictions could be considered statements about expected behaviors of the variables. The theoretical framework could be thought of as a description of all the variables that will be deliberately attended to plus the mechanisms conjectured to account for these relationships.
In Martha’s case, the most obvious variables are the responses teachers give to questions about their analysis of the videos and the features observed in their teaching practices. The mechanism of primary interest is the (mental and social) process that transforms the skills, knowledge, and attention involved in analyzing videos into particular kinds of teaching practices—or vice versa. The definition of conceptual teaching she adopted from previous studies gave her a clue about the mechanisms—about how and why learning to analyze videos might affect classroom teaching. The definition included attending to key learning moments in a lesson and tracking students’ thinking during these moments. Martha predicted that if teachers learned to attend to these aspects of teaching when viewing videos, they might attend to them when planning and implementing their own teaching.
As Martha reviewed the literature, she identified a number of variables that might affect the likelihood and extent of this translation. Here are some examples: how well teachers understand the mathematics in the videos and the mathematics they will teach; the nature of the videos themselves; the number of opportunities teachers have to analyze videos and the ways in which these opportunities are structured; teachers’ analysis of videos and their teaching practices before the learning opportunities begin; and how much time they have to apply what they learn to their own teaching.
Martha identified these additional variables because she learned they might have a direct influence on the mechanisms that could explain the relationship between analyzing videos and teaching. Some variables might support these mechanisms, and some might interfere. Martha’s task at this point in her work is to identify and describe all the variables that could play a meaningful role in the outcome of her study. This means to identify each variable for which it is possible to establish a clear and direct connection between the variable and the relationship she planned to investigate. Using the outcome of this task, Martha then needs to update her description of the mechanisms that could account for the relationships she expects to see and review her predictions and theoretical framework with these variables and mechanisms in mind.
Exercise 3.6
Review the predictions that Martha made and identify the variables that play a role in these predictions. Even though you might not be immersed in this literature, think about the alignment between the variables included in the predictions and those that could impact the relationships in which Martha is interested. Are there other missing variables that should be included in her predictions?
How Do You Know When You Have Finished Building Your Theoretical Framework?
The question of when your theoretical framework is finished could be answered in several ways. First, it is never really finished. As you continue to write your evolving research paper, you will continue strengthening your framework. You might even refine the framework as you write the final draft of your paper, after you have collected and analyzed your data. Furthermore, if you do follow-up studies, you will continue to build your framework.
A second answer is that you should invest the time and effort to build a theoretical framework that is as finished as possible at each point in the research process. As you write each draft of your evolving research paper, you should feel as if you have the strongest, most robust rationale you can have for your current predictions. In other words, you should feel that with each succeeding draft you have finished building your framework, even though you are quite sure you have not.
A third answer addresses a common, related question: “How do I know when I have included enough ideas and borrowed from enough sources? Would including another idea or citing another source be useful?” The answer is that you should include only those ideas that contribute to building a stronger framework. When you wonder whether you should include another idea or reference, ask yourself whether doing so would make your framework stronger in all the ways we described earlier.
Exercise 3.7
In 2–3 pages (single spaced), write out the plan for your study. The plan should include your research questions, your predictions of the answers, your rationale for the predictions (i.e., your theoretical framework), and your imagined plan for testing the predictions. Be as explicit and precise as you can. Be sure you have identified the critical variables and described the mechanism(s) that could explain the phenomena, the relationships, and/or the changes you predict. Look back to see if the logic connecting the parts is obvious. Ask yourself whether the tests you plan are what anyone familiar with your framework would expect (i.e., there should be no surprises).
Part IV. Refining a Theoretical Framework: A Scholarly Dialogue
As we noted above, conversations with colleagues and other experts can help you refine your theoretical framework by clarifying your predictions and digging into the details of the rationales you develop to justify those predictions. This is as true for experienced researchers as it is for beginning researchers. The dialogue below is an example of how two colleagues, Adrian (A) and Corin (C), work together to gradually formulate a testable hypothesis. Some of their conversation will look familiar as they refine their prediction through multiple steps of discussion:
Narrowing the focus of their prediction.
Making their prediction more testable.
Being more specific about what they want to study.
Engaging their prediction in cycles of refinements.
Determining the appropriate level/grainsize of their prediction (zoom in, zoom out).
Adding more predictions.
Thinking about underlying mechanisms (i.e., what explains the relationships between their variables).
Putting their predictions on a continuum (going from black and white to grey).
In addition, they construct their theoretical framework to match their hypotheses through multiple steps:
Defining and rationalizing their variables.
Re-evaluating their initial rationales in response to changes in their initial predictions.
Asking themselves “why” questions about predictions and rationales.
Finding empirical evidence and theory that better supports their evolving predictions.
Keeping in mind what they are going to be measuring.
Making sure their rationales support each link in their chain of reasoning.
Identifying underlying mechanisms.
Making sure that statements are included in their rationale if and only if they directly support their predictions and are essential to the argument.
They begin with the following hypothesis:
Prediction: Students will exhibit more persistence in mathematical course taking in high school if they work in groups.
Brief Description of Rationale: When people work in groups, they feel more competent and learn better (Cohen & Lotan, 2014 ; Jansen, 2012). When people feel more competent, they persist in additional mathematical course taking (Bandura & Schunk, 1981 ; Dweck, 1986 ).
So, do we think this hypothesis is testable?
Well actually, who these students are is probably something we need to be more specific about.
Good point, and also, since Algebra 2 is the bridge to additional course taking (i.e., the first course students don’t have to take), perhaps we should target Algebra 2. How about if we change our prediction to the following: Algebra 2 students will exhibit more mathematical persistence in mathematical course taking in high school if they work in groups in Algebra 2.
Okay, but another problem is that it would take a long time to collect data that would inform a prediction about the courses students take, and over that amount of time I’m not sure we could even tell if groupwork was responsible. What if we limited our prediction to: Algebra 2 students will exhibit more mathematical persistence in Algebra 2 if they work in groups.
Good idea! But when we talk about persistence, do we mean students don’t quit, or that they don’t drop the course, or productively struggle during class, or turn in their homework, or is it something else we mean? To me, what would be testable about mathematical persistence would be persistence at the problem level, such as when students get stuck on a problem, but they don’t give up.
I agree. So, let’s predict the following: Algebra 2 students will exhibit more mathematical persistence in Algebra 2 when they get stuck on problems if they work in groups. That’s something I think we could test.
Yes, but I think we need to be even more specific about what we mean by mathematical persistence when students get stuck on problems.
Hmm, what if we focused specifically on mathematical persistence that involves staying engaged in trying to solve a problem for the duration of a problem-solving session or until the problem gets solved? But that also makes me wonder if we want to be focusing on persistence at the individual level or at the group level?
Umm, I think we should focus on persistence at the individual level, because that’s more consistent with our original interest in persistence in course taking, which is about individual students, not about groups.
Okay, that makes sense. So then how about this for a prediction: If Algebra 2 students work in groups, they will be more likely to stay engaged in trying to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem.
To this point in the dialogue, Adrian and Corin are developing a theoretical framework by sharpening what they mean by their prediction and making sure their prediction is testable. In the next part, they return to their original idea to make sure they have not strayed too far by making their prediction more precise. The dialogue illustrates how making predictions should support the goal of understanding the relationship between variables and the mechanisms for change.
Yes, I’m liking the way this prediction is evolving. However, I also feel like our prediction is now so focused that we’ve lost a bit of our initial idea of competence and learning, which is what we were initially interested in. Could we do something to bring those ideas back? Perhaps we could create more predictions to get at more of those ideas?
Great idea! Okay, so to help us see what we are missing now, let’s look back at the initial links in our chain of reasoning. We initially said that Working in Groups leads to Feeling Competent & Learning Better leads to Persistence in Math Course Taking. But our chain of reasoning has changed. I think it’s more like this: Working in Groups on Problems leads to Staying Engaged in Problem Solving leads to Greater Sense of Competence and Learning Better leads to More Persistence in Course Taking.
Okay, so if that’s the case, it looks like our new prediction just tests the first link in this chain, the link between Working in Groups on Problems and Staying Engaged in Problem Solving. It looks like there are three other potential predictions we could make; we could make a prediction about the relationship between Staying Engaged in Problem Solving and having a Greater Sense of Competence, between Staying Engaged in Problem Solving and Learning Better, and between having a Greater Sense of Competence/Learning Better and More Persistence in Course Taking.
Clearly that’s too many predictions for us to tackle in one study and actually I am aware of several studies that already address the third prediction. So, we can use those studies as part of our rationale and don’t need to study that link.
I agree. Let’s just add one prediction, one about the link between Staying Engaged and Sense of Competence. In our initial prediction, we just had a vague connection between Working in Groups and Sense of Competence. But in our new prediction, we were more specific that working in groups helps students stay engaged until the end of a problem-solving session. So, I guess we could say for a second prediction then that When Algebra 2 students stay engaged in problem solving until the end of a problem-solving session, they develop a greater sense of competence.
Okay so we will have two predictions to examine with our study: Prediction 1 is: If Algebra 2 students work in groups, they will be more likely to stay engaged in trying to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem. This prediction deals with the first link in our chain of reasoning. And then Prediction 2 is: If Algebra 2 students try to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem, they will be more likely to develop a sense of competence. Oh, as soon as I finished stating that prediction, the thought just came to me, “sense of competence about what?”
How about if we focused on sense of competence in being able to solve similar problems in the future? Actually, maybe that’s too limited. Maybe we should expand our prediction a bit more so we include a sense of competence that’s at least somewhat closer to more course taking? Something like sense of competence that involves feeling capable of understanding future Algebra 2 concepts. That’s at least bigger than sense of competence at solving similar problems. If students feel they’re capable of understanding future Algebra 2 concepts, then they will probably be more likely to persist in course taking too.
Okay, that makes sense. So, then our Prediction 2 could be: If Algebra 2 students try to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem, they will be more likely to feel they will be capable of understanding future Algebra 2 concepts.
Oh, I just had an additional idea! What if we changed the two predictions one more time to allow for more or less of the variables? For example, Prediction 1 could be: The more Algebra 2 students work in groups, the more likely they will stay engaged in trying to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem.
Yes, great. So, that would mean Prediction 2 could be: The more Algebra 2 students try to solve problems for the duration of a problem-solving session or until they solve the problem, the more likely they will feel they are capable of understanding future Algebra 2 concepts.
So, I think we’re happy with our predictions for now, but I think we need to work on our rationales for those predictions because they no longer apply very well.
Okay, to recap, our original chain of reasoning was Working in Groups leads to Feeling Competent & Learning Better leads to Persistence in Math Course Taking. Our initial rationales were the following: For the link between working in groups and feeling competent, we based that link on Cohen and Lotan’s ( 2014 ) book on Designing Groupwork, in which they explain why and how all students can feel competent through their engagement in groupwork. We also based this link on that 2012 Jansen study that found that groupwork helped students enact their competence in math. Then, for the link between competence and persistence, we based that link on the Bandura and Schunk ( 1981 ) study and on the work by Carol Dweck ( 1986 ) that show that children who feel more competent in arithmetic, tend to persist more.
Corin and Adrian have looked back at their initial research idea. In doing so, they illustrated how developing a theoretical framework involves developing and refining a chain of reasoning. They continue by working on developing rationales for their predictions.
Okay, so let’s think if any of our previous rationales still work. How about Elizabeth Cohen’s work? I still think her work applies because it shows that groupwork can affect engagement. But now that I think about it, another part of her work indicates that groupwork needs particular norms in order to be effective. So maybe we should tighten up our predictions to focus just on groupwork that has particular norms?
But, on the other hand, what about Jo Boaler’s ( 1998 ) “Open and Closed Mathematics” article? In that study, students at the Phoenix Park School did not have much structure, and in spite of that, groupwork worked quite well for those students, better than individual work did for students at the Amber Hill School who had highly structured instruction.
That’s a good point. So maybe we should leave our predictions about groupwork as is (i.e., not focus on particular norms). Also, the ideas in the Boaler article would be good to add to our theoretical framework because it deals with secondary students, which aligns better with the ages of the Algebra 2 students we are planning on studying.
Okay, so we’re adding the ideas in the Boaler article. I also think we need to find literature that specifies the kind of engagement we want to focus on. Looking at the engagement literature would sharpen our thinking about the engagement we are most interested in. We should consider Brigid Barron’s ( 2003 ) study, “When Smart Groups Fail.” In her study, students produced better products if they engaged with each other and with the content. But that makes me think that we are mostly just focused on the latter, namely on how individuals engage with the content.
I agree we’re focused on individuals’ engagement with the content. Come to think of it, the fact that we’re focused on how individuals engage with content rather than how groups engage further justifies why we’re not looking at groupwork norms. But let me ask a question we need to answer. Why are we focusing on how individuals engage with content? It’s not just a preference. It’s because we think individual engagement with content is related to feeling capable. So, our decision to focus on individual engagement aligns with our predictions. And even though we’re not including Barron’s work in our framework, considering her work helped sharpen our thinking about what we’re focusing on.
You know, we are kind of in a weird space because we’re focusing on individual engagement with content at the same time as we are predicting that groupwork leads to more engagement. In other words, we are and aren’t taking a social perspective. But what this reminds me of is how, from the perspective of the theory of constructivism, even though individuals have to make sense of things for themselves, social interactions are what drives sense making. In fact, here’s a quote from von Glasersfeld ( 1995 ): “Piaget has stressed many times that the most frequent cause of accommodation is the interaction” (p. 66). So, I think we can use constructivism as a theoretical justification for predicting that the social activity of groupwork is what is related to individual engagement with content.
Interesting! Yes, makes sense. When you were describing that, I had another insight from constructivism. You know how when someone experiences a perturbation, it also creates a need in them to resolve the perturbation, right? So maybe perturbations are the mechanism explaining why groupwork leads to more individual engagement with content. Groupwork potentially generates perturbations, meaning the person engages more to try to resolve those perturbations.
Okay, now that we have brought in the idea of perturbations as potentially being the mechanism that drives how working in groups leads to staying more engaged, perhaps we need to reconsider what we will be measuring in our study. Will it be perturbations, or will it be staying engaged that we should be measuring?
I think what we are saying is that the need to resolve perturbations is part of the underlying mechanism, but measuring the need to resolve perturbations would be difficult if not impossible. So, instead, I think we should focus on measuring the variable staying engaged , a variable we can measure. And then if we find that more working in groups leads to more staying engaged, that also gives us more evidence that our theoretical framework with perturbations as a mechanism is viable. In other words, mechanisms are part of our framework and by testing our prediction, we are testing our theoretical framework (i.e., our rationales) too.
This final part of the dialogue illustrates that the rationale for a study continues to develop as the predictions continue to be refined and testability continues to be considered. In other words, the development of the predictions and rationale (i.e., the theoretical framework) should be iterative and ongoing.
Through their discussion, Adrian and Corin have refined both their predictions and their rationales. In the process, the key ideas they have drawn on contributed to their rationales and thus to constructing their theoretical framework.
Part V. Distinctions Between Rationales, Theoretical Frameworks, and Literature Reviews
We have introduced a number of terms that play critical roles in the scientific inquiry process. Because they refer to related and sometimes overlapping ideas, keeping straight their meanings and uses can be challenging. It might be helpful to revisit each of them briefly to describe how they are similar to, and different from, each other.
To distinguish between rationales, theoretical frameworks, and literature reviews, it is useful to consider the roles they play as you plan and conduct a study compared to the roles they play when you write the report of your study.
Thinking Through a Study
The chronology of the thinking process often moves through many cycles of identifying a research problem or asking a question, and then reading the literature to learn more about the problem, and then refining and narrowing the scope of a question that would add to or extend what is known, and then predicting (guessing) an answer to the question and asking yourself why you predicted this answer and writing a first draft of your rationale, and then reading the literature to improve your rationale, and then realizing you can refine the question further along with specifying a clearer and more targeted prediction, and then reading the literature to further improve your rationale, and then realizing you can refine the question further along with a clearer and more targeted prediction, and so on.
The primary activity that generates more specific and clearer hypotheses is searching and reviewing literature . You can return to the literature as often as you need to build your rationales . As your rationales develop, they morph into your theoretical framework . The theoretical framework is a coherent argument that threads together the individual rationales and explains why your predictions are the best predictions the field can make at this time.
If you have one research question and one prediction you will have one rationale. In this case, your rationale is essentially the same as your theoretical framework. If you have more than one research question, you will have multiple predictions and multiple rationales. As you develop rationales for each prediction, you might find lots of overlap. Maybe the literatures you read to refine each prediction and develop each rationale overlap, and maybe the arguments you piece together include many of the same elements. Your theoretical framework emerges from weaving the rationales together into one coherent argument. Although this process is more complicated than the thinking process for one prediction, it is more common. If you find few connections among the rationales for each prediction, we recommend stepping back and asking whether you are conducting more than one study. It might make more sense to sort the questions into two or more studies because the rationales for the predicted answers are drawing from different literatures.
Writing the Evolving Research Paper
We recommend that you write drafts of the research report as you think through your study and make decisions about how to proceed. Although your thinking will be fluid and evolving, we recommend that you follow the conventions of academic writing as you write drafts. For example, we recommend that you structure the paper using the five typical major sections of a journal article: introduction, theoretical framework, methods, results, and discussion. Each of these sections will go through multiple drafts as you plan your study, collect the data, analyze the data, and interpret the results.
In the introduction, you will present the research problem you are studying. This includes describing the problem, explaining why it is significant, defining the special terms you use, and often presenting the research questions you will address along with the answers you predict. Sometimes the questions and predictions are part of the next section—the theoretical framework.
In the theoretical framework, you will present your best arguments for expecting the predicted answers to the research questions. You will not trace the many cycles in which you engaged to get to the best versions of your arguments but rather present the latest and best version. The report of a study does not describe the chronology of the back-and-forth messiness always involved in thinking through all aspects of the study. What you learned from reviewing the literature will be an integral part of your arguments. In other words, the review of research will be included in the presentation of your theoretical framework rather than in a separate section.

