Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what are the benefits of group work.
“More hands make for lighter work.” “Two heads are better than one.” “The more the merrier.”
These adages speak to the potential groups have to be more productive, creative, and motivated than individuals on their own.

Benefits for students
Group projects can help students develop a host of skills that are increasingly important in the professional world (Caruso & Woolley, 2008; Mannix & Neale, 2005). Positive group experiences, moreover, have been shown to contribute to student learning, retention and overall college success (Astin, 1997; Tinto, 1998; National Survey of Student Engagement, 2006).
Properly structured, group projects can reinforce skills that are relevant to both group and individual work, including the ability to:
- Break complex tasks into parts and steps
- Plan and manage time
- Refine understanding through discussion and explanation
- Give and receive feedback on performance
- Challenge assumptions
- Develop stronger communication skills.
Group projects can also help students develop skills specific to collaborative efforts, allowing students to...
- Tackle more complex problems than they could on their own.
- Delegate roles and responsibilities.
- Share diverse perspectives.
- Pool knowledge and skills.
- Hold one another (and be held) accountable.
- Receive social support and encouragement to take risks.
- Develop new approaches to resolving differences.
- Establish a shared identity with other group members.
- Find effective peers to emulate.
- Develop their own voice and perspectives in relation to peers.
While the potential learning benefits of group work are significant, simply assigning group work is no guarantee that these goals will be achieved. In fact, group projects can – and often do – backfire badly when they are not designed , supervised , and assessed in a way that promotes meaningful teamwork and deep collaboration.
Benefits for instructors
Faculty can often assign more complex, authentic problems to groups of students than they could to individuals. Group work also introduces more unpredictability in teaching, since groups may approach tasks and solve problems in novel, interesting ways. This can be refreshing for instructors. Additionally, group assignments can be useful when there are a limited number of viable project topics to distribute among students. And they can reduce the number of final products instructors have to grade.
Whatever the benefits in terms of teaching, instructors should take care only to assign as group work tasks that truly fulfill the learning objectives of the course and lend themselves to collaboration. Instructors should also be aware that group projects can add work for faculty at different points in the semester and introduce its own grading complexities .
Astin, A. (1993). What matters in college? Four critical years revisited. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Caruso, H.M., & Wooley, A.W. (2008). Harnessing the power of emergent interdependence to promote diverse team collaboration. Diversity and Groups. 11, 245-266.
Mannix, E., & Neale, M.A. (2005). What differences make a difference? The promise and reality of diverse teams in organizations. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 6(2), 31-55.
National Survey of Student Engagement Report. (2006). http://nsse.iub.edu/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report/docs/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report.pdf .
Tinto, V. (1987). Leaving college: Rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
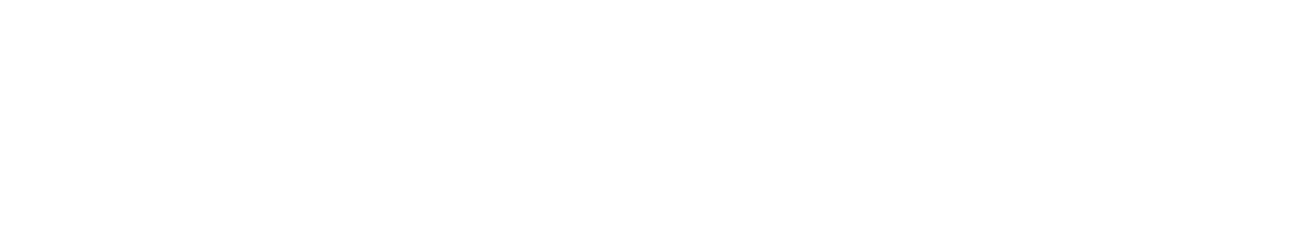
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
Many students have had little experience working in groups in an academic setting. While there are many excellent books and articles describing group processes, this guide is intended to be short and simply written for students who are working in groups, but who may not be very interested in too much detail. It also provides teachers (and students) with tips on assigning group projects, ways to organize groups, and what to do when the process goes awry.
Some reasons to ask students to work in groups
Asking students to work in small groups allows students to learn interactively. Small groups are good for:
- generating a broad array of possible alternative points of view or solutions to a problem
- giving students a chance to work on a project that is too large or complex for an individual
- allowing students with different backgrounds to bring their special knowledge, experience, or skills to a project, and to explain their orientation to others
- giving students a chance to teach each other
- giving students a structured experience so they can practice skills applicable to professional situations
Some benefits of working in groups (even for short periods of time in class)
- Students who have difficulty talking in class may speak in a small group.
- More students, overall, have a chance to participate in class.
- Talking in groups can help overcome the anonymity and passivity of a large class or a class meeting in a poorly designed room.
- Students who expect to participate actively prepare better for class.
Caveat: If you ask students to work in groups, be clear about your purpose, and communicate it to them. Students who fear that group work is a potential waste of valuable time may benefit from considering the reasons and benefits above.
Large projects over a period of time
Faculty asking students to work in groups over a long period of time can do a few things to make it easy for the students to work:
- The biggest student complaint about group work is that it takes a lot of time and planning. Let students know about the project at the beginning of the term, so they can plan their time.
- At the outset, provide group guidelines and your expectations.
- Monitor the groups periodically to make sure they are functioning effectively.
- If the project is to be completed outside of class, it can be difficult to find common times to meet and to find a room. Some faculty members provide in-class time for groups to meet. Others help students find rooms to meet in.
Forming the group
- Forming the group. Should students form their own groups or should they be assigned? Most people prefer to choose whom they work with. However, many students say they welcome both kinds of group experiences, appreciating the value of hearing the perspective of another discipline, or another background.
- Size. Appropriate group size depends on the nature of the project. If the group is small and one person drops out, can the remaining people do the work? If the group is large, will more time be spent on organizing themselves and trying to make decisions than on productive work?
- Resources for students. Provide a complete class list, with current email addresses. (Students like having this anyway so they can work together even if group projects are not assigned.)
- Students that don't fit. You might anticipate your response to the one or two exceptions of a person who really has difficulty in the group. After trying various remedies, is there an out—can this person join another group? work on an independent project?
Organizing the work
Unless part of the goal is to give people experience in the process of goal-setting, assigning tasks, and so forth, the group will be able to work more efficiently if they are provided with some of the following:
- Clear goals. Why are they working together? What are they expected to accomplish?
- Ways to break down the task into smaller units
- Ways to allocate responsibility for different aspects of the work
- Ways to allocate organizational responsibility
- A sample time line with suggested check points for stages of work to be completed
Caveat: Setting up effective small group assignments can take a lot of faculty time and organization.
Getting Started
- Groups work best if people know each others' names and a bit of their background and experience, especially those parts that are related to the task at hand. Take time to introduce yourselves.
- Be sure to include everyone when considering ideas about how to proceed as a group. Some may never have participated in a small group in an academic setting. Others may have ideas about what works well. Allow time for people to express their inexperience and hesitations as well as their experience with group projects.
- Most groups select a leader early on, especially if the work is a long-term project. Other options for leadership in long-term projects include taking turns for different works or different phases of the work.
- Everyone needs to discuss and clarify the goals of the group's work. Go around the group and hear everyone's ideas (before discussing them) or encourage divergent thinking by brainstorming. If you miss this step, trouble may develop part way through the project. Even though time is scarce and you may have a big project ahead of you, groups may take some time to settle in to work. If you anticipate this, you may not be too impatient with the time it takes to get started.
Organizing the Work
- Break up big jobs into smaller pieces. Allocate responsibility for different parts of the group project to different individuals or teams. Do not forget to account for assembling pieces into final form.
- Develop a timeline, including who will do what, in what format, by when. Include time at the end for assembling pieces into final form. (This may take longer than you anticipate.) At the end of each meeting, individuals should review what work they expect to complete by the following session.
Understanding and Managing Group Processes
- Groups work best if everyone has a chance to make strong contributions to the discussion at meetings and to the work of the group project.
- At the beginning of each meeting, decide what you expect to have accomplished by the end of the meeting.
- Someone (probably not the leader) should write all ideas, as they are suggested, on the board, a collaborative document, or on large sheets of paper. Designate a recorder of the group's decisions. Allocate responsibility for group process (especially if you do not have a fixed leader) such as a time manager for meetings and someone who periodically says that it is time to see how things are going (see below).
- What leadership structure does the group want? One designated leader? rotating leaders? separately assigned roles?
- Are any more ground rules needed, such as starting meetings on time, kinds of interruptions allowed, and so forth?
- Is everyone contributing to discussions? Can discussions be managed differently so all can participate? Are people listening to each other and allowing for different kinds of contributions?
- Are all members accomplishing the work expected of them? Is there anything group members can do to help those experiencing difficulty?
- Are there disagreements or difficulties within the group that need to be addressed? (Is someone dominating? Is someone left out?)
- Is outside help needed to solve any problems?
- Is everyone enjoying the work?
Including Everyone and Their Ideas
Groups work best if everyone is included and everyone has a chance to contribute ideas. The group's task may seem overwhelming to some people, and they may have no idea how to go about accomplishing it. To others, the direction the project should take may seem obvious. The job of the group is to break down the work into chunks, and to allow everyone to contribute. The direction that seems obvious to some may turn out not to be so obvious after all. In any event, it will surely be improved as a result of some creative modification.
Encouraging Ideas
The goal is to produce as many ideas as possible in a short time without evaluating them. All ideas are carefully listened to but not commented on and are usually written on the board or large sheets of paper so everyone can see them, and so they don't get forgotten or lost. Take turns by going around the group—hear from everyone, one by one.
One specific method is to generate ideas through brainstorming. People mention ideas in any order (without others' commenting, disagreeing or asking too many questions). The advantage of brainstorming is that ideas do not become closely associated with the individuals who suggested them. This process encourages creative thinking, if it is not rushed and if all ideas are written down (and therefore, for the time-being, accepted). A disadvantage: when ideas are suggested quickly, it is more difficult for shy participants or for those who are not speaking their native language. One approach is to begin by brainstorming and then go around the group in a more structured way asking each person to add to the list.
Examples of what to say:
- Why don't we take a minute or two for each of us to present our views?
- Let's get all our ideas out before evaluating them. We'll clarify them before we organize or evaluate them.
- We'll discuss all these ideas after we hear what everyone thinks.
- You don't have to agree with her, but let her finish.
- Let's spend a few more minutes to see if there are any possibilities we haven't thought of, no matter how unlikely they seem.
Group Leadership
- The leader is responsible for seeing that the work is organized so that it will get done. The leader is also responsible for understanding and managing group interactions so that the atmosphere is positive.
- The leader must encourage everyone's contributions with an eye to accomplishing the work. To do this, the leader must observe how the group's process is working. (Is the group moving too quickly, leaving some people behind? Is it time to shift the focus to another aspect of the task?)
- The leader must encourage group interactions and maintain a positive atmosphere. To do this the leader must observe the way people are participating as well as be aware of feelings communicated non-verbally. (Are individuals' contributions listened to and appreciated by others? Are people arguing with other people, rather than disagreeing with their ideas? Are some people withdrawn or annoyed?)
- The leader must anticipate what information, materials or other resources the group needs as it works.
- The leader is responsible for beginning and ending on time. The leader must also organize practical support, such as the room, chalk, markers, food, breaks.
(Note: In addition to all this, the leader must take part in thc discussion and participate otherwise as a group member. At these times, the leader must be careful to step aside from the role of leader and signal participation as an equal, not a dominant voice.)
Concerns of Individuals That May Affect Their Participation
- How do I fit in? Will others listen to me? Am I the only one who doesn't know everyone else? How can I work with people with such different backgrounds and expericnce?
- Who will make the decisions? How much influence can I have?
- What do I have to offer to the group? Does everyone know more than I do? Does anyone know anything, or will I have to do most of the work myself?
Characteristics of a Group that is Performing Effectively
- All members have a chance to express themselves and to influence the group's decisions. All contributions are listened to carefully, and strong points acknowledged. Everyone realizes that the job could not be done without the cooperation and contribution of everyone else.
- Differences are dealt with directly with the person or people involved. The group identifies all disagreements, hears everyone's views and tries to come to an agreement that makes sense to everyone. Even when a group decision is not liked by someone, that person will follow through on it with the group.
- The group encourages everyone to take responsibility, and hard work is recognized. When things are not going well, everyone makes an effort to help each other. There is a shared sense of pride and accomplishment.
Focusing on a Direction
After a large number of ideas have been generated and listed (e.g. on the board), the group can categorize and examine them. Then the group should agree on a process for choosing from among the ideas. Advantages and disadvantages of different plans can be listed and then voted on. Some possibilities can be eliminated through a straw vote (each group member could have 2 or 3 votes). Or all group members could vote for their first, second, and third choices. Alternatively, criteria for a successful plan can be listed, and different alternatives can be voted on based on the criteria, one by one.
Categorizing and evaluating ideas
- We have about 20 ideas here. Can we sort them into a few general categories?
- When we evaluate each others' ideas, can we mention some positive aspects before expressing concerns?
- Could you give us an example of what you mean?
- Who has dealt with this kind of problem before?
- What are the pluses of that approach? The minuses?
- We have two basic choices. Let's brainstorm. First let's look at the advantages of the first choice, then the disadvantages.
- Let's try ranking these ideas in priority order. The group should try to come to an agreement that makes sense to everyone.
Making a decision
After everyone's views are heard and all points of agreement and disagreement are identified, the group should try to arrive at an agreement that makes sense to everyone.
- There seems to be some agreement here. Is there anyone who couldn't live with solution #2?
- Are there any objections to going that way?
- You still seem to have worries about this solution. Is there anything that could be added or taken away to make it more acceptable? We're doing fine. We've agreed on a great deal. Let's stay with this and see if we can work this last issue through.
- It looks as if there are still some major points of disagreement. Can we go back and define what those issues are and work on them rather than forcing a decision now.
How People Function in Groups
If a group is functioning well, work is getting done and constructive group processes are creating a positive atmosphere. In good groups the individuals may contribute differently at different times. They cooperate and human relationships are respected. This may happen automatically or individuals, at different times, can make it their job to maintain the atmospbere and human aspects of the group.
Roles That Contribute to the Work
Initiating —taking the initiative, at any time; for example, convening the group, suggesting procedures, changing direction, providing new energy and ideas. (How about if we.... What would happen if... ?)
Seeking information or opinions —requesting facts, preferences, suggestions and ideas. (Could you say a little more about... Would you say this is a more workable idea than that?)
Giving information or opinions —providing facts, data, information from research or experience. (ln my experience I have seen... May I tell you what I found out about...? )
Questioning —stepping back from what is happening and challenging the group or asking other specific questions about the task. (Are we assuming that... ? Would the consequence of this be... ?)
Clarifying —interpreting ideas or suggestions, clearing up confusions, defining terms or asking others to clarify. This role can relate different contributions from different people, and link up ideas that seem unconnected. (lt seems that you are saying... Doesn't this relate to what [name] was saying earlier?)
Summarizing —putting contributions into a pattern, while adding no new information. This role is important if a group gets stuck. Some groups officially appoint a summarizer for this potentially powerful and influential role. (If we take all these pieces and put them together... Here's what I think we have agreed upon so far... Here are our areas of disagreement...)
Roles That Contribute to the Atmosphere
Supporting —remembering others' remarks, being encouraging and responsive to others. Creating a warm, encouraging atmosphere, and making people feel they belong helps the group handle stresses and strains. People can gesture, smile, and make eye-contact without saying a word. Some silence can be supportive for people who are not native speakers of English by allowing them a chance to get into discussion. (I understand what you are getting at...As [name] was just saying...)
Observing —noticing the dynamics of the group and commenting. Asking if others agree or if they see things differently can be an effective way to identify problems as they arise. (We seem to be stuck... Maybe we are done for now, we are all worn out... As I see it, what happened just a minute ago.. Do you agree?)
Mediating —recognizing disagreements and figuring out what is behind the differences. When people focus on real differences, that may lead to striking a balance or devising ways to accommodate different values, views, and approaches. (I think the two of you are coming at this from completely different points of view... Wait a minute. This is how [name/ sees the problem. Can you see why she may see it differently?)
Reconciling —reconciling disagreements. Emphasizing shared views among members can reduce tension. (The goal of these two strategies is the same, only the means are different… Is there anything that these positions have in common?)
Compromising —yielding a position or modifying opinions. This can help move the group forward. (Everyone else seems to agree on this, so I'll go along with... I think if I give in on this, we could reach a decision.)
Making a personal comment —occasional personal comments, especially as they relate to the work. Statements about one's life are often discouraged in professional settings; this may be a mistake since personal comments can strengthen a group by making people feel human with a lot in common.
Humor —funny remarks or good-natured comments. Humor, if it is genuinely good-natured and not cutting, can be very effective in relieving tension or dealing with participants who dominate or put down others. Humor can be used constructively to make the work more acceptable by providing a welcome break from concentration. It may also bring people closer together, and make the work more fun.
All the positive roles turn the group into an energetic, productive enterprise. People who have not reflected on these roles may misunderstand the motives and actions of people working in a group. If someone other than the leader initiates ideas, some may view it as an attempt to take power from the leader. Asking questions may similarly be seen as defying authority or slowing down the work of the group. Personal anecdotes may be thought of as trivializing the discussion. Leaders who understand the importance of these many roles can allow and encourage them as positive contributions to group dynamics. Roles that contribute to the work give the group a sense of direction and achievement. Roles contributing to the human atmosphere give the group a sense of cooperation and goodwill.
Some Common Problems (and Some Solutions)
Floundering —While people are still figuring out the work and their role in the group, the group may experience false starts and circular discussions, and decisions may be postponed.
- Here's my understanding of what we are trying to accomplish... Do we all agree?
- What would help us move forward: data? resources?
- Let's take a few minutes to hear everyone's suggestions about how this process might work better and what we should do next.
Dominating or reluctant participants —Some people might take more than their share of the discussion by talking too often, asserting superiority, telling lengthy stories, or not letting others finish. Sometimes humor can be used to discourage people from dominating. Others may rarely speak because they have difficulty getting in the conversation. Sometimes looking at people who don't speak can be a non-verbal way to include them. Asking quiet participants for their thoughts outside the group may lead to their participation within the group.
- How would we state the general problem? Could we leave out the details for a moment? Could we structure this part of the discussion by taking turns and hearing what everyone has to say?
- Let's check in with each other about how the process is working: Is everyone contributing to discussions? Can discussions be managed differently so we can all participate? Are we all listening to each other?
Digressions and tangents —Too many interesting side stories can be obstacles to group progress. It may be time to take another look at the agenda and assign time estimates to items. Try to summarize where the discussion was before the digression. Or, consider whether there is something making the topic easy to avoid.
- Can we go back to where we were a few minutes ago and see what we were trying to do ?
- Is there something about the topic itself that makes it difficult to stick to?
Getting Stuck —Too little progress can get a group down. It may be time for a short break or a change in focus. However, occasionally when a group feels that it is not making progress, a solution emerges if people simply stay with the issue.
- What are the things that are helping us solve this problem? What's preventing us from solving this problem?
- I understand that some of you doubt whether anything new will happen if we work on this problem. Are we willing to give it a try for the next fifteen minutes?
Rush to work —Usually one person in the group is less patient and more action-oriented than the others. This person may reach a decision more quickly than the others and then pressure the group to move on before others are ready.
- Are we all ready-to make a decision on this?
- What needs to be done before we can move ahead?
- Let's go around and see where everyone stands on this.
Feuds —Occasionally a conflict (having nothing to do with the subject of the group) carries over into the group and impedes its work. It may be that feuding parties will not be able to focus until the viewpoint of each is heard. Then they must be encouraged to lay the issue aside.
- So, what you are saying is... And what you are saying is... How is that related to the work here?
- If we continue too long on this, we won't be able to get our work done. Can we agree on a time limit and then go on?
For more information...
James Lang, " Why Students Hate Group Projects (and How to Change That) ," The Chronicle of Higher Education (17 June 2022).
Hodges, Linda C. " Contemporary Issues in Group Learning in Undergraduate Science Classrooms: A Perspective from Student Engagement ," CBE—Life Sciences Education 17.2 (2018): es3.
- Designing Your Course
- A Teaching Timeline: From Pre-Term Planning to the Final Exam
- The First Day of Class
- Group Agreements
- Classroom Debate
- Flipped Classrooms
- Leading Discussions
- Polling & Clickers
- Problem Solving in STEM
- Teaching with Cases
- Engaged Scholarship
- Devices in the Classroom
- Beyond the Classroom
- On Professionalism
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
- Professional
- International
Select a product below:
- Connect Math Hosted by ALEKS
- My Bookshelf (eBook Access)
Sign in to Shop:
My Account Details
- My Information
- Security & Login
- Order History
- My Digital Products
Log In to My PreK-12 Platform
- AP/Honors & Electives
- my.mheducation.com
- Open Learning Platform
Log In to My Higher Ed Platform
- Connect Math Hosted by Aleks
Business and Economics
Accounting Business Communication Business Law Business Mathematics Business Statistics & Analytics Computer & Information Technology Decision Sciences & Operations Management Economics Finance Keyboarding Introduction to Business Insurance & Real Estate Management Information Systems Management Marketing
Humanities, Social Science and Language
American Government Anthropology Art Career Development Communication Criminal Justice Developmental English Education Film Composition Health and Human Performance
History Humanities Music Philosophy and Religion Psychology Sociology Student Success Theater World Languages
Science, Engineering and Math
Agriculture & Forestry Anatomy & Physiology Astronomy & Physical Science Biology - Majors Biology - Non-Majors Chemistry Cell/Molecular Biology & Genetics Earth & Environmental Science Ecology Engineering/Computer Science Engineering Technologies - Trade & Tech Health Professions Mathematics Microbiology Nutrition Physics Plants & Animals
Digital Products
Connect® Course management , reporting , and student learning tools backed by great support .
McGraw Hill GO Greenlight learning with the new eBook+
ALEKS® Personalize learning and assessment
ALEKS® Placement, Preparation, and Learning Achieve accurate math placement
SIMnet Ignite mastery of MS Office and IT skills
McGraw Hill eBook & ReadAnywhere App Get learning that fits anytime, anywhere
Sharpen: Study App A reliable study app for students
Virtual Labs Flexible, realistic science simulations
Inclusive Access Reduce costs and increase success
LMS Integration Log in and sync up
Math Placement Achieve accurate math placement
Content Collections powered by Create® Curate and deliver your ideal content
Custom Courseware Solutions Teach your course your way
Professional Services Collaborate to optimize outcomes
Remote Proctoring Validate online exams even offsite
Institutional Solutions Increase engagement, lower costs, and improve access for your students
General Help & Support Info Customer Service & Tech Support contact information
Online Technical Support Center FAQs, articles, chat, email or phone support
Support At Every Step Instructor tools, training and resources for ALEKS , Connect & SIMnet
Instructor Sample Requests Get step by step instructions for requesting an evaluation, exam, or desk copy
Platform System Check System status in real time
Why Group Work is Critical for Active Classroom Learning
Give students the ability to teach each other and take learning into their own hands with group work and the active learning approach with tips in this article..

