

thesis (n.)
late 14c., "unaccented syllable or note, a lowering of the voice in music," from Latin thesis "unaccented syllable in poetry," later (and more correctly) "stressed part of a metrical foot," from Greek thesis "a proposition," also "downbeat" (in music), originally "a setting down, a placing, an arranging; position, situation" (from reduplicated form of PIE root *dhe- "to set, put").
The sense in logic of "a formulation in advance of a proposition to be proved or debated" is attested by 1570s (contrasted to hypothesis ; in rhetoric it is opposed to antithesis ); that of "dissertation presented by a candidate for a university degree" is from 1650s. The uncertainty of the prosodic sense might have kept it from being established in English. Related: Thetic ; thetical ; thetically .
Entries linking to thesis
*dhē- , Proto-Indo-European root meaning "to set, put."
It forms all or part of: abdomen ; abscond ; affair ; affect (v.1) "make a mental impression on;" affect (v.2) "make a pretense of;" affection ; amplify ; anathema ; antithesis ; apothecary ; artifact ; artifice ; beatific ; benefice ; beneficence ; beneficial ; benefit ; bibliothec ; bodega ; boutique ; certify ; chafe ; chauffeur ; comfit ; condiment ; confection ; confetti ; counterfeit ; deed ; deem ; deface ; defeasance ; defeat ; defect ; deficient ; difficulty ; dignify ; discomfit ; do (v.); doom ; -dom ; duma ; edifice ; edify ; efface ; effect ; efficacious ; efficient ; epithet ; facade ; face ; facet ; facial ; -facient ; facile ; facilitate ; facsimile ; fact ; faction (n.1) "political party;" -faction ; factitious ; factitive ; factor ; factory ; factotum ; faculty ; fashion ; feasible ; feat ; feature ; feckless ; fetish ; -fic ; fordo ; forfeit ; -fy ; gratify ; hacienda ; hypothecate ; hypothesis ; incondite ; indeed ; infect ; justify ; malefactor ; malfeasance ; manufacture ; metathesis ; misfeasance ; modify ; mollify ; multifarious ; notify ; nullify ; office ; officinal ; omnifarious ; orifice ; parenthesis ; perfect ; petrify ; pluperfect ; pontifex ; prefect ; prima facie ; proficient ; profit ; prosthesis ; prothesis ; purdah ; putrefy ; qualify ; rarefy ; recondite ; rectify ; refectory ; sacrifice ; salmagundi ; samadhi ; satisfy ; sconce ; suffice ; sufficient ; surface ; surfeit ; synthesis ; tay ; ticking (n.); theco- ; thematic ; theme ; thesis ; verify .
It is the hypothetical source of/evidence for its existence is provided by: Sanskrit dadhati "puts, places;" Avestan dadaiti "he puts;" Old Persian ada "he made;" Hittite dai- "to place;" Greek tithenai "to put, set, place;" Latin facere "to make, do; perform; bring about;" Lithuanian dėti "to put;" Polish dziać się "to be happening;" Russian delat' "to do;" Old High German tuon , German tun , Old English don "to do."
Trends of thesis
More to explore, share thesis.
updated on March 20, 2024
Trending words
- 2 . research
- 3 . philadelphia
- 6 . authority
- 7 . algorithm
- 9 . geography
Dictionary entries near thesis
- English (English)
- 简体中文 (Chinese)
- Deutsch (German)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Italiano (Italian)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- Português (Portuguese)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese)
- 1.1 Etymology
- 1.2 Pronunciation
- 1.3.1 Derived terms
- 1.3.2 Related terms
- 1.3.3 Translations
- 1.4 References
- 1.5 Further reading
- 1.6 Anagrams
- 2.1 Etymology
- 2.2 Pronunciation
- 3.1 Etymology
- 3.2 Pronunciation
- 3.3.1 Declension
- 3.3.2 Descendants
- 3.4 References
From Late Middle English thesis ( “ lowering of the voice ” ) [ 1 ] and also borrowed directly from its etymon Latin thesis ( “ proposition, thesis; lowering of the voice ” ) , from Ancient Greek θέσῐς ( thésis , “ arrangement, placement, setting; conclusion, position, thesis; lowering of the voice ” ) , from τῐ́θημῐ ( títhēmi , “ to place, put, set; to put down in writing; to consider as, regard ” ) [ 2 ] [ 3 ] (ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *dʰeh₁- ( “ to do; to place, put ” ) ) + -σῐς ( -sis , suffix forming abstract nouns or nouns of action, process, or result ) . The English word is a doublet of deed .
Sense 1.1 (“proposition or statement supported by arguments”) is adopted from antithesis . [ 2 ] Sense 1.4 (“initial stage of reasoning”) was first used by the German philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762–1814), and later applied to the dialectical method of his countryman, the philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770–1831).
The plural form theses is borrowed from Latin thesēs , from Ancient Greek θέσεις ( théseis ) .
Pronunciation
- ( Received Pronunciation ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθiːsɪs/ , ( archaic ) /ˈθɛsɪs/
| Audio ( ): | ( ) |
- ( General American ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθisɪs/
- Rhymes: -iːsɪs
- Hyphenation: the‧sis
- ( Received Pronunciation ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθiːsiːz/
- ( General American ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθisiz/
- Rhymes: -iːsiːz
- Hyphenation: the‧ses
thesis ( plural theses )
- ( rhetoric ) A proposition or statement supported by arguments .
