- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course

Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 7 Class 10 Coordinate Geometry
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT Book for 2023-2024 Boards.
Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 7 Class 10 Coordinate Geometry. All questions have been solved in an easy to understand way with detailed explanation of each and every step.
Answers to optional exercise is also given
In Coordinate Geometry of Class 9, we learned what is x and y coordinate of a point.
In this chapter, we will learn
- Coordinates of points in x-axis (x, 0) and y-axis (0, y)
- How to find distance between two points using Distance Formula
- Checking if points form a triangle, or an isoceles triangle, or a square, rectangle. (To do this, we need to learn properties of parallelogram )
- Checking if 3 points are collinear using Distance Formula
- Finding points equidistant to given points
- Then, we will learn about Section Formula - Finding coordinates of a point that divides line joining two points in some ratio
- Finding coordinates of mid-point of a line using Section Formula
- Finding ratio when coordinates of point of intersection is given
- Using properties of parallelogram to do some questions on Section Formula (like finding coordinates of a point, when 4 vertices of parallelogram are given)
- Finding Area of triangle when coordinates of all 3 vertices are given
- Proving 3 points collinear using Area of Triangle Formula
- Finding Area of Quadrialteral using Area of Triangle Formula (dividing Quadrilateral into 2 triangles and finding area)
Click on an exercise link below to study from the NCERT Way.
Or you can click on a topic link below Concept wise to learn the Teachoo way.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- Math Article
- Coordinate Geometry For Class 10

Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Notes
Cbse class 10 maths coordinate geometry notes:- download pdf here, class 10 maths chapter 7 coordinate geometry notes.
The complete notes on coordinate geometry for Class 10 are provided here. Coordinate geometry teaches us the location of a point on a plane. For example, the coordinates of a point are (x, y), where x-coordinate (abscissa) denotes the distance of a point from the y-axis and y-coordinate (ordinate) denotes the distance of the point from the x-axis. Now we will learn to find the distance between two points and the area of a triangle using the distance formula when the coordinates of the points are given. Go through the below article and learn the points on the coordinate plane, distance formulas, section formulas and so on with a detailed explanation.
Students can refer to the short notes and MCQ questions along with a separate solution pdf of this chapter for quick revision from the links below:
- Coordinate Geometry Short Notes
- Coordinate Geometry MCQ Practice Questions
- Coordinate Geometry MCQ Practice Solutions
Basics of Coordinate Geometry
For more information on the basics of coordinate geometry, watch the below video.

To know more about Coordinate Geometry, visit here .
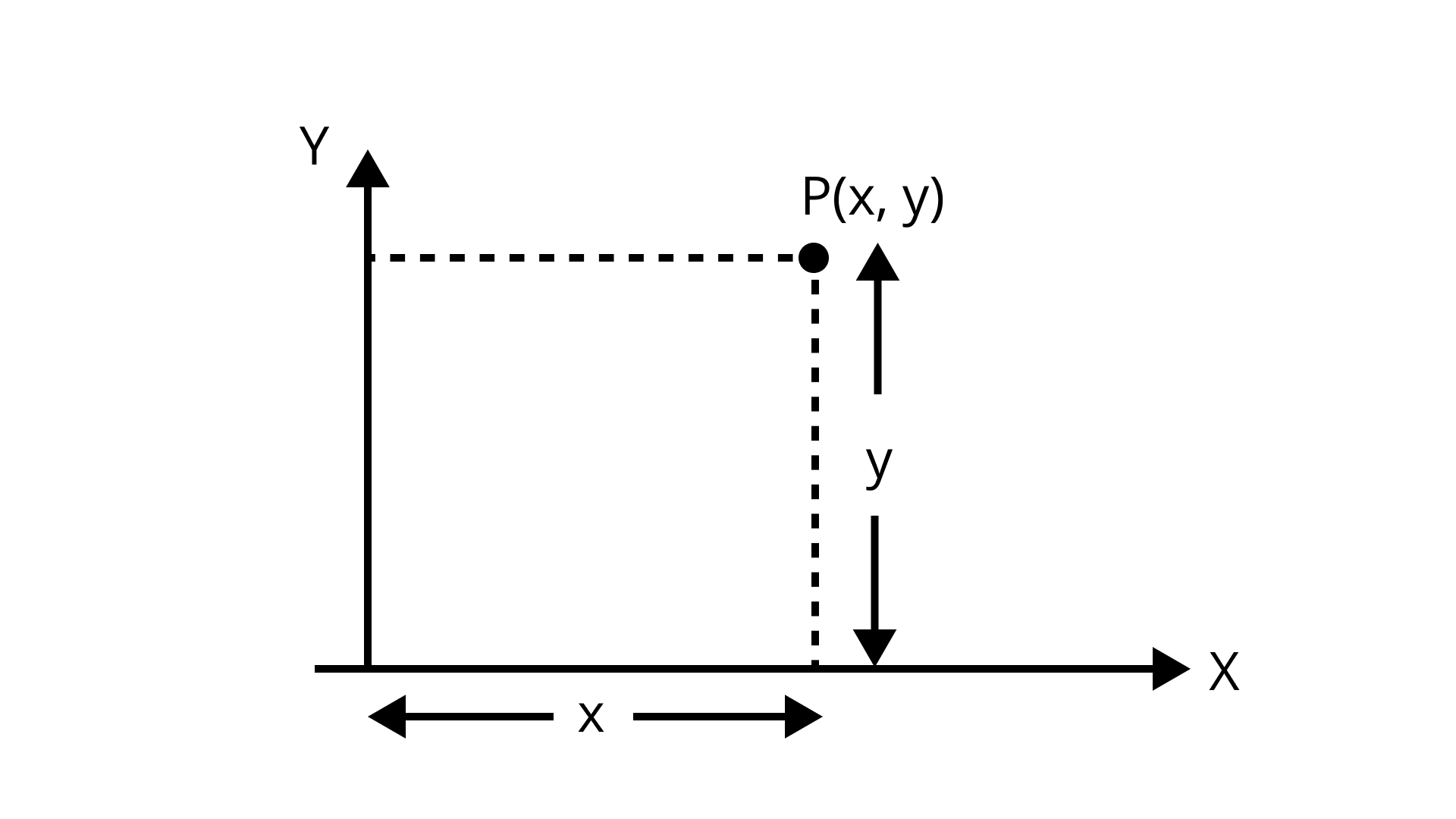
Points on a Cartesian Plane
A pair of numbers locate points on a plane called the coordinates . The distance of a point from the y-axis is known as abscissa or x-coordinate. The distance of a point from the x-axis is called ordinate or y-coordinate.

Example: Consider a point P(3, 2), where 3 is the abscissa, and 2 is the ordinate. 3 represents the distance of point P from the y-axis, and 2 represents the distance of point P from the x-axis.
Distance Formula
Distance between two points on the same coordinate axes.
The distance between two points that are on the same axis (x-axis or y-axis) is given by the difference between their ordinates if they are on the y-axis, else by the difference between their abscissa if they are on the x-axis.

Distance AB = 6 – (-2) = 8 units
Distance CD = 4 – (-8) = 12 units
Distance between Two Points Using Pythagoras Theorem

Let P(x 1 , y 1 ) and Q(x 2 , y 2 ) be any two points on the cartesian plane.
Draw lines parallel to the axes through P and Q to meet at T.
ΔPTQ is right-angled at T.
By Pythagoras Theorem ,
PQ 2 = PT 2 + QT 2
= (x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 – y 1 ) 2
Distance between any two points (x 1 , y 1 ) and (x 2 , y 2 ) is given by
Where d is the distance between the points (x 1 ,y 1 ) and (x 2 ,y 2 ).
To know more about Distance Formula, visit here .
Section Formula
If the point P(x, y) divides the line segment joining A(x 1 , y 1 ) and B(x 2 , y 2 ) internally in the ratio m:n , then, the coordinates of P are given by the section formula as:
For more information on Section Formula, watch the below video
To know more about Section Formula, visit here .
Finding Ratio given the points
To find the ratio in which a given point P(x, y) divides the line segment joining A(x 1 , y 1 ) and B(x 2 , y 2 ),
- Assume that the ratio is k : 1
- Substitute the ratio in the section formula for any of the coordinates to get the value of k.
When x1, x2 and x are known, k can be calculated. The same can be calculated from the y- coordinate also.
Example: Find the ratio when point (– 4, 6) divide the line segment joining the points A(– 6, 10) and B(3, – 8)?
Solution: Let the ratio be m:n.
We can write the ratio as:
m/n : 1 or k:1
Suppose (-4, 6) divide the line segment AB in k:1 ratio.
Now using the section formula, we have the following;
-4 = (3k-6)/(k+1)
– 4k – 4 = 3k – 6
k : 1 = 2 : 7
Thus, the required ratio is 2:7.
The midpoint of any line segment divides it in the ratio 1 : 1 .

The coordinates of the midpoint(P) of line segment joining A(x 1 , y 1 ) and B(x 2 , y 2 ) is given by
Example: What is the midpoint of line segment PQ whose coordinates are P (-3, 3) and Q (1, 4), respectively.
Solution: Given, P (-3, 3) and Q (1, 4) are the points of line segment PQ.
Using midpoint formula, we have;
= (-2/2, 1/2)
= (-1, 1/2)
Points of Trisection
To find the points of trisection P and Q, which divides the line segment joining A(x 1 , y 1 ) and B(x 2 , y 2 ) into three equal parts:
i) AP : PB = 1 : 2
ii) AQ : QB = 2 : 1
Example: Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining the points A(2, – 2) and B(– 7, 4).
Solution: Let P and Q divide the line segment AB into three parts.
So, P and Q are the points of trisection here.
Let P divides AB in 1:2, thus by section formula, the coordinates of P are (1, 0)
Let Q divides AB in 2:1 ratio, then by section formula, the coordinates are (-4,2)
Thus, the point of trisection for line segment AB are (1,0) and (-4,2).
Centroid of a Triangle
If A(x 1 , y 1 ), B(x 2 , y 2 ), and C(x 3 , y 3 ) are the vertices of a ΔABC, then the coordinates of its centroid(P) are given by
Example: Find the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are given as (-1, -3), (2, 1) and (8, -4)
Solution: Given,
The coordinates of the vertices of a triangle are (-1, -3), (2, 1) and (8, -4)
The Centroid of a triangle is given by:
G = ((x 1 +x 2 +x 3 )/3 , (y 1 +y 2 +y 3 )/3 )
G = ((-1+2+8)/3 , (-3+1-4)/3)
G =( 9/3 , -6/3)
G = (3, -2)
Therefore, the centroid of a triangle, G = (3, -2)
Learn more: Centroid of a Triangle
Area from Coordinates
Area of a triangle given its vertices.
If A(x 1 , y 1 ),B(x 2 , y 2 ) and C(x 3 , y 3 ) are the vertices of a Δ ABC, then its area is given by
Where A is the area of the Δ ABC.
Example: Find the area of the triangle ABC whose vertices are A(1, 2), B(4, 2) and C(3, 5).
Using the formula given above,
Area = 9/2 square units.
Therefore, the area of a triangle ABC is 9/2 square units.
To know more about the Area of a Triangle, visit here .
Collinearity Condition
If three points A, B and C are collinear and B lies between A and C, then,
- AB + BC = AC. AB, BC, and AC can be calculated using the distance formula.
- The ratio in which B divides AC, calculated using the section formula for both the x and y coordinates separately, will be equal.
- The area of a triangle formed by three collinear points is zero.
Video Lesson on Coordinate Geometry Toughest Problems

Coordinate Geometry for Class 10 Problems
Determine the distance between the pair of points (a, b) and (-a, -b)
Let the given points be A(a, b) and B(-a, -b)
We know that the distance formula is:
AB = √[(x 2 -x 1 ) 2 +(y 2 -y 1 ) 2 ]
(x 1 , y 1 ) = (a, b)
(x 2 , y 2 ) = (-a, -b)
Now, substitute the values in the distance formula, we get
AB = √[(-a-a) 2 +(-b-b) 2 ]
AB = √[(-2a) 2 + (-2b) 2 ]
AB = √[4a 2 +4b 2 ]
AB = √[4(a 2 +b 2 )]
AB = √4. √[a 2 +b 2 ]
AB = 2.√[a 2 +b 2 ].
Hence, the distance between two points (a, b) and (-a, -b) is 2√[a 2 +b 2 ].
Determine the ratio in which the line segment joining the points A(1, -5) and B(-4, 5) is divided by the x-axis. Also, find the coordinates of the point of division.
Given that, the point P is on the x-axis. Hence, the y-coordinate is 0. Hence, the point is of the form P(x, 0).
Now, we have to find the ratio. Let the ratio be k:1.

Given Points: A(1, -5) and B = (-4, 5).
(x 1 , y 1 ) = (1, -5)
(x 2 , y 2 ) = (-4, 5)
m 1 = k, m 2 = 1
We know that the section formula is:
y= [m 1 y 2 +m 2 y 1 ]/[m 1 +m 2 ]
Now, substitute the values in the section formula, we get
y = [k(5) + 1(-5)]/[k+1]
y = [5k-5]/[k+1]
(5k-5)/(k+1) = 0
Hence, the ratio k:1 = 1:1
Finding x-coordinate:
x= [m 1 x 2 +m 2 x 1 ]/[m 1 +m 2 ]
x = [k(-4) + 1(1)]/(k+1)
Now, substitute k=1 in the above equation, we get
x = [1(-4) + 1(1)]/(1+1)
x = (-4+1)/2
Hence, the coordinate of the point is P(x, 0) = P(-3/2, 0).
Related Articles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry MCQs
- Important Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Two Dimensional Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinate Geometry Formulas
Stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to learn all Maths-related concepts easily by exploring more videos.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
It helped me a lot. thank you
Yes it helped me a lot too 😊
It become much helpful for me.
Thank you Byjus! You helped me a ton!
very helpful thank you !! :))
Thank you a lot. Helped me a lot. Notes is given so systematically, I actually took Mathematics textbook from my seniors and as the syllabus was reduced even this chapter pages were also removed. So finally I found Byjus notes and this has helped me. Thank you.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
NCERT solutions for class 10 Maths chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry all exercises in Hindi and English Medium revised for session 2024-25. Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 solution is simplified and modified as per the new NCERT textbooks published for academic year 2024-25.
Class 10th Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1 Solutions
- Class 10 Maths Exercise 7.1 in English
- Class 10th Maths Exercise 7.1 in Hindi
10th Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.2 Solutions
- Class 10 Maths Exercise 7.2 in English
- Class 10th Maths Exercise 7.2 in Hindi
Class 10th Maths Chapter 7 Solutions for State Boards
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.2
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.4
- Class 10th Maths Chapter 7 NCERT Book
- Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
| Class: 10 | Maths |
| Chapter 7: | Coordinate Geometry |
| Content: | NCERT Exercises Solutions |
| Mode: | Online Videos and Text Format |
| Academic Session: | Year 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
It is useful for UP Board as well as CBSE, MP Board Schools in Hindi Medium and English medium in PDF format to free download. UP Board High School students are now using NCERT Books for school exams. Download UP Board Solutions and NCERT Solutions Apps 2024-25 based on updated NCERT Solutions for the new session 2024-25. There is overall summery about coordinate geometry for class 10, which will help the students to know more about this chapter.
Exam based NCERT solutions for class 10 Maths chapter 7 coordinate geometry exercises from 7.1 and 7.2 are given to free download. All the contents are in updated format for academic session 2024-25. Offline Apps based on these solutions are also for new session. Join the Discussion Forum to discuss your doubts and respond the questions asked by your friends.

ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. If the distance between the points (4, k) and (1, 0) is 5, then what can be the possible values of k? [CBSE 2017] THREE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. The area of a triangle is 5 sq units. Two of its vertices are (2, 1) and (3, -2). If the third vertex is (7/2, y), find the value of y. [CBSE 2017] 2. Show that triangle ABC, where A(-2, 0), B(2, 0), C(0, 2) and triangle PQR where (-4, 0), Q(4, 0), R(0, 4) are similar triangles. [CBSE 2017] FOUR MARKS QUESTIONS 1. If a≠b≠0, prove that the points (a, a²), (b, b²), (0, 0) will not be collinear. [CBSE 2017]
In Coordinate geometry, we study that the distance of a point from the y-axis is called its x-coordinate, or abscissa (abscissa is a Latin word which means cut off) and the distance of a point from the x-axis is called its y-coordinate, or ordinate (ordinate is a Latin word which means keep it in order). Abscissa and ordinate collectively forms coordinate of a point in Cartesian system. The coordinates of a point on the x-axis are of the form (x, 0), and of a point on the y-axis are of the form (0, y). For more question on coordinate geometry, go through NCERT exemplar problems for Class 10 Maths.
Rene Descartes (1596 – 1650) was a French philosopher, mathematician whose work ‘La geometrie’ includes his application of algebra to geometry from which we now have Cartesian geometry.
What is the main objective of Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry in class 10 Maths?
Objectives of Coordinate Geometry To find the distance between two different points whose co-ordinates are given and finding the co-ordinates of a point, which divides the line segment joining two points in a given ratio internally. To find the co-ordinates of the mid-point of the join of two points to get the co-ordinates of the centroid of a triangle with given vertices.
How can one get good marks in class 10 Chapter 7 Maths?
For examination purpose, we have to do only first three exercises. Exercise 7.4 is an optional one, given only for extra practice. Out of exercise 7.1, and 7.2, if a student complete the first exercise thoroughly he can score good marks in entire chapter 7 of class 10 Maths.
What are the Important Results in Chapter 7 Class 10 Maths Coordinate Geometry?
Based on class 10 Maths Chapter 7, the Important Results in Coordinate Geometry are as follows: 1. The co-ordinates of the origin are (0, 0) 2. The y co-ordinate of every point on the x-axis is 0 and the x co-ordinate of every point on the y-axis is 0. 3. The two axes XOX’ and YOY’ divide the plane into four parts called quadrants.
What are the important examples of class 10 Maths chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry?
Example number 4, 5, 9, 10 and 14 are considered as important examples of 10th Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry as these are frequently asked in board exams as well as school tests.
What are the main topics to study in chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Maths?
In chapter 7 (Coordinate Geometry) of class 10th math, Students will study:
1) Distance Formula (To find distance between two points P(x₁, y₁) and Q(x₂, y₂)). 2) Section Formula.
How many exercises are there in chapter 7 of 10 Maths?
There are 2 exercises (exercise 7.1, and 7.2) in chapter 7 (Coordinate Geometry) of class 10 Maths and exercise 7.3 and 7.4 are now deleted from syllabus.
Does chapter 7 (Coordinate Geometry) of class 10 math contain any Theorem?
No, chapter 7 (Coordinate Geometry) of class 10 math doesn’t contain any Theorem.
« Chapter 6: Triangles
Chapter 8: introduction to trigonometry ».
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry (Book Solutions)
- Textbook Solutions

NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths - Coordinate Geometry - Free PDF Download
NCERT(National Council of Educational Research and Training) has published various editions to provide a standard text for the students preparing for the Class 10th board exam. Each year an attempt is made to put the latest revision with additional material which makes the book more comprehensive. In this regard, NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths is one of the most reliable available with current exam-oriented questions which have been designed and created books with utmost care. A unique feature of this book is that it is filled with various practice problems to enhance the working of the readers and at the same time develop their skills for the exam. Moreover, it offers the latest questions to make the task more difficult and interesting.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for CBSE Class10 Mathematics Chapter 7 – COORDINATE GEOMETRY (Examples, Easy Methods and Step by Step Solutions)
EXERCISE 7.1
1. The distance of point $P(2,3)$ from the $x - axis $ is
Correct Answer: B.
Ans: The perpendicular distance of the point $P(2,3)$ from the $x - {\text{axis}}$ will be equal to the $y$ coordinate. So, the distance of the point $P(2,3)$ from the $x - {\text{axis}}$ is $3$ units.
Hence, the distance of the point $P(2,3)$ from the $x - {\text{axis}}$ is $3$ units.
2. The distance between the points $A(0,6)$ and $B(0, - 2)$ is
Correct answer: B.
Ans: $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ are two points respectively, the distance between them is given as:
$AB = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}}$
Given points are $A(0,6)$ and $B(0, - 2)$.
$AB = \sqrt {{{(0 - 0)}^2} + {{( - 2 - 6)}^2}}$
Hence, the distance between the points $A(0,6)$ and $B(0, - 2)$ is $8.$
3. The distance of point $P(- 6,8)$ from the origin is
(B) $2\sqrt 7$
Correct answer: C.
Ans: The distance between any two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $AB = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}}$.
Given points are $O(0,0)$ and $P( - 6,8)$.
$OP = \sqrt {{{( - 6 - 0)}^2} + {{(8 - 0)}^2}}$
$OP = \sqrt {100}$
Therefore, the distance of $P( - 6,8)$ from origin is $10$.
4. The distance between the points $(0,5)$ and $( - 5,0)$ is
(B) $5\sqrt 2$
(C) $2\sqrt 5$
Ans: Distance between two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ are as follows:
Given points are $(0,5)$ and $( - 5,0)$.
$AB = \sqrt {{{( - 5 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 5)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {50}$
$AB = 5\sqrt 2$
Hence, the distance between $(0,5)$ and $( - 5,0)$ is $5\sqrt 2$.
5. $AOBC$ is a rectangle whose three vertices are vertices $ A(0,3), O(0,0)$ and $B(5,0).$ The length of its diagonal is
(C) $\sqrt {34}$
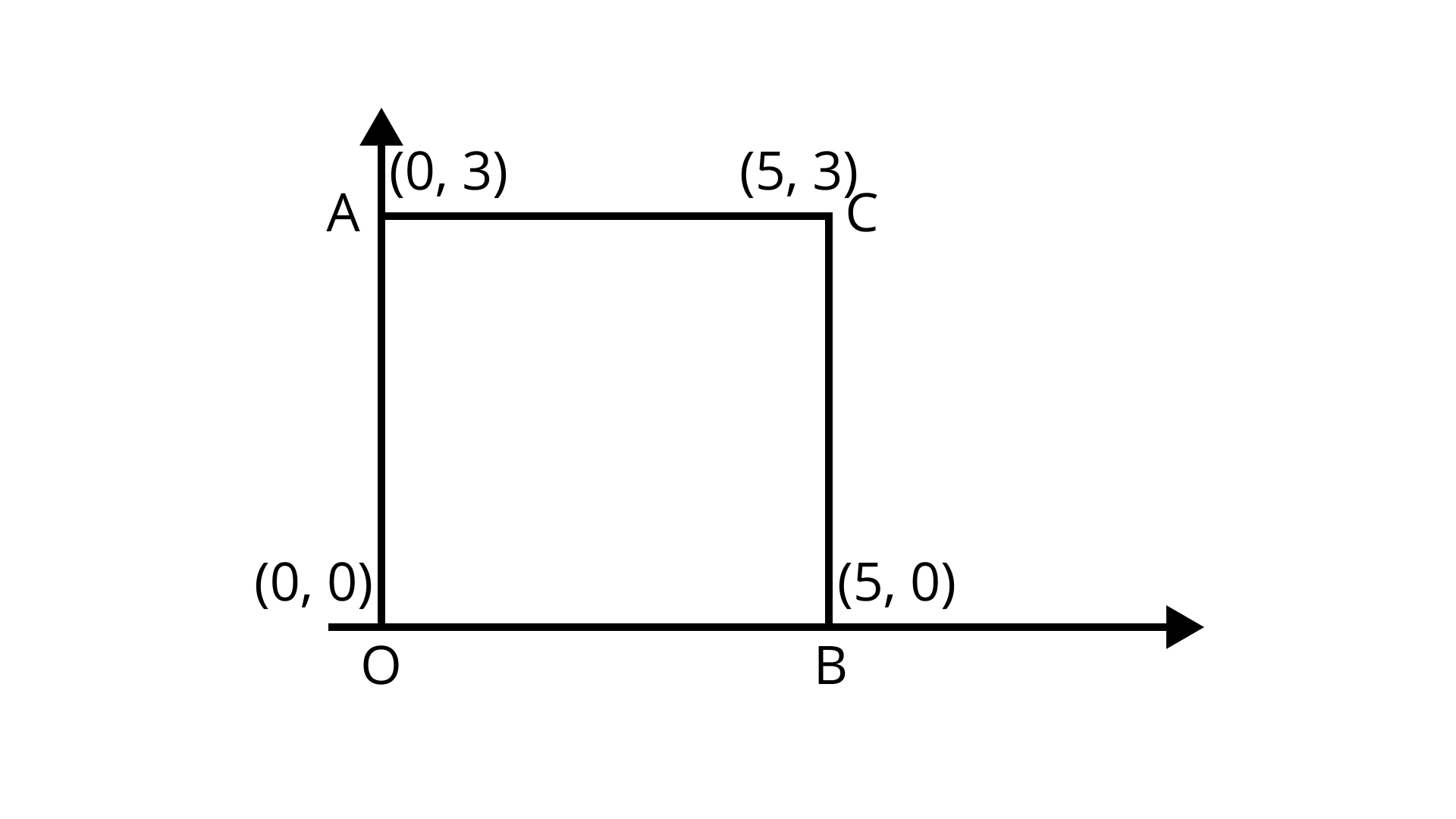
The distance between any two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $AB = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}}$
Given points are $ A(0,3), O(0,0)$ and $B(5,0).$
$AB = \sqrt {{{(5 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 3)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {34}$
Hence, the length of its diagonal is $\sqrt {34}$.
Question 6: The perimeter of a triangle with vertices $ (0,4), (0,0)$ and $(3,0)$ is
(D) $7 + \sqrt 5$
Ans: Perimeter of triangle $\Delta ABC = AB + BC + AC$.
$(0,4), (0,0)$ and $C(3,0)$ are the three vertices of $\Delta ABC.$
Two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ are at distance as below
$\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{{(0 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 4)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow AB = 4$
$\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{{(3 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 4)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow AC = 5$
$\Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{{(3 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow BC = 3$
Perimeter of $\Delta ABC = 4 + 5 + 3$
Perimeter of $\Delta ABC = 12 cm$
Hence, the perimeter of a triangle with vertices $ (0,4), (0,0)$ and $(3,0)$ is $12cm$.
7. The area of a triangle with vertices $A(3,0), B(7,0)$ and $C(8,4)$ is
Ans: $ A(3,0), B(7,0)$ and $C(8,4)$ are the three vertices of $\Delta ABC.$
Area of triangle $\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]$
Area of triangle $\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3\left( {0 - 4} \right) + 7\left( {4 - 0} \right) + 8\left( {0 - 0} \right)} \right]$
$\Delta ABC = 8 sq.units$
Hence, the area of a triangle with vertices $A(3,0), B(7,0)$ and $C(8,4)$ is $8 sq.units$.
8. The points $(- 4,0), (4,0), (0,3)$ are the vertices of a
(A) Right triangle
(B) Isosceles triangle
(C) Equilateral triangle
(D) Scalene triangle
Ans: Two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ are at a distance, which is derived as follows:
$\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{{(4 + 4)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow AB = 8$
$\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{{(0 + 4)}^2} + {{(3 - 0)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{{(0 - 4)}^2} + {{(3 - 0)}^2}}$
$\Rightarrow BC = 5$
$AC = BC = 5 cm\: and\: AB = 8 cm{\text{.}}$
Hence, the points $ ( - 4,0), (4,0), (0,3)$ are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
9. The point which divides the line segment joining the points $(7, - 6)$ and $(3,4)$ in ratio $1:2$ internally lies in the
(A) I quadrant
(B) II quadrant
(C) III quadrant
(D) IV quadrant
Correct answer: D.
Ans: As $x = \dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$ and $y = \dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$
Here, ${m_1} = 1, {m_2} = 2$ .
$\Rightarrow (x,y) = \left( {\dfrac{{1(3) + 2(7)}}{{1 + 2}},\dfrac{{1(4) + 2( - 6)}}{{1 + 2}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow (x,y) = \left( {\dfrac{{17}}{3},\dfrac{{ - 8}}{3}} \right)$
Hence, we can conclude by saying that the line segment is divided by the line joining $(7, - 6)$ and $(3,4)$ in ratio $1:2$ internally lies in IV quadrant.
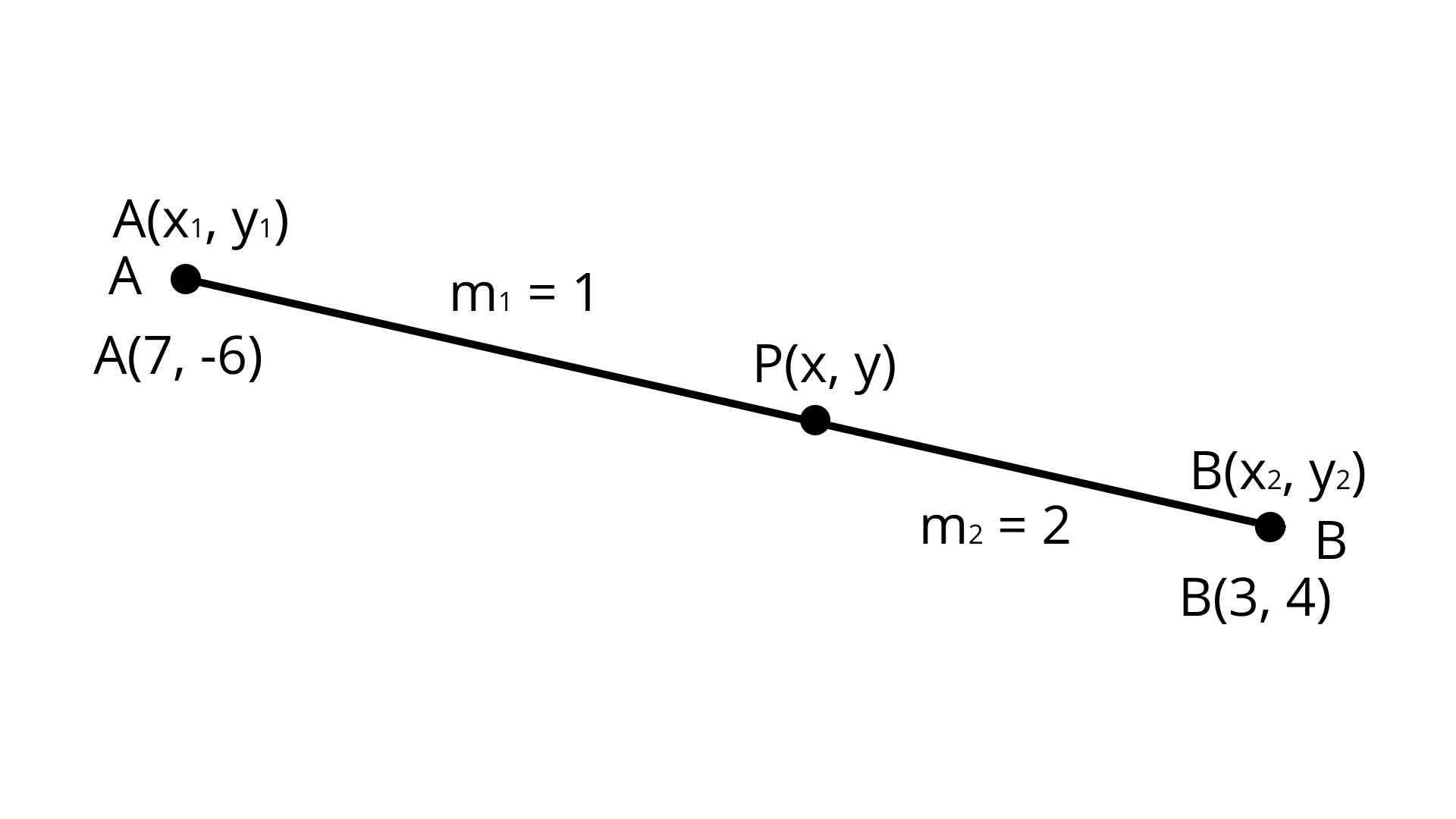
10. The point which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points $A( -2, -5)$ and $B(2,5)$ is
(A) $(0, 0)$
(B) $(0, 2)$
(C) $(2, 0)$
(D) $( - 2, 0)$
Correct answer: A.
Ans: Through the midpoint of $AB$, the perpendicular bisector of AB passes.
The midpoint of the line joining $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
Mid-point $= \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Mid-point $= \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2 + 2}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 5 + 5}}{2}} \right)$
Mid-point $= \left( {0, 0} \right)$
Hence, the point lying on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points $A(- 2, - 5)$ and $B(2, 5)$ is $\left( {0, 0} \right)$.
11. The fourth vertex $D$ of a parallelogram $ABCD$ whose three vertices are $A( - 2, 3), B(6, 7)$ and $C(8, 3)$ is
(A) $(0, 1)$
(B) $(0, - 1)$
(C) $( - 1, 0)$
(D) $(1, 0)$
Ans:
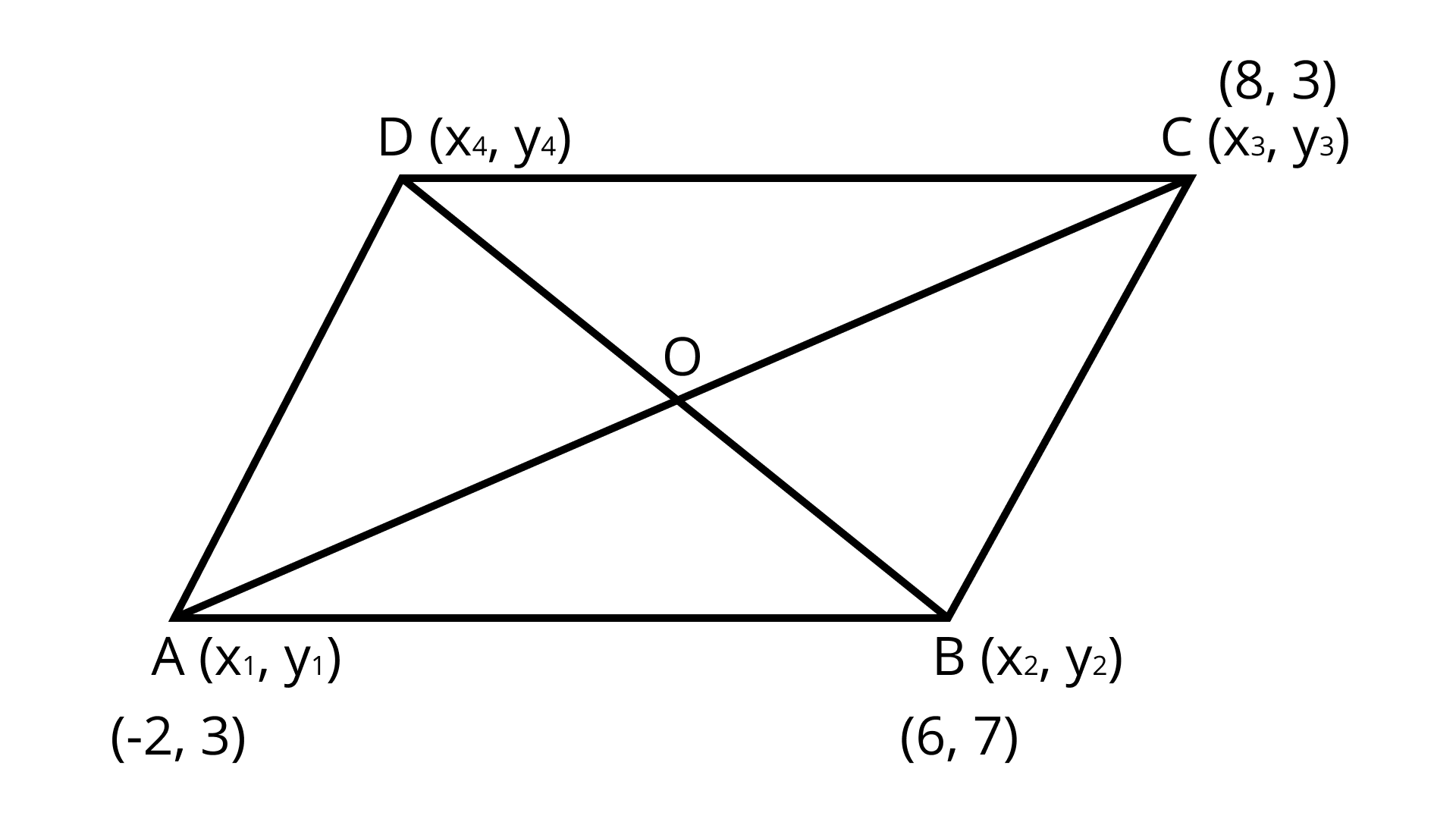
Note that the diagonals $AC$ and $BD$ of parallelogram $ABCD$ bisect each other. So, the midpoint of $AC$ is equal to the midpoint of $BD$.
The midpoint of $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2 + 8}}{2},\dfrac{{3 + 3}}{2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_4} + 6}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_4} + 7}}{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( {3,3} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_4} + 6}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_4} + 7}}{2}} \right)$
Now, compare both sides:
$\dfrac{{{x_4} + 6}}{2} = 3$ and $\dfrac{{{y_4} + 7}}{2} = 3$
${x_4} = 0$ and ${y_4} = - 1$
$({x_4},{y_4}) = (0, - 1)$
Hence, the fourth vertex $D$ of a parallelogram $ABCD$ is $(0, - 1)$.
12. If the point $P(2, 1)$ lies on the line segment joining points $A(4, 2)$ and $B(8, 4)$ then
(A) $AP = \dfrac{1}{3}AB$
(B) $AP = PB$
(C) $PB = \dfrac{1}{3}AB$
(D) $AP = \dfrac{1}{2}AB$
Let ${m_1} = k,{m_2} = 1$.
As $x = \dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$ and $y = \dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$ ,
$\Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{k(8) + 1(4)}}{{k + 1}}$ and $1 = \dfrac{{k(4) + 1(2)}}{{k + 1}}$
$\Rightarrow 8k + 4 = 2k + 2$ and $4k + 2 = k + 1$
$\Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}$ and $k = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}$
So, $\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}$
$\Rightarrow AP = - 1$, which means $1$ part outside $AB.$
And $PB = 3$
$\Rightarrow AP = 1x$ unit and $AB = 3x - 1x = 2x$ units.
So, $AP = \dfrac{1}{2}AB$.
Hence, $AP = \dfrac{1}{2}AB$.
13. If $P\left( {\dfrac{a}{3},4} \right)$ is the midpoint of the line segment joining the points $Q(- 6, 5)$ and $R(- 2, 3)$ then the value of $a$ is
Ans: $P({x_1},{y_1})$ and $Q({x_2},{y_2})$ equation’s midpoint is given by $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{a}{3},4} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{a}{3},4} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 6 - 2}}{2},\dfrac{{5 + 3}}{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{3} = \dfrac{{ - 8}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a = - 12$
Hence, $a = - 12$.
14. The perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points $A(1, 5)$ and $B(4, 6)$ cuts the y-axis at
(A) $(0, 13)$
(B) $(0, - 13)$
(C) $(0, 12)$
(D) $(13, 0)$
Ans: The point where the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining $A(1, 5)$ and $B(4, 6)$ cuts the y-axis $P(0, y).$
$\Rightarrow A{P^2} = B{P^2}$
$\Rightarrow 1 + {(y - 5)^2} = 16 + {(y - 6)^2}$
$\Rightarrow 1 + {y^2} - 10y + 25 = 16 + {y^2} - 12y + 36$
$\Rightarrow y = 13$
So, the point $P(0, y) = (0, 13)$.
15. The coordinates of the point which is equidistant from the three vertices of the $\Delta AOB$ as shown in the Fig. 7.1 is
(A) $(x,y)$
(B) $(y,x)$
(C) $\left( {\dfrac{x}{2},\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)$
(D) $\left( {\dfrac{y}{2},\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)$
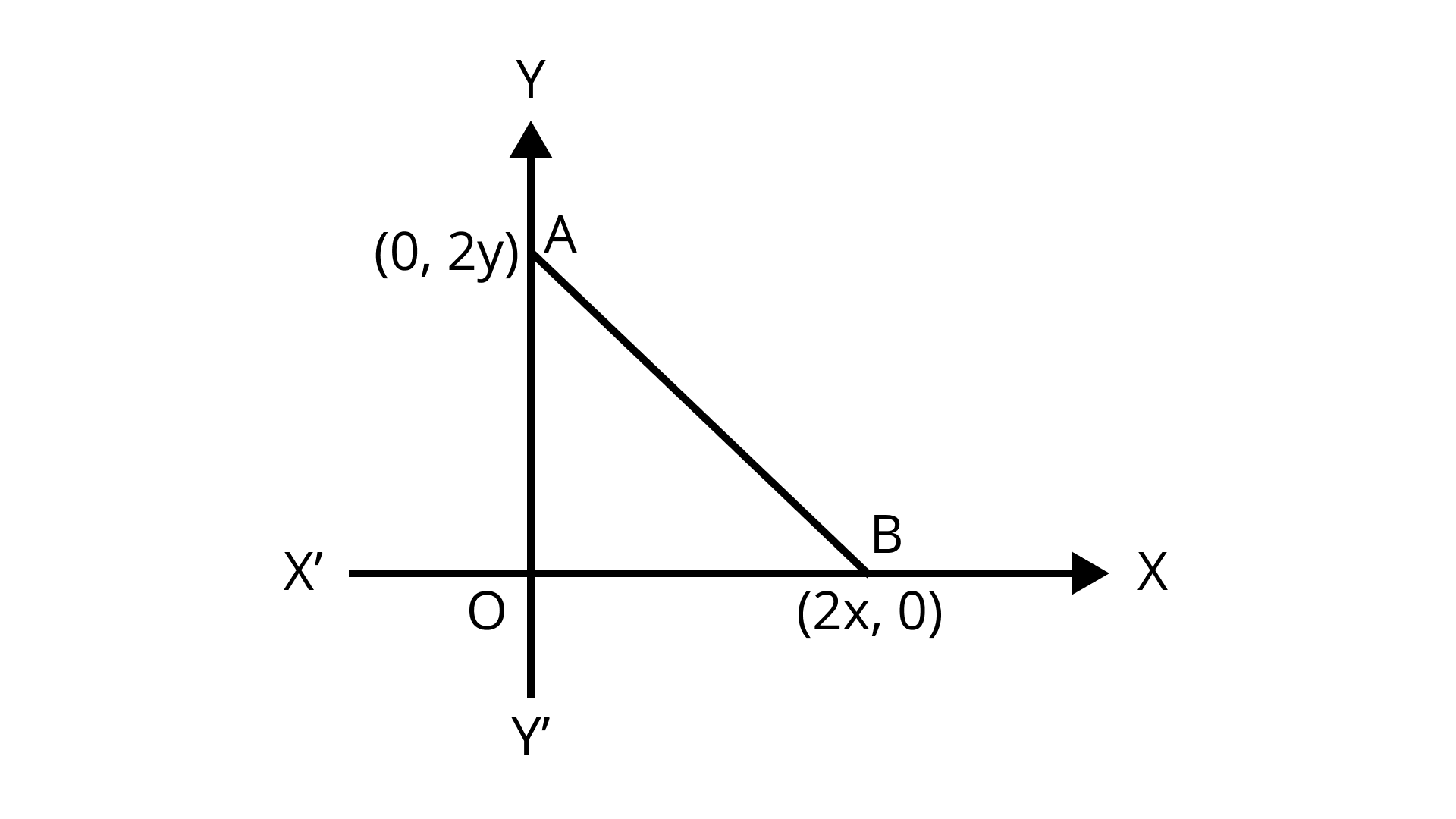
Correct answer: A.
Ans: I n any right-angled triangle, the mid-point of the hypotenuse will be equidistant from all the three vertices of the triangle.
Midpoint of $A(0,2y)$ and $B(2x,0)$ is $\left( {\dfrac{{2x + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{0 + 2y}}{2}} \right) = (x, y)$.
Hence, the coordinates of the point which is equidistant from the three vertices of the $\Delta AOB$ is $(x, y)$.
16. A circle drawn with origin as the center passes through $\left( {\dfrac{{13}}{2},0} \right).$ The point which does not lie in the interior of the circle is
(A) $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{4},1} \right)$
(B) $\left( {2,\dfrac{7}{3}} \right)$
(C) $\left( {5,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
(D) $\left( { - 6,\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$
Ans: The distance between any two points $A({x_1},{y_1})$ and $B({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $AB = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}}$ .
The radius of the circle is $\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{13}}{2} - 0} \right)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}} = 6.5$ units.
Consider the point given in option A,
The distance of $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{4},1} \right)$ from origin is $\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{4} - 0} \right)}^2} + {{(1 - 0)}^2}} = 1.25$ units.
As the distance $1.25 < 6.5$, the point $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{4},1} \right)$ lies in the interior of the given circle.
Consider the point given in option B.
The distance of $\left( {2,\dfrac{7}{3}} \right)$from origin is $\sqrt {{{\left( {2 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{7}{3} - 0} \right)}^2}} = 3.0731$ units.
As the distance $3.0731 < 6.5$, the point $\left( {2,\dfrac{7}{3}} \right)$ lies in the interior of the given circle.
Consider the point given in option C,
The distance of $\left( {5,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$ from origin is $\sqrt {{{(5 - 0)}^2} + {{\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2} - 0} \right)}^2}} = 5.0249$units.
As the distance $5.0249 < 6.5$ , the point $\left( {5,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$ lies in the interior of the given circle.
Consider the point given in option D,
The distance of $\left( { - 6,\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$ from origin is $\sqrt {{{( - 6 - 0)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{5}{2} - 0} \right)}^2}} = 6.5$ units.
As the distance $6.5 = 6.5$, the point $\left( { - 6,\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$ lies on the given circle.
Hence, the point which does not lie in the interior of the circle is $\left( { - 6,\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$.
17. A line intersects the y-axis and x-axis at the points $P$ and $Q$ respectively. If $(2, - 5)$ is the midpoint of $PQ$ then the coordinates of $P$ and $Q$ are, respectively
(A) $(0, - 5)$ and $(2,0)$
(B) $(0,10)$ and $( - 4,0)$
(C) $(0,4)$ and $( - 10,0)$
(D) $(0, - 10)$ and $(4,0)$
Ans: As $P$ lies on y-axis, the coordinates of $P$ will be $(0, y).$
As $Q$ lies on x-axis, the coordinates of $Q$ will be $(x, 0).$
The midpoint of $P({x_1},{y_1})$ and $Q({x_2},{y_2})$ is given by $\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right) = (2, - 5)$
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{0 + x}}{2},\dfrac{{y + 0}}{2}} \right) = (2, - 5)$
$\Rightarrow x = 4 and y = - 10$
Hence, the coordinates of $P$ and $Q$ are $(0, - 10)$ and $(4,0)$.
18. The area of a triangle with vertices (a,b + c), (b,c + a) and (c,a + b) is
(A) ${(a + b + c)^2}$
(C) a + b + c
Correct Answer: B
Ans: That area of triangle $\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]$.
Vertices are (a,b + c), (b,c + a) and (c,a + b).
Area = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {a\{ c + a - \left( {a + b} \right)\} + b\{ a + b - (b + c)\} + c\{ b + c - (c + a)\} } \right]$
Area = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {a\left( {c - b} \right) + b(a - c) + c(b - a)} \right]$
Area = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {ac - ab + ab - bc + bc - ac} \right]$
Hence, Area of triangle = 0.
19. If the distance between the points $(4,p)$ and $(1,0)$ is $5$ then the value of $p$ is
(A) $4$ only
(B) $ \pm 4$
(C) $ - 4$ only
Correct answer: B.
Given $AB = 5$units
$\Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( 5 \right)^2}$
$\Rightarrow {(4 - 1)^2} + {(p - 0)^2} = 25$
$\Rightarrow 9 + {(p)^2} = 25$
$\Rightarrow {(p)^2} = 16$
$\Rightarrow p = \pm 4$
Hence, $p = \pm 4.$
20. If the points $A(1,2), O(0,0)$ and $C(a,b)$ are collinear, then
(A) $a = b$
(B) $a = 2b$
(C) $2a = b$
(D) $a = - b$
Ans: Area of triangle $\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]$.
Area of a triangle is zero if the points are collinear.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right] = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1\left( {0 - b} \right) + 0\left( {b - 2} \right) + a\left( {2 - 0} \right)} \right] = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}( - b + 2a) = 0$
$\Rightarrow 2a = b$
Hence, $2a = b.$
EXERCISE 7.2 1. $\Delta ABC$ With vertices $A( - 2, 0), B(2, 0)$ and $C(0, 2)$ is similar to $\Delta DEF$ with vertices $D (- 4, 0),E(4,0)$ and $F$ $(0, 4)$
Ans: The statement is False.
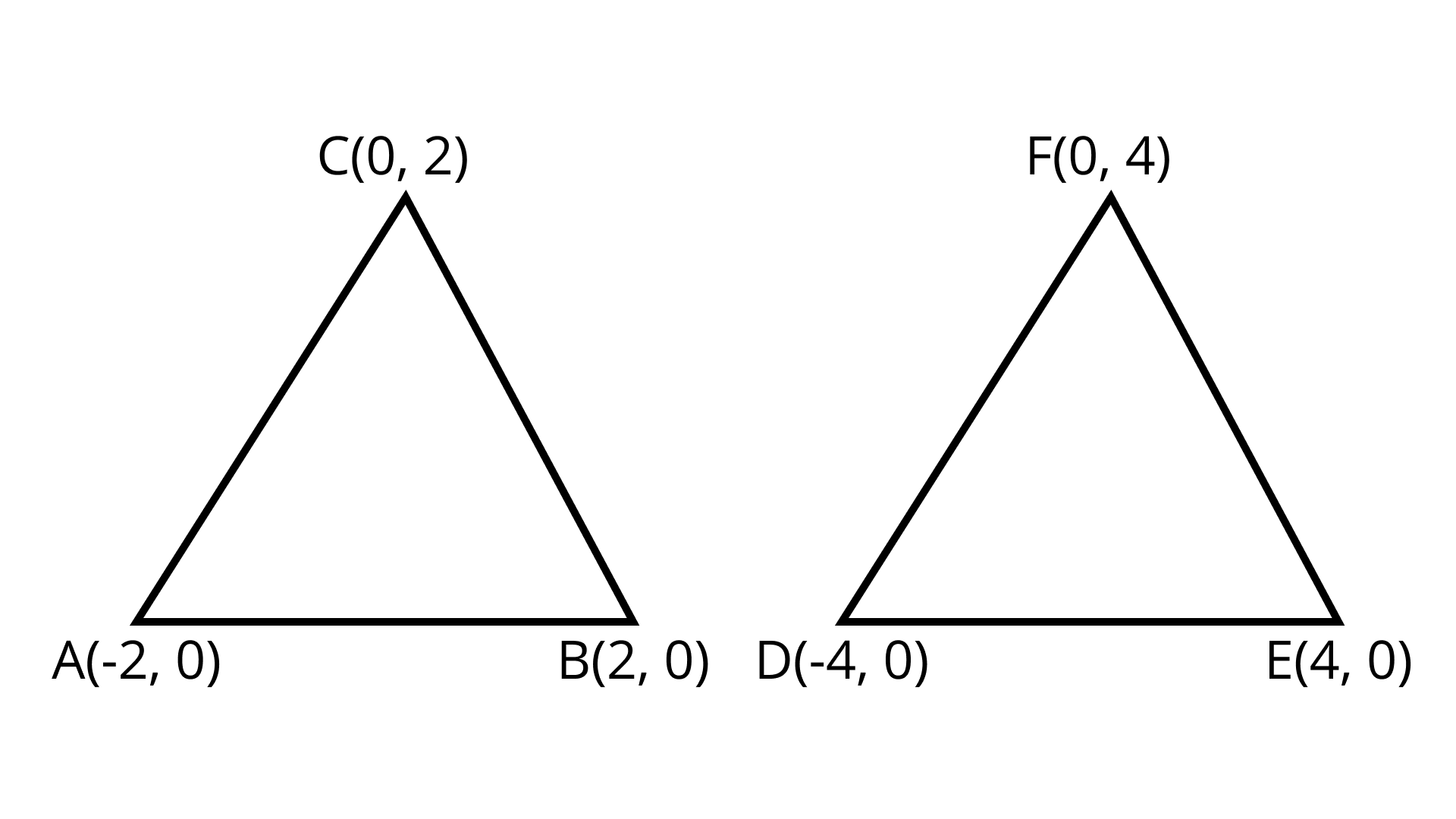
Distance Formula $= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
In $\Delta ABC$ , $AB = \sqrt {{{(2 + 2)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(4)}^2}} = 4$
$AC = \sqrt {{{(0 + 2)}^2} + {{(2 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {(4 + 4)} = 2\sqrt 2$
in $\Delta DEF$ , $DE = \sqrt {{{(4 + 4)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(8)}^2}} = 8$
$EF = \sqrt {{{(0 - 4)}^2} + {{(4 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {16 + 16} = \sqrt {32} = 4\sqrt 2$
$DF = \sqrt {{{(0 + 4)}^2} + {{(4 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {16 + 16} = 4\sqrt 2$
Here, $\dfrac{{AB}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{EF}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{DF}}$
$\dfrac{4}{8} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{4\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence, $\Delta ABC$ is similar to $\Delta DEF$.
2. Point $P( - 4,2)$ lies on the line segment joining the points $A( - 4,6)$ and $B( - 4, - 6)$
Ans: The statement is True The given points $A( - 4, 6)$ and $B( - 4, - 6)$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 4, 6)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = ( - 4, - 6)$
$\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = ( - 4, 2)$
Point $P( - 4, 2)$ lie on line AB if the area of triangle $ABP = 0$
$\dfrac{1}{2}[ - 4( - 6 - 2) - 4(2 - 6) - 4(6 + 6)]$
$\dfrac{1}{2}[ - 4( - 8) - 4( - 4) - 4(12)]$
$[32 + 16 - 48]$ $= 0$
$\therefore P( - 4, 2)$ Must lie on line joining, $AB$
3. The points $(0, 5), (0, - 9)$ and $(3, 6)$ are collinear.
Ans: The statement is False The given points area $(0, 5),(0, - 9)$ and $(3, 6)$
If the point area is collinear then the area of triangle is 0.
${x_1} = 0, {x_2} = 0, {x_3} = 3$
${y_1} = 5, {y_2} = 9, {y_3} = 6$
$= \dfrac{1}{2} [0 ( - 9 - 6) + 0 (6 - 5) + 3 (5 + 9)]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[0 + 0 + 42]$
$= \dfrac{{42}}{2} = 21$
Area of triangle $= 21$
Here the area of the triangle is not equal to zero.
Hence, the point is not collinear.
4. Point $ P\left( {0, 2} \right)$ is the point of intersection of y–axis and perpendicular bisector of line segment joining the points $A ( - 1, 1)$ and $B (3, 3)$
If the point ${\text{P}}$ is a perpendicular bisector of the line joining the point $A( - 1, 1)$ and $B(3, 3)$ then it must be mid-point of $AB$.
Mid - point of $AB = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 1, 1)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (3, 3)$
It does not represent point P
Hence, the given statement is false.
5. Points $A \left( {3, 1} \right), B \left( {12, -2} \right) and C \left( {0, 2} \right)$ cannot be the vertices of a triangle.
Ans: The statement is True If they are not the vertices of a triangle then
Area of $\Delta ABC = 0$
${x_1} = 3, {x_2} = 12, {x_3} = 0$
${y_1} = 1, {y_2} = - 2, {y_3} = 2$
Let us find the area of $\Delta ABC$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[3( - 2 - 2) + 12(2 - 1) + 0(1 + 2)]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[3( - 4) + 12(1) + 0]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[ - 12 + 12]$
$= \dfrac{0}{2}$
Hence, they are collinear or not the vertices of a triangle.
6. Points $A \left( {4, 3} \right), B \left( {6, 4} \right), C \left( {5, --6} \right) and D \left( {--3, 5} \right)$ are the vertices of a parallelogram. Ans: The statement is False The given points area $A(4,3),B(6,4),C(5, - 6),D( - 3,5)$ Distance between $AB = \sqrt {{{(6 - 4)}^2} + {{(4 - 3)}^2}}$ $AB = \sqrt {{{(2)}^2} + {{(1)}^2}} = \sqrt 5$
Distance between $BC = \sqrt {{{(5 - 6)}^2} + {{( - 6 - 4)}^2}}$ $BC = \sqrt {1 + 100} = \sqrt {101}$
Distance between $CD = \sqrt {{{( - 3 - 5)}^2} + {{(5 + 6)}^2}}$
$CD = \sqrt {64 + 121} = \sqrt {185}$
Distance between $DA = \sqrt {{{(4 + 3)}^2} + {{(3 - 5)}^2}}$
$DA = \sqrt {49 + 4} = \sqrt {53}$
Here, opposite sides are not equal i.e.
$AB \ne CD,BC \ne DA$
Hence, it is not a parallelogram
7. A circle has its Centre at the origin and a point $P\left( {5, 0} \right)$ lies on it. The point $Q\left( {6, 8} \right)$ lies outside the circle.
Ans: The statement is True. The center of the circle is $O(0,0)$