Whenever I conduct observations of faculty members, my suggestion is usually the same: can these students take a more hands-on approach to this lesson? Can they grapple with or solve the problem together, without interference from you?
Across various disciplines, instructors are moving away from lecturing, choosing instead to promote active learning . In a typical active learning classroom, the instructor will design an activity (geared toward the day’s instruction), divide students into groups, ask them to solve a problem together, and then present their findings.
The success of such an approach relies heavily on the division of groups:
- How well students are matched
- How effectively do you explain the assignment’s outcomes
- Which methods do you employ to distribute their labor
Below are some suggestions for facilitating useful group work in your classroom.
Why Groups?
Before breaking students up, it’s important that they understand why group work is important. Too often, instructors feel compelled to manage students’ learning—lecturing course content, fielding questions, and responding to raised hands. Although this model can court some useful participation (usually from self-motivated, front row-types), it also creates a dynamic that centralizes the instructor and makes him or her responsible for all the learning.
In opting for student-centered learning—as opposed to the traditional lecture/discussion model—you are placing the responsibility of “learning” onto the learner. Rather than lecturing your class, telling them what they need to know, you are asking them to grapple with the course’s key concepts and arrive at original conclusions.
In doing so, you are not shirking your responsibilities; instead, you are guiding students toward mastery—creating an arena in which they must take an active role in their own learning.
In an active learning classroom, the instructor functions as a facilitator: designing the day’s activity, giving instructions, and checking in with each group’s progress. This model thwarts any hope of passive learning. Participation is not optional; it’s necessary. Students cannot “zone out” during your lecture; they cannot remain silent in the back row or surreptitiously text under their desks. Working collaboratively, they must “solve” the central problems of the day’s lesson and practice accountability for their own understanding.
Engaging effectively with their fellow students, they are modeling skills that will be vital in their future workplaces. Rather than passively “paying attention” to their instructor, they are obligated to communicate their ideas, practice interdependence, and take on leadership roles.
Avoiding Complaints Before They Arise
In making group work an integral part of your classroom instruction, you’ll find that complaints are common and usually come in the following varieties:
- “Can’t we just do it by ourselves?”
- “Can I be in a group with X and Y, my two best friends?”
- “Can we just keep the same groups we had last time?”
- “How about we just team up with the people sitting around us?”
There is a simple answer to all of these questions: “No.”
While the how of assigning groups is up to you, the instructor, it’s a good idea to vary the makeup of groups from class to class. There is good to be found in working with the same team consistently: relationships are forged, communication becomes fluent, strengths are appraised, and labor is divided accordingly. Nevertheless, students seek familiarity in group work because they wish to be comfortable and, thus, take a more passive role in their own learning.
Pushing your students into unfamiliar learning environments—regularly asking them to meet and collaborate with new colleagues—can have deep pedagogical value. Apart from the challenge of the day’s lesson, you are offering them a “meta-challenge” to surmount: collaborating with a new crop of near-strangers, adjusting to their various strengths, deficits, and learning styles.
Methods of Division
The easiest (and fairest) way to divide students involves the use of a randomized selection tool. Many LMS platforms, such as Canvas, have options for setting groups and will (objectively) split your roster into whatever configuration you choose. This method is particularly effective for classes that rely heavily on active learning; as students drag their feet, disappointed that they’re being separated from their pals, remind them that this lottery-style selection process could always swing their way next time.
For a more directed division, consider making each team a microcosm of the classroom at large. As you well know, every class roster contains students with different aptitudes, points of view, and cultural backgrounds. While the semester progresses—and you “get to know” them—why not use group work to create intellectual conflict? Should you opt for this approach, consider the following suggestions:
- Never cluster all of your A-level students together. Instead, group them alongside peers of different proficiency levels. Reciprocally, this will provide a strong model for struggling students and press the “A's” to work on their leadership and communication skills.
- In courses that stress discussion or debate, try experimenting with diversity. Once you’ve established a spirit of collaboration and safety in your classroom, try creating cross-sections of race, gender, ethnicity, sexual orientation, political leaning, class background, and/or disciplinary interest. Put students into conversation with alternative points of view. Disclaimer: know thyself. This sort of academic intercourse can only work with instructors who share a strong rapport with students and sculpt an environment of mutual respect, approachability, and tolerance. Do not enter potentially volatile territory unless you’re sure you can sensitively facilitate disagreements.
Legitimate Complaints
Every so often, though, interpersonal conflict mucks up your best-laid plans. Two students who used to date or grew apart in high school “absolutely cannot and will not work together”. This will make them “uncomfortable”.
In these cases, it’s worth examining that word: uncomfortable. While there are a great many avenues for intellectual discomfort—that is, pushing students beyond the “safe” boundaries of critical thought—this is something different. There is no scholarly value in forcing two clashing students together. On the contrary, the hostility that passes between them will only prompt silence and an awkward group dynamic.
In order to identify these contentious relationships ahead of time—and reduce the likelihood of an “in-class scene”—you may prefer to have students self-report. Offer them an opportunity, at the beginning of the term, to inform you (anonymously!) of any conflicts that might impede collaboration. Students with legitimate concerns will identify them and you’ll be able to address them throughout the semester.
Group work can be more complicated and may require more time than traditional lectures, but the benefits to transforming a classroom into an active experience can’t be undersold. Pushing students to take ownership of their work and an active role in their own learning won’t just improve your course, it will help students become independent thinkers and learners.

Professor Ray Dademo is an adjunct professor of English at Rutgers University, Montclair State University, and Middlesex County College. He holds an MFA in Nonfiction Writing from Columbia University and a BA in English from Fordham University. His pedagogy involves the use of cinematic literacy as an entry point for composition studies. He has recently co-authored an article for the CEA Critic, titled "Narrating the Moviegoing Experience: Reframing Film for First-Year Composition.
- Something went wrong loading this content.

Center for Educational Effectiveness
Engaging student groups, planning instruction & learning activities ( read full series ), what is it.
Having students engage with collaborative assignments and projects is considered a “high-impact practice,” which means that it is an approach that can support deep learning, significant achievement gains, and positive differential impact on historically underserved student populations ( AAC&U, 2022 ).
Working with others is foundational to many dimensions of learning. It prepares students for future jobs and studies by cultivating transferable skills such as interpersonal skills (i.e., active listening and effective communication), organizational skills (leading meetings, establishing processes), and individual and group time management (AAC&U, 2018; Finelli et al., 2011). The benefits of students groups are well-documented in the literature, and include the following: exposure to multiple perspectives, increased openness to diversity, increased occupational awareness, increased problem-solving abilities, persistence, and engagement with complex and challenging objectives ( Baepler et al., 2016 ).
- + Positive association between how often faculty engage students in cooperative learning and changes to students’ openness to diversity and challenges (Trolian & Parker, 2022; Loes et. al., 2018).
Teaching Strategies
- Define a clear and specific purpose for group work. This is important because it helps us to make decisions every step of the way – who should be working together, how big the groups should be, how we will assess learning, etc.
- Determine how groups will be formed . Three of the most common approaches are student-selected groups, random groups, and instructor-selected groups – each with its own advantages.
- Build a foundation for group work . Before having students dive into a group assignment or activity, consider setting aside some time for them to establish a positive group dynamic (e.g., a group contract). Doing so can help students discuss topics more freely, hold each other accountable, and address conflicts if they arise.
- Consider how you will monitor and assess student learning. Whether a short-term or longer-term activity, including some formative assessments provides accountability for students and helps you monitor student learning. These might include having each group do a short verbal share-out of what they discussed or asking groups to turn in notes, a graphic organizer, or solutions.
Students say ...
- “My instructor set up group folders in google drive. This really helped our group stay organized and accountable to each other.”
- “The professor gave us feedback on the group project as we completed stages. This helped us make changes and corrections before submitting the final project.”
- How do intentionally structure your group activities for equity and student success?
- What formative assessments do you use to monitor student learning? How do you use the results to intervene or reteach?
- Office of Curriculum, Assessment and Teaching Transformation >
- Teaching at UB >
- Course Development >
- Teach Your Course >
Facilitating group work to enhance student learning.
On this page:
The importance of group work.
Group work refers to learning experiences in which students work together on the same task. Group work can help build a positive and engaging learning community through peer learning and teaching.
Promoting peer interactions can positively affect learning experiences by preparing students for work beyond the classroom. According to Constructivism, when students work together to solve problems, they construct knowledge together, rather than passively absorbing information. Students learn more effectively working cooperatively in diverse groups as opposed to working exclusively in a heterogeneous class, working in competition with other students, or working alone (Hattie, 2008). Some benefits include:
- Collaborating to break apart and solve complex tasks
- Deepening understandings and clarifying misconceptions with peer support
- self-regulation and self-reflection
- communication and time management
- project management and conflict resolution
Advantages and Disadvantages
While working collaboratively has the potential to improve student outcomes, it requires the instructor to carefully organize, guide and maintain a positive and productive work environment. Despite the substantial benefits group work offers, there are also disadvantages, especially if not implemented effectively.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| More can be accomplished than working alone | Time wasted waiting on others |
| Less work than working alone | More work than working alone |
| Share knowledge and skills | Unequal support of ideas |
| Equal exchange of information | Conflict over roles and responsibilities |
| Team commitment and social support is motivating | Unequal participation is demotivating |
| Supportive and productive collaboration | Lack of productivity and miscommunication |
For group work to be successful, you need to thoughtfully plan and organize how it will benefit your students. Group work must be designed to enhance student skills and abilities towards achieving learning outcomes.
Additional Resources
Designing successful group work.
The suggestions below will help you design a successful collaborative learning experience for your students. Prior to incorporating group work, take the time to consider strategies that can help avoid potential challenges. Remember to teach effective group work just as you teach content knowledge.
- Consider having students create group contracts for high-stakes assignments and complex projects. These are also beneficial when the same group will be working together over an extended period.
- Provide students with guidelines or templates to ensure that they address aspects of collaboration that may alleviate future concerns, such as potential problems with effective solutions.
- Plan appropriate group composition, size and activity duration. Smaller groups of 3-5 students tend to be more efficient.
- Promote positive interdependence where each member of the group feels a sense of respect, accountability and inclusivity. Ask each group to define their expectations, goals, roles and responsibilities.
- Establish effective group structures and communication in which students share their knowledge and skills, motivate themselves and others, and respect multiple perspectives or opinions.
- Give resources and strategies for project development, team building and conflict resolution.
Creating Group Work Projects
Assigning tasks that foster genuine teamwork and simulate real-life scenarios can help to prepare students for professional situations that will require collaboration. To design an engaging and community-oriented classroom, it is necessary to create opportunities for students to work together in your course. Students can accomplish this through:
- authentic assessments that foster autonomy and demonstrate learning
- discussions that foster critical thinking, equity and inclusivity
- investigations to analyzing problems and identifying solutions
- activities that incorporate active learning
- brainstorming to practice divergent thinking and innovation
The following examples provide you opportunities and ideas to integrate group work successfully into your course.
Authentic Assessments
Design projects that allow groups to demonstrate their learning in a variety of methods and modalities. Authentic assessments allow groups and individuals to show what they have learned and how they can transfer this knowledge and apply their new understandings to specific concepts. Construct group work intentionally and align it to the course’s learning outcomes. Here are some examples of group oriented authentic assessments:
- Case studies
- Designing a textbook
- Presentations
- Experiential learning
- Problem-based learning
- Innovation sprints
Discussions
Discussions are a great way to build collaboration into your course. Discussions allow students to practice higher order thinking skills in a variety of ways and can help students achieve many types of learning outcomes. Having a structure in place will help ensure that discussions are meaningful, effective and engaging. The benefits of discussions include:
- Deepening understanding
- Developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Learning to navigate difficult conversations
- Strengthening oral communication and active listening
- Applying newly learned concepts and skills to authentic contexts
Group Investigation
Study groups.
Strategies to design successful group projects.
How to build effective collaboration in your course.
Video that helps you move group work to an online environment.
Assessing Group Work
In addition to evaluating the group’s output, determine how groups functioned, how individuals contributed to the group itself, as well evaluate both the process and product. This is not always easy, but these general principles can guide you:
- Instructor assessment of group
- Individual assignments
- Quizzes or individual write ups
- Self-assessments
- Student assessment of group or group members
- Student assessment of self
- Provide criteria for assessment
- Assess process as well as product
- Give group feedback and individual feedback when possible
- Monitor each group’s progress and address issues that may arise
Additional resources
Video series for structuring online groups.
Learn how to assess group work equitably.
Overview of the various methods to grade group work successfully and fairly.
Collaboration in Online Learning
Collaborative online learning activities allow students to support each other by asking critical questions and clarifying misunderstandings. It is through this collaboration that students can learn to listen thoughtfully and value the contributions of their peers. Using appropriate and intuitive technology tools helps create an engaging and supportive learning community. The following are a variety of tools available to connect you with your students and to help your students collaborate with their peers.
UB Learns: Collaboration
Share ideas individually and collaboratively.
Assign students to groups within the UB Learns course.
- How to Create Groups in UB Learns
Group Assignments
Can set assignments for group submissions.
Discussion Forums
See below for detailed information.
Additional Collaboration Tools
Communication tools can support both student and instructor presence whether your class is synchronous or asynchronous.
Store, share and edit documents, spreadsheets, presentations and surveys (among other features). It is ideal for working collaboratively in real time.
Text and chat in real time (individuals or groups).
Create, communicate and collaborate in real time.
Virtual interactive bulletin board.
Record instruction videos.
Create a unique hashtag that students can use to talk about class, share links, etc.
Store, share and edit university-related documents in UB Box.
Video conferencing software for synchronous classes and office hours.
UB faculty shares how you can successfully enhance your course with technology.
Third party digital tools you can integrate into your course to strengthen collaboration.
Discussions are usually an important component of a course regardless of the modality. Online discussions can be conducted in two primary ways:
- Synchronously: All students participate in the discussion at the same time, in the same virtual space.
- Asynchronously: All students participate in the discussion on their own time, but according to a schedule.
In an online course, discussion boards can be a primary point of connection for collaboration among students. They can serve a variety of purposes, including as a place for students to:
- submit assignments for other students to review and give feedback
- ask questions that can be read and answered by peers, the TA and/or the instructor
- communicate with their peers formally or informally
- create posts and responses that can be counted towards participation or homework grades
- discuss a topic with a small group or with the whole class
- collaborate on group assignments
Tips for Using Discussion Forums
- Establish criteria and expectations, both general and specific. Include grading, if applicable.
- Strategically monitor and interact with the discussion board. Guide and prompt students as needed.
Determine the complexity of the discussion questions ( Bloom's Taxonomy ). Use meaningful, open-ended questions and prompts.
Create opportunities for autonomy and incorporate UDL principles . Give students choices such as the question they answer or the delivery method they complete (ex: written or video response).
Uses of Discussion Forums
- Asking questions
- Answering questions
- Comprehension of content
- Ice Breakers
- Introductions
- Jigsaw activity
- Peer feedback
- Reflections
- Sharing ideas and resources
- Small groups and conversations
Building a Discussion Board in UB Learns
A guide to building a discussion forum in UB Learns.
A guide to creating a discussion forum from Brightspace.
A handout that gives an overview of the best practices to consider when designing a discussion board for your course.
Ways to create significant discussions in your course.
How to set criteria and expectations for discussions.
Integrate Student Collaboration Into Your Course Design
- Are there opportunities for the instructor to engage with students?
- Are there class activities that foster communication between students?
- Are there various modalities for students to communicate and collaborate?
- Step 2 : Identify areas where you could further integrate student collaboration into your course design.
- Step 3 : Begin to build or revise a student collaboration activity or project.
Learn how to plan, facilitate and assess classroom discussions.
How to prepare students to engage with and support peers who may share different views and perspectives.
Research article that reviews the changing cultural landscape of higher education classrooms.
Strategies to navigate difficult discussions in the classroom.
Blog that shares the challenges and successes of group work.
Better resources for classroom management.
Set clear expectations for class interactions.
Build and support a learning community.
Create opportunities for collaboration.
Provide opportunities to learn and share from a diverse range of resources.
For further information about group work, see the following readings.
- Hattie, J. (2012). Visible learning for teachers (1st ed.). Routledge.
- Loes, C., Culver, K., & Trolian, T. (2018). How collaborative learning enhances students’ openness to diversity. The Journal of Higher Education (Columbus), 89(6), 935–960. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221546.2018.1442638
Center for Teaching
Group work: using cooperative learning groups effectively.
|
|
| Brame, C.J. & Biel, R. (2015). Setting up and facilitating group work: Using cooperative learning groups effectively. Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. Retrieved [todaysdate] from http://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/setting-up-and-facilitating-group-work-using-cooperative-learning-groups-effectively/. |
Many instructors from disciplines across the university use group work to enhance their students’ learning. Whether the goal is to increase student understanding of content, to build particular transferable skills, or some combination of the two, instructors often turn to small group work to capitalize on the benefits of peer-to-peer instruction. This type of group work is formally termed cooperative learning, and is defined as the instructional use of small groups to promote students working together to maximize their own and each other’s learning (Johnson, et al., 2008).
Cooperative learning is characterized by positive interdependence, where students perceive that better performance by individuals produces better performance by the entire group (Johnson, et al., 2014). It can be formal or informal, but often involves specific instructor intervention to maximize student interaction and learning. It is infinitely adaptable, working in small and large classes and across disciplines, and can be one of the most effective teaching approaches available to college instructors.
What can it look like?
What’s the theoretical underpinning, is there evidence that it works.
- What are approaches that can help make it effective?
Informal cooperative learning groups In informal cooperative learning, small, temporary, ad-hoc groups of two to four students work together for brief periods in a class, typically up to one class period, to answer questions or respond to prompts posed by the instructor.
Additional examples of ways to structure informal group work
Think-pair-share
The instructor asks a discussion question. Students are instructed to think or write about an answer to the question before turning to a peer to discuss their responses. Groups then share their responses with the class.

Peer Instruction
This modification of the think-pair-share involves personal responses devices (e.g. clickers). The question posted is typically a conceptually based multiple-choice question. Students think about their answer and vote on a response before turning to a neighbor to discuss. Students can change their answers after discussion, and “sharing” is accomplished by the instructor revealing the graph of student response and using this as a stimulus for large class discussion. This approach is particularly well-adapted for large classes.

In this approach, groups of students work in a team of four to become experts on one segment of new material, while other “expert teams” in the class work on other segments of new material. The class then rearranges, forming new groups that have one member from each expert team. The members of the new team then take turns teaching each other the material on which they are experts.

Formal cooperative learning groups
In formal cooperative learning students work together for one or more class periods to complete a joint task or assignment (Johnson et al., 2014). There are several features that can help these groups work well:
- The instructor defines the learning objectives for the activity and assigns students to groups.
- The groups are typically heterogeneous, with particular attention to the skills that are needed for success in the task.
- Within the groups, students may be assigned specific roles, with the instructor communicating the criteria for success and the types of social skills that will be needed.
- Importantly, the instructor continues to play an active role during the groups’ work, monitoring the work and evaluating group and individual performance.
- Instructors also encourage groups to reflect on their interactions to identify potential improvements for future group work.
This video shows an example of formal cooperative learning groups in David Matthes’ class at the University of Minnesota:
There are many more specific types of group work that fall under the general descriptions given here, including team-based learning , problem-based learning , and process-oriented guided inquiry learning .
The use of cooperative learning groups in instruction is based on the principle of constructivism, with particular attention to the contribution that social interaction can make. In essence, constructivism rests on the idea that individuals learn through building their own knowledge, connecting new ideas and experiences to existing knowledge and experiences to form new or enhanced understanding (Bransford, et al., 1999). The consideration of the role that groups can play in this process is based in social interdependence theory, which grew out of Kurt Koffka’s and Kurt Lewin’s identification of groups as dynamic entities that could exhibit varied interdependence among members, with group members motivated to achieve common goals. Morton Deutsch conceptualized varied types of interdependence, with positive correlation among group members’ goal achievements promoting cooperation.
Lev Vygotsky extended this work by examining the relationship between cognitive processes and social activities, developing the sociocultural theory of development. The sociocultural theory of development suggests that learning takes place when students solve problems beyond their current developmental level with the support of their instructor or their peers. Thus both the idea of a zone of proximal development, supported by positive group interdependence, is the basis of cooperative learning (Davidson and Major, 2014; Johnson, et al., 2014).
Cooperative learning follows this idea as groups work together to learn or solve a problem, with each individual responsible for understanding all aspects. The small groups are essential to this process because students are able to both be heard and to hear their peers, while in a traditional classroom setting students may spend more time listening to what the instructor says.
Cooperative learning uses both goal interdependence and resource interdependence to ensure interaction and communication among group members. Changing the role of the instructor from lecturing to facilitating the groups helps foster this social environment for students to learn through interaction.
David Johnson, Roger Johnson, and Karl Smith performed a meta-analysis of 168 studies comparing cooperative learning to competitive learning and individualistic learning in college students (Johnson et al., 2006). They found that cooperative learning produced greater academic achievement than both competitive learning and individualistic learning across the studies, exhibiting a mean weighted effect size of 0.54 when comparing cooperation and competition and 0.51 when comparing cooperation and individualistic learning. In essence, these results indicate that cooperative learning increases student academic performance by approximately one-half of a standard deviation when compared to non-cooperative learning models, an effect that is considered moderate. Importantly, the academic achievement measures were defined in each study, and ranged from lower-level cognitive tasks (e.g., knowledge acquisition and retention) to higher level cognitive activity (e.g., creative problem solving), and from verbal tasks to mathematical tasks to procedural tasks. The meta-analysis also showed substantial effects on other metrics, including self-esteem and positive attitudes about learning. George Kuh and colleagues also conclude that cooperative group learning promotes student engagement and academic performance (Kuh et al., 2007).
Springer, Stanne, and Donovan (1999) confirmed these results in their meta-analysis of 39 studies in university STEM classrooms. They found that students who participated in various types of small-group learning, ranging from extended formal interactions to brief informal interactions, had greater academic achievement, exhibited more favorable attitudes towards learning, and had increased persistence through STEM courses than students who did not participate in STEM small-group learning.
The box below summarizes three individual studies examining the effects of cooperative learning groups.

