Something went wrong when searching for seed articles. Please try again soon.
No articles were found for that search term.
Author, year The title of the article goes here

LITERATURE REVIEW SOFTWARE FOR BETTER RESEARCH
“Litmaps is a game changer for finding novel literature... it has been invaluable for my productivity.... I also got my PhD student to use it and they also found it invaluable, finding several gaps they missed”
Varun Venkatesh
Austin Health, Australia

As a full-time researcher, Litmaps has become an indispensable tool in my arsenal. The Seed Maps and Discover features of Litmaps have transformed my literature review process, streamlining the identification of key citations while revealing previously overlooked relevant literature, ensuring no crucial connection goes unnoticed. A true game-changer indeed!
Ritwik Pandey
Doctoral Research Scholar – Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning

Using Litmaps for my research papers has significantly improved my workflow. Typically, I start with a single paper related to my topic. Whenever I find an interesting work, I add it to my search. From there, I can quickly cover my entire Related Work section.
David Fischer
Research Associate – University of Applied Sciences Kempten
“It's nice to get a quick overview of related literature. Really easy to use, and it helps getting on top of the often complicated structures of referencing”
Christoph Ludwig
Technische Universität Dresden, Germany
“This has helped me so much in researching the literature. Currently, I am beginning to investigate new fields and this has helped me hugely”
Aran Warren
Canterbury University, NZ
“I can’t live without you anymore! I also recommend you to my students.”
Professor at The Chinese University of Hong Kong
“Seeing my literature list as a network enhances my thinking process!”
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
“Incredibly useful tool to get to know more literature, and to gain insight in existing research”
KU Leuven, Belgium
“As a student just venturing into the world of lit reviews, this is a tool that is outstanding and helping me find deeper results for my work.”
Franklin Jeffers
South Oregon University, USA
“Any researcher could use it! The paper recommendations are great for anyone and everyone”
Swansea University, Wales
“This tool really helped me to create good bibtex references for my research papers”
Ali Mohammed-Djafari
Director of Research at LSS-CNRS, France
“Litmaps is extremely helpful with my research. It helps me organize each one of my projects and see how they relate to each other, as well as to keep up to date on publications done in my field”
Daniel Fuller
Clarkson University, USA
As a person who is an early researcher and identifies as dyslexic, I can say that having research articles laid out in the date vs cite graph format is much more approachable than looking at a standard database interface. I feel that the maps Litmaps offers lower the barrier of entry for researchers by giving them the connections between articles spaced out visually. This helps me orientate where a paper is in the history of a field. Thus, new researchers can look at one of Litmap's "seed maps" and have the same information as hours of digging through a database.
Baylor Fain
Postdoctoral Associate – University of Florida

We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
10 Best Literature Review Tools for Researchers

Boost your research game with these Best Literature Review Tools for Researchers! Uncover hidden gems, organize your findings, and ace your next research paper!
Researchers struggle to identify key sources, extract relevant information, and maintain accuracy while manually conducting literature reviews. This leads to inefficiency, errors, and difficulty in identifying gaps or trends in existing literature.
Table of Contents
Top 10 Literature Review Tools for Researchers: In A Nutshell (2023)
| 1. | Semantic Scholar | Researchers to access and analyze scholarly literature, particularly focused on leveraging AI and semantic analysis |
| 2. | Elicit | Researchers in extracting, organizing, and synthesizing information from various sources, enabling efficient data analysis |
| 3. | Scite.Ai | Determine the credibility and reliability of research articles, facilitating evidence-based decision-making |
| 4. | DistillerSR | Streamlining and enhancing the process of literature screening, study selection, and data extraction |
| 5. | Rayyan | Facilitating efficient screening and selection of research outputs |
| 6. | Consensus | Researchers to work together, annotate, and discuss research papers in real-time, fostering team collaboration and knowledge sharing |
| 7. | RAx | Researchers to perform efficient literature search and analysis, aiding in identifying relevant articles, saving time, and improving the quality of research |
| 8. | Lateral | Discovering relevant scientific articles and identify potential research collaborators based on user interests and preferences |
| 9. | Iris AI | Exploring and mapping the existing literature, identifying knowledge gaps, and generating research questions |
| 10. | Scholarcy | Extracting key information from research papers, aiding in comprehension and saving time |
#1. Semantic Scholar – A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
Not all scholarly content may be indexed, and occasional false positives or inaccurate associations can occur. Furthermore, the tool primarily focuses on computer science and related fields, potentially limiting coverage in other disciplines.
#2. Elicit – Research assistant using language models like GPT-3
However, users should be cautious when using Elicit. It is important to verify the credibility and accuracy of the sources found through the tool, as the database encompasses a wide range of publications.
Additionally, occasional glitches in the search function have been reported, leading to incomplete or inaccurate results. While Elicit offers tremendous benefits, researchers should remain vigilant and cross-reference information to ensure a comprehensive literature review.
#3. Scite.Ai – Your personal research assistant
Scite.Ai is a popular literature review tool that revolutionizes the research process for scholars. With its innovative citation analysis feature, researchers can evaluate the credibility and impact of scientific articles, making informed decisions about their inclusion in their own work.
However, while Scite.Ai offers numerous advantages, there are a few aspects to be cautious about. As with any data-driven tool, occasional errors or inaccuracies may arise, necessitating researchers to cross-reference and verify results with other reputable sources.
Rayyan offers the following paid plans:
#4. DistillerSR – Literature Review Software
Despite occasional technical glitches reported by some users, the developers actively address these issues through updates and improvements, ensuring a better user experience.
#5. Rayyan – AI Powered Tool for Systematic Literature Reviews
However, it’s important to be aware of a few aspects. The free version of Rayyan has limitations, and upgrading to a premium subscription may be necessary for additional functionalities.
#6. Consensus – Use AI to find you answers in scientific research
With Consensus, researchers can save significant time by efficiently organizing and accessing relevant research material.People consider Consensus for several reasons.
Consensus offers both free and paid plans:
#7. RAx – AI-powered reading assistant
#8. lateral – advance your research with ai.
Additionally, researchers must be mindful of potential biases introduced by the tool’s algorithms and should critically evaluate and interpret the results.
#9. Iris AI – Introducing the researcher workspace
Researchers are drawn to this tool because it saves valuable time by automating the tedious task of literature review and provides comprehensive coverage across multiple disciplines.
#10. Scholarcy – Summarize your literature through AI
Scholarcy’s ability to extract key information and generate concise summaries makes it an attractive option for scholars looking to quickly grasp the main concepts and findings of multiple papers.
Scholarcy’s automated summarization may not capture the nuanced interpretations or contextual information presented in the full text.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, conducting a comprehensive literature review is a crucial aspect of any research project, and the availability of reliable and efficient tools can greatly facilitate this process for researchers. This article has explored the top 10 literature review tools that have gained popularity among researchers.
Q1. What are literature review tools for researchers?
Q2. what criteria should researchers consider when choosing literature review tools.
When choosing literature review tools, researchers should consider factors such as the tool’s search capabilities, database coverage, user interface, collaboration features, citation management, annotation and highlighting options, integration with reference management software, and data extraction capabilities.
Q3. Are there any literature review tools specifically designed for systematic reviews or meta-analyses?
Meta-analysis support: Some literature review tools include statistical analysis features that assist in conducting meta-analyses. These features can help calculate effect sizes, perform statistical tests, and generate forest plots or other visual representations of the meta-analytic results.
Q4. Can literature review tools help with organizing and annotating collected references?
Integration with citation managers: Some literature review tools integrate with popular citation managers like Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote, allowing seamless transfer of references and annotations between platforms.
By leveraging these features, researchers can streamline the organization and annotation of their collected references, making it easier to retrieve relevant information during the literature review process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Fiona Doyle
- Coil Spring
New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at Ai2.
Analyze research papers at superhuman speed
Search for research papers, get one sentence abstract summaries, select relevant papers and search for more like them, extract details from papers into an organized table.

Find themes and concepts across many papers
Don't just take our word for it.
.webp)
Tons of features to speed up your research
Upload your own pdfs, orient with a quick summary, view sources for every answer, ask questions to papers, research for the machine intelligence age, pick a plan that's right for you, get in touch, enterprise and institutions, common questions. great answers., how do researchers use elicit.
Over 2 million researchers have used Elicit. Researchers commonly use Elicit to:
- Speed up literature review
- Find papers they couldn’t find elsewhere
- Automate systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- Learn about a new domain
Elicit tends to work best for empirical domains that involve experiments and concrete results. This type of research is common in biomedicine and machine learning.
What is Elicit not a good fit for?
Elicit does not currently answer questions or surface information that is not written about in an academic paper. It tends to work less well for identifying facts (e.g. "How many cars were sold in Malaysia last year?") and in theoretical or non-empirical domains.
What types of data can Elicit search over?
Elicit searches across 125 million academic papers from the Semantic Scholar corpus, which covers all academic disciplines. When you extract data from papers in Elicit, Elicit will use the full text if available or the abstract if not.
How accurate are the answers in Elicit?
A good rule of thumb is to assume that around 90% of the information you see in Elicit is accurate. While we do our best to increase accuracy without skyrocketing costs, it’s very important for you to check the work in Elicit closely. We try to make this easier for you by identifying all of the sources for information generated with language models.
How can you get in contact with the team?
You can email us at [email protected] or post in our Slack community ! We log and incorporate all user comments, and will do our best to reply to every inquiry as soon as possible.
What happens to papers uploaded to Elicit?
When you upload papers to analyze in Elicit, those papers will remain private to you and will not be shared with anyone else.
How accurate is Elicit?
Training our models on specific tasks, searching over academic papers, making it easy to double-check answers, save time, think more. try elicit for free..
Your personal research assistant
Zotero is a free, easy-to-use tool to help you collect, organize, annotate, cite, and share research.
Available for Mac, Windows, Linux, and iOS
Just need to create a quick bibliography? Try ZoteroBib .
Meet Zotero.
Collect with a click..
Zotero automatically senses research as you browse the web. Need an article from JSTOR or a preprint from arXiv.org? A news story from the New York Times or a book from a library? Zotero has you covered, everywhere.
Organize your way.
Zotero helps you organize your research any way you want. You can sort items into collections and tag them with keywords. Or create saved searches that automatically fill with relevant materials as you work.
Cite in style.
Zotero instantly creates references and bibliographies for any text editor, and directly inside Word, LibreOffice, and Google Docs. With support for over 9,000 citation styles, you can format your work to match any style guide or publication.
Stay in sync.
Zotero can optionally synchronize your data across devices, keeping your files, notes, and bibliographic records seamlessly up to date. If you decide to sync, you can also always access your research from any web browser.
Collaborate freely.
Zotero lets you co-write a paper with a colleague, distribute course materials to students, or build a collaborative bibliography. You can share a Zotero library with as many people you like, at no cost.
Zotero is open source and developed by an independent, nonprofit organization that has no financial interest in your private information. With Zotero, you always stay in control of your own data.
Still not sure which program to use for your research? See why we think you should choose Zotero .
Ready to try Zotero?

10 Open Science Tools for Literature Review You Should Know about
Here are 10 literature search tools that will make your scientific literature search faster and more convenient. All of the presented literature review software is free and follows Open Science principles.
Traditionally, scientific literature has been tucked away behind paywalls of academic publishers. Not only is the access to papers often restricted, but subscriptions are required to use many scientific search engines. This practice discriminates against universities and institutions who cannot afford the licenses, e.g. in low-income countries. Closed publishing also makes it hard for persons not affiliated with research institutes, such as freelance journalists or the public, to learn about scientific discoveries.
The proportion of research accessible publicly today at no cost varies between disciplines . While in the biomedical sciences and mathematics, the majority of research published between 2009 and 2015 was openly accessible, this held true only for around 15 percent of publications in chemistry. Luckily, the interest in open access publishing is steadily increasing and has gained momentum in the past decade or so.
Many governmental funding bodies around the world nowadays require science resulting from grant money they provided to be available publicly for free. The exact requirements vary and UNESCO is currently developing a framework that specifies standards for the whole area of Open Science.
Once I started my research on the topic, I was astonished by just how many free Open Science tools for literature review already exist! Read on below for 10 literature search tools — from a search engines for research papers, over literature review software that helps you quickly find open access versions of papers, to tools that help you save the correct citation in one click.
Tools for Literature review
First, an overview of the literature search tools in this blog post:
ScienceOpen
- Citation Gecko
- Local Citation Network
ResearchRabbit
- Open Access Button
- EndNote Click
Read by QxMD
I divided the tools into four categories:
Search engines for research papers
- Literature review software based on citation networks
- Locating open access scientific papers, and
- Other tools that help in the literature review
Here, we go!
The best place to start a scientific literature search is with a search engine for research papers. Here are two you might not have heard of!
Want to perform a literature search and don’t want to pay for Web of Science or Scopus or perhaps you are tired of the limited functionality of the free Google Scholar ? ScienceOpen is many things, among others a search engine for research papers. Despite being owned by a private company, this scientific search engine is freely accessible with visually appealing and functional design. Search results are clearly labelled for type of publication, number of citations, altmetrics scores etc. and allow for filtering. You can also access citation metrics, i.e., display which publications have cited a certain paper.
Recommended by a reader of the blog (thank you!), the Lens is a search tool that doesn’t only allow you to search the scholarly literature but patents too! Millions of patents from over 95 jurisdictions can be searched. The Lens is run by the non-profit social enterprise Cambia. The search engine is free to use for the public, though charges occur for commercial use and to get additional functionality.

Literature Review software based on citation networks
The next category of tools we will be looking at are a bit more advanced than a simple search engine for research papers. These literature search tools help you discover scientific literature you may have missed by visualising citation networks.
Citation Gecko
The literature search tool Citation Gecko is an open source web app that makes it easier to discover relevant scientific literature than your average keyword-based search engine for research papers. It works in the following way: First you upload about 5-6 “seed papers”. The program then extracts all references in and to these seed papers and creates a visual citation network. The nodes are displayed in different colours and sizes depending on whether the papers are citing a seed paper or are cited by it and how many, respectively. By combing through the citation network, you can discover new papers that may be relevant for your scientific literature search. You can also increase your citation network step by step by including more seed papers.
This literature review tool was developed by Barney Walker , and the underlying citation data is provided by Crossref and Open Citations .
Local Citation Network
Similar to Citation Gecko, Local Citation Network is an open source tool that works as a scientific search engine on steroids. Local Citation Network was developed by Physician Scientist Tim Wölfle. This literature review tool works best if you feed it with a larger library of seed papers than required for Citation Gecko. Therefore, Wölfle recommends using it at the end of your scientific literature search to identify papers you may have missed.
As an alternative to the literature search tools Citation Gecko and Local Citation Network, a reader of the blog recommended ResearchRabbit . It’s free to use and looks like a versatile piece of literature review software helping you build your own citation network. ResearchRabbit lets you add labels to the entries in your citation network, download PDFs of papers and sign up for email alerts for new papers related to your research topic. Instead of a tool to use only once during your scientific literature search, ResearchRabbit seems to function more like a private scientific library storing (and connecting) all the papers in your field.
Run by (former) researchers and engineers, ResearchRabbit is partly financed through donations but their website does not state where the core funding of this literature review software originates from.
Locating open access scientific papers
You may face the problem in your scientific literature search that you don’t have access to every research paper you are interested in. I highly recommend installing at least one of the open access tools below so you can quickly locate freely accessible versions of the scientific literature if available anywhere.
Open Access Button
Works like the scientific search engine Sci-hub but is legal: You enter the DOI, link or citation of a paper and the literature review tool Open Access Button displays it if freely accessible anywhere. To find an open access version, Open Access Button searches thousands of repositories, for example, preprint servers, authors’ personal pages, open access journals and other aggregators such as the COnnecting REpositories service based at The Open University in the UK ( CORE ), the EU-funded OpenAire infrastructure, and the US community initiative Share .
If the article you are looking for isn’t freely available, Open Access Button asks the author to share it to a repository. You can enter your email address to be notified once it has become available.
Open Access Button is also available as browser plugin, which means that a button appears next to an article whenever a free version is available. This search engine for research papers is funded by non-profit foundations and is open source.
Unpaywall
Unpaywall is a search engine for research papers similar to Open Access Button — but only available as browser plugin. If the article you are looking at is behind a paywall but freely accessible somewhere else, a green button appears on the right side of the article. I installed it recently and regret not having done it sooner, it works really smoothly! I think the plugin is a great help in your scientific literature search.
Unpaywall is run by the non-profit organisation Our Research who has created a fleet of open science tools.
EndNote Click
Another browser extension that lets you access the scientific literature for free if available is EndNote Click (formerly Kopernio). EndNote Click claims to be faster than other search engines for research papers bypassing redirects and verification steps. I personally don’t find the Unpaywall or Open Access Button plugins inconvenient to use but I’d encourage you to try out all of these scientific search engines and see what works best for you.
One advantage of EndNote Click that a reader of the blog told me about is the side bar that appears when opening a paper through the plugin. It lets you, for example, save citations quickly, avoiding time-consuming searches on publishers’ websites.
As the reference manager, EndNote Click is part of the research analytics company Clarivate.
Other tools for literature review
This last category of literature search tools features a tool that creates a personalised feed of scientific literature for you and another that makes citing the scientific literature effortless.
Available as an app or in a browser window, the literature review tool Read lets you create a personalised feed that is updated daily with new papers on research topics or from journals of your choice. If there is an openly accessible version of an article, you can read it with one click. If your institution has journal subscriptions, you can also link them to your Read profile. Read has been created by the company QxMD and is free to use.
CiteAs
You discovered a promising paper in your scientific literature search and want to cite it? CiteAs is a convenient literature review tool to obtain the correct citation for any publication, preprint, software or dataset in one click. Funded by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, CiteAs is operated partly by the non-profit Our Research .
Beyond literature review tools
There you have it, 10 tools for literature review that are all completely free and follow Open Science principles.
Of course, finding a great literature review tool, such as a search engine for research papers or a citation tool, is only one essential part in the whole process of writing a scientific paper. If you would like to learn a complete process to write a scientific article step by step, then you’ll love our free training. Simply click on the orange button below to watch it now (or sign up to watch it later).

Share article
© Copyright 2018-2024 by Anna Clemens. All Rights Reserved.
Photography by Alice Dix
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

5 literature review tools to ace your research (+2 bonus tools)

Table of Contents
Your literature review is the lore behind your research paper . It comes in two forms, systematic and scoping , both serving the purpose of rounding up previously published works in your research area that led you to write and finish your own.
A literature review is vital as it provides the reader with a critical overview of the existing body of knowledge, your methodology, and an opportunity for research applications.

Some steps to follow while writing your review:
- Pick an accessible topic for your paper
- Do thorough research and gather evidence surrounding your topic
- Read and take notes diligently or you can use ChatPDF tool for this
- Create a rough structure for your review
- Synthesis your notes and write the first draft
- Edit and proofread your literature review
To make your workload a little lighter, there are many literature review AI tools. These tools can help you find academic articles through AI and answer questions about a research paper.
Best literature review tools to improve research workflow
A literature review is one of the most critical yet tedious stages in composing a research paper. Many students find it an uphill task since it requires extensive reading and careful organization .
Using some of the best literature review tools listed here, you can make your life easier by overcoming some of the existing challenges in literature reviews. From collecting and classifying to analyzing and publishing research outputs, these tools help you with your literature review and improve your productivity without additional effort or expenses.
1. SciSpace
SciSpace is an AI for academic research that will help find research papers and answer questions about a research paper. You can discover, read, and understand research papers with SciSpace making it an excellent platform for literature review. Featuring a repository with over 270 million research papers, it comes with your AI research assistant called Copilot that offers explanations, summaries , and answers as you read.
Get started now:
Find academic articles through AI
SciSpace has a dedicated literature review tool that finds scientific articles when you search for a question. Based on semantic search, it shows all the research papers relevant for your subject. You can then gather quick insights for all the papers displayed in your search results like methodology, dataset, etc., and figure out all the papers relevant for your research.
Identify relevant articles faster
Abstracts are not always enough to determine whether a paper is relevant to your research question. For starters, you can ask questions to your AI research assistant, SciSpace Copilot to explore the content and better understand the article. Additionally, use the summarize feature to quickly review the methodology and results of a paper and decide if it is worth reading in detail.