The literature you choose to include to present your theoretical framework is not all the literature you reviewed for conducting your study. Rather, the literature cited in your paper should be the literature that contributed to building your theoretical framework, and only that literature. In other words, the theoretical framework places the boundaries on what you should review in the paper.
Beginning researchers are often tempted to review much of what they read. Researchers put lots of time into reading, and leaving lots of it out when writing the paper can make all that reading feel like a waste of time. It is not a waste of time; it is always part of the research process. But, reviewing more than you need in the paper becomes a distraction and diverts the reader from the main points.

What should you do if the editor of the journal requires, or recommends, a section titled “review of research”? We recommend you create a somewhat more elaborated review for this section and then show exactly how you used the literature to build your rationale in the theoretical framework section.
Reviewers notice when the theoretical framework and the literature reviewed do not provide sufficient justification for the research questions (or the hypotheses). We found that about 13% of JRME reviews noted an especially important gap—the research questions in a paper were not sufficiently motivated. We expect the same would be true for other research journals. Reviewers also note when manuscripts either do not have an explicit theoretical framework or when they seem to be juggling more than one theoretical framework.
Part VI. Moving to Methods
A significant benefit of building rich and precise theoretical frameworks is the guidance they provide for selecting and creating the methods you will use to test your hypotheses. The next phase in the process of scientific inquiry is crafting your methods: choosing your research design, selecting your sample, developing your measures, deciding on your data analysis strategies, and so on. In Chap. 4 , we discuss how you can do this in ways that keep your story coherent.
Bandura, A., & Schunk, D. H. (1981). Cultivating competence, self-efficacy, and intrinsic interest through proximal self-motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 41 , 586–598. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.41.3.586
Article Google Scholar
Barron, B. (2003). When smart groups fail. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 12 (3), 307–359. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327809JLS1203_1
Biddle, B. J., & Anderson, D. S. (1986). Theory, methods, knowledge, and research on teaching. In M. C. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching: A project of the American Educational Research Association . Macmillan.
Google Scholar
Boaler, J. (1998). Open and closed mathematics: Student experiences and understandings. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 29 , 41–62.
Cai, J., Morris, A., Hohensee, C., Hwang, S., Robison, V., Cirillo, M., Kramer, S. L., & Hiebert, J. (2019c). Theoretical framing as justifying. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 50 (3), 218–224. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.50.3.0218
Cohen, E. G., & Lotan, R. A. (2014). Designing groupwork: Strategies for the heterogenous classroom (3rd ed.). Teachers College Press.
Colquitt, J. A., & Zapata-Phelan, C. P. (2007). Trends in theory building and theory testing: A five-decade study of the academy of management journal. The Academy of Management Journal, 50 (6), 1281–1303.
Dweck, C. S. (1986). Motivational processes affecting learning. American Psychologist, 41 , 1040–1048. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.41.10.1040
Kerlinger, F. N. (1964). Foundations of behavioral research: Educational and psychological inquiry . Holt, Rinehardt, & Winston.
Kersting, N. B., Givvin, K., Sotelo, F., & Stigler, J. W. (2010). Teacher’s analysis of classroom video predicts student learning of mathematics: Further explorations of a novel measure of teacher knowledge. Journal of Teacher Education , 61(1–2), 172–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487109347875 , 172.
Kersting, N. B., Givvin, K. B., Thompson, B., Santagata, R., & Stigler, J. (2012). Developing measures of usable knowledge: Teachers’ analyses of mathematics classroom videos predict teaching quality and student learning. American Educational Research Journal, 49 (3), 568–590. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831212437853
Oxford University Press. (2021). Theory. In Lexico.com dictionary . Lexico.com . https://www.lexico.com/en/definition/theory
Praetorius, A.-K., & Charalambous, C. (2022). Moving the field forward with respect to theorizing teaching: An introduction. In A.-K. Praetorius & C. Charalmabous (Eds.), Expert perspectives on theorizing teaching: Current status, problematic issues, and aspirations . Springer.
von Glasersfeld, E. (1995). Radical constructivism: A way of knowing and learning . Falmer Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
James Hiebert, Anne K Morris & Charles Hohensee
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
Jinfa Cai & Stephen Hwang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Hiebert, J., Cai, J., Hwang, S., Morris, A.K., Hohensee, C. (2023). Building and Using Theoretical Frameworks. In: Doing Research: A New Researcher’s Guide. Research in Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_3
Published : 03 December 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-19077-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-19078-0
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Make a Conceptual Framework

6-minute read
- 2nd January 2022
What is a conceptual framework? And why is it important?
A conceptual framework illustrates the relationship between the variables of a research question. It’s an outline of what you’d expect to find in a research project.
Conceptual frameworks should be constructed before data collection and are vital because they map out the actions needed in the study. This should be the first step of an undergraduate or graduate research project.
What Is In a Conceptual Framework?
In a conceptual framework, you’ll find a visual representation of the key concepts and relationships that are central to a research study or project . This can be in form of a diagram, flow chart, or any other visual representation. Overall, a conceptual framework serves as a guide for understanding the problem being studied and the methods being used to investigate it.
Steps to Developing the Perfect Conceptual Framework
- Pick a question
- Conduct a literature review
- Identify your variables
- Create your conceptual framework
1. Pick a Question
You should already have some idea of the broad area of your research project. Try to narrow down your research field to a manageable topic in terms of time and resources. From there, you need to formulate your research question. A research question answers the researcher’s query: “What do I want to know about my topic?” Research questions should be focused, concise, arguable and, ideally, should address a topic of importance within your field of research.
An example of a simple research question is: “What is the relationship between sunny days and ice cream sales?”
2. Conduct a Literature Review
A literature review is an analysis of the scholarly publications on a chosen topic. To undertake a literature review, search for articles with the same theme as your research question. Choose updated and relevant articles to analyze and use peer-reviewed and well-respected journals whenever possible.
For the above example, the literature review would investigate publications that discuss how ice cream sales are affected by the weather. The literature review should reveal the variables involved and any current hypotheses about this relationship.
3. Identify Your Variables
There are two key variables in every experiment: independent and dependent variables.
Independent Variables
The independent variable (otherwise known as the predictor or explanatory variable) is the expected cause of the experiment: what the scientist changes or changes on its own. In our example, the independent variable would be “the number of sunny days.”
Dependent Variables
The dependent variable (otherwise known as the response or outcome variable) is the expected effect of the experiment: what is being studied or measured. In our example, the dependent variable would be “the quantity of ice cream sold.”
Next, there are control variables.
Control Variables
A control variable is a variable that may impact the dependent variable but whose effects are not going to be measured in the research project. In our example, a control variable could be “the socioeconomic status of participants.” Control variables should be kept constant to isolate the effects of the other variables in the experiment.
Finally, there are intervening and extraneous variables.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Intervening Variables
Intervening variables link the independent and dependent variables and clarify their connection. In our example, an intervening variable could be “temperature.”
Extraneous Variables
Extraneous variables are any variables that are not being investigated but could impact the outcomes of the study. Some instances of extraneous variables for our example would be “the average price of ice cream” or “the number of varieties of ice cream available.” If you control an extraneous variable, it becomes a control variable.
4. Create Your Conceptual Framework
Having picked your research question, undertaken a literature review, and identified the relevant variables, it’s now time to construct your conceptual framework. Conceptual frameworks are clear and often visual representations of the relationships between variables.
We’ll start with the basics: the independent and dependent variables.
Our hypothesis is that the quantity of ice cream sold directly depends on the number of sunny days; hence, there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the independent variable (the number of sunny days) and the dependent and independent variable (the quantity of ice cream sold).
Next, introduce a control variable. Remember, this is anything that might directly affect the dependent variable but is not being measured in the experiment:
Finally, introduce the intervening and extraneous variables.
The intervening variable (temperature) clarifies the relationship between the independent variable (the number of sunny days) and the dependent variable (the quantity of ice cream sold). Extraneous variables, such as the average price of ice cream, are variables that are not controlled and can potentially impact the dependent variable.
Are Conceptual Frameworks and Research Paradigms the Same?
In simple terms, the research paradigm is what informs your conceptual framework. In defining our research paradigm we ask the big questions—Is there an objective truth and how can we understand it? If we decide the answer is yes, we may be working with a positivist research paradigm and will choose to build a conceptual framework that displays the relationship between fixed variables. If not, we may be working with a constructivist research paradigm, and thus our conceptual framework will be more of a loose amalgamation of ideas, theories, and themes (a qualitative study). If this is confusing–don’t worry! We have an excellent blog post explaining research paradigms in more detail.
Where is the Conceptual Framework Located in a Thesis?
This will depend on your discipline, research type, and school’s guidelines, but most papers will include a section presenting the conceptual framework in the introduction, literature review, or opening chapter. It’s best to present your conceptual framework after presenting your research question, but before outlining your methodology.
Can a Conceptual Framework be Used in a Qualitative Study?
Yes. Despite being less clear-cut than a quantitative study, all studies should present some form of a conceptual framework. Let’s say you were doing a study on care home practices and happiness, and you came across a “happiness model” constructed by a relevant theorist in your literature review. Your conceptual framework could be an outline or a visual depiction of how you will use this model to collect and interpret qualitative data for your own study (such as interview responses). Check out this useful resource showing other examples of conceptual frameworks for qualitative studies .
Expert Proofreading for Researchers
Whether you’re a seasoned academic or not, you will want your research paper to be error-free and fluently written. That’s where proofreading comes in. Our editors are on hand 24 hours a day to ensure your writing is concise, clear, and precise. Submit a free sample of your writing today to try our services.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 2
- Integration of a theoretical framework into your research study
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Roberta Heale 1 ,
- Helen Noble 2
- 1 Laurentian University , School of Nursing , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- 2 Queens University Belfast , School of Nursing and Midwifery , Belfast , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Roberta Heale, School of Nursing, Laurentian University, Ramsey Lake Road, Sudbury, P3E2C6, Canada; rheale{at}laurentian.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2019-103077
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Often the most difficult part of a research study is preparing the proposal based around a theoretical or philosophical framework. Graduate students ‘…express confusion, a lack of knowledge, and frustration with the challenge of choosing a theoretical framework and understanding how to apply it’. 1 However, the importance in understanding and applying a theoretical framework in research cannot be overestimated.
The choice of a theoretical framework for a research study is often a reflection of the researcher’s ontological (nature of being) and epistemological (theory of knowledge) perspective. We will not delve into these concepts, or personal philosophy in this article. Rather we will focus on how a theoretical framework can be integrated into research.
The theoretical framework is a blueprint for your research project 1 and serves several purposes. It informs the problem you have identified, the purpose and significance of your research demonstrating how your research fits with what is already known (relationship to existing theory and research). This provides a basis for your research questions, the literature review and the methodology and analysis that you choose. 1 Evidence of your chosen theoretical framework should be visible in every aspect of your research and should demonstrate the contribution of this research to knowledge. 2
What is a theory?
A theory is an explanation of a concept or an abstract idea of a phenomenon. An example of a theory is Bandura’s middle range theory of self-efficacy, 3 or the level of confidence one has in achieving a goal. Self-efficacy determines the coping behaviours that a person will exhibit when facing obstacles. Those who have high self-efficacy are likely to apply adequate effort leading to successful outcomes, while those with low self-efficacy are more likely to give up earlier and ultimately fail. Any research that is exploring concepts related to self-efficacy or the ability to manage difficult life situations might apply Bandura’s theoretical framework to their study.
Using a theoretical framework in a research study
Example 1: the big five theoretical framework.
The first example includes research which integrates the ‘Big Five’, a theoretical framework that includes concepts related to teamwork. These include team leadership, mutual performance monitoring, backup behaviour, adaptability and team orientation. 4 In order to conduct research incorporating a theoretical framework, the concepts need to be defined according to a frame of reference. This provides a means to understand the theoretical framework as it relates to a specific context and provides a mechanism for measurement of the concepts.
In this example, the concepts of the Big Five were given a conceptual definition, that provided a broad meaning and then an operational definition, which was more concrete. 4 From here, a survey was developed that reflected the operational definitions related to teamwork in nursing: the Nursing Teamwork Survey (NTS). 5 In this case, the concepts used in the theoretical framework, the Big Five, were the used to develop a survey specific to teamwork in nursing.
The NTS was used in research of nurses at one hospital in northeastern Ontario. Survey questions were grouped into subscales for analysis, that reflected the concepts of the Big Five. 6 For example, one finding of this study was that the nurses from the surgical unit rated the items in the subscale of ’team leadership' (one of the concepts in the Big Five) significantly lower than in the other units. The researchers looked back to the definition of this concept in the Big Five in their interpretation of the findings. Since the definition included a person(s) who has the leadership skills to facilitate teamwork among the nurses on the unit, the conclusion in this study was that the surgical unit lacked a mentor, or facilitator for teamwork. In this way, the theory of teamwork was presented through a set of concepts in a theoretical framework. The Theoretical Framework (TF)was the foundation for development of a survey related to a specific context, used to measure each of the concepts within the TF. Then, the analysis and results circled back to the concepts within the TF and provided a guide for the discussion and conclusions arising from the research.
Example 2: the Health Decisions Model
In another study which explored adherence to intravenous chemotherapy in African-American and Caucasian Women with early stage breast cancer, an adapted version of the Health Decisions Model (HDM) was used as the theoretical basis for the study. 7 The HDM, a revised version of the Health Belief Model, incorporates some aspects of the Health Belief Model and factors relating to patient preferences. 8 The HDM consists of six interrelated constituents that might predict how well a person adheres to a health decision. These include sociodemographic, social interaction, experience, knowledge, general and specific health beliefs and patient preferences, and are clearly defined. The HDM model was used to explore factors which might influence adherence to chemotherapy in women with breast cancer. Sociodemographic, social interaction, knowledge, personal experience and specific health beliefs were used as predictors of adherence to chemotherapy.
The findings were reported using the theoretical framework to discuss results. The study found that delay to treatment, health insurance, depression and symptom severity were predictors to starting chemotherapy which could potentially be adapted with clinical interventions. The findings from the study contribute to the existing body of literature related to cancer nursing.
Example 3: the nursing role effectiveness model
In this final example, research was conducted to determine the nursing processes that were associated with unexpected intensive care unit admissions. 9 The framework was the Nursing Role Effectiveness Model. In this theoretical framework, the concepts within Donabedian’s Quality Framework of Structure, Process and Outcome were each defined according to nursing practice. 10 11 Processes defined in the Nursing Role Effectiveness Model were used to identify the nursing process variables that were measured in the study.
A theoretical framework should be logically presented and represent the concepts, variables and relationships related to your research study, in order to clearly identify what will be examined, described or measured. It involves reading the literature and identifying a research question(s) while clearly defining and identifying the existing relationship between concepts and theories (related to your research questions[s] in the literature). You must then identify what you will examine or explore in relation to the concepts of the theoretical framework. Once you present your findings using the theoretical framework you will be able to articulate how your study relates to and may potentially advance your chosen theory and add to knowledge.
- Kalisch BJ ,
- Parent M , et al
- Strickland OL ,
- Dalton JA , et al
- Eraker SA ,
- Kirscht JP ,
- Lightfoot N , et al
- Harrison MB ,
- Laschinger H , et al
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Patient and public involvement Not required.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Topic Guide - Developing Your Research Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- APA 7th Edition
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
Importance of Theory
Strategies for developing the theoretical framework, structure and writing style, writing tip, another writing tip, yet another writing tip, still yet another writing tip.
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- 10. Proofreading Your Paper
- Writing Concisely
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Study
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Bibliography
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounding assumptions. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework introduces and describes the theory that explains why the research problem under study exists.
Abend, Gabriel. "The Meaning of Theory." Sociological Theory 26 (June 2008): 173–199; Swanson, Richard A. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines . San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers 2013.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
By virtue of its applicative nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges associated with a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework . College of Education. Alabama State University; Corvellec, Hervé, ed. What is Theory?: Answers from the Social and Cultural Sciences . Stockholm: Copenhagen Business School Press, 2013; Asher, Herbert B. Theory-Building and Data Analysis in the Social Sciences . Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1984; Drafting an Argument . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Jarvis, Peter. The Practitioner-Researcher. Developing Theory from Practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1999.
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research problem. Identify the assumptions from which the author(s) addressed the problem.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, your work is expected to test the validity of that existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism Theory, which categorizes perceived differences among nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism Theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the disputed split between southern and northern Sudan that led to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Based upon the above example, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as an answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [i.e., justify the application of your choice of a particular theory and explain why alternative constructs were rejected. I could choose instead to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among ethnic conflict theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
Just as a research problem in your paper requires contextualization and background information, a theory requires a framework for understanding its application to the topic being investigated. When writing and revising this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks , concepts, models, or theories . As noted in the example above, there will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the theory you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory. Although the past tense can be used to describe the history of a theory or the role of key theorists, the construction of your theoretical framework is happening now.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory inadequately explains a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework . College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. "A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research." Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article . Inside Higher Education; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Weick, Karl E. “The Work of Theorizing.” In Theorizing in Social Science: The Context of Discovery . Richard Swedberg, editor. (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2014), pp. 177-194.
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Elsewhere
An increasingly important trend in the social and behavioral sciences is to think about and attempt to understand research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories developed within your particular discipline, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbents in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be more engaged in the research topic.
CohenMiller, A. S. and P. Elizabeth Pate. "A Model for Developing Interdisciplinary Research Theoretical Frameworks." The Qualitative Researcher 24 (2019): 1211-1226; Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Don't Undertheorize!
Do not leave the theory hanging out there in the introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you describe should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the review of pertinent literature and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose supports analysis of the research problem or, if appropriate, how the theoretical framework was found to be inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in newspapers and popular magazines and in non-academic settings. However, the difference between theory and hypothesis in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested assumptions that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory; critical race theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis . About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis . Slideshare presentation.
Be Prepared to Challenge the Validity of an Existing Theory
Theories are meant to be tested and their underlying assumptions challenged; they are not rigid or intransigent, but are meant to set forth general principles for explaining phenomena or predicting outcomes. Given this, testing theoretical assumptions is an important way that knowledge in any discipline develops and grows. If you're asked to apply an existing theory to a research problem, the analysis may include the expectation by your professor that you should offer modifications to the theory based on your research findings. Indications that theoretical assumptions may need to be modified can include the following:
- Your findings suggest that the theory does not explain or account for current conditions or circumstances,
- The study reveals a finding that is significantly incongruent with what the theory attempts to explain or predict, or
- Your analysis reveals that the theory overly generalizes behaviors or actions without taking into consideration specific factors [e.g., factors related to culture, nationality, history, gender, ethnicity, age, geographic location, legal norms or customs , religion, social class, socioeconomic status, etc.].
Philipsen, Kristian. "Theory Building: Using Abductive Search Strategies." In Collaborative Research Design: Working with Business for Meaningful Findings . Per Vagn Freytag and Louise Young, editors. (Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018), pp. 45-71; Shepherd, Dean A. and Roy Suddaby. "Theory Building: A Review and Integration." Journal of Management 43 (2017): 59-86.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2022 8:49 AM
- URL: https://leeuniversity.libguides.com/research_study_guide
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
A patient-centered conceptual model of aya cancer survivorship care informed by a qualitative interview study.