What are approaches that can help make group work effective?
Preparation
Articulate your goals for the group work, including both the academic objectives you want the students to achieve and the social skills you want them to develop.
Determine the group conformation that will help meet your goals.
- In informal group learning, groups often form ad hoc from near neighbors in a class.
- In formal group learning, it is helpful for the instructor to form groups that are heterogeneous with regard to particular skills or abilities relevant to group tasks. For example, groups may be heterogeneous with regard to academic skill in the discipline or with regard to other skills related to the group task (e.g., design capabilities, programming skills, writing skills, organizational skills) (Johnson et al, 2006).
- Groups from 2-6 are generally recommended, with groups that consist of three members exhibiting the best performance in some problem-solving tasks (Johnson et al., 2006; Heller and Hollabaugh, 1992).
- To avoid common problems in group work, such as dominance by a single student or conflict avoidance, it can be useful to assign roles to group members (e.g., manager, skeptic, educator, conciliator) and to rotate them on a regular basis (Heller and Hollabaugh, 1992). Assigning these roles is not necessary in well-functioning groups, but can be useful for students who are unfamiliar with or unskilled at group work.
Choose an assessment method that will promote positive group interdependence as well as individual accountability.
- In team-based learning, two approaches promote positive interdependence and individual accountability. First, students take an individual readiness assessment test, and then immediately take the same test again as a group. Their grade is a composite of the two scores. Second, students complete a group project together, and receive a group score on the project. They also, however, distribute points among their group partners, allowing student assessment of members’ contributions to contribute to the final score.
- Heller and Hollabaugh (1992) describe an approach in which they incorporated group problem-solving into a class. Students regularly solved problems in small groups, turning in a single solution. In addition, tests were structured such that 25% of the points derived from a group problem, where only those individuals who attended the group problem-solving sessions could participate in the group test problem. This approach can help prevent the “free rider” problem that can plague group work.
- The University of New South Wales describes a variety of ways to assess group work , ranging from shared group grades, to grades that are averages of individual grades, to strictly individual grades, to a combination of these. They also suggest ways to assess not only the product of the group work but also the process. Again, having a portion of a grade that derives from individual contribution helps combat the free rider problem.
Helping groups get started
Explain the group’s task, including your goals for their academic achievement and social interaction.
Explain how the task involves both positive interdependence and individual accountability, and how you will be assessing each.
Assign group roles or give groups prompts to help them articulate effective ways for interaction. The University of New South Wales provides a valuable set of tools to help groups establish good practices when first meeting. The site also provides some exercises for building group dynamics; these may be particularly valuable for groups that will be working on larger projects.
Monitoring group work
Regularly observe group interactions and progress , either by circulating during group work, collecting in-process documents, or both. When you observe problems, intervene to help students move forward on the task and work together effectively. The University of New South Wales provides handouts that instructors can use to promote effective group interactions, such as a handout to help students listen reflectively or give constructive feedback , or to help groups identify particular problems that they may be encountering.
Assessing and reflecting
In addition to providing feedback on group and individual performance (link to preparation section above), it is also useful to provide a structure for groups to reflect on what worked well in their group and what could be improved. Graham Gibbs (1994) suggests using the checklists shown below.

The University of New South Wales provides other reflective activities that may help students identify effective group practices and avoid ineffective practices in future cooperative learning experiences.
Bransford, J.D., Brown, A.L., and Cocking, R.R. (Eds.) (1999). How people learn: Brain, mind, experience, and school . Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press.
Bruffee, K. A. (1993). Collaborative learning: Higher education, interdependence, and the authority of knowledge. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Cabrera, A. F., Crissman, J. L., Bernal, E. M., Nora, A., Terenzini, P. T., & Pascarella, E. T. (2002). Collaborative learning: Its impact on college students’ development and diversity. Journal of College Student Development, 43 (1), 20-34.
Davidson, N., & Major, C. H. (2014). Boundary crossing: Cooperative learning, collaborative learning, and problem-based learning. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25 (3&4), 7-55.
Dees, R. L. (1991). The role of cooperative leaning in increasing problem-solving ability in a college remedial course. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 22 (5), 409-21.
Gokhale, A. A. (1995). Collaborative Learning enhances critical thinking. Journal of Technology Education, 7 (1).
Heller, P., and Hollabaugh, M. (1992) Teaching problem solving through cooperative grouping. Part 2: Designing problems and structuring groups. American Journal of Physics 60, 637-644.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Smith, K.A. (2006). Active learning: Cooperation in the university classroom (3 rd edition). Edina, MN: Interaction.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Holubec, E.J. (2008). Cooperation in the classroom (8 th edition). Edina, MN: Interaction.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Smith, K.A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory. Journl on Excellence in College Teaching 25, 85-118.
Jones, D. J., & Brickner, D. (1996). Implementation of cooperative learning in a large-enrollment basic mechanics course. American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference Proceedings.
Kuh, G.D., Kinzie, J., Buckley, J., Bridges, B., and Hayek, J.C. (2007). Piecing together the student success puzzle: Research, propositions, and recommendations (ASHE Higher Education Report, No. 32). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Love, A. G., Dietrich, A., Fitzgerald, J., & Gordon, D. (2014). Integrating collaborative learning inside and outside the classroom. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25 (3&4), 177-196.
Smith, M. E., Hinckley, C. C., & Volk, G. L. (1991). Cooperative learning in the undergraduate laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education 68 (5), 413-415.
Springer, L., Stanne, M. E., & Donovan, S. S. (1999). Effects of small-group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 96 (1), 21-51.
Uribe, D., Klein, J. D., & Sullivan, H. (2003). The effect of computer-mediated collaborative learning on solving ill-defined problems. Educational Technology Research and Development, 51 (1), 5-19.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1962). Thought and Language. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.

Teaching Guides
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules
- The Student Experience
- Financial Aid
- Degree Finder
- Undergraduate Arts & Sciences
- Departments and Programs
- Research, Scholarship & Creativity
- Centers & Institutes
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Guarini School of Graduate & Advanced Studies
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Tuck School of Business
Campus Life
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Athletics & Recreation
- Student Groups & Activities
- Residential Life
- [email protected] Contact & Department Info Mail
- Diversity Statement
- Impact Reports
- Experiential Learning
- Gateway Initiative
- Online Learning
- Apgar Award for Innovation in Teaching
- Annual Reports
- Consultation
- Universal Design for Learning Institute
- Graduate Student and Postdoc Programs
- Learning Fellows Program
- New Faculty Programs
- On-Demand Seminars
- Resources for New Faculty
- Teaching & Learning Principles
- Preparing to Teach: Exploring Beliefs
- Knowledge for Teaching
- Student Development
- Recommended Reading
- Course Design - Getting Started
- Learning Outcomes
- Planning for Assessment
- Syllabus Guide
- Universal Design in Education
- Resilient Course Design
- Wellbeing in Course Design
- Academic Continuity During Disruption
- Nuts & Bolts
- First Day of Class
- Effective Lecturing
Student Group Work
- Inclusive Teaching
- Creating Accessible Materials
- Anti-Racist Pedagogy
- Teaching With Generative AI
- Formative Assessments
- Grading & Feedback
- Saving Time While Grading
- End-of-Term Evaluations
- Classroom Observations
- Other Sources of Teaching Support
- Schedules, Calendars, Maps
- Reserving the Teaching Center
- Funding Opportunities
- News & Events
Search form
- Teaching & Learning Foundations
- Course Design & Preparation
- Evaluating Teaching & Learning
- Dartmouth References
Group work has been shown to support deep learning, long-term information retention, strengthened communication and teamwork skills, and a greater sense of purpose and dedication to course materials––if groups are formed thoughtfully and given clear parameters ( Monson ; Oakley et. al. ; Davis ). Many students and faculty alike have (or have heard) horror stories about group work gone awry. But, research and student feedback show that with a bit of preparation, clear guidelines, and mechanisms for group troubleshooting in place, group work can be more than worth the effort.
Setting Groups Up for Success
"Professors have three major responsibilities concerning the implementation of [group work]––forming groups, training students to be effective collaborators, and managing collaborative groups." ––B.W. Speck
There are many ways to use student groups in your classes, from informal, short-term think-pair-share duos to small discussion groups that are formed and disbanded each class session, writing circles that persist for an entire essay cycle, and formal, long-term groups collaborating on a major course assignment. All of them require some level of instructor guidance on how groups should be formed, how group work should be approached, and what the goals of the work are. In some cases, asking students to turn to a classmate and share a question or comment is sufficient preparation. In others, much more scaffolding needs to be in place if students are to navigate their work successfully as a group. See the figure below for a quick overview of what such scaffolding might look like, based on the duration and goals of group work.
three-panel_detailed_storyboard.png
For the purposes of this article, we will focus on groups that will be working together for a week or more, because the length and complexity of the work such groups do together requires more planning and support. While the specific needs of such groups will depend upon the nature of the assignment, subject matter, and course learning objectives, the literature on group formation and collaborative student work provides some important considerations that are relevant to many cases, across disciplines. Here, these considerations are broken out into three categories: group formation, group training, and group management.
Note: COVID has, predictably, affected students' experience of group work, and not only due to the pivot to remote learning. For an in depth discussion of COVID and student group work, see "Student Teamwork During COVID-19: Challenges, Changes, and Consequences" ( Wildman, et. al. ). Click here to see a summary of the paper's key insights .
Group Formation
For long-term collaborations, groups should be created by instructors .
Student-selected groups are more likely to lead to "social slacking" and self-segregation .
Additionally, student-selected groups are less likely to lead to interdependence and collaboration . Students in the same group may end up breaking apart the project and working separately, or, one student may end up bearing the brunt of the workload.
One study indicated that "students found by a two-to-one ratio that their worst group work experiences were with self-formed groups" ( Feitchner and Davis ).
Self-selected groups tend to be homogeneous in terms of student skill-level and subject-matter experience, gender, and race.
For many types of group work, the ideal group size is 3-4 students .
Exceptions include groups formed for team-based-learning , which works well with 5-7 students, and ensemble practices in the arts , which range widely in group size. STEM-specific studies suggest groups of 3-5.
These smaller sizes help ensure that every group member has a meaningful role, while also making sure that there are enough perspectives represented to prevent inquiry from stalling (see group training, below, for resources on group roles).
In general: "The less skilful the group members, the smaller the groups should be. The shorter amount of time available, the smaller the groups should be" ( Davis ).
Groups thrive when their members are diverse (in terms of skill, prior subject-matter experience, and, yes, demographics).
More specifically, "groups that are gender-balanced, are ethnically diverse, and have members with different problem-solving approaches have been shown to exhibit enhanced collaboration" ( Wilson, Brickman, and Brame ).
Conversely, minority group members are most successful––in your class, and in their academic lives more generally––when they aren't isolated.
Isolated students may not feel empowered to speak and contribute at the same level as their fellow group members. "Studies have shown that when members of at-risk minority groups are isolated in project teams, they tend either to adopt relatively passive roles within the team or are relegated to such roles, thereby losing many of the benefits of the team interactivity" ( Heller and Hollobaugh qtd in Oakley et. al. ).
We know, for example, that men are 1.6x more likely to speak in class than women ( Lee and McCabe 2021). This issue is compounded by isolation within groups.
In fact, such unsuccessful group experiences may contribute to student retention issues: "The isolation these individuals feel within their teams could also contribute to a broader sense of isolation in the student body at large, which may in turn increase the dropout risk" ( Heller and Hollobaugh qtd in Oakley et. al. ).
There is some evidence that teamwork- or working-style has more of an impact on group cohesion than prior academic experience or skill with the subject matter.
"Generally, groups that are gender-balanced, are ethnically diverse, and have members with different problem-solving approaches have been shown to exhibit enhanced collaboration. The data on academic performance as a diversity factor do not point to a single conclusion" ( Wilson, Brickman, and Brame ).
And, finally, from a logistical viewpoint: if you don't provide dedicated group working time in class, group members will need common blocks of free time to meet outside of class.
X-hours can be fantastic as dedicated group-work time, if your course plan allows.
Group Training
"When a professor assumes that students will automatically work well together and provides little or no training in group success, groups can fall apart." ––B.W. Speck
Students express higher levels of satisfaction when instructors are explicit about the process and expectations of group work.
Setting expectations can help ameliorate student aversion to group work rooted in past negative experiences ( Felder and Brent 1996).
Groups tend not to differentiate between "social loafers" and team members who are struggling with the project or course content, exhibiting destructive behavior toward group members who fall into either category equally. By being transparent about the benefits of group work as well as the expectations about how group work should proceed, instructors can prevent much of this potential for group dysfunction ( Freeman and Greenacre ).
Giving students individual (rotating) roles within their group can help instill individual ownership of the project as well as foster collaboration and interdependence.
For instance, Oakley et. al. outline a four person team using the following roles:
Coordinator - "keeps everyone on task and makes sure everyone is involved."
Recorder - "prepares the final solution to be turned in."
Monitor - "checks to make sure everyone understands both the solution and the strategy used to get it."
Checker - "double-checks it before it is handed in."
Other roles might include:
Encourager - "encourages group members to continue to think through their approaches and ideas. The Encourager uses probing questions to help facilitate deeper thinking, and group-wide consideration of ideas" ( Fournier ).
Questioner - "pushes back when the team comes to consensus too quickly, without considering a number of options or points of view. The questioner makes sure that the group hears varied points of view, and that the group is not avoiding potentially rich areas of disagreement" ( Fournier ).
Reflector / Strategy Analyst - "observes team dynamics and guides the consensus-building process (helps group members come to a common conclusion)" ( Fournier ).
Spokesperson / Presenter - "presents the group's ideas to the rest of the class. The Spokesperson should rely on the recorder's notes to guide their report" ( Fournier ).
Requiring group members to rotate through these roles during the term "can help students develop communications skills in a variety of areas rather than relying on a single personal strength" ( Fournier ).
Functional groups develop "norms," "charters," or social contracts with agreed upon behaviors, values, and conflict-management practices.
For example, The 3 Be's of Collaborative Writing B.W. Speck uses with collaborative writing groups:
Be Responsible
Be Organized
3beswriting0.png

The University of Connecticut Writing Center offers this group contract template to be used after forming groups, but before assigning roles as a means to "prevent group discord" and "create a consensus on expectations.
Group Management
Even the most strategically formed groups may still fail if they aren't given sufficient guidance, or management. Some of the most important things to consider when determining how you and your students will work together to manage groups are:
Group Persistence (will students stay in a single group all term, or will groups be formed and reformed throughout the term?)
Motivation (what scaffolding needs to be in place to keep groups motivated?)
"To promote both accountability and autonomy, instructors should create milestones and deadlines for groups but also provide time for the students to expressly assign duties and roles to meet those deadlines" ( Wilson, Brickman, and Brame ).
Dartmouth faculty member, Professor Deborah Brooks, recommends building in opportunities for Peer Recognition .
For discussion groups, you may want to consider occasional opportunities for peer shout outs (for example, a student might want to shout out a group member who helped them understand something in a new way).
For longer, more formal group projects, peer awards can offer groups a fun way to recognize and celebrate their work as well as providing faculty some insight into the way groups worked together.
Assessment (how will group and individual work be assessed? how will students assess their own work and the group as a whole?)
Although it may not be appropriate for all types of group work to be graded, for group projects or assignments, it can be beneficial to assess both the work of the group as a whole and the work of individual group members.
Felder and Brent suggest:
Giving "individual tests that cover all of the material on the team assignments and projects" ( Felder and Brent 2007).
Making "groups responsible for seeing that non-contributors don't get credit" ( Felder and Brent 2007).
Using "peer ratings to make individual adjustments to team assignment grades" ( Felder and Brent 2007).
In addition to assessment via grading, it is important to structure in opportunities for student and group self-assessment.
"Once or twice during the group work task," Barbara Gross Davis suggests, "ask group members to discuss two questions: What action has each member taken that was helpful for the group? What action could each member take to make the group even better?" ( Davis ).
Felder and Brent suggest making plans for "periodic self-assessment of team functioning" every few weeks via written responses to questions such as ( Felder and Brent 2007):
How well are we meeting our goals and expectations?
What are we doing well?
What needs improvement?
What (if anything) will we do differently next time?
Troubleshooting (what happens when groups encounter a problem? what if a group fails to cohere?)
Make a contingency plan to chart out what happens when
Students drop the course, leaving groups too small or imbalance
A group fails to cohere.
Some research suggests that giving students the ability to "fire" a group member who isn't contributing can be an effective strategy ( Felder and Brent 2007).
But resist the urge to dissolve and reform groups frequently.
Studies have shown that:
"It takes at least [one month] for the teams to encounter problems, and learning to work through the problems is an important part of teamwork skill development" ( Felder and Brent 2007).
Build in opportunities for students to tell you how the group work is going:
"Conduct a midterm assessment to find out how students feel about teamwork" ( Felder and Brent 2007).
and, Opportunities for Reflection and Feedback ( will students have a chance to reflect on their group work? how will students report what's happening in their group to you? how will you provide feedback to groups?)
Thomas Wenzel notes that peer- and self-assessment, combined with instructor observations, are critical in courses using group work not only to identify dysfunctional groups but also to identify the contributions of each group member ( Wenzel ).
See this Team Peer Assessment developed by Angela R. Linse of the Schreyer Institute for Teaching Excellence
See the final pages of Oakley et. al. for a useful set of reflective and evaluative worksheets. Namely:
Evaluation of Progress Toward Effective Team Functioning
Team Member Evaluation Form
Peer Rating of Team Members
Autorating System
Note: peer rating and assessment are likely to be most useful as a conversation starter regarding group dynamics and norms.
Team Formation Tool
The Team Formation Tool, a Canvas app developed at Dartmouth, is a survey-based tool for the creation of optimized student groups. With the Team Formation Tool, instructors can create custom surveys designed to sort students into groups based on a cluster of predetermined criteria including time zone, teamwork and working style, preferred time of day to study, and more.
To learn more about the Team Formation Tool, read the overview here or contact [email protected] . To have the Team Formation Tool installed in your Canvas course, submit a Canvas Support Request here , and enter Team Formation Tool Installation in the Short Description of Problem field.
Additional Resources
Using Student Groups in Your Teaching
Episode 073 - Team Based Learning with Jim Sibley , Teaching in Higher Ed Podcast
Babson College Group Project Survival Guide
Effective Strategies for Cooperative Learning .
CBE––Life Sciences Education evidence-based teaching guide for Group Work .
Alison Burke's article, " How to Use Groups Effectively ."
Curated list of resources about Collaborative Learning & Group Work
Curated list of podcast episodes about group learning
Teach Remotely: Collaborative Projects discussion, facilitated by DCAL
Davis, Barbara Gross. Tools for Teaching. Vol. 1st ed, Jossey-Bass, 1993. EBSCOhost, search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,url,uid&db=nlebk&AN=26088&site=ehost-live&scope=site.
Feichtner, S. B., and E. A. Davis. "Why Some Groups Fail: A Survey of Students' Experiences with Learning Groups." Journal of Management Education, vol. 9, no. 4, Nov. 1984, pp. 58–73. DOI.org (Crossref), doi: 10.1177/105256298400900409 .
Felder, Richard M., and Rebecca Brent. "Navigating the Bumpy Road to Student-Centered Instruction." College Teaching, vol. 44, no. 2, Apr. 1996, pp. 43–47. DOI.org (Crossref), doi: 10.1080/87567555.1996.9933425 .
Felder, Richard M., and Rebecca Brent. "Cooperative Learning." Active Learning, edited by Patricia Ann Mabrouk, vol. 970, American Chemical Society, 2007, pp. 34–53. DOI.org (Crossref), doi: 10.1021/bk-2007-0970.ch004 .
Fournier, Eric. "Using Roles in Group Work." Washington University in St. Louis Center for Teaching and Learning, https://ctl.wustl.edu/resources/using-roles-in-group-work/ . Accessed 2 Feb. 2021.
Freeman, Lynne, and Luke Greenacre. "An Examination of Socially Destructive Behaviors in Group Work." Journal of Marketing Education - J Market Educ, vol. 33, Apr. 2011, pp. 5–17. ResearchGate, doi: 10.1177/0273475310389150 .
Gaunt, Helena, and Danielle Shannon Treacy. "Ensemble Practices in the Arts: A Reflective Matrix to Enhance Team Work and Collaborative Learning in Higher Education." Arts and Humanities in Higher Education, vol. 19, no. 4, SAGE Publications, Oct. 2020, pp. 419–44. SAGE Journals, doi: 10.1177/1474022219885791 .
Hassanien, Ahmed. "Student Experience of Group Work and Group Assessment in Higher Education." Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, vol. 6, no. 1, July 2006, pp. 17–39. DOI.org (Crossref), doi: 10.1300/J172v06n01_02 .
Heller, Patricia, and Mark Hollabaugh. "Teaching Problem Solving through Cooperative Grouping. Part 2: Designing Problems and Structuring Groups." American Journal of Physics, vol. 60, no. 7, American Association of Physics Teachers, July 1992, pp. 637–44. aapt.scitation.org (Atypon), doi: 10.1119/1.17118 .
Monson, Renee. "Groups That Work: Student Achievement in Group Research Projects and Effects on Individual Learning." Teaching Sociology, vol. 45, no. 3, SAGE Publications Inc, July 2017, pp. 240–51. SAGE Journals, doi: 10.1177/0092055X17697772 .
Oakley, Barbara, et al. "Turning Student Groups into Effective Teams." Journal of Student Centered Learning, vol. 2, no. 1, 2004, pp. 9-34. https://www.engr.ncsu.edu/wp-content/uploads/drive/1ofGhdOciEwloA2zofffqkr7jG3SeKRq3/2004-Oakley-paper(JSCL).pdf
Speck, Bruce W. Facilitating Students' Collaborative Writing. Jossey-Bass, 2002, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/ERIC-ED466716/pdf/ERIC-ED466716.pdf , Accessed 2 Feb 2021
Wenzel, Thomas J. "Evaluation Tools To Guide Students' Peer-Assessment and Self-Assessment in Group Activities for the Lab and Classroom." Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 84, no. 1, 2007, p. 182.
Wildman, Jessica, et al. "Student Teamwork During COVID-19: Challenges, Changes, and Consequences." Small Group Research, vol. 0, no. 0, 2021, pp. 1–16.
Wilson, KJ, et al. "Evidence Based Teaching Guide: Group Work." CBE Life Science Education, http://lse.ascb.org/evidence-based-teaching-guides/group-work/ . Accessed 2 Feb. 2021.
- Our Mission
Setting Up Effective Group Work
Truly collaborative group work is complex and messy, so we have a few tips and tools to get students working interdependently.

