Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
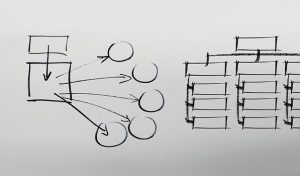
A formula for a good argument
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
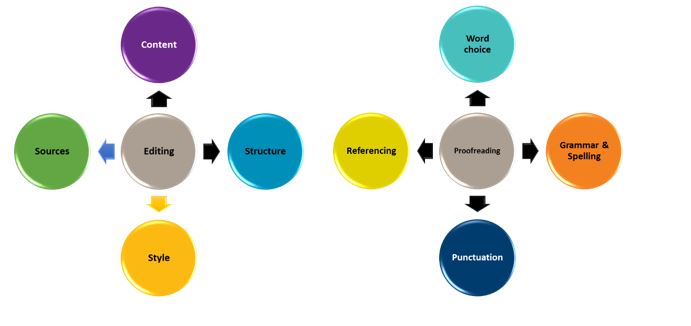
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Understanding the Assignment
There are four kinds of analysis you need to do in order to fully understand an assignment: determining the purpose of the assignment , understanding how to answer an assignment’s questions , recognizing implied questions in the assignment , and recognizing the disciplinary expectations of the assignment .
Always make sure you fully understand an assignment before you start writing!
Determining the Purpose
The wording of an assignment should suggest its purpose. Any of the following might be expected of you in a college writing assignment:
- Summarizing information
- Analyzing ideas and concepts
- Taking a position and defending it
- Combining ideas from several sources and creating your own original argument.
Understanding How to Answer the Assignment
College writing assignments will ask you to answer a how or why question – questions that can’t be answered with just facts. For example, the question “ What are the names of the presidents of the US in the last twenty years?” needs only a list of facts to be answered. The question “ Who was the best president of the last twenty years and why?” requires you to take a position and support that position with evidence.
Sometimes, a list of prompts may appear with an assignment. Remember, your instructor will not expect you to answer all of the questions listed. They are simply offering you some ideas so that you can think of your own questions to ask.
Recognizing Implied Questions
A prompt may not include a clear ‘how’ or ‘why’ question, though one is always implied by the language of the prompt. For example:
“Discuss the effects of the No Child Left Behind Act on special education programs” is asking you to write how the act has affected special education programs. “Consider the recent rise of autism diagnoses” is asking you to write why the diagnoses of autism are on the rise.
Recognizing Disciplinary Expectations
Depending on the discipline in which you are writing, different features and formats of your writing may be expected. Always look closely at key terms and vocabulary in the writing assignment, and be sure to note what type of evidence and citations style your instructor expects.
About Writing: A Guide Copyright © 2015 by Robin Jeffrey is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Composing Effective Writing Assignments
Invisible text for formatting
Resources for Teaching Writing
Course & assignment design, examples of effective writing assignments.
- Scaffolding Writing to Support Student Learning
- Creating Assignments for Miami Plan Capstone Courses
- Teaching Literature Reviews
- Using Threshold Concepts to Design Assignments and Courses
- Teaching Grammar Rhetorically
- Structuring Purposeful Group & Team Work
- Mentoring Graduate Writers
Feedback & Assessment
- Using ePortfolio Assignments
- Giving Feedback to Writers
- Facilitating Meaningful Online Discussions
- Engaging Students in Effective Peer Response
Teaching Online and with AI
- Providing Online Writing Support
- Teaching Resources and Lesson Plans
Writing is a valuable educational tool for learning. In the classroom, writing can help students grapple with and understand content more deeply and help students learn disciplinary ways of knowing and communicating. For instructors, writing can help evaluate students’ understanding of course content, and help assess students’ prior knowledge and gauge how well they’re understanding current material.
In this resource, we provide some recommendations based on best practices in writing studies research to help you compose meaningful writing assignments that promote deep learning. You can also view our companion resource “ Scaffolding Writing to Support Student Learning ” to see more ideas on how to scaffold and teach writing day-to-day in your courses.
Before we get started , we encourage you to pull up the writing assignment you are reworking, or to open a new document as you plan a brand new assignment. Take some notes as you read through each step and engage with our questions. Planning course assignments is a learning activity just like any other that benefits from writing about it.
Recommendations for Composing Effective Writing Assignments
- Identify your learning goals for the course. We often assign writing because we think we should, or because that’s how we were taught in school, or for some other reason unrelated to the purpose of the course. But sometimes writing, or more likely the type of writing we assign, isn’t the best way for students to learn, achieve, and demonstrate learning of course goals. Therefore, we suggest you start at the end by first identifying your course goals; then consider how you could use writing to achieve and assess those goals. Defining your goals and then aligning assignments to those goals leads to assignments that are targeted and cohesive within your course. (In this process, you may also find that writing isn’t the best way to assess your learning goals; yet read on, because writing has many other uses.)
- Explicitly articulate the audience for an assignment. Oftentimes students will write assignments with their teacher in mind as the audience, even as they will write for a broad array of audiences in the workplace. To encourage your students to explore the real power and impact of the writing they will do in the world, consider more explicitly identifying audiences in each of your assignments. Will a CEO be reading this business memo? Concerned parents in a school district? Eligible voters across an entire county with various interests? A important first section in an assignment prompt can be articulating audience, even if that’s asking students to identify and describe audiences themselves.
- Differentiate between declarative and procedural knowledge in your course. When determining course goals, remember that there are two types of knowledge: declarative knowledge (knowing “about” something, such as what the various parts of a microscope are) and procedural knowledge (knowing “how to” do something, such as actually using the microscope during a lab). Procedural knowledge tends to lag behind declarative knowledge. Knowing about something doesn’t necessarily mean that you know how to do something with that knowledge. Declarative knowledge is often learned through reading and lecture. Procedural knowledge requires practice, and if complex, requires practice of the component parts while building to the whole, with ongoing feedback and additional practice of those parts. It can be helpful to determine which kind of knowledge you want students to learn in your course, and then which assignments can teach which specific knowledge. Consider using this declarative and procedural knowledge worksheet as a place to get started.
- problem-focused activities
- critical thinking skills
- case studies
- synthesized reviews of literature
- assigned positions
- real world applications
Consider reframing your writing assignments to more closely appear as one of these tasks.
- Name assignments to illustrate the goals and genre. In line with the above, research also indicates that giving your assignments relevant, descriptive names (rather than “Paper 1”) can improve students’ disciplinary knowledge and knowledge transfer. For example, “Company Stakeholder Analysis” or “Marketing Change Plan” to get at some of the more specifics of what the assignment entails and is about.
- Think about how many assignments you have in the course, and how long students will need to complete this writing assignment. A lot of faculty organize their courses into units or modules, with a set number of weeks for each. Keeping in mind the kinds of declarative and procedural knowledge you wish students to learn, take stock of how many units and assignments you have overall, and think about how long students will need to complete your desired writing assignment. To do so, also consider what component skills students will need to require each task, and how much class time you might need to devote to those skills. Check out this backwards planning worksheet to help keep track of skills, tasks, and assignments in your course as you plan.
- Explain expectations clearly. Research shows that providing clear expectations can improve student engagement and the quality of their final product (Anderson et al 2016). Clear expectations can include identifying the purpose of the assignment, how it relates to other assignments/other courses, audiences for the assignment, grading criteria, and more. Try to include clear expectations in every assignment for improved clarity and to help students meet your expectations. You can even ask students to help write and codify instructions with you, helping provide them with agency in the process.
Explore the following examples to see effective writing assignments from various areas of study at Miami. These examples include the instructor’s rationale to help you reflect on your own writing assignments. Note that these assignments expand beyond the typical “research paper” assignment and engage students with important critical thinking and problem-solving.
We’ll keep adding assignments here to provide a truly representative sample of writing across the curriculum at Miami.
Economics 344: Country Report Project
Created by: Dr. Ling Shao , Assistant Teaching Professor
Context from Faculty
ECO 344 is a general elective for economics major, but it is a required course for International Studies major and International Business minor. Therefore, students enrolled in the course come from a variety of majors besides economics. They have varied levels of preparedness in math and economics training. For this reason, the course is not heavy in math. Instead, it focuses on presenting essential international trade and international macroeconomic theories in a relatively simple way. The Country Report Project (CRP) is created so that students can apply their learning of these theories to real world data and policy discussions.
The CRP is a series of assignments closely tied to the weekly content of the course. I chose this format over a single big project after learning about the merits of scaffolding. Students will have a country to work on. Depending on the number of students, it can be done individually or as a group. The country will either be assigned by the instructor or be decided by students themselves. It works well in both face-to-face and online classes. I used the CRP in Fall 2019, Spring 2020, and Summer 2020.
Sample Assignment for Economics 344
Module 1 | discussion.
For this discussion, please decide on a country that you are interested in and use the World Trade Organization (WTO) database to look at actual data on your country’s exports and imports.
Discuss the following questions based on your country’s data:
- Does your country run a surplus or deficit in total merchandise trade? How about the balances on certain smaller categories of merchandise trade such as agriculture and manufactures?
- Please include a data table in your discussion with exports and imports side by side to support your responses.
Module 2 | Discussion
For this discussion, please continue to use your country’s trade data that you have obtained. You will discuss winners and losers from trade based on your country’s top exports and top imports. Relate it to the specific-factors model. In addition, you can share any knowledge of your country’s attitude toward trade and comment if it makes sense from an economic perspective. Any trade protests you have witnessed or read about you can share as well.
This discussion will be completed through a video recording:
- 2 - 3 minutes
- Must show yourself
- You can use a few powerpoint slides if it helps make your discussion easier to follow, but it is not required.
Please respond to at least two videos from your classmates. Comment on the substance of the discussion with a critique, a question, a suggestion, or anything you see fit.
Module 3 | Discussion
For this discussion, you will discuss your country’s tariff policy. Please visit the World Trade Organization’s website. From the homepage, click “WTO membership” box in the upper middle. Find and click on the country of your interest. On the country page, please click on the pdf link under “Tariff profile” on the lower left side. Please respond to the following questions and include a screen capture of the pdf in your discussion:
- In the summary box at the top of the pdf, what is the country’s average MFN tariff rate in the most recent year?
- How does the MFN tariff compare to other summary tariff stats (e.g., final bound, trade weighted average)?
- In part A.2 of the pdf, find the product group that has the highest MFN tariff. What is that product group’s share of imports? Who do you think benefits from the tariff on the product? Who do you think is hurt by the tariff?
You must also respond to at least two posts from your classmates. Comment on your impression of their country’s tariff policy and whether their response to the winners and losers of tariff makes sense or not.
Module 4 | Discussion
Below are a few tariff case studies:
- History of U.S. Steel Protectionism
- Welfare Cost of U.S.-China Trade War
Module 5 | Discussion
For this discussion, please decide on a country (excluding the U.S.) that you are curious about and explore the history of its exchange rate policy using this paper. Click on the red PDF icon to access the paper. Please discuss the following questions:
- How many different exchange rate regimes does your country have over time?
- Select one regime change and provide some historical background on this change.
- What is the current exchange rate policy in your country?
- How has your country’s currency been performing against the U.S. dollar in the past year?
You must also comment on at least two posts from your classmates.
Module 6 | Discussion
In this discussion, you will select a country (other than the U.S.) and get exchange rates and inflation data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Then you will use the data to rest if relative PPP holds between your country and the U.S. Then discuss the following questions using the data:
- Compare your country’s inflation rates to the U.S.
- Briefly summarize how your country’s currency has been performing against the dollar over time.
- Test to see how well relative PPP holds up using the data from your country and the US.
You must also respond to at least one post from your classmates. Comment on whether the data looks right or not, and whether their understanding of relative PPP is correct or not.
Module 7 | Discussion
For this discussion, imagine you are an advisor from the International Monetary Fund and you are assigned to advise the central bank of an emerging economy on macroeconomic policy issues. Some research beyond the textbook may be necessary. Please discuss the following in a video (must show yourself; dress properly; use of PPT and visuals allowed; 3 - 4 minutes):
- What data would you collect about this economy to help you make recommendations?