- 1766 , [ Oliver Goldsmith ], “The Conclusion”, in The Vicar of Wakefield: [ … ] , volume II, Salisbury, Wiltshire: [ … ] B. Collins, for F [ rancis ] Newbery , [ … ] , →OCLC , pages 218–219 : I told them of the grave, becoming, and ſublime deportment they ſhould aſſume upon this myſtical occaſion, and read them two homilies and a theſis of my own compoſing, in order to prepare them.
- ( mathematics , computer science ) A conjecture , especially one too vague to be formally stated or verified but useful as a working convention.
- ( logic ) An affirmation , or distinction from a supposition or hypothesis .
- ( philosophy ) In the dialectical method of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel : the initial stage of reasoning where a formal statement of a point is developed ; this is followed by antithesis and synthesis .
- ( music , prosody , originally ) The action of lowering the hand or bringing down the foot when indicating a rhythm ; hence, an accented part of a measure of music or verse indicated by this action; an ictus , a stress . Antonym: arsis
- ( music , prosody , with a reversal of meaning ) A depression of the voice when pronouncing a syllables of a word ; hence, the unstressed part of the metrical foot of a verse upon which such a depression falls , or an unaccented musical note .
Derived terms
- all but thesis
- bachelor's thesis
- Church-Turing thesis
- conflict thesis
- doctoral thesis
- graduate thesis
- Habakkuk thesis
- master's thesis
- Merton thesis
- private language thesis
- thesis defense
- thesis statement
Related terms
Translations.
| (tʻez) , (tézis), (palažénnje), (téza) (téza), (tézis) / (leon dim ), / (leon tai ) / (lùndiǎn), / (lùntí) , , (tezisi) (thésis) , (tēze), (ろんだい, rondai), (しゅちょう, shuchō), (ていりつ, teiritsu) (teje), (nonje), (ronje) (North Korea) (teza) (tɛ́zis), (položénije) , , , , (téza), (tézys), (polóžennja) |
| (ʔuṭrūḥa) (atenaxosutʻyun), (disertacʻia), (diplomayin ašxatankʻ) (dysjertácyja), (dysertácyja), (dyplómnaja rabóta) (disertácija) , / (leon man ) / (lùnwén) , , , , ; ; , (diserṭacia) , , , , , (only a doctoral thesis) (mahāśodh nibandh) (téza) , (postgraduate), (ろんぶん, ronbun) (dissertasiä), (diplomdyq jūmys) (nɨkkheepaʼbɑt) (nonmun), (ronmun) (North Korea) (dissertatsiya) (wi tha nyā ni phon) (disertacija) or , (pâyân-nâme), , , (dissertácija), (diplómnaja rabóta) , , , (dissertatsiya) (wít-tá-yaa-ní-pon), (bpà-rin-yaa-ní-pon), (ní-pon) , , (dysertácija), (dyplómna robóta) , , |
| (thésis) |
- ^ “ thē̆sis, n. ”, in MED Online , Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan , 2007 .
- ^ “ thesis, n. ”, in Lexico , Dictionary.com ; Oxford University Press , 2019–2022 .
Further reading
- “ thesis ”, in The Century Dictionary [ … ] , New York, N.Y.: The Century Co. , 1911 , →OCLC .
- “ thesis ”, in Webster’s Revised Unabridged Dictionary , Springfield, Mass.: G. & C. Merriam , 1913 , →OCLC .
- Heists , Sethis , heists , shiest , shites , sithes , thises
From Latin thesis , from Ancient Greek θέσις ( thésis , “ a proposition, a statement, a thing laid down, thesis in rhetoric, thesis in prosody ” ) .
| Audio: | ( ) |
thesis f ( plural theses or thesissen , diminutive thesisje n )
- Dated form of these . Synonyms: dissertatie , proefschrift , scriptie
From Ancient Greek θέσις ( thésis , “ a proposition, a statement, a thing laid down, thesis in rhetoric, thesis in prosody ” ) .
- ( Classical Latin ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈtʰe.sis/ , [ˈt̪ʰɛs̠ɪs̠]
- ( modern Italianate Ecclesiastical ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈte.sis/ , [ˈt̪ɛːs̬is]
thesis f ( genitive thesis ) ; third declension
| Case | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| | ||
Descendants
- → Dutch: thesis
- → Armenian: թեզ ( tʻez )
- → Dutch: these
- → Persian: تز ( tez )
- → Romanian: teză
- → Turkish: tez
- Galician: tese
- Italian: tesi
- English: thesis
- Portuguese: tese
- Spanish: tesis
- “ thesis ”, in Charlton T. Lewis and Charles Short ( 1879 ) A Latin Dictionary , Oxford: Clarendon Press
- thesis in Gaffiot, Félix ( 1934 ) Dictionnaire illustré latin-français , Hachette.