Simple Summary
1. introduction, 2.1. recruitment, 2.2. interview approach, 2.3. analysis, 3.1. overall themes, 3.2. care coordination and healthcare system navigation support.
“So there really wasn’t much time. Or was there? I didn’t know to ask that question. Okay, I know this is growing—is there enough time for me to get a consultation? I don’t know if maybe I could have waited a few days. I just don’t know, because I didn’t know that question to ask... But I just went ahead and signed away because I felt like I was—I hate to say the word bullied, but I felt like I was in a corner. I was like oh my god—this cancer’s bigger than me, just get it out, kill it! Do what you need to do.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I, I mostly blamed myself for my inexperience in hospitals, I guess. But yeah, I felt like people weren’t necessarily completely clear, well, telling me exactly what I had to do. What I should do. Like when I should ask for help or when I didn’t need to, that sort of thing.”— Participant 2, female, renal cell carcinoma, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I felt like I had to be the care coordinator. I had to make sure everybody knew what the other was doing. Proactively ask for appointments—like okay, I’m going to have to get radiation next. And they’re like oh, you can wait for that until the week before, and I was like, but what if I don’t like [the provider]? You’re going to put me in a box. So I had to just be proactive to get the kind of care that I wanted to get. And I felt like my care coordinator, which is exhausting.”— Participant 4, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I was first getting treatment somewhere and I didn’t feel completely taken care of there. As a nurse practitioner, I felt like I was asking—I was supposed to be a patient then, I wasn’t supposed to be a health care provider. So I felt like I was directing my care and I was reminding them of things. It didn’t feel like the right fit for me with my oncologist and the care team, so I ended up after getting a second opinion switching to another hospital.”— Participant 3, female, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“Gosh, that’s really why I became an advocate—I just couldn’t believe the lack of treating me as a holistic person. I understand that I guess to be an oncologist you’re going to meet patients who ultimately die from it, and I get that they’re trying to make sure that you don’t die, and that is of course great, you kind of need that. But what about a nurse navigator or even like the nurse? There was no follow up... there needs to be a middle person. Whether it be that nurse or that social worker, and it should be mandatory that every AYA... have an initial conversation [with them] and then determine if you want to work with them...The follow ups just go through the cracks.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I felt like my oncologist was very good at giving me medications to deal with nausea and other side effects when I needed them...But I had to research online what are things that I could use and then go and ask for it, as opposed to someone presenting me with “these are all the resources” or “these are things you should consider, let us know what you need”. I felt like the latter would have been much more helpful. I went to [other specialty cancer centers, and] both of those hospitals did provide that. Like “here’s your coordinator, here’s a whole pamphlet, here’s all the resources we have. Here’s how you use each one”. So I thought that was really cool.”— Participant 4, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
3.3. Mental Health Support
“Definitely anxiety, depression for sure. I think those would be the biggest two that I’ve had to deal with. It’s an everyday struggle … Anxious about my cancer getting worse or also having cancer in my family or friends, since I already know what it feels like, having cancer. I wouldn’t want any of my loved ones to go through the same thing.”— Participant 6, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“Cancer is trauma, and even though a lot may not equate it with that term, because they just don’t know, a lot of us have PTSD. And that’s not talked about enough… every experience in the AYA community matters. So that might be why someone would not [talk to a researcher about their cancer experience], because they might feel like you could talk to someone better. It’s really about insecurity, but also too how they’ve been treated throughout their treatment. It can be hard to discuss and be traumatic. I can now verbally talk about it without bursting into tears, but not everyone can.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“Obviously having cancer kind of like fucks you up mentally. But I’ve been going to therapy, I actually take an antianxiety med now.”— Participant 8, female, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 15–19 years old at diagnosis .
“Like I thought, I thought I was alone for like five years … Post treatment I actually had a really bad depressive episode, because I was just in such despair because I thought I was alone and no one else was like me. And I did hours of searching and finally found a couple of organizations that led me to other things. But I would have liked to have those resources [earlier], I wouldn’t have felt so alone.”— Participant 8, female, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 15–19 years old at diagnosis .
“I actually learned about the support groups from Instagram … just as a young Black woman, [it was important] to see other women of color that were young and that looked like me, because I was not seeing that at my cancer center. So that was a huge support for me. Also, just by sharing my story, it allowed me to pay it forward to other young adults and also inspired me to get involved in advocacy work.”— Participant 9, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
3.4. Peer Support and Making “Cancer Friends”
“It’s bad enough I’m an AYA, it’s bad enough I’m Black, it’s bad enough I’m a woman, it’s bad enough that I am an only child. I feel like all of these things were hitting me—and I have cancer, and now I literally have no one? It’s been hard.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“So, I think at the time the quintessential experience of being the youngest person at the cancer center in the waiting room, you know, not seeing anybody else my age unless they were in a caregiver capacity... And just feeling like I was the only person my age that had cancer and was getting treatment. And so the experience was very different when you are under 40. I didn’t know other people that had gone through that at the time.”— Participant 10, male, testicular cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“As I was nearing the end of chemotherapy, I was feeling like I couldn’t really talk to my friends the same, and I didn’t really have people to relate to, and I felt like an astronaut. My brain was foggy, I really wanted to talk to someone about [my side effects and stuff] without worrying people. I remember Stupid Cancer was the big [AYA organization] at the time, and I saw that they had in-person Meetups. I decided to go … and then I instantly was like oh, maybe this [is] a window into a community I didn’t even know existed. I didn’t picture people in their 20s and 30s with cancer hanging out before this. That was the beginning of making cancer friends, [we have fun but] also if someone does need to vent about their situation, treatment, insurance, or relationships going away because of cancer, you’re the perfect [person] to talk to about it.”— Participant 11, male, testicular cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I went through a lot of side effects. I literally had the motherlode of side effects and what was very hurtful was when my oncologist would be like yeah, you know, a lot of patients get that. Well, it’s my first time seeing my tongue turn black, so you might want to have some sort of—I don’t know, like compassion for how freaked out I would be. Even my throat would swell and I had difficulty swallowing. ‘Oh, I’ve seen it before, I’ve seen worse.’ Well, I’ve never seen worse.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I wish that that there was an AYA program at the hospital to tell me about these resources. To tell me like, hey, there’s a Gilda’s Club, it’s 10 to 15 min from here. There’s a meeting once a month. You can go and meet people your own age. It’s safe. People are really cool. Check it out. And now you can join these virtually. Just having somebody to say to me that is totally normal to feel that way. There are other people your age that get treatment here and you can meet them. That would have been really awesome.”— Participant 10, male, testicular cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I think just introducing for patients, that adolescent young adult oncology exists, and there is support out there for AYA’s. I didn’t really dive into the AYA support community until after treatment and got connected to a lot of resources and a lot of friends that way. But I think if I had known that resources like that existed while I was going through treatment, it would have been helpful just to know that I wasn’t alone and all these amazing organizations exist.”— Participant 12, female, osteosarcoma, 15–19 years old at diagnosis .
3.5. Empathic Communication about Fertility Preservation
“When I got diagnosed in the hospital … they had brought in a blood specialist and he described leukemia to me … After he left one of the interns immediately asked me, like so do you have any kids? And I was like no. And he was like, have you thought about freezing your eggs? And I’m like, dude, this dude just told me about cancer, like I haven’t, I can’t talk about kids right now like. You know?”— Participant 13, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“The timing was rushed because it was overwhelming. I feel like if you sit down with anybody, man, woman, whatever, and tell them you might not be able to have kids, that’s pretty heavy and something you want to sit with. And … it’s not like it was free to go get the sperm banking done and have it stored. But I was like well, if I don’t do this, that might be it, I might never have kids. Even if I don’t want them at the moment, taking the option off just seemed scary. So yeah, I would have liked to have had more time.”— Participant 11, male, testicular cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“Everything for me happened within like three days, so there was no, no ability to like, I don’t even know what it’s called. But to … freeze my eggs, I didn’t have that option because of the type of cancer I had everything had to be done so quickly. The only thing I was told in regards to fertility is you may not be able to have kids. There’s a high likelihood with the chemotherapy you are receiving that you may not be able to have children after this. There was no offering of like any type of resources. I only found that out afterwards, [about] all like the different type of programs for patients.”— Participant 15, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“We talked about [fertility preservation] in [my support] group before and I guess, well, I mean for guys it’s easy, so they’re super on top of it as far as when we spoke about it. But a lot of [women] who were in similar positions to me where it was all just really sad. From my experience [the doctors] were like, okay, you’re here now, here’s your doctor, here’s your treatment. Oh, by the way there’s this [fertility preservation option], we kind of want to get started right now, so could you just not [have kids] … It wasn’t a huge deal, but I was a little sad.”— Participant 14, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“There should have been a follow up call [after my diagnosis]. Because that was a really intense moment. My first time as the patient … Why wasn’t there a follow up? Like hey, I know you just heard a lot of information, let’s talk about this. I feel like I should have at least been required to get a consultation with an infertility specialist, even though it wouldn’t have been covered under my insurance. I feel that conversation should at least have been had so they could make sure I was really making the best decision for myself at that time. Sorry, I get really passionate and very angered about it.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I lost my fertility. No one prepared me for that. I didn’t receive initial counseling going into that surgery or coming out of it. I didn’t expect to experience that kind of grief, because I was single all this time, and childless, and now I am chronically single and barren forever. None of my doctors cared to see how that would affect me.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I don’t really have trouble communicating with [doctors]. I’m a lawyer and I did a lot of research, so I generally got the comments that ‘oh, you’re so knowledgeable, you’re an easy patient.’ [But] I don’t think they necessarily answered all my questions, or gave me all the resources that were available, or were upfront about side effects, which I found frustrating…[the doctors failed] to mention fertility resources [so] I found my own stuff … I certainly wouldn’t say I got most of my information from my oncologist, but I found it in other places.”— Participant 4, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“My oncologist is very respectful of my wishes in terms of wanting to have another baby … but then [she] also wasn’t afraid to tell me, you know, we can only do one round of harvesting your eggs, because it’s not safe to do more. She did a really good job acknowledging my dream and weighing that accordingly, [so] I’m not risking life … but I’m still able to try to, you know, preserve my fertility before having this definitive surgery.”— Participant 5, female, ovarian cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“Before I started chemo, my social worker came to talk to me in the hospital room and she just wanted me to know like hey, your doctors want you to do chemo, but you don’t have to do it right now, you can work on the fertility thing, if it’s important to you. So she made me feel comfortable that it was okay to delay the treatment.”— Participant 7, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
3.6. Financial Burden and Need for Support
“We needed help, we had help from family and friends, but again, the financial burden … is just a nightmare. You got the financial burden, you got the paperwork. You’re supposed to be focusing on your health.”— Participant 5, female, ovarian cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I worked in fine dining and didn’t have any insurance … And then the diagnosis alone racked up I think tens of thousands of [dollars in] debt and I was just through biopsies and scans and you know. I was going to, which is laughable, but it was called free clinic. It took a long time before I was diagnosed; go get bloodwork, come back in two weeks, schedule another appointment for two weeks later. And debt was mounting.”— Participant 16, male, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“I probably know more about the American health services than I ever wanted to know … it’s just not the way I would have liked to have learned it.”— Participant 8, female, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 15–19 years old at diagnosis .
“With my age I am able to be on my dad’s insurance and it is a really good insurance plan. So it hasn’t been like insanely expensive or anything … But as I approach my 26th birthday, the cutoff [of staying on my parents’ insurance], I have lots of concerns with finding good health care on my own.”— Participant 14, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
3.7. Quality of Life
“When I was first diagnosed I was studying for a board license for civil engineering. I was still thinking I’m going to be in chemo for eight hours, I’ll have a lot of time to study at the hospital. It wasn’t like that at all. That’s when I was in denial, and I think after that, that’s when depression hit me. I was like you know what? It’s over, I’m just going to keep my job now. There’s no way I can study for the exam … Sometimes in my back of my mind I’m still thinking I want to be a licensed engineer and all I have to do is pass that exam. I start dreaming that when I pass the exam, I’m going to get my promotion and travel more, which I used to do before diagnosis … I guess career-wise I still think about getting my license, even if I don’t keep working in the engineering field, I want to feel accomplished. I want to be able to say even through or despite cancer, I was still able to accomplish that.”— Participant 6, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“So because I got sick, at least with my internship hours, I could have been done last December. But I was going through treatment. And my friend and I were collecting hours and going to school at the same time. She already finished herself, got certified, she’s my boss right now. She’s my supervisor. We were like at the same level, she’s already above me. So and she doesn’t treat me any lower, but I’m still a little upset sometimes because I could have been there by now if I hadn’t gotten sick.”— Participant 13, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“I’ve been a dog groomer on and off for about 10 years. And I when I was finally able to get back into work [right after my surgery], I felt like they didn’t understand what I was going through. Like I was very anxious, and there’s a lot of sounds in a grooming salon. And it was really putting me on edge. And I started to wear earplugs to deal with that. And then I started getting like looks from my coworkers and like I just started to feel less and less welcome there. And I just gave up on it and I ended up quitting that job. I just didn’t feel very good there anymore.”— Participant 2, female, renal cell carcinoma, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I did officially go back up to my regular hours, but there are some days that I take time off for appointments. I try to schedule for example my scans in one day, for example, so I only have to take one day off whenever I can…It’s not just cancer that we deal with, we still have to deal with what other people go through as well, for example taking time out for dental and eye doctor appointments. I still have to take time off for that.”— Participant 6, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I had never been to the hospital before. And so I had to go through getting my diagnosis. Going through all these different procedures. And every one alone. They transferred me because they didn’t have the resources where I live to treat me. They transferred me to Houston, so my life got uprooted. My job put on hold. I had to move about five hours away so I could get treatment.”— Participant 13, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
3.8. Information about and Support Mitigating Side Effects and Late Effects
“The important elements for young adult cancer care compared to the typical cancer patient that you think of, like 50, 60, 70, they’re worried more about the here and now, and they don’t necessarily have to worry about side effects 20, 30 years down the road, because life expectancy, they won’t be there. I was diagnosed at 25. God willing, I’ll be alive for 50 more years beyond that. I don’t want to be dealing with side effects for years on end, so if there’s an option that’s a little bit more conservative treatment, which will possibly result in less side effects but maybe instead of saying it’s 100% certain, it’s 80% certain. That’s a 20% difference, so I think addressing that in terms that are easily understood by young adults, and also not in a talk down to manner, is super important.”— Participant 17, male, testicular cancer, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“Oh, and then the thing I always forget are the other secondary effects of treatment. I had to have both shoulders and both hips replaced, and I had no idea that was going to be in my future whatsoever, at the time of treatment.”— Participant 18, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“I have osteoporosis and I’m not even 25 yet, so that’s kind of concerning for the future.”— Participant 14, female, leukemia, 20–29 years old at diagnosis .
“The one thing I do deal with is, because of all the surgery I’ve had, I have chronic nerve pain, nerve damage, so that’s not fun to deal with. I wish I would have known that it was a possibility, because I was not told that it was a possibility that this could happen.”— Participant 19, female, sarcoma, 15–19 years old at diagnosis .
“I’ve got major issues with the majority of my organs. I have liver damage. I have heart failure. I was in a wheelchair for a while. I was on bedrest for a very long time right after everything. I am disabled. I am on disability. And I do not have the energy I once did. Napping and every couple days just being totally exhausted is kind of part of my life.”— Participant 20, female, leukemia, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“I have permanent damage—I don’t feel my feet, my toes from the upper balls to my toes. Sometimes the numbness goes up my legs… and I’ve fallen, actually almost fractured my ankle in January because I didn’t feel my foot. It was so sudden and severe, and … no one seemed to take it as seriously as I did, which is frustrating.”— Participant 1, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
3.9. Attention to the Unique Needs of Young Adults
“[My center had] an AYA program. Granted, they have so much volume because they have a special unit, so I think volume begets resources. But they have providers who are knowledgeable and not just oncologists, but lots of different providers who are knowledgeable about issues that AYA’s face, especially fertility. Sometimes we respond differently to drugs. If every center could have somebody who has a special research focus, to keep up to date on AYA’s. Or a pamphlet, a website, that even would have been helpful. I feel like there’s many ways to skin the cat, but it’s just providing age-appropriate information.”— Participant 4, female, breast cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
“But I definitely wanted more [young adult] support specifically. And not just in general cancer support, I went through this huge ordeal; it’s completely life changing. And I just, to me the more support I’m getting I feel more in control and I have more power.”— Participant 5, female, ovarian cancer, 30–39 years old at diagnosis .
4. Discussion
4.1. care coordination and healthcare system navigation, 4.2. mental health support, 4.3. aya peer support, 4.4. empathic communication about fertility preservation, 4.5. financial burden, 4.6. quality of life, 4.7. education and support regarding side effects and late effects, 4.8. attention to the unique needs of young adults, 4.9. limitations, 4.10. implications for cancer survivors, 5. conclusions, supplementary materials, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, acknowledgments, conflicts of interest.
- Nekhlyudov, L.; Mollica, M.A.; Jacobsen, P.B.; Mayer, D.K.; Shulman, L.N.; Geiger, A.M. Developing a Quality of Cancer Survi-vorship Care Framework: Implications for Clinical Care, Research, and Policy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019 , 111 , djz089. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Andersen, R.M. Revisiting the Behavioral Model and Access to Medical Care: Does it Matter? J. Health Soc. Behav. 1995 , 36 , 1–10. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Moore, A.R. Qualitative Study of Factors Contributing to Fertility Service Use Among Cancer Survivors of Reproductive Age in the US. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia Southern University, Statesboro, GA, USA, 2021. Volume 2353. [ Google Scholar ]
- Canzona, M.R.; Victorson, D.E.; Murphy, K.; Clayman, M.L.; Patel, B.; Puccinelli-Ortega, N.; McLean, T.W.; Harry, O.; Little-Greene, D.; Salsman, J.M. A Conceptual Model of Fertility Concerns Among Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer. Psycho-Oncology 2021 , 30 , 1383–1392. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bober, S.L.; Varela, V.S. Sexuality in Adult Cancer Survivors: Challenges and Intervention. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012 , 30 , 3712–3719. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Danhauer, S.C.; Canzona, M.; Tucker-Seeley, R.D.; Reeve, B.B.; Nightingale, C.L.; Howard, D.S.; Puccinelli-Ortega, N.; Little-Greene, D.; Salsman, J.M. Stakeholder-Informed Conceptual Framework for Financial Burden Among Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer. Psycho-Oncology 2021 , 31 , 597–605. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Courneya, K.S.; Friedenreich, C.M. Framework PEACE: An organizational model for examining physical exercise across the cancer experience. Ann. Behav. Med. 2001 , 23 , 263–272. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Strauser, D.R.; Jones, A.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Tansey, T.; Chan, F. Career Development of Young Adult Cancer Survivors: A Conceptual Framework. J. Vocat. Rehabil. 2015 , 42 , 167–176. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Le Boutillier, C.; Archer, S.; Barry, C.; King, A.; Mansfield, L.; Urch, C. Conceptual Framework for Living with and Beyond Cancer: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. Psycho-Oncology 2019 , 28 , 948–959. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Matheson, L.; Boulton, M.; Lavender, V.; Collins, G.; Mitchell-Floyd, T.; Watson, E. The Experiences of Young Adults with Hodgkin Lymphoma Transitioning to Survivorship: A Grounded Theory Study. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2016 , 43 , E195–E2014. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Haase, J.E. The Adolescent Resilience Model as a Guide to Interventions. J. Pediatr. Oncol. Nurs. 2004 , 21 , 289–299. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kroenke, C.H. A Conceptual Model of Social Networks and Mechanisms of Cancer Mortality, and Potential Strategies to Improve Survival. Transl. Behav. Med. 2018 , 8 , 629–642. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Luberto, C.M.; Hall, D.L.; Chad-Friedman, E.; Park, E.R. Theoretical Rationale and Case Illustration of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Fear of Cancer Recurrence. J. Clin. Psychol. Med. Settings 2019 , 26 , 449–460. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Warner, E.L.; Kent, E.E.; Trevino, K.M.; Parsons, H.M.; Zebrack, B.J.; Kirchhoff, A.C. Social Well-Being Among Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancer 2016 , 122 , 1029–1037. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Clinical Oncology Society of Australia Model of Survivorship Care Working Group. Model of Survivorship Care: Critical Components of Cancer Survivorship Care in Australia Position Statement ; Clinical Oncology Society of Australia Model of Survivorship Care Working Group: Sydney, Australia, 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor, R.M.; Pearce, S.; Gibson, F.; Fern, L.; Whelan, J. Developing a Conceptual Model of Teenage and Young Adult Experiences of Cancer through Meta-Synthesis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2013 , 50 , 832–846. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Fern, L.A.; Taylor, R.M.; Whelan, J.; Pearce, S.; Grew, T.; Brooman, K.; Starkey, C.; Millington, H.; Ashton, J.; Gibson, F. The Art of Age-Appropriate Care: Reflecting on a Conceptual Model of the Cancer Experience for Teenagers and Young Adults. Cancer Nurs. 2013 , 36 , E27–E38. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Hammond, C. Against a Singular Message of Distinctness: Challenging Dominant Representations of Adolescents and Young Adults in Oncology. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2017 , 6 , 45–49. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Reflecting on reflexive thematic analysis. Qual. Res. Sport Exerc. Health 2019 , 11 , 589–597. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Byrne, D. A worked example of Braun and Clarke’s approach to reflexive thematic analysis. Qual. Quant. 2021 , 56 , 1391–1412. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Neubauer, B.E.; Witkop, C.T.; Varpio, L. How phenomenology can help us learn from the experiences of others. Perspect. Med. Educ. 2019 , 8 , 90–97. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tong, A.; Sainsbury, P.; Craig, J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2007 , 19 , 349–357. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cactus Cancer Society. About Us. 2022. Available online: https://cactuscancer.org/about/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Palinkas, L.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; Green, C.A.; Wisdom, J.P.; Duan, N.; Hoagwood, K. Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2015 , 42 , 533–544. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Institute, N.C. Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/aya (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Black & White Cancer Survivors Foundation. BWCSF. 2014. Available online: https://www.blackandwhitecancersurvivorsfoundation.com/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Teen Cancer America. Teen Cancer America. Available online: https://teencanceramerica.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Young Adult Survivors United. Young Adult Survivors United. 2022. Available online: https://www.yasurvivors.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Testicular Cancer Foundation. TCF. 2022. Available online: https://www.testicularcancer.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Sisters Network Inc. A National African American Breast Cancer Survivorship Organization. 2022. Available online: https://www.sistersnetworkinc.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Imerman Angels. Imerman Angels Your One-on-One Cancer Support Community. 2020. Available online: https://imermanangels.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Creswell, J.W.; Klassen, A.C.; Clark, V.L.P.; Smith, K.C.; The Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research. Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in Health Sciences , 2nd ed.; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011.
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches ; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, G.W.; Stern, S.A.; Hilton, L.; Tucker, J.S.; Kennedy, D.P.; Golinelli, D.; Wenzel, S.L. When, where, why and with whom homeless women engage in risky sexual behaviors: A framework for understanding complex and varied decision-making processes. Sex Roles 2009 , 61 , 536–553. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Toward an Experimental Ecology of Human Development. Am. Psychol. 1977 , 32 , 513–531. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Spradley, J.P. Asking Descriptive Questions, in The Ethnographic Interview ; Wadsworth Group: St Albans Ln, NC, USA, 1979. [ Google Scholar ]