Research supports what we probably already knew about student collaboration: It’s integral to learning. We know that collaboration helps students build their interpersonal and social and emotional skills. We know that students don’t learn facts in a vacuum; social learning helps them build a more meaningful understanding of the world.
Everyone loves collaboration. But simply bring up group work and... that’s a different conversation. Group work is one of the most common types of student collaboration. It’s also complicated and messy, and never quite works out as well as we’d like. Some students feel like they’re doing most of the work. Others feel left out. Motivation wanes. Assignments get cobbled together, and nobody feels like they have real ownership of the work.
Or worse yet: Nobody feels a strong sense of ownership of the learning.
Collaborative group work is complex and messy by nature—it’s supposed to be that way. Working through that complexity is part of what we want students to experience. But if we really want to promote and model positive collaboration, it’s worth taking a second look at how we structure and assign group work to our students.
Practical Tips
If you’re designing an activity, lesson, or unit that involves collaborative group work, here are a few ideas to consider.
1. Ask yourself: Does this assignment actually need to involve group work? Can the tasks be broken down into meaningful, equitable parts? Before anything else, decide exactly what you want students to learn and make sure it’s suited to group collaboration. If the work doesn’t break down easily (and equitably), maybe it’s worth considering a different route.
2. Break down the work for students ahead of time. Effective group work takes a lot of scaffolding. Don’t expect students to know how to divvy up the work on their own. Working together to break down and delegate responsibilities is one of the most challenging tasks for any group, even for adults. Breaking down tasks ahead of time models for students how it can be done. Over time, consider transferring some of this responsibility to them.
Make sure the distribution of work—what each student’s roles and responsibilities will be—is very clear to everyone. Do your best to create tasks that are interdependent—the kind that require kids to work both independently and together.
3. Give students a framework to understand their roles and responsibilities. Traditional group work roles (think: timekeeper or note taker) tend to be administrative. While that division is well-intentioned, the roles don’t (usually) serve our learning goals directly and fall short of supporting true collaboration.
What if we structured the roles differently? When students share ownership of what they’re learning, everyone should have multiple roles to play: one task to own individually; a role in supporting a peer; and the responsibility to assess both themselves and someone else in their group. Interdependence is key. You can check out this graphic organizer for an example of how this might look in a group of four students.
The work of collaborating in groups can be difficult to coordinate and challenging to complete. But it’s also a great opportunity to practice communication and collaboration skills. Visual brainstorming tools, such as mind maps and virtual corkboards, can help students get organized and comfortable sharing their ideas.
Using a digital tool can be a big help. The three online tools below are specifically for group brainstorming. Kids can add text, videos, and images at any time (remotely or during class). And by organizing group work visually, students will develop valuable presentation skills while working creatively as a part of their team.
Mural : Designed for multiple users to share ideas, Mural allows kids to work together on projects in class or remotely. Students can watch their boards grow as group members add text, videos, and images. In addition, they can move and revise items during the brainstorming process as if they were moving Post-it notes around. The paid version allows teachers to create secure rooms, or folders, to house mural boards and control sharing.
MindMeister : Great for older kids, this mind-mapping website has a simple interface with extensive sharing functionality. Students can browse through premade templates or build their own map by choosing a main theme and building out nodes with notes, images, attachments, and links. Bonus: Any node can contain team assignments, due dates, and email reminders, so groups can easily visualize and organize their interdependent responsibilities. Stormboard : Students create and add “stickies” to a virtual whiteboard where group members (or a whole class) can comment and vote. These stickies can be text, images, or videos, and users can color-code and rearrange them on the board to easily organize ideas as they brainstorm.
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Benefits of Group Work
Dr. lori mcdonald.
- September 9, 2020

Henry Ford once said, “Coming together is a beginning, staying together is progress, and working together is success.” I think it is safe to say that he certainly knew something about the importance of teamwork! There is so much to be gained by having students work in groups in the classroom. Studies have shown that students who participate in group work demonstrate greater achievement than those who work alone. Therefore, it is important that teachers understand the benefits of group work and the best ways to use it in the classroom.
What are the Benefits of Group Work?
For students.
The benefits of group work for students are vast! First of all, students are able to learn how to plan and manage their time when working. Group work also allows students to be exposed to a wide variety of perspectives and ideas. Most importantly, students learn how to work with other students. This is a critically important skill that will be necessary in any career placement .
Other benefits include:
- Improved social skills including cooperation and conflict resolution skills
- Complex tasks can be broken down into smaller, more manageable steps
- Accountability
- Giving and getting feedback from peers
- Students are able to utilize individual strengths to assume roles and responsibilities for the group
For Teachers
The benefits of group work do not stop with the students. Group work gives teachers a fantastic opportunity to monitor and observe as students collaborate. This enables teachers to see their students’ growth in action as students apply learning and analyze situations and decisions. Teachers can offer guidance and correction as needed.
By observing students working in groups, teachers are able to identify strengths and areas of concern, both academically and socially. Teachers are also able to assign more complex projects when using group work because students are able to combine their efforts.
Group work also provides a more authentic learning experience than teachers are typically able to provide in a traditional learning environment. On a side note, there is also a smaller number of projects to grade when students are working together.
For Classroom Management
Will your classroom be louder when students are participating in group work? Yes! Is louder always a bad thing? No! Always remember, the one doing the talking is the one doing the learning. As long as students’ discussions are on-task, the talking that is going on is very productive and beneficial. Also, students are more likely to be on-task when motivated by a group work project. Students develop responsibility and self-discipline that are beneficial to the class as a whole.
Which Students Benefit from Group Work the Most?
It’s hard to say which students actually benefit the most from group work because there are benefits for so many different groups of students, especially when groups are of varying ability levels.
Above Grade-Level Students
These students benefit from group work because they get to exercise and develop leadership skills. They also get to teach others within their groups, which is one of the best ways to enrich learning.
Struggling Students
These students benefit by seeing the modeled academic behaviors of their peers. The discussions that take place during the group work can enrich the learning of struggling students.
On Grade-Level Students
These students, perhaps, benefit the most because they are right in the middle. They can benefit by learning from their above grade-level peers and can also enrich their own learning by peer tutoring the struggling students.
Others that benefit from group work include English language learners that are enriched by being immersed in academic dialogue. Students that lack motivation benefit by being encouraged in observing how motivated students perform and by the shared workload. Socially-challenged students benefit from increased social interaction. The list goes on and on.
Ways to Use Group Work in Your Class
First of all, group work can be done in every grade level, but different grade levels require different procedures and preparation. There are some basics that must be established before implementing group work in your class regardless of the grade level.
It is important that groups for group work include a wide variety of ability levels in order to truly reap the benefits of group work. Also, the teacher must invest time up front in establishing routines, procedures, and behavioral expectations for group work.
Other important steps in preparing for group work:
- Assign roles for each student
- Physically arrange classroom in a way that supports group work
- Design a task that is challenging for students
- Decide on group size
- Allot ample time for the task
- Ask for input from the students
- Establish grading procedures and communicate expectations
Examples of group work projects:
- Class escape room project – This is a great and timely option for utilizing group work. Escape rooms have become so popular, and it is a really fun way to implement group work. Escape rooms can be adapted to any subject area or grade level by applying newly acquired knowledge or skills.
- Debate – Students can be put into groups to debate historical issues. By assigning students to an argument, they can research and work with their group to defend their perspective.
- Complex math problems – Very complex, multi-step math problems can be completed in groups. Again, assigning each student a specific role.
- Economic projects – Students can experiment with economics by setting up virtual economic systems that they will monitor and maintain together.
- Science projects – A wide variety of science skills can be explored in group settings with students assigned to roles like recording data, analyzing data, conducting experiments, etc.
With the amount of benefits that can be reaped from group work, it is very important that teachers know how to do this and give students the opportunity to break from the daily norm to explore this fresh, exciting, and socially-enriching way to learn.
“Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn.” – Ben Franklin
- #ClassroomManagement , #GroupWork
More in Classroom Management

The Impact of Classroom Design
Have you ever walked into a room and immediately felt the energy of…

Are Student Behavior Charts Beneficial?
One classroom management strategy that has stood the test of time is the…

Incorporating Punch Cards into Your Classroom
Punch cards are a simple and smart classroom management tool that keeps your…
The Importance of Art Class
In today’s technology-driven classrooms, art remains an important component of student development. Despite often being the first to be cut from…
Advertisement
Who benefits from group work in higher education? An attachment theory perspective
- Published: 15 April 2016
- Volume 73 , pages 175–187, ( 2017 )
Cite this article

- Shiri Lavy 1
13k Accesses
23 Citations
7 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Several studies have pointed to the benefits of learning in groups. However, surprisingly little research has been conducted regarding what role relationship-related personality traits play in the effectiveness of this kind of student learning. Such personality factor can potentially buffer the students’ effectiveness in groups. The present study focused on attachment orientations—personal characteristics of individuals that reflect internal models of relationships—and assessed their impact on different aspects of students’ feelings and functioning in higher-education study groups. It was hypothesized that individuals with interpersonal difficulties (characterized by high attachment anxiety or avoidance) will not benefit from a learning group and that they may exhibit poorer performance in group projects. Participants ( N = 244) were college students enrolled in courses that included a group project. They completed measures of their attachment orientations, instrumental and socio-emotional functioning in the group, and satisfaction from the group. Additionally, their GPA and grade in the group project were assessed. Results indicated negative associations of attachment anxiety and avoidance with students’ self-reported instrumental and socio-emotional functioning in the group. However, attachment anxiety was associated with higher grades in the group task. Attachment avoidance was not associated with students’ grades. The study’s findings generally suggest that attachment insecurities do not obscure students’ actual performance in group projects, contrary to students’ self-perceptions. Implications for group learning are discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Fostering the X-Factor in Pakistan’s university students

Peer Interaction Types for Social and Academic Integration and Institutional Attachment in First Year Undergraduates