- English terms derived from Proto-Indo-European
- English terms derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *dʰeh₁-
- English terms inherited from Middle English
- English terms derived from Middle English
- English terms borrowed from Latin
- English terms derived from Latin
- English terms derived from Ancient Greek
- English doublets
- English 2-syllable words
- English terms with IPA pronunciation
- English terms with audio links
- Rhymes:English/iːsɪs
- Rhymes:English/iːsɪs/2 syllables
- Rhymes:English/iːsiːz
- Rhymes:English/iːsiːz/2 syllables
- English lemmas
- English nouns
- English countable nouns
- English nouns with irregular plurals
- en:Rhetoric
- English terms with quotations
- en:Mathematics
- en:Computer science
- en:Philosophy
- English contranyms
- Dutch terms derived from Latin
- Dutch terms derived from Ancient Greek
- Dutch terms with audio links
- Dutch lemmas
- Dutch nouns
- Dutch nouns with Latin plurals
- Dutch nouns with plural in -en
- Dutch feminine nouns
- Dutch dated forms
- Latin terms derived from Proto-Indo-European
- Latin terms derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *dʰeh₁-
- Latin terms borrowed from Ancient Greek
- Latin terms derived from Ancient Greek
- Latin 2-syllable words
- Latin terms with IPA pronunciation
- Latin lemmas
- Latin nouns
- Latin third declension nouns
- Latin feminine nouns in the third declension
- Latin feminine nouns
- Word of the day archive
- English entries with language name categories using raw markup
- Pages with 3 entries
- Terms with Armenian translations
- Terms with Asturian translations
- Terms with Azerbaijani translations
- Terms with Belarusian translations
- Terms with Bulgarian translations
- Terms with Catalan translations
- Terms with Cantonese translations
- Mandarin terms with redundant transliterations
- Terms with Mandarin translations
- Terms with Czech translations
- Terms with Danish translations
- Terms with Dutch translations
- Terms with Esperanto translations
- Terms with Estonian translations
- Terms with Finnish translations
- Terms with French translations
- Terms with Galician translations
- Terms with Georgian translations
- Terms with German translations
- Terms with Ancient Greek translations
- Terms with Hungarian translations
- Terms with Italian translations
- Terms with Japanese translations
- Terms with Korean translations
- Terms with Latin translations
- Terms with Macedonian translations
- Terms with Malay translations
- Terms with Maori translations
- Terms with Norwegian Bokmål translations
- Terms with Persian translations
- Terms with Polish translations
- Terms with Portuguese translations
- Russian terms with non-redundant manual transliterations
- Terms with Russian translations
- Terms with Serbo-Croatian translations
- Terms with Slovak translations
- Terms with Slovene translations
- Terms with Spanish translations
- Terms with Swedish translations
- Terms with Tagalog translations
- Terms with Turkish translations
- Terms with Ukrainian translations
- Terms with Vietnamese translations
- Terms with Arabic translations
- Terms with Gujarati translations
- Terms with Hebrew translations
- Terms with Indonesian translations
- Terms with Kazakh translations
- Terms with Khmer translations
- Terms with Kyrgyz translations
- Terms with Lao translations
- Terms with Latvian translations
- Terms with Lithuanian translations
- Terms with Norwegian Nynorsk translations
- Terms with Romanian translations
- Terms with Tajik translations
- Terms with Thai translations
- Terms with Uzbek translations
- Terms with Middle English translations
Navigation menu
Look up a word, learn it forever.
Other forms: theses
A thesis is the most important or foundational idea of an argument. If the thesis of your paper is that chocolate ice cream is better than vanilla, you'll need to back that up with plenty of sundae-based research.
The noun thesis has more than one important sense to it. One definition of thesis is that it is the most important or foundational idea of an argument, presentation, or piece of writing. But it can also mean a large work of art, criticism, or scientific research that represents original research and is generally the final requirement for an academic degree.
- noun an unproved statement put forward as a premise in an argument see more see less type of: assumption , premise , premiss a statement that is assumed to be true and from which a conclusion can be drawn
- noun a treatise advancing a new point of view resulting from research; usually a requirement for an advanced academic degree synonyms: dissertation see more see less type of: tractate , treatise a formal exposition
Vocabulary lists containing thesis
A thorough survey of various textbooks, assignments, content area standards, and examinations yields the following list of words compiled by Jim Burke . You cannot expect to succeed on assignments if you do not understand the directions.
Persuade yourself to study this list of words related to argumentative writing. You'll learn all about making claims, supporting arguments with evidence, and maintaining an objective tone. It's no fallacy that reviewing these words will improve your credibility as a writer.
To improve your fluency in English Language Arts and Reading (ELAR), learn this academic vocabulary list that includes words selected from the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) state standards.
Sign up now (it’s free!)
Whether you’re a teacher or a learner, vocabulary.com can put you or your class on the path to systematic vocabulary improvement..
Words and phrases
Personal account.
- Access or purchase personal subscriptions
- Get our newsletter
- Save searches
- Set display preferences
Institutional access
Sign in with library card
Sign in with username / password
Recommend to your librarian
Institutional account management
Sign in as administrator on Oxford Academic
thesis noun
- Hide all quotations
What does the noun thesis mean?
There are seven meanings listed in OED's entry for the noun thesis . See ‘Meaning & use’ for definitions, usage, and quotation evidence.
thesis has developed meanings and uses in subjects including
Entry status
OED is undergoing a continuous programme of revision to modernize and improve definitions. This entry has not yet been fully revised.
