Top 257 Good Persuasive Essay Topics [Tips & Prompts]

What if your teacher assigned you to write an essay about anything you like? It would excite you at first. You’d consider endless opportunities to express yourself and show your writing skills…
…But then, you start looking for a good persuasive essay idea, and nothing seems to stand out.
Don’t worry:
We have a list of good persuasive essay topics for you! IvyPanda’s team compiled these great ideas that you can explore in detail. Use them for academic writing or public speaking—they would sound convincing either way. And don’t forget to check out our tips on composing a perfect persuasive essay.
Let’s get started and see if you like anything!
- ✋ What Is a Good Topic?
- 📌 Top-12 Topics
- 🎉 Funny Essay Topics
- 🎈 For Elementary Students
- 👩🏫 For Middle & High School
- 🎓 For College
- 🦉 For Higher English
- 🏈 Sports Topics
- 🩺 Health Topics
- 📲 Social Media Topics
- 🎹 Music Topics
- 💖 Love & Family Topics
- ✔ 60 More Topics
- 💁♀️ 6 Tips on Writing
- 📜 5 Writing Prompts

✋ What is a Good Persuasive Topic?
We can start by understanding what some good persuasive topics ideas are. A lot of people think that persuasive writing is the same thing as the argumentative one. They cannot be more wrong.
Argumentative one is a type of writing that presents arguments without trying to convince anyone. Moreover, it shows both sides of a dispute. There are numerous beautiful essay examples that demonstrate it.
Persuasive writing is a piece of academic writing, which attempts to persuade that the presented viewpoint is more legitimate than any other. The word “persuade” derives from the Latin word “persuadere,” which means “to convince.” This type of essay doesn’t only describe a situation. It takes a stand and delivers a point.

You can use a good persuasive essay topic for both writing and speech preparation. Public speaking can become a lot more engaging when you have a convincing title. Here you can find one that can serve as an exceptional speech idea.
A persuasive topic is good if:
- It serves the purpose. You should be able to develop the topic. Check if there is room for discussion and analysis. For that, make sure there are plenty of primary and secondary sources available. It’s a good idea to check it out before picking your topic.
- It’s engaging for you. Remember that it’s you who will have to write your essay. So, pick something that genuinely interests you. Make sure you will be able to write about it with ease.
- It’s relevant to your readers. Always keep in mind the people who will read your paper. Who is your target audience? Pick a topic that resonates with your audience. Choose something that matters to them.
- It’s unique. One of the best things you can do when coming up with ideas is to stay original and fresh. Of course, it’s quite challenging to find a completely unique topic. However, even if it is more or less common, attempt to find an unusual perspective on the issue.

📌 Top-12 Good Persuasive Essay Ideas
- Is the Internet safe for young kids?
- Should we abolish zoos?
- Can animal testing be ethical?
- Is euthanasia a human right?
- Do public libraries need more funding?
- Is green energy reliable?
- Can we remain anonymous online?
- Is gender a social construct?
- How can debt be relieved for college students?
- Is there a point to political debates?
- Did the 2020 pandemic change the world?
- What is better – high school or middle school?
🎉 Funny Persuasive Essay Topics
Writing about something funny and entertaining is always more pleasant. Not only it puts you in a good mood, but also it helps you to train your sense of humor and stay creative. For your audience, it is even more exciting to read something fun.
This list of funny persuasive essay topics ideas will help you to start your essay. Or it can assist with brainstorming and generating your unique funny ideas.
- Girls do not like gossiping more than boys do. It is a widespread belief, but do you think it depends on gender? Or is it a stereotype that we keep perpetuating? If you ask any man if he gossips, the answer will most probably be negative. However, it is not valid. Men gossip as well. The difference is that they don’t consider their conversations as gossiping.
- Why should people eat less junk food? There are so many good reasons why people should eat less junk food. You can start with listing health benefits, the financial aspects of it. Add data about the inability to check sanitary norms and allergy restrictions. It is a straightforward and exciting topic to write about.
- Everyone should know how to cook.
- Why do smokers have more acquaintances?
- Why parents should stop lying about Santa Claus .
- People should live together before getting married.

- The color of your hair does not affect your IQ. There is a common stereotype that your hair color can somehow determine your IQ. This stereotype has been reinforced by Hollywood movies, magazines, and even by some ordinary people. Can it be true? Find some good scientific explanation for the position you hold.
- Why is social media great for you?
- Regular exercise can help you be happy .
- Netflix can help you grow as an individual.
- Why should homework not be given to kids?
- Overprotection can make your child fail in life . Every parent should allow kids to make mistakes. Unfortunately, that is how we learn. Without this valuable experience, we cannot succeed as adults. We will not be able to make crucial decisions because we will be so afraid of failure. Parents should be able to teach their kids that failure is normal because it is a part of life.
- Physical attractiveness can help you succeed .
😊 Good Persuasive Essay Topics
When you are trying to find a persuasive essay topic, it may not work for you. The task is either too simple or way too hard. This list is arranged based on your academic level. Hopefully, it will help you to navigate and find the topic for a persuasive essay.
🎈 Persuasive Essay Topics for Elementary Students
Being able to persuade others is a vital skill. To do that, we need to learn how to express our thoughts and ideas logically and coherently. Your sentences and words should be straight to the point.
These skills should be trained even at elementary school. This list can help you to come up with the topic for the next elementary school essay.

- School uniform is a good idea . If you disagree with this statement, you can easily change it to be what you agree with. There are plenty of reasons why a school uniform is a great idea. First, it teaches kids to obey authority. They will wear uniforms for the rest of their life no matter what professional path they will use. Second of all, it helps to balance economic differences between kids. Some parents cannot afford expensive clothing, while others can.
- School breaks should be longer.
- Watching TV is good for you.
- Why there should be no homework .
- Eating vegetables is good for your health .
- Why every child should be allowed to have a pet . Having a pet lets you experience what it is to be an adult. It teaches you responsibility. If you have a pet, you can share the lessons you have learned.
- Summer and Winter are the best seasons.
- Kids should be allowed to play computer games.
- I should be able to go to bed when I want to.
- Kids should be able to vote.
- My parents should pay me for doing chores.
- Why having a piggy bank can help you in life. Financial education should start at a very early age. Kids should be able to understand the value of money and what it means to save. If you have a piggy bank, you can share what benefits it has for you.
- Students should be able to give grades to teachers.
- Should we get paid for good grades?
- Having a big family has more benefits than disadvantages.
- Cats are better than dogs.
- Students should be allowed to pick their teachers.
- Using a cell phone at school should be allowed .
- Why learning another language is good for you. Do you like traveling? Or watching movies and cartoons? Learning another language can help you to do so while using a foreign language. It also provides you with a competitive edge and an advantage in the future.
- Everyone should have a hobby.
👩🏫 Persuasive Essay Topics for Middle & High School
Middle and high school is a place where you can learn and train the essential life skills. There is learning how to count, write, and communicate with others. Besides all of this, you can learn how to be convincing and persuasive. Essay writing is a great way to do that.
So, if you can choose your essay topic, try to go for a persuasive essay topic.

- Smoking is bad for you .
- The school day should start later in the day.
- Households should be obliged to recycle .
- Books should be replaced with tablets. Books are the things of the past. Having to carry heavy books is not necessary anymore. A tablet can contain hundreds of books. It is also better for the environment and forest preservation. If you agree with this statement, choose this persuasive essay topic.
- The Internet is the best invention of the 20th century . Pretty much everyone will agree with you. A modern world would be so much more difficult without the Internet. It elevates communication to another level and provides information. Some people disagree with these statements. They think that the Internet is not the best invention of the 20th century.
- Smoking should be banned in all public spaces.
- Why city life is better than country life.
- The Internet should be free for everyone. It is a critical component of modern life. Such things as applying for taxes, looking for a job, working are impossible nowadays without access to the Internet. Even applying to university, or for scholarships to support your studies cannot be done without it. Consequently, it should be free.
- Should tattoos be illegal?
- Women should be allowed to breastfeed in public.
- Eating chocolate is healthy .
- Animal dissection is inhumane.
- Cities should have a free bike-sharing.
- Video games promote violence . Video games are sometimes connected to violent actions. Kids who play video games are more likely to engage in intense activity. Elaborate on this view or argue against it.
- Social Media is bad for your self-image.
- Who do you consider your hero, and why?
- Texting while driving should be illegal.
- Why zoos should be banned . Lots of individuals love going to zoos. However, look at it from an ethical perspective. You will see why zoos should be forbidden for a large number of reasons. In this essay, you can give your personal opinion. For example, tell your reader why keeping animals in cages is inhumane.

- Gender divided schools are bad for kids.
- The benefits of having younger siblings.
🎓 Persuasive Essay Ideas for College
Choosing a persuasive essay idea for the college level is a real challenge. We’ve already done the hardest part for you and created a list of interesting topics. See if anything looks persuasive enough for your next paper or a public talk.
- How should Americans solve the gun violence issue in the United States?
- One policy that should be implemented in the educational sector.
- Why should public universities have free tuition?
- The death penalty is an ineffective way to prosecute .
- Hunting is not an ethical hobby. Many people believe that it is not a decent hobby because it makes animals suffer. Sometimes an animal can survive the shot but later on experience a prolonged and painful death. Find arguments that support this point of view. You can think that there is nothing wrong with hunting. Then highlight that love for animals and this hobby are not two mutually exclusive concepts.
- Vegetarianism does not save animals.
- Mcdonalds should not be an official sponsor of any sporting event.
- The world should have free borders.
- Abstract art is not art.
- Online learning is best for students and teachers .
- The importance of equal representation of genders and races in the police.
- Capital punishment should be abolished .
- Churches should be required to pay taxes. This debate continues for decades. A lot of people believe that churches should be stripped of their tax-exempt charity status. One of the reasons is that the Catholic Church is the wealthiest organization in the world.
- Teachers should be paid more .
- Americans should speak more languages.
- Beauty contests are bad for teenage girls’ self-image. This type of competition degrades women to mere sexual objects. Those who are not able to participate in such contests end up being affected as well. They feel that they are not good enough. Explore some other arguments about why beauty contests are not good for teenagers.
- Standardized tests should be banned.
- Why should there be only one currency in the world?
- Pets should be allowed to join children at school.
- Why cyberbullying should become a crime .
🦉 Persuasive Essay Topics for Higher English
College students majoring in English can use one of these topics for their essays. Writing a persuasive speech or paper starts with picking the right idea.
Check out this great list of creative and unusual topics for essay writing. Our ideas can help you to deliver an outstanding result that will pleasantly surprise your readers.
- The question of authority is the focus of The Giver by Lois Lowry.
- Why abortions should be allowed.

- People should be charged for racial slurs.
- Guns should not be allowed on College Campuses .
- Elementary schools should focus on teaching how to type, not handwrite.
- Security cameras at a workplace are an invasion of privacy .
- College football should be banned. It is just too dangerous.
- Parents should never lie to their kids. In this essay, you can explain what happens to kids when their parents lie to them. Later in life, it may create a colossal distrust. You can also talk about common lies parents tell their kids such as Santa, dead pet, or swallowing chewing gum.
- Illegal immigration benefits the American economy .
- Do we live in the society predicted by Ray Bradberry in Fahrenheit 451?
- Should priests be allowed to get married?
- Does the government have a right to choose what it censors?
- How the current tax system overburdens middle-class citizens.
- Religious beliefs do not define a person.
- Being egoistic should be encouraged. Being selfish is usually seen as a negative trait. However, psychologists believe that being selfish can make you a better individual. Find arguments that support this point of view. You can claim that being selfish can help you stay healthy or even have better relationships. There are many good arguments you can make that will persuade your readers.
- Sexual desire does not define human behavior.
- Equal rights between men and women are impossible to attain. Elaborate on the topic expressing this or the opposing view. Provide both arguments and counterarguments, striving to convince your reader.
- Women are better at collaborating and executing than men.
- There is a danger in being neutral.
- Should all residents receive free health care?
🎈 Great Persuasive Essay Topics according to Theme
We organized our topics thematically as well. It could help you to search for the right one as you may have to write a persuasive essay for a specific class.
Maybe you have a passion for music, or sports, or a healthy lifestyle. Then, you can go to a theme you like the most. Select a good persuasive essay topic that works.
🏈 Persuasive Essay Topics about Sports
Who does not like sports? Okay, maybe some individuals do not enjoy it. However, most students choose not to write essays about it.
Do you know why?
Mainly because it is hard to find the topic. It is especially problematic when you want to find a good one. This list will give you some fresh persuasive essay ideas.
- Don’t generalize college athletes . There is a common belief that all college athletes are not very smart. In this essay, you should provide reasoning on why this statement is wrong.

- Cheerleading should also be regarded as a sport.
- Only women should be allowed to train female teams.
- Universities should stop spending so much money on sports programs . This essay topic is another debate in American society. A lot of people believe that spending this amount of money on sports does not make sense. We could redirect this money to academics and financial support for students in need. The best schools in the USA do not have large sports programs, explain why.
- Not every sportsperson can be a good coach.
- Every college athlete should get insurance .
- Women should be allowed to compete against men.
- An issue of homophobia in sports.
- Cheerleaders should wear different costumes because the current ones are sexist.
- Why parents should let their kids play extreme sports . Think about why parents should allow their children to participate in such activities. First, you can write about why kids want to do extreme sports. Second, you can elaborate on why parents do not want to let that. You will be surprised at what you might find.
- Fame is the main factor in getting a sports-related career.
- College athletes should get paid as much as the professional ones .
- Chess should become an Olympic sport.
- Sports help with managing depression and anxiety.
- Michael Jordan is the most successful athlete of all time .
🩺 Persuasive Health Topics
This particular section has some ideas of the persuasive essay topics about health. Each section has about five titles.
Let’s see what health topics you can use:
Medical Persuasive Essay Topics
- Everyone should have a right to euthanasia .
- The importance of talking to kids about sex .
- Healthcare should be free. First and foremost, free healthcare can save millions of lives. So, it creates a foundation for a right and just society. Some of the poorest people cannot afford to pay their medical bills. It creates even more inequality in society.
- Talking about childhood cancer is essential to fight it.
- Why marijuana should not be legalized . There is a popular belief that marijuana is not dangerous. However, some scientists disagree with this statement. In this essay, you can persuade your readers not to support the legalization of the drug. Or you can do the opposite. Convince them that it is not harmful and can be beneficial for your health.

Persuasive Essay Topics on Healthy Lifestyle
- Your eating habits affect your personality.
- Seven harmful effects of junk food .
- The vegetarian diet is the healthiest one.
- Unhealthy foods taste so good because it’s a manipulation. This topic is a funny one, but many people probably had the same type of questions. Why do unhealthy foods taste so good? Not only it pleases our taste buds, but it also triggers brain chemicals to start reacting.
- Poor nutrition and life expectancy connection.
Persuasive Essay Topics on Mental Health
- Misuse of ADHD medication among college students.
- Stigma and discrimination affect gay men’s mental health.
- Does playing music during pregnancy increase a baby’s IQ?
- Playing with Barbie dolls can later manifest in eating disorders . Girls who played with Barbie dolls are convinced that their bodies are not perfect. They feel as if they need to diet. An impossible ideal of Barbie creates a disturbance in body image. Society needs to see that playing with skinny dolls does not cause eating disorders. It increases the risks of having low self-esteem. This essay can provide a fresh look at something as innocent as playing with a doll.
- The stigma associated with mental illness has to be eliminated.
Persuasive Essay Topics on Depression
- The connection between perfectionism and anxiety.
- Teenage Depression is more common than you think . Some individuals believe that teenagers nowadays have very unrealistic expectations. They claim the media and Social Media continuously promote a message about “feeling good.” Many people do not teach their kids vital skills on how to manage their lives under pressure. Find some data that can show how regular the issue is. Prove your point with facts and opinions from trustworthy sources.
- Every school should have a mechanism to help students with mental health issues.
- Recognizing the symptoms, signs, and risk factors of OCD is important .
- The reasons why everyone should have a psychologist. There are plenty of reasons why everyone should see a therapist. An essay can discuss some of them and maybe convince people to start therapy.