- Leech, B.L. Asking Questions: Techniques for Semistructured Interviews. PS Polit. Sci. Polit. 2002 , 35 , 665–668. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saunders, B.; Sim, J.; Kingstone, T.; Baker, S.; Waterfield, J.; Bartlam, B.; Burroughs, H.; Jinks, C. Saturation in qualitative research: Exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Qual. Quant. 2018 , 52 , 1893–1907. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guba, E.G. ERIC/ECTJ Annual Review Paper: Criteria for Assessing the Trustworthiness of Naturalistic Inquiries. Educ. Commun. Technol. 1981 , 29 , 75–91. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Krefting, L. Rigor in qualitative research: The assessment of trustworthiness. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1991 , 45 , 214–222. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Crozier, G.; Denzin, N.; Lincoln, Y. Handbook of Qualitative Research , 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamilton, A.B.; Finley, E.P. Qualitative methods in implementation research: An introduction. Psychiatry Res. 2019 , 280 , 112516. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Maietta, R.; Mihas, P.; Swartout, K.; Petruzzelli, J.; Hamilton, A. Sort and Sift, Think and Shift: Let the Data Be Your Guide an Applied Approach to Working With, Learning From, and Privileging Qualitative Data. Qual. Rep. 2021 , 26 , 2045–2060. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Friese, S. Qualitative Data Analysis with ATLAS.ti , 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saldaña, J. The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers , 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheung, C.K.; Zebrack, B. What do adolescents and young adults want from cancer resources? Insights from a Delphi panel of AYA patients. Support. Care Cancer 2017 , 25 , 119–126. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Avutu, V.; Lynch, K.A.; Barnett, M.E.; Vera, J.A.; Glade Bender, J.L.; Tap, W.D.; Atkinson, T.M. Psychosocial Needs and Pref-erences for Care among Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Patients (Ages 15–39): A Qualitative Study. Cancers 2022 , 14 , 710. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Osborn, M.; Johnson, R.; Thompson, K.; Anazodo, A.; Albritton, K.; Ferrari, A.; Stark, D. Models of care for adolescent and young adult cancer programs. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019 , 66 , e27991. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bibby, H.; White, V.; Thompson, K.; Anazodo, A. What Are the Unmet Needs and Care Experiences of Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer? A Systematic Review. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2017 , 6 , 6–30. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Magni, C.; Veneroni, L.; Silva, M.; Casanova, M.; Chiaravalli, S.; Massimino, M.; Clerici, C.A.; Ferrari, A. Model of Care for Ado-lescents and Young Adults with Cancer: The Youth Project in Milan. Front. Pediatr. 2016 , 4 , 88. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gorin, S.S.; Haggstrom, D.; Han, P.K.J.; Fairfield, K.M.; Krebs, P.; Clauser, S.B. Cancer Care Coordination: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Over 30 Years of Empirical Studies. Ann. Behav. Med. 2017 , 51 , 532–546. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Smith, S.; Mooney, S.; Cable, M.; Taylor, R.M. The Blueprint of Care for Teenagers and Young Adults with Cancer , 2nd ed.; Teenage Cancer Trust: London, UK, 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gupta, A.A.; Papadakos, J.K.; Jones, J.M.; Amin, L.; Chang, E.K.; Korenblum, C.; Mina, D.S.; McCabe, L.; Mitchell, L.; Giuliani, M.E. Reimagining care for adolescent and young adult cancer programs: Moving with the times. Cancer 2016 , 122 , 1038–1046. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shapiro, J. “Violence” in medicine: Necessary and unnecessary, intentional and unintentional. Philos. Ethics Hum. Ities Med. 2018 , 13 , 7. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Salmond, S.; Dorsen, C. Time to Reflect and Take Action on Health Disparities and Health Inequities. Orthop. Nurs. 2022 , 41 , 64–85. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Casanova-Perez, R.; Apodaca, C.; Bascom, E.; Mohanraj, D.; Lane, C.; Vidyarthi, D.; Beneteau, E.; Sabin, J.; Pratt, W.; Weibel, N.; et al. Broken down by bias: Healthcare biases experienced by BIPOC and LGBTQ+ patients. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2021 , 2021 , 275–284. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gannon, T.; Phillips, B.; Saunders, D.; Berner, A.M. Knowing to Ask and Feeling Safe to Tell-Understanding the Influences of HCP-Patient Interactions in Cancer Care for LGBTQ+ Children and Young People. Front. Oncol. 2022 , 12 , 891874. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Desai, M.J.; Gold, R.S.; Jones, C.K.; Din, H.; Dietz, A.C.; Shliakhtsitsava, K.; Martinez, M.E.; Vaida, F.; Su, H.-C.I. Mental Health Outcomes in Adolescent and Young Adult Female Cancer Survivors of a Sexual Minority. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2021 , 10 , 148–155. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Eisape, A.; Nogueira, A. See Change: Overcoming Anti-Black Racism in Health Systems. Front. Public Health 2022 , 10 , 895684. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Alegría, M.; Green, J.G.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Loder, S. Disparities in Child and Adolescent Mental Health and Mental Health Services in the US ; William, T., Ed.; Grant Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, P.S.; Lane, M.; Olfson, M.; Pincus, H.A.; Wells, K.B.; Kessler, R.C. Twelve-Month Use of Mental Health Services in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005 , 62 , 629–640. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Schellinger, S.E.; Anderson, E.W.; Frazer, M.S.; Cain, C.L. Patient Self-Defined Goals: Essentials of Person-Centered Care for Serious Illness. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2018 , 35 , 159–165. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zebrack, B. Information and service needs for young adult cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2008 , 16 , 1353–1360. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- LaRosa, K.N.; Stern, M.; Bleck, J.; Lynn, C.; Hudson, J.; Reed, D.R.; Quinn, G.P.; Donovan, K.A. Adolescent and Young Adult Patients with Cancer: Perceptions of Care. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2017 , 6 , 512–518. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Yabroff, K.R.; Gansler, T.; Wender, R.C.; Cullen, K.J.; Brawley, O.W.; Gansler, T. Minimizing the burden of cancer in the United States: Goals for a high-performing health care system. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019 , 69 , 166–183. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Reed, D.; Block, R.G.; Johnson, R. Creating an Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Program: Lessons Learned from Pediatric and Adult Oncology Practice Bases. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014 , 12 , 1409–1415. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ferrari, A.; Thomas, D.; Franklin, A.R.K.; Hayes-Lattin, B.M.; Mascarin, M.; van der Graaf, W.; Albritton, K.H. Starting an Ad-olescent and Young Adult Program: Some Success Stories and Some Obstacles to Overcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010 , 28 , 4850–4857. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zebrack, B.J.; Corbett, V.; Embry, L.; Aguilar, C.; Meeske, K.A.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; Block, R.; Zeman, D.T.; Cole, S. Psychological distress and unsatisfied need for psychosocial support in adolescent and young adult cancer patients during the first year fol-lowing diagnosis. Psychooncology 2014 , 23 , 1267–1275. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tai, E.; Buchanan, N.; Townsend, J.; Fairley, T.; Moore, A.; Richardson, L.C. Health status of adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. Cancer 2012 , 118 , 4884–4891. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kent, E.E.; Parry, C.; Montoya, M.J.; Sender, L.S.; Morris, R.A.; Anton-Culver, H. “You’re too young for this”: Adolescent and young adults’ perspectives on cancer survivorship. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2012 , 30 , 260–279. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Miedema, B.; Hamilton, R.; Easley, J. From “invincibility” to “normalcy”: Coping strategies of young adults during the cancer journey. Palliat. Support Care 2007 , 5 , 41–49. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zebrack, B.; Kent, E.E.; Keegan, T.H.; Kato, I.; Smith, A.W.; AYA Hope Study Collaborative Group. “Cancer sucks,” and other ponderings by adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2014 , 32 , 1–15. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pannier, S.T.; Warner, E.L.; Fowler, B.; Fair, D.; Salmon, S.K.; Kirchhoff, A.C. Age-Specific Patient Navigation Preferences Among Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer. J. Cancer Educ. 2019 , 34 , 242–251. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zebrack, B.J. Psychological, social, and behavioral issues for young adults with cancer. Cancer 2011 , 117 (Suppl. S10), 2289–2294. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Zebrack, B.J.; Block, R.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; Embry, L.; Aguilar, C.; Meeske, K.A.; Li, Y.; Butler, M.; Cole, S. Psychosocial service use and unmet need among recently diagnosed adolescent and young adult cancer patients. Cancer 2013 , 119 , 201–214. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- D’agostino, N.M.; Edelstein, K. Psychosocial challenges and resource needs of young adult cancer survivors: Implications for program development. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2013 , 31 , 585–600. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bender, J.L.; Puri, N.; Salih, S.; D’agostino, N.M.; Tsimicalis, A.; Howard, A.F.; Garland, S.N.; Chalifour, K.; Drake, E.K.; Marrato, A.; et al. Peer Support Needs and Preferences for Digital Peer Navigation among Adolescent and Young Adults with Cancer: A Canadian Cross-Sectional Survey. Curr. Oncol. 2022 , 29 , 1163–1175. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zebrack, B.; Bleyer, A.; Albritton, K.; Medearis, S.; Tang, J. Assessing the health care needs of adolescent and young adult cancer patients and survivors. Cancer 2006 , 107 , 2915–2923. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Choi, E.; Becker, H.; Kim, S. Unmet needs in adolescents and young adults with cancer: A mixed-method study using social media. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2022 , 64 , 31–41. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Benedict, C.; Thom, B.; Friedman, D.N.; Pottenger, E.; Raghunathan, N.; Kelvin, J.F. Fertility information needs and concerns post-treatment contribute to lowered quality of life among young adult female cancer survivors. Support. Care Cancer 2018 , 26 , 2209–2215. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Benedict, C.; Shuk, E.; Ford, J.S. Fertility issues in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2016 , 5 , 48–57. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guy, G.P.; Yabroff, K.R.; Ekwueme, D.U.; Smith, A.W.; Dowling, E.C.; Rechis, R.; Nutt, S.; Richardson, L.C. Estimating the health and economic burden of cancer among those diagnosed as adolescents and young adults. Health Aff. 2014 , 33 , 1024–1031. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lu, A.D.; Zheng, Z.; Han, X.; Qi, R.; Zhao, J.; Yabroff, K.R.; Nathan, P.C. Medical Financial Hardship in Survivors of Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer in the United States. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021 , 113 , 997–1004. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Young Adults and the Affordable Care Act: Protecting Young Adults and Eliminating Burdens on Families and Businesses. Programs and Initiatives. 2022. Available online: https://www.cms.gov/CCIIO/Resources/Files/adult_child_fact_sheet (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Ayanian, J.Z.; Weissman, J.S.; Schneider, E.C.; Ginsburg, J.A.; Zaslavsky, A.M. Unmet Health Needs of Uninsured Adults in the United States. JAMA 2000 , 284 , 2061–2069. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Landwehr, M.S.; Watson, S.E.; Macpherson, C.F.; Novak, K.A.; Johnson, R.H. The cost of cancer: A retrospective analysis of the financial impact of cancer on young adults. Cancer Med. 2016 , 5 , 863–870. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Han, X.; Jemal, A.D. The Affordable Care Act and Cancer Care for Young Adults. Cancer J. 2017 , 23 , 194–198. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Quinn, G.P.; Goncalves, V.; Sehovic, I.; Bowman, M.L.; Reed, D.R. Quality of life in adolescent and young adult cancer patients: A systematic review of the literature. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2015 , 6 , 19–51. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Magasi, S.; Marshall, H.K.; Winters, C.; Victorson, D. Cancer Survivors’ Disability Experiences and Identities: A Qualitative Exploration to Advance Cancer Equity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022 , 19 , 3112. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Janssen, S.H.M.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; van der Meer, D.J.; Manten-Horst, E.; Husson, O. Adolescent and Young Adult (AYA) Cancer Survivorship Practices: An Overview. Cancers 2021 , 13 , 4847. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- White, V.; Skaczkowski, G.; Thompson, K.; Bibby, H.; Coory, M.; Pinkerton, R.; Nicholls, W.; Orme, L.M.; Conyers, R.; Phillips, M.B.; et al. Experiences of Care of Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer in Australia. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2018 , 7 , 315–325. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Wilkinson, J. Young people with cancer—How should their care be organized? Eur. J. Cancer Care 2003 , 12 , 65–70. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Albritton, K.H.; Wiggins, C.H.; Nelson, H.E.; Weeks, J.C. Site of Oncologic Specialty Care for Older Adolescents in Utah. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007 , 25 , 4616–4621. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Marshall, S.; Grinyer, A.; Limmer, M. The Experience of Adolescents and Young Adults Treated for Cancer in an Adult Setting: A Review of the Literature. J. Adolesc. Young-Adult Oncol. 2018 , 7 , 283–291. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Flanagin, A.; Frey, T.; Christiansen, S.L.; AMA Manual of Style Committee. Updated Guidance on the Reporting of Race and Ethnicity in Medical and Science Journals. JAMA 2021 , 326 , 621–627. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Linas, B.P.; Assoumou, S.A. Laying the Foundation for a New and Inclusive Science. JAMA Netw. Open 2022 , 5 , e2148540. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Stewart, J.; Krows, M.L.; Schaafsma, T.T.; Heller, K.B.; Brown, E.R.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Brown, C.E.; Leingang, H.; Liou, C.; Bershteyn, A.; et al. Comparison of Racial, Ethnic, and Geographic Location Diversity of Participants Enrolled in Clinic-Based vs 2 Remote COVID-19 Clinical Trials. JAMA Netw. Open 2022 , 5 , e2148325. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Number (%) | |
|---|---|
| Female | 21 (84) |
| Male | 4 (16) |
| White | 19 (76) |
| Black | 2 (8) |
| Middle Eastern/North African | 1 (4) |
| Other | 3 (12) |
| Hispanic/Latinx | 6 (24) |
| Not Hispanic/Latine/x | 19 (76) |
| 20–29 | 8 (32) |
| 30–39 | 12 (48) |
| 40–49 | 5 (20) |
| 15–19 | 4 (16) |
| 20–29 | 10 (40) |
| 30–39 | 11 (44) |
| Less than 2 years | 3 (12) |
| At least 2, but less than 5 years | 8 (32) |
| At least 5, but less than 10 years | 11 (44) |
| 10 or more years | 3 (12) |
| Less than 2 years | 5 (20) |
| More than 2, but less than 5 years | 12 (48) |
| More than 5, but less than 10 years | 5 (20) |
| 10 or more years | 3 (12) |
| Breast | 5 (20) |
| Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma | 1 (4) |
| Hodgkin’s Lymphoma | 4 (16) |
| Leukemia | 7 (28) |
| Lung | 1 (4) |
| Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) | 1 (4) |
| Osteosarcoma | 1 (4) |
| Ovarian | 1 (4) |
| Sarcoma | 1 (4) |
| Testicular | 3 (12) |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Figueroa Gray, M.S.; Shapiro, L.; Dorsey, C.N.; Randall, S.; Casperson, M.; Chawla, N.; Zebrack, B.; Fujii, M.M.; Hahn, E.E.; Keegan, T.H.M.; et al. A Patient-Centered Conceptual Model of AYA Cancer Survivorship Care Informed by a Qualitative Interview Study. Cancers 2024 , 16 , 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173073
Figueroa Gray MS, Shapiro L, Dorsey CN, Randall S, Casperson M, Chawla N, Zebrack B, Fujii MM, Hahn EE, Keegan THM, et al. A Patient-Centered Conceptual Model of AYA Cancer Survivorship Care Informed by a Qualitative Interview Study. Cancers . 2024; 16(17):3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173073
Figueroa Gray, Marlaine S., Lily Shapiro, Caitlin N. Dorsey, Sarah Randall, Mallory Casperson, Neetu Chawla, Brad Zebrack, Monica M. Fujii, Erin E. Hahn, Theresa H. M. Keegan, and et al. 2024. "A Patient-Centered Conceptual Model of AYA Cancer Survivorship Care Informed by a Qualitative Interview Study" Cancers 16, no. 17: 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173073
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, supplementary material.
ZIP-Document (ZIP, 126 KiB)
Further Information
Mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
- Open access
- Published: 31 August 2024
Employing a synergistic bioinformatics and machine learning framework to elucidate biomarkers associating asthma with pyrimidine metabolism genes
- Dihui Zhang 1 na1 ,
- Xiaowei Pu 2 na1 ,
- Man Zheng 3 ,
- Guanghui Li 3 &
- Jia Chen 2
Respiratory Research volume 25 , Article number: 327 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Asthma, a prevalent chronic inflammatory disorder, is shaped by a multifaceted interplay between genetic susceptibilities and environmental exposures. Despite strides in deciphering its pathophysiological landscape, the intricate molecular underpinnings of asthma remain elusive. The focus has increasingly shifted toward the metabolic aberrations accompanying asthma, particularly within the domain of pyrimidine metabolism (PyM)—a critical pathway in nucleotide synthesis and degradation. While the therapeutic relevance of PyM has been recognized across various diseases, its specific contributions to asthma pathology are yet underexplored. This study employs sophisticated bioinformatics approaches to delineate and confirm the involvement of PyM genes (PyMGs) in asthma, aiming to bridge this significant gap in knowledge.
Employing cutting-edge bioinformatics techniques, this research aimed to elucidate the role of PyMGs in asthma. We conducted a detailed examination of 31 PyMGs to assess their differential expression. Through Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA), we explored the biological functions and pathways linked to these genes. We utilized Lasso regression and Support Vector Machine-Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) to pinpoint critical hub genes and to ascertain the diagnostic accuracy of eight PyMGs in distinguishing asthma, complemented by an extensive correlation study with the clinical features of the disease. Validation of the gene expressions was performed using datasets GSE76262 and GSE147878.
Our analyses revealed that eleven PyMGs—DHODH, UMPS, NME7, NME1, POLR2B, POLR3B, POLR1C, POLE, ENPP3, RRM2B, TK2—are significantly associated with asthma. These genes play crucial roles in essential biological processes such as RNA splicing, anatomical structure maintenance, and metabolic processes involving purine compounds.
Conclusions
This investigation identifies eleven PyMGs at the core of asthma's pathogenesis, establishing them as potential biomarkers for this disease. Our findings enhance the understanding of asthma’s molecular mechanisms and open new avenues for improving diagnostics, monitoring, and progression evaluation. By providing new insights into non-cancerous pathologies, our work introduces a novel perspective and sets the stage for further studies in this field.
Introduction
Asthma, a chronic and complex disease, affects over 300 million individuals globally, with projections suggesting an increase to 400 million by 2025 [ 1 ]. Characterized by pervasive airway inflammation and intricate cellular dynamics, asthma presents significant global health challenges, as indicated by the Global Asthma Network (GAN) with prevalence rates of 10.5% among children and 4.4% among adults [ 2 ]. The disease manifests through symptoms such as airway hyperresponsiveness, eosinophilic infiltration, reversible airflow obstruction, airway remodeling, mucus hypersecretion, and goblet cell hyperplasia [ 3 ]. Despite extensive research, the underlying mechanisms of asthma remain poorly understood, a consequence of its multifactorial nature involving genetic, environmental, infectious, immunological, and dietary components. Current therapeutic approaches primarily target symptom control, often leaving a considerable number of patients undermanaged [ 4 ]. This gap underscores the critical need for an in-depth investigation into the genetic and molecular bases of asthma, which could revolutionize our understanding of its onset and progression [ 5 ]. Advancements in this field promise to shift from merely managing symptoms to altering the disease trajectory, potentially transforming asthma treatment and significantly enhancing patient care worldwide [ 6 ].
PyM plays a pivotal role in the synthesis, degradation, and recycling of critical pyrimidine nucleobases, such as cytosine and uracil, which are crucial to nucleic acid structures. Beyond its foundational role in nucleic acid synthesis, PyM is intricately linked to broader aspects of energy metabolism through its biosynthetic and catabolic pathways, encompassing both de novo and salvage routes [ 7 ]. These pathways are particularly vital in rapidly dividing cells [ 8 ]. Disruptions in PyM pathways can lead to a range of inherited metabolic and autoimmune inflammatory disorders, including asthma. Recent studies highlight the role of microRNAs, notably miR-146a and miR-155, in promoting asthma by downregulating genes that typically suppress cell proliferation [ 9 ]. Furthermore, modulation of these microRNAs through TSHR-mediated pathways reveals insights into the fibroproliferative characteristics of asthma. Research by Madera-Salcedo et al. has shown that inflammation-induced hypermethylation of PPP2R2B (B55ß) leads to resistance to apoptosis in the absence of cytokines [ 10 ]. Concurrently, Zhu et al. demonstrated how UBE2T exacerbates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by influencing PyM [ 11 ]. This research aims to dissect the role of PyMGs in asthma immunotherapy, seeking to uncover new therapeutic opportunities by investigating purinosome formation and the glutamine pyrimidine metabolism pathway [ 12 ]. Despite significant progress, the impact of PyM on the immunogenic landscape and its critical role in enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapies for asthma remain poorly understood. This study is committed to a comprehensive assessment of PyMGs and their integration with immunotherapeutic strategies in asthma, potentially leading to transformative clinical advancements.
The Asthma Initiative heralds a transformative leap in biomedical research, integrating comprehensive transcriptomic sequencing with detailed clinical annotations to elucidate the transcriptional and molecular intricacies of asthma [ 13 , 14 , 15 ]. This project employs cutting-edge bioinformatics to navigate vast datasets, aiming to unveil the complex pathophysiological foundations of the disease. Notably, the role of PyMGs in the asthma schema remains underexplored. Our study addresses this oversight by utilizing asthma-specific datasets from the GEO to investigate the impact and relevance of PyMGs on asthma pathogenesis, as illustrated in Fig. 1 . Through this focused analysis, we aim to enhance our understanding of asthma’s molecular basis and pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies.
Materials and methods
The methodologies proposed by Zi-Xuan Wu et al. in 2023 were employed in this study [ 16 ].
GEO was searched for mRNA expression. Series: GSE76262 and GSE147878. Platform: GPL13158 and GPL6480. Strategy for searching (‘Parkinson’ [MeSH] mRNA [All Fields] and normal) AND (‘Homo sapiens’ [Organism] AND ‘Non-coding RNA profiling by array’ [Filter]). Specifically, this investigation harnessed the datasets GSE76262 and GSE147878, underpinned by the GPL13158 and GPL6480 platform. GSE76262 functioned as the training cohort, while GSE147878 constituted the testing group (Table 1 ). We also identified PyMGs from the MSigDB (Table S1).
Analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
Our methodology for extracting precise mRNA profiles involved the utilization of Perl scripts to meticulously match and sort transcriptional data from the GSE76262 dataset. Following normalization procedures, we applied stringent criteria for identifying differential expression among PyMGs: FDR < 0.05 and |log2FC|≥ 1. This rigorous approach enabled the isolation of significantly altered PyMGs for further scrutiny. To elucidate the intricate relationships among these genes, Pearson's correlation coefficient was harnessed, leveraging the corrplot package in R for comprehensive correlation analysis. This step was pivotal in highlighting genes with statistically significant associations within the identified modules.
GO and KEGG analysis
To elucidate the biological implications and pathway involvements of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), we conducted comprehensive Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. Employing the R programming language, we investigated the impact of differentially expressed PyMGs on biological processes (BP), molecular functions (MF), and cellular components (CC). This analysis aimed to delineate the overarching biological themes and molecular pathways influenced by these genes, thereby enhancing our understanding of their roles in disease pathology and identifying potential therapeutic targets. Through this multi-faceted approach, we not only categorized the DEGs but also shed light on the intricate interplay between purine metabolism and its broader biological and clinical significance.
Model construction and analysis of immune cell infiltration
In our pursuit of a predictive model characterized by unparalleled precision and reliability, we utilized the glmnet package for Lasso regression analysis, complemented by cross-validation, to refine and enhance our model. This methodology effectively mitigated overfitting, thereby boosting the model's predictive capability for complex biological datasets. For further validation, we employed the sophisticated SVM-RFE algorithm using the e1071 package, meticulously constructing a machine learning model. Cross-validation was pivotal in assessing the model's error rates and accuracy, ensuring its robustness and dependability. The Random Forest algorithm, renowned for its efficacy in ensemble learning, was integral to our analysis. By generating multiple decision trees and aggregating their predictions, it minimized overfitting risks and enhanced model generalization. The algorithm's distinctive feature—random feature selection and bootstrap sampling—fostered diversity among decision trees, thus improving the model's overall accuracy. Utilizing the randomForest and ggplot2 packages, we concentrated on analyzing differentially expressed genes, identifying key genes crucial for disease classification. In the final phase, we ranked the significance of these feature genes using an integrated approach that synthesized insights from Lasso regression, Random Forest, and SVM models. This provided a nuanced understanding of their roles in disease pathology. Furthermore, the CIBERSORT algorithm enabled us to analyze the immune cell composition, offering deeper insights into the immune landscape associated with the disease. This comprehensive and rigorous analytical approach not only augmented the accuracy of disease classification but also unveiled new avenues for understanding the molecular basis of the disease.
GSEA and GSVA
To elucidate the functional dynamics and pathway alterations across a spectrum of samples, we employed Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA). These powerful methodologies enabled the identification of functionally related gene sets and pathway changes, utilizing quantitative scores and visual representations to highlight active biological processes and pathways within various risk stratifications. Using R, we thoroughly investigated the impact of differentially expressed PyMGs on BP, MF, CC, and pathways, providing a granular understanding of their roles in disease mechanisms. This approach allowed us to uncover the intricate biological themes and molecular pathways influenced by these genes, thereby enhancing our comprehension of their involvement in disease pathology.
Drug-gene interactions in asthma
As bioinformatics in asthma research progresses towards pinpointing viable biomarkers, the construction of biological models and the identification of effective markers for disease diagnostics have become increasingly critical. Grasping the clinical relevance of these biomarkers is essential for crafting targeted therapeutic approaches. Anticipating drug reactions based on these pivotal markers is fundamental for the development of future preventative measures and therapeutic regimens for asthma. In this vein, validated biomarkers stand as crucial reference points. Thus, precise prediction of drug-gene interactions holds paramount significance. In this study, the Drug-Gene Interaction database (DGIdb) ( https://dgidb.genome.wustl.edu/ ) was utilized to forecast interactions between the identified hub genes and prospective therapeutic agents, highlighting the potential for targeted intervention strategies in asthma management.
Investigation of shared miRNAs and lncRNAs in asthma
The regulatory landscape of genetics is profoundly influenced by non-coding RNA transcripts, particularly microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). miRNAs modulate gene expression by enhancing or repressing mRNA degradation and translation, while lncRNAs, consisting of over 200 nucleotides, orchestrate a multitude of cellular processes through mechanisms such as chromosomal modifications, transcriptional activation, and interference. Recent studies have illuminated the extensive interplay between miRNAs and lncRNAs, fostering a competitive binding scenario among miRNAs, lncRNAs, and other regulatory entities. This interaction has led to the concept of competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), where lncRNAs can regulate gene expression by sequestering miRNAs. In light of these findings, our investigation aims to determine whether specific miRNAs and lncRNAs share regulatory mechanisms and developmental pathways in Asthma, potentially unveiling novel avenues for understanding and treating this complex condition.
Establishment of a common mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA network in asthma
To elucidate the interactive landscape among mRNA, miRNA, and lncRNA entities in Asthma, we sourced target gene information from miRTarBase and PrognoScan, databases renowned for providing empirically validated miRNA-lncRNA-target interactions. By intersecting the target genes of common mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA interactions with Asthma-associated genes, we established a regulated network. This network was visualized using Cytoscape software, providing a graphical representation of the molecular interplay critical to Asthma pathophysiology.
Mendelian randomization analysis
To ensure the independence of exposure and outcome variables in our genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data, we engaged in an association analysis via the TwoSampleMR package in R. Designating NME7 and POLR2B-related expression as the exposure and Asthma as the outcome, we aimed to explore potential causal relationships. The analysis entailed: 1. Instrumental Variables (IVs) Configuration: NME7 and POLR2B-related expressions were screened with a P-value threshold of < 5 × 10^-8 to identify strongly associated exposures. 2. Independence Configuration: Linkage disequilibrium (LD) between SNPs was calculated using the PLINK clustering method, excluding SNPs with LD coefficient r^2 > 0.001 and within 10,000 kb to ensure SNP independence and reduce pleiotropic biases. 3. Statistical Strength Configuration: The robustness of instrumental variables was assessed using the F-statistic (F = β^2/SE^2), with variables having F < 10 deemed inadequate to mitigate confounding effects.
Leveraging GWAS data, SNPs associated with the instrumental variables were identified, and through the “harmonise_data” function within TwoSampleMR, we aligned allelic directions of exposure and outcome, excluding incompatible SNPs. The inverse variance-weighted (IVW) method served as the cornerstone for causal inference, employing the variance of instrumental variables as weights to determine causal dynamics, thereby advancing our understanding of the genetic architecture underlying disease states.
Active components-targets docking
ADCY4 and PNPT1 were docked to verify the accuracy of principal components and prediction targets. The protein configurations of the core targets were obtained from the Uniprot database by using the minimum resolution (Resolution) and the source (Method) as X-ray as the screening condition, and the crystal structure of these protein configurations were obtained from the RCSB PDB database). 2D structures of 6 active components of core targets were obtained from PubChen database, and these 2D structures were minimized by chem3d software. The binding strength and activity of active components and targets were evaluated by SYBYL2.0 software, and the active components of binding TotalScore greater than 3 were selected for sub-docking. Then imported the crystal into the Pymol 2.4 for dehydration, hydrogenation, and separation of ligands; it then imported AutoDockTools 1.5.6 to construct the docking grid box for each target. Docking was completed by Vina 1.1.2 software, and the molecules with the lowest binding energy in the docking conformation were selected to observe the binding effect by matching with the original ligands and intermolecular interactions (such as hydrophobicity, cation-π, anion-π, π-π stacking, hydrogen bonding, etc.). Finally, the Pymol2.4 software was utilized to visualize the molecular docking.
Identification of DEGs and principal component analysis
Among the 31 examined PyMGs, several exhibited significant differences in expression levels. Furthermore, gene clustering analysis revealed distinct clusters in the treatment and control groups. Notable PyMGs in the treatment group included DHODH, POLE, UCK2, ENTPD1, NT5E, UPB1, ENPP1, TXNRD1, while control group PyMGs comprised PNPT1, POLR3F, PRIM2, POLR2C, POLR2G, POLR1D, POLR2B (Fig. 2 a). Correlation analysis was conducted among these PyMGs, and a correlation matrix was generated for visualization (Fig. 2 b) (Table S2).

