

18CPS13/23 C Programming For Problem Solving Question Papers
Computer graphics opengl mini projects, download final year projects, 18cps13/23 c programming for problem solving – cps vtu question papers.
Download the First-Year Engineering VTU question papers and VTU CBCS notes of C Programming For Problem Solving – CPS (Common to all branches).
| University Name |
| Visvesvaraya Technological University (VTU), Belagavi |
| Branch Name |
| Common to all Branches |
| Semester |
| First-Year Engineering |
| Subject Code and Subject Name |
| 18CPS13/23 C Programming For Problem Solving – CPS |
| Type of Material |
| Semester End Examination VTU Question Papers |
| Scheme of Examination |
| 2018 CBCS Scheme |
| Marks Distribution |
| 40 Marks for Continuous Internal Assessment and 60 Marks for Semester end examination |
Click the below link to download the 18CPS13-23 C Programming For Problem Solving – CPS VTU Question Papers
Dec 2019 Jan 2020, Dec 2018 Jan 2019
Click the below link to download the 17CPS13/23 and 15CPS13/23 C Programming For Problem Solving – CPS VTU Question Papers
Dec 2019 Jan 2020, Dec 2018 / Jan 2019
Click Here to download the 2018 scheme First Year P-Cycle (Common to all Dept.) VTU CBCS Notes
Click Here to download the 2018 scheme First Year C-Cycle (Common to all Dept.) VTU CBCS Notes
Here you can download the 2018 scheme VTU question papers of C Programming For Problem Solving – CPS of First-Year Engineering branch. If you like the material share it with your friends. Like the Facebook page for regular updates and YouTube channel for video tutorials.
Related Posts
Welcome to vtupulse.com, computer graphics and image processing mini projects -> click here, download final year project -> click here.
This will close in 12 seconds

- Problem Solving Through C (BCA) 1st Sem Previous Year Solved Question Paper 2022
- Problem Solving Through C (BCA)
Unlock success in BCA 1st Semester with our comprehensive 'Problem Solving Through C' solved question paper for 2022. Access detailed solutions to previous year questions for effective preparation.
1. What is a flowchart ? Draw a flowchart to find out total number of students in a class who have scored more than 60%.
2. what is a constant discuss different types of constants used in c language., 3. discuss the structure of a c program with the help of an example program., 4. discuss various arithmetic and assignment operators available in c language. give appropriate examples., 5. discuss various looping statements used in c language., 6. what are the different ways to pass parameters to a function explain with the help of examples., 7. how to use switch, break and continue statements in a program give example code., 8. define a function to print ith fibonacci where term i is passed as argument to the function. use this function to print first n fibonacci terms., 9. write a program to find greatest element in each row of a two-dimensional array., 10. how to declare an array (single and double dimensional) how to access individual values in an array how to initialize an array during compile time and run time give appropriate example code., 11. what is a pointer how to use pointers with double dimensional array write a program to print all the elements of a two-dimensional array using pointers., 12. how to all allocate memory dynamically discuss various functions used., 13. discuss the following string handling functions with the help of example code :, 14. write a program to copy a string from one character array to another without using any build-in string handling function., 15. how to use array of structures explain with the help of an example code., 16. how to create, open and close a file in a c program discuss various functions used to write into a file., 17. differentiate between local and global variables., 18. what are date flow diagrams give example., 19. what logical operators are available in c language, 20. what is a union give example., 21. how are structures different from arrays , 22. what is the use of static storage class .
Learn With Studynotes

BCA Degree Problem Solving using C Previous Question Paper

Degree Previous Question Paper for BCA Problem Solving using C
Problem Solving using C Previous Question Papers – Calicut University UG degree course second semester BCA Problem Solving using C old year question papers are available to download.
University : Calicut University
Course : BCA (Bachelor of Computer Applications )
Semester : 2 Semester
Subject : Problem Solving using C
Problem Solving using C Previous Question Paper
From the links below, you can download Degree Problem Solving using C previous question papers for the second semester BCA Degree Course Examination .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
VTU C Programming for Problem Solving Question Papers 1st sem CHEMISTRY_CYCLE 2018 CBCS scheme
18CPS13 Question Paper
VTU C Programming for Problem Solving AUG 2022 Question Paper
C programming for problem solving question papers, vtu c programming for problem solving jan 2019 question paper, vtu c programming for problem solving jan 2020 question paper, vtu c programming for problem solving july 2019 question paper, vtu c programming for problem solving mar 2022 question paper, vtu c programming for problem solving sep 2020 question paper, last updated : monday january 23, 2023.
- VTU last year question papers
- VTU E Learning
- VTU Time Table New
- Model Question Papers New
- VTU Syllabus New
- VTU Results
- VTU Question Bank
- VTU Revaluation Results
- SGPA to Percentage
VTU Updates
- VTU NON-CBCS Results New
- SSP Scholarship 2023 New
- Cloud Computing vtu question papers New
- Machine Learning Syllabus New
- 18CS71-AiML VTU Question Papers New
- Machine Learning VTU Question Papers New
- Web Technology Syllabus New
- VTU change of college Procedure New
- VTU MTech Syllabus New
- VTU MBA Results New
- VTU Notes New
- VTU PhD TimeTable New
- VTU Academic Calendar 2023 Odd Sem
- VTU Updates New
- Infosys Recruitment 2022 New
- Cyber Security Syllabus New
- MBA in USA for Engineering Students New