📲 Social Media Persuasive Essay Topics
Social Media has a considerable impact on the world we live in. Therefore, in the past years, essay topics about it became increasingly popular.
A Social Media persuasive topic should be intriguing, controversial, and relatable.
- The negative effects of Social Media .
- What makes a successful Social Media marketing plan. Some many different tricks and tips help to make a successful social media marketing plan. However, stick to the essential ones. What you are trying to do and what you want to achieve should be the focus. In the world of marketing, it is called S.M.A.R.T. goals.
- The importance of attention getter in writing an Instagram post.
- Don’t forget to live your life, not only to document it for Social Media.
- Teenagers spend too much time on Social Media . In the modern world, almost everyone has a device. People spend a lot of time looking at the screen. Teenagers spend even more. Explain whether it is a problem or how it can be changed. What are the dangers of spending too much time on Social Media?
- A specific purpose of Social Media.
- The positive effects of Social Media.
- Social Media addiction among older people . You might be surprised, but social media addiction exists even among older people. First, talk about what is considered social media addiction. Then talk about how it can be changed. Why should it be changed?
- The reasons why Twitter is popular among celebrities.
- Social Media opened new possibilities for business.
- The world cannot survive without Social Media.
- Social Media promotes cyberbullying.
- Social Media strengthens relationships between people . Despite a lot of negative effects, one thing remains clear: social media helps people to stay in touch. The world we live in today became much smaller because of social media.
- Social Media and Networking Sites are a great help in your professional development.
- Social Media is a social problem.
- Social Comparison caused by Social Media is something we cannot avoid.
- Social Media Influencers are not celebrities.
- The Internet heavily affects News .
- Social Media should not be allowed in the workplace.

🎹 Persuasive Topics on Music
Everyone loves music—both listening to it and reading about it. Imagine how pleasantly surprised your peers will be if you choose a persuasive essay topic on it. Choose an artist or a genre and get creative.
- Hard Rock music is the music of violence.
- Rap music is not music—it’s poetry. A lot of people believe that rap isn’t music but poetry. Do you agree? If you do, then this topic is excellent for you. Look at the history of rap music. You will find some great arguments that support this view. What was the purpose of the first songs?
- Some people have an addiction to music.
- Depressive songs can be triggering for people with mental issues. Sad music usually goes hand-in-hand with depression. If you aren’t feeling well, it is quite reasonable if you choose sad music. However, researchers say that sad music can worsen your condition, so you should be careful. There are a lot of great experiments that demonstrate this idea and prove this point. Your essay can be quite helpful for those battling with their emotions and feelings.
- Music does not always have a positive effect.
- Kids should not listen to death metal.
- Hip hop dancing is a mainstream American culture now.
- Why music talent shows are so popular in America .
- Kids who listen to hip hop music are more rebellious than the rest. Rap music is heavily scrutinized. Kids who listen to rap and hip-hop may be more rebellious than others. It can happen since that such music often advocates violence and rebellion.
- The Negative view of women in hip hop music videos is outdated.
- The similarities between ballet and hip hop .
- The music can influence our behavior .
- The positive aspects of playing a musical instrument.
- Classical music and intelligence.
- The music reflects society and its authenticity.
- The positive effects of Mozart’s music on babies. There are so many advantages when it comes to listening to classical music. That’s why many parents in the United States start playing classical music to kids at a very early age.

- Blacks express themselves through music for centuries.
- Even plants grow better with classical music.
- Jazz is an extinct music genre.
- Reasons why most people do not like country music.
💖 Persuasive Essay Topics about Love & Family
All we need is love. It is a very famous song, and it is so true. Here’s a list of topics about love and family for you to be able to get inspired.
- Love is more than a set of chemical reactions. What is love? A lot of writers, scientists, philosophers, artists tried to answer this question. According to science, love is no more than a set of chemical reactions in the brain. Can it be true? You can argue that love is more sophisticated than any chemical reaction. Finding arguments that support this viewpoint should not be complicated. Or take the opposite stand.
- Everyone needs love.
- Why men do not understand women.
- It is not a good idea to live together before marriage.
- Hitting kids should be a crime. Children cannot make a connection between their actions and physical. Therefore, any form of aggression to children should become illegal. The only thing they feel is pain, so kids should not be physically punished. You can talk about the short-term and long-term effects of childhood traumas caused by caregivers.
- Every parent should talk to kids about sex.
- Why can people be happy only if they have love in their life?
- Love is the only way we can fight racism.
- Why parents should not drink and smoke in front of their children.
- Are marriage bonds are more reliable than any other relationship?
- The concept of love is different from culture to culture .
- The love between Romeo and Juliet was not mature.
- A love of a woman is different .
- Looking beyond imperfections is essential for success in marriage.
- Sacrifice is an element in family life. To build a happy family, we may need to learn the quality of sacrifice. In your essay, you can talk about why it may be necessary. What does it help to achieve? You can include your life examples and show the benefits of sacrifice.

- The changing landscape of love and marriage .
- Love and marriage are incompatible .
- Can parents leave their kids at home alone before 13 years old?
- Teenagers should have more free time.
✔ 60 More Persuasive Essay Topics
In this section, you can find 60 more persuasive essay topics.
1. Persuasive Essay Topics: UK
Choosing a good persuasive essay topic can be difficult. For UK students and students interested in UK culture, finding this section can be such a relief. These ten topics were waiting for you:
- Why Are UK Universities Better than the ones in the USA’s ones? It is a very subjective idea. Though it has a place to exist. If you think that UK universities are better, develop this idea into a persuasive essay.
- Why are UK musicians so famous in America?
- Brexit will help the UK to prosper.
- Why some believe that Shakespeare didn’t write his plays . You have probably heard this point of view before. However, you do not have to agree with it. You could find good arguments to demonstrate this common belief. Explain your position and why people think this way.
- Scotland’s version of UK history is different.
- The UN and International Peace .
- British and English are not synonyms.
- The history of the Northern Ireland crisis.
- Difficult relationships between the United Kingdom and the EU.
2. Persuasive Essay Topics: Philippines
- The effects of globalization on poverty in The Philippines.
- Death penalty laws in The Philippines are cruel.
- Critical issues in the Philippines should be resolved immediately.
- Benefits of a nationwide smoking ban in the Philippines.
- The quality of education in the Philippines should be higher.
3. Persuasive Essay Topics: Canada
- The impact of immigration on the geography of Canada is exceptional. Did you know that Canada receives more than 200.000 immigrants per year? Discuss how it affects economic geography in Canada. Where do most immigrants decide to reside? What happens to the job market?

- Canadian immigration is marked with a history of discrimination.
- Democratic racism in Canada is apparent.
- Canada is in denial about the issue of gender inequality .
- The most famous Canadian women and their achievements are underappreciated.
4. Persuasive Essay Topics: Social Science
- There is a connection between mental illness and aging.
- There are effects of violent movies on psychology. Absolutely everything that people see and watch affects their psychology. It affects us in one way or the other. Unfortunately, nowadays, violence is one of the most common forms of entertainment. This essay can persuade people to watch less violent movies.
- We have to deal with the social issues of families in poverty .
- Technology positively impacts society.
- There are negative consequences of individualism .
5. LGBT+ Persuasive Essay Topics
- Social problems in relation to the LGBT population is still an issue.
- LGBT labor and employment discrimination issues . Unfortunately, the LGBT community still faces discrimination. Besides showing the state of affairs, try to change your reader’s attitude. Make them see it as a social issue.
- The effects of cyberbullying on the LGBT community are significant.
- There is a Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender discrimination in the Hispanic community.
- The causes of homosexual discrimination in American society .
6. Emotional Persuasive Essay Topics
- The importance of the use of ethos, pathos, logos in essay writing.
- The reasons why we should protect the environment.
- Should older people be allowed to drive?
- Is access to the internet a human right?
- The American dream is no longer attainable.
7. Deep Persuasive Essay Topics
- Should graffiti be considered a form of art?
- Stereotypes of American citizens .
- Why the debate over free education for all students should be over.
- Why is it important to teach Shakespeare in school?
- Art and music therapy should be covered by health insurance.
8. Harry Potter: Persuasive Essay Topics
- Does the sorting hat know more than humans?
- Is there a deeper meaning in Harry Potter and The Sorcerer’s Stone?
- A theme of love and betrayal in J.K.Rowling’s books is prominent. A lot of critics believe that Harry Potter is not about magic but love. It is a recurring theme in the whole series.

- Hogwarts: a home away from home.
- We should discuss the symbolism of deathly hallows more.
9. Fashion: Persuasive Essay Topics
- Eco-friendly clothing is the next type of fashion.
- Why is a style more important than fashion?
- What does your choice of dress tell about you?
- Fashion photography is a form of art, as well.
- What are the concepts of beauty in the fashion industry?
10. Domestic Violence: Persuasive Essay Topics
- We have to take into account a cross-cultural perspective on domestic abuse. Different cultures approach domestic violence with varying levels of tolerance. In multicultural families, it can be a challenging problem to address. In your essay, you should try to explain why, in some places, people tolerate domestic violence. Elaborate on why, in other areas, it is forbidden.
- Domestic violence against women is a prominent problem.
- Domestic abuse against men exists too. Not everyone understands, but domestic violence against men is an issue. However, people discuss it less commonly, and men do not like to share their experiences. Why? They prefer to maintain their sharp facade. However, domestic abuse is damaging to everyone.
- There is significant emotional abuse in low-income families.
- Child abuse is still a problem .
11. Persuasive Agriculture Topics
- How urban agriculture affects the economy .
- The agricultural effects on wild animals.
- Should GMO organisms in farming be allowed?
- The issue of agricultural modernization in third world countries .
- Organic farming should be the only type of farming.
👩🏫 6 Tips on Writing a Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is one of the most common types of academic writing. You, as a student, will be required to master it. The goal is to present a distinct opinion on a topic and illustrate it with arguments and evidence. Hopefully, by the end of this section, you will be able to write a good persuasive essay.

As you already can guess from the name, in the essay, you have to is to persuade (convince) others. Attempts to make people feel and think a certain way. To be able to do that, you need to have a good grasp of logos, pathos, and ethos.
Even heard of it?
A Greek philosopher Aristotle discovered this theory. A good speech that can convince others depends on three elements, which are:
- Logos refers to the part responsible for logical persuasion;
- Pathos refers to the part responsible for emotional appeal;
- Ethos refers to the extent readers are willing to trust the writer.

So, you should determine and implement logos, pathos, and ethos in your essay. You might not be able to use the third one, though. It deals with your social status and reputation.
Now let’s understand what makes a persuasive essay so great:
- Your distinctive position supported by both arguments and counterarguments.
- A compelling style that influences your reader.
- An adequate organization that ensures the natural progression of your argumentation.
📜 5 Persuasive Writing Prompts
In this section, we will give you some good ideas for using both logos and pathos. It is essential to remember about these components if you are writing a persuasive essay. These five persuasive writing prompts will help you to start:
- Immigrants are not a threat to American society. This is such a familiar debate. Some politicians and regular people see immigrants as a threat to American society. Present several facts that argue against the idea. Elaborate on the increase in human capital, innovation, science. Appeal to the fact that America is a country that was built by immigrants.
- The immoral aspect of eating animals. Have you ever heard about the Animal Rights movement? It exists, and it states that causing suffering to animals is immoral. You can argue for or against it. You can say that humans were created to eat meat. Or claim that the Bible says we should be vegetarians. There are many logos and pathos arguments that you can make if you decide to choose this topic.
- Having a lot of friends is impossible. A lot of times, people confuse who is their friend and who is their acquaintance. In this essay, try to find a good definition of who you would call a friend. Friendship requires a lot of time and effort. Is it possible to maintain a lot of friendship relationships?
- Sexual orientation is determined in childhood. A lot of people believe that sexual orientation is determined later in life. However, most LGBTQ+ persons state that it is not valid. They say that their sexual orientation became evident to them even when they were kids. You can develop this argument and include some personal stories of people you know.
- Capital punishment is a crime. In this essay, you can give your opinion about capital punishment. Choose the position you genuinely believe in and support it with evidence. One thing is clear; capital punishment is a susceptible subject. No matter what view you have, you will most probably meet some opposition. Stick to logical arguments and try not to appeal too much to pathos.

Thank you for reading this article! Do not hesitate to share our persuasive essay topics with your friends and fellow students. And leave a comment below—we’d be happy to learn your opinion.
🔗 References
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- Writing Resources: Writing Center Handouts, Hamilton College
- Ten Timeless Persuasive Writing Techniques: Brian Clark, Copyblogger
- How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay, Easy Step-by-Step Guide: Malcolm Gladwell, MasterClass
- Persuasive Essay, Examples and Definition of Persuasive Essay: Literary Devices, Definition and Examples of literary Items
- Persuasive Essay Outline: HCC Learning Web
- How To Write A Persuasive Essay: Writing Guides, Ultius
- Tips To Write An Effective Persuasive Essay: Melissa Burns, The College Puzzle
- Tips for Organizing an Argumentative Essay: Judith L. Beumer Writing Center
- Counterargument: Gordon Harvey (adapted from The Academic Essay: A Brief Anatomy), for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- 60 Persuasive Essay and Speech Topics: K12 Reader
- 434 Good Persuasive Topics for Speech or Essay: My Speech Class
- How to Write Persuasive Essays: Matrix Education
- 31 Powerful Persuasive Writing Techniques: Writtent
- A CS Research Topic Generator or How To pick A Worthy Topic In 10 Seconds: Purdue University
- Topic Ideas Generator: Online Research Library Questia
- English Grammar, Grammar Rules and Tips: Grammarist, English Grammar, Usage, and Style Blog
- How Do I Cite Sources: Plagiarism.org
- Writing Essays: Learning Development, Plymouth University
- Citation Style and Reference Formats: C. Rodkin, Association for Computing Machinery
- Effective Writing Grammar Rules: Grammar Book
- The Basics of Essay Writing: UNSW Current Students
- Share via Facebook
- Share via X
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via email
By clicking "Post Comment" you agree to IvyPanda’s Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions . Your posts, along with your name, can be seen by all users.
Really amazing article. It’s really helpful. Thanks for sharing.
Thanks for the feedback. We really appreciate your opinion!