Learn in your preferred language
A big barrier non-native English speakers face while conducting a literature review is that a significant portion of scientific literature is published in English. But with SciSpace Copilot, you can review, interact, and learn from research papers in any language you prefer — presently, it supports 75+ languages. The AI will answer questions about a research paper in your mother tongue.
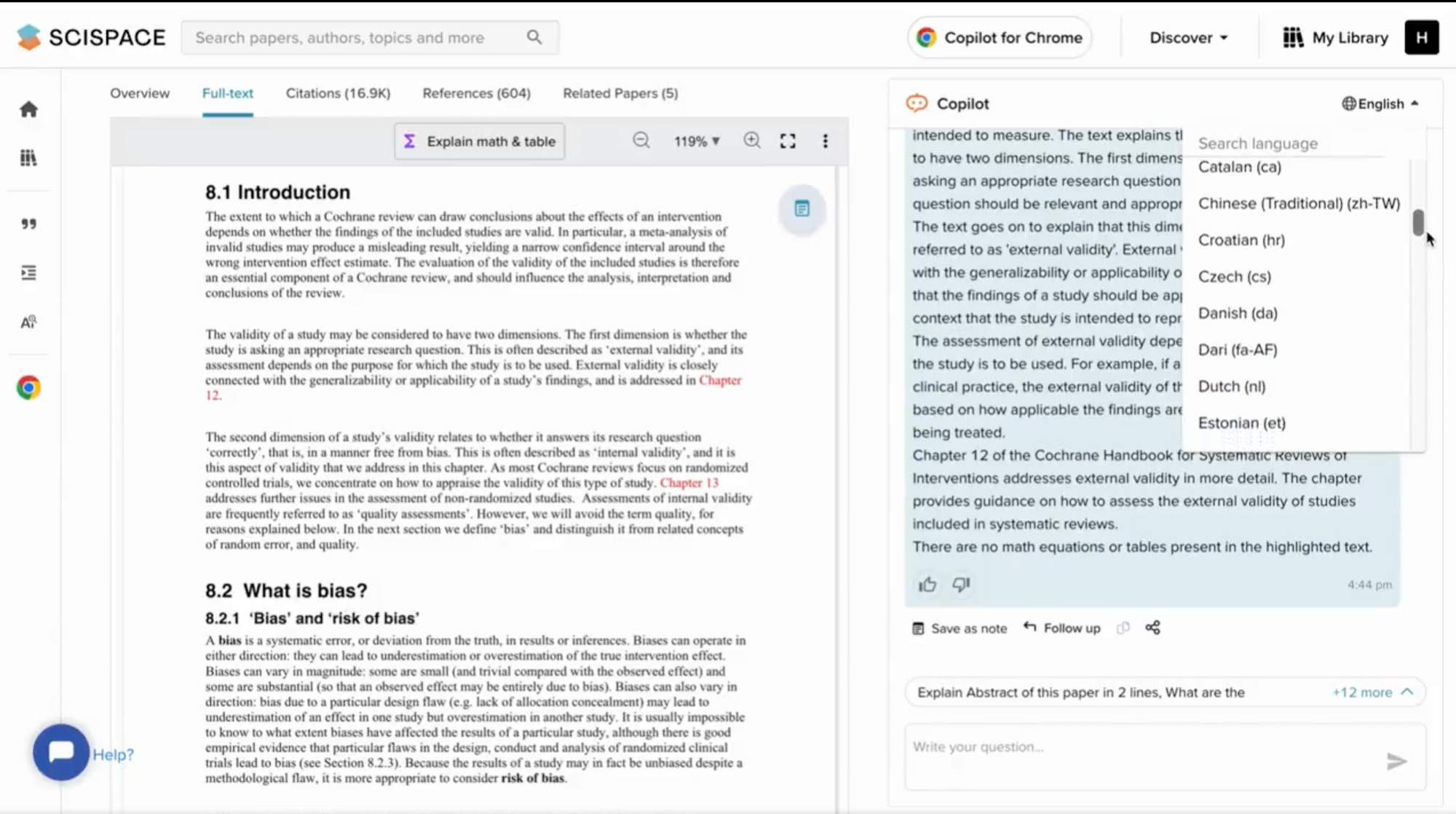
Integrates with Zotero
Many researchers use Zotero to create a library and manage research papers. SciSpace lets you import your scientific articles directly from Zotero into your SciSpace library and use Copilot to comprehend your research papers. You can also highlight key sections, add notes to the PDF as you read, and even turn helpful explanations and answers from Copilot into notes for future review.
Understand math and complex concepts quickly
Come across complex mathematical equations or difficult concepts? Simply highlight the text or select the formula or table, and Copilot will provide an explanation or breakdown of the same in an easy-to-understand manner. You can ask follow-up questions if you need further clarification.

Discover new papers to read without leaving
Highlight phrases or sentences in your research paper to get suggestions for related papers in the field and save time on literature reviews. You can also use the 'Trace' feature to move across and discover connected papers, authors, topics, and more.
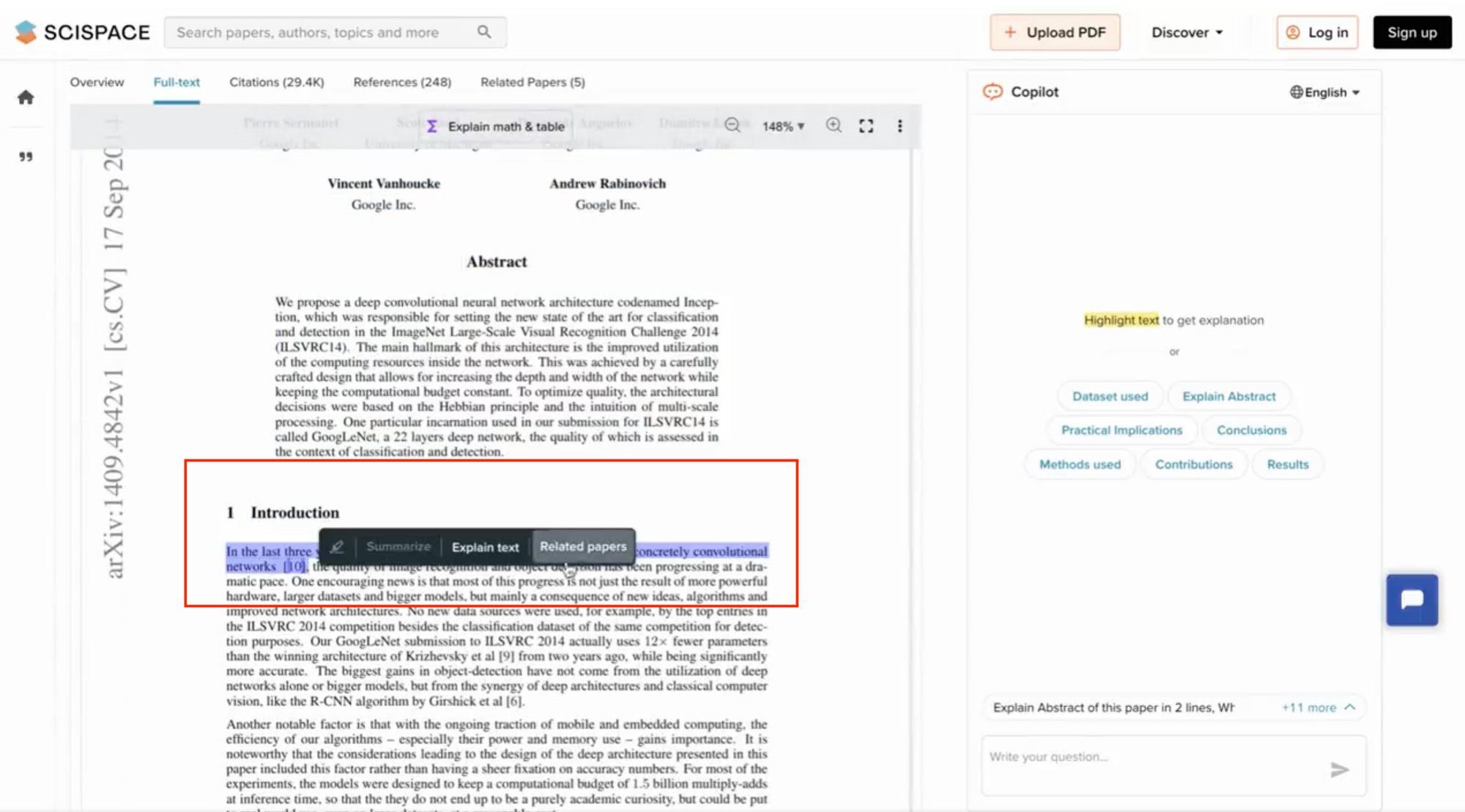
SciSpace Copilot is now available as a Chrome extension , allowing you to access its features directly while you browse scientific literature anywhere across the web.
Get citation-backed answers
When you're conducting a literature review, you want credible information with proper references. Copilot ensures that every piece of information provided by SciSpace Copilot is backed by a direct reference, boosting transparency, accuracy, and trustworthiness.
Ask a question related to the paper you're delving into. Every response from Copilot comes with a clickable citation. This citation leads you straight to the section of the PDF from which the answer was extracted.
By seamlessly integrating answers with citations, SciSpace Copilot assures you of the authenticity and relevance of the information you receive.
2. Mendeley
Mendeley Citation Manager is a free web and desktop application. It helps simplify your citation management workflow significantly. Here are some ways you can speed up your referencing game with Mendeley.
Generate citations and bibliographies
Easily add references from your Mendeley library to your Word document, change your citation style, and create a bibliography, all without leaving your document.
Retrieve references
It allows you to access your references quickly. Search for a term, and it will return results by referencing the year, author, or source.
Add sources to your Mendeley library by dragging PDF to Mendeley Reference Manager. Mendeley will automatically remove the PDF(s) metadata and create a library entry.
Read and annotate documents
It helps you highlight and comment across multiple PDFs while keep them all in one place using Mendeley Notebook . Notebook pages are not tied to a reference and let you quote from many PDFs.
A big part of many literature review workflows, Zotero is a free, open-source tool for managing citations that works as a plug-in on your browser. It helps you gather the information you need, cite your sources, lets you attach PDFs, notes, and images to your citations, and create bibliographies.
Import research articles to your database
Search for research articles on a keyword, and add relevant results to your database. Then, select the articles you are most interested in, and import them into Zotero.
Add bibliography in a variety of formats
With Zotero, you don’t have to scramble for different bibliography formats. Simply use the Zotero-Word plug-in to insert in-text citations and generate a bibliography.
Share your research
You can save a paper and sync it with an online library to easily share your research for group projects. Zotero can be used to create your database and decrease the time you spend formatting citations.
Sysrev is an AI too for article review that facilitates screening, collaboration, and data extraction from academic publications, abstracts, and PDF documents using machine learning. The platform is free and supports public and Open Access projects only.
Some of the features of Sysrev include:
Group labels
Group labels can be a powerful concept for creating database tables from documents. When exported and re-imported, each group label creates a new table. To make labels for a project, go into the manage -> labels section of the project.
Group labels enable project managers to pull table information from documents. It makes it easier to communicate review results for specific articles.
Track reviewer performance
Sysrev's label counting tool provides filtering and visualization options for keeping track of the distribution of labels throughout the project's progress. Project managers can check their projects at any point to track progress and the reviewer's performance.
Tool for concordance
The Sysrev tool for concordance allows project administrators and reviewers to perform analysis on their labels. Concordance is measured by calculating the number of times users agree on the labels they have extracted.
Colandr is a free, open-source, internet-based analysis and screening software used as an AI for academic research. It was designed to ease collaboration across various stages of the systematic review procedure. The tool can be a little complex to use. So, here are the steps involved in working with Colandr.
Create a review
The first step to using Colandr is setting up an organized review project. This is helpful to librarians who are assisting researchers with systematic reviews.
The planning stage is setting the review's objectives along with research queries. Any reviewer can review the details of the planning stage. However, they can only be modified by the author for the review.
Citation screening/import
In this phase, users can upload their results from database searches. Colandr also offers an automated deduplication system.
Full-text screening
The system in Colandr will discover the combination of terms and expressions that are most useful for the reader. If an article is selected, it will be moved to the final step.
Data extraction/export
Colandr data extraction is more efficient than the manual method. It creates the form fields for data extraction during the planning stage of the review procedure. Users can decide to revisit or modify the form for data extraction after completing the initial screening.
Bonus literature review tools
SRDR+ is a web-based tool for extracting and managing systematic review or meta-analysis data. It is open and has a searchable archive of systematic reviews and their data.
7. Plot Digitizer
Plot Digitizer is an efficient tool for extracting information from graphs and images, equipped with many features that facilitate data extraction. The program comes with a free online application, which is adequate to extract data quickly.
Final thoughts
Writing a literature review is not easy. It’s a time-consuming process, which can become tiring at times. The literature review tools mentioned in this blog do an excellent job of maximizing your efforts and helping you write literature reviews much more efficiently. With them, you can breathe a sigh of relief and give more time to your research.
As you dive into your literature review, don’t forget to use SciSpace ResearchGPT to streamline the process. It facilitates your research and helps you explore key findings, summary, and other components of the paper easily.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is rrl in research.
RRL stands for Review of Related Literature and sometimes interchanged with ‘Literature Review.’ RRL is a body of studies relevant to the topic being researched. These studies may be in the form of journal articles, books, reports, and other similar documents. Review of related literature is used to support an argument or theory being made by the researcher, as well as to provide information on how others have approached the same topic.
2. What are few softwares and tools available for literature review?
• SciSpace Discover
• Mendeley
• Zotero
• Sysrev
• Colandr
• SRDR+
3. How to generate an online literature review?
The Scispace Discover tool, which offers an excellent repository of millions of peer-reviewed articles and resources, will help you generate or create a literature review easily. You may find relevant information by utilizing the filter option, checking its credibility, tracing related topics and articles, and citing in widely accepted formats with a single click.
4. What does it mean to synthesize literature?
To synthesize literature is to take the main points and ideas from a number of sources and present them in a new way. The goal is to create a new piece of writing that pulls together the most important elements of all the sources you read. Make recommendations based on them, and connect them to the research.
5. Should we write abstract for literature review?
Abstracts, particularly for the literature review section, are not required. However, an abstract for the research paper, on the whole, is useful for summarizing the paper and letting readers know what to expect from it. It can also be used to summarize the main points of the paper so that readers have a better understanding of the paper's content before they read it.
6. How do you evaluate the quality of a literature review?
• Whether it is clear and well-written.
• Whether Information is current and up to date.
• Does it cover all of the relevant sources on the topic.
• Does it provide enough evidence to support its conclusions.
7. Is literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research and provide a background for the rest of your work.
8. What are the sources for a literature review?
• Reports
• Theses
• Conference proceedings
• Company reports
• Some government publications
• Journals
• Books
• Newspapers
• Articles by professional associations
• Indexes
• Databases
• Catalogues
• Encyclopaedias
• Dictionaries
• Bibliographies
• Citation indexes
• Statistical data from government websites
9. What is the difference between a systematic review and a literature review?
A systematic review is a form of research that uses a rigorous method to generate knowledge from both published and unpublished data. A literature review, on the other hand, is a critical summary of an area of research within the context of what has already been published.
Suggested reads!
Types of essays in academic writing Citation Machine Alternatives — A comparison of top citation tools 2023
QuillBot vs SciSpace: Choose the best AI-paraphrasing tool
ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

Accelerate your research with the best systematic literature review tools
The ideal literature review tool helps you make sense of the most important insights in your research field. ATLAS.ti empowers researchers to perform powerful and collaborative analysis using the leading software for literature review.

Finalize your literature review faster with comfort
ATLAS.ti makes it easy to manage, organize, and analyze articles, PDFs, excerpts, and more for your projects. Conduct a deep systematic literature review and get the insights you need with a comprehensive toolset built specifically for your research projects.

Figure out the "why" behind your participant's motivations
Understand the behaviors and emotions that are driving your focus group participants. With ATLAS.ti, you can transform your raw data and turn it into qualitative insights you can learn from. Easily determine user intent in the same spot you're deciphering your overall focus group data.

Visualize your research findings like never before
We make it simple to present your analysis results with meaningful charts, networks, and diagrams. Instead of figuring out how to communicate the insights you just unlocked, we enable you to leverage easy-to-use visualizations that support your goals.
Paper Search – Access 200+ Million Papers with AI-Powered Insights
Unlock access to over 200 million scientific papers and streamline your research with our cutting-edge AI-powered Paper Search 2.0. Easily find, summarize, and integrate relevant papers directly into your ATLAS.ti Web workspace.