If point $P(5,0)$ lies on the circle then the distance between $O(0, 0)$ and $P(5, 0)$ is the radius of the circle $OP = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$OP = \sqrt {{{(5 - 0)}^2} + {{(0 - 0)}^2}}$
$OP = \sqrt {{{(5)}^2}} = 5$
Radius of circle $= 5$
If point $Q(6, 8)$ is outside the circle then the distance between $O (0,0)$ and $Q (6,8)$ is greater than the Radius of the circle
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (0, 0)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (6, 8)$
$OQ = \sqrt {{{(6 - 0)}^2} + {{(8 - 0)}^2}}$
$OQ = \sqrt {36 + 64}$
$= \sqrt {100} = 10$
Here point $OQ$ is greater than the radius of circle.
Hence, point $Q(6, 8)$ lies outside the circle.
8. The point $A(2, 7)$ lies on the perpendicular bisector of line segment joining the points $P(6, 5)$ and $Q(0, - 4)$
Ans: The statement is False. If point $A(2, 7)$ is bisector then it must be mid-point of the line joining the points $P(6, 5)$ and $Q(0, - 4)$
Mid - point of $PQ = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (6,5)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (0, - 4)$
$= \left( {\dfrac{{6 + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{5 - 4}}{2}} \right) = \left( {3,\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
Hence, A does not lies on bisector.
9. Point $C \left( {5, -3} \right)$ is one of the two points of trisection of the line segment joining the points $A \left( {7, - 2} \right)$ and B $\left( {1, - 5} \right)$ Ans: The statement is True
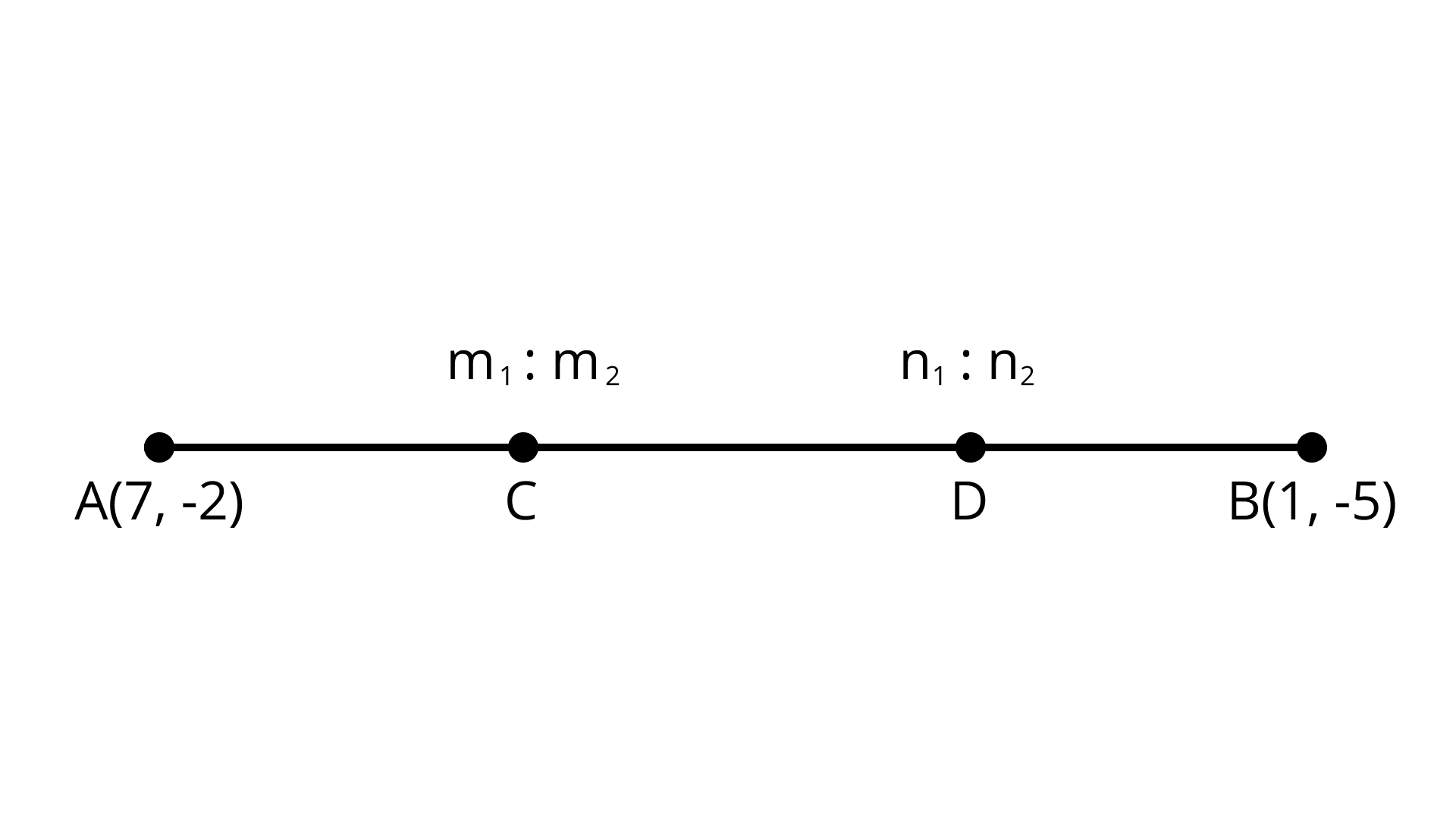
Let the two point of trisection are C, D
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (7, - 2)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (1, - 5)$
${m_1} = 1,{m_2} = 2$ $\because$ C divide in ratio 1:2
$C = \left( {\dfrac{{1 \times 1 + 2 \times 7}}{{1 + 2}},\dfrac{{1 \times \left( { - 5} \right) + 2 \times \left( { - 2} \right)}}{{1 + 2}}} \right)$
$C = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + 14}}{3},\dfrac{{ - 5 - 4}}{3}} \right)$
$C = (5, - 3)$
${n_1} = 2,{n_2} = 1$ $\because$ C divide in ratio 2:1
$D = \left( {\dfrac{{2 \times 1 + 1 \times 7}}{{2 + 1}},\dfrac{{2 \times \left( { - 5} \right) + 1 \times \left( { - 2} \right)}}{{2 + 1}}} \right)$
$D = \left( {\dfrac{{2 + 7}}{3},\dfrac{{ - 10 - 2}}{3}} \right)$
$D = (3, - 4)$
Hence, the given statement is true.
10. Points $A( - 6,10), B ( - 4,6)$ and $C (3, - 8)$ are collinear such that $AB = \dfrac{2}{9}AC$ Ans: The statement is True.
If the points $A( - 6,10), B( - 4,6)$ and $C(3, - 8)$ are collinear then area of $\Delta ABC = 0$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}[ - 84 + 72 + 12]$
Hence, ${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$ are collinear
Distance between $AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {{{( - 4 + 6)}^2} + {{(6 - 10)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {4 + 16} = \sqrt {20} = 2\sqrt 5$
Distance between $AC = \sqrt {{{(3 + 6)}^2} + {{( - 8 - 10)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {81 + 324}$
$= \sqrt {405}$
$AC = 9\sqrt 5$
Hence, $\dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 5 }}{{9\sqrt 5 }}$
$AB = \dfrac{2}{9}AC$
11. The point $P( - 2, 4)$ lies on a circle of radius $6$ and Centre $C(3, 5)$
Ans: The statement is False The radius of the circle is $6$ and Centre $C (3, 5)$
If point $P (- 2,4)$ lies on the circle then the distance between the Centre and point $P$ is equal to the radius of the circle. Distance between $PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 2,4)$ $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (3,5)$
$PC = \sqrt {{{(3 + 2)}^2} + {{(5 - 4)}^2}}$
$PC = \sqrt {25 + 1} = \sqrt {26}$
$PC \ne radius (6)$
Hence, point $P ( - 2, 4)$ not lies on the circle with Centre$C (3, 5)$.
12. The points A(- 1, - 2),B(4, 3),C(2, 5)$ and D( - 3, 0) in that order form a rectangle.
Ans: The statement is True The given points are A( - 1, - 2),B(4,3),C(2,5) and D( - 3,0) Length of $AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {{{(4 + 1)}^2} + {{(3 + 2)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {50} = 5\sqrt 2$
Length of $BC = \sqrt {{{(2 - 4)}^2} + {{(5 - 3)}^2}}$
$BC = \sqrt {4 + 4} = \sqrt 8 = 2\sqrt 2$
Length of $CD = \sqrt {{{( - 3 - 2)}^2} + {{(0 - 5)}^2}}$
$CD = \sqrt {25 + 25} = \sqrt {50} = 5\sqrt 2$
$DA = \sqrt {4 + 4} = \sqrt 8 = 2\sqrt 2$
$AB = CD,BC = DA$
Length of $AC = \sqrt {{{(2 + 1)}^2} + {{(5 + 2)}^2}}$
$AC = \sqrt {9 + 49} = \sqrt {58}$
Length of $BD = \sqrt {{{( - 3 - 4)}^2} + {{(0 - 3)}^2}}$
$BD = \sqrt {49 + 9} = \sqrt {58}$
$AC = BD$ (Diagonals)
Hence, $ABCD$ is a rectangle as
$AB = CD,BC = DA,AC = BD$
EXERCISE 7.3
1. Name the type of triangle formed by the points $A( - 5,6),B( - 4, - 2),C(7,5)$
Ans: ${\text{ABC}}$ is a scalene triangle. Given vertices are $A( - 5, 6), B( - 4, - 2), C(7, 5)$
Distance formula $= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
Distance of $AB = \sqrt {{{( - 4 - ( - 5))}^2} + {{( - 2 - 6)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {{{(1)}^2} + {{( - 8)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {1 + 64}$
$= \sqrt {65}$
$= \sqrt {{{(11)}^2} + {{(7)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {121 + 49}$
$= \sqrt {170}$
Distance of $AC = \sqrt {{{(7 - ( - 5))}^2} + {{(5 - 6)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {{{(12)}^2} + {{( - 1)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {144 + 1}$
$= \sqrt {145}$
$AB \ne BC \ne AC$
Therefore, $ABC$ is a scalene triangle.
2. Find the points on the x-axis which are at a distance of $2\sqrt 5$ from the point $ (7, - 4)$. How many such points are there Ans: Point are $(9, 0)$ and $(5, 0)$ Let point on $x$-axis is $(x, 0)$ $\left[ {\because {\text{ }}y is zero on - axis} \right]$
Given point $(7, - 4)$
Distance $= 2\sqrt 5$
$2\sqrt 5 = \sqrt {{{(7 - x)}^2} + {{( - 4, - 0)}^2}}$
Squaring both sides
${(2\sqrt 5 )^2} = {(7 - x)^2} + {( - 4)^2}$ $20 = 49 + {x^2} - 14x + 16$ ${x^2} - 14x + 65 - 20 = 0$ ${x^2} - 14x + 45 = 0$ ${x^2} - 9x - 5x + 45 = 0$ $x(x - 9) - 5(x - 9) = 0$ $(x - 9)(x - 5) = 0$ $x = 9, x = 5$
Point are $(9,0)$ and $(5,0)$ Hence, two points are there.
3. What type of a quadrilateral do the points $A(2, - 2), B(7,3), C(11, - 1), D(6, - 6)$ taken in that order, form?
Ans: Rectangle Let the points be $A(2, - 2), B(7,3), C(11, - 1), D(6, - 6)$ of a quadrilateral $ABCD$
$AB = \sqrt {{{(7 - 2)}^2} + {{(3 + 2)}^2}} = \sqrt {{5^2} + {5^2}} = \sqrt {25 + 25} = \sqrt {50}$
$BC = \sqrt {{{(7 - 11)}^2} + {{( - 1 - 3)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(4)}^2} + {{( - 4)}^2}} = \sqrt {16 + 16} = \sqrt {32}$
$CD = \sqrt {{{(6 - 11)}^2} + {{( - 6 + 1)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{( - 5)}^2} + {{( - 5)}^2}} = \sqrt {25 + 25} = \sqrt {50}$
$DA = \sqrt {{{(6 - 2)}^2} + {{( - 6 + 2)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(4)}^2} + {{( - 4)}^2}} = \sqrt {16 + 16} = \sqrt {32}$
$AC = \sqrt {{{(11 - 2)}^2} + {{( - 1 + 2)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(9)}^2} + {{(1)}^2}} = \sqrt {81 + 1} = \sqrt {82}$
$BD = \sqrt {{{(6 - 7)}^2} + {{( - 6 - 3)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(1)}^2} + {{( - 9)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 81} = \sqrt {82}$
$AS, AB = CD$ and $BC = DA$ and $AC = BD$
Hence, the quadrilateral is a rectangle.
4. Find the value of a, if the distance between the points $A( - 3, - 14)$ and $B(a, - 5)$ is $9 units$
Ans: $- 3$ Here, points are $A( - 3, - 14)$ and $B(a, - 5)$
Distance $= 9$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 3, - 14)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (a, - 5)$
$9 = \sqrt {{{(a + 3)}^2} + {{( - 5 + 14)}^2}}$
Squaring both sides we get
${(9)^2} = {(a + 3)^2} + {(9)^2}$
${(a + 3)^2} = 0$
$\Rightarrow a + 3 = 0$
$a = - 3$
Value of a is $- 3$
5. Find a point which is equidistant from the points $A( - 5, 4)$ and $B( - 1, 6)$? How many such points are there?
Ans: Infinite numbers of points are there Let ${\text{P }}(x, y)$ is a point which is equidistant from point $A( - 5, 4)$ and $B( - 1, 6)$ i.e. $PA = PB$
$P{A^2} = P{B^2}$
${( - 5 - x)^2} + {(4 - y)^2} = {( - 1 - x)^2} + {(6 - y)^2}$
$25 + {x^2} + 10x + 16 + {y^2} - 8y = 1 + {x^2} + 2x + 36 + {y^2} - 12y$
$\left[ {Using:{{(a + b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab;{{(a - b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right]$
$25 + 10x + 16 - 8y = 1 + 2x + 36 - 12y$
$10x - 8y + 41 - 2x + 12y - 37 = 0$
$8x + 4y + 4 = 0$
Dividing by 4 we get
$2x + y + 1 = 0 \ldots ..(1)$
Mid - point of $AB = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 5 - 1}}{2},\dfrac{{4 + 6}}{2}} \right)$
$= ( - 3,5)$
Put point $( - 3,5)$ in eqn. (1)
$2( - 3) + 5 + 1$
Mid-point of $AB$ satisfy equation (1)
Hence, infinite numbers of points are there.
6. Find the coordinates of the point Q on the x-axis which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points $ A\left( {--5,--2} \right) and B \left( {4,--2} \right)$ Name the type of triangle formed by the points Q, A and B.
Ans: $\Delta ABQ$ Is an isosceles triangle. Use distance formula $= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
Let $Q(x,0)$$\left[ {\because On - axis y coordinate is zero} \right]$
$Q$ Lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line AB i.e.
$A{Q^2} = B{Q^2}$
${(x - 5)^2} + {(0 + 2)^2} = {(x - 4)^2} + {(0 + 2)^2}$
${x^2} + 25 - 10x + 4 = {x^2} + 16 - 8x + 4$
$29 - 10x = 20 - 8x$
$29 - 20 = - 8x + 10x$
$\dfrac{9}{2} = x$
$\therefore$ The co-ordinate of $Q$ is $(4.5,0)$
$\because AQ = BQ$ And $Q$ lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line AB
$\therefore \Delta ABQ$ Is an isosceles triangle.
7. Find the value of $m$ if the points $A(5,1), B( - 2, - 3), C(8,2m)$ are collinear.
Ans: $m = \dfrac{{19}}{{14}}$ Given points are $A(5,1),B( - 2, - 3),C(8,2m)$
If points are collinear then the area of triangle $= 0$
$\Rightarrow 5( - 3 - 2m) - 2(2m - 1) + 8(1 + 3) = 0$
$\Rightarrow - 15 - 10m - 4m + 2 + 32 = 0$
$\Rightarrow - 14m + 19 = 0$
$\Rightarrow 14m = 19$
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{19}}{{14}}$
8. If the point $A (2, - 4)$ is equidistant from $P (3, 8)$ and $Q ( - 10, y)$ , find the values of y. Also find distance PQ.
Ans: $13\sqrt 2 Units$ or$\sqrt {290} Units$ Given: Point $A (2, - 4)$ is equidistant from $P (3,8)$ and $Q ( - 10,y)$
Square both sides
$A{P^2} = A{Q^2}$
${(3 - 2)^2} + {(8 + 4)^2} = {( - 10 - 2)^2} + {(y + 4)^2}$ (Using distance formula)
${(1)^2} + {(12)^2} = {(12)^2} + {(y)^2} + {(4)^2} + 2 \times y \times 4 \left\{ {Q{{(a + b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right\}$
$1 + 144 = 144 + {y^2} + 16 + 8y$
${y^2} + 8y + 15 = 0$
${y^2} + 3y + 5y + 15 = 0$
$y \times (y + 3) + 5 \times (y + 3) = 0$
$(y + 5)(y + 3) = 0$
$y = - 5,{\text{ }}y = - 3$
Case-I when $y = - 5$ , $ PQ = \sqrt {{{( - 10 - 3)}^2} + {{( - 5 - 8)}^2}} = \sqrt {169 + 169} = 13\sqrt 2$ Units
Case-II when $y = - 3$ , $PQ = \sqrt {{{( - 10 - 3)}^2} + {{( - 3 - 8)}^2}} = \sqrt {169 + 121} = \sqrt {290}$ Units
9. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are $( - 8, 4),( - 6, 6),( - 3, 9)$ Ans: $30{\text{ Sq}}{\text{. Units}}$ Given vertices are $( - 8, 4),( - 6, 6),( - 3, 9)$
${x_1} = - 8{x_2} = - 6{x_3} = - 3$ ${y_1} = 4{y_2} = 6{y_3} = 9$ We know that area of triangle is
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[24 + 30 + 6]$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}[60]$ $= 30 Sq. Units$
10. In what ratio does the x–axis divide the line segment joining the points $( - 4, - 6)$ and $( - 1, 7)$? Find the coordinates of the point of division.
Ans: $Co - ordinate of P\left( {\dfrac{{ - 34}}{{13}},0} \right)$
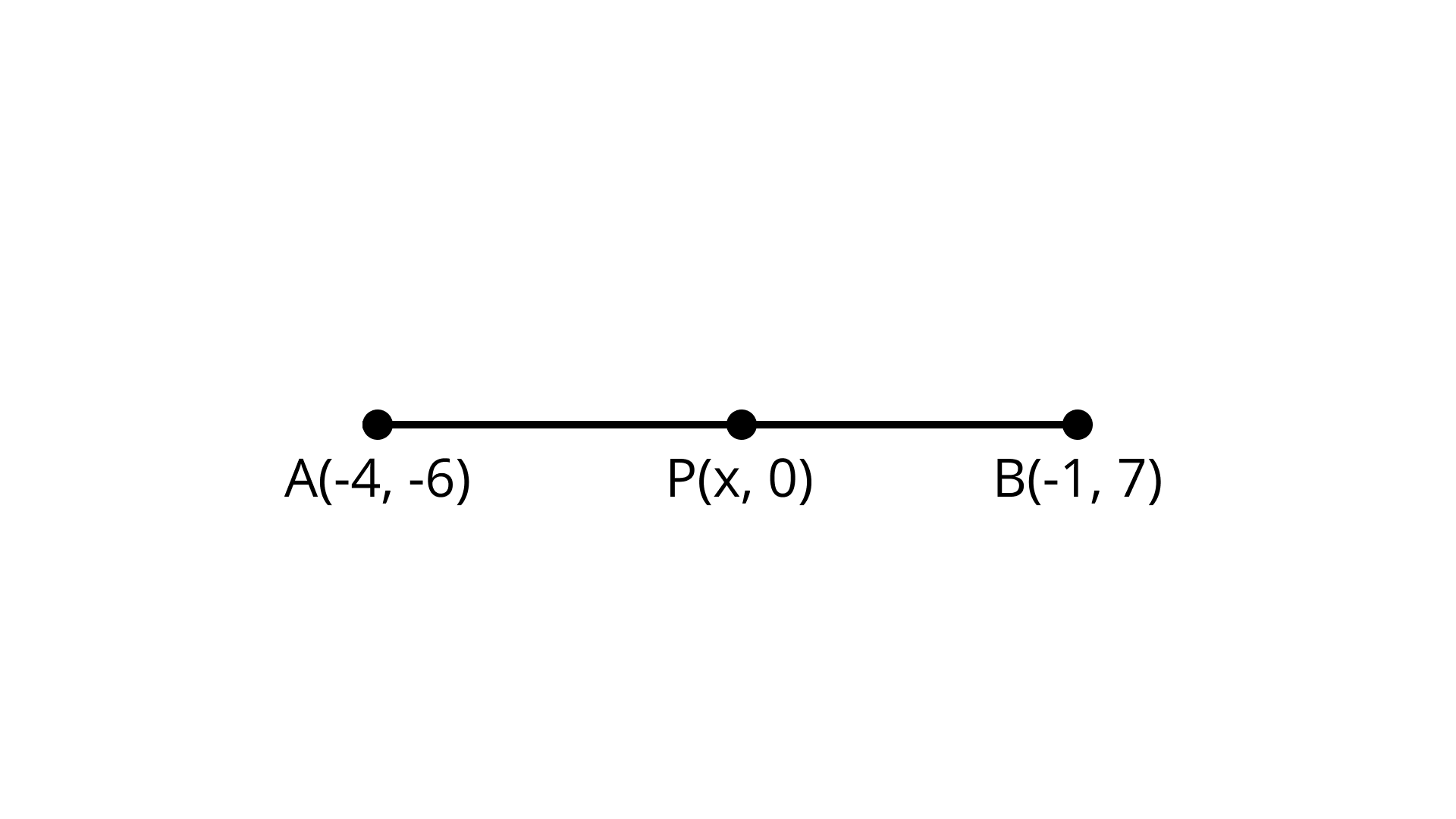
Let the point on $x$ -axis $(x,0)$ when divides the given points $( - 4, - 6)$ and $( - 1, 7)$ in the
Ratio $k:1$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = A( - 4, - 6)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = B( - 1,7)$
${m_1} = k,{m_2} = 1$
Using section formula, we have $P(x,0) = \left[ {\dfrac{{ - k - 4}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{7k - 6}}{{k + 1}}} \right]$
By comparing the left-hand side and the right-hand side we get $\dfrac{{7k - 6}}{{k + 1}} = 0$
$7k - 6 = 0$
$k = \dfrac{6}{7}$
$x = \dfrac{{ - k - 4}}{{k + 1}} = \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{6}{7} - 4}}{{\dfrac{6}{7} + 1}} = \dfrac{{ - 6 - 28}}{{6 + 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 34}}{{13}}$
The required ratio is $6:7$ $Co - ordinate of P\left( {\dfrac{{ - 34}}{{13}},0} \right)$
11. Find the ratio in which the point $P\left( {\dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{5}{{12}}} \right)$ divides the line segment joining the points $ A\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)$ and $B (2, - 5)$.
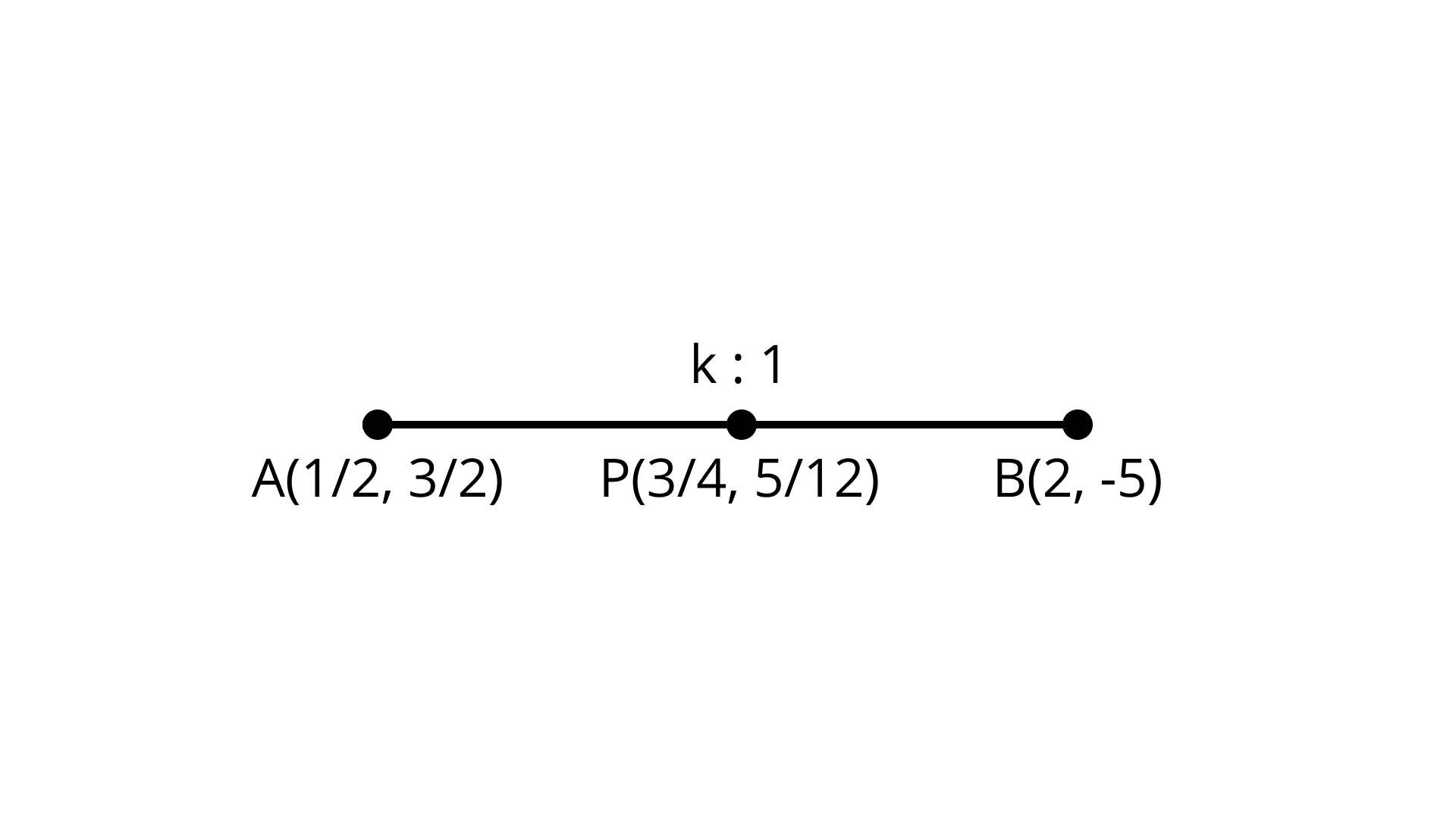
Let the point $P\left( {\dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{5}{{12}}} \right)$ divides the line segment joining the joining the points $A\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)$ and
$B(2, - 5)$ In the ratio $k:1$.
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (2, - 5)$
Using section formula, we have
$\left( {\dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{5}{{12}}} \right) = \left[ {\dfrac{{2k + 1/2}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{ - 5k + 3/2}}{{k + 1}}} \right]$
$\left( {\dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{5}{{12}}} \right) = \left[ {\dfrac{{4k + 1}}{{2k + 1}},\dfrac{{ - 10k + 3}}{{2k + 2}}} \right]$
$\dfrac{{4k + 1}}{{2k + 1}} = \dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{{ - 10k + 3}}{{2k + 2}} = \dfrac{5}{{12}}$
$16k + 4 = 6k + 6 - 120k + 36 = 10k + 10$
$16k - 6k = 6 - 4 - 130k = - 26$
$k = \dfrac{2}{{10}} = \dfrac{1}{5}$
Therefore the required ratio is $1:5$
12. If $P (9a - 2, - b)$ divides line segment joining $A (3a + 1, - 3)$ and $B (8a,5)$ in the ratio $3:1$, find the values of a and b.
Ans: $a = 1$ and $b = - 3$
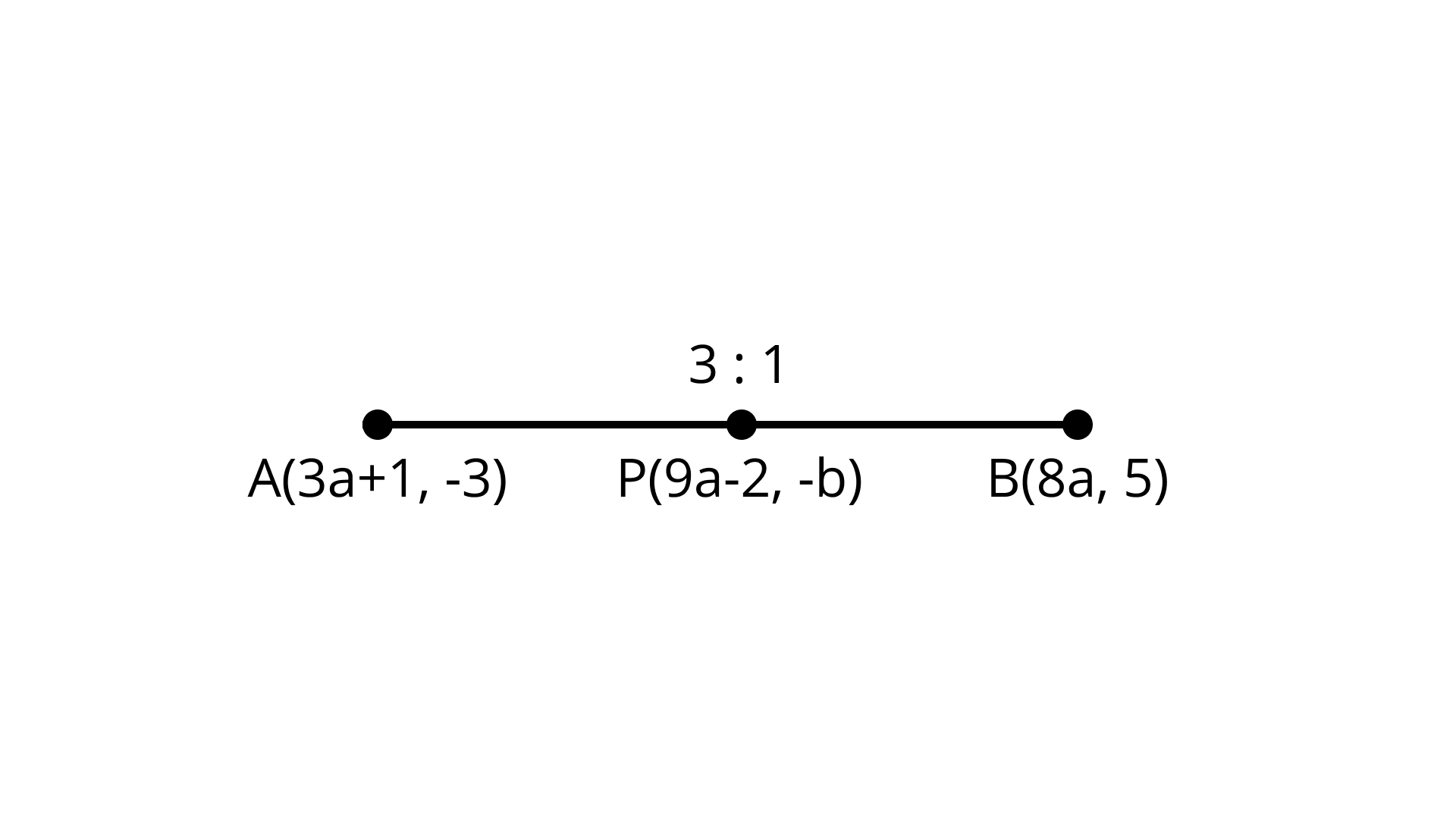
Point $P (9a - 2, - b)$ divides line segment joining the points $A (3a + 1, - 3)$ and $B (8a,5)$
In ration $3:1$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (3a + 1, - 3)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (8a,5)$
${m_1} = 3,{m_2} = 1$
$(9a - 2, - b) = \left[ {\dfrac{{24a + 3a + 1}}{4},\dfrac{{15 - 3}}{4}} \right]$
$(9a - 2, - b) = \left[ {\dfrac{{27a + 1}}{4},\dfrac{{12}}{4}} \right]$
Equate left-hand side and the right-hand side we get $9a - 2 = \dfrac{{27a + 1}}{4}, - b = \dfrac{{12}}{4}$
$36a - 8 = 27a + 1, - b = 3$
$9a = 9,b = - 3$
$a = \dfrac{9}{9}$
$a = 1$ And $b = - 3$
13. If $P(a, b)$ is the mid-point of the line segment joining the points $A(10, - 6)$ and $B(k, 4)$ and $a - 2b = 18$ , find the value of k and the distance AB.
Ans: $2\sqrt {61}$
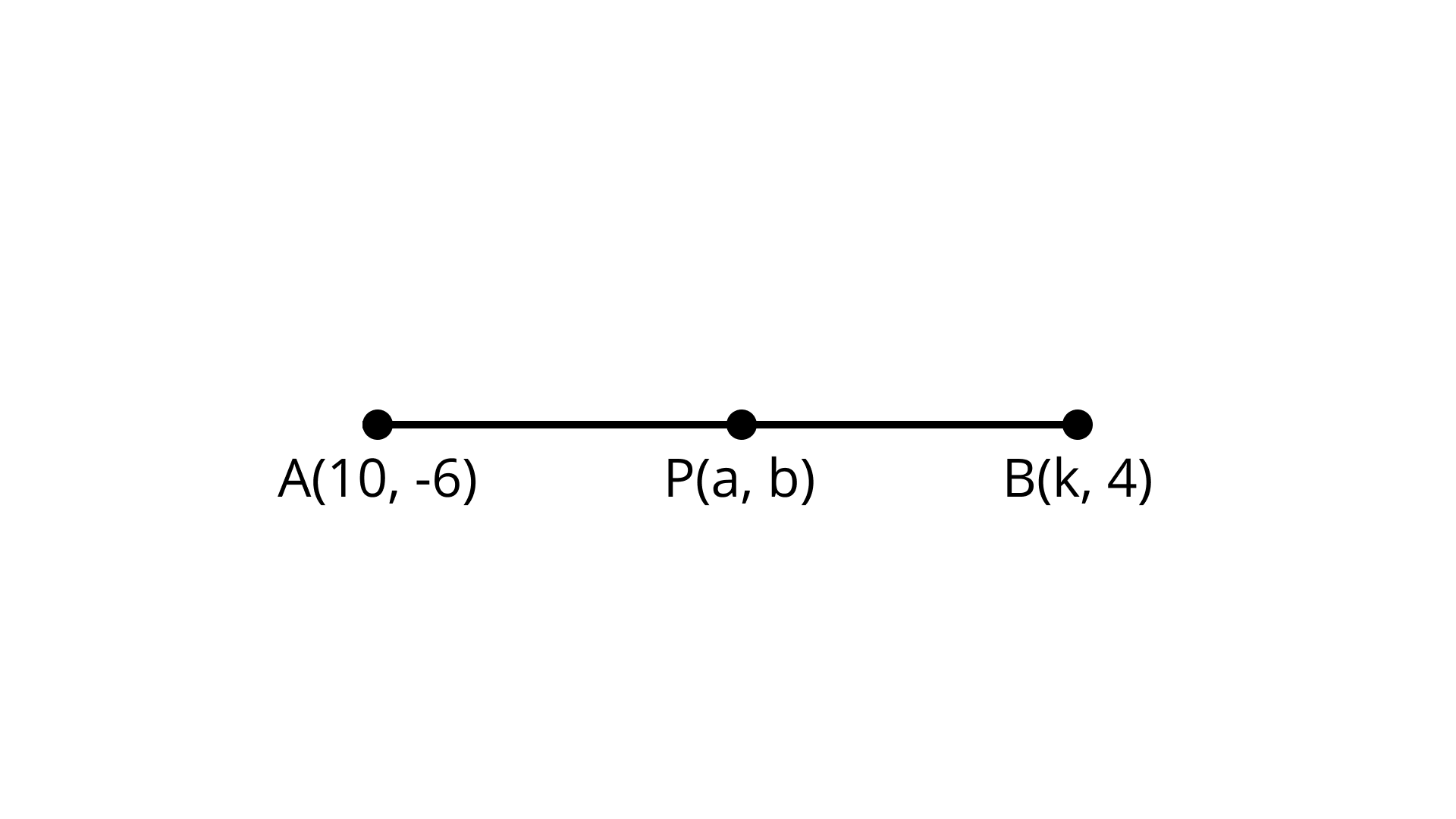
Mid - point formula: $x = \dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},y = \dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}$
Point $P(a, b)$ divide $A(10, - 6)$ and $B(k, 4)$ in two equal parts. $a = \dfrac{{10 + k}}{2},b = \dfrac{{ - 6 + 4}}{2} = \dfrac{{ - 2}}{2} = - 1$
Given: $a - 2b = 18$
Put $b = - 1$
$a - 2( - 1) = 18$
$a = 18 - 12$
$a = 16$
Now, $a = \dfrac{{10 + k}}{2}$
$16 = \dfrac{{10 + k}}{2}$
$32 = 10 + k$
$32 - 10 = k$
$22 = k$
$\therefore A(10, - 6), B(22, 4)$
$AB = \sqrt {{{(22 - 10)}^2} + {{(4 + 6)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {{{(12)}^2} + {{(10)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {144 + 100}$
$= \sqrt {244}$
$= 2\sqrt {61}$
14: The Centre of a circle is $A(2a, a - 7)$. Find the values of a if the circle passes through the point $B(11, - 9)$ and has diameter $10\sqrt 2$ units.
Ans: $a = 5, 3$
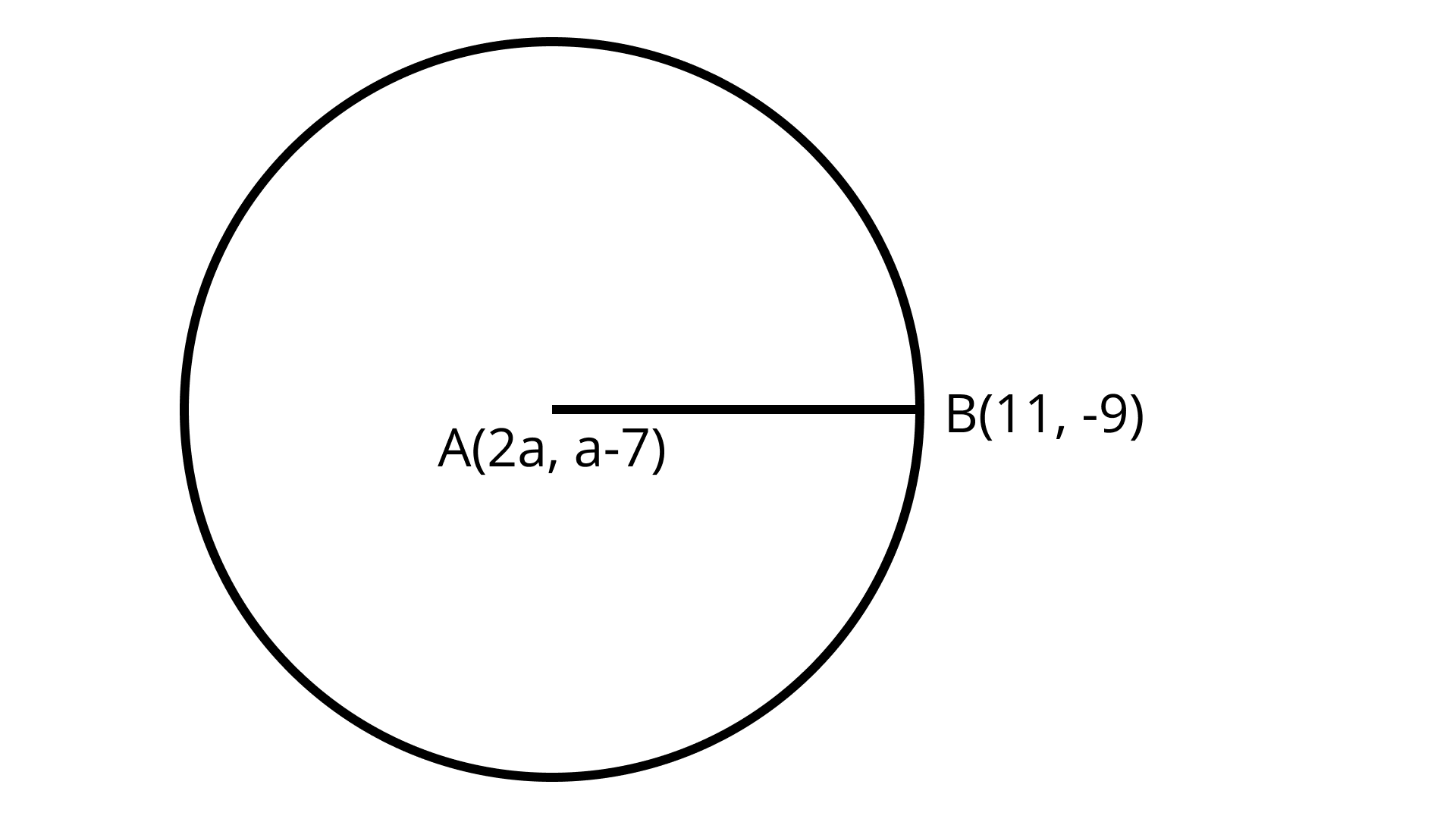
Distance formula $= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$ Given points area $A(2a, a - 7)$ and $B(11, - 9)$
Diameter $= 10 \sqrt 2$
Radius $= \dfrac{{10\sqrt 2 }}{2} = 5\sqrt 2$
Distance $= 5\sqrt 2$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (2a, a - 7)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (11, - 9)$
$= \sqrt {{{(11 - 2a)}^2} + {{( - 9 - a + 7)}^2}} = (5\sqrt 2 )$
Squaring both sides ${(11 - 2a)^2} + {( - 2 - a)^2} = {(5\sqrt 2 )^2}$
$121 + 4{a^2} - 44a + 4 + {a^2} + 4a = 50$
$502 - 40a + 125 - 50 = 0$
$5{a^2} - 40a + 75 = 0$
Dividing by 5 we get
${a^2} - 8a + 15 = 0$
${a^2} - 5a - 3a + 15 = 0$
$a(a - 5) - 3(a - 5) = 0$
$(a - 5)(a - 3) = 0$
15. The line segment joining the points $A(3, 2)$ and $B(5, 1)$ is divided at the point P in the ratio 1:2 and it lies on the line $3x - 18y + k = 0$. Find the value of k.
Ans: $k = 19$
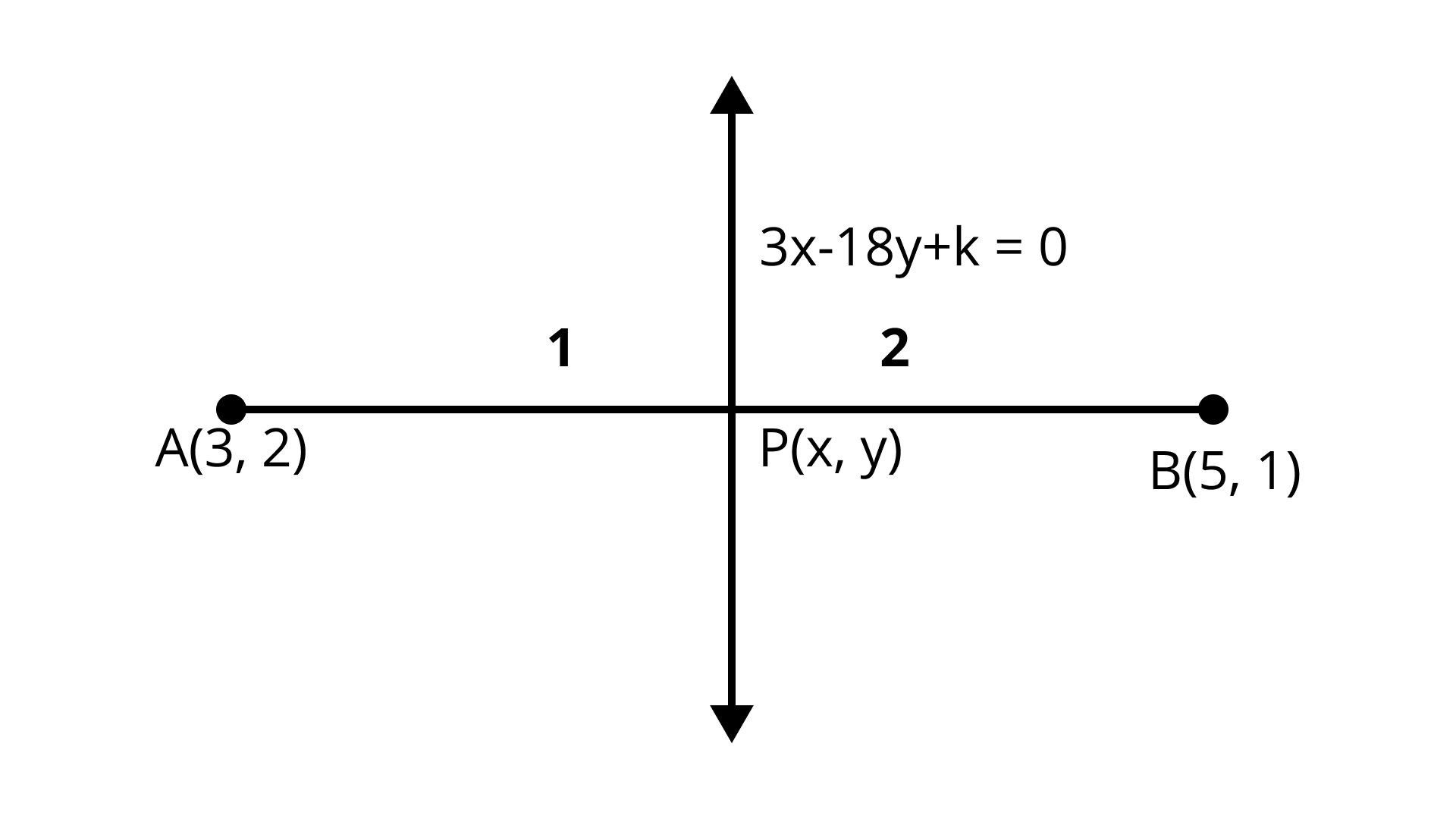
Here points $A(3, 2)$ and $B(5, 1)$ is divided at the point $P$ in the ratio 1:2
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (3,2),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (5, 1)$
${m_1} = 1,{m_2} = 2$ By section formula we have $P(x,y) = \left[ {\dfrac{{1 \times 5 + 2 \times 3}}{{1 + 2}},\dfrac{{1 \times 1 + 2 \times 2}}{{1 + 2}}} \right]$
$= \left[ {\dfrac{{5 + 6}}{3},\dfrac{{1 + 4}}{3}} \right]$
$= \left[ {\dfrac{{11}}{3},\dfrac{5}{3}} \right]$
Line is $3x - 18y + k = 0 \ldots \ldots (1)$
Put point $P\left( {\dfrac{{11}}{3},\dfrac{5}{3}} \right)$ in $(1)$
$Put x = \dfrac{{11}}{3},y = \dfrac{5}{3}$
$3\left( {\dfrac{{11}}{3}} \right) - 18\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}} \right) + k = 0$
$11 - 30 + k = 0$
$ - 19 + k = 0$
16. If $D\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2},\dfrac{5}{2}} \right),E\left( {7,3} \right) and F\left( {\dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{7}{2}} \right)$ dare the midpoints of sides of $\Delta ABC$ find the area of the $\Delta ABC$.
Ans: $11Sq. Units$ Units
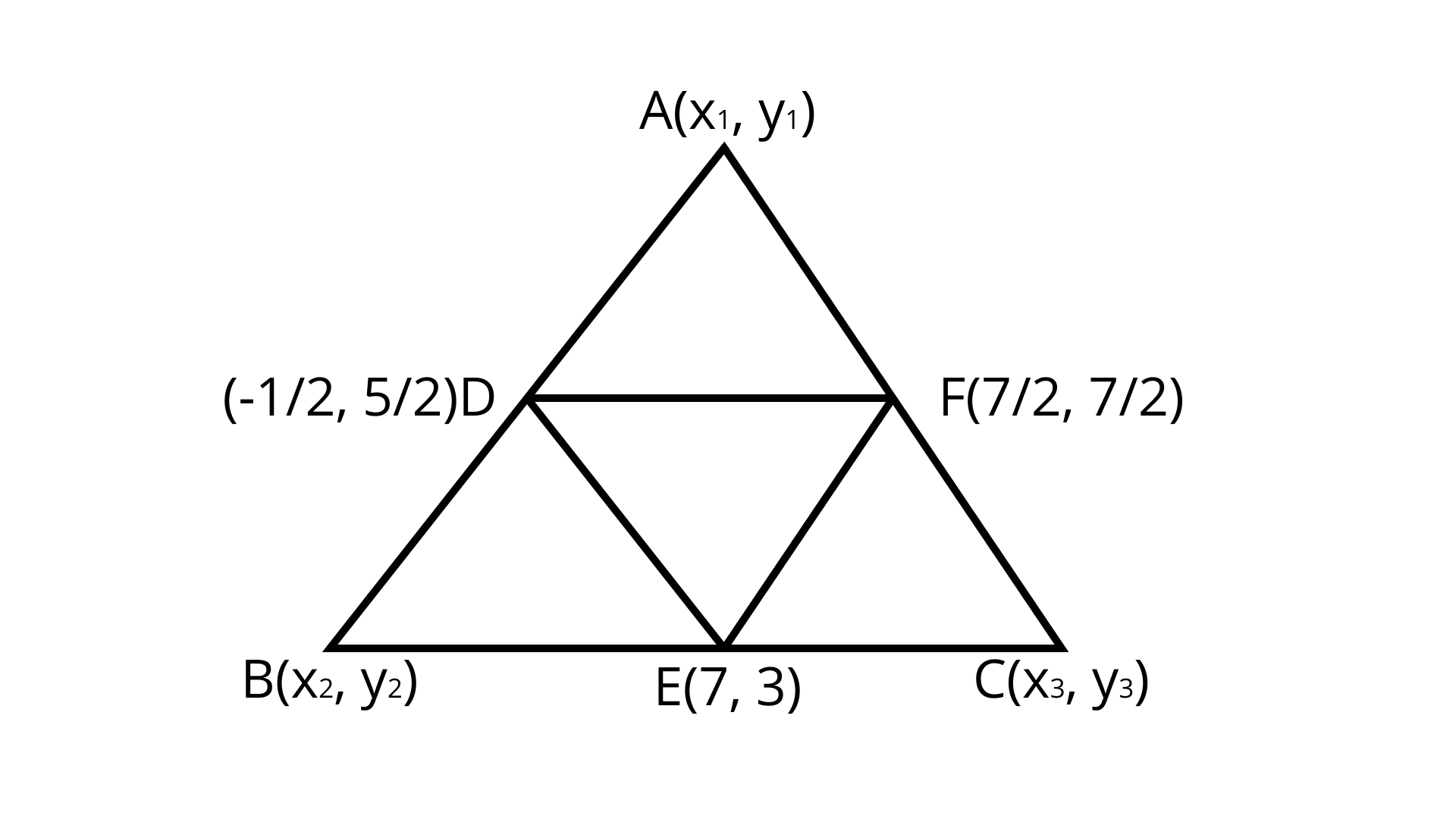
$D$ Is mid-point of $AB$ using mid-point formula:
$- \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{5}{2} = \dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}$
${x_1} + {x_2} = - 1 \ldots \ldots $ (1)
$5 = {y_1} + {y_2} \ldots (2)$
${\text{E}}$ Is mid-point of BC using mid-point formula: $\dfrac{{{x_2} + {x_3}}}{2} = 7,\dfrac{{{y_2} + {y_3}}}{2} = 3$
${x_2} + {x_3} = 14 \ldots \ldots (3)$
${y_2} + {y_3} = 6 \ldots .(4)$
${\text{F}}$ is mid-point of ${\text{AB}}$ using mid-point formula:
$\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_3}}}{2} = \dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_3}}}{2} = \dfrac{7}{2}$
${x_1} + {x_3} = 7 \ldots .(5)$
${y_1} + {y_3} = 7 \ldots \ldots (6)$
Simplifying the above equations for values of ${x_1},{y_1},{x_2},{y_2},{x_3}$ and ${y_3}$
${x_1} + {x_2} = - 1$
${x_3} + {x_3} = 14$ {Using $(1)$ and $(3)\}$
${x_1} - {x_3} = - 15 \ldots ..\left( 7 \right)$
Adding equation (5) and (7)
$2{x_1} = - 8$
${x_1} = - 4$
Put ${x_1} = 4$ in (1) we
$- 4 + {x_2} = - 1$
${x_2} = - 1 + 4 = 3$
Put ${x_2} = 3$ in (3)
$3 + {x_3} = 14$
${x_3} = 11$
Using equation (4) from equation (4) ${y_1} - {y_3} = --1 .....(8)$ Adding equation (6) and (8) $2{y_1} = 6$ ${y_1} = 3$ Put ${y_1} = 3$ in eqn. (2) $5 - 3 = {y_2}$ $2 = {y_2}$ Put ${y_2} = 2$ in eqn. (4) $2 + {y_3} = 6$ ${y_3} = 6 - 2$ ${y_3} = 4$ Hence, ${x_1} = - 4$ y $1 = 3$ ${x_2} = 3{y_2} = 2$ ${x_3} = 11{y_3} = 4$ $A = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 4,3),B = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (3,2),C = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = (11,4)$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}[( - 4)( - 2) + 3(1) + 11(1)]$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}[8 + 3 + 11]$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}[22]$ $= 11 Sq.Units$
17. The points $A\left( {2,9} \right), B\left( {a,5} \right), C \left( {5,5} \right)$ are the vertices of a $\Delta ABC$ right angled at B. Find the values of a and hence the area of $\Delta ABC$
Ans: $8 Sq. Units$
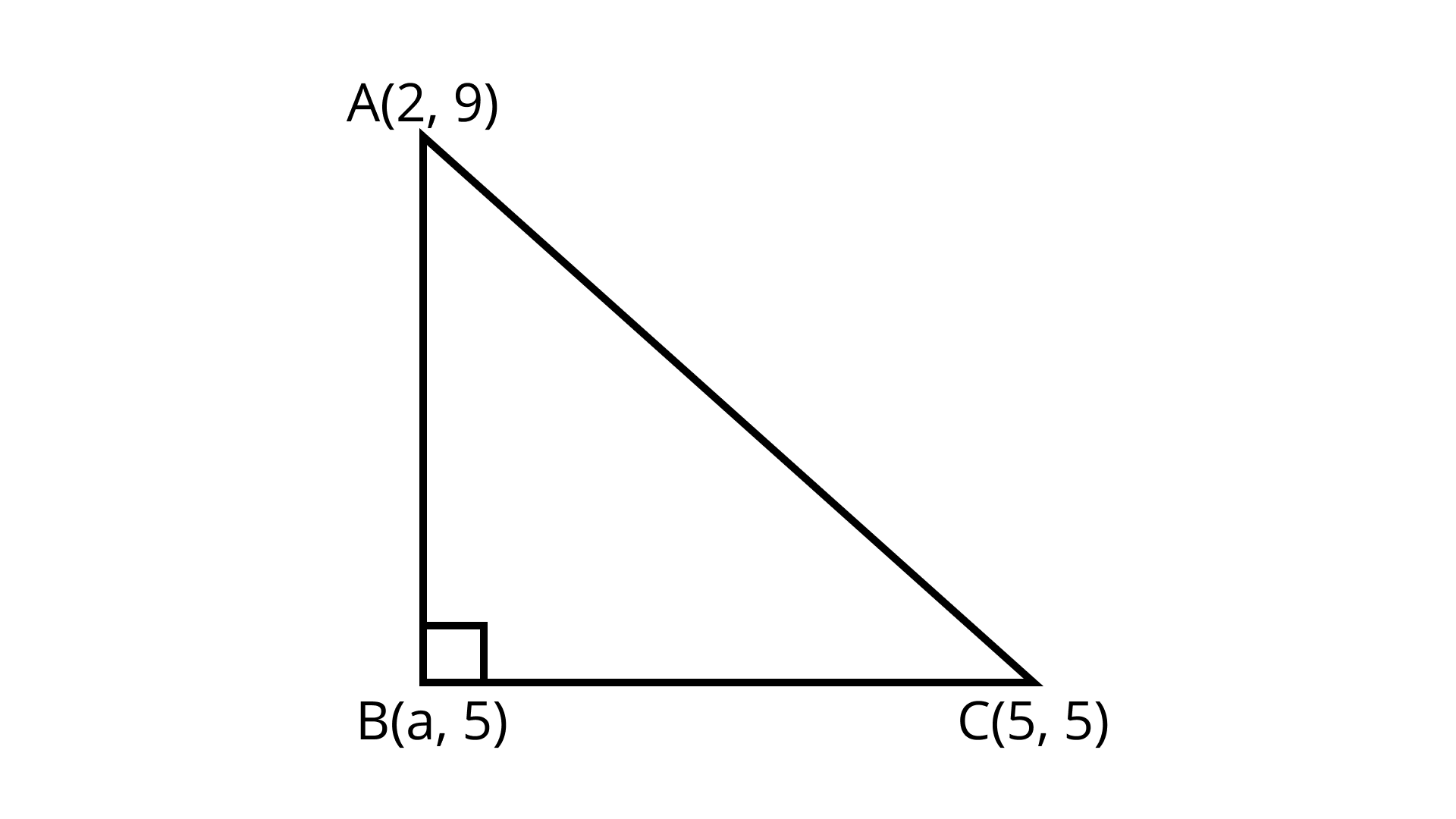