What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
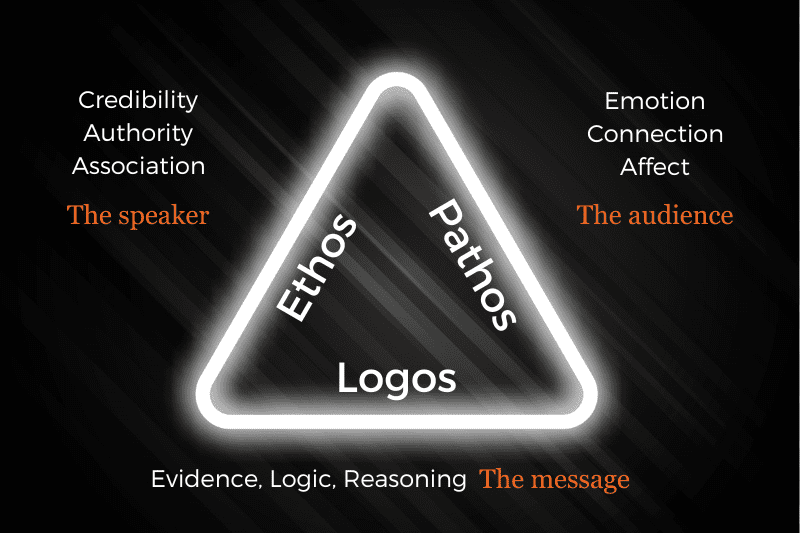
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing is an essential skill, it is useful whether you are selling something, writing for a cause, for business purposes, or even for your class! Persuasive writing can be described as an argument or piece of writing that an author uses to convince his audience of a point or topic. This could potentially be to call the reader to action, or it could merely be to convince the reader of an opinion or view.
Topic & Thesis
The first step in persuasive writing is choosing what you want to write about. Usually, the most natural and most effective topics focus on something specific, rather than an extremely broad topic. More specific topics generally can be explained and supported more easily than extremely broad topics.
After you have determined your topic, you should then develop your thesis. A thesis is the primary argument that your essay will attempt to support. Theses should be arguable points, not facts; for example, if you are selling something, your thesis will be “why you should buy this.”
Click here for a list of Persuasive Writing Topics
The next part of writing effective persuasive essays is choosing your supporting points. Supporting points are the reasons used to prove and support thesis. Support is the largest part of your essay, and it is used to show your reader why your thesis is true. Within these supporting points, you should include facts, logic, expert opinions, and statistics to further your point and thesis. Additionally, you can use emotion evoking stories to attempt to connect with your audience. Research should be done to support your points.
Your supporting points should be mapped out before you begin to write your essay, developing an outline is a good way of doing this. The structure of your supporting points is critical; one supporting point should usually lead to another, although they don’t always have to.
After you have determined your topic and thesis, you should begin to target and make research your audience. In order to convince somebody of something using writing, you must first know the impact the writing will make on that person and you must also understand who you are writing to. For example, one might take a different approach in writing to industrialists about climate change than when writing to college students about the same subject.
Choosing an audience is extremely important, and is a crucial step that many people forget to take into consideration when writing. Many people think that they are writing to everyone when they write persuasively, this may be true for some subjects, like “why breathing oxygen is important,” but for most, there is usually a target that you may not even realize. The reason this step is so important is that different audiences will have different reactions to what you write, and you want to target the right reactions – you want to connect with people.
The next step in this process is to attempt to identify what the beliefs and characteristics of the audience you are writing to are. This includes the reasons why your audience might disagree with your views or what inhibitions they would have before doing what you are trying to persuade them. Also, it is important to know why this cause is relevant to an audience.
Understanding your audience is also vital because it is imperative not to offend your audience, as this will definitely turn them off to any persuasion.
Modes of Persuasion
The next step in persuasive writing is knowing how to connect with your audience. There are three basic ways to do this, which are known as the modes of persuasion.
Persuasion through the authority of the author, known as Ethos ,
Ethos can be developed by choosing language that is appropriate for the audience and topic (also means choosing proper level of vocabulary), making yourself sound fair or unbiased, introducing your expertise or pedigree, and by using correct grammar and syntax.
Persuasion through use of logic and facts, known as Logos ,
Logos can be developed by citing facts and statistics (very important), using advanced and well-developed language, using historical incidents, analogies, and by constructing logical arguments.
Persuasion through use of emotion and sympathy, known as Pathos
Pathos can be developed by using meaningful language, emotional tone, emotion-evoking examples, stories of emotional events, and implied meanings.
Much of the work in persuasive writing is knowing how to use these methods effectively.
Counterarguments
Anticipating and responding to arguments against your point are important parts of persuasive writing. A response to counter arguments varies based on the validity of the counterargument.
In some cases, when a counterargument is completely frivolous, you can completely dismiss it using facts and logic. However, sometimes you may have to concede some parts – or even the entire argument to the opposing point. In these situations, it is important to show the audience why this argument is not important or less important to the big picture of your argument. Acknowledging counterarguments contributes to Ethos, and makes the author seem more fair and balanced in the eyes of the reader.
More Tips and Techniques for Persuasive Writing
Using Sympathy:
Drawing sympathy (using pathos) from your audience is one of the most effective forms of persuasion. This is especially true if your paper is focused around a certain problem or is a passionate topic. This technique is called using pathos. You can use this to draw both negative and positive emotions.
Emotions are a powerful tool. To use your audience’s emotion to your advantage, you must understand why something is important to your audience. Then you should focus on this importance, and make your audience feel the emotions associated with it. After you draw on their emotions, you should present your thesis as a solution to their pain or pleasure.
If you are writing about wind as a source of renewable energy, to an audience of predominately older people, you could describe to them the consequences their children will face if this level of harm towards the environment persists. In this case, the fate of your audience’s children is important to your audience. After you have drawn upon their sympathy, you should present to your audience why wind power will offer a solution to this.
If you are writing about equal rights to a predominately white audience, you could try to place your audience in the shoes of someone who is being discriminated against. After you have drawn upon your audience’s sympathy, you could show them why policies about equal rights are important.
Make Your Reader a Part of Something:
Feeling like a part of a group or club makes everyone feels good. Make your reader feel like they are a part of a group of people by agreeing with your thesis, while seemingly excluding those who don’t.
If your topic is convincing readers of climate change, you could make your readers feel like a part of a progressive group, enlighten people by agreeing with you.
Look into the Future:
Making assumptions about the future gives your audience a clear choice in deciding what to think after reading your writing. This technique can be especially useful if you are attempting to call your audience to action. Painting a grim future for the inaction of your thesis can be a powerful tool for persuading your audience; likewise, you should describe a brighter future where your thesis is enacted. I.e., this is what will happen if you listen to me, this is what will happen if you don’t.
However, this technique should only be used if you can adequately convince your readers that what you are saying will happen or is likely to happen. Misusing this technique can discredit your entire essay and make you seem like a fool!
Popular Articles
- Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition and Examples
- Modes of Persuasion: Ethos
- Ethos, Pathos, and Logos ‒ Examples
- Modes of Persuasion: Pathos
Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Ethos, Pathos, Logos, Kairos: The Modes of Persuasion and How to Use Them
General Education

Ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos all stem from rhetoric—that is, speaking and writing effectively. You might find the concepts in courses on rhetoric, psychology, English, or in just about any other field!
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising.
Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they’re used, and how to identify them!
What Are the Modes of Persuasion?
As you might have guessed from the sound of the words, ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos go all the way back to ancient Greece. The concepts were introduced in Aristotle’s Rhetoric , a treatise on persuasion that approached rhetoric as an art, in the fourth century BCE.
Rhetoric was primarily concerned with ethos, pathos, and logos, but kairos, or the idea of using your words at the right time, was also an important feature of Aristotle’s teachings.
However, kairos was particularly interesting to the Sophists, a group of intellectuals who made their living teaching a variety of subjects. The Sophists stressed the importance of structuring rhetoric around the ideal time and place.
Together, all four concepts have become the modes of persuasion, though we typically focus on ethos, pathos, and logos.

What Is Ethos?
Though you may not have heard the term before, ‘ethos’ is a common concept. You can think of it as an appeal to authority or character—persuasive techniques using ethos will attempt to persuade you based on the speaker’s social standing or knowledge. The word ethos even comes from the Greek word for character.
An ethos-based argument will include a statement that makes use of the speaker or writer’s position and knowledge. For example, hearing the phrase, “As a doctor, I believe,” before an argument about physical health is more likely to sway you than hearing, “As a second-grade teacher, I believe.”
Likewise, celebrity endorsements can be incredibly effective in persuading people to do things . Many viewers aspire to be like their favorite celebrities, so when they appear in advertisements, they're more likely to buy whatever they're selling to be more like them. The same is true of social media influencers, whose partnerships with brands can have huge financial benefits for marketers .
In addition to authority figures and celebrities, according to Aristotle, we’re more likely to trust people who we perceive as having good sense, good morals, and goodwill —in other words, we trust people who are rational, fair, and kind. You don’t have to be famous to use ethos effectively; you just need whoever you’re persuading to perceive you as rational, moral, and kind.

What Is Pathos?
Pathos, which comes from the Greek word for suffering or experience, is rhetoric that appeals to emotion. The emotion appealed to can be a positive or negative one, but whatever it is, it should make people feel strongly as a means of getting them to agree or disagree.
For example, imagine someone asks you to donate to a cause, such as saving rainforests. If they just ask you to donate, you may or may not want to, depending on your previous views. But if they take the time to tell you a story about how many animals go extinct because of deforestation, or even about how their fundraising efforts have improved conditions in the rainforests, you may be more likely to donate because you’re emotionally involved.
But pathos isn’t just about creating emotion; it can also be about counteracting it. For example, imagine a teacher speaking to a group of angry children. The children are annoyed that they have to do schoolwork when they’d rather be outside. The teacher could admonish them for misbehaving, or, with rhetoric, he could change their minds.
Suppose that, instead of punishing them, the teacher instead tries to inspire calmness in them by putting on some soothing music and speaking in a more hushed voice. He could also try reminding them that if they get to work, the time will pass quicker and they’ll be able to go outside to play.
Aristotle outlines emotional dichotomies in Rhetoric . If an audience is experiencing one emotion and it’s necessary to your argument that they feel another, you can counterbalance the unwanted emotion with the desired one . The dichotomies, expanded upon after Aristotle, are :
- Anger/Calmness
- Friendship/Enmity
- Fear/Confidence
- Shame/Shamelessness
- Kindness/Unkindness
- Pity/Indignation
- Envy/Emulation
Note that these can work in either direction; it’s not just about swaying an audience from a negative emotion to a positive one.
However, changing an audience's emotion based on false or misleading information is often seen as manipulation rather than persuasion. Getting into the hows and whys requires a dive into the ethics of rhetoric , but suffice to say that when you attempt to deceive an audience, that is manipulation.
If you really want to get an audience fired up about something, you can inspire righteous anger, which may or may not be manipulation. If somebody is offended that you’ve asked them for something, you can try making them feel sorry for you by turning indignation into pity— that’s manipulation.

What Is Logos?
Logos comes from a Greek word of multiple meanings, including “ground,” “speech,” and “reason.” In rhetoric, it specifically refers to having a sense of logic to your persuasion; logos-based rhetoric is founded in logic and reason rather than emotion, authority, or personality.
A logic-based argument appeals to a person’s sense of reason— good logos-based rhetoric will persuade people because the argument is well-reasoned and based in fact. There are two common approaches to logos: deductive and inductive arguments.
Deductive arguments build on statements to reach a conclusion —in effect, the conclusion is reached in reverse. A common method is to propose multiple true statements which are combined to reach a conclusion, such as the classic method of proving that Socrates is mortal.
All men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, therefore Socrates must be mortal.
That’s not really a case that needs to be argued, but we can apply the same framework to other arguments as well. For example, we need energy to live. Food gives the body energy. Therefore, we need food to live.
All of this is based on things we can prove, and results in a conclusion that is true , not just theorized. Deductive reasoning works on the assumption that A = B, B = C, so therefore A = C. But this also supposes that all the information is true, which is not always the case.
Sometimes the conclusions you reach with deductive reasoning can be valid, as in the reasoning makes sense, but the conclusion may not be necessarily true. If we return to the Socrates argument, we could propose that:
All men eat apples. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates must eat apples.
The problem is that we can’t prove that all men eat apples —some do, some don’t. Some might eat an apple once but never again. But based on our arguments, the conclusion that Socrates must eat apples is valid.
A strong deductive argument for logos-based reasoning will be composed of provable facts that can reach a provable conclusion. However, a valid but not entirely sound argument can also be effective—but be wary of shifting from persuasion to manipulation!
Another approach to logos-based rhetoric is inductive reasoning, which, unlike deductive reasoning, results in a probable argument rather than a definite one. That doesn’t mean that it is less effective—many scientific concepts we accept as truth are inductive theories simply because we cannot travel back in time and prove them— but rather that inductive reasoning is based on eliminating the impossible and ending in an argument that is based in sound logic and fact, but that may not necessarily be provable.
For example, all people with a cough have a cold. Kelly has a cough. Therefore, Kelly likely has a cold.
Our conclusion is likely , but not absolute. It’s possible that Kelly doesn’t have a cold—not because she doesn't have a cough, but because there are other possible causes, such as having allergies or having just breathed in some dust. The conclusion that she has a cold is likely based on data, but not absolute.
Another example would be that Kelly picks her nose. Kelly is a woman, therefore all women must pick their nose.
Inductive reasoning is based on generalizations. The first example, in which Kelly likely has a cold, makes sense because it’s based on something provable—that a sampling of people who have a cough have colds—and followed up with a likely conclusion. In the second example, this is a less sensible conclusion because it’s based on extrapolation from a single reference point.
If we reverse the claim and say that all women pick their noses, and Kelly is a woman, therefore Kelly must pick her nose, that would be more sound logic. Still not necessarily true—not all women pick their noses—but a more sound example of inductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning can still be incredibly effective in persuasion, provided that your information is well-reasoned. Inductive reasoning creates a hypothesis that can be tested; its conclusion is not necessarily true, but can be examined.
As always, be wary of venturing into manipulation, which is more likely to be based on erroneous or misleading facts.

What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the Greek word for the opportune moment, which is precisely what it means in rhetoric. According to this principle, the time in which an argument is deployed is as important as the argument itself. An argument at the wrong time or to the wrong audience will be wasted; to be effective, you must also consider when you are speaking and to whom.
In effect, kairos means choosing the correct rhetorical device to match the audience and space in which you’re attempting to persuade. If you wanted to persuade people to go vegetarian, the middle of a hot dog-eating contest is probably not the right time. Likewise, you’re probably not going to persuade a room of data-driven scientists of something by appealing to pathos or ethos; logos is probably your best bet.
In essence, kairos asks you to consider the context and atmosphere of the argument you’re making. How can you deploy your argument better considering time and space? Should you wait, or is time of the essence?
As Aristotle famously said, “Anybody can become angry—that is easy, but to be angry with the right person and to the right degree and at the right time and for the right purpose, and in the right way—that is not within everybody's power and is not easy.”
The goal of kairos is to achieve exactly that. Effective use of kairos strengthens your persuasion ability by considering how people are already feeling based on context. How can you influence or counteract that? Or maybe pathos isn’t the right approach—maybe cold hard facts, using logos, is more suited. Kairos works in conjunction with the other modes of persuasion to strengthen your argument, so as you’re putting a persuasive piece together, consider how and when it’ll be deployed!

How to Identify Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Understanding how the modes of persuasion work can make you better at identifying and picking them out. Not only is a better understanding of them useful for composing your own arguments, but it’s also beneficial when seeing other people’s arguments. When you understand how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos work, you’re less susceptible to them.
Advertising is one of the places we see the modes of persuasion most often. Looking at each of these advertisements, you can see how they use each mode of persuasion to convince audiences to convince an audience of something.
Using celebrities is a classic example of ethos, which uses authority or recognition to convince an audience of something. In this case, celebrities like Michelle Obama, Lin-Manuel Miranda, and Janelle Monáe discuss the importance of voting.
It doesn’t matter that they’re not politicians or political scientists; audiences find them appealing and genuine. When they speak of the importance of voting, audiences listen because they like what these figures have to say . If talented, famous people like this are taking the time to vote, it must be important!
Historians or those well-versed in politics might make different arguments about why audiences should vote, but in this case, the goal is to inspire people. When we see people we admire doing things, we want to do them too; hence the reason that ethos works so well.
ASPCA’s commercials are some of the most infamous examples of pathos in advertising. Sarah McLachlan’s “Angel” plays over footage of abused animals in shelters, encouraging viewers to donate money to support the organization.
It’s not hard to understand why it works; both the song and the imagery are heartbreaking! You can’t help but feel sad when you see it, and that sadness, when followed up by a prompt to donate, encourages you to take immediate action. And these ads are effective— the campaign raised millions of dollars for ASPCA .
By appealing to our emotions and making us feel sad, this advertisement encourages us to act. That’s a classic use of ethos—it influences our feelings through the one-two punch of sad music and imagery, encouraging us to perform the desired action.
In some cases, emotion and authority aren’t the right tactic. Logos often appears in tech advertisements, such as this one for the iPhone XS and XR.
Notice how the advertisement focuses on product shots and technological terms. Most audiences won’t know what an A12 bionic neural engine is, but it sounds impressive. Likewise, that “12 MPf/1.8 wide-angle lens, with larger, deeper 1.4 micron pixels” is pretty meaningless to most people, but the numbers suggest that this phone is something special because it uses scientific-sounding language.
It doesn’t matter whether audiences really understand what’s being said or not. What matters is that they feel confident that the ad is selling them something they need —in this case, impressive technological specifications that make this phone an improvement over others.
Kairos should ideally factor into all uses of the modes of persuasion, but timeliness can also be a big selling point. In this Christmas-themed M&Ms advertisement, the company uses timely humor to forge a connection between the holidays and M&Ms.
Because these commercials have been running for such a long time, there’s also a nostalgic attachment to them. Just as people look forward to new Budweiser advertisements during the Super Bowl, others look forward to seeing M&Ms or the Coca-Cola polar bear during the holidays.
Though this commercial doesn’t go out of its way to tell you the benefits of M&Ms, it does forge a connection between M&Ms and Christmas, encouraging people to purchase them around the holidays.

Examples of the Modes of Persuasion
Now that you’ve had some exposure to how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos function and what they can do, you can test your ability to recognize them using the images below!