How common is the noun thesis ?
| 1750 | 1.6 |
| 1760 | 1.8 |
| 1770 | 2.6 |
| 1780 | 1.9 |
| 1790 | 1.7 |
| 1800 | 1.9 |
| 1810 | 1.4 |
| 1820 | 1.3 |
| 1830 | 1.3 |
| 1840 | 1.8 |
| 1850 | 2.0 |
| 1860 | 1.8 |
| 1870 | 2.6 |
| 1880 | 2.9 |
| 1890 | 3.7 |
| 1900 | 4.2 |
| 1910 | 5.7 |
| 1920 | 8.2 |
| 1930 | 13 |
| 1940 | 15 |
| 1950 | 19 |
| 1960 | 24 |
| 1970 | 27 |
| 1980 | 27 |
| 1990 | 25 |
| 2000 | 23 |
| 2010 | 23 |
How is the noun thesis pronounced?
British english, u.s. english, where does the noun thesis come from.
Earliest known use
Middle English
The earliest known use of the noun thesis is in the Middle English period (1150—1500).
OED's earliest evidence for thesis is from before 1398, in a translation by John Trevisa, translator.
thesis is a borrowing from Greek.
Etymons: Greek θέσις .
Nearby entries
- thesaurus, n. 1823–
- thesaury, n. a1639–1708
- these, n. a1600–48
- these, pron. & adj. Old English–
- Thesean, adj. 1815–
- Theseid, n. 1725–
- Theseium, n. 1819–
- these-like, adj. 1644–
- thesial, adj. 1654
- thesicle, n. 1863–
- thesis, n. a1398–
- thesis-novel, n. 1934–
- thesis-play, n. 1902–
- thesmophilist, n. 1644–
- Thesmophorian, adj. 1891–
- Thesmophoric, adj. 1788–
- thesmothete, n. 1603–
- thesocyte, n. 1887–
- thesp, n. 1962–
- Thespian, adj. & n. 1675–
- Thespianism, n. 1914–
Thank you for visiting Oxford English Dictionary