Distance formula $= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$\Delta ABC$ is a right angle triangle by using Pythagoras theorem
${(AC)^2} = {(BC)^2} + {(AB)^2}$
$\left[ {{{(5 - 2)}^2} + {{(5 - 9)}^2}} \right] = \left[ {{{(2 - a)}^2} + {{(9 - 5)}^2}} \right] + \left[ {{{(a - 5)}^2} + {{(5 + 5)}^2}} \right]$
${(3)^2} + {( - 4)^2} = 4 + {a^2} - 4a + {(4)^2} + {a^2} + 25 - 10a$
$9 + 16 = 4 + {a^2} - 4a + 16 + {a^2} + 25 - 10a$
$25 = 2{a^2} - 14a + 45$
$2{a^2} - 14a + 45 - 25 = 0$
$2{a^2} - 14a + 20 = 0$
Dividing by 2 we have
${a^2} - 7a + 10 = 0$
${a^2} - 5a - 2a + 10 = 0$
$a(a - 5) - 2(a - 5) = 0$
$(a - 5)(a - 2) = 0$
$a = 5,a = 2$
$a = 5$ Is not possible because if $a = 5$ then point $B$ and $C$ coincide.
$\therefore a = 2$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[2(5 - 5) + 2(5 - 9) + 5(9 - 5)]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[0 - 8 + 20]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[16]$
$= 8 Sq. Units$
18. Find the coordinates of the point R on the line segment joining the points $P\left( {--1,3} \right)$ and $Q\left( {2,5} \right)$ such that $PR = \dfrac{3}{5}PQ$
Ans: $\left( {\dfrac{4}{5},\dfrac{{21}}{5}} \right)$
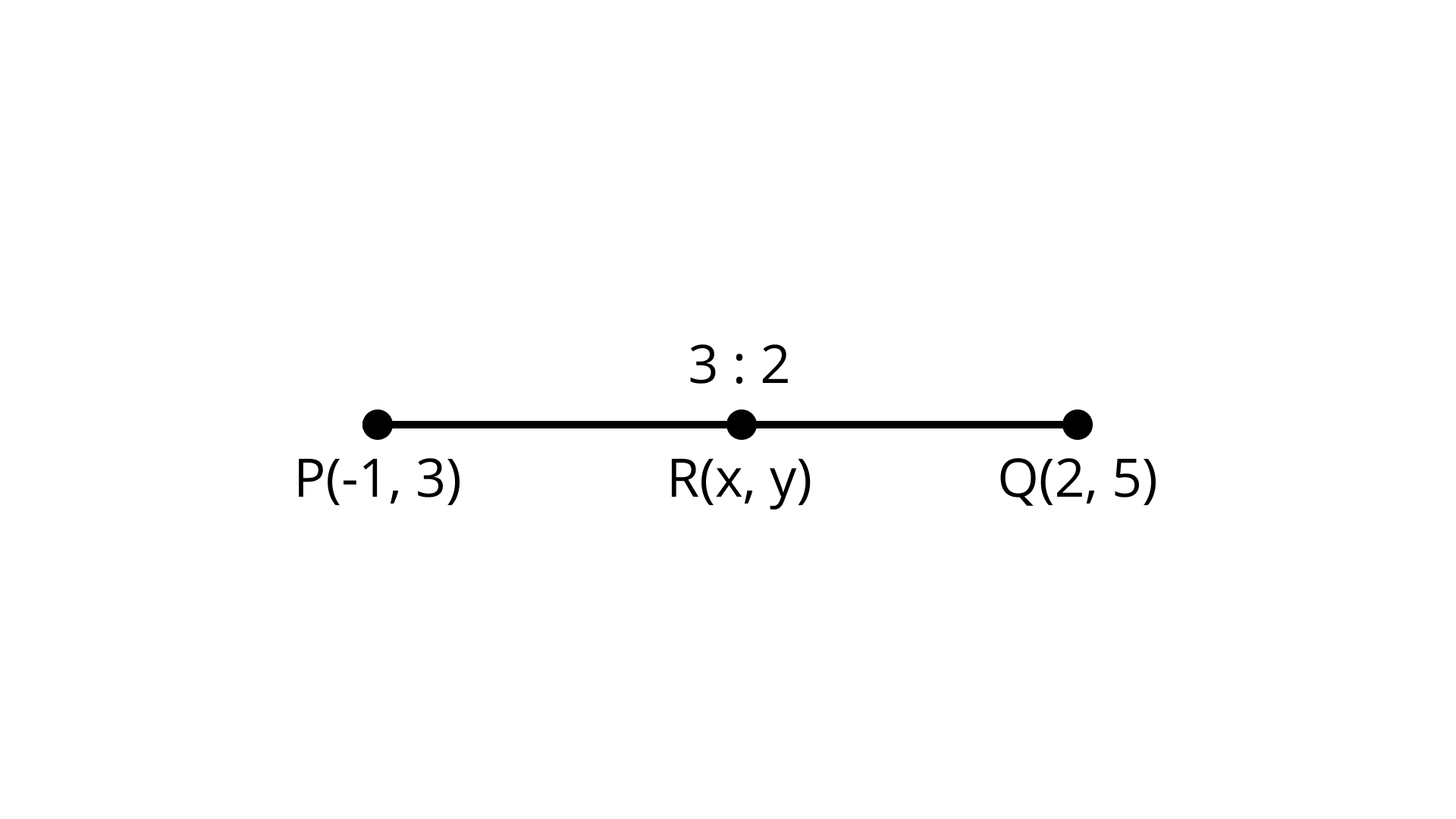
According to question let $R = (x,y)$ and $PR = \dfrac{3}{5}PQ$
$\dfrac{{PQ}}{{PR}} = \dfrac{3}{5}$
${\text{R}}$ Lies on $PQ \therefore {\text{ }}PQ = PR + RQ$
$\dfrac{{PR + PQ}}{{PR}} = \dfrac{5}{3}$
On dividing separately we get $1 + \dfrac{{RQ}}{{PR}} = \dfrac{5}{3}$
$\dfrac{{RQ}}{{PR}} = \dfrac{5}{3} - 1 = \dfrac{2}{3}$
$\Rightarrow PR:RQ = 3:2$
Hence, $R$ divides PQ in ratio 3: 2 using section formula we have
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = ( - 1, 3)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (2, 5)$
${m_1} = 3,{m_2} = 2$
$R(x,y) = \left( {\dfrac{{6 - 2}}{5},\dfrac{{15 + 6}}{5}} \right)$
$R(x,y) = \left( {\dfrac{4}{5},\dfrac{{21}}{5}} \right)$
Here co- ordinates of ${\text{R}}$ is $\left( {\dfrac{4}{5},\dfrac{{21}}{5}} \right)$
19. Find the values of k if the points $A(k + 1, 2k), B(3k, 2k + 3)$ and $C(5k - 1, 5k)$are collinear.
Ans: $2,\dfrac{1}{2}$ If points $A(k + 1, 2k),B(3k, 2k + 3)$ and $C(5k - 1, 5k)$ are collinear then area of triangle is equal to zero
$[(k + 1)(2k + 3 - 5k) + 3k(5k - 2k) + (5k - 1)(2k - 2k - 3)] = 0$
$[(k + 1)(3 - 3k) + 3k(3k) + 5(k - 1)( - 3)] = 0$
$\left[ {3k - 3{k^2} + 3 - 3k + 9{k^2} - 15k + 3} \right] = 0$ $6{k^2} - 15k + 6 = 0$ $6{k^2} - 12k - 3k + 6 = 0$ $6k(k - 2) - 3(k - 2) = 0$ $(k - 2)(6k - 3)$ $k = 2,k = \dfrac{3}{6}$ $= \dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence, values of ${\text{k}}$ are $2,\dfrac{1}{2}$
20. Find the ratio in which the line $2x + 3y - 5 = 0$ divides the line segment joining the points $A(8, - 9)$ and $B(2,1)$. Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Ans: $P\left( {\dfrac{8}{3},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right)$
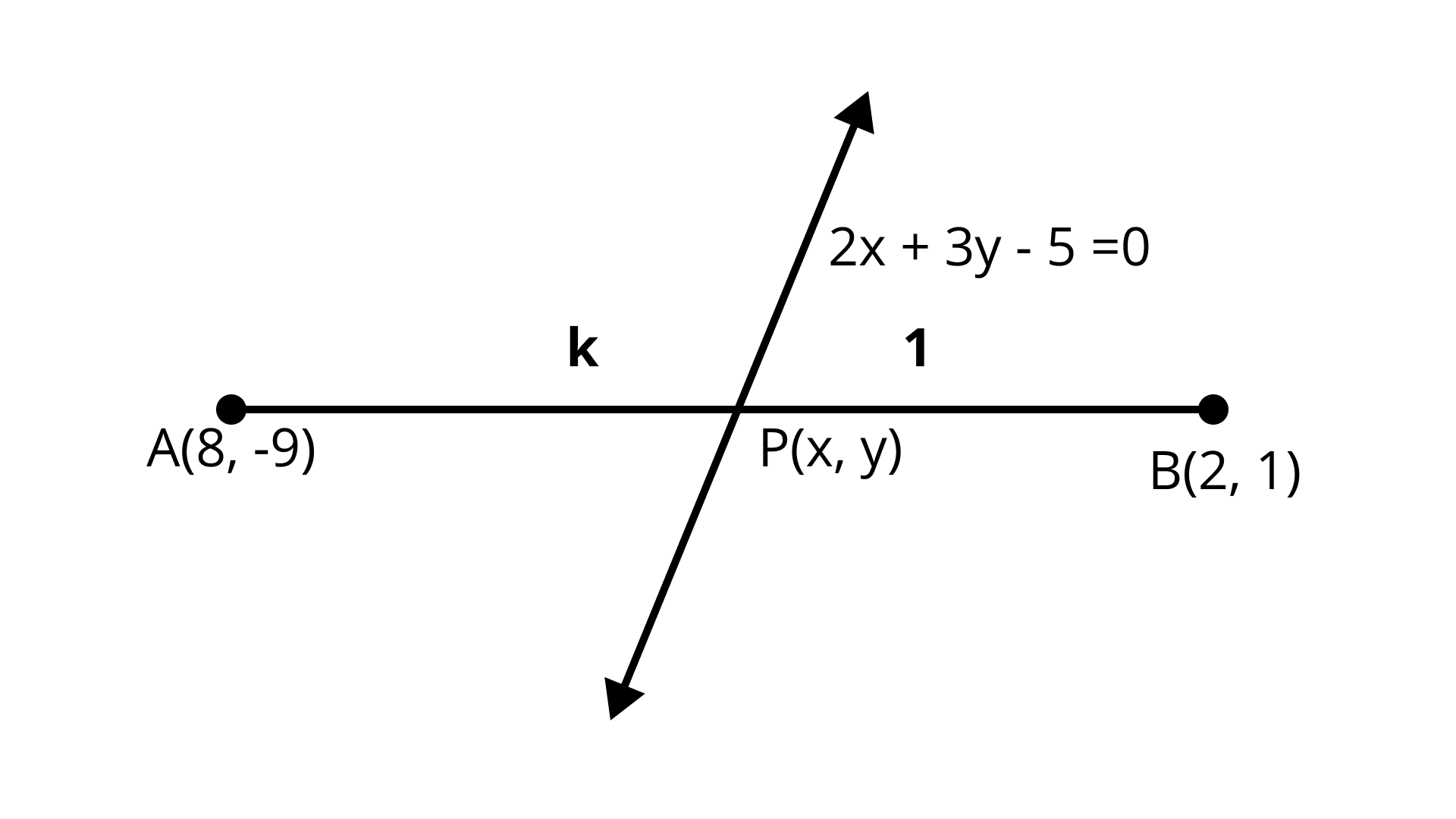
Let point $P(x, y)$ divides the line segment joining the points $A(8, - 9)$ and $B(2, 1)$ in ratio $k:1$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (8, - 9)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (2,1)$
${m_1}:{m_2} = k:1$
Using section formula we have $P(x,y) = \left[ {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right]$
Given equation is $2x + 3y - 5 = 0 \ldots (2)$
Put values of $x$ and $y$ in eqn. (2) $2\left[ {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}}} \right] + 3\left[ {\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right] - 5 = 0$
$2(2k + 3) + 3(k - 9) - 5(k + 1) = 0$ $4k + 16 + 3k - 27 - 5k - 5 = 0$ $2k - 16 = 0$ $k = 8$
Hence, P divides the line in ration $8:1$ put ${\text{k}} = 5$ in eqn. (1) $(x, y) = \left[ {\dfrac{{2(8)}}{{8 + 1}},\dfrac{{8 - 9}}{{8 + 1}}} \right]$ Required point is $P\left( {\dfrac{8}{3},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right)$
EXERCISE 7.4:
1. If $( - 4, 3)$ and $(4, 3)$ are two vertices of an equilateral triangle, find the coordinates of the third vertex, given that the origin lies in the interior of the triangle.
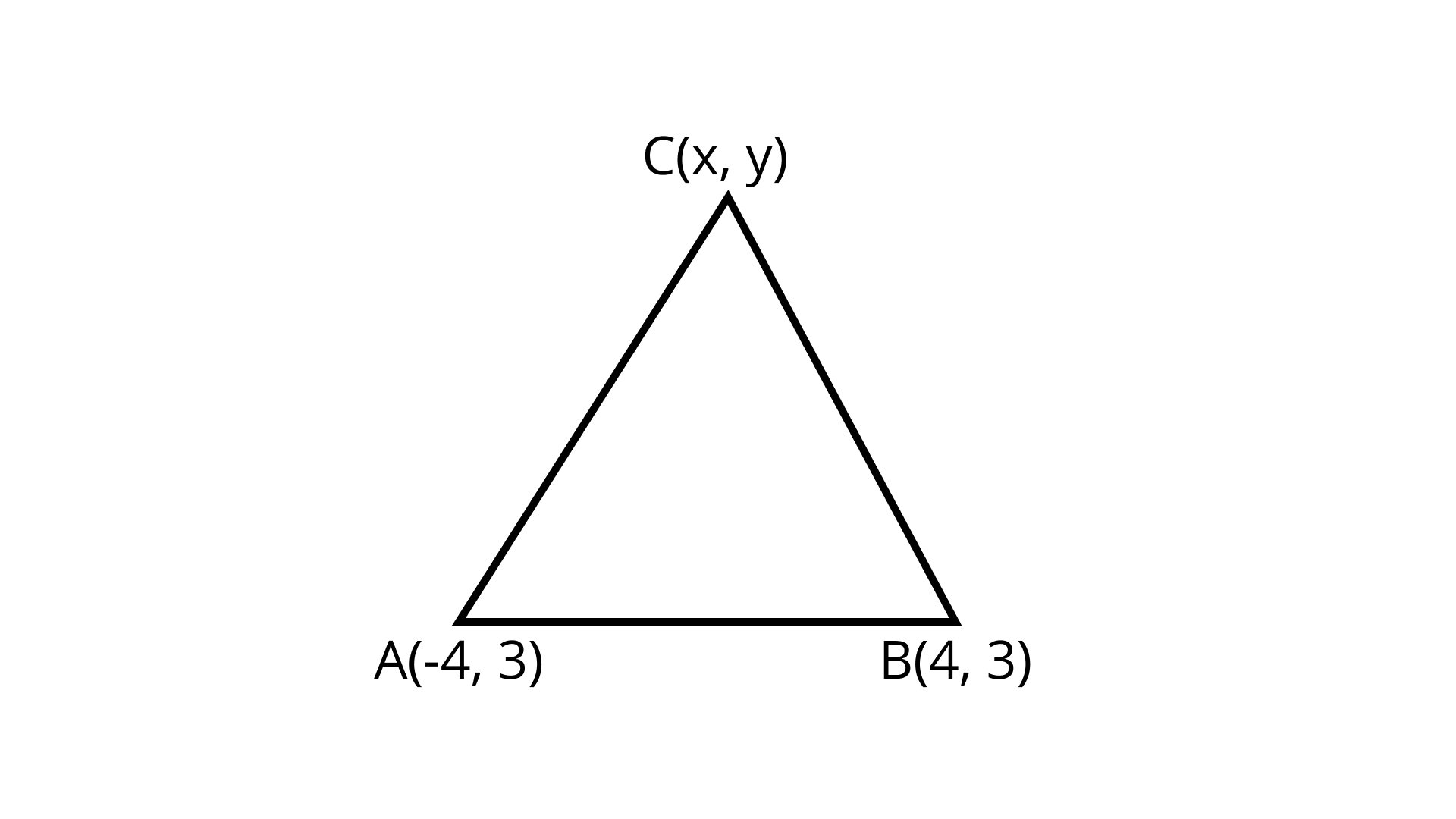
Ans: $\left( {0,3 - 4\sqrt 3 } \right)$
In equilateral triangle $AB = BC = AC$
$AC = \sqrt {{{(x + 4)}^2} + {{(y - 3)}^2}}$
$AC = \sqrt {{x^2} + 16 + 8x + {y^2} + 9 - 6y}$
$\left( {\because {\text{ }}{{(a + b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab{\text{and}}\left[ {{{(a - b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right]} \right)$
$BC = \sqrt {{{(x - 4)}^2} + {{(y - 3)}^2}}$
$BC = \sqrt {{x^2} + 16 - 8x + {y^2} + 9 - 6y}$ $\left( {\because {{(a - b)}^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)$
${\text{AC}} = {\text{BC}}$
$\sqrt {{x^2} + 16 + 8x + {y^2} + 9 - 6y} = \sqrt {{x^2} + 16 - 8x + {y^2} + 9 - 6y}$
Squaring both side
$8x + 8x = 0$
$C = (0,y)$
Length of $AB = \sqrt {{{(4 + 4)}^2} + {{(3 - 3)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {{{(8)}^2}} = 8$
$\sqrt {{x^2} + 16 + 8x + {y^2} + 9 - 6y} = 8$
Put$x = 0$, squaring both side
$0 + 16 + 0 + {y^2} + 9 - 6y = 64$
${y^2} - 6y + 25 - 64 = 0$
${y^2} - 6y - 39 = 0$
$y = \dfrac{{6 \pm \sqrt {36 + 156} }}{2}$
$y = \dfrac{{6 - 8\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ (For origin in the interior we take the only term with negative sign)
$y = 3 - 4\sqrt 3$ 2. $A(6,1),B(8,2)$ and $C(9,4)$ are three vertices of a parallelogram $ABCD$. If $E$ is the midpoint of $DC$ , find the area of $\Delta ADE$.
Ans: $\dfrac{3}{4}sq \times units$
The given points $A(6,1), B(8,2)$ and $C(9,4)$ let $D(x,y)$
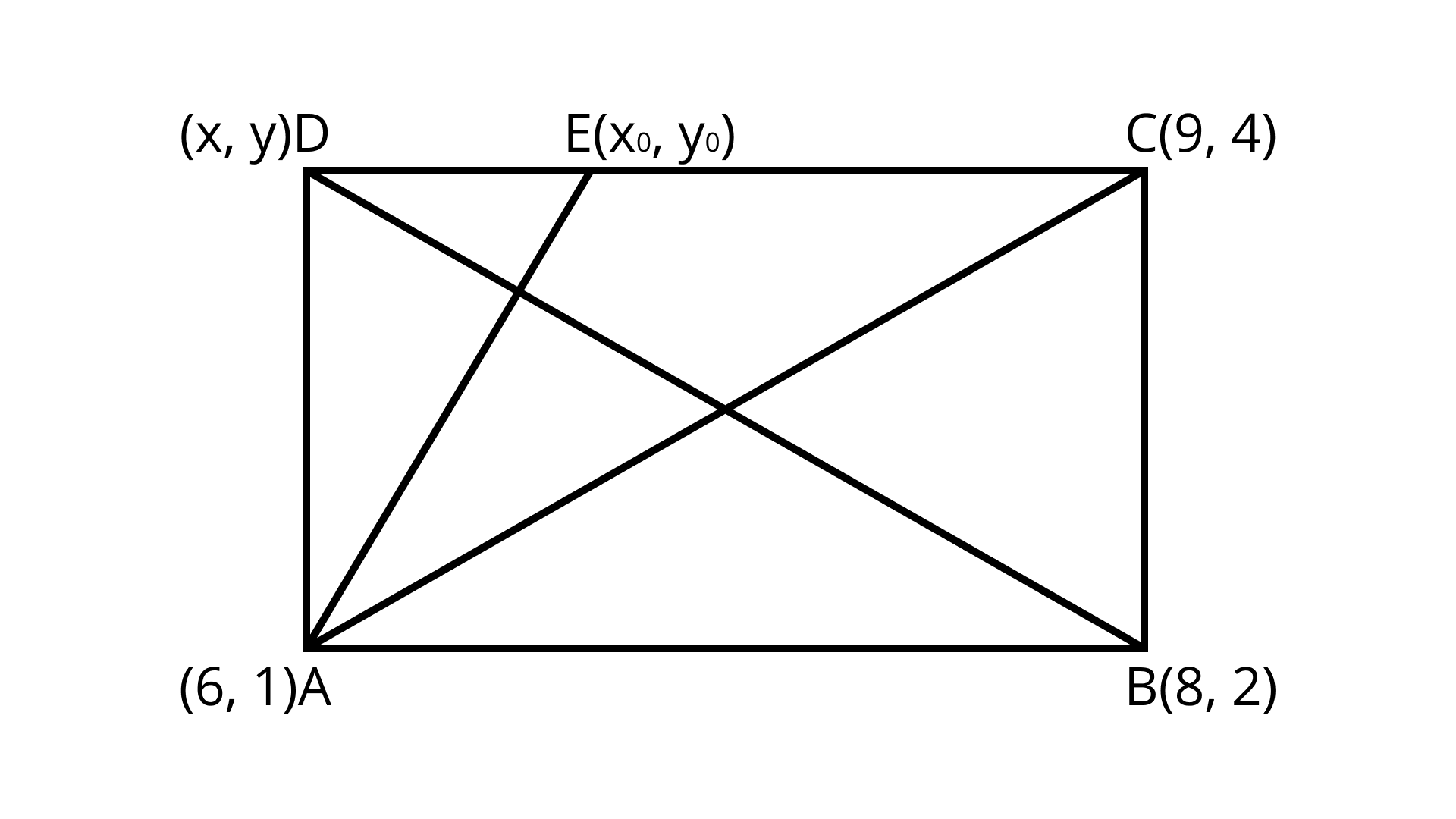
As the diagonal of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Here mid-point of ${\text{AC}} = $ mid-point of BD
$\left( {\dfrac{{6 + 9}}{2},\dfrac{{1 + 4}}{2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{8 + x}}{2},\dfrac{{2 + y}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{2},\dfrac{5}{2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{8 + x}}{2},\dfrac{{2 + y}}{2}} \right)$
$\dfrac{{15}}{2} = \dfrac{{8 + x}}{2}\dfrac{{2 + y}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2}$
$x = 7y = 3$
E is the mid-point of CD
Let $E\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{7 + 9}}{2},\dfrac{{3 + 4}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{16}}{2},\dfrac{2}{7}} \right)$
$E = \left( {8,\dfrac{7}{2}} \right)$
Area of $\Delta ADE = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6\left( {\dfrac{7}{2} - 3} \right) + 8(3 - 1) + 7\left( {1 - \dfrac{7}{2}} \right)} \right]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 8 \times 2 + 7 \times \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3 + 16 - \dfrac{{35}}{2}} \right]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{6 + 32 - 35}}{2}} \right]$
Area of $\Delta ADE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{3}{2}$ $= \dfrac{3}{4}sq units$
(i) The points $A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ and $C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are the vertices of $\Delta ABC$. The median from $A$ meets $BC$ at D. find the coordinates of the point $D$.
(ii) The points $A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ and $C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are the vertices of $\Delta ABC$. Find the coordinates of the point $P$ on AD such that $AP:PD = 2:1$
(iii) The points $A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ and $C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are the vertices of $\Delta ABC$. Find the coordinates of points $Q$ and $R$ on medians $BE$ and $CF$, respectively such that $BQ:QE = 2:1$ and $CR:RF = 2:1$
(iv) The points $A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ and $C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are the vertices of $\Delta ABC.$ what are the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle $ABC?$
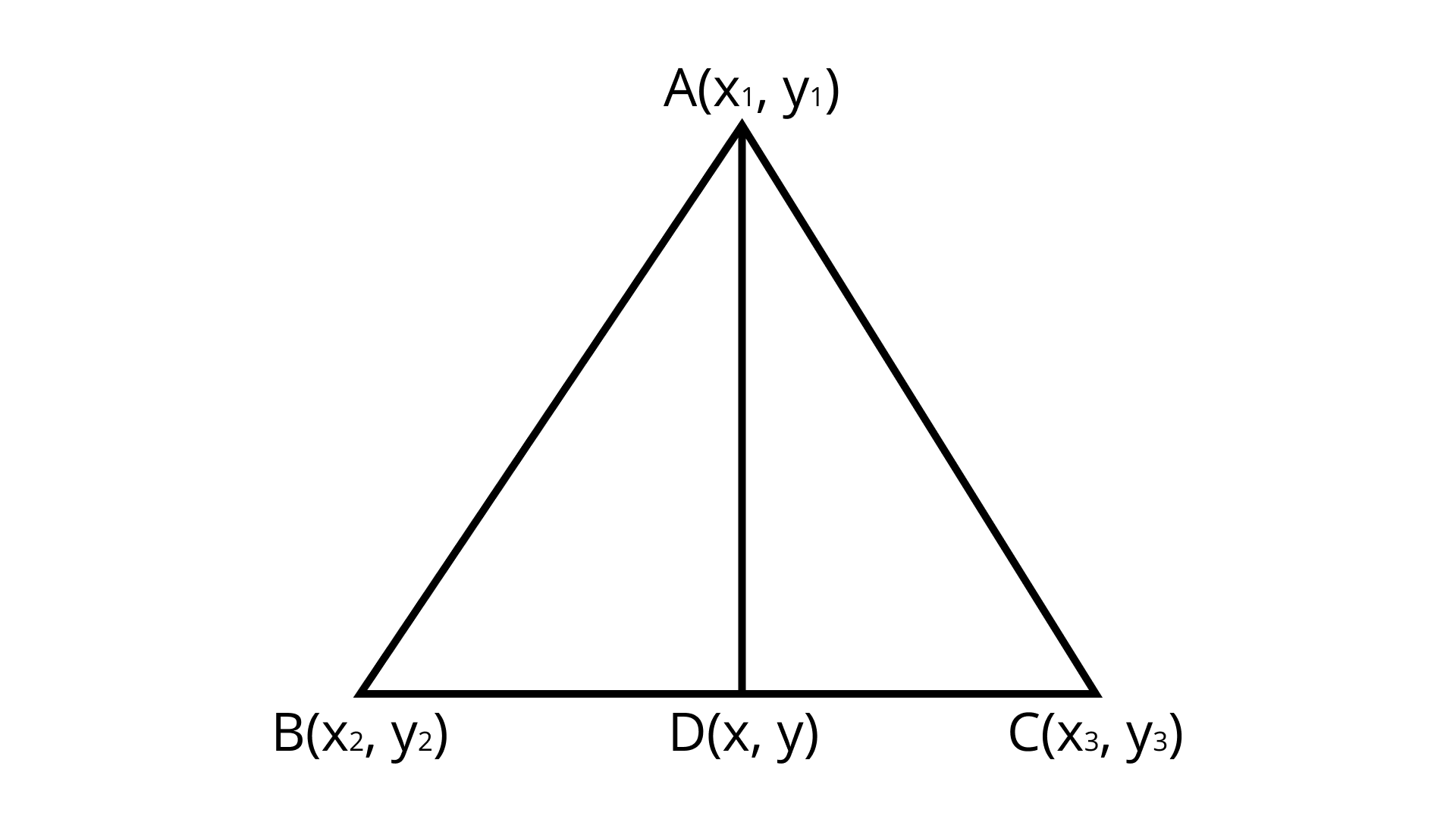
${\text{D}}$ Is the mid-point of ${\text{BC}}$
mid - point formula $= \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Coordinates of $D(x,y) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_2} + {x_3}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_2} + {y_3}}}{2}} \right)$ $\left( {{\text{By midpoint formula}}} \right)$
(ii) Explanation:
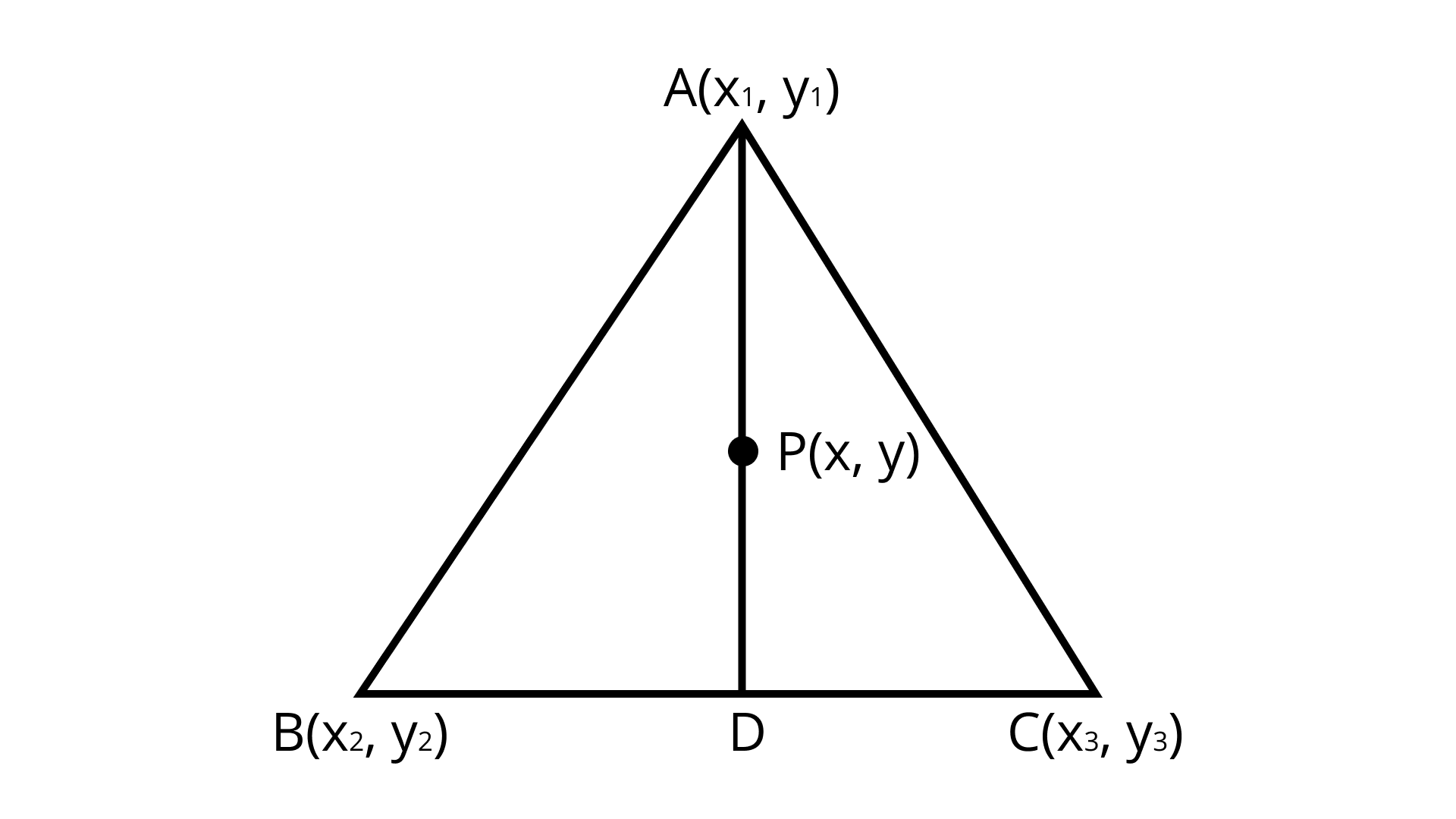
Section formula $= \left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
$D = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_2} + {x_3}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_2} + {y_3}}}{2}} \right)$ (By Midpoint formula)
$P = \left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
$P = \left( {\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{x_2} + {x_3}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {x_1}}}{{2 + 1}},\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{y_2} + {y_3}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {x_1}}}{{2 + 1}}} \right)$
$P = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)$
(iii) Explanation:
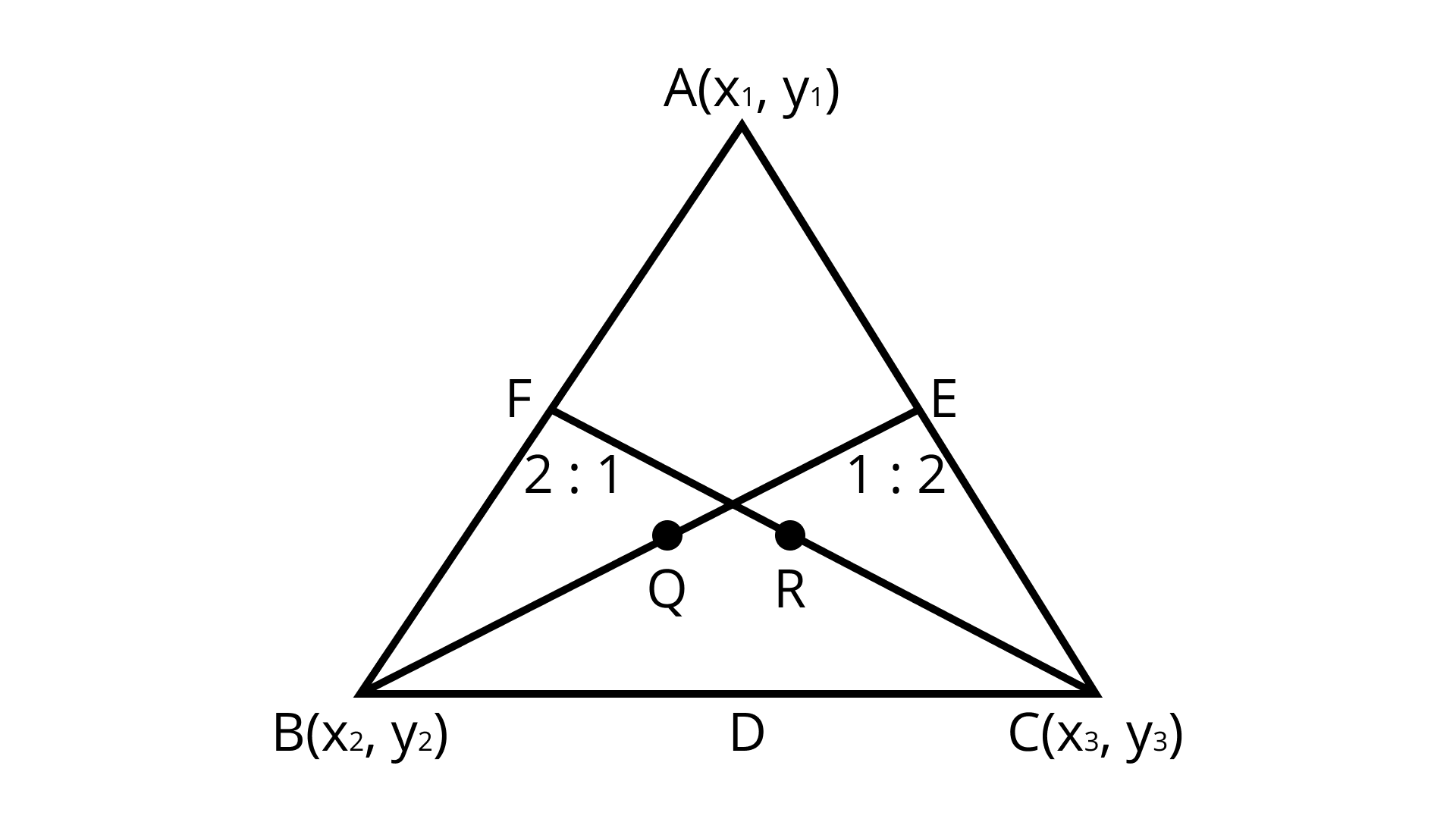
${\text{E}}$ is mid-point of ${\text{AC}}$
$E = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_3}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_3}}}{2}} \right)$
Q divides ${\text{BF}}$ at $ 2:1$
$Q = \left( {\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{x_1} + {x_3}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {x_2}}}{{2 + 1}},\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{y_1} + {y_3}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {y_2}}}{{2 + 1}}} \right)$
$Q = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)$
$R$ Divides CF at $ 2:1$ $R = \left( {\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{x_1} + {x_2}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {x_3}}}{{2 + 1}},\dfrac{{2 \times \dfrac{{\left( {{y_1} + {y_2}} \right)}}{2} + 1 \times {y_3}}}{{2 + 1}}} \right)$
$R = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)$
(iv) Explanation:
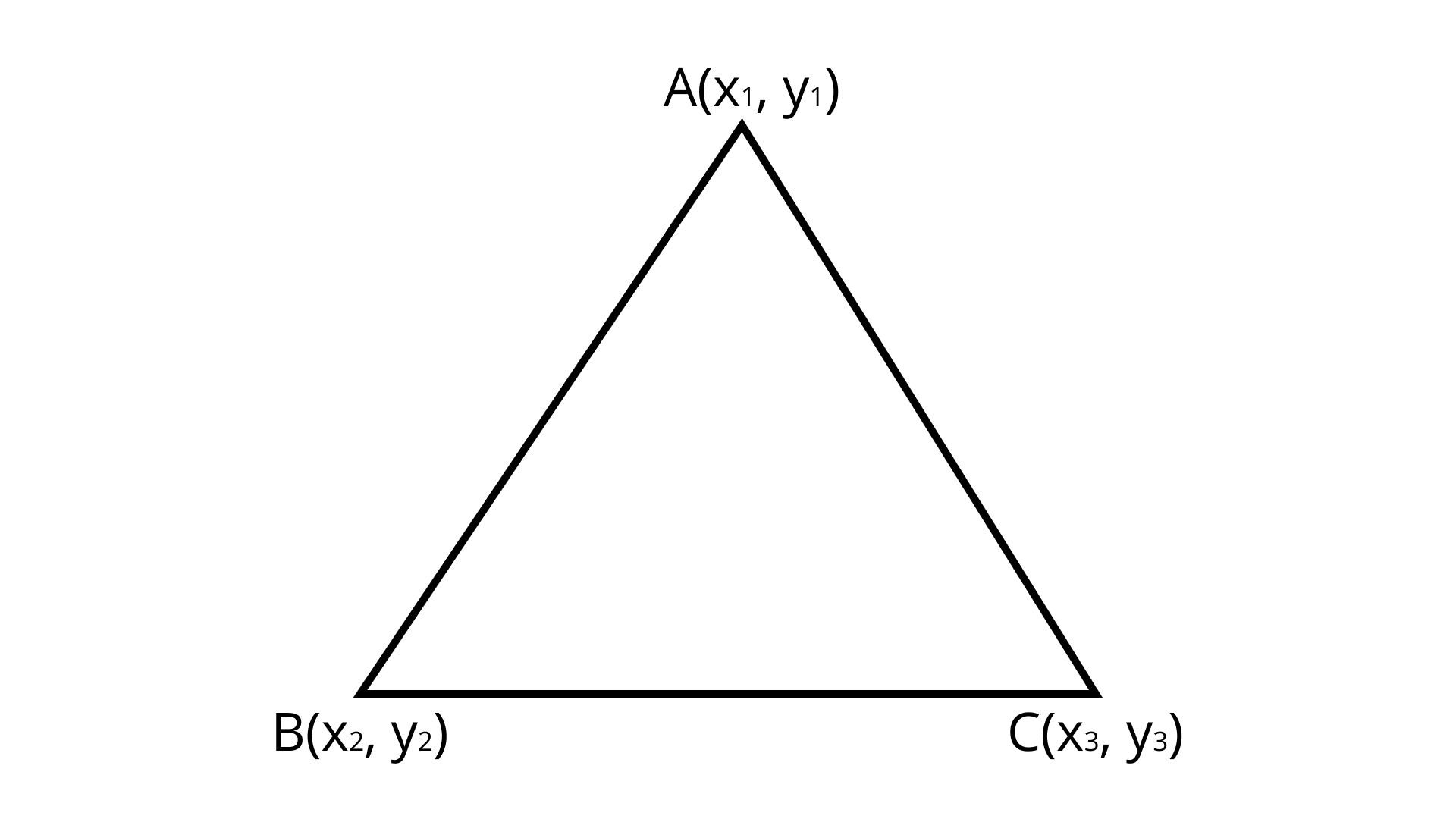
Co-ordinate of centroid
$= \left( {\dfrac{{{\text{ Sumof all coondinates of all vertices }}}}{3},\dfrac{{{\text{ Sum of all coordinates of all vertices }}}}{3}} \right)$
Centroid: The centroid is the center point of the triangle which is the intersection of the medians of a Triangle. $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ Coordinates of centroid $= \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right)$
4. If the points $A(1, - 2),B(2,3),C(a,2)$ and $D( - 4, - 3)$ form a parallelogram, find the value of $a$ and height of the parallelogram taking $AB$ as base.
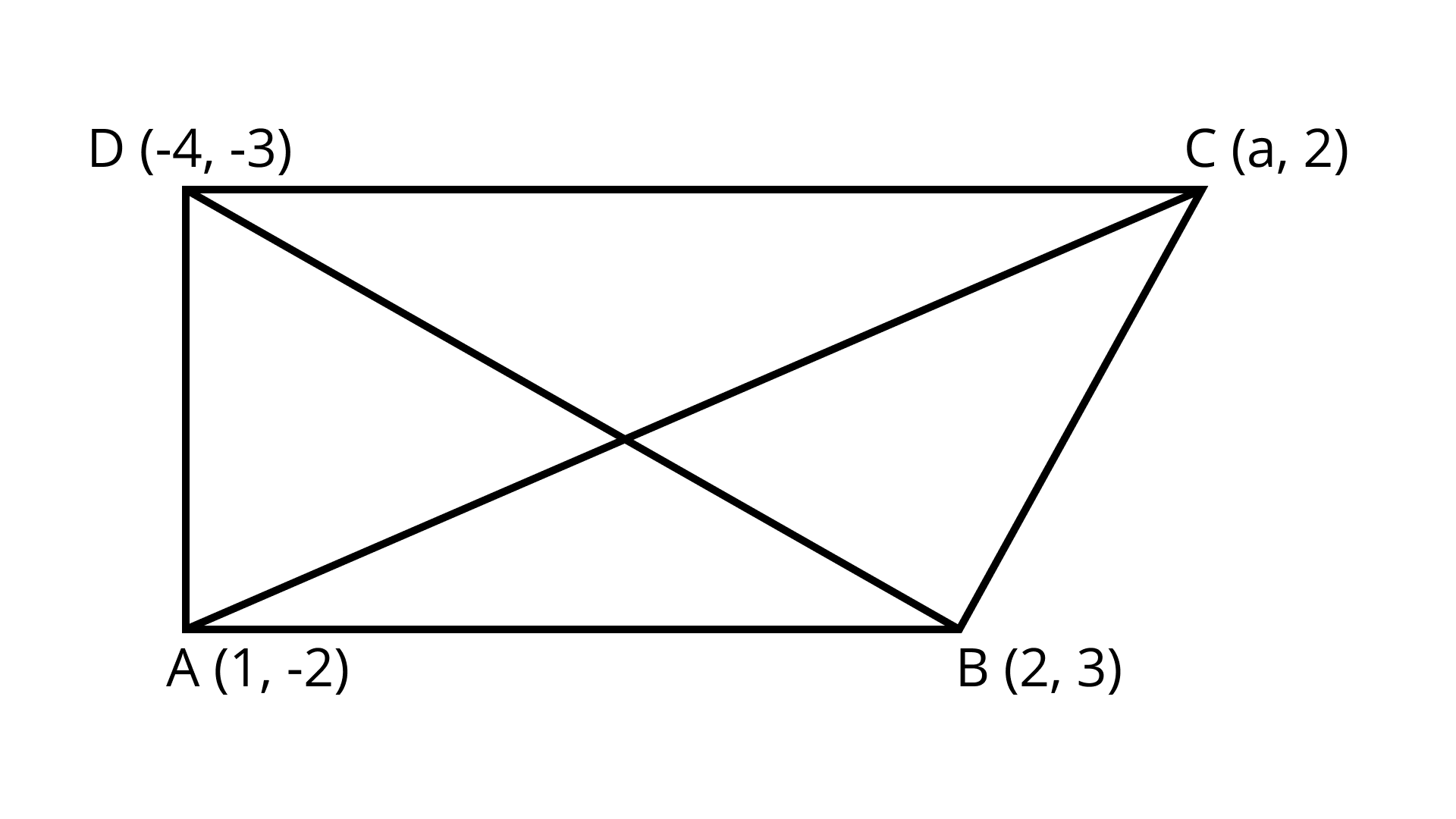
Ans: ${\text{a}} = - 3$ and height =$\dfrac{{24\sqrt {26} }}{{13}}$
We know that diagonals bisect each other
Hence, mid-point of ${\text{AC}} = $ Mid-point of BD $\left( {\dfrac{{1 + a}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 2 + 2}}{2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2 - 4}}{2},\dfrac{{3 - 3}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {\dfrac{{1 + a}}{2},0} \right) = ( - 1,0)$
$\dfrac{{1 + a}}{2} = - 1$
$1 + a = - 2$
$C( - 3,2)$
Area of $\Delta {\text{ABC}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[1(3 - 2) + 2(2 + 2) + ( - 3)( - 2 - 3)]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[1 + 2(4) + 15]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {24} \right) = 12{\text{ sq Units}}$
Area of parallelogram $= 2 \times $ Area of $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$
Area of parallelogram $= 2 \times 12 = 24{\text{ sq }}{\text{Units}}$ Length of $AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {{{(2 - 1)}^2} + {{(3 + 2)}^2}}$
$AB = \sqrt {1 + 25} = \sqrt {26}$ Units
Area of parallelogram = Base $ \times $ height $\dfrac{{24}}{{{\text{ Base }}}} = $ Height Height $= \dfrac{{24}}{{AB}}$
Height $= \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt {26} }} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt {26} }}{{\sqrt {26} }}$
$\dfrac{{24\sqrt {26} }}{{13}}$ Units
Questions 5: Students of a school are standing in rows and columns in their playground for a drill practice.${\text{A}}$ , $ {\text{B}}$ , $ {\text{C}}$ And ${\text{D}}$ are the positions of four students as shown in figure. Is it possible to place Jaspal in the Drill in such a way that he is equidistant from each of the four students ${\text{A}},{\text{B}},{\text{C}}$ and ${\text{D}}$ ? If so, what? Should be his position?
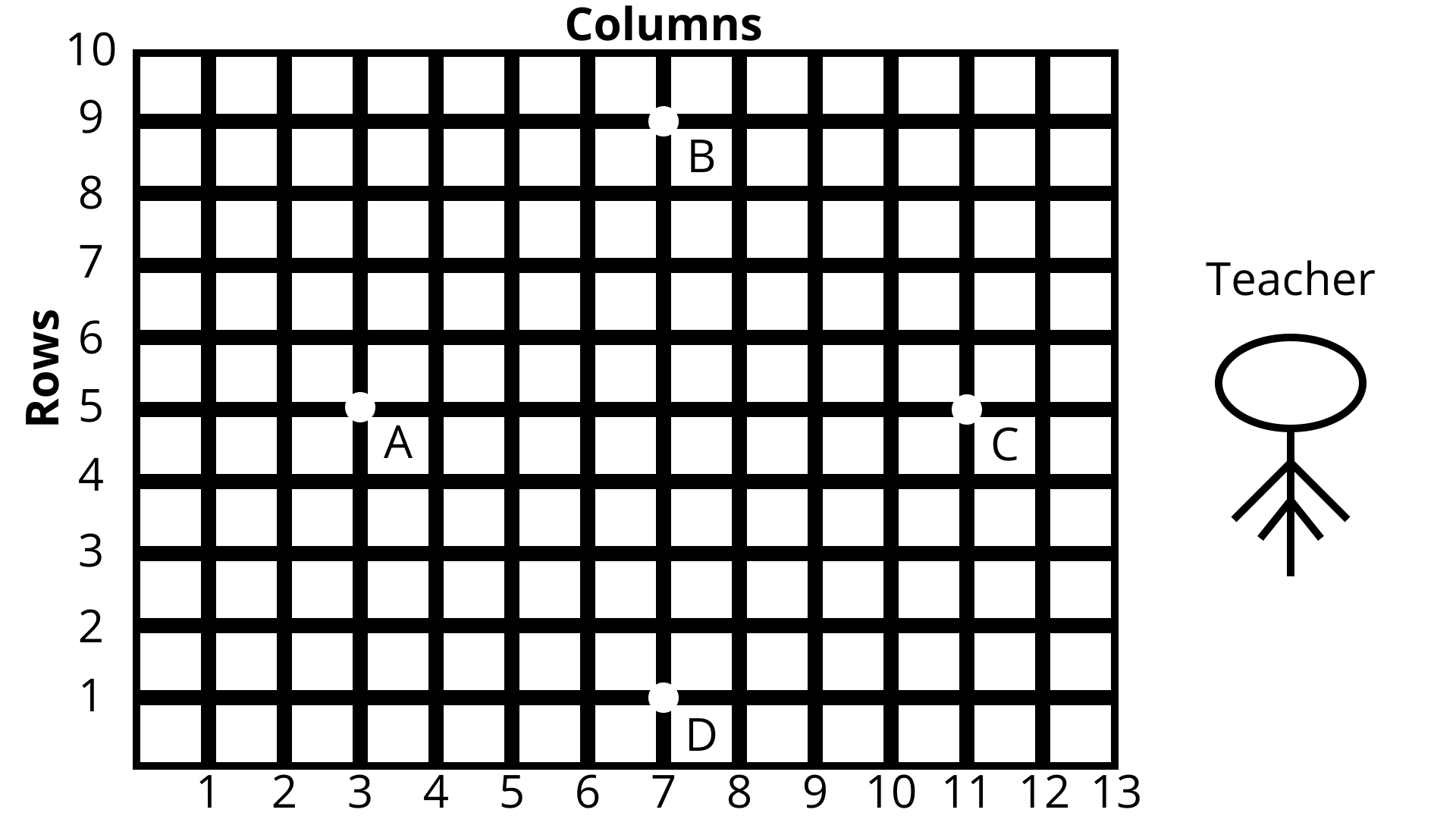
Length of ${\text{AB}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
${\text{AB}} = \sqrt {{{(7 - 3)}^2} + {{(9 - 5)}^2}}$
${\text{AB}} = \sqrt {16 + 16}$ $= \sqrt {32} = 4\sqrt 2$
Length of ${\text{BC}} = \sqrt {{{(11 - 7)}^2} + {{(5 - 9)}^2}}$
${\text{BC}} = \sqrt {16 + 16}$
$= \sqrt {32}$
$= 4\sqrt 2$
Length of ${\text{CD}} = \sqrt {{{(7 - 11)}^2} + {{(1 - 5)}^2}}$
${\text{CD}} = \sqrt {16 + 16}$
Length of ${\text{AD}} = \sqrt {{{(3 - 7)}^2} + {{(5 - 1)}^2}}$
${\text{AD}} = \sqrt {16 + 16}$
Length of ${\text{AC}} = \sqrt {{{(11 - 3)}^2} + {{(5 - 5)}^2}}$
$AC = \sqrt {(8)}$
Length of ${\text{BD}} = \sqrt {{{(7 - 7)}^2} + {{(1 - 9)}^2}}$
${\text{BD}} = \sqrt {64}$
${\text{AB}} = {\text{BC}} = {\text{AD}},{\text{AC}} = {\text{BD}}$
Hence, ABCD is square
The diagonals cut each other at mid-point, which is the equidistance from all four corners of square. Mid – point of ${\text{AC}} = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = (3,5)$
$\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = (11,5)$
${\text{AC}} = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 11}}{2},\dfrac{{5 + 5}}{2}} \right)$
${\text{AC}} = (7,5)$
This should be the position of Jaspal.
6 .Ayush starts walking from his house to the office. Instead of going to the office directly, he goes to a bank first, from there to his daughter’s school and then reaches the office. What is the extra distance travelled by Ayush in reaching his office? (Assume that all distances covered are in straight lines). If the house is situated at $(2,4)$ , bank at $(5,8)$ , school at $(13,14)$ and office at $\left( {13,{\text{ }}26} \right)$ and coordinates are in ${\text{km}}$.
Ans: The given point are $(2,4),(5,8),(13,14),(13,26)$
Distance between house and bank
$= \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {{{(5 - 2)}^2} + {{(8 - 4)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {9 + 16} = 5{\text{ Km}}$
Distance between bank and school
$= \sqrt {{{(13 - 5)}^2} + {{(14 - 8)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {64 + 36}$
$= \sqrt {100} = 10{\text{ Km}}$
Distance between school and office $= \sqrt {{{(13 - 13)}^2} + {{(26 - 14)}^2}}$ $= \sqrt {{{(12)}^2}} = 12{\text{ Km}}$
Distance between office and house $= \sqrt {{{(13 - 2)}^2} + {{(26 - 14)}^2}}$
$= \sqrt {121 + 484}$
$= \sqrt {605}$
$= 24 \cdot 59{\text{ Km}}$
Total distance covered from house to bank, bank to school, school to office $= 5 + 10 + 12 = 27$
Extra distance covered$= 27 - 24.59 = 2.41{\text{km}}$
Contents of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Mathematics The book contains a plethora of question papers and hence is a useful study material for the readers. This book has a total of 885 questions along with answers in 4 topics namely;
Numerical Operations
Coordinate Geometry
Trigonometry
The book also contains detailed solutions to all the questions along with detailed answers. The exam pattern of the board exam also gets covered in the book. A detailed outline along with solutions is given for each chapter so that the students can easily understand the working of the chapters.
Free Download of the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Mathematics
The book is quite flexible as it allows the students to download the entire book from their account for free. They can also read the book offline and can take notes from the questions and answers. The book also provides various chapter-wise revision notes which help in enhancing the learning of the students and also in building a strong foundation of the book. Furthermore, this book contains comprehensive revision notes and chapter-wise notes in all the subjects. It also contains questions to solve the problems.
Coordinate Geometry in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Mathematics
Coordinate Geometry is an important chapter in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths for students of 10th Class. Coordinate Geometry is a vital portion of basic geometry. The chapter is a complete and detailed treatment of the subject. Coordinate Geometry in NCERT is one of the most important concepts taught at the secondary level. Coordinate Geometry and also coordinate geometry courses with various concepts are discussed in this chapter.
Coordinate Geometry is a section of Algebra, and it includes linear geometry. This chapter discusses all the points that a student should learn and understand before they enter the world of trigonometry. If students enter the world of trigonometry without understanding basic geometry, the calculations may seem difficult to them.
Questions and Solutions in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Mathematics
The book also includes the problems that students will face after a brief overview of the subject. The solutions to all of these problems are provided in this chapter. The chapter includes not only questions but also the solutions to these questions.
The most important part of this chapter is coordinate geometry. Coordinate geometry is an important chapter in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths.
Topics covered in the chapter.
Coordinate Plane
It is the most important part of coordinate geometry. In this chapter, you will learn to construct coordinate planes and understand the concepts of parallel and perpendicular lines. We will also understand the concept of distance and find the distance between two points. You will also understand the definitions of coordinate axes.
Points and Lines
It is the next important topic of the chapter. In this section, you will learn about points and lines. We will learn to understand the concept of the point-line system and its properties. You will also learn the fundamental idea of a line that will be used to understand coordinate geometry.
Angles and Triangles
In this section, we will learn the concept of angle and triangle. You will learn to understand the concepts of the law of sines and cosines.
Trigonometry
It is a part of coordinate geometry. In this chapter, you will learn to understand the concept of ratio and degree. You will learn to understand the concept of the unit circle and different types of radii. You will also learn the conversion between degrees and radians. You will learn to use basic trigonometry formulas to solve algebraic equations.
Graphing with Graphs
It is a very important chapter in coordinate geometry. In this chapter, we will learn to construct the graphing of coordinates of points and find the points for any given line. We will also learn to draw the graphs of various coordinate systems. Graphs are very helpful in giving an accurate view of the given topic. They help us to visualize and understand it intuitively. The problem of graphing can be solved by using graphs. They help us to understand the underlying concepts easily.
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Mathematics
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry solved by expert Maths teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Vedantu is a platform that provides free NCERT Solutions and other study materials for students. You can download NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths to help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Subjects like Science, Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution Class 10 Science, Maths solutions, and solutions of other subjects that are available on Vedantu only.

FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry (Book Solutions)
1. How should I tackle questions of the form "Which line is parallel to line BAB and intersects line ABC at point D?"
As a general rule, if several lines have the same gradient then any line on that line will intersect the desired line. For example, let us consider the line:
AB = DC (1)
Let us take the line CBA, which intersects AB at point D. If C is taken to be the line parallel to AB and having the same gradient, then line CBA intersects line AB at point D.Another example would be if you wanted to find a line which intersects a line at a particular angle.
2. Can I Download NCERT Maths Exemplar for my Class?
To download NCERT Maths Exemplar Question Paper, just click on the download button and fill up the required information. After the download, you will get a .doc or .pdf format file of the NCERT maths question paper. The entire NCERT Exemplar is free to download from Vedantu’s website or app and use example question paper for Class 10 Maths. The PDF file can be opened in Adobe Reader and MS Word. You can save the PDF file as a print-ready file and share it with your friends. We recommend that you print it and keep it with your notes and books. You can study from the NCERT Exemplar question paper for better understanding and preparation.
3. What is the Main Objective of the Subject?
It helps students to know more about the basics of the concept of Geometry. It also helps students to develop their logic, judgment, and creativity. Moreover, it prepares students for other branches of science and to understand the basics of Mathematics. The main topics covered in the subject are-
Fundamentals of Geometry, Projective Geometry, Descriptive Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, Spatial Relations, Functions, Vector Calculus, Coordinates and Curves, Maths Review (Maths for Class 10), Algebra, Pre-Algebra, Geometric Algebra, Vector, Tensor, Matrix and General Calculus, Differential Geometry, Topology.
4. What Aspects of Mathematics should be Covered?
Every subject has different aspects which are to be covered. Mathematics, which is one of the most difficult subjects, has various aspects to be covered. Students should be taught a particular aspect of mathematics to cover all the aspects of that subject. For example, they should be taught how to write mathematical symbols; they should be taught how to read and interpret mathematical symbols; they should be taught how to apply mathematics; they should be taught how to understand mathematical concepts; they should be taught how to apply mathematics; they should be taught how to study
mathematics; etc.
5. What is a Study Guide?
NCERT Study Guides are carefully prepared books with chapters and subchapters, that enable a student to read a text and gain a deep understanding of the topics taught. Often the best feature of NCERT Study Guides is that they are accessible and interesting. These study guides are then studied carefully by our experts at www.vedantu.com. They now prepare notes for the children and the teachers to refer from. We possess a massive section for resources where you can find almost anything.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry . These Assignments for Grade 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 10 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry class 10 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Coordinate Geometry assignments in Pdf for grade 10th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 10 important questions and answers for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 will be really helpful for standard 10th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 10th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Download in Pdf