There are a few things to notice about this image:
- The anonymous figure
- The language
- The use of a statistic
Can you figure out which mode of persuasion this represents?
The fact that the figure is anonymous tells us it’s probably not ethos. While we might be influenced by a person who’s in shape, there’s not really an appeal here based on the person—they’re just an image to support the ad.
“DOMINATE” is a pretty loaded word, suggesting that this may have elements of pathos.
However, take a look at that statistic. Whether it’s true or not, a hard statistic like that suggests that this ad is using logos to appeal to viewers. You can draw out an argument from there—75% of users lose weight within weeks. You’re a user. Therefore, you will likely lose weight within weeks.

What do you notice about this image?
- The way the text frames the woman’s body
- The name of the perfume
- The color choice
What mode of persuasion is this?
Again, we don’t know who the model is, and perfume isn’t going to make us look like her, so we can count ethos out.
The ad seems pretty intent on making us look at certain things—the woman’s lips and chest in particular. What is it trying to make us feel?
“FORBIDDEN FRUIT” has a connotation of sensuality.
Red is a color commonly associated with passion.
When you combine the photo, the framing, the perfume name, and the color, you get a strong sense of sex appeal from the advertisement. This makes it an example of pathos—the ad is trying to make us feel a certain way . If we buy this perfume, maybe we would feel attractive, too.

How about this advertisement?
- A serious-looking photo
- Text promising “no more back pain”
- “Doctor recommended.”
Seeing a doctor might make you tempted to think the answer is logos, but there’s no appeal to logic here.
“No more back pain,” is a nice promise, but there’s no attempt to appeal to emotions, so it can’t be pathos.
What’s important in this image is the combination of the doctor in the image and the line “doctor recommended.” This doctor might not be famous, but he does have authority, making this an example of ethos.
Our confidence in this treatment grows because we trust that a doctor understands how to address back pain.

What mode of persuasion is this? Think about:
- The framing
She does look fashionable and the ad mentions stylists, so it’s possible that this is ethos.
There are no statistics or arguments being made, so the answer probably isn’t logos.
Pathos is possible, but despite having a heavily made-up model, this ad is far less about sex appeal than the previous one.
But the text mentions a specific holiday—New Year’s—suggesting that this is kairos. Kairos can, and often should, be combined with all the modes of persuasion to be even more effective. In this case, the model’s appearance could suggest either ethos or pathos in addition to kairos. The message here is that you should act now, at the beginning of the year, to take advantage of the deal and to start the year off with a new style, much like the one the model is sporting.

Key Tips for Identifying Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Now that you know the difference between all the modes of persuasion, you’ll have a much easier time identifying them. If you run into trouble, you can always ask questions about what you’re seeing, hearing, or reading to understand what mode of persuasion it’s using.
#1: Is It Related to a Specific Time?
If the argument is based on a specific day or context, such as Valentine’s Day or appealing only to a select group of people, such as people with dogs, it’s more likely to be kairos.
#2: Does It Involve a Celebrity or Authority Figure?
Celebrities are often a dead giveaway that an argument is using ethos. But authority figures, such as doctors, dentists, or politicians, can also be used to appeal to ethos. Even regular, everyday people can work, particularly when combined with pathos, to appeal to you based on a mutual connection you have.
#3: Does It Involve Statistics?
Statistics are a huge clue that an argument is using logos. But logos can also just be a logical argument, such as that if plants need water, and it’s hard to remember to water them, you should buy an automatic plant waterer. It makes perfect sense, making you more likely to buy it, rather than changing your habits to remember to water your plants more frequently.
#4: Does It Influence Your Emotions?
If an argument tries to change your emotions, whether by making you sad, happy, angry, or something else entirely, it’s a good indicator that it’s using pathos. Sex appeal is one of the biggest examples of pathos in advertising, appearing everywhere from makeup ads to car commercials to hamburger advertisements.
What’s Next?
Need help understanding the historical context for The Great Gatsby to perfect your kairos-based argument?
You can always combine the modes of persuasion with literary devices to make your arguments even stronger!
Learn how to say "good morning" in Japanese ! Even if it's not a mode of persuasion, it's just good manners.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
What Are Ethos, Logos, and Pathos?
Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of persuasion. We’ll be covering what they mean and how to include them in your writing.

Quick Summary on Using Ethos, Logos, and Pathos in Your Writing
- Ethos , logos , and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer’s credibility, logos appeals to the audience’s reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions.
- These three concepts, also known as the rhetorical triangle , three rhetorical appeals , or three modes of persuasion , were coined by Aristotle in his explanation of what makes rhetoric effective.
Ethos vs. Logos vs. Pathos
To understand what ethos, logos, and pathos are, you must first know what rhetoric is.
Rhetoric is defined by the Oxford Dictionary as “the art of effective or persuasive speaking or writing.” Aristotle defined rhetoric as “the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion.” In simpler terms, rhetoric is the effectiveness of the words (spoken or written) you choose to convey a message or change your audience’s perspective.
According to Aristotle, there are three means by which your rhetoric can be more powerful and that’s through the use of ethos, logos, and pathos. Knowing how to apply these three elements of persuasion can make your writing more compelling, so we’re going to teach you exactly what they mean and how to use them.
What Is Ethos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
Ethos establishes the writer’s credibility or authority. Imagine you’re at a climate change conference to learn how you can help planet Earth. Whose speech would you find more trustworthy—that of a CEO of a gas company that has profited millions of dollars by drilling for oil, or a speech by the CEO of a non-profit that helps clean oceans?
Ethos “appeals to the writer’s credibility, authority, or character” to get the audience to trust them.
My non-profit organization started with just one volunteer—me. I’d walk up and down the beaches collecting trash. Then, a friend joined me. The following week, that friend brought a friend. And then another. Until it grew to what it is today—an organization with more than 300 volunteers who have helped remove more than 15,000 pounds (6.8 tons) of trash from the beaches and the oceans. So, I know quite a bit on getting people together for a good cause.
Consider word choice, spelling, and grammar when incorporating ethos to your writing. It’s hard to trust a writer when their text is riddled with errors. Depending on what you’re writing, it may be a good idea to explicitly explain why you’re trustworthy and your expertise in the area you’re writing about.
To ensure your writing is error-free, try using LanguageTool as your writing assistant. This multilingual spelling and grammar checker can detect various types of mistakes in your writing and suggest stylistic improvements.
What Is Logos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The word logic is derived from the word logos. As you might have imagined, logos is the “appeal to the reader’s logic.” This means that you use facts, data, and statistics to support your reasoning.
Using logos in your writing is effective because it provides evidence that makes it difficult for your audience to disagree with you. Proper use of logos in your writing requires thorough research. The following example includes logos:
According to NASA and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), “the influence of human activity on the warming of the planet has evolved from theory to established fact.” This can be proven through data collected from ice cores, rocks, and tree rings as well as modern equipment, like satellites.
What Is Pathos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The last of the three elements of persuasion we’ll be discussing is pathos, which appeals to the audience’s emotions. In other words, writers try to persuade their audience by having them feel a certain way. Consider the following example:
Climate change is already happening all around us. But let’s pretend that we’re at the liberty of not having to worry about it because its effects won’t be evident in our lifetimes. What about your children? Or your children’s children? Imagine the life they will live as they have to endure extreme heat, catastrophic hurricanes, unprecedented rainfalls, and more. Climate change may not affect you personally, but it will affect those you love.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Makes For Effective Writing
Depending on what you’re writing and how you’re writing it, you may find yourself using more of either ethos, logos, or pathos. Truly effective writing finds a way to incorporate all three, even if one or two are used just a bit. As you read, try to recognize ethos, logos, and pathos. This will help you better incorporate it into your writing.

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to header right navigation
- Skip to site footer

Farnam Street
Mastering the best of what other people have already figured out
Ethos, Logos and Pathos: The Structure of a Great Speech
“A speech is like a love affair. Any fool can start it, but to end it requires considerable skill.” — Lord Mancroft
The structure of a great oral argument has been passed down through the ages, starting with Aristotle. Not only is it an incredibly valuable skill to have, it’s important to know how you’re being persuaded when you’re a part of the audience. So using Sam Leith’s Words Like Loaded Pistols as our guide, let’s discuss Aristotle’s three modes of persuasion: Ethos, Logos, and Pathos.
But before we get into the specifics of the three modes, we need to decide on the structure of our argument itself. How? By doing the work required to have an opinion .
This phase is referred to as invention , but it’s not about making something up, it’s more about the information gathering or research phase of your work.
Invention is doing your homework: thinking up in advance exactly what arguments can be made both for and against a given proposition, selecting the best on your own side, and finding counterarguments to those on the other.
This research phase should not be limited to the subject matter, it should also include your audience. If there is one theme that resonates throughout Leith’s book, it’s that you must know your audience; their interests, prejudices and expectations. Without that grounding, you’re already setting yourself up for failure. (In other words, your moving speech on why we all need to take a social media holiday may not resonate at the Twitter shareholder meeting.)
Ethos is about establishing your authority to speak on the subject, logos is your logical argument for your point and pathos is your attempt to sway an audience emotionally. Leith has a great example for summarizing what the three look like.
Ethos: ‘Buy my old car because I’m Tom Magliozzi.’ Logos: ‘Buy my old car because yours is broken and mine is the only one on sale.’ Pathos: ‘Buy my old car or this cute little kitten, afflicted with a rare degenerative disease, will expire in agony, for my car is the last asset I have in the world, and I am selling it to pay for kitty’s medical treatment.’
The first part of ethos is establishing your credentials to be speaking to the audience on the specific subject matter. It’s the verbal equivalent of all those degrees hanging up in your doctor’s office. And once you’ve established why you are an authority on the subject, you need to build rapport. Ethos, when everything is stripped away, is about trust.
Your audience needs to know (or to believe, which in rhetoric adds up to the same thing) that you are trustworthy, that you have a locus standi to talk on the subject, and that you speak in good faith. You need your audience to believe that you are, in the well-known words, ‘A pretty straight kind of guy.’
So if you’re a politician and you’re speaking about reforming the legal system, it’s great to be a lawyer or a judge, but it’s even better to be a lawyer or a judge who comes from the same community as your audience. Between two speakers with identical credentials, the more closely relatable one will win the audience.
You’ll even see a reverse ethos appeal at times, an attack on an opponent which questions their credentials and trustworthiness and serves to alienate them from the audience. To head that off, it’s best to establish your ethos early on, both to give your attackers more of a challenge and to create a hook for your logos to hang on.
Here’s how Leith describes logos , the next link in the chain:
If ethos is the ground on which your argument stands, logos is what drives it forward: it is the stuff of your arguments, the way one point proceeds to another, as if to show that the conclusion to which you are aiming is not only the right one, but so necessary and reasonable as to be more or less the only one.
Think of this as the logic behind your argument. You want your points to seem so straightforward and commanding that your audience can’t conceive of an alternative.
Aristotle had a tip here: He found that the most effective use of logos is to encourage your audience to reach the conclusion to your argument on their own, just moments before your big reveal. They will relish in the fact that they were clever enough to figure it out, and the reveal will be that much more satisfying.
Another logos trick used often is the much abused syllogism.
The syllogism is a way of combining two premises and drawing a fresh conclusion that follows logically from them. The classic instance you always hear quoted is the following: All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.
While you need to take care with the syllogisms you use — false syllogisms can lead to obvious logical fallacies — they can be a powerful tool for helping your audience draw certain conclusions.
Aristotle also advocated the use ‘commonplaces’, or accepted premises shared with the audience. The best arguments are soaked in them.
Associated with these general topics are ‘commonplaces’ (topos is Greek for a ‘place’). Any form of reasoning has to start from a set of premises, and in rhetoric those premises are very often commonplaces. A commonplace is a piece of shared wisdom: a tribal assumption. In the use of commonplaces, you can see where logos and ethos intersect. Commonplaces are culturally specific, but they will tend to be so deep-rooted in their appeal that they pass for universal truths. They are, in digested form, the appeal to ‘common sense.’ You get nowhere appealing to commonplaces alien to your audience. The wise persuader starts from one or two commonplaces he knows he has in common with his audience – and, where possible, arrives at one too.
Your use of commonplaces is also a good point to interject pathos , as many of these common beliefs can illicit an emotional response. Let’s dig into pathos .
Your logical argument will be that much more persuasive if it’s wrapped up with a good dose of emotion. Because of the way we use the word pathos in the modern world, you may be thinking of something dramatic and sad. But pathos is more nuanced than that; it can be humor, love, patriotism, or any emotional response.
The key here once again is to know your audience . If you are trying to evoke a sense of anger or sadness regarding mankind’s role in the decline of the honeybee, you might not get the response you want from the bee allergy support group.
You can even invoke pathos by admitting a wrong. ( We all make mistakes …) This can be a clever way to put your opponent off balance.
This is the figure, called paromologia in the Greek, where you concede, or appear to concede, part of your opponent’s point. It turns what is often necessity to advantage, because it makes you look honest and scrupulous, takes the wind out of your opponent’s sails, and allows you to shift the emphasis of the argument in a way finally favorable to you. It’s the equivalent of a tactical retreat, or of the judo fighter using an opponent’s momentum against him.
Another tool you can use with pathos is something the ancients called aposiopesis.
Aposiopesis – a sudden breaking off as if at a loss for words – can be intended to stir pathos. And even where something appears merely decorative – a run of alliteration or a mellifluously turned sentence – it serves to commend the speech more easily to memory, and to give pleasure to the audience. Delight is an end, as well as a means.
And we can’t forget joy and laughter. A well received joke can help you both connect with the audience (ethos) and bring home the pathos appeal.
… the joke can do more than just perk up a drowsing audience. It can be a powerful rhetorical tool. It participates in the pathos appeal inasmuch as it stirs an audience’s emotions to laughter – but more importantly, it participates in the ethos appeal, inasmuch as laughter is based on a set of common assumptions. As Edwin Rabbie argues in ‘Wit and Humour in Roman Rhetoric,’ ‘Jokes usually presuppose (even rest on) a significant amount of shared knowledge.
Ultimately, the three modes of persuasion are interconnected. It’s helpful not to think of them in a linear way but more like three overlapping circles. If you can create something with ethos, logos, and pathos peppered throughout, and tie it all into your audience’s belief system, you will have a very strong argument.
While Aristotle’s three persuasive appeals make appearances throughout the book, there is so much more to Words Like Loaded Pistols . Leith goes into depth regarding the five parts of rhetoric and the three branches of oratory. He also spend considerable time explaining the different figures, also known as the ‘flowers of rhetoric, which can be thought of as the literary weapons you can use in your war of words. If you have an interest in making your own presentations or speeches better, or in understanding the techniques a speaker is using when you are in the audience then this book is definitely worth the read. In the meantime check out our post on Wartime Rhetoric for some inspiration.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos – A Simple Guide

4-minute read
- 12th April 2023
Ethos, logos, and pathos are three essential components of persuasive communication . They’ve been used for centuries by great communicators to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. In this simple guide, we’ll take a closer look at these three components using examples from famous writing and speeches.
What Is Ethos?
Ethos is a persuasive appeal based on the credibility or character of the speaker or writer. It refers to the trustworthiness, expertise, or authority that they bring to the argument. It’s crucial in establishing the credibility of the speaker or writer and can be built in through a variety of means, such as reputation and sources, or language and tone.
How To Use Ethos
Ethos can be established through the speaker or writer’s reputation: if they are known for being knowledgeable, honest, and trustworthy, this can lend credibility to their argument. For example, in his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, Martin Luther King Jr. established his ethos by highlighting his role as a civil rights leader and his personal experience with racial injustice.
Another way you can achieve ethos in speech or writing is through the use of credible sources. For example, Rachel Carson established ethos in her book Silent Spring by providing extensive scientific evidence to support her argument that pesticides were harming the environment.
Finally, ethos can be accomplished through the use of language and tone . Using a professional and respectful tone can create the impression of credibility and authority. For instance, in his second inaugural address, President Abraham Lincoln employed ethos by using a solemn, reflective tone to convey the gravity of the situation.
What Is Logos?
Logos is a persuasive appeal based on logic and reasoning. It refers to the use of evidence and logical arguments to support the speaker or writer’s position.
How To Use Logos
One way you can implement logos in your speech or writing is through the use of statistics and data. When writing, or constructing a speech, try to incorporate reliable and credible stats or figures to strengthen your claims or argument and persuade your audience.
You can also employ examples and analogies to achieve logos. These can make your argument more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. For example, in his book The Tipping Point , Malcolm Gladwell uses the example of “the broken windows” theory to illustrate his argument that small changes can have a big impact on social behavior.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Finally, logos can be established through the use of logical arguments . To ensure you have a logical argument, you should have a clear statement with definitions, examples, and evidence to support it. For instance, in his essay “Civil Disobedience,” Henry David Thoreau made a logical argument that individuals have a moral obligation to resist unjust laws.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is a persuasive appeal based on emotion. It refers to the use of language and imagery that elicits an emotional response. Pathos can be used to create a sense of urgency, inspire empathy, or evoke a particular mood.