- What exchange rate policy would you suggest, fixed or floating? Why?
- Would you recommend the country open up its capital market (e.g., stock market) to foreign investors or not? Why?
- If the central bank wants to know whether or not it can use monetary policy to influence domestic economics, what would you say?
Please vote for your favorite advisor (other than yourself) by posting a reply. Explain briefly what made you decide to vote for him/her.
Module 8 | Discussion
For this discussion, you will select a country (other than the U.S.) to explore its current account.
Current Account Data:
- Go to IMF BOP data site
- Click on the table titled “1. Balance of Payments Analytic Presentation by Country”
- In the country drop-down menu, select your country
- Is the current account in surplus or deficit in recent years? Any trends?
- Out of TB, NFIA, and NUT, what seems to be the determining factor of your country’s CA outcome? Is this consistent with your country’s development and income status? Why?
You must also respond to at least one post from your classmates. Please comment on whether their data analysis is correct or not and the explanation provided makes sense or not.
Economics 347: Economics of Developing Countries Analysis
Created by: Dr. Janice Kinghorn , Teaching Professor & Assessment Director
Context from the HCWE
This assignment breaks down a complex semester-long analysis into more manageable parts, by having students focus on one or two concepts they are learning each week as they build to the full analysis. The assignment explains the purpose/objectives of the assignment, specifies an audience and genre, provides detailed instructions, and describes explicitly how economists think and write so that students can practice and model those disciplinary ways of knowing.
Sample Assignment for Economics 347
The objective of this project is to allow you to apply ideas and concepts we discuss in class to a specific context - a developing country. Through completing the steps in the project you should gain a better understanding of:
- The usefulness of standard development indicators for understanding the economy of a country
- The difficulties in finding and using standard development indicators in low income countries
- The process of generating hypothesis about development by examining data
- How economists use theory to better understand development experiences
- How economists use evidence to make arguments
- How to communicate like an economist
Students will choose a developing country to work on during the semester and complete a series of assignments, mostly memos, applying what we talk about in class to that country. Through that process I expect students to become experts on their particular country and thus be able to develop a thesis about economic development and write a strong argumentative essay using economic theory to make an argument supported by evidence by the end of the term.
The implied audience for the memos and the final paper is the U.S. ambassador to that country. Remember that the ambassador is busy so it is your job to provide just enough, and never too much information. The communication should be concise, easy to read, and clearly convey your point. More detail on how to write a business memo is at http://www.fsb.miamioh.edu/fsb/content/programs/howe-writing-initiative/HWI-handout-memo.html . Another source on how to write a business memo is here.
General Notes: In the assignments I often ask you to describe. Economists tend to describe by using graphs and tables. As you are learning the field of economics, I want you to follow this convention. Of course your graphs and tables must be correct, clearly labeled, your source data must be cited in a way the reader can easily find it, and they must be original. Excellent graphs and tables will clearly communicate to the reader without making the reader work too hard to understand your point. The objective is not to demonstrate to the instructor that you found the requested data - I’m assuming you did that - rather to make a clear point with that data.
I will assume that you mean everything you write. Be careful that you don’t use generalizations for stylistic reasons that you can not back up. Be careful of using vague words that you can not define. For example, “country X’s growth rate was huge” would be more appropriately written as “country X’s growth rate averaged 6% over the past ten years”.
I expect all data and claims to be sourced (APA style). Remember that I am trying to teach you to write like an economist, so in this project I’m not only concerned that you know things, but that you can appropriately write about them.
General Grading Criteria : Most assignments, unless otherwise specified, will be graded based on:
- Is the memo on time, complete, and conforming to requirements?
- Is the memo professional - free of errors, easy to read, shows evidence of thoughtful tailoring to the audience
- Is the work properly cited?
- Do the claims demonstrate that the student can accurately apply the course concepts?
- Does the application go beyond formulaic to add to an understanding of the country’s experience?
Assignment 1: Millennium Development Goals
Choose a country, which must be approved by your instructor. You must choose a low or middle income country, NOT a high income country. See http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-and-lending-groups#High_income (Links to an external site.). to check and see if your country is high income. You must choose a country with a population of greater than five million. You may not choose a country in which you have lived. You may not choose a country in which war, political instability, or other political factors make the economic situation highly atypical (your instructor will make the judgement about which countries to exclude for this reason). No more than 3 people may choose the same country, and you may benefit from discussing your country with others who are also doing research, but your assignments must be entirely your own. See the shared Google doc linked under the assignment to “sign up” for a country.
Once you have received approval for your country, investigate how well that country achieved the Millenium Development Goals. 1. Choose two goals that you would argue were a success for that country. a. Describe why you can claim they were successful (with evidence) and b. how they were successful (find at least one credible, high quality source). 2. Describe two that they still need to work on, and give evidence for your claim. You might find it helpful to consult http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/Host.aspx?Content=Data/snapshots.htm .
Assignment 2: Income
- Describe the income, over time, and in context of your country. In class we discuss ways to measure income, so in this assignment I will not specify which you are to use, but you must justify why you chose the measure you did. You must use a professional looking graph that you have created (not copied from the internet) to communicate. You will need to choose what is meant by over time and in context. We will talk about this in class, but in general I want you to make your description meaningful by the inclusion of time and context.
- Describe the HDI for your country, and comment on the individual components. Pick one other indicator of development that is interest to you, not income or the components of HDI, and describe it for your country. The United Nations publishes data on the HDI at http://hdr.undp.org/en/data .
Assignment 3: Models of Development
We discussed models of development in chapters 3 and 4. Choose two of the models and discuss why they might be applicable to the development experience of your country. This is different from the other assignments because it asks you to apply models to the situation of the country that you have been learning about. To make your argument about applicability you will likely want to use historical experiences, as you are discussing change over time or historical conditions that have an effect on the country today. This assignment may require more library research than the others. In your final paper you will need to use theory to make an argument, so this is an opportunity to try that out. You do not need to stick with what you write for this assignment in your final paper, but you may do so.
Be sure your argument does not rely on “economist x writing in journal y thinks this model is applicable”, rather I want you to make the arguments and provide the evidence yourself. Note that the argument and evidence does not need to be complex - but it does need to be specific, and evidence does need to back up the argument. Because this assignment may be difficult, please discuss with with me if you are having difficulty. This is a great time to come to office hours to brainstorm ideas. You may also want to reach out to the business librarian at this point to help you find high quality resources for background research. You can find more information at https://libguides.lib.miamioh.edu/ECO347 .
Assignment 4: Poverty and Inequality
Describe the level of poverty and inequality in your country using standard measures of income and multidimensional poverty (UNDP has this data) that we discussed in class. Do you see any indication that there is a kuznets curve? What are the characteristics of those living in poverty (gender, ethnic origin, age, etc.)?
Assignment 5: Demographic Situation
a. Create a population pyramid for your country. The U.S. Census has this data at https://www.census.gov/data-tools/demo/idb/informationGateway.php. If your excel skills are a bit rusty you can find tutorials on the web. One is at https://www.census.gov/data-tools/demo/idb/informationGateway.php. b. How may the demographic situation in your country affect development? I have not specified what I mean by “demographic situation” so you have some latitude to choose which concept/measure from our class discussion is relevant for your country. You will need to be sure and describe (see the notes above for hints on how economists describe) the situation and make an argument connecting it to development. Note that I have also not specified how you must define “development”, so you will have to make that decision thinking about our discussion at the beginning of the term, but be sure you are intentional both in your work and in your communication.
Assignment 6: Thesis Statement
Develop a thesis about economic development in your country. Unlike the other assignments, the product is not a memo, but a one-sentence thesis. In the prior assignments you were asked to explain something that is straightforward once you did the research to find the “facts”. This assignment is different in that it asks you to take your understanding of “facts” and develop an argument by using what you know about the country and what you know about the theory of development. The following examples may get your thinking started:: country x can improve development indicator y by taking z action, country x is underdeveloped because of action y, X is a binding constraint on development of country y. A thesis is a statement of an argument. A good thesis:
- Tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- Serves as a road map for the paper; tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- Is usually a single sentence that presents your argument to the reader in a nutshell (for this assignment you are required to submit a single sentence).
For more help with writing a good thesis see this handout from the Howe center http://miamioh.edu/hcwe/handouts/thesis-statements/index.html . You are also encouraged to take advantage of the consultations available at the center. More information is at Howe Writing Center . Note that all students in this class may use the Howe Center for Business Writing, even if you are not an FSB student. If you have not looked at the resources our business librarian has put together when you were doing assignment 3 you may want to do so now. See https://libguides.lib.miamioh.edu/ECO347 . Assignment 6 will be graded based on how many times it takes you to get it right. If you submit an excellent thesis on the first try, you will get full credit. If you are asked to revise your thesis you must submit the first thesis and the revision. The more time it takes for you to get it right, the lower the grade, however you may not write the paper until you get this right.
Assignment 7: Draft
Submit a complete draft of your paper. A complete draft will 1. Have all parts complete (bibliography, footnotes, etc.) 2. Be well proofread (it should not by any means be your first draft). Details of the paper are below. For information about how to properly cite an idea or a direct quote see here. You must make sure you are fully aware of Miami’s policy on plagiarism and take steps to prevent it. Please also review the FSB’s interpretation of the Miami policy.
Assignment 8: Peer Review
Peer review at least two students’ papers. The peer review will happen in class and you will receive instructions about what I want you to do. This assignment asks you to report on your learnings from that exercise. Write a memo describing 1. two pieces of feedback you received on your paper and how you will respond to them. Note that you do not have to accept the feedback, but if you choose not to make changes based on feedback please note your reasoning. Also describe 2. Two pieces of feedback you gave to each of two classmates and why you think this feedback would make their paper more effective.
Assignment 9: Final Paper
Your final paper should be no more than 1500 words (strictly enforced) not including bibliography (APA style) and good papers are often less. I will not specify a minimum number of sources but your sources should be sufficiently diverse so that you are confident you have an understanding of multiple perspectives and your arguments and evidence are properly sourced. I will check your sources - that is, I will find them and evaluate their quality, so be sure your citations provides enough information that I can easily find them, and make sure you are comfortable with their quality (do you know who the author is? Is the author qualified? Is the argument/evidence subject to peer review or editorial review?)
The format of the paper should be an argumentative essay - you will make an argument, supported by evidence, to substantiate your thesis. More information about this type of writing can be found here .
Because this paper is the culmination of your semester-long effort to apply class material to your country it should be grounded in theories and concepts we used in this class. A paper which may be otherwise excellent but does not reflect the learning in this class this term will not be accepted.
Rubric for Assignment 9 Final Paper
| Excellent Work | Average | Poor | |
| Clarity | Grammar, spelling, and style make it easy for the reader to follow. Uses words correctly and avoids jargon unless it is the most precise word. | Occasional (2 or 3 per page) grammar, spelling or style problems. Tendency to use vague words or excessive jargon. | Problems in grammar, spelling or style that interfere with the author's statements. (Multiple problems in each paragraph). |
| Evidence/accuracy | All claims made are appropriately sourced and correct. Evidence is complete, accurate and compelling. | One claim may be unsourced or vague, but the vast majority are complete and accurate. Student may not have used the strongest evidence. | More than one claim unsourced or vague, or evidence weak. |
| Relevance/Significance | Topic is significant to both the course and in larger senses (e.g., to individual, to the region). Makes a case for that significance. | Topic is obviously central to the course. | Achieves learning objectives minimally. Topic choice is only vaguely related to the assignment. |
| Depth/Breadth | Response displays a full understanding of the complexity of the issue addressed and multiple points of view. Recognizes varied interpretations and implications. | Of the following 2 tasks, does one well and the other partially or does both partially a) Recognizing varied points of view b) Exploring the topic in depth from one point of view. | Of the following 2 tasks, does one well and the other not at all or does both minimally a) Recognizing varied points of view b) Exploring the topic in depth from one point of view. . |
| Graphs/tables | Graphs and tables are appropriate to purpose, successful in enhancing reader’s understanding, clear and easy to read, and properly sourced. | Graphs and tables are mostly appropriate, with one or more communication issues or may be not optimal for advancing argument. | Graphs and tables not easy to read or contain errors. Content is unnecessary for enhancing understanding. |
Assignment 10: Class presentation
The audience for the presentation is your classmates. Your objective is to teach them something about development by showing them how a concept we discussed is class applies to your country. Parts of the presentation are:
- Background: give the class enough information about your country so that they can understand the argument you will make, but they do not necessarily need to know everything about the country that you have learned - be strategic in what you want to share.