Advantages of Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics Coordinate Geometry assignments for Grade 10, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics Coordinate Geometry textbooks for Class 10 .
- All Mathematics Coordinate Geometry assignments for Class 10 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Coordinate Geometry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry in Grade 10, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Grade 10 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 10 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 10 Physics Assignments

Class 10 Assignments Download Pdf

Class 10 Mathematics Assignments
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry [Latest edition]
Online mock tests.

Advertisements
Solutions for chapter 7: coordinate geometry.
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CBSE, Karnataka Board NCERT for Mathematics Class 10.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.1 [Pages 161 - 162]
Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(2, 3), (4, 1)
(−5, 7), (−1, 3)
(a, b), (− a, − b)
Find the distance between the points (0, 0) and (36, 15). Can you now find the distance between the two towns A and B discussed in Section 7.2.
Determine if the points (1, 5), (2, 3) and (− 2, − 11) are collinear.
Check whether (5, - 2), (6, 4) and (7, - 2) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
In a classroom, 4 friends are seated at the points A, B, C and D as shown in the following figure. Champa and Chameli walk into the class and after observing for a few minutes, Champa asks Chameli, “Don’t you think ABCD is a square?” Chameli disagrees.
Using distance formula, find which of them is correct.

Name the type of quadrilateral formed, if any, by the following points, and give reasons for your answer:
(- 1, - 2), (1, 0), (- 1, 2), (- 3, 0)
Name the type of quadrilateral formed, if any, by the following point, and give reasons for your answer:
(− 3, 5), (3, 1), (0, 3), (− 1, − 4)
(4, 5), (7, 6), (4, 3), (1, 2)
Find the point on the x-axis which is equidistant from (2, - 5) and (- 2, 9).
Find the values of y for which the distance between the points P (2, -3) and Q (10, y) is 10 units.
If Q (0, 1) is equidistant from P (5, − 3) and R (x, 6), find the values of x. Also find the distance QR and PR.
Find a relation between x and y such that the point (x, y) is equidistant from the point (3, 6) and (− 3, 4).
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.2 [Page 167]
Find the coordinates of the point which divides the join of (–1, 7) and (4, –3) in the ratio 2 : 3.
Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining (4, -1) and (-2, -3).
To conduct Sports Day activities, in your rectangular shaped school ground ABCD, lines have been drawn with chalk powder at a distance of 1 m each. 100 flower pots have been placed at a distance of 1 m from each other along AD, as shown in the following figure. Niharika runs `1/4` th the distance AD on the 2 nd line and posts a green flag. Preet runs `1/5` th the distance AD on the eighth line and posts a red flag. What is the distance between both the flags? If Rashmi has to post a blue flag exactly halfway between the line segment joining the two flags, where should she post her flag?

Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points (-3, 10) and (6, - 8) is divided by (-1, 6).
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining A (1, − 5) and B (− 4, 5) is divided by the x-axis. Also, find the coordinates of the point of division.
If (1, 2), (4, y), (x, 6) and (3, 5) are the vertices of a parallelogram taken in order, find x and y.
Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is the diameter of circle whose centre is (2, − 3) and B is (1, 4)
If A and B are (− 2, − 2) and (2, − 4), respectively, find the coordinates of P such that `AP = 3/7 AB` and P lies on the line segment AB.
Find the coordinates of the points which divide the line segment joining A (- 2, 2) and B (2, 8) into four equal parts.
Find the area of a rhombus if its vertices are (3, 0), (4, 5), (− 1, 4) and (− 2, −1) taken in order.
[ Hint: Area of a rhombus = `1/2` (product of its diagonals)]
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.3 [Page 170]
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are: (2, 3), (-1, 0), (2, -4)
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are: (–5, –1), (3, –5), (5, 2)
In each of the following find the value of ' k ', for which the points are collinear.
(7, -2), (5, 1), (3, - k )
(8, 1), ( k , -4), (2, -5)
Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0, -1), (2, 1) and (0, 3). Find the ratio of this area to the area of the given triangle
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices, taken in order, are (-4, -2), (-3, -5), (3, -2) and (2, 3).
median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas. Verify this result for ΔABC whose vertices are A (4, - 6), B (3, - 2) and C (5, 2).
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.4 [Pages 171 - 172]
Determine the ratio in which the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divides the line segment joining the points A(2, – 2) and B(3, 7).
Find a relation between x and y if the points (x, y), (1, 2) and (7, 0) are collinear.
Find the centre of a circle passing through the points (6, − 6), (3, − 7) and (3, 3).
The two opposite vertices of a square are (− 1, 2) and (3, 2 ). Find the coordinates of the other two vertices.
The class X students of a secondary school in Krishinagar have been allotted a rectangular plot of land for their gardening activity. Saplings of Gulmohar are planted on the boundary at a distance of 1 m from each other. There is a triangular grassy lawn in the plot as shown in the following figure. The students are to sow seeds of flowering plants on the remaining area of the plot.

(i) Taking A as origin, find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle.
(ii) What will be the coordinates of the vertices of Δ PQR if C is the origin?
Also calculate the areas of the triangles in these cases. What do you observe?
The vertices of a ΔABC are A (4, 6), B (1, 5) and C (7, 2). A line is drawn to intersect sides AB and AC at D and E respectively, such that `(AD)/(AB) = (AE)/(AC) = 1/4`Calculate the area of the ΔADE and compare it with the area of ΔABC. (Recall Converse of basic proportionality theorem and Theorem 6.6 related to ratio of areas of two similar triangles)
Let A (4, 2), B (6, 5) and C (1, 4) be the vertices of ΔABC.
(i) The median from A meets BC at D. Find the coordinates of point D.
(ii) Find the coordinates of the point P on AD such that AP: PD = 2:1
(iii) Find the coordinates of point Q and R on medians BE and CF respectively such that BQ: QE = 2:1 and CR: RF = 2:1.
(iv) What do you observe?
(v) If A(x 1 , y 1 ), B(x 2 , y 2 ), and C(x 3 , y 3 ) are the vertices of ΔABC, find the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle.
ABCD is a rectangle formed by the points A(-1, -1), B(-1, 4), C(5, 4) and D(5, -1). P, Q, R and S are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Is the quadrilateral PQRS a square? a rectangle? or a rhombus? Justify your answer.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 10 chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Mathematics Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Mathematics Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board 7 (Coordinate Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics Class 10 chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry are Section Formula, Graphs of Linear Equations, Distance Formula, Coordinate Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, Basic Geometric Constructions, Area of a Triangle, Section Formula, Graphs of Linear Equations, Distance Formula, Coordinate Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, Basic Geometric Constructions, Area of a Triangle, Section Formula, Graphs of Linear Equations, Distance Formula, Coordinate Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, Basic Geometric Constructions, Area of a Triangle.
Using NCERT Mathematics Class 10 solutions Coordinate Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Class 10 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Coordinate Geometry Mathematics Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.