Everything you need to elevate your literature review
Import and organize literature data.
Import and analyze any type of text content – ATLAS.ti supports all standard text and transcription files such as Word and PDF.
Analyze with ease and speed
Utilize easy-to-learn workflows that save valuable time, such as auto coding, sentiment analysis, team collaboration, and more.
Leverage AI-driven tools
Make efficiency a priority and let ATLAS.ti do your work with AI-powered research tools and features for faster results.
Visualize and present findings
With just a few clicks, you can create meaningful visualizations like charts, word clouds, tables, networks, among others for your literature data.
The faster way to make sense of your literature review. Try it for free, today.
A literature review analyzes the most current research within a research area. A literature review consists of published studies from many sources:
- Peer-reviewed academic publications
- Full-length books
- University bulletins
- Conference proceedings
- Dissertations and theses
Literature reviews allow researchers to:
- Summarize the state of the research
- Identify unexplored research inquiries
- Recommend practical applications
- Critique currently published research
Literature reviews are either standalone publications or part of a paper as background for an original research project. A literature review, as a section of a more extensive research article, summarizes the current state of the research to justify the primary research described in the paper.
For example, a researcher may have reviewed the literature on a new supplement's health benefits and concluded that more research needs to be conducted on those with a particular condition. This research gap warrants a study examining how this understudied population reacted to the supplement. Researchers need to establish this research gap through a literature review to persuade journal editors and reviewers of the value of their research.
Consider a literature review as a typical research publication presenting a study, its results, and the salient points scholars can infer from the study. The only significant difference with a literature review treats existing literature as the research data to collect and analyze. From that analysis, a literature review can suggest new inquiries to pursue.
Identify a focus
Similar to a typical study, a literature review should have a research question or questions that analysis can answer. This sort of inquiry typically targets a particular phenomenon, population, or even research method to examine how different studies have looked at the same thing differently. A literature review, then, should center the literature collection around that focus.
Collect and analyze the literature
With a focus in mind, a researcher can collect studies that provide relevant information for that focus. They can then analyze the collected studies by finding and identifying patterns or themes that occur frequently. This analysis allows the researcher to point out what the field has frequently explored or, on the other hand, overlooked.
Suggest implications
The literature review allows the researcher to argue a particular point through the evidence provided by the analysis. For example, suppose the analysis makes it apparent that the published research on people's sleep patterns has not adequately explored the connection between sleep and a particular factor (e.g., television-watching habits, indoor air quality). In that case, the researcher can argue that further study can address this research gap.
External requirements aside (e.g., many academic journals have a word limit of 6,000-8,000 words), a literature review as a standalone publication is as long as necessary to allow readers to understand the current state of the field. Even if it is just a section in a larger paper, a literature review is long enough to allow the researcher to justify the study that is the paper's focus.
Note that a literature review needs only to incorporate a representative number of studies relevant to the research inquiry. For term papers in university courses, 10 to 20 references might be appropriate for demonstrating analytical skills. Published literature reviews in peer-reviewed journals might have 40 to 50 references. One of the essential goals of a literature review is to persuade readers that you have analyzed a representative segment of the research you are reviewing.
Researchers can find published research from various online sources:
- Journal websites
- Research databases
- Search engines (Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar)
- Research repositories
- Social networking sites (Academia, ResearchGate)
Many journals make articles freely available under the term "open access," meaning that there are no restrictions to viewing and downloading such articles. Otherwise, collecting research articles from restricted journals usually requires access from an institution such as a university or a library.
Evidence of a rigorous literature review is more important than the word count or the number of articles that undergo data analysis. Especially when writing for a peer-reviewed journal, it is essential to consider how to demonstrate research rigor in your literature review to persuade reviewers of its scholarly value.
Select field-specific journals
The most significant research relevant to your field focuses on a narrow set of journals similar in aims and scope. Consider who the most prominent scholars in your field are and determine which journals publish their research or have them as editors or reviewers. Journals tend to look favorably on systematic reviews that include articles they have published.
Incorporate recent research
Recently published studies have greater value in determining the gaps in the current state of research. Older research is likely to have encountered challenges and critiques that may render their findings outdated or refuted. What counts as recent differs by field; start by looking for research published within the last three years and gradually expand to older research when you need to collect more articles for your review.
Consider the quality of the research
Literature reviews are only as strong as the quality of the studies that the researcher collects. You can judge any particular study by many factors, including:
- the quality of the article's journal
- the article's research rigor
- the timeliness of the research
The critical point here is that you should consider more than just a study's findings or research outputs when including research in your literature review.
Narrow your research focus
Ideally, the articles you collect for your literature review have something in common, such as a research method or research context. For example, if you are conducting a literature review about teaching practices in high school contexts, it is best to narrow your literature search to studies focusing on high school. You should consider expanding your search to junior high school and university contexts only when there are not enough studies that match your focus.
You can create a project in ATLAS.ti for keeping track of your collected literature. ATLAS.ti allows you to view and analyze full text articles and PDF files in a single project. Within projects, you can use document groups to separate studies into different categories for easier and faster analysis.
For example, a researcher with a literature review that examines studies across different countries can create document groups labeled "United Kingdom," "Germany," and "United States," among others. A researcher can also use ATLAS.ti's global filters to narrow analysis to a particular set of studies and gain insights about a smaller set of literature.
ATLAS.ti allows you to search, code, and analyze text documents and PDF files. You can treat a set of research articles like other forms of qualitative data. The codes you apply to your literature collection allow for analysis through many powerful tools in ATLAS.ti:
- Code Co-Occurrence Explorer
- Code Co-Occurrence Table
- Code-Document Table
Other tools in ATLAS.ti employ machine learning to facilitate parts of the coding process for you. Some of our software tools that are effective for analyzing literature include:
- Named Entity Recognition
- Opinion Mining
- Sentiment Analysis
As long as your documents are text documents or text-enable PDF files, ATLAS.ti's automated tools can provide essential assistance in the data analysis process.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
What Will You Do Differently?
Please help your librarians by filling out this two-minute survey of today's class session..
Professor, this one's for you .
Introduction
Literature reviews take time. here is some general information to know before you start. .
- VIDEO -- This video is a great overview of the entire process. (2020; North Carolina State University Libraries) --The transcript is included --This is for everyone; ignore the mention of "graduate students" --9.5 minutes, and every second is important
- OVERVIEW -- Read this page from Purdue's OWL. It's not long, and gives some tips to fill in what you just learned from the video.
- NOT A RESEARCH ARTICLE -- A literature review follows a different style, format, and structure from a research article.
| Reports on the work of others. | Reports on original research. | |
| To examine and evaluate previous literature. | To test a hypothesis and/or make an argument. May include a short literature review to introduce the subject. |
- Next: Evaluate >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 1:42 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
All-in-one Literature Review Software
Start your free trial.
Free MAXQDA trial for Windows and Mac
Your trial will end automatically after 14 days and will not renew. There is no need for cancelation.
MAXQDA The All-in-one Literature Review Software
MAXQDA is the best choice for a comprehensive literature review. It works with a wide range of data types and offers powerful tools for literature review, such as reference management, qualitative, vocabulary, text analysis tools, and more.
Document viewer
Your analysis.
As your all-in-one literature review software, MAXQDA can be used to manage your entire research project. Easily import data from texts, interviews, focus groups, PDFs, web pages, spreadsheets, articles, e-books, and even social media data. Connect the reference management system of your choice with MAXQDA to easily import bibliographic data. Organize your data in groups, link relevant quotes to each other, keep track of your literature summaries, and share and compare work with your team members. Your project file stays flexible and you can expand and refine your category system as you go to suit your research.
Developed by and for researchers – since 1989

Having used several qualitative data analysis software programs, there is no doubt in my mind that MAXQDA has advantages over all the others. In addition to its remarkable analytical features for harnessing data, MAXQDA’s stellar customer service, online tutorials, and global learning community make it a user friendly and top-notch product.
Sally S. Cohen – NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing
Literature Review is Faster and Smarter with MAXQDA

Easily import your literature review data
With a literature review software like MAXQDA, you can easily import bibliographic data from reference management programs for your literature review. MAXQDA can work with all reference management programs that can export their databases in RIS-format which is a standard format for bibliographic information. Like MAXQDA, these reference managers use project files, containing all collected bibliographic information, such as author, title, links to websites, keywords, abstracts, and other information. In addition, you can easily import the corresponding full texts. Upon import, all documents will be automatically pre-coded to facilitate your literature review at a later stage.
Capture your ideas while analyzing your literature
Great ideas will often occur to you while you’re doing your literature review. Using MAXQDA as your literature review software, you can create memos to store your ideas, such as research questions and objectives, or you can use memos for paraphrasing passages into your own words. By attaching memos like post-it notes to text passages, texts, document groups, images, audio/video clips, and of course codes, you can easily retrieve them at a later stage. Particularly useful for literature reviews are free memos written during the course of work from which passages can be copied and inserted into the final text.

Find concepts important to your generated literature review
When generating a literature review you might need to analyze a large amount of text. Luckily MAXQDA as the #1 literature review software offers Text Search tools that allow you to explore your documents without reading or coding them first. Automatically search for keywords (or dictionaries of keywords), such as important concepts for your literature review, and automatically code them with just a few clicks. Document variables that were automatically created during the import of your bibliographic information can be used for searching and retrieving certain text segments. MAXQDA’s powerful Coding Query allows you to analyze the combination of activated codes in different ways.
Aggregate your literature review
When conducting a literature review you can easily get lost. But with MAXQDA as your literature review software, you will never lose track of the bigger picture. Among other tools, MAXQDA’s overview and summary tables are especially useful for aggregating your literature review results. MAXQDA offers overview tables for almost everything, codes, memos, coded segments, links, and so on. With MAXQDA literature review tools you can create compressed summaries of sources that can be effectively compared and represented, and with just one click you can easily export your overview and summary tables and integrate them into your literature review report.

Powerful and easy-to-use literature review tools
Quantitative aspects can also be relevant when conducting a literature review analysis. Using MAXQDA as your literature review software enables you to employ a vast range of procedures for the quantitative evaluation of your material. You can sort sources according to document variables, compare amounts with frequency tables and charts, and much more. Make sure you don’t miss the word frequency tools of MAXQDA’s add-on module for quantitative content analysis. Included are tools for visual text exploration, content analysis, vocabulary analysis, dictionary-based analysis, and more that facilitate the quantitative analysis of terms and their semantic contexts.
Visualize your literature review
As an all-in-one literature review software, MAXQDA offers a variety of visual tools that are tailor-made for qualitative research and literature reviews. Create stunning visualizations to analyze your material. Of course, you can export your visualizations in various formats to enrich your literature review analysis report. Work with word clouds to explore the central themes of a text and key terms that are used, create charts to easily compare the occurrences of concepts and important keywords, or make use of the graphical representation possibilities of MAXMaps, which in particular permit the creation of concept maps. Thanks to the interactive connection between your visualizations with your MAXQDA data, you’ll never lose sight of the big picture.
AI Assist: literature review software meets AI
AI Assist – your virtual research assistant – supports your literature review with various tools. AI Assist simplifies your work by automatically analyzing and summarizing elements of your research project and by generating suggestions for subcodes. No matter which AI tool you use – you can customize your results to suit your needs.
Free tutorials and guides on literature review
MAXQDA offers a variety of free learning resources for literature review, making it easy for both beginners and advanced users to learn how to use the software. From free video tutorials and webinars to step-by-step guides and sample projects, these resources provide a wealth of information to help you understand the features and functionality of MAXQDA for literature review. For beginners, the software’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive help center make it easy to get started with your data analysis, while advanced users will appreciate the detailed guides and tutorials that cover more complex features and techniques. Whether you’re just starting out or are an experienced researcher, MAXQDA’s free learning resources will help you get the most out of your literature review.

Free MAXQDA Trial for Windows and Mac
Get your maxqda license, compare the features of maxqda and maxqda analytics pro, faq: literature review software.
Literature review software is a tool designed to help researchers efficiently manage and analyze the existing body of literature relevant to their research topic. MAXQDA, a versatile qualitative data analysis tool, can be instrumental in this process.
Literature review software, like MAXQDA, typically includes features such as data import and organization, coding and categorization, advanced search capabilities, data visualization tools, and collaboration features. These features facilitate the systematic review and analysis of relevant literature.
Literature review software, including MAXQDA, can assist in qualitative data interpretation by enabling researchers to organize, code, and categorize relevant literature. This organized data can then be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and themes, helping researchers draw meaningful insights from the literature they’ve reviewed.
Yes, literature review software like MAXQDA is suitable for researchers of all levels of experience. It offers user-friendly interfaces and extensive support resources, making it accessible to beginners while providing advanced features that cater to the needs of experienced researchers.
Getting started with literature review software, such as MAXQDA, typically involves downloading and installing the software, importing your relevant literature, and exploring the available features. Many software providers offer tutorials and documentation to help users get started quickly.
For students, MAXQDA can be an excellent literature review software choice. Its user-friendly interface, comprehensive feature set, and educational discounts make it a valuable tool for students conducting literature reviews as part of their academic research.
MAXQDA is available for both Windows and Mac users, making it a suitable choice for Mac users looking for literature review software. It offers a consistent and feature-rich experience on Mac operating systems.
When it comes to literature review software, MAXQDA is widely regarded as one of the best choices. Its robust feature set, user-friendly interface, and versatility make it a top pick for researchers conducting literature reviews.
Yes, literature reviews can be conducted without software. However, using literature review software like MAXQDA can significantly streamline and enhance the process by providing tools for efficient data management, analysis, and visualization.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Brevo . To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook . To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of literature review , a. habitat loss and species extinction: , b. range shifts and phenological changes: , c. ocean acidification and coral reefs: , d. adaptive strategies and conservation efforts: .
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review .
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.
Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as yo u go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free!
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research | Cite feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface. It also allows you auto-cite references in 10,000+ styles and save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research | Cite” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.

- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references in 10,000+ styles into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.

The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 22+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, academic integrity vs academic dishonesty: types & examples, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , the ai revolution: authors’ role in upholding academic..., the future of academia: how ai tools are..., how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide).
10 free online tools for scientific research

X min read
As the landscape of scientific research evolves, the shift towards online tools has introduced a sea of resources that can profoundly impact the productivity and effectiveness of scientific endeavors.
The key is to identify tools that enhance your research without complicating your process.
While diving into this ocean of resources, there are several important things to look for:
- Ease of Use: Opt for tools with intuitive interfaces.
- Artificial Intelligence: Look for AI integration to automate and enhance research tasks.
- Data Security: Ensure compliance with the latest data security and privacy standards.
- Software Integration: Favor tools that offer seamless integration with existing systems.
- Accuracy: Verify that the tools provide precise and correct information.
- Free Access: Confirm that there’s a genuinely free offer, not just a trial period that requires future payment.
With these criteria in mind, let’s explore ten free online tools that could become indispensable for your scientific research.
1. Semantic Scholar
Powered by AI, Semantic Scholar is a free, nonprofit research tool that stands out for its smart search capabilities.
It sifts through millions of publications to bring you the most relevant and impactful studies, cutting down the time you’d typically spend on literature review.
With a focus on AI, Semantic Scholar offers personalized recommendations, citation summaries, and key phrase extractions that make keeping up with your field’s latest a breeze.
Visit Semantic Scholar
2. Connected Papers
Connected Papers offers a unique visual take on research, building an interactive graph that shows the connections between scientific papers.
It’s like having a bird’s-eye view of the research landscape, allowing you to trace the development of ideas and how they relate to one another. This can uncover pivotal papers that might otherwise slip through the cracks.
Visit Connected Papers
3. Scholarcy
Scholarcy is your AI-powered reading companion, making sense of complex academic papers by breaking them down into digestible summaries.
Imagine having the ability to absorb the core themes and conclusions of a dense, 30-page document in a matter of minutes. Scholarcy makes this a reality, highlighting the methodology, results, and discussions that are central to understanding the paper’s contribution to the field.
This tool is perfect for researchers who are pressed for time but need to stay ahead of the curve. With Scholarcy, you can easily grasp the essence of lengthy publications and build a knowledge base faster than ever.
Visit Scholarcy
4. Consensus
Imagine if you could quickly gauge the consensus of the scientific community on a particular topic. That’s exactly what Consensus aims to do.
Powered by the sophisticated GPT-4 model, Consensus operates as a dynamic search engine that delivers not just search results but a synthesized understanding of where the scientific agreement lies on complex subjects.
With its AI-driven analysis, it reviews multiple studies and delivers a consensus view, helping to inform your research stance.
It’s like a digital synthesis of expert opinions at your fingertips.
Visit Consensus
5. Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit is more than just a tool; it’s your research exploration partner. It helps you discover and organize literature in a personalized research landscape.
The magic of Research Rabbit lies in its ability to learn and adapt to your research behavior, suggesting not just content but also potential pathways your research could take.
It’s much like having a personal librarian who not only knows your research interests but also suggests connections you might not have considered, leading to innovative ideas and directions.
Visit Research Rabbit
6. Audemic.io
Audemic.io stands out in the digital research tools space by transforming the way we consume scientific literature. It leverages the power of audio to make research papers accessible in a format that’s perfect for the multitasking researcher.
Whether you’re commuting or running an experiment, Audemic.io ensures that you can keep up with the latest publications by listening, making the continuous learning process a seamless part of your daily routine.
Visit Audemic.io
Zotero revolutionizes the way researchers manage their references.
Zotero is a haven for anyone looking to organize their sources, offering an intuitive platform for collecting, organizing, and citing research materials. With it, you can easily create bibliographies and in-text citations in a variety of citation styles, which are essential for manuscript preparation.
Zotero holds the distinction of being the oldest tool on this list. Having stood the test of time since its inception in 2006, it proves that a tool does not require all the bells and whistles, or even AI technology, to remain relevant and useful in the fast-paced world of academic research.
Its continued popularity underscores the fact that reliability, ease of use, and a user-focused approach never go out of style.
Visit Zotero
8. Protocols.io
Protocols.io is an indispensable tool for researchers who understand that the devil is often in the details—particularly when it comes to experimental protocols. This platform allows for the creation, sharing, and collaborative refinement of protocols.
Not only does it provide a dynamic space for protocol management, but it also seamlessly integrates with SciNote —a comprehensive electronic lab notebook—allowing for an efficient transition from planning to execution.
Visit Protocols.io
9. Scite.ai
Scite.ai takes a novel approach to assessing the reliability of scientific papers.
Using a sophisticated AI, it analyzes citation contexts to provide “Smart Citations,” allowing researchers to see how a paper has been cited, and if its findings have been supported or contradicted.
This insight is crucial in gauging the impact and reliability of research findings , offering a new dimension to the citation analysis that goes beyond mere numbers.
Visit Scite.ai
10. SciNote ELN
Managing research data effectively is critical, and SciNote ELN is the online tool designed for this task.
It’s an electronic lab notebook that helps you keep your research data organized and secure. With features that support project management, team collaboration, and inventory tracking, SciNote is not just a digital notebook—it’s a central hub for managing all aspects of your research projects.
It’s designed to bring order to the complexity of research data, ensuring that every finding and experiment is documented comprehensively.
Visit SciNote ELN
Final Thoughts
In the current research landscape, these tools are more than conveniences; they’re necessities for staying current, connected, and creative in your work.
Whether you’re looking to manage data, streamline processes, or consume literature in innovative ways, the digital solutions available can significantly enhance the efficiency and impact of your research.
Each of these tools offers a unique angle on the research process, tailored to save time, foster collaboration, and enhance discovery.
By incorporating these into your workflow, you embrace a future where technology and science go hand in hand, creating a symbiosis that propels both forward.
Whether through AI-powered summaries or visual mapping of the literature, these tools embody the innovative spirit of the scientific community. By leveraging these resources, researchers can stand on the shoulders of the digital giants to reach new heights in their academic and professional pursuits.
Related articles

8 Habits of Happy Researchers
- March 2, 2021 |
- Fun in the lab
Do you ever feel like your work should be better organized? Are you frustrated when you spend time searching for “lost” samples or results? How many of these happy – researchers’- habits have you already developed?

Are You a Scientist or a Researcher?
- January 11, 2021 |
Is there a difference between scientists and researchers? Is one an occupation and the other a mission or lifestyle? Does it really matter in the end?

Lab Digitalization Quiz – How does your organization rank?
- July 16, 2020 |
Take the quiz and see how your lab ranks in comparison to others and which are the key activities your peers are taking to pave their way forward. Get insight and take the lead!
SciNote Reviews
Connect with us, get scinote eln.
Top-rated cloud-based electronic lab notebook (ELN) software.
- Premium plans
- Free electronic lab notebook for individual users
- Lab notebook app for mobile
Contact SciNote
- [email protected]
- US HQ +1 234-200-2648
- EU HQ +386 1-235-09-60
SciNote, LLC
- 3000 Parmenter St. Middleton, WI USA POB 620828
Support & Resources
- Knowledge Base
- Downloadable Resources
- Release Notes
- SciNote Blog
- Join our referral program NEW
Contact Support
SciNote Newsletter
Receive SciNote ELN news, webinars and articles.
Revolutionize Your Research with Jenni AI
Literature Review Generator
Welcome to Jenni AI, the ultimate tool for researchers and students. Our AI Literature Review Generator is designed to assist you in creating comprehensive, high-quality literature reviews, enhancing your academic and research endeavors. Say goodbye to writer's block and hello to seamless, efficient literature review creation.

Loved by over 3 million academics

Endorsed by Academics from Leading Institutions
Join the Community of Scholars Who Trust Jenni AI

Elevate Your Research Toolkit
Discover the Game-Changing Features of Jenni AI for Literature Reviews
Advanced AI Algorithms
Jenni AI utilizes cutting-edge AI technology to analyze and suggest relevant literature, helping you stay on top of current research trends.
Get started

Idea Generation
Overcome writer's block with AI-generated prompts and ideas that align with your research topic, helping to expand and deepen your review.
Citation Assistance
Get help with proper citation formats to maintain academic integrity and attribute sources correctly.