Principal Component Analysis. a Analysis of difference. b Analysis of correlation
Enrichment analysis of PyMGs
GO enrichment analysis identified 290 core target genes, encompassing BP, MF, and CC. The MF category primarily involved nucleoside binding (GO: 0001882), catalytic activity, acting on RNA (GO: 0140098), ribonucleoside binding (GO: 0032549). The CC category was mainly associated with transferase complex, transferring phosphorus-containing groups (GO: 0061695), nuclear chromosome (GO: 0000228), RNA polymerase complex (GO: 0030880). The BP category included RNA splicing (GO: 0008380), anatomical structure homeostasis (GO: 0060249), purine-containing compound metabolic process (GO: 0072521). KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the upregulated genes were primarily involved in Pyrimidine metabolism (hsa00240), Huntington's disease (hsa05016), Purine metabolism (hsa00230) (Fig. 3 and Table S3a, b).

For PyMGs, GO, and KEGG analyses were performed. a The GO circle illustrates the scatter map of the selected gene’s logFC. b The KEGG barplot and bubble illustrates the scatter map of the logFC of the indicated gene
Model construction
In our study, we meticulously established a gene signature by employing LASSO and Cox regression analysis, judiciously selecting the optimal value, as depicted in Fig. 4 a, b. To validate the precision and reliability of our model, we constructed a machine learning model using SVM-RFE. This model demonstrated exceptional accuracy, achieving a score of 0.863, and maintained a minimal error rate of 0.137, as shown in Fig. 4 c, d. Some key genes were screened by random forest tree, including NME7, POLR3C, ENTPD4, ENPP1, UCKL1, etc. (Fig. 4 e, f). The intersection of the 11 PyMGs identified by LASSO, RF and SVM revealed strong concordance (Fig. 4 g). Upon evaluating the model in relation to the 11 hub genes, we observed notably high accuracy rates for each gene: DHODH (AUC = 0.680), UMPS (AUC = 0.823), NME7 (AUC = 0.776), NME1 (AUC = 0.767), POLR2B (AUC = 0.672), POLR3B (AUC = 0.775), POLR1C (AUC = 0.637), POLE (AUC = 0.699), ENPP3 (AUC = 0.679), RRM2B (AUC = 0.744), TK2 (AUC = 0.720) (Fig. 4 f). Remarkably, an AUC of 0.934 (95% CI 0.887−0.973) was achieved in dataset GSE76262, underscoring the high accuracy and robustness of our prediction model (Fig. 4 g) (Table 1 and S4). In evaluating the performance of our study, particularly with regard to the AUC, a detailed analysis of Fig. 4 demonstrates an impressive AUC value of 0.934, underscoring the high accuracy of our model. Addressing concerns about the lower AUC values observed for certain genes, it is essential to consider the influence of individual genetic variations on these outcomes. Despite these variations, it is important to note that the aggregated AUC values for these genes consistently approximate a significant benchmark of 0.7. This collective result substantiates the overall credibility, precision, and robustness of our predictive model, affirming its utility in both clinical and research contexts.