To continue reading, please sign in below or purchase a subscription. After purchasing, please sign in below to access the content.
Meaning & use
Pronunciation, compounds & derived words, entry history for thesis, n..
thesis, n. was first published in 1912; not yet revised.
thesis, n. was last modified in December 2023.
Revision of the OED is a long-term project. Entries in oed.com which have not been revised may include:
- corrections and revisions to definitions, pronunciation, etymology, headwords, variant spellings, quotations, and dates;
- new senses, phrases, and quotations which have been added in subsequent print and online updates.
Revisions and additions of this kind were last incorporated into thesis, n. in December 2023.
Earlier versions of this entry were published in:
OED First Edition (1912)
- Find out more
OED Second Edition (1989)
- View thesis in OED Second Edition
Please submit your feedback for thesis, n.
Please include your email address if you are happy to be contacted about your feedback. OUP will not use this email address for any other purpose.
Citation details
Factsheet for thesis, n., browse entry.

- Login | Register
Prefixes and suffixes for research writing
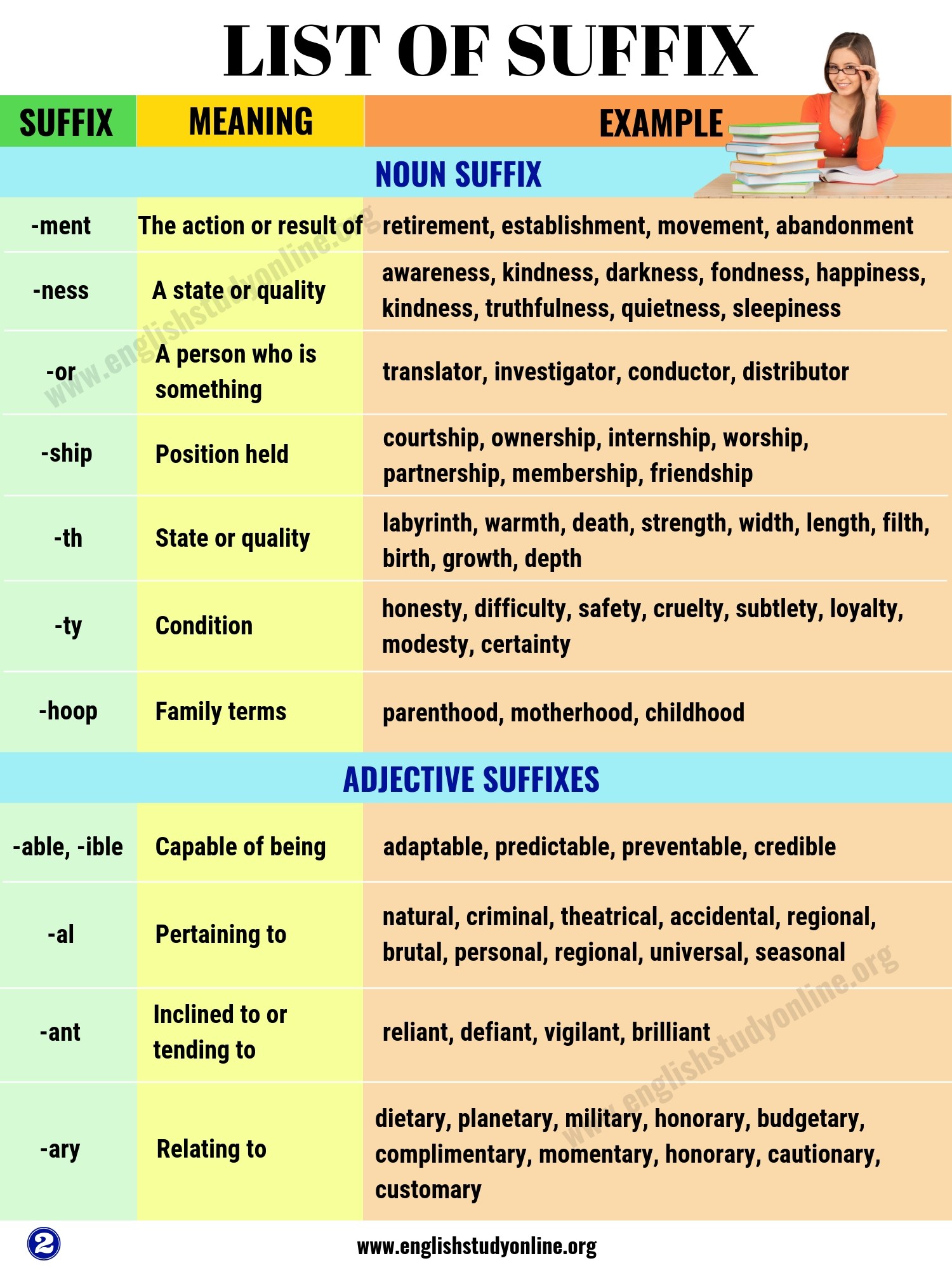
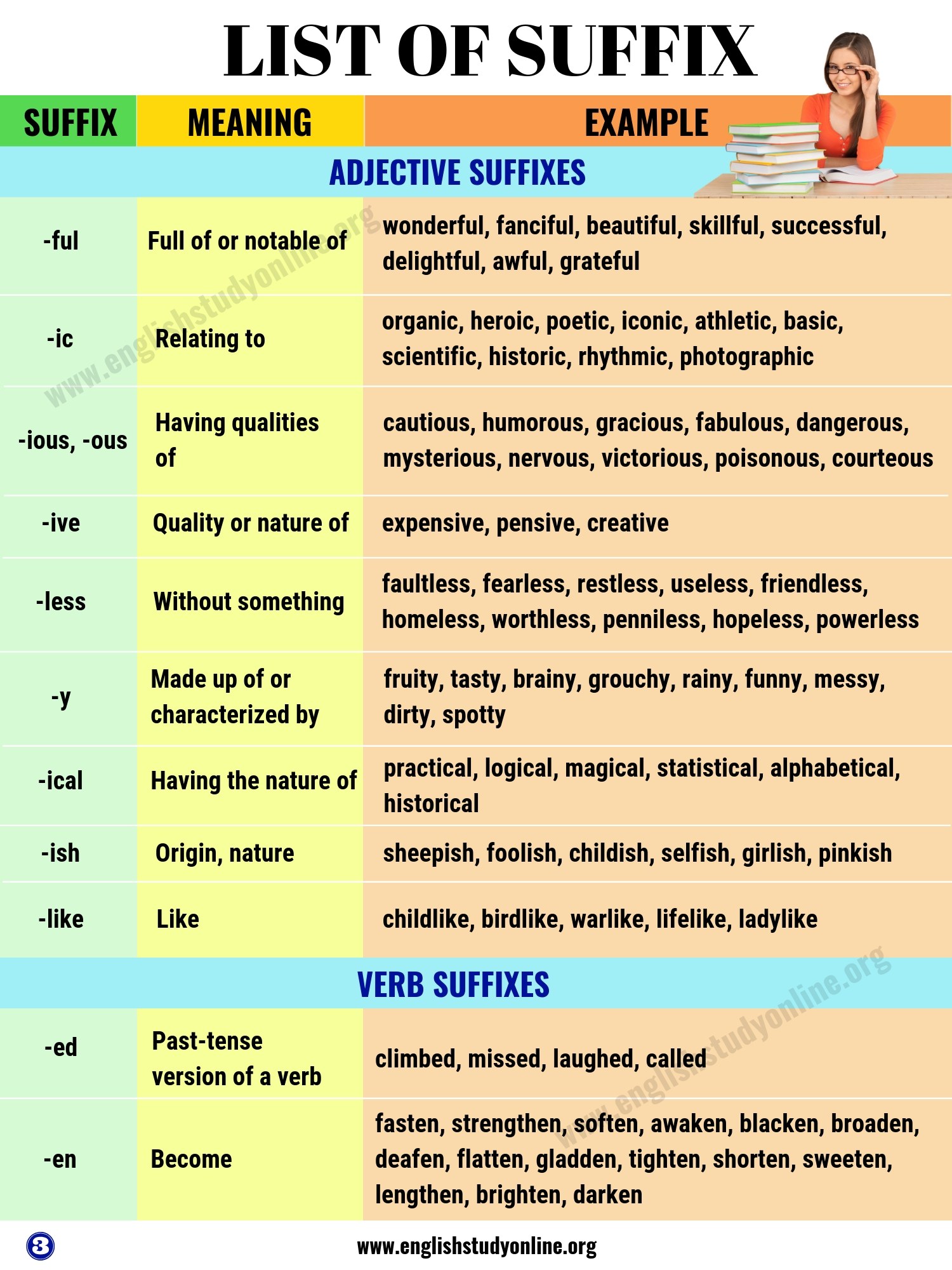
Many words are made up of a root word and an affix . An affix is a word part that is attached to the beginning or the end of a root word; this affix then changes the meaning of the root word.