Our Pledge to Academic Integrity
At Jenni AI, we are deeply committed to the principles of academic integrity. We understand the importance of honesty, transparency, and ethical conduct in the academic community. Our tool is designed not just to assist in your research, but to do so in a way that respects and upholds these fundamental values.
How it Works
Start by creating your account on Jenni AI. The sign-up process is quick and user-friendly.
Define Your Research Scope
Enter the topic of your literature review to guide Jenni AI’s focus.
Citation Guidance
Receive assistance in citing sources correctly, maintaining the academic standard.
Easy Export
Export your literature review to LaTeX, HTML, or .docx formats
Interact with AI-Powered Suggestions
Use Jenni AI’s suggestions to structure your literature review, organizing it into coherent sections.
What Our Users Say
Discover how Jenni AI has made a difference in the lives of academics just like you

I thought AI writing was useless. Then I found Jenni AI, the AI-powered assistant for academic writing. It turned out to be much more advanced than I ever could have imagined. Jenni AI = ChatGPT x 10.

Charlie Cuddy
@sonofgorkhali
Love this use of AI to assist with, not replace, writing! Keep crushing it @Davidjpark96 💪

Waqar Younas, PhD
@waqaryofficial
4/9 Jenni AI's Outline Builder is a game-changer for organizing your thoughts and structuring your content. Create detailed outlines effortlessly, ensuring your writing is clear and coherent. #OutlineBuilder #WritingTools #JenniAI

I started with Jenni-who & Jenni-what. But now I can't write without Jenni. I love Jenni AI and am amazed to see how far Jenni has come. Kudos to http://Jenni.AI team.

Jenni is perfect for writing research docs, SOPs, study projects presentations 👌🏽

Stéphane Prud'homme
http://jenni.ai is awesome and super useful! thanks to @Davidjpark96 and @whoisjenniai fyi @Phd_jeu @DoctoralStories @WriteThatPhD
Frequently asked questions
What exactly does jenni ai do, is jenni ai suitable for all academic disciplines, is there a trial period or a free version available.
How does Jenni AI help with writer's block?
Can Jenni AI write my literature review for me?
How often is the literature database updated in Jenni AI?
How user-friendly is Jenni AI for those not familiar with AI tools?
Jenni AI: Standing Out From the Competition
In a sea of online proofreaders, Jenni AI stands out. Here’s how we compare to other tools on the market:
Feature Featire
COMPETITORS
Advanced AI-Powered Assistance
Uses state-of-the-art AI technology to provide relevant literature suggestions and structural guidance.
May rely on simpler algorithms, resulting in less dynamic or comprehensive support.
User-Friendly Interface
Designed for ease of use, making it accessible for users with varying levels of tech proficiency.
Interfaces can be complex or less intuitive, posing a challenge for some users.
Transparent and Flexible Pricing
Offers a free trial and clear, flexible pricing plans suitable for different needs.
Pricing structures can be opaque or inflexible, with fewer user options.
Unparalleled Customization
Offers highly personalized suggestions and adapts to your specific research needs over time.
Often provide generic suggestions that may not align closely with individual research topics.
Comprehensive Literature Access
Provides access to a vast and up-to-date range of academic literature, ensuring comprehensive research coverage.
Some may have limited access to current or diverse research materials, restricting the scope of literature reviews.
Ready to Transform Your Research Process?
Don't wait to elevate your research. Sign up for Jenni AI today and discover a smarter, more efficient way to handle your academic literature reviews.
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
AI-Based Literature Review Tools
- Dialogues: Insightful Facts
- How to Craft Prompts
- Plugins / Extensions for AI-powered Searches
- Cite ChatGPT in APA / MLA
- AI and Plagiarism
- ChatGPT & Higher Education
- Author Profile
Selected AI-Based Literature Review Tools
Disclaimer:
- The guide is intended for informational purposes. It is advisable for you to independently evaluate these tools and their methods of use.
- The free version of Research GPT is available in Dimensions Analytics (TAMU). It only covers the open-access publications in Dimensions. To explore it select the OA filter first. AI research assistant is also available in Statista (TAMU).
- See news about their AI Assistant (Beta): Web of Science , Scopus , Ebsco , ProQues t, OVID , Dimensions , JStor , Westlaw , and LexisNexis .
Suggestions:
- Please keep these differences in mind when exploring AI-powered academic search engines.

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- https://www.openread.academy/
- Accessed institutionally by Harvard, MIT, University of Oxford, Johns Hopkins, Stanford, and more. ..
- AI-powered Academic Searching + Web Searching - Over 300 million papers and real-time web content.
- Trending and Topics - Browse them to find the latest hot papers. Use Topic to select specific fields and then see their trending.
- Each keyword search or AI query generates a synthesis report with citations. To adjust the search results, simply click on the Re-Generate button to refresh the report and the accompanied citations. After that click on Follow-Up Questions to go deeper into a specific area or subject.
- Use Paper Q&A to interact with a text directly. Examples: " What does this paper say about machine translation ?" ; "What is C-1 in Fig.1?"
- When you read a paper, under Basic Information select any of the following tools to get more information: Basic Information > Related Paper Graph> Paper Espresso > Paper Q&A , and > Notes. The Related Paper Graph will present the related studies in a visual map with relevancy indication by percentage.
- Click on Translation to put a text or search results into another language.
- Read or upload a document and let Paper Espresso analyze it for you. It will organize the content into a standard academic report format for easy reference: Background and Context > Research Objectives and Hypotheses > Methodology > Results and Findings > Discussion and Interpretation > Contributions to the field > Structure and Flow > Achievements and Significance , and > Limitations and Future Work.
SEMANTIC SCHOLAR
- SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE SEARCH ENGINE - finding semantically similar research papers.
- " A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature." <https://www.semanticscholar.org/>. But login is required in order to use all functions.
- Over 200 millions of papers from all fields of science, the data of which has also served as a wellspring for the development of other AI-driven tools.
The 4000+ results can be sorted by Fields of Study, Date Range, Author, Journals & Conferences
Save the papers in your Library folder. The Research Feeds will recommend similar papers based on the items saved.
Example - SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality Total Citations: 22,438 [Note: these numbers were gathered when this guide was created] Highly Influential Citations 2,001 Background Citations 6,109 Methods Citations 3,273 Results Citations 385
Semantic Reader "Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual." It "uses artificial intelligence to understand a document’s structure and merge it with the Semantic Scholar’s academic corpus, providing detailed information in context via tooltips and other overlays ." <https://www.semanticscholar.org/product/semantic-reader>.
Skim Papers Faster "Find key points of this paper using automatically highlighted overlays. Available in beta on limited papers for desktop devices only." <https://www.semanticscholar.org/product/semantic-reader>. Press on the pen icon to activate the highlights.
TLDRs (Too Long; Didn't Read) Try this example . Press the pen icon to reveal the highlighted key points . TLDRs "are super-short summaries of the main objective and results of a scientific paper generated using expert background knowledge and the latest GPT-3 style NLP techniques. This new feature is available in beta for nearly 60 million papers in computer science, biology, and medicine..." < https://www.semanticscholar.org/product/tldr>
- AI-POWERED RESEARCH ASSISTANT - finding papers, filtering study types, automating research flow, brainstorming, summarizing and more.
- " Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers’ workflows. Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review. If you ask a question, Elicit will show relevant papers and summaries of key information about those papers in an easy-to-use table." <https://elicit.org/faq#what-is-elicit.>; Find answers from 175 million papers. FAQS
- Example - How do mental health interventions vary by age group? / Fish oil and depression Results: [Login required] (1) Summary of top 4 papers > Paper #1 - #4 with Title, abstract, citations, DOI, and pdf (2) Table view: Abstract / Interventions / Outcomes measured / Number of participants (3) Relevant studies and citations. (4) Click on Search for Paper Information to find - Metadata about Sources ( SJR etc.) >Population ( age etc.) >Intervention ( duration etc.) > Results ( outcome, limitations etc.) and > Methodology (detailed study design etc.) (5) Export as BIB or CSV
- How to Search / Extract Data / List of Concept Search -Enter a research question >Workflow: Searching > Summarizing 8 papers> A summary of 4 top papers > Final answers. Each result will show its citation counts, DOI, and a full-text link to Semantic Scholar website for more information such as background citations, methods citation, related papers and more. - List of Concepts search - e.g. adult learning motivation . The results will present a list the related concepts. - Extract data from a pdf file - Upload a paper and let Elicit extract data for you.
- Export Results - Various ways to export results.
- How to Cite - Includes the elicit.org URL in the citation, for example: Ought; Elicit: The AI Research Assistant; https://elicit.org; accessed xxxx/xx/xx
CONSENSUS.APP
ACADEMIC SEARCH ENGINE- using AI to find insights in research papers.
"We are a search engine that is designed to accept research questions, find relevant answers within research papers, and synthesize the results using the same language model technology." <https://consensus.app/home/blog/maximize-your-consensus-experience-with-these-best-practices/>
- Example - Does the death penalty reduce the crime? / Fish oil and depression / (1) Extracted & aggregated findings from relevant papers. (2) Results may include AIMS, DESIGN, PARTICIPANTS, FINDINGS or other methodological or report components. (3) Summaries and Full Text
- How to Search Direct questions - Does the death penalty reduce the crime? Relationship between two concepts - Fish oil and depression / Does X cause Y? Open-ended concepts - effects of immigration on local economics Tips and search examples from Consensus' Best Practice
- Synthesize (beta) / Consensus Meter When the AI recognizes certain types of research questions, this functionality may be activated. It will examine a selection of some studies and provide a summary along with a Consensus Meter illustrating their collective agreement. Try this search: Is white rice linked to diabetes? The Consensus Meter reveals the following outcomes after analyzing 10 papers: 70% indicate a positive association, 20% suggest a possible connection, and 10% indicate no link.
Prompt “ write me a paragraph about the impact of climate change on GDP with citations “
CITATIONS IN CONTEXT
Integrated with Research Solutions.
Over 1.2 billion Citation Statements and metadata from over 181 million papers suggested reference.
How does it work? - "scite uses access to full-text articles and its deep learning model to tell you, for a given publication: - how many times it was cited by others - how it was cited by others by displaying the text where the citation happened from each citing paper - whether each citation offers supporting or contrasting evidence of the cited claims in the publication of interest, or simply mention it." <https://help.scite.ai/en-us/article/what-is-scite-1widqmr/>
EXAMPLE of seeing all citations and citation statements in one place
More information: Scite: A smart citation index that displays the context of citations and classifies their intent using deep learning
Scholar GPT - By awesomegpts.ai
- " Enhance research with 200M+ resources and built-in critical reading skills. Access Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, Arxiv, and more, effortlessly ."
- Dialogue prompts suggested on the page: - Find the latest research about AI. - I'll provide a research paper link; Please analyze it. - I will upload a PDF paper; Use critical skills to read it. - Type "LS" to list my built-in critical reading list.
- To access it, in your ChatGPT account > Select " Explore GPTs > Scholar GPT
- GPT3.5 by OpenAI. Knowledge cutoff date is September 2021.
- Input/ Output length - ChatGPT-3.5 allows a maximum token limit of 4096 tokens. According to ChatGPT " On average, a token in English is roughly equivalent to 4 bytes or characters. English words are typically around 5 characters long. This means that, very roughly, you could fit around 800 to 1000 English words within 4096 tokens."
- According to ChatGPT, the generated responses are non-deterministic by default. So if you run the searches again and get slightly or very different results, it's likely due to this factor.
- ChatGPT may find non-existent references.
- According to this study < https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2304/2304.06794.pdf > "ChatGPT cites the most-cited articles and journals, relying solely on Google Scholar's citation counts" within the field of environmental science.
- See a case of using ChatGPT40 to extract a PDF file below.
- Example - "INTERVIEW WITH CHATGPT" as a Research Method & Teaching Tool Some researchers began to use this approach to obtain their research data. Try this Google Scholar search link "interview with ChatGPT" or see two articles below: (1) Chatting about ChatGPT: how may AI and GPT impact academia and libraries? BD Lund, T Wang - Library Hi Tech News, 2023 (2) An interview with ChatGPT: discussing artificial intelligence in teaching, research, and practice , G Scaringi, M Loche - 2023
Increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) Increased risk of premature birth Increased risk of low birth weight Increased risk of respiratory problems in newborns Increased risk of respiratory problems in infants exposed to secondhand smoke Increased risk of developing asthma and other respiratory illnesses later in life for infants exposed to secondhand smoke [Note : ChatGPT may generate non-existent references or false knowledge. To find out why Large Language Models hallucinate, check out this Wiki article: Hallucination (artificial intelligence) and this blog post - A Gentle Introduction to Hallucinations in Large Language Models by Adrian Tam ]
Infant death Neonatal mortality (referring specifically to deaths within the first 28 days of life) Perinatal mortality (referring to deaths occurring during the period from 22 completed weeks of gestation to 7 completed days after birth) Early childhood mortality (referring to deaths occurring within the first five years of life) Child mortality (referring to deaths occurring before the age of 18) [Press the Regenerate button to get more.]
- Example - RELATED WORDS What are the related words of infant mortality? Neonatal mortality, Post-neonatal mortality, Stillbirths, Low birth weight, Malnutrition, Infectious diseases, Vaccination, Maternal health, Access to healthcare, Poverty, Social inequality, Sanitation, Hygiene, Water quality, Childbirth complications, Congenital abnormalities, Birth defects, Maternal age, Under-five mortality, Child mortality, Perinatal mortality, Preterm birth, Low birth weight, Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), Maternal mortality, Postnatal care, Malnutrition, Immunization, Access to healthcare, Clean water and sanitation, Congenital anomalies, Infant health disparities, Infant mortality rate (IMR), Infant survival.
(("Infant Death"[Mesh] OR "Sudden Infant Death Syndrome"[Mesh] OR "Infant Mortality"[Mesh] OR "Perinatal Mortality"[Mesh] OR "Neonatal Mortality"[Mesh] OR "Fetal Mortality"[Mesh] OR "Infant Death" OR "Sudden Infant Death Syndrome" OR "Infant Mortality" OR "Perinatal Mortality" OR "Neonatal Mortality" OR "Fetal Mortality") AND ("Risk Factors"[Mesh] OR "Etiology"[Mesh] OR "Prevention and Control"[Mesh] OR "Interventions"[Mesh] OR "Public Health"[Mesh] OR "Health Disparities"[Mesh] OR "Healthcare Disparities"[Mesh] OR "Poverty"[Mesh] OR "Malnutrition"[Mesh] OR "Infection"[Mesh] OR "Congenital Abnormalities"[Mesh] OR "Prematurity"[Mesh] OR "Low Birth Weight"[Mesh] OR "Maternal Education"[Mesh] OR "Maternal Health"[Mesh] OR "Risk Factors" OR "Etiology" OR "Prevention and Control" OR "Interventions" OR "Public Health" OR "Health Disparities" OR "Healthcare Disparities" OR "Poverty" OR "Malnutrition" OR "Infection" OR "Congenital Abnormalities" OR "Prematurity" OR "Low Birth Weight" OR "Maternal Education" OR "Maternal Health")) Comments and Suggestions: #1 -This search string may not work on all database platforms. For example, Medline (OVID) may not be able to run it, Medline & CINAHL (EBSCO) can run it without any problems while PubMed will run it but it will indicate which MeSH terms are not indexed. See PubMed's search History and Details under Advanced . #2 - This is just one possible combination. You may need to adjust it based on your task and the databases you are using . #3 - It might be easier if you break the task into 3 parts: ask for synonyms > ask for thesauri terms > and ask it to combine them.
Examples - DATABASE RECOMMENDATIONS Heath Science - Which databases to use to find articles on the EFFECTS OF MATERNAL SMOKING ON INFANT DEATH? PubMed: This is a database of biomedical literature from the National Library of Medicine. It includes articles from medical journals and other sources on a wide range of health-related topics. Embase: This is a database of biomedical literature that covers more international and pharmaceutical content than PubMed. It includes articles from medical journals and other sources on a wide range of health-related topics. Cochrane Library : This is a collection of databases that provides systematic reviews and meta-analyses of healthcare interventions, including interventions related to maternal smoking and infant death. Scopus: This is a multidisciplinary database that covers research from a wide range of fields, including health sciences. It includes articles from scientific journals, books, and conference proceedings. Web of Science: This is a database that covers research from a wide range of fields, including health sciences. It includes articles from scientific journals, books, and conference proceedings. CINAHL: This is a database of nursing and allied health literature, including articles on maternal smoking and infant death. [Note: The response above was copied and pasted directly from ChatGPT. No editing was added.] Education -- I am doing a meta-analysis on k-12 STEM education. What databases should I use? ERIC : This is a database of education research and information, including articles from journals, reports, and conference papers. It is a commonly used database for educational research. Education Source : This is a comprehensive database of education research and information, including articles from journals, books, and conference papers. Web of Science: This is a multidisciplinary database that covers research from a wide range of fields, including education. It includes articles from scientific journals, books, and conference proceedings. Scopus: This is another multidisciplinary database that covers research from a wide range of fields, including education. It includes articles from scientific journals, books, and conference proceedings. PsycINFO: This is a database of psychology research, including articles from journals, books, and dissertations. It can be useful for research on STEM education that includes psychological factors. Cochrane Library : This is a collection of databases that provides systematic reviews and meta-analyses of healthcare interventions including interventions related to education. [Author's note: You could also ask for the GREY LITERATURE sources related to the topic above,]
Example: ACT-AS-AN-EXPERT PROMPT Here's an alternative way to consolidate all the questions into a single consultation by using this popular Act-As-An-Expert prompt, aka, system message prompt: I am going to conduct a systematic review on games and mathematics related to K-12 education I want you to act as a systematic review expert . I will ask you some questions related to my research topic and you advise me on how to do it.
[You may ask one question at a time] My first question is "which databases should I use?" My second question is "what are the relevant subject terms, descriptors and key words?" My third question is "how to do data extraction?" ..... , .... Please note that the above prompts are merely for illustrative purposes. Actual questions may contain more specific instructions. As an example, for the first question, could you provide guidance on how to identify relevant publications? Specifically, can you provide a list of the primary databases and grey literature sources related to my topic?
Example - GREY LITERATURE Please show me all the resources that offer grey literature for conducting research in the field of education ERIC (Education Resources Information Center): https://eric.ed.gov/ OpenGrey: http://www.opengrey.eu/ British Education Index: https://www.ebscohost.com/academic/british-education-index WorldCat: https://www.worldcat.org/ ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global: https://www.proquest.com/products-services/pqdtglobal.html EThOS (Electronic Theses Online Service): https://ethos.bl.uk/ Institutional Repositories of universities and academic institutions (search for specific institution repositories) American Educational Research Association (AERA): https://www.aera.net/ National Education Association (NEA): https://www.nea.org/ Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD): http://www.ascd.org/ RAND Corporation: https://www.rand.org/ National Center for Education Research (NCER): https://ies.ed.gov/ncer/ National Center for Education Statistics (NCES): https://nces.ed.gov/ European Educational Research Association (EERA): https://www.eera-ecer.de/ UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP): http://www.iiep.unesco.org/ Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): https://www.oecd.org/education/ Education Development Center (EDC): https://www.edc.org/ National Institute for Educational Policy Research (NIER) - Japan: https://www.nier.go.jp/ Australian Council for Educational Research (ACER): https://www.acer.org/ Canadian Education Association (CEA): https://www.cea-ace.ca/ My topic is about stem education. Which grey literature databases should I use? STEM Education Research Centre (SERC) Grey Literature Database National STEM Education Research Repository (NSERR) National Science Digital Library (NSDL) STEM Education Resource Center (SERC) GrayLit Network STEM Education Grey Literature Library
See other Comparison Examples under Bing AI.
Examples - ZERO SHOT, ONE SHOT & FEW SHOT PROMPTING for literature review See the examples on the left panel- How to Fine Tune Prompts
Example- using ChatGPT4o to Extract sections from PDF
I am going to upload a PDF file. Please extract its Research Objectives, Hypotheses,Methodology and findings for me, and then save it into a text file. ChatGPT40 : Yes, you can upload the PDF..... The uploaded document appears to be a paper titled "......" I'll begin by searching for and extracting the relevant sections. Extracting Sections: Research Objectives and Hypotheses, Methodology, Results and Findings Let me start with the extraction. The information has been saved into a text file. You can download it using the link below:Download Extracted_Info.txt
Bing Chat / Copilot
- Bing Chat has become Copilot.
- CONVERSATIONAL LLM 4.0 + SEARCH ENGINE. Connects to the Internet.
- Three conversation modes: More Creative, More Balanced or More Precise.
- Comparison - Prompt: My topic is about psychology. Which grey literature databases should I use? More Precise - PsycExtra, NIH Library and links to library guides, .gov and .org websites More Balanced - PsycExtra and three main research guides that mention psychology grey literature sources. More Creative- PsycExtra, LILACS, and Worldcat + definition of grey literature + suggestions on searching for professional association websites, newsletters, magazines, standards and guidelines, and other sources that may contain relevant information for your topic.
- Some examples below were tested in Bing Chat only.
- Example - factors of infant mortality Infant mortality is a term that refers to the death of infants before their first birthday. The leading causes of infant mortality include birth asphyxia, pneumonia, congenital malformations, term birth complications such as abnormal presentation of the fetus umbilical cord prolapse, or prolonged labor, neonatal infection, diarrhea, malaria, measles, and malnutrition1. Many situational factors lead to infant mortality such as the pregnant woman’s level of education, environmental conditions, political infrastructure, and level of medical support1. In the United States, a primary determinant of infant mortality risk is infant birth weight with lower birth weights increasing the risk of infant mortality. The determinants of low birth weight include socioeconomic, psychological, behavioral and environmental factors2.
- Example: PEER REVIEWED SOURCES I need to find some peer reviewed articles about infant mortality? The answer includes 5 articles. The first one is “Causes of death and infant mortality rates among full-term births in the United States between 2010 and 2012: An observational study” by Neha Bairoliya and Günther Fink1. A click on " Tell me more about the first article " leads to this summary: " The first article is titled “Causes of death and infant mortality rates among full-term births in the United States between 2010 and 2012: An observational study” and was published in PLOS Medicine on March 20, 2018. The authors are Neha Bairoliya and Günther Fink. The study used linked birth and death records for the period 2010–2012 to identify the state- and cause-specific burden of infant mortality among full-term infants (born at 37–42 weeks of gestation) in the United States. The researchers found that the full-term infant mortality rate (FTIMR) was 2.2 per 1,000 live births overall and ranged between 1.29 (Connecticut) and 3.77 (Mississippi) at the state level. Sudden unexpected death in infancy (SUDI) accounted for 43% of FTIM; congenital malformations and perinatal conditions accounted for 31% and 11.3% of FTIM, respectively. The largest mortality differentials between states with good and states with poor FTIMR were found for SUDI, with particularly large risk differentials for deaths due to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and suffocation." More searches: Please find five empirical studies focusing on the factors influencing adult learners engaged in online education. Please locate five scholarly articles on stress management among college students site:pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