How To Use Pathos
Vivid imagery is a great way in which a writer or speaker can implement pathos. Using descriptive language to paint a picture in your audience’s mind is a powerful and persuasive skill. For example, in his poem “Dulce et Decorum Est,” Wilfred Owen used vivid imagery to describe the horrors of war and elicit an emotional response in his readers.
Pathos can also be accomplished by using personal anecdotes. The power of storytelling is an invaluable skill for any writer or speaker because it creates rapport and an emotional connection with your audience. For example, in her TED talk “The Power of Vulnerability,” Brene Brown shares personal stories about her struggles with shame and vulnerability to inspire empathy and connection with her audience.
Finally, pathos can be established through the use of rhetorical questions and appeals to shared values. A good example can be heard in Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech. He poses his biggest question to his audience (and the world): “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” In response to this rhetorical question, he beautifully tries to persuade the audience to work together toward a common goal, stating, “It means that we’ve got to stay together. We’ve got to stay together and maintain unity.”
Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting change in the world.
Interested in learning how to elevate your writing with more literary devices? Check our other articles .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Pathos, Logos, and Ethos
Most people are able to drive a car without fully understanding how the car operates. Making an argument is the same way. Most of us attempt to persuade people every day without understanding how persuasion works. Learning how a strong argument is crafted empowers us to better communicate and persuade others to understand our viewpoints.
What Are Pathos, Logos, and Ethos?
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader.
Pathos , or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and stories that evoke emotion. Authors can desire a range of emotional responses, including sympathy, anger, frustration, or even amusement.
Logos , or the appeal to logic, means to appeal to the audiences’ sense of reason or logic. To use logos, the author makes clear, logical connections between ideas, and includes the use of facts and statistics. Using historical and literal analogies to make a logical argument is another strategy. There should be no holes in the argument, also known as logical fallacies, which are unclear or wrong assumptions or connections between ideas.
Ethos is used to convey the writer’s credibility and authority. When evaluating a piece of writing, the reader must know if the writer is qualified to comment on this issue. The writer can communicate their authority by using credible sources; choosing appropriate language; demonstrating that they have fairly examined the issue (by considering the counterargument); introducing their own professional, academic or authorial credentials; introducing their own personal experience with the issue; and using correct grammar and syntax.
Sample Paragraph
Imagine this: a small dog sits in a dark, cold garage. His hair is matted and dirty; he is skinny and weak from going days without food. There is no water for him to drink, no person to give him love and no blanket to keep him warm at night. 1 While this might be a hard scenario to imagine, it is not an uncommon one in America today. According to the Humane Society of the United States, nearly 1,000,000 animals are abused or die from abuse every year. 2 As a veterinarian with 30 years of experience, I have seen how even one incident of abuse can affect an animal for the rest of its life. 3 As a society, we need to be more aware of this terrible problem and address this issue before it gets worse.
1 Pathos: the author paints a vivid picture to evoke a feeling from the reader—sadness and pity for the abused animal.
2 Logos: the author uses a startling statistic to appeal to our intellect. Keep in mind that these three strategies can often overlap. This sentence qualifies as both Logos and Ethos because it cites a reputable organization, so we know the author is using credible sources.
3 Ethos: the author establishes their own credibility by stating their occupation and experience.>
How Do I Know if the Author is Using Pathos, Logos or Ethos?
Pathos—does the writer appeal to the emotions of their reader.
- Do they use individuals’ stories to “put a face” on the problem you’re exploring? For example, using an individual’s story about losing their home during the mortgage crisis of the 2008 Recession may be more powerful than using only statistics.
- Do they use charged language or words that carry appropriate connotations? For example, if a writer describes a gun as a “sleek, silver piece of sophisticated weaponry,” they are delivering a much different image than if she writes, “a cold hunk of metal, dark and barbaric and ready to kill.”
Logos—does the writer appeal to the rational mind by using logic and evidence?
- Do they include facts and statistics that support their point? It’s more convincing to tell the reader that “80% of students have committed some form of plagiarism,” than simply saying that “Lots of students have plagiarized.”
- Do they walk us through the logical quality of their argument? Do they show us how ideas connect in a rational way? For example: “English students have been able to raise their overall grade by meeting with peer tutors, so it’s safe to assume that math students could also benefit from frequent tutoring sessions.” This example points out that logically, if the result has been seen in one situation, then it should be seen in a different but similar situation.
- Hasty generalizations: “Even though the movie just started, I know it’s going to be boring.”
- Slippery Slope: “If the government legalizes marijuana, eventually they’ll legalize all drugs.”
- Circular Argument: “Barack Obama is a good communicator because he speaks effectively.”
Ethos—is this writer trustworthy?
- What are their credentials? Are they an expert in the field? Have they written past essays, articles or books about this topic?
- Do they use reputable sources? Do they support her statements with sources from established publications like The New York Times or a government census report? Do they fail to mention any sources?
- Are they a fair-minded person who has considered all sides of this issue? Have they acknowledged any common ground they share with the opposite side? Do they include a counterargument and refutation?
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer .
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay .

Writing a Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays convince readers to accept a certain perspective. Writing a persuasive essay therefore entails making an argument that will appeal to readers, so they believe what you say has merit. This act of appealing to readers is the art of persuasion, also known as rhetoric. In classical rhetoric, persuasion involves appealing to readers using ethos, pathos, and logos.
In this tutorial, we refer to the sample persuasive draft and final paper written by fictional student Maggie Durham.
THE ART OF PERSUASION
Ethos refers to establishing yourself as a credible source of information. To convince an audience of anything, they must first trust you are being earnest and ethical. One strategy to do this is to write a balanced discussion with relevant and reliable research that supports your claims. Reliable research would include quoting or paraphrasing experts, first-hand witnesses, or authorities. Properly citing your sources, so your readers can also retrieve them, is another factor in establishing a reliable ethos. When writing for academic purposes, expressing your argument using unbiased language and a neutral tone will also indicate you are arguing fairly and with consideration of others having differing views.
When you appeal to your readers’ emotions, you are using pathos. This appeal is common in advertising that convinces consumers they lack something and buying a certain product or service will fulfill that lack. Emotional appeals are subtler in academic writing; they serve to engage a reader in the argument and inspire a change of heart or motivate readers toward a course of action. The examples you use, how you define terms, any comparisons you draw, as well as the language choices you use can draw readers in and impact their willingness to go along with your ideas.
Consider that one purpose of persuasion is to appeal to those who do not already agree with you, so it will be important to show that you understand other points of view. You will also want to avoid derogatory or insulting descriptions or remarks about the opposition. You wouldn’t want to offend the very readers you want to persuade.
Establishing an appeal of logos is to write a sound argument, one that readers can follow and understand. To do this, the facts and evidence you use should be relevant, representative, and reliable, and the writing as a whole should be well organized, developed, and edited.
STEPS FOR WRITING PERSUASIVELY
Step one: determine the topic.
The first step in writing a persuasive essay is to establish the topic. The best topic is one that interests you. You can generate ideas for a topic by prewriting, such as by brainstorming whatever comes to mind, recording in grocery-list fashion your thoughts, or freewriting in complete sentences what you know or think about topics of interest.
Whatever topic you choose, it needs to be:
- Interesting : The topic should appeal both to you and to your intended readers.
- Researchable : A body of knowledge should already exist on the topic.
- Nonfiction : The information about the topic should be factual, not based on personal opinions or conspiracy theories.
- Important : Your reader should think the topic is relevant to them or worthy of being explored and discussed.
Our sample student Maggie Durham has selected the topic of educational technology. We will use Maggie’s sample persuasive draft and final paper as we discuss the steps for writing a persuasive essay.
Step Two: Pose a Research Question
Once you have a topic, the next step is to develop a research question along with related questions that delve further into the first question. If you do not know what to ask, start with one of the question words: What? Who? Where? When? Why? and How? The research question helps you focus or narrow the scope of your topic by identifying a problem, controversy, or aspect of the topic that is worth exploration and discussion. Some general questions about a topic would be the following:
- Who is affected by this problem and how?
- Have previous efforts or polices been made to address this problem? – What are they?
- Why hasn’t this problem been solved already?
For Maggie’s topic of educational technology, potential issues or controversies range from data privacy to digital literacy to the impact of technology on learning, which is what Maggie is interested in. Maggie’s local school district has low literacy rates, so Maggie wants to know the following:
- Are there advantages and/or disadvantages of technology within primary and secondary education?
- Which types of technology are considered the best in terms of quality and endurance?
- What types of technology and/or programs do students like using and why?
- Do teachers know how to use certain technologies with curriculum design, instruction, and/or assessment?
Step Three: Draft a Thesis
A thesis is a claim that asserts your main argument about the topic. As you conduct your research and draft your paper, you may discover information that changes your mind about your thesis, so at this point in writing, the thesis is tentative. Still, it is an important step in narrowing your focus for research and writing.
The thesis should
1. be a complete sentence,
2. identify the topic, and
3. make a specific claim about that topic.
In a persuasive paper, the thesis is a claim that someone should believe or do something. For example, a persuasive thesis might assert that something is effective or ineffective. It might state that a policy should be changed or a plan should be implemented. Or a persuasive thesis might be a plea for people to change their minds about a particular issue.
Once you have figured out your research question, your thesis is simply the answer. Maggie’s thesis is “Schools should supply technology aids to all students to increase student learning and literacy rates.” Her next step is to find evidence to support her claim.
Step Four: Research
Once you have a topic, research question, and thesis, you are ready to conduct research. To find sources that would be appropriate for an academic persuasive essay, begin your search in the library. The Purdue Global Library has a number of tutorials on conducting research, choosing search teams, types of sources, and how to evaluate information to determine its reliability and usefulness. Remember that the research you use will not only provide content to prove your claim and develop your essay, but it will also help to establish your credibility as a reliable source (ethos), create a logical framework for your argument (logos), and appeal to your readers emotionally (pathos).
Step Five: Plan Your Argument; Make an Outline
Once you have located quality source information—facts, examples, definitions, knowledge, and other information that answers your research question(s), you’ll want to create an outline to organize it. The example outline below illustrates a logical organizational plan for writing a persuasive essay. The example outline begins with an introduction that presents the topic, explains the issue, and asserts the position (the thesis). The body then provides the reasoning for the position and addresses the opposing viewpoints that some readers may hold. In your paper, you could modify this organization and address the opposing viewpoints first and then give the reasoning for your viewpoints, or you can alternate and give one opposing viewpoint then counter that with your viewpoint and then give another opposing viewpoint and counter that with your viewpoint.
The outline below also considers the alternatives to the position—certainly, there are other ways to think about or address the issue or situation. Considering the alternatives can be done in conjunction with looking at the opposing viewpoints. You do not always have to disagree with other opinions, either. You can acknowledge that another solution could work or another belief is valid. However, at the end of the body section, you will want to stand by your original position and prove that in light of all the opposing viewpoints and other perspectives, your position has the most merit.
Sample Outline of a Persuasive Argument
- 1. Introduction: Tell them what you will tell them.
- a. Present an interesting fact or description to make the topic clear and capture the reader’s attention.
- b. Define and narrow the topic using facts or descriptions to illustrate what the situation or issue is (and that is it important).
- c. Assert the claim (thesis) that something should be believed or done about the issue. (Some writers also briefly state the reasons behind this claim in the thesis as Maggie does in her paper when she claims that schools should supply tablets to students to increase learning , engagement, and literacy rates ).
- 2. Body: Tell them.
- a. Defend the claim with logical reasons and practical examples based on research.
- b. Anticipate objections to the claim and refute or accommodate them with research.
- c. Consider alternate positions or solutions using examples from research.
- d. Present a final point based on research that supports your claim in light of the objections and alternatives considered.
- 3. Conclusion: Tell them what you told them.
- a. Recap the main points to reinforce the importance of the issue.
- b. Restate the thesis in new wording to reinforce your position.
- c. Make a final remark to leave a lasting impression, so the reader will want to continue this conversation and ideally adopt the belief or take the action you are advocating.
In Maggie’s draft, she introduced the topic with facts about school ratings in Texas and then narrowed the topic using the example of her local school district’s literacy rates. She then claimed the district should provide each student a tablet in order to increase learning (and thus, literacy rates).
Maggie defends her claim with a series of examples from research that proved how access to tablets, technology-integrated curriculums, and “flipped classrooms” have improved literacy rates in other districts. She anticipates objections to her proposal due to the high cost of technology and counter argues this with expert opinions and examples that show partnerships with businesses, personalized curriculums that technology makes possible, and teacher training can balance the costs. Maggie included an alternative solution of having students check out tablets from the library, but her research showed that this still left students needing Wi-Fi at home while her proposal would include a plan for students to access Wi-Fi.
Maggie concluded her argument by pointing out the cost of not helping the students in this way and restated her thesis reaffirming the benefits, and then left the reader with a memorable quote.
Click here to see Maggie’s draft with feedback from her instructor and a peer. Sample Persuasive Draft
Feedback, Revision, and Editing
After you write a draft of your persuasive essay, the next step is to have a peer, instructor, or tutor read it and provide feedback. Without reader feedback, you cannot fully know how your readers will react to your argument. Reader feedback is meant to be constructive. Use it to better understand your readers and craft your argument to more appropriately appeal to them.
Maggie received valuable feedback on her draft from her instructor and classmate. They pointed to where her thesis needed to be even more specific, to paragraphs where a different organization would make her argument more convincing, to parts of the paper that lacked examples, sentences that needed revision and editing for greater clarity, and APA formatting that needed to be edited.
Maggie also took a critical look at her paper and looked back at her writing process. One technique she found helpful was to read her paper aloud because it let her know where her wording and organization were not clear. She did this several times as she revised and again as she edited and refined her paper for sentence level clarity and concision.
In the end, Maggie produced a convincing persuasive essay and effective argument that would appeal to readers who are also interested in the way technology can impact and improve student learning, an important topic in 2014 when this paper was written and still relevant today.
Click here to see Maggie’s final draft after revising and editing. Sample Persuasive Revised
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
- Speech Crafting →
Examples of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Persuasive Speeches

Ever fumbled for words while convincing someone to sign up for your club or buy something you're promoting on stage?
It happens. For this reason, Aristotle came up with three essential tools you can use in your everyday speech to persuade people for almost anything: ethos, pathos, and logos.
Here are some vivid examples of ethos, pathos, and logos to help you understand what they are and how to use them in your arguments.
The Three Tools That Guide Your Speech
Ethos, pathos, and logos are Greek words that make up the rhetorical triangle. Aristotle was the first to come up with them and wrote these concepts in his book, Rhetoric .
You can use them in any argument if you want to drive your point across or sell something: an idea, a product, or a brand.
Whether it is a sales pitch, a compelling argument, or a speech, these three modes of persuasion can sway your audience's perspective. Their presence since ancient times depicts their strength and significance.
Ethos is Greek for “character,” "credibility," or "authority." It refers to a person's character when they are presenting an argument.
The stronger the character or, the more influential the speaker is, the more they can change someone’s point of view regarding a particular subject.
You wouldn’t be enraptured, hanging on to her every word when J.K Rowling was giving a TED talk if she wasn’t a famous author, right?
Therefore, many brands and companies try to get celebrities to advertise for them. When people become fans, they religiously love what the celebrity loves and hates what the celebrity doesn't like.
This is the power of ethos. Here is how to establish ethos in a speech .