A prefix is a word part that is added to the beginning of a word to create a new meaning. For example, if the prefix “un” is added to the root word “happy”, we get a new word that has the opposite meaning to happy: “unhappy”.
A suffix is a word part that is added to the end of a word to create a new meaning. For example, if we take the root word “care”, we can change its meaning by adding the suffix “ful”, to give us the word “careful” (meaning “cautious” or “paying attention”). Alternatively, we could add the suffix “less” to “care”, to give us a word with a very different meaning: “careless” (meaning “not concerned” or “lacking in attention”).
Many words that we use in science use prefixes and suffixes that are derived from Greek or Latin. While this may seem complicated, once you become familiar with some of these prefixes and suffixes you will often be able to work out the meaning of scientific words, even if they are new to you.
Consider this example:
The word part “cyte” is derived from the Greek word for “cell”.
The word part “erythro” is derived from the Greek word for “red”.
The word “erythrocyte” means “red blood cell”.
The word “leucocyte” means “white blood cell” (the word part “leuco” being derived from the Greek word for “white”).
Note that some affixes can act as suffixes or as prefixes, depending on the word they are being used in.
For example, in the word “cytology”, meaning “the study of cells”, the word part “cyte” appears at the beginning of the word, rather than at the end as it does in “erythrocyte”. The word part “ology” comes from the Greek word that means “the study of”.
Look at the list of affixes below. Then, based on this list, answer the following questions.
- Endo – within
- Exo – outside
- Iso – equal
- Macro – large
- Micro – small
- Ology – the study of
- Therm – temperature
- What is the term for an animal’s skeleton that is inside its body?
- What is the term for an animal’s skeleton that is outside its body?
- What is the term for a process in which a system changes, for example, its pressure or volume, but the temperature remains the same?
- If the word part “osteo” comes from the Greek word for “bone”, what is the scientific name for a “bone cell”?
- What is the word part missing from the list of affixes that is needed to make a word that means the study of tiny living things?
Answers are below.
________________________________________________________________________________
- What is the term for an animal’s skeleton that is inside its body? “endoskeleton”
- What is the term for an animal’s skeleton that is outside its body? “exoskeleton”
- What is the term for a process in which a system changes, for example, its pressure or volume, but the temperature remains the same? “isothermal”
- If the word part “osteo” comes from the Greek word for “bone”, what is the scientific name for a “bone cell”? “osteocyte”
- What is the word part missing from the list of affixes that is needed to make a word that means the study of tiny living things? “bio”
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of suffix
(Entry 1 of 2)
Definition of suffix (Entry 2 of 2)
transitive verb
Did you know?
What are prefixes , suffixes , and combining forms ?
Prefixes and suffixes are both kinds of affixes . That is, they are word parts that attach to the beginning or end of a word or word base (a word stripped down to its simplest form) to produce a related word or an inflectional form of a word. Examples are in- in informal and both re- and -ing in reporting .
A third kind of affix is called an infix . Infixes are inserted into a word or word base. English uses very few infixes, but a couple examples are the plural-making s in words like cupsful and passersby , and various swear words, like damn in informal constructions like guaran-damn-tee .
A combining form is a form of a word that only appears as part of another word. There are a number of kinds of combining forms, each classified by what kind of word results when the form is used. For example, -wise in clockwise is an adverb combining form; -like in birdlike is an adjective combining form; -graph in photograph is a noun combining form; and -lyze in electrolyze is a verb combining form.
Combining forms are similar to affixes but can have a bit more lexical substance to them. Unlike affixes, combining forms are substantial enough to form a word simply by connecting to an affix, such as when the combining form cephal- joins with the suffix -ic to form cephalic . A combining form can also differ from an affix in its being derived from an independent word. For example, para- is a combining form in the word paratrooper because in that word it represents the word parachute . Para- is a prefix, however, in the words paranormal and paramedic . A combining form can also be distinguished historically from an affix by the fact that it is borrowed from another language in which it is descriptively a word or a combining form, such as the French mal giving English the mal- in malfunction .
Examples of suffix in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'suffix.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
borrowed from New Latin suffīxum, noun derivative from neuter of Latin suffīxus, past participle of suffīgere "to fasten from below, attach to the top of," from suf-, assimilated form of sub- sub- + fīgere "to drive in, insert, fasten" — more at fix entry 1
derivative of suffix entry 1
1720, in the meaning defined above
1778, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to suffix

A Pair of Suffixes and The History of...
A Pair of Suffixes and The History of 'Ditto'
Word Matters, Episode 79

A Comprehensive Guide to Forming...
A Comprehensive Guide to Forming Compounds
Everything you need to know
Dictionary Entries Near suffix
sufficient reason
sufflaminate
Cite this Entry
“Suffix.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/suffix. Accessed 4 Sep. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of suffix.
Kids Definition of suffix (Entry 2 of 2)
More from Merriam-Webster on suffix
Nglish: Translation of suffix for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of suffix for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about suffix
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), games & quizzes.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of thesis in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I wrote my thesis on literacy strategies for boys .
- Her main thesis is that children need a lot of verbal stimulation .
- boilerplate
- composition
- corresponding author
- dissertation
- essay question
- peer review
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
thesis | American Dictionary
Examples of thesis, collocations with thesis.