The ERIC Thesaurus contains nearly 12,000 terms, including more than 4,500 descriptors and 7,000 synonyms1. You can use the term “Academic Achievement” or its synonyms such as “Educational Achievement”, “Student Achievement”, “Academic Performance”, “Academic Success”, “Learning Achievement” and more. [ Note : The follow-up responses include some additional sources. See two below: https://www.powerthesaurus.org/academic_achievement https://eric.ed.gov/?ti=Achievement+Gap including https://eric.ed.gov/?ti=Academic+Achievement |
My topic is about psychology. Which grey literature databases should I use?
ChatGPT PsycEXTRA : This database is produced by the American Psychological Association (APA) and includes grey literature such as conference papers, white papers, and government reports. OpenGrey : This database provides access to grey literature produced in Europe, including reports, theses, and conference papers Grey Literature Report : This database is produced by The New York Academy of Medicine and includes reports, conference papers, and other grey literature on health and biomedical topics, including psychology. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global : This database provides access to graduate-level research, including theses and dissertations related to psychology. Google Scholar: While not exclusively a grey literature database, Google Scholar can be a useful tool for finding conference papers and other grey literature related to psychology. National Technical Information Service (NTIS) : This database provides access to technical reports produced by U.S. government agencies, including those related to psychology. Bing AI - [asked in the Precise mode] For psychology, some recommended grey literature databases include PsycEXTRA and PsyArXiv . PsycEXTRA is a database of grey literature material relating to psychology, behavioral sciences and health. PsyArXiv is a psychology archive designed to facilitate rapid dissemination of psychological research. What other models have been developed based on SERVQUAL?
ChatGPT SERVPERF: This is a modified version of SERVQUAL that measures service performance instead of service quality. It was developed by Cronin and Taylor (1992) and is based on the same five dimensions as SERVQUAL. SERVPERF-GAP: This model, developed by Caruana and Ewing (2006), extends the SERVQUAL model to include three additional gaps that can occur when customers evaluate service quality. E-SERVQUAL: This model, developed by Parasuraman et al. (2005), adapts the SERVQUAL scale to measure the quality of online services. SERVCO: This is a modified version of SERVQUAL that includes a sixth dimension, "cost," in addition to the five original dimensions. It was developed by Sureshchandar et al. (2002) to address the importance of cost in service quality evaluation. SERVQ-HC: This is a modified version of SERVQUAL that is specifically designed for evaluating the quality of health care services. It was developed by Cronin et al. (2000) and includes 20 items across five dimensions. Bing AI The Nordic model of service quality2. The hierarchical model of service quality3. The American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI)4.
Bing AI Sidebar - CHAT, THINK, & WRITE
- Examples of Using AI sidebar to Recap Google Scholar findings
Chat - If you highlight a study in the search results of Google Scholar, you will be prompted with a question by AI sidebar asking if you want to send the selected text to it. If you choose to do so, you can then select either EXPLAIN or EXPAND to learn more about the chosen article. It's worth noting that EXPAND provides more detailed information. You can then click on any of the follow-up links to delve further into the selected article or topic. If the text of the chosen study is written in a foreign language, the AI sidebar can also provide an explanation of the text in English. Another option for extracting the key points from a selected article is to submit the URL of the PDF. Insights - Use the insights button to get more ideas about the topic. Compose - Tell the Edge sidebar your topic and let its Compose tool to generate a draft for you. Google Scholar Button- See also the Plugins and Extension page for how to perform a combined search using Google, Google Scholar, and ChatGPT .
Example: FINDING SIMILAR ARTICLES Find similar articles like this one - [then paste in the abstract ] Note - Use this prompt with Bing chat since real-time web info is required.
Examples: SUMMARIZE + REFERENCE Use a basic prompt like " Please summarize . ..." or add a REFERENCE TEXT that provides the necessary information about what you want it to focus or how the summary or resolution should look like. The reference could be a quote, an excerpt, a partial sentence, a conversation, an abstract, a code snippet and so on. Formula : Specify a role > assign a task > provide a reference text. Example#1 - Scholarly Journal Quote
STEP 1 Prompt: As a research assistant specializing in renewable energy, your task is to locate comparable research studies based on the provided abstract from an article: "This paper discusses the perspective of renewable energy (wind, solar, wave and biomass) in the making of strategies for a sustainable development. Such strategies typically involve three major technological changes: energy savings on the demand side, efficiency improvements in the energy production, and replacement of fossil fuels by various sources of renewable energy."
Bing Chat then found 3 documents: the ScienceDirect paper where the abstract came from and two other documents from un.org and frontiersin.org respectively.
STEP 2 Prompt: Please synthesize the findings of the three studies provided above.
Bing Chat: "Sure! Here is a synthesis of the findings from the three studies:
All three studies emphasize the importance of renewable energy in achieving sustainable development and mitigating climate change. They all discuss various strategies and actions that can be taken to increase the use of renewable energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Henrik Lund’s paper discusses the perspective of renewable energy (wind, solar, wave and biomass) in the making of strategies for a sustainable development. Such strategies typically involve three major technological changes: energy savings on the demand side, efficiency improvements in the energy production, and .....
The United Nations outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to transform our energy systems and speed up the shift to renewable energy: Make renewable energy technology a global public good, Improve global access to components and raw materials......
“Sustainable Energy Transition for Renewable and Low Carbon Grid” discusses that a sustainable global electricity transition will entail increased use of renewable energy sources particularly wind and solar, nuclear energy as a low carbon energy source, electrification of transport and.......
In summary , these studies suggest that transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial for sustainable development and mitigating climate change. This can be achieved through various strategies such as increasing energy efficiency, improving access to renewable technology and materials, leveling the playing field for renewables, ending fossil fuel subsidies, and redirecting investments towards renewables." Example #2 Y ou are an expert researcher, given the following article, please discuss its key findings. Reference: How Large Language Models are Transforming Machine-Paraphrased Plagiarism at https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03568 This is another way to put REFERENCE TEXT. As a side not, role specifying or the use of persona is important as it can impact the level of responses obtained. Just imagine if the designated role were " You are a high school student... ." Example #3 Please read this article and summarize it f or me - "Who Should I Trust: AI or Myself? Leveraging Human and AI Correctness Likelihood to Promote Appropriate Trust in AI-Assisted Decision-Making" and then find 5 similar studies and please also summarize each for me.

CONNECTED PAPERS
- RELATED STUDIES
- Uses visual graphs or other ways to show relevant studies. The database is connected to the Semantic Scholar Paper Corpus which has compiled hundreds of millions of published papers across many science and social science fields.
- See more details about how it works .
- Example - SERVQUAL and then click on SELECT A PAPER TO BUILD THE GRAPH > The first paper was selected. Results: (1) Origin paper - SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality + Connected papers with links to Connected Papers / PDF / DOI or Publisher's site / Semantic Scholar / Google Scholar. (2) Graph showing the origin paper + connected papers with links to the major sources . See above. (3) Links to Prior Works and Derivative Works See the detailed citations by Semantic Scholar on the origin SERVQUAL paper on the top of this page within Semantic Scholars.
- How to Search Search by work title. Enter some keywords about a topic.
- Download / Save Download your saved Items in Bib format.
PAPER DIGEST
- SUMMARY & SYNTHESIS
- " Knowledge graph & natural language processing platform tailored for technology domain . <"https://www.paperdigest.org/> Areas covered: technology, biology/health, all sciences areas, business, humanities/ social sciences, patents and grants ...

- LITERATURE REVIEW - https://www.paperdigest.org/review/ Systematic Review - https://www.paperdigest.org/literature-review/
- SEARCH CONSOLE - https://www.paperdigest.org/search/ Conference Digest - NIPS conference papers ... Tech AI Tools: Literature Review | Literature Search | Question Answering | Text Summarization Expert AI Tools: Org AI | Expert search | Executive Search, Reviewer Search, Patent Lawyer Search...
Daily paper digest / Conference papers digest / Best paper digest / Topic tracking. In Account enter the subject areas interested. Daily Digest will upload studies based on your interests.
RESEARCH RABBIT
- CITATION-BASED MAPPING: SIMILAR / EARLY / LATER WORKS
- " 100s of millions of academic articles and covers more than 90%+ of materials that can be found in major databases used by academic institutions (such as Scopus, Web of Science, and others) ." See its FAQs page. Search algorithms were borrowed from NIH and Semantic Scholar.
The default “Untitled Collection” will collect your search histories, based on which Research Rabbit will send you recommendations for three types of related results: Similar Works / Earlier Works / Later Works, viewable in graph such as Network, Timeline, First Authors etc.
Zotero integration: importing and exporting between these two apps.
- Example - SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality [Login required] Try it to see its Similar Works, Earlier Works and Later Works or other documents.
- Export Results - Findings can be exported in BibTxt, RIS or CSV format.
CITING GENERATIVE AI
- How to cite ChatGPT [APA] - https://apastyle. apa.org/blog /how-to-cite-chatgpt
- How to Cite Generative AI [MLA] https://style. mla.org /citing-generative-ai/
- Citation Guide - Citing ChatGPT and Other Generative AI (University of Queensland, Australia)
- Next: Dialogues: Insightful Facts >>
- Last Updated: Sep 13, 2024 2:15 PM
- URL: https://tamu.libguides.com/c.php?g=1289555

How to Master at Literature Mapping: 5 Most Recommended Tools to Use
This article is also available in: Turkish , Spanish, Russian , and Portuguese
After putting in a lot of thought, time, and effort, you’ve finally selected a research topic . As the first step towards conducting a successful and impactful research is completed, what follows it is the gruesome process of literature review . Despite the brainstorming, the struggle of understanding how much literature is enough for your research paper or thesis is very much real. Unlike the old days of flipping through pages for hours in a library, literature has come easy to us due to its availability on the internet through Open Access journals and other publishing platforms. This ubiquity has made it even more difficult to cover only significant data! Nevertheless, an ultimate solution to this problem of conglomerating relevant data is literature mapping .

Table of Contents
What is Literature Mapping?
Literature mapping is one of the key strategies when searching literature for your research. Since writing a literature review requires following a systematic method to identify, evaluate, and interpret the work of other researchers, academics, and practitioners from the same research field, creating a literature map proves beneficial. Mapping ideas, arguments, and concepts in a literature is an imperative part of literature review. Additionally, it is stated as an established method for externalizing knowledge and thinking processes. A map of literature is a “graphical plan”, “diagrammatic representation”, or a “geographical metaphor” of the research topic.
Researchers are often overwhelmed by the large amount of information they encounter and have difficulty identifying and organizing information in the context of their research. It is recommended that experts in their fields develop knowledge structures that are richer not only in terms of knowledge, but also in terms of the links between this knowledge. This knowledge linking process is termed as literature mapping .
How Literature Mapping Helps Researchers?
Literature mapping helps researchers in following ways:
- It provides concrete evidence of a student’s understanding and interpretation of the research field to share with both peers and professors.
- Switching to another modality helps researchers form patterns to see what might otherwise be hidden in the research area.
- Furthermore, it helps in identifying gaps in pertinent research.
- Finally, t lets researchers identify potential original areas of study and parameters of their work.
How to Make a Literature Map?
Literature mapping is not only an organizational tool, but also a reflexive tool. Furthermore, it distinguishes between declarative knowledge shown by identifying key concepts, ideas and methods, and procedural knowledge shown through classifying these key concepts and establishing links or relationships between them. The literature review conceptualizes research structures as a “knowledge production domain” that defines a productive and ongoing constructive element. Thus, the approaches emphasize the identity of different scientific institutions from different fields, which can be mapped theoretically, methodologically, or fundamentally.
The two literature mapping approaches are:
- Mapping with key ideas or descriptors: This is developed from keywords in research topics.
- Author mapping: This is also termed as citation matching that identifies key experts in the field and may include the use of citations to interlink them.
Generally, literature maps can be subdivided by categorization processes based on theories, definitions, or chronology, and cross-reference between the two types of mapping. Furthermore, researchers use mind maps as a deductive process, general concept-specific mapping (results in a right triangle), or an inductive process mapping to specific concepts (results in an inverted triangle).
What are Different Literature Mapping Methods?
The different types of literature mapping and representations are as follows:
1. Feature Mapping:
Argument structures developed from summary registration pages.
2. Topic Tree Mapping:
Summary maps showing the development of the topic in sub-themes up to any number of levels.
3. Content Mapping:
Linear structure of organization of content through hierarchical classification.
4. Taxonomic Mapping:
Classification through standardized taxonomies.
5. Concept Mapping:
Linking concepts and processes allows procedural knowledge from declarative information. With a basic principle of cause and effect and problem solving, concept maps can show the relationship between theory and practice.
6. Rhetorical Mapping:
The use of rhetoric communication to discuss, influence, or persuade is particularly important in social policy and political science and can be considered a linking strategy. A number of rhetorical tools have been identified that can be used to present a case, including ethos, metaphor, trope, and irony.
7. Citation Mapping:
Citation mapping or matching is a research process established to specifically establish links between authors by citing their articles. Traditional manual citation indexes have been replaced by automated databases that allow visual mapping methods (e.g. ISI Web of Science). In conclusion, citation matching in a subject area can be effective in determining the frequency of authors and specific articles.
5 Most Useful Literature Mapping Tools
Technology has made the literature mapping process easier now. However, with numerous options available online, it does get difficult for researchers to select one tool that is efficient. These tools are built behind explicit metadata and citations when coupled with some new machine learning techniques. Here are the most recommended literature mapping tools to choose from:
1. Connected Papers
a. Connected Papers is a simple, yet powerful, one-stop visualization tool that uses a single starter article.
b. It is easy to use tool that quickly identifies similar papers with just one “Seed paper” (a relevant paper).
c. Furthermore, it helps to detect seminal papers as well as review papers.
d. It creates a similarity graph not a citation graph and connecting lines (based on the similarity metric).
e. Does not necessarily show direct citation relationships.
f. The identified papers can then be exported into most reference managers like Zotero, EndNote, Mendeley, etc.
2. Inciteful
a. Inciteful is a customizable tool that can be used with multiple starter articles in an iterative process.
b. Results from multiple seed papers can be imported in a batch with a BibTex file.
c. Inciteful produces the following lists of papers by default:
- Similar papers (uses Adamic/Adar index)
- “Most Important Papers in the Graph” (based on PageRank)
- Recent Papers by the Top 100 Authors
- The Most Important Recent Papers
d. It allows filtration of results by keywords.
e. Importantly, seed papers can also be directly added by title or DOI.
a. Litmaps follows an iterative process and creates visualizations for found papers.
b. It allows importing of papers using BibTex format which can be exported from most reference managers like Zotero, EndNote, Mendeley. In addition, it allows paper imports from an ORCID profile.
c. Keywords search method is used to find Litmaps indexed papers.
d. Additionally, it allows setting up email updates of “emergent literature”.
e. Its unique feature that allows overlay of different maps helps to look for overlaps of papers.
f. Lastly, its explore function allows finding related papers to add to the map.
4. Citation-based Sites
a. CoCites is a citation-based method for researching scientific literature.
b. Citation Gecko is a tool for visualizing links between articles.
c. VOSviewer is a software tool for creating and visualizing bibliometric networks. These networks are for example journals, may include researchers or individual publications, which can be generated based on citation, bibliographic matching , co-citation, or co-authorship relationships. VOSviewer also offers text mining functionality that can be used to create and visualize networks of important terms extracted from a scientific literature.
5. Citation Context Tools
a. Scite allow users to see how a publication has been cited by providing the context of the citation and a classification describing whether it provides supporting or contrasting evidence for the cited claim.
b. Semantic Scholar is a freely available, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature.
Have you ever mapped your literature? Did you use any of these tools before? Lastly, what are the strategies and methods you use for literature mapping ? Let us know how this article helped you in creating a hassle-free and comprehensive literature map.
It’s very good and detailed.
It’s very good and clearly . It teaches me how to write literature mapping.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
- Thought Leadership
- Trending Now
How Enago Academy Contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Through Empowering Researchers
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a universal call to action to end…