Problem Solving Through Programming In C
- Formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems
- Translate the algorithms to programs (in C language)
- Test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors
- Implement conditional branching, iteration and recursion
- Decompose a problem into functions and synthesize a complete program using divide and conquer approach
- Use arrays, pointers and structures to formulate algorithms and programs
- Apply programming to solve matrix addition and multiplication problems and searching and sorting problems
- Apply programming to solve simple numerical method problems, namely rot finding of function, differentiation of function and simple integration
| Course Status : | Completed | ||
| Course Type : | Elective | ||
| Duration : | 12 weeks | ||
| Category : | |||
| Credit Points : | 3 | Undergraduate/Postgraduate | |
| Start Date : | 25 Jul 2022 | ||
| End Date : | 14 Oct 2022 | ||
| Enrollment Ends : | 08 Aug 2022 | ||
| Exam Date : | 29 Oct 2022 IST |
| Automatic variables can be accessed within the same block because their scope is always local to the function in which they are declared. | Static variables can be accessed within the same block because their scope is also restricted to the function in which they are declared. | |
| The lifetime of an automated variable is local (limited), and it lasts just until the function is finished running. At that point, the variables are destroyed. | Static variable’s life time is not limited. Since it’s scope is local but the variable will be live (exist) till the program’s execution. | |
| Automatic variables create a new each time when program’s execution enters in the function and destroys when leaves. | Static variable create once, when programme’s execution enters in the function first time, destroys when programme’s execution finishes, they do not again. |
Q3. What is meant by array of structures?
Ans. An array of structure in C-programming is a collection of different datatype variable, grouped together under a single name.
The structural declaration is as follows:

Here, struct is the keyword
tagname specifies name of structure
member 1, member 2 specifies the data items that make up structure.
Q4. What is a pointer ? How is a pointer initialised?
Ans. Pointers : The address of other variables is stored in pointers, which are variables. Our entire data set is kept in the computer’s memory, which is broken up into tiny bytes. Every time we use a variable, it is stored at any memory location because each of these bytes has a unique address.
Initialisation of Pointer Variables
The initialisation of the pointer variable is simple like other variable but in the pointer variable, we assign the address instead of value.
Its system is:

Here in the above example, we have a pointer variable and another is a simple integer variable and we have assigned the pointer variable with the address of the ‘var1’. That means the pointer variable ‘ptr’ now has the address of the variable ‘var1′.
If we want to access the pointer variable, then we have to understand the most important thing that if the ‘*’ asterisk sign is before the pointer variable, this means the pointer variable is now pointing to the value at the location instead of the pointing to location.
Q5. Describe the use and limitations of the function getc.
Ans. The Use of the Function Getc: Both the input-output operations getc and putc use characters. These functions are used for a variety of stream-based input-output operations. To read a character from a stream and move the stream file pointer to the following character in the input stream, use the getc function. To output a character to the output stream, use the putc function.
Limitation of the Function Get: The main drawback getc (), putc () functions are file handling function in C-programming language which is used to read a character from a file (getc) and display on standard output or write into a file (putc).

getc functions is used to read a character from a file. In a C-programme, we read a character as below.

putc function is used to display a character on standard output or is used to write into a file. In a C-programme, we can use putc as below.

Section B: C-Programming Short Question Answer
Q6. What is a data structure? Why is an array called a data structure? Write a program to read a matrix of size mxn and print its transpose.
Ans. An array is a data structure that is designed to store a group of objects of the same or different types. So, they are needed in C programming to store multiple values of same data type. Through arrays, we can represent many instances in one variable.
Array in Data Structure: An array is a linear data structure that collects elements of the same data type and stores them in contiguous and adjacent memory locations. Array work on an index system starting from O to (n – 1), where n is the size of the array.
Program to read a matrix of size m*n and print its transpose

Q7. Describe the three logical bitwise operators what is the purpose of each what types of operands are required by each of the logical bitwise operators?
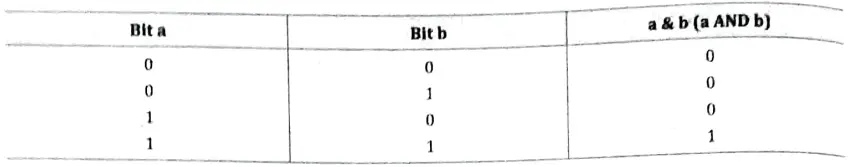
Ans. Bitwise AND Operator : This operator is represented as ‘& and is different than &&, the logical AND operator. The & operator operates on two operands. While operating upon these two operands, they are compared on a bit-by-bit basis. Hence, both the operands must be of the same type (either char or int). The second operand is often called an AND Mask. The & operator operates on a pair of bits to yield a resultant bit. The rules that decide the value of the resultant bit are shown below:
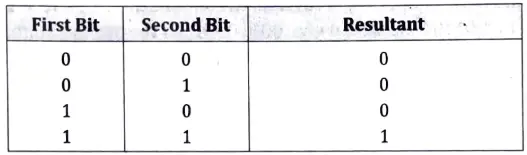
This can be represented in a more understandable form as a ‘Truth Table’ shown below:
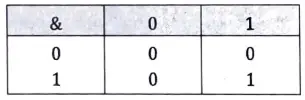
The example given below shows more clearly what happens while ANDing one operand with another. The rules given in the figure are applied to each pair of bits one by one.
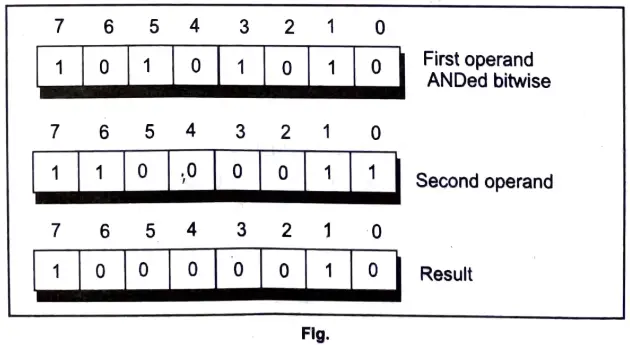
Thus, it must be clear that the operation is being performed on individual bits and the operation performed on one pair of bits is completely independent of the operation performed on the other pairs.
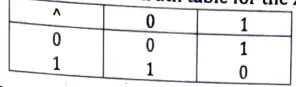
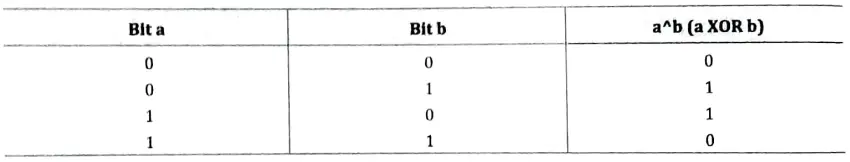
Bitwise XOR Operator : The XOR operator is represented as ’^’ and is also called an exclusive OR operator. The OR operator returns 1, when any one of the two bits or both the bits are 1, whereas XOR returns 1 only if one of the two bits is 1. The truth table for the XOR operator is given below :
XOR operator is used to toggle a bit ON or OFF. A number XORed with another number twice gives the original number. This is shown in the following program :