There are tons of examples of ethos in advertisements, movies, speeches, and daily life. Highlighted below are some of them.
Albus Dumbledor used ethos in the movie The Goblet of Fire when he went against the Ministry of Magic to tell his students how Cedric Diggory died. He knew they would believe him because he was Headmaster. He said:
"I think, therefore, you have the right to know exactly how he died. You see, Cedric Diggory was murdered by Lord Voldemort. The Ministry of Magic does not wish me to tell you this. But I think to do so would be an insult to his memory."
In a commercial, you’d see 4 out of 5 dentists recommending a particular toothpaste. That's how brands convince viewers to buy their products by backing them up with credible people.
As a physics student, you tune in to a TED talk by Brian Greene and believe everything he says because he’s a theoretical physicist and a string theorist.
Pathos is Greek for “emotion,” “suffering,” or “experience.” This rhetorical strategy appeals to people's feelings when used in an argument.
It invokes people’s senses, nostalgia, memory, and experiences. It is used in ads and videos to persuade people to follow a call to action.
When pathos is embedded in a message, it moves people, driving them to take action. Pathos can trigger any intended emotion in people, such as sympathy, pity, and empathy.
Why do you think romance sells so much, be it novels, movies, or stories? It pulls at the reader’s heartstrings, connects them to the characters, and makes them want something similar.
Below are some examples of pathos in everyday life, movies, and ads.
An excellent way to convince people to donate to a puppy shelter is to show them how brutally they'll die if they don't donate.
The Evian commercial in which adults look like toddlers when they look at their reflections depicts the "bandwagon effect." Light-heartedly, it uses feel-good emotion to convince people to buy their water.
In their ad, IKEA convinces people to opt for home delivery for £3.95 by showing a person stuck in traffic after buying from the brand. This appeals to people because we like comfort, right?
Unlike ethos and pathos, logos rely on logic. It is a Greek word that means “logic” or “reason.” It uses logical reasons to convince people about something.
When you use logos in your everyday speech or arguments, you try to mention facts or data to support your idea.

While ethos uses the speaker's credibility to persuade people about something, pathos uses emotion to trigger people. Logos simply relies on logic and cuts to the chase.
You can easily persuade an audience using reason and logic in your argument; however, emotions do get the best of us as humans. For this reason, there are three modes of persuasion.
The following are a few examples of Logos.
Al Gore, a renowned environmentalist, used logos in his speech “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” in 2019. He tells people what exactly is happening that is causing climate change and cites scientific research and experts in his speech as well:
"I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face."
In the Versatile Stain Remover ad by OxiClean, you see Billy Mays use the stain remover to clean different products to showcase the product's ability as a stain remover.
An iPhone commercial shows the smartphone's different features that make it stand out from the rest.
Some More Examples of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Almost everyone uses these three modes of persuasion in one form or the other in their arguments. Let’s see how famous people have used them through time.
"During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife.
Pixar went on to create the world's first computer-animated feature film, Toy Story and is now the most successful animation studio in the world.
In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple's current renaissance."
—Steve Jobs, 2005
Steve Jobs, the co-founder of Apple, relies heavily on ethos here. He uses his authority as a founder of successful tech companies to show people why they should listen to him.
"I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations.
Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality."
—Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
Martin Luther King Jr. was famous for fighting for civil rights. In the above excerpt from his speech “I Have a Dream,” he uses pathos to empathize with his audience.
He informs them that he understands they have suffered a lot and have come out of a painful time. This evokes emotion in the audience, and they can connect with King easily.
"Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be.
But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better-adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature that would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders.
In such a case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favored the individuals of any of the species by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement."
—Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species, 1859
Charles Darwin appeals to logic or logos in his book Origin of the Species by talking about the rationale of natural selection.
He talks about how species have evolved with time to better adapt to their environment, a.k.a survival of the fittest. You can see how he uses a logical argument to talk about natural selection.
Conclusion: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Ethos, pathos, and logos have survived the test of time and are used almost everywhere today. You can find them embedded in commercials, movies, speeches, TED talks, and day-to-day arguments.
These three tools of persuasion appeal to different aspects of humanity: authority, emotion, and logic. When used together, they form a solid argument that can convince anyone of its gist.
Ethos uses the speaker’s authority or credibility to persuade the audience. Pathos uses emotion to trigger people to take action. On the other hand, logos rely on facts and logic to drive a point across.
All three are very important to use in any argument.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case.
Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning takes a specific representative case or facts and then draws generalizations or conclusions from them. Inductive reasoning must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. In other words, the facts you draw on must fairly represent the larger situation or population. Example:
In this example the specific case of fair trade agreements with coffee producers is being used as the starting point for the claim. Because these agreements have worked the author concludes that it could work for other farmers as well.
Deductive reasoning begins with a generalization and then applies it to a specific case. The generalization you start with must have been based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence.Example:
In this example the author starts with a large claim, that genetically modified seeds have been problematic everywhere, and from this draws the more localized or specific conclusion that Mexico will be affected in the same way.
Avoid Logical Fallacies
These are some common errors in reasoning that will undermine the logic of your argument. Also, watch out for these slips in other people's arguments.
Slippery slope: This is a conclusion based on the premise that if A happens, then eventually through a series of small steps, through B, C,..., X, Y, Z will happen, too, basically equating A and Z. So, if we don't want Z to occur A must not be allowed to occur either. Example:
In this example the author is equating banning Hummers with banning all cars, which is not the same thing.
Hasty Generalization: This is a conclusion based on insufficient or biased evidence. In other words, you are rushing to a conclusion before you have all the relevant facts. Example:
In this example the author is basing their evaluation of the entire course on only one class, and on the first day which is notoriously boring and full of housekeeping tasks for most courses. To make a fair and reasonable evaluation the author must attend several classes, and possibly even examine the textbook, talk to the professor, or talk to others who have previously finished the course in order to have sufficient evidence to base a conclusion on.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: This is a conclusion that assumes that if 'A' occurred after 'B' then 'B' must have caused 'A.' Example:
In this example the author assumes that if one event chronologically follows another the first event must have caused the second. But the illness could have been caused by the burrito the night before, a flu bug that had been working on the body for days, or a chemical spill across campus. There is no reason, without more evidence, to assume the water caused the person to be sick.
Genetic Fallacy: A conclusion is based on an argument that the origins of a person, idea, institute, or theory determine its character, nature, or worth. Example:
In this example the author is equating the character of a car with the character of the people who built the car.
Begging the Claim: The conclusion that the writer should prove is validated within the claim. Example:
Arguing that coal pollutes the earth and thus should be banned would be logical. But the very conclusion that should be proved, that coal causes enough pollution to warrant banning its use, is already assumed in the claim by referring to it as "filthy and polluting."
Circular Argument: This restates the argument rather than actually proving it. Example:
In this example the conclusion that Bush is a "good communicator" and the evidence used to prove it "he speaks effectively" are basically the same idea. Specific evidence such as using everyday language, breaking down complex problems, or illustrating his points with humorous stories would be needed to prove either half of the sentence.
Either/or: This is a conclusion that oversimplifies the argument by reducing it to only two sides or choices. Example:
In this example where two choices are presented as the only options, yet the author ignores a range of choices in between such as developing cleaner technology, car sharing systems for necessities and emergencies, or better community planning to discourage daily driving.
Ad hominem: This is an attack on the character of a person rather than their opinions or arguments. Example:
In this example the author doesn't even name particular strategies Green Peace has suggested, much less evaluate those strategies on their merits. Instead, the author attacks the characters of the individuals in the group.
Ad populum: This is an emotional appeal that speaks to positive (such as patriotism, religion, democracy) or negative (such as terrorism or fascism) concepts rather than the real issue at hand. Example:
In this example the author equates being a "true American," a concept that people want to be associated with, particularly in a time of war, with allowing people to buy any vehicle they want even though there is no inherent connection between the two.
Red Herring: This is a diversionary tactic that avoids the key issues, often by avoiding opposing arguments rather than addressing them. Example:
In this example the author switches the discussion away from the safety of the food and talks instead about an economic issue, the livelihood of those catching fish. While one issue may affect the other, it does not mean we should ignore possible safety issues because of possible economic consequences to a few individuals.
Ethos or the ethical appeal is based on the character, credibility, or reliability of the writer. There are many ways to establish good character and credibility as an author:
- Use only credible, reliable sources to build your argument and cite those sources properly.
- Respect the reader by stating the opposing position accurately.
- Establish common ground with your audience. Most of the time, this can be done by acknowledging values and beliefs shared by those on both sides of the argument.
- If appropriate for the assignment, disclose why you are interested in this topic or what personal experiences you have had with the topic.
- Organize your argument in a logical, easy to follow manner. You can use the Toulmin method of logic or a simple pattern such as chronological order, most general to most detailed example, earliest to most recent example, etc.
- Proofread the argument. Too many careless grammar mistakes cast doubt on your character as a writer.
Pathos , or emotional appeal, appeals to an audience's needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. Pathos can also be understood as an appeal to audience's disposition to a topic, evidence, or argument (especially appropriate to academic discourse).
Argument emphasizes reason, but used properly there is often a place for emotion as well. Emotional appeals can use sources such as interviews and individual stories to paint a more legitimate and moving picture of reality or illuminate the truth. For example, telling the story of a single child who has been abused may make for a more persuasive argument than simply the number of children abused each year because it would give a human face to the numbers. Academic arguments in particular benefit from understanding pathos as appealing to an audience's academic disposition.
Only use an emotional appeal if it truly supports the claim you are making, not as a way to distract from the real issues of debate. An argument should never use emotion to misrepresent the topic or frighten people.
Project Types We Cover
- Admissions Essay
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Research Paper
- Book Reviews
- Personal Statement
- Ph.D Dissertation
- Proofreading
Academic Fields & Subjects
- Programming
- Computer Science
- Other projects we help with
- Our Experts
- Plagiarism Checker
- Writing Tips
- Ethos Pathos and Logos
Persuasive Essay Using Ethos Pathos and Logos
By: Henrique Bertulino

You may not know it but you need logos, ethos, pathos, and even kairos to come up with a good essay. Basically, these things, also called modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals, can help you convince your audience and support your arguments. These four elements of persuasion were even described by Aristotle in his Rhetoric, and he definitely knew how to be persuasive. Now you can get a short summary of the ancient philosopher's research and use his knowledge in your favor!
Understanding Logos, Ethos, and Pathos
Examples of logos, examples of ethos , examples of pathos , bonus: what is kairos.
So, what are logos, ethos, and pathos? You can see them as three elements of an effective persuasive message, which can come in handy for your argumentative essay. You're using them already, there's no doubt, but you're just doing it unknowingly for now. But by knowing them well and using them purposefully you can get as convincing and confident as by using a professional rhetorical approach. Also, knowing the structure of your persuasion will improve the structure of your speech overall, both written and spoken. So get to know logos, ethos, pathos, and kairos better.
What Is Logos?
Logos is the persuasive technique appealing to the rational part. It's related to the facts you use to support your argument and make your idea look more attractive to the audience. Logos is usually called a "logical appeal", and it comes in the form of the citation of statistics, facts, charts, graphs, etc. It makes your statement more reliable and legit by using undoubtful things that can be checked and measured.
There are different rational modes of thinking to use, here are some examples:
- Deductive reasoning — going from a broad, general claim to a specific point.
- Inductive reasoning — using some specific examples to support a broad generalization.
- Comparison — highlighting the strength of your claim by comparing your case with a similar one in which the fairness of your position is clearer.
- Cause/effect thinking — basing your position on making assumptions about the future, making predictions that prove you're right.
- Exemplification — listing many examples of evidence to support your opinion.
- Coherent thought — structuring your thoughts properly so that they are easy to receive and understand.
Let’s pretend you need to write an argumentative essay reflecting global warming. Here are some examples of logos you can use to make your arguments stronger.
- The average surface temperature of the Earth has risen about 2.05 degrees Fahrenheit since the late 19th century.
- NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment have data showing that Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019.
- When it comes to surface ocean waters, their level of acidity has increased by about 30% since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.
What Is Ethos
Ethos is another important brick in the wall of your persuasion, it appeals to your character and evaluates your opinion in terms of your trustworthiness. It relies on your credibility as a speaker and decreases or increases the level of trust that the audience has towards you depending on how reliable you are as a source. Ethos is not only related to your own authority and achievements but also to the values or ideologies that your potential listener or reader may share.
There are several ways to show people your credibility, such as:
- Describing more than one opinion and providing counterarguments to show that you're knowledgeable and open to other positions.
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the beliefs that matter to the audience, which may also include using special language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles, to build the bond.
- Demonstrating your reputation, expertise, experience, or academic knowledge in a field.
Let’s continue with your discussion paper on global warming. Here are some examples of ethos that can support your argument.
- I have a degree in Biology and I can assure you the way this company disposes of its waste can harm the environment.
- My family has a business related to fishing and I can say that for the last 15 years, the level of water quality has been decreasing dramatically.
- As I've spent the last summer as a volunteer for a non-profit environmental organization, I know that the effect of global warming is even more dreadful than the media portray it.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos focuses your audience's attention on their emotions and how your writing corresponds with them. It appeals to such things as empathy, imagination, feelings, fears, etc. Combined with two other modes, this emotional one can help you build a strong argument that will convince any audience that you're right.
Here are some examples of what can help you:
- Describing things, people, places, events, and ideas in an expressive and relatable way.
- Creating vivid images that make readers not only understand but also feel your claim.
- Sharing personal stories to build a stronger connection with your readers.
- Using emotionally charged vocabulary to reflect a specific mindset and create a specific atmosphere.
- Appealing to the facts that may affect your audience and their lives so that they can actually relate to the things you're saying.
As we keep going with your imaginary discussion essay about global warming, let's see what pathos examples can be useful.
- Due to global warming hurricanes will become stronger and more intense, which is a life-threatening change.
- Extreme heat affects not only people's health, but also energy consumption, agricultural industry, and economics.
- Obviously, the rising of the temperature leads to declining water supplies, which means the price of just an ordinary water bottle will increase drastically in no time.
This one is way less-used but still present. Kairos stands for "right time". And it basically refers to the optimal moment to take action. You can make your claim stronger by building a connection between your position and the actual situation you and your audience are in right now. Your logos, ethos, and pathos need to be served in a perfect moment to strike effectively, and that's when kairos comes into play.
User ratings:
User ratings is 4.4 stars.
4.4 /5 ( 28 Votes)

Head of Customer Success
I'm a medical doctor and brand manager. The process of getting into Med school and studying at it made me learn and apply many strategies to keep my productivity high while spending less time and effort. As a working student, I had to figure out how to study smarter, not harder. During this period, my interest in neurology and psychiatry, as well as my aspiration to help others, intensified. At Studybay, I use my knowledge, skills, and experience to develop helpful solutions for students and make their study paths more productive and fun.
Add Your Comment
We are very interested to know your opinion
Frankly speaking, when I started reading about Ethos, Logos, Pathos, and Kairos, I could not understand what they are and how they can be used in essay writing. However, after reading your notes, everything has become clear. It will be very easier to me to teach my students how these rhetorical appeals are used in essay writing. Thank you very much.
Jean Bosco Twahirwa
This is a detailed lesson about the use of persuasive strategies in essay writing. Shout out to you; hats off! May I have another detailed example of a full written essay about inclusive education? That will be kind of you, guys.
TWAHIRWA Jean Bosco
Such an enlightening article! It not only explained the importance of ethos, pathos, and logos but also showcased how they work together to make arguments more convincing. I feel more confident in my argumentative essay writing after reading this.
I never realized how much of an impact my use of ethos, pathos, and logos made in my writing until I read this article.
I’ve used the techniques in this article for my latest essay and noticed a significant improvement in its persuasive power.
I found this extremely helpful in improving my essay writing skills. The examples provided were spot-on and helped me better grasp the importance of ethos, pathos, and logos in persuasive writing. Highly recommended!