These are words often used in combination with thesis .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of thesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
put something off
to decide or arrange to delay an event or activity until a later time or date

It’s not really my thing (How to say you don’t like something)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add thesis to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add thesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Definition of Suffix
Types of suffix, examples of suffix in literature, example #1: waiting for godot (by samuel beckett).
“No, personally I do not need them any more. ( Estragon takes a step towards the bones .) But . . . ( Estragon stops short ) . . . He is therefore the one to ask . ( Estragon turns towards Lucky, hesitates .) ( in raptures ). Mister! ( Lucky bows his head .) Reply! Do you want them or don’t you? ( Silence of Lucky. To Estragon .) They’re yours. ( Estragon makes a dart at the bones, picks them up and begins to gnaw them .)… It’s a scandal ! Silence . Flabbergasted, Estragon stops gnawing , looks at Pozzo and Vladimir in turn. Pozzo outwardly calm .”
Example #2: Gulliver’s Travels (by Jonathan Swift)
“Two days after this adventure , the emperor, having ordered that part of his army which quarters in and about his metropolis, to be in readiness , took a fancy of diverting himself in a very singular manner. He desired I would stand like a Colossus, with my legs as far asunder as I conveniently could. He then commanded his general (who was an old experienced leader, and a great patron of mine) to draw up the troops in close order, and march them under me …”

Example #3: Heart of Darkness (by Joseph Conrad)
“We were on deck at the time, and the headman of my wood-cutters, lounging near by, turned upon him his heavy and glittering eyes…I assure you that never, never before, did this land, this river, this jungle, the very arch of this blazing sky, appear to me so hopeless and so dark, so impenetrable to human thought, so pitiless to human weakness . … he did not know exactly in what direction .”
Example #4: Macbeth (by William Shakespeare)
“And fixed his head upon our battlements . As whence the sun ‘gins his reflection Shipwracking storms and direful thunders break… As cannons overcharged with double cracks, So they doubly redoubled strokes upon the foe. Except they meant to bathe in reeking wounds .”
Example #5: Ode to Autumn (by John Keats)
“Season of mists and mellow fruitfulness , Close bosom-friend of the maturing sun… To bend with apples the moss’d cottage- trees , And fill all fruit with ripeness to the core; Thee sitting careless on a granary floor, Thy hair soft-lifted by the winnowing wind…”
Function of Suffix
Related posts:, post navigation.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||














IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
thesis. (n.). late 14c., "unaccented syllable or note, a lowering of the voice in music," from Latin thesis "unaccented syllable in poetry," later (and more correctly) "stressed part of a metrical foot," from Greek thesis "a proposition," also "downbeat" (in music), originally "a setting down, a placing, an arranging; position, situation" (from reduplicated form of PIE root *dhe-"to set, put").
Thesis definition: a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, especially one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections. See examples of THESIS used in a sentence.
The meaning of THESIS is a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view; especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree. How to use thesis in a sentence.
thesis (plural theses) (rhetoric) A proposition or statement supported by arguments. (by extension) A lengthy essay written to establish the validity of a thesis (sense 1.1), especially one submitted in order to complete the requirements for a non- doctoral degree in the US and a doctoral degree in the UK; a dissertation.
A thesis is the most important or foundational idea of an argument. If the thesis of your paper is that chocolate ice cream is better than vanilla, you'll need to back that up with plenty of sundae-based research. ... One definition of thesis is that it is the most important or foundational idea of an argument, presentation, or piece of writing ...
THESIS meaning: 1. a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done for a higher…. Learn more.
Thesis definition: . See examples of THESIS used in a sentence.
There are seven meanings listed in OED's entry for the noun thesis. See 'Meaning & use' for definitions, usage, and quotation evidence. thesis has developed meanings and uses in subjects including. prosody (Middle English) music (Middle English) rhetoric (late 1500s) logic (late 1500s) education (late 1700s) philosophy (1830s)
A suffix is a word part that is added to the end of a word to create a new meaning. For example, if we take the root word "care", we can change its meaning by adding the suffix "ful", to give us the word "careful" (meaning "cautious" or "paying attention").
The meaning of SUFFIX is an affix occurring at the end of a word, base, or phrase. How to use suffix in a sentence. What are prefixes, suffixes, and combining forms?
thesis in American English. (ˈθisɪs) noun Word forms: plural -ses (-siz) 1. a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, esp. one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections. He vigorously defended his thesis on the causes of war. 2. a subject for a composition or essay. 3.
thesis (that…) a statement or an opinion that is discussed in a logical way and presented with evidence in order to prove that it is true. The basic thesis of the book is fairly simple. These latest findings support the thesis that sexuality is determined by nature rather than choice.
THESIS definition: 1. a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done for a higher…. Learn more.
A suffix is not a word, but it adds to and changes the meaning of a root or base word, making the word longer. It also shows the way a word is used, formed, and changed into another word with a different meaning to suit the text and time of the context.In addition, a suffix also transforms the grammatical role of lexis by changing nouns into adjectives or making verbs of nouns - the reason ...
She's doing research for her Ph.D. thesis in political science. synonyms: dissertation, treatise similar words: article, composition, discourse, essay, exposition, monograph, paper: definition 3: the opening of a dialectical argument or process, followed by antithesis and resolved in synthesis.
plural theses / ˈθiːˌsiːz/. Britannica Dictionary definition of THESIS. [count] 1. : a long piece of writing on a particular subject that is done to earn a degree at a university. She wrote her thesis on Renaissance Nativity scenes. a master's/doctoral thesis on the effects of global warming. 2. formal : a statement that someone wants to ...