The development of the PyMGs signature. a Regression of the 11 Asthma-related genes using LASSO. b Cross-validation is used in the LASSO regression to fine-tune parameter selection. c , d Accuracy and error of this model. e , f : RF. g Venn. h AUC of 10 hub genes. i AUC of train group
Gene set enrichment analysis
In this study, the AUC of each gene in the test group, the Rank ranking of each gene, and the results of the test group validation were observed. We found that NME7 and POLR2B may be the most relevant genes. Through literature evaluation and analysis of hub gene sensitivity within the model, it was determined that NME7 and POLR2B may be the most relevant genes to Asthma. In terms of GO analysis, NME7 was found to be associated with CC ribosome, MF cytokine receptor activity, MF structural constituent of ribosome. On the other hand, POLR2B was primarily involved in the CC mitochondrial protein containing complex, CC organellar ribosome, CC ribosomal subunit (Fig. 5 a). In KEGG analysis, NME7 was mainly associated with cytokine cytokine receptor interaction, neuroactive ligand receptor interaction, oxidative phosphorylation, while POLR2B was involved in neuroactive ligand receptor interaction, oxidative phosphorylation, parkinsons disease (Fig. 5 b) (Table S5).

GSEA of Analysis in NME7 and POLR2B. a GO. b KEGG
Analysis of immune cells
In this investigation, we explore the nuanced role of the immune microenvironment in the onset and progression of asthma, a complex condition shaped by the dynamics of immune cell interactions. Our extensive analysis was designed to unravel the expression patterns and interrelations of these cells, utilizing violin plots to vividly delineate the differential expression profiles of immune cells in control versus asthma-impacted tissues. These graphical representations distinctly showcased an upregulation of activated mast cells, eosinophils, and both resting and activated dendritic cells in the control samples. Conversely, tissues afflicted by asthma exhibited heightened levels of CD8 T cells, follicular helper T cells, and both M0 and M2 macrophages, illuminating the altered or engaged immune response mechanisms in asthma. This endeavor aimed to elucidate the potential genetic interplays with, or influences by, the immune microenvironment in asthma, striving to enrich our comprehension of the disease's pathophysiological underpinnings. The results, showcased in Fig. 6 a, reveal a complex symbiosis between immune cells and genetic factors, broadening our understanding of the intricate immune-genetic interplay in asthma. In addition, we added NME7 and POLR2B to the immune infiltration analysis of their respective genes alone.

Expression of Immune cells. a Expression of immune cells in different clusters. b NME7. c POLR2B
In the GO analysis, NME7 was primarily associated with CC septin cytoskeleton, BP negative regulation of myoblast proliferation, BP axonemal central apparatus assembly, MF olfactory receptor binding, CC iga immunoglobulin complex. POLR2B was mainly involved in the MF udp xylosyltransferase activity, BP regulation of mirna catabolic process, BP positive regulation of mirna catabolic process, CC fancm mhf complex, MF glycine n acyltransferase activity (Fig. 7 a). In terms of KEGG analysis, NME7 was mainly associated with glycosaminoglycan degradation, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, renin angiotensin system, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis lacto and neolacto series, asthma, sulfur metabolism. POLR2B was involved in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis heparan sulfate, linoleic acid metabolism, arachidonic acid metabolism, taste transduction, retinol metabolism, nitrogen metabolism (Fig. 7 b).
GSVA of Analysis in NME7 and POLR2B. a GO. b KEGG
Drug-gene interactions
Some drugs were predicted to interact with the eleven hub genes, including leflunomide, teriflunomide, vidofludimus, chembl1164954, leucovorin (Table S6) (Fig. 8 ). The investigation unveiled eleven PyMGs—DHODH, UMPS, NME7, NME1, POLR2B, POLR3B, POLR1C, POLE, ENPP3, RRM2B, TK2—significantly associated with asthma. According to rank, NME7 and POLR2B were selected for molecular docking. To verify the credibility of our results. We performed molecular docking of NME7 and POLR2B with CHEMBL1164954, LEFLUNOMIDE, TERIFLUNOMIDE, ZALCITABINE (Table 2 and Fig. 9 ).

Drug-gene interactions. Red circles are up-regulated genes, green hexagons are down-regulated genes, and blue squares are associated drugs

Molecular docking results. a UMPS. b DHODH
Identification of common RNAs and construction of miRNA-lncRNA shared genes network
A total of 212 miRNAs and 241 lncRNAs associated with Asthma were identified from three databases (Table S7a, b). Table S7 shows the matching of these genes against the corresponding miRNA database. These databases include miRanda [ 17 ], miRDB [ 18 ], and TargetScan [ 19 ]. When the corresponding database matched the relevant miRNA, the score was marked as 1. It can be seen that when all three databases can be matched, it is 3 points. The miRNA was matched by spongeScan database [ 20 ] to obtain the corresponding lncRNA data. The miRNA-lncRNA-gene network was constructed by intersecting these non-coding RNAs with the shared genes obtained through Lasso regression and SVM-RFE. The network consisted of 190 lncRNAs, 182 miRNAs, and some common genes, including the 11 hub genes (NME7, TK2, UMPS, POLE, ENPP3, POLR1C, DHODH, RRM2B, POLR3B, NME1, POLR2B) (Fig. 10 ).

miRNAs-LncRNAs shared Genes Network. Red circles are mrnas, blue quadrangles are miRNAs, and green triangles are lncRNAs
Validation of hub genes
To enhance the confidence and prediction accuracy of the model, GSE147878 dataset was used for validation. The GSE147878 analysis further confirming their potential relevance to Asthma (Fig. 11 ).

eleven hub genes were validated
Model verification
The Boxplots depicted the residual expression patterns of these genes in Asthma (Fig. 12 a). There are some differences in the proportions of the four different modes (Fig. 12 b, c). The PyMGs' diagnostic capacity in distinguishing Asthma from control samples revealed a satisfactory diagnostic value, with an AUC of RF: 0.967; SVM: 0.919; XGB: 0.943; GLM: 0.933 (Fig. 12 c). An AUC of 1.000 (95% CI 1.000–1.000) in GSE147878 (Fig. 12 d).