We can use XOR operator to check whether a given year is leap or not. The following program shows how this can be done :

Bitwise OR Operator : Operator is represented as ‘|’. The rules that give the value of the resulting bit obtained after ORing of two bits is shown in the truth table below :
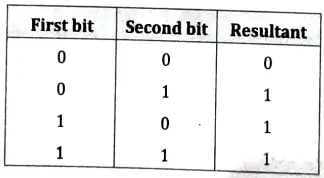
Bitwise OR operator is usually used to put ON a particular bit in a number,
Let us would consider be the bit pattern 11000011.If we want to put ON bit number 3, then the OR mask to be used would be 00001000. Note that all the other bits in the mask are set 0 and only the bit, which we want to set ON in the resulting value is set to 1.
There are three basic operands i.e. AND, OR and NOT. Every complex logical expression can be built using a combination of these operands.
Q8. What is the relationship between an array name and a pointer? How is an array name interpreted when it appears as an argument to a function? How can a function return a pointer to its calling routine?
Ans. Interpretation of Array Name: When an array name appears as an argument to a function, it in fact, passes the base address of the array which is the location of the first element of the array in the memory. That means, the array is passed by address which means that the function it is passed to, can change the values stored in the original array.
For example:

Here, the array name ‘c’ is passed as an argument to function display’ as – display (c [2]);A Function Returning a Pointer: In order for a function to return a pointer to its calling routine, the return type of function should be a pointer to another function. For this, we need to define a type which represents that particular function pointer.
Type def return type (* function_pointer_name) (argument type_1, argument_type_2, ……..,argument _type_n):
This creates a type which represents a pointer for a particular function.

Output: Hello Bachelorexam!!
Section C: C-Programming
Q9. (a) Character string in C are automatically terminated by the null character. Explain how this feature helps in string manipulations.
Ans. Strings are usually one-dimensional array of characters terminated by a null character ‘\0’. In fact, we do not place the null character at the end of a string constant. But the c compiler automatically places the ‘\0′ at the end of the string when it initialises the array. In c, strings are just a sequence of characters accessed via a pointer to the first character:. There is no space in a pointer to store the length so we need some indication of where the end of the string is. Hence, it was decided to indicate this by a null character.
This feature widely helps in string manipulations because programs that manipulate string often need to compute a character string’s length. The function ‘strlen’ in the standard library takes a string as its argument and returns the string’s length expressed as an integer. The length computation starts at the beginning of the string and examine each character in order until it reaches the null character. The function is represented as–strlen (S1);
There are some other functions also that manipulate null – terminated strings:
1. strcpy (S1, S2); – It copies string S2 into string S1.
2. strcat (S1, S2); – It concatenates string S2 onto the end of string S1. (15 x 3 = 45)
3. strcmp (S1, S2); – It returns 0 if S1 and S2 are the same; less than 0 if S1 < S2 and greater than 0 if S1 > S2.
4. strchr (S1, ch); – It returns a pointer to the first occurrence of character ch in string S1
5. strstr (S1, S2); -It returns a pointer to the first occurrence of string S2 in string S1.
(b). Main is a user defined function. How does is differ from other uses-defined functions?
Ans. The main () function is a user-defined function but it is different from other user-defined functions in the following ways:
- 1. The compilers of most of the programming languages are so designed that the main () function constitutes the entry point of the program execution. It defines the point from which the program has to start executing itself though there are many other sub-routines and other user-defined functions included in the program.
- 2. The main () function is the controlling section of our code because even though the control of the program is shifted to the UDF (User Defined Function) during the program execution after a function call from main (), once it’s execution is completed, the control is transferred back to the main () function with some or no return value (as in the case of a void function).
- 3. The main () function provides a platform for calling the first user-defined function in the program.
- 4. It has got its own functionality and structural features with respect to the usage of syntaxes Which cannot be changed by the end user unless he writes his own compiler. But the UDF’s have functions and structures designed by the user or programmer.
- 5. The main () has function definition (the code of a function() but it doesn’t have any function declaration. Though we often use int main () or void main (), these declarations are not compulsory. But a UDF should have such declarations.
- 6. A main () function is a user-defined function in C that means we can pass parameters to the main () function according to the requirement of a program. This function is used to invoke the programming code at the run time, not at the compile time of a program. It provides a platform for calling the first user defined function in the program.
Q10. (a) Compare the working of the function strcat and strncat. Write a program, which read your name from the keyboard and outputs a list of ASCII codes, which represent your name.
Ans. C-Strcat
This function is a concatenation string function. strcat() function concatenates the destination string at the end of the source string. This means it connects two strings. Destination String is appended at the end of source string.
Here is below example:
Source String is: src
Destination String is: city
Syntax for strcat() -strcat(source, destination);