- Reporting Research
AI Assistance in Academia for Searching Credible Scholarly Sources
The journey of academia is a grand quest for knowledge, more specifically an adventure to…
- Language & Grammar
Best Plagiarism Checker Tool for Researchers — Top 4 to choose from!
While common writing issues like language enhancement, punctuation errors, grammatical errors, etc. can be dealt…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats were achieved!
It’s beginning to look a lot like success! Some of the greatest opportunities to research…

- Manuscripts & Grants
Writing a Research Literature Review? — Here are tips to guide you through!
Literature review is both a process and a product. It involves searching within a defined…
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

Which among these features would you prefer the most in a peer review assistant?
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 10:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
- Mission and history
- Platform features
- Library Advisory Group
- What’s in JSTOR
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
JSTOR’s interactive research tool
JSTOR invites you to explore an interactive research tool in beta. Developed in collaboration with our community, this tool employs generative AI and other technologies to empower people to deepen and expand their research with JSTOR’s trusted corpus.
In developing this tool, we are not selling any content to large language model (LLM) providers. The data sent to selected LLM providers when JSTOR users interact with our research tool is stored temporarily and is not used for training LLMs. For more details, please refer to our FAQ .
Sign up for the beta
Do you have questions, comments, or concerns? We want to hear from you! Please email [email protected] to share your feedback.
Table of contents
- About JSTOR’s interactive research tool (beta)
Frequently asked questions
Exploring new technologies at ithaka, legal notices, about the tool (beta).
The tool appears on the content page for journal articles, book chapters, and research reports, and as an addition to JSTOR’s standard keyword search. The tool helps you do the following:
Assess content relevance
The tool supports your ability to skim text by highlighting key points and arguments so you can assess its relevance. It also highlights why the text is related to your search terms.
Deepen your research
Discover related topics, enrich your reading with similar content from the JSTOR corpus, and try new ways of searching.
Be conversational
Use natural, conversational language to ask questions and get quick answers about what you’re reading or researching.
- JSTOR’s interactive research tool (beta)
- Beta program
With the release of this tool, we aim to equip students, faculty, researchers, and librarians with innovative tools that facilitate engagement with complex content and enrich research and learning. This early release harnesses the power of generative AI to help users:
- Discover new topics and content within the JSTOR corpus, enabling exploration of additional possible paths of inquiry.
- Be conversational by asking questions about the text being viewed.
- Search JSTOR in a new way with a semantic search-powered capability that works better for natural language queries than traditional keyword search.
JSTOR stays up to date on the latest technologies and applies them in ways that best serve our users. JSTOR has previously applied machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to optimize the research experience. For example, we have created a citation graph to link all articles on JSTOR, and used ML to improve the relevance of search results and recommendations. As we extend our knowledge and application of new technologies to generative AI, we expect to iterate and evolve as we learn. By volunteering for our limited beta test, you will help us define the long-term scope of this exciting new tool.
At present, the tool can be used with journal articles, book chapters, and research reports found on JSTOR. Images and text-based primary sources on JSTOR are not yet included.
To start, we are using only the contents of the document being viewed to generate responses. Over time, as we learn from and improve upon the accuracy of responses, we might extend this to use the content of other relevant documents in the JSTOR corpus.
The beta release of our interactive research tool uses GPT-4o-mini from OpenAI , Claude 3 Haiku from Anthropic via Amazon Bedrock, and the open source all-MiniLM-L6-v2 sentence transformer model . We are actively exploring alternatives and expect to evolve the models we use as our environment develops.
We are monitoring and continuously improving accuracy using the following methods:
- Subject matter experts from a range of academic disciplines conduct in-depth, ongoing evaluations of the tool’s output. These evaluations help us ensure that generated content is useful and accurate.
- Users provide in-tool feedback that we use to identify areas for improvement. All interactions with the beta tool offer users the opportunity to provide a thumbs up or thumbs down rating. For thumbs down ratings, the user can provide further detail to explain their response.
- We assess model performance for our specific use cases using industry-standard metrics for Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Additionally, we continuously integrate new evaluation metrics specifically developed for Large Language Model (LLM) use cases.
JSTOR handles all personal information, including information provided to this tool, in accordance with our privacy policy . JSTOR does not sell user data, nor does it share content or user data from its platform for the purposes of training third-party large language models (LLMs). For more information about JSTOR’s privacy practices and the practices of the LLMs used by the tool, see “Data collection and use” in the Legal notices section of this page.
As a nonprofit service, JSTOR’s financial model is designed to recover our costs and support sustainable growth to meet the emerging needs of the education community. As we learn more about what it costs to deploy and maintain the use of generative AI and other new technologies on our platform, we will evaluate how to bring these powerful capabilities forward as equitably and sustainably as possible.
JSTOR maintains physical, technical, and administrative safeguards to protect the content we hold. We are a SOC2 compliant organization whose data security practices and measures are audited annually by independent third parties.
Content is only processed internally and with the OpenAI API and Anthropic Claude API via Amazon Bedrock. Please note that OpenAI API and Amazon Bedrock only temporarily store data for the processing purposes and do not use the submitted data to train their models or enhance their services. For more information on OpenAI’s data security practices, please consult the OpenAI Trust Portal and Amazon Bedrock policy .
Technology has always been an incredible accelerator for ITHAKA’s mission to improve access to knowledge and education. As a trusted provider of scholarly materials, we have a responsibility to leverage content, technology, and deep subject matter expertise to chart a path forward that makes the use of AI safe, effective, and affordable for our constituents.
- We honor our values first and foremost. JSTOR provides users with a credible, scholarly research and learning experience. Generative AI must enhance that credibility, not undermine it.
- We will listen closely and proceed cautiously. We recognize the concerns associated with generative AI and are pursuing this work mindful of the very real considerations at hand. Our first step is to deepen our collective understanding through research and implementation in close collaboration with our community. We will use these tools safely and well.
- We empower people, we do not replace them. These tools should not be used to “do the work.” They should be designed to help people, especially students, deepen and expand their work.
- We will enable our systems to interact with users in ways that are comfortable. Traditionally, it has been the users’ responsibility to adapt to restricted language and structures to provide computers with inputs; computers can now interact effectively with users in natural language, and we should take advantage of that.
- We will lead with care. We will deeply consider the aspirations and trepidations of the many communities we serve.
As we learn about and pursue this latest technology, we look forward to your engagement and insights to ensure we continue to deliver high-quality, trusted, impactful services that improve access to knowledge and education for people everywhere. Learn more about how ITHAKA is exploring emerging technologies below .
JSTOR’s interactive research tool is referred to as a “beta” feature because it is still in rapid development and in need of user feedback to help us develop it into the best tool it can be. By “limited” we mean that access to this feature will be offered to a limited number of testers to ensure that our product and technology teams can best understand how users interact with these new features.
During the beta phase, we will work with engaged users to explore capabilities, foster innovation, refine functionality, and reveal limitations. As the tool evolves based on this work, its features may change. In this early stage of development, the ability of the tool will be limited, and its functionality less stable than other tools on JSTOR. In addition to product research and refinement, the following will occur:
- Quality assessment: Generating high-quality output with generative AI models can be challenging, as they may produce incorrect or undesirable results in certain scenarios. By limiting the user base initially, we can better manage output quality and ensure generated content aligns with our standards before exposing it to a broader audience.
- Feedback: The limited rollout enables us to gather valuable feedback from our community. This feedback helps identify and address any concerns, issues, or sensitivities before scaling up.
- Safety and legal considerations: Limiting the user base at the start allows us to explore areas of concern, make policy decisions based on experience, evaluate potential risks, and implement necessary precautions.
- Scalability and infrastructure: By initially limiting the number of users, we can ensure our infrastructure handles the demand while maintaining a stable user experience. Gradual expansion allows us to monitor and optimize systems before opening them up to a larger user base.
There are two ways to sign up:
- Users who are signed into a personal account and have institutional authentication on JSTOR will be shown a pop-up that asks if they would like to sign up to try the tool.
- Submit your interest via our signup form , using the email associated with your personal JSTOR account . Please note that access to the beta is currently only available to users who have access to JSTOR through an institution.
Note that access to our testing environment will be limited so we can create a controlled learning experience where our product and technology teams can best study user interaction with these new features.
We are not able to provide a timeframe for access to the tool. We will notify you if and when access to the pre-release features become available for you to explore.
While we aspire to offer more open and immediate access in the future, it’s important that we limit user access in these early stages of development. This will allow us to:
- Manage performance and ensure a good experience
- Gain initial feedback from users
- Improve the experience in reaction to feedback
We are not able to guarantee access to the tool. Access to our testing environment will be limited so we can create a controlled learning experience to best understand user interaction with these new features. The long-term integration of generative AI with JSTOR will be determined by what we learn through beta testing.
ITHAKA offers a portfolio of nonprofit services, including JSTOR, Portico, and Constellate, aligned around a shared mission to improve access to knowledge globally as affordably and sustainably as possible. Technology is central to achieving this goal. Through Ithaka S+R ’s research, insights from Constellate ’s text analysis experts, and ongoing enhancements to JSTOR’s research and learning tools, we are actively exploring the use of generative AI and other emerging technologies to advance education and scholarship.
Approaching generative AI together
JSTOR and ITHAKA’s founding president, Kevin Guthrie, shares his thoughts about our mission-driven approach to deploying new technologies to improve the learning and research experience for JSTOR users.
Generative AI and higher education
Ithaka S+R is working to uncover the implications of generative AI for higher education and discover its potential to support instructors, students, and researchers.
Sharing insights and learnings
We’re continuously sharing insights from real-world applications, usage, and user feedback. Stay updated on our latest findings on our blog.
Please keep the following in mind as you explore generative AI on JSTOR.
Data collection and use
By using JSTOR’s generative AI tool you consent to JSTOR collecting any data that you choose to share with the tool. JSTOR retains your conversation history in our logs and uses it in de-identified form, in accordance with our privacy policy , to maintain and improve the tool. We won’t ask you for any personal information, and request that you not share any in your conversations.
Any data that is sent to OpenAI (which includes your prompt as well as some or all of the text of the content being viewed) is used only for generating the response. They do not use this to further train their models, nor do they retain the data for more than 30 days, in accordance with OpenAI’s own API data usage policies .
Beta limitations
This AI tool is currently in a beta state, therefore its features are subject to change without notice as we develop it. Current user experience may vary and may not be reflective of the tool’s future capabilities. Users should not rely on its outputs without conducting independent research. The tool should not be used to seek professional advice, including but not limited to legal, financial, and medical advice.
Offensive materials and language
This evolving beta feature is built on JSTOR’s digital archive, which includes millions of items, spanning centuries and representing a wide range of ideas and perspectives. Given the historical nature of the materials on JSTOR, content items will reflect the era in which they were produced and/or the perspectives of the content creators, including the language, ideas or other cultural standards of the time. Some content items may consist of or contain outdated language and ideas that are no longer in use and may be considered offensive, and the beta feature may repeat this when it summarizes or describes that content. Such responses reflect the views of the original content creators through the underlying content and not the views of JSTOR or its employees.
Any suggestions, ideas, or other information you would like to share regarding the tool may be used to improve, enhance, or develop its features. By submitting user feedback, you agree that such feedback becomes the sole property of JSTOR, and waive any rights, including intellectual property rights, related to the feedback.
Extract key information from research papers with our AI summarizer.
Get a snapshot of what matters – fast . Break down complex concepts into easy-to-read sections. Skim or dive deep with a clean reading experience.

Summarize, analyze, and organize your research in one place.
Features built for scholars like you, trusted by researchers and students around the world.
Summarize papers, PDFs, book chapters, online articles and more.
Easy import
Drag and drop files, enter the url of a page, paste a block of text, or use our browser extension.
Enhanced summary
Change the summary to suit your reading style. Choose from a bulleted list, one-liner and more.
Read the key points of a paper in seconds with confidence that everything you read comes from the original text.
Clean reading
Clutter free flashcards help you skim or diver deeper into the details and quickly jump between sections.
Highlighted key terms and findings. Let evidence-based statements guide you through the full text with confidence.
Summarize texts in any format
Scholarcy’s ai summarization tool is designed to generate accurate, reliable article summaries..
Our summarizer tool is trained to identify key terms, claims, and findings in academic papers. These insights are turned into digestible Summary Flashcards.
Scroll in the box below to see the magic ⤸

The knowledge extraction and summarization methods we use focus on accuracy. This ensures what you read is factually correct, and can always be traced back to the original source .
What students say
It would normally take me 15mins – 1 hour to skim read the article but with Scholarcy I can do that in 5 minutes.
Scholarcy makes my life easier because it pulls out important information in the summary flashcard.
Scholarcy is clear and easy to navigate. It helps speed up the process of reading and understating papers.
Join over 400,000 people already saving time.
From a to z with scholarcy, generate flashcard summaries. discover more aha moments. get to point quicker..

Understand complex research. Jump between key concepts and sections. Highlight text. Take notes.

Build a library of knowledge. Recall important info with ease. Organize, search, sort, edit.

Bring it all together. Export Flashcards in a range of formats. Transfer Flashcards into other apps.

Apply what you’ve learned. Compile your highlights, notes, references. Write that magnum opus 🤌

Go beyond summaries
Get unlimited summaries, advanced research and analysis features, and your own personalised collection with Scholarcy Library!

With Scholarcy Library you can import unlimited documents and generate summaries for all your course materials or collection of research papers.

Scholarcy Library offers additional features including access to millions of academic research papers, customizable summaries, direct import from Zotero and more.

Scholarcy lets you build and organise your summaries into a handy library that you can access from anywhere. Export from a range of options, including one-click bibliographies and even a literature matrix.
Compare plans
Summarize 3 articles a day with our free summarizer tool, or upgrade to Scholarcy Library to generate and save unlimited article summaries.
Import a range of file formats
Export flashcards (one at a time)
Everything in Free
Unlimited summarization
Generate enhanced summaries
Save your flashcards
Take notes, highlight and edit text
Organize flashcards into collections
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i use scholarcy, what if i’m having issues importing files, can scholarcy generate a plain language summary of the article, can scholarcy process any size document, how do i change the summary to get better results, what if i upload a paywalled article to scholarcy, is it violating copyright laws.
How to Use AI for Literature Review (2024): Complete 7 Step Guide for Researchers
Jc Chaithanya
13 min read
What is a Literature Review and Why Does It Matter?
Different types of literature review, method 1: using multiple ai tools for literature review, method 2: using elephas for literature review, advantages of using ai for literature review, the traditional approach: manual literature review, the new kid on the block: ai literature review, comparing the two approaches, common concerns and misconceptions about ai in literature review, things to keep in mind while using ai for literature review, conclusion , 1. can gpt-4 do a literature review , 2. can you use ai to do a literature review, 3. what is the ai tool to summarize the literature review.
Literature reviews are a crucial yet time-consuming part of academic research.
With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), researchers now have tools that can significantly streamline this process. This guide explores how AI can be effectively utilized to enhance and accelerate literature reviews.
We'll cover the following key aspects:
- The role of AI in literature reviews
- Specific AI tools designed for academic research, such as Elephas
- Best practices for integrating AI into your research workflow
- Potential benefits and limitations of AI-assisted literature reviews
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a student embarking on your first major project, this guide will provide practical insights on leveraging AI to improve your literature review process.
So let's get started.

When researchers start a new project , they don't just jump in blindly. They first look at what others have already figured out. That's where a literature review comes in handy.
It's like piecing together a puzzle. You gather all the bits of information from different studies, articles, and books. Then you start to see the big picture. What do we know so far? Where are the gaps? Are there any hot debates going on?
All these will translate to
It connects their work to the bigger conversation in their field
It stops researchers from reinventing the wheel
It helps them spot new angles to explore
It shows they've done their homework
By digging into existing research, scholars can push knowledge forward. They're not starting from scratch, but building on what's already there. Plus, a good literature review is super helpful for other researchers too.
It gives them a quick way to catch up on a topic without having to read through piles of separate studies. This saves time and helps guide future research efforts.

Literature reviews can take on various forms depending on their purpose and approach. Below are some of the most popular types of literature reviews:
Narrative Review: This review gives a broad summary of existing studies on a topic but doesn't adhere to a rigid structure. It's often used to provide general insights without analyzing the specifics deeply.
Systematic Review: A systematic review follows a well-defined method to gather, assess, and interpret all available research on a particular question, aiming to reduce bias and provide a more accurate picture of the subject.
Meta-Analysis: This method uses statistical techniques to combine findings from several studies. The goal is to derive a stronger conclusion by merging the data and providing more robust results.
Scoping Review: A scoping review maps out the main ideas and gaps in a field of research, helping to identify where more studies are needed and suggesting potential directions for future research .
Critical Review: This type of review critically examines the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, offering new perspectives or challenging previously accepted theories.
Well, each type offers unique insights based on the research objective, shaping the direction of further inquiry of the research.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Use AI for Literature Review
Using AI for literature review can significantly streamline your research process. Let's explore two methods: a multi-tool approach and using Elephas, an all-in-one assistant.

1. Identify Your Research Topic and Keywords
The first step is defining your research area. Use Perplexity AI for topic exploration and generating research questions. This AI tool helps you uncover new angles for research topics by analyzing vast amounts of data quickly.
2. Search for Relevant Articles
Start your literature search by heading to Elicit.org. Export the articles based on categories like abstract, author, title, and publication date. You can also use other AI-powered search tools like Semantic Scholar or Google Scholar to broaden your sources.
3. Generate Summaries and Key Themes with GPT-4o
After gathering your articles, use GPT-4o to analyze the abstracts and generate key themes. Input the abstracts with prompts like, “ Please summarize the key themes from these articles. ” This step saves hours of manual reading and gives you a thematic overview.
4. Draft an Initial Literature Review with Copy.ai
Use Copy.ai to create a first draft of your literature review. Its AI-powered writing features allow you to generate sections of the review quickly and in a structured format. Copy.ai can assist in writing specific sections, such as background or methodology, based on the keywords and themes you provide.
5. Refine with Smart Writing Tools
Use AI tools like Jasper or Writesonic to refine your literature review. These tools help to paraphrase content, improve readability, and adapt the tone to meet academic standards. The rewrites from these tools can help make the content more engaging and coherent.
6. Organise References Using Reference Managers
As you finalise your draft, integrate reference management tools like Mendeley or Zotero. These tools can store and organise all the references cited in your paper, and AI integration allows for easy reference generation.
7. Use Perplexity AI for Final Checks
Before submission, use Perplexity AI again to check for any gaps in the research or identify potential new areas to explore. It can provide suggestions based on the latest publications and research trends.

Elephas offers an all-in-one solution for conducting literature reviews. Here’s how you can use it:
1. Search the Web with Elephas
Elephas’ web search feature allows you to find relevant articles directly within the tool. Simply input your research terms, and it will pull up related papers, articles, and sources for you to analyse.
2. Analyse Key Themes
Using integrated AI models like GPT-4 or Claude, you can analyse the abstracts or summaries of these papers to identify key themes.
3. Generate a Literature Review
With Elephas’ Smart Write feature, you can create a well-structured literature review in just a few prompts. It pulls in the key themes and drafts a coherent review, ensuring that all relevant abstracts are referenced accurately.
4. Organise with Super Brain
Elephas’ Super Brain feature helps you manage the knowledge from the papers, documents, and research you’re using. It organises and categorises the data for easy access during the writing process.
5. Refine and Customise Tone
Elephas allows you to refine the review by using its multiple writing modes (Zinsser, Friendly, Professional, or Viral Mode). You can ensure that the literature review matches your preferred tone and style.
6. Manage References and Citations
With the help of Super Brain, you can manage references and citations within the text, simplifying the process of creating a bibliography.
By using Elephas, you can significantly speed up the literature review process while maintaining high quality. It’s a comprehensive all-in-one AI tool, making it one of the best solutions for conducting literature reviews.