Model verification. a Residual expression patterns. b , c Model expression patterns ( d ) AUC of model. e AUC of test group
In our exploration of the intrinsic connection between NME7 and POLR2B, and asthma forest plots were meticulously employed to visually articulate the associations. For NME7, the all SNPs (rs73078636, rs10178845, rs11071559, rs2460555, rs7734635, rs5743618, etc.) conspicuously positioned itself to the right of the confidence interval, indicating a positive association. (Fig. 13 a). In the case of POLR2B, all SNPs (rs10178845, rs11071559, rs2460555, rs7734635, rs5743618, rs61957178, rs4795399, etc.) were all situated to the right of the confidence interva, suggesting a similar trend of association with asthmal (Fig. 13 b). Further dissecting the heterogeneity inherent in our analysis, the funnel plot tailored to asthma revealed a deviation from the expected symmetrical distribution, albeit maintaining a general symmetry. This nuanced observation was further scrutinized through sensitivity analysis, employing a “leave-one-out” approach. Remarkably, the omission of any individual SNP from the analysis had a negligible effect on the results of the Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) analysis, indicating that the remaining SNPs consistently mirrored the outcomes of the aggregate dataset. Substantiating the validity of our findings, the MR-Egger regression analysis was invoked, providing a solid foundation that bolsters both the robustness and authenticity of our results and the methodologies applied. This Mendelian randomization analysis unequivocally confirms the intimate association of NME7 and POLR2B with asthma. Hence, it delineates a potential pathway to modulate the incidence, evolution, and progression of asthma by intervening in the functions of NME7 and POLR2B, presenting a promising avenue for therapeutic intervention and a deeper understanding of the disease mechanism.

Mendelian Randomization Analysis. a NME7. b POLR2B
Discussions
Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways, presents a significant global health challenge, with the Global Asthma Network (GAN) study reporting prevalence rates of 10.5% in children and 4.4% in adults [ 21 ]. Characterized by airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, mucus hypersecretion, and remodeling, the pathophysiology of asthma is complex, resulting from a multifaceted interplay of genetic and environmental factors [ 22 ]. Despite the availability of treatments primarily aimed at symptomatic relief, a substantial proportion of patients remain inadequately managed, highlighting the urgent need for advanced therapeutic interventions [ 23 ]. In this context, the identification of asthma biomarkers through comprehensive bioinformatic analysis is a critical endeavor. This approach aims to unravel the complex mechanisms underlying asthma and uncover novel therapeutic targets, potentially shifting asthma management towards early detection and precise disease characterization [ 24 ]. PyM is essential for the synthesis, breakdown, and utilization of key pyrimidine nucleobases, such as cytosine and uracil, which are integral to nucleic acid structures and energy metabolism [ 8 ]. Dysregulation of PyM pathways is implicated in various inherited metabolic disorders, including autoimmune inflammatory diseases [ 9 ]. Recent studies have highlighted the role of microRNAs, such as miR-146a and miR-155, in modulating cell proliferation in asthma by targeting genes that inhibit cell growth, and the TSHR-mediated regulation of these microRNAs in asthma's fibroproliferative pathology [ 10 ]. Additionally, research has identified dysregulation in PPP2R2B (B55ß) through inflammation-driven hypermethylation, affecting apoptosis resistance, and the role of UBE2T in exacerbating hepatocellular carcinoma by influencing PyM [ 12 ]. This study focuses on PyMGs and their relevance in asthma immunotherapy, exploring new therapeutic avenues through the investigation of purinosome formation and the glutamine pyrimidine metabolism pathway [ 25 ]. Despite advancements, the impact of PyM on the immunogenic landscape and its role in modulating immunotherapy efficacy in asthma remains to be fully elucidated. Our research aims to conduct a thorough analysis of PyMGs and their interaction with immunotherapeutic strategies in asthma, paving the way for groundbreaking clinical progress.
In our comprehensive study, we identified a network of 31 DEGs intricately associated with PyMGs in asthma. Utilizing a rigorous analytical framework that combines DEG analysis, Lasso regression, and SVM-RFE, we identified eleven critical PyMGs: DHODH, UMPS, NME7, NME1, POLR2B, POLR3B, POLR1C, POLE, ENPP3, RRM2B, and TK2. These genes have demonstrated significant diagnostic relevance in asthma, a finding further validated by external datasets, underscoring their essential role in the disease's pathogenesis. However, our research also revealed a significant gap in understanding the interaction between these genes and specific transcription factors, especially within the context of purine metabolism. Notably, NME7 and POLR2B emerged as key mediators in the link between asthma and PyMGs. Further investigation into their biological functions indicated their involvement in various immune-related processes, including RNA splicing, anatomical structure homeostasis, and the metabolic processing of purine-containing compounds. This finding suggests that PyMGs may regulate a broad spectrum of biological pathways, particularly those related to immune responses, thereby potentially influencing the pathophysiological progression of asthma. Our results propose that these genes are crucial in understanding asthma’s progression and could unveil new avenues for therapeutic targeting, presenting promising opportunities for future research and the development of treatment strategies. This underscores the paramount importance of PyMGs within the molecular landscape of asthma, indicating a novel direction in the quest to understand and mitigate this complex disease.
The investigation into PyM, a cornerstone of cellular energy balance and proliferation, has revealed its extensive implications across various diseases and metabolic disorders. In the intricate landscape of asthma pathogenesis, recent research has highlighted the critical roles of NME7 and POLR2B in shaping the molecular framework of this disease. Asthma, characterized by chronic airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, and reversible airflow obstruction, arises from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors [ 26 ]. Identifying NME7 and POLR2B as key players in this intricate narrative adds a new dimension to our understanding of asthma's origins and potential therapeutic avenues. NME7, associated with intracellular signaling and cellular differentiation pathways, has been significantly linked to asthma [ 27 ]. Its role in modulating signal transduction pathways underscores its impact on the inflammatory cascade and airway smooth muscle cell dynamics, which are integral to asthma's pathophysiology [ 28 ]. However, the precise mechanisms by which NME7 influences asthma require further elucidation. The gene's association with asthma suggests that any deviation in NME7's expression or functionality could exacerbate the inflammatory environment, leading to increased asthma symptoms and airway structural changes [ 29 ]. Similarly, POLR2B, a vital component of the RNA polymerase II complex essential for mRNA synthesis, has been identified as a gene of interest in asthma research. Its fundamental role in gene expression regulation positions POLR2B as a key mediator in asthma by controlling genes involved in immune responses and airway inflammation [ 30 ]. Changes in POLR2B expression or function could alter the transcriptional profile of asthma-related genes, influencing disease severity and the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, analyses of the GSE147878 dataset have highlighted PyM-related markers as emerging prognostic indicators in asthma, representing a dynamic frontier in genomic exploration. These insights pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies in asthma management, heralding the advent of personalized medicine in contemporary healthcare. This body of research not only deepens our understanding of asthma's molecular etiology but also underscores the potential of targeted genetic and molecular interventions in revolutionizing asthma treatment paradigms.
Asthma, a chronic disorder, is characterized by persistent airway inflammation and increased reactivity, resulting from a complex interplay between host immune mechanisms and environmental factors within the pulmonary environment. The pathogenesis of asthma is marked by an imbalance between the innate and adaptive immune systems in the airways [ 31 ]. Environmental triggers—such as allergens, pollutants, and respiratory pathogens—induce airway epithelial cells to initiate an immune response, characterized by the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This response recruits various innate immune cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, and innate lymphoid cells, leading to acute inflammation [ 32 ]. Simultaneously, dysregulation of adaptive immune responses, particularly within T-helper (Th) cell subsets, plays a crucial role in sustaining chronic inflammation and structural changes characteristic of asthma [ 33 ]. A shift towards Th2-dominated responses, marked by the secretion of interleukins (IL)-4, IL-5, and IL-13, promotes eosinophilic inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, and excessive mucus production [ 34 ]. Additionally, recent studies have highlighted the significant roles of aberrant Th17 and regulatory T cell (Treg) functions in modulating airway inflammation and remodeling, adding complexity to our understanding of asthma’s immunology. Our analysis, utilizing violin plot visualizations, has identified distinct immune cell expression profiles. The control group exhibited higher levels of activated mast cells, eosinophils, and both resting and activated dendritic cells. In contrast, the treatment group showed increased levels of CD8 T cells, follicular helper T cells, and both M0 and M2 macrophages. These findings provide deeper insights into the immune landscape of asthma. These observations underscore the importance of elucidating immune pathways to advance innovative therapeutic strategies. Immunomodulatory interventions, aimed at reducing inflammation and correcting immune dysregulation, present a promising avenue for novel asthma treatments. This research heralds a new era in targeted therapeutic interventions, poised to reshape the future of asthma therapy by emphasizing the critical role of immune pathways in understanding and managing the disease.
The merging of asthma research with metabolic studies marks a groundbreaking phase in medical science, energized by the adoption of advanced bioinformatics techniques. This shift has significantly broadened our understanding of the molecular complexity and diverse pathological expressions of asthma [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. The scientific community's collaborative efforts have been crucial in deciphering the molecular foundations and clinical spectrum of this disease. Our research represents a pivotal advancement in this burgeoning field, highlighting the critical role of PyMGs within the asthma paradigm. Utilizing extensive datasets from the GEO, specifically GSE76262 and GSE147878, we have applied a comprehensive suite of analytical tools, including GO, KEGG, and GSEA. These tools have enabled the development of a sophisticated predictive model that illuminates the intricate role of PyMGs in asthma's etiology. Our work establishes a foundational theoretical framework while also opening new pathways for investigating the metabolic imbalances at the heart of asthma and developing targeted therapeutic approaches. However, the necessity for further empirical research to confirm the mechanisms proposed in our findings is paramount. Such validation, achievable through rigorous in vivo and in vitro testing, is essential to deepen our understanding of asthma. These exacting scientific endeavors are vital for progressing towards effective treatment solutions, shaping the future of asthma research and therapeutic development.
Within the complex landscape of asthma, PyMGs play a central role, orchestrating a broad array of biological interactions, pathways, signaling cascades, and regulatory mechanisms. At the core of asthma's molecular framework, PyMGs underlie the synthesis of key biomolecules such as DHODH, UMPS, NME7, NME1, POLR2B, POLR3B, POLR1C, POLE, ENPP3, RRM2B, and TK2, which are crucial in essential physiological processes and metabolic regulation related to asthma. Notably, NME7 and POLR2B are distinguished by their significant regulatory effects on metabolic pathways, profoundly influencing asthma's pathophysiological terrain. Our investigations into PyMGs highlight their vital role in the metabolic imbalances characteristic of asthma, proposing the targeting of these pathways as a viable therapeutic strategy.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [GEO] repository. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ .
Abbreviations
Gene ontology
Traditional Chinese medicine
Molecular functions
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
Gene expression omnibus
Pyrimidine metabolism genes
Biological processes
Cellular components
Differentially expressed genes
Gomez JL. Epigenetics in asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019;19(12):56.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lauzon-Joset JF, Marsolais D, Tardif-Pellerin E, Patoine D, Bissonnette EY. CD200 in asthma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;112:141–4.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Cormier M, Lemiere C. Occupational asthma. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2020;24(1):8–21.
Pinyochotiwong C, Chirakalwasan N, Collop N. Nocturnal asthma. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021;39(2):78–88.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Khan DA, Oppenheimer JJ, Lee GB, Fineman SM. Asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123(4):416–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Katwa U, Kabra SK. Advances in asthma. Indian J Pediatr. 2018;85(8):641–2.
Garavito MF, Narvaez-Ortiz HY, Zimmermann BH. Pyrimidine metabolism: dynamic and versatile pathways in pathogens and cellular development. J Genet Genomics. 2015;42(5):195–205.
El KM. Pyrimidine metabolism in schistosomes: a comparison with other parasites and the search for potential chemotherapeutic targets. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;213:55–80.
Article Google Scholar
Pfenninger KH. Plasma membrane expansion: a neuron’s Herculean task. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(4):251–61.
Woeller CF, Roztocil E, Hammond C, Feldon SE. TSHR signaling stimulates proliferation through PI3K/Akt and induction of miR-146a and miR-155 in thyroid eye disease orbital fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60(13):4336–45.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Madera-Salcedo IK, Sanchez-Hernandez BE, Svyryd Y, Esquivel-Velazquez M, Rodriguez-Rodriguez N, Trejo-Zambrano MI, Garcia-Gonzalez HB, Hernandez-Molina G, Mutchinick OM, Alcocer-Varela J, et al. PPP2R2B hypermethylation causes acquired apoptosis deficiency in systemic autoimmune diseases. JCI Insight. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.126457 .
Zhu Z, Cao C, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Liu L, Wu D, Sun J. UBE2T-mediated Akt ubiquitination and Akt/beta-catenin activation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development by increasing pyrimidine metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(2):154.
Yuan Y, Li N, Fu M, Ye M. Identification of critical modules and biomarkers of ulcerative colitis by using WGCNA. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1611–28.
Xu M, Kong Y, Chen N, Peng W, Zi R, Jiang M, Zhu J, Wang Y, Yue J, Lv J, et al. Identification of immune-related gene signature and prediction of CeRNA network in active ulcerative colitis. FRONT IMMUNOL. 2022;13:855645.
Wu Y, Liu X, Li G. Integrated bioinformatics and network pharmacology to identify the therapeutic target and molecular mechanisms of Huangqin decoction on ulcerative Colitis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):159.
Wu Z, Liu P, Huang B, Deng S, Song Z, Huang X, Yang J, Cheng S. A novel Alzheimer’s disease prognostic signature: identification and analysis of glutamine metabolism genes in immunogenicity and immunotherapy efficacy. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):6895.
De Carvalho TR, Giaretta AA, Teixeira BF, Martins LB. New bioacoustic and distributional data on Bokermannohyla sapiranga Brandao et al., 2012 (Anura: Hylidae): revisiting its diagnosis in comparison with B. pseudopseudis (Miranda-Ribeiro, 1937). Zootaxa. 2013;3746:383–92.
Chen Y, Wang X. miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(D1):D127–31.
Mon-Lopez D, Tejero-Gonzalez CM. Validity and reliability of the TargetScan ISSF Pistol & Rifle application for measuring shooting performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(11):1707–12.
Furio-Tari P, Tarazona S, Gabaldon T, Enright AJ, Conesa A. spongeScan: a web for detecting microRNA binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W176–80.
Williams EJ, Berthon BS, Stoodley I, Williams LM, Wood LG. Nutrition in asthma. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;43(5):646–61.
Guerau-de-Arellano M, Britt RJ. Sterols in asthma. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(10):792–9.
Quirt J, Hildebrand KJ, Mazza J, Noya F, Kim H. Asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018;14(Suppl 2):50.
King-Biggs MB. Asthma. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(7):C49–64.
Liu C, Gu C, Huang W, Sheng X, Du J, Li Y. Targeted UPLC-MS/MS high-throughput metabolomics approach to assess the purine and pyrimidine metabolism. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019;1113:98–106.
Sedova L, Bukova I, Bazantova P, Petrezselyova S, Prochazka J, Skolnikova E, Zudova D, Vcelak J, Makovicky P, Bendlova B, et al. Semi-lethal primary ciliary dyskinesia in rats lacking the Nme7 gene. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083810 .
Sedova L, Prochazka J, Zudova D, Bendlova B, Vcelak J, Sedlacek R, Seda O. Heterozygous Nme7 mutation affects glucose tolerance in male rats. Genes. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071087 .
Ren X, Rong Z, Liu X, Gao J, Xu X, Zi Y, Mu Y, Guan Y, Cao Z, Zhang Y, et al. The protein kinase activity of NME7 activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to promote one-carbon metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2022;82(1):60–74.
Sun Y, Li S, Li H, Yang F, Bai Y, Zhao M, Guo J, Zhao M, Zhou P, Khor CC, et al. TNFRSF10A-LOC389641 rs13278062 but not REST-C4orf14-POLR2B-IGFBP7 rs1713985 was found associated with age-related macular degeneration in a Chinese population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54(13):8199–203.
Li XL, Xie Y, Chen YL, Zhang ZM, Tao YF, Li G, Wu D, Wang HR, Zhuo R, Pan JJ, et al. The RNA polymerase II subunit B (RPB2) functions as a growth regulator in human glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;674:170–82.
Wang H, Jia Y, Gu J, Chen O, Yue S. Ferroptosis-related genes are involved in asthma and regulate the immune microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1087557.
Yip W, Hughes MR, Li Y, Cait A, Hirst M, Mohn WW, McNagny KM. Butyrate shapes immune cell fate and function in allergic asthma. Front Immunol. 2021;12:628453.
Shamji MH, Sharif H, Layhadi JA, Zhu R, Kishore U, Renz H. Diverse immune mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis with and without asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(3):791–801.
Strzelak A, Ratajczak A, Adamiec A, Feleszko W. Tobacco smoke induces and alters immune responses in the lung triggering inflammation, allergy, asthma and other lung diseases: a mechanistic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15051033 .
Huang F, Yu J, Lai T, Luo L, Zhang W. The combination of bioinformatics analysis and untargeted metabolomics reveals potential biomarkers and key metabolic pathways in asthma. Metabolites. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010025 .
Chen ST, Yang N. Constructing ferroptosis-related competing endogenous RNA networks and exploring potential biomarkers correlated with immune infiltration cells in asthma using combinative bioinformatics strategy. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):294.
Wu Z, Cai Z, Shi H, Huang X, Cai M, Yuan K, Huang P, Shi G, Yan T, Li Z. Effective biomarkers and therapeutic targets of nerve-immunity interaction in the treatment of depression: an integrated investigation of the miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks. Aging. 2022;14(8):3569–96.
Download references
The Second “Xinglin Scholars-Nursing Youth” Program of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2023HLXL09); Science and Technology Development Project (Nursing Special Project), Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 23HLZX06.
Author information
Dihui Zhang and Xiaowei Pu contributed equally to this article as the first author.
Authors and Affiliations
Orthopedics department The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou, 510000, China
Dihui Zhang
Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, 200021, China
Xiaowei Pu & Jia Chen
Dongying People’s Hospital (Dongying Hospital of Shandong Provincial Hospital Group), Dongying, 257091, Shandong, People’s Republic of China
Man Zheng & Guanghui Li
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dihui Zhang and Xiaowei Pu drafted and revised the manuscript. Dihui Zhang and Man Zheng were in charge of data collection. Dihui Zhang and Xiaowei Pu were in charge of design of frame. Jia Chen and Guanghui Li conceived and designed this article, in charge of syntax modification and revised of the manuscript. All the authors have read and agreed to the final version manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Guanghui Li or Jia Chen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, D., Pu, X., Zheng, M. et al. Employing a synergistic bioinformatics and machine learning framework to elucidate biomarkers associating asthma with pyrimidine metabolism genes. Respir Res 25 , 327 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02954-4
Download citation
Received : 29 March 2024
Accepted : 17 August 2024
Published : 31 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02954-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Pyrimidine metabolism-related genes (PyMGs)
- Lasso regression
- Bioinformatics
Respiratory Research
ISSN: 1465-993X
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Scientists Discover “Completely Different” New Risk Factor for Heart Disease
A new study has settled a prolonged dispute within the medical community by showing that mutations associated with clonal hematopoiesis heighten the risk of atherosclerosis in affected individuals.
In addition to the established risk factors for cardiovascular disease—such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity—another factor must now be considered: clonal hematopoiesis. This condition, caused by acquired mutations in blood stem cells, has already been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
However, until now it was uncertain if clonal hematopoiesis was a cause or consequence of cardiovascular disease . Now, a new study published in Nature Medicine and carried out by researchers at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) resolves this critical debate by establishing clonal hematopoiesis as a new risk factor for atherosclerosis—the formation of lesions in the arterial wall that underlies most cardiovascular disorders.
In a second study, published in the European Heart Journal , the CNIC scientists propose the ancient medication colchicine as the central plank of personalized strategies to alleviate the effects of clonal hematopoiesis associated with acquired mutations in the TET2 gene. The results of these important studies will be presented today at the European Society of Cardiology meeting in London, UK.