- Maharashtra Board Question Bank with Solutions (Official)
- Balbharati Solutions (Maharashtra)
- Samacheer Kalvi Solutions (Tamil Nadu)
- NCERT Solutions
- RD Sharma Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions
- TS Grewal Solutions
- ICSE Class 10 Solutions
- Selina ICSE Concise Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- CBSE Study Material
- Maharashtra State Board Study Material
- Tamil Nadu State Board Study Material
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Study Material
- Mumbai University Engineering Study Material
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Entrance Exams
- Video Tutorials
- Question Papers
- Question Bank Solutions
- Question Search (beta)
- More Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Shaalaa App
- Ad-free Subscriptions
Select a course
- Class 1 - 4
- Class 5 - 8
- Class 9 - 10
- Class 11 - 12
- Search by Text or Image
- Textbook Solutions
- Study Material
- Remove All Ads
- Change mode

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 – Coordinate Geometry

Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7, Coordinate Geometry, cover all exercises from the NCERT textbook . Prepared by experts at Infinity Learn, these solutions provide comprehensive study material for students preparing for the CBSE Class 10 board examination. Available for easy access and download, these class 10 coordinate geometry solutions offer detailed step-by-step answers to various questions in the textbook. Practicing these coordinate geometry class 10 NCERT solutions will help students master the topics covered in chapter 7 of class 10 maths.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---

These coordinate geometry class 10 PDF solutions are essential for understanding the concepts of coordinate geometry in class 10. By referring to the NCERT solutions for class 10 maths chapter 7, students can enhance their preparation for chapter 7 maths class 10. This chapter 7 class 10 maths content is a valuable resource for attaining perfection in the topics involved. Get your class 10 maths coordinate geometry solutions today and excel in your exams.
Download Coordinate Geometry Class 10 PDF NCERT Solutions
Download PDF for Free. Study without Internet (Offline)
Grade --- Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Class 6 Class 7 Class 8 Class 9 Class 10 Class 11 Class 12
Target Exam JEE NEET CBSE
Preferred time slot for the call --- 9 am 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm 6 pm 7 pm 8pm 9 pm 10pm
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Are you a Sri Chaitanya student? No Yes
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
This NCERT Solutions include all the exercise questions from the NCERT textbook for class 10 chapter 7. Diagrammatic representations and alternate methods ensure a thorough understanding of the concepts in class 10 chapter 7 maths. By solving these coordinate geometry class 10 solutions, you will become familiar with important formulas and standards. This NCERT solution for class 10 maths chapter 7 features various examples to help you relate geometry and numerical concepts to real-life situations.
Infinity Learn offers NCERT study materials created by the country’s top teachers. You can access these materials on the Infinity Learn website or through the Infinity Learn app. Additionally, Infinity Learn provides solutions for other textbooks, available free of cost, to offer students more practice problems. Visit the Infinity Learn website or download the app to access all the study materials for maths chapter 7 class 10, including coordinate geometry class 10 NCERT solutions and coordinate geometry class 10 solutions.
More Resources for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 English

FAQs on Coordinate Geometry Class 10 NCERT Solutions
What are the benefits of ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 7 for cbse term i exams.
For self-evaluation, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 provides answers with thorough descriptions as per the period limit specified by the board. Students will gain valuable experience solving these problems, allowing them to complete the assignment on time. As a result, it's evident that NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 are critical for high exam scores. Students will become more comfortable with writing tests and will be better prepared to confront them.
Mention the topics covered in Chapter 7 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths?
Introduction to coordinate geometry, distance formula, section formula, and triangle area are all covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7. Students will be able to tackle complex problems if they learn these NCERT solutions thoroughly.
Is it compulsory to complete all of the exercises in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7?
Yes, all of the exercises in Chapter 7 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths must be practiced because they contain multiple questions to answer that may appear in the CBSE first term examination. This gives them more confidence in the CBSE Syllabus for 2021-22, which has been updated term by term.
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 7 with Solutions
January 6, 2023 by Sastry CBSE
Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths Coordinate Geometry with Answers
Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry. According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Carries 20 Marks.
You can also download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. If the distance between the points (4, k) and (1,0) is 5, then what can be the possible values of it? [CBSE 2017] Answer: Let A (4, k), B (1, 0) AB = 5 given ⇒ \(\sqrt{(4-1)^2+(k-0)^2}\) = 5 ⇒ \(\sqrt{3^2+k^2}\) = 5 ⇒ k 2 + 9 = 25 ⇒ k 2 = 25 – 9 = 16 ∴ k = ± 4
Question 2. Find the distance of a point P(x, y) from the origin. Answer: Using distance formula for distance between A (x 1 , y 1 ) and B (x 2 , y 2 ) AB = \(\sqrt{\left(x_2-x_1\right)^2+\left(y_2-y_1\right)^2}\) ∴ Reqd. distance = \(\sqrt{(x-0)^2+(y-0)^2}\) = \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
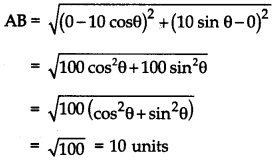
Question 7. If the point (0, 2) is equidistant from the points (3, k) and (k, 5), find the value of k. Answer: Let the points be P(0, 2), A(3, k) and B(k, 5). Now, PA = PB or, PA 2 = PB 2 ⇒ (3 – 0) 2 + (k – 2) 2 = (k – 0) 2 + (5 – 2) 2 ⇒ 9 + (k – 2) 2 = k 2 + 9 ⇒ k 2 = (k – 2) 2 ⇒ k = ± (k – 2) k = (k – 2) (impossible) ∴ k = – (k – 2) = – k + 2 or 2k = 2 or k = 1.
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions Short Answer Type-1
Question 1. Find the value of x for which the distance between the point P (2, – 3) and Q (x, 5) is 10 unit. Answer: According as given PQ = 10 units ⇒ \(\sqrt{(2-x)^2+(-3-5)^2}\) = 10 Squaring both sides, we have 4 + x 2 – 4x + 64 = 100 ⇒ x 2 – 4x – 32 = 0 ⇒ x 2 – 8x + 4x – 32 = 0 ⇒ x (x – 8) + 4 (x – 8) = 0 ⇒ (x – 8) (x + 4) = 0 ⇒ x = 8 or x = – 4.
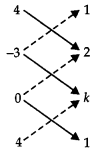
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions Short Answer Type-2
(ii) Using mid-point formula, The coordinates of D are = \(\left(\frac{1+4}{2}, \frac{7+2}{2}\right)\) = \(\left(\frac{5}{2}, \frac{9}{2}\right)\)
(iii) Area of ∆ ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) |1(2 – 4) + 4(4 – 7) – 4(7 – 2)| = \(\frac{1}{2}\) |- 2 – 12 – 20| = \(\frac{1}{2}\) |- 34| = 17 sq. units
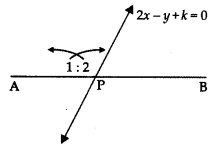
Question 6. If a ≠ b ≠ 0, prove that the point (a, a 2 ), (b, b 2 ) (0, 0) will not be collinear. [CBSE 2017] Answer: Let A(a, a 2 ), B(b, b 2 ), O(0, 0) be given points ⇒ ar ∆ABO = \(\frac{1}{2}\)|x 1 (y 2 – y 3 ) + x 2 (y 3 – y 1 ) +x 3 (y 1 – y 2 )| ⇒ = \(\frac{1}{2}\)|a(b 2 ) + b(- a 2 ) + 0| = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ab(b – a) ≠ 0 as a ≠ b ≠ 0 ∴ Given points are not collinear
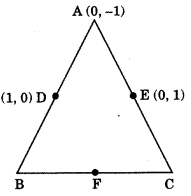
Question 16. Prove that the area of a triangle with vertices (t, t – 2), (t+2, t+2) and (t+3, t) is independent oft [CBSE Delhi 2016] Answer: Let A(t, t – 2), B(t + 2, t + 2) and C(t + 3, t) be the vertices of the given triangle. We know that the area of the triangle having vertices (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) and (x 3 , y 3 ) is \(\frac{1}{2}\) |x 1 (y 2 – y 3 ) + x 3 (y 3 – y 1 ) + x 3 (y 1 – y 2 )| ∴ Area of ∆ABC = |\(\frac{1}{2}\) [x 1 (y 2 – y 3 ) + x 2 (y 3 – y 1 ) + x 3 (y 1 – y 2 )l = |\(\frac{1}{2}\) [t(t + 2 – t) + (t + 2) (t – t + 2) + (t + 3) (t – 2 – t – 2)]| = |\(\frac{1}{2}\) (2t + 2t + 4 – 4t – 12) = |- 4| = 4 square units Hence, the area of the triangle with given vertices is independent of t.
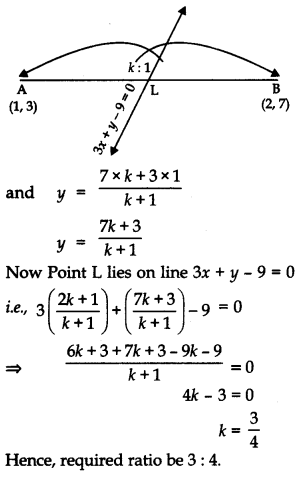
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions HOTS
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option out of four given in each of the following:
Question 1. The ratio of the distances of point P(3, 4) from origin to that from y-axis is (a) 3:5 (b) 5:3 (c) 5:4 (d) 3:4 Answer: (c) 5:4
Question 2. AOBC is a rectangle whose three vertices are A(0, 4), O(0, 0) and B(3, 0). The length of its diagonal is (a) 25 units (b) 5 units (c) 3 units (d) 4 units Answer: (b) 5 units
Question 3. The distance between A(10 cos θ, 0) and B(0, 10 sin θ) is (a) √10 units (b) 10 units (c) 5 units (d) 10 sin θ cos θ Answer: (b) 10 units
Question 4. Perimeter of the triangle formed by the points O(0, 0), A(A, 0) and B(0, b) is: (a) a + b (b) ab (c) a + b + 2√ab (d) a + b + \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\) Answer: (d) a + b + \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
Question 5. The points (-8, 0), (8, 0), (0, 5) are the vertices of a (a) right triangle (b) isosceles triangle (c) equilateral triangle (d) scalene triangle Answer: (b) isosceles triangle
Question 6. The points (-2, 2), (8, -2) and (-4, -3) are the vertices of a (a) equilateral triangle (b) isosceles triangle (c) right triangle (d) none of these Answer: (c) right triangle
Question 7. The points (1, 7), (4, 2), (-1, 1) and (-4, 4) are the vertices of a (a) parallelogram (b) rhombus (c) rectangle (d) square Answer: (d) square
Question 8. The line segment joining the points (2, -3) and (5, 6) is divided by x-axis in the ratio (a) 2:1 (b) 3:1 (c) 1:2 (d) 1:3 Answer: (a) 2:1
Question 9. The line segment joining the points (3, 5) and (-4,2) is divided by y-axis in the ratio (a) 5 : 3 (b) 3 : 5 (c) 4 : 3 (d) 3 : 4 Answer: (d) 3 : 4
Question 10. If (3, 2), (4, k) and (5, 3) are collinear then k is equal to (a) \(\frac{3}{2}\) (b) \(\frac{2}{5}\) (c) \(\frac{5}{2}\) (d) \(\frac{3}{5}\) Answer: (c) \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Question 11. If the points (p, 0), (0, q) and (1, 1) are collinear then \(\frac{1}{p}+\frac{1}{q}\) is equal to (a) – 1 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 0 Answer: (b) 1
Question 12. The coordinates of reflection of Q(- 1, -3) in x- axis are (a) (1, 3) (b) (-1,3) (c) (1, -3) (d) none of these Answer: (b) (-1,3)
Question 13. The distance between the points (-3, 0) and (3, 0) is (a) 3 units (b) 3√2 units (c) 2√3 units (d) 6 units Answer: (d) 6 units
Question 14. If P\(\left(\frac{a}{3}, 4\right)\) is the mid point of the line segment joining the points A(-6, 5) and B(-2, 3), then value of a is (a) – 4 (b) – 12 (c) 12 (d) – 6 Answer: (b) – 12
Question 15. The fourth vertex D of a parallelogram ABCD whose three vertices are A(-2, 3), B(6, 7) and C(8, 3) is: (a) (0, 1) (b) (0, -1) (c) (1, 0) (d) (-1, 0) Answer: (b) (0, -1)
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Distance of point P(a, b) from origin is __________ . Answer: \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
Question 2. Coordinates of mid point joining P(α, β) and Q(γ, δ) are __________. Answer: \(\left(\frac{\alpha+\gamma}{2}, \frac{\beta+\delta}{2}\right)\)
Question 3. For given three points A, B, C if out of three possible distances AB, BC and CA the length of the greatest distance is equal to sum of other two distances then the points A, B, C are said to be __________ . Answer: collinear
Question 4. For given four points A, B, C, D if lengths AB, BC, CD and DA are all equal then ABCD is necessarily a __________ . Answer: rhombus
Question 5. For given four points A, B, C, D if lengths AB = BC = CD = DA and AC ≠ BD then ABCD is a __________ but not __________ . Answer: rhombus, square
Question 6. For proving ABCD to be a __________ . It is sufficient to show that opposite sides are equal. Answer: parallelogram
Question 7. For given four points A, B, C, D if AB = CD, BC = DA and AC ≠ BD then ABCD is a __________ but not __________ . Answer: parallelogram, rectangle
Question 8. If area of a triangle is zero square units then its vertices are __________ . Answer: collinear
Question 9. The distance between (α, β) and (- α, – β) is __________ . Answer: 2\(\sqrt{\alpha^2+\beta^2}\)
Question 10. If the point P(x, y) divides the line segment joining A(x 1 , y 1 ) and B(x 2 , y 2 ) in the ratio m: n the value of y – x = __________ . Answer: \(\frac{m\left(y_2-x_2\right)+n\left(y_1+x_1\right)}{m+n}\)
Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 10 maths, free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- Choose class
- No notification
Sign-in to access many more resources
- Question Bank /
Class 10 Maths Extra Questions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
AglaSem is an Indian edtech company that specializes in education related services and products. It provides all important study material and resources for free to students.
ENTER YOUR EDUCATION
Bookmarked exams.
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments For Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry
Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry have been developed for Standard 10 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry from our website as we have provided all topic wise assignments free in PDF format which can be downloaded easily. Students are recommended to do these assignments daily by taking printouts and going through the questions and answers for Grade 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry. You should try to do these test assignments on a daily basis so that you are able to understand the concepts and details of each chapter in your Mathematics Coordinate Geometry book and get good marks in class 10 exams.
Question. The lines, x = 2 and y = 3 are (A) parallel to each other (B) perpendicular to each other (C) neither parallel nor perpendicular to each other (D) none of these
Question. The lines, x = –2 and y = 3 intersect at the point ________. (A) (-2,3) (B) (2,-3) (C) (3,-2) (D) (-3,2)
Question. The point equidistant from vertices of a triangle is called (A) circumcentre (B) incentre (C) orthocenter (D) none of these
Question. The slope of the line joining the points (2, k – 3) and (4,-7) is 3. Find k. (A) -10 (B) -6 (C) -2 (D) 10
Question. The distance between the points (3, 4) and (6, –3) is. (A) √58 (B) √68 (C) √78 (D) √98
Question. If A and B are (1, 4) and (5, 2) respectively, then the co-ordinates of P when AP/PB = 3/4 is (A) (19/7 , 22/7) (B) (20/7 , 21/7) (C) (21/7 , 22/7) (D) (21/7 , 23/7)
Question. If the coordinates of the mid-points of the sides of a triangle are (1, 2) (0, –1) and (2, –1). Then the sum of x coordinates of its vertices of the triangle is (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
Question. The centre of a circle is C(2,-3) and one end of the diameter AB is A(3,5) . Find the coordinates of the other end B. (A) (1,-11) (B) (5,2) (C) (1,8) (D) none of these
Question. Find λ , if the line 3x – λy + 6 = 0 passes through the point (–3,4). (A) 3/4 (B) -3/4 (C) 4/3 (D) -4/3
Question. Find the area of the triangle formed by the line 5x – 3y + 15 = 0with coordinate axes. (A) 15cm 2 (B) 5 cm 2 (C) 8 cm 2 (D) 15/2 cm 2
Question. The point P lying in the fourth quadrant which is at a distance of 4 units from X-axis and 3 units from Y-axis is__________. (A) (4,-3) (B) (4,3) (C) (3,-4) (D) (-3,4)
Question. In what ratio does the line 4x+3y -13 = 0 divide the line segment joining the points (2, 1) and (1, 4)? (A) 3 : 2 internally (B) 2 : 3 externally (C) 2 : 3 internally (D) 3 : 2 externally
Question. The points on X-axis which are at a distance of 13 units from (-2,3) is ________. (A) (0,0), (-2,-3) (B) (0,0), (-4,0) (C) (0,0), (2,3) (D) none of these
Question. If (5, 3), (4, 2) and (1, –2) are the mid points of sides of triangle ABC, then the area of ΔABCis (A) 2 sq. units (B) 3 sq. units (C) 1 sq. units (D) 4 sq. units
Question. The points (a,b +c), (b,c +a) and (c,a + b) (A) are collinear (B) form a scalene triangle (C) form an equilateral triangle (D) none of these
Coordinate Geometry
A point in 2-D plane (let’s say XY plane) is represented by its coordinates (x,y) Here x is the distance of a point from the x-axis and is called y-coordinate. y is the distance of a point from the and is called its .
Distance Formula : the distance between the points P(x 1 ,y 1 ) and Q(x 2 ,y 2 ) is PQ=
This is called distance formula. F
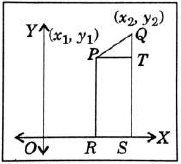
Area of a triangle : the area of ABC is the numerical value of the expression F

Section Formula : the coordinates of the point P(x,y) which divides the line segment joining the points A(x 1 ,y 1 ) and B(x 2 ,y 2 ) internally, in the ratio m 1 :m 2 are

This is known as section formula. F

Special Case -: if P is mid point then m 1 :m 2 =1:1
Now, the coordinates of mid point
In order to prove that a given figure is a : i) Square, prove that four sides are equal and the diagonals are equal. ii) Rhombus, prove that the four sides are equal. iii) Rectangle, prove the opposite sides are equal and the diagonals are also equal. iv) Parallelogram, prove that the opposite sides are equal. The point of intersection of the medians of a triangle is called its called its centroid. The coordinates of the centroid of the triangle whose are (x 1 ,y 1 ) ,(x 2 ,y 2 ) and (x 3 ,y 3 ) are given by
For three points to be collinear, i) The sum of the distances between two pairs of points is equal to the distance third pair of points. Three given points A(x 1 ,y 1 ) ,B(x 2 ,y 2 ) and C(x 3 ,y 3 ) are collinear if ABC =0.
Question. Find the condition that the point (x, y) may lie on the line joining (3, 4) and (-5, – 6). Solution. Since the point P (x, y) lies on the line joining A (3, 4) and B (-5, -6). Therefore, P, A andB are collinear points.

Hence, the point (x, y) lies on the line joining (3,4) and (-5, -6), if 5x – 4y+1 = 0
Question. Show that the points A(3, 5), B(6, 0), C(1, -3) and D (-2, 2) are the vertices of a square ABCD. Solution. Let A( 3,5), B(6, 0), C(1, -3 ) and D(-2, 2) be the angular points of a quadrilateral ABCD. Join AC and BD
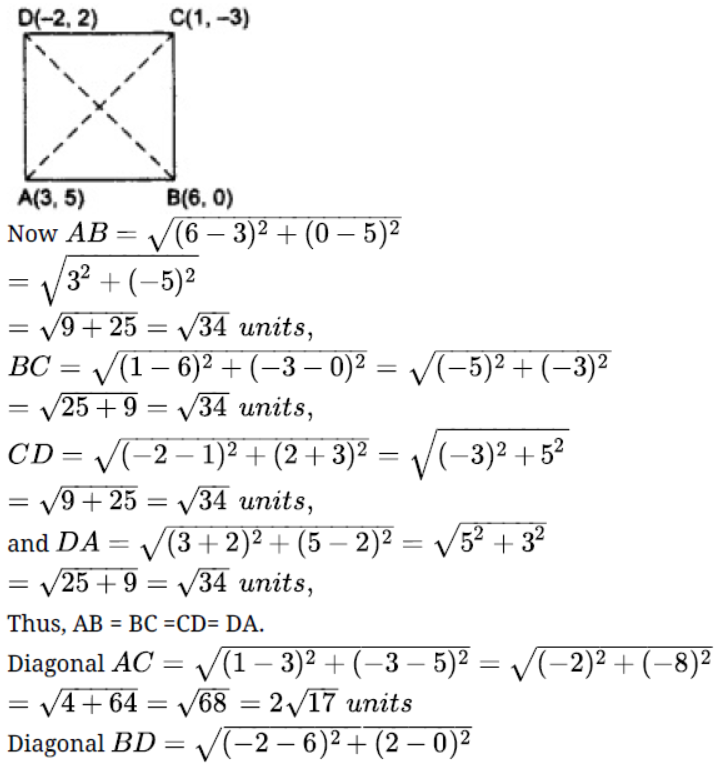
Thus, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which all sides are equal and the diagonals are equal. Hence, quad. ABCD is a square.
Question. If P (x, y) is any point on the line joining the points A(a,0) and B(0, b), then show that x/a + y/b = 1 Solution. It is given that the point P (x, y) lies on the line segment joining points A (a, 0) and B (0, b).Therefore, points P (x, y), A (a, 0) and B (0, b) are collinear points.

Question. A (4, 2), B (6, 5) and C (1, 4) are the vertices of ΔABC. Solution.

i. The median from A meets BC in D. Find the coordinates of the point D.
i. Median AD of the triangle will divide the side BC in two equal parts. So D is the midpoint of side BC.
ii. Find the coordinates of point P on AD such that AP : PD = 2:1.

iii. Find the coordinates of the points Q and R on medians BE and CP respectively such that BQ : QE = 2 :1 and CR: RF =2: 1.
Median BE of the triangle will divide the side AC in two equal parts. So E is the midpoint of side AC.
iv. What do you observe? Now we may observe that coordinates of point P, Q are same. So, all these are representing same point on the plane i.e. centroid of the triangle.
Question. Find the lengths of the medians of a ΓABC whose vertices are A(0, -1) B(2, 1) and C(0,3). Solution. Let D, E, F be the midpoint of the side BC, CA and AB respectively in ΔABC

Question. The area of triangle formed by the points (p, 2 – 2p), (1, p, 2 p ) and (-4 -p, 6 – 2p) is 70 sq. units. How many integral values of p are possible. Solution.
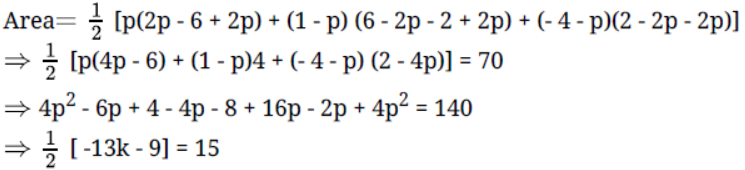
Question. Find the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are (0,6), (8,12) and (8,0). Solution. Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ), (x 3 , y 3 ) are

Question. Point A is on x-axis, point B is on y-axis and the point P lies on line segment AB, such that P (4, – 5) and AP : PB = 5 : 3. Find the coordinates of point A and B. Solution. Let coordinates of A are (x, 0) and coordinates of B are (0, y)

Question. If the points A(x, 2), B(- 3, – 4), C(7, – 5) are collinear, then find the value of x. Solution. Since the points are collinear, then, Area of triangle = 0

Practice Exercise :
Question. Prove that(4,-1),(6,0),(7,2)&(5,1) are the vertices of a rhombus .Is it a square? Solution. Proof
Question. Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is diameter of a circle whose Centre is(2,-3)and B is(1,4) Solution. (3,-10)
Question. Find the centroid of triangle whose vertices are (3,-7), (-8,6) and (5,10). Solution. (0,3)
Question. If A (-2,4),B(0,0),C(4,2) are the vertices of a ΔABC, then find the length of median through the vertex A. Solution. 5 units
Question. Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0,-1),(2,1) and (0,3).Find the ratio of this area to the area of the given triangle. Solution. 1:4
Question. Determine the ratio in which the point P(a,-2) divides the line joining of points(-4,3) and B(2,-4).Also find the value of a. Solution. a=2/7
Question. If the point C(-1,2) divides internally the line segment joining A(2,5)and in the ratio 3:4. Find the Co- ordinates of B. Solution. B(-5,-2)
Question. Show that points (1,1), (4,4) ,(4,8)and (1,5) are the vertices of a parallelogram. Solution. Proof
Question. Find the value of p, for which the points(-1,3),(2,p) & (5,-1)are collinear Solution. p=1
Question. If the points(-1,3),(1,-1)and(5,1)are the vertices of a triangle .Find the length of the median through the first vertex. Solution. 5
Question. Find the center of a circle passing through the points (6,-6), (3,-7)and(3,3). Solution. (3,-2)
Question. If the distance between the points (3,0) and (0,y)is 5 units and y is positive ,what is the value of y? Solution. 4
Question. If the points(x ,y),(-5,-2)and(3,-5)are collinear r, then prove that 3x+8y+31=0. Solution. Proof
Question. A line intersects y–axis and x-axis at the points P and Q respectively. If (2,-5) is the midpoint of PQ, then find the coordinates of P and Q respectively. Solution. (0,-10) and(4,0)
Question. Show that the three points (a,a) ,(-a,-a) &(-a√3 , a√3) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle. Solution. Proof
Question. Find the value of k, if the point P (2, 4) is equidistant from the points (5, k) and (k, 7). Solution. K=3
Question. If the point A(0,2)is equidistant from the points B (3,p) and C(p,5),find p .Also find the length of AB. Solution. P=1, AB=√10
Question. Find the distance between the points A and B in the following : A(a, 0), B(0, a) Solution. A(a, 0), B(0, a)

Question. Find the perpendicular distance of A(5,12) from the y-axis. Solution. The point on the y-axis is (0,12) Distance between (5,12) and (0,12)
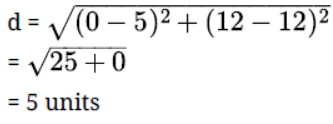
Question. Find the distance of the point (- 4, – 7) from the y-axis. Solution. Points are (- 4, – 7) and (0, – 7)

Question. Find the distance between the points: A(-6, -4) and B(9, -12) Solution. The given points are A(-6, -4) and B(9, -12) Then, (x 1 = -6, y 1 = -4) and (x 2 = 9, y 2 = -12)

Question. Show that four points (0, -1), (6, 7), (-2, 3) and (8, 3) are the vertices of a rectangle. Also,find its area. Solution. Let A (0 – 1), B (6, 7), C (-2, 3) and D (8, 3) be the given points. Then,
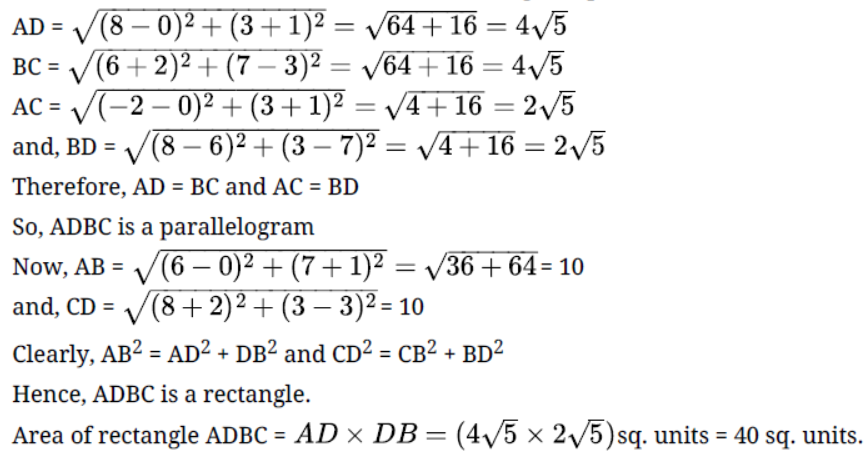
Question. Find the co-ordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining the points A(1,- 2) and B(- ,4). Solution.

Question. Find the distance between the points A and B in the following:A(1,-3), B(4, 1) Solution. A(1, -3), B(4, 1)

Question. If the points A (a, -11), B (5, b), C (2, 15) and D (1, 1) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD, find the values of a and b.

Solution. Let A(a, -11), B(5, b), C(2, 15) and D(1, 1) be the given points. We know that diagonals of parallelogram bisect each other. Therefore, Coordinates of mid-point of AC = Coordinates of mid-point of BD

Hence value of a and b is equal to 4 and 3 respectively.
Question. Find the coordinates of the point , where the line x – y = 5 cuts Y-axis. Solution. x – y = 5 is a given line x – y = 5 cuts Y-axis. Put x = 0 in the equation of line x- y = 5 ⇒ (0) – y = 5 ⇒ y = – 5 Therefore , the point is (0,-5)cuts x – y = 5 at Y-axis..
Question. If the point A(2, –4) is equidistant from P(3, 8) and Q(–10, y) then find the values of y. Also find distance PQ. Solution. According to the question,we are given that, PA = QA ⇒ PA 2 = QA 2 ⇒ (3 – 2) 2 + (8 + 4)2 = (–10 – 2) 2 + (y + 4) 2 ⇒ 12 + 12 2 = (–12) 2 + y 2 + 16 + 8y ⇒ y 2 + 8y + 16 – 1 = 0 ⇒ y 2 + 8y + 15 = 0 ⇒ y 2 + 5y + 3y + 15 = 0 ⇒ y(y + 5) + 3(y + 5) = 0 ⇒ (y + 5) (y + 3) = 0 ⇒ y + 5 = 0 or y + 3 = 0 ⇒ y = –5 or y = –3 So, the co–ordinates are P(3, 8), Q1(–10, –3), Q2(–10, –5).
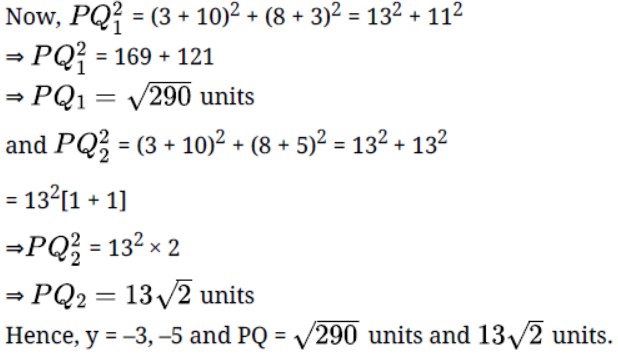
Question. Find the value of ‘k’ if the points (7, –2), (5, 1), (3, k) are collinear. Solution. (7, –2), (5, 1), (3, k)

Question. Find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices (0, 4), (0,0) and (3,0). Solution. Here, A→ (0,4),B→ (0,0),C→ (3,0)

Question. Find the area of a quadrilateral PQRS whose vertices area P(- 5, 7), Q(- 4, – 5), R (-1, – 6) and S(4, 5). Solution. Area PQRS = ar PQS + ar QRS
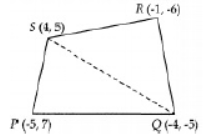
Hence, area PQRS = 53 + 19 = 72 sq. units
Question. The point R divides the line segment AB where A(-4, 0), B(0, 6) are such that AR =3/4 A B. Find the coordinates of R. Solution.
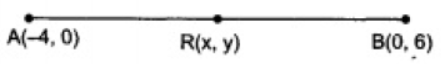
Question. Prove that the lines joining the middle points of the opposite sides of a quadrilateral and the join of the middle points of its diagonals meet in a point and bisect one another. Solution. Let OBCD be the quadrilateral P, Q, R, S be the mid-points of OB, CD, OD and BC.