AI is changing the game for researchers tackling literature reviews. Now, we've got smart tools that can do a lot of the heavy lifting for us. Let's explore some advantages of using AI for literature review.
Time Efficiency: AI dramatically speeds up the review process. It can analyze thousands of articles in minutes, a task that would take humans days or weeks to complete.
Comprehensive Coverage: AI can thoroughly scan vast databases, ensuring no relevant study slips through the cracks.
Pattern Recognition: AI literature tools excel at identifying trends and connections across multiple studies, often spotting insights that humans might overlook.
Bias Reduction: AI approaches each piece of literature objectively, helping to minimize human biases that can creep into manual reviews.
Multilingual Capabilities: Language barriers become less of an issue. AI can process and analyze research in multiple languages, broadening the scope of reviews.
Data Visualization: Many AI tools can generate clear, insightful visualizations of complex data, making it easier to grasp key findings at a glance.
Continuous Updating: In rapidly evolving fields, AI can keep literature reviews current by continuously incorporating newly published research.
While AI brings these impressive benefits to the table, it's important to remember that it's not a wise move to use AI extensively and limit your human touch in the review.
The ideal approach is to combine AI with your critical thinking and domain knowledge. As AI technology continues to advance, its role in streamlining and improving literature reviews is only set to grow, opening up exciting new possibilities for more comprehensive and efficient research processes.
Manual Literature Review vs AI Literature Review
In the world of research, literature reviews play a crucial role. They help researchers understand what's already known about a topic and identify gaps in knowledge. Today, we're seeing a shift in how these reviews are conducted, with AI tools coming in and helping researchers to reduce their overall workflow. But what is actually better: manual literature review or AI-assisted literature reviews?

Manual literature reviews have been the standard for a long time. Here's what they typically involve:
They take detailed notes on each source
Researchers spend hours reading through papers and articles
Key themes and patterns are identified through careful analysis
Connections between different studies are made based on the expertise
This method has its strengths. It allows for deep understanding and critical thinking. Researchers can pick up on subtle nuances that might be important. However, it's also very time-consuming and can be limited by the researcher's ability to process large amounts of information.

AI-assisted literature reviews are changing the game. Here's how they work:
AI tools can quickly scan thousands of articles
Key themes and patterns are automatically extracted
They use advanced algorithms to identify relevant studies
Connections between studies are made based on data analysis
The speed and efficiency of AI reviews are impressive. They can process far more information than a human could in the same amount of time. This means researchers can get a broader view of their field quickly. AI tools are also great at spotting trends and connections that humans might miss.
When we look at manual and AI literature reviews side by side, we see some interesting differences:
Time efficiency: AI is much faster, potentially saving weeks of work
Scope: AI can cover a broader range of sources
Depth of analysis: Manual reviews often provide deeper insights
Bias: AI can help reduce human bias, but may have its own algorithmic biases
Flexibility: Manual reviews can adapt more easily to unique research needs
Language: AI can work across multiple languages, expanding the scope of research
It's important to note that AI isn't perfect. It might miss context or nuances that a human would catch. That's why many researchers are now using a hybrid approach.
They use AI to do the initial heavy lifting, then apply their own expertise to refine and interpret the results.
In the end, whether manual or AI-assisted, the goal of a literature review remains the same: to build a solid foundation for new research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.

There are many concerns and misconceptions about using AI in literature reviews. It's natural to have doubts about new technology, especially when it comes to something as crucial as research.
One big worry is that AI might replace human researchers. But that's not really the case. AI is a powerful tool, but it can't match the critical thinking and deep understanding that humans bring to the table, at least for now. It's more of a helper than a replacement.
Accuracy Concerns: There's a misconception that AI might misinterpret or miss important information. Modern AI tools are actually quite accurate, but they do need proper setup and oversight to perform at their best.
Over-reliance on Technology: Some worry researchers might become too dependent on AI, losing their own analytical skills. In reality, AI frees up time for deeper analysis and creative thinking.
Data Privacy Issues: Concerns about data security and privacy are valid. It's crucial to use AI tools that adhere to strict data protection standards.
Limited to Quantitative Analysis: Many think AI can only handle numbers and statistics. Actually, advanced AI can process qualitative data too, including complex text analysis.
High Costs: While some AI tools can be expensive, many affordable options exist. The efficiency gains often outweigh the initial investment.
Complexity of Use: There's a belief that AI tools are too complicated for the average researcher. In fact, many are designed with user-friendly interfaces.
When using AI for literature reviews, there are several key points to keep in mind. Let's check out these important considerations that might get you into trouble if not checked properly when using AI for a literature review.
Quality Control: While using AI, you need to always double-check the results it generates. Take the time to review the selected articles and ensure they're truly relevant to your research.
Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in academic work is still a hot topic. Be mindful of ethical concerns, particularly around plagiarism and AI-generated content. Make sure your work is original and properly cited.
Stay Updated: Keep an eye on the latest developments in AI tools for literature reviews. What's new in the AI market and what’s outdated will help inform you to make the most of these tools.
Define Clear Parameters: Be specific about your research questions, keywords, and inclusion criteria. The more precise your input, the more relevant your results will be.
Understand AI Limitations: AI is great at processing large amounts of data, but it might miss nuances or context that a human would catch.
Maintain a Critical Perspective: Don't accept AI-generated summaries or analyses at face value. Apply your critical thinking skills. Question the results, look for potential biases, and consider alternative interpretations.
Document Your Process: Keep detailed records of how you used AI in your review. Note which tools you used, what parameters you set, and how you verified the results. This transparency is vital for the credibility of your work.
These tips may be generic and known to everyone, but many researchers, while using AI in their literature writing or revising process, still make these mistakes. Using AI is not wrong, but it's about finding the right balance between technological assistance and human expertise.
You know, it's pretty amazing how AI is shaking things up in the world of research. If you're knee-deep in literature reviews, learning to use AI could be a game-changer for you. It's like having a super-smart assistant who never gets tired and can spot connections you might miss.
There are a bunch of ways to go about it - you could mix and match different AI tools, or go for an all-in-one solution. The trick is finding what clicks for you. Just remember, AI is incredibly helpful, but it's not all good. You've still got to bring your expertise to the table.
As AI keeps evolving, it's opening up new possibilities for research. Who knows what breakthroughs we might see? So, getting comfortable with AI for literature reviews now could really set you up for the future.
It's an exciting time to be a researcher, that's for sure!
Yes, GPT-4 can help with a literature review by summarizing research papers, analyzing content, and identifying key themes. It speeds up the process by offering relevant insights from sources, but human expertise is still needed to ensure accuracy and a comprehensive understanding.
Yes, AI can assist in conducting a literature review by automating tasks such as summarizing research papers, analyzing large amounts of data, and highlighting important findings. This aids in streamlining the review process, although human judgment is essential for interpreting and validating the results effectively.
AI tools like Elephas, designed for summarizing literature reviews, help streamline the process by providing features such as offline support, multiple language models, and web search integration. These tools can quickly summarize key insights and trends across academic papers and other research sources.
AI assistant
Sign up now
Get a deep dive into the most important AI story of the week. Deliverd to your inbox for free!

Meet Elephas - Your AI-Powered Knowledge Assistant. Your Personal ChatGPT for all your files. Transform information overload into actionable insights. Organize vast knowledge. Access ideas efortlessly. Save 10 hours a week
You may also want to read

Top 10 Best AI Tools for Literature Review (Free + Paid)
Pinned Post

What’s New from Apple? iPhone 16 with AI, Apple Watch Series 10, and More!
iPhone Productivity

Jenni AI Review HONEST Review (2024): Is it the Best AI Writing Assistant for Research Papers
Previous Post
This week: the arXiv Accessibility Forum
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computers and Society
Title: mapping technical safety research at ai companies: a literature review and incentives analysis.
Abstract: As artificial intelligence (AI) systems become more advanced, concerns about large-scale risks from misuse or accidents have grown. This report analyzes the technical research into safe AI development being conducted by three leading AI companies: Anthropic, Google DeepMind, and OpenAI. We define safe AI development as developing AI systems that are unlikely to pose large-scale misuse or accident risks. This encompasses a range of technical approaches aimed at ensuring AI systems behave as intended and do not cause unintended harm, even as they are made more capable and autonomous. We analyzed all papers published by the three companies from January 2022 to July 2024 that were relevant to safe AI development, and categorized the 61 included papers into eight safety approaches. Additionally, we noted three categories representing nascent approaches explored by academia and civil society, but not currently represented in any papers by the three companies. Our analysis reveals where corporate attention is concentrated and where potential gaps lie. Some AI research may stay unpublished for good reasons, such as to not inform adversaries about security techniques they would need to overcome to misuse AI systems. Therefore, we also considered the incentives that AI companies have to research each approach. In particular, we considered reputational effects, regulatory burdens, and whether the approaches could make AI systems more useful. We identified three categories where there are currently no or few papers and where we do not expect AI companies to become more incentivized to pursue this research in the future. These are multi-agent safety, model organisms of misalignment, and safety by design. Our findings provide an indication that these approaches may be slow to progress without funding or efforts from government, civil society, philanthropists, or academia.
| Subjects: | Computers and Society (cs.CY) |
| Cite as: | [cs.CY] |
| (or [cs.CY] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Open access
- Published: 11 September 2024
Adult co-creators’ emotional and psychological experiences of the co-creation process: a Health CASCADE scoping review protocol
- Lauren McCaffrey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2524-977X 1 ,
- Bryan McCann 1 ,
- Maria Giné-Garriga 2 ,
- Qingfan An 3 ,
- Greet Cardon 4 ,
- Sebastien François Martin Chastin 1 , 4 ,
- Rabab Chrifou 4 ,
- Sonia Lippke 5 ,
- Quentin Loisel 1 ,
- Giuliana Raffaella Longworth 2 ,
- Katrina Messiha 6 ,
- Mira Vogelsang 1 ,
- Emily Whyte 1 &
- Philippa Margaret Dall 1
Systematic Reviews volume 13 , Article number: 231 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
63 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
There is a growing investment in the use of co-creation, reflected by an increase in co-created products, services, and interventions. At the same time, a growing recognition of the significance of co-creators’ experience can be detected but there is a gap in the aggregation of the literature with regard to experience. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review is to uncover the breadth of existing empirical research on co-creation experience, how it has been defined and assessed, and its key emotional and psychological characteristics in the context of co-created products, services, or interventions among adults.
The development of the search strategy was guided by the research question, Arksey, and O’Malley’s scoping review methodology guidelines, and through collaboration with members of the Health CASCADE consortium. The results of the search and the study inclusion process will be reported in full and presented both narratively and by use of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses extension for scoping review (PRISMA-ScR) flow diagram. Comprehensive searches of relevant electronic databases (e.g. Scopus) will be conducted to identify relevant papers. Snowball searches to identify additional papers through included full-text papers will be done using the artificial intelligence tool, namely, Connected Papers. All review steps will involve at least two reviewers. Studies in English, Dutch, Chinese, Spanish, and French, published from the year 1970 onwards, will be considered. Microsoft Excel software will be used to record and chart extracted data.
The resulting scoping review could provide useful insights into adult co-creators’ experience of participating in the co-creation process. An increased understanding of the role of emotional and psychological experiences of participating in co-creation processes may help to inform the co-creation process and lead to potential benefits for the co-creators and co-created outcome.
Systematic review registration
10.5281/zenodo.7665851.
Peer Review reports
Co-creation can be defined as “any act of collective creativity that involves a broad range of relevant and affected actors in creative problem-solving that aims to produce a desired outcome” [ 1 ]. Co-creation is increasingly acknowledged as a promising approach to address complex ‘wicked’ societal problems and develop more contextually relevant interventions to improve outcomes in a variety of settings [ 2 ]. By facilitating communication across sectors, integrating diverse forms of knowledge and expertise, and enabling local ownership, co-creation can be useful in a broad range of fields including, healthcare, community, and education [ 3 ].
The co-creation process is guided by participatory methodologies [ 4 ]. The goal of participatory research is to engage all those who are the subject of the research in all stages of the research [ 5 ]. Participatory research acknowledges the value of their contribution in a practical and collaborative way [ 5 ]. Co-creation builds on these participatory methodologies, to address the power imbalances stemming from social inequities and uses empowerment approaches to address and meet the needs of citizens [ 3 ]. Co-creation is more specific than the broad concept of participation, which also refers to passive involvement [ 6 ]. The ultimate goal of co-creation is to actively involve all relevant and affected stakeholders in all aspects of the co-creation process, such as planning or conducting [ 7 ].
Whilst the co-creation behaviour of participants in a co-creation process is mostly documented in the co-creation literature, the emotional and psychological experience of participating in the co-creation process has been given less attention [ 8 , 9 ]. Co-creation behaviour is argued to comprise multiple behavioural dimensions that fall under two higher-order factors, namely, participation behaviour and citizenship behaviour [ 10 ]. The behavioural dimensions of participation behaviour include information seeking and sharing, responsible behaviour, and personal interaction. The dimensions of citizenship behaviour include feedback, advocacy, helping, and tolerance [ 10 ]. On the other hand, the co-creators’ experiences of participating in the co-creation process, hereby shortened to co-creation experience, capture co-creators’ emotional and psychological states; highlight the interactive component; and involve a continuous process as opposed to a single fixed-time event [ 9 ]. In brief, the co-creation experience, as defined for the purposes of this review, is the co-creators’ emotional and psychological states during active participation and interaction when engaging in the co-creation process [ 9 ]. Co-creation experience differs from co-creation behaviour due to its focus on the feelings and cognitions derived from the act of undertaking the co-creation behaviour [ 9 ].
Research indicates that active involvement in the co-creation process can have profound positive effects on increased health and performance outcomes, satisfaction, and well-being [ 11 , 12 ]. For example, Leask et al. [ 13 ] reported older adults having positive experiences engaging with the co-creation of a health intervention, describing that participants’ role as co-researchers made it enjoyable, interesting, and rewarding. Similar findings from Rooijen et al. [ 14 ] indicated that participants felt empowered, liked the interactive characteristic of meetings, and felt they were valued contributors with a shared responsibility for the project. Positive emotional states like happiness or gratitude can foster trust, which is important for building relationships, whereas negative emotional states, like anger, uncertainty, and frustration, can decrease trust [ 15 ]. Building relationships is an important aspect of the co-creation process, in which experiencing positive emotions helps to create new relationships [ 16 ]. Therefore, positive emotions could also contribute to the functioning of the co-creation group(s) and the successful development of products like intervention components, tools, and further actions.
There are instances when co-creators can experience the co-creation process negatively. There exists some research to indicate how failed co-created services recovered can impact co-creators in terms of future intention to co-create, role clarity, and motivation [ 17 ]. However, there might be a lack of, or a lack of visibility of, literature documenting the negative emotional and psychological experiences associated with the co-creation process because of publication bias. Individual and interpersonal experience including group dynamics are central to the creation of value and innovation and this justifies the need to study the role of human experience in the context of co-creation [ 18 , 19 ]. Figure 1 provides a visual depiction of the proposed connection between co-creation experience and the other elements of co-creation.

Suggested model of the relationship between co-creation experience, processes, behaviour, outcomes, impact, and future co-creation
However, so far, there is a gap regarding the aggregation of the literature pertaining to co-creation experience. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review is to uncover the breadth of existing empirical research on co-creation experience, how it has been defined, and assessed and its key characteristics in the context of co-created products, services, or interventions among adults. As the focus is on the participant’s experience of the process and not the outcome, no limits have been applied to the co-creation context. Scoping reviews are exploratory in nature and systematically map available literature on a broad topic to identify key concepts, theories, sources of evidence, and research gaps [ 20 ]. A scoping review has been identified as an appropriate means to address this broad research question given that, to the authors’ knowledge, there has been no systematic review of co-creation experience literature, the phenomenon is not well understood or utilised, and studies span a wide variety of fields. The aim of the current scoping review is to deliver an evidence-based review of co-creators’ experiences of co-creating. This review will guide future research to advance evidence-based co-creation methods and inform guidance aimed at enhancing positive experiences for those participating in co-creation.
Research question
What is the current state of the science regarding adult co-creators’ emotional and psychological experiences of participating in co-creation?
The objectives of this review are to:
Determine the extent of research on co-creation experience.
Uncover the range of and key characteristics of emotional and psychological experiences documented in the literature to date.
Identify any explicit or implicit underlying psychological theories drawn upon to explain the potential mechanism of the experience of co-creation.
Document any tools or technology used during the co-creation process that impacted the experience during co-creation or to make co-creation more successful .
Methodology
This scoping review protocol is reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Protocols (PRISMA-P) checklist (see Additional file 1).
Search strategy
The search strategy comprises three main stages (see Fig. 2 ). The first stage involved searching the newly created Health CASCADE Co-creation Database. This database was created by members of the Health CASCADE network and was aimed at collecting in one place the entire corpus of literature pertaining to participatory research and co-creation (1). This database was created using CINAHL, PubMed and all databases accessible via ProQuest through Glasgow Caledonian University (GCU) institutional licence (17 databases in total, APA PsycArticles®, APA PsycInfo®, Art, Design & Architecture Collection, British Periodicals, Coronavirus Research Database, Early Modern Books, Ebook Central, Entertainment Industry Magazine Archive, Humanities Index, Periodicals Archive Online, ProQuest One AcademicTrial-Limited time only, PTSDpubs, SciTech Premium Collection, Social Science Premium Collection, Sports Medicine & Education Index, The Vogue Archive, and The Women's Wear Daily Archive). The key search terms used in this search strategy are found in Table 1 . ASReview, an artificial intelligence (AI) aided platform that helps find relevant records was used for screening the records to be included in this database. The AI performs a textual analysis of the provided records, based on active learning and prioritization. Given the large volume of records retrieved from PubMed, CINAHL, and all databases available through ProQuest with GCU access, AI was necessary to speed up the screening process. There are over 13,000 records contained in this database, with all titles and abstracts containing at least one of the search terms.