The Predictive Effect of Teachers’ Emotional Support on Chinese Undergraduate Students’ Online Learning Gains: An Examination of Self-determination Theory
Ainsworth, M. D. S., Blehar, M., Waters, E., & Wall, S. (1978). Patterns of attachment . Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Google Scholar
Al-Yagon, M., & Mikulincer, M. (2004). Socioemotional and academic adjustment among children with learning disorders: The meditational role of attachment-based factors. The Journal of Special Education, 38 , 111–123.
Article Google Scholar
Barry, B., & Stewart, G. L. (1997). Composition, process, and performance in self-managed groups: The role of personality. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82 , 62–78.
Bartholomew, K., & Horowitz, L. M. (1991). Attachment styles among young adults: A test of a four category model. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 226–244.
Belbin, R. M. (2012). Team roles at work. Emergence of a team role language (pp. 19–32). New York: Routledge. (Chapter 3) .
Bertucci, A., Conte, S., Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2010). The impact size of cooperative groups on achievement, social support, and self-esteem. Journal of General Psychology, 137 , 256–272.
Boud, D. (2014). Making the move to peer learning. In D. Boud, R. Cohen, & J. Sampson (Eds.), Peer learning in higher education: Learning from and with each other (pp. 1–20). New York: Routledge.
Bowlby, J. (1969/1982). Attachment and loss, Vol. I: Attachment. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Bradley, B. H., Klotz, A. C., Postlethwaite, B. E., & Brown, K. G. (2013). Ready to rumble: How team personality composition and task conflict interact to improve performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98 (2), 385.
Brennan, K. A., Clark, C. L., & Shaver, P. R. (1998). Self-report measurement of adult attachment. In J. A. Simpson & W. S. Rholes (Eds.), Attachment theory and close relationships (pp. 46–76). New York: Guilford.
Cassidy, J., & Kobak, R. R. (1988). Avoidance and its relation to other defensive processes. In J. Belsky & T. Nezworski (Eds.), Clinical implications of attachment (pp. 300–323). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Cohen, E. G. (1994). Restructuring the classroom: Conditions for productive small groups. Review of Educational Research, 64 , 1–35.
DeBerard, M. S., Spielmans, G. I., & Julka, D. L. (2004). Predictors of academic achievement and retention among college freshmen: A longitudinal study. College Student Journal, 38 , 66–80.
Doyle, A. B., & Markiewicz, D. (2005). Parenting, marital conflict, and adjustment from early- to mid-adolescence: Mediated by adolescent attachment style? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 34 , 97–110.
Druskat, V. U., & Kayes, D. C. (2000). Learning versus performance in short-term project teams. Small Group Research, 31 , 328–353.
Fass, M. E., & Tubman, J. G. (2002). The influence of parental and peer attachment on college students’ academic achievement. Psychology in the Schools, 39 , 561–574.
Felder, R. M., & Brent, R. (1996). Navigating the bumpy road to student-centered instruction. College Teaching, 44 , 43–47.
Fraley, R. C., & Spieker, S. J. (2003). Are infant attachment patterns continuously or categorically distributed? A taxometric analysis of strange situation behavior. Developmental Psychology, 39 , 387–404.
Fuendeling, J. M. (1998). Affect regulation as a stylistic process within adult attachment. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 15 , 291–322.
Furnham, A., Batey, M., & Martin, N. (2011). How would you like to be evaluated? The correlates of students’ preferences for assessment methods. Personality and Individual Differences, 50 , 259–263.
Furnham, A., Christopher, A., Garwood, J., & Martin, N. (2008). Ability, demography, learning style and personality trait correlates of student preferences for assessment method. Educational Psychology, 28 , 15–27.
Gaudet, A. D., Ramer, L. M., Nakonechny, J., Cragg, J. J., & Ramer, M. S. (2010). Small-group learning in an upper-level university biology class enhances academic performance and student attitudes toward group work. Public Library of Science One, 5 , 1–9.
Gregory, R., & Thorley, L. (2013). Introduction. In R. Gregory & L. Thorley (Eds.), Using group-based learning in higher education (pp. 19–23). New York: Routledge.
Harms, P. D. (2011). Adult attachment styles in the workplace. Human Resource Management Review, 21 , 285–296.
Hazan, C., & Shaver, P. R. (1987). Romantic love conceptualized as an attachment process. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52 , 511–524.
Hazan, C., & Shaver, P. R. (1990). Love and work: An attachment-theoretical perspective. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 59 , 270–280.
Holt, L. J. (2014). Attitudes about help-seeking mediate the relation between parent attachment and academic adjustment in first-year college students. Journal of College Student Development, 55 (4), 418–423.
Janssen, J., Kirschner, F., Erkens, G., Kirschner, P. A., & Paas, F. (2010). Making the black box of collaborative learning transparent: Combining process-oriented and cognitive load approaches. Educational Psychology Review, 22 , 139–154.
Jenkins-Guarnieri, M. A., Wright, S. L., & Hudiburgh, L. M. (2012). The relationships among attachment style, personality traits, interpersonal competency, and Facebook use. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 33 (6), 294–301.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. (2003). Training for cooperative group work. In M. West, D. Tjosvold, & K. Smith (Eds.), International handbook of organizational teamwork and cooperative working (pp. 167–183). London: Wiley.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. (2005). New developments in social interdependence theory. Psychology Monographs, 131 , 285–358.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. Educational Researcher, 38 , 365–379.
Lavy, S., Azaiza, F., & Mikulincer, M. (2012). Attachment patterns of Arabs and Jews in Israel: Are we really so different? Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Issues, 49 , 184–193.
Lavy, S., Bareli, Y., & Ein-Dor, T. (2014). The effects of attachment heterogeneity and team cohesion on team functioning. Small Group Research, 44 , 1–23.
Lawler, E. E., Mohrman, S. A., & Ledford, G. E. (1995). Creating high performance organizations: Practices and results of employee involvement and total quality management in Fortune 1000 companies . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Littman Ovadia, H., Oren, L., & Lavy, S. (2013). Attachment and autonomy in the workplace – new insights. Journal of Career Assessment, 21 , 502–518. doi: 10.1177/1069072712475282 .
Lopez, F. G., Mauricio, A. M., Gormley, B., Simko, T., & Berger, E. (2001). Adult attachment orientations and college student distress: The mediating role of problem coping styles. Journal of Counseling and Development, 79 , 459–464.
Mattanah, J. F., Hancock, G. R., & Brand, B. L. (2004). Parental attachment, separation-individuation, and college student adjustment: A structural equation analysis of mediational effects. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 51 (2), 213.
Mikulincer, M., & Florian, V. (2000). Exploring individual differences in reactions to mortality salience: Does attachment style regulate terror management mechanisms? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79 , 260–273.
Mikulincer, M., Florian, V., & Tolmacz, R. (1990). Attachment styles and fear of personal death: A case study of affect regulation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58 , 273–280.
Mikulincer, M., & Shaver, P. R. (2007). Attachment patterns in adulthood: Structure, dynamics, and change . New York: Guilford Press.
Mitchell, P., Wynia, M., Golden, R., McNellis, B., Okun, S., Webb, C. E. et al. (2012). Core principles & values of effective team-based health care. Retrieved on 12 Nov 2013. http://217ewmp01.blackmesh.com/~/media/Files/Perspectives-Files/2012/Discussion-Papers/VSRT-Team-Based-Care-Principles-Values.pdf .
Moss, E., & St-Laurent, D. (2001). Attachment at school age and academic performance. Developmental Psychology, 37 , 863–874.
Neuman, G. A., Wagner, S. H., & Christiansen, N. D. (1999). The relationship between work-team personality composition and the job performance of teams. Group and Organization Management, 24 (1), 28–45.
Noftle, E. E., & Shaver, P. R. (2006). Attachment dimensions and the big five personality traits: Associations and comparative ability to predict relationship quality. Journal of Research in Personality, 40 (2), 179–208.
Ortiz, A., Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. (1996). The effect of positive goal and resource interdependence on individual performance. Journal of Social Psychology, 136 , 243–249.
Peeters, M. A., Rutte, C. G., Tuijl, H. F., & Reymem, I. M. (2006). The big five personality traits and individual satisfaction with the group. Small Group Research, 37 , 187–211.
Pfaff, E., & Huddelston, P. (2003). Does it matter if I hate group work? What impacts students attitudes towards group work. Journal of Marketing Education, 25 , 37–45.
Quimby, J. L., & O’Brien, K. M. (2006). Predictors of well-being among nontraditional female students with children. Journal of Counseling and Development: JCD, 84 (4), 451.
Richards, D. A., & Schat, A. C. H. (2011). Attachment at (not to) work: Applying attachment theory to explain individual behavior in organizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96 , 169–182.
Rom, E., & Mikulincer, M. (2003). Attachment theory and group processes: The association between attachment style and group—related representation, goals, memories, and functioning. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84 , 1220–1235.
Sadikaj, G., Moskowitz, D. S., & Zuroff, D. C. (2015). Felt security in daily interactions as a mediator of the effect of attachment on relationship satisfaction. European Journal of Personality, 29 (2), 187–200.
Shaver, P. R., & Brennan, K. A. (1992). Attachment styles and the “Big Five” personality traits: Their connections with each other and with romantic relationship outcomes. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 18 (5), 536–545.
Shaver, P. R., & Mikulincer, M. (2002). Attachment-related psychodynamics. Attachment and Human Development, 4 , 133–161.
Shaw, J. B. (2004). A fair go for all? The impact of intra-group diversity and diversity-management skills on student experiences and outcomes in team-based class projects. Journal of Management Education, 28 , 139–169.
Slavin, R. E., Leavey, M., & Madden, N. A. (1982). Combining cooperative learning and individualized instruction: Effects on student mathematics achievement, attitudes and behaviors . Baltimore: Center for Organization of Schools.
Smith, E. R., Murphy, J., & Coats, S. (1999). Attachment to groups: Theory and management. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77 , 94–110.
Springer, L., Stanne, M. E., & Donovan, S. S. (1999). Effects of small group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 69 , 21–51.
Sterns, H. L., & Spokus, D. M. (2013). Lifelong learning and the world of work. In P. Taylor (Ed.), Older workers in an ageing society: Critical topics in research and policy (pp. 89–109). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Susskind, A. M., & Borchgrevink, C. P. (1999). Team-based interaction in the foodservice instructional laboratory: An exploratory model of team composition, team-member interaction, and performance. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 10 , 22–29.
Tasa, K., Sears, G. J., & Schat, A. C. (2011). Personality and teamwork behavior in context: The cross-level moderating role of collective efficacy. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32 (1), 65–85.
Tribe, D. M. (2013). An overview from higher education. In R. Gregory & L. Thorley (Eds.), Using group-based learning in higher education (pp. 25–35). New York: Routledge.
Webb, N. M. (1982a). Peer interaction and learning in cooperative small groups. Journal of Educational Psychology, 74 , 642–655.
Webb, N. M. (1982b). Group composition, group interaction and achievement in cooperative small groups. Journal of Educational Psychology, 74 , 475–484.
Wright, S. L., Perrone-McGovern, K. M., Boo, J. N., & White, A. V. (2014). Influential factors in academic and career self-efficacy: Attachment, supports, and career barriers. Journal of Counseling and Development, 92 (1), 36–46.
Download references
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Benjamin Zemelman and Tali Ducas for their assistance in collecting data and material for the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Leadership and Policy in Education, The University of Haifa, 199 Abba Khoushy Ave., Mount Carmel, 3498838, Haifa, Israel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shiri Lavy .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Lavy, S. Who benefits from group work in higher education? An attachment theory perspective. High Educ 73 , 175–187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-016-0006-z
Download citation
Published : 15 April 2016
Issue Date : February 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-016-0006-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Study groups
- Attachment theory
- Attachment styles
- Attachment orientations
- Collaborative groups
- Effectiveness
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Implementing Group Work in the Classroom
Group work can be an effective method to motivate students, encourage active learning, and develop key critical-thinking, communication, and decision-making skills. But without careful planning and facilitation, group work can frustrate students and instructors, and feel like a waste of time. Use these suggestions to help implement group work successfully in your classroom.
Preparing for Group Work
- Think carefully about how students will be physically arranged in groups. Will it be easy for groups to form and for all students to be comfortable? Also think about how the layout of your classroom will impact volume. Will students be able to hear one another clearly? How can you moderate the activity to control volume?
Set clear guidelines on professional, civil conduct between and among students to respect people’s differences and create an inclusive environment.
Talk to students about their past experiences with group work and allow them to establish some ground rules for successful collaboration. This discussion can be successfully done anonymously through the use of note cards.
Designing the Group Activity
- Identify the instructional objectives. Determine what you want to achieve through the small group activity, both academically (e.g., knowledge of a topic) and socially (e.g., listening skills). The activity should relate closely to the learning objective(s) and class content, and must be designed to help students learn, not simply to occupy their time. When deciding whether or not to use group work for a specific task, consider these questions: What is the objective of the activity? How will that objective be furthered by asking students to work in groups? Is the activity challenging or complex enough that it requires group work? Will the project require true collaboration? Is there any reason why the assignment should not be collaborative?
- Make the task challenging. Consider giving a relatively easy task early in the term to arouse students’ interest in group work and encourage their progress. In most cases collaborative exercises should be stimulating and challenging. By pooling their resources and dealing with differences of opinion that arise, groups of students can develop a more sophisticated product than they could as individuals. See our teaching tip “ Group work in the Classroom: Small-Group Tasks ” for some ideas.
- Allocate essential resources across the group so that group members are required to share information (e.g., the jigsaw method ). Or, to come up with a consensus, randomly select one person to speak for the group, or assign different roles to group members so that they are all involved in the process (e.g., recorder, spokesperson, summarizer, checker, skeptic, organizer, observer, timekeeper, conflict resolver, liaison to other groups).
- Another strategy for promoting interdependence is specifying common rewards for the group, such as a group mark. See the CTE teaching tip “ Methods for Assessing Group Work ” for more information.
- Decide on group size. The size you choose will depend on the number of students, the size of the classroom, the variety of voices needed within a group, and the task assigned. Groups of four-five tend to balance the needs for diversity, productivity, active participation, and cohesion. The less skillful the group members, the smaller the groups should be (Gross Davis, 1993).
- To vary group composition and increase diversity within groups, randomly assign students to groups by counting off and grouping them according to number.
- For some group tasks, the diversity within a group (e.g., gender, ethnicity, level of preparation) is especially important, and you might want to assign students to groups yourself before class. Collect a data card from each student on the first day of class to glean important information about their backgrounds, knowledge, and interests. Alternately, ask students to express a preference (e.g., list three students with whom they would most like to work or two topics they would most like to study), and keep their preferences in mind as you assign groups.
- Allow sufficient time for group work. Recognize that you won't be able to cover as much material as you could if you lectured for the whole class period. Cut back on the content you want to present in order to give groups time to work. Estimate the amount of time that subgroups need to complete the activity. Also plan for a plenary session in which groups’ results can be presented or general issues and questions can be discussed.
- Design collaborative work in multiple forms: pairs, small groups, large groups, online synchronously, online asynchronously, etc. Some students might be better at contributing after they have had time to digest material, while others might be better at thinking on the spot. Other students will defer to others in large groups but actively contribute in pairs. All roles should be valued and included.
Introducing the Group Activity
- Share your rationale for using group work. Students must understand the benefits of collaborative learning. Don't assume that students know what the pedagogical purpose is. Explicitly connect these activities to larger class themes and learning outcomes whenever possible.
- Have students form groups before you give them instructions. If you try to give instructions first, students may be too preoccupied with deciding on group membership to listen to you.
- Facilitate some form of group cohesion. Students work best together if they know or trust each other, at least to some extent. Even for brief group activities, have students introduce themselves to their group members before attending to their task. For longer periods of group work, consider introducing an icebreaker or an activity designed specifically to build a sense of teamwork.
- Explain the task clearly. This means both telling students exactly what they have to do and describing what the final product of their group work will look like. Explaining the big picture or final goal is important, especially when the group work will take place in steps (such as in snowballing or jigsaw ). Prepare written or visual instructions (e.g., charts, sequential diagrams) for students. Remember to include time estimations for activities.
- Set ground rules for group interaction. Especially for extended periods of group work, establish how group members should interact with one another, including principles such as respect, active listening, and methods for decision making. Consider making a group contract. See Group Decision Making , a CTE teaching tip prepared for students working in groups, and Making Group Contracts .
- Let students ask questions. Even if you believe your instructions are crystal clear, students may have legitimate questions about the activity. Give them time to ask questions before they get to work.
Monitoring the Group Task
- Monitor the groups but do not hover. As students do their work, circulate among the groups and answer any questions raised. Also listen for trends that are emerging from the discussions, so that you can refer to them during the subsequent plenary discussion. Avoid interfering with group functioning — allow time for students to solve their own problems before getting involved. You might consider leaving the room for a short period of time. Your absence can increase students’ willingness to share uncertainties and disagreements (Jaques, 2000).
- Be slow to share what you know. If you come upon a group that is experiencing uncertainty or disagreement, avoid the natural tendency to give the answers or resolve the disagreement. If necessary, clarify your instructions, but let students struggle — within reason — to accomplish the task (Race, 2000).
- Clarify your role as facilitator. If students criticize you for not contributing enough to their work, consider whether you have communicated clearly enough your role as facilitator.
Ending the Group Task
Provide closure to the group activities. Students tend to want to see how their work in small groups was useful to them and/or contributed to the development of the topic. You can end with a plenary session in which students do group reporting. Effective group reporting “can make the difference between students’ feeling that they are just going through their paces and the sense that they are engaged in a powerful exchange of ideas” (Brookfield & Preskill, 1999, p. 107).
- Oral reports: Have each group give one idea and rotate through the groups until no new ideas arise. Or have each group give their most surprising or illuminating insights or their most challenging question. You can record ideas raised to validate their value.
- Written reports: Have each group record their ideas and either present them yourself or have a group member do so. One variation on this is to have groups record their conclusions on a section of the blackboard or on flipchart paper that is then posted on the wall. Students then informally circulate around the room and read each other’s answers. Alternately, you can ask students to move around the room in small groups, rotating from one set of comments to another and adding their own comments in response. Another variation on written reports is to have students write brief comments on Post-it notes or index cards. Collect them, take a few minutes to process them or put them in sequence, then summarize their contents.
- Model how you want students to participate. When responding to students’ answers, model the respect and sensitivity that you want the students to display towards their classmates. Be ready to acknowledge and value opinions different from your own. Be willing to share your own stories, critique your work, and summarize what has been said.
- Connect the ideas raised to course content and objectives. Recognize that groups might not come up with the ideas you intended them to, so be willing to make your lecture plans flexible. Wherever possible, look for a connection between group conclusions and the course topic. However, be aware that misconceptions or inaccurate responses need to be clarified and corrected either by you or by other students.
- Don’t provide too much closure. Although the plenary session should wrap up the group work, feel free to leave some questions unanswered for further research or for the next class period. This openness reflects the nature of knowledge.
- Ask students to reflect on the group work process. They may do so either orally or in writing. This reflection helps them discover what they learned and how they functioned in the group. It also gives you a sense of their response to group work.
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
- Brookfield, S.D., & Preskill, S. (1999). Discussion as a Way of Teaching: Tools and Techniques for Democratic Classrooms. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
- Gross Davis, B. (1993). Tools for Teaching. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
- Jaques, D. (2000). Learning in Groups: A Handbook for Improving Group Work, 3rd ed. London: Kogan Page.
- Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Smith, K. A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching , 25(3&4), 85-118.
- Race, P. (2000). 500 Tips on Group Learning. London: Kogan Page.
- Roberson, B., & Franchini, B. (2014). Effective task design for the TBL classroom. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25(3&4), 275-302.
CTE teaching tips
- Group Work in the Classroom: Small-Group Tasks
- Group Work in the Classroom: Types of Small Groups
- Making Group Contracts
- Methods for Assessing Group Work
Other resources
- Journal on Excellence in College Teaching (2014). Special Focus Issue: Small-Group Learning in Higher Education — Cooperative, Collaborative, Problem-Based, and Team-Based Learning .
- Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Smith, K.A. (2006). Active learning: Cooperation in the university classroom (3 rd edition). Edina, MN: Interaction.
- Silberman, M. (1996). Active Learning: 101 Strategies to Teach Any Subject. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Course Implementation ,
- Request a Consultation
- Workshops and Virtual Conversations
- Technical Support
- Course Design and Preparation
- Observation & Feedback
Teaching Resources
Using Roles in Group Work
Resource overview.
How using roles can improve group work in your class
While collaborative learning through group work has been proven to have the potential to produce stronger academic achievement than other kinds of learning environments (Johnson, Johnson, & Smith, 2006), it can be challenging to implement successfully because many students come to college without the tools they need to automatically succeed in collaborative learning contexts. One way of providing supportive structures to students in a collaborative learning environment is through assigning roles within group work.
Potential Benefits of Using Assigned Roles in Group Work
Assigning group roles can be a beneficial strategy for successful group work design for a number of reasons:
- Group roles offer an opportunity for high quality, focused interactions between group participants. Participants are more likely to stay on task and pay closer attention to the task at hand when their roles in the collaboration are clear and distinct.
- Group roles provide all students with a clear avenue for participation. Students are less likely to feel left out or unengaged when they have a particular duty that they are responsible for completing. Along the same lines, assigning group roles reduces the likelihood of one individual completing the task for the whole group, or “taking over,” to the detriment of others’ learning.
- Group roles encourage individual accountability. Group members are more likely to hold each other accountable for not completing work if a particular task is assigned to them.
- Group roles allow students to strengthen their communicative skills, especially in areas that they are less confident in volunteering for.
- Group roles can help disrupt stereotypical and gendered role assignments, which can be common in group learning. For example, Hirshfield and Chachra (2015) found that in first-year engineering courses, female students tended to undertake less technical roles and more communicative roles than their male colleagues. By assigning roles during group work, and by asking students to alternate these roles at different points in the semester, students can work past gendered assumptions about themselves and their groupmates.
POGIL: A Model for Role Assignments in Collaborative Learning
One small group learning methodology where the use of group roles is well-defined and researched is the Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) method . The POGIL method calls for groups of three or four students who work in a team on process-oriented guided inquiry activities in which students construct their knowledge through interactions with others. Traditional POGIL roles for group members are provided below (POGIL, 2016).
- Manager or Facilitator : Manages the group by helping to ensure that the group stays on task, is focused, and that there is room for everyone in the conversation.
- Recorder : Keeps a record of those who were in the group, and the roles that they play in the group. The recorder also records critical points from the small group’s discussion along with findings or answers.
- Spokesperson or Presenter : Presents the group’s ideas to the rest of the class. The Spokesperson should rely on the recorder’s notes to guide their report.
- Reflector or Strategy Analyst : Observes team dynamics and guides the consensus-building process (helps group members come to a common conclusion).
Other Highly Adaptable Roles to Consider
You can adapt roles for different kinds of group tasks. While the POGIL model is a useful place to start, you may find that the tasks associated with your discipline require other kinds of roles for effective group learning. Adding to or reframing POGIL roles can be beneficial in these contexts. Below are some suggestions for additional roles that might be valuable to a variety of learning situations.
- Encourager : Encourages group members to continue to think through their approaches and ideas. The Encourager uses probing questions to help facilitate deeper thinking, and group-wide consideration of ideas.
- Questioner : Pushes back when the team comes to consensus too quickly, without considering a number of options or points of view. The questioner makes sure that the group hears varied points of view, and that the group is not avoiding potentially rich areas of disagreement.
- Checker : Checks over work in problem-solving contexts before the group members finalize their answers.
Strategies for Effective Facilitation of Group Roles
The following suggestions are strategies for effective facilitation of group roles. These strategies are helpful in a wide variety of group work situations, but are essential for group work that will last beyond a single class period, or constitute a significant portion of student grades.
- Be transparent about why you are assigning group roles. This kind of transparency can increase student buy-in by helping them recognize the value in establishing group roles
- Provide students with a list of roles and brief definitions for each role at the beginning of the group work activity. Make it clear which tasks are associated with which roles.
- Alternatively, you may find it helpful, especially in advanced-level classes, to encourage students to develop their own roles in groups based on the tasks that they feel will be critical to the group’s success. This strategy provides the students with a larger level of autonomy in their learning, while also encouraging them to use proven structures that will help them be successful.
- Roles can be assigned randomly through a variety of strategies, from who has the next birthday to color-coded post-it notes, or a place card that points out roles based on where everyone is sitting.
- Circulate early in the class period to be sure that everyone has been assigned a role, and that everyone is clear about what their responsibilities include.
- Be willing to reinforce the given roles throughout the activity. For roles to work, students have to feel as though they will be held accountable for fulfilling those roles. Therefore, it is critical for you to step in if you see someone taking over someone else’s role or not fulfilling their assigned role. Often gentle reminders about who is supposed to be doing what can be useful interventions. For example, if someone is talking over everyone and not listening to their other groupmates, you might say something like “Remember, as a spokesperson, your job is to represent the ideas of everyone in the group.”
- Talk with students individually if their speech or conduct could be silencing, denigrating, or excluding others. Remember: your silence on this issue may be read as endorsement.
- Changing things up regularly is imperative. If you use group roles frequently, mixing up roles throughout the semester can help students develop communication skills in a variety of areas rather than relying on a single personal strength.
- If this is a long-term group assignment, be sure to provide structures for individual feedback for the instructor and other group member on group dynamics. This could be a formal or informal check in, but it’s critical for students to have a space to voice concerns related to group dynamics—especially if this assignment counts for a large portion of their final grade. This feedback might be provided through an anonymous survey in paper form or through a web-based tool like Qualtrics or a Google form. These check-ins can reduce student anxiety about the potential for uneven group participation.
Overall, using assigned roles in group work provides students with a supportive structure that promotes meaningful collaborative learning. While group learning can be challenging to implement effectively, using roles can mitigate some of the challenges associated with learning in groups, while offering students the opportunity to develop a variety of communication skills that will be critical to their success in college and their future careers.
Burke, Alison. (2011). Group work: How to use groups effectively. The Journal of Effective Teaching , 11(2), 87-95.
Beebe, S.A., & Masterson, J.T. (2003). Communicating in small groups . Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Cheng, W. Y., Lam, S. F., & Chan, C. Y. (2008). When high achievers and low achievers work in the same group: The roles of group heterogeneity and processes in project‐based learning. British Journal of Educational Psychology , 78 (2), 205-221.
Eberlein, T., Kampmeier, J., Minderhout, V., Moog, R.S., Platt, T., Varma-Nelson, P., White, H.B. (2008). Pedagogies of engagement in science: A comparison of PBL, POGIL and PLTL. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 36 (4), 262-73.
Hale, D., & Mullen, L. G. (2009). Designing process-oriented guided-inquiry activities: A new innovation for marketing classes. Marketing Education Review , 19 (1), 73-80.
Hirshfield, L., & Chachra, D. (2015). Task choice, group dynamics and learning goals: Understanding student activities in teams. 2015 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference: Launching a New Vision in Engineering Education Proceedings, FIE 2015 , 1-5.
Johnson, C. (2011). Activities using process‐oriented guided inquiry learning (POGIL) in the foreign language classroom. Die Unterrichtspraxis/Teaching German , 44 (1), 30-38.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., and Smith, K.A. (2006). Active learning: Cooperation in the university classroom . Edina, MN: Interaction.
Moog, R.S. (2014). Process oriented guided inquiry learning. In M.A. McDaniel, R. F. Frey, S.M. Fitzpatrick, & Roediger, H.L. (Eds.). Integrating cognitive science with innovative teaching in STEM disciplines (147-166). St. Louis: Washington University in St. Louis Libraries.
The POGIL Project. (2017). https://pogil.org/
Springer, L., Stanne, M.E., & Donovan, S.S. (1999). Effects of small-group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 96 (1), 21-51.

Education resources › Blog › 10 advantages and disadvantages of classroom group work

10 advantages and disadvantages of classroom group work
- Leadership & teamwork
- The science of learning
Written by the InnerDrive team | Edited by Bradley Busch
The use of group work in the classroom is one of the most widely researched and implemented teaching approaches in the world. Numerous research studies have shown the benefits of collaborative learning on academic performance, communication skills, and confidence.
However, our understanding of how group work facilitates learning and why group work is only effective in certain situations is still limited. And like with all teaching strategies, the disadvantages need to be taken into consideration.
Amongst educators, there is a growing debate surrounding the efficacy of group work due to the potential for laziness, unequal workload, conflict between students, and a loss of focus on the task at hand. So, we took a look at the pros and cons of implementing group work into the classroom to determine how effective it really is.

10 advantages and disadvantages of group work
5 advantages of group work, a new perspective .
The phrase “two heads are better than one” certainly has some merit. Researchers found that if students are able to work together , for example on a problem-solving task, they are more likely to experiment with different techniques in order to try and solve it. They can also learn faster from positive and negative feedback.
Students also learn better by discussing and questioning each other’s opinions and reasoning as this allows them to develop different perspectives of how they can go about completing a task. Research shows this promotes cognitive restructuring , enhancing academic, social, and emotional learning as a result.
Personal satisfaction
Working in a group can be tough. So, when students are able to overcome all the conflict, stress, and long hours that come with group assignments, the end result of getting a good grade can be extremely satisfying and motivating.
Research shows that students who contribute to group discussion and engage with the assigned problem-solving task are highly dedicated to figuring out a solution. When they find that solution, students report feeling extremely satisfied with their role in making that decision compared to students who weren’t as involved. This leads to a more positive depiction of their group learning experience.
Teamwork skills
Teamwork is a staple part of academic life and allows students to explore complex tasks that they otherwise wouldn’t have done if they had been alone, enhancing both their individual and collective learning. This is because working in a group exposes students to new perspectives, styles of thinking, and disagreement.
This provides students with an opportunity to improve their communication skills, collaboration and provides a larger capacity for brainstorming different ideas. This not only contributes to a more holistic approach to learning but can help group productivity as well.
Enhancing learning
A survey showed that 97% of students reported that working in a group environment has helped facilitate their learning and collaborative skills in some way. Some students suggested that group work served as a learning process in itself; that is, they learnt about groups by working in a group.
Research also shows that learning in a group leads to better memory recall and understanding. This is because students remember more from group discussions than if they listened to the same content in a more instructional format.
However, these benefits are only felt if:
- Clear goals are set
- There is clear leadership
- Each member is assigned a specific role
- There’s equal participation from all group members
- The task is relevant to syllabus content
Although this study was conducted with university students, these findings are still relevant to other educational levels.
Learning to overcome conflict
Some teachers argue that conflict during group work can actually be a good thing as it is representative of experiences students will have in their future workplaces. By experiencing it in a more controlled setting, students learn about communication skills and how to resolve interpersonal issues more safely.
Group work also allows students to develop a better understanding of themselves and how their peers view them. By gaining constructive feedback from their peers about how well they did on a task and how well they worked as part of the group, students are better equipped to evaluate their social skills and behaviour.
5 disadvantages of group work
Anyone who has done group work knows that is can have its fair share of disadvantages. Let’s take a look at why.
Presence of conflict
When working with others, it’s natural that disagreement will arise due to differences in opinions. Some students find it difficult to accept criticism from their peers and struggle to get on board with ideas that aren’t their own.
Moreover, students who are quiet often have difficulty expressing their ideas in a group and may feel uncomfortable working with people they don’t normally speak to. As a result, they may be seen as lazy, creating conflict.
Research shows that the presence of conflict in group work can negatively impact the students’ enjoyment of that class, inhibit their individual learning, and increase stress levels. This is because students felt that compromising and coming to an agreement was an extremely difficult and draining process. This led to many students developing a fear of conflict.
Unequal participation
In group work, you’ll often observe a large discrepancy in participation between the different group members. With a lot of group projects, it’s common to find 1-2 students taking the bulk of the workload, whilst other members essentially freeload. This can lead to conflict and breed bitterness amongst the different group members – especially if the student feels others are being rewarded for their hard work.
Research shows that this is more evident in larger groups as individuals tend to diffuse the responsibility of tasks onto others as grades typically don’t consider individual contribution. Other times, a student may just give their peers the answer without explaining how they worked it out. Consequently, no real knowledge and understanding have been gained.
Avoiding the task
When working in a group, it’s quite common for students to go off-topic, especially if the task involves discussion. Some students may use that time to gossip, do other tasks, or loaf around. This results in the group work session being less effective and productive .
As a teacher, it’s difficult to make sure everyone is doing the task they’re supposed to for the entire session, not just as you approach their table to see how they’re doing. For some teachers, it feels that they have to micromanage the task in order for the task to be effective, diminishing the purpose of working in a group.
Time consuming
Working in a team can be extremely time-consuming as a student. Not only do meetings have to be scheduled outside of class hours but they have to co-ordinate with everyone’s schedule. For sixth-form students in particular, this can be quite difficult due to already being overscheduled .
Researchers have even argued whether the time-consuming nature of group work made the strategy ineffective. As a result, more research is emerging about when not to use group work in the classroom and suggest that for simpler tasks, students complete them individually.
Individual needs are dominated by the needs of the group
Not all students learn at the same speed. Some may need more time to fully understand the task and process the information they’re being taught. On the flip side, some students may grasp the material very quickly.
Therefore, when working as a group, certain students are either forced to hurry up their learning to the extent that they either learn nothing or resort to copying. Alternatively, those who work faster may actually be going too fast, attempting to move onto the next task before everyone is ready. This can lead to conflict as students may get frustrated by the learning process.
Final thoughts
Group learning can be effective regardless of people’s socioeconomic status or whether they’re put into a group with the same people throughout the year. However, the advantages of this active learning environment are only observed when it is done right.
Group size, how groups are assigned and how the teacher manages the groups can have both a positive and negative impact on learning. Due to the potential disadvantages, some research suggests that group work should only be used in moderation by allowing simpler tasks to be completed individually and more complex tasks to be completed in groups.
For tips on how to engage your students in the classroom, take a look at our blogs on how to create a psychologically smart classroom and why you should interleave your teaching .
About the editor

Bradley Busch
Bradley Busch is a Chartered Psychologist and a leading expert on illuminating Cognitive Science research in education. As Director at InnerDrive, his work focuses on translating complex psychological research in a way that is accessible and helpful. He has delivered thousands of workshops for educators and students, helping improve how they think, learn and perform. Bradley is also a prolific writer: he co-authored four books including Teaching & Learning Illuminated and The Science of Learning , as well as regularly featuring in publications such as The Guardian and The Telegraph.
Jump to section:
Recommended The science of learning reads

How much does prior knowledge help?