- Problem/thesis: Share with the class what your thesis is, and also why it is important (what is the larger development issue that is at stake)
- Argument: Clearly make your argument in a way your classmates will easily follow
- Evidence: Convince your classmates that you are correct
Your presentation should be no longer than ten minutes, and you should expect to answer questions. You are expected not only to give a professional presentation but also be professional during your classmates’ presentations. That means your demeanor should indicate to the speaker that you are interested, you should not come in late while someone is speaking, you should occasionally raise your hand to ask questions.
Rubric for Assignment 10 Class Presentation
| Excellent Work | Average | Poor | |
| Background | Provided just enough useful information for audience to understand the rest of the presentation. Information is correct, engaging, and easy to understand. | Left out some useful context or included some unnecessary detail. Audience may have some confusion over the point. | Left out important context and/or cluttered presentation with too much information. Audience may have had to struggle to retain main point. |
| Thesis | Thesis is communicated clearly. Discussion explains why this is an important development issue both to the country and to the field. | Thesis is communicated clearly. Discussion of importance is somewhat vague or importance assumed. | Unclear thesis or unclear or trivial discussion of importance. |
| Argument | Argument is clear, easy to follow, and sophisticated enough to strongly support thesis. | Argument may be slightly hard to follow, vague, or not strongly support thesis (in other words, not strongly convincing. | Argument may be hard to follow, vague, or weakly support thesis (in other words, not convincing) |
| Evidence | Presented clearly, all graphs and tables and easy to read and make a clear and relevant point. Presentation is not cluttered with data that does not directly support argument. | Presented mostly clearly. Tables and graphs may be not optimized for presentation format or may show opportunities for improvement. | Difficult to read or follow, or does not support argument. |
| Presentation Conventions | Respected presentation conventions: turned in on time, made effort to avoid technological issues delaying class, student was professional in the classroom. | Mostly respected the conventions. | Violated one or more of the conventions. |
Due Dates: Fall 2019
A late assignment is an inferior assignment, thus you will receive a 20% reduction per day for an assignment submitted past the due date. Please see Canvas for updated due dates.
History: Dear Reader Memo
Created by: Dr. Erik Jensen , Associate Professor of History
The Dear Reader memo, sometimes called a Writer’s Note, is an assignment developed by Nancy Sommers, Harvard Writing Project , that establishes communication between the writer and the instructor and/or peers (whoever will read the draft) about the state of the draft and the writer’s perceptions of it, both positive and negative, and provides an opportunity for the writer to ask the reader for specific advice. A Dear Reader memo gives the writer an opportunity to reflect on their writing process and in later drafts often includes information about what was revised and why. Instructors should provide a prompt explaining what they want students to include in their memo and should also assign some points or other incentive for completing it.
Sample Assignment
Submit a “Dear Reader” memo (maximum 250 words) at the same time as the draft and a new “Dear Reader” memo at the same time as the final version, but always as a separate document to its own location on Canvas.
The memo for the draft is your opportunity to tell me and your peer reviewer the three aspects of your draft that you are most concerned about, so that we can focus our attention and comments on those three things in particular. (For instance, you might wonder if your organization makes sense, or you might wonder about some particular pieces of evidence that you use.) Your peer reviewer and I will comment on other areas, too, if we see problems and issues in your draft, but your memo should highlight three areas, in particular.
The memo for the final version is your opportunity to tell me how you’ve incorporated my feedback and that of your peer reviewer into this final version. You should highlight specific revisions that you’ve made. You can also use this memo to justify your reasons for not making certain changes that I or your peer reviewer may have recommended, but with which you disagreed.
- Due with your peer-reviewable draft on Tuesday, November 17, by class. Submitted either entirely via Canvas, or by hard copy in class and via Canvas (if we are face to face).
- Due with your polished final draft by Tuesday, December 8, at 5:00pm. Submitted electronically, via Canvas.
History 111: Primary Source Analysis Essay
Created by: Dr. Lindsay Schakenbach Regele , Robert H. and Nancy J. Blayney Assistant Professor of History
This is a scaffolded writing assignment for the class HST111 Survey of American History I. It's intended to introduce students (usually students who are new to history as a discipline) to primary source analysis and thesis-writing in the historical discipline. I created several pre-paper assignment deadlines to get students thinking about their document ahead of time and enable me to help students work through any interpretive issues they were having. Also, I allow students to select their own document to hopefully spark feelings of curiosity and ownership.
Sample Assignment for History 111
*Please read through the assignment description, guidelines and rubric. Following this information, there is a timeline for completing the assignment.
Primary sources form the base that supports historians’ reconstructions of the past. Historians are always trying to discover both the meaning and the significance of a piece of historical evidence. By meaning, we are trying to reconstitute what that document might have meant (or how it might have been understood) by the historical actors in that era. By significance, we attempt to relate how that evidence contributes to a particular interpretation of the past.
This assignment will give you practice in interpreting historical evidence . A good document analysis will focus upon both the text itself (with attention to the specifics and nuances of language used) and the context (the broader picture of the history of that period that informs the document. Never will simply describing what happened be sufficient as an historical interpretation of a document. No outside research is needed for this, just a familiarity with the material in your textbook.
Choose ONE primary source document from your Voices of Freedom book.
In 3-5 double-spaced pages, address the following sets of questions:
- Who wrote the document, and for whom was it written? What does this suggest about the point of view reflected in the document and any potential biases?
- Why was the document written, and how does the style/structure help or hinder its purpose?
- What do the document's author, audience, and style tell us about the historical context in which this document was produced?
- What other kinds of sources would you want to examine to corroborate the document’s claims and understand its context?
Begin your essay with a sentence or two about the author, the date and title of the text, the occasion for which the text was written, and the general subject of the document. If the author's identity is unknown, try to determine as much as you can about the type of person who was responsible for the production of the document. If the document was written after the events it describes, explain what impact that might have had on its construction.
In your introductory paragraph, present a brief summary of your interpretation of the author’s perspective, method, and purpose in writing the text. Your introduction should include a thesis statement that makes an argument about the document’s significance for understanding that period of American history (a good thesis statement requires evidence to support, and could be argued against).
In the body of your essay, you may find that the most efficient and effective way to discuss and analyze the text is to move step by step through the text. After all, that is how the author intended the text to be read or heard. As you present the points that the author makes (offer quotations from the text as evidence for your discussion), you will construct your own analysis, building and developing your interpretation as your essay progresses. Give yourself time to revise your essay, so that you can go back through the essay and refine your interpretation.
In your essay, use the simple past tense to describe what the author wrote: this serves to remind both you and your readers that the author wrote for an audience of his/her contemporaries. Whenever possible, use sentence constructions with the active voice rather than passive voice. Active verbs reiterate the author’s active role in creating the text and the argument, and they encourage you to make connections and draw conclusions about the author and the text.
The essay will be graded according to the following rubric*:
- Builds on the preparatory work you’ve done /100
- Makes a cogent thesis statement /50
- Demonstrates an understanding of the document's main points by successfully answering the questions /200 (50 points for each question)
- Supports the thesis statement with clearly written and well-organized evidence from the documents /200
- Total /500 *Please see the sample essays for what a “cogent thesis statement” and “well-organized evidence,” etc., look like.
In order to help you prepare your essay, I’m asking you to do some work ahead of time. This will help ensure that you understand both the assignment and the document you’ve chosen. It will also allow me to intervene if there are major questions or misunderstandings about the documents. (I expect you to struggle with them a little bit—Primary sources are difficult!)
- Before September 11 , select your document and read through the examples of successful essays that I’ve posted
- On the Canvas discussion board, post your selection and answer the questions that follow the document., DUE Friday, Sept. 11
- Look through other students’ posts, and post 5-7 sentences reflecting on your thoughts after reading other students’ choices and if you would like to change the document you have selected (which you are permitted to do) DUE Friday, Sept. 18
- Upload your answers to the assignment questions (Word document; these can be in draft note form), DUE Friday, October 16
- Upload final primary source analysis essay (Word document), DUE Friday, November 6
History 198: Continuity/Change Essay
I focused extensively in this course on creating a writing-feedback-rewriting framework. HST 198 (“World History since 1500”) engaged students at all levels of the curriculum, both majors and non-majors. I developed a scaffolded approach to the writing assignments that followed this template:
- A best-effort draft
- “Dear Reader” memo for the draft
- Peer review memo about your partner’s draft
- Polished final draft with “Dear Reader” memo for the polished, final draft in which the writer addresses instructor comments on the draft as well as peer reviewer’s comments
Note: I used this framework for all three courses I taught during the same semester—HST 198 (“World History since 1500”), HST 331 (“Nineteenth-century Europe”), and HST 410 (“Twentieth-century Germany”). Each of these classes, which I taught all in one semester, has two or three writing assignments. I’ve provided one sample for HST 198 below.
Sample Assignment for History 198
- Due as a peer-reviewable draft on Tuesday, November 17, by class. Submitted either entirely via Canvas, or by hard copy in class and via Canvas (if we are face to face).
- Due as a polished final draft by Tuesday, December 8, at 5:00pm. Submitted electronically, via Canvas.
Why am I having you write this Essay?
This assignment hones your ability to present a clear argument that is supported by evidence and written in a manner that is accessible to people who may have a limited background in the subject matter. This is a job skill. Whether submitting grant proposals for a non-profit organization or assessing business models for a consulting firm, an ability to write thoughtfully and persuasively will serve you well.
By prompting you to examine the explicit, implicit, and perhaps even unconscious arguments, assumptions, and experiences represented in the five texts for our course, this essay also encourages you to do the historian’s work of interpreting and presenting a vision of the past. This is an unavoidably subjective enterprise, and it makes your engaged and critical reading of these texts so important.
Other than in its expanding size and power, the general nature and purpose of the state has not changed that much over the past five hundred years. Based on your readings and comparison of The Death of Woman Wang, The History of Mary Prince, Abina and the Important Men, Spider Eaters, and The Origins of the Modern World, do you agree or disagree? Why?
The Process
In a well-organized essay of around 2,000 words (roughly 7 pages, double-spaced), answer the question based on your reading of the five assigned texts from this course. You must include at least fourteen (14) direct quotations from the texts, with at least four (4) coming from Spider Eaters; at least four (4) coming from The Origins of the Modern World; and at least two (2) coming from each of the three remaining texts. Explain each quotation’s relevance to your larger argument.
Since this is an historical essay, use dates in order to provide the necessary context for a given quotation, event, or trend. You should cite the source of the quotation in a footnote or an endnote. Here’s an example:
In Chapter 5, Robert Marks argues that transformations in economic production led to the emergence of new forms of identity, noting that "industrialization created new social classes, especially the urban working class and the capitalist class."[1] (This example also highlights the fact that you should introduce every quotation.) For subsequent quotations that come from the same source as the preceding quotation, do this.[2]
Focus on the prompt. Your answer to it constitutes your thesis, which your entire essay should then seek to support. If a piece of information does not advance your thesis, do not include it. You can just as easily write an "A" paper that disagrees with the prompt as one that agrees with it. The skill, clarity, and integrity with which you craft your argument determines your grade.
- No quotation should be longer than 40 words (i.e. NO block quotations).
- Introduce each quotation so that the reader knows who has written the words that appear within the quotation marks and can put those words in context.
- Always underline the title of a book, like this, or place it in italics, like this.
The Audience
Provide enough background information so that a person will understand the logic of your argument and the relevance of your examples even without having read any of the five texts in question.