Let the coordinates of O,B, C, D are (0, 0), (x, 0), (x, y) and (0, y) Coordinates of P are (x/2 ,0) Coordinates of Q are (x/2 , y) Coordinates of R are (0,y/2) Coordinates of S are (x , y/2) Coordinates of mid-point of PQ are

Since, the coordinates of the mid-point of PQ = coordinates of mid-point of RS. PQ and RS bisect each other.
Question. In the given triangle ABC as shown in diagram D, E and F are the mid-points of AB, BC and AC respectively. Find the area of ΔDEF. Solution.
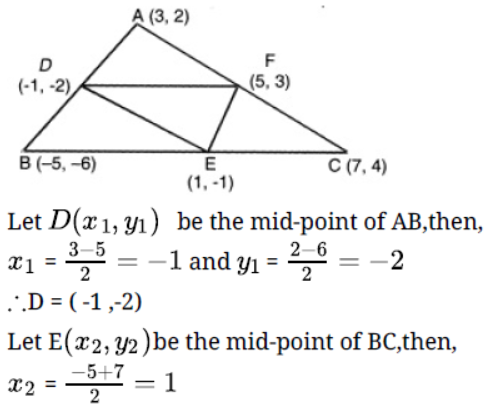
Question. Find the value of m for which the points with coordinates (3, 5), (m, 6) and (1/2 , 15/2) are collinear. Solution. If points are collinear, then one point divides the other two in the same ratio. Let point (m, 6) divides the join of (3, 5) and (1/2 , 15/2) in the ratio k: 1.
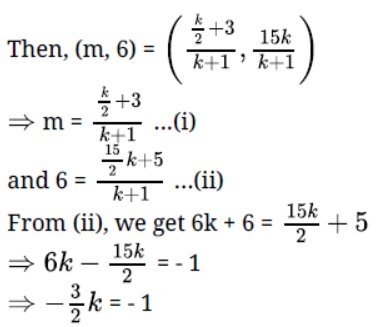
Question. If origin is the mid-point of the line segment joined by the points (2, 3) and (x, y) then find the value of (x, y). Solution.

Question. Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are given below: (3, -5), (-7, 4), (10,-2). Solution. The given vertices of triangle are (3, -5), (-7, 4) and (10, -2). Let (x, y) be the coordinates of the centroid. Then

Question. Find the number of points on x-axis which are at a distance of 2 units from (2, 4). Solution. Distance of the point (2, 4) from x-axis is 4 units. There is no point on x-axis which is at a distance of 2 units from the given point.
Question. Name the type of quadrilateral formed, if any, by the following points, and give reasons for your answer: (-1, -2), (1, 0), (-1, 2), (-3, 0) (4) Solution. (-1, -2), (1, 0), (-1, 2), (-3, 0) Let A→ (-1, -2), B→ (1, 0) C→ (-1, 2) and D→ (-3, 0)
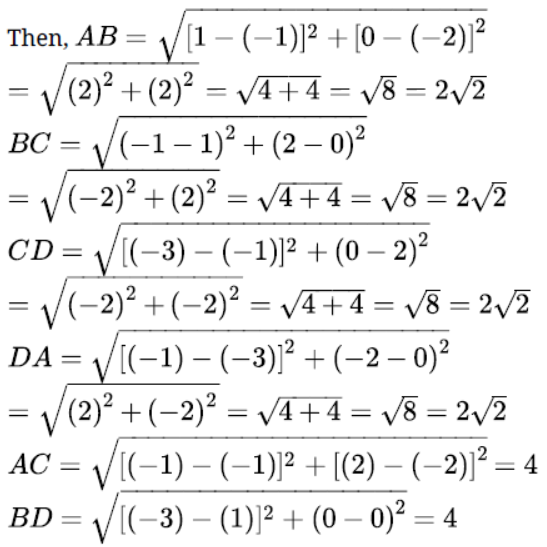
Since AB = BC = CD = DA (i.e., all the four sides of the quadrilateral ABCD are equal) and AC = BD (i.e. diagonals of the quadrilateral ABCD are equal). Therefore, ABCD is a square.
Question. Find the area of the triangle with vertices (0 ,0) (6 ,0) and (0 ,5). Solution. We have to find the area of the triangle with vertices (0 ,0) (6 ,0) and (0 ,5). Area of triangle
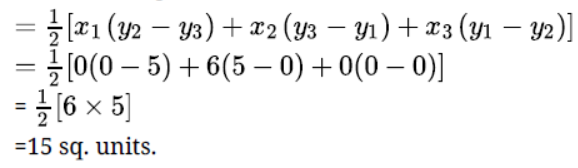
Question. Prove that the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle ABC, with vertices A(x 1 , y 1 ), B(x 2 , y 2 ) and C(x 3 , y 3 ) are given by (x 1 + x 2 + x 3 /3 , y 1 + y 2 + y 3 /3) 12 Solution. Let the coordinates of vertices of ΔABC be A(x 1 , y 1 ), B(x 2 , y 2 ) and C(x 3 , y 3 ) respectively. Let D be the midpoint of BC. Using section formula, coordinates of D will be

Now since centroid G will divide the line joining A and D in the ratio of 2 : 1, therefore again using section formula, coordinates of G will be
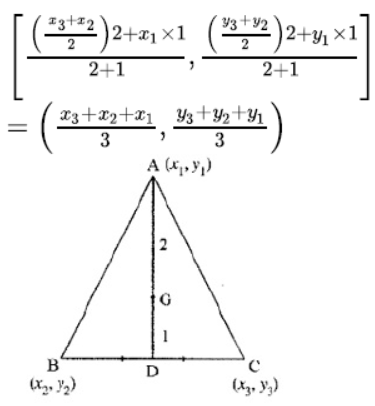
Question. The centre of a circle is (2a, a -7). Find the values of a, if the circle passes through the point (11, -9) and has diameter 10√2 units. Solution. Diameter of a circle = 10√2 units ⇒ Radius of a circle = 5√2 units Let the centre of a circle be O(2a, a – 7) which passes through the point P(11, -9). ⇒ OP is the radius of the circle. ⇒ OP = 5√2 units ⇒ OP 2 = (5√2) 2 ⇒ (11 – 2a) 2 + (-9 – a + 7) 2 = 50 ⇒ 121 + 4a 2 – 44a + (-2 – a) 2 = 50 ⇒ 121 + 4a2 – 44a + 4 + a 2 + 4a = 50 ⇒ 5a 2 – 40a + 125 = 50 ⇒ 5a 2 – 40a + 75 = 0 ⇒ a 2 – 8a + 15 = 0 ⇒ a2 – 5a – 3a + 15 = 0 ⇒ a(a – 5) -3(a – 5) =0 ⇒ (a – 5)(a – 3) = 0 ⇒ a – 5 = 0 or a – 3 = 0 ⇒ a = 5 or a = 3
Question. Find the area of the rhombus if its vertices are (3, 0), (4, 5), (-1, 4) and (-2, -1) taken in order. Solution. Let A (3, 0), B (4, 5), C (-1, 4) and D (-2, -1)

Question. If the points P (-3, 9), Q (a, b) and R (4, -5) are collinear and a + b = 1, find the values of a and b. Solution. It is given that the points P (-3, 9), Q (a, b) and R(4,-5) are collinear.
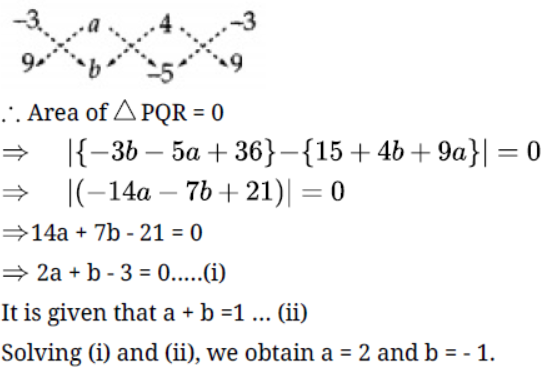
Question. Find the area of a triangle ABC with A(1, – 4) and mid-points of sides through A being (2, -1) and (0, -1). 1 Solution.

Question. If the points (0, 0), (1, 2) and (x, y) are collinear,then find x. Solution. The points are collinear, then area of triangle = 0

Question. Find the lengths of the medians of a ΔABC having vertices at A (0, -1), B (2, 1) and C (0, 3). Solution.

Let A(0, -1), B(2, 1) and C(0, 3) be the given points.
Question. Find the distance of the point (α ,β) from y-axis. Solution. Distance of the point (α ,β) from y-axis is the positive value of its x-coordinate. ∴ Distance = lαl
Question. If the centre of circle is (2a, a – 7) then find the values of a if the circle passes through the point (11, –9) and has diameter 10√2 units. Solution. Let C(2a, a – 7) be the centre of the circle and it passes through the point P(11, –9).

∴ PQ = 10√2 ⇒ CP = 5√2 ⇒ CP2 = (5√2) 2 = 50 ⇒ (2a – 11)2 + (a – 7 + 9)2 = 50 ⇒ (2a) 2 + (11) 2 – 2(2a) (11) + (a + 2) 2 = 50 ⇒ 4a 2 + 121 – 44a + (a) 2 + (2) 2 + 2(a)(2) = 50 ⇒ 5a 2 – 40a + 125 = 50 ⇒ a 2 – 8a + 25 = 10 ⇒ a 2 – 8a + 25 – 10 = 0 ⇒ a 2 – 8a + 15 = 0 ⇒ a 2 – 5a – 3a + 15 = 0 ⇒ a(a – 5) –3(a – 5) = 0 ⇒ (a – 5) (a – 3) = 0 ⇒ a – 5 = 0 or a – 3 = 0 ⇒ a = 5 or a = 3 Hence, the required values of a are 5 and 3.
Question. If the centre and radius of circle is (3, 4) and 7 units respectively, then what is the position of the point A(5,8) with respect to circle? Solution. Distance of the point, from the centre

Question. Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle passing through the points (0, 0), (-2, 1) and (-3, 2). Also, find its radius.
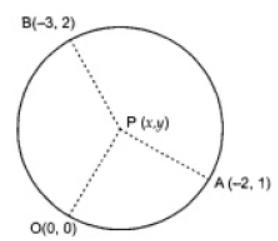
Solution. Let P (x, y) be the centre of the circle passing through the points O (0, 0), A (-2, 1) and B (-3, 2). Then,

Question. If the coordinates of the mid-points of the sides of a triangle are (1, 1), (2, -3) and (3,4), find the vertices of the triangle. Solution. Let A(x 1 , y 1 ), B(x 2 , y 2 ) and C(x 3 , y 3 ) be the vertices of Let D(1, 1), E(2, -3) and F(3, 4) be the mid-points of sides BC, CA and AB respectively. Since, D is the mid-point of BC Similarly E and F are the mid-points of CA and AB respectively. ⇒ x1 + x 2 = 6 and y 1 + y 2 = 8 …(iii) From (i), (ii) and (iii) we get x 2 + x 3 + x 1 + x 3 + x 1 + x 2 = 2 + 4 + 6 and, y 2 + y 3 + y1 + y 3 + y 1 + y 2 = 2 +(-6) + 8 ⇒ 2(x 1 + x 2 + x 3 ) = 12 and 2(y 1 + y 2 + y 3 ) = 4 ⇒ x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 6 and y 1 + y 2 + y 3 = 2 …(iv) From (i) and (iv) we get x 1 + 2 = 6 and y 1 + 2 = 2 ⇒ x 1 = 6 – 2 y 1 = 2 – 2 ⇒ x 1 = 4 y 1 = 0 So the coordinates of A are (4, 0) From (ii) and (iv) we get x 2 + 4 = 6 and y 2 + (-6) = 2 ⇒ x 2 = 2 ⇒ y 2 – 6 = 2 ⇒ y 2 = 8 So the coordinates of B are (2, 8) From (iii) and (iv) we get 6 + x 3 = 6 and 8 + y 3 = 2 ⇒ x 3 = 6 – 6 ⇒ y 3 = 2 – 8 ⇒ x 3 = 0 ⇒ y 3 = -6 So the coordinates of c are (0, -6) Hence, the vertices of triangle ABC are: A(4, 0), B(2, 8) and C(0, -6)
Question. Find the distance between the points P (-4, 7) and Q(2, -5). Solution. The given points are P (-4, 7) and Q(2, -5). Then, x 1 = -4, y 1 = 7 and x 2 = 2, y 2 = -5.

Question. Find the point on the X-axis which is equidistant from the points (-1,0) and (5,0) Solution. Let A(x,o) be any point on the X-axis , which is equidistant from points (-1,0) and (5,0). ⇒ (x + 1) 2 = (x – 5) 2 A(x,o) be any point on the X-axis , which is equidistant from points (-1,0) and (5,0). ⇒ x 2 + 2x + 1 = x 2 – 10x + 25 ⇒ 2x + 1 = -10x + 25 ⇒ 2x + 10x = 25 – 1 ⇒ 12x = 24
Question. Find value(s) of y for which the distance between the points P (2, –3) and Q (10, y) is 10 units. Solution. Let P (2, –3) and Q (10, y) be the two given points such that PQ = 10. ∴ PQ = √(10 – 2) 2 + (y + 3) 2 = 10 (given) ⇒ PQ 2 = 64 + y 2 + 6 y + 9 = 100 ⇒ y 2 + 6y – 27 = 0 ⇒ y2 + 9y – 3y – 27 = 0 ⇒ y (y + 9) – 3 (y + 9) = 0 ⇒ (y + 9) (y – 3) = 0 ⇒ y = – 9 or y = 3 Ans.
Question. Find the ratio in which the join of (–3, 10) and (6, –8) is divided by (–1, 6). Solution. Let the given points be A(–3, 10), B(6, –8) and C(–1, 6).

Question. Prove that the points (2, –2), (–3, 8) and (–1, 4) are collinear. Solution. Let Δ be the area of the triangle formed by given three points A(2, –2), B(–3, 8) and C(–1, 4).

Question. Show that the points (1, –1), (5, 2) and (9, 5) are collinear. Solution. Let A(1, –1), B(5, 2) and C(9, 5) be the given points.

Question. Find the coordinates of the circumcentre of the triangle whose vertices are (8, 6), (8, –2) and (2, –2). Also, find its circum-radius. Solution. We know circumcentre of a triangle is equidistant from the vertices of a triangle. Let A(8, 6), B(8, –2) and C(2, –2) be the vertices of a given triangle and let P(x, y) be the circumcentre of this triangle. Then, PA = PB = PC ⇒ PA 2 = PB 2 = PC 2 Now, PA 2 = PB 2 ⇒ (x– 8) 2 + (y – 6) 2 = (x – 8)2 + (y + 2) 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 – 16x – 12 y + 100 = x 2 + y 2 – 16x + 4y + 68 ⇒ 16y = 32 ⇒ y = 2. and PB 2 = PC 2 ⇒ (x – 8) 2 + (y + 2) 2 = (x – 2) 2 + (y + 2) 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 – 16x + 4y + 68 = x 2 + y 2 – 4x + 4y + 8 ⇒ 12x = 60 ⇒ x = 5 So, the coordinates of the circumcentre P are (5, 2). Also, circum-radius = PA = PB = PC √(5 – 8) 2 + (2 – 6) 2 = √(-3) 2 + (-4) 2 √9 + 16 = √25 = 5 units Ans.
Question. Find the distance between the points : (i) A (0, 0), B (–5, 12) (ii) A (5, –8), B(–7, –3) (iii) P (cos α, –sin α), Q( – cos α, sin α) (iv) P (a + b, a – b), Q (a – b, a + b) Solution. (i) AB = √(-5 – 0)2 + (12 – 0) 2
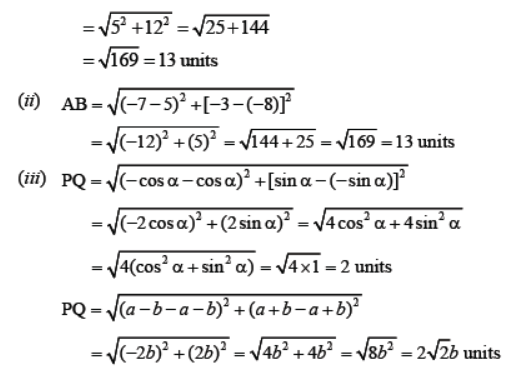
Question. Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices taken in order are (–4, –2), (–3, –5), (3, –2), (2, 3). Solution. Let A(–4, –2), B(–3, –5), C(3, –2) and D (2, 3) be the given points. Now, area of quad. ABCD = ar (ΔABD) + ar (ΔBCD) For ar (ΔABD) : A(–4, –2), B(–3, –5), D(2, 3)
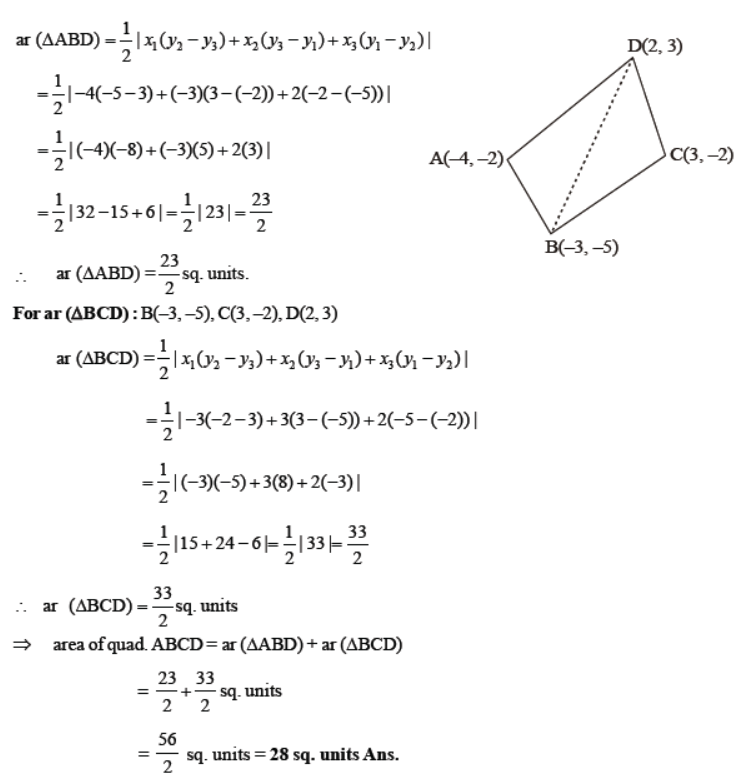
Question. Check whether (5, –2), (6, 4) and (7, –2) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle. Solution. Let A(5, –2), B(6, 4) and C(7, –2) be the vertices of a ΔABC. AB = √(6 – 5)2 + (4 + 2)2 = √12 + 62 = √ 1 + 36 = √37

Question. If A(5, –1), B(–3, –2) and C(–1, 8) are the vertices of ΔABC, find the length of medians through A and the coordinates of the centroid. Solution. Let AD be the median through the vertex A of ΔABC. Then, D is the mid-point of BC. So, the coordinates of D are (-3/2 , -2 + 8/2) i.e. (–2, 3).
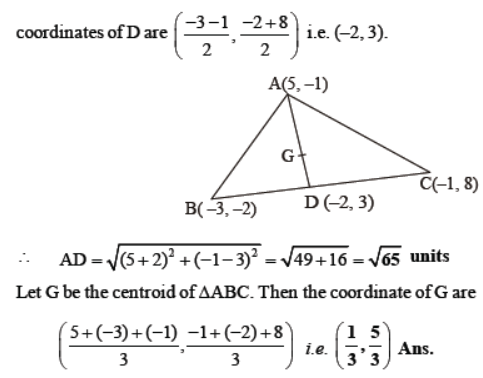
Question. Show that (1, –2), (3, 0), (1, 2) and (–1, 0) are the vertices of a square. Solution. Let A(1, –2), B(3, 0), C(1, 2) and D(–1, 0) be the given points.

Question. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are (–5, –1), (3, –5), (5, 2). Solution. Let A(–5, –1), B(3, –5), C(5, 2) be the given points.

Question. Find the co-ordinates of the points of trisection of the line joining the points (4, –1) and (–2, –3). Solution. Let C and D be the points of trisection of AB

Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry as per CBSE NCERT pattern
All students studying in Grade 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry should download the assignments provided here and use them for their daily routine practice. This will help them to get better grades in Mathematics Coordinate Geometry exam for standard 10. We have made sure that all topics given in your textbook for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry which is suggested in Class 10 have been covered ad we have made assignments and test papers for all topics which your teacher has been teaching in your class. All chapter wise assignments have been made by our teachers after full research of each important topic in the textbooks so that you have enough questions and their solutions to help them practice so that they are able to get full practice and understanding of all important topics. Our teachers at https://www.assignmentsbag.com have made sure that all test papers have been designed as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern. These question banks have been recommended in various schools and have supported many students to practice and further enhance their scores in school and have also assisted them to appear in other school level tests and examinations. Its easy to take print of thee assignments as all are available in PDF format.
Some advantages of Free Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry
- Solving Assignments for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 helps to further enhance understanding of the topics given in your text book which will help you to get better marks
- By solving one assignments given in your class by Mathematics Coordinate Geometry teacher for class 10 will help you to keep in touch with the topic thus reducing dependence on last minute studies
- You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected in your Mathematics Coordinate Geometry class test
- You will be able to revise all topics given in the ebook for Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry as all questions have been provided in the question banks
- NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Workbooks will surely help you to make your concepts stronger and better than anyone else in your class.
- Parents will be able to take print out of the assignments and give to their child easily.
All free Printable practice assignments are in PDF single lick download format and have been prepared by Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry teachers after full study of all topics which have been given in each chapter so that the students are able to take complete benefit from the worksheets. The Chapter wise question bank and revision assignments can be accessed free and anywhere. Go ahead and click on the links above to download free CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments PDF.

You can download free assignments for class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry from https://www.assignmentsbag.com
You can get free PDF downloadable assignments for Grade 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry from our website which has been developed by teachers after doing extensive research in each topic.
On our website we have provided assignments for all subjects in Grade 10, all topic wise test sheets have been provided in a logical manner so that you can scroll through the topics and download the worksheet that you want.
You can easily get question banks, topic wise notes and questions and other useful study material from https://www.assignmentsbag.com without any charge
Yes all test papers for Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 are available for free, no charge has been put so that the students can benefit from it. And offcourse all is available for download in PDF format and with a single click you can download all assignments.
https://www.assignmentsbag.com is the best portal to download all assignments for all classes without any charges.
Related Posts

Capital Small Alphabet Matching Assignments Download PDF

Assignments For Class 5 Science

Assignments For Class 9 Mathematics Lines and Angles
Search This Blog
Cbse mathematics.
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12. A complete resource centre of mathematics for students and teachers
Featured Posts
Linear programming class xii chapter 12, math assignment class x ch-7 | coordinate geometry.
Math Assignment, Class X,

ASSIGNMENT FOR 10 STANDARD COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Questions based on distance formula.
a) (5, -12) Ans [13]
Find the type of triangle ABC formed whose vertices are A(1, 0), B(-5, 0)and C(-2, 5)
Questions based on the section formula and mid-point formula.
In what ratio the line segment joining the points (3, -5) and (-1, 6) divided by the line y = x ?
Answer: 8:7
Points A(-1,y) and B(5, 7) lie on a circle with centre O(2, -3y) such that AB is a diameter of the circle. Find the value of y. Also find the radius of the circle.
Answer: y = -1, Radius = 5
Find the ratio in which the point (8/5, y) divides the line segment joining the points (1, 2) and (2, 3). Also, find the value of y.
Answer: 3 : 2, y = 13/5
Point P divides the line segment joining the points A(4, -5) and B(1, 2) in the ratio 5 : 2. Find the coordinates of point P.
Answer : (13/7, 0)
AD is a median of triangle ABC with vertices A(5, -6), B(6, 4) and C(0,0). Find length AD ?
P(-2, 5) and Q(3, 2) are two points. Find the coordinates of the point R on line segment PQ such that PR = 2QR.
Answer: R(4/3, 3)
Question 37
Find a relation between x and y such that the points P(x, y) is equidistant from the points A(7, 1) and B(3, 5)
Answer: x - y - 2 = 0
ABCD is a rectangle formed by the points A(-1, -1), B(-1, 6), C(3, 6) and D(3, -1). P, Q, R and S are mid-points of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Show that diagonals of the quadrilateral PQRS bisect each other.
Find the coordinates of P,Q,R,S by using mid point formulas.
Find the coordinates of mid points of diagonals PR and QS which are same and are equal to (1, 5/2)
As the coordinates of mid points of PR and QS both are equal ⇒ Diagonals bisects each other.
Questions based on the centroid of triangle
Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are given below
a) A(4,7), B(2,1), C(3,6) Ans [3, 14/3] b) A(2,3), B(4,5), C(3,4) Ans [3,4]
Download Pdf Form of the Assignments
Questions deleted from cbse syllabus, post a comment, breaking news, popular post on this blog, lesson plan maths class 10 | for mathematics teacher.

Lesson Plan Math Class X (Ch-8) | Trigonometry

Class XI Maths Formulas | Basics | Assignments

- Assignment 10 15
- Assignment 11 12
- Assignment 12 15
- Assignment 8 8
- Assignment 9 5
- Lesson plan 10 15
- Lesson Plan 12 14
- Lesson Plan 8 10
- Maths 10 20
- Maths 11 21
- Maths 12 18
SUBSCRIBE FOR NEW POSTS
Get new posts by email:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The topics that are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 are Introduction to Coordinate Geometry, Distance Formula, Section Formula and Area of the Triangle. By learning these NCERT solutions thoroughly, students will be able to solve complex problems easily.
Practice Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry. The centre of a circle is (2a, a - 7). Find the values of a, if the circle passes through the point (11, -9) and has a diameter 10√ 2 units. Find the ratio in which the line 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 divides the line segment joining the points (8, -9) and (2, 1).
Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 7 Class 10 Coordinate Geometry. All questions have been solved in an easy to understand way with detailed explanation of each and every step. Answers to optional exercise is also given. In Coordinate Geometry of Class 9, we learned what is x and y coordinate of a point.
To know more about Coordinate Geometry, visit here. Points on a Cartesian Plane. A pair of numbers locate points on a plane called the coordinates.The distance of a point from the y-axis is known as abscissa or x-coordinate.The distance of a point from the x-axis is called ordinate or y-coordinate. Example: Consider a point P(3, 2), where 3 is the abscissa, and 2 is the ordinate. 3 represents ...
Solution: Question 24. If the coordinates of points A and B are (-2, -2) and (2, - 4) respectively, find the coordinates of P such that AP = 3/7 AB, where P lies on the line segment AB. Solution: Question 25. Find the coordinates of a point P on the line segment joining A (l, 2) and B (6,7) such that AP=2/5AB.
10th Maths Chapter 7 Solutions. Exam based NCERT solutions for class 10 Maths chapter 7 coordinate geometry exercises from 7.1 and 7.2 are given to free download. All the contents are in updated format for academic session 2024-25. Offline Apps based on these solutions are also for new session.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 7 Class 10 Maths, "Coordinate Geometry" covers the following four exercises: Exercise 7.1 - This exercise contains 10 questions, students are introduced to the concept of the Cartesian Plane, plotting points on the plane, and finding the coordinates of a point. Students learn how to identify the quadrants of the ...
Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 depicts Coordinate Geometry which is the branch of Mathematics. It helps us to exactly locate a given point with the help of an ordered pair of numbers. Coordinate geometry is also well known as Cartesian Geometry. It helps in finding the distance between two points whose coordinates are given.
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry solved by expert Maths teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Ex 7.1 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing homework. Exercise 7.1 Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.in Teachers. Detailed answers of all the questions in Chapter 7 Maths Class 10 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 7.1 Provided in NCERT Textbook
Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Coordinate Geometry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf. Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams.
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-II (3 Marks) Question 20. Find that value(s) of x for which the distance between the points P(x, 4) and Q(9, 10) is 10 units. (2011D) Solution: PQ = 10 …Given PQ 2 = 10 2 = 100 … [Squaring both sides
Using NCERT Mathematics Class 10 solutions Coordinate Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Class 10 ...
COORDINATE GEOMETRY 155 7 7.1 Introduction In Class IX, you have studied that to locate the position of a point on a plane, we require a pair of coordinate axes. The distance of a point from the y-axis is called its x-coordinate, or abscissa.The distance of a point from the x-axis is called its y-coordinate, or ordinate.The coordinates of a point on the x-axis are of the form
These coordinate geometry class 10 PDF solutions are essential for understanding the concepts of coordinate geometry in class 10. By referring to the NCERT solutions for class 10 maths chapter 7, students can enhance their preparation for chapter 7 maths class 10. This chapter 7 class 10 maths content is a valuable resource for attaining perfection in the topics involved.
Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Extra Questions Short Answer Type-2. Question 1. Two friends Seema and Aditya work in the same office at Delhi. In the Christmas vacations, both decided to go to their hometowns represented by Town A and Town B respectively in the figure given below. Town A and Town B are connected by trains from the same station C ...
COORDINATE GEOMETRY CHAPTER 7 (A) Main Concepts and Results Distance Formula, Section Formula, Area of a Triangle. • The distance between two points P (x 1, y 1) and Q (x2, y 2) is ( )( )2 2 xx y y21 2 1-- + • The distance of a point P (x,y) from the origin is xy22+ • The coordinates of the point P which divides the line segment joining the points
Download Class 10 Maths Extra Questions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry free from Aglasem Docs. aglasem.com. Login. Number of coins ... Class 10 Maths Extra Questions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry More Detail. Maths Question Bank AglaSem Class 10. Save to library Add Notes Download 1 / 1. Updated On ...
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Assignments Set H. Coordinate Geometry. A point in 2-D plane (let's say XY plane) is represented by its coordinates (x,y) Here x is the distance of a point from the x-axis and is called y-coordinate. y is the distance of a point from the and is called its . Distance Formula : the distance between ...
The y - coordinate of a point is its perpendicular distance from the x - axis measured along the y - axis (positive along the positive direction of the y - axis and negative along the negative direction of the y - axis). For the point P, it is. 3 and for Q, it is -2. The y - coordinate is also called the ordinate.
Math Assignment Class X Ch-7 | Coordinate Geometry. By CBSE MATHEMATICS May 09, 2022. Math Assignment, Class X, Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry. Extra questions of chapter 7 class 10 Coordinate Geometry with answer and hints to the difficult questions. Important and useful math assignment for the students of class 10. ASSIGNMENT FOR 10 STANDARD.