Before concatenation destination string = Bombay
After concatenation destination string = Bombay + Nagpur
C-strncat(): This strncat() function is used when u need to concatenate some portion of one string at the end of another string. Here we can give a number of characters that have to concatenate.
Syntax for strncat(): strncat(source, destination, number_of_character)

Before concatenation destination string = Bombay
After concatenation destination string= Bombay + Na
In the example there are 3 characters from destination string is append to source string.
Program that reads the name from the keyboard and outputs a list of ASCII codes which represent the name:

Enter your name: Bachelorexam
| b | 66 |
| a | 97 |
| c | 99 |
| h | 104 |
| e | 101 |
| l | 108 |
| o | 111 |
| r | 114 |
| e | 101 |
| x | 120 |
| a | 97 |
| m | 109 |
(b) What are the rules that govern the passing of arrays to function? Use recursive function calls to evaluate
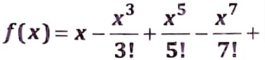
Ans. Rules Governing the Passing of Arrays to Function
In G, there are several times when we are required to pass an array to a function argument. For example, we have a function to sort a list of numbers: it is more efficient to pass these numbers as an array to function than passing them as variables since the number of elements the user has is not fixed and passing numbers as an array will allow our function to work for any number of values.
The rules that govern the passing of arrays to function are as under:
- 1. In G, an array when passed as a function argument is always treated as a pointer by a function.
- 2. Ways to pass an array to a function in Care Formal parameters as pointer, Formal parameters as sized arrays and formal parameters as unsized arrays.
- 3. It is possible to return an array from a function by changing return type of function to pointer of data type of the array.
- 4. To pass an entire array to a function, only the name of the array is passed as an argument such as result=calculateSum(num);
C-Program to use recursive calls to evaluate
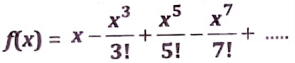
Q11. (a) Explain the meaning and purpose of the following:
(i) Struct keyword
(ii) Typedef keyword
(iii) Size of operator
Ans. (i) Struct Keyword: A user-defined datatype called a structure is used in C to store variables of various data kinds. In C, the word “struct” is used to define a structure. The user must then type the structure’s name after the struct keyword. The data types and the names of the members are then defined inside curly brackets.

‘struct’ keyword is used to create a structure. We can use this data type to store dates of different attributes of different data types.
(ii) Typedef Keyword: In C programming, the typedef keyword is used to give an existing data type a new name. To redefine a term that already exists, use the typedef keyword. When using datatype names in programmes becomes challenging, typedef is used with user-defined datatypes, which function similarly to creating a command alias.
The typedef keyword gives a meaningful name to the existing data type which helps other users to understand the program more easily. It can be used with structures to increase code readability and we don’t have to type struct again and again. The typedef keyword can also be used with pointers to declare multiple pointers in a single statement. It can be used with arrays to declare any number of variables.
(ii) Size of Operator: Size of is a much-used operator in the C. It is a compile-time unary operator which can be used to compute the size of its operand. The result of size of is of the unsigned integral type which is usually denoted by size_t. Size of can be applied to any data type, including primitive types such as integer and floating-point types, pointer types or compound datatypes such as structure, union, etc.
When size of() is used with the data types, it simply returns the amount of memory allocated to that data type. The output can be different on different machines like a 32-bit system can show different output while a 64-bit system can show different of same data types.
Syntax with Parameters: Size of operator in C has various styles for representation:
- 1. Type: Type is the variable passed in the function to represent the type of data type to be used. size of(type)
- 2. Variable-name: variable-name is the variable passed to the function for determining the bytes occupied by the memory.
- size of(variable-name)
- 3. Expression: It is the parameter that is passed to the functionality for determining the bytes in the memory to compute the values for the expression.
size of (expression)
(b) Write a function that receive a sorted array of integers and an integer value and inserts the value in its correct place.
Ans. Function in C that receive a sorted array of integers and an integer value and inserts the value in its correct place

Q12. (a) Define auto and register variables in the content of ‘C’: What is the basic difference between these two variables?
Ans. Auto Variable : It is a variable that is defined with the auto specifier within a function or block and is a member of the automatic storage class. If no storage class is specified, all variables defined within a function or block by default belong to automatic storage class. Automatic storage class variables are exclusive to the block in which they are defined and are removed upon block exit.
The following C program demonstrates the visibility level of auto variables :

In the above program we see three definitions for variable i.
So, there could be more than one variable with the same name if these variables are defined in different blocks. Thus, there will be no error here and the program will compile and execute successfully. The printf in the inner most block will print 3 and the variable i defined in the inner most block gets destroyed as soon as control exits from the block. Now control comes to the second outer block and prints 2 then comes to the outer block and prints 1. Here, automatic variable must always be initialised properly, otherwise we are likely to get unexpected results because automatic variables are not given any initial value by the compiler.
Register Variable : The register specifier declares a variable of register storage class called as register variable. Variables belonging to register storage class are local to the block which they are defined in and get destroyed on exit from the block. A register declaration is equivalent to an auto declaration, but hints that the declared variable will be accessed frequently, therefore they are placed in CPU registers, not in memory. Only a few variables are actually placed into registers, and only certain types are eligible; the restrictions are implementation-dependent. However, if a variable is declared as register, the unary & (address of) operator may not be applied to it, explicitly or implicitly. Register variables are also given no initial value by the compiler.
The following piece of code is trying to get the address of variable i into pointer variable P but it won’t succeed because i is declared register, therefore following piece of code won’t compile and exit with error “error : address of register variable requested.”