The awkward AI homework question

How much should research inform teaching practice?

Neuromyths and how to combat them: An educator’s guide

What do teachers want? Free evidence-informed CPD

The psychology of ‘Aha!’ moments: 5 ways to develop insight

9 common thinking biases in Education
11 min read

The Spiral Curriculum: A complete overview
Be the first to know about the key Teaching & Learning research and how to apply it. Sign up to receive our free resources directly in your inbox.
Center for Teaching Innovation
Resource library.
- Examples of Collaborative Learning or Group Work Activities
- Getting Started with Designing Group Work Assignments
- Getting Started with Evaluating Group Work
- Team-Based Learning Collaborative
Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning can occur peer-to-peer or in larger groups. Peer learning, or peer instruction, is a type of collaborative learning that involves students working in pairs or small groups to discuss concepts or find solutions to problems. Similar to the idea that two or three heads are better than one, educational researchers have found that through peer instruction, students teach each other by addressing misunderstandings and clarifying misconceptions.
Why use collaborative learning?
Research shows that educational experiences that are active, social, contextual, engaging, and student-owned lead to deeper learning. The benefits of collaborative learning include:
- Development of higher-level thinking, oral communication, self-management, and leadership skills.
- Promotion of student-faculty interaction.
- Increase in student retention, self-esteem, and responsibility.
- Exposure to and an increase in understanding of diverse perspectives.
- Preparation for real life social and employment situations.
Considerations for using collaborative learning
- Introduce group or peer work early in the semester to set clear student expectations.
- Establish ground rules for participation and contributions.
- Plan for each stage of group work.
- Carefully explain to your students how groups or peer discussion will operate and how students will be graded.
- Help students develop the skills they need to succeed, such as using team-building exercises or introducing self-reflection techniques.
- Consider using written contracts.
- Incorporate self -assessment and peer assessment for group members to evaluate their own and others' contributions.
Getting started with collaborative learning
Shorter in-class collaborative learning activities generally involve a three-step process. This process can be as short as five minutes, but can be longer, depending on the task at hand.
- Introduce the task. This can be as simple as instructing students to turn to their neighbor to discuss or debate a topic.
- Provide students with enough time to engage with the task. Walk around and address any questions as needed.
- Debrief. Call on a few students to share a summary of their conclusions. Address any misconceptions or clarify any confusing points. Open the floor for questions.
For larger group work projects, here are some strategies to help ensure productive group dynamics:
- Provide opportunities for students to develop rapport and group cohesion through icebreakers , team-building, and reflection exercises.
- Give students time to create a group work plan allowing them to plan for deadlines and divide up their responsibilities.
- Have students establish ground rules . Students can create a contract for each member to sign. This contract can include agreed-upon penalties for those who fail to fulfill obligations.
- Assign roles to members of each group and change the roles periodically. For example, one student can be the coordinator, another the note-taker, another the summarizer, and another the planner of next steps.
- Allow students to rate each other’s quality and quantity of contributions. Use these evaluations when giving individual grades, but do not let it weigh heavily on a student's final grade. Communicate clearly how peer assessment will influence grades.
- Check in with groups intermittently but encourage students to handle their own issues before coming to you for assistance.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.17(1); Spring 2018
Kristy J. Wilson
† Biology Department, College of Arts and Sciences, Marian University, Indianapolis, IN 46222
Peggy Brickman
‡ Department of Plant Biology, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602
Cynthia J. Brame
§ Center for Teaching and Department of Biological Sciences, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37203
This essay introduces an evidence-based teaching guide presenting research and resources related to group work. The guide provides links to key articles accompanied by summaries organized by teaching challenge and an instructor checklist. In addition to describing the guide, the article identifies areas for further research.
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics faculty are increasingly incorporating both formal and informal group work in their courses. Implementing group work can be improved by an understanding of the extensive body of educational research studies on this topic. This essay describes an online, evidence-based teaching guide published by CBE—Life Sciences Education ( LSE ). The guide provides a tour of research studies and resources related to group work (including many articles from LSE ). Instructors who are new to group work, as well as instructors who have experienced difficulties in implementing group work, may value the condensed summaries of key research findings. These summaries are organized by teaching challenges, and actionable advice is provided in a checklist for instructors. Education researchers may value the inclusion of empirical studies, key reviews, and meta-analyses of group-work studies. In addition to describing key features of the guide, this essay also identifies areas in which further empirical studies are warranted.
INTRODUCTION
Group work is one of the most widely used and deeply researched teaching approaches in the college classroom. Group work that promotes students’ collaboration to achieve shared learning goals has been shown to increase student achievement, persistence, and attitudes toward science (e.g., Springer et al ., 1999 ; Tanner et al ., 2003 ; Johnson and Johnson, 2009 ; Johnson et al ., 2014 ). It can provide opportunities for students to explain their reasoning to one another and to themselves, thereby promoting the cognitive restructuring that leads to learning (e.g., Kagan, 2014 ). It offers opportunities for formative assessment and feedback with peers to shape that learning (e.g., Johnson and Johnson, 2009 ). It also provides students with an avenue to incorporate diverse viewpoints and to develop communication and teamwork skills that are especially important in scientific collaboration and professional fields (e.g., Lamm et al. , 2012 ).
However, anyone who has worked in a group or used group work in courses has experienced challenges. These challenges, if left unchecked, can prevent effective learning and result in poor-quality products, unequal distribution of workload, and escalating conflict among team members (e.g., Feichtner and Davis, 1984 ). In this article, we describe an evidence-based teaching guide that we have created to condense, summarize, and provide actionable advice from research findings (including many articles from CBE—Life Sciences Education [ LSE ]). The guide can be found on the American Society for Cell Biology website ( https://lse.ascb.org/evidence -based-teaching-guides/group-work ), and a link will be listed on the LSE home page to direct users to a complete list of guides as this feature grows. We have included several useful features in the guide: a landing page that indicates starting points for instructors ( Figure 1 ), syntheses of observations from the literature ( Figure 2 ), summaries of and links to selected papers ( Figure 3 ), and an instructor checklist that details recommendations and points to consider. The guide is meant to aid instructors who are new to group work as well as instructors who have tried group work and experienced difficulties or want to improve their students’ experiences and outcomes. Researchers interested in exploring this area will also appreciate our efforts to identify empirical studies, informative reviews, and unanswered questions for which additional research is warranted. Some of the questions that we have considered in developing the guide are highlighted in the following sections.

Screenshot representing the landing page of the guide, which provides readers with an overview of choice points.

Screenshot showing an example description of overall conclusions that can be drawn about an element of group work, based on a synthesis of the literature.

Screenshots representing (A) summaries and links to important papers and (B) other resources.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF FORMING PERMANENT VERSUS TEMPORARY GROUPS?
The guide begins by separating findings, recommendations, and resources for formal, permanent groups from informal, temporary groups. During formal group work, students work in persistent groups for an extended period on a collaborative project, while in informal group work, ad hoc groups work together on an in-class problem or question for periods ranging from a few minutes to a full class session ( Johnson et al ., 2014 ). Formal group work requires more planning and coordination, but the benefits are that it can help students work together to reach important course objectives. Informal group work, on the other hand, is easy to incorporate into classes of any size and in any space. Informal group work can be an effective supplement to lecture, allowing learners to process information, and is often an essential part of, or used in conjunction with, classic active-learning techniques (e.g., Tanner et al. , 2003 ).
Three elements that are particularly important to consider in structuring formal group work are task interdependence, individual accountability, and reward interdependence ( Johnson and Johnson, 2009 ). Task interdependence refers to the degree to which group members must work together to complete the assigned task. For optimal group benefit and motivation, tasks should not be able to be completed by just one or two group members, but rather should require contributions from all group members (e.g., Gillies, 2013 ). Individual accountability, or the understanding that group members will be responsible for the work they specifically contribute, reduces social free-riding in group settings and encourages members to contribute. Reward interdependence can be accomplished through several mechanisms, including shared grades, for which individual students earn a final grade that relies on scores earned by their team members on a test or assignment, or certificates of recognition that students can earn if their average team scores on quizzes or other individual assignments exceed a pre-established criterion ( Serrano and Pons, 2007 ).
Notably, the very distinction between the types of group work points to an unanswered research question:
Are there specific types of outcomes that are better met with informal group work rather than formal group work, or vice versa?
SHOULD INSTRUCTORS FORM GROUPS OR LET STUDENTS SELF-SELECT THEIR OWN GROUPS?
When planning formal group work, the literature suggests that instructors should form small groups (typically three to five students), considering student characteristics that can contribute to effective group processes and performance (e.g., Treen et al. , 2016 ; and other references within the Group Size section of the guide). Generally, groups that are gender balanced, are ethnically diverse, and have members with different problem-solving approaches have been shown to exhibit enhanced collaboration (see references within the Group Composition section of the guide). Within these generic observations, however, there are a number of unanswered questions for which further research is needed:
- What are the different impacts for ethnic majority and minority students in ethnically diverse groups? If so, what are they, and why do they occur?
- Does context determine effective gender composition for groups? If so, is it a generalizable context (e.g., physics groups work best with one composition, while biology groups work best with another composition)? Alternatively, does the effectiveness of different group gender compositions depend on the measure being used (e.g., creativity of final product, effectiveness of group communication)? Are there task features or group structures that can mitigate disadvantages of particular gender mixes?
- The data on academic performance as a diversity factor also do not point to a single conclusion. What features of group work lead to benefits for high-, mid-, or low-performing students? Will these features be combined to benefit mixed-ability groups? Do homogeneous or heterogeneous groups provide a greater advantage?
- What are effective steps to take to support students with different disabilities while they participate in group work?
WHAT CAN INSTRUCTORS DO TO PROMOTE QUALITY GROUP EXPERIENCES?
There are a number of common problems that students and instructors experience when involved in group work. The most commonly reported problem is uneven workload (free-riding or overbearing students). However, groups also experience other types of social conflict and lack of cohesion that can result in production of “Frankenstein products” that are a conglomeration of individual student efforts without integration and synthesis of ideas. There are several practices and resources that can help ensure that groups function more effectively. Students report greater satisfaction with group work if the instructor has implemented methods to monitor and manage groups ( Chapman and Van Auken, 2001 ; and other references within Setting Group Norms ). Suggested methods include providing an opportunity for students to discuss their expectations for group work and setting group norms. For group work that spans multiple days or weeks, providing opportunities for identifying individual effort and allowing students to evaluate their peers can allow for ongoing adjustments to group dynamics. Assigning specific roles to students within groups can emphasize interdependence, and prompting students to provide elaborated explanations during discussions can help promote learning gains ( Gillies, 2013 ). Even with these recommendations, there are many unanswered questions.
- Findings from research studies on peer evaluation have clearly identified several methods to identify dysfunctional groups. What are the potential solutions to address dysfunctional groups and under what conditions are these solutions effective? When is it more effective to disband a dysfunctional group rather than enforce mediation?
- What is the best method to deal with persistent free-riders?
WHAT TASKS ARE IDEAL FOR PROMOTING EFFECTIVE GROUP WORK?
We describe a number of formalized group-work pedagogies with defined criteria and tasks that instructors can consider. These include problem-based learning, team-based learning, process-oriented guided inquiry learning, case-based learning, and peer-led team learning, all of which have descriptions and biology-relevant papers linked within the Formalized Pedagogies section of the guide. Instructors considering these approaches should consider forming a team of instructors, administrators, and/or staff to address the attendant time and resource needs. For any group task, it is important to consider why group work is being used in a particular situation and how it meets the instructor’s learning goals for students. To help promote student buy-in and student learning, these goals should be shared with students, along with an explanation of how the group work aligns with these goals.
Effective group tasks should challenge groups to solve highly complex or ill-structured problems that require the collaboration of the group to solve (e.g., Scager et al. , 2016 ; and other references within the Task Features section). In addition, tasks that engage student interest, such as by using contemporary issues relevant to students’ lives and generating products for an audience outside the classroom, can increase students’ motivation (e.g., Schmidt et al. , 2011 ). With this general recommendation in mind, however, there are a number of unanswered questions:
- Typically, a task’s relevance to students’ lives increases task value and thus student motivation. What are the best ways to structure relevant tasks in the biology classroom? Do these features differ by major or level of student?
- Does a students-as-producers approach, wherein students generate new knowledge for an external audience, impact motivation for all students or only some? Does the relative size of the product/student contribution matter (e.g., one figure on a poster vs. entire infographic for congressional representative)?
- How do different group tasks or task instructions affect cognitive development of knowledge structures and their use? What tasks support development of declarative knowledge (what), procedural knowledge (how), and conceptual knowledge (when/why)?
- Students lie at various places along the novice–expert continuum. How do we match scaffolding to student needs?
WHEN NOT TO USE GROUP WORK
We finish this summary to our guide by cautioning that group work is not a panacea for learning. A great deal of research has defined the type of tasks for which group work is more effective than individual learning. Groups of students show greater gains than individual students for tasks that are complex and ill-defined with multiple possible correct answers ( Kirschner et al. , 2011 ), but for simpler tasks that require recall, definitions, or looking up information, students exhibit greater gains when they work on their own. Thus, maximizing the benefits of group work requires that instructors attend to the learning goals they want their students to attain and, if applicable, the group-work structures that they put in place to help the students reach those goals.
Acknowledgments
We thank William Pierce and Thea Clarke for their efforts in producing the Evidence-Based Teaching Guides website and the American Society for Cell Biology for hosting the site.
- Chapman K. J., Van Auken S. (2001). Creating positive group experiences: An examination of the role of the instructor on students’ perceptions of group projects . Journal of Marketing Education , , 117–127. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feichtner S. B., Davis E. A. (1984). Why some groups fail: A survey of students’ experiences with learning groups . Journal of Management Education , , 58–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M. (2013). Structuring cooperative group work in classrooms . International Journal of Educational Research , , 35–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning . Educational Researcher , , 365–379. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T., Smith K. A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory . Journal on Excellence in College Teaching , , 85–118. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kagan S. (2014). Kagan structures, processing, and excellence in college teaching . Journal on Excellence in College Teaching , ( 3–4 ), 119–138. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kirschner F., Paas F., Kirschner P. A. (2011). Task complexity as a driver for collaborative learning efficiency: The collective working-memory effect . Applied Cognitive Psychology , ( 4 ), 615–624. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamm A. J., Shoulders C., Roberts T. G., Irani T. A., Snyder J. L., Brendemuhl B. J. (2012). The influence of cognitive diversity on group problem solving strategy . Journal of Agricultural Education , , 18–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Scager K., Boonstra J., Peeters T., Vulperhorst J., Wiegant F. ( Collaborative learning in higher education: Evoking positive interdependence 2016). ( 4 ),. ar69 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schmidt H. G., Rotgans J. I., Yew E. H. J. (2011). The process of problem-based learning: What works and why . Medical Education , , 792–806. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Serrano J. M., Pons R. M. (2007). Cooperative learning: We can also do it without task structure . Intercultural Education , ( 3 ), 215–230. [ Google Scholar ]
- Springer L., Stanne M. E., Donovan S. S. (1999). Effects of small-group learning in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis . Review of Educational Research , , 21–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tanner K., Chatman L. S., Allen D. (2003). Approaches to cell biology teaching: Cooperative learning in the science classroom—beyond students working in groups . Cell Biology Education , , 1–5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Treen E., Atanasova C., Pitt L., Johnson M. (2016). Evidence from a large sample on the effects of group size and decision-making time on performance in a marketing simulation game . Journal of Marketing Education , , 130–137. [ Google Scholar ]
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work.

- Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking. Similarly, the question of why some group work is successful and other group work results in the opposite is still unsolved. The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students’ experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work ends up being a positive experience resulting in successful learning, while in other cases, the result is the reverse, are of interest. Data were collected through a study-specific questionnaire, with multiple choice and open-ended questions. The questionnaires were distributed to students in different study programs at two universities in Sweden. The present result is based on a reanalysis and qualitative analysis formed a key part of the study. The results indicate that most of the students’ experiences involved group work that facilitated learning, especially in the area of academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that served as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions facilitate or hamper students’ learning, as well as impact their experiences with group work.
Introduction
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in most educational systems, from compulsory education to higher education. The overarching purpose of group work in educational practice is to serve as an incentive for learning. For example, it is believed that the students involved in the group activity should “learn something.” This prerequisite has influenced previous research to predominantly focus on how to increase efficiency in group work and how to understand why some group work turns out favorably and other group work sessions result in the opposite. The review of previous research shows that in the 20th century, there has been an increase in research about students’ cooperation in the classroom ( Lou et al., 1996 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). This increasing interest can be traced back to the fact that both researchers and teachers have become aware of the positive effects that collaboration might have on students’ ability to learn. The main concern in the research area has been on how interaction and cooperation among students influence learning and problem solving in groups ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ).
Two approaches concerning learning in group are of interest, namely cooperative learning and collaborative learning . There seems to be a certain amount of confusion concerning how these concepts are to be interpreted and used, as well as what they actually signify. Often the conceptions are used synonymously even though there are some differentiations. Cooperative group work is usually considered as a comprehensive umbrella concept for several modes of student active working modes ( Johnson and Johnson, 1975 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ), whereas collaboration is a more of an exclusive concept and may be included in the much wider concept cooperation ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Cooperative learning may describe group work without any interaction between the students (i.e., the student may just be sitting next to each other; Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ), while collaborative learning always includes interaction, collaboration, and utilization of the group’s competences ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ).
At the present time, there is strong scientific support for the benefits of students learning and working in groups. In addition, the research shows that collaborative work promotes both academic achievement and collaborative abilities ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to Gillies and Boyle (2011) , the benefits are consistent irrespective of age (pre-school to college) and/or curriculum. When working interactively with others, students learn to inquire, share ideas, clarify differences, problem-solve, and construct new understandings. Gillies (2003a , b ) also stresses that students working together are more motivated to achieve than they would be when working individually. Thus, group work might serve as an incentive for learning, in terms of both academic knowledge and interpersonal skills. Nevertheless, studies about what occur in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking in the literature, especially when it comes to addressing the students’ points of view, with some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Similarly, the question of why some group work turns out successfully and other work results in the opposite is still unsolved. In this article, we hope to contribute some new pieces of information concerning the why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while others result in the opposite.
Group Work in Education
Group work is frequently used in higher education as a pedagogical mode in the classroom, and it is viewed as equivalent to any other pedagogical practice (i.e., whole class lesson or individual work). Without considering the pros and cons of group work, a non-reflective choice of pedagogical mode might end up resulting in less desirable consequences. A reflective choice, on the other hand, might result in positive experiences and enhanced learning ( Galton et al., 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Group Work as Objective or Means
Group work might serve different purposes. As mentioned above, the overall purpose of the group work in education is that the students who participate in group work “learn something.” Learning can be in terms of academic knowledge or “group knowledge.” Group knowledge refers to learning to work in groups ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare might be of equal importance as academic knowledge, or they may even be prerequisites for learning. Thus, the group and the group work serve more functions than just than “just” being a pedagogical mode. Hence, before group work is implemented, it is important to consider the purpose the group assignment will have as the objective, the means, or both.
From a learning perspective, group work might function as both an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities) and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement) or both ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). If the purpose of the group work is to serve as an objective, the group’s function is to promote students’ development of group work abilities, such as social training and interpersonal skills. If, on the other hand, group work is used as a means to acquire academic knowledge, the group and the collaboration in the group become a base for students’ knowledge acquisition ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). The group contributes to the acquisition of knowledge and stimulates learning, thus promoting academic performance. Naturally, group work can be considered to be a learning environment, where group work is used both as an objective and as the means. One example of this concept is in the case of tutorial groups in problem-based learning. Both functions are important and might complement and/or even promote each other. Albeit used for different purposes, both approaches might serve as an incentive for learning, emphasizing different aspect knowledge, and learning in a group within an educational setting.
Working in a Group or as a Group
Even if group work is often defined as “pupils working together as a group or a team,” ( Blatchford et al., 2003 , p. 155), it is important to bear in mind that group work is not just one activity, but several activities with different conditions ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). This implies that group work may change characteristics several times during a group work session and/or during a group’s lifetime, thus suggesting that certain working modes may be better suited for different parts of a group’s work and vice versa ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). It is also important to differentiate between how the work is accomplished in the group, whether by working in a group or working as a group.
From a group work perspective, there are two primary ways of discussing cooperation in groups: working in a group (cooperation) or working as a group (collaboration; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Situations where students are sitting together in a group but working individually on separate parts of a group assignment are referred to as working in a group . This is not an uncommon situation within an educational setting ( Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ). Cooperation between students might occur, but it is not necessary to accomplish the group’s task. At the end of the task, the students put their separate contributions together into a joint product ( Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2010 , 2011a ). While no cooperative activities are mandatory while working in a group, cooperative learning may occur. However, the benefits in this case are an effect of social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) and are not caused by cooperation. In this situation, social facilitation alludes to the enhanced motivational effect that the presence of other students have on individual student’s performance.
Working as a group, on the other hand, causes learning benefits from collaboration with other group members. Working as a group is often referred to as “real group work” or “meaningful group work,” and denotes group work in which students utilizes the group members’ skills and work together to achieve a common goal. Moreover, working as a group presupposes collaboration, and that all group members will be involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, the utilization of the group’s competence, and the presence of problem solving and reflection. According to Granström (2006) , working as a group is a more uncommon activity in an educational setting. Both approaches might be useful in different parts of group work, depending on the purpose of the group work and type of task assigned to the group ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). Working in a group might lead to cooperative learning, while working as group might facilitate collaborative learning. While there are differences between the real meanings of the concepts, the terms are frequently used interchangeably ( Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Previous Research of Students’ Experiences
As mentioned above, there are a limited number of studies concerning the participants’ perspectives on group work. Teachers often have to rely upon spontaneous viewpoints and indications about and students’ experiences of group work in the form of completed course evaluations. However, there are some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). To put this study in a context and provide a rationale for the present research, a selection of studies focusing on pupils’ and/or students’ experiences and conceptions of group work will be briefly discussed below. The pupils’ and/or students inside knowledge group work may present information relevant in all levels of educational systems.
Hansen (2006) conducted a small study with 34 participating students at a business faculty, focusing on the participants’ experiences of group work. In the study different aspects of students’ positive experiences of group work were identified. For example, it was found to be necessary that all group members take part and make an effort to take part in the group work, clear goals are set for the work, role differentiation exists among members, the task has some level of relevance, and there is clear leadership. Even though Hansen’s (2006) study was conducted in higher education, these findings may be relevant in other levels in educational systems.
To gain more knowledge and understand about the essence behind high-quality group work, Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) turned their focus toward students’ experiences and conceptions of group work in higher education. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating their students’ points of view and how the students assess working in groups. Do the students’ appreciate group projects or do they find it boring and even as a waste of time? Would some students prefer to work individually, or even in “the other group?” The study was a part of a larger research project on group work in education and only a small part of the data corpus was analyzed. Different critical aspects were identified as important incitements for whether the group work turned out to be a success or a failure. The students’ positive, as well as negative, experiences of group work include both task-related (e.g., learning, group composition, participants’ contribution, time) and socio-emotional (e.g., affiliation, conflict, group climate) aspects of group work. The students described their own group, as well as other groups, in a realistic way and did not believe that the grass was greener in the other group. The same data corpus is used in this article (see under Section The Previous Analysis). According to Underwood (2003) and Peterson and Miller (2004) , the students’ enthusiasm for group work is affected by type of task, as well as the group’s members. One problem that recurred frequently concerned students who did not contribute to the group work, also known as so-called free-riders ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Students are, in general, reluctant to punish free-riders and antipathy toward working in groups is often associated with a previous experience of having free-riders in the group ( Peterson and Miller, 2004 ). To accomplish a favorable attitude toward group work, the advantages of collaborative activities as a means for learning must be elucidated. Furthermore, students must be granted a guarantee that free-riders will not bring the group in an unfavorable light. The free-riders, on the other hand, must be encouraged to participate in the common project.
Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) were also interested in students’ experiences and conceptions of high-quality and low-quality group work in school and how students aged 13–16 describe good and bad group work? Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) show that the students seem to have a clear conception of what constitutes group work and what does not. According to the students, genuine group work is characterized by collaboration on an assignment given by the teacher. They describe group work as working together with their classmates on a common task. The students are also fully aware that successful group work calls for members with appropriate skills that are focused on the task and for all members take part in the common work. Furthermore, the results disclose what students consider being important requisites for successful versus more futile group work. The students’ inside knowledge about classroom activities ended up in a taxonomy of crucial conditions for high-quality group work. The six conditions were: (a) organization of group work conditions, (b) mode of working in groups, (c) tasks given in group work, (d) reporting group work, (e) assessment of group work, and (f) the role of the teacher in group work. The most essential condition for the students seemed to be group composition and the participants’ responsibilities and contributions. According to the students, a well-organized group consists of approximately three members, which allows the group to not be too heterogeneous. Members should be allotted a reasonable amount of time and be provided with an environment that is not too noisy. Hence, all six aspects are related to the role of the teacher’s leadership since the first five points concern the framework and prerequisites created by the teacher.
Näslund (2013) summarized students’ and researchers’ joint knowledge based on experience and research on in the context of shared perspective for group work. As a result, Näslund noticed a joint apprehension concerning what constitutes “an ideal group work.” Näslund (2013) highlighted the fact that both students and researchers emphasized for ideal group work to occur, the following conditions were important to have: (a) the group work is carried out in supportive context, (b) cooperation occurs, (c) the group work is well-structured, (d) students come prepared and act as working members during the meetings, and (e) group members show respect for each other.
From this brief exposition of a selection of research focusing on students’ views on group work, it is obvious that more systematic studies or documentations on students’ conceptions and experiences of group work within higher education are relevant and desired. The present study, which is a reanalysis of a corpus of data addressing the students’ perspective of group, is a step in that direction.
Aim of the Study
The overarching knowledge interest of this study is to enhance the body of knowledge regarding group work in higher education. The aim of this article is to add knowledge and understanding of what the essence behind successful group work in higher education is by focusing on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups , an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work until the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, are of interest.
Materials and Methods
To capture university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, an inductive qualitative approach, which emphasizes content and meaning rather than quantification, was used ( Breakwell et al., 2006 ; Bryman, 2012 ). The empirical data were collected through a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire and a qualitative content analysis was performed ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
Participants
All participating students attended traditional university programs where group work was a central and frequently used pedagogical method in the educational design. In addition, the participants’ programs allowed the students to be allocated to the same groups for a longer period of time, in some cases during a whole semester. University programs using specific pedagogical approaches, such as problem-based learning or case method, were not included in this study.
The participants consisted of a total of 210 students, 172 female and 38 male, from two universities in two different cities (approximately division: 75 and 25%). The students came from six different populations in four university programs: (a) The Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology, (b) The Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program, (c) Social Work Program, and (d) The Bachelor’s Programs in Biology. The informants were studying in their first through eighth terms, but the majority had previous experiences from working in other group settings. Only 2% of the students had just started their first term when the study was conducted, while the vast majority (96%) was participating in university studies in their second to sixth semester.
The teacher most frequently arranged the group composition and only a few students stated that they have had any influence on the group formation. There were, with a few exceptions, between 6 and 10 groups in each of the programs included in this study. The groups consisted of between four to eight members and the differences in sizes were almost proportionally distributed among the research group. The groups were foremost heterogeneous concerning gender, but irrespective of group size, there seems to have been a bias toward more women than men in most of the groups. When there was an underrepresented sex in the group, the minority mostly included two students of the same gender. More than 50% of the students answered that in this particularly group, they worked solely with new group members, i.e., students they had not worked with in previous group work during the program.
To collect data about students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire was constructed. The questionnaire approached the students’ experiences regarding the specific group work they were working in at the time of the data collection (spring 2006), not their experiences of group work in general. The questionnaire contained a total of 18 questions, including both multiple choice and open-ended questions. The multiple choice questions concerned background variables and information about the present group. The seven open-ended questions were designed to gather data about the students’ experiences and perceptions of group work in higher education. The questionnaires were distributed to the different populations of students (some populations studied at the same program) at two universities in Sweden. During the time the questionnaires were completed, the researcher or an assistant was present to answer possible questions. In all, 210 students answered the questionnaire.
The previous analysis
As described above (Section Previous Research of Students’ Experiences) a previous analysis based on the same data corpus revealed that most of the students included in the study found group work to be an enjoyable and stimulating working method ( Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ). The data were analyzed using a qualitative content analysis based on three different research questions. There were two main criticisms of the previous study presented from other researchers. The criticism conveyed applied mostly to the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group and second to the fact that the results were mostly descriptive. To counter this criticism and to elaborate on the analysis, a further analysis was conducted.
The present analysis
The present analysis (or reanalysis) was conducted by using an inductive qualitative content analysis based on three open-ended research questions:
(1) In what ways does group work contribute to your learning?
(2) What positive experiences have you had while working in your present group?
(3) What negative experiences have you had while working in your present group?
Each question corresponds to one aspect of the research’s objective, but together, they might support and enrich each other and unravel new information based on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work. Research question 1, listed above, was not included in the first analysis and is being investigated for the first time in this study, while the other two questions are being reanalyzed. An inductive, qualitative content analysis is applicable when the aim of the research is a description of the meaning or of a phenomenon in conceptual form ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
The analysis was carried out over several steps, following the basic principles of an inductive, qualitative content analysis ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). The steps included three phases: preparation, organizing, and reporting ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Each question was treated as a unit of analysis and was thus analyzed separately. In the preparation phase, the researcher tried to make sense of the data by becoming familiar with the data corpus. In the current study, this included transcription and thorough reading of the answers. An open coding system composed of marginal notes and headings began the second phase, which included organizing the data. This second phase, in turn, included open coding, creating categories, and abstraction. The notes and the headings from the open coding were transferred to coding sheets and then grouped into categories. Categories were formed through the interpretation of the codes that described the same meaning or phenomenon. Finally, an abstraction process began, where a general description of the grouped categories formed an abstraction (see Table 1 ). An abstraction was denominated using the content-characteristic words for this paper: learning, study-social function, and organization . The third phase, reporting , addressed the presentation of the process of analysis and the results.
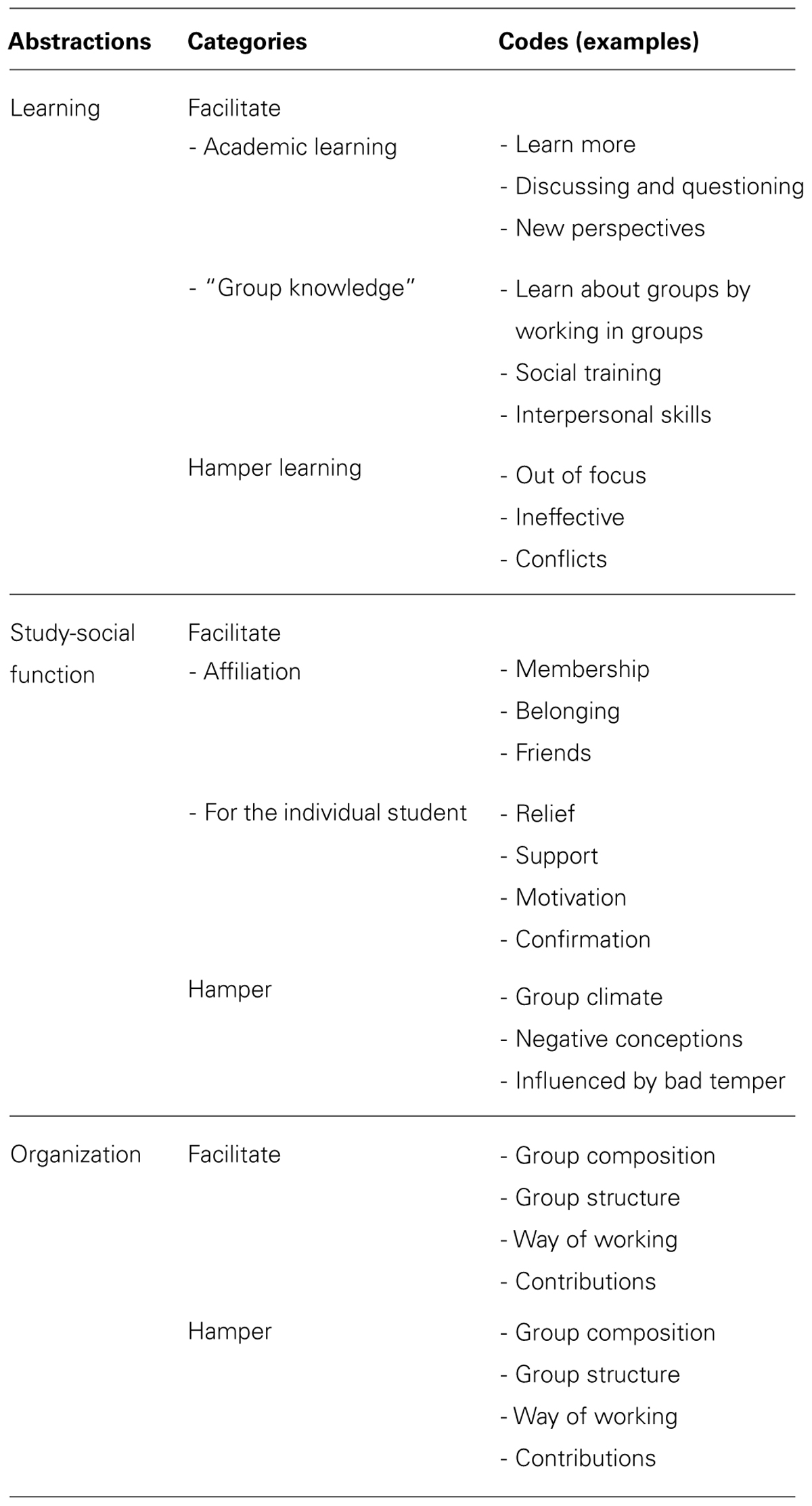
TABLE 1. Examples from the organization phase of the coding process.
The final aim of this study is to present the phenomenon studied in a model or conceptual map of the categories ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). In following these procedures, we aim to expand our understanding of the existing work and to counter the second part of the criticisms, which included criticisms stating that the results were mostly descriptive in nature. To counter the criticisms regarding the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group, the qualitative abstraction that emerged from the qualitative content analysis was compared to background information by using SPSS. Three background variables were used: gender, cities, and programs.
Ethics and Quality
The ethical principles provided by the British Psychology Society have formed a guideline [ British Psychology Society (BPS), 2006 ] for the present study. The ethical principles, which emphasize the concern for participants’ interest, have been applied throughout the study [ American Psychological Association (APA), 2002 ; British Psychology Society (BPS), 2004 ; Barett, 2007 ]. To facilitate trustworthiness, a thorough description of the analysis process has been presented ( Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Translated citations are also included to increase trustworthiness.
As described above, the analysis resulted in three abstraction emerging: learning, study-social function , and organization . Each abstraction includes both a positive variant (i.e., facilitating learning, study-social function, and/or organization) as well as a negative alternative (i.e., hampering learning, study-social function, and/or organization). The results will be presented in three different sections, with each section corresponding to one abstraction. However, we would like to call attention to the fact that one fifth (20%, including missing value 8%) of the students included in this study did not perceive and/or mention any negative experiences at all in their present group. From a general point of view, there is no difference with respect to gender or city regarding the distribution of positive and negative experiences concerning the abstractions, neither concerning different programs nor the distribution of negative experiences (all p > 0.05). In contrast, there is a difference between the various programs and the distribution of positive experiences (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). The students from the social work program display a higher amount of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with the other programs.
The majority of the students (97%) responded that working in group somehow facilitated learning, academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both. They learned more or different things when working in groups than they would have if working alone. By discussing and questioning each other’s points of view and listening to their fellow students’ contributions, thus obtaining different perspectives, the participants experienced an enhanced academic learning, compared to working alone. “I learn much more by working in groups than working individually. I obtain more through interaction with the other group members.” Academic knowledge is not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gain advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work in group courses strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus learning about groups by working in groups. “Through practical knowledge demonstrate several of the phenomena we read about in theory (group psychology and sociology).”
The results show no difference when considering either gender or city. However, when comparing the four programs included in the study and the types of learning, a difference occurs (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). A division into two parts seems to generate the difference. On the one hand, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program emphasize academic knowledge. On the other hand, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities single handed, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning.
Even though the participants did not expressly report that group work hampered learning, they often mentioned that they perceived group work as being ineffective due to loss of focus and the presence of conflicts, thereby hampering conceivable learning. One respondent stated, “that you sometimes are out of focus in the discussion and get side-tracked instead of considering the task.” Another offered the following perspective: “Occasionally, it is too little task related and feels unnecessary sometimes. Individual work is, in certain situations, preferable.” Group work might be perceived as ineffective and time consuming considering long working periods with tedious discussions. One participant stated, “The time aspect, everything is time consuming.” The absence or presence of conflicts in the group affects students’ experiences, and conflicts not handled may influence learning in a negative way. The students perceived that it was difficult to come to an agreement and experience those conflicts and the need to compromise hampered individual learning. Accordingly, the absence of conflicts seemed to be an important incitement for learning. However, fear of conflicts can lead to reduced learning and cause negative experiences, but to a considerably lesser extent than does the presence of actual conflicts. “A great fear of conflicts sometimes raises an oppressive atmosphere.” “Fear of conflicts leads to much not made known.”
A Study-Social Function
Group work also has an important study - social function according to the students. They describe their membership in groups as an important aspect of affiliation. In general, the total number of students at a program is approximately 60–80 or more. In contexts with a large population of students, the smaller group gives the participants an opportunity to feel affiliated with the group and to each other. “Feels safe to have a certain group to prepare oneself together with before, for instance, an upcoming seminar.” The group gives the individual student a platform of belonging, which might serve as an important arena for learning ( facilitate ) and finding friends to spend leisure time with. Many of the participants also reported feeling a positive atmosphere in the group, which is important for the satisfaction of being in the group together with the fellow students.
To be a member of a group may also serve as a function of relief, both academically and socially, for the individual student. The participants reported that many of the tasks assigned by the university teachers are difficult to handle on their own. “The others explain to me. We help one another.” However, the students reported that they helped and supported each other, even if the task did not demand cooperation. “As a student, you get more active. You help one another to extract the groups’ common knowledge. Forward info if somebody is missing.” Being a member of a group also affects students’ motivation to study. They prepare themselves by reading texts and other material before the next group session. Group work may also have positive effects on achievement. Students’ total amount of time and effort on their work may also increase. Through group work, the participants also get confirmation of who they are and what their capacities are.
Being a member of a group also has its downside, which often has to do with the group climate and/or group processes, both of which have multiple and complex features. Many students reported that both the group climate and group processes might be the source of negative conceptions of the group and hamper learning. “Process losses.” The respondents described negative conceptions based on the feeling of not having enough time to get to know each other in the group or being in situations where no cooperation occurred. Other students referred to the fact that the group’s life is too long, which may lead to group members not only wearing each other out, but also having a negative effect on each other’s mood. “Influenced by each other’s mood.” Examples of negative experiences are process losses in general, including insufficient communication, unclear roles, and problems with one group member. As mentioned above, the students from the Social Work Program display a higher number of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with students from the other programs.
Organization
O rganization concerns the structure of group work and includes different aspects, all describing group work from different angles. The aspects are relevant no matter how the participants perceive the group work, whether as positive or negative. Unlike the other two abstractions (learning and study-social function), organization includes the same aspects no matter what the experiences are, namely group composition , group structure , way of working and contributions.
Whether the group is composed in a homogeneous or heterogeneous way seems to be experienced in both a positive and negative sense. A well-thought-out group composition , including both group size and mix of members, is essential. A just large-enough group for the task, consisting of a population of members that is not too heterogeneous, facilitates a joyful experience and learning. A homogeneous mix of members might be perceived as positive, as the students feel that they have similar life situations, opinions, and skills, thereby causing positive conditions for collaboration within the group. Conversely, in a group with a heterogeneous mix, different members contribute with different knowledge and/or prior experiences, which can be used in the group for collective and collaborative learning. “Good group composition, distribution of age groups that leads to fruitful discussions.”
An additional facilitating prerequisite is that the group develops adequate ways of working together, which includes a well-organized group structure . Well-working groups are characterized as having developed adequate ways of working together, while groups that work less well together lack a developed way of cooperation. “Well-organized working group with clear and distinct rules and structure.” Preparation and attendance for group work are aspects mentioned as facilitating (and hampering) incitements. Group work in educational settings sometimes entails that you, as a student, are forced to read and learn within a certain period of time that is beyond your control. Some participants find the pressure positive, hence “increase the pressure to read chapters in time.” The members’ contribution to the group is also a central factor for the students’ apprehension of how the group works. This is, in short, about how much each member ought to contribute to the group and to the work. Groups considered to be well-working are ones where all members contribute to the group’s work, but the content of the contribution may vary according to the single member’s qualifications. “We work well together (most of us). Everybody participates in different ways and seems committed.” “Good, everybody participates the same amount. We complement each other well.”
The same prerequisites can lead to the reverse result, i.e., hampering learning and stirring up negative experiences. If the group members are too identical (a homogeneous group composition ), it might lead to a lack of opinions, which several participants perceived as being negative. “That we do not get a male perspective about the subject. We are all girls, at the age of 20, which also means that we have pretty much the same experiences that may be seen as both positive and negative. The negative is the lack of opinion.” If the group is considered to be too small, students seems to find it troublesome, as the relationships are few, but there are also few people who are available to handle the workload allotted to the group. Nevertheless, a group that is too large could also lead to negative experiences. “It is far too large a group.”
A lack of group structure might lead to a lower degree of satisfaction with the group’s way of working . A commonly expressed point of view seen in the students’ answers involved the occurrences of when all members did not attend the meetings (absence). In these cases, it was also viewed that the work in the group often was characterized as unstructured. “Sometimes a bit unclear structures, some students have difficulties with coming in time.” Not attending or coming unprepared or badly prepared to the group work is other aspect that is commented on. “Low degree of fellowship, punctuality is a problem, an insecure group.” Some students find it frustrating to prepare for a certain time decided that is beyond their control. “A necessity to read certain chapters within a specific period of time is never stimulating.”
One characteristic of groups that are not working well is that contribution varies among the members. In group work, students with different levels of ambition are assembled, which may result in different levels of interest and commitment, as well as differences in the willingness to take on responsibilities or part of the workload of the group’s work. Some members are active and do much of the work, while others barely contribute at all. “Some don’t do anything while others pull the heaviest burden. Two out of three prepare before the meeting, the rest think that they are able to read during the group work and do not supply the group with anything else other than delays and frustration.” A common answer seen in the questionnaires that concerns negative experiences of group work as they relate to contribution is: “Everybody does not contribute just as much.” or “There is always someone who just glides along and doesn’t take part.”
Summary of the Results
The results are summarized in a model illustrating the relationship between abstractions (i.e., learning, study-social function, and organization) and result (i.e., enhanced or reduced learning), as well as positive or negative experiences (see Figure 1 ).
FIGURE 1. A model illustrating the relationship between abstractions and result .
The figure shows that all three abstractions may facilitate or hamper learning as well as the experiences of group work. To piece together, the difficult and extensive jigsaw puzzle concerning why some group work result in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases the result is the reverse is still not solved. In this article, we propose that the prerequisites learning, study-social function, and organization influence learning and experiences of working in group, thus, providing additional pieces of information to the jigsaw puzzle (Figure 2 ).
FIGURE 2. Pieces of jigsaw puzzle influence learning and experiences.
The current study focuses on university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view, as well as how the students’ assess learning when working in groups. The analysis resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations. Each abstraction also included a positive and a negative variant. In other words, all three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work.
Learning in Group Work
The result shows that the majority of the students (97%) experience that working in group facilitated learning, either academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both, accordingly confirming previous research ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to the students, they learn more or different things when working in groups compared with working individually. Academic knowledge was not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gained advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work might strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus the students were learning about groups by working in groups. This implies that group work, from a learning perspective, serves several functions for the students ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Group work also seems to have an important study-social function for the university students, hence confirming that group work serves more functions than just being a pedagogical mode.
Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare seem to be highly important, and may even be essential prerequisites for learning. Accordingly, group work functions as both as an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities), and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement), or both, for the students ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). Moreover, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Program for Human Resources seem to use group work more as means for obtaining academic knowledge. In contrast, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities alone, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning, thus using group work as an objective, as a means, or as a combination of both. One interpretation might be that the type of task assigned to the students differs in various programs. This can be valid both concerning the purpose of group work (group work as objective or as the means), but also arrangement (working in a group or as a group; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Another possible explanation might be that the main emphasis in the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the Program for Human Resources is on product and academic knowledge, while in the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program, the process is more articulated and demanded. However, this is only speculation and further research is needed.
Even though the participants did not explicitly state that group work hampered learning, they mentioned that they perceived group work to be ineffective due to the loss of focus and/or the presence of conflicts with other group members, thereby hampering conceivable learning. This may also be an effect of the purpose or arrangement of the group work ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Experiences of Group Work
The results revealed that several aspects of group work are important incentives for learning. In addition, this study revealed students’ experiences of group work (i.e., facilitating or hampering positive/negative experiences), which is in line with the previous studies on students’ experiences of working in groups ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Group composition, group structure, ways of working, and participants’ contributions are aspects put forward by the university students as either facilitating or hampering the positive experience of group work ( Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Several of the aspects bear reference to whether the group members work in a group or as a group ( Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, utilization of the group’s competence, and includes problem solving and reflection. All group members are involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). According to the results, not all groups are working as a group but rather working in a group, which, according to Granström (2006) , is common in an educational setting.
Due to problems with group composition, members’ contributions, and group structure, including rules and ways of cooperation, some students end up with negative experiences of group work. Additionally, the university students allude to the fact that a well-functioning supportive study-social context is an essential prerequisite not only for positive experiences of group work, but also for learning ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Both working in a group and working as group might be useful in different parts of the group work ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ) and cause learning. Hence working in a group causes cooperative learning based on social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) while working as group causes learning benefits through collaboration with other group members. Although both approaches might cause positive or negative experiences, a conceivable interpretation is that working as a group has a greater potential to enhance positive experiences. The findings suggest a need for further research to fully understand why some group work causes positive experiences and other instances of group work cause negative experiences.
The findings in the current study develop the findings from Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) . First, it shows that it is possible to assemble all groups in to a joint research group (see below). Second, a thorough reanalysis, using an inductive qualitative content analysis, resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations as either facilitating or hampering learning, and experiences.
Methodological Considerations
There are some limitations in the current study and most of them have to do with the construction of the study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire. First, the questions do not discriminate between (a) the type of group work, (b) the purpose with the group work, (c) the structure of the group work (i.e., extent and/or time); or (d) ways of working in the group (i.e., cooperation or collaboration). Second, the design of the questionnaire does not facilitate comparison between the populations included in the group. The questionnaire treated group work as one activity and did not acknowledge that group work can serve different functions and include various activities ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). This simplification of the phenomena group work causes criticism concerning whether or not it is possible to assemble these populations into a joint research group. An elaborated description of the analysis process and the comparison to three background variables has been used to counter this criticism. The thin results from the comparison, indicate that based on the question used in the study-specific questionnaire, it is possible to assemble the results into a corpus of joint results.
Conclusion/Concluding Remarks
The results indicate that most of the students’ experienced that group work facilitated learning, especially concerning academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that serve as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work. By listening to the university students’ voices and elucidating their experiences and conceptions, we have been able to add new knowledge and understanding of what the essence is behind successful group work in higher education. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, can be of use for further development of group work as a pedagogical practice.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Ph.D. Faculty Program Director, Charlotta Einarsson, for her contribution to the design of this study and contribution to early stages of the data analysis and manuscript.
American Psychological Association (APA). (2002). The Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct . Available at: http://www.apa.org/ethics/code2002.html
Baines, E., Blatchford, P., and Chowne, A. (2007). Improving the effectiveness of collaborative group work in primary schools: effects on science attainment. Br. Educ. Res. J. 33, 663–680. doi: 10.1080/01411920701582231
CrossRef Full Text
Barett, M. (2007). “Practical and ethical issues in planning research,” in Research Methods in Psychology , eds G. Breakell, S. Hammond, C. Fife-Schaw, and J. A. Smith (London: Sage Publications), 24–48.
Baron, R. S. (1986). Distraction-conflict theory: progress and problems. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 19, 1–40. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60211-7
Bennet, N., and Dunne, E. (1992). Managing Classroom Groups. Hemel Hempstead: Simon & Schuster Education.
Blatchford, P., Kutnick, P., Baines, E., and Galton, M. (2003). Toward a social pedagogy of classroom group work. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 153–172. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00078-8
Breakwell, G. M., and Hammond, F., Fife-Schaw, C., and Smith, J. A. (eds). (2006). Research Methods in Psychology . London: Sage Publications.
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2004). Code of Conduct, Ethical Principles, and Guidelines . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/document-download-area/document-download.cfm?file_uuid=6D0645CC-7E96-C67F-D75E2648E5580115&ext=pdf
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2006). Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/the-society/code-of-conduct/code-of-conduct_home.cfm
Bryman, A. (2012). Social Research Methods . Oxford: University Press.
Cantwell, R. H., and Andrews, B. (2002). Cognitive and psychological factors underlying secondary school students’ feeling towards group work. Educ. Psychol. 22, 75–91. doi: 10.1080/01443410120101260
Elo, S., and Kyngäs, H. (2007). The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 62, 107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x
Pubmed Abstract | Pubmed Full Text | CrossRef Full Text
Galton, M., and Williamson, J. (1992). Group Work in the Primary Classroom . London: Routledge.
Galton, M. J., Hargreaves, L., and Pell, T. (2009). Group work and whole-class teaching with 11–14-years-old compared. Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 119–147. doi: 10.1080/03057640802701994
Gillies, R. M. (2003a). The behaviours, interactions, and perceptions of junior high school students during small-group learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 95, 137–147. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.137
Gillies, R. M. (2003b). Structuring cooperative group work in classrooms. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 35–49. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00072-7
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2010). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning: Issues of implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 26, 933–940. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2009.10.034
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2011). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning (CL): a two-year follow-up. Teach. Educ. 1, 63–78. doi: 10.1080/10476210.2010.538045
Graneheim, U. H., and Lundman, B. (2003). Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ. Today 24, 105–112. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001
Granström, K. (2006). “Group phenomena and classroom management in Sweden,” in Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice, and Contemporary Issues , eds C. M. Evertson and C. S. Weinstein (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 1141–1160.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2008). A scheme for understanding group processes in problem-based learning. High. Educ. 55, 505–518. doi: 10.1007/s10734-007-9071-7
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2010). “Group work is not one, but a great many processes – understanding group work dynamics,” in Group Theory: Classes, Representation and Connections, and Applications , ed. C. W. Danellis (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 153–166.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011a). Research on Group Work in Education . New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011b). “Research on group work in education,” in Emerging Issues in Compulsory Education [Progress in Education. Volume 20 ], ed R. Nata (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 25–44.
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Einarsson, C. (2007). “Is the grass greener in the other group? Students’ experiences of group-work” [“Är gräset grönare i den andra gruppen? Studenters erfarenheter av grupparbete”] [Published in Swedish], in Interaction on the Edge 2. Proceedings from the 5th GRASP Conference , ed. J. Näslund (Linköping: Linköping University).
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Granström, K. (2012). Teachers’ leadership and students’ experience of group work. Teach. Teach. Theor. Pract. 3, 345–363. doi: 10.1080/13540602.2012.629842
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Hempel, A. (2013), Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] . Lund: Studentlitteratur.
Hansen, R. S. (2006). Benefits and problems with student teams: suggestions for improving team projects. J. Educ. Bus. 82, 11–19. doi: 10.3200/JOEB.82.1.11-19
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (1975). Learning Together and Alone. Cooperative, Competitive and Individualistic Learning (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall).
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (2004). Assessing Students in Groups: Promoting Group Responsibility and Individual Accountability . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Kutnick, P., and Beredondini, L. (2009). Can the enhancement of group work in classrooms provide a basis for effective communication in support of school-based cognitive achievement in classrooms of young learners? Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 71–94. doi: 10.1080/03057640902836880
Lou, Y., Abrami, P. C., Spence, J. C., Poulsen, C., Chambers, B., and d’Apllonia, S. (1996). Within-class grouping: a meta analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 66, 423–458. doi: 10.3102/00346543066004423
Mayring, P. (2000). Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 1:2. Available at: http://qualitative-research.net/fqs/fqs-e/2-00inhalt-e.htm_140309
Näslund, J. (2013). “Pupils’ and students’ view on group work” [Published in Swedish: Elevers och studenters syn på grupparbete] in Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] , eds E. Hammar Chiriac and A. Hempel (Lund: Studentlitteratur), 233–242.
Peterson, S, and Miller, J. A. (2004). Quality of college students’ experiences during cooperative learning. Soc. Psychol. Learn. 7, 161–183.
Underwood, J. D. M. (2003). Student attitudes towards socially acceptable and unacceptable group working practices. Br. J. Psychol. 94, 319–337. doi: 10.1348/000712603767876253
Uziel, L. (2007). Individual differences in the social facilitation effect: a review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Person. 41, 579–601. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2006.06.008
Webb, N. M., and Palincsar, A. S. (1996). “Group processes in the classroom,” in Handbook of Educational Psychology , eds D. C. Berliner and R. C. Calfee (New York: Macmillan), 841–873.
Zajonc, R. B. (1980). “Compresence,” in Psychology of Group Influence , ed. P. B. Paulus (New York, NY: Lawrence Erlbaum), 35–60.
Keywords : group work, collaborative learning, cooperative learning, higher education, students’ perspectives, qualitative research
Citation: Hammar Chiriac E (2014) Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work. Front. Psychol. 5 :558. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00558
Received: 30 Mar 2014; Accepted: 20 May 2014; Published online: 05 June 2014.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2014 Hammar Chiriac. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eva Hammar Chiriac, Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, SE-581 83 Linköping, Sweden e-mail: [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Teaching & Learning
When should you use group work?