About Prefix and Suffix Words . This page lists all the words created by adding prefixes, suffixes to the word `thesis`. For each word, youwill notice a blue bar below the word. The longer the blue bar below a word, the more common/popular the word. Very short blue bars indicate rare usage.
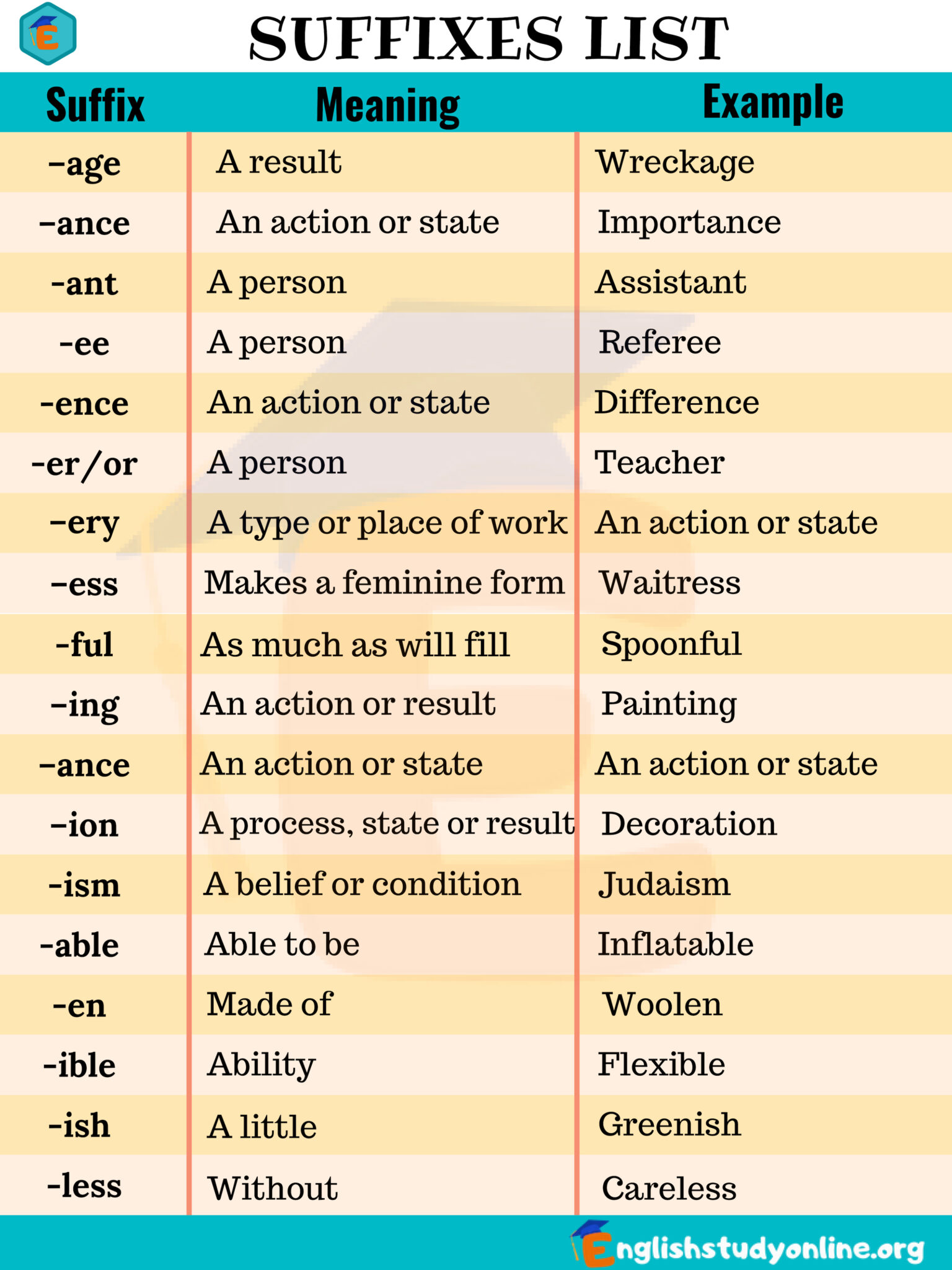
A suffix is a letter or group of letters attached to the end of a word, making a new word or altering the original word's tense, meaning, or part of speech.For example, adding -ness to the adjective "happy" creates the noun "happiness.". List of Noun Suffixes. Learn a useful list of noun suffixes with their meaning and examples in English-al ...
Suffix definition. A suffix is a series of letters that is added to the end of a root word and modifies or expands the meaning of the original word.. Suffixes can also be used in English to show if a word is a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb.. Difference between a prefix and a suffix. A prefix is a letter or group of letters that is attached to the beginning of a word.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
1 thesis (on something) a long piece of writing completed by a student as part of a university degree, based on their own research Students must submit a thesis on an agreed subject within four years.
This thesis focuses on the deviation of ergodic sums for a substitution dynamical systems with a matrix that admits eigenvalues of modulus larger than 1. Specifically, we concentrate on substitutions with non-conjugated eigenvalues. At first, we define the a-minimals letters and the dominant letters of a word to study its broken associated line.