Difference between Auto and Register Variables
| ldentifier | Auto. | Register. | |
| Access time | Slower than register. | Fastest. | |
| Storage | Memory/Cache. | CPU register. | |
| No. of variables | Large variables can be Created. | Very few variables can be created. |
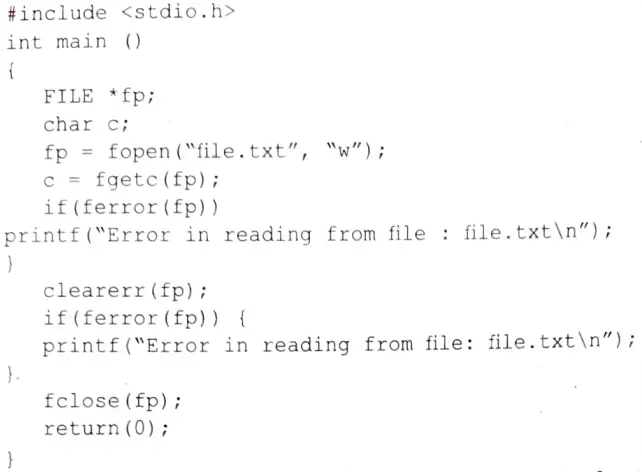
(b) Give examples of using feof and ferror in a program.
Ans. feof() function in C
In C language, when we are using a stream that links with a file, then we are required to determine that we have come to the end of a file. To solve the problem, we have to compare an integer value to the EOE value. Through the feof() function, we determine whether EOF of a file has occurred or not. The prototype of this function is:
int feof(FlLE* filename);
It returns the value zero when end of the file has not occurred, otherwise it returns 1.
Parameters: FILE* filename
Return type: int(0 or 1)
Example:

Ferror() function in C
The C library function int ferror(FILE *stream) tests the error indicator for the given stream. Following is the declaration for ferror() function.

Parameters:
Stream: This is the pointer to a FILE object that identifies the stream.
Return Value: If the error indicator associated with the stream was set, the function returns a non zero value else, it returns a zero value.
Example: The following example shows the usage of ferror() function.
Q13. (a) What do you know about bitwise operator? Explain about some bit wise operators by providing the examples for each?
Ans. Bitwise Operations : Using bitwise operators, operations can be carried out at the bit level in the C programming language. Byte-level operations, which define the bitwise operators’ logical equivalents, the AND, OR, and NOT operators, stand in contrast to bitwise operations. These operators operate on groups of eight bits (referred to as bytes) rather than single bits. This is because a byte is often the smallest addressable memory (i.e., data having a specific memory address) unit. This is true for bitwise operators as well, thus even though they only work with one bit at a time, they are unable to handle inputs smaller than bytes.
Bitwise Operators
C provides six operators for bit manipulation.
1. Bitwise AND “&” : The bitwise AND operator is a single ampersand: &. It is just a representation of AND which does its work on the bits of the operands rather than the truth value of the operands. Bitwise binary AND does the logical AND (as shown in the table below) of the bits in each position of a number in its binary form.
For instance, working with a byte (the char type): 0
The most significant bit of the first number is 1 and that of the second number is also 1 so the most significant bit of the result is 1; in the second most significant bit, the bit of second number is zero, so we have the result as 0.
2. Bitwise OR “|” : Similar to bitwise AND, bitwise OR (inclusive or) is applied to only operators at the bit level. Its result is a 1 if one of the either bits is 1 and zero only when both bits are 0. It symbol is “ | ” which can be called a pipe.

3. Bitwise XOR “^” : The Bitwise xOR (exclusive or) performs a logical XOR function, which is equivalent to adding two bits and discarding the carry. The result is zero only when we have two zeroes or two ones. XOR can be used to toggle the bits between 1 and 0. Thus, i = i^1 when used in a loop toggles its values between 1 and 0.
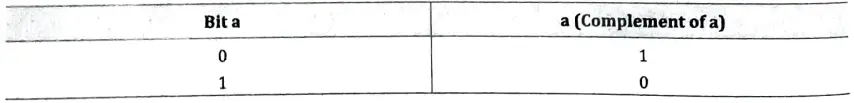
4. Bitwise NOT “~” Jone’s complement (unary) : The one’s complement (~) or the bitwise complement gets us the complement of a given number. Thus we get the bits inverted, for every bit 1, the result is bit 0 and conversely for every bit 0, we have a bit 1. This operation should not be confused with logical negation “!”.
5. Shift Operators : There are two bitwise shift operators. They are :
(a) Right Shift Operator : The symbol of right shift operator is ‘>>’, For its operation, it requires two operands. It shifts each bit in its left operand to the right. The number following the operator decides the number of places the bits are shifted (.e. the right operand). Thus, by doing ch >> 3, all the bits will be shifted to the right by three places and so on.
Example : If the variable ch contains the bit pattern 11100101, then ch >> 1 with produce the result 01110010 and ch >> 2 will produce 00111001.
Here blank spaces are generated simultaneously on the left when the bits are shifted to the right When performed on an unslgped type, the operation performed is a logical shift, causing the blanks to be filled by 0s (zeros). When performed on a signed type, an arithmetic shift is performed, cuSing the blank lo be filled with the sign bit of the left operand, Right shift can be used to divide a bit pattern by 2.
(b) Left Shift Operator : The symbol of left operator is ‘<<‘, It shifts each bit in its left-hand sperand to the lett by the number of positions indicated by the right-hand operand. It works opposite to that of the shit operator, Thus by doing ch << 1 in the above example, we have 11001010. Blank spaces generated are filled up by zeroes as above. Left shift can be used to multiply an integer in multiples of 2.
6. Bitwise Assignment Operators : C provides a compound assignment operator for each binary arithmetic and bitwise operation (i.e. cach operation which accepts two operands). Each of the compound bitwise assignment operators perform the appropriate binary operation and store the result in the left operand.
The bitwise assignment operators are as follows :