Upgrade your writing skills!
Try our AI essay writer from Studybay today!
- My Storyboards
The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
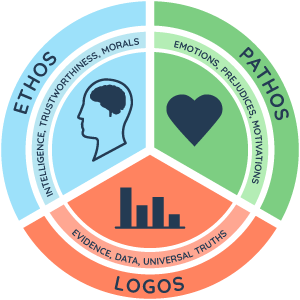
Rhetoric Definition
Rhetoric is using language in an effective manner with the aim to persuade or motivate an audience. Rhetoric is applicable to both speaking and writing.
In high school, the ELA Common Core State Standards require students to develop formal writing skills, creating essays and arguments that are well-thought-out and syntactically varied. They also require students to effectively use persuasive writing strategies to defend a claim or point of view.
A great way to enhance students' understanding of effective arguments is to teach the Aristotelian concepts of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos . This requires a basic working knowledge of rhetoric. A key to strong persuasive writing is the ability to dissect and validate, or debunk, the rhetoric of other arguments.
What is Ethos?
Ethos refers to the credibility of a speaker or writer. It establishes trust and authority on a particular topic. The definition of ethos focuses on character, expertise, reliability, and reputation. When a speaker utilizes ethos, they demonstrate their qualifications, morals, and knowledge to influence an audience.
For example, Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech exemplifies strong ethos. As an influential civil rights activist, MLK established his reputation and character. His credibility compelled audiences nationwide to support the civil rights movement. MLK highlighted his educated background and referred to respected documents like the Constitution to showcase his expertise on racial injustice. This enhanced his ethical appeal.
Ethos appeals to:
- Intelligence
- Perception of trustworthiness

What is Pathos?
Pathos evokes emotion in an audience to persuade them. The pathos definition involves appealing to sympathies, imagination, and personal connections. Pathos sways an audience by targeting desires, biases, and motivations. Instead of relying solely on statistics, pathos utilizes vivid language, imagery, and metaphors.
In literature, Charles Dickens leveraged pathos effectively in his novels. For example, Oliver Twist depicts the appalling conditions of orphanages and child labor. Dickens magnified feelings of outrage and empathy through emotive descriptions of Oliver's miserable circumstances. This made the public determined to correct social injustices impacting children.
Pathos appeals to:
- Emotions and feelings
- Biases and prejudices
- Motivations

What is Logos?
Logos utilizes facts, data, and logical reasoning to construct a persuasive argument. The logos definition focuses on credibility rooted in rationality rather than emotion. Logos establishes an argument as logical and sound through citing evidence, testimonies, and statistics, and providing context. Unlike pathos, logos avoids sentimentality in favor of objective explanations.
For instance, a scientific paper delivers logos by presenting methodical research and empirical evidence. The paper avoids unverified assumptions or subjective viewpoints. Through precise language and factual details, the author systematically supports their hypothesis with logical analysis of experiments and results. This logos strengthens the paper's central thesis.
Logos utilizes:
- Statistics and Data
- Universal truths
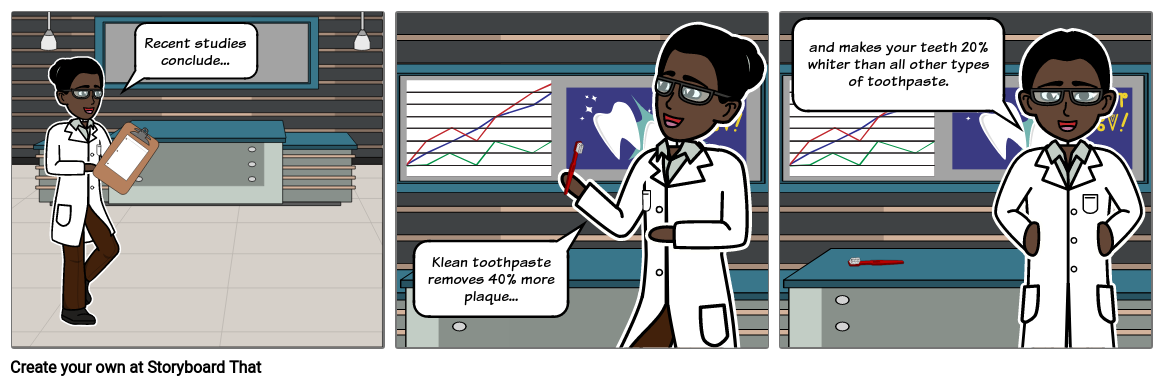
Rhetorical Strategies and Devices
The successful implementation of ethos, pathos, and logos in writing or speech depends on the effectiveness of different rhetorical strategies . There are many different rhetorical strategies (and rhetorical fallacies!) that can strengthen or weaken an argument. A few of the more familiar strategies to students include:
| Rhetorical Questions | encourages audience to think about an obvious answer |
| Analogy | establishes a more familiar concept to explain a more complicated or remote subject |
| Rebuttal | disproves or refuses an assertion |
| Antithesis | uses strongly contrasting words, images, or ideas |
| Parallelism | repeats a grammatical structure to emphasize an important idea |
| Repetition | repeats a specific word or phrase to ensure that the audience pays attention |
| Loaded Words | uses the connotations of words to play on the audience’s emotions |
| Restatement | expresses the same idea but in different words to clarify or emphasize |
| Understatement or Overstatement | use to be ironic, call attention to an idea, or to emphasize an idea through exaggeration |

By recognizing the tactics of a persuasive argument, students learn to use it themselves and recognize these tactics in daily life. One excellent way to teach and review the concepts of ethos, pathos, and pathos is through a storyboard.
In the following example storyboard, each concept is briefly explained and then shown in action. When students create a definition or example board like this, classroom concepts are reinforced, and students have the chance to demonstrate them creatively.

By incorporating the visual elements of a storyboard as well as text, even students who struggle creating organized written thoughts can demonstrate mastery of the subject. Additionally, teachers can immediately see and respond to inaccuracies, allowing them to use class time to assess and correct, rather than handing back graded work a day or two later.
Using Storyboards In Your Classroom
- Use storyboards to create advertisements for products using Ethos, Pathos, or Logos to convince potential buyers.
- Use a storyboard to create an “argument diagram” of a famous speech. Students can break the speech up into tactics, then show an example of those tactics in each cell.
- Ask students to create a persuasive storyboard about a topic that is important to them. Require them to use one, or all, of the tactics in the rhetorical triangle.
- Have students collaborate and promote an unpopular school rule, consequence, homework, or even cafeteria food. Have them utilize rhetorical tactics and strategies in their promotion. Having to flip a negative idea into a positive one is also a great way to teach propaganda.
- Give students an empty storyboard as part of an assessment and ask them to explain and give an example of each: ethos, pathos, logos.
Related Activities
Check out these ethos, pathos, logos activities from our guides on Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , The Tragedy of Julius Caesar , and "Letter from Birmingham Jail" .
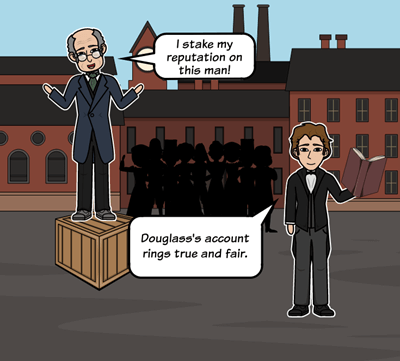
Related Resources
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos in I Have a Dream Speech
- Rhetorical Strategies in Declaration of Independence
- Types of Propaganda
- Text Analysis Storyboard Templates
| Proficient 33 Points | Emerging 25 Points | Beginning 17 Points | |
|---|---|---|---|
How to Incorporate Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Group Discussions and Debates in the Classroom
Introduction and explanation.
Begin by introducing ethos, pathos, and logos as rhetorical strategies used to persuade an audience. Explain that incorporating these strategies in group discussions and debates can enhance the effectiveness of arguments and promote critical thinking.
Teach the Concepts
Provide clear definitions and examples of ethos, pathos, and logos. Illustrate how each strategy appeals to different aspects of persuasion: ethos focuses on credibility, pathos appeals to emotions, and logos emphasizes logical reasoning.
Analyze Real-World Examples
Engage students in analyzing real-world examples of group discussions, debates, or persuasive speeches. Encourage them to identify instances of ethos, pathos, and logos used by the speakers to support their arguments.
Practice Identifying Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Assign group activities or provide sample texts where students can identify and analyze the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. Guide discussions on how the application of these strategies influences the effectiveness and persuasiveness of the arguments presented.
Structured Debate or Discussion
Divide students into groups and assign a debate or discussion topic relevant to the curriculum or current events. Instruct each group to incorporate ethos, pathos, and logos into their arguments and encourage them to support their viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
Reflection and Feedback
After the debate or discussion, facilitate a reflection session where groups can evaluate their use of ethos, pathos, and logos. Provide constructive feedback on their application of these strategies and encourage students to reflect on how they can improve their persuasive skills in future discussions or debates.
Frequently Asked Questions about The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
What is the rhetorical triangle.
The Rhetorical Triangle is a framework developed by Aristotle to analyze the elements of persuasive writing and speaking. It consists of three key elements: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos. Ethos refers to the credibility of the speaker or writer, Pathos appeals to emotions, and Logos appeals to logic.
Why is it important to understand the Rhetorical Triangle?
Understanding the Rhetorical Triangle is essential for effective communication, particularly in persuasive writing and speaking. By analyzing the use of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in an argument, one can identify the strengths and weaknesses of the argument and ultimately develop stronger persuasive writing and speaking skills.
How can the Rhetorical Triangle be applied in the classroom?
The Rhetorical Triangle can be applied in the classroom to teach students how to develop persuasive writing and speaking skills. Teachers can introduce students to the concepts of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos and provide examples of each. Students can then practice identifying these elements in various texts and speeches and apply them in their own writing and speaking.
Pricing for Schools & Districts
Limited Time
- 10 Teachers for One Year
- 2 Hours of Virtual PD
30 Day Money Back Guarantee • New Customers Only • Full Price After Introductory Offer • Access is for 1 Calendar Year
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Limited Time. New Customers Only
Back to school special!
Purchase orders must be received by 9/6/24.
30 Day Money Back Guarantee. New Customers Only. Full Price After Introductory Offer. Access is for 1 Calendar Year
Generating a Quote
This is usually pretty quick :)
Quote Sent!
Email Sent to
Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
You may be surprised to learn that much of your life consists of constructing arguments. If you ever plead a case to your parents—in order to extend your curfew or to get a new gadget, for example—you are using persuasive strategies. When you discuss music with friends and agree or disagree with them about the merits of one singer compared to another, you are also using strategies for persuasion.
Indeed, when you engage in these "arguments" with your parents and friends, you are instinctively using ancient strategies for persuasion that were identified by the Greek philosopher Aristotle a few thousand years ago. Aristotle called his ingredients for persuasion pathos , logos , and ethos .
Persuasion Tactics and Homework
When you write a research paper , write a speech , or participate in a debate , you also use the persuasion strategies mentioned above. You come up with an idea (a thesis) and then construct an argument to convince readers that your idea is sound.
You should become familiar with pathos, logos, and ethos for two reasons: First, you need to develop your own skills at crafting a good argument so that others will take you seriously. Second, you must develop the ability to identify a really weak argument, stance, claim, or position when you see or hear it.
Logos Defined
Logos refers to an appeal to reason based on logic. Logical conclusions come from assumptions and decisions derived from weighing a collection of solid facts and statistics . Academic arguments (research papers) rely on logos.
An example of an argument that relies on logos is the argument that smoking is harmful based on the evidence that, "When burned, cigarettes create more than 7,000 chemicals. At least 69 of these chemicals are known to cause cancer, and many are toxic," according to the American Lung Association. Notice that the statement above uses specific numbers. Numbers are sound and logical.
An everyday example of an appeal to logos is the argument that Lady Gaga is more popular than Justin Bieber because Gaga's fan pages collected 10 million more Facebook fans than Bieber's. As a researcher, your job is to find statistics and other facts to back up your claims. When you do this, you are appealing to your audience with logic or logos.
Ethos Defined
Trustworthiness is important in research. You must trust your sources, and your readers must trust you. The example above concerning logos contained two examples that were based on hard facts (numbers). However, one example comes from the American Lung Association. The other comes from Facebook fan pages. You should ask yourself: Which of these sources do you suppose is more credible?
Anyone can start a Facebook page. Lady Gaga may have 50 different fan pages, and each page may contain duplicate "fans." The fan page argument is probably not very sound (even though it seems logical). Ethos refers to the credibility of the person posing the argument or stating the facts.
The facts provided by the American Lung Association are probably more persuasive than those provided by fan pages since the American Lung Association has been around for more than 100 years. At first glance, you might think that your own credibility is out of your control when it comes to posing academic arguments, but that is incorrect.
Even if you write an academic paper on a topic that is outside your area of expertise, you can improve your credibility—using ethos to persuade—by coming across as a professional by citing credible sources and making your writing error-free and concise.
Pathos Defined
Pathos refers to appealing to a person by influencing his emotions. Pathos is involved in the strategy of convincing the audience by invoking feelings through their own imaginations. You appeal through pathos when you try to convince your parents of something. Consider this statement:
"Mom, there is clear evidence that cellphones save lives in emergency situations."
While that statement is true, the real power lies in the emotions that you will likely invoke in your parents. What mother wouldn't envision a broken-down automobile perched by the side of a busy highway upon hearing that statement?
Emotional appeals are extremely effective, but they can be tricky. There may or may not be a place for pathos in your research paper . For example, you may be writing an argumentative essay about the death penalty.
Ideally, your paper should contain a logical argument. You should appeal to logos by including statics to support your view such as data that suggests that the death penalty does/does not cut down on crime (there's plenty of research both ways).
Use Appeals to Emotion Sparingly
You may also use pathos by interviewing someone who witnessed an execution (on the anti-death penalty side) or someone who found closure when a criminal was executed (on the pro-death penalty side). Generally, however, academic papers should employ appeals to emotions sparingly. A long paper that is purely based on emotions is not considered very professional.
Even when you are writing about an emotionally charged, controversial issue like the death penalty, you can't write a paper that is all emotion and opinion. The teacher, in that circumstance, will likely assign a failing grade because you haven't provided a sound (logical) argument.
- “ What's In a Cigarette? ” American Lung Association,
- Words, Phrases, and Arguments to Use in Persuasive Writing
- Convince Me: A Persuasive Writing Activity
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- How Can You Stretch a Paper to Make it Longer?
- Research Note Cards
- Finding Sources for Death Penalty Research
- Understanding the Progressive Era
- Finding Statistics and Data for Research Papers
- Tips for Typing an Academic Paper on a Computer
- Strategies for Writing a 20-Page Paper
- How to Find Trustworthy Sources
- How to Narrow the Research Topic for Your Paper
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- How to Write a News Article That's Effective
- What Is a Bibliography?
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Writing — Persuasive Writing: The Power of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Persuasive Writing: The Power of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
- Categories: Writing
About this sample

Words: 870 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 870 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Table of contents
Using ethos, pathos, and logos together, counterarguments.
- Professional qualifications, expertise, and experience
- Personal reputation, character, and integrity
- Third-party endorsements, testimonials, and references
- Common values, beliefs, and interests
- Create empathy, compassion, or sympathy
- Trigger fear, anger, or sadness
- Stir hope, inspiration, or joy
- Connect with the audience's values, beliefs, and experiences
- Present facts, data, and statistics
- Use reasoning, deductions, and analogies
- Use examples, anecdotes, and case studies
- Address counterarguments and refute objections
- Establish your ethos first, to gain the audience's trust and respect
- Use pathos to engage the audience's emotions and values, but avoid manipulating or exploiting them
- Use logos to provide evidence, reasoning, and counterarguments, but avoid being too technical or dry
- Integrate ethos, pathos, and logos seamlessly, so that they reinforce each other and create a persuasive synergy
- Acknowledge the counterarguments and show that you understand the other side's perspective (ethos)
- Anticipate the emotional reactions that the counterarguments may trigger and address them proactively (pathos)
- Provide evidence, reasoning, and examples to refute the counterarguments and strengthen your position (logos)
- Use rhetorical questions, analogies, or metaphors to reframe the counterarguments and show their weaknesses (logos)