Academic Integrity
If you are strapped for time before the final version is due, *request an extension,* which in this case might mean asking for an Incomplete for the semester. An “I” is far preferable to a conviction for academic dishonesty. Know the policies stated in the student handbook regarding academic integrity. For this assignment, you should not use any source other than the assigned text (in paper or e-book format) and the in-class discussions. If you have any questions at all about what is appropriate to use, please see me.
Grading (and Peer-Review) Rubric
- Is the thesis clear, and does it address the prompt?
- Does the introductory section provide a “roadmap” that succinctly summarizes the author’s main points and organization of the essay?
- If the essay acknowledges the opposing argument, is that acknowledgment brief and concluded with a reiteration of the thesis?
- What pieces of evidence support the argument?
- What types of evidence might be missing?
- Does the author include at least the minimum number of quotations, and does the author effectively frame each one to show how it supports the argument?
- Does the essay stay focused on its thesis and adhere to its organizational roadmap?
- Are transitions between the paragraphs smooth, and does each paragraph have a topic sentence and clear focus?
- Does the essay have a forceful conclusion?
- Are the quotations, dates, and historical context accurate? Are words and names spelled correctly? Peer reviewers: Circle anything that looks suspicious, so that the author knows to double check it.
- Has the author written clearly – avoiding repetition, using comfortable vocabulary, and employing passive voice only where it makes sense to do so?
History 331: Power Essay
I focused extensively in all three courses [taught during one semester] on creating a writing-feedback-rewriting framework. I developed two or three writing assignments in each class. The three courses—HST 198 (“World History since 1500”), HST 331 (“Nineteenth-century Europe”), and HST 410 (“Twentieth-century Germany”)—engaged students at all levels of the curriculum, both majors and non-majors. For all three classes, I developed a scaffolded approach to the writing assignments that followed the same template:
Sample Assignment for History 331
By prompting you to make an argument about which sets of forces you think had the greatest impact on people’s lives during a particular period of time, this essay also emboldens you to “do history,” which entails interpreting, presenting, and supporting with evidence your vision of the past.
The state (governments, judicial systems, laws, national and local bureaucracies) shaped people's lives in the 19th century more profoundly than did broader cultural, social, economic, or environmental forces or non-state institutions. Based on do you agree or disagree? Why?
In a well-organized essay of around 3,000 words (roughly 10-11 pages, double-spaced), answer the question based on your reading of The Transformation of the World, The Communist Manifesto, and A Doll’s House. You must include at least fourteen (14) direct quotations from The Transformation of the World, at least eight (8) of which must come from the last nine chapters (Chapter XI through the Conclusion), and from five different ones among those last nine. In addition, you must include at least three (3) direct quotations from The Communist Manifesto and three (3) from A Doll’s House. Explain each quotation’s relevance to your larger argument.
In Chapter VII, on "Frontiers," Osterhammel seems to downplay the pervasiveness of territorial acquisitions, when he writes, "In nineteenth-century Europe, especially outside Russia, colonial landgrabs on a large scale became a rarity."[1] (This example also highlights the fact that you should introduce every quotation.) For subsequent quotations that come from the same source as the preceding quotation, do this.[2]
Provide enough background information so that a person will understand the logic of your argument and the relevance of your examples even without having read The Communist Manifesto, A Doll’s House, or The Transformation of the World.
- What pieces evidence support the argument?
- Are they the strongest pieces of evidence
References: 1. Jürgen Osterhammel, The Transformation of the World: A Global History of the Nineteenth Century, trans. Patrick Camiller (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2014), 323. 2. Ibid.,115.
HST 410: Dictatorship Essay
Sample assignment for history 410.
- Due as a peer-reviewable draft on Tuesday, November 19, by class. Submitted either entirely via Canvas, or by hard copy in class and via Canvas (if we are face to face).
The individual motivations for cooperating with, opposing, or simply tolerating the Nazi and East German regimes were broadly similar. Based on your reading of Kershaw and Funder, do you agree or disagree? Why?
When you are looking at cooperation, opposition, or toleration/submission, you will want to consider an array of motivations, including patriotism, peer pressure, familial ties, material desire, longing for greater rights, obedience, and so on. Our class discussions will play a central role in helping us to think through these motivations.
In a well-organized essay of around 3,000 words (roughly 10-11 pages, double-spaced), answer the question based on your reading of The End and Stasiland. You must include at least sixteen (16) direct quotations, eight (8) of which must come from Kershaw and eight (8) of which must come from Funder. Draw these quotations from different chapters throughout both works, rather than from just a single chapter or section. Explain each quotation’s relevance to your larger argument.
In his discussion of the role of Jews during the Revolutions of 1848, Elon notes the multi-generational nature of this involvement when he writes, "An older generation of Jewish militants found a role as well." [1] (This example also highlights the fact that you should introduce every quotation.) For subsequent quotations that come from the same source as the preceding quotation, do this.[2]
Provide enough background information so that a person will understand the logic of your argument and the relevance of your examples even without having read The End or Stasiland.
References: 1 . Amos Elon, The Pity of It All: A Portrait of the German-Jewish Epoch , 1743-1933 (New York: Picador, 2002), 163. 2. Ibid.,197.
Gerontology 354: Rhetorical Analysis
Created by: Dr. Kate de Medeiros, Professor & O'Toole Family Professorship
For this undergraduate class, students work on a final persuasive paper based on a controversy of their choice over the course of the semester. I wanted them to read carefully to see how written language can be used to set a tone, to subtly persuade, to speak with authority, to leave one with a certain emotion, and so on. They first complete the rhetorical analysis on controversy articles from the “Opposing Viewpoints” database. After they write their draft, they use the same rhetorical analysis steps to provide a peer review on a classmate’s paper.
Sample Assignment from Gerontology 354
A critical part of writing well is learning to read with a discerning eye. A rhetorical analysis is a close reading of someone else’s work where you pay very close attention to not only what the writer says, but how the writer uses language – word choices, sentence structures, opposing arguments, tone, arguments structure, and others – to convey their point.
- Navigate to the “Opposing Viewpoints” database via the library’s website. Here is a brief video that shows you how to do this in case you are not familiar.
- Select a topic that is different than your own but is related to aging.
- Read the viewpoint essay for the topic you selected. Write or paste the title of the essay here, as well as the url.
- Who is the intended audience of this piece? How do you know? I am not asking you to simply guess based on the title, but see if there are subtle ways that the author conveys this.
- What is the purpose of the piece – the thesis? Either copy a sentence that you believe is the thesis or rephrase in your own words.
- What is the effect the author intends to have on readers? How do you know? Include “evidence” in your response (e.g., copy a sentence, some phrases – whatever makes your case.)
- What are the main arguments that the author uses to support his/her case? (You can cut and paste sentences from the text or explain in your own words.) Does the author bring up counter-arguments? (You can cut and paste sentences from the text or explain in your own words.) Overall, how effective would you say the author’s arguments are? Please explain your response.
- Does the author support his/her argument with additional information or data? Please give examples. How believable/reliable is that data? Please explain.
- Overall, what feelings are you left with after reading the piece (e.g., anger, sadness, outrage, etc.) Since emotions in a text are a direct result of the specific words, among other things, find words in the essay that contribute to your feelings.
- Another effective strategy that writers use is varied sentence length. Focus on one paragraph in the essay. How long are each of the sentences? Is there any relationship you see between sentence length and the message and/or emotions conveyed? Explain your answer and provide support.
- After reading this, what, if any, of the literary devices would you apply to your own work? What literary devices in this piece would you not apply to your own work. Please explain.
- In your opinion, was the essay a good piece of writing? Why or why not? (There is no right answer but be sure to support your response with clear examples and/or explanations.)
Gerontology 602: Theory Project
Created by: Dr. Jennifer Kinney , Professor and Director of Graduate Studies
Sample Assignment for Gerontology 602
At this point in the semester you have a good overview of gerontology (in large part on de Medeiros, 2017) and are beginning to read a variety of genre (journal articles, encyclopedia entries, book chapters) written for an academic gerontology audience. Over the remainder of the semester you will continue to learn about gerontological theory and its application. During this time, in addition to your assigned out-of-class reading and our class sessions, you will complete a theory project. For this project, you will explore a specific gerontological concept that you are particularly interested in/that will be most helpful to you as you prepare to be a gerontologist. Specifically, you will document the development of the concept in gerontology and its theoretical underpinnings. You will complete the project in specific steps, and receive feedback/be evaluated on each step of the project. For several of the steps you will revise your work based on the feedback you get from your peers and/or me, and incorporate the feedback into a revision that is included in the final step of the project. At the end of the semester you will present an overview of your paper to the class.
Specific instructions for each step of the project (1-8) are listed below.
Step 1: Your Initial Idea
Pick a contemporary concept in gerontology in which you are particularly interested. If a topic does not immediately come to mind, you might think about: 1) your previous work with/on behalf of older adults; 2) what interested you when you were applying to graduate school; 3) new interests that have emerged through your classwork, GA work, and other experiences and/or an area that you would like to learn more about. For Step 1, please turn in the following:
- List the top 1- 3 ideas or concepts that you have learned from your prior knowledge/experience related to gerontology.
- For each of the concepts listed, how does your prior knowledge relate to what we have read so far or what you are interested in learning more about?
- What do you need to know (e.g., more theories, applicable examples) to gain more insight into the concept/theory that you are most interested in?
Step 1 of your theory project is due during week 4 of the semester and is worth 5 possible points (2% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 2: Identifying and Reflecting on Your Topic
Last week, I asked you to start thinking about a topic you'd like to explore. Now I am asking you to commit to that topic.
- Step 2 Product: Write a 1-2 paragraph description of what concept you plan to explore, and why you chose that concept. The audience for this concept description is me— your course instructor/a gerontology faculty member. Because of the audience, this should be well thought out and well written. You will get feedback from me about your concept description and should take this feedback into account when you complete Step 3.
- How much of your topic relies on your previous learning or experience?
- What new information/perspective do you hope to gain through your topic?
- How do you hope to apply your topic to your future work in the GTY program?
- What additional challenges will you need to face (e.g., mastering a new literature, changing previous ways of thinking) to accomplish your goal for this project?
Your concept description and reflection (in one document) is due during week 5 of the semester and is worth 15 possible points (7% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 3: Contemporary Thinking on Your Topic
- Step 3 Product: For three of the sources (i.e., articles or book chapters) you identified, prepare a summary. You can either prepare a 1-page narrative summary for each source, or you can use a modified version of the Howe Writing Center matrix (similar to the one we have used in class).
Regardless of the format you choose, your summary should include definition of the key concept(s); what lens/perspective/theory the authors use to contextualize and/or ground the concept; and the purpose, major points/findings, and what you learned from each source. The audience for the summary(ies) is primarily yourself and your instructor/consultant who will give you feedback about your ideas (as opposed to the quality of your writing). Be sure that your ideas/writing are clear enough that another reader can understand what you are saying.
Your summary(ies) and the three sources are due during week 7 of the semester and is worth 30 possible points (14% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 4: Looking Back/Historical Influences
- Step 4 Product: Prepare one combined summary for the three sources you identified. In contrast to your summaries from Step 3, which could be in the form of an narrative for each source or a modified version of the Howe Writing Center matrix (either one matrix per source, or one matrix with all three sources), the focus of your Step 4 summary should be how the articles “talk” to one another (e.g., how your concept developed from the earliest to the most recent article, the gerontological lens/perspective/theory used in each source, the commonalities and discrepancies across the three sources), and it should be in the form of one narrative or one matrix for all three sources. The summary (whether it is a narrative or matrix) can address the following topics:
- definitions of the concept
- how the concept is used in the conceptualization/research
- strengths and weaknesses in how the concept is defined/used
- suggestions to improve how the concept is conceptualized/measured
Note: the above topics are suggestions; you should modify them to address the points you want to make in your paper.
The audience for the summary of historical sources matrix is primarily yourself and your instructor/consultant who will give you feedback about your ideas (as opposed to the quality of your writing). Again, make sure that your ideas/writing are clear enough that another reader can understand what you are saying.