(b) Define a macro that receives an array and the number of elements in the array as arguments. Write a program using this macro to print out the elements of an array.
Ans. Macro Defining the Array
A marco is a piece of code in a program that is replaced by the value of the macro. Marco is defined by #define directive. Whenever a macro name is encountered by the compiler, it replaces the name with the definition of the macro. Macro definitions need not be terminated by a semi-colon(;).
A macro that receives an array and the number of elements in the array as arguments is defined as:
Program in C using macro to print out the elements of an array

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
EnggTree.com
Your Success is our Mission
- Question Papers

CS3251 Programming in C Question Papers 2021 Regulation
- 2021 Regulation
Share with Your Friends:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
CS3251 PC Question Paper
We are providing the CS3251 Programming in C Question Papers ( First and are Exclusively Available on our Website ) below for your examination success. use our Materials to score good marks in the examination. Best of Luck.
| Regulation | |
| Subject Code | |
| Subject Name | |
| Semester |
CS3251 Programming in C Previous Year Question Papers Download Links :
| CS3251 Programming in C | Apr May 2022 Question Paper | |
| CS3251 Programming in C | Nov Dec 2022 Question Paper | |
| CS3251 Programming in C | Apr May 2023 Question Paper | |
| CS3251 Programming in C | Nov Dec 2023 Question Paper |
CS3251 Programming in C Other Useful Links :
| CS3251 Programming in C Syllabus | |
| CS3251 Programming in C Question Papers | |
| CS3251 Programming in C Lecture Notes | |
| CS3251 Programming in C Two Mark Questions | Coming Soon |
| CS3251 Programming in C Question Bank |
Search Terms :
cs3251 programming in c question paper,
cs3251 programming in c question papers pdf,
cs3251 programming in c question papers pdf download
cs3251 pc question paper,
cs3251 programming in c nov dec 2023 question paper,
cs3251 programming in c apr may 2023 question paper,
cs3251 programming in c jan 2024 question paper,
cs3251 last sem question paper pdf download,
cs3251 previous year question papers
cs3251 programming in c qp pdf,
cs3251 pc qp,
cs3251 pc qp download
cs3251 pc qp pdf
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Stories
Cec365 wireless sensor network design question papers 2021 regulation, ce3003 prefabricated structures question papers 2021 regulation, cw3551 data and information security question papers 2021 regulation.
- September 2024
- August 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- January 2022
- November 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- November 2019
- Academic Performance
- AU Syllabus
- Duplicate Certificate
- Internal Marks
- Malpractice
- Notes & QP
- Recent Notifications
- Transcripts
- WH (With-Held)
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org

Programming in C (CS8251) Notes, Question Papers & Syllabus
APR/MAY 2023 EXAMS
| NOTES/QB | MATERIAL |
| QN BANK | |
| NOTES | |
| QN’ PAPERS | |
| SYLLABUS |
Engineering Graphics (GE3251) [EG] Notes, Question Papers & Syllabus
Basic electrical, electronics and instrumentation engineering (be3252) [beeie] notes, question papers & syllabus, electric circuit analysis (ee3251) [eca] notes, question papers & syllabus.
Trusted by 1.7 Million Students & 25,000+ Faculty Members - Download App
- C Data Types
- C Operators
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
- C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
- C Interview Questions
AKTU (UPTU) Previous Year Solved Papers | C Programming
This article contains the previous year papers of AKTU for the subject of Fundamentals of C Programming .