Stages of search strategy
The Health CASCADE Co-creation Database was searched using free-text terms relating to co-creation experience (see Table 2 ). Search terms have been developed in reference to the research question and through consultation with members of the Health CASCADE consortium. The search will be piloted to check the appropriateness of keywords and to ensure known studies are identified.
The second stage of the search strategy is to use both sets of search terms (see Tables 1 and 2 ) in Scopus using the Boolean operator AND to combine the two sets. This is to provide additional robustness to the search. Due to the large volume of records retrieved (> 35,000) when combining the two sets of search terms, it is necessary to omit some search terms used to create the Health CASCADE Co-creation Database. Four search terms will be retained “co-creat*”, “co-production”, “co-design” and “experience-based design”. These search terms are specifically chosen because co-production and co-design are commonly used interchangeably with the term co-creation [ 21 ]. In addition, “experience-based design” is retained due to the obvious focus on the experience. We will include articles that meet our inclusion criteria for co-creation, regardless of the terminology used to describe the methodology. For pragmatic reasons, sources of unpublished empirical studies (including grey literature, theses, and dissertations) will not be searched for. The draft search strategy for Scopus is available in Additional file 2.
The final stage of the search is to employ snowballing to capture any additional articles that may be potentially missed. An artificial intelligence tool called Connected Papers [ 22 ] will be used to identify papers that (1) the included paper has cited (backward reference searching), and (2) papers that have since cited the included paper (forward reference searching).
The article selection process is considered an iterative process, whereby the search strategy will be initially broad and then refined based on abstracts retrieved and as reviewer familiarity with the literature increases. The concept of co-creation is defined differently depending on the setting and context and is often used interchangeably with similar, yet distinct concepts, but equally lacking a clear universal understanding [ 21 ]. Therefore, to account for the overlaps in terminology a broad scope will be initially implemented.
As recommended by Arksey and O’Malley [ 23 ], decisions on how to set search parameters will be made after a general scope of the field has been gained. Hence, this stage will require the reviewer(s) to engage in a reflexive way and repeat steps to ensure a comprehensive literature search with more sensitive searches [ 23 , 24 ].
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
All study participants in the included papers must be adults, described as people aged 18 years and over with no upper limit. Children/adolescents are not included in this study as research indicates that there are differences between their emotional experiences in terms of emotional intensity and stability [ 25 ].
Empirical articles (i.e. primary research studies) include any qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method research designs that include a description of the co-created product, service, or intervention and an evaluation of the co-creators’ co-creation experience. Although scoping reviews can draw on evidence from non-empirical sources, this review imposes limits to include empirical sources only as empirical sources would be most useful and appropriate for contributing to an evidence-based understanding of co-creation methods.
Any context that involves the co-creation of a product, service, or intervention will be considered.
The Health CASCADE Co-creation Database is limited to searching records between 1st January 1970 and 1st December 2021. The search in Scopus will include records from 1st January 1970 until the date of the search.
The Health CASCADE Co-creation Database is limited to only include materials that are written in English. However, for the search conducted in Scopus, publications in English, Spanish, Dutch, French, and Chinese languages will also be considered, as the research team has proficient fluency in these languages.
Data extraction
Following the database search, articles will be exported as a CSV file for removal of duplicates in Excel. The articles will be imported and screened in Rayyan. The title and abstract of all studies will be screened independently by several reviewers (LMcC, QA, QL, EW, GRL, RC, and MV) and irrelevant studies will be removed. All titles and abstracts will be double-screened. Full-text articles of studies identified as potentially relevant for inclusion will subsequently be sought and screened by several reviewers (LMcC, QA, QL, EW, GRL, RC, MV, and KM) against the agreed set of criteria. Differences of opinion regarding inclusion or exclusion will be resolved by discussion and reaching a consensus or by a third reviewer. The results of the search and the study inclusion process will be reported in full in the final scoping review and presented both narratively and by use of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses extension for scoping review (PRISMA-ScR) flow diagram.
To determine the extent of research on co-creation experience (objective 1), details about co-creation more generally will first be extracted. This includes:
Study’s definition of co-creation and co-creation experience (if available).
The context or setting.
Data about the participants (number, type, and characteristics of co-creators’ involved).
Description of the co-creation process undertaken (including number of sessions, level of participation).
Purpose of co-creation.
Outcome of the co-created intervention, service, or product.
The key characteristics of psychological and emotional experience including positive and negative components (objective 2) will be extracted.
The psychological theory underpinning the co-creation experience identified by the authors of the studies (objective 3) will be recorded.
Information about the technology or tools that had an impact on the co-creation experience (objective 4) will be extracted.
Additional descriptive information such as discipline and date of publication will also be extracted.
The above-extracted information will be entered into an Excel spreadsheet developed by the authors. This data extraction Excel spreadsheet may be modified and revised as necessary during the process of extracting data from the included evidence sources to ensure that key findings relevant to the review question are addressed.
Quality assessment
There exists debate as to whether a scoping review should contain an assessment of study quality [ 26 ]. A quality assessment component will be included in this review in relation to the sufficiency of reporting the process of co-creating an intervention, service, or product. This tool (see Table 3 ) has been adapted from Leask et al.’s [ 4 ] ‘checklist for reporting intervention co-creation’ and Eyles et al.’s [ 27 ] amended version of a checklist for reporting non-pharmacological interventions. The reason for including this checklist is two-fold. Firstly, the scoping review may contain a variety of study designs and the focus is not solely on the outcomes, but rather on the process [ 27 ]. Secondly, as explained above, the concept of co-creation is used interchangeably with other similar overlapping concepts, such that some processes may be described as co-creation when they are in fact not (according to the definition used in this review) or vice versa. Therefore, by incorporating this checklist, it will become clearer as to the type or extent of co-creation processes that were implemented and whether they were clearly reported within each individual source of empirical evidence. However, given that a scoping review aims to present an overview of the extant literature on a particular topic without synthesis from individual studies, no study will be excluded on the basis of the quality of reporting co-created interventions.
Strategy for data analysis
The PRISMA-ScR will be used to guide the reporting of the scoping review [ 28 ]. Whilst, the synthesis of the results from included sources of evidence is more appropriately done with a systematic review, the analysis of data in scoping reviews is generally descriptive in nature [ 29 ]. A narrative summary of extracted data will be produced along with the tabulated and/or charted results described in relation to the review question and objectives. Descriptive techniques, such as basic coding of data to particular categories, are recommended as a useful approach when the purpose is to identify concepts or key characteristics related to the concept [ 20 ]. Data will be analysed using the well-established method of thematic analysis [ 30 ]. This method is characterised by identifying and reporting recurring themes within the data and is a suitable analytic method because it allows for patterns of experience to be recorded, such as understanding adults’ experiences of participating in co-creation. We intend to extract relevant co-creation experience data from the result sections of articles, including verbatim participant quotations. For quantitative data, such as questionnaires, we will attempt to extract the item statements and code them alongside the qualitative data.
The purpose of this scoping review is to uncover the breadth of existing empirical research on co-creation experience with a focus on emotional aspects and from a psychological perspective. An increased understanding of the role of experiences of participating in co-creation processes may help to inform the development and use of co-creation processes and lead to potential benefits for the co-creators’ and co-created outcome.
This scoping review has some limitations, which reflect the balance between conducting a wide search to discover the breadth of existing literature and the pragmatic constraints of conducting the review. This scoping review searches for published peer-reviewed work from SCOPUS and the Health CASCADE Co-creation Database. Other databases could be searched but for pragmatic reasons, these two databases were selected for their breadth and relevancy. Another limitation is that it was necessary to restrict the search terms for capturing ‘co-creation’ for the search in Scopus to maintain a manageable number of records retrieved to screen by the research team. However, authors may use different terms or descriptions. For instance, variations of terms like co-creation, co-design, and co-production, whether written with a dash or space can affect the number of articles retrieved. Boundaries on the search terms relating to experience were also formed, for example, specific emotions were not included in the search string, due to the large range of possible emotions that can be experienced, which would make the search unwieldy. We also have not used any of the advanced search features of the databases, such as proximity searching, which could potentially improve the specificity.
A strength of this review is the comprehensive snowballing search strategy to capture additional relevant papers. The results will be submitted to a peer-reviewed journal and to scientific conferences. The plan for dissemination includes digital science communication platforms and presentations.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Artificial intelligence
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis–extension for scoping reviews
Agnello DM, Loisel QEA, An Q, et al. Establishing a health CASCADE–curated open-access database to consolidate knowledge about co-creation: novel artificial intelligence–assisted methodology based on systematic reviews. J Med Internet Res. 2023;25(1): e45059. https://doi.org/10.2196/45059 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
von Heimburg D, Cluley V. Advancing complexity-informed health promotion: a scoping review to link health promotion and co-creation. Health Promot Int. 2020;36(2):581–600.
Article Google Scholar
Sherriff S, Miller H, Tong A, Williamson A, Muthayya S, Sally R, et al. Building trust and sharing power for co-creation in Aboriginal health research: a stakeholder interview study. Evid Policy J Res Debate Pract. 2019.
Leask CF, Sandlund M, Skelton DA, Altenburg TM, Cardon G, Chinapaw MJM, et al. Framework, principles and recommendations for utilising participatory methodologies in the co-creation and evaluation of public health interventions. Res Involv Engagem. 2019;5(1):2.
Wright MT, Springett J, Kongats K. What is participatory health research? In: Wright MT, Kongats K, editors. Participatory Health Research. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018.
Voorberg WH, Bekkers VJJM, Tummers LG. A systematic review of co-creation and co-production: Embarking on the social innovation journey. Public Manag Rev. 2015;17(9):1333–57.
Torfing J, Sørensen E, Røiseland A. Transforming the public sector into an arena for co-creation: Barriers, drivers, benefits, and ways forward. Adm Soc. 2016;51(5):795–825.
Leclercq T, Hammedi W, Poncin I. Ten years of value cocreation: an integrative review. Rech Appl En Mark Engl Ed. 2016;31(3):26–60.
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Meng F, So KKF. Cocreation experience in peer-to-peer accommodations: Conceptualization and scale development. J Travel Res. 2021;60(6):1333–51.
Yi Y, Gong T. Customer value co-creation behavior: scale development and validation. J Bus Res. 2012;66(9):1279–84.
Partouche-Sebban J, Rezaee Vessal S, Bernhard F. When co-creation pays off: the effect of co-creation on well-being, work performance and team resilience. J Bus Ind Mark. 2021;37(8).
Sharma S, Conduit J, Rao HS. Hedonic and eudaimonic well-being outcomes from co-creation roles: a study of vulnerable customers. J Serv Mark. 2017;31(4/5):397–411.
Leask CF, Sandlund M, Skelton DA, Chastin SF. Co-creating a tailored public health intervention to reduce older adults’ sedentary behaviour. Health Educ J. 2017;76(5):595–608.
van Rooijen M, Lenzen S, Dalemans R, Beurskens A, Moser A. Stakeholder engagement from problem analysis to implementation strategies for a patient-reported experience measure in disability care: a qualitative study on the process and experiences. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):53–65.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Dunn JR, Schweitzer ME. Feeling and believing: the influence of emotion on trust. J Personal Soc Psychol Manag Proc. 2005;88(5):736–48.
Waugh CE, Fredrickson BL. Nice to know you: positive emotions, self–other overlap, and complex understanding in the formation of a new relationship. J Posit Psychol. 2006;1(2):93–106.
Dong B, Evans KR, Zou S. The effects of customer participation in co-created service recovery. J Acad Mark Sci. 2008;36(1):123–37.
Ramaswamy V. It’s about human experiences… and beyond, to co-creation. Ind Mark Manag. 2011;40(2):195–6.
Ramaswamy V. Co-creation of value — towards an expanded paradigm of value creation. Mark Rev St Gallen. 2009;26(6):11–7.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020Oct;18(10):2119–26.
Halvorsrud K, Kucharska J, Adlington K, Rüdell K, Brown Hajdukova E, Nazroo J, et al. Identifying evidence of effectiveness in the co-creation of research: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the international healthcare literature. J Public Health. 2021;43(1):197–208.
Tarnavsky-Eitan, A, Smolyansky E, Knaan-Harpaz I, Perets S. Connected Papers. 2020. https://www.connectedpapers.com/about . Accessed 26 May 2022.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):69.
Bailen NH, Green LM, Thompson RJ. Understanding emotion in adolescents: a review of emotional frequency, intensity, instability, and clarity. Emot Rev. 2019;11(1):63–73.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85.
Eyles H, Jull A, Dobson R, Firestone R, Whittaker R, Te Morenga L, et al. Co-design of mHealth delivered interventions: a systematic review to assess key methods and processes. Curr Nutr Rep. 2016;5(3):160–7.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Aromataris E, Munn Z. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews. In: JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020.
Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic analysis: a practical guide. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications Ltd; 2021.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The Health CASCADE consortium.
The PhD studies of Lauren McCaffrey are funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement n° 956501.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Health and Life Sciences, Glasgow Caledonian University, Glasgow, UK
Lauren McCaffrey, Bryan McCann, Sebastien François Martin Chastin, Quentin Loisel, Mira Vogelsang, Emily Whyte & Philippa Margaret Dall
Faculty of Psychology, Education and Sport Sciences Blanquerna, Universitat Ramon Llull, Barcelona, Spain
Maria Giné-Garriga & Giuliana Raffaella Longworth
Department of Community Medicine and Rehabilitation, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
Department of Movement and Sports Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium
Greet Cardon, Sebastien François Martin Chastin & Rabab Chrifou
Department of Psychology and Methods, Jacobs University Bremen, Bremen, Germany
Sonia Lippke
Department of Public and Occupational Health, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam Public Health Research Institute, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Katrina Messiha
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LMcC coordinated and conceived the study. LMcC, PMD, BMcC, and MGG have made substantive contributions to developing this protocol and the review question. LMcC, PMD, BMcC, MGG, QA, QL, EW, GRL, MV, RC, and KM jointly developed the search strategy. LMcC drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lauren McCaffrey .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: prisma-p 2015 checklist., additional file 2: search strategy–scopus., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
McCaffrey, L., McCann, B., Giné-Garriga, M. et al. Adult co-creators’ emotional and psychological experiences of the co-creation process: a Health CASCADE scoping review protocol. Syst Rev 13 , 231 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02643-9
Download citation
Received : 10 August 2022
Accepted : 22 August 2024
Published : 11 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02643-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Co-creation experience
- Psychological response
- Scoping review
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Author Biographies
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
The turkish government’s ambivalent policy response to the new influx of afghan migrants through the public policy tools, share and cite.
Bermek, S. The Turkish Government’s Ambivalent Policy Response to the New Influx of Afghan Migrants through the Public Policy Tools. Soc. Sci. 2024 , 13 , 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13090487
Bermek S. The Turkish Government’s Ambivalent Policy Response to the New Influx of Afghan Migrants through the Public Policy Tools. Social Sciences . 2024; 13(9):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13090487
Bermek, Sevinç. 2024. "The Turkish Government’s Ambivalent Policy Response to the New Influx of Afghan Migrants through the Public Policy Tools" Social Sciences 13, no. 9: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13090487
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a full-time researcher, Litmaps has become an indispensable tool in my arsenal. The Seed Maps and Discover features of Litmaps have transformed my literature review process, streamlining the identification of key citations while revealing previously overlooked relevant literature, ensuring no crucial connection goes unnoticed.
6. Consensus. Researchers to work together, annotate, and discuss research papers in real-time, fostering team collaboration and knowledge sharing. 7. RAx. Researchers to perform efficient literature search and analysis, aiding in identifying relevant articles, saving time, and improving the quality of research. 8.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at Ai2. Semantic Scholar uses groundbreaking AI and engineering to understand the semantics of scientific literature to help Scholars discover relevant research.
Over 2 million researchers have used Elicit. Researchers commonly use Elicit to: Speed up literature review. Find papers they couldn't find elsewhere. Automate systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Learn about a new domain. Elicit tends to work best for empirical domains that involve experiments and concrete results.
research assistant. Zotero is a free, easy-to-use tool to help you collect, organize, annotate, cite, and share research. Download. Available for Mac, Windows, Linux, and iOS. Just need to create a quick bibliography? Try ZoteroBib.
Citation Gecko . The literature search tool Citation Gecko is an open source web app that makes it easier to discover relevant scientific literature than your average keyword-based search engine for research papers. It works in the following way: First you upload about 5-6 "seed papers". The program then extracts all references in and to these seed papers and creates a visual citation network.
3. Zotero. A big part of many literature review workflows, Zotero is a free, open-source tool for managing citations that works as a plug-in on your browser. It helps you gather the information you need, cite your sources, lets you attach PDFs, notes, and images to your citations, and create bibliographies.
Finalize your literature review faster with comfort. ATLAS.ti makes it easy to manage, organize, and analyze articles, PDFs, excerpts, and more for your projects. Conduct a deep systematic literature review and get the insights you need with a comprehensive toolset built specifically for your research projects.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
These tools provide researchers with an option to at least partially automate some of their literature review work which can save a lot of time. Things to keep in mind: Very little independent research has been done to test the reliability, scope, and accuracy of these tools. In our own testing of tools that provide summaries of articles, we ...
Literature reviews take time. Here is some general information to know before you start. VIDEO -- This video is a great overview of the entire process. (2020; North Carolina State University Libraries) --The transcript is included. --This is for everyone; ignore the mention of "graduate students". --9.5 minutes, and every second is important.
Our Literature Review Generator is an AI-powered tool that streamlines and simplifies the creation of literature reviews by automatically collecting, analyzing, summarizing, and synthesizing all the relevant academic sources on a specific topic within the parameters you define. It saves you additional time by highlighting themes, trends, and ...
Literature review software is a tool designed to help researchers efficiently manage and analyze the existing body of literature relevant to their research topic. MAXQDA, a versatile qualitative data analysis tool, can be instrumental in this process.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
1. Semantic Scholar. Powered by AI, Semantic Scholar is a free, nonprofit research tool that stands out for its smart search capabilities. It sifts through millions of publications to bring you the most relevant and impactful studies, cutting down the time you'd typically spend on literature review. With a focus on AI, Semantic Scholar offers ...
Welcome to Jenni AI, the ultimate tool for researchers and students. Our AI Literature Review Generator is designed to assist you in creating comprehensive, high-quality literature reviews, enhancing your academic and research endeavors. Say goodbye to writer's block and hello to seamless, efficient literature review creation.
AI-POWERED RESEARCH ASSISTANT - finding papers, filtering study types, automating research flow, brainstorming, summarizing and more. " Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers' workflows. Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review.
Here are the most recommended literature mapping tools to choose from: 1. Connected Papers. a. Connected Papers is a simple, yet powerful, one-stop visualization tool that uses a single starter article. b. It is easy to use tool that quickly identifies similar papers with just one "Seed paper" (a relevant paper). c.
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
Here are the tools that I use to manage my literature sources when I write the literature review for my research. Mendeley. Mendeley is a free reference management tool that can help you to capture the bibliographic information of the articles you read, keep their copies in PDFs, highlight and comment on the most relevant information.
JSTOR invites you to explore an interactive research tool in beta. Developed in collaboration with our community, this tool employs generative AI and other technologies to empower people to deepen and expand their research with JSTOR's trusted corpus. In developing this tool, we are not selling any content to large language model (LLM) providers.
Our Excel export feature generates a literature synthesis matrix for you, so you can. Compare papers side by side for their study sizes, key contributions, limitations, and more. Export literature-review ready data in Excel, Word, RIS or Markdown format. Integrates with your reference manager and 'second brain' tools such as Roam, Notion ...
Scholarcy's AI summarization tool is designed to generate accurate, reliable article summaries. Our summarizer tool is trained to identify key terms, claims, and findings in academic papers. These insights are turned into digestible Summary Flashcards. Scroll in the box below to see the magic ⤸. The knowledge extraction and summarization ...
5. Refine with Smart Writing Tools. Use AI tools like Jasper or Writesonic to refine your literature review. These tools help to paraphrase content, improve readability, and adapt the tone to meet academic standards. The rewrites from these tools can help make the content more engaging and coherent. 6. Organise References Using Reference Managers
As artificial intelligence (AI) systems become more advanced, concerns about large-scale risks from misuse or accidents have grown. This report analyzes the technical research into safe AI development being conducted by three leading AI companies: Anthropic, Google DeepMind, and OpenAI. We define safe AI development as developing AI systems that are unlikely to pose large-scale misuse or ...
Method A literature search was conducted using legitimate databases, indexing services, and directories including PubMed/MEDLINE (Ovid®), EMBASE (Ovid®), google scholar and WorldCat to retrieve ...
However, so far, there is a gap regarding the aggregation of the literature pertaining to co-creation experience. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review is to uncover the breadth of existing empirical research on co-creation experience, how it has been defined, and assessed and its key characteristics in the context of co-created products, services, or interventions among adults.
Nonetheless, this literature has not substantially explored the Turkish government's attitude towards the new influx of migrants. For this purpose, the article draws upon qualitative research based on secondary and grey literature (including semi-structured interviews with representatives from migration-related NGOs in Turkey).