Your summary of historical sources is due during week 9 of the semester and is worth 30 possible points (14% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 5: Constructing your “Story”
- Step 5 Product: Develop a “blueprint” of the story you want to tell your audience, which is other scholars in gerontology. This blueprint can take the form of a traditional outline, a “forensic or concept map," or any other format that “works” for you. Although you should keep in mind that the audience for your final paper is other scholars in gerontology, the audience for the blueprint is yourself and your instructor/peers who will give you feedback about your ideas.
Your blueprint is due during week 10 of the semester and is worth 30 possible points (14% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 6: Putting it all Together
- Step 6 Product: Develop your blueprint into a 5-10 ish- page paper. This academic paper should be written for other gerontology scholars. The purpose of this paper is to explain the evolution of gerontological thinking about your concept, with an emphasis on the lenses/perspectives/theories that informed this thinking, and for you to speculate (in an informed way) about how this concept will continue to develop in gerontology.
Your paper is due during week 12 of the semester and you should bring a copy to class, where a peer will be assigned to give you feedback. Your draft is worth 40 possible points (19% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 7: Peer Review
- Step 7 Product: You will be assigned as a peer reviewer for one of your classmates. Carefully read the draft of their paper, and provide written feedback. You will be given specific guidelines for the feedback. Your peer feedback is due during week 13 of the semester and is worth 20 possible points (10% of the written theory project, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 8: The Finish Line
- Step 8 Product: Using the feedback you received, prepare, revise and finalize your paper. Your final paper is due during exam week. Your final paper is worth 40 possible points (20% of the assignment, which is worth a total of 210 points).
Step 9: Final Oral Presentation
- have an appropriate powerpoint presentation that uses minimal text and instead uses engaging graphics/images when appropriate.
- be well rehearsed so that it sounds confident but not scripted.
- final paper. Remember, we as an audience do not need to know everything. Instead, you should present a coherent story of why your concept matters.
NOTE: The presentation must not exceed 12 minutes. I will cut you off at the 12 minute mark. It is important to be mindful of other people's time so staying within the allotted time is key.
The presentation will occur during the last week of classes and will be worth a total of 25 possible points.
Gerontology 702: Weekly Synthesis Assignment
The synthesis exercise was based on our observation that students had a tendency to summarize literature, not synthesize ideas. Through this exercise, I wanted to force students to read two very different articles to come up with a synthesis that somehow brought together key ideas from both. We did this weekly. Although difficult for them at first, they gradually became more comfortable with and proficient at synthesizing literature as the semester progressed.
Sample Assignment for Gerontology 702
I borrow this definition of a literature "synthesis": "Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. In synthesis, you search for the links between various materials in order to make your point." A synthesis is not just a mere summary. It is an integrated analysis whereby you should demonstrate not only that you read and understood the readings, but also that you can pull key points together in some cohesive way. The readings will often not be obviously related. However, find a way to be true to their essence while also using them to build a new observation or idea.
synthesis: Article 1 and 2
Your synthesis should be at least 2 paragraphs long.
Avoid using block quotes (taking large chunks of direct text in quotations.) Everything should be in your own words with proper citation using APA formatting.
You should demonstrate a deep reading and understanding of some major points.
Bring these points together to pull together something related to gerontology.
Remember, this is a theory course. You should not focus on methods, on study design, findings, or anything outside of theory.
Use only the articles assigned for that week. Do not bring in outside readings or sources.
Gerontology 702: Reverse Genealogy Assignment
I found that students, even doctoral students, were not reading critically. This assignment came about during the Fellows program with relation to understanding how to build on past work when writing an article, especially in the literature review. I wanted students to clearly see what the “bones” of an article looked like by looking at its foundation – the references. It was very successful. Students were surprised to see the connections between the articles cited and the final article, which they were given after completing this exercise.
Attached is a reference list for a gerontology article. Using only this list, attempt to make sense of what the article is about and what are the major influencing literatures cited. Pay close attention to details such as: what journals are cited, what "classic" works (if any) are included, whether there are topics that you could group together, what authors are cited. You do not need to upload this — you can have hand drawn diagrams or notes if that is easier. Be prepared to discuss during class.
Gerontology 705: Genre Analysis
Sample assignment for gerontology 705.
The purpose of this activity is to explain the conventions of a particular sub-genre of gerontological writing (e.g., abstract, introduction, method, discussion) and relate these conventions to the work that the genre does for the gerontologists who use it. The main question the analysis should address is why the genre takes the shape(s) that it does given what gerontologists are trying to accomplish when they use that genre. Doing this type of analysis for different genre will enable us to: 1) articulate what that genre “looks like” in gerontology and 2) be able to more successfully create documents in that genre.
After you have carefully engaged with the exemplars/examples from the genre, identify their commonalities using the categories and questions of analysis identified by Sojna Foss (2018) as a starting point:
- What conditions (situations) call for this genre?
- What prompts this sort of document to be written?
- What is the exigence—the need or reason for a given action or communication?
- Who usually creates this genre—people doing what?
- What sort of content (substance) is typically contained in this genre?
- What do these texts tend to talk about or say?
- Is there information that is typically present (or not present) in these texts?
- What form does this sort of genre take and what does it look like (length, page layout, color, font)?
- How are its parts organized?
- What language does it use?
- Are there specialized terms?
- How are references/citations used in the text?
- What “moves” (e.g., transitions, signposting) are made?
- What tone/voice does it take (formal, informal, dense, light; passive, active)?
- What elements make this genre what it is?
- What are the common denominations of the genre (for example, what makes a resume a resume?
- For each characteristic you identify in 1-3 above, you might ask “If I took out this characteristic, would it still be recognizable as this genre?”
Your analysis should “tell the story” of the genre, including how what the genre needs to accomplish leads to the shape it typically takes; how this genre is most often used; and the features that your analysis indicates are required; features that appear to be optional. A good analysis includes a clear explanation of who uses the genre and for what purpose(s), conclusions based on comparison of several exemplars/examples of the genre; accurate assessments of the genre’s key elements; a clear organizational structure that includes a logical progression through the elements of the genre that your analysis highlights.
The source for the genre analysis guidelines: Foss, Sonja K. 2018. Rhetorical Criticism: Exploration and Practice 5th edition . Long Grove, IL: Waveland
Resources/Further Reading
- Anderson, P., Anson, C. M., Gonyea, R.M., & Paine, C. (2016). “How to create high-impact writing assignments that enhance learning and development and reinvigorate WAC/WID programs: What almost 72,000 undergraduates taught us.” Across the Disciplines, 13(4). DOI: https://doi.org/10.37514/ATD-J.2016.13.4.13
- Hyland, K. (2013). Writing in the university: Education, knowledge, and reputation. Language Teaching, 46(1), 53-70.
- Swales, J. (2004). Research genres: Explorations and applications. Cambridge University Press.
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning, meaning and identity. Cambridge University Press.
Howe Center for Writing Excellence
The mission of the HCWE is to ensure that Miami supports its students in developing as effective writers in college, and fully prepares all of its graduates to excel as clear, concise, and persuasive writers in their careers, communities, and personal lives.
Popular Destinations
- Howe Writing Across The Curriculum
- Howe Writing Center
- Advanced Writing
- Faculty Writing Fellows
151 S. Campus Ave King Library Oxford, OH 45056 [email protected] 513-529-6100
2022 Writing Program Certificate of Excellence

2022 Exemplary Enduring WAC Program

501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Writing Across the Curriculum
Ask a question
- Research & Assessment
- Writing Plans
- WEC Liaisons
- Academic Units
- Engage with WEC
- Teaching Resources
- Teaching Consultations
- Faculty Writing Resources

- Designing Effective Writing Assignments
One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in their learning. In this section, you can read about key principles of assignment design, review examples of effective writing assignments, and use a checklist to guide your own designs. You can also consult with a Writing Across the Curriculum Program team member . We’re happy to think with you about your writing assignment, whether it is in the inkling stage or undergoing a few minor tweaks.
What makes an assignment effective?
A good deal of educational research points to the benefits of writing assignments that exhibit the following features:
Meaningful tasks. A task is given meaning by its relevance to and alignment with the learning aims in the course. What counts as meaningful in one course context might not be meaningful in another. As Eodice, Geller, and Lerner (2016) have shown, meaningful writing assignments do occur across all disciplines and they are typically ones that “offer students opportunities to engage with instructors, peers, and texts and are relevant to past experiences and passions as well as to future aspirations and identities.”
Maximized learning time. As Linda Suskie argues, effectiveness is determined by the “learning payoff,” not by size of the assignment. Will students learn four times as much on an assignment that takes 20 hours outside of class than one that takes 5? Longer research-based assignments and elaborate class activities (mock conferences, debates, poster sessions, etc.) can greatly maximize learning, but there must be an appropriate level of writing and learning time built into the task. Term papers are much more effective when students have time to draft and revise stages of the assignment, rather than turning in one final product at the end.

Logical sequencing. A writing task that includes discrete stages (research, drafting, review, revising, etc.) is more likely to be an effective learning experience than one that only specifies the final product. Furthermore, these stages are more effective when they are scaffolded so simpler tasks precede more complex tasks. For example, a well-sequenced 10-12 page essay assignment might involve discrete segments where students generate a central inquiry question, draft and workshop a thesis statement, produce a first draft of the essay, give and receive feedback on drafts, and submit a revision. Read more about sequencing assignments .
Clear criteria will help students connect an assignment’s relevance to larger scale course outcomes. The literature on assignment design strongly encourages instructors to make the grading criteria explicit to students before the assignment is collected and assessed. A grading scheme or rubric that is handed out along with the assignment can provide students with a clear understanding of the weighted expectations and, thus help them decide what to focus on in the assignment. It becomes a teaching tool, not just an assessment tool.
Forward-thinking activities more than backward-thinking activities. Forward-thinking activities and assignments ask students to apply their learning rather than simply repeat it. The orientation of many writing prompts is often backward, asking students to show they learned X, Y, and Z. As L. Dee Fink (2013) points out, forward-thinking assignments and activities look ahead to what students will be able to do in the future having learned about X, Y, and Z. Such assignments often utilize real-world and scenario-based problems, requiring students to apply their learning to a new situation. For Grant Wiggins (1998) , questions, problems, tests, and assignments that are forward-thinking often:
- Require judgment and innovation. Students have to use knowledge and skills to solve unstructured problems, not just plug in a routine.
- Ask students to do the subject. Beyond recitation and replication, these tasks require students to carry out explorations, inquiry, and work within specific disciplines.
- Replicate workplace and civic contexts. These tasks provide specific constraints, purposes, and audiences that students will face in work and societal contexts.
- Involve a repertoire of skills and abilities rather than the isolation of individual skills.
Feel free to use this assignment checklist , which draws on the principles and research described on this page.
- African American & African Studies
- Agronomy and Plant Genetics
- Animal Science
- Anthropology
- Applied Economics
- Art History
- Carlson School of Management
- Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
- Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering
- College of Biological Sciences
- Communication Studies
- Computer Science & Engineering
- Construction Management
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Dental Hygiene
- Apparel Design
- Graphic Design
- Product Design
- Retail Merchandising
- Earth Sciences
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Environmental Sciences, Policy and Management
- Family Social Science
- Fisheries, Wildlife, and Conservation Biology
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Geography, Environment and Society
- German, Nordic, Slavic & Dutch
- Health Services Management
- Horticultural Science
- Hubbard School of Journalism and Mass Communication
- Industrial and Systems Engineering
- Information Technology Infrastructure
- Mathematics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Medical Laboratory Sciences
- Mortuary Science
- Organizational Leadership, Policy, and Development
- Political Science
- School of Architecture
- School of Kinesiology
- School of Public Health
- Spanish and Portuguese Studies
- Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences
- Theatre Arts & Dance
- Youth Studies
- New Enrollments for Departments and Programs
- Legacy Program for Continuing Units
- Writing in Your Course Context
- Syllabus Matters
- Mid-Semester Feedback Strategies
- Writing Assignment Checklist
- Scaffolding and Sequencing Writing Assignments
- Informal, Exploratory Writing Activities
- 5-Minute Revision Workshops
- Reflective Memos
- Conducting In-Class Writing Activities: Notes on Procedures
- Now what? Responding to Informal Writing
- Teaching Writing with Quantitative Data
- Commenting on Student Writing
- Supporting Multilingual Learners
- Teaching with Effective Models of Writing
- Peer Response Protocols and Procedures
- Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning
- Conferencing with Student Writers
- Designing Inclusive Writing Assigments
- Addressing a Range of Writing Abilities in Your Courses
- Effective Grading Strategies
- Designing and Using Rubrics
- Running a Grade-Norming Session
- Working with Teaching Assistants
- Managing the Paper Load
- Teaching Writing with Sources
- Preventing Plagiarism
- Grammar Matters
- What is ChatGPT and how does it work?