A fter spending so long teaching children sitting in rows, facing the front, during the pandemic, it wouldn’t be a surprise if some of us had forgotten just how powerful group work can be.
Often teachers find the idea of pupils sitting quietly and working independently more appealing than the noise and activity that comes from group work - not least because we are forever being told that we should be trying to cut down on the distractions that can create excessive cognitive load.
However, we may not need to worry about that quite as much as we might think. In a 2011 study, Femke Kirschner and colleagues show that “the collective working memory effect” means that collaborative learning is likely to be more effective than individual learning when the complexity of the learning material is high.
In other words, when the task is particularly tricky, with multiple aspects and chunks of information, more heads can be better than one.
More on teaching and learning:
- What’s the best way to tackle low attendance?
- Is this the best way to teach writing in KS3?
- When it comes to catch-up, do the children know best?
But, despite these benefits, there is still a time and a place for group work, as a 2019 study by Jimmy Zambrano and colleagues shows.
The researchers set out to determine whether learning in groups is still more effective than individual learning when you take prior knowledge into account. They found that when learners have gaps in their knowledge, collaborative learning is likely to be more effective than individual learning. In this instance, the prior knowledge of one pupil can fill the gap of another.
How teachers can make the most of group work
However, the reverse is true when pupils have the complete prior knowledge needed for a task - in this scenario, individual learning is more likely to be superior to collaborative learning.
So, when planning group work, teachers must first ask themselves if the task is complex enough to warrant collaborative thinking, and then consider the knowledge that each pupil will bring to the task.
If pupils have the prerequisite knowledge and understanding to achieve success individually, then a collaborative task may not be the best choice, as pupils will not need the input from each other - unless the task is particularly complex.
But if you know that pupils’ prior knowledge will have gaps, and in different areas, then a collaborative task is likely to be much more effective than leaving pupils to toil over the task on their own.
In this case, it is important to choose collaborative tasks in which success relies on pupils contributing in different ways, filling each other’s gaps in prior knowledge, effectively cutting down the load on the collective working memory.
Overall, the key takeaway is that if a task is broad and differentiated, with gaps here and there for different pupils, then collaborative learning is likely to be rich and rewarding.
There are, though, nuances to consider around this.
There will always be children who sit in a group, panicked, feeling unable to contribute because of the large gaps in their knowledge. To mitigate against this, teachers could give these children a preliminary task around specific knowledge that will then support them to contribute.
Equally, we shouldn’t throw any pupils into collaborative group work without giving them instructions on how to collaborate effectively and manage shared thinking. This includes how to capture and evaluate each other’s ideas, as well as how to take turns and listen to each other.
If we can do that, then we will help children to develop abilities that will prove valuable not just in group tasks but throughout their lives.
Beth Budden is an assistant headteacher at John Ball Primary School, in south-east London, and a PhD candidate at IOE/UCL. She blogs at [email protected] and tweets @bethbudden
You need a Tes subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content:.
- Unlimited access to all Tes magazine content
- Exclusive subscriber-only stories
- Award-winning email newsletters
Already a subscriber? Log in
You need a subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content, including:.
topics in this article


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hold one another (and be held) accountable. Receive social support and encouragement to take risks. Develop new approaches to resolving differences. Establish a shared identity with other group members. Find effective peers to emulate. Develop their own voice and perspectives in relation to peers. While the potential learning benefits of group ...
The benefits of group work include the following: Students engaged in group work, or cooperative learning, show increased individual achievement compared to students working alone. For example, in their meta-analysis examining over 168 studies of undergraduate students, Johnson et al. (2014) determined that students learning in a collaborative ...
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students' ability to learn is still lacking.
This is a report of the third phase of a research study on students' groupwork. The two earlier phases of the research focused on the assessment and outcome of students' groupwork in general, but at this phase the focus is on Active Learning Classrooms (ALCs). At this phase the author surveyed faculty and students about the effectiveness of ...
Asking students to work in small groups allows students to learn interactively. Small groups are good for: Some benefits of working in groups (even for short periods of time in class) Students who have difficulty talking in class may speak in a small group. More students, overall, have a chance to participate in class.
Group work can be more complicated and may require more time than traditional lectures, but the benefits to transforming a classroom into an active experience can't be undersold. Pushing students to take ownership of their work and an active role in their own learning won't just improve your course, it will help students become independent ...
Define a clear and specific purpose for group work. This is important because it helps us to make decisions every step of the way - who should be working together, how big the groups should be, how we will assess learning, etc.; Determine how groups will be formed.Three of the most common approaches are student-selected groups, random groups, and instructor-selected groups - each with its ...
Group Work That Works. Educators weigh in on solutions to the common pitfalls of group work. Mention group work and you're confronted with pointed questions and criticisms. The big problems, according to our audience: One or two students do all the work; it can be hard on introverts; and grading the group isn't fair to the individuals.
The Importance of Group Work. Group work refers to learning experiences in which students work together on the same task. Group work can help build a positive and engaging learning community through peer learning and teaching. Promoting peer interactions can positively affect learning experiences by preparing students for work beyond the classroom.
This paper will discuss the use of group work in higher education. Keywords: Group work, collaborative learning, higher education pedagogy. Teaching and learning in higher education are changing. Active learning has become an important focus in this time of pedagogical change. While the term encompasses a broad array of practices, collaborative ...
Many instructors from disciplines across the university use group work to enhance their students' learning. Whether the goal is to increase student understanding of content, to build particular transferable skills, or some combination of the two, instructors often turn to small group work to capitalize on the benefits of peer-to-peer instruction.
For many types of group work, the ideal group size is 3-4 students. Exceptions include groups formed for team-based-learning, which works well with 5-7 students, and ensemble practices in the arts, which range widely in group size. STEM-specific studies suggest groups of 3-5. These smaller sizes help ensure that every group member has a ...
2. Break down the work for students ahead of time. Effective group work takes a lot of scaffolding. Don't expect students to know how to divvy up the work on their own. Working together to break down and delegate responsibilities is one of the most challenging tasks for any group, even for adults. Breaking down tasks ahead of time models for ...
The benefits of group work do not stop with the students. Group work gives teachers a fantastic opportunity to monitor and observe as students collaborate. This enables teachers to see their students' growth in action as students apply learning and analyze situations and decisions. Teachers can offer guidance and correction as needed.
Several studies have pointed to the benefits of learning in groups. However, surprisingly little research has been conducted regarding what role relationship-related personality traits play in the effectiveness of this kind of student learning. Such personality factor can potentially buffer the students' effectiveness in groups. The present study focused on attachment orientations—personal ...
Small group learning may be defined as a group of learners demonstrating three common characteristics; active participation, a specific task and reflection. This article provides an overview of small group learning and teaching, describes the characteristics of this form of small group work, benefits, problems, potential causes of less than ...
Group work can be an effective method to motivate students, encourage active learning, and develop key critical-thinking, communication, and decision-making skills. But without careful planning and facilitation, group work can frustrate students and instructors, and feel like a waste of time. Use these suggestions to help implement group work ...
The POGIL method calls for groups of three or four students who work in a team on process-oriented guided inquiry activities in which students construct their knowledge through interactions with others. Traditional POGIL roles for group members are provided below (POGIL, 2016). Manager or Facilitator: Manages the group by helping to ensure that ...
The use of group work in the classroom is one of the most widely researched and implemented teaching approaches in the world. Numerous research studies have shown the benefits of collaborative learning on academic performance, communication skills, and confidence.. However, our understanding of how group work facilitates learning and why group work is only effective in certain situations is ...
Collaborative Learning. Collaborative learning can occur peer-to-peer or in larger groups. Peer learning, or peer instruction, is a type of collaborative learning that involves students working in pairs or small groups to discuss concepts or find solutions to problems. Similar to the idea that two or three heads are better than one, educational ...
Informal group work can be an effective supplement to lecture, allowing learners to process information, and is often an essential part of, or used in conjunction with, classic active-learning techniques (e.g., Tanner et al., 2003 ). Three elements that are particularly important to consider in structuring formal group work are task ...
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in most educational systems, from compulsory education to higher education. The overarching purpose of group work in educational practice is to serve as an incentive for learning. For example, it is believed that the students involved in the group activity should "learn something.".
Group work is important in education because it benefits students in that it helps them to learn about the way that others think. Students are able to learn from each other and share their ideas ...
Abstract and Figures. Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working ...
A fter spending so long teaching children sitting in rows, facing the front, during the pandemic, it wouldn't be a surprise if some of us had forgotten just how powerful group work can be.. Often teachers find the idea of pupils sitting quietly and working independently more appealing than the noise and activity that comes from group work - not least because we are forever being told that we ...