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 730 words
1 pages / 554 words
1 pages / 567 words
2 pages / 1119 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Writing
Writing is not merely a means of communication; it is a multifaceted tool that influences cognitive, emotional, and social dimensions of human experience. This essay will investigate the impact of writing on cognitive skills [...]
The movie Freedom Writers is based on the true story of a teacher, Erin Gruwell, who inspired her at-risk students to overcome their personal struggles and societal barriers through writing. The film explores various themes [...]
Agatha Christie is a name synonymous with mystery and detective fiction. Her works have transcended time, captivating readers and spawning numerous adaptations in various media. However, what is less known about this literary [...]
When applying to the University of Pittsburgh, the application essay serves as a pivotal component that can significantly influence an applicant's admission prospects. This essay is not merely a requirement but an opportunity [...]
As a writer, I have always found it challenging to articulate my thoughts and ideas in a way that truly captures the essence of who I am and what I believe in. The art of writing has been a lifelong passion of mine, one that has [...]
Kurt Vonnegut, the acclaimed American author known for his dark humor and satirical wit, has left an indelible mark on the literary world with his unique writing style. Through an analysis of Vonnegut's works, one can discern [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Ethos Pathos Logos Example in Literature
This essay about the strategic use of logos in literature demonstrates how authors employ logical reasoning and factual evidence to enhance their narratives’ impact and depth. Through examples from works like George Orwell’s “Animal Farm,” Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar,” Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice,” and Rebecca Skloot’s “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks,” the essay elucidates how logos engages readers intellectually, enriching their understanding and fostering deeper engagement with the text. By recognizing and understanding the implementation of logos, readers can interrogate ideas and appreciate the literary craftsmanship on a more profound level, turning passive reading into an active dialogue with the text.
How it works
When we dive into the rich tapestry of literature, we often find ourselves ensnared not just by the eloquence of the prose or the complexity of character development, but also by the meticulous structure of the arguments presented. This is where logos comes into play—a rhetorical device that beckons us to lean into our logical faculties and be persuaded by reason. Logos, a term derived from Greek meaning “word” or “reason,” is one of the chief techniques a writer employs to engage the intellect of readers, convincing them through logical explanation and factual evidence.
By exploring various examples of logos in literature, we gain a deeper understanding of how authors craft their narratives to not only tell a story but also to argue, inform, and persuade.
Take, for instance, George Orwell’s “Animal Farm,” a narrative ripe with political undertones and ethical questions. Orwell doesn’t just spin a yarn about farm animals; he constructs a logical critique of totalitarianism. In the novella, the pig Old Major delivers a rousing speech that sets the foundation of the animals’ uprising. Old Major’s argument is methodical and clear: he presents a series of grievances regarding the exploitation of animals by humans, backed by observations and concluded with the reasoning that the removal of man will lead to a utopia for animals. His use of logos is not just in the listing of complaints but in the causal connection he draws between human behavior and animal misery— a logical pathway that convinces his animal audience of the necessity for a revolt.
Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar” provides another profound canvas where logos is masterfully employed. The play is particularly memorable for the funeral orations by Brutus and Mark Antony, which are classic studies in persuasive speech. Brutus attempts to justify Caesar’s assassination to the Roman populace using a series of reasoned arguments, appealing to the citizens’ desire for freedom from tyranny. He logically argues that Caesar’s ambition would have hurt Rome, presenting his case with such rational calmness that the crowd is swayed. Yet, this is juxtaposed by Mark Antony’s speech, which, while famously known for its pathos, cleverly employs logos to dismantle Brutus’ arguments. Antony slyly introduces facts and rhetorical questions that expose the flaws in Brutus’ logic, showing that Caesar’s actions were often for Rome’s benefit, thus stirring doubts about the justification of the assassination.
In the realm of classic English literature, Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice” subtly showcases logos through the interactions of its characters, particularly in the evolving relationship between Elizabeth Bennet and Mr. Darcy. During Darcy’s first, failed proposal, he uses logical arguments to explain his actions and feelings. He talks about overcoming his objections to her family’s lower social standing due to his overwhelming love for her. This moment is crucial, as it lays bare Darcy’s internal conflict and rationalizations, making his feelings for Elizabeth palpable and his character more nuanced. Austen’s use of logos here serves to deepen our understanding of Darcy, presenting his vulnerabilities and justifications in a way that resonates with the reader’s sense of reason.
Non-fiction also utilizes logos extensively, as seen in Rebecca Skloot’s “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks.” Skloot presents a compelling narrative that also serves as an investigative critique of ethical standards in scientific research. Through meticulous documentation, interviews, and historical context, Skloot constructs a logical argument about the exploitation of Henrietta Lacks. By presenting facts and data surrounding the scientific use of Lacks’ cells, alongside the lack of consent and the impact on her family, Skloot not only informs but also builds a logical case for the need for ethical reform in medical research.
These examples illustrate how effectively logos can be woven into literature to enhance the narrative’s impact and depth. It engages readers by appealing to their intellect, challenging them to rethink assumptions and consider different perspectives through rational discourse. The use of logos enriches the reading experience, providing layers of understanding that go beyond the emotional or superficial readings of a text.
In conclusion, the strategic use of logos in literature is not merely about crafting logical arguments or presenting evidence; it’s about enhancing the persuasive power of the narrative. It invites readers into a dialogue, engaging them intellectually and sometimes morally. As we traverse through different genres and eras in literature, recognizing and understanding the implementation of logos not only enhances our appreciation of literary craftsmanship but also deepens our engagement with the text. It turns passive reading into an active interrogation of ideas, fostering a richer interaction with the works we explore.
Cite this page
Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature. (2024, May 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature." PapersOwl.com , 1 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/ [Accessed: 25 Aug. 2024]
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature." PapersOwl.com, May 01, 2024. Accessed August 25, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature," PapersOwl.com , 01-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/. [Accessed: 25-Aug-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/ [Accessed: 25-Aug-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
How to use Ethos, Pathos and Logos in a Persuasive Essay
Oct 21, 2023 | 0 comments

Oct 21, 2023 | Blog | 0 comments
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three types of persuasion that an author or speaker can use to convince the audience. Ethos is the appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Pathos is the appeal to emotion, and it’s a way of convincing an audience of an argument by creating an emotional response. Logos is the appeal to logic, and it uses logical reasoning as its main tool for persuasion.
This article will discuss using these three modes when writing your essay. The difference between ethos, pathos, and logos will be elaborated by ethos, pathos, and logos examples.
Table of Contents
People Also Read
- What Is a Blue Book?- All You Need to Know as a Student
- The Role Of Feedback And Reflection In Improving Diagnostic Essay Writing Skills
- Understanding the Limitations of Survey-based Studies
What Is Logos?
The third and final aspect of ethos, logos, is an appeal to logic. It attempts to persuade readers by using reason, rationality, and facts. You can use logos to present evidence for your thesis statement—using statistics or examples from the world around you—or it can be used as a standalone approach. Either way, logos are best when backed up by evidence from the real world.
Logos makes sense because it appeals to our rational minds: we use logic every day to make decisions (or not). We ask ourselves, “Is this a good idea?” or “Will this benefit me?” We weigh the pros and cons before acting on impulse; we think about consequences before making purchases; we run through a cost-benefit analysis before investing our time or money into something new. Logos tries its hardest not just because it makes sense but because it works!
Examples of Logos
Logos are often used in essays to support a claim, explain why something is true, or give an example. For example:
- “I can’t wait for our next meeting because it will be fun.” (explanation)
- “That’s not fair! You’re supposed to let me go first.” (reasoning)
Logos are especially useful when persuading someone or making your point clear. They’re also good for showing that you understand how things work or what makes them important. For example:
- “I know that many people think they need a degree to get a job in this field, but I think most employers value experience over education anyway.” (logical reasoning)
What Is Ethos
Ethos is an appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Ethos is the Greek word for “character.” The rhetoric must establish trust with an audience to persuade them effectively. Effective ethos will make your audience feel more comfortable with you and more likely to believe what you say.
To establish ethos, you can refer to other people who have similar credentials, experience, or knowledge as yourself or else provide evidence that shows how your expertise has been beneficial in similar situations before (this makes it easier for others to accept your knowledge because they know how much experience you have).
Examples of Ethos
Examples of Ethos:
- Speeches (e.g., Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech)
- Advertisements (e.g., Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign)
- Literature and poetry (e.g., Edgar Allan Poe’s “ The Raven “)
- Journalism (e.g., the New York Times’ coverage of Hurricane Harvey)
- Politics (e.g., Donald Trump’s presidential inauguration speech)
In daily life, you can use examples of ethos to persuade people to get what you want or do what you ask them to do.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is all about the emotional connection between the speaker and the audience. It’s an appeal to the senses and feelings of an audience, often through pity or sympathy.
Essentially, pathos is all about persuasion through emotion: it’s how you can use pathos in your writing (and in life) to influence people—and get them on your side.
Because when we’re moved by something, whether it be a person’s suffering or a cause we believe in, we are more likely to act on that feeling than if there were no emotion.
So, what emotions does pathos evoke? There are many ways for writers and speakers alike to use pathos in their work—but these three methods of persuasion will probably come up most often: empathy, fear, guilt/shame.
Examples of Pathos
Here are some examples of how you can use pathos in various forms of writing:
- In advertising, an emotional appeal is often used to persuade viewers that a product will improve their lives. For example, one advertisement might portray a family enjoying time together using their new vacuum cleaner. Another advertisement might show a man alone at home watching TV and eating potato chips—but he could be happy if only he had this new brand of hot sauce!
- In speeches or debates, an emotional appeal is often used to encourage people to take action on something important to them or others. An activist might speak about how many animals have died yearly because they were trapped in animal testing labs—and ask everyone listening what they will do. A politician might talk about how his opponent’s policies won’t truly help people who need jobs; instead, he’ll ensure everyone has health insurance and gets paid more money for working full-time than if they were unemployed!
- Legal cases can include stories from witnesses or victims who experienced suffering because someone else committed wrongdoings against them (or even themselves). If you want someone else punished for stealing your car stereo system when all you did was walk outside your house one day and then come back later when there was nothing left where it should’ve been…then tell us why we should care!
Bonus: What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the right time to deliver your message.
It’s used in persuasive writing to take advantage of your audience’s current state of mind so they’re more likely to listen and act on whatever you’re trying to get across.
The best way to use kairos is by connecting with your reader emotionally—you want them to relate what you have written with their own experiences so that they can connect with what you are saying, whether it be about a product or an idea.
Examples of Kairos
Kairos is a Greek word meaning “the right or opportune moment (the supreme moment).” When the time is right, you do the right thing.
One of the most classic uses of kairos was in ancient Greece, when people would use it before speaking to kings and royalty. If someone had something important to say, they waited for a kairotic moment where both parties were available and in an appropriate mood to hear their speech.
You can use Kairos when you need to take advantage of an opportunity as soon as it arises. It’s similar to timeliness, but rather than just being on time, it’s more like jumping into action before anyone else has thought about doing so themselves! This can be useful when trying out new ideas or coming up with innovative solutions because you can come up with them before anyone else does, which means that other people will start thinking about them (which could give them ideas).
Final Thoughts on Ethos Pathos and Logos
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three important elements to consider when writing your essay.
- Ethos is the writer’s credibility, which you can establish by using facts and figures that are credible and relevant to the topic being discussed.
- Pathos is an appeal to emotion to create a connection with the reader, who will feel compelled to agree with your argument. Opening paragraphs of essays often use pathos because they set expectations for what will come later in the essay.
- Logos refers to appeals based on logic or reason rather than emotions or feelings—and, as such, relies on strong arguments supported by evidence (facts). You can use logos in any part of your essay, but especially at the end, where you want readers who did not initially agree with your point of view to change their minds after reading your supporting evidence.
Get Help from our Experts with your essay.
Our company is a professional writing service that helps students with essay writing. We have been offering this type of help to students for over 20 years, so we know what works and what does not in terms of academic success. Our team consists of highly qualified experts ready to provide you with the best possible assistance at any process stage, from initial brainstorming to final editing. In addition, we use advanced tools such as Grammarly to ensure that your written composition is flawless and fully consistent with all academic standards.
We can help you in many ways:
- Developing an outline for your essay by guiding how it should look and where each paragraph should go;
- Writing an entire paper from scratch if you don’t have enough time or confidence;
- Revising existing essays according to your instructions (you can find examples here);

I am dedicated to creating engaging blog posts that provide valuable insights and advice to help students excel in their studies. From study tips to time management strategies, my goal is to empower students to reach their full potential.
- Best 10 Persuasive Essay Examples for Students in 2024
- Revolutionizing Essay Writing with AI Essay Writers: An Analytical Perspective

Most Popular Articles
Racism thesis statement example, how to rephrase a thesis statement, capstone project topic suggestions, how to write an abortion essay, should students wear school uniforms essay, list causal essay topics write, respect essay, signal words, great synonyms, informative speech examples, essay writing guide, introduction paragraph for an essay, argumentative essay writing, essay outline templates, write an autobiographical essay, personal narrative essay ideas, descriptive essay writing, how to write a reflective-essay, how to write a lab report abstract, how to write a grant proposal, point of view in an essay, debate topics for youth at church, theatre research paper topics, privacy overview.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
There is a Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender discrimination in the Hispanic community. The causes of homosexual discrimination in American society. 6. Emotional Persuasive Essay Topics. The importance of the use of ethos, pathos, logos in essay writing. The reasons why we should protect the environment.
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Persuasion through use of emotion and sympathy, known as Pathos. Pathos can be developed by using meaningful language, emotional tone, emotion-evoking examples, stories of emotional events, and implied meanings. Much of the work in persuasive writing is knowing how to use these methods effectively.
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising. Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they're ...
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
Ethos is about establishing your authority to speak on the subject, logos is your logical argument for your point and pathos is your attempt to sway an audience emotionally. Leith has a great example for summarizing what the three look like. Ethos: 'Buy my old car because I'm Tom Magliozzi.'. Logos: 'Buy my old car because yours is ...
Pathos is a rhetorical device that involves the use of emotional appeals to persuade an audience. It is one of the three modes of persuasion identified by Aristotle, alongside ethos and logos. Pathos is about connecting with your audience on an emotional level, appealing to their values, desires, fears, and hopes.
Conclusion. Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting ...
Tips for Applying Logos in Your Writing. Strategy 1 — State the facts. Statistics, data, and other irrefutable facts make ideal evidence. "Twenty-seven percent of college students will experience back pain at some point due to the weight of their textbooks.". Strategy 2 — Show that it would be unreasonable not to take your side.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader. Pathos, or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and ...
The thesis should. 1. be a complete sentence, 2. identify the topic, and. 3. make a specific claim about that topic. In a persuasive paper, the thesis is a claim that someone should believe or do something. For example, a persuasive thesis might assert that something is effective or ineffective.
It uses logical reasons to convince people about something. When you use logos in your everyday speech or arguments, you try to mention facts or data to support your idea. While ethos uses the speaker's credibility to persuade people about something, pathos uses emotion to trigger people. Logos simply relies on logic and cuts to the chase.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Ethos, Pathos, Logos Created by: Brandon Everett Summer 2019 An appeal is an author's attempt to earn audience approval. Authors will utilize specific devices and techniques to appeal to emotion, values, character, and reason in their writing in order to make their arguments more persuasive.
Pathos. Pathos, or emotional appeal, appeals to an audience's needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. Pathos can also be understood as an appeal to audience's disposition to a topic, evidence, or argument (especially appropriate to academic discourse). Argument emphasizes reason, but used properly there is often a place for emotion as well.
You may not know it but you need logos, ethos, pathos, and even kairos to come up with a good essay. Basically, these things, also called modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals, can help you convince your audience and support your arguments. These four elements of persuasion were even described by Aristotle in his ...
Ethos refers to the credibility of a speaker or writer. It establishes trust and authority on a particular topic. The definition of ethos focuses on character, expertise, reliability, and reputation. When a speaker utilizes ethos, they demonstrate their qualifications, morals, and knowledge to influence an audience.
A dive into classical rhetoric introduces us to three stalwarts of persuasive communication: Ethos, Logos, and Pathos. While these Greek terms might sound like the stuff of ancient lore, understanding their practical application reveals their timeless relevance in shaping opinion, driving action, and forging connections.
Pathos refers to appealing to a person by influencing his emotions. Pathos is involved in the strategy of convincing the audience by invoking feelings through their own imaginations. You appeal through pathos when you try to convince your parents of something. Consider this statement:
Persuasive writing is a powerful tool that can change people's minds, attitudes, and behaviors. However, not all persuasive writing is equally effective. To make your message compelling and convincing, you need to use various techniques, such as ethos, pathos, and logos. Ethos refers to credibility, trustworthiness, and authority; pathos refers ...
Ethos Pathos Logos Example in Literature. When we dive into the rich tapestry of literature, we often find ourselves ensnared not just by the eloquence of the prose or the complexity of character development, but also by the meticulous structure of the arguments presented. This is where logos comes into play—a rhetorical device that beckons ...
Ethos is the appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Pathos is the appeal to emotion, and it's a way of convincing an audience of an argument by creating an emotional response. Logos is the appeal to logic, and it uses logical reasoning as its main tool for persuasion.
uofl.edu/writingcenter [email protected] (502)852-2173 Logos, Ethos, Pathos, Kairos Pathos (Greek for "suffering" or "experience") Focuses attention on the values and beliefs of the intended audience. Appeals to the audience's capacity for empathy, often by using an imaginable story to exemplify logical appeals. Whereas logos and ethos appeal to our mental capacities for logic ...