- Incorporating ChatGPT into Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- Restricting ChatGPT Use in Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- What do we mean by "writing"?
- How can I teach writing effectively in an online course?
- What are the attributes of a "writing-intensive" course at the University of Minnesota?
- How can I talk with students about the use of artificial intelligence tools in their writing?
- How can I support inclusive participation on team-based writing projects?
- How can I design and assess reflective writing assignments?
- How can I use prewritten comments to give timely and thorough feedback on student writing?
- How can I use online discussion forums to support and engage students?
- How can I use and integrate the university libraries and academic librarians to support writing in my courses?
- How can I support students during the writing process?
- How can I use writing to help students develop self-regulated learning habits?
- Submit your own question
- Short Course: Teaching with Writing Online
- Five-Day Faculty Seminar
- Past Summer Hunker Participants
- Resources for Scholarly Writers
- Consultation Request
- Faculty Writing Groups
- Further Writing Resources
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Weekly Updates
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
- Rhetorical Analysis
What is "Academic" Writing?

Written by L. Lennie Irvin

Introduction: The Academic Writing Task
As a new college student, you may have a lot of anxiety and questions about the writing you’ll do in college. That word “academic,” especially, may turn your stomach or turn your nose. However, with this first year composition class, you begin one of the only classes in your entire college career where you will focus on learning to write. Given the importance of writing as a communication skill, I urge you to consider this class as a gift and make the most of it. But writing is hard, and writing in college may resemble playing a familiar game by completely new rules (that often are unstated). This chapter is designed to introduce you to what academic writing is like, and hopefully ease your transition as you face these daunting writing challenges.
So here’s the secret. Your success with academic writing depends upon how well you understand what you are doing as you write and then how you approach the writing task. Early research done on college writers discovered that whether students produced a successful piece of writing depended largely upon their representation of the writing task. The writers’ mental model for picturing their task made a huge difference. Most people as they start college have wildly strange ideas about what they are doing when they write an essay, or worse—they have no clear idea at all. I freely admit my own past as a clueless freshman writer, and it’s out of this sympathy as well as twenty years of teaching college writing that I hope to provide you with something useful. So grab a cup of coffee or a diet coke, find a comfortable chair with good light, and let’s explore together this activity of academic writing you’ll be asked to do in college. We will start by clearing up some of those wild misconceptions people often arrive at college possessing. Then we will dig more deeply into the components of the academic writing situation and nature of the writing task.
Myths about Writing
Though I don’t imagine an episode of MythBusters will be based on the misconceptions about writing we are about to look at, you’d still be surprised at some of the things people will believe about writing. You may find lurking within you viral elements of these myths—all of these lead to problems in writing.
Myth #1: The “Paint by Numbers” myth
Some writers believe they must perform certain steps in a particular order to write “correctly.” Rather than being a lock-step linear process, writing is “recursive.” That means we cycle through and repeat the various activities of the writing process many times as we write.
Myth #2: Writers only start writing when they have everything fgured out
Writing is not like sending a fax! Writers figure out much of what they want to write as they write it. Rather than waiting, get some writing on the page—even with gaps or problems. You can come back to patch up rough spots.
Myth #3: Perfect first drafts
We put unrealistic expectations on early drafts, either by focusing too much on the impossible task of making them perfect (which can put a cap on the development of our ideas), or by making too little effort because we don’t care or know about their inevitable problems. Nobody writes perfect first drafts; polished writing takes lots of revision.
Myth #4: Some got it; I don’t—the genius fallacy
When you see your writing ability as something fixed or out of your control (as if it were in your genetic code), then you won’t believe you can improve as a writer and are likely not to make any efforts in that direction. With effort and study, though, you can improve as a writer. I promise.
Myth #5: Good grammar is good writing
When people say “I can’t write,” what they often mean is they have problems with grammatical correctness. Writing, however, is about more than just grammatical correctness. Good writing is a matter of achieving your desired effect upon an intended audience. Plus, as we saw in myth #3, no one writes perfect first drafts.
Myth #6: The Five-Paragraph Essay
Some people say to avoid it at all costs, while others believe no other way to write exists. With an introduction, three supporting paragraphs, and a conclusion, the five paragraph essay is a format you should know, but one which you will outgrow. You’ll have to gauge the particular writing assignment to see whether and how this format is useful for you.
Myth #7: Never use “I”
Adopting this formal stance of objectivity implies a distrust (almost fear) of informality and often leads to artificial, puffed-up prose. Although some writing situations will call on you to avoid using “I” (for example, a lab report), much college writing can be done in a middle, semi-formal style where it is ok to use “I.”
The Academic Writing Situation
Now that we’ve dispelled some of the common myths that many writers have as they enter a college classroom, let’s take a moment to think about the academic writing situation. The biggest problem I see in freshman writers is a poor sense of the writing situation in general. To illustrate this problem, let’s look at the difference between speaking and writing.
When we speak, we inhabit the communication situation bodily in three dimensions, but in writing we are confined within the twodimensional setting of the flat page (though writing for the web—or multimodal writing—is changing all that). Writing resembles having a blindfold over our eyes and our hands tied behind our backs: we can’t see exactly whom we’re talking to or where we are. Separated from our audience in place and time, we imaginatively have to create this context. Our words on the page are silent, so we must use punctuation and word choice to communicate our tone. We also can’t see our audience to gauge how our communication is being received or if there will be some kind of response. It’s the same space we share right now as you read this essay. Novice writers often write as if they were mumbling to themselves in the corner with no sense that their writing will be read by a reader or any sense of the context within which their communication will be received.
What’s the moral here? Developing your “writer’s sense” about communicating within the writing situation is the most important thing you should learn in freshman composition. Figure 1, depicting the writing situation, presents the best image I know of describing all the complexities involved in the writing situation.
Looking More Closely at the “Academic Writing” Situation
Writing in college is a fairly specialized writing situation, and it has developed its own codes and conventions that you need to have a keen awareness of if you are going to write successfully in college. Let’s break down the writing situation in college:
- Who’s your audience? Primarily the professor and possibly your classmates (though you may be asked to include a secondary outside audience).
- What’s the occasion or context? An assignment given by the teacher within a learning context and designed to have you learn and demonstrate your learning.
- What’s your message? It will be your learning or the interpretation gained from your study of the subject matter.
- What’s your purpose? To show your learning and get a good grade (or to accomplish the goals of the writing assignment).
- What documents/genres are used? The essay is the most frequent type of document used.
So far, this list looks like nothing new. You’ve been writing in school toward teachers for years. What’s different in college? Lee Ann Carroll, a professor at Pepperdine University, performed a study of student writing in college and had this description of the kind of writing you will be doing in college:
What are usually called ‘writing assignments’ in college might more accurately be called ‘literacy tasks’ because they require much more than the ability to construct correct sentences or compose neatly organized paragraphs with topic sentences. . . . Projects calling for high levels of critical literacy in college typically require knowledge of research skills, ability to read complex texts, understanding of key disciplinary concepts, and strategies for synthesizing, analyzing, and responding critically to new information, usually within a limited time frame. (3–4)
Academic writing is always a form of evaluation that asks you to demonstrate knowledge and show proficiency with certain disciplinary skills of thinking, interpreting, and presenting. Writing the paper is never “just” the writing part. To be successful in this kind of writing, you must be completely aware of what the professor expects you to do and accomplish with that particular writing task. For a moment, let’s explore more deeply the elements of this college writing “literacy task.”
Knowledge of Research Skills
Perhaps up to now research has meant going straight to Google and Wikipedia, but college will require you to search for and find more in-depth information. You’ll need to know how to find information in the library, especially what is available from online databases which contain scholarly articles. Researching is also a process, so you’ll need to learn how to focus and direct a research project and how to keep track of all your source information. Realize that researching represents a crucial component of most all college writing assignments, and you will need to devote lots of work to this researching.
The Ability to Read Complex Texts
Whereas your previous writing in school might have come generally from your experience, college writing typically asks you to write on unfamiliar topics. Whether you’re reading your textbook, a short story, or scholarly articles from research, your ability to write well will be based upon the quality of your reading. In addition to the labor of close reading, you’ll need to think critically as you read. That means separating fact from opinion, recognizing biases and assumptions, and making inferences. Inferences are how we as readers connect the dots: an inference is a belief (or statement) about something unknown made on the basis of something known. You smell smoke; you infer fire. They are conclusions or interpretations that we arrive at based upon the known factors we discover from our reading. When we, then, write to argue for these interpretations, our job becomes to get our readers to make the same inferences we have made.
The Understanding of Key Disciplinary Concepts
Each discipline whether it is English, Psychology, or History has its own key concepts and language for describing these important ways of understanding the world. Don’t fool yourself that your professors’ writing assignments are asking for your opinion on the topic from just your experience. They want to see you apply and use these concepts in your writing. Though different from a multiple-choice exam, writing similarly requires you to demonstrate your learning. So whatever writing assignment you receive, inspect it closely for what concepts it asks you to bring into your writing.
Strategies for Synthesizing, Analyzing, and Responding Critically to New Information
You need to develop the skill of a seasoned traveler who can be dropped in any city around the world and get by. Each writing assignment asks you to navigate through a new terrain of information, so you must develop ways for grasping new subject matter in order, then, to use it in your writing. We have already seen the importance of reading and research for these literacy tasks, but beyond laying the information out before you, you will need to learn ways of sorting and finding meaningful patterns in this information.
In College, Everything’s an Argument: A Guide for Decoding College Writing Assignments
Let’s restate this complex “literacy task” you’ll be asked repeatedly to do in your writing assignments. Typically, you’ll be required to write an “essay” based upon your analysis of some reading(s). In this essay you’ll need to present an argument where you make a claim (i.e. present a “thesis”) and support that claim with good reasons that have adequate and appropriate evidence to back them up. The dynamic of this argumentative task often confuses first year writers, so let’s examine it more closely.
Academic Writing Is an Argument
To start, let’s focus on argument. What does it mean to present an “argument” in college writing? Rather than a shouting match between two disagreeing sides, argument instead means a carefully arranged and supported presentation of a viewpoint. Its purpose is not so much to win the argument as to earn your audience’s consideration (and even approval) of your perspective. It resembles a conversation between two people who may not hold the same opinions, but they both desire a better understanding of the subject matter under discussion. My favorite analogy, however, to describe the nature of this argumentative stance in college writing is the courtroom. In this scenario, you are like a lawyer making a case at trial that the defendant is not guilty, and your readers are like the jury who will decide if the defendant is guilty or not guilty. This jury (your readers) won’t just take your word that he’s innocent; instead, you must convince them by presenting evidence that proves he is not guilty. Stating your opinion is not enough—you have to back it up too. I like this courtroom analogy for capturing two importance things about academic argument: 1) the value of an organized presentation of your “case,” and 2) the crucial element of strong evidence.