Fundamentals of Programming with C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2016-17 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2015-16 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A
- AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B
Register Here for Free
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- How to Delete Discord Servers: Step by Step Guide
- Google increases YouTube Premium price in India: Check our the latest plans
- California Lawmakers Pass Bill to Limit AI Replicas
- Best 10 IPTV Service Providers in Germany
- 15 Most Important Aptitude Topics For Placements [2024]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
B.C.A study
Bca full study material for mgkvp university, c programming previous year paper.
B.C.A. Second semester
Examination, 2019
First paper
( C Programming )
Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 75
Note: Attempt any five questions. All question carry equal marks.
Note: The answer to short answer type questions should not exceed 200 words and the answer to long answer type questions should not exceed 500 words .
1. (A) What is an array? What are the merits and demerits of array in C? Differentiate between one dimensional and two dimensional arrays with suitable example.
(B) write a program to compute the sum of diagonal elements of a square matrix.
2. (A) write a program to find the maximum of an array.
(B) Explain the following briefly :
(i) Sorting (ii) Memory representation of array
3. (A) What is the difference between the function malloc() and calloc()?
(B) What is a pointer in reference to C language? How do you declare pointers? Explain using a suitable example.
4. (A) Explain the term “calling function by reference”. How do you declare pointers? Explain using a suitable example.
(B) Write a program to read two integer X and Y and swap the contents of the variable x and Y using pointers.
5. (A) what is a structure? Explain the components of a structure.
(B) what is the difference between a structure variable and a union variable? What are the difference between structure and array?
6. (A) Write a short notes on nested structure.
(B) What are embedded structure? Give an appropriate example for embedded structure.
7. (A) Write C program to implement the following library function in C.
(i) Strcpy (ii) strcat
(B) Write a program inn C that takes a string as input and find out the frequency of each character in the string.
8. (A) what do you understood by built-in-function? How are they different from user defined function?
(B) Discuss basic file handling function.
year – 2017
Examination, 2017
Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 75
- (A) How we can access elements of one dimensional array? Write a program in C language to illustrate operation of an array.
(B) Write a program to short the elements of an array.
2. (A) What are the characteristics of two-dimensional array?
How we declare a two dimensional array in C language ?
Explain with an example.
3.(A) What is the role of indirection operator? How we can
define and declare pointers in C language?
(B) Write a program in C language to demonstrate the concept of pointers in C.
4.(A) What is dynamic memory allocation? Mention the limitation of static memory allocation also. Explain mallo ( ) and calloc( ) function .
(B) Mention the difference between “ call by value” and “call by reference” by writing a C program.
5.(A) In what way is a string different from a character array? Explain with example, how we can define, declare and initialize string in C program.
(B) Write the functionality of strlen( ) and strcpy( ) using C program. Do not use library function.
6. (A) Why we use structure? How we can access member variable ad member function of a structure?
(B) Write C program to demonstrate the use of union.
(C ) Mention the difference between a Union and a structure.
7. (A) Why we use “File in ‘C’ Language? Explain the Operating modes of files.
(B) Explain the following file function with example:
(i) fopen( ) (ii) fclose( )
(iii) feof( ) (iv) fseek( )
8. Write a program in C using a pointers to implement a linked list. Also perform the function of inserting & deleting a mode from it
year – 2016
B.C.A. Second semester
Examination, 2016
- (A) What is “Array” data structure? How can we define one dimensional and two dimensional array.
(B) Write a program in C language to compute addition of two matrix.
2.(A) Explain the row major and column major memeory representation of array. Also mention how we can compute the address of an element in each case.
(B) Write a C program to show how array can be used as a function argument.
3.(A) What is a pointer? How does it help in dynamic memeory allocation.
(B) Write short notes on:
(i) Array and Pointer
(ii) Functions and pointers
4.(A) What is ‘String’? how can we declare and initialize a string variable?
(B) Explain with example the following string function-
(i) Strlen( ) (ii) strcpy( )
(iii) strcat( ) (iv) strcmp( )
(v) strstr
5.(A) Impliment the following string function without using library function :
(i) Copy the string
(ii) compute the length of the string
(iii) Reverse the string.
(B) what is function? What is function definition and function call?
6.(A) What is structure? How can we access element of a structure?
(B) What is union? Mention its advantages.
(C) Mention the difference between structure and union with example.
7.(A) What is pre-process? What is its advantages? Explain any three pre-process in C.
(B) Explain the bit wise AND, OR and NOT operation. Mention the role of shift operators.
8.(A) How do we declare a file in a C program? Explain the opening modes of file.
(B) Explain the following file function with example-
(i) fopen( )
(ii) fclose( )
(iii ) feof( )
(iv) fgetc( )
(v ) fputc( )
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING CPROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C R19 Regulation B.Tech JNTUK-kakinada Old question papers previous question papers download
PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING CPROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C,R19 Regulation, B.Tech , JNTUK,OLD Question papers, Previous ,Question , papers, download, R16, R13, R10, R07
| Sub. Name | Month | Year | Download Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 01 | 2020 | |
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 11 | 2020 | |
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 08 | 2021 | |
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 12 | 2021 | |
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 04 | 2022 | |
| PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C | 09 | 2022 |
If you have any old question paper not updated on our website please send email to [email protected] with question paper as attachment.
Jntuh old question papers click here, for other subject question papers click here, if you don't find something you are searching for contact us.
| Other Subjects R19 Regulation |
|---|
| Other Subjects in Different Regulations |
|---|