Acquired mutations in blood cell lineages: a new cause of atherosclerosis
An adult person produces hundreds of thousands of blood cells every day. This high rate of cell division unavoidably entails the accumulation of DNA mutations in the dividing cells. These mutations are known as somatic mutations, and are acquired, not inherited. “Although most somatic mutations are innocuous, some give the affected cells a competitive advantage that allows them to expand and progressively accumulate, generating clonal populations of mutated blood cells, a phenomenon known as clonal hematopoiesis,” explained José Javier Fuster, who led the Nature Medicine study, for which it has received support from Fundación “la Caixa” .
These mutations had already been proposed as a possible risk factor for cardiovascular disease; however, the exact nature of the relationship remained unclear. As Dr. José Javier Fuster, coordinator of the CNIC “Novel Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis” program, explained, “some earlier studies suggested that somatic mutations linked to clonal hematopoiesis contribute directly to cardiovascular disease and thereby accelerating the development of atherosclerosis. On the other hand, others proposed that it is atherosclerosis that causes clonal hematopoiesis by increasing the proliferation of blood stem cells and thereby generating a higher proportion of mutated blood cells.”
The Nature Medicine study clarifies the relationship between clonal hematopoiesis and atherosclerosis through a longitudinal analysis of data from the PESA-CNIC-Santander study. PESA (Progression of Early Subclinical Atherosclerosis) is a prospective study of more than 4000 apparently healthy middle-aged participants who have undergone periodic examinations using advanced imaging technology since 2010 to detect the presence and progression of asymptomatic atherosclerosis.

PESA is a collaborative initiative of the CNIC and Santander Bank. “The PESA study has already made very important contributions to our understanding of cardiovascular disease, and its longitudinal nature and unique characteristics provide an ideal framework for carrying out this important study on the relationship between clonal hematopoiesis and atherosclerosis,” said Dr. Valentín Fuster, CNIC General Director, principal investigator on the PESA study, and co-lead author on the Nature Medicine study.
The researchers used high-sensitivity DNA sequencing technology to detect somatic mutations in blood samples and assessed the presence and progression of atherosclerosis detected with noninvasive imaging techniques in the PESA participants. “The study was a multidisciplinary effort involving specialists in basic science and cardiology, together with the specialized technical expertise of the Bioinformatics, Genomics, and Clinical Trials Units at the CNIC,” said José Javier Fuster.
The results of the study clearly demonstrate that participants who had mutations linked to clonal hematopoiesis at the start of the study were more likely to develop atherosclerosis in the following years. On the other hand, the presence and extent of atherosclerosis had no influence on the expansion of mutated blood cells. “These results indicate that the mutations contribute to the development of atherosclerosis but are not a consequence of it,” explained co-first author Miriam Díez-Díez. “However, it remains possible that other factors, such as genetic profile or lifestyle, might modulate the effects of clonal hematopoiesis, and future studies are planned to examine this possibility,” added Beatriz L. Ramos-Neble, the other co-first author on the study.
The results of the study have clear clinical implications and identify clonal hematopoiesis as a cardiovascular risk factor completely different from the traditional risk factors studied in recent decades. This novelty holds promise for the development of new strategies for the prevention of cardiovascular disorders. “By demonstrating that the mutations linked to clonal hematopoiesis precede atherosclerosis and contribute to its development, our research suggests that blocking the effects of these somatic mutations could help to prevent cardiovascular disease,” claimed Dr. José Javier Fuster. The second CNIC study, published in the European Heart Journal , lays the groundwork for this.
An ancient drug to alleviate a new cardiovascular risk factor
The best-characterized mutations linked to clonal hematopoiesis are those that affect the TET2 gene. In a 2017 study published in Science , Dr. José Javier Fuster’s team showed that mutations in TET2 accelerate the development of atherosclerosis in animal models. In the new study published in the European Heart Journal , the CNIC group, in partnership with the team led by Dr. Pradeep Natarajan at the Broad Institute in Boston, shows that the adverse effects of TET2 mutations on cardiovascular health can be alleviated by treatment with the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine.
The CNIC team demonstrated that administration of colchicine to animals with TET2 mutations slows the development of atherosclerosis to a rate similar to that seen in non-mutated animals. In parallel, the Broad Institute scientists showed that individuals with TET2 mutations and who had been treated with colchicine for other conditions had a lower risk of myocardial infarction than untreated patients with similar mutations.
Plant preparations containing colchicine have been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine, and the drug is used in modern medicine to treat inflammatory conditions such as gout. “Colchicine is a very cheap medicine, available throughout the world, and is approved for the prevention of cardiovascular disease by the European Medicines Agency and by the FDA in the USA. There is, therefore, no major obstacle to its use for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in people with TET2 mutations,” emphasized Dr. María Ángeles Zuriaga, who conducted the experimental studies at the CNIC and is the first author on the European Heart Journal study.
Dr. José Javier Fuster underlined the important implications of the study for personalized medicine. “In clonal hematopoiesis, each mutated gene acts through different mechanisms and will therefore likely require specific interventions to target its effects. This study lays the groundwork for using colchicine for/in the personalized prevention of cardiovascular disease of carriers of mutations in TET2 , but new clinical trials will be needed to conclusively demonstrate its effectiveness in these individuals.”
References: “Unidirectional association of clonal hematopoiesis with atherosclerosis development” by Miriam Díez-Díez, Beatriz L. Ramos-Neble, Jorge de la Barrera, J. C. Silla-Castro, Ana Quintas, Enrique Vázquez, M. Ascensión Rey-Martín, Benedetta Izzi, Lucía Sánchez-García, Inés García-Lunar, Guiomar Mendieta, Virginia Mass, Nuria Gómez-López, Cristina Espadas, Gema González, Antonio J. Quesada, Ana García-Álvarez, Antonio Fernández-Ortiz, Enrique Lara-Pezzi, Ana Dopazo, Fátima Sánchez-Cabo, Borja Ibáñez, Vicente Andrés, Valentín Fuster and José J. Fuster, 30 August 2024, Nature Medicine . DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03213-1
“Colchicine prevents accelerated atherosclerosis in TET2-mutant clonal haematopoiesis” by María A Zuriaga, Zhi Yu, Nuria Matesanz, Buu Truong, Beatriz L Ramos-Neble, Mari C Asensio-López, Md Mesbah Uddin, Tetsushi Nakao, Abhishek Niroula, Virginia Zorita, Marta Amorós-Pérez, Rosa Moro, Benjamin L Ebert, Michael C Honigberg, Domingo Pascual-Figal, Pradeep Natarajan and José J Fuster, 30 August 2024, European Heart Journal . DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae546
The PESA study is cofunded by the CNIC and Santander Bank. The two studies were additionally funded by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación e Universidades (PLEC2021-008194), the Spanish cardiovascular research network (CIBERCV), Fundación “la Caixa” (LCF/PR/HR17/52150007; LCF/PR/HR22/52420011), and Fundación ‘La Marató TV3’ (202314-31).
Related Articles
Covid toll: big jump in cardiovascular-related deaths reported by american heart association, recent research reveals a simple trick to lower heart disease risk, coffee’s link to raised cholesterol depends on drinker’s sex plus brewing method, daily coffee may benefit the heart and help you live longer – here’s how much to drink, covid-19 infections increase risk of serious heart conditions up to a year later, pfizer covid-19 vaccine associated with increased risk of carditis (heart inflammation), new research finds eating lots of avocados has public health benefits for issues like obesity, the latest research on coffee and your risk for heart rhythm problems – good news, popular energy drinks’ harmful effects on heart revealed in new research.
“In addition to the established risk factors for cardiovascular disease—such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity—another factor must now be considered: clonal hematopoiesis.” What they call established risk factors I, now eighty years of age, call co-symptoms.
The group photo suggests instead of researching clonal hematopoiesis they probably should be researching allergy/gout related obesity, likely related to the theme of the article via high serum levels of uric acid and/or low levels of calcium (as per ionic, not blood serum, testing). As to the presence of mutated red blood cells, lacking the skills and resources to do genetic testing I can only suspect “…the formation of lesions in the arterial wall that underlies most cardiovascular disorders.” is caused by uric acid crystallizing in the smooth muscle tissue lining the affected arteries, caused by low core temperature due to metabolic syndrome.
Bottom line: more great research undermined by mainstream medicine’s failure to recognize and research Dr. Arthur F. Coca’s kind of allergies since the early 1930s. I’ve never tried colchicine for my own mostly asymptomatic gout but I’ve read it can have serious side effects.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the study, so you need to get this right. Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena.
What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
Guiding the research design: A theoretical framework can guide the selection of research methods, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures. By outlining the key concepts and assumptions underlying the research questions, the theoretical framework can help researchers to identify the most appropriate research design for their study.
For instance, conceptual frameworks can address how the current study will fill gaps in the research, resolve contradictions in existing literature, or suggest a new area of study. While a literature review describes what is known and not known about the phenomenon, the conceptual framework leverages these gaps in describing the current study ...
A conceptual framework in research is used to understand a research problem and guide the development and analysis of the research. It serves as a roadmap to conceptualize and structure the work by providing an outline that connects different ideas, concepts, and theories within the field of study. A conceptual framework pictorially or verbally ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
Conceptual Framework Methodology is a research method that is commonly used in academic and scientific research to develop a theoretical framework for a study. It is a systematic approach that helps researchers to organize their thoughts and ideas, identify the variables that are relevant to their study, and establish the relationships between ...
What is a framework? Understanding their purpose, value, ...
The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that ...
Developing a conceptual framework in research. A conceptual framework is a representation of the relationship you expect to see between your variables, or the characteristics or properties that you want to study. Conceptual frameworks can be written or visual and are generally developed based on a literature review of existing studies about ...
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz. Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George. Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review.
A conceptual framework in research is not just a tool but a vital roadmap that guides the entire research process. It integrates various theories, assumptions, and beliefs to provide a structured approach to research. By defining a conceptual framework, researchers can focus their inquiries and clarify their hypotheses, leading to more ...
framework is a generative source of thinking, planning, conscious action, and reflection throughout the research process. A conceptual framework makes the case for why a study is significant and relevant and for how the study design (including data collection and analysis methods) appropri - ately and rigorously answers the research questions.
The Importance of Research Frameworks. Researchers may draw on several elements to frame their research. Generally, a framework is regarded as "a set of ideas that you use when you are forming your decisions and judgements" 13 or "a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is used to plan or decide something." 14 Research frameworks may consist of a single formal theory or part thereof ...
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and presenting the key ideas, theories, and relationships that underpin a research study or academic argument. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher, guiding the investigation and helping to connect various concepts logically and coherently.
conceptual and theoretical frameworks. As conceptual defines the key co ncepts, variables, and. relationships in a research study as a roadmap that outlines the researcher's understanding of how ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
Researching Theoretical Frameworks - Research Process
Theoretical frameworks contain the arguments that define the contribution of research studies. They do this in two ways, by showing how your study extends what is known and by setting the parameters for your contribution. ... The major source for ideas that will shape the framework is the research literature. That said, conversations with ...
Steps to Developing the Perfect Conceptual Framework. Pick a question. Conduct a literature review. Identify your variables. Create your conceptual framework. 1. Pick a Question. You should already have some idea of the broad area of your research project. Try to narrow down your research field to a manageable topic in terms of time and resources.
Integration of a theoretical framework into your research ...
A research framework provides an underlying structure or model to support our collective research efforts. Up until now, we've referenced, referred to and occasionally approached research as more of an amalgamated set of activities. But as we know, research comes in many different shapes and sizes, is variable in scope, and can be used to ...
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways: An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically. The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
Purpose: Conceptual models provide frameworks to illustrate relationships among patient-, provider-, system-, and community-level factors that inform care delivery and research. Existing models of cancer survivorship care focus largely on pediatric or adult populations whose needs differ from adolescents and young adults (AYAs). We developed a patient-centered conceptual model of AYA ...
The merging of asthma research with metabolic studies marks a groundbreaking phase in medical science, energized by the adoption of advanced bioinformatics techniques. This shift has significantly broadened our understanding of the molecular complexity and diverse pathological expressions of asthma [35,36,37]. The scientific community's ...
"The PESA study has already made very important contributions to our understanding of cardiovascular disease, and its longitudinal nature and unique characteristics provide an ideal framework for carrying out this important study on the relationship between clonal hematopoiesis and atherosclerosis," said Dr. Valentín Fuster, CNIC General ...