Academic Writing Is an Analysis
We now turn our attention to the actual writing assignment and that confusing word “analyze.” Your first job when you get a writing assignment is to figure out what the professor expects. This assignment may be explicit in its expectations, but often built into the wording of the most defined writing assignments are implicit expectations that you might not recognize. First, we can say that unless your professor specifically asks you to summarize, you won’t write a summary. Let me say that again: don’t write a summary unless directly asked to. But what, then, does the professor want? We have already picked out a few of these expectations: You can count on the instructor expecting you to read closely, research adequately, and write an argument where you will demonstrate your ability to apply and use important concepts you have been studying. But the writing task also implies that your essay will be the result of an analysis. At times, the writing assignment may even explicitly say to write an analysis, but often this element of the task remains unstated.
So what does it mean to analyze? One way to think of an analysis is that it asks you to seek How and Why questions much more than What questions. An analysis involves doing three things:
- Engage in an open inquiry where the answer is not known at first (and where you leave yourself open to multiple suggestions).
- Identify meaningful parts of the subject.
- Examine these separate parts and determine how they relate to each other.
An analysis breaks a subject apart to study it closely, and from this inspection, ideas for writing emerge. When writing assignments call on you to analyze, they require you to identify the parts of the subject (parts of an ad, parts of a short story, parts of Hamlet’s character), and then show how these parts fit or don’t fit together to create some larger effect or meaning. Your interpretation of how these parts fit together constitutes your claim or thesis, and the task of your essay is then to present an argument defending your interpretation as a valid or plausible one to make. My biggest bit of advice about analysis is not to do it all in your head. Analysis works best when you put all the cards on the table, so to speak. Identify and isolate the parts of your analysis, and record important features and characteristics of each one. As patterns emerge, you sort and connect these parts in meaningful ways. For me, I have always had to do this recording and thinking on scratch pieces of paper. Just as critical reading forms a crucial element of the literacy task of a college writing assignment, so too does this analysis process. It’s built in.
Three Common Types of College Writing Assignments
We have been decoding the expectations of the academic writing task so far, and I want to turn now to examine the types of assignments you might receive. From my experience, you are likely to get three kinds of writing assignments based upon the instructor’s degree of direction for the assignment. We’ll take a brief look at each kind of academic writing task.
The Closed Writing Assignment
- Is Creon a character to admire or condemn?
- Does your advertisement employ techniques of propaganda, and if so what kind?
- Was the South justified in seceding from the Union?
- In your opinion, do you believe Hamlet was truly mad?
These kinds of writing assignments present you with two counter claims and ask you to determine from your own analysis the more valid claim. They resemble yes-no questions. These topics define the claim for you, so the major task of the writing assignment then is working out the support for the claim. They resemble a math problem in which the teacher has given you the answer and now wants you to “show your work” in arriving at that answer.
Be careful with these writing assignments, however, because often these topics don’t have a simple yes/no, either/or answer (despite the nature of the essay question). A close analysis of the subject matter often reveals nuances and ambiguities within the question that your eventual claim should reflect. Perhaps a claim such as, “In my opinion, Hamlet was mad” might work, but I urge you to avoid such a simplistic thesis. This thesis would be better: “I believe Hamlet’s unhinged mind borders on insanity but doesn’t quite reach it.”
The Semi-Open Writing Assignment
- Discuss the role of law in Antigone.
- Explain the relationship between character and fate in Hamlet.
- Compare and contrast the use of setting in two short stories.
- Show how the Fugitive Slave Act influenced the Abolitionist Movement.
Although these topics chart out a subject matter for you to write upon, they don’t offer up claims you can easily use in your paper. It would be a misstep to offer up claims such as, “Law plays a role in Antigone” or “In Hamlet we can see a relationship between character and fate.” Such statements express the obvious and what the topic takes for granted. The question, for example, is not whether law plays a role in Antigone, but rather what sort of role law plays. What is the nature of this role? What influences does it have on the characters or actions or theme? This kind of writing assignment resembles a kind of archeological dig. The teacher cordons off an area, hands you a shovel, and says dig here and see what you find.
Be sure to avoid summary and mere explanation in this kind of assignment. Despite using key words in the assignment such as “explain,” “illustrate,” analyze,” “discuss,” or “show how,” these topics still ask you to make an argument. Implicit in the topic is the expectation that you will analyze the reading and arrive at some insights into patterns and relationships about the subject. Your eventual paper, then, needs to present what you found from this analysis—the treasure you found from your digging. Determining your own claim represents the biggest challenge for this type of writing assignment.
The Open Writing Assignment
- Analyze the role of a character in Dante’s The Inferno.
- What does it mean to be an “American” in the 21st Century?
- Analyze the influence of slavery upon one cause of the Civil War.
- Compare and contrast two themes within Pride and Prejudice .
These kinds of writing assignments require you to decide both your writing topic and you claim (or thesis). Which character in the Inferno will I pick to analyze? What two themes in Pride and Prejudice will I choose to write about? Many students struggle with these types of assignments because they have to understand their subject matter well before they can intelligently choose a topic. For instance, you need a good familiarity with the characters in The Inferno before you can pick one. You have to have a solid understanding defining elements of American identity as well as 21st century culture before you can begin to connect them. This kind of writing assignment resembles riding a bike without the training wheels on. It says, “You decide what to write about.” The biggest decision, then, becomes selecting your topic and limiting it to a manageable size.
Picking and Limiting a Writing Topic
Let’s talk about both of these challenges: picking a topic and limiting it. Remember how I said these kinds of essay topics expect you to choose what to write about from a solid understanding of your subject? As you read and review your subject matter, look for things that interest you. Look for gaps, puzzling items, things that confuse you, or connections you see. Something in this pile of rocks should stand out as a jewel: as being “do-able” and interesting. (You’ll write best when you write from both your head and your heart.) Whatever topic you choose, state it as a clear and interesting question. You may or may not state this essay question explicitly in the introduction of your paper (I actually recommend that you do), but it will provide direction for your paper and a focus for your claim since that claim will be your answer to this essay question. For example, if with the Dante topic you decided to write on Virgil, your essay question might be: “What is the role of Virgil toward the character of Dante in The Inferno?” The thesis statement, then, might be this: “Virgil’s predominant role as Dante’s guide through hell is as the voice of reason.” Crafting a solid essay question is well worth your time because it charts the territory of your essay and helps you declare a focused thesis statement.
Many students struggle with defining the right size for their writing project. They chart out an essay question that it would take a book to deal with adequately. You’ll know you have that kind of topic if you have already written over the required page length but only touched one quarter of the topics you planned to discuss. In this case, carve out one of those topics and make your whole paper about it. For instance, with our Dante example, perhaps you planned to discuss four places where Virgil’s role as the voice of reason is evident. Instead of discussing all four, focus your essay on just one place. So your revised thesis statement might be: “Close inspection of Cantos I and II reveal that Virgil serves predominantly as the voice of reason for Dante on his journey through hell.” A writing teacher I had in college said it this way: A well tended garden is better than a large one full of weeds. That means to limit your topic to a size you can handle and support well.
Three Characteristics of Academic Writing
I want to wrap up this section by sharing in broad terms what the expectations are behind an academic writing assignment. Chris Thaiss and Terry Zawacki conducted research at George Mason University where they asked professors from their university what they thought academic writing was and its standards. They came up with three characteristics:
- Clear evidence in writing that the writer(s) have been persistent, open-minded, and disciplined in study. (5)
- The dominance of reason over emotions or sensual perception. (5)
- An imagined reader who is coolly rational, reading for information, and intending to formulate a reasoned response. (7)
Your professor wants to see these three things in your writing when they give you a writing assignment. They want to see in your writing the results of your efforts at the various literacy tasks we have been discussing: critical reading, research, and analysis. Beyond merely stating opinions, they also want to see an argument toward an intelligent audience where you provide good reasons to support your interpretations.
The Format of the Academic Essay
Your instructors will also expect you to deliver a paper that contains particular textual features. The following list contains the characteristics of what I have for years called the “critical essay.” Although I can’t claim they will be useful for all essays in college, I hope that these features will help you shape and accomplish successful college essays. Be aware that these characteristics are flexible and not a formula, and any particular assignment might ask for something different.
Characteristics of the Critical Essay
“Critical” here is not used in the sense of “to criticize” as in find fault with. Instead, “critical” is used in the same way “critical thinking” is used. A synonym might be “interpretive” or “analytical.”
- It is an argument, persuasion essay that in its broadest sense MAKES A POINT and SUPPORTS IT. (We have already discussed this argumentative nature of academic writing at length.)
- The point (“claim” or “thesis”) of a critical essay is interpretive in nature. That means the point is debatable and open to interpretation, not a statement of the obvious. The thesis statement is a clear, declarative sentence that often works best when it comes at the end of the introduction.
- Organization: Like any essay, the critical essay should have a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. As you support your point in the body of the essay, you should “divide up the proof,” which means structuring the body around clear primary supports (developed in single paragraphs for short papers or multiple paragraphs for longer papers).
- Support: (a) The primary source for support in the critical essay is from the text (or sources). The text is the authority, so using quotations is required. ( b) The continuous movement of logic in a critical essay is “assert then support; assert then support.” No assertion (general statement that needs proving) should be left without specific support (often from the text(s)). (c) You need enough support to be convincing. In general, that means for each assertion you need at least three supports. This threshold can vary, but invariably one support is not enough.
- A critical essay will always “document” its sources, distinguishing the use of outside information used inside your text and clarifying where that information came from (following the rules of MLA documentation style or whatever documentation style is required).
- Whenever the author moves from one main point (primary support) to the next, the author needs to clearly signal to the reader that this movement is happening. This transition sentence works best when it links back to the thesis as it states the topic of that paragraph or section.
- A critical essay is put into an academic essay format such as the MLA or APA document format.
- Grammatical correctness: Your essay should have few if any grammatical problems. You’ll want to edit your final draft carefully before turning it in.
As we leave this discussion, I want to return to what I said was the secret for your success in writing college essays: Your success with academic writing depends upon how well you understand what you are doing as you write and then how you approach the writing task. Hopefully, you now have a better idea about the nature of the academic writing task and the expectations behind it. Knowing what you need to do won’t guarantee you an “A” on your paper—that will take a lot of thinking, hard work, and practice—but having the right orientation toward your college writing assignments is a first and important step in your eventual success.
- How did what you wrote in high school compare to what you have/will do in your academic writing in college?
- Think of two different writing situations you have found yourself in. What did you need to do the same in those two situations to place your writing appropriately? What did you need to do differently?
- Think of a writing assignment that you will need to complete this semester. Who’s your audience? What’s the occasion or context? What’s your message? What’s your purpose? What documents/genres are used? How does all that compare to the writing you are doing in this class?
Works Cited
This essay was written by L. Lennie Irvin and published in Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Volume 1, a peer-reviewed open textbook series for the writing classroom; it appears here with minor changes. This material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 International License . Please keep this information on this material if you use, adapt, and/or share it.
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Report a Concern
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Lyle Cleeland and Lisa Moody

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write, and edit your assignments.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements before you begin researching and writing your assignments.
The assessment task description (located in your subject outline) provides key information about an assessment item, including the question. It is essential to scan this document for topic, task, and limiting words. If there are any elements you do not understand, you should clarify these as early as possible.
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g. discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope or parameters of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, a particular jurisdiction (this would be relevant then to which laws, codes or standards you consulted) or a timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
| Task word | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments, or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments, or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise; instead, you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia’s asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The marking criteria or rubric , is an important document to look at before you begin your assignment. This outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The assessment task description will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
For a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics, visit the chapter Managing Assessments .
Preparing your ideas
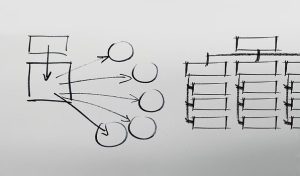
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is:
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is Academic Writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment items you prepare will require an academic writing style. Sometimes this feels awkward when you begin. However, it is good to know that practice at academic writing reduces this feeling.
| Academic writing | Non-academic writing |
| Is clear, concise and well-structured. | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed. |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under ten in full. | Writes numbers under ten as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full. |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed). | Uses humour – puns, sarcasm. |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- “Evidence suggests that…”). | Writes in first person “I think”, “I found”. |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject. | Uses colloquial language e.g., “mate”. |
Thesis statements
One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your working thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument, or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. It is found in the introduction paragraph. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Lets your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The premise is the key argument or position.