COMMENTS
delQP6Write a C function isprime(num) that accepts an integer argument and returns 1 if the argument is a prime or 0 o. herwise. Write a program that invokes this function to generate prime numbers between the giv. 20156Write a c-program using function to check whether the given number is prim. 4 M,VTU ModelQP.
Click the below link to download the 18CPS13-23 C Programming For Problem Solving - CPS VTU Question Papers. Click the below link to download the 17CPS13/23 and 15CPS13/23 C Programming For Problem Solving - CPS VTU Question Papers. Click Here to download the 2018 scheme First Year P-Cycle (Common to all Dept.) VTU CBCS Notes.
Marks: 100 Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each module. MODULE 1 1 a Explain different types of computer. (6Marks) b What is Software? Explain different types of software. (6 Marks) c With a neat diagram explain the basic structure of a computer (8 Marks) OR 2 a Explain a general structure of C program with ...
JettyStudy. Problem Solving Through C (BCA) Problem Solving Through C (BCA) 1st Sem Previous Year Solved Question Paper 2022. Unlock success in BCA 1st Semester with our comprehensive 'Problem Solving Through C' solved question paper for 2022. Access detailed solutions to previous year questions for effective preparation. 1. What is a flowchart ?
This C Exercise page contains the top 30 C exercise questions with solutions that are designed for both beginners and advanced programmers. It covers all major concepts like arrays, pointers, for-loop, and many more. So, Keep it Up! Solve topic-wise C exercise questions to strengthen your weak topics.
Problem Solving using C Previous Question Papers - Calicut University UG degree course second semester BCA Problem Solving using C old year question papers are available to download. University : Calicut University. Course : BCA (Bachelor of Computer Applications ) Semester : 2 Semester. Subject : Problem Solving using C.
This video explained a Discussion of Problem Solving Using C Previous Year Question Papers BCA April 2022 Exam 2020 admission Detailed Discussion Notes QP P...
3rd semester problem solving using c question paper. Other 100% (1) Prepare for your exam. C program 2021. ... Question 1/10 What does a C program to find the area of a circle and square do? Practice quiz. Lecture notes. Date Rating. year. Ratings. Module 1 Problem solving using c. 15 pages. 2021/2022.
Download VTU C Programming for Problem Solving of 1st semester Chemistry Cycle with subject code 18CPS13 2018 scheme Question Papers. ... VTU C Programming for Problem Solving AUG 2022 Question Paper C Programming for Problem Solving Question Papers Download VTU 18CPS13 Aug 2022 Question paper. A d v e r t i s e m e n t.
Learners enrolled: 29073. ABOUT THE COURSE : This course is aimed at enabling the students to. Formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic and logical problems. Translate the algorithms to programs (in C language) Test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors. Implement conditional branching, iteration and recursion.
Section A: C-Programming Very Short Question Answers. Q1. Explain the need for array variables. Ans. As opposed to defining distinct variables for each value, arrays are used to hold numerous values in a single variable. The data type must be specified along with the array name and square brackets [to build an array].
PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C (Common to EEE, ME, ECE, CSE, CSE-CS&T, EIE, IT, ECT, Auto Eng, Min Eng, ... Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any five Questions one Question from Each Unit All Questions Carry Equal Marks 1. a) UNIT-I ... Write a C program to generate Fibonacci series using recursive functions. (7M)
51 M3-R4: PROGRAMMING AND PROBLEM SOLVING THROUGH 'C' LANGUAGE Model Question Paper NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER SHEET only, attached to the question paper, as per the instructions contained therein.
Week 1. Lecture 1 : Introduction. Lecture 2 : Idea of Algorithms. Lecture 3 : Flow Chart and Pseudocode. Lecture 4 : Introduction to Programming Language Concepts. Lecture 5 : Variables and Memory. Week 2. Lecture 6 : Types of Software and Compilers. Lecture 7 : Introduction to C Programming Language.
CS3251 PC Question Paper. We are providing the CS3251 Programming in C Question Papers ( First and are Exclusively Available on our Website ) below for your examination success. use our Materials to score good marks in the examination. Best of Luck. Regulation.
k 0Assignment 12The due dat. for submitting this assignment has passed. Due on 2020-04. 22, 23:59 IST. As per our records you have not submitted this assignment.1) W. 3a) Stringb) Array. ) Characterd) Struc. wers:d) StructureWeek 6Week 7We. Week 11Week 12Lecture 56 : Structure (Co.
Anna University MCQ Q&A, Notes, Question Bank, Question Paper for Programming in C (CS8251) [PC] semester exams. Download App; More Menu. AU News; Notes & QP; Results; Internal Marks; Timetable; Syllabus. Syllabus (R2021) ... PREVIOUS POST Anna University Special Case - Nov/Dec 2022 Examinations. NEXT POST Anna University Internal Marks ...
Paper download link: Paper | Sem 2 | 2014-15 B.Tech. (SEM-II) THEORY EXAMINATION 2014-15 COMPUTER SYSTEM & PROGRAMMING IN C Time: 3hrs Total Marks: 100 Note:- Attempt all questions. Marks are indicated against each question.
7. (a) Write a C program to display the contents of the file in reverse order. [5+5] (b) Write a C program to copy the contents from one file to another file. 8. Write a C program to count no.of characters, spaces, lines, words of a file. [10] 9. (a) Discuss command line arguments in detail with examples. [5+5] (b) Write a short notes on
B.C.A. Second semester. Examination, 2019. First paper. ( C Programming ) Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 75. Note: Attempt any five questions. All question carry equal marks. Note: The answer to short answer type questions should not exceed 200 words and the answer to long answer type questions should not exceed 500 words.
Studying Programming for Problem Solving using C ES1201 at Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Kakinada? ... C Important Questions. 3 pages. 2021/2022. None. 2021/2022 None. Save. Poc Important Questions -1. 2 pages. 2022/2023. ... Question Paper. 24 pages. 2021/2022. None. 2021/2022 None. Save. Ppsc course objectives. 1 page. 2022/2023.
JNTUK B.Tech PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING CPROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING USING C R19 Regulation B.Tech JNTUK-kakinada Old question papers previous question papers download
FYBCS C Programming Sem - I (2021-22) Question Paper - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 1. The document is an internal assessment from the academic year 2021-2022 for a Class FYBCS semester 1 'C' programming subject from Padmashri Manibhai Desai Mahavidyalaya. It contains 4 questions assessing knowledge of 'C' programming concepts like operators ...
The Consortium of NLUs held the CLAT on June 19, 2022, for entry into undergraduate and postgraduate programs. Approximately 10,434 candidates registered for CLAT PG, and the exam was conducted in pen-and-paper format. It serves 2 purposes. Firstly, it is a gateway to enter into prestigious national universities of India for the Masters program.