A key element of your thesis statement should be included in the topic sentence of each paragraph.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have a clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task. This is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
No one’s writing is the best quality on the first few drafts, not even professional writers. It is strongly advised that you accept that your first few drafts will feel rough. Ultimately, it is the editing and review processes which lead to good quality ideas and writing.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement.
Writing introductions
An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic elements:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic and key information that reader needs to understand your thesis statement.
- Scope of discussion (key points discussed in body paragraphs).
- A thesis statement (see section above).
The below example demonstrates the different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) Digital technology is now widely utilised in health settings, by health professionals. Within the public health field, doctors and nurses need to engage with ongoing professional development relating to digital technology in order to ensure efficient delivery of services to patients and communities. 3) Clearly, information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but some health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/overview | 2 Scope of what will be covered | 3 The thesis statement
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis statement and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) Clearly, communication of individuals and organisations is substantially influenced or affected by information technology across professions. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for public health professionals, so that they become more familiar with the particular digital technologies 3) In addition, the patients and communities being served by public health professionals benefit when communication technologies are effectively implemented. 4) The Australian health system may never be completely free of communication problems, however, ensuring appropriate and timely professional development, provision of resource sand infrastructure will enhance service provision and health outcomes.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-3 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 4 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are adapted from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified Topic Sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by moving from general information to the specific details. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
The first sentence of the paragraph is the Topic Sentence. This is the main idea of the paragraph and tells the reader what you will discuss in more detail below. Each Topic Sentence should address one aspect of your overall argument.
Supporting Sentences
Supporting Sentences provide more explanation, evidence, data, analogies, and/or analysis of the main idea.
Linking/Concluding Sentence
Some paragraphs are best linked to the following paragraph through a Linking/Concluding Sentence. Not every paragraph lends itself to this type of sentence.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic (where appropriate)?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Also avoid overly long sentences, which happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. Address only one key idea per sentence. See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation.
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to the transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations .
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
What is paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing. Note: paraphrasing generally means that the rewritten section is the same or a similar length to the original.
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example, change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in-text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people, often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences. However, the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques.
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen et al.’s (2016) research results suggest that there is a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This is corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicate that students with higher levels of procrastination also report greater levels of anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e. statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate that you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
Creating an Argument
What does this mean.
In academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence from valid scholarly sources.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence.
- Plan your argument.
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument.
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
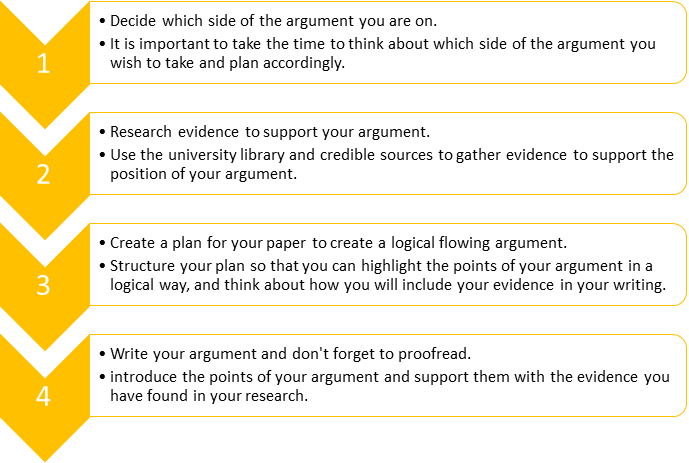
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing.
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that… • …is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because… • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that…. • This evidence demonstrates that… • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that… |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates… • This evidence clearly demonstrates…. • This is important/significant because… • This data highlights… |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that… • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because… • Consequently, this leads to…. • The research presented therefore indicates… |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment.
- Proofreading considers the finer details.
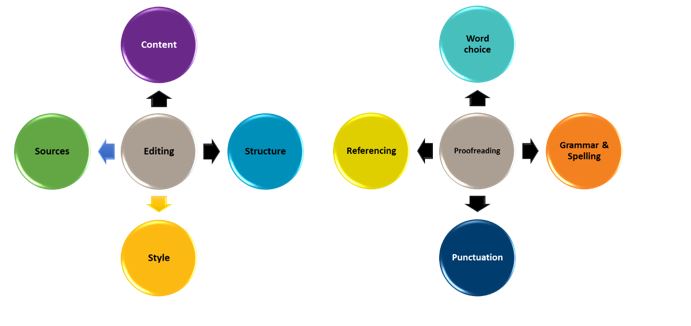
As can be seen in the figure above, there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in third person, not first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
During proofreading, it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation, and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas, or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (For more information on referencing, refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proofreading. Combining these skills and practising them can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing Education Perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1), 5-22.
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2023 by Lyle Cleeland and Lisa Moody is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.5 Understanding the Writing Assignment
Before you begin working on an essay or a writing assignment, don’t forget to spend some quality time analyzing the assignment sheet. By closely reading and breaking down the assignment sheet, you are setting yourself up for an easier time planning and composing the assignment.
Understanding what you need to do
- First , carefully read the assignment sheet and search for the required page length, due dates, and other submission-based information.
- Second , determine the genre of the assignment
- Third , identify the core assignment questions that you need to answer
- Fourth , locate the evaluation and grading criteria
Identifying Writing Requirements & Disciplinary Expectations
Some instructors offer indications of what certain parts of the essay/composition should contain. Does the assignment sheet offer suggestions or requirements for the Intro paragraph? For the thesis statement? For the structure or content of the body paragraphs or conclusion paragraphs?
Depending on the discipline in which you are writing, different features and formats of your writing may be expected. Always look closely at key terms and vocabulary in the writing assignment, and be sure to note what type of evidence and citation style your instructor expects.
- Does the essay need to be in MLA, APA, CMS, or another style?
- Does the professor require any specific submission elements or formats?
Writing Genre
What, in the broadest sense, are you being asked to do? What writing genre is expected?
- Narrative – The act of telling a story through an essay. Also note that narrative includes the act of writing about yourself, which is exceptionally difficult for most writers but is nonetheless required for many circumstances in and out of college.
- Analysis – Analysis questions often contain words like how, in what ways, and what are some of the ____. Analysis asks you to examine small pieces of the larger whole and indicate their meaning or significance.
- Synthesis – If you are asked to draw from and connect several different sources, then you will be synthesizing.
- Argument – Any text in which you are attempting to get a reader to accept your claim. Argument is persuasive writing, and it can include things like argument-based research papers or critiques/evaluations of others’ work.
- Explanation – Any text in which you merely report (as opposed to attempting to persuade) is going to be an explanation paper. None of your own opinions is being sought. Summaries, annotations, and reports are often explanatory.
- Compare and Contrast – This essay is usually between two ideas. The primary aim of comparing and contrasting in college writing is to clarify meaningful, non-obvious features of similarity and difference.
Answer the Assignment Questions & Implied Questions
Sometimes, a list of prompts or questions may appear with an assignment. Likely, your instructor will not expect you to answer all of the questions listed. They are simply offering you some ideas so that you can think of your questions to ask.
- Circle all assignment questions that you see on the assignment sheet
- Put a star next to the question that is either the most important OR that you will pursue in creating the assignment
A prompt may not include a clear ‘how’ or ‘why’ question, though one is always implied by the language of the prompt. For example:
“Discuss the effects of the No Child Left Behind Act on special education programs” is asking you to write how the act has affected special education programs. “Consider the recent rise of autism diagnoses” is asking you to write why the diagnoses of autism are on the rise.
Identifying Evaluation Criteria
Many assignment sheets contain a grading rubric or some other indication of evaluation criteria for the assignment. You can use these criteria to both begin the writing process and to guide your revision and editing process. If you do not see any rubric or evaluation criteria on the assignment sheet — ask!
Attributions
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
This chapter has additions, edits, and organization by James Charles Devlin.
2.5 Understanding the Writing Assignment Copyright © by James Charles Devlin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: planning your assignments.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback










.png)

.png)
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Understanding Writing Assignments. Before you can begin any writing assignment, you need to know exactly what you are being asked to do. The first step is understanding the terms your instructor has used. Luckily, the same terms appear over and over in writing assignments, whether for research papers, lab reports, or essay exams.
Introduction. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
Determining the Purpose. The wording of an assignment should suggest its purpose. Any of the following might be expected of you in a college writing assignment: Summarizing information. Analyzing ideas and concepts. Taking a position and defending it. Combining ideas from several sources and creating your own original argument.
the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment. 2.
hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and. growth, in their writing. Cour. es. and assignments should be planned with this in mi. d. Three principles are paramount:1. Name what you want and imagine students doing itHowever free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has com.
Composing Effective Writing Assignments. Writing is a valuable educational tool for learning. In the classroom, writing can help students grapple with and understand content more deeply and help students learn disciplinary ways of knowing and communicating. ... Move writing assignments from open-topic "research papers" to specific meaning ...
Understanding the question is the first and most important step when starting your assignments and helps to ensure that your research and writing is more focused and relevant. This means understanding both the individual words, and also the general scope of the question. A common mistake students make with their assignments is to misinterpret ...
Designing Effective Writing Assignments. One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in ...
A literature review is a piece of academic writing that summarizes, describes, and evaluates a topic through analysis of other authors' works. A literature review examines a topic through two or more works, and these works can be books, scholarly articles, presentations, dissertations, or other published materials.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
These kinds of writing assignments present you with two counter claims and ask you to determine from your own analysis the more valid claim. They resemble yes-no questions. These topics define the claim for you, so the major task of the writing assignment then is working out the support for the claim.
1. Reflective Papers. These assignments typically require students to think about their own experiences that demonstrate a specific concept and/or principle. For instance, a student might write about their own struggle with self-harm at a young age and reflect on the circumstances that contributed to this.
Writing Assignments Lyle Cleeland and Lisa Moody. Figure 57. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. ... These words define the scope or parameters of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, a particular jurisdiction (this would be relevant then to which laws ...
Understanding what you need to do. First, carefully read the assignment sheet and search for the required page length, due dates, and other submission-based information. Second, determine the genre of the assignment. Third, identify the core assignment questions that you need to answer. Fourth, locate the evaluation and grading criteria.
Assignment Planning - Guidelines. This template is designed to assist you with the collection and organisation of information into your notes and to plan the structure of your work before you start writing your first draft. The Assignment Planning - Guidelines has four stages: Stage #1 - Collecting Information.
With regular writing practice and targeted feedback, over time they will become more authoritative participants and contributors in your field. Designing successful writing assignments involves some or all of the following six strategies: Explicitly State Assignment Goals. Tie Assignment Goals to Course Goals.
Assignment. Definition: Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. ... For example, a writing assignment may be ...
Strive for Clarity in Your Assignment Sheet. Use "active voice" commands as you write your assignment sheet. It might feel more polite to write, "You might try comparing A to B," but students need to see "Compare A to B.". Use language that your students will understand. Students may not know exactly what you want when they see ...
Writing assignments are often used to support the goals of Writing in the Disciplines (WID), also called writing to communicate. Writing assignments of this sort are designed to introduce or give students practice with the writing conventions of a discipline and to help them game familiarity and fluency with specific genres and formats typical of a given discipline.
Below I share an approach to designing writing assignments that came together when I was teaching full time in the SOSC Core as a Harper-Schmidt Fellow. It prepares students to succeed on their SOSC essays by breaking down the writing process into the essential steps that college-level writing demands and giving students time to attend to each one.
Definition. This type of expository writing defines a subject. For example, you might write a piece that defines a historic figure by exploring their actions, motivations, and circumstances. ... As a student, many of your writing assignments are pieces of expository writing. Presenting facts in a logical, clear way is a much different task from ...
Writing an introduction can be the most difficult part of your assignment because it is where you lay out everything you will cover in what follows. The purpose of an introduction is to clearly tell the reader about the main themes and concepts in your assignment, as well as how you